Patents
Literature
167 results about "Protein stability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein Stability. Protein stability is the net balance of forces, which determine whether a protein will be its native folded conformation or a denatured (unfolded or extended) state. The net stability of proteins is quite small and is the difference between two large opposing forces.
T cell receptor-like antibodies specific for a wti peptide presented by hla-a2
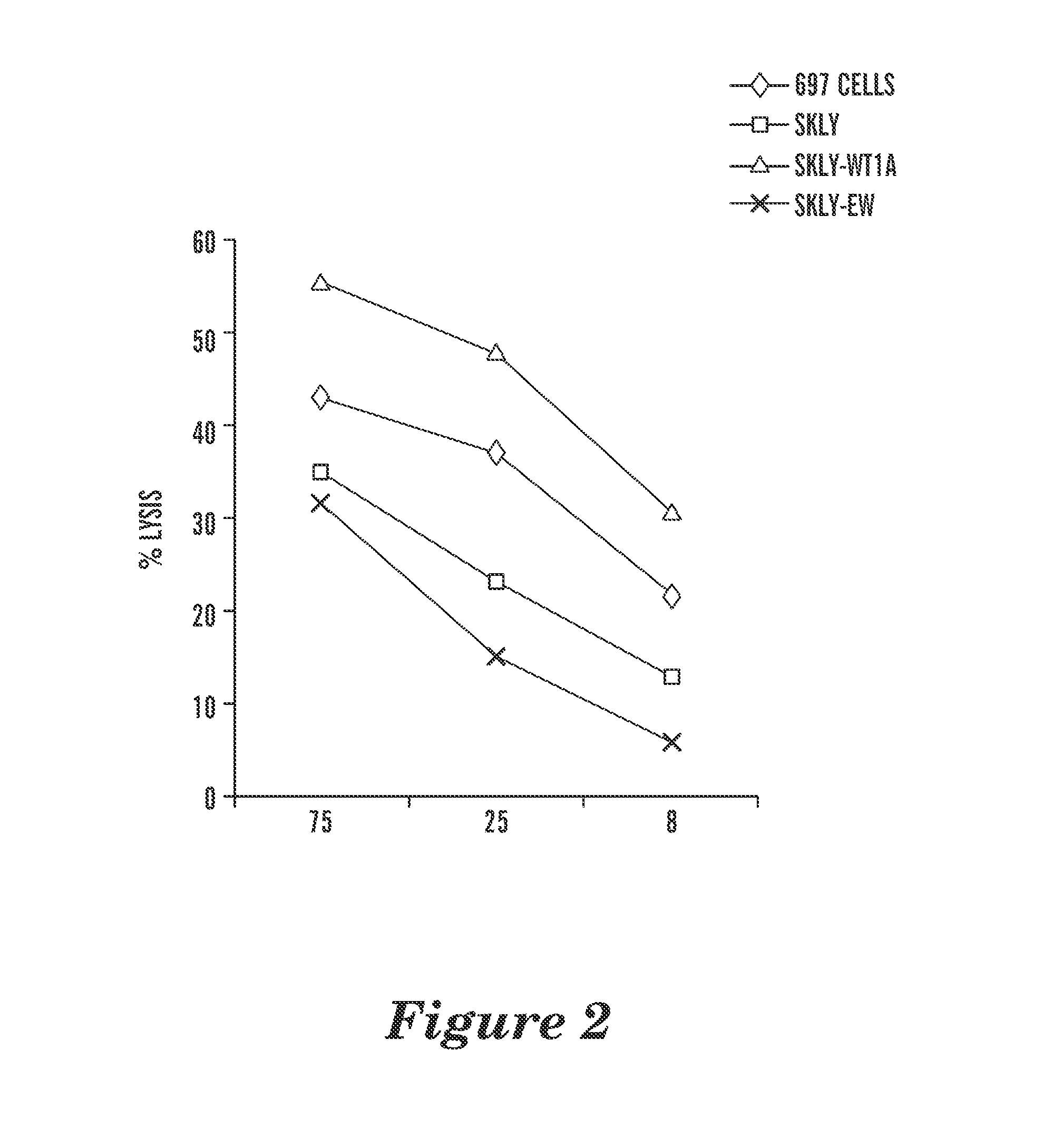
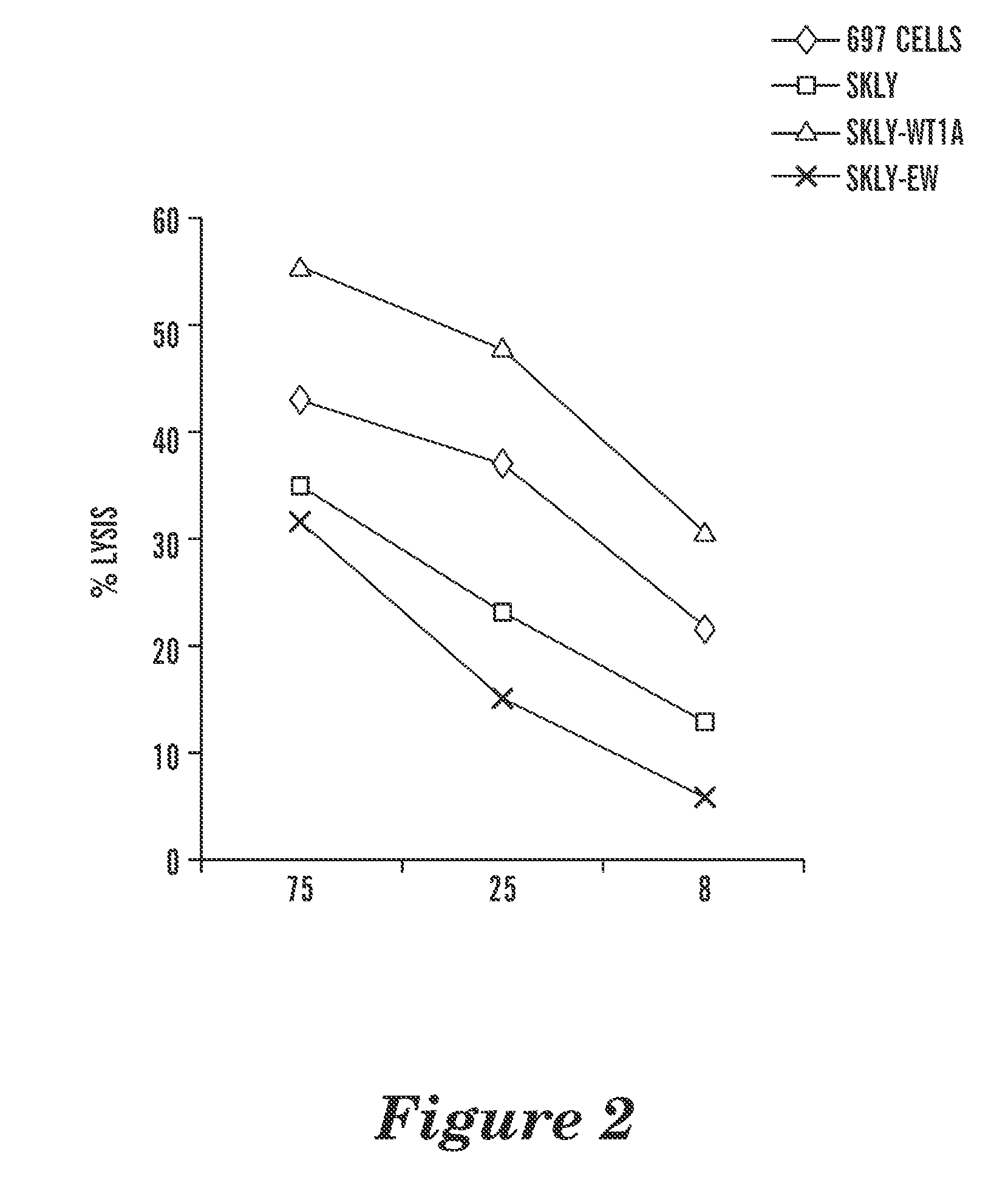
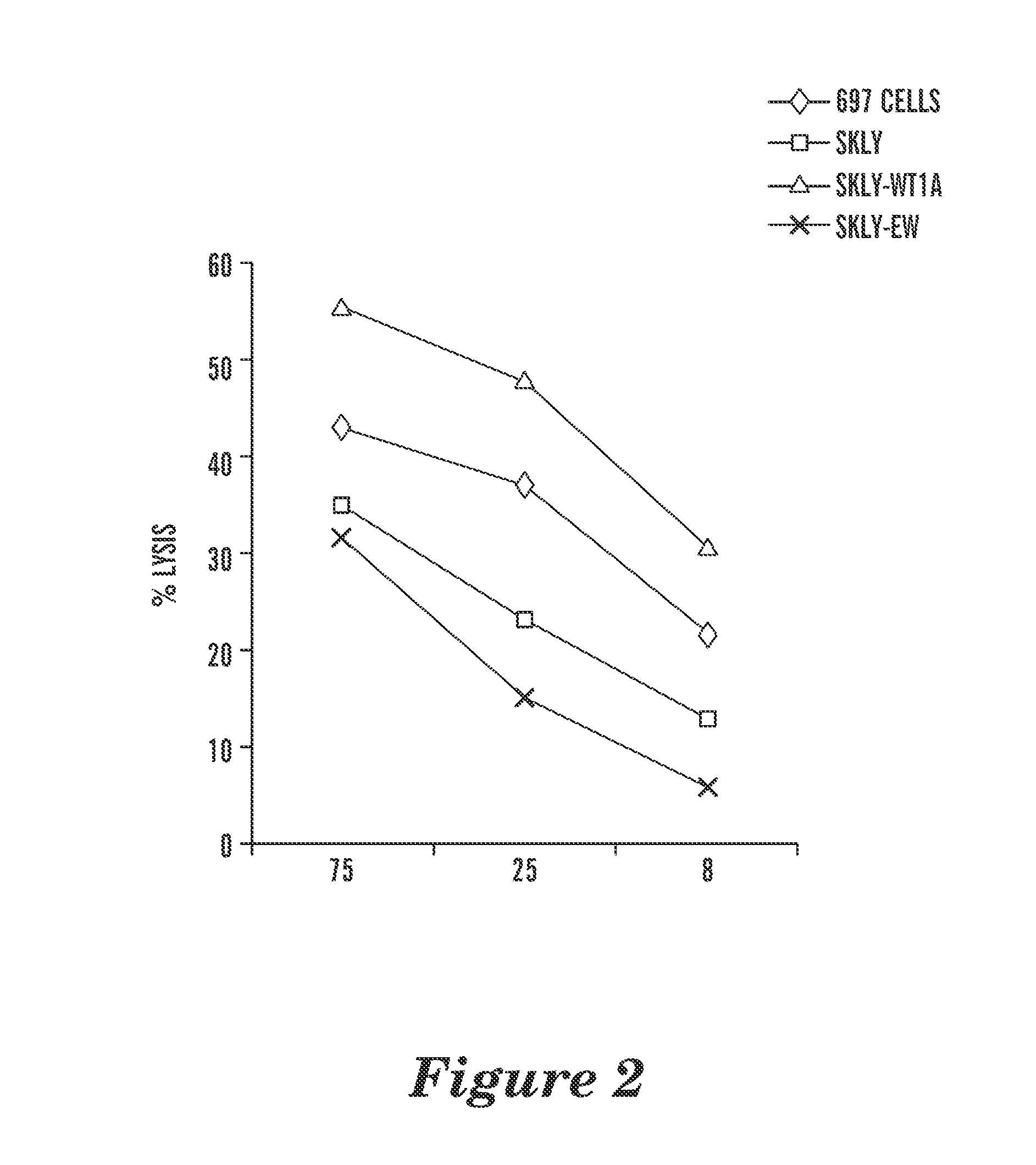
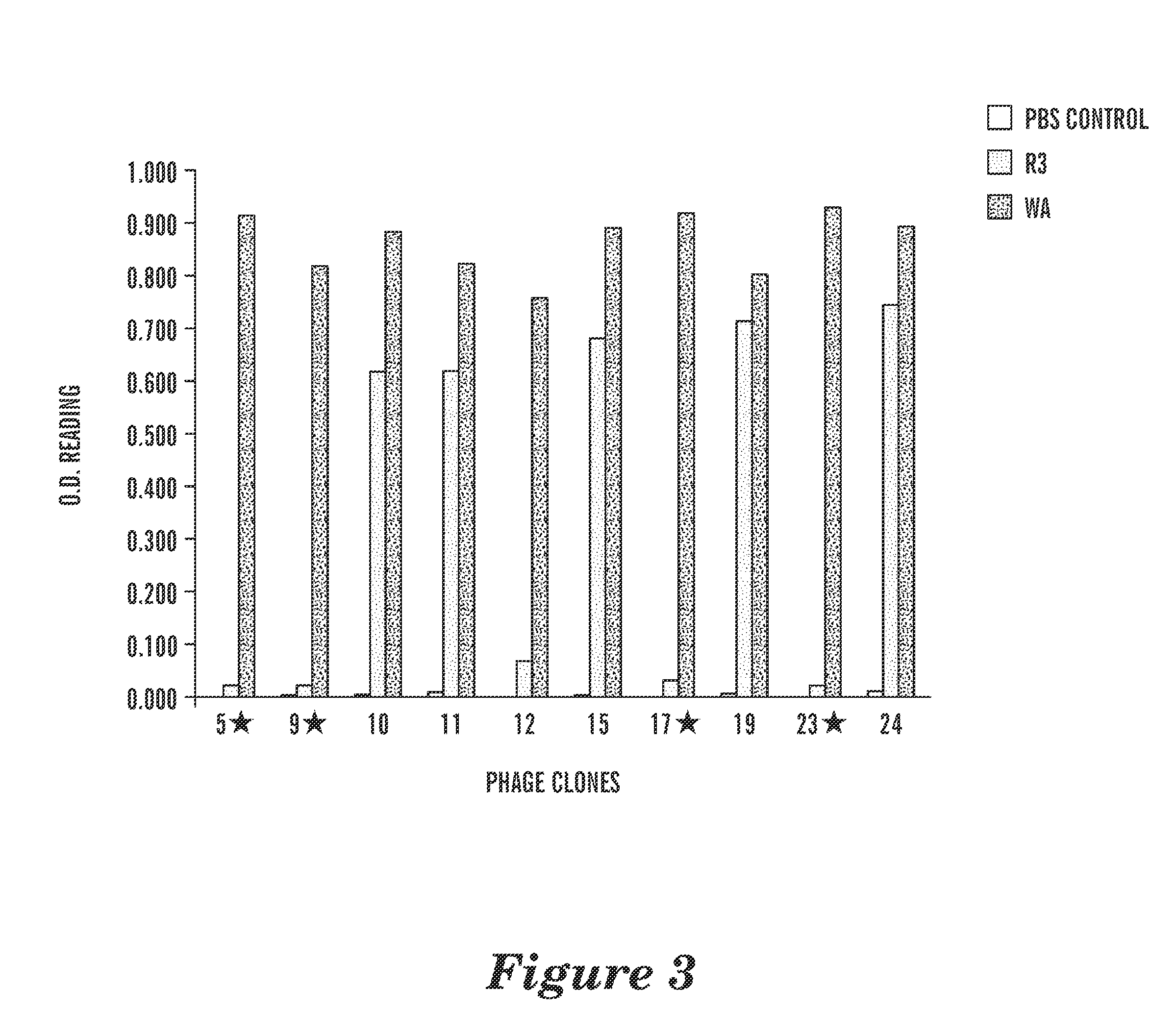
The present invention provides antigen binding proteins that specifically bind to Wilms' tumor protein (WT1), including humanized, chimeric and fully human antibodies against WT1, antibody fragments, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), fusion proteins, and conjugates thereof. The antigen binding proteins and antibodies bind to HLA-A0201-restricted WT1 peptide. Such antibodies, fragments, fusion proteins and conjugates thereof are useful for the treatment of WT1 associated cancers, including for example, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, chronic myelocytic leukemia, multiple myeloma, acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid / myelogenous leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). In more particular embodiments, the anti-WT1 / A antibodies may comprise one or more framework region amino acid substitutions designed to improve protein stability, antibody binding and / or expression levels.
Owner:EUREKA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
Anti-CD19 Antibodies
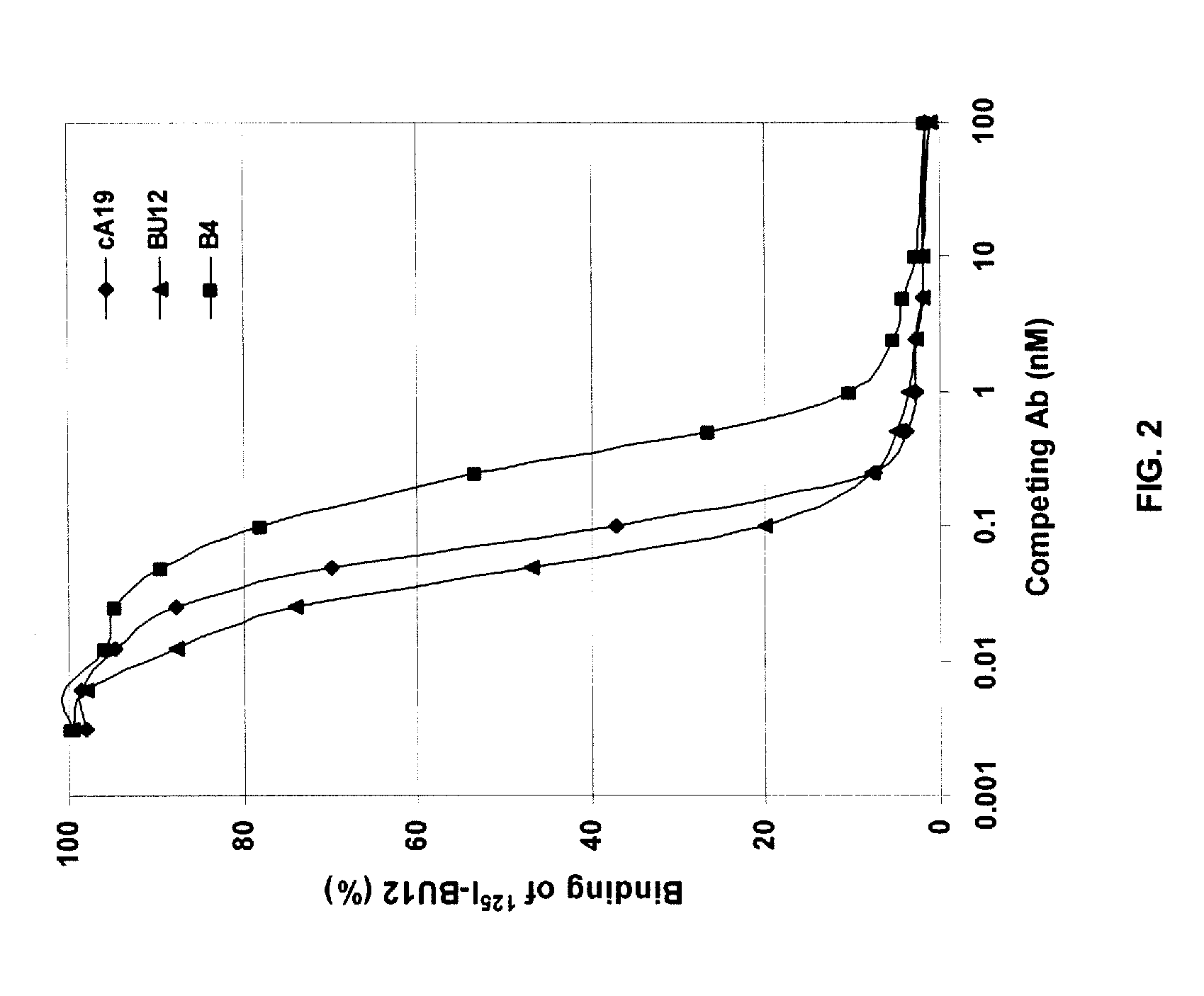
The present invention provides humanized, chimeric and human anti-CD19 antibodies, anti-CD19 antibody fusion proteins, and fragments thereof that bind to a human B cell marker. Such antibodies, fusion proteins and fragments thereof are useful for the treatment and diagnosis of various B-cell disorders, including B-cell malignancies and autoimmune diseases. In more particular embodiments, the humanized anti-CD19 antibodies may comprise one or more framework region amino acid substitutions designed to improve protein stability, antibody binding and / or expression levels. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the substitutions comprise a Ser91Phe substitution in the hA19 VH sequence.
Owner:IMMUNOMEDICS INC
Stable spray-dried protein formulations
InactiveUS6956021B1Improve protein stabilityImprove stabilityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicinePhospholipid
Spray-dried particles having improved protein stability are produced by spray-drying a mixture including a protein, a phospholipid and an organic-aqueous co-solvent. Spray-dried particles which include at least 1 weight % phospholipid, having a tap density of less than 0.4 g / cm3 can be prepared. The particles can be delivered to the pulmonary system of a patient.
Owner:CIVITAS THERAPEUTICS
Stabilization of aqueous compositions of proteins with displacement buffers
InactiveUS20100028372A1Improve stabilityImproves pH stabilityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsAnalytical chemistryProtein stability
An aqueous composition having increased protein stability is obtained by: a. determining a pH at which the protein has stability at the desired temperature; b. adding to the composition at least one displacement buffer wherein the displacement buffer has a pKa that is at least 1 unit greater or less than the pH of step (a); and c. adjusting the pH of the composition to the pH of step (a); wherein the aqueous composition does not comprise a conventional buffer at a concentration greater than about 2 mM and wherein the conventional buffer has a pKa that is within 1 unit of the pH of step (a).
Owner:ARECOR LTD
Methods and compositions for preventing oxidative degradation of proteins
InactiveUS20050276823A1Improve the immunityExtend product shelf lifePharmaceutical delivery mechanismImmunoglobulinsScavengerProtein oxidation
Methods and compositions for preventing oxidative damage to proteins, particularly antibodies, are provided. The compositions include a combination of metal chelators, such as DTPA, EGTA, and / or DEF, and can further include one or more free radical scavengers, particularly scavengers of oxygen radicals. Methods for enhancing protein stability using the compositions of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDAREX INC
T cell receptor-like antibodies specific for a WT1 peptide presented by HLA-A2
The present invention provides antigen binding proteins that specifically bind to Wilms' tumor protein (WT1), including humanized, chimeric and fully human antibodies against WT1, antibody fragments, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), fusion proteins, and conjugates thereof. The antigen binding proteins and antibodies bind to HLA-A0201-restricted WT1 peptide. Such antibodies, fragments, fusion proteins and conjugates thereof are useful for the treatment of WT1 associated cancers, including for example, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, chronic myelocytic leukemia, multiple myeloma, acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid / myelogenous leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). In more particular embodiments, the anti-WT1 / A antibodies may comprise one or more framework region amino acid substitutions designed to improve protein stability, antibody binding and / or expression levels.
