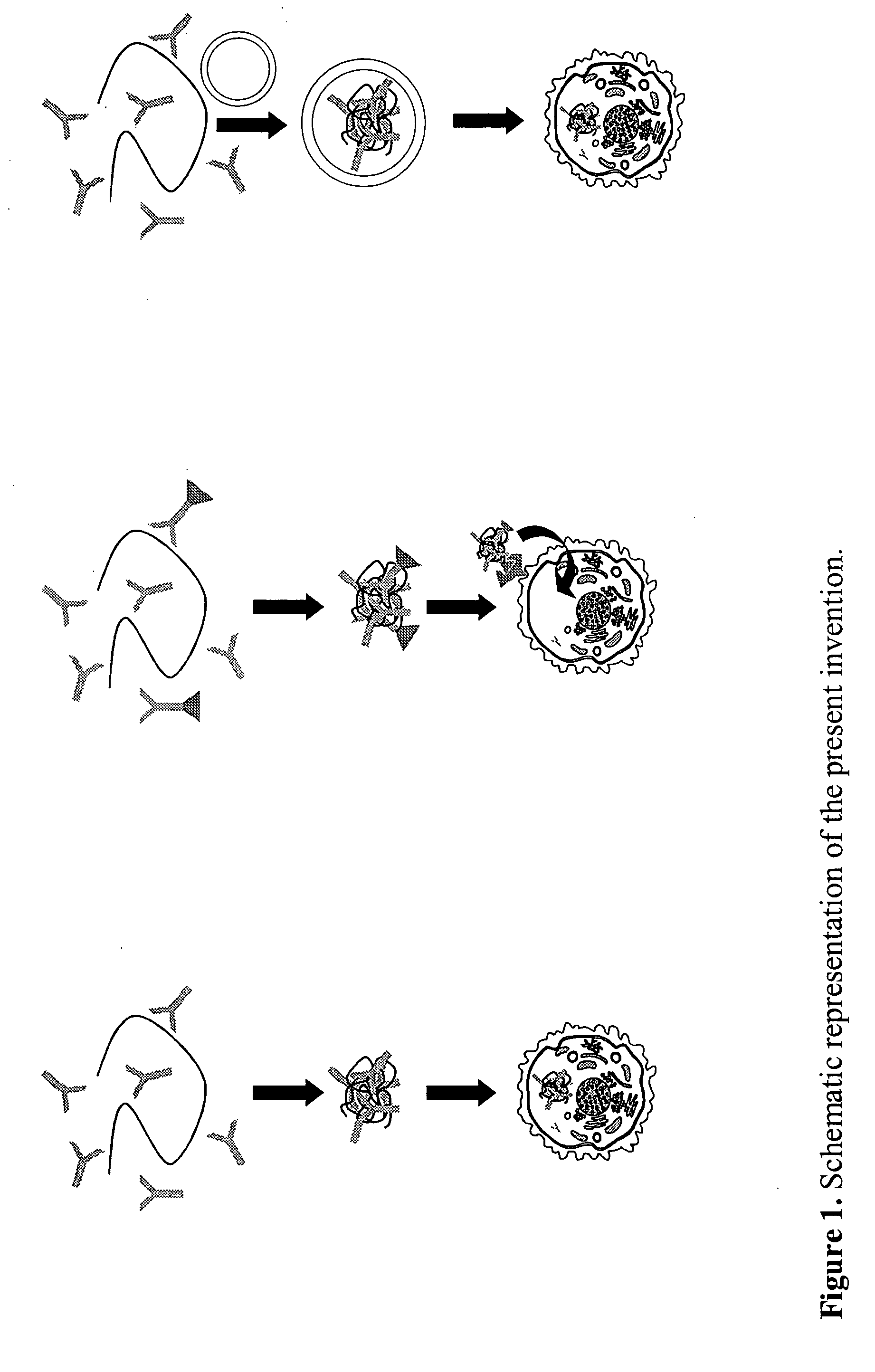
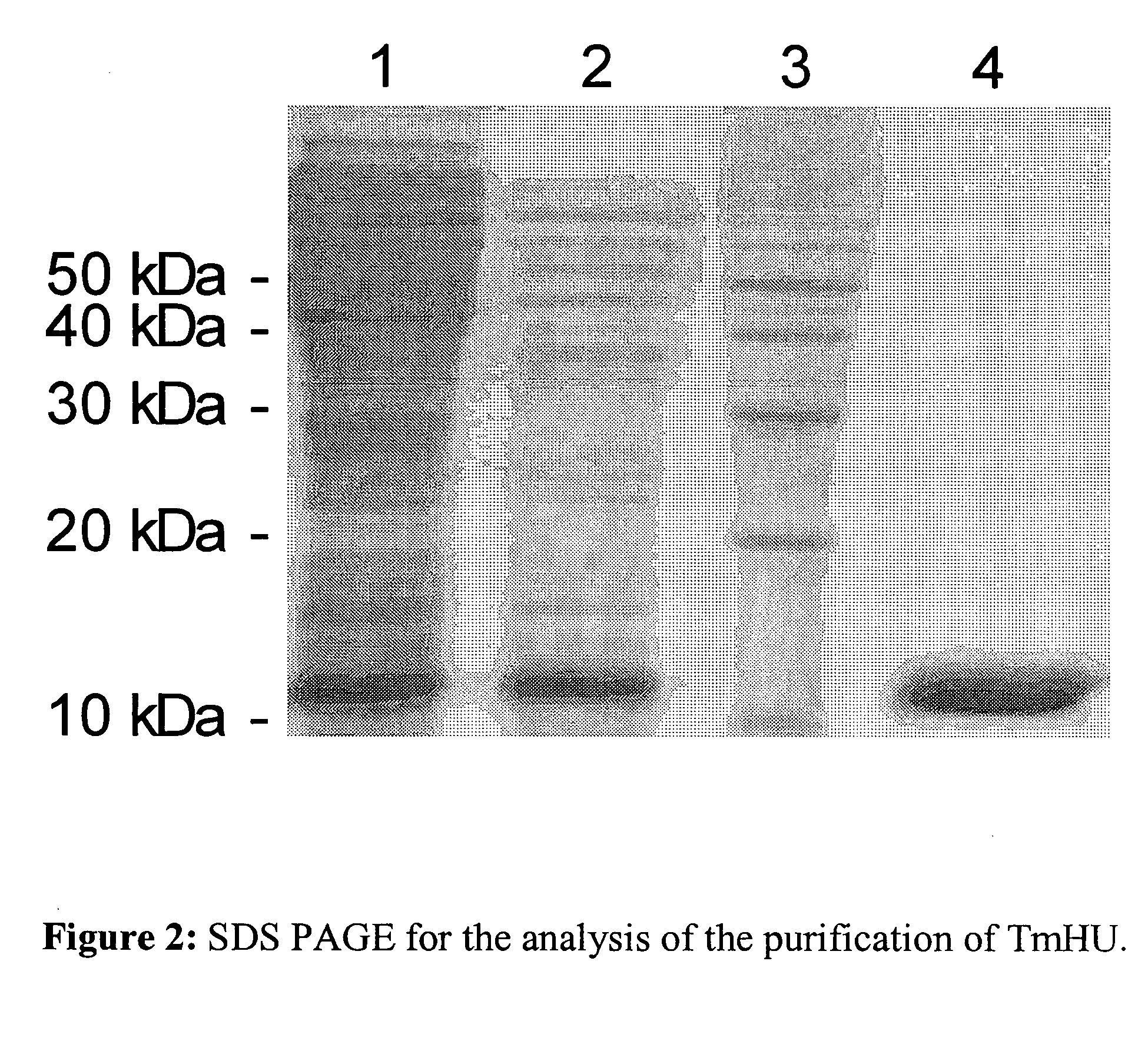
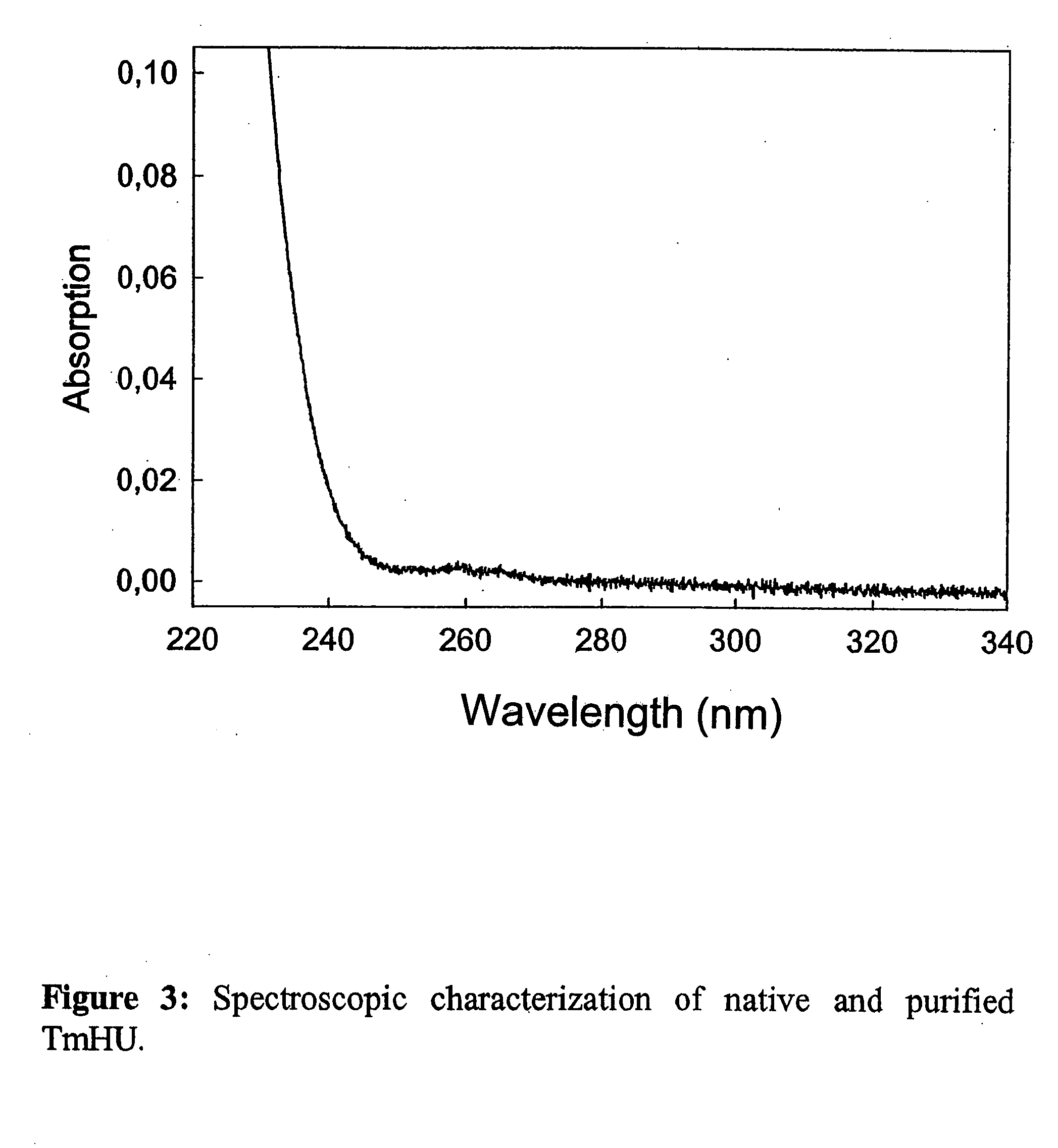
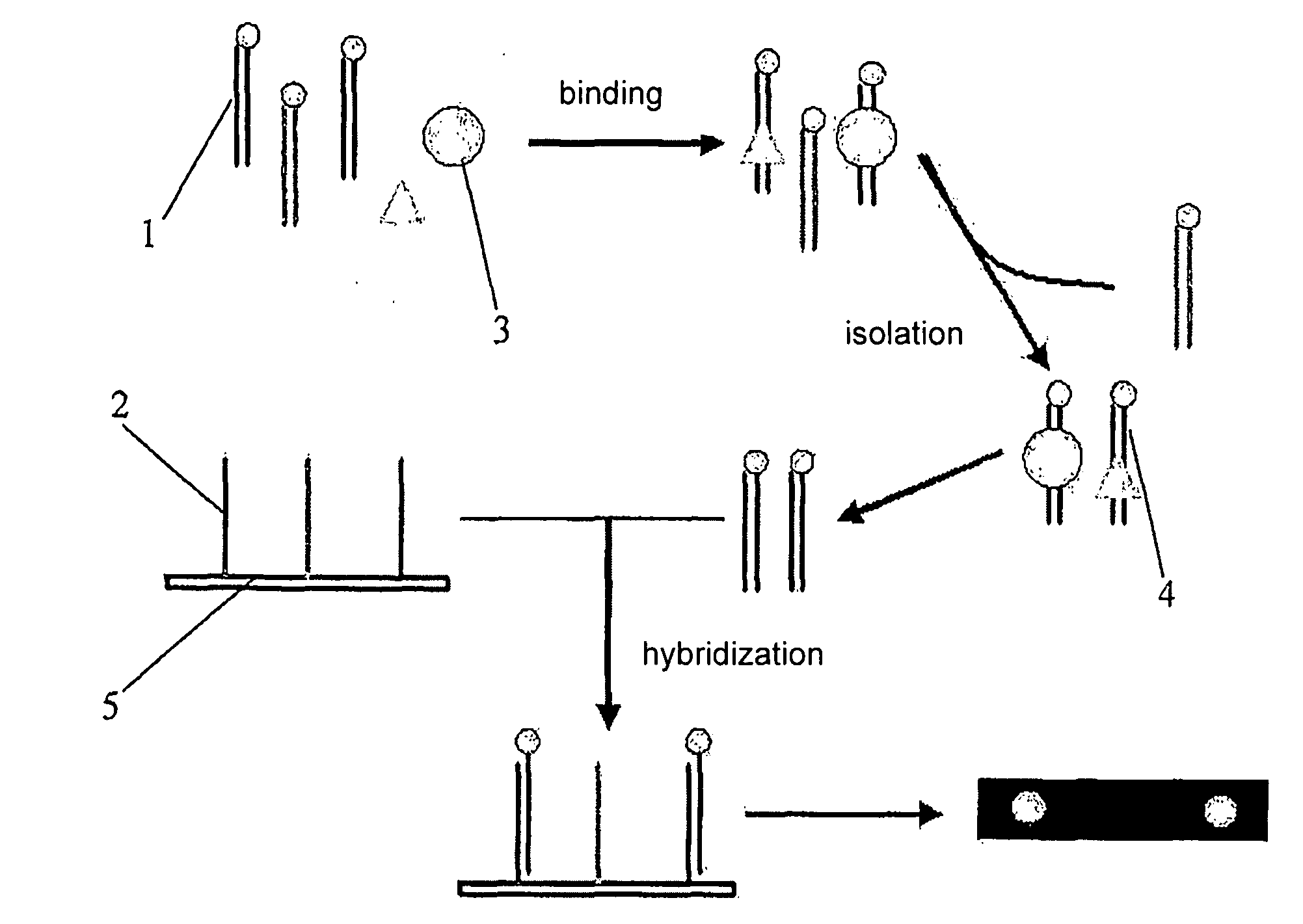
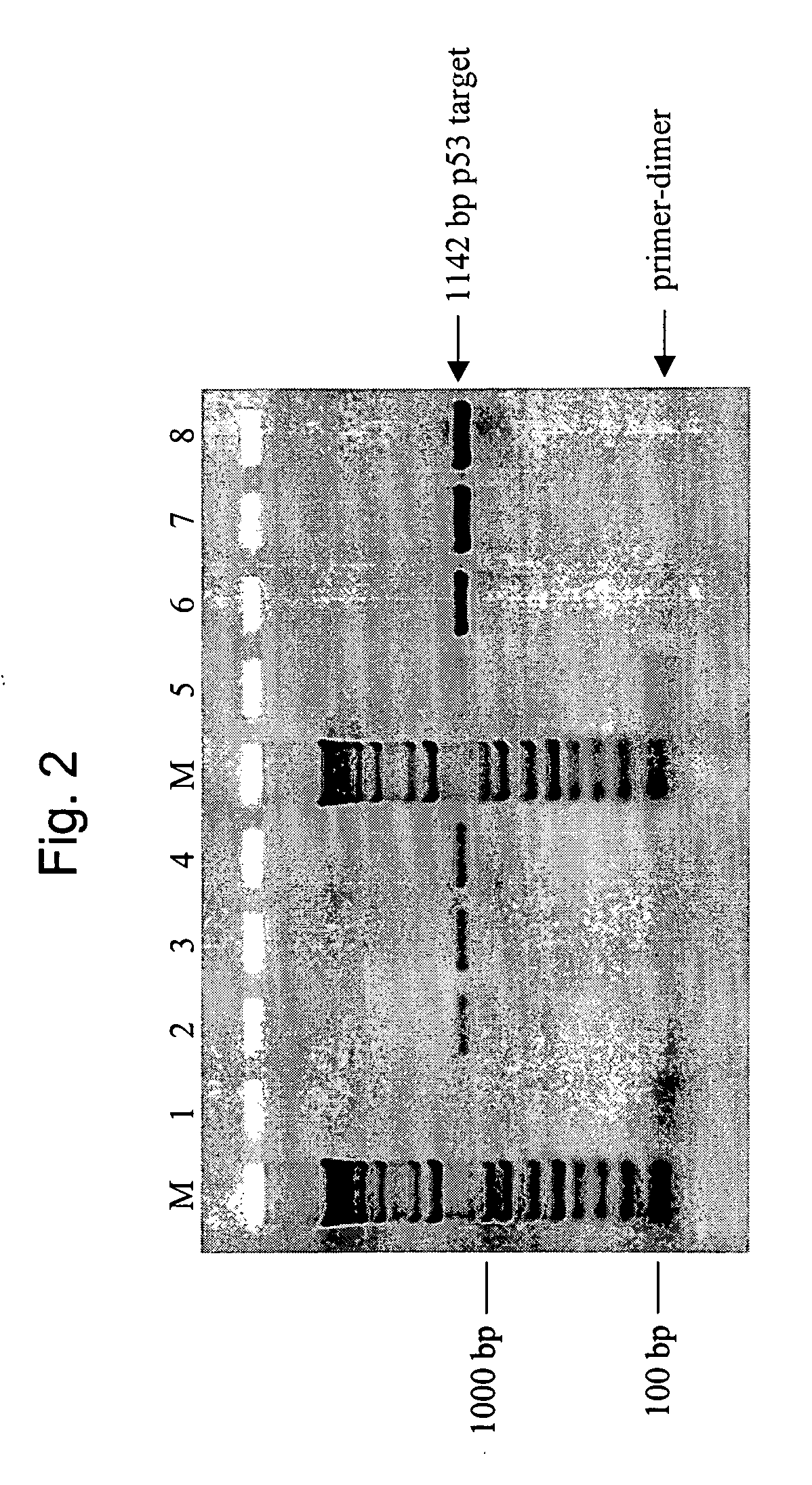
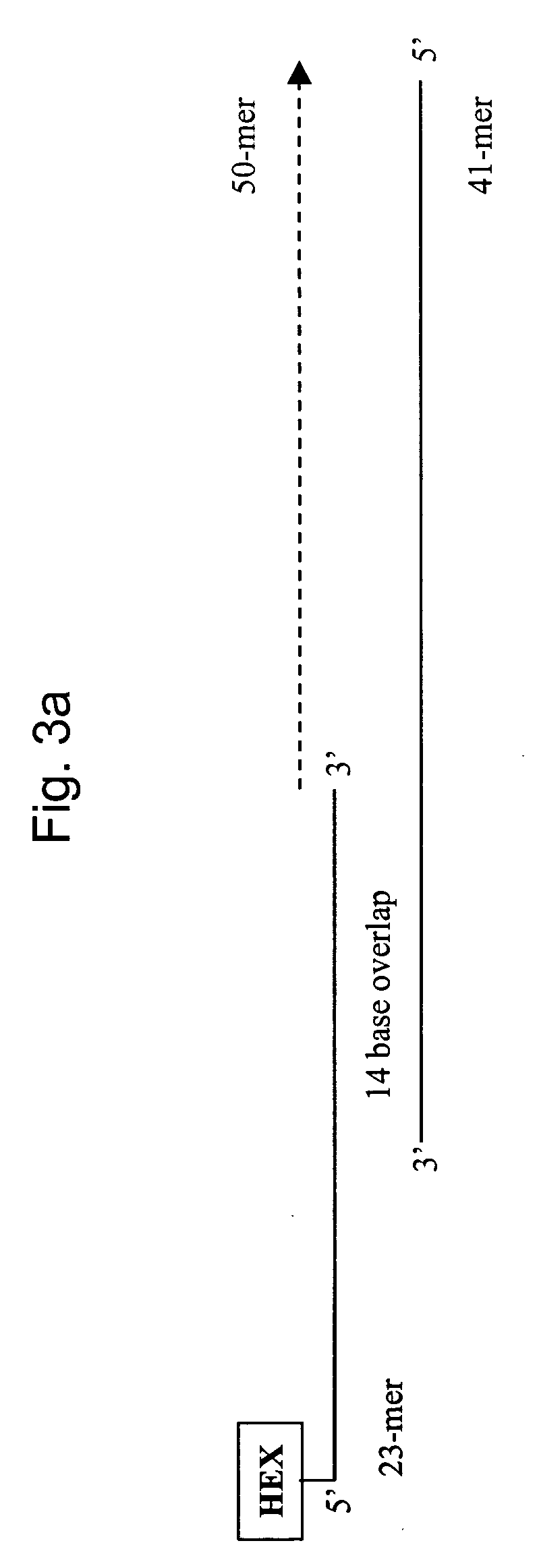
Patents
Literature
69 results about "Nucleic acid binding protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
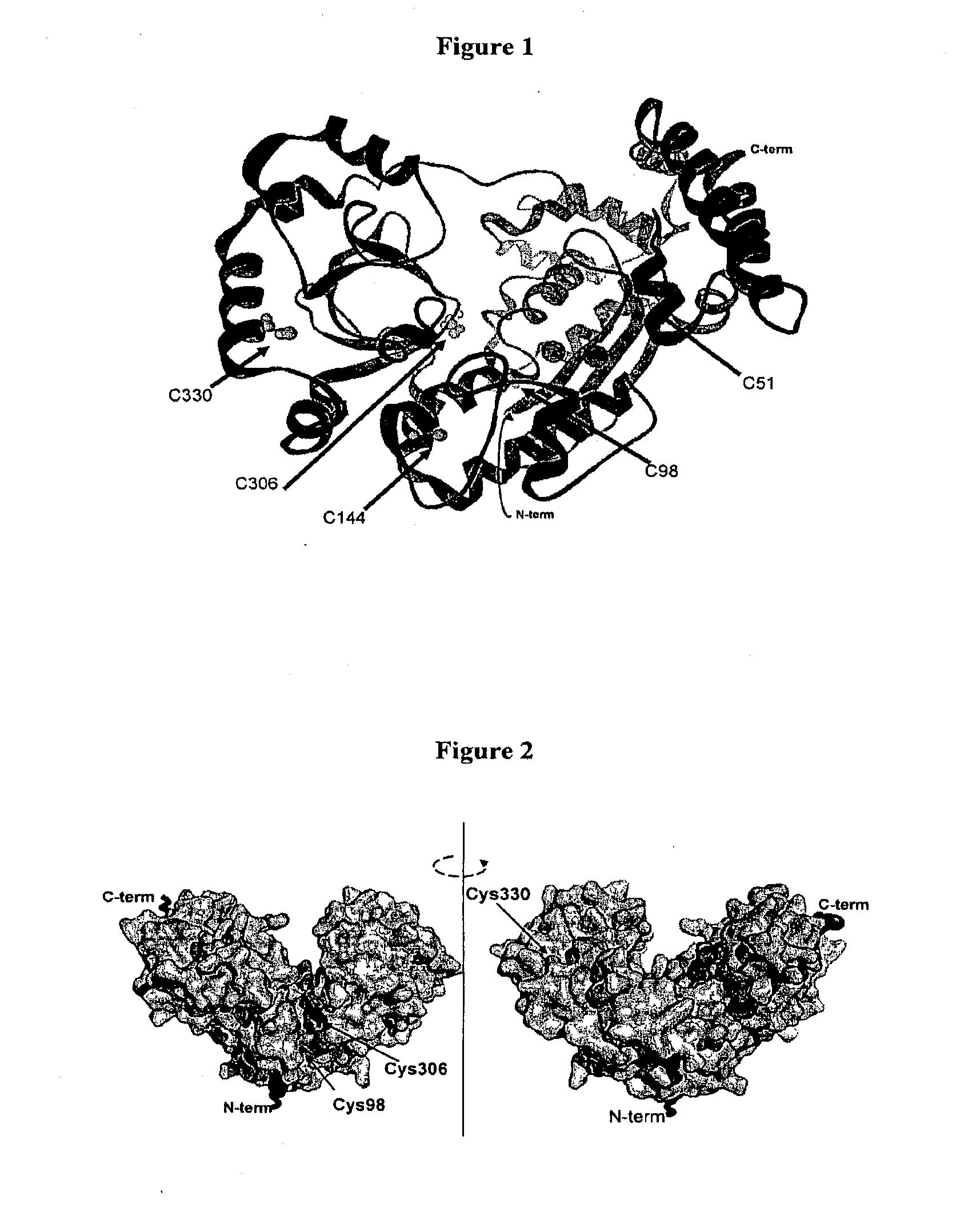
Normal Function. The CNBP gene (also known as ZNF9) provides instructions for making a protein called CCHC-type zinc finger nucleic acid binding protein. This protein has seven regions, called zinc finger domains, which are thought to attach (bind) to specific sites on DNA and its chemical cousin, RNA.
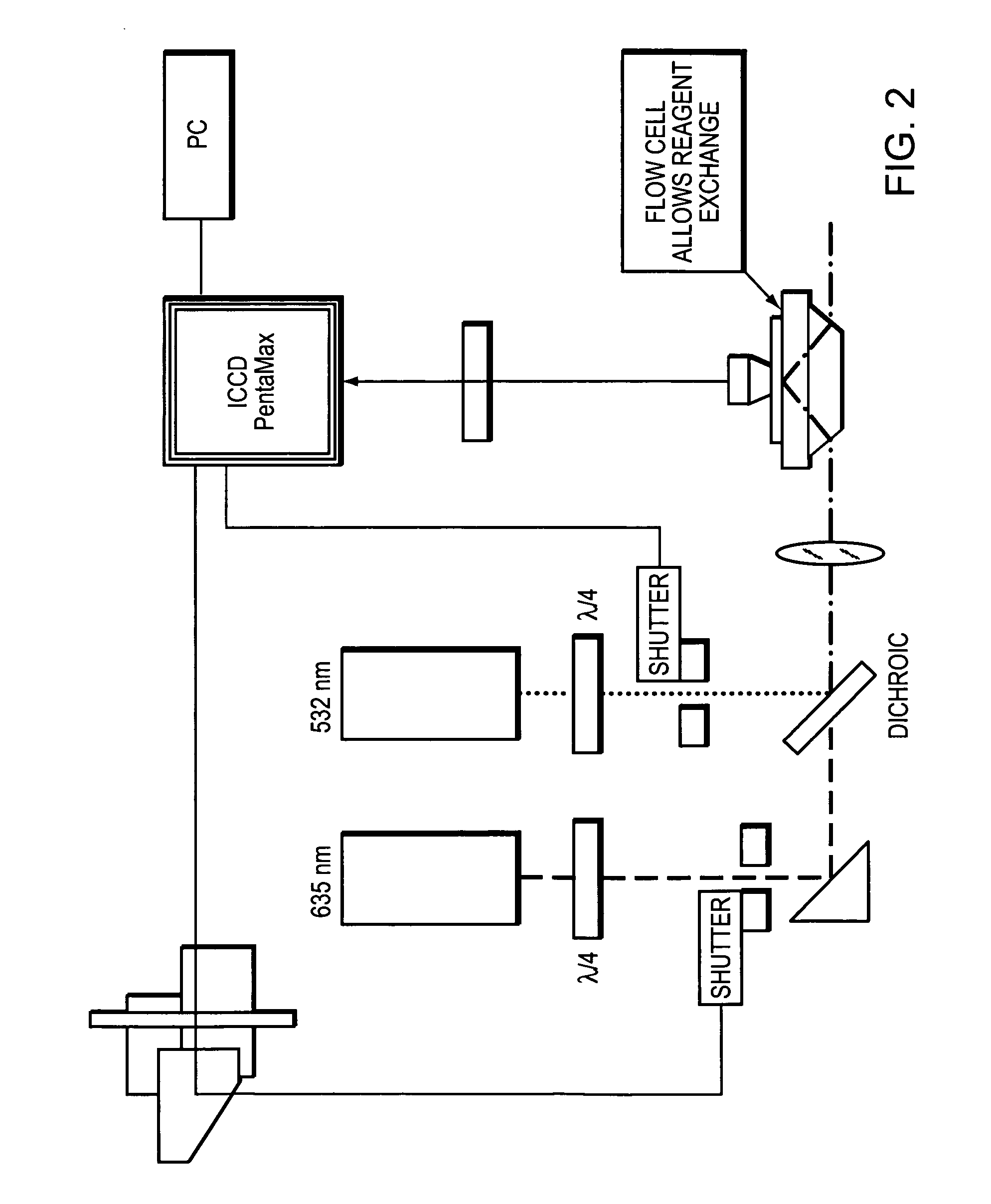
Use of single-stranded nucleic acid binding proteins in sequencing
InactiveUS20060024678A1Stabilizing sequencingIncrease speedMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingSingle strand
The invention provides methods for stabilizing a nucleic acid sequencing reaction. Generally, methods of the invention include exposing a target nucleic acid to a single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein and performing a sequencing reaction.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Nucleic acid binding proteins
Disclosed herein are methods for designing DNA binding proteins comprising a plurality of zinc fingers and methods for binding the proteins to target nucleotide sequences in cells.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
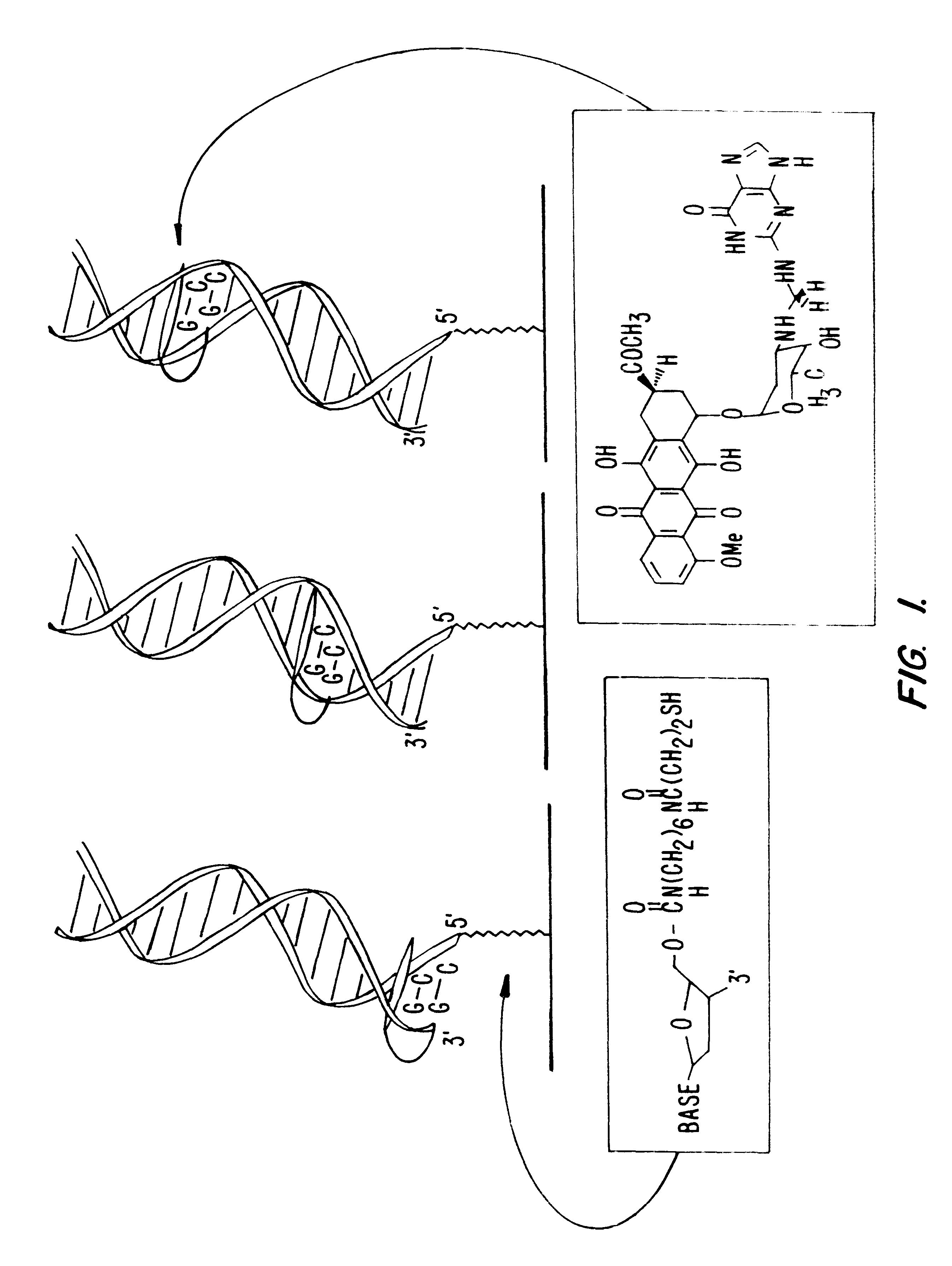
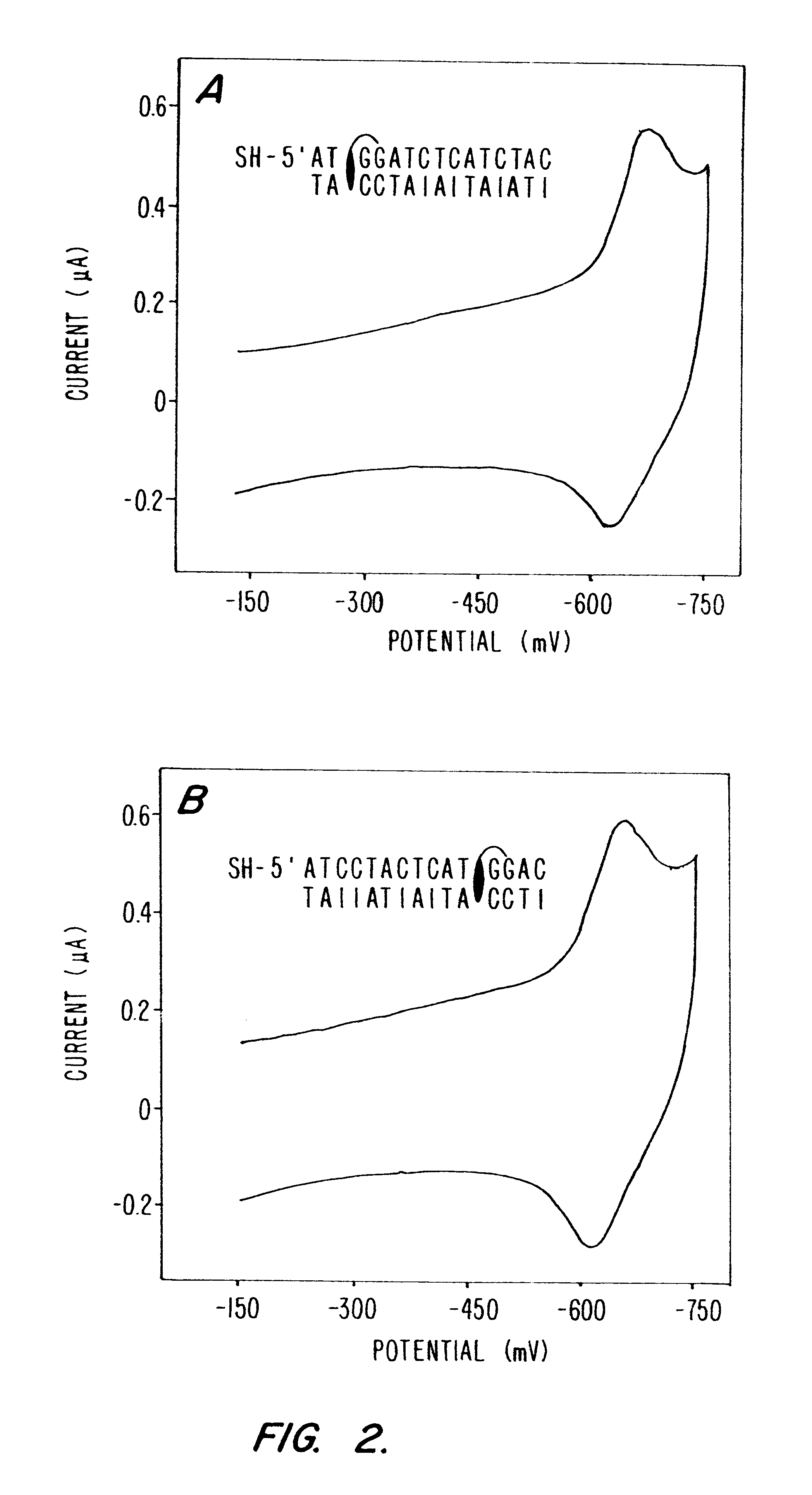
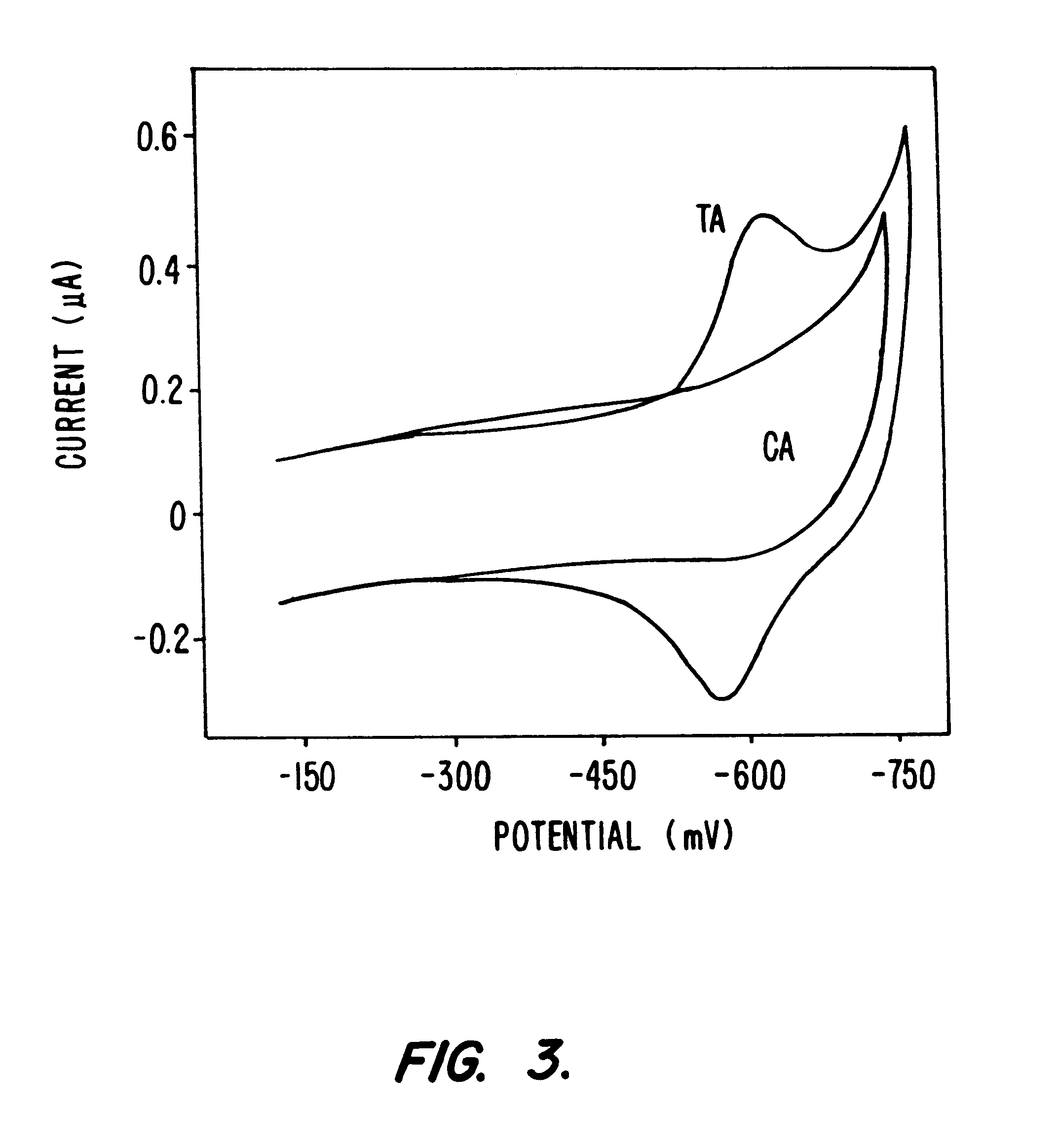
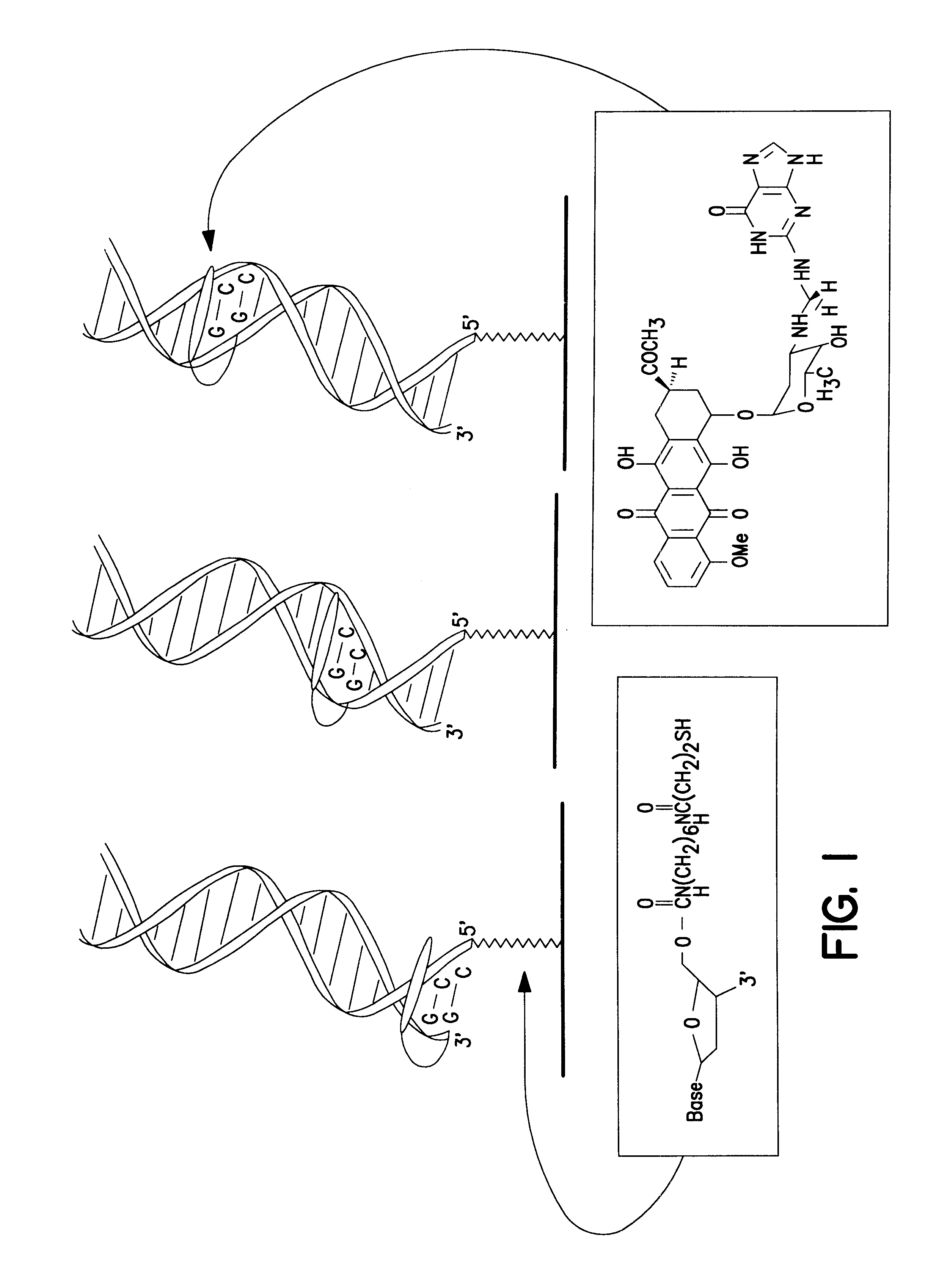
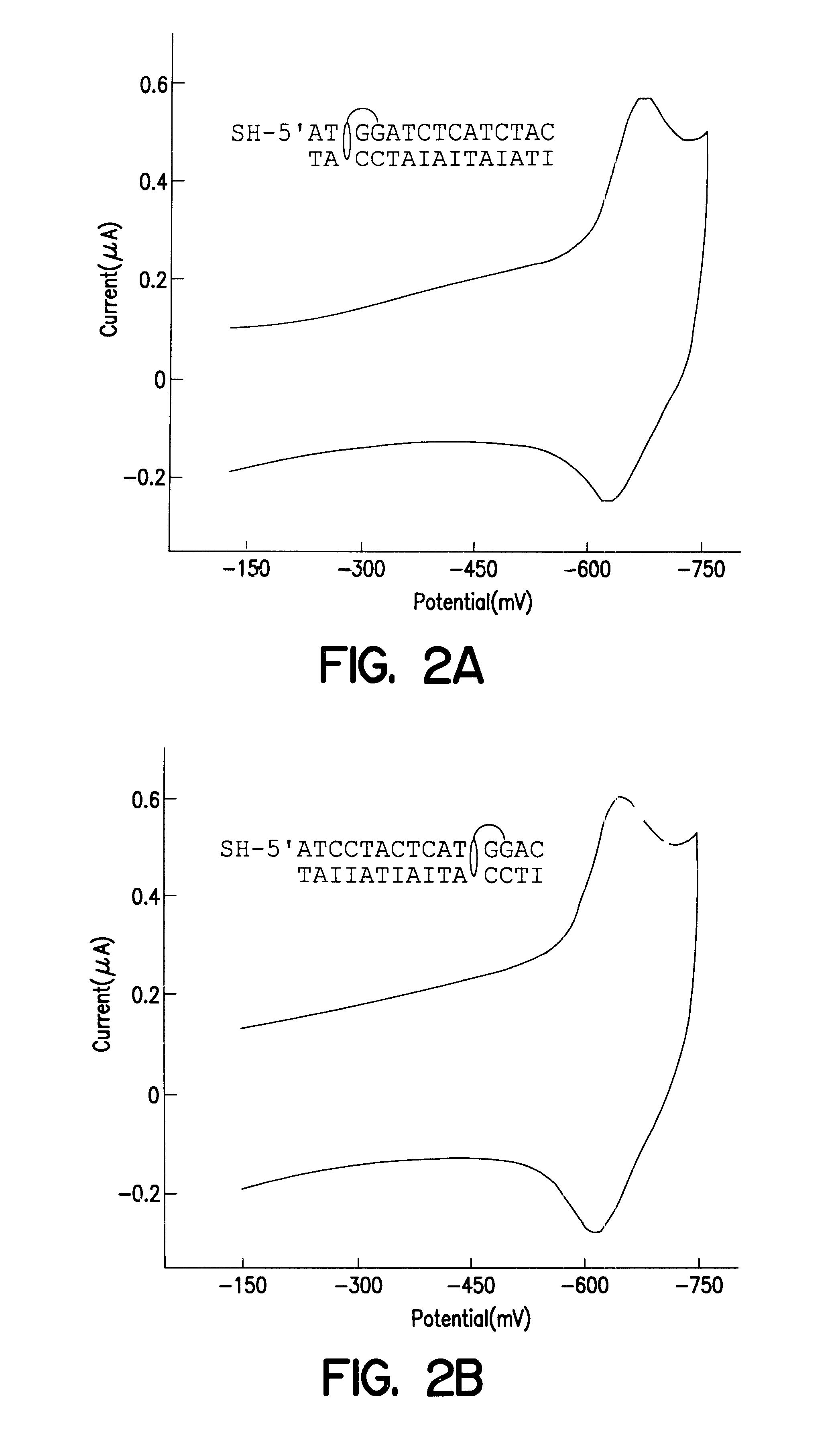
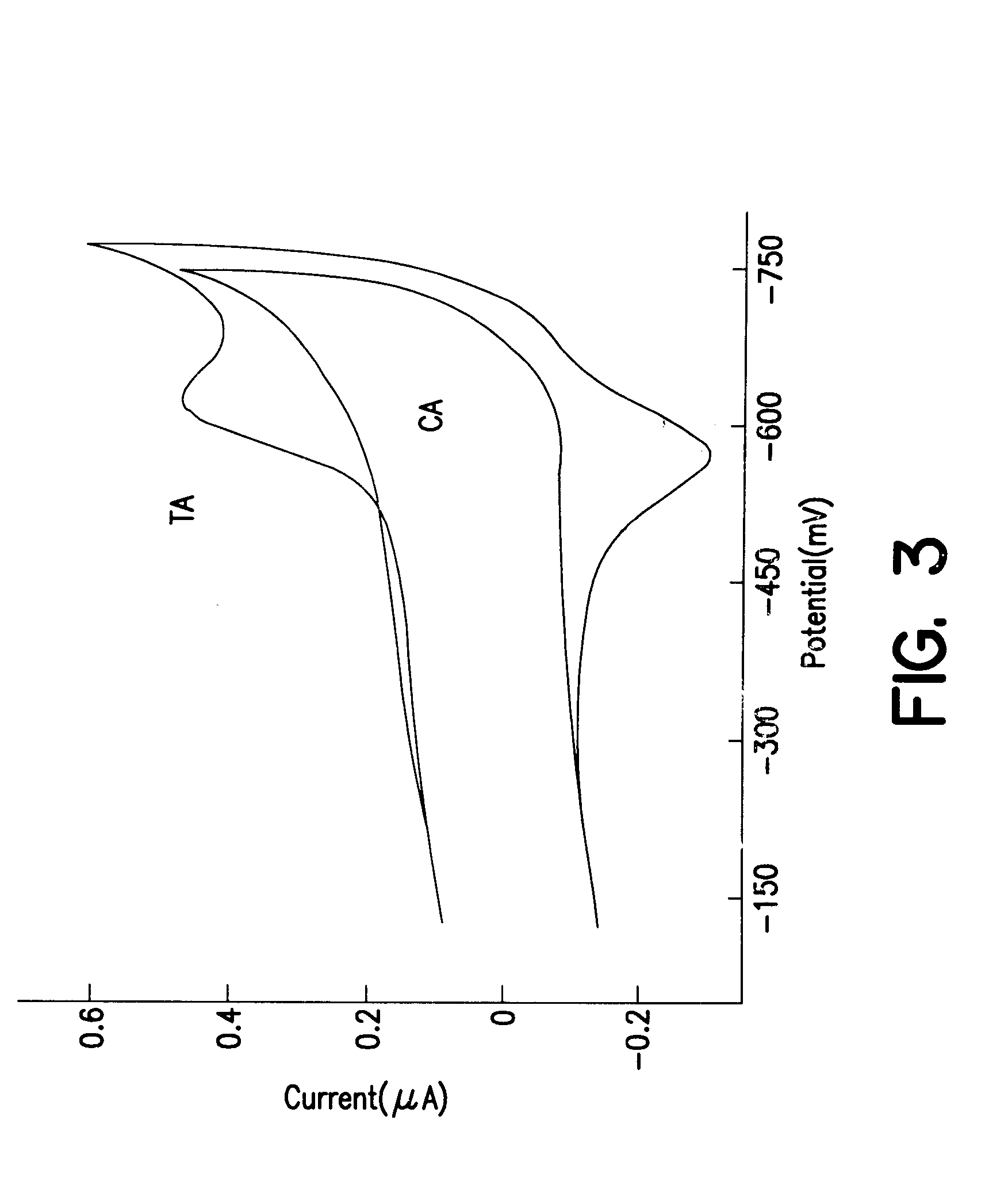
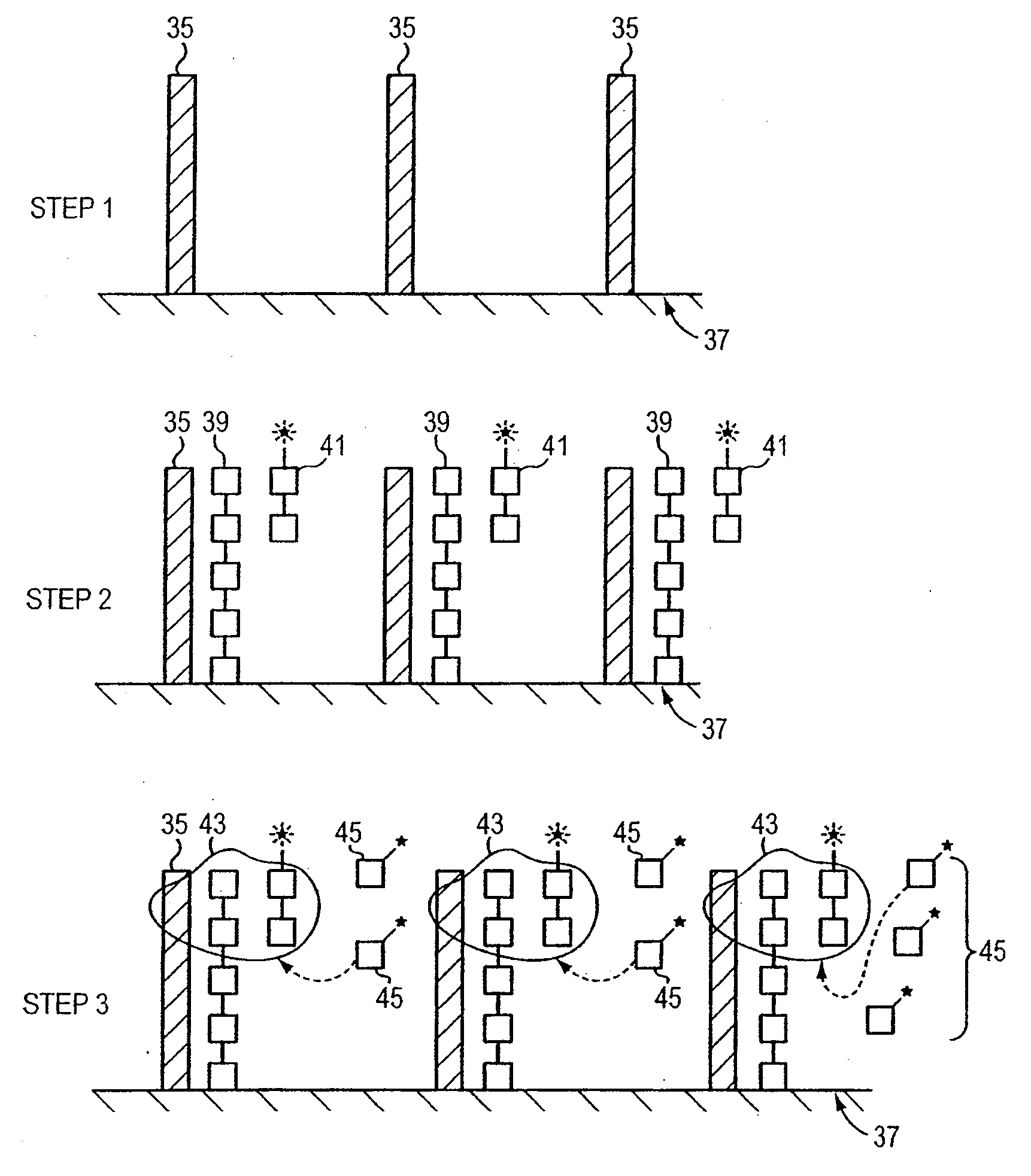
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
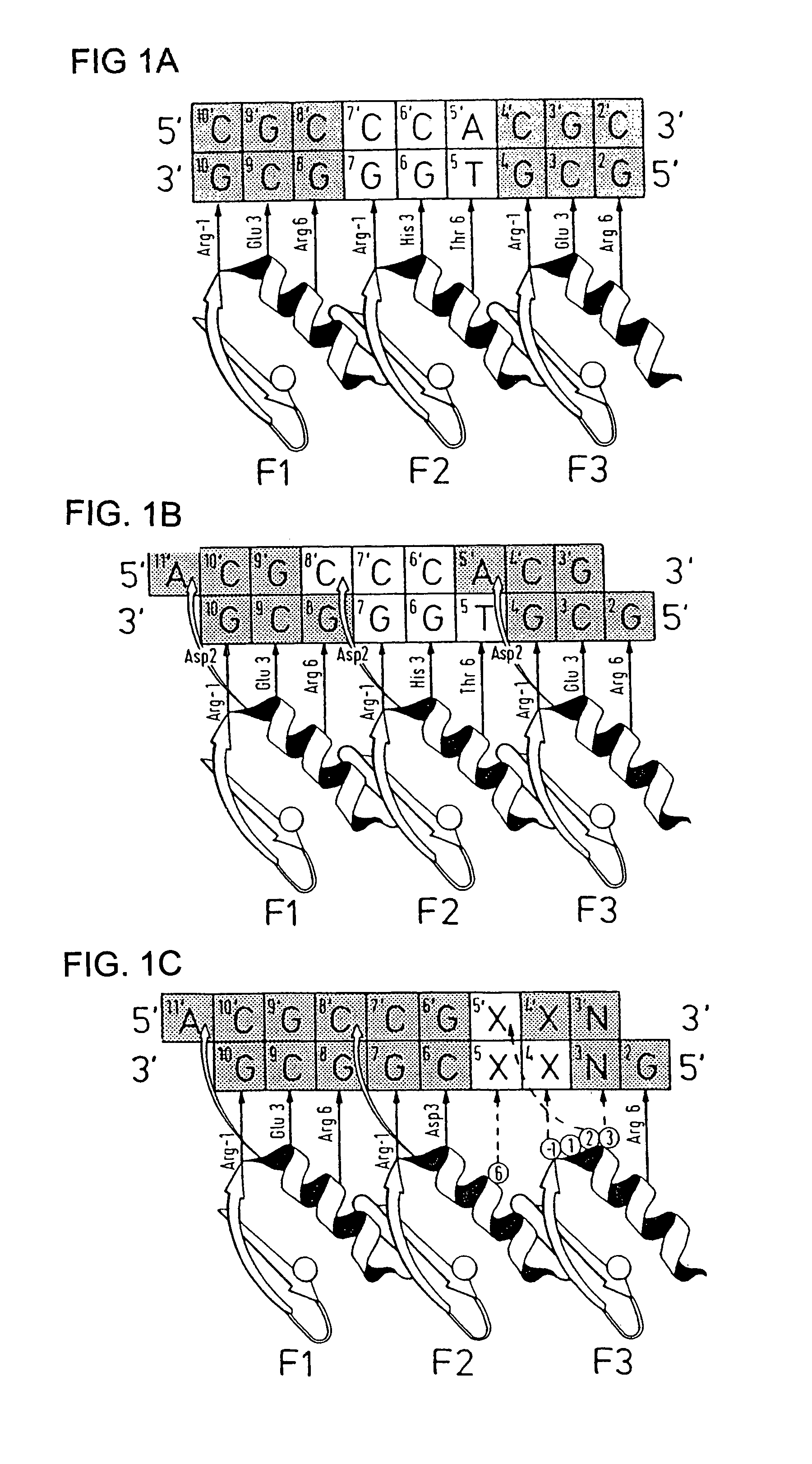
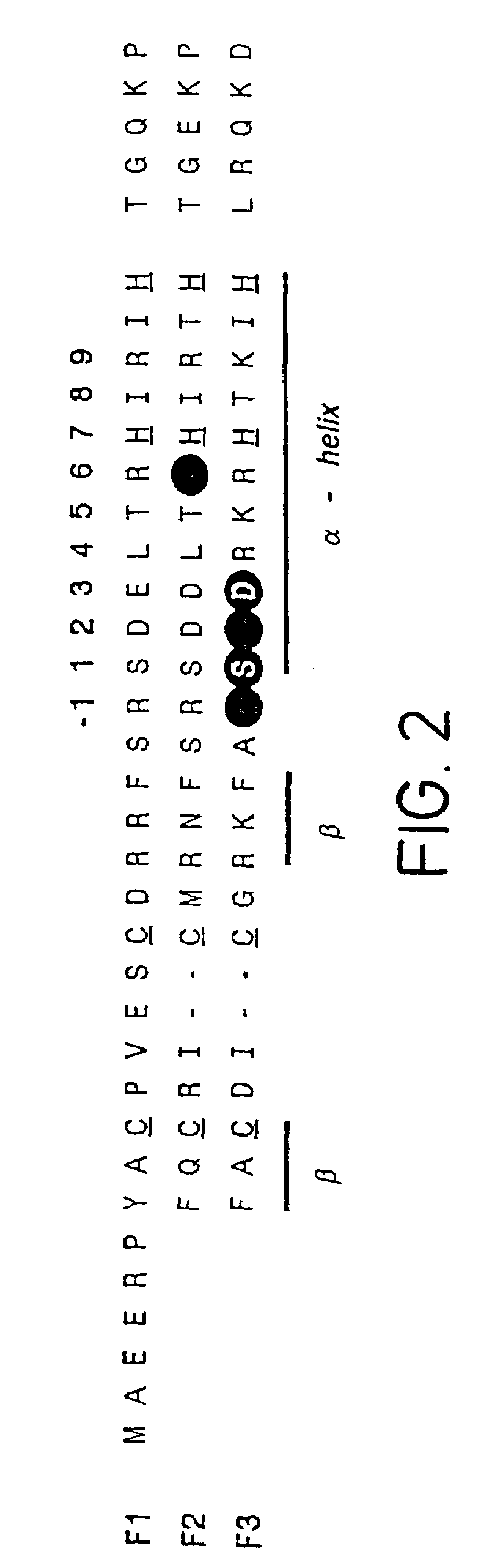
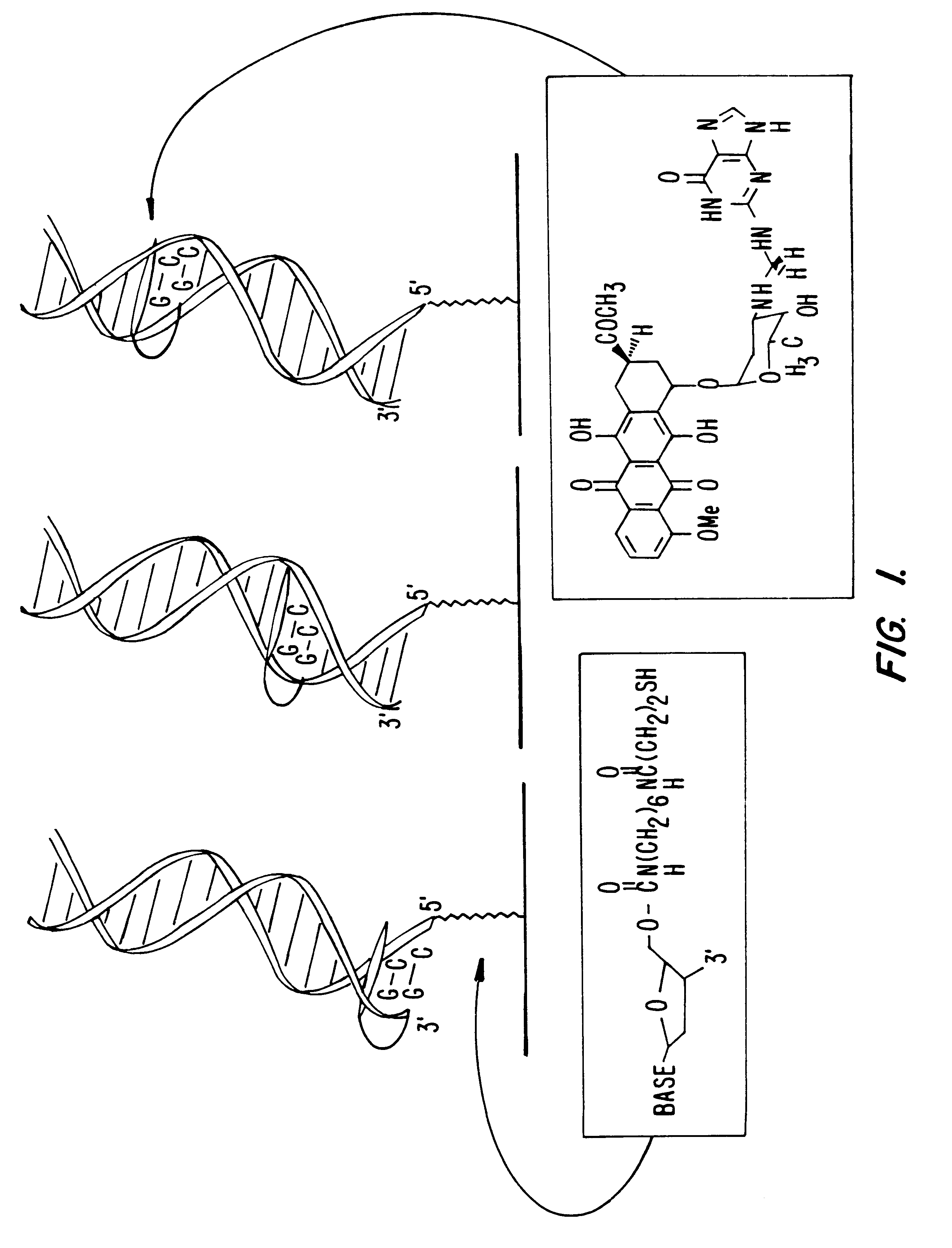
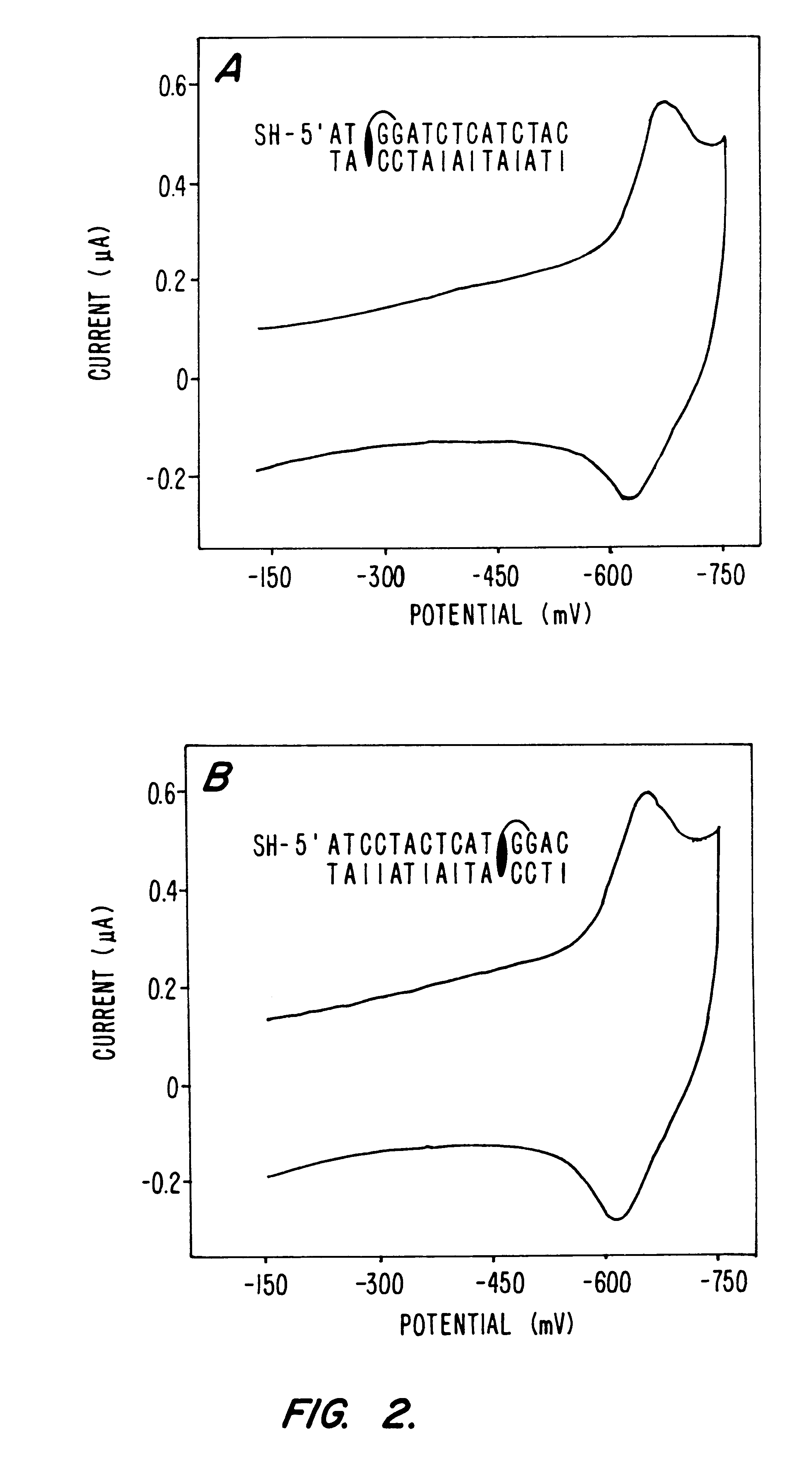
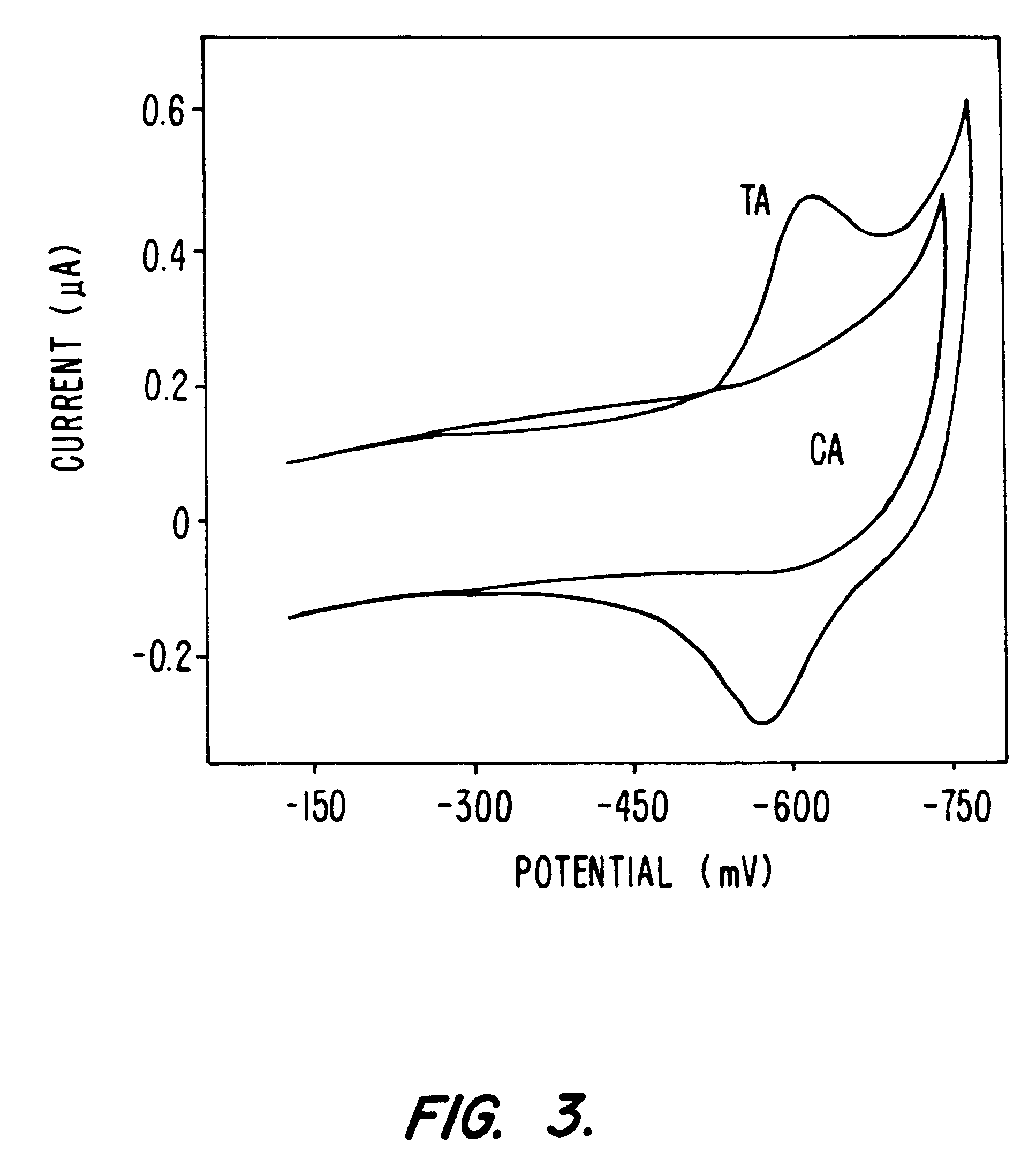
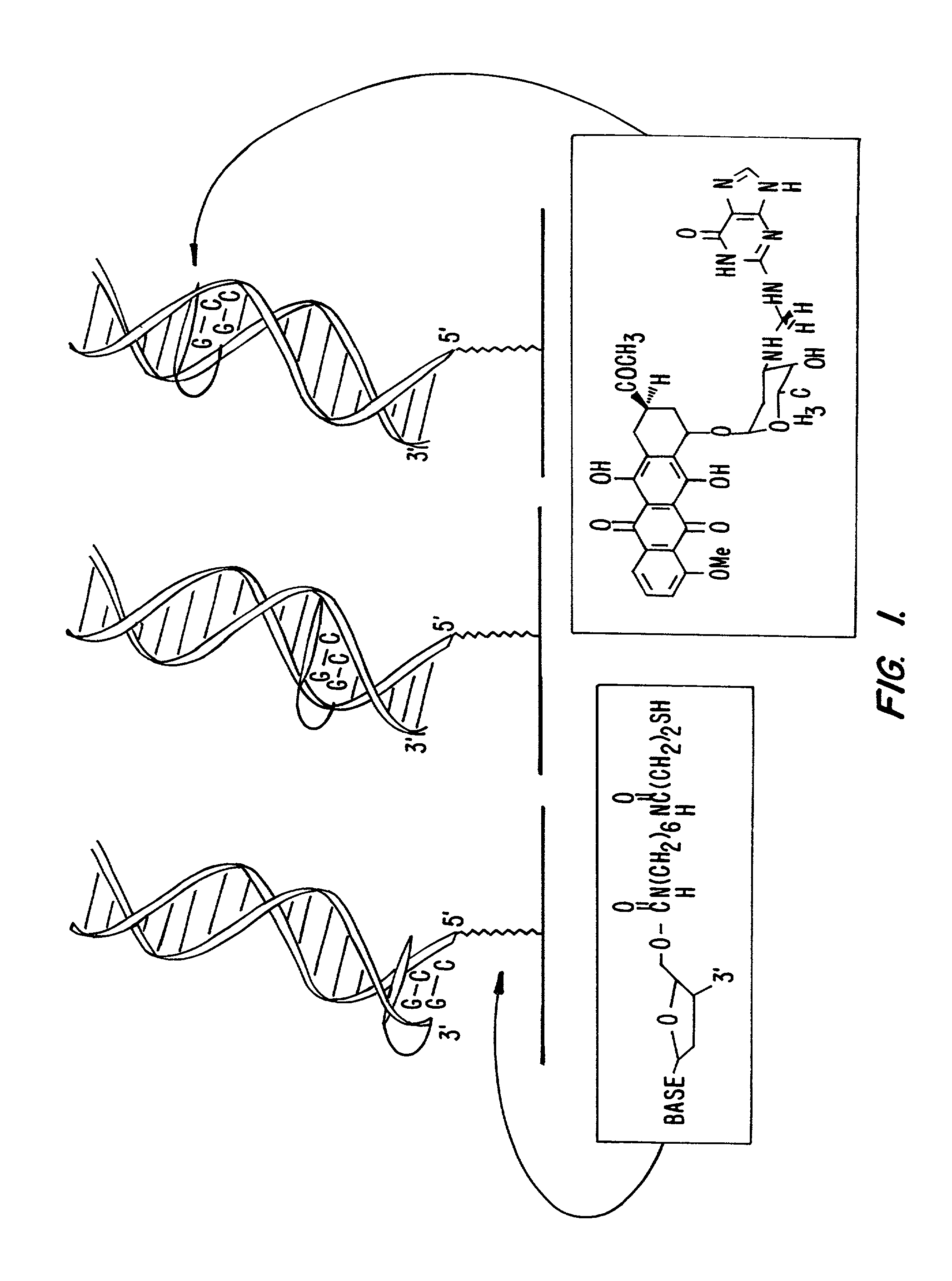
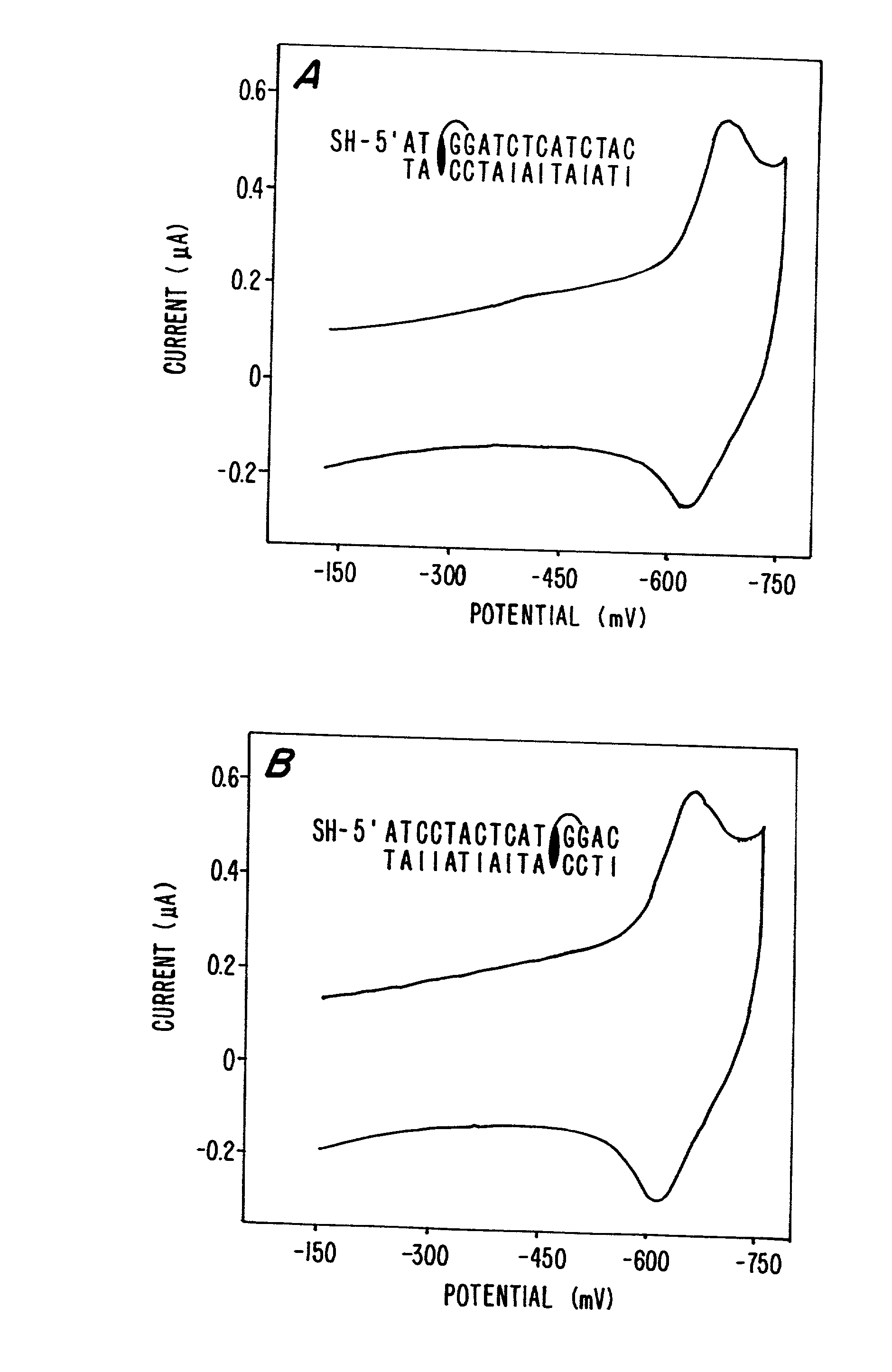
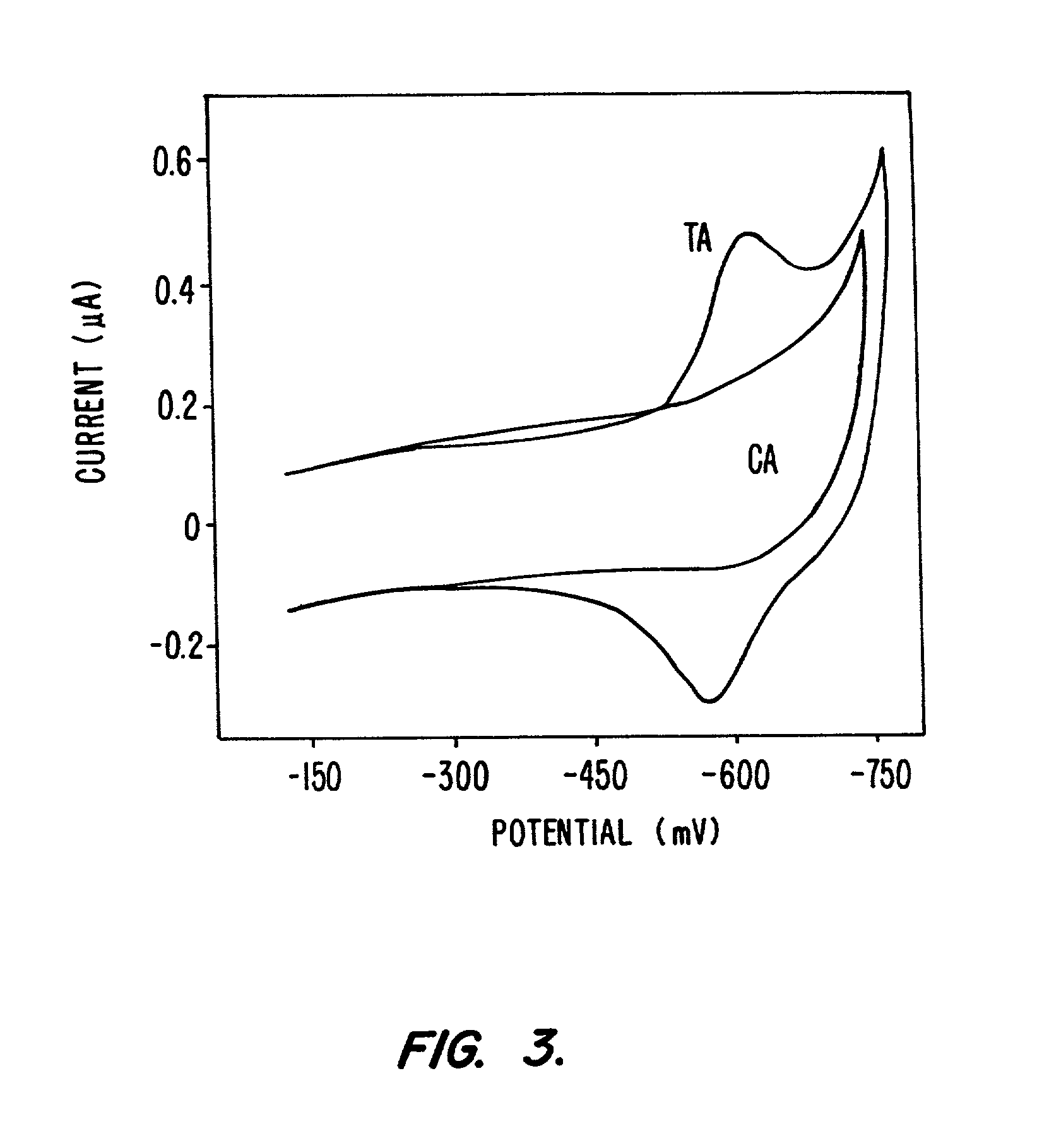
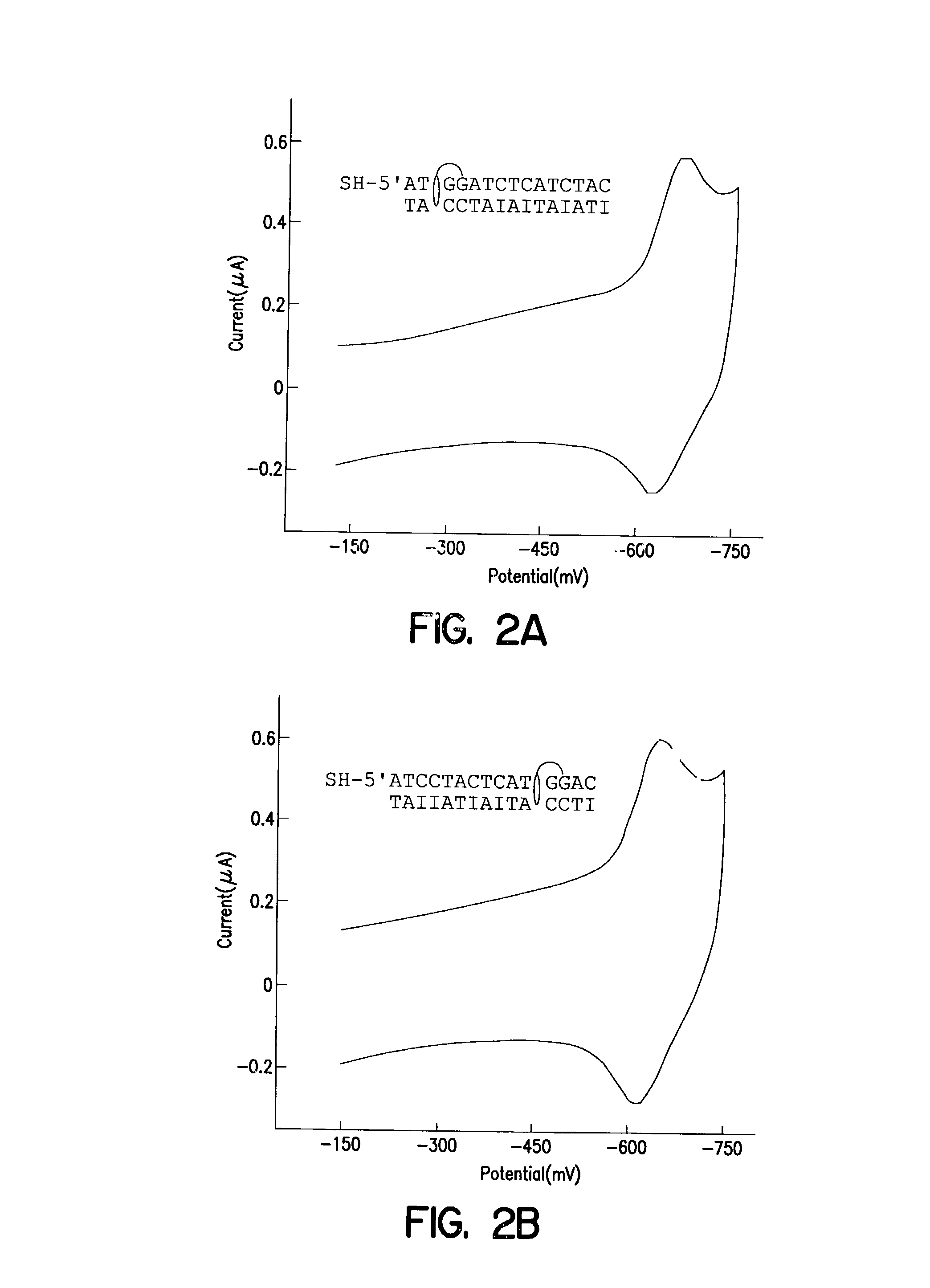
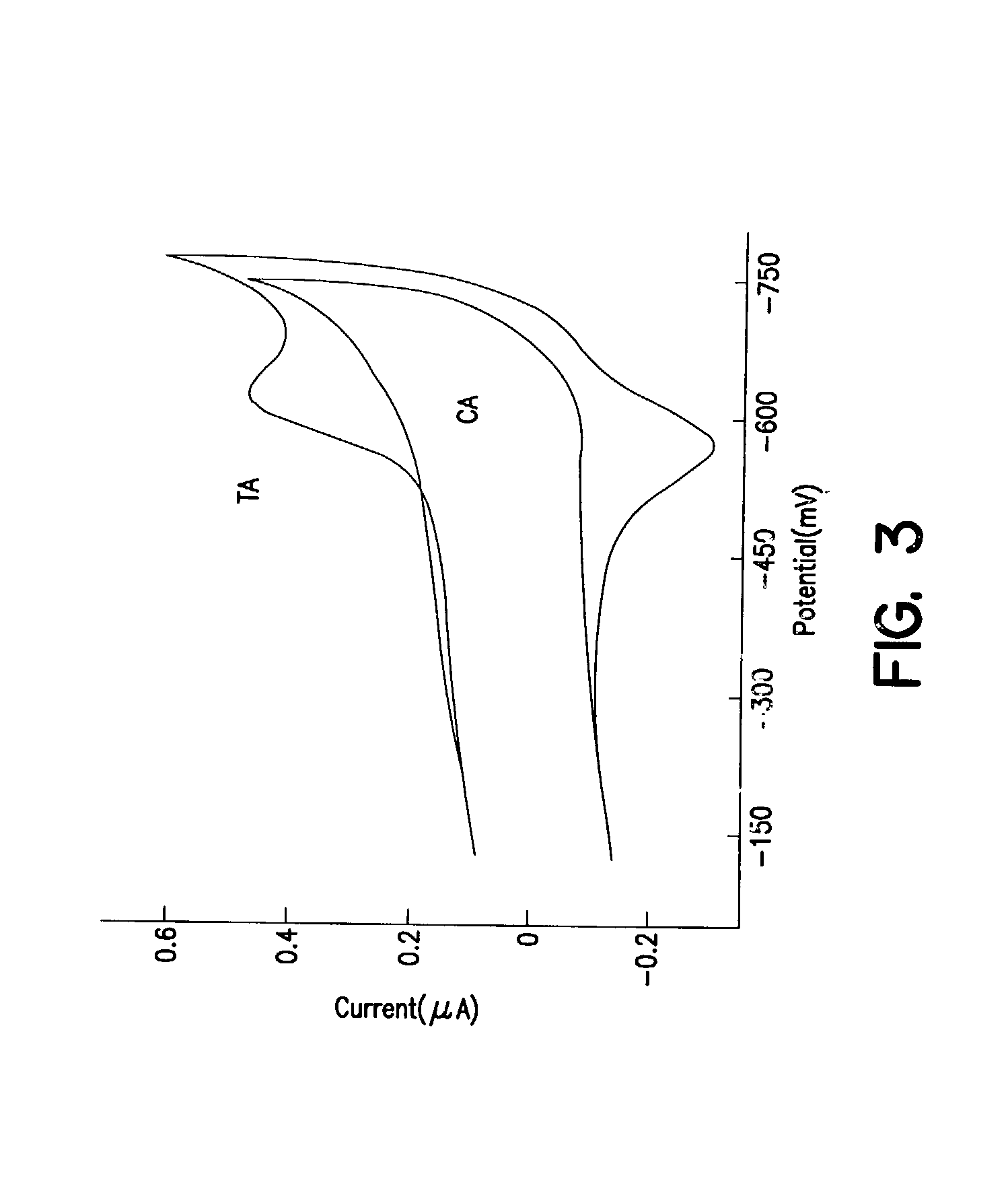
Compositions and methods for electrochemical detection and localization of genetic point mutations and other base-stacking perturbations within oligonucleotide duplexes adsorbed onto electrodes and their use in biosensing technologies are described. An intercalative, redox-active moiety (such as an intercalator or nucleic acid-binding protein) is adhered and / or crosslinked to immobilized DNA duplexes at different separations from an electrode and probed electrochemically in the presence or absence of a non-intercalative, redox-active moiety. Interruptions in DNA-mediated electron-transfer caused by base-stacking perturbations, such as mutations or binding of a protein to its recognition site are reflected in a difference in electrical current, charge and / or potential.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Novel hot start nucleic acid amplification
