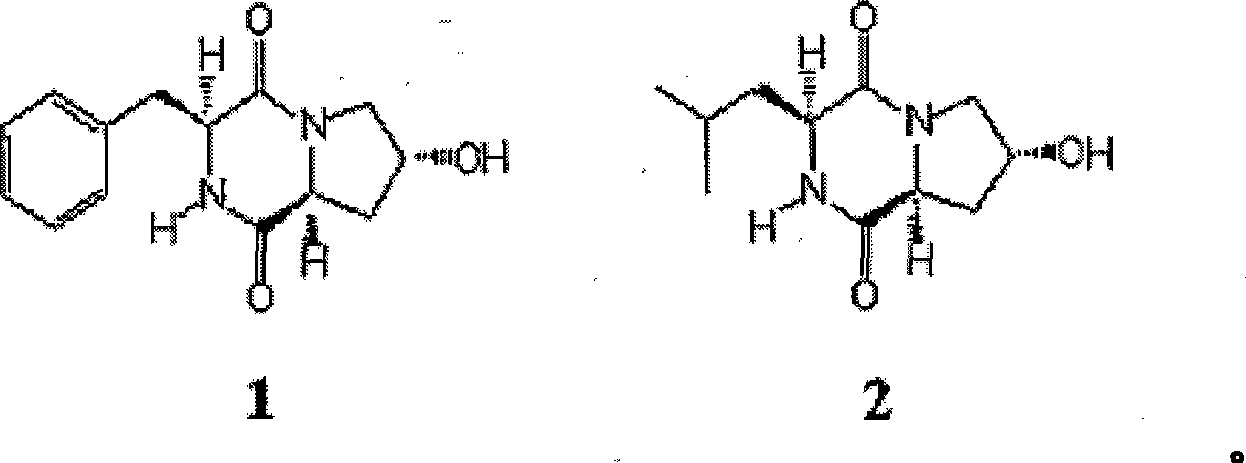
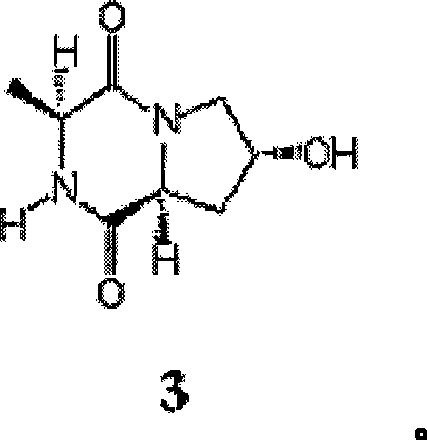
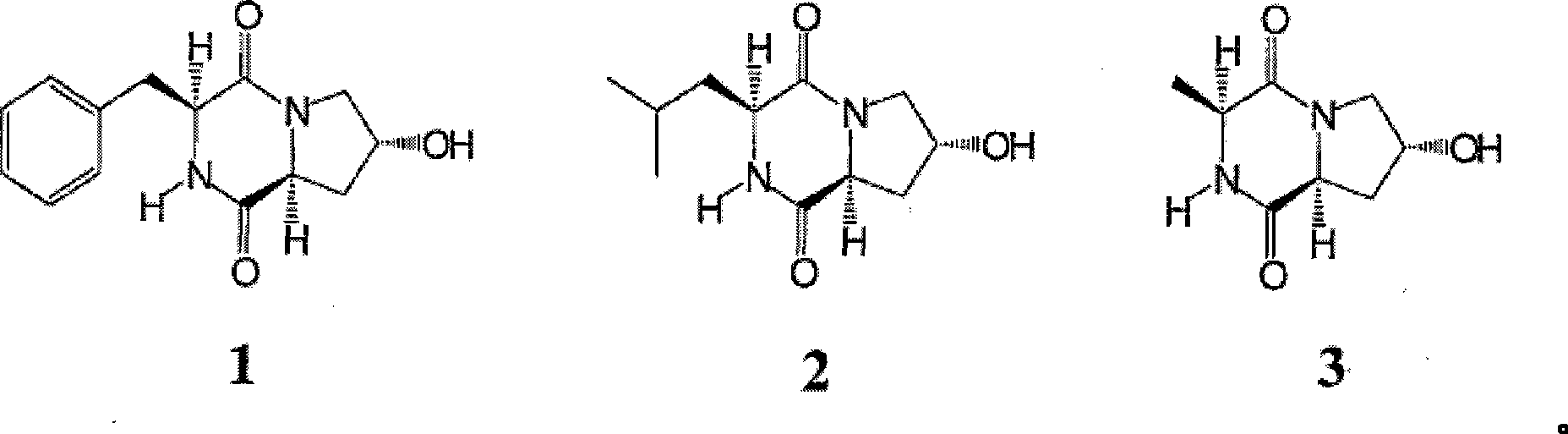
Patents
Literature
1106 results about "Secondary