Owner:EUREKA THERAPEUTICS INC +1
EphA2, hypoproliferative cell disorders and epithelial and endothelial reconstitution
InactiveUS20050049176A1Convenient treatmentReduces and avoids unwanted effectPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticCell layerInflammatory Bowel Diseases
The present invention relates to methods and compositions designed for the treatment, management, or prevention of a hypoproliferative cell disorder, especially those disorders relating to the destruction, shedding, or inadequate proliferation of epithelial and / or endothelial cells, particularly interstitial cystitis (IC) and lesions associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). The methods of the invention comprise the administration of an effective amount of one or more agents that are antagonists of EphA2. In certain embodiments, the EphA2 antagonistic agent of the invention decreases EphA2-endogenous ligand binding, upregulates EphA2 gene expression and / or translation, increases EphA2 protein stability or protein accumulation, decreases EphA2 cytoplasmic tail phosphorylation, promotes EphA2 kinase activity (other than autophosphorylation or ligand-mediated EphA2 signaling), increases proliferation of EphA2 expressing cells, increases survival of EphA2 expressing cells, and / or maintains / reconstitutes epithelial and / or endothelial cell layer integrity. The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more EphA2 antagonistic agents of the invention either alone or in combination with one or more other agents useful for therapy for a hypoproliferative cell disorder. Diagnostic methods and methods for screening for therapeutically useful agents are also provided.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
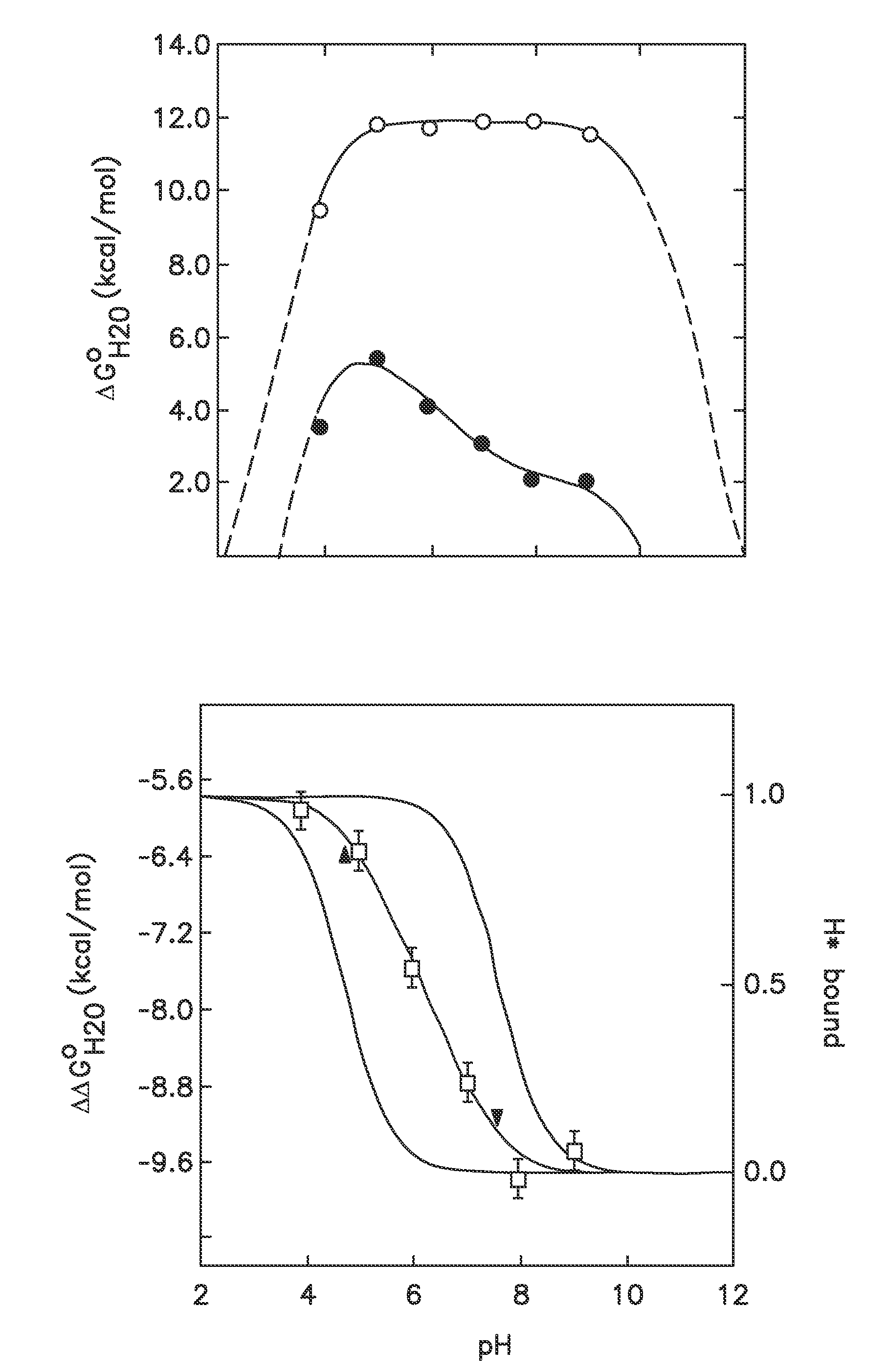
Stable Aqueous Systems Comprising Proteins
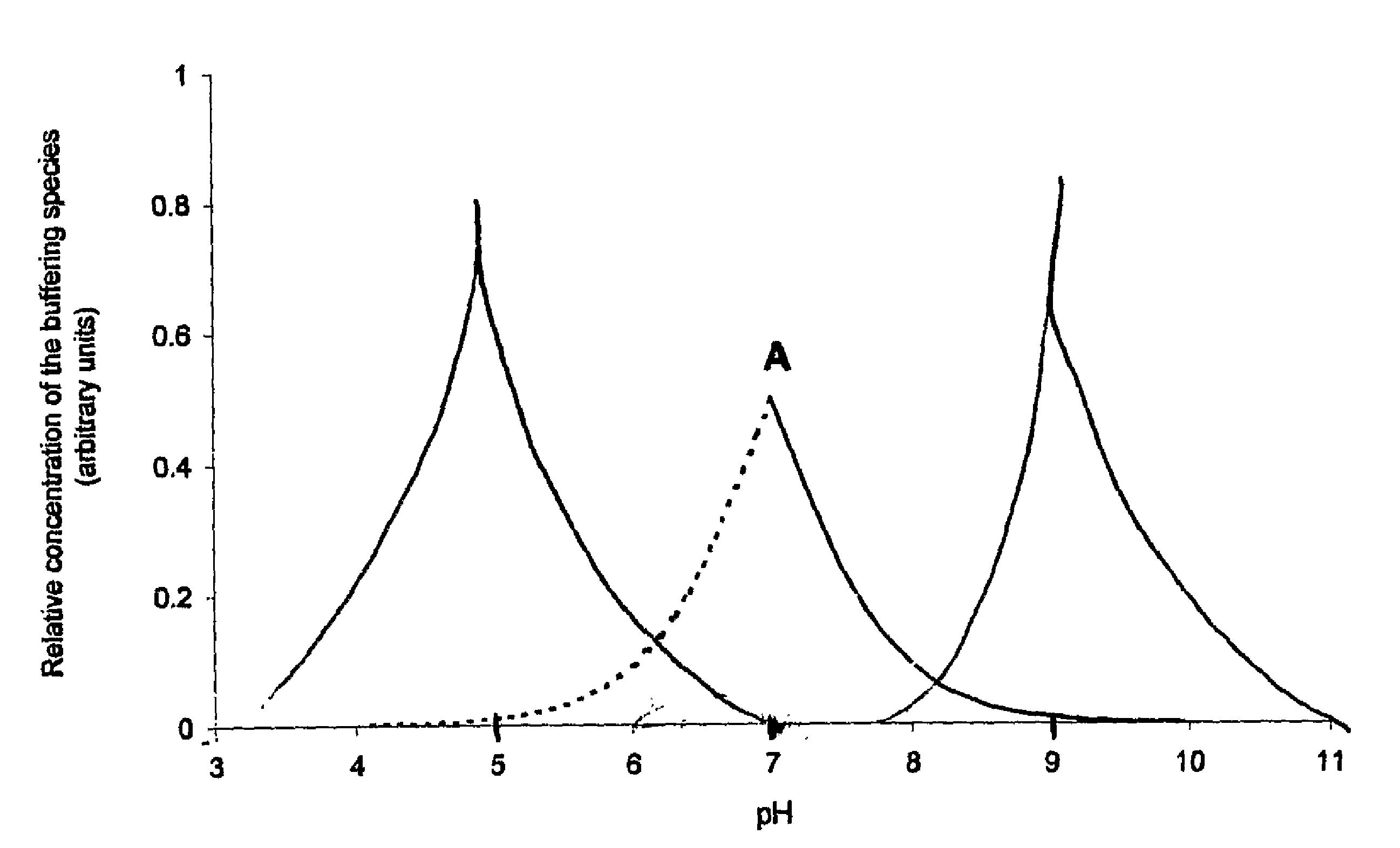
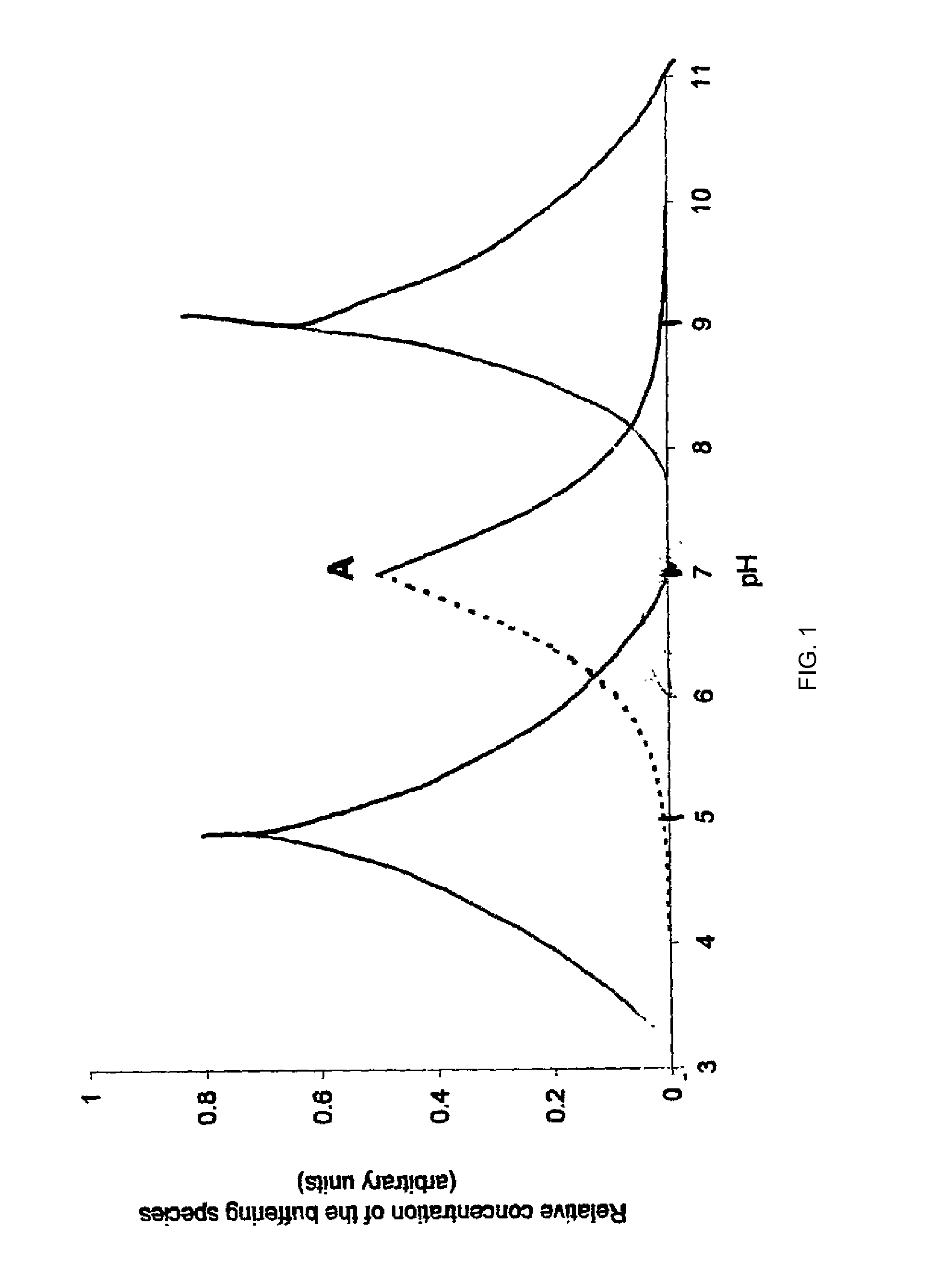
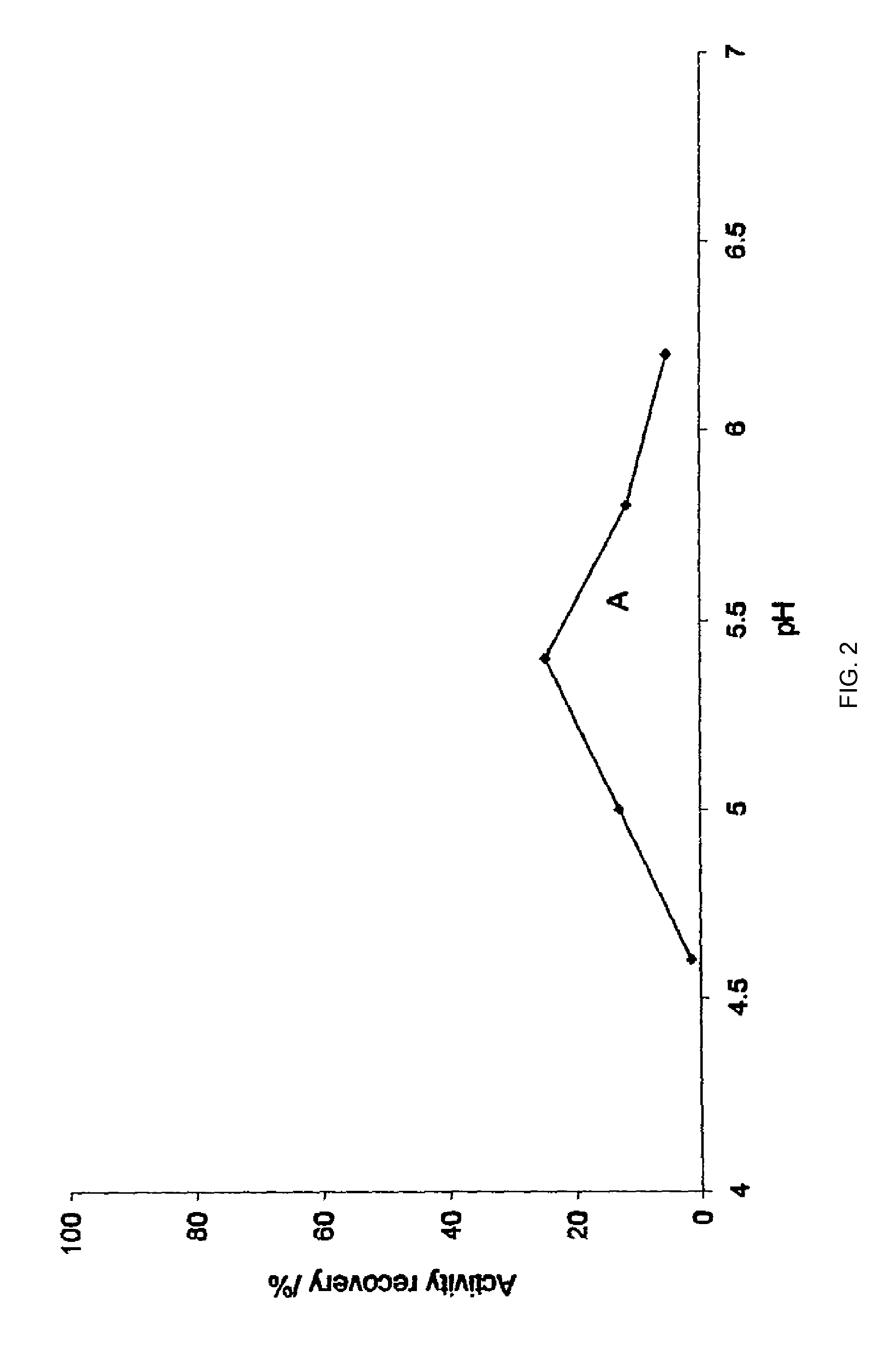
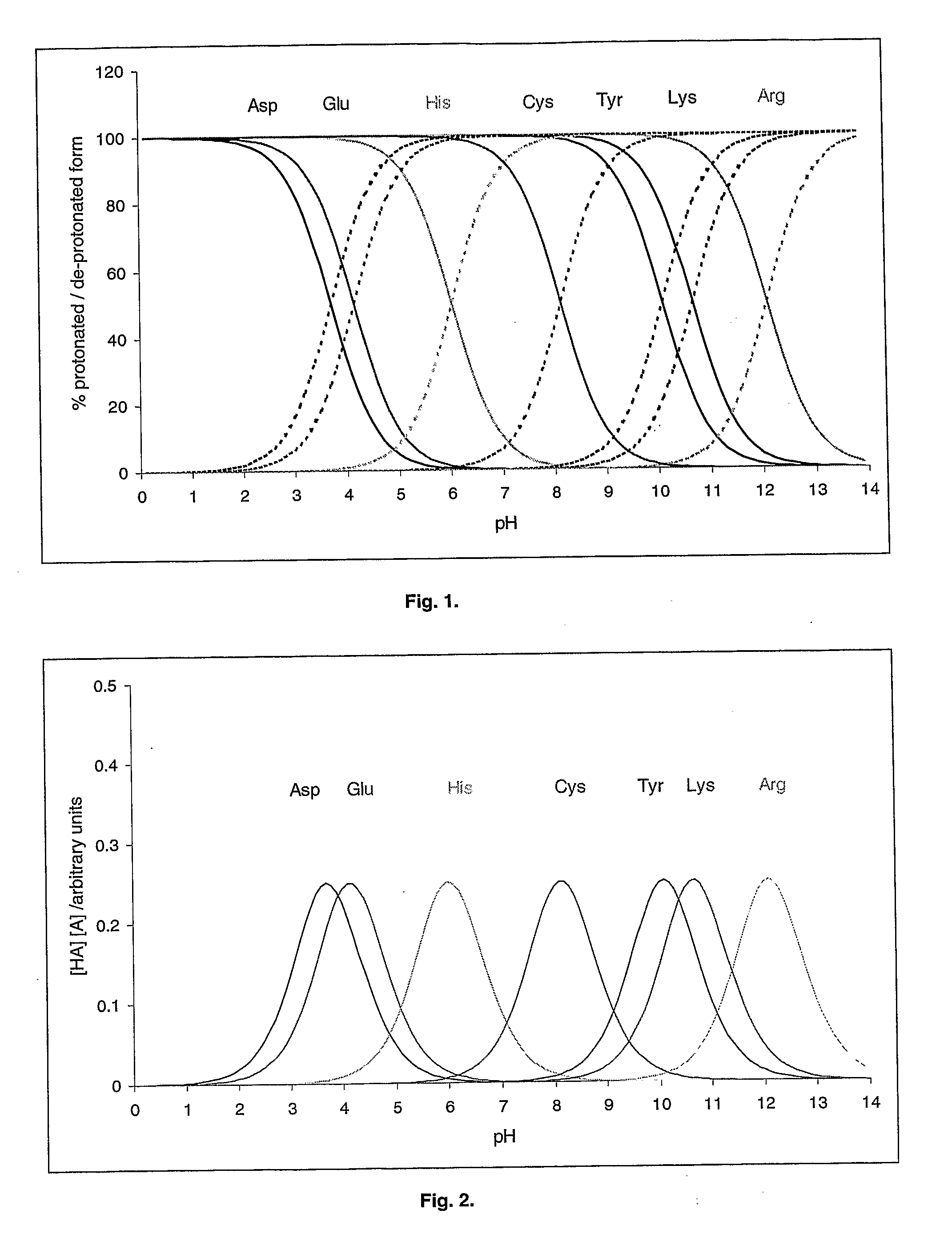
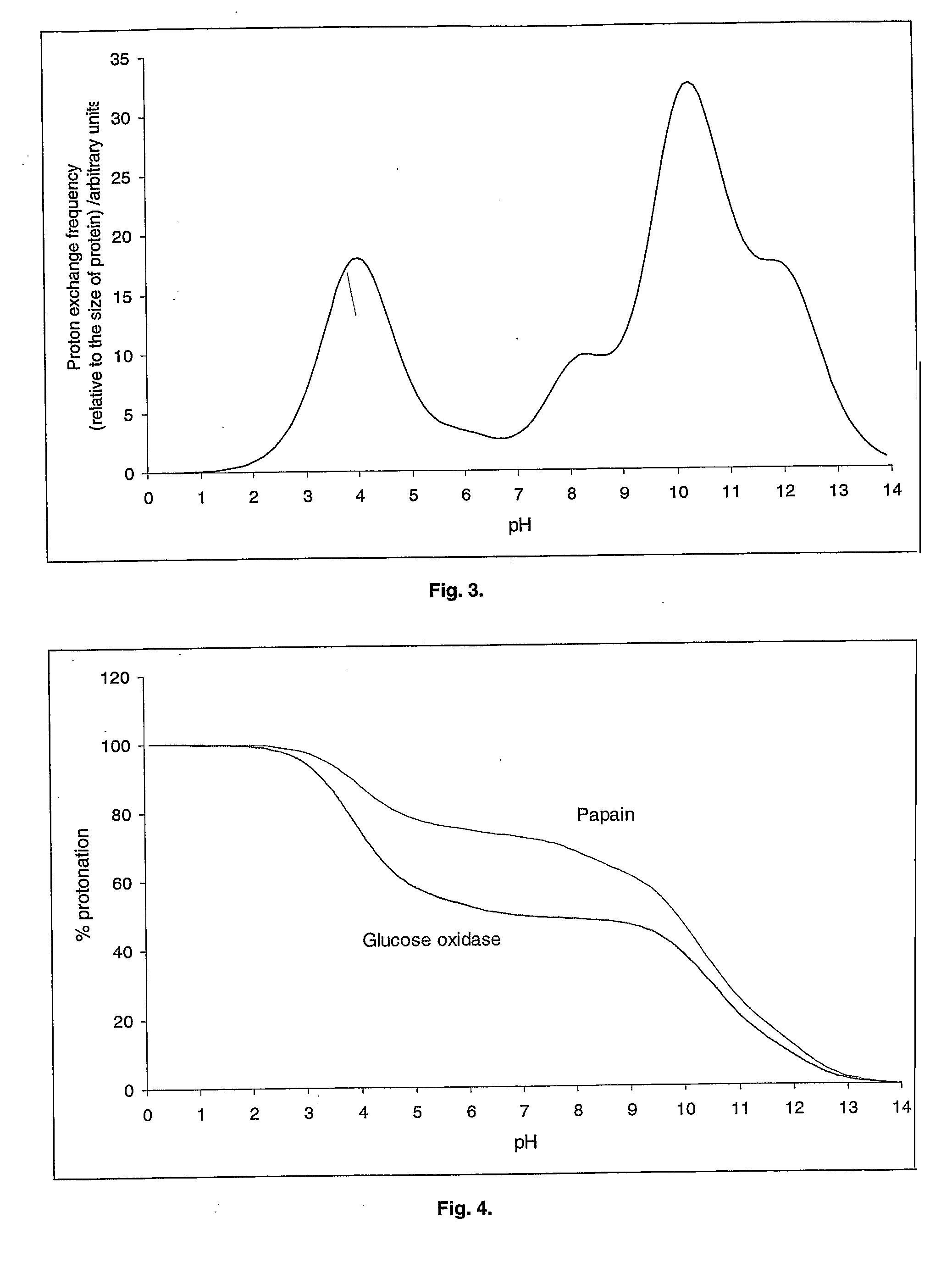
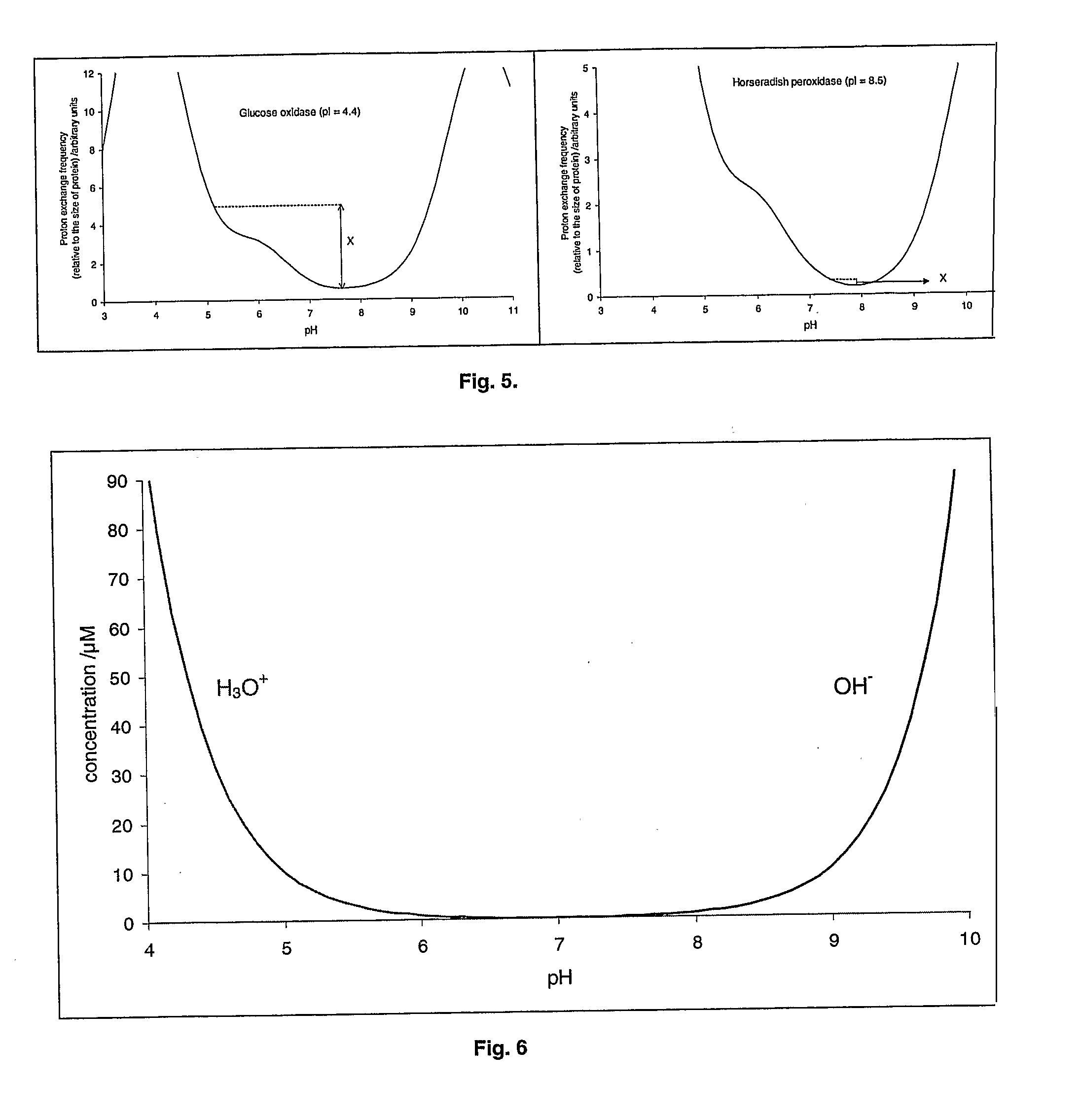
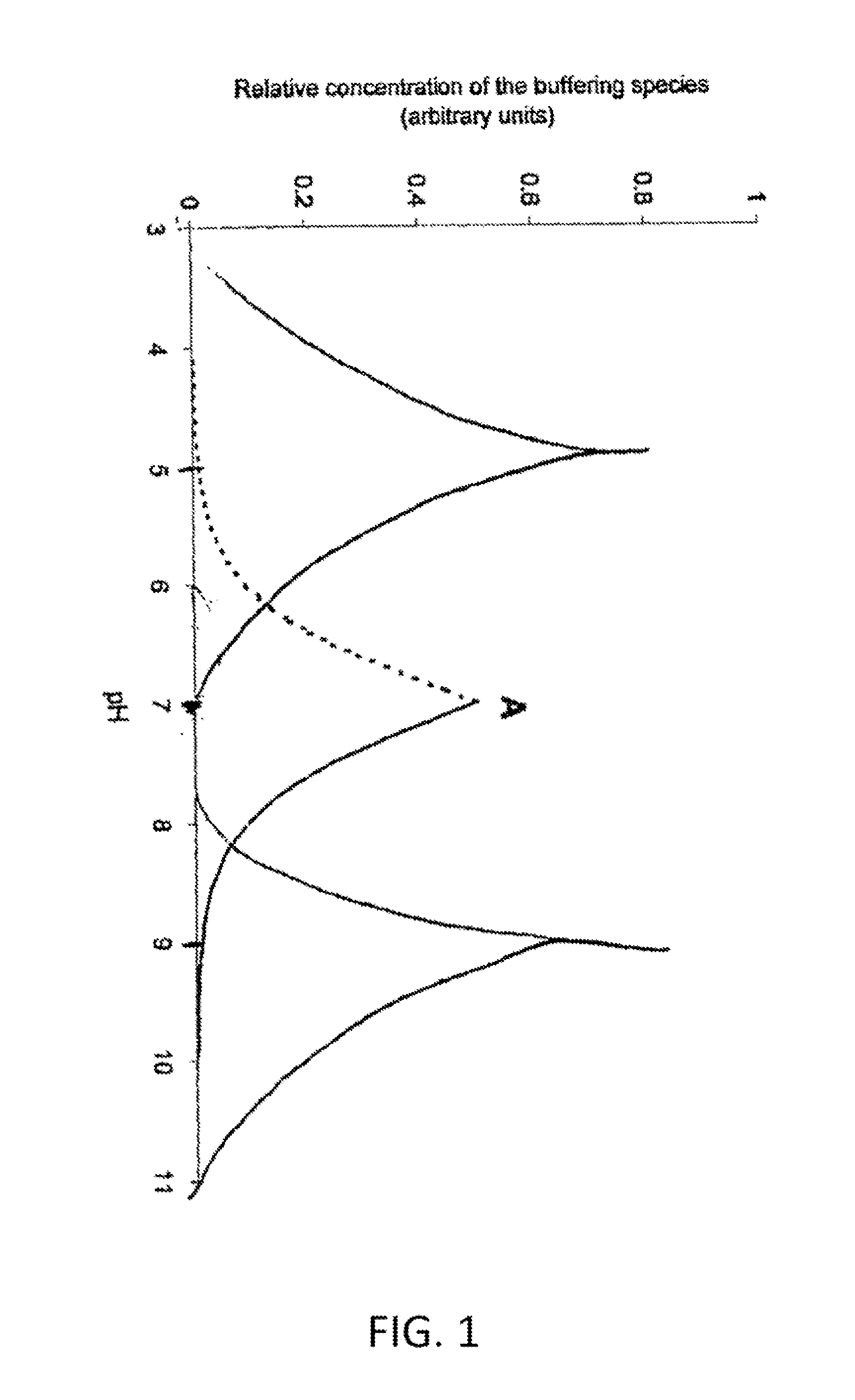
An aqueous system comprises a protein and one or more stabilising agents, characterised in that (i) the one or more stabilising agents have ionisable groups capable of exchanging protons with the protein and with the ionised products of water dissociation; (ii) the ionisable groups include first groups that are positively charged when protonated and uncharged when deprotonated, and second groups that are uncharged when protonated and negatively charged when deprotonated; and (v) the pH of the composition is within a range of protein stability that is at least 50% of the maximum stability of the protein with respect to pH.
Owner:ARECOR LTD
Stabilization of Aqueous Compositions of Proteins with Displacement Buffers
InactiveUS20150071879A1Improve stabilityImproves pH stabilityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsAnalytical chemistryProtein stability
An aqueous composition having increased protein stability is obtained by: a. determining a pH at which the protein has stability at the desired temperature; b. adding to the composition at least one displacement buffer wherein the displacement buffer has a pKa that is at least 1 unit greater or less than the pH of step (a); and c. adjusting the pH of the composition to the pH of step (a); wherein the aqueous composition does not comprise a conventional buffer at a concentration greater than about 2 mM and wherein the conventional buffer has a pKa that is within 1 unit of the pH of step (a).
