Chip for non-label detecting DNA bindin, preparation and use method thereof
A protein-binding and labeling detection technology, which is applied in the direction of biological testing, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of low-abundance protein loss, improve detection efficiency and sensitivity, disadvantages, etc., achieve comprehensive biological significance, save detection costs, and avoid pollution effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
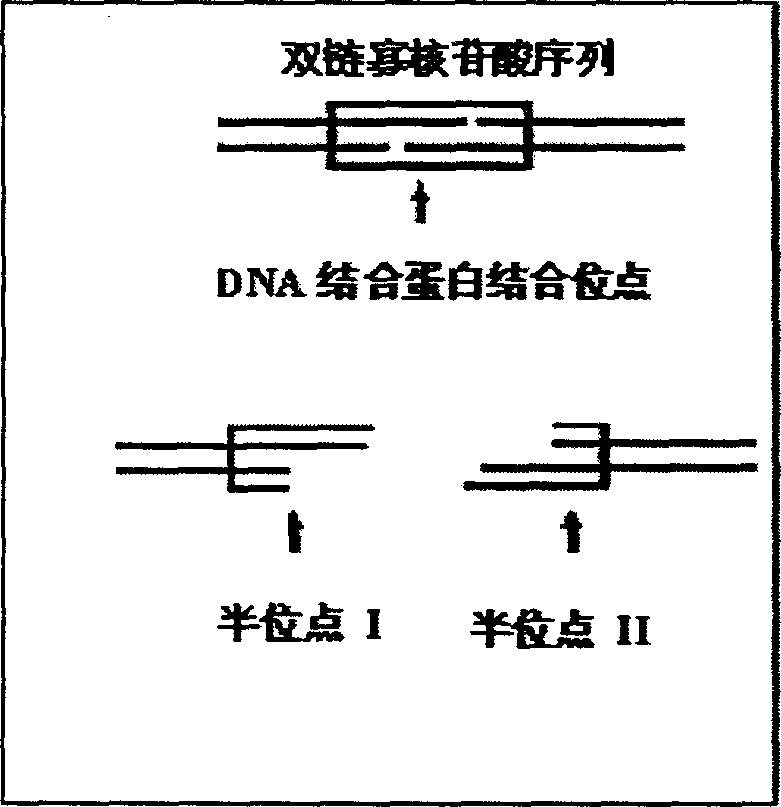
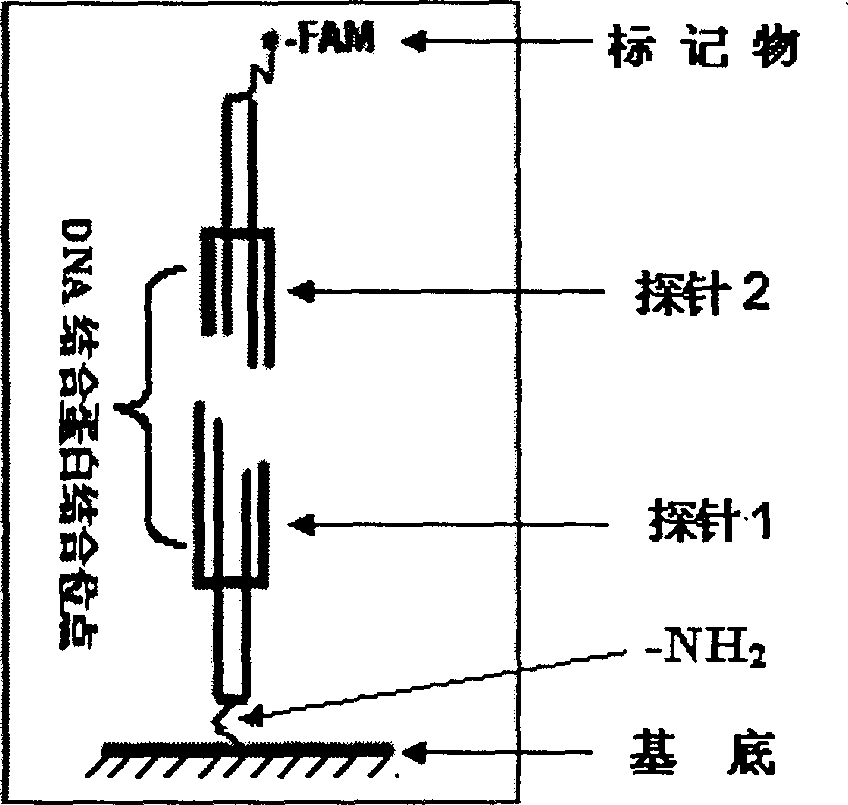
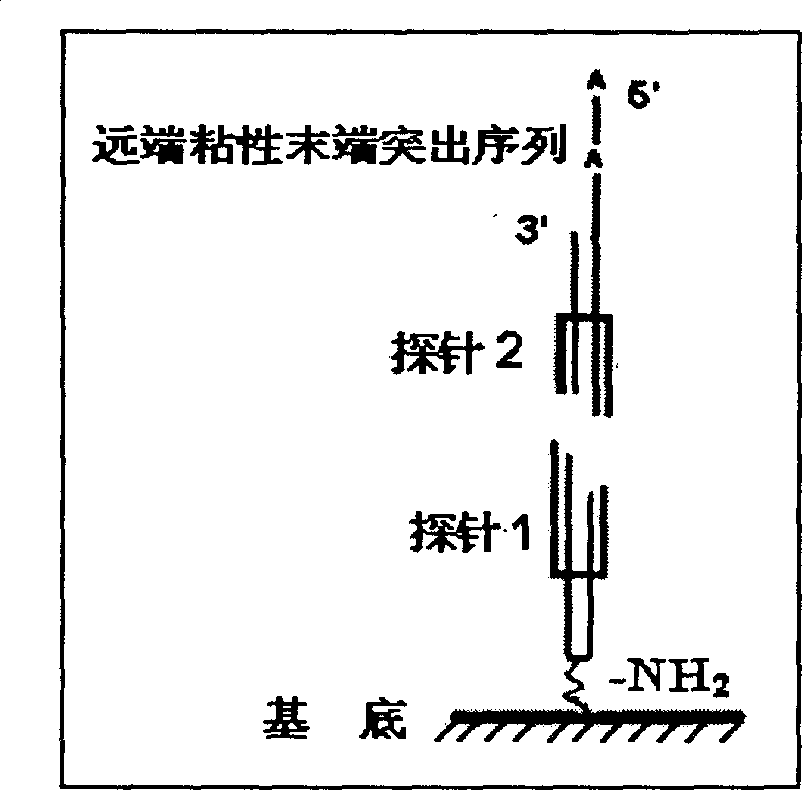
[0025] Refer to attached figure 1 , 2 3. A chip for non-labeled detection of DNA-binding proteins, the structure of which has a double-stranded oligonucleotide probe, and the sequence of the double-stranded oligonucleotide probe is specific to the DNA recognition sequence of the detected DNA-binding protein. Designed to be divided into two half-site fragments I and II with cohesive ends between the recognition site containing the DNA-binding protein to be tested, i.e. probe 1 and probe 2 (such as figure 1 ), one of the double-stranded oligonucleotide fragments, probe 1, is immobilized on the substrate, and the other double-stranded oligonucleotide fragment, probe 2, introduces a label (-FAM) (such as figure 2 ). Or probe 2 does not label any fluorescent groups, but it is designed as a protruding sticky end away from the 5' end of the half site, and the base sequence of the protruding end is 3'-ANNA-5' (wherein N represents any base )(Such as image 3 ). Example 1 Prepara...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 Preparation and application method of a chip for non-labeled detection of DNA-binding proteins
[0039]1. Preparation of probes
[0040] The design and preparation of the probe are basically the same as in Example 1, except that the probe 2 does not label any fluorescent groups, but its distal end is designed as a protruding sticky end, and the base sequence of the protruding end is 3'-ANNA- 5' (where N represents any base) (such as image 3 ).
[0041] 2. The preparation and hybridization of the microarray are the same as in Example 1.
[0042] 3. Incorporation of fluorescent molecules
[0043] After hybridization, the chip was exposed to DNA polymerase 1 large fragment (Klenow enzyme) extension system at 37°C for 1 hour, and fluorescently labeled deoxyuridine adenosine triphosphate (such as Cy3-dUTP) was introduced. Wash free Cy3-dUTP (such as Figure 5 ).
[0044] 4. Fluorescent signal detection and result analysis
[0045] Also utilize the incorpora...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com