ActiveUS20080138878A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandNucleic acid binding protein
Methods and compositions for performing nucleic acid duplication and amplification reactions are provided. A single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein is selected and provided in the reaction mixture which is assembled at a low, nonstringent temperature to include all of the necessary reagents for successful nucleic acid duplication or amplification reactions. By incorporating a single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein into the reaction mixture at low temperature, the generation of nonspecific products such as amplification products is improved despite the reaction mixture having been fully assembled at a nonstringent temperature.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Screening system for zinc finger polypeptides for a desired binding ability
InactiveUS6733970B2Determining affinityDetermining specificitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingZinc
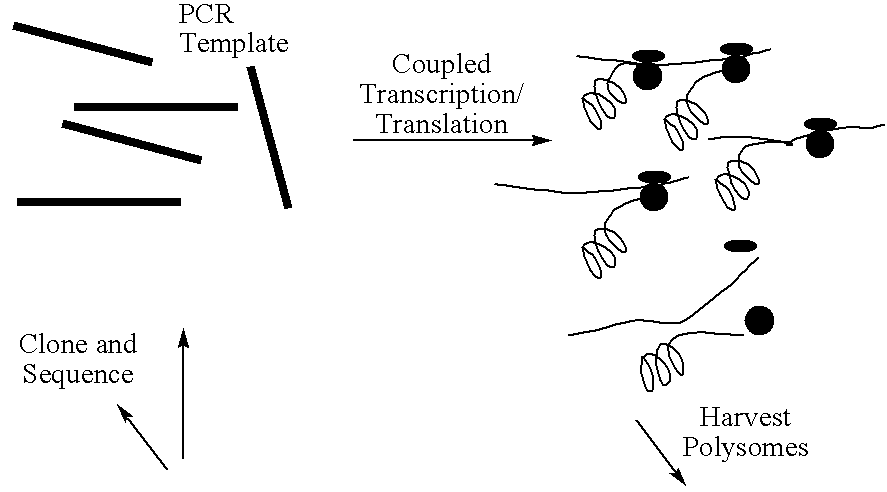
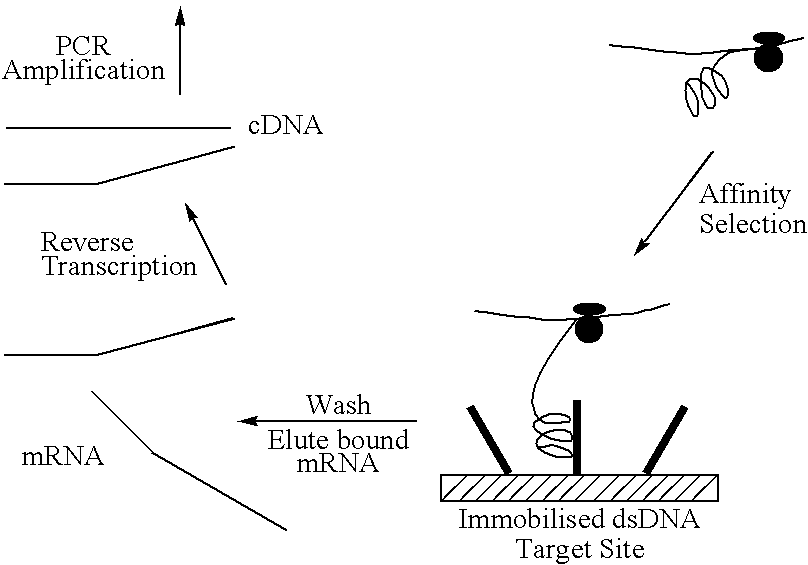
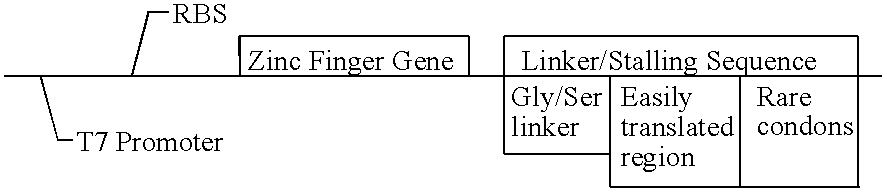
This invention relates to a method for producing a zinc finger nucleic acid binding protein comprising preparing a zinc finger protein according design rules, varying the protein at one or more positions, and selecting variants which bind to a target nucleic acid sequence by polysome display.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD +1
Enzyme mutant
InactiveUS20120100530A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesNucleotideADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to constructs comprising a nucleic acid binding protein and a surface. At least one native accessible cysteine residue is removed from the binding protein. The binding protein is attached to the surface via one or more accessible cysteine residues. The removal of other accessible cysteine residues from the protein allows control attachment to the surface. The constructs can be used to generate transmembrane pores having a nucleic acid binding protein attached thereto. Such pores are particularly useful for sequencing nucleic acids. The enzyme handles the nucleic acid in such a way that the pore can detect each of its component nucleotides by stochastic sensing.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
Assays for measuring nucleic acid binding proteins and enzyme activities