Owner:ARECOR LTD
Methods and systems for increasing protein stability
InactiveUS20130129727A1High expressionEasy to purifyBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsSerum protein albuminHalf-life
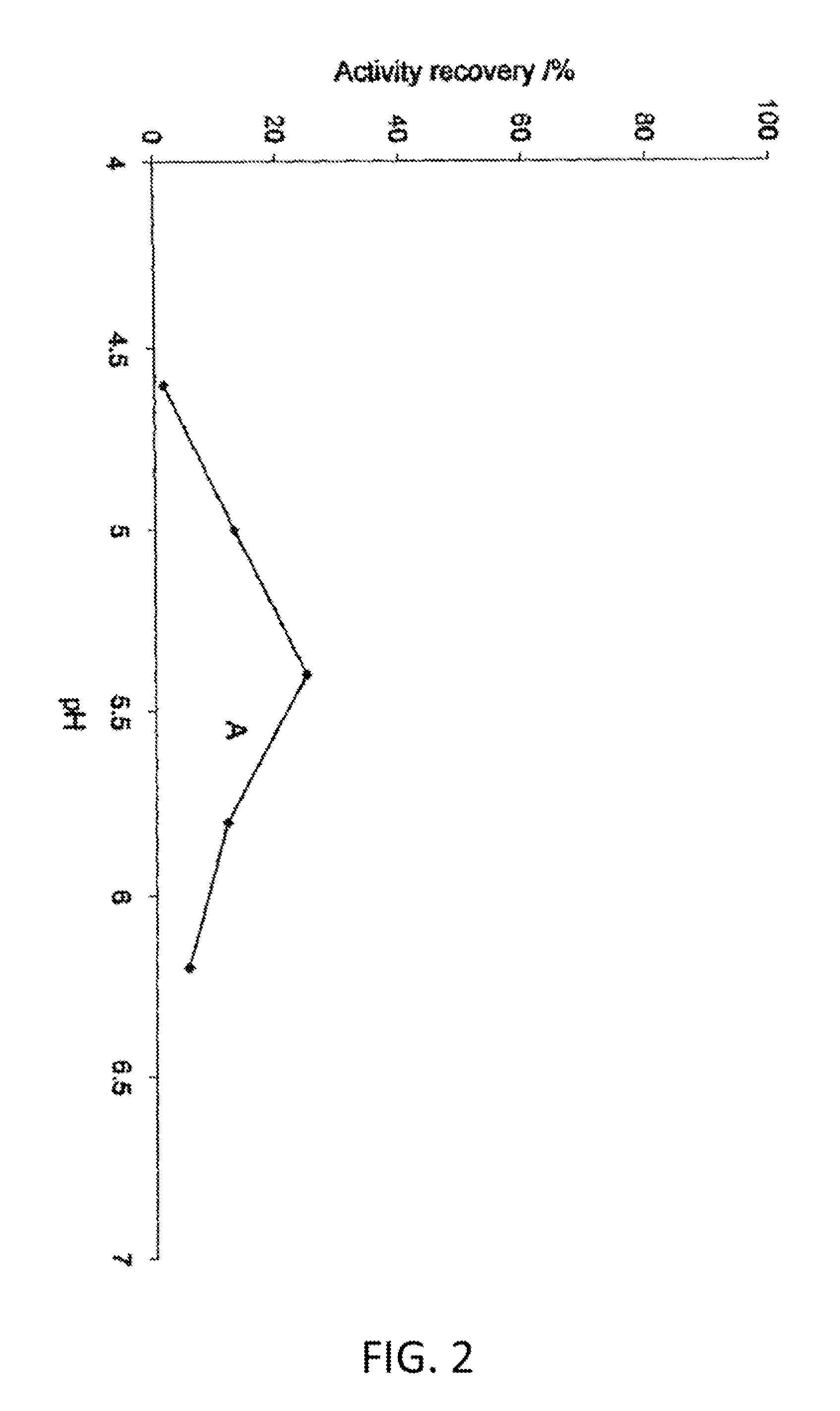
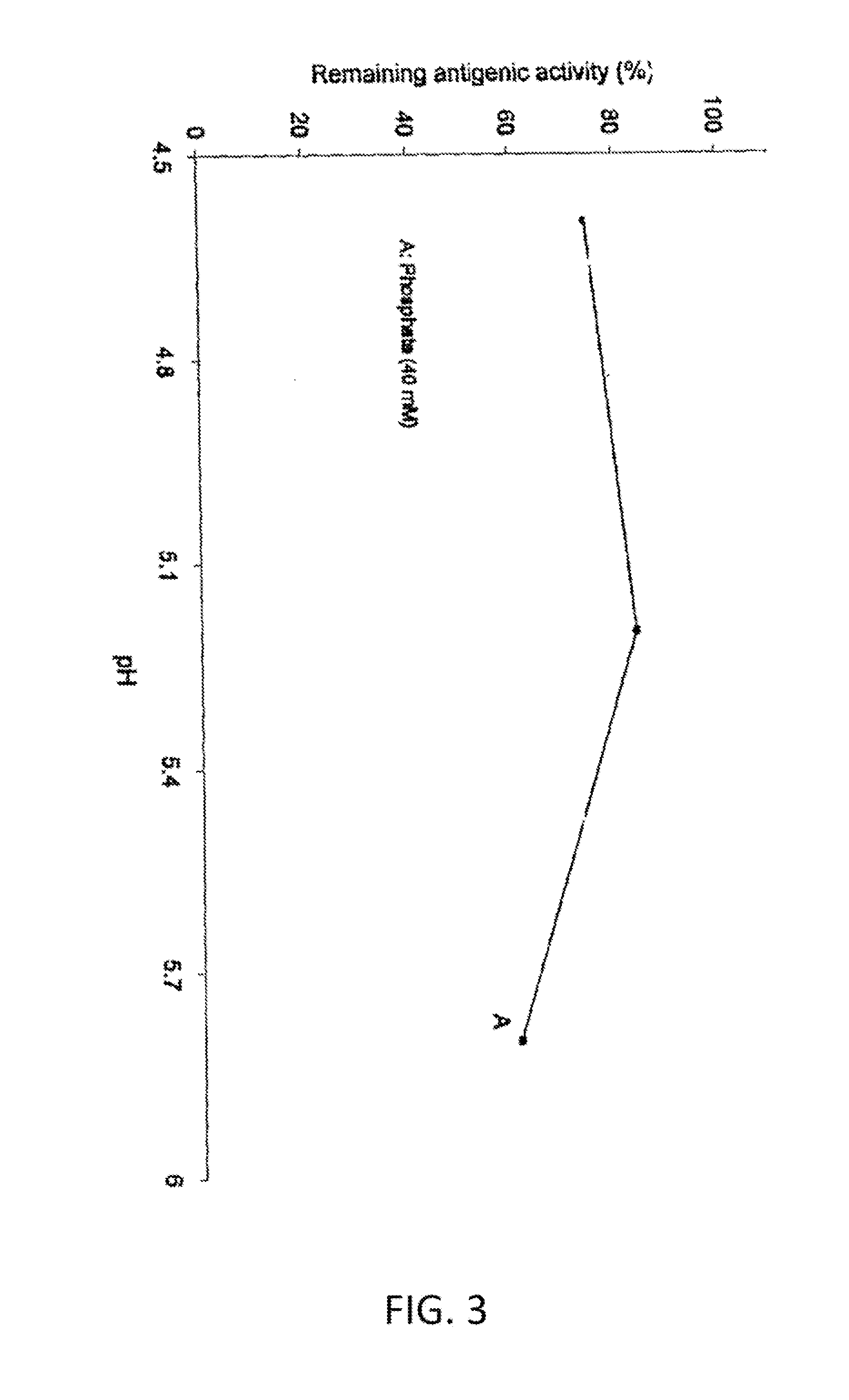
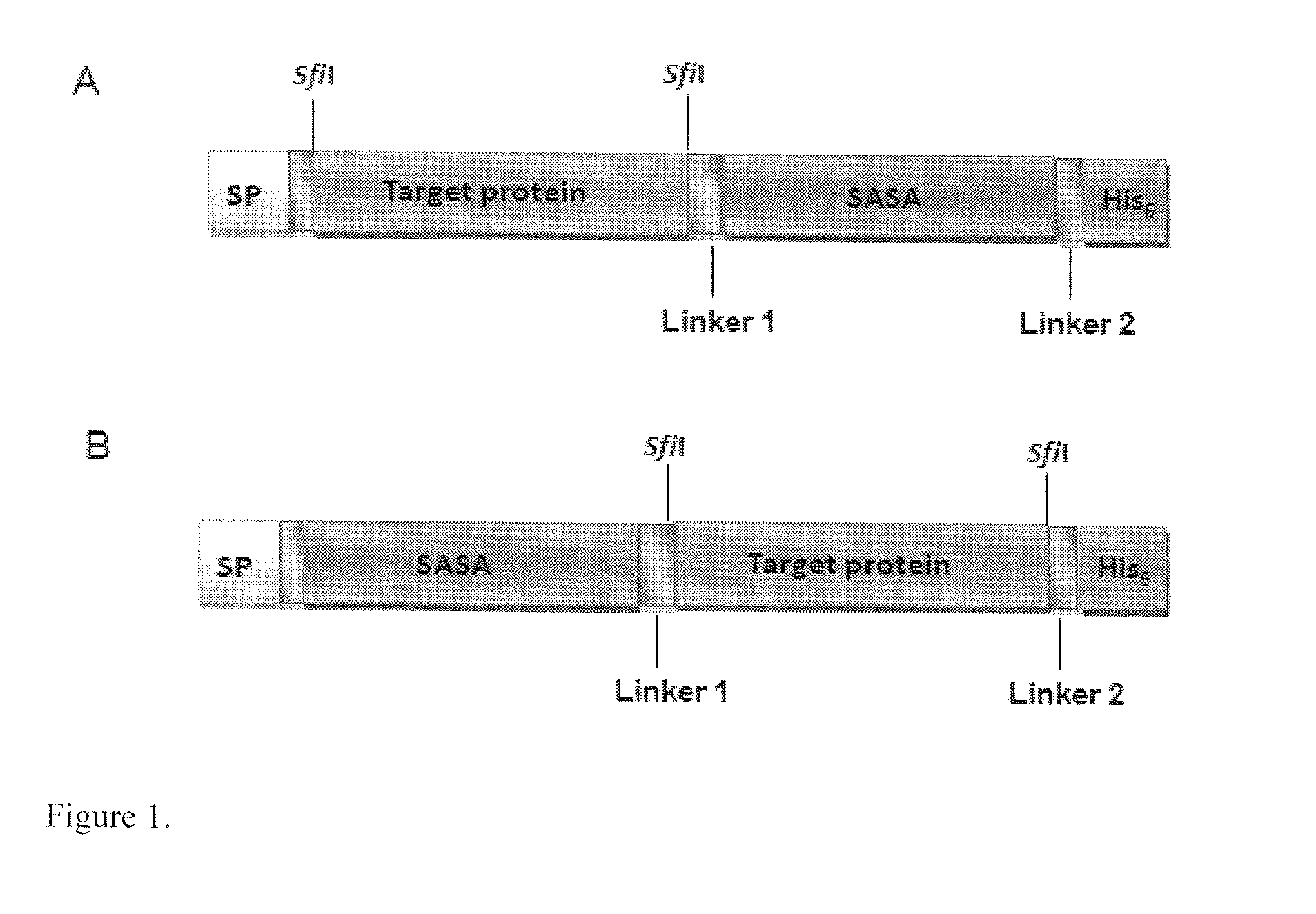
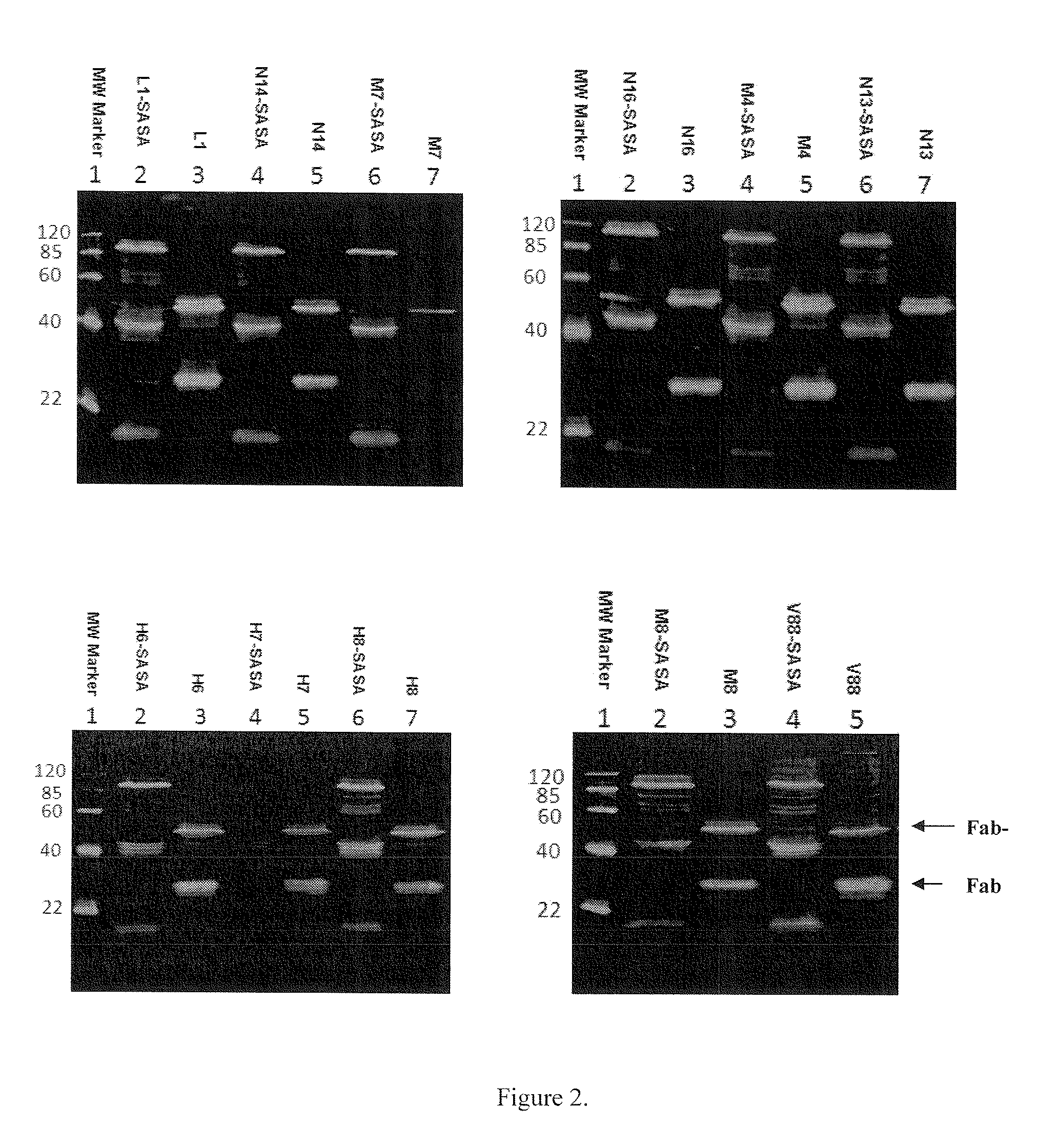
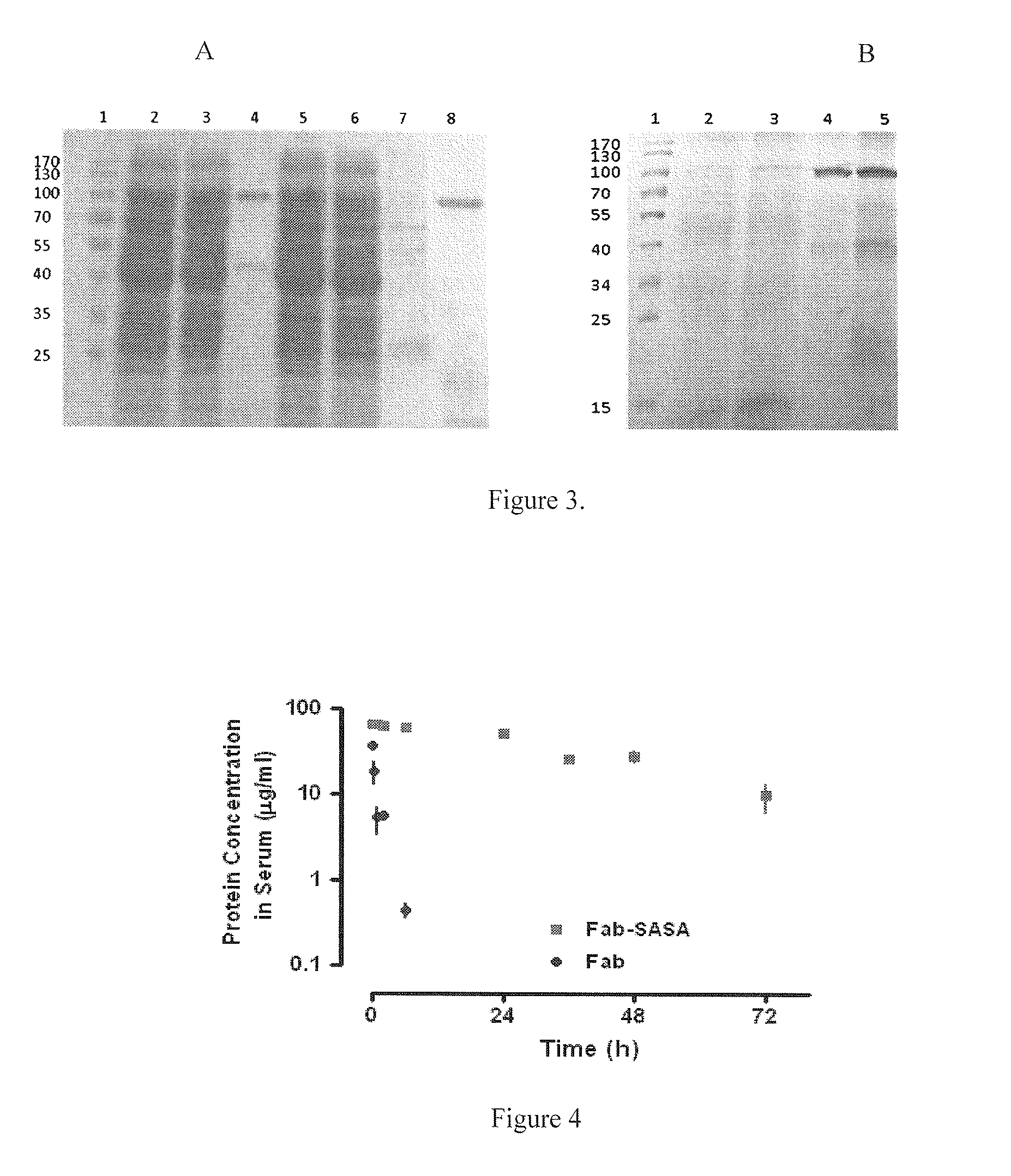
Methods and systems for increasing stability of a target polypeptide in a serum are described. The methods and systems utilize a fusion protein comprising a single-domain antibody against a serum albumin (SASA), the target polypeptide and optionally a linker. The fusion protein has a significantly prolonged serum half life in comparison with the target polypeptide alone. The SASA fusion tag also facilitates the expression and purification of the fusion protein. This allows direct in vivo screening or utilization of the target polypeptide for its biological activity or efficacy regardless of its intrinsic serum half life, which has significantly increased the number of candidates for the development of novel protein based diagnosis or treatment.
Owner:NANJING GENSCRIPT BIOTECH CO LTD
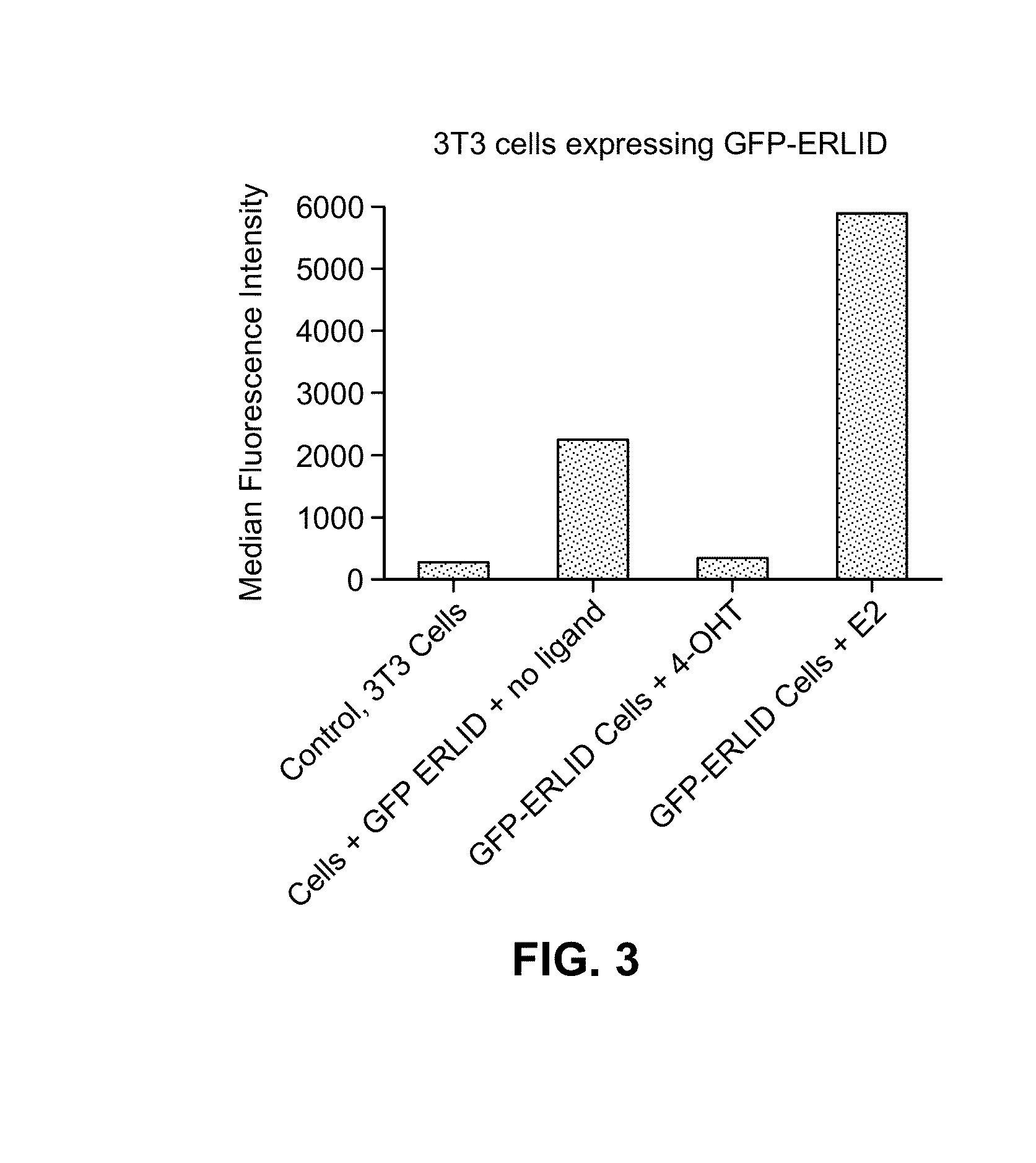
Estrogen-receptor based ligand system for regulating protein stability
Disclosed herein are systems, methods and compositions for rapidly and reversibly destabilizing a target protein in vitro or in vivo, in the presence or absence of a cell-permeable, synthetic molecule or ligand.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
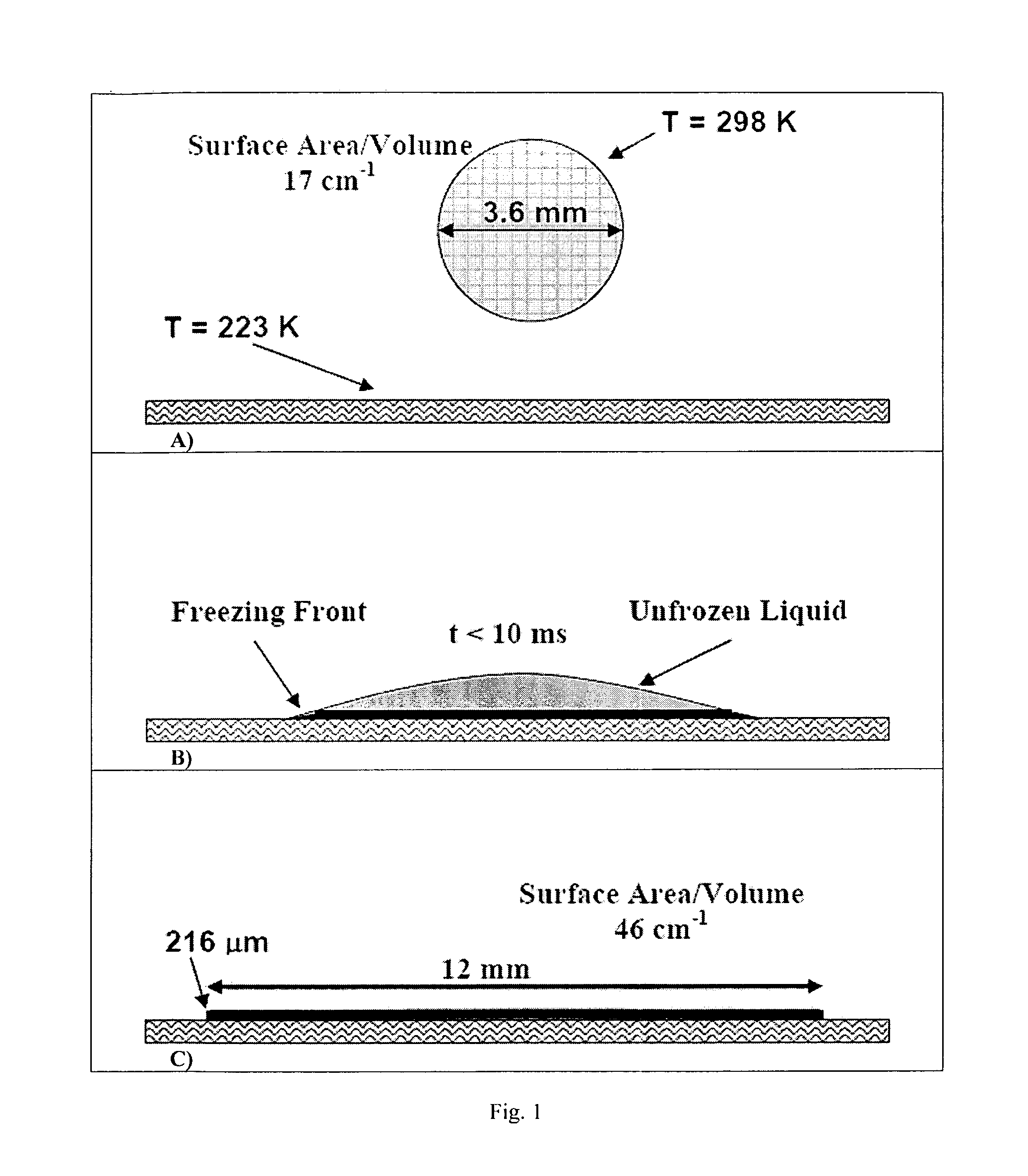
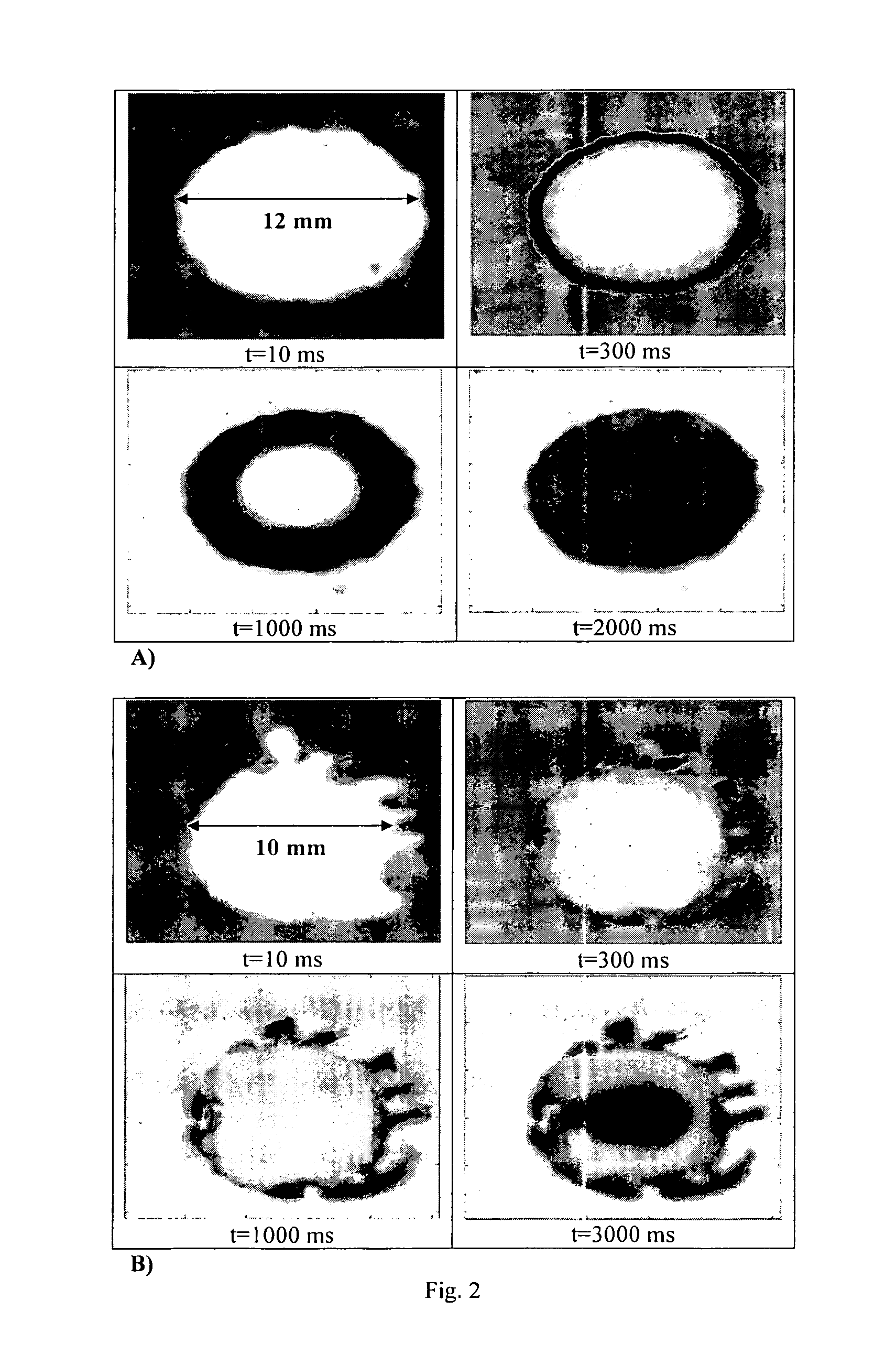
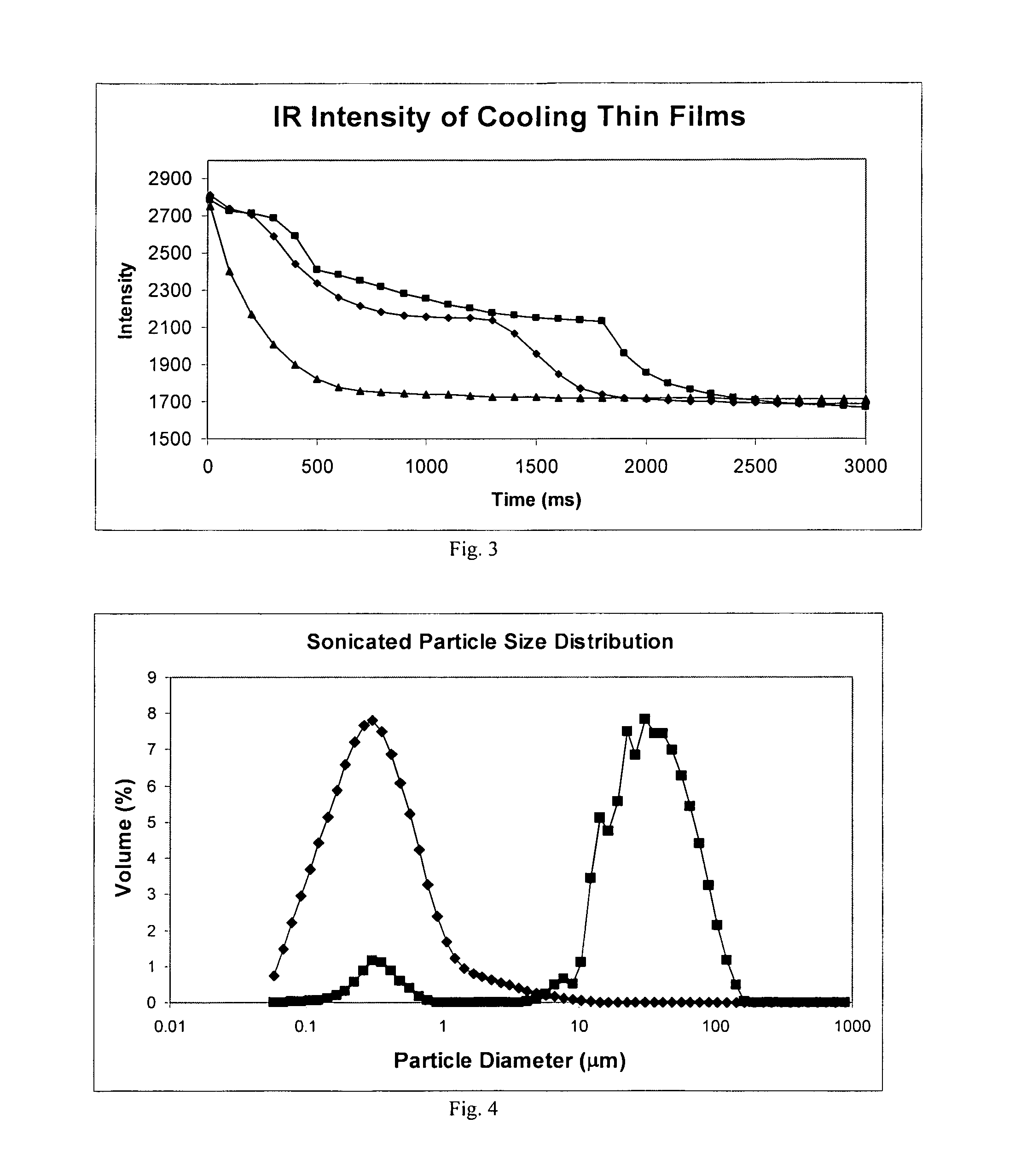
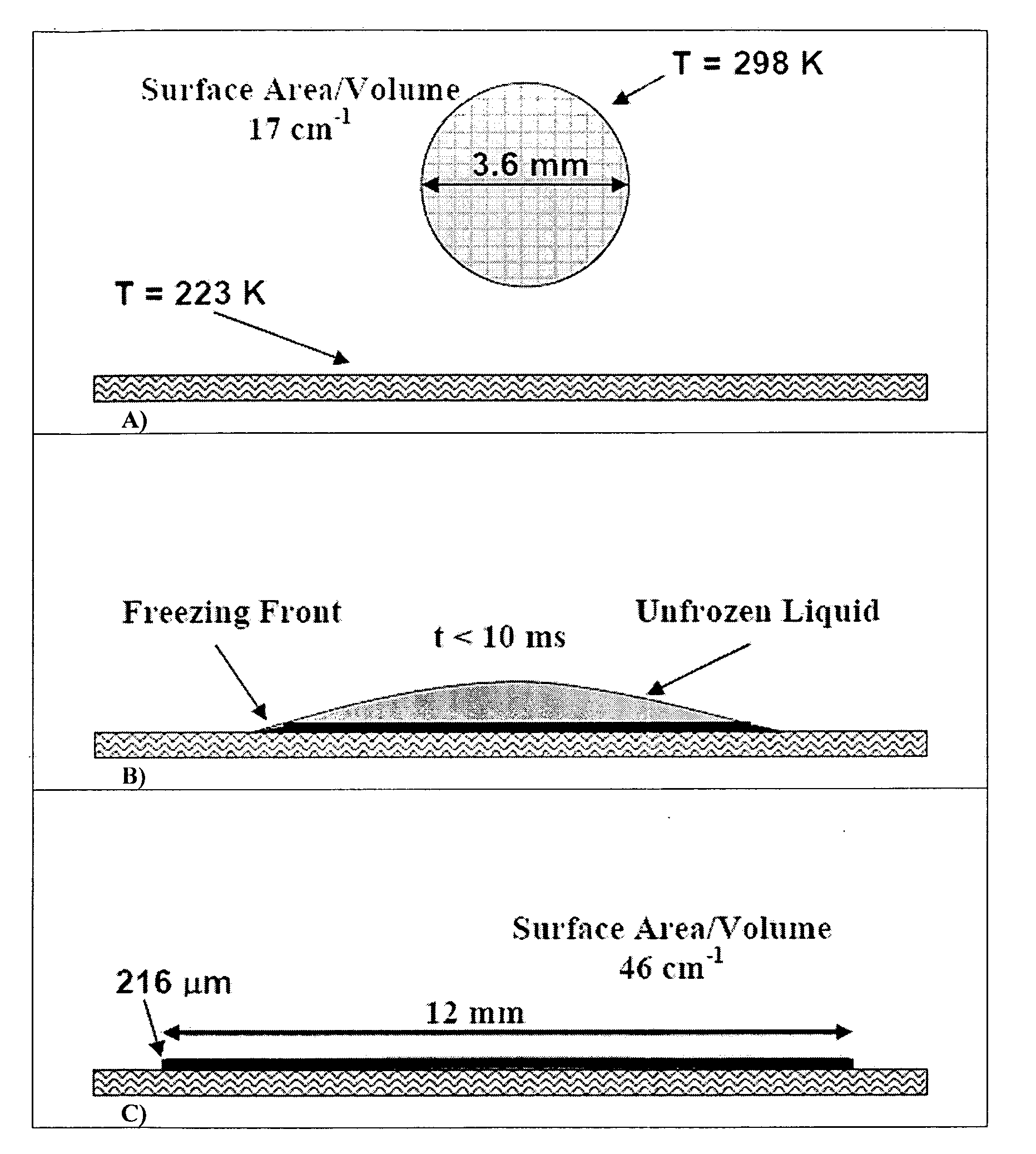
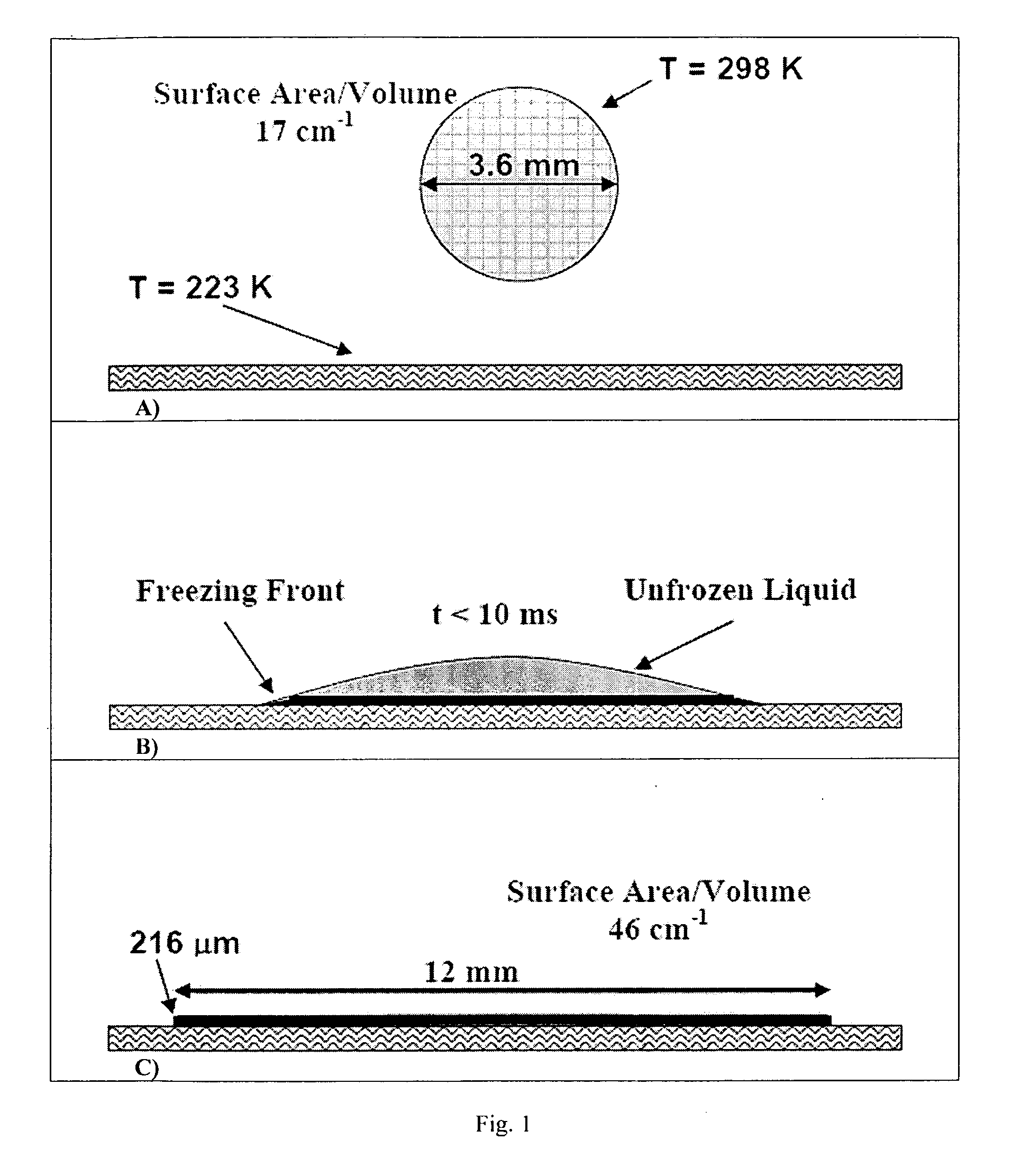
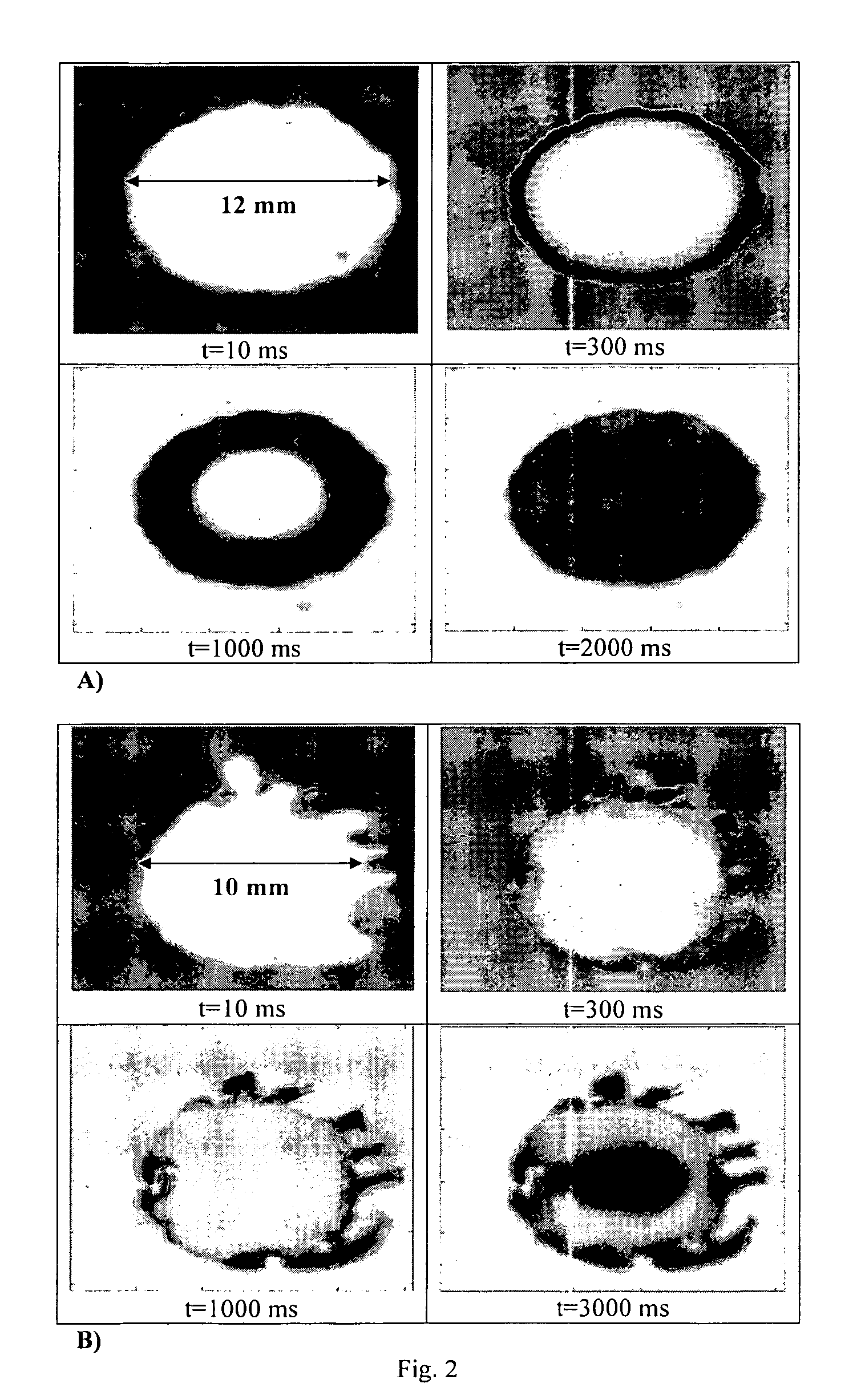
Formation of stable submicron peptide or protein particles by thin film freezing
ActiveUS8968786B2Simple and efficient and robust processPowder deliveryNervous disorderVapor liquidMicrometer
The present invention includes compositions and methods for preparing micron-sized or submicron-sized particles by dissolving a water soluble effective ingredient in one or more solvents; spraying or dripping droplets solvent such that the effective ingredient is exposed to a vapor-liquid interface of less than 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 200, 400 or 500 cm−1 area / volume to, e.g., increase protein stability; and contacting the droplet with a freezing surface that has a temperature differential of at least 30° C. between the droplet and the surface, wherein the surface freezes the droplet into a thin film with a thickness of less than 500 micrometers and a surface area to volume between 25 to 500 cm−1.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Combinations of therapeutic agents for treating melanoma