metabolite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Secondary metabolites are organic compounds produced by bacteria, fungi, or plants which are not directly involved in the normal growth, development, or reproduction of the organism. Unlike primary metabolites, absence of secondary metabolites does not result in immediate death, but rather in long-term impairment of the organism's survivability, fecundity, or aesthetics, or perhaps in no significant change at all. Specific secondary metabolites are often restricted to a narrow set of species within a phylogenetic group. Secondary metabolites often play an important role in plant defense against herbivory and other interspecies defenses. Humans use secondary metabolites as medicines, flavorings, pigments, and recreational drugs.
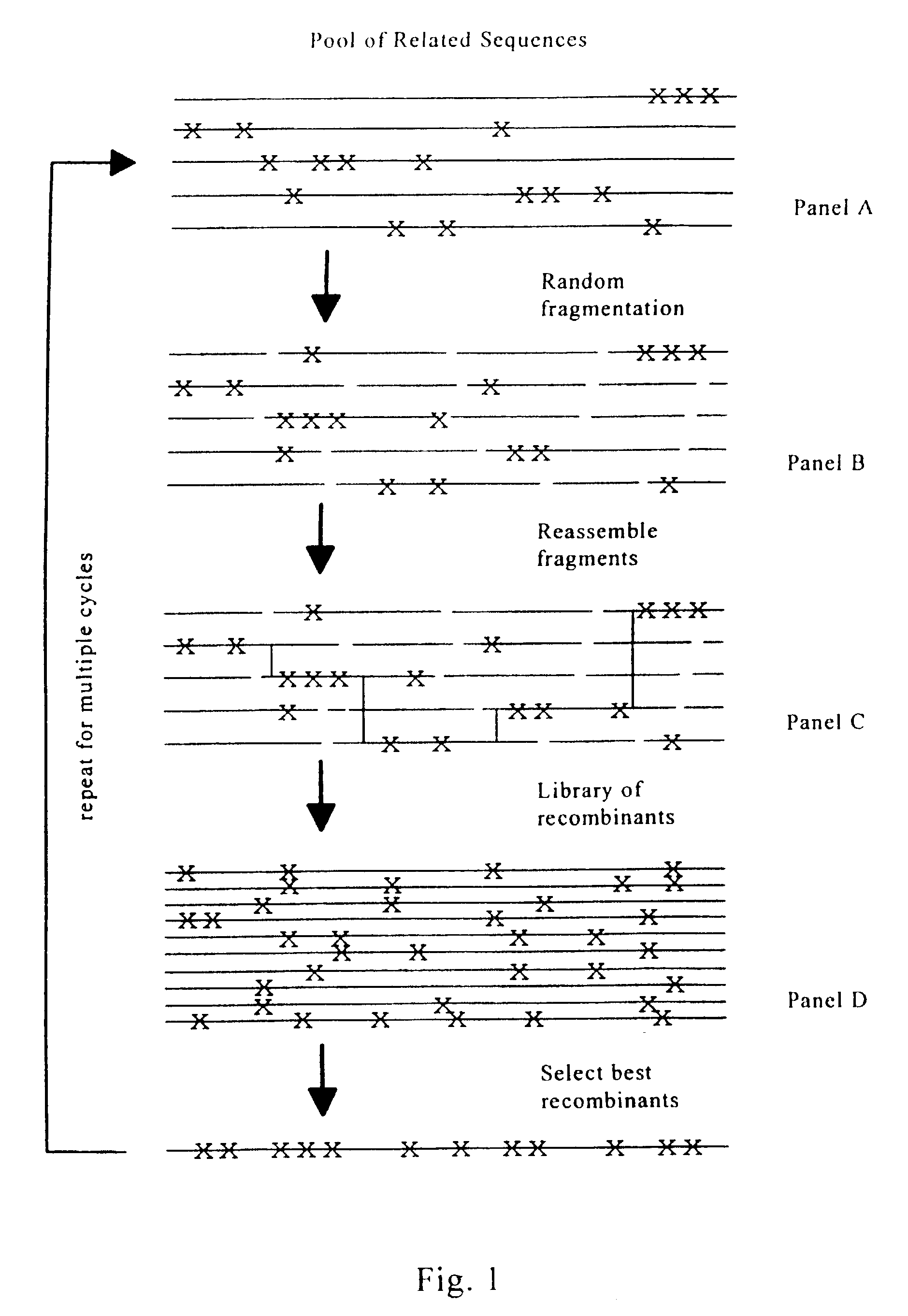
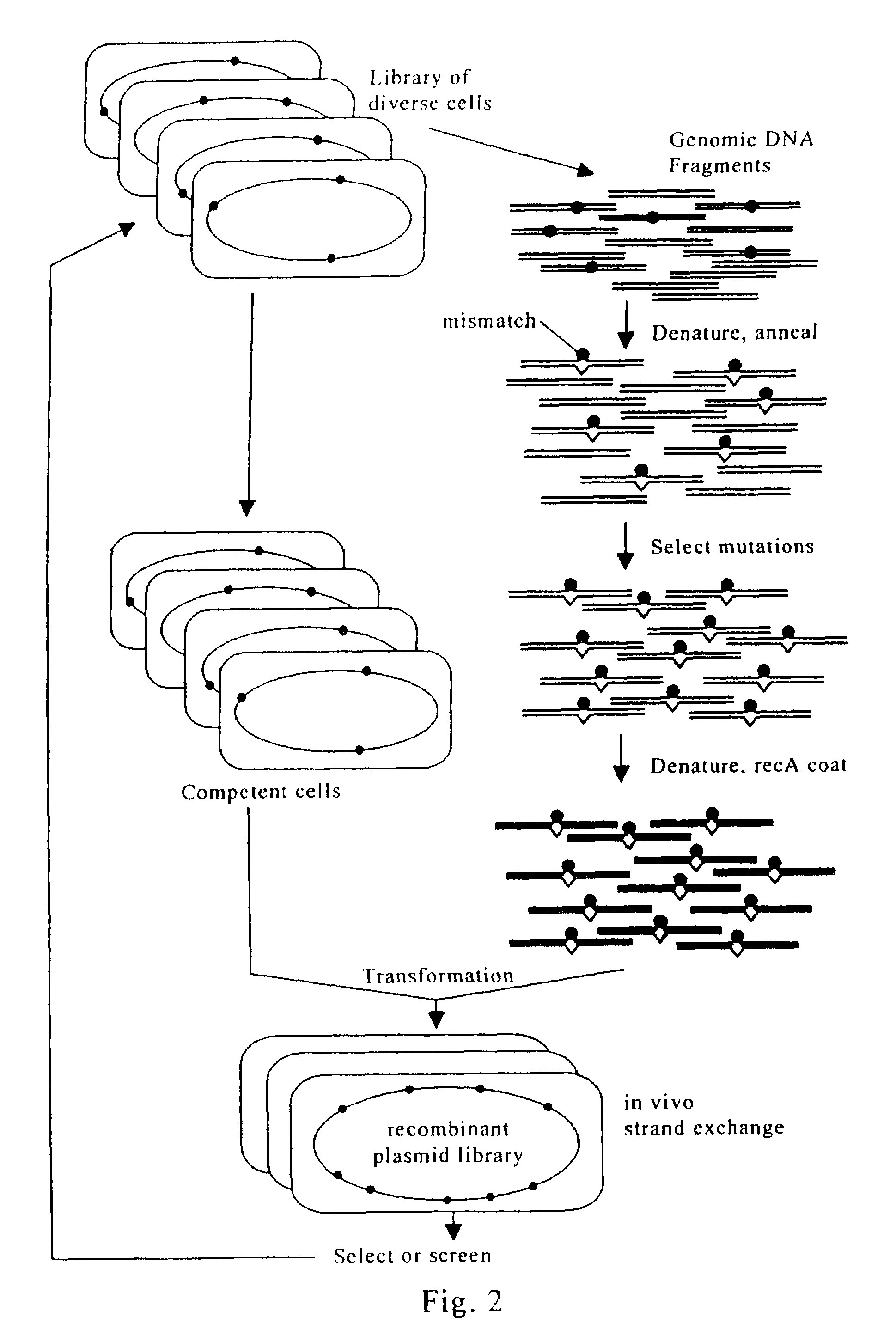
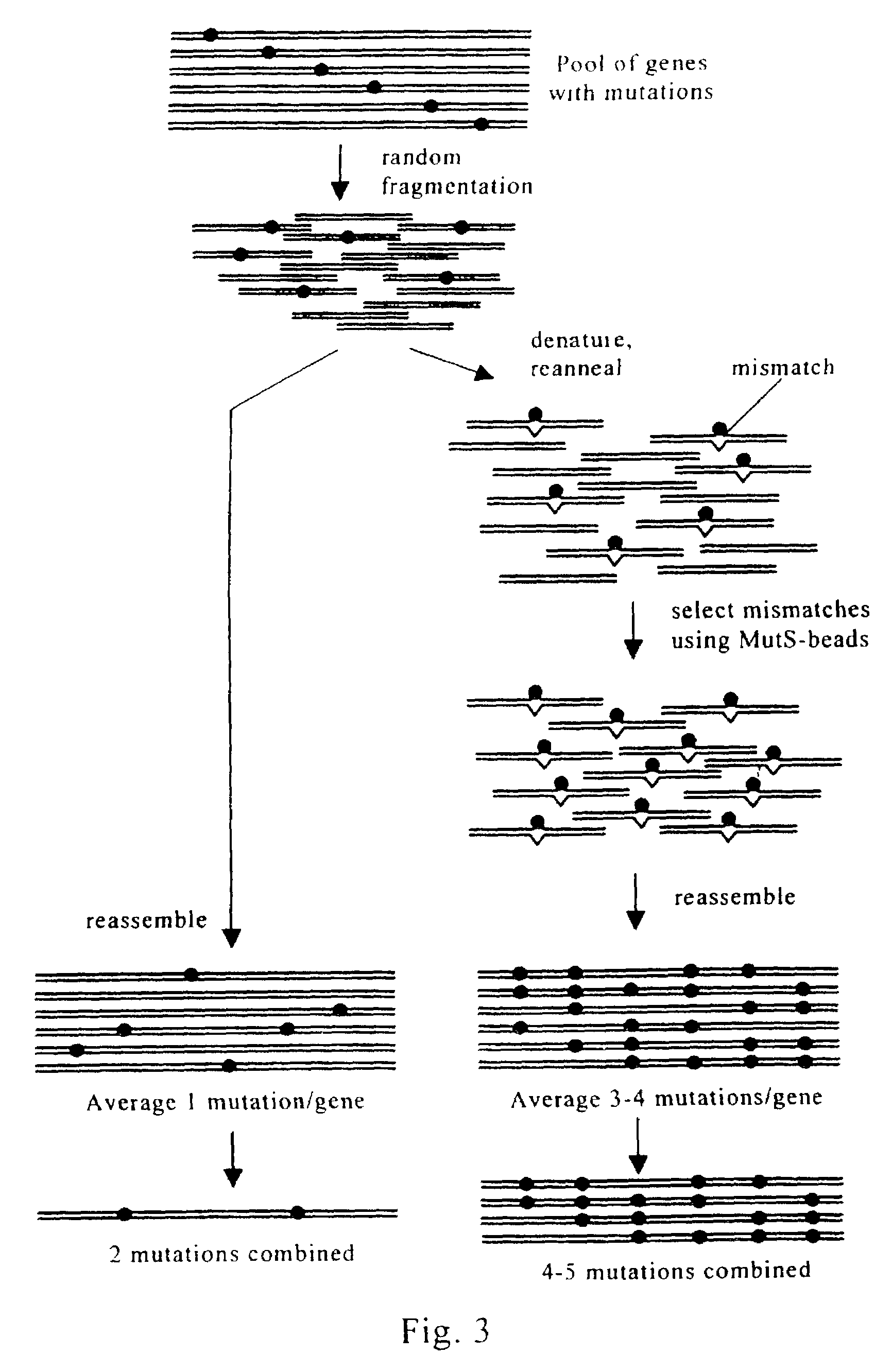
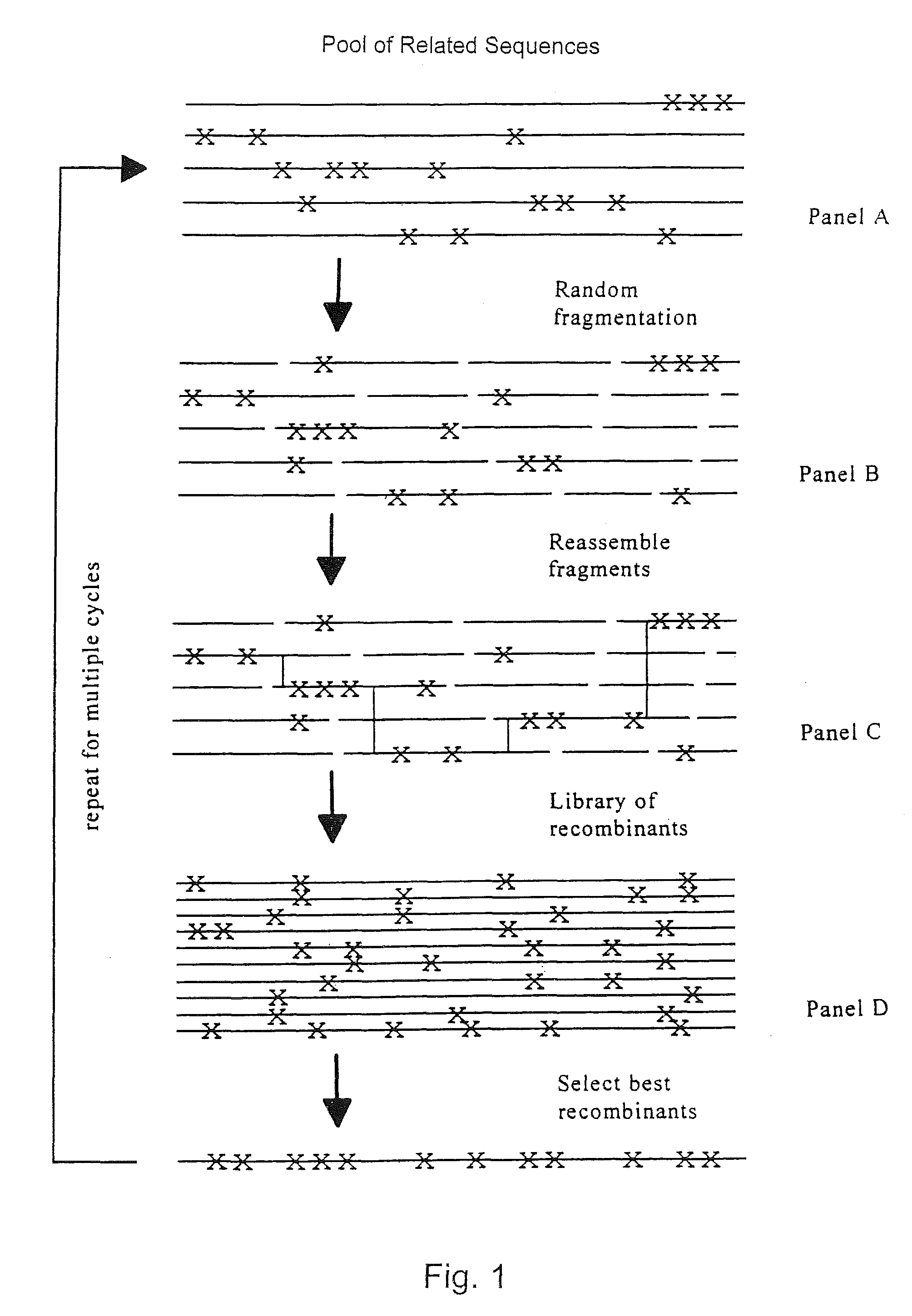
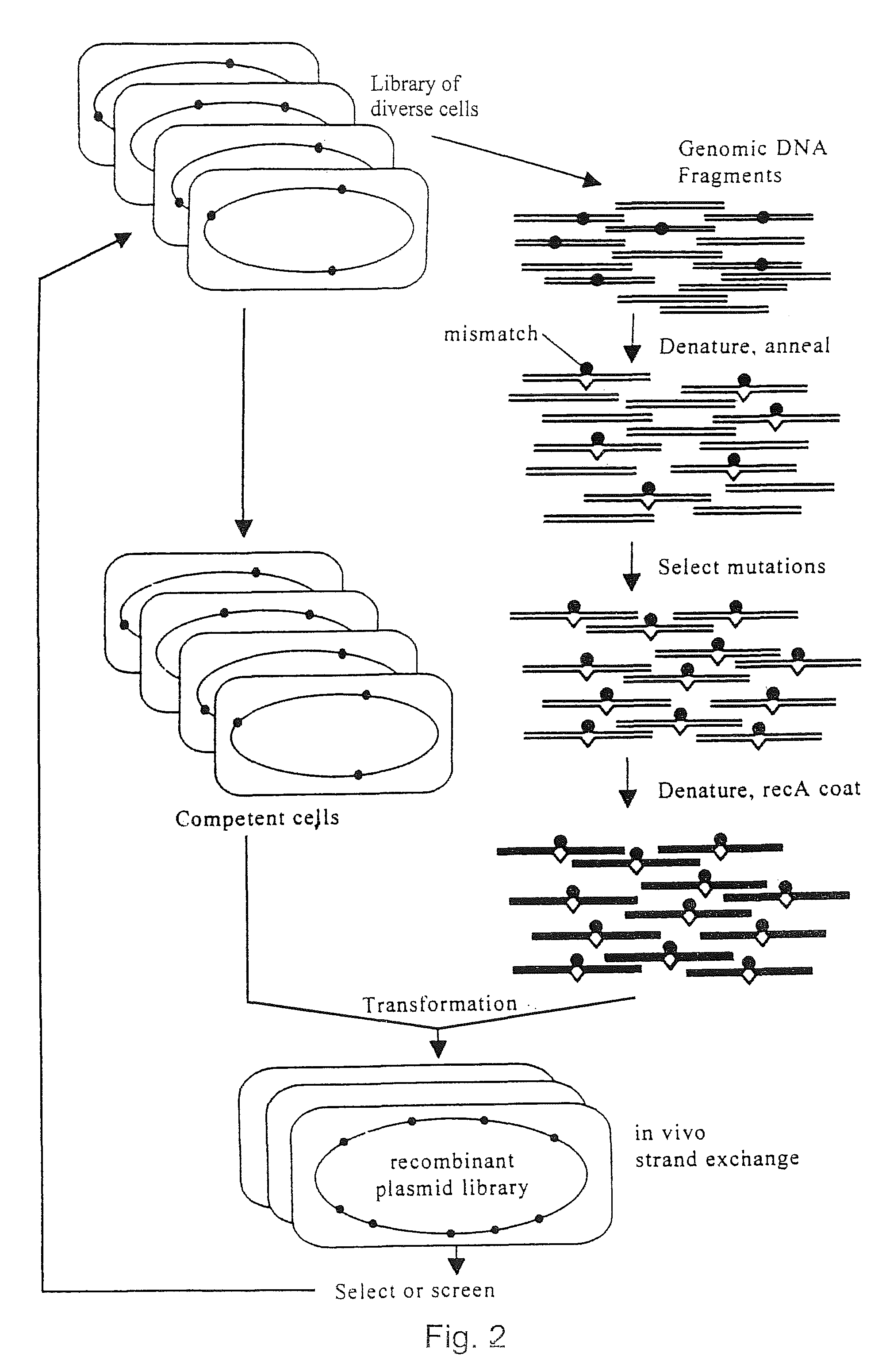