InactiveUS6312896B1Simple and accurate and reliable assayEfficient transferSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein insertionNucleic acid binding protein
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Methods and compositions related to the use of sequence-specific endonucleases for analyzing nucleic acids under non-cleaving conditions
The invention relates to methods, products and systems for analyzing nucleic acid molecules using a nucleic acid binding protein such as a sequence-specific endonuclease. The methods can be used to obtain sequence information about the nucleic acid molecules.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
Nucleic acid mapping using linear analysis
InactiveUS20050112620A1Microbiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsNucleic acid mappingLinear analysis
The invention relates to the use of nucleic acid binding agents for labeling polymers such as nucleic acid molecules. The nucleic acid binding agents are nucleic acid binding proteins that bind nucleic acid molecules non-specifically, in some embodiments.
Owner:U S GENOMICS INC
Methods for attaching proteins to lipidic microparticles with high efficiency
InactiveUS7022336B2Extended shelf lifeOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesAntibody fragmentsMicroparticle
The invention provides methods of attaching proteins to lipidic microparticles with efficiencies of at least 77%. The proteins are attached to linker molecules comprising a hydrophilic domain and a hydrophobic domain. The proteins can be antibodies, antibody fragments, hormones, growth factors, enzymes, or nucleic acid binding proteins, or other proteins. The proteins can be chemically conjugated to the linker molecules, or they can be fused to the linker molecules by recombinant techniques.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Compositions and their uses directed to nucleic acid binding proteins
InactiveUS20050153336A1Modulate expressionSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseNucleic acid binding protein
Compounds, compositions and methods are provided for modulating the expression of STAT2. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acid encoding STAT2. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of STAT2 expression and for diagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions associated with expression of STAT2 are provided.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
InactiveUS6461820B1Material nanotechnologySugar derivativesNucleic acid binding proteinElectron transfer