ActiveUS9408885B2Less side effectsRemarkable effectHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsCarboplatinDocetaxel
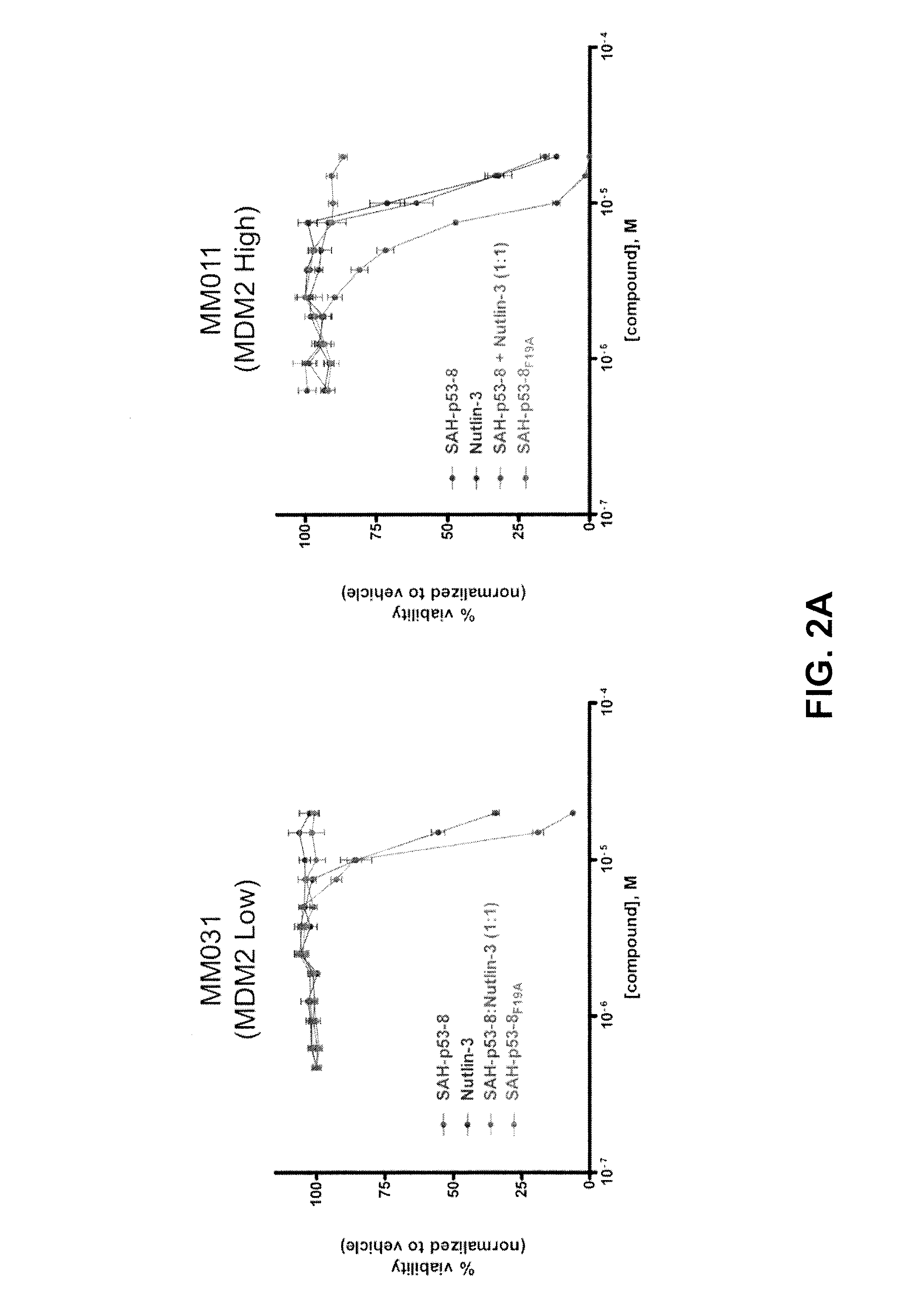
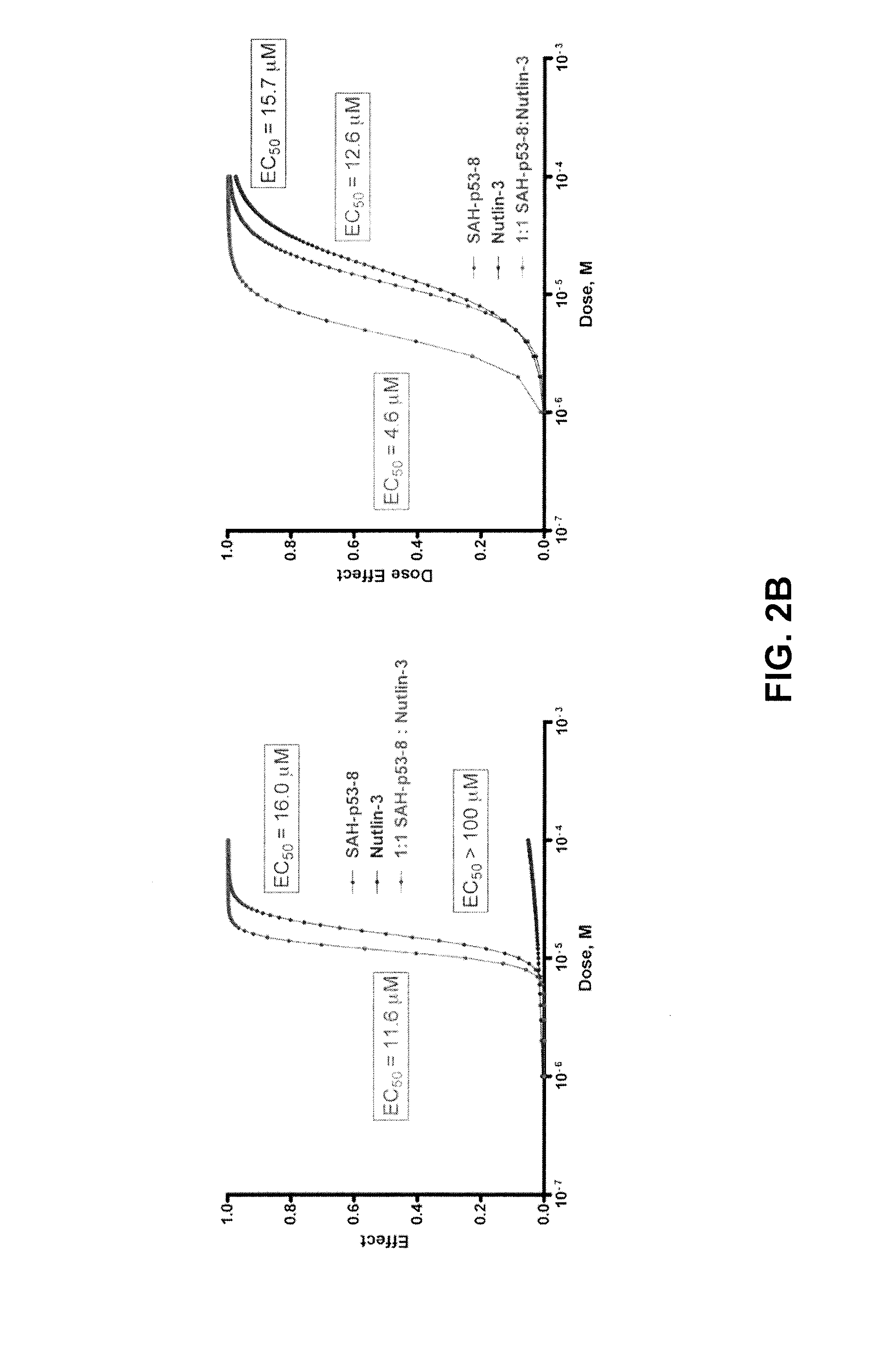
The present disclosure relates to the field of oncology, more particularly to the field of melanoma. Provided are methods of treating melanoma, particularly advanced cutaneous melanoma, with a combination of pharmaceutical agents comprising MDM4-specific antagonists (such as an inhibitor of the MDM4-p53 interaction or a molecule that decreases MDM4 protein stability) or MDM4-MDM2 dual inhibitors (i.e., molecules that disrupt the interactions between p53 and MDM2 and p53 and MDM4) and one or more chemotherapeutic agents such as for example alkylating agents (i.e., Dacarbazine (DITC) or melphalan), alkylating-like agents (i.e., cisplatin or carboplatin) or mitotic inhibitors (taxanes docetaxel or paclitaxel) and PI3K-AKT, B-RAF and MEK inhibitors. Further provided are pharmaceutical formulations of MDM4-specific antagonists (be it an inhibitor of the MDM4-p53 interaction or a molecule that decreases MDM4 protein stability) or MDM4-MDM2 dual inhibitors (i.e., molecules that disrupt the interactions between p53 and MDM2 and p53 and MDM4) and a pharmaceutical formulation of one or more chemotherapeutic agents such as for example alkylating agents (i.e., Dacarbazine (DITC) or melphalan), alkylating-like agents (i.e., cisplatin or carboplatin) or mitotic inhibitors (taxanes docetaxel or paclitaxel) and B-RAF and MEK inhibitors.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Method for testing milk protein stability
The present invention discloses an inspection method of milk protein stability. Said method includes the following steps: preparing sample to be inspected, preheating sample, high-temperature treatment, constant temperature treatment, cooling treatment, making detection and analysis and judging result. Said method can be used for controlling raw material milk quality for processing milk product.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
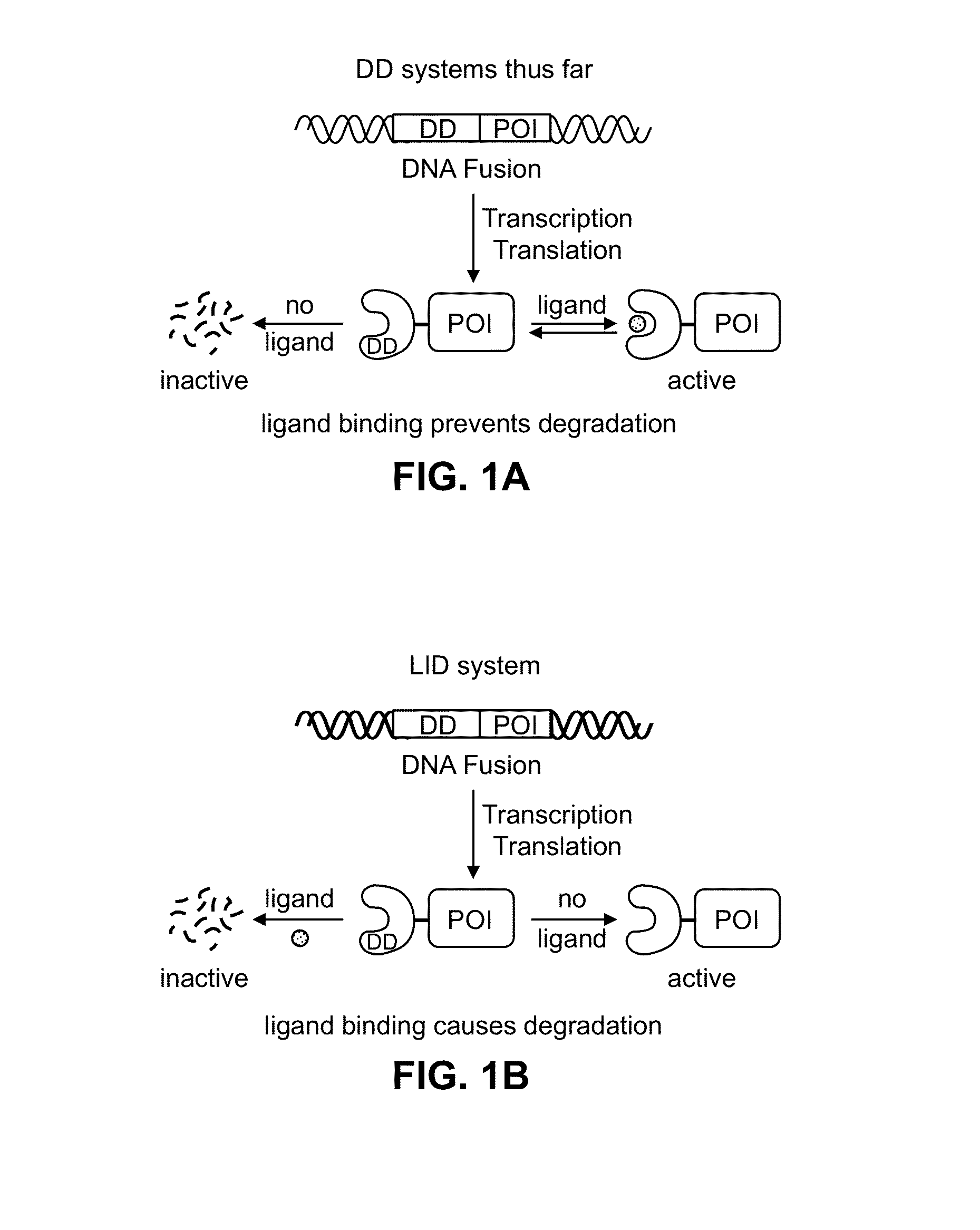
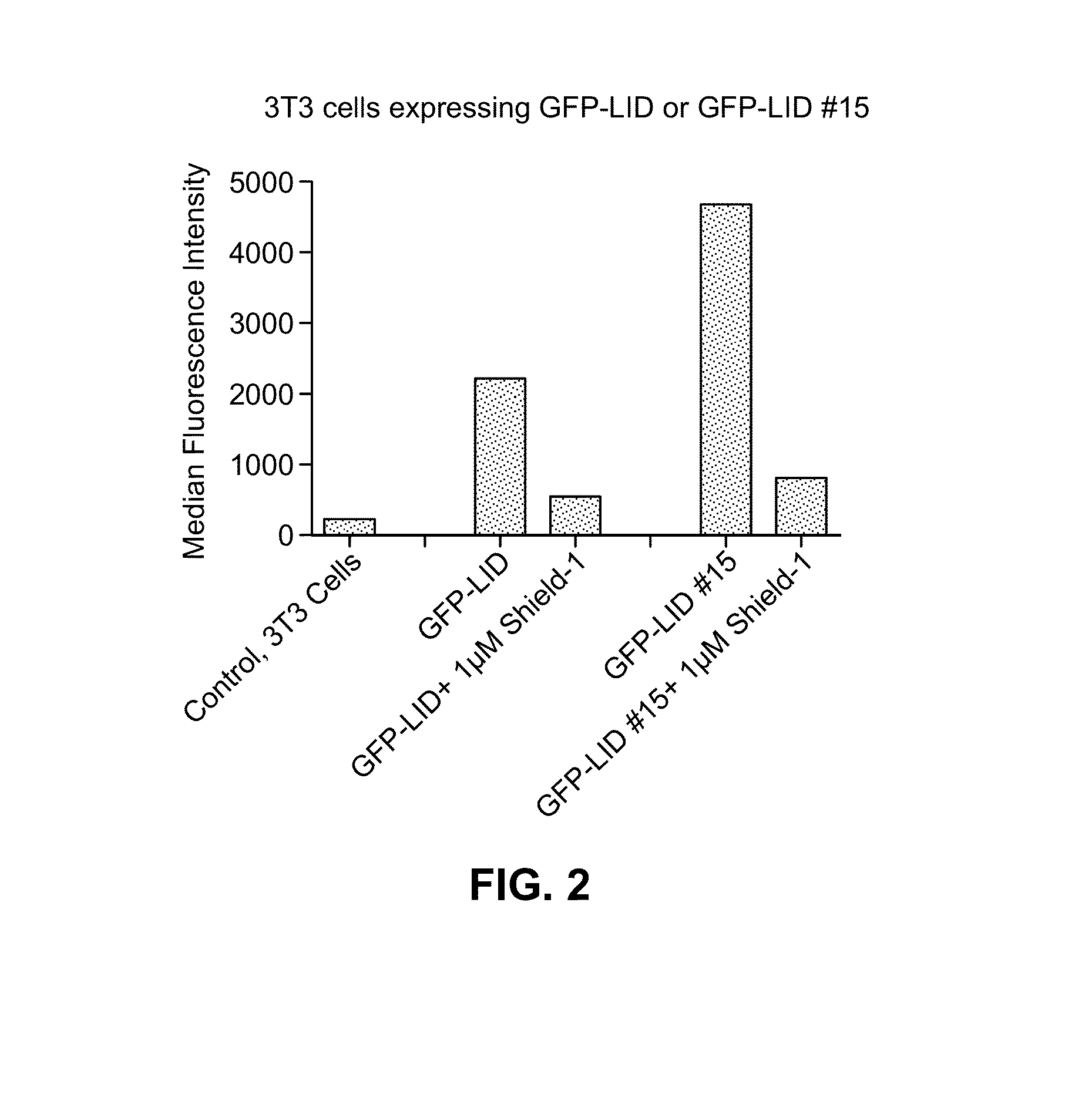
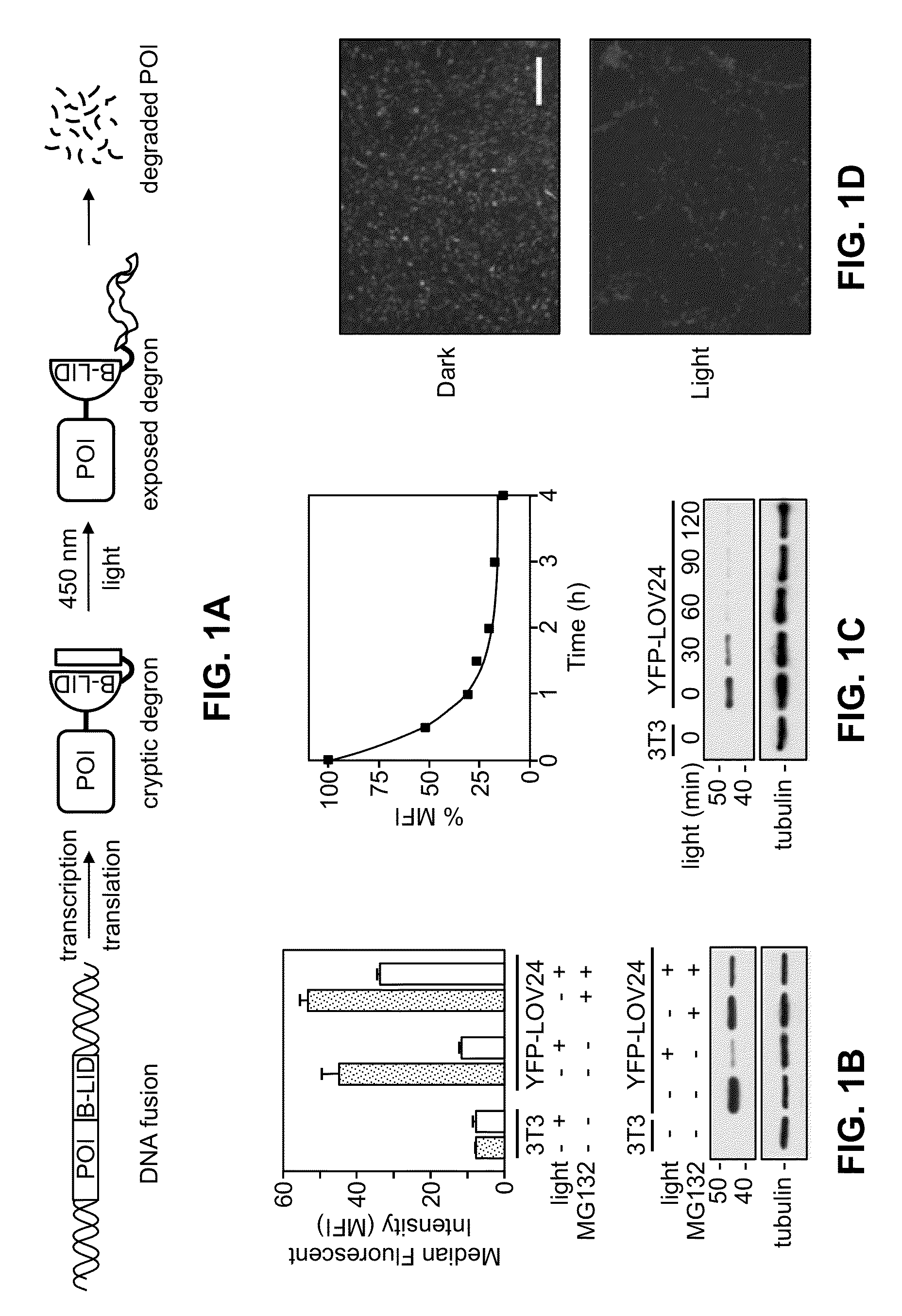
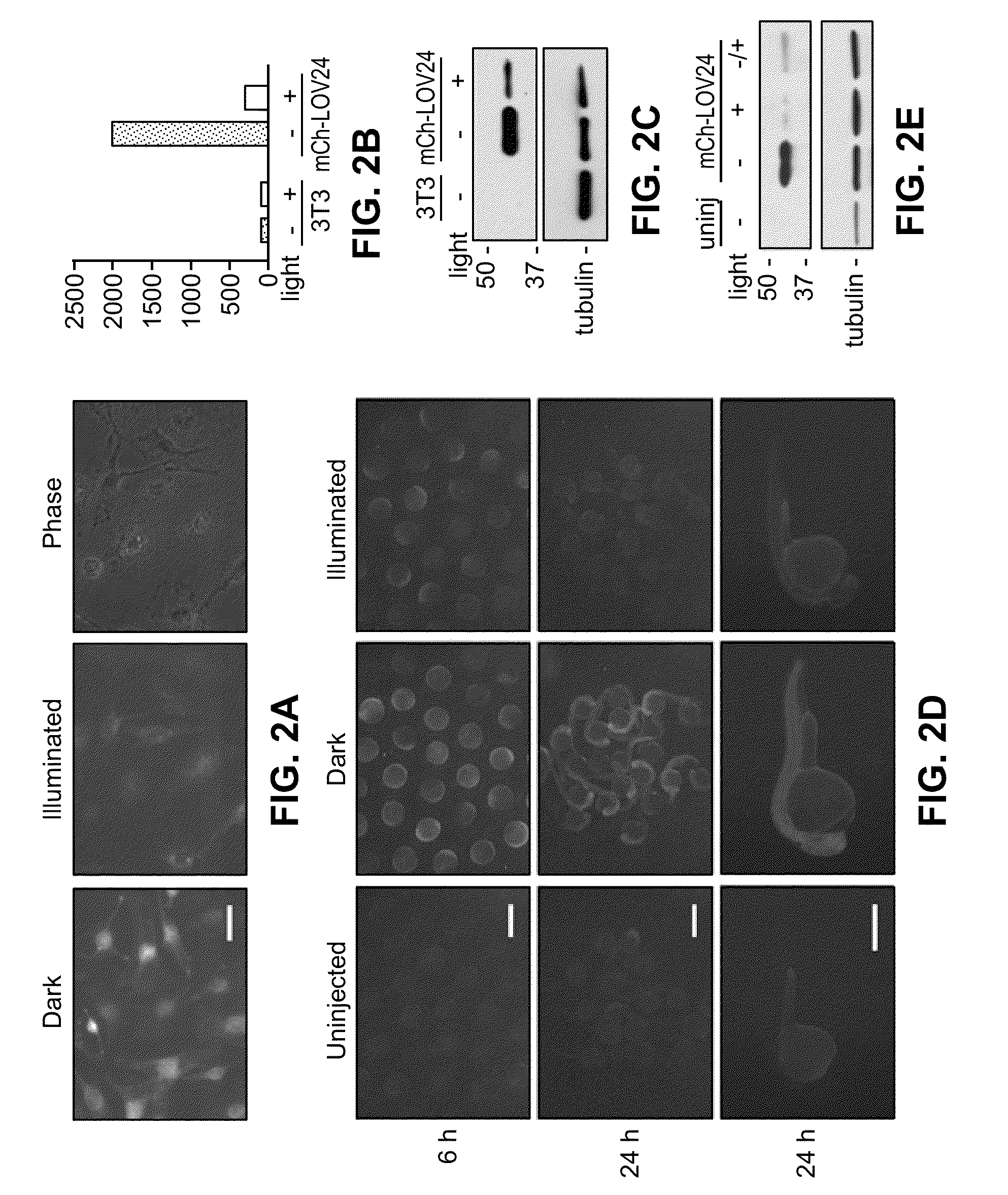
Light-inducible system for regulating protein stability
Disclosed herein are a light-inducible system and method for rapidly and reversibly modulating protein stability and function. This system and method employs conditionally stable protein domains that regulate the degradation of a fusion protein depending upon the presence or absence of a particular light source.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
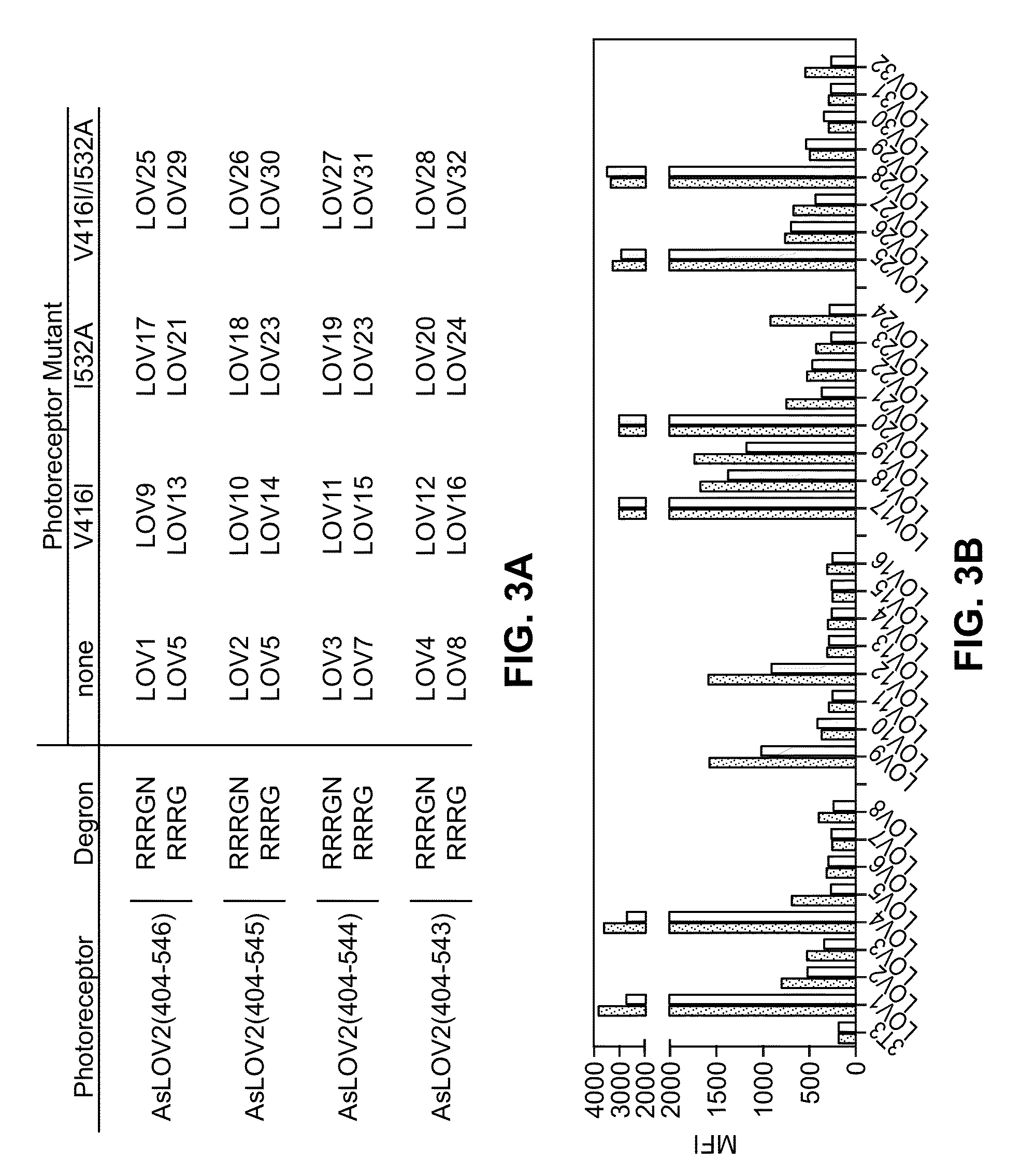
Methods and systems for designing stable proteins
InactiveUS20120265513A1Improve protein stabilityImprove thermal stabilityAnalogue computers for chemical processesProteomicsProtein structureThermophilic organism
