Transmembrane Dps (starvation-induced DNA binding protein) and application
A protein-binding and starvation-induced technology, applied in the field of starvation-induced DNA-binding proteins, can solve the problems of improper protein assembly, improper assembly, solubility and protein stability, and achieve good water solubility, uniform size, Easy to purify effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
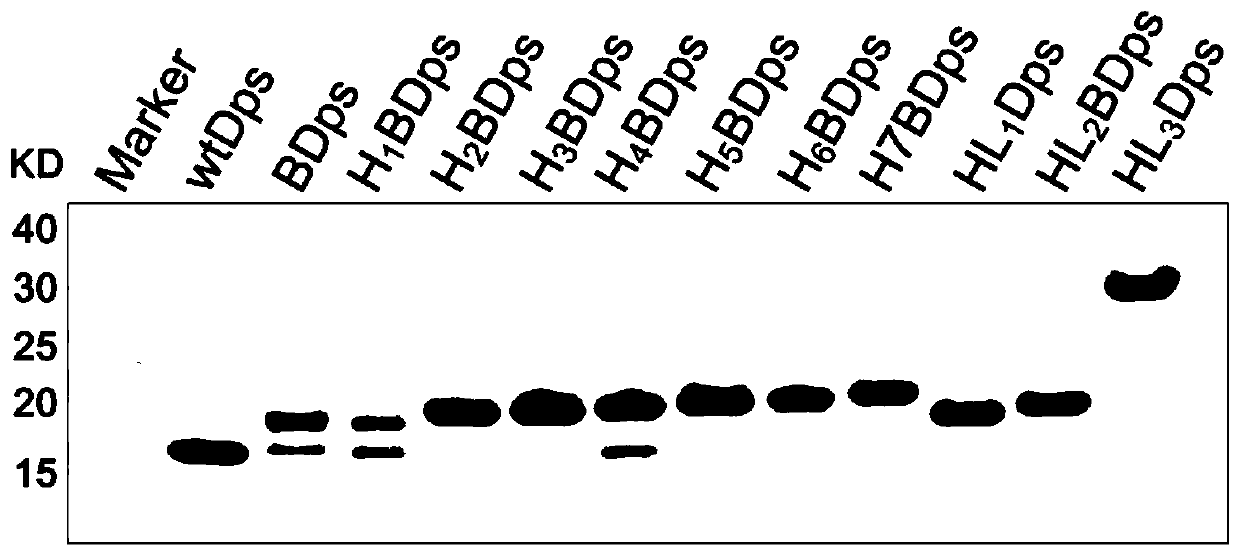
[0034] A transmembrane starvation-induced DNA-binding protein, the protein is sequentially fused with 1 Avitag and X His at the N-terminal or C-terminal of Dps; or sequentially fused with Y GGGGS and 6 His at the N-terminal or C-terminal of Dps His; said X is any natural number from 1 to 7; said Y is 1 or 2 or 3.
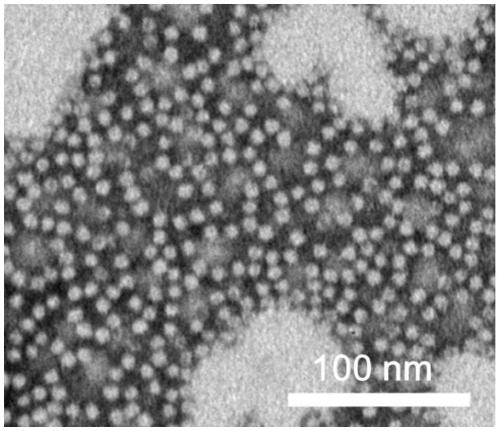
[0035] In the embodiment of the present invention, one Avitag and two His fusion proteins are sequentially fused to the N-terminus of Listeria-derived Dps 2 BDps is taken as an example for illustration, the H 2 The DNA sequence of BDps is shown in SEQ ID NO.1.
[0036] The Dps protein can be Dps protein from different species, and can also be some protein nanocages with a spherical structure.
Embodiment 2
[0038] A method for preparing a transmembrane starvation-induced DNA-binding protein, comprising the steps of:
[0039] The embodiment of the present invention is illustrated by taking the Dps protein derived from prokaryotes as an example, and the Dps protein derived from other species can also complete the present invention;
[0040] Using Listeria genomic DNA as a template, amplify the wtDps nucleotide sequence (the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2), and the primers for amplifying the wtDps nucleotide sequence are: 5'CATATGAAAACAATCAACTCAGTAG3' and 5'CTCGAGTTATTCTAATGGAGCTTTT3' .
[0041] Design primers to sequentially add 1 Avitag and X His nucleotide sequences to the N-terminal of Dps, or design primers to sequentially add Y GGGGS and 6 His nucleotide sequences to the N-terminal of Dps; Add enzyme cleavage sites and corresponding protective bases, select double enzyme cleavage sites NdeI and Xho I, perform PCR amplification, detect by agarose gel electrophores...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Detection of the transmembrane ability of starvation-induced DNA-binding proteins:
[0061] First, modify the Alex555 fluorescent dye on the surface of the protein. Specific steps: take wtDps as the reference concentration at 2 mg / ml, adjust the molar concentration of the fusion protein prepared in Example 2 to be consistent with wtDps, and the feed ratio of protein and Alex555 is corresponding to one protein ball 12 fluorescent molecules, the reaction buffer is 0.1M sodium bicarbonate, shake at 600rpm / min at 25°C for 1h, then stand overnight at 4°C, dialyze into PBS solution to remove free Alex555, then pass through SDS-PAGE, optical density instrument GS900 For imaging, the image J software was used for grayscale analysis to quantify the protein concentration, and the fluorescence spectrophotometer was used to detect the modification of the dye in the sample, which was used to correct the results of flow cytometry.
[0062] Choose skin fibroblast HFF-1 and African gre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com