Compositions and methods for electrochemical detection and localization of genetic point mutations and other base-stacking perturbations within oligonucleotide duplexes adsorbed onto electrodes and their use in biosensing technologies are described. An intercalative, redox-active moiety (such as an intercalator or nucleic acid-binding protein) is adhered and / or crosslinked to immobilized DNA duplexes at different separations from an electrode and probed electrochemically in the presence or absence of a non-intercalative, redox-active moiety. Interruptions in DNA-mediated electron-transfer caused by base-stacking perturbations, such as mutations or binding of a protein to its recognition site are reflected in a difference in electrical current, charge and / or potential.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Use of Single-Stranded Nucleic Acid Binding Proteins In Sequencing
InactiveUS20080032307A1Improved speed and accuracy and precisionImproved speed and fidelity and processivityMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides methods for stabilizing a nucleic acid sequencing reaction. Generally, methods of the invention include exposing a target nucleic acid to a single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein and performing a sequencing reaction.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
Lateral flow methods and devices for detection of nucleic acid binding proteins
InactiveUS20070015166A1Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBody fluidNucleic acid binding protein
Methods and devices are provided for detecting the presence or absence of nucleic acid binding proteins, such as NMP22, and other proteins, in bodily fluids.
Owner:DATASCOPE INVESTMENT
Method of high flux screening, capturing and separating target molecule from complex composition matter such as traditional Chinese medicine and chemical mixture
InactiveCN1590560AImprove bindingIncrease transcriptionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA Microarray ChipDisease
A process for high-flux screening, capturing and separation of target moleculae from complex substance (Chinese medicine or chemical mixer) includes preparing a ds DNA microarray chip to make its probe have a binding sites of dsDNA bindin, measuring the affinity of the sites, creating the standard affinity parameter system, mixing the microarray chip with said complex substance, reacting, detecting the affinity variation, screening the varied targets, linking them to the surface of chromatographic column, filling the complex substance in it, capturing the effective moleculae by probes, eluting and collecting the effective moleculae.
Owner:王进科 +2
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
InactiveUS6649350B2Highly accurateSensitive highBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyNucleic acid binding proteinElectron transfer
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Use of Single-Stranded Nucleic Acid Binding Proteins in Sequencing
InactiveUS20100173363A1Improved speed and accuracy and precisionImproved speed and fidelity and processivityMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme stabilisationSingle strandNucleic acid sequencing