Methods and computing systems for generating a protein stability lookup table and a predictive model. These methods and systems are useful for predicting the thermal stability of a protein sequence and for predicting mutations that may enhance the thermal stability of a protein given its amino acid sequence and / or three dimensional structure. The protein stability lookup table and a predictive model are based on a combination and analysis of related protein sequences and, where available, protein structure data, and relative stability data from mesophilic and thermophilic organisms and experimentally determined stability changes of wild type proteins and their mutants.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
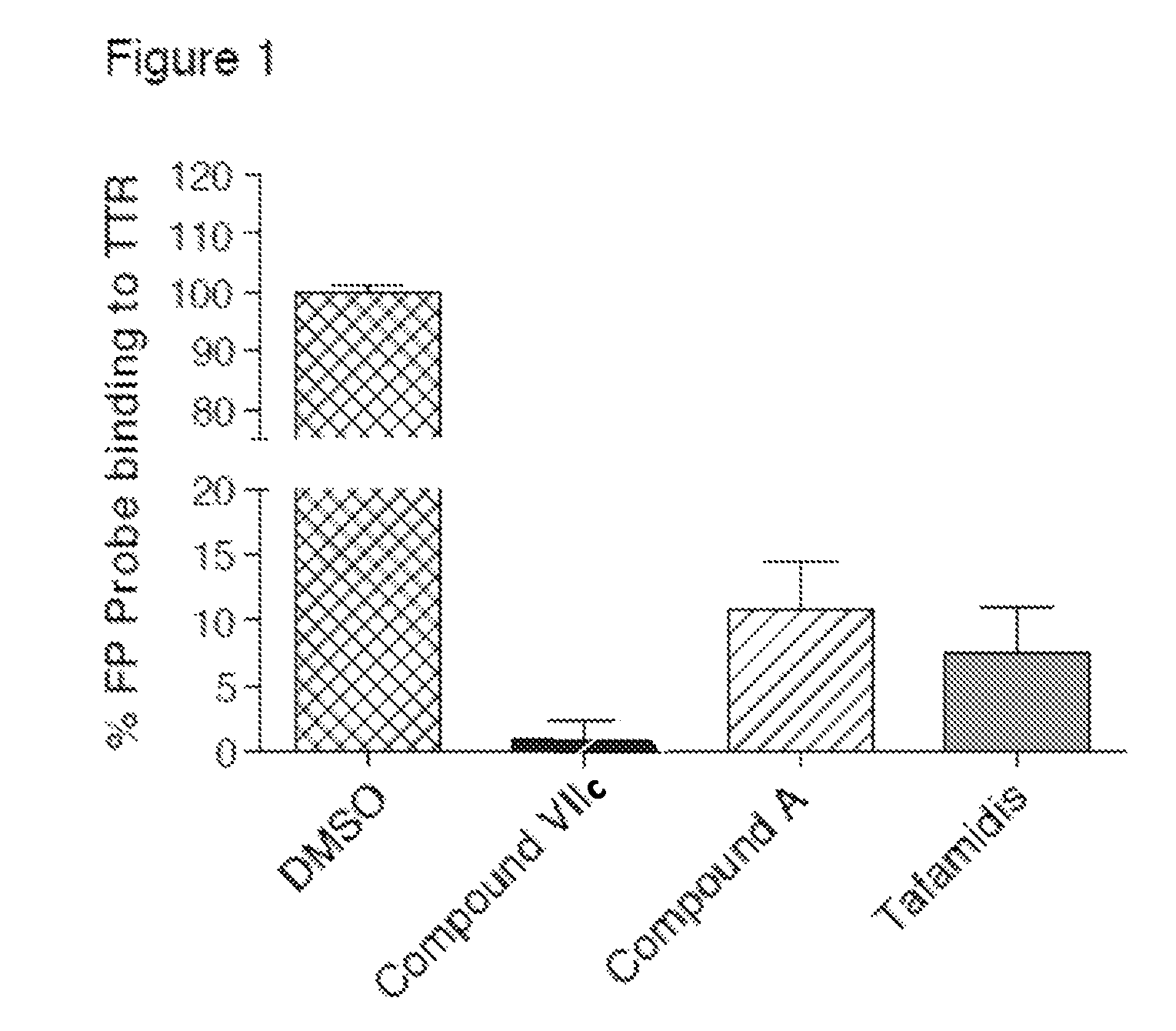
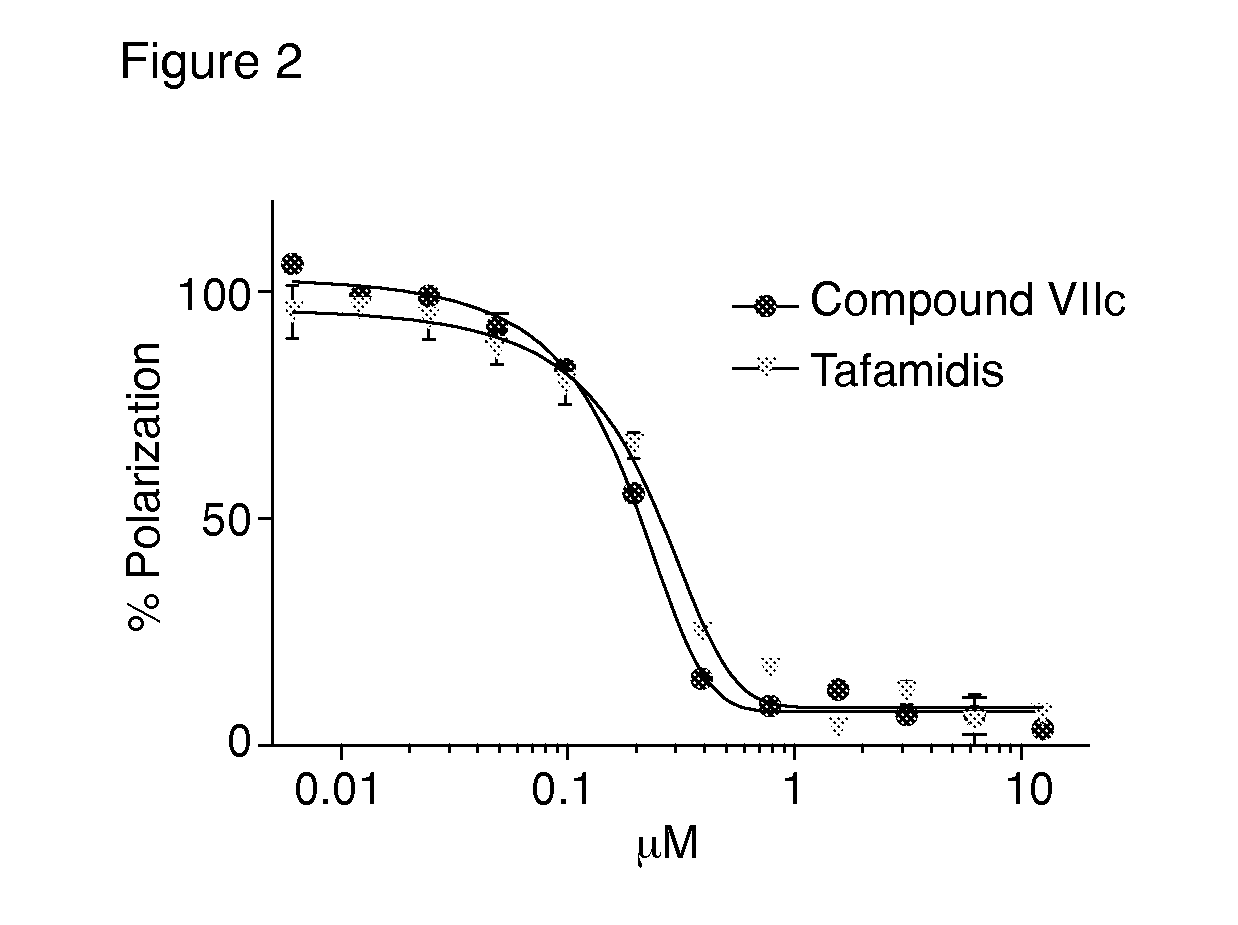
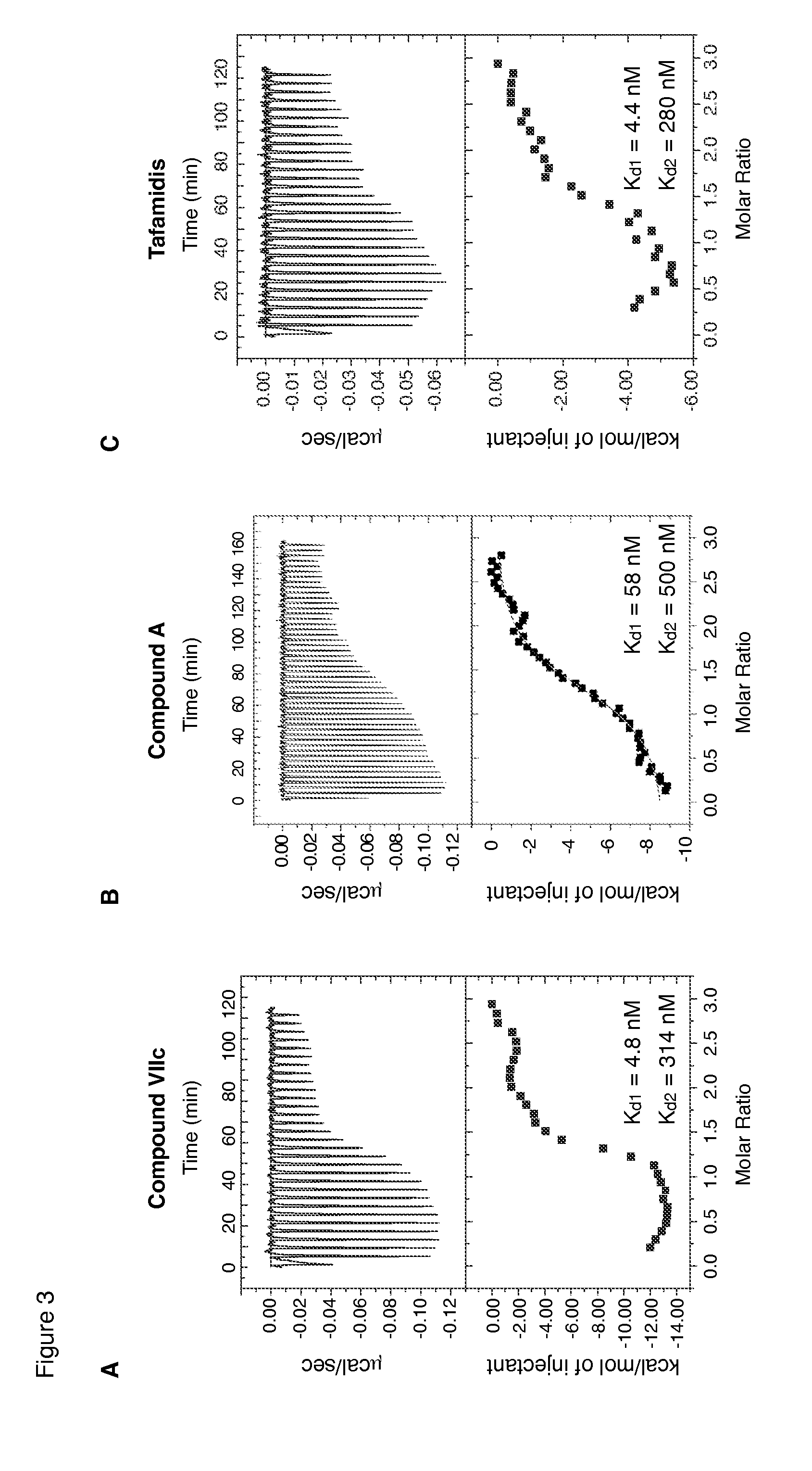
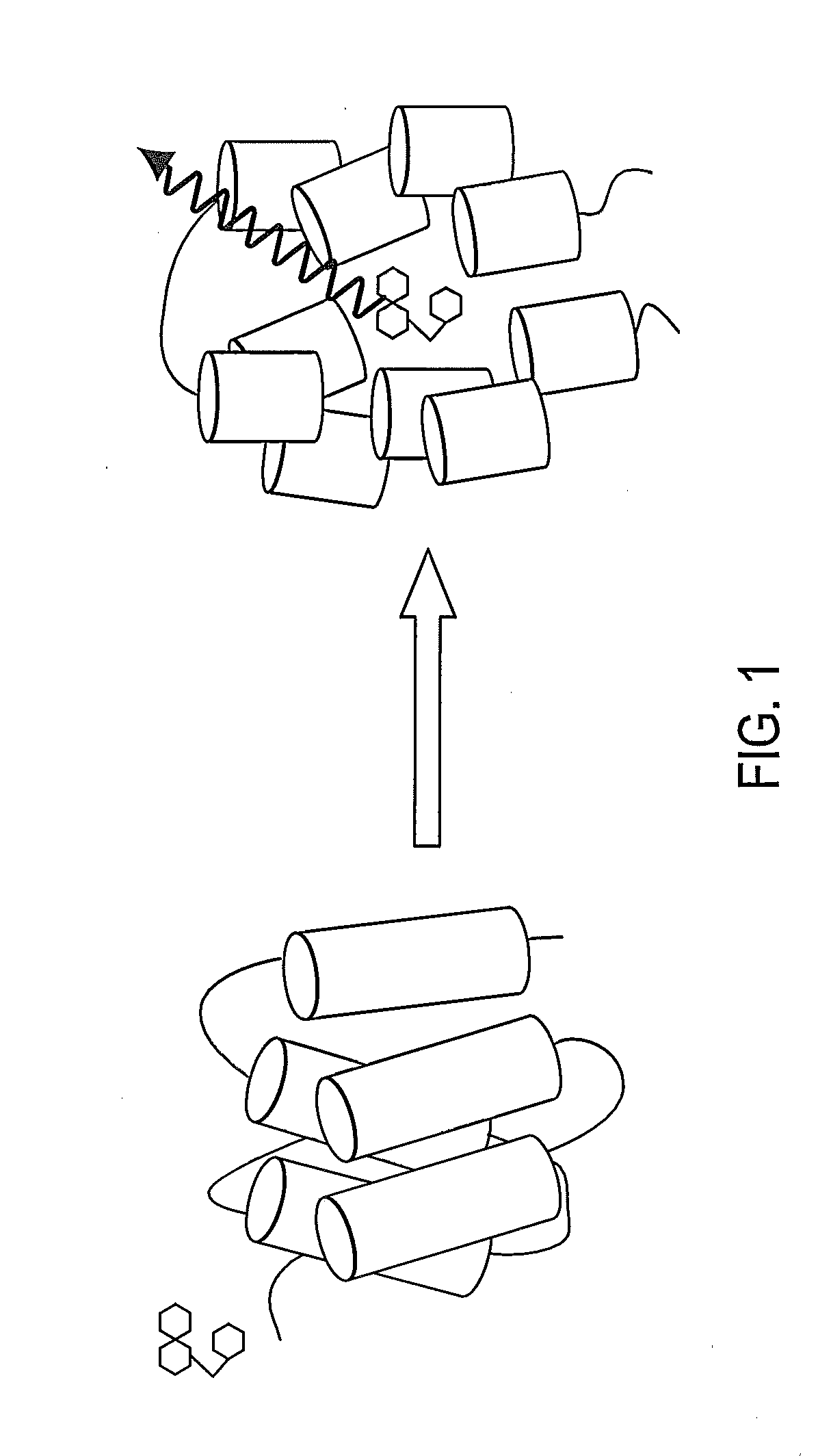
Compounds and compositions that bind and stabilize transthyretin and their use for inhibiting transthyretin amyloidosis and protein-protein interactions
ActiveUS9169214B2Improve stabilityDecreasing aggregate formationOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderProtein targetOrganic chemistry
Disclosed herein are compounds and compositions thereof which find use in increasing stability of proteins particularly proteins that tend to misfold and form aggregates. Also provided herein are methods for using these compounds and compositions for increasing stability of proteins and thereby decreasing aggregate formation by these proteins. Also disclosed herein are heterobifunctional compounds that include a TTR binding compound connected to a targeting moiety via a linker, for use in disrupting PPIs of a target protein.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
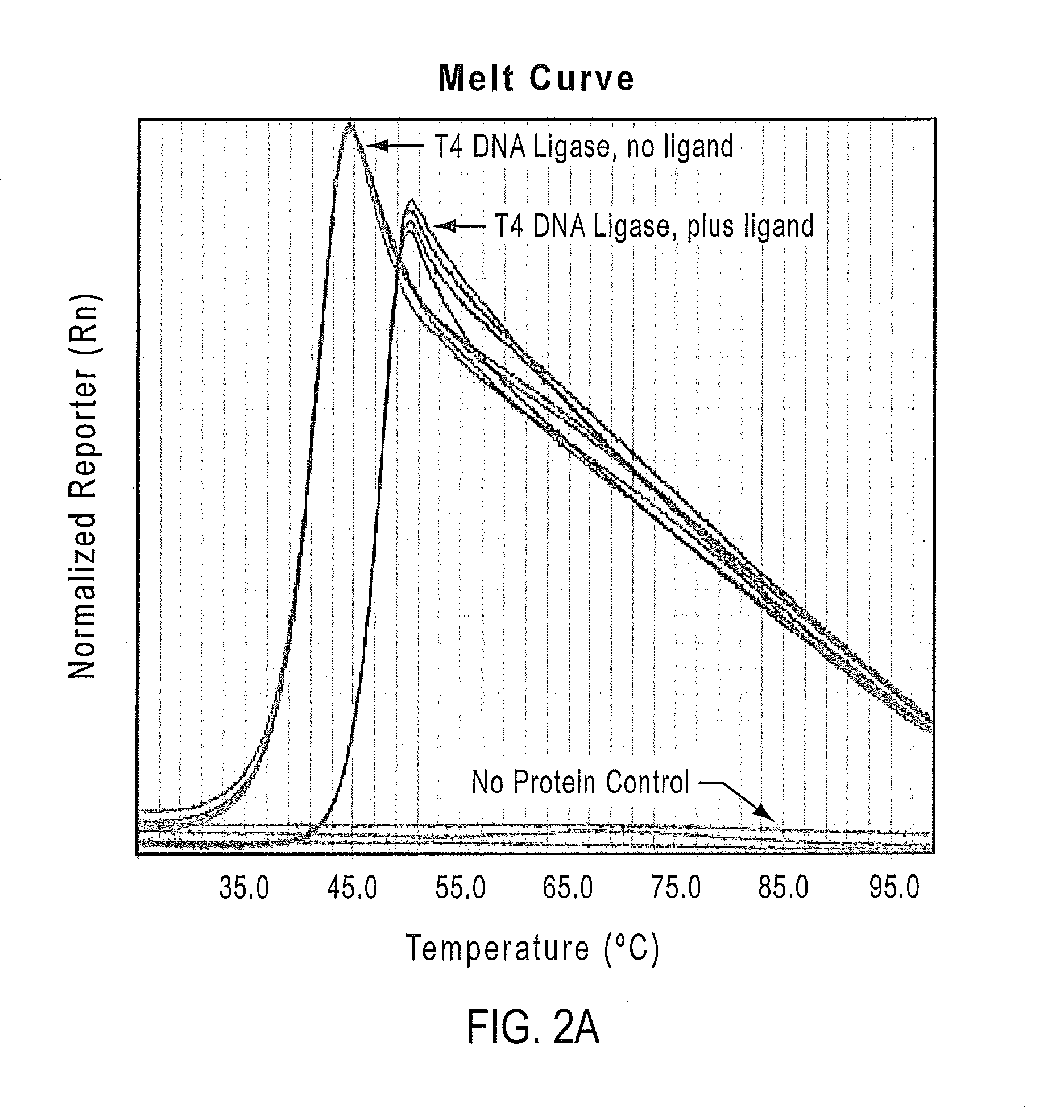
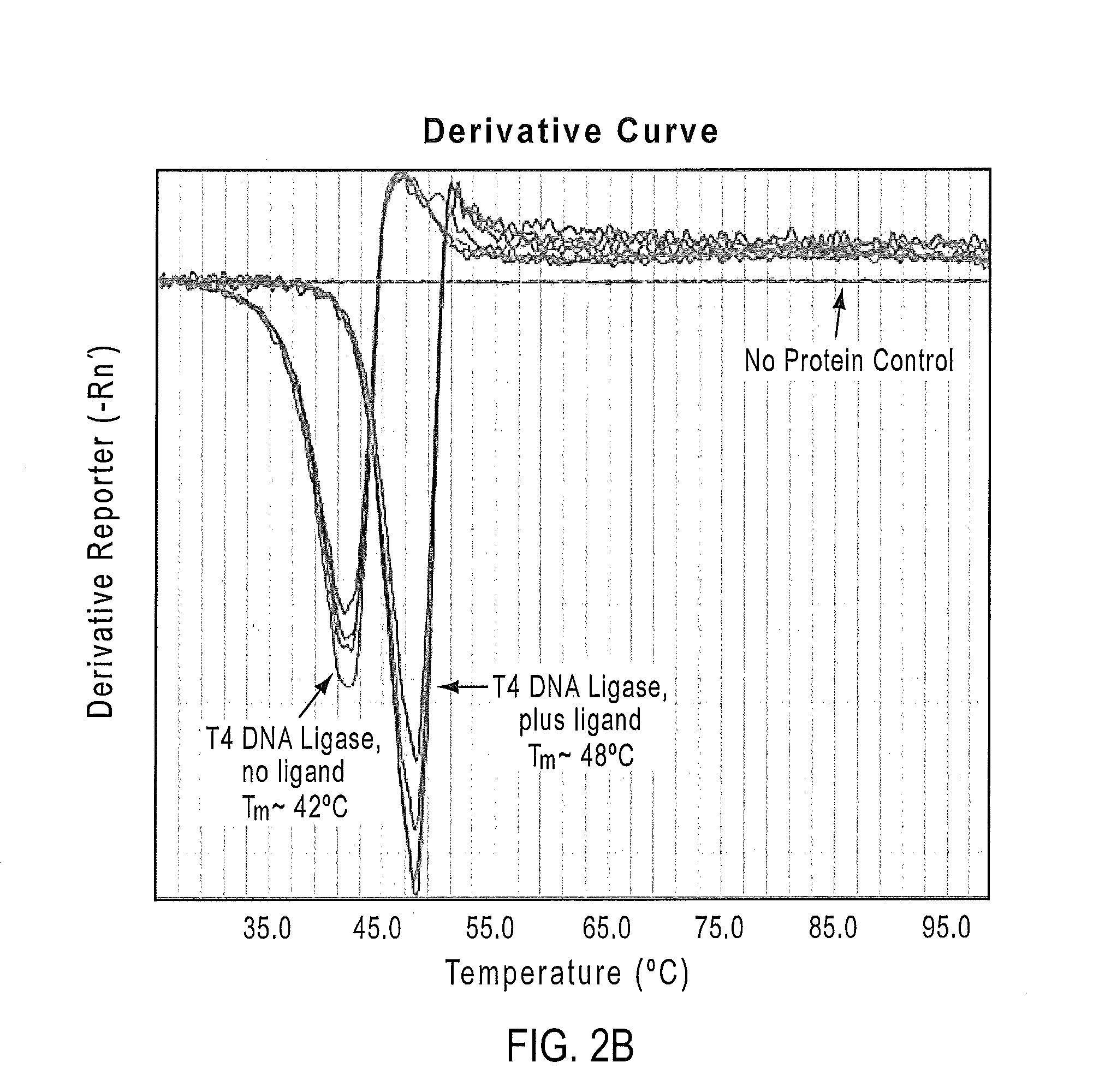
Methods for dye selection for protein melt temperature determinations
ActiveUS20140315190A1Methine/polymethine dyesMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceMelt temperature
According to the present teachings, compositions, kits, and methods for protein melt analysis are provided that utilizing one or more fluorophore dyes. In some embodiments, a method comprises preparing a sample by mixing at least one protein with two or more dyes, and applying a controlled heating, while recording the fluorescence emission of the sample. The methods can be used, for example, for screening conditions for optimized protein stability, screening for ligands that bind and enhance protein stability (e.g., protein-protein interactions), screening for mutations for enhanced stability, screening crystallization conditions for protein stability, screening storage conditions for protein stability, and screening conditions in which a protein will be used (e.g., production conditions, treatment conditions, etc.) for protein stability.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
