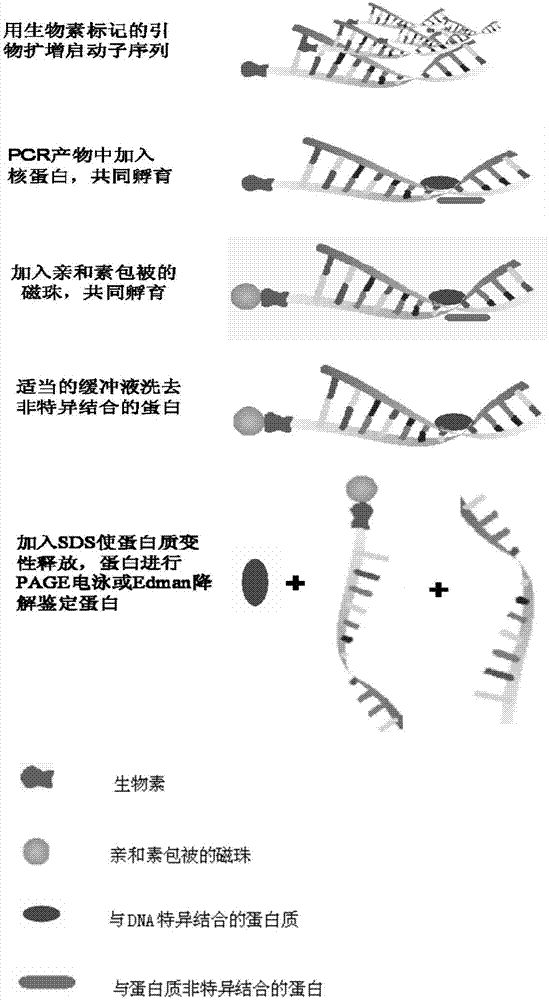
Method for separating DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) binding protein and accurately positioning DNA binding site
A technology for binding proteins and binding sites, which is applied in the field of DNA binding proteins, can solve the problems of complex operation, low efficiency, and unnecessary use, and achieve the effect of simple method and short cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
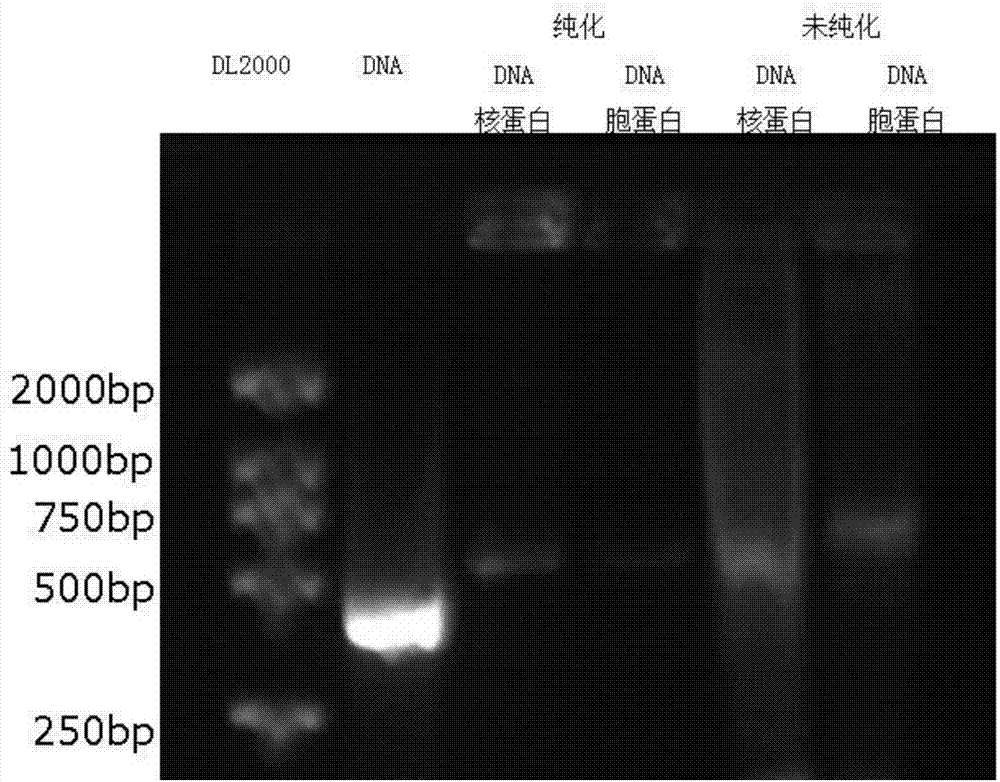
[0042] Example 1 Isolation of hCLP46 gene promoter CpG island binding protein and localization of binding site
[0043] 1. Amplification of hCLP46 promoter region
[0044] Apply Primer Premier 5.0 to design primers (Table 1), 100 μL reaction system contains 10 μL of 10×PCR Buffer, 8 μL of 2.5mM dNTP mix, 4.0 μL of 10uM upstream and downstream primers, 2.0 μL of U937 DNA, 1.0 μL of 5U / μL Taq (TakaRa ) and 71.0 μL ddH2O. After the mixture was mixed and centrifuged, the amplification reaction was performed on a PCR machine (95°C for 3 min; 95°C for 30 s, 59°C for 30 s, 72°C for 1 min, 45 cycles; 72°C for 5 min; 4°C forever).
[0045] Table 1 hCLP46 promoter amplification primers
[0046]
[0047]
[0048] 2. U937 cell cytoplasmic protein and nuclear protein extraction
[0049] U937 cells were cultured according to the above method, and nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins were extracted using a nuclear and cytoplasmic protein extraction kit (Nanjing Kaiji). The simple steps ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com