The invention provides methods for stabilizing a nucleic acid sequencing reaction. Generally, methods of the invention include exposing a target nucleic acid to a single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein and performing a sequencing reaction.
Owner:FLUIDIGM CORP
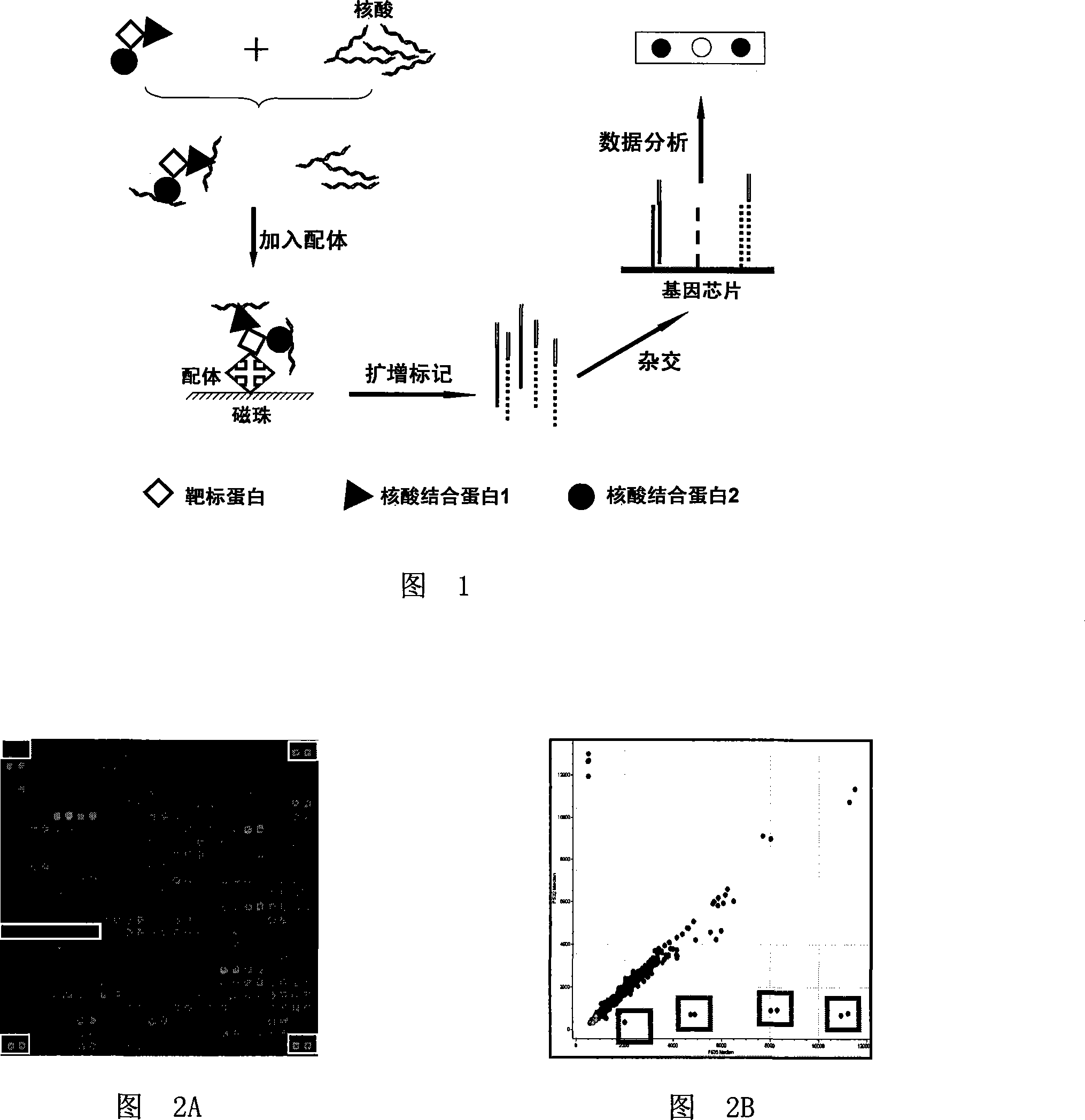
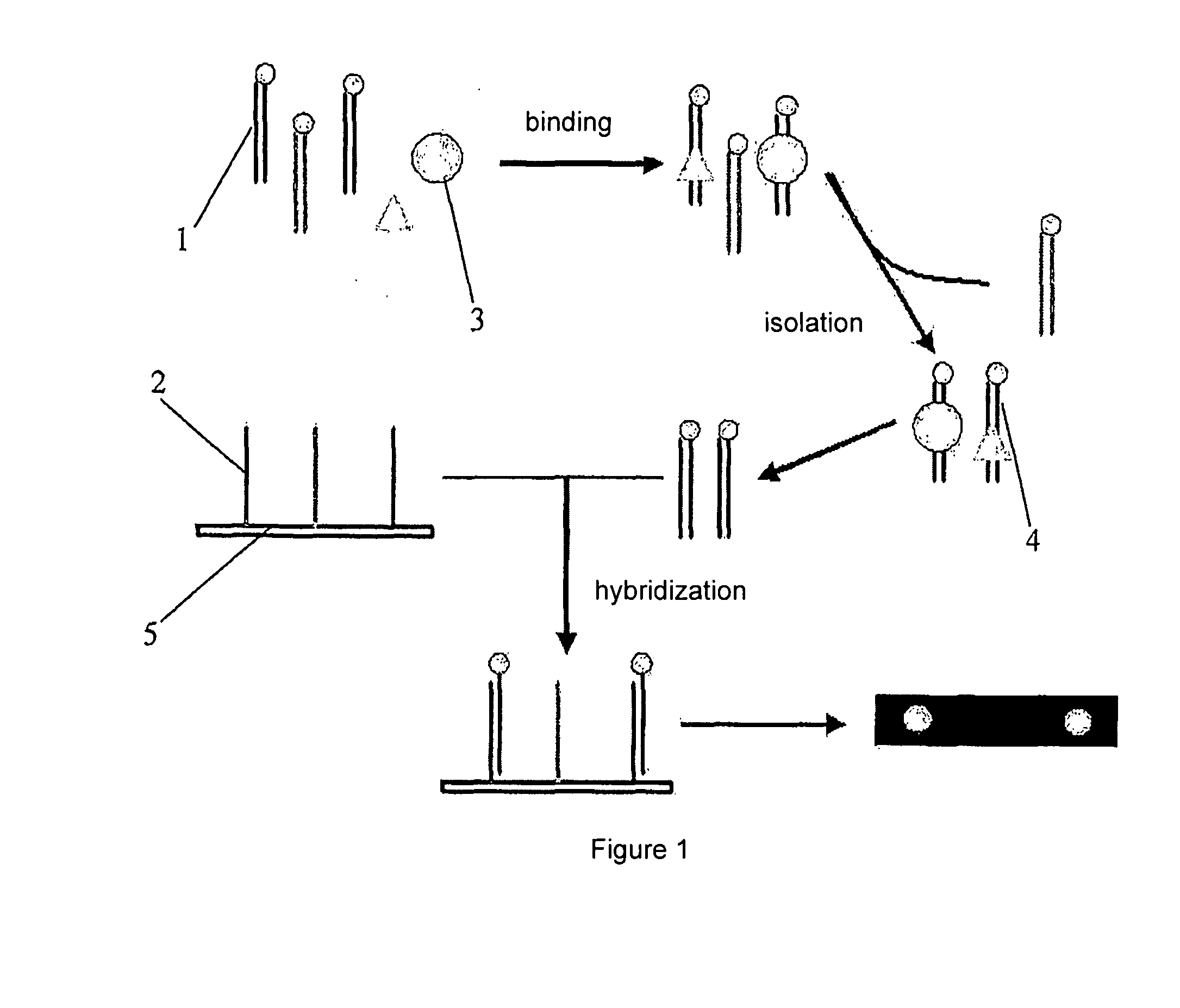
Method for detecting if interaction between nucleic acid conjugated protein -target protein exist based on biological chip
ActiveCN101236209AImprove throughputHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtein targetConjugated protein
The invention discloses a method of detecting whether an interaction exists between nucleic acid protein and target protein based on biochip. The method comprises the following steps: (1)adding a plurality of groups of nucleic acid acquisition probes into a biological sample system containing the target protein to form a target-protein-nucleic-acid-conjugated-protein-nucleic-acid-acquisition-probe compound, and the nucleic acid acquisition probes containing at least one section of sequence capable of integrating with the nucleic acid conjugated protein; (2) separating the target-protein-nucleic-acid-conjugated-protein-nucleic-acid-acquisition-probe compound through molecules capable of specifically integrating with the target protein, and then recovering the nucleic acid acquisition probes; (3) carrying out hybridization of the nucleic acid acquisition probes recovered in the step 2 and a plurality of single chain immobilized probes which are fixed on the substrate of the biochip and are corresponding to the nucleic acid acquisition probes, and the nucleic acid sequence of the immobilized probes complementing the corresponding nucleic acid acquisition probes or one chain of the nucleic acid acquisition probes; (4) detecting the hybridization results to see whether the interaction exists between the nucleic acid conjugated protein and the target protein.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
Assays for measuring nucleic acid binding proteins and enzyme activities
InactiveUS20020146722A1Simple and accurate and reliable assaySimple and accurate and reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptide preparation methodsAssayNucleic acid binding protein
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Rapid and sensitive assay for the detection and quantification of coregulators of nucleic acid binding factors
InactiveUS20080044826A1Facilitating and stabilizing spectroscopic interactionMeasurable change in fluorescenceNanotechSugar derivativesPost translationalFluorescence
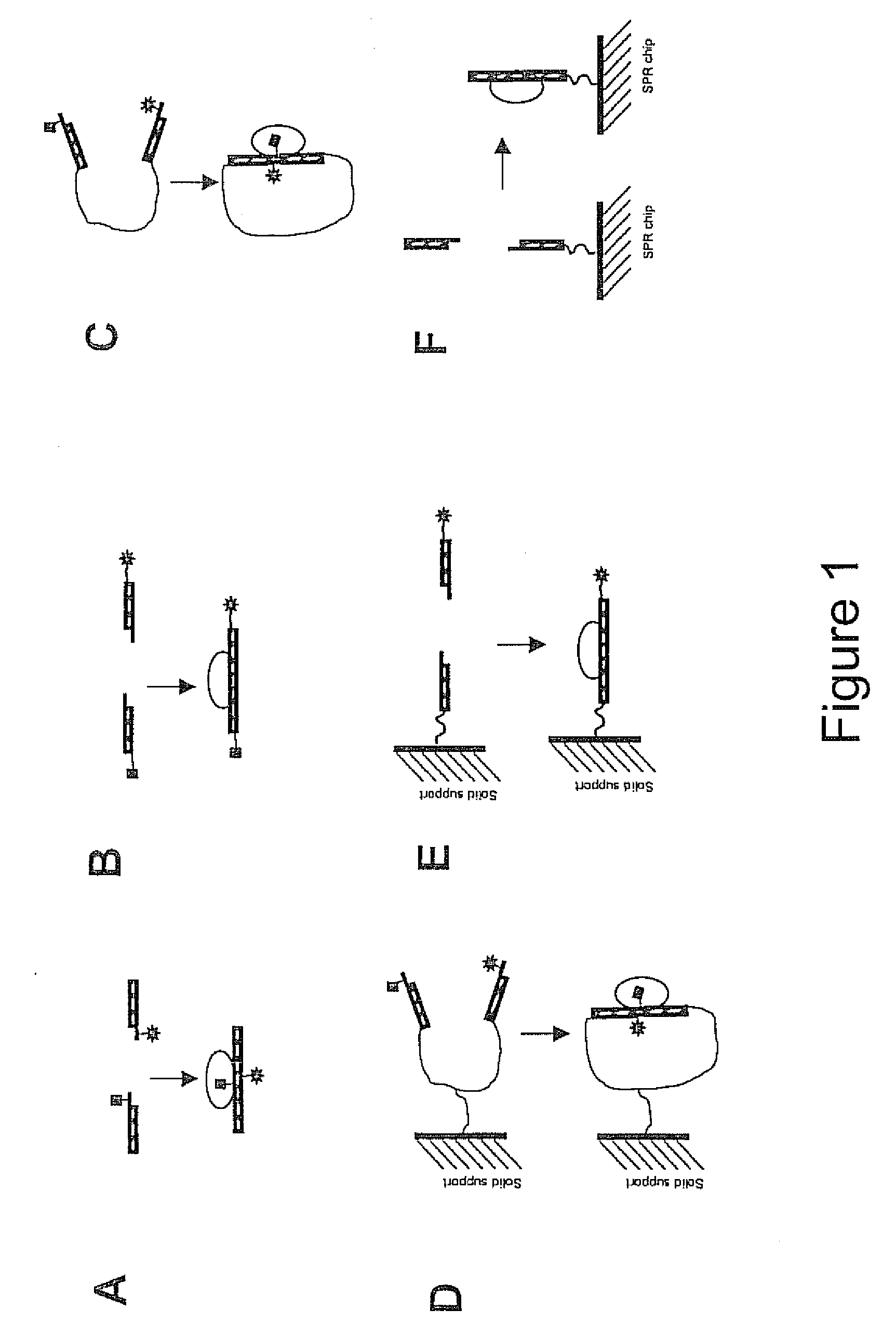
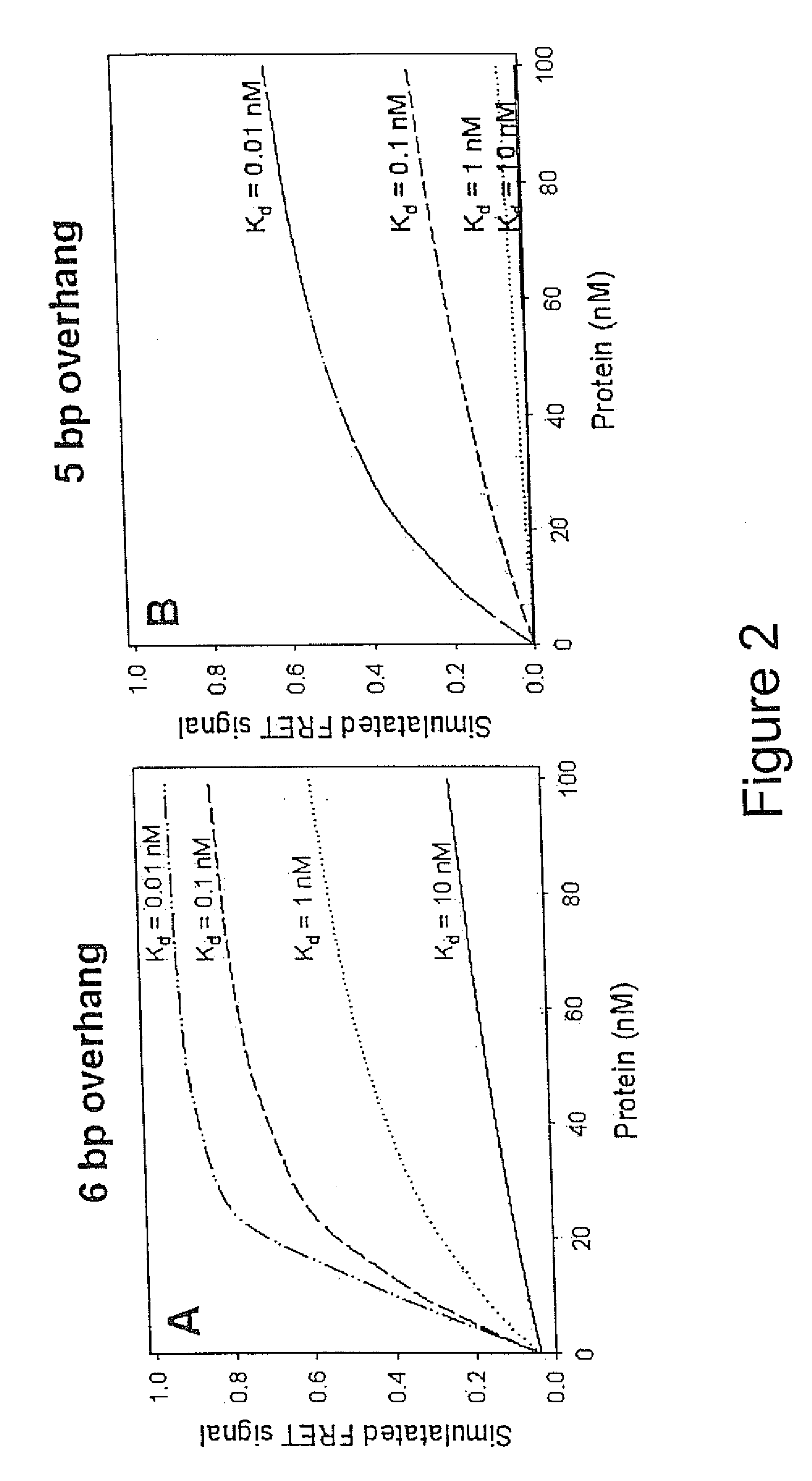