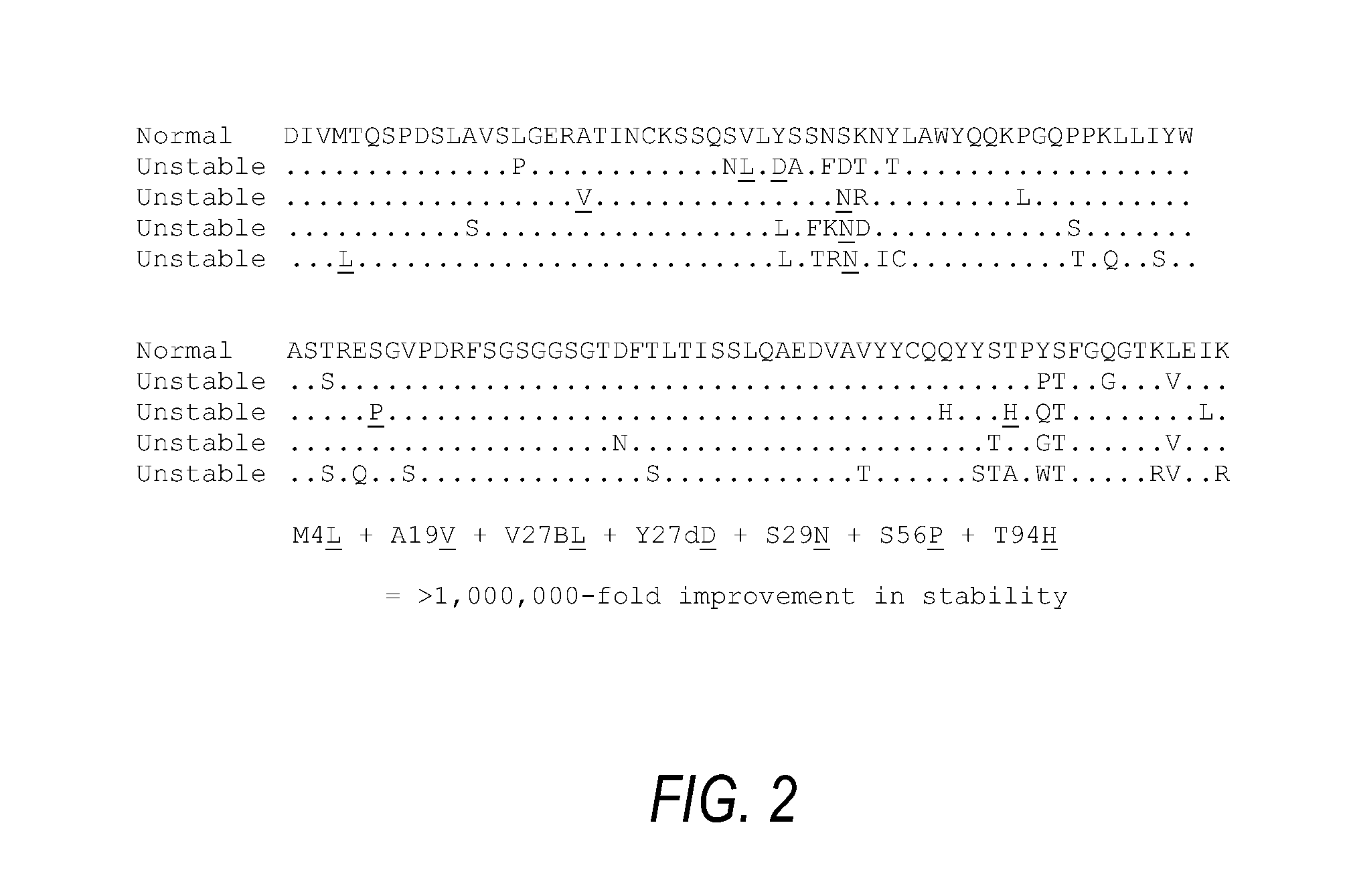
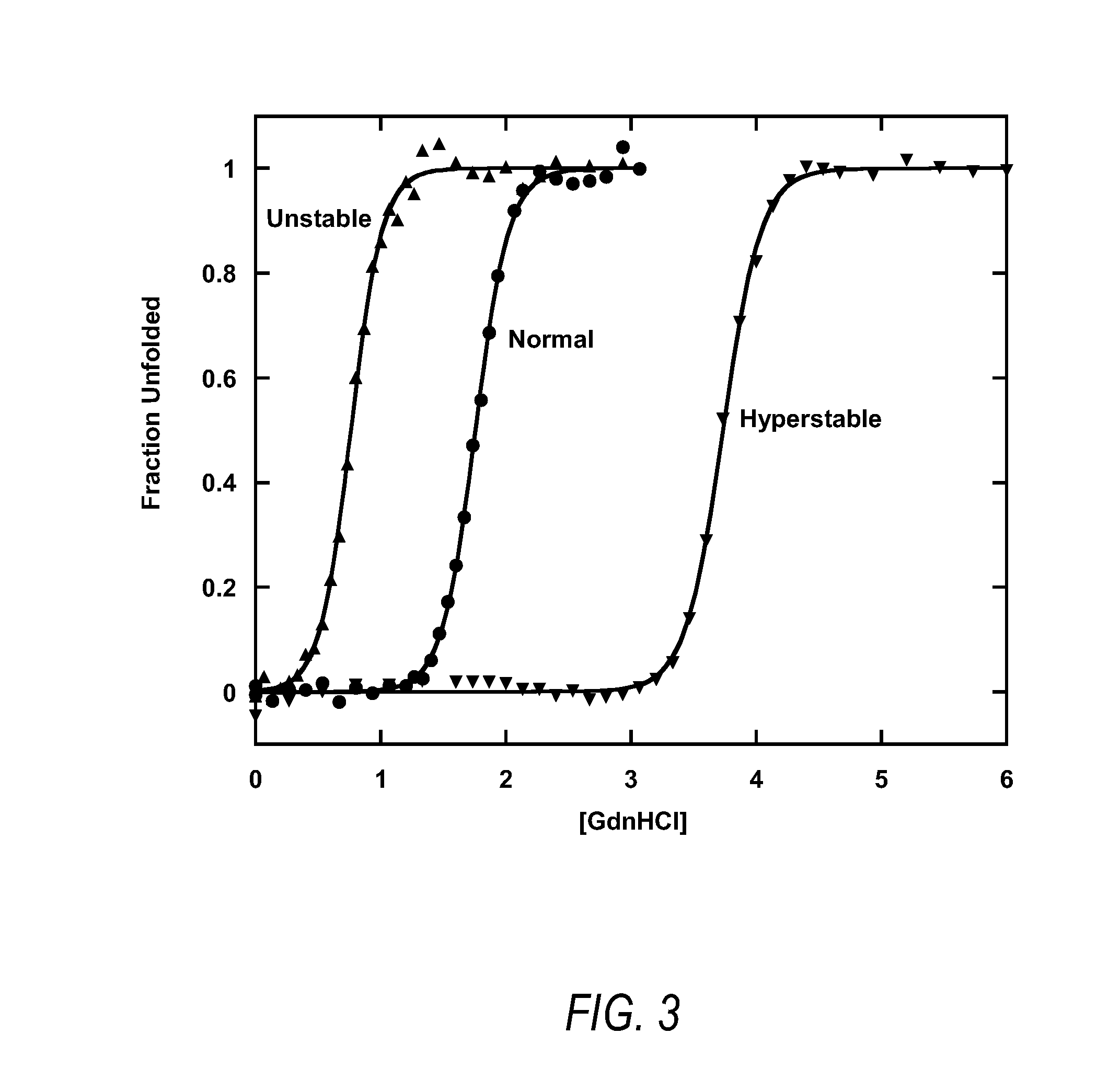
Methods for systematic control of protein stability
InactiveUS20110130324A1Improve stabilityFacilitate therapeutic and diagnostic and other usPeptide/protein ingredientsLibrary screeningCell biologyAntibody
Methods and compositions to control the stability of proteins with special emphasis on antibodies and proteins with antibody-like structures, e.g., having an “immunoglobulin-like” fold, are described. Controlling the stability facilities different applications for a protein with the same function, but different stability.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Alginate lyase gene algp and its preparation method and expression
ActiveCN105296454AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionVibrio vulnificusAlginate lyase
The invention relates to alginate lyase gene algp and its preparation method and expression and discloses alginate lyase of Vibrio vulnificus origin, which has good protein stability and high bioactivity. The invention also discloses alginate lyase gene algp, a carrier and a host cell containing the alginate lyase gene algp, and a method of recombinant expression of the alginate lyase. The technical scheme enables large-scale production of recombinant alginate lyase at lower cost.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
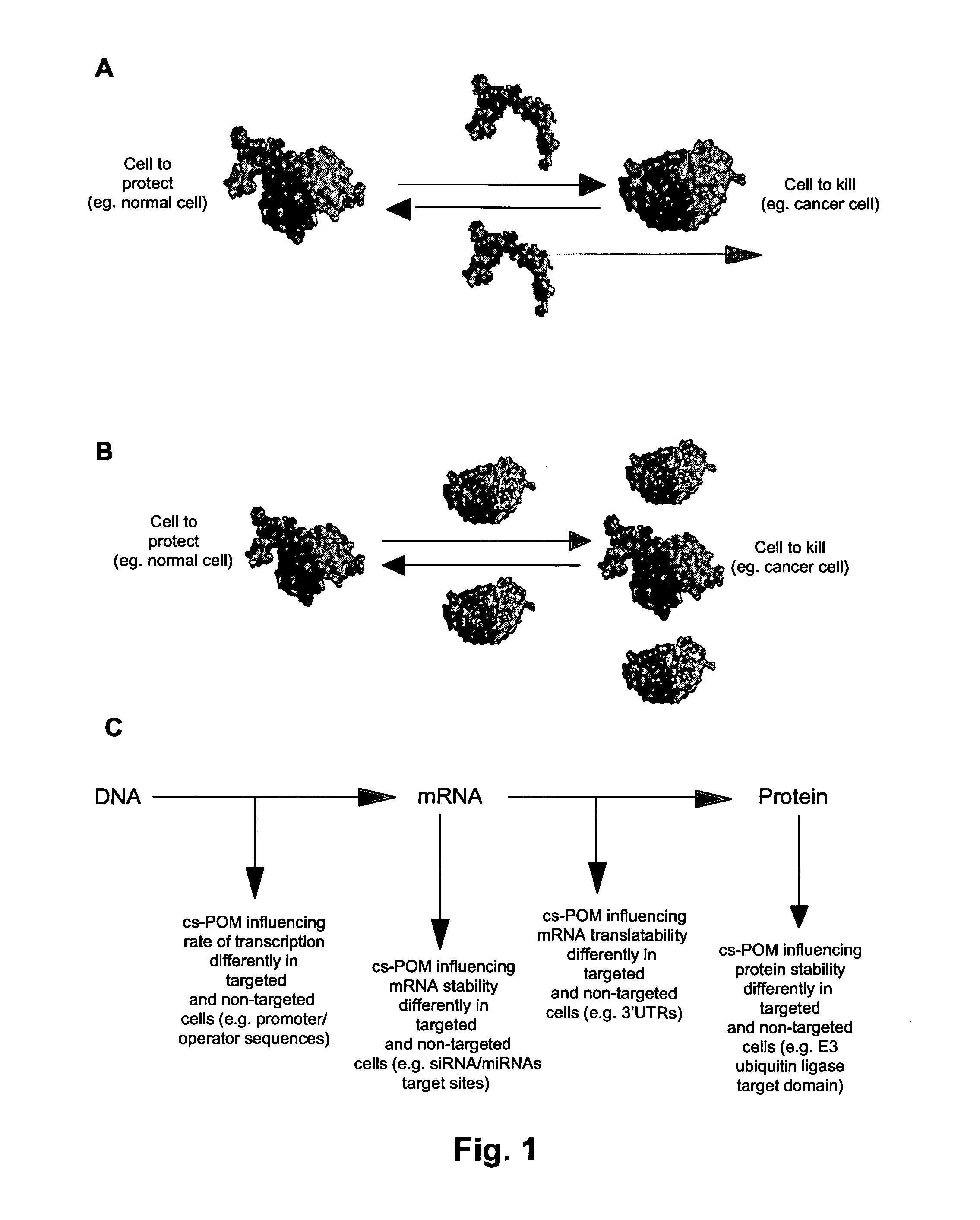
Systems and methods for diminishing cell growth and inducing selective killing of target cells
ActiveUS9555127B2Promote growthReduced growth rateOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCancer cellHost chromosome
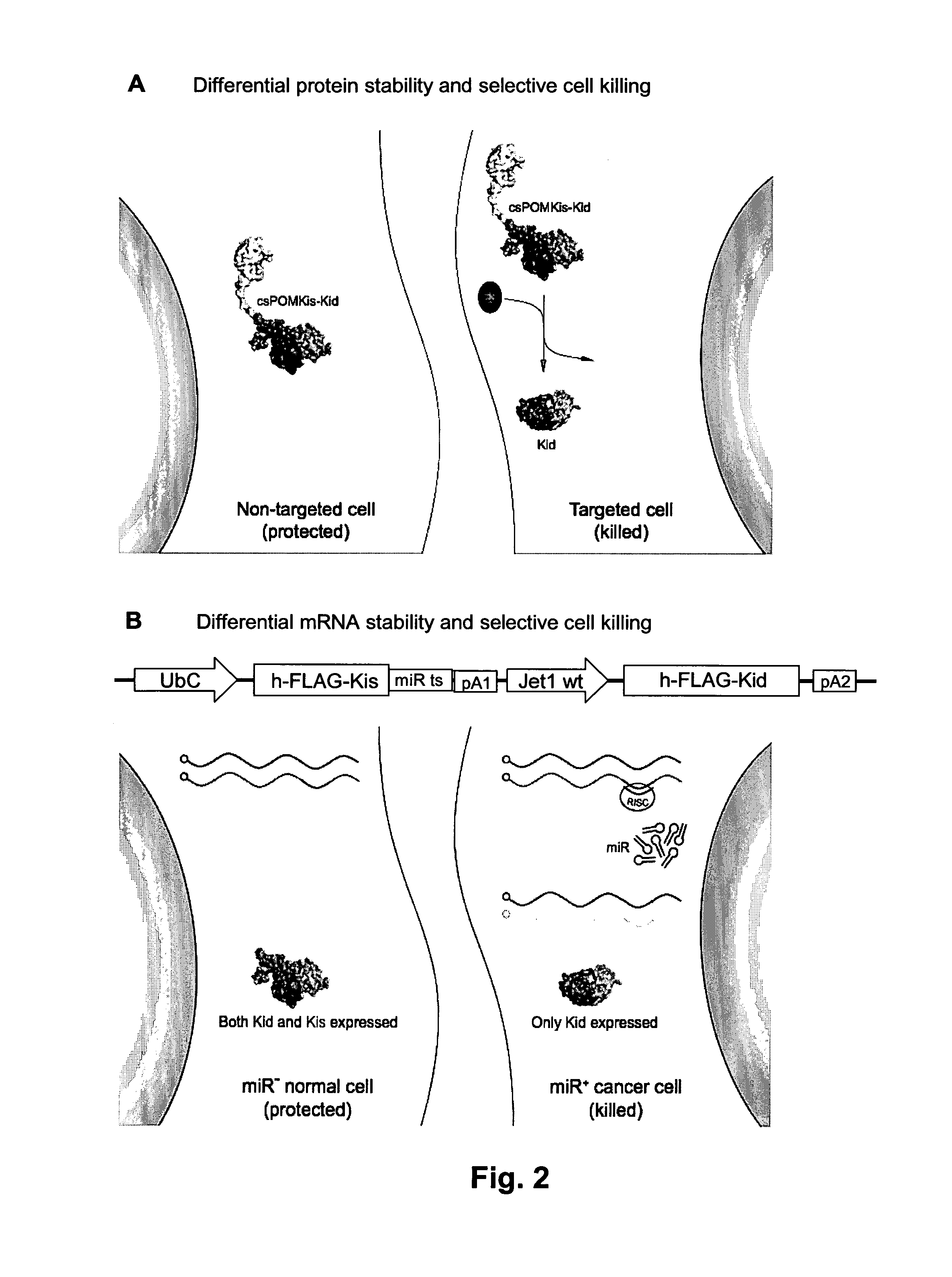
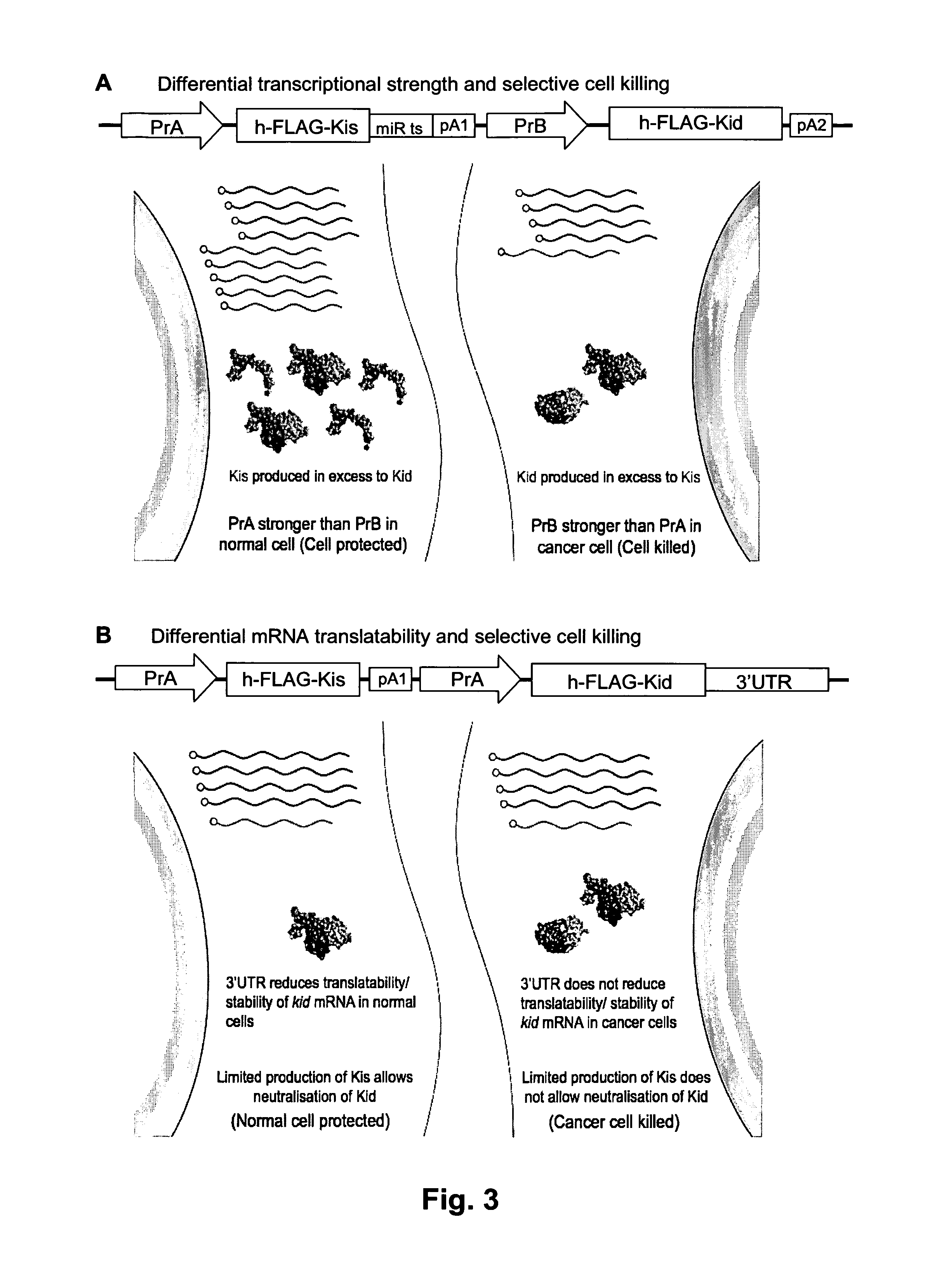
The invention relates to a biological system for diminishing cell growth or inducing selective killing of target cells, in particular pathogenic bacterial or fungal cells, or cancer cells. The biological system is based on toxin-antitoxin systems, as found in prokaryotic plasmids and their host chromosomes. The biological system comprises a vehicle with a first nucleic acid sequence or amino acid sequence encoding for a prokaryotic toxin of a prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin pair, and a second nucleic acid sequence or amino acid sequence encoding for the corresponding prokaryotic antitoxin of the prokaryotic toxin-antitoxin pair. The system is characterized in that the toxin and / or the antitoxin is operably linked to a protein output modifier (POM) that comprises a nucleic acid sequence or amino acid sequence that modifies the relative rate of transcription, mRNA stability, mRNA translatability or protein stability of the toxin and / or antitoxin.
Owner:CUEVA MENDEZ GUILLERMO DE LA +1
T cell receptor-like antibodies specific for a wti peptide presented by hla-a2
The present invention provides antigen binding proteins that specifically bind to Wilms' tumor protein (WT1), including humanized, chimeric and fully human antibodies against WT1, antibody fragments, chimeric antigen receptors (CARs), fusion proteins, and conjugates thereof. The antigen binding proteins and antibodies bind to HLA-A0201-restricted WT1 peptide. Such antibodies, fragments, fusion proteins and conjugates thereof are useful for the treatment of WT1 associated cancers, including for example, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, prostate cancer, chronic myelocytic leukemia, multiple myeloma, acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid / myelogenous leukemia (AML) and myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS). In more particular embodiments, the anti-WT1 / A antibodies may comprise one or more framework region amino acid substitutions designed to improve protein stability, antibody binding and / or expression levels.
Owner:MEMORIAL SLOAN KETTERING CANCER CENT +1
Formation of stable submicron peptide or protein particles by thin film freezing
ActiveUS20100247506A1Simple and efficient and robustSimple and efficient and robust processNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsVapor liquidAdditive ingredient
The present invention includes compositions and methods for preparing micron-sized or submicron-sized particles by dissolving a water soluble effective ingredient in one or more solvents; spraying or dripping droplets solvent such that the effective ingredient is exposed to a vapor-liquid interface of less than 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 200, 400 or 500 cm−1 area / volume to, e.g., increase protein stability; and contacting the droplet with a freezing surface that has a temperature differential of at least 30° C. between the droplet and the surface, wherein the surface freezes the droplet into a thin film with a thickness of less than 500 micrometers and a surface area to volume between 25 to 500 cm−1.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for Incorporating Internal Polar and Ionizable Groups in Proteins
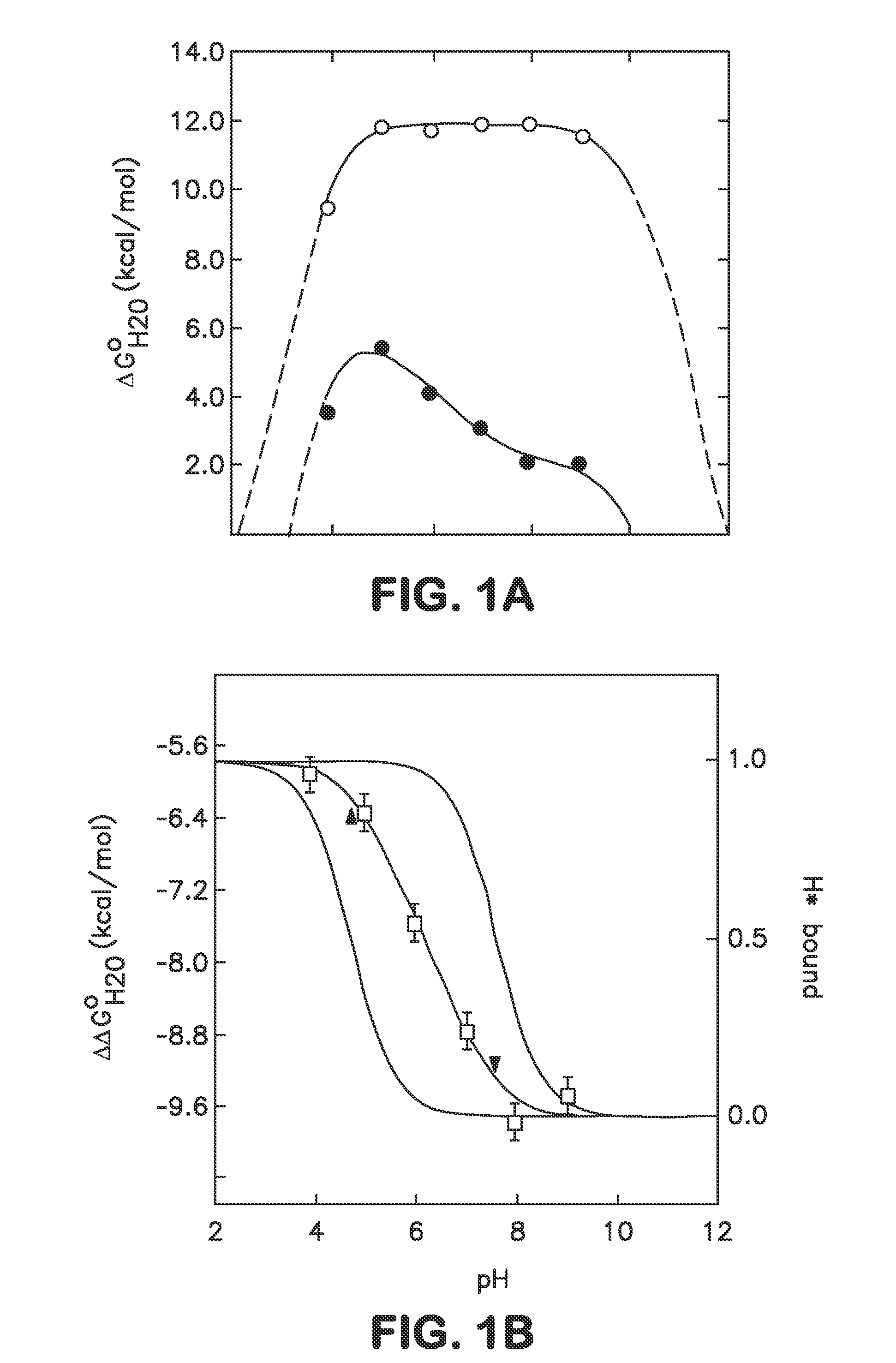
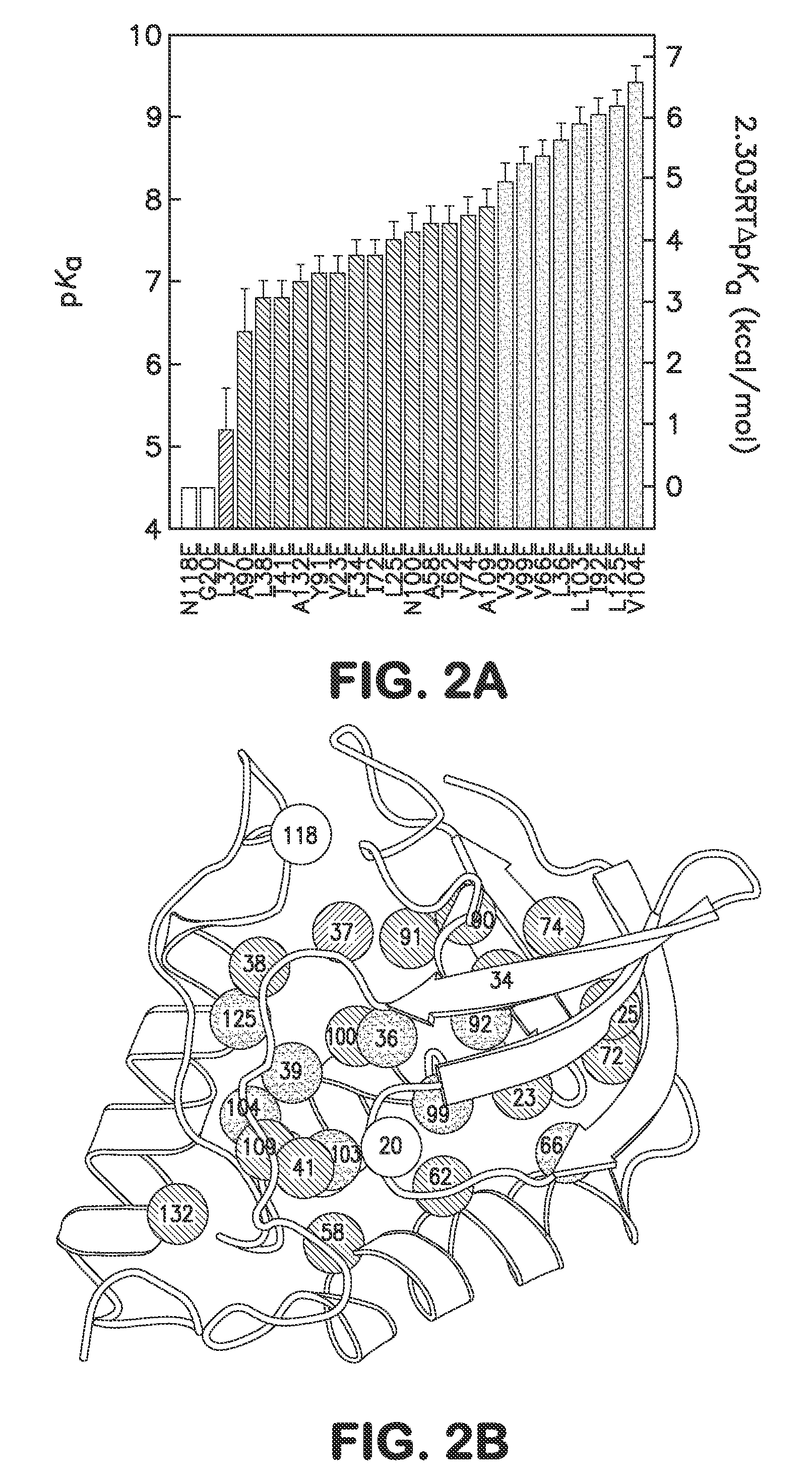
ActiveUS20120258518A1High thermodynamic stabilityImprove accuracyHydrolasesPeptide preparation methodsElectricityCrystallography
Internal polar and ionizable groups are essential for enzymatic catalysis, proton transport, redox reactions, and many other functional properties of proteins. To engineer novel enzymes or to modify the function of existing ones, and to build switches that can be used to modify the stability of proteins in response to changes in pH, it is necessary to introduce polar or ionizable groups or to modify the properties of existing ones. However, internal polar and ionizable groups usually destabilize proteins. The disclosure provides new methods that allow the introduction of polar and ionizable groups into the interior of proteins, as well as new methods for improving the accuracy of pKa of an internal amino acid of a protein, and methods for mapping the folding free energy landscape of a protein.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Preparation method of walnut oil
InactiveCN106665890AImprove qualityGood colorFatty-oils/fats refiningFatty-oils/fats productionWaxOil separation
The invention discloses a preparation method of walnut oil. The preparation method of the walnut oil comprises the following steps: carrying out careful selecting, carrying out washing, carrying out sterilization, carrying out peeling, carrying out pressing, and carrying out ultrasonic extraction. According to the preparation method of the walnut oil, the preparation is carried out at 45 DEG C, and the walnut kernel peel is removed before pressing by using alkaline liquor, so that the qualities and the color of the walnut oil are improved; and ultrasonic extraction is adopted so as to increase yield rate, reduce oil content rate of the oil cakes, balance protein in the walnut oil and the oil cakes so as to ensure protein stability in the oil cakes, and improve wax-oil separation effect. The preparation method of the walnut oil is simple in processes; and the walnut oil which is clear, transparent and bright in color, free of impurities, rich in nutrition and high in oil yield can be prepared without the step of carrying out decoloring by adopting the preparation method.
Owner:迪庆香格里拉舒达有机食品有限公司
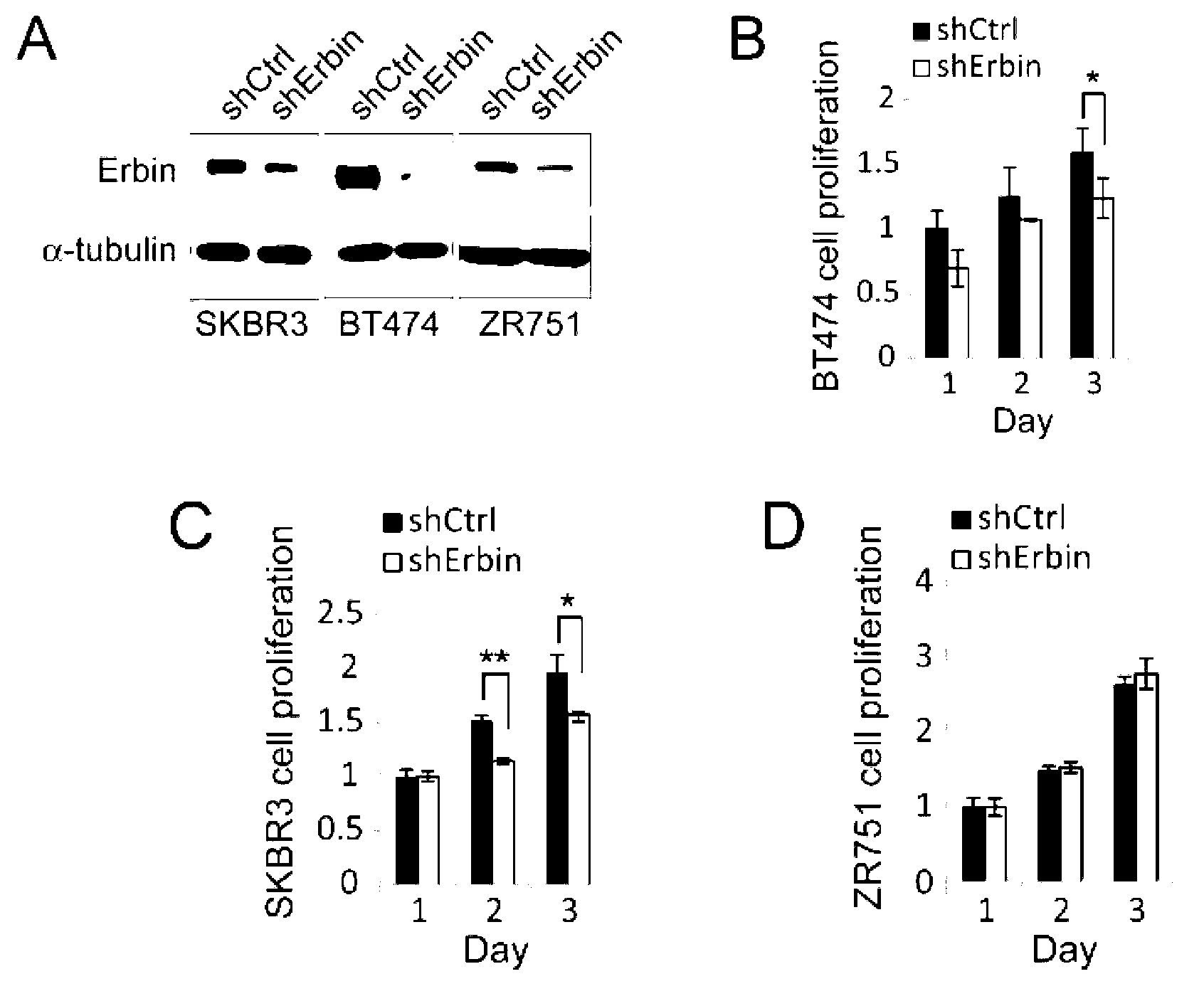
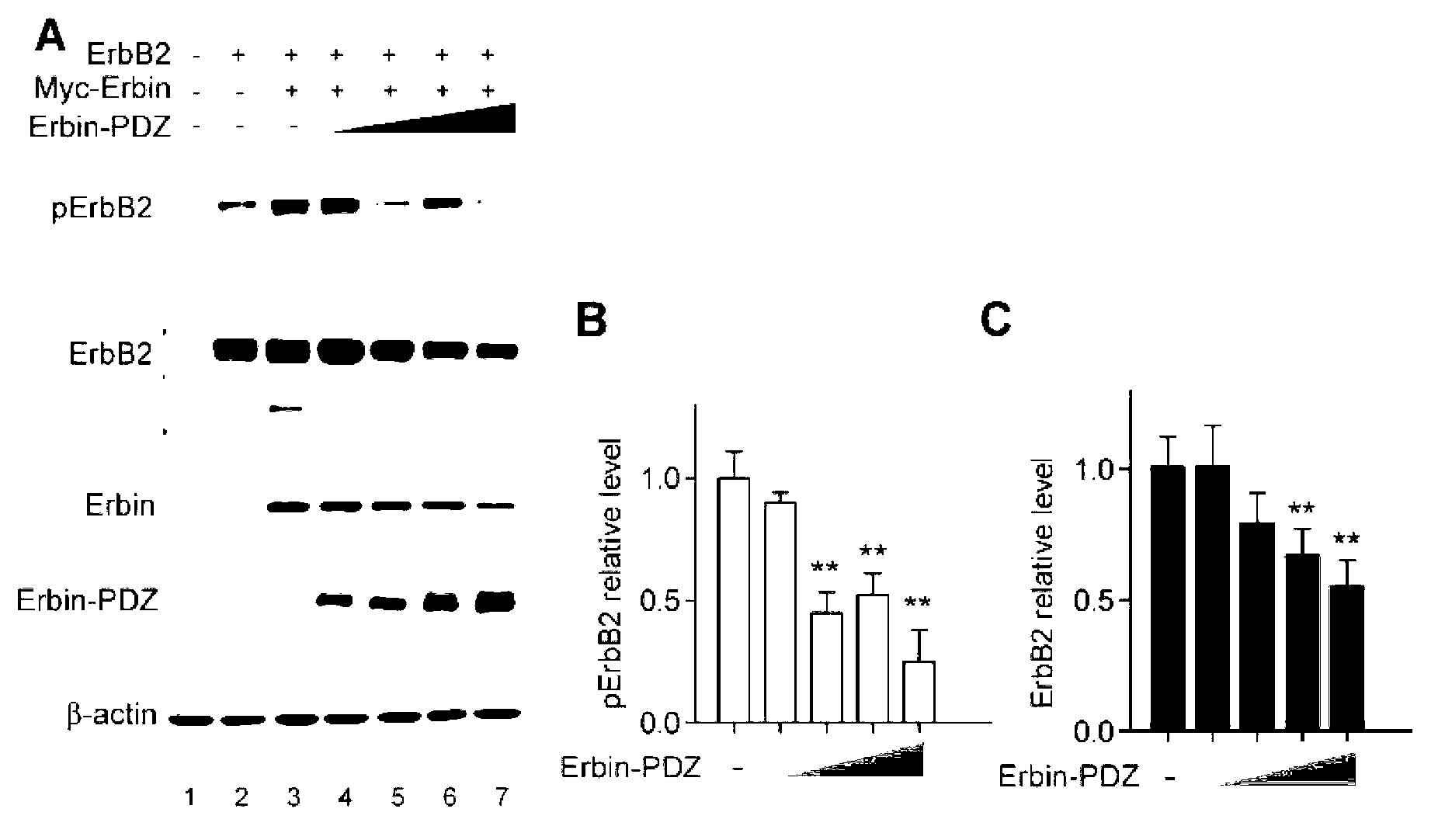
Application of Erbin inhibitor in preparation of antitumor drug
InactiveCN103212077AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthKinase activity
The invention provides application of an Erbin inhibitor in preparation of an antitumor drug. The inhibitor is specifically a compound capable of lowering expression of Erbin or interfering Erbin-ErbB2 interaction. The Erbin-Erbin interaction is crucial to tumor-prompting action and carcinogenic action of ErbB2; the ErbB2 dependent cancer cell proliferation or tumor growth can be inhibited by over-expressing a PDZ structural segment of Erbin or excessively giving tail-end polypeptide segments to the ErB2 in the cell. The invention provides a novel way of treating ErbB2 positive tumors, i.e., a way of inhibiting protein stability and kinase activity of the ErbB2 by reducing the expression of Erbin or interfering with the combination of ErBin and ErbB2, so that the tumor-prompting action and carcinogenic action of the ErbB2 are inhibited.
Owner:梅林 +4
Method to Assess Stability of Proteins
InactiveUS20090298186A1Reduce consumptionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionThermal denaturationFluorescence
A method for determining conformational stability of proteins detects the change in free sulfhydryls accessible to reaction with a fluorescent probe after combined chemical and thermal denaturation. The method is useful in any application where the stability and integrity of a protein preparation is useful information. The method can be used to screen protein variants for desirable stability profile.