Biosensors and methods to determine the activity of any and all nucleic acid binding factors, proteins, cellular events, nucleic acid binding protein coregulators, or fragments thereof, based upon the stabilization of the interaction of two nucleic acid components, which together comprise a complete nucleic acid binding element, by the binding of a nucleic acid binding factor are provided. Preferably, a fluorescence donor is attached to a nucleic acid comprising one portion or component of a complete nucleic acid binding element and a fluorescence acceptor is attached to a nucleic acid comprising the other portion or component of the same complete binding element. Alternatively, a solid substrate is attached to a nucleic acid comprising one portion of a binding element and a detectable label is attached to a nucleic acid comprising the other portion of the same binding element. Binding of a nucleic acid binding factor to the nucleic acid components affects a change in luminescence or the association of the detectable label with the solid substrate. These biosensors and methods may also be used to detect mediating nucleic acid binding factor coregulators, post-translational modifications and cellular events, to diagnose diseases and / or screen for drugs or other ligands that mediate the activity of nucleic acid binding factors.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
Compositions and methods for electrochemical detection and localization of genetic point mutations and other base-stacking perturbations within oligonucleotide duplexes adsorbed onto electrodes and their use in biosensing technologies are described. An intercalative, redox-active moiety (such as an intercalator or nucleic acid-binding protein) is adhered and / or crosslinked to immobilized DNA duplexes at different separations from an electrode and probed electrochemically in the presence or absence of a non-intercalative, redox-active moiety. Interruptions in DNA-mediated electron-transfer caused by base-stacking perturbations, such as mutations or binding of a protein to its recognition site are reflected in a difference in electrical current, charge and / or potential.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
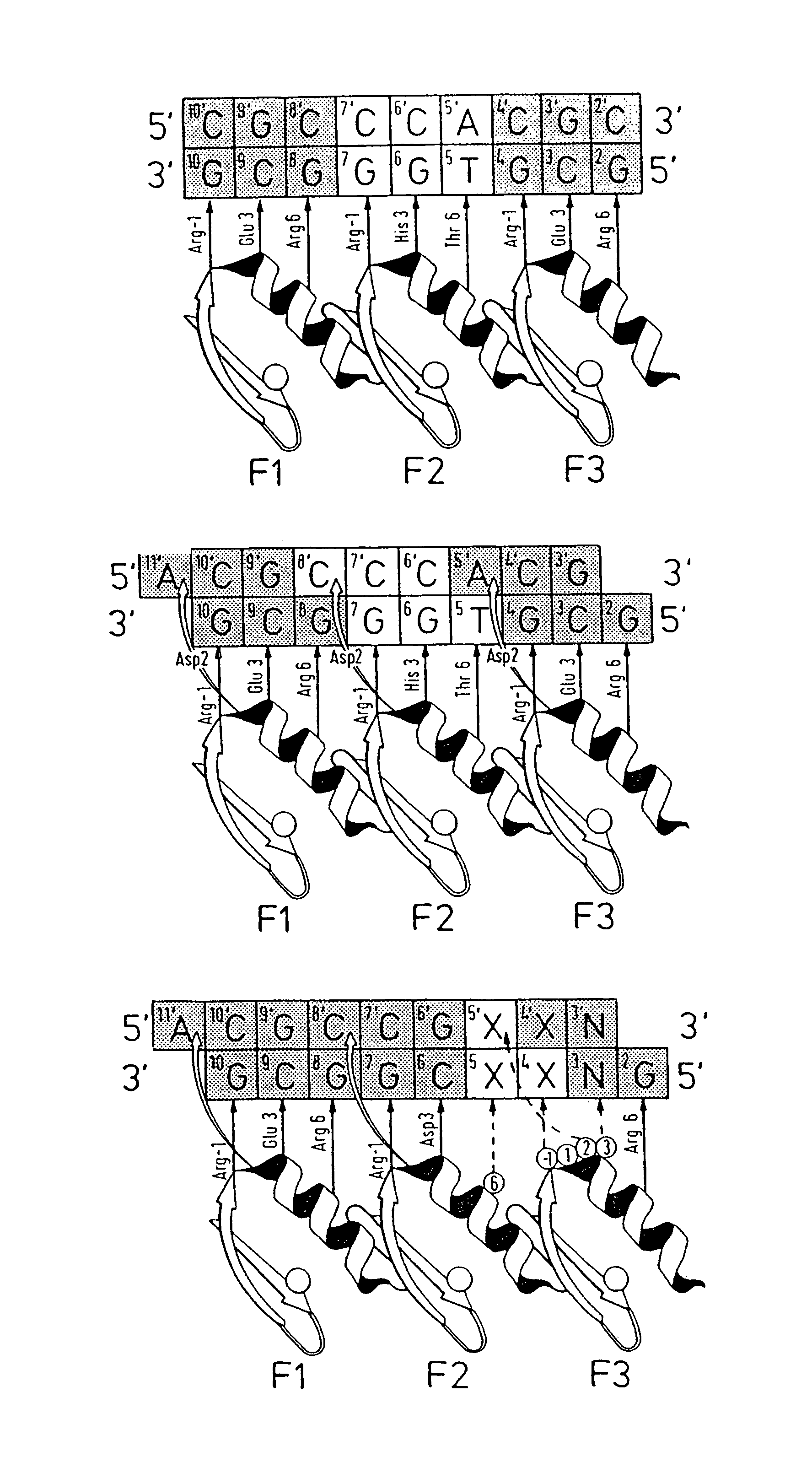
Nucleic acid binding proteins
InactiveUS6977154B1Preferential bindingStrong specificityHydrolasesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid sequencingZinc
The invention provides a method for producing a zinc finger polypeptide which binds to a target nucleic acid sequence containing a modified base but not to an identical sequence containing an equivalent unmodified base.
Owner:GENDAQ +1
Method for transfer of molecular substances with prokaryontic nucleic acid-binding proteins
InactiveUS20050170504A1Improve efficiencyUndesirable effectOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsThermal stabilityNucleic acid binding protein
The invention relates to a method for the transfer of molecular substances, for example proteins or nucleic acids in cells, in the case of using DNA combined with a possible gene expression. A prokaryotic nucleic acid-binding protein is used for the transfer, which is preferably obtained from a thermostable organism. Where the substance to be transferred is a nucleic acid, the protein forms a reversible complex with the nucleic acid. The prokaryotic protein condenses and compacts the nucleic acids. Said nucleic acids can be taken up in the target cells after suitable incubation.
Owner:ACGT PREGENOMICS
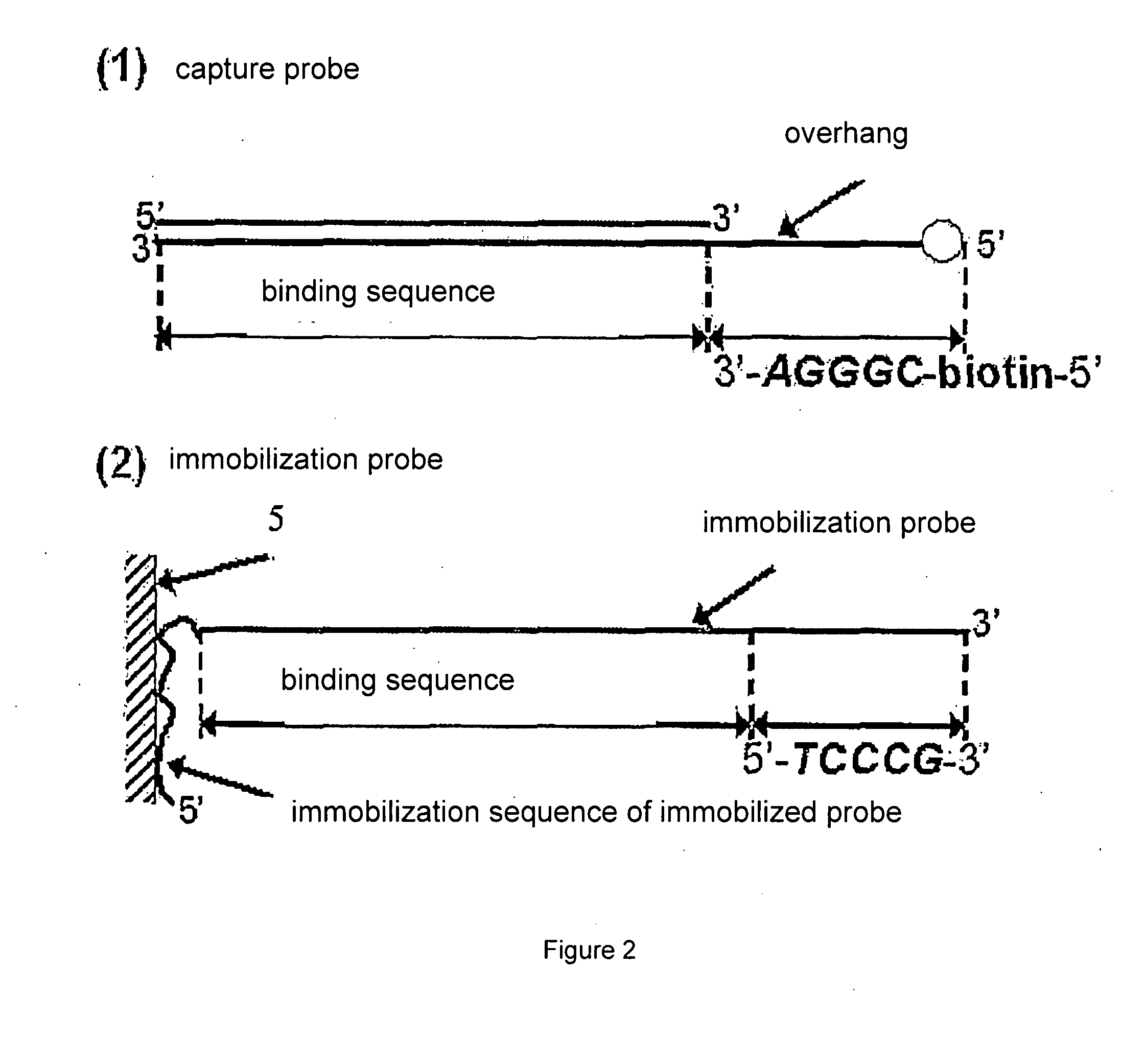
Testing Method of Nucleic Acid Binding Protein Based on Biochip
InactiveUS20090018025A1Improve throughputSensitive highMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationSingle strandNucleic acid binding protein
A testing method of nucleic acid binding protein based on biochip, comprises the following steps: 1. puts a plurality of groups solution including nucleic acid captured probes into biological sample including a plurality of nucleic acid binding protein to be test, and thus forming nucleic acid captured probe-nucleic acid binding protein complexes; such nucleic acid captured probe includes at least a segment of binding sequence which can bind with aimed nucleic acid binding protein; 2. separates such nucleic acid captured probe-nucleic acid binding protein complexes, then recoveries nucleic acid captured probes; 3. hybridizes the nucleic acid captured probes according to step 2 with a plurality of single strand blotting probes on biochip substrate; the sequence of such blotting probe compensates with such nucleic acid captured probe or one of its strand; 4. detects the result of hybridization.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
Methods and compositions for linking binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins
ActiveUS7851216B2Longer gapGap variableFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesBinding domainNucleic acid binding protein
We describe a method of producing a modified nucleic acid binding polypeptide, the method comprising the steps of: (a) providing a nucleic acid binding polypeptide comprising a plurality of nucleic acid binding modules; (b) selecting a first binding domain consisting of one or two contiguous nucleic acid binding modules; (c) selecting a second binding domain consisting of one or two contiguous nucleic acid binding modules; and (d) introducing a flexible linker sequence to link the first and second binding domains, the flexible linker sequence comprising five or more amino acid residues. Use of structured linkers, alone or in combination with flexible linkers, is also disclosed.
Owner:GENDAQ +1
Electrochemical sensor using intercalative, redox-active moieties
InactiveUS20020146716A1Highly accurateSensitive highMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProtein insertionElectron transfer
Compositions and methods for electrochemical detection and localization of genetic point mutations, common DNA lesions and other base-stacking perturbations within oligonucleotide duplexes adsorbed onto electrodes and their use in biosensing technologies are described. An intercalative, redox-active moiety (such as an intercalator or nucleic acid-binding protein) is adhered and / or crosslinked to immobilized DNA duplexes at different separations from an electrode and probed electrochemically in the presence or absence of a non-intercalative, redox-active moiety. Interruptions in DNA-mediated electron-transfer caused by base-stacking perturbations, such as mutations or binding of a protein to its recognition site are reflected in a difference in electrical current, charge and / or potential.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for transfer of molecular substances with prokaryotic nucleic acid-binding proteins
InactiveUS7435595B2Improve efficiencyUndesirable effectOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleic acid binding proteinDNA
The invention relates to a method for the transfer of molecular substances, for example proteins or nucleic acids in cells, in the case of using DNA combined with a possible gene expression. A prokaryotic nucleic acid-binding protein is used for the transfer, which is preferably obtained from a thermostable organism. Where the substance to be transferred is a nucleic acid, the protein forms a reversible complex with the nucleic acid. The prokaryotic protein condenses and compacts the nucleic acids. Said nucleic acids can be taken up in the target cells after suitable incubation.
Owner:ACGT PREGENOMICS
Sequence-specific nuclear acid binding protein based nucleic acid detecting and ribotyping method and application thereof
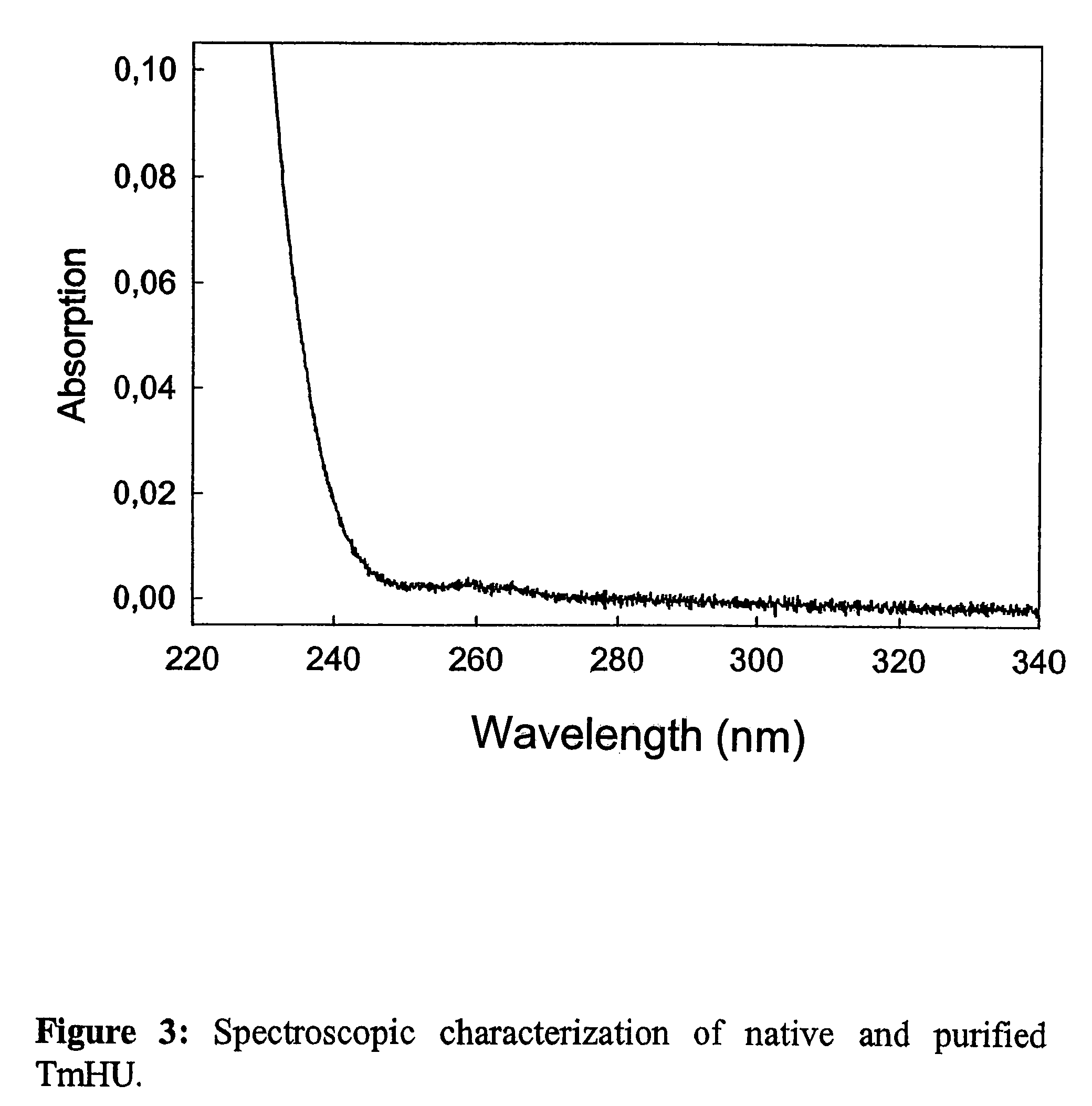
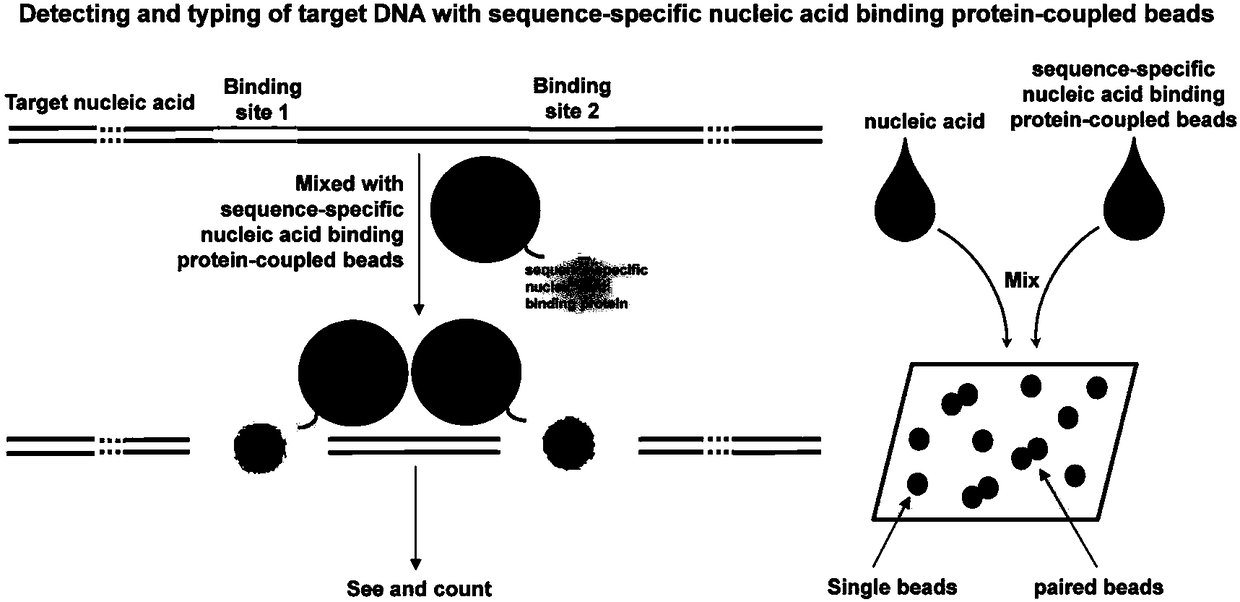
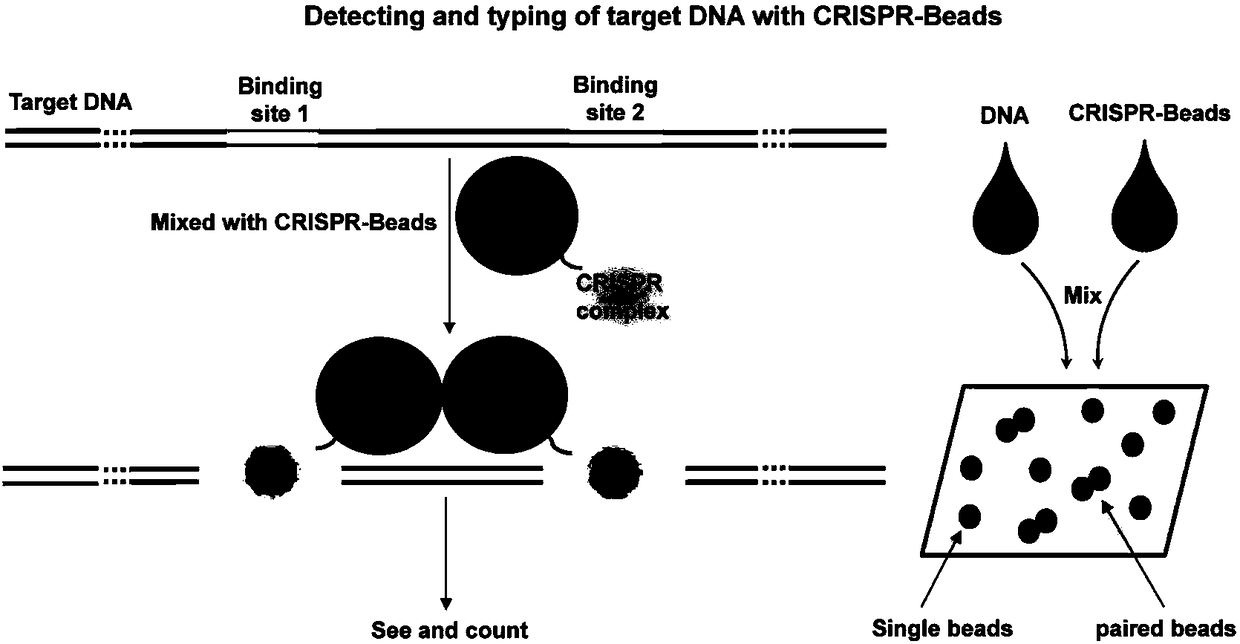
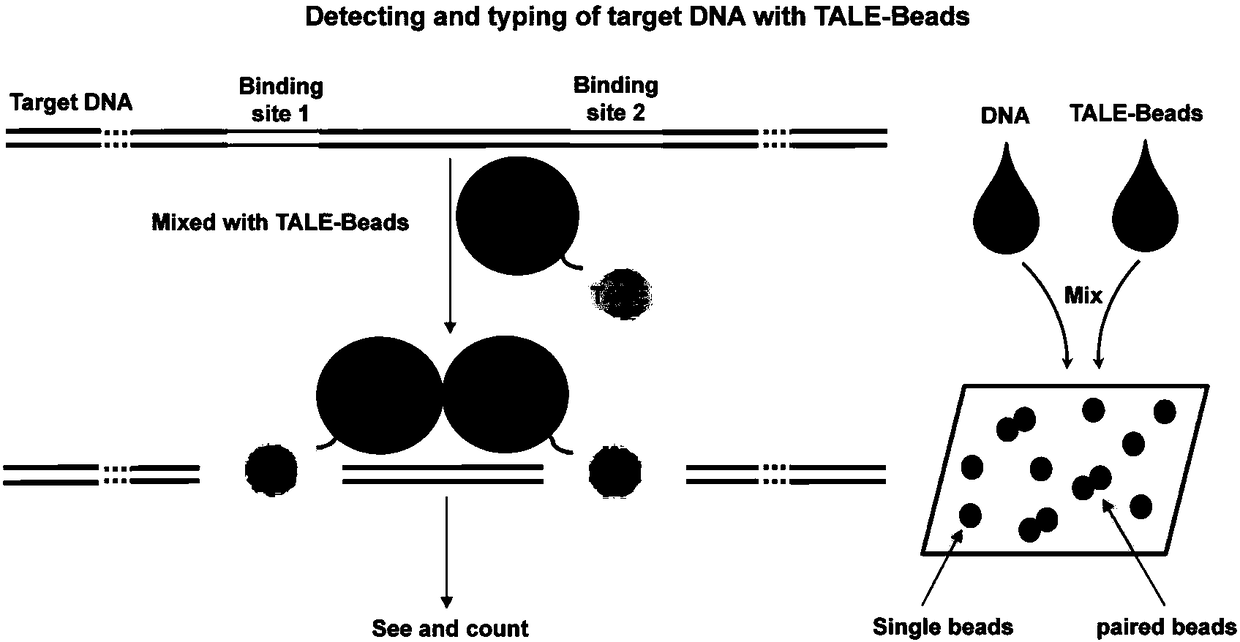
The invention discloses a sequence-specific nuclear acid binding protein based nucleic acid detecting and ribotyping method and application thereof. The method is characterized in that nucleic acid tobe detected is mixed with microspheres of which the surfaces are provided with sequence-specific nuclear acid binding protein, sequence-specific nuclear acid binding protein and microspheres, and then incubation is performed under room temperature; the microspheres are observed through a microscope tool, to realize the nucleic acid detecting and ribotyping. With the adoption of the method, even fm-level DNA can be quickly and simply without the complex, time-consumption and high-cost processes such as nucleic acid amplification and nucleic acid hybridization in traditional nucleic acid detection. According to the method, the properties of sequence-specific nuclear acid binding protein on specific recognizing and binding of nucleic acid molecules are utilized, so that the key bottleneck problems such as nucleic acid hybridization and amplification in the current fields of nucleic acid detecting and ribotyping are successfully avoided; the visual, digital and super-sensitive quick detection of nucleic acid is realized; and the method is extremely high in value of wide application in the field of nucleic acid detection.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Gene editing composition or kit for in vivo gene therapy
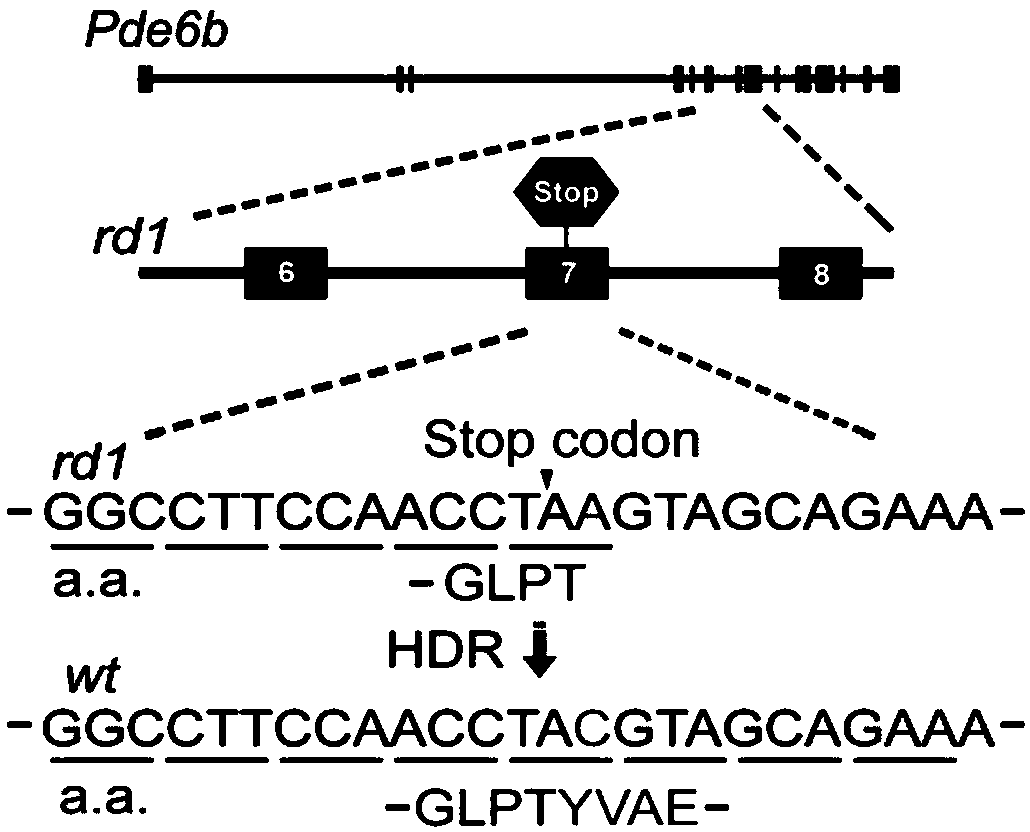
The present invention provides gene editing compositions or kits for in vivo gene therapy. A gene editing composition or kit provided in the invention comprises 1) an sgRNA linked to a nucleic acid molecule of a binding protein targeting a mutant gene or a coding sequence thereof, 2) a template nucleic acid or code sequence thereof for repairing a mutant gene of inter, 3) a nuclease guided by sgRNA or coding sequence thereof, and 4) a protein fused with a nucleic acid bin protein capable of promoting homologous recombination or coding sequence thereof, wherein that nucleic acid binding proteinis capable of binding to the nucleic acid molecule in the above 1). The invention also relates to the use of sgRNA, compositions or kits for the treatment of diseases caused by gene mutations, such as hereditary diseases. The sgRNA, composition or kit of the invention can effectively improve the efficiency of homologous recombination repair, and can also realize homologous recombination repair innon-dividing cells.
Owner:合肥星眸生物科技有限公司
Novel hot start nucleic acid amplification
ActiveUS20060029952A1Improve responseMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSingle strandNucleic acid binding protein
Methods and compositions for performing nucleic acid duplication and amplification reactions are provided. A single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein is selected and provided in the reaction mixture which is assembled at a low, nonstringent temperature to include all of the necessary reagents for successful nucleic acid duplication or amplification reactions. By incorporating a single-stranded nucleic acid binding protein into the reaction mixture at low temperature, the generation of nonspecific products such as amplification products is improved despite the reaction mixture having been fully assembled at a nonstringent temperature.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com