Owner:BRIGHAM BURKE MICHAEL +1
Quantitative, high-throughput screening method for protein stability
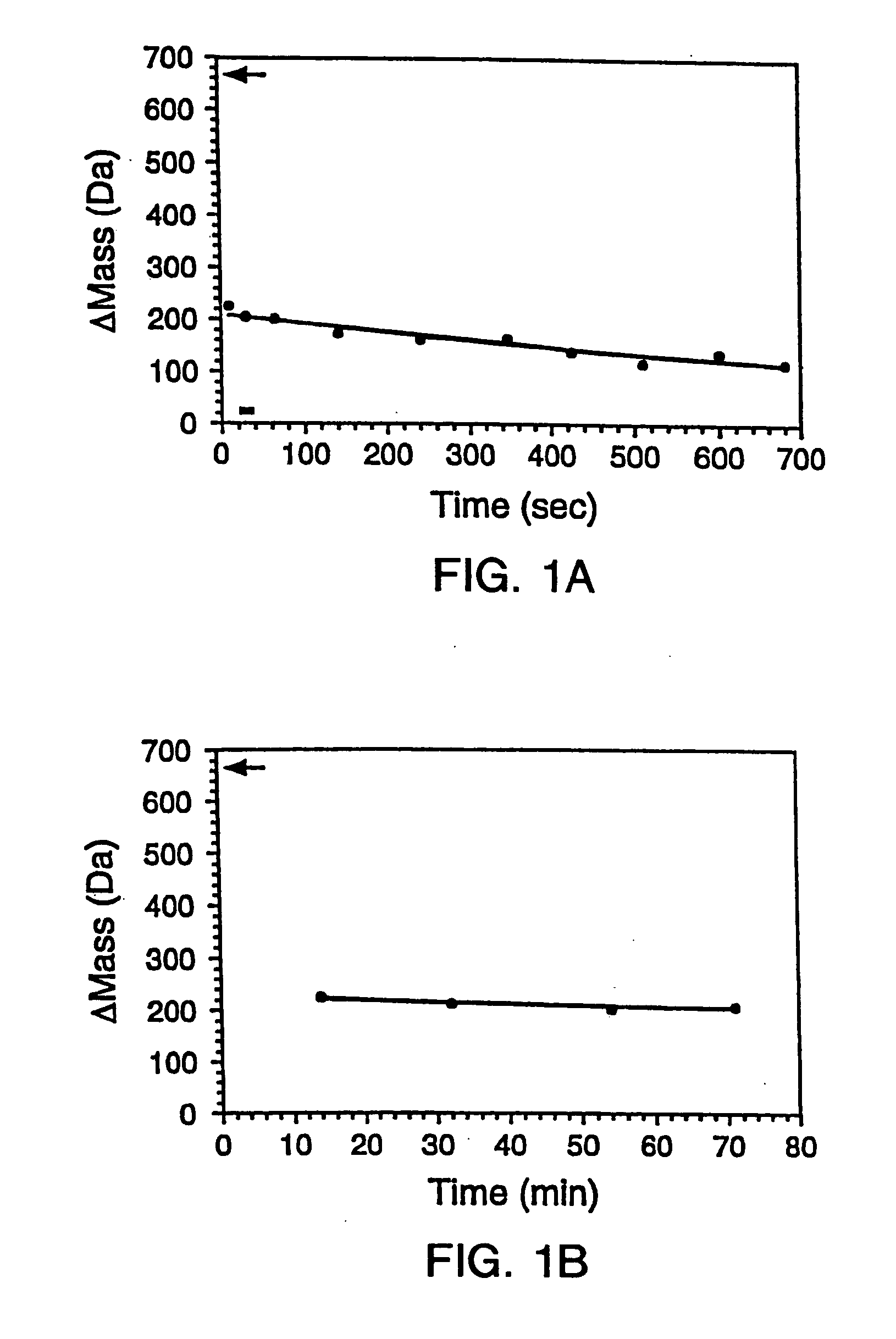
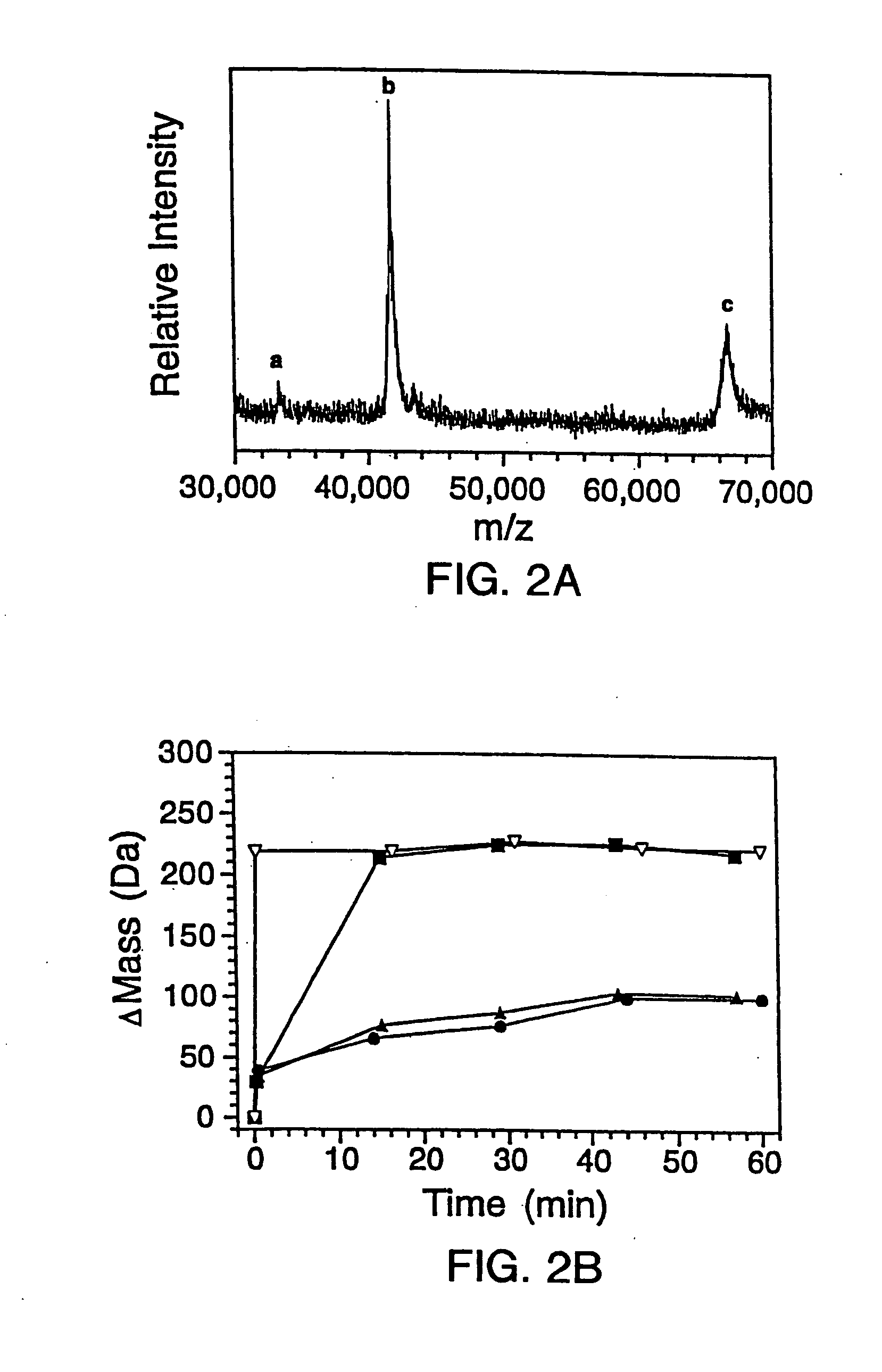
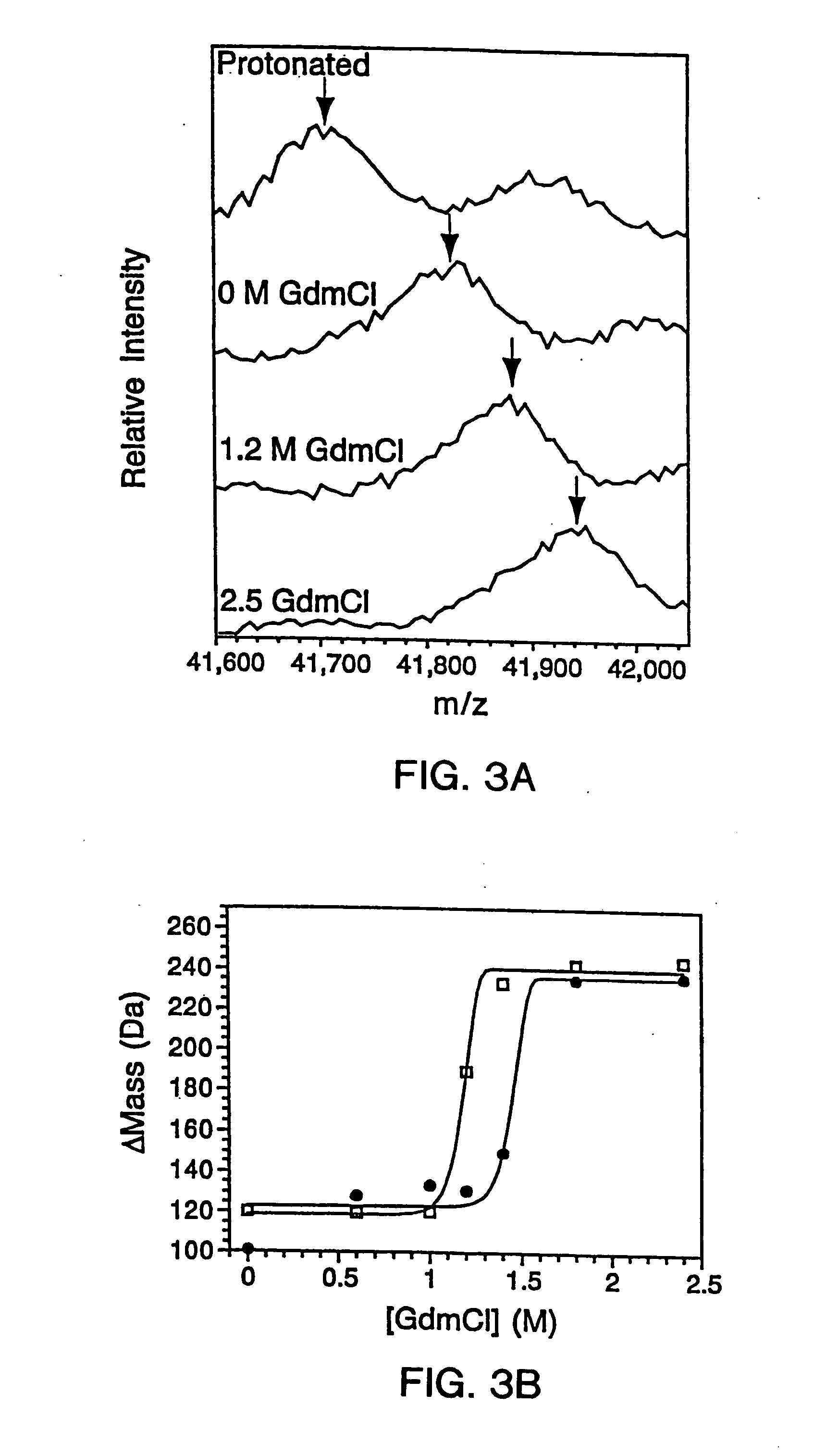
InactiveUS20070099305A1Improve completenessImprove stabilityDisease diagnosisBiological testingLaser desorption ionization mass spectrometryHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
In proteomic research, it is often necessary to screen a large number of polypeptides for the presence of stable structure. Described herein are methods (referred to as MALDI MS-HX and SUPREX) for measuring the stability of proteins in a rapid, high-throughput fashion. The method employs hydrogen exchange to estimate the stability of quantities of unpurified protein extracts, using matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry. A method of quantitatively determining the stability of a test protein under native conditions is disclosed. The method includes the steps (a) providing a test protein; (b) contacting the protein with an exchange buffer comprising a denaturant and deuterium, the exchange buffer having a denaturant concentration; (c) contacting the test protein with a mass spectrometry matrix medium; (d) determining a change in mass of the test protein by mass spectrometry; (e) varying the denaturant concentration of the exchange buffer; (f) repeating steps (a)-(e) a desired number of times; and (g) quantitatively determining protein stability based on the change in mass of the test protein as a function of denaturant concentration, whereby the stability of a test protein under native conditions is quantitatively determined.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Stable kallikrein-1 injection
ActiveCN101596311AImprove stabilityEasy to manufacturePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismPhosphateSerum albumin
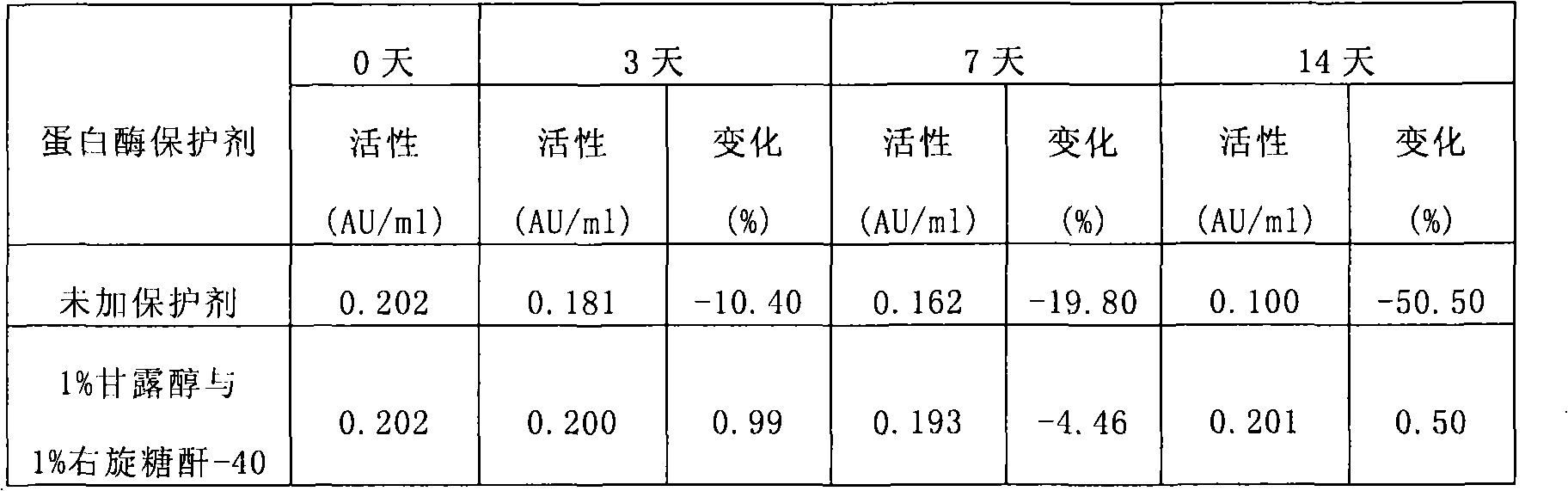
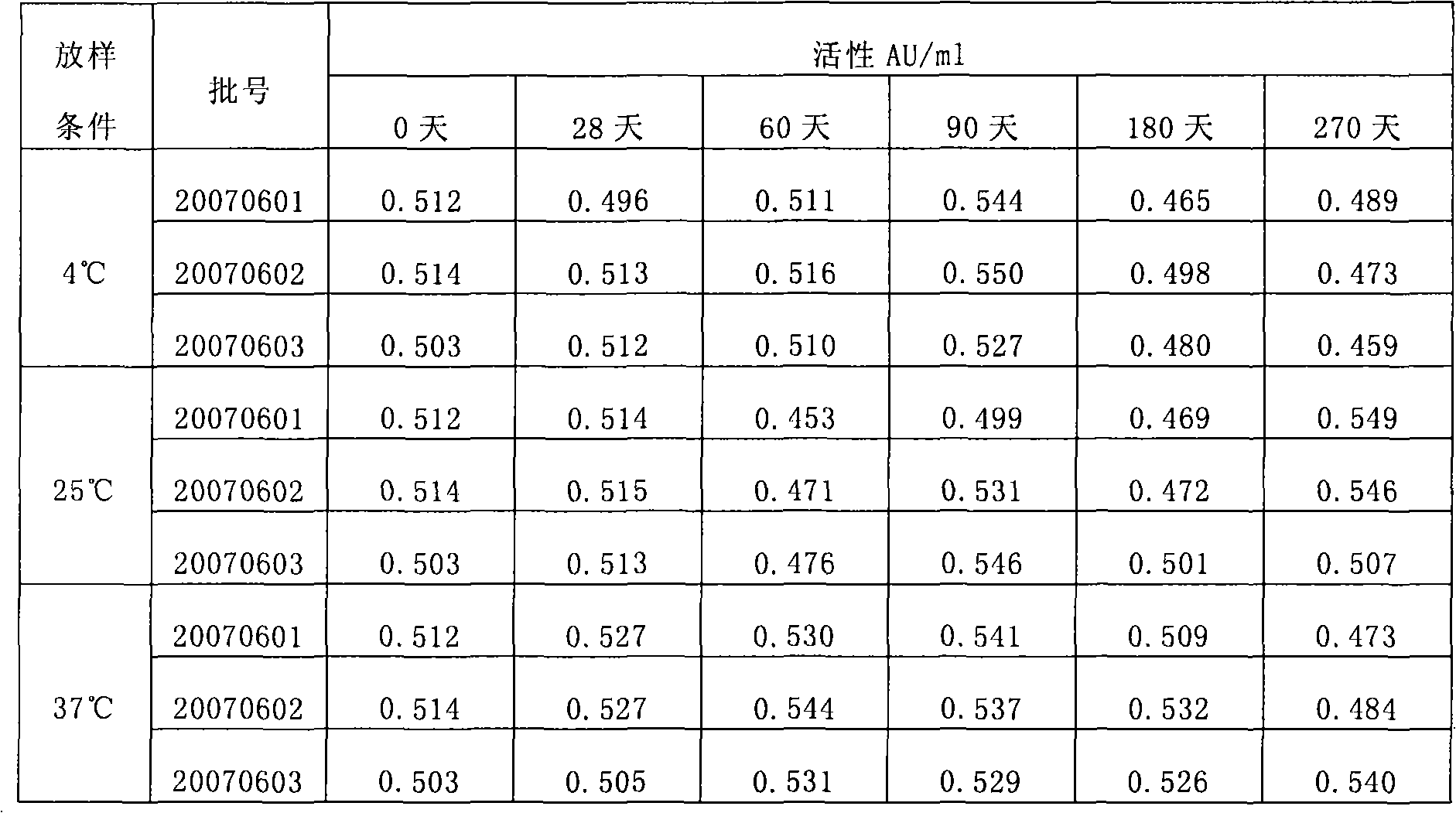
The invention discloses a stable kallikrein-1 injection containing 0.05-40.00 AU / ml of kallikrein-1(1), 10-50 mmol / L of phosphate buffer (2) with the pH value of 6.0 to 8.0, 0.01-0.2 mol / L of sodium chloride (3) and 0.01-20 w / v percent of proteinase protective agent (4). The stable kallikrein-1 injection has good protein stability, contains no human serum albumin as a protective agent, avoids increasing the potential hazards of leading in exogenous viruses and has simple and convenient preparation and low cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI TENRY PHARMCEUTICAL CO LTD
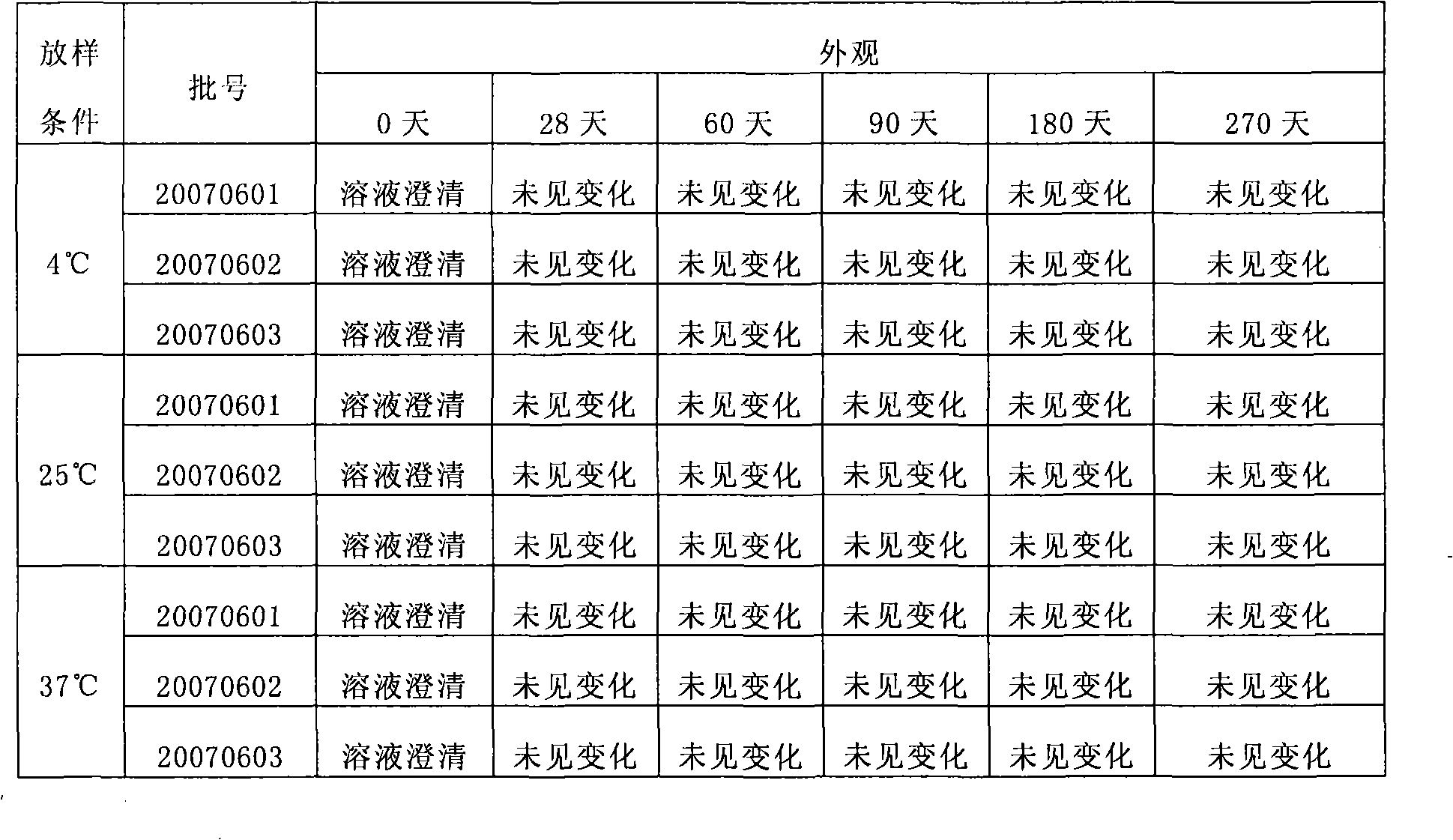
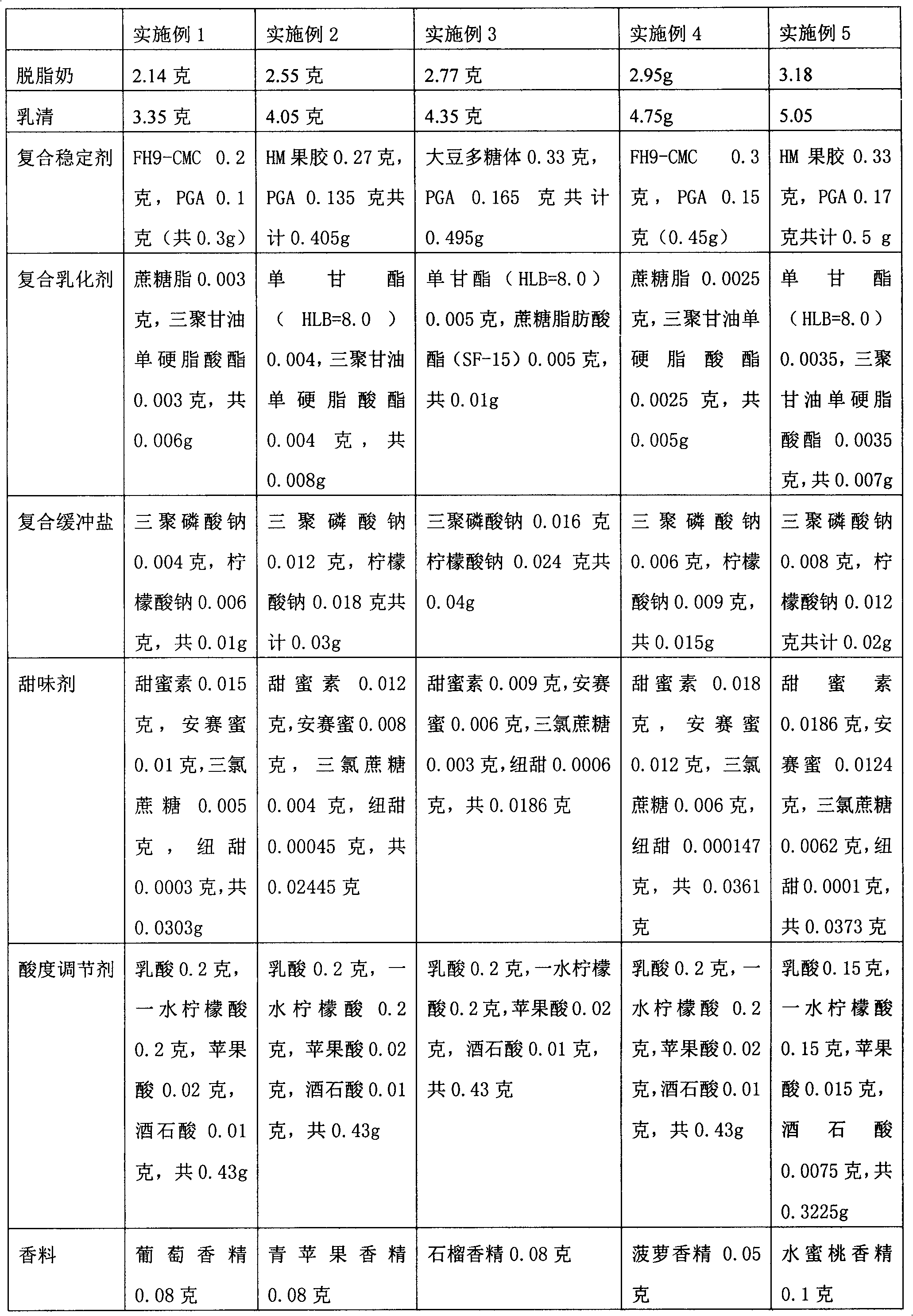
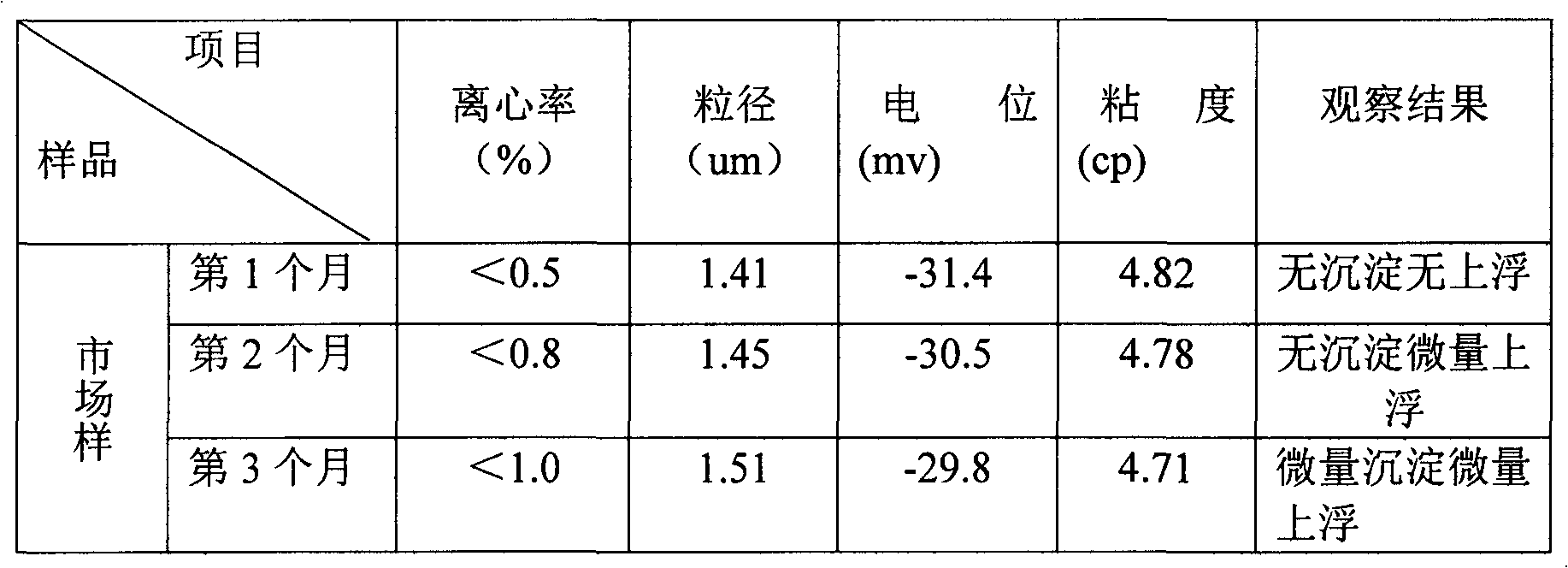
Fat-free and sugar-free acid milk beverage and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an acid milk beverage, in particular to a fat-free and sugar-free acid milk beverage and a preparation method thereof. The acid milk beverage has the following formulas according to the protein content: 2.130g-3.175g of defatted milk powder, 3.3g-5g of salted whey powder, 0.3g-0.5g of compound stabilizer, 0.05g-0.01g of compound emulsifying agent, 0.01g-0.04g of compound buffer salt, 0.0186g-0.0373g of sweetener, 0.3225g-0.43g of acidity regulator, 0.01-0.1g of spices and the balance of water. From the formula, the product does not contain fat and sugar, and the protein stability is similar to the product containing fat and sugar on the market; and from the taste, in the product, the sweetener can replace cane sugar without containing energy, and the taste is similar to the product containing fat and sugar on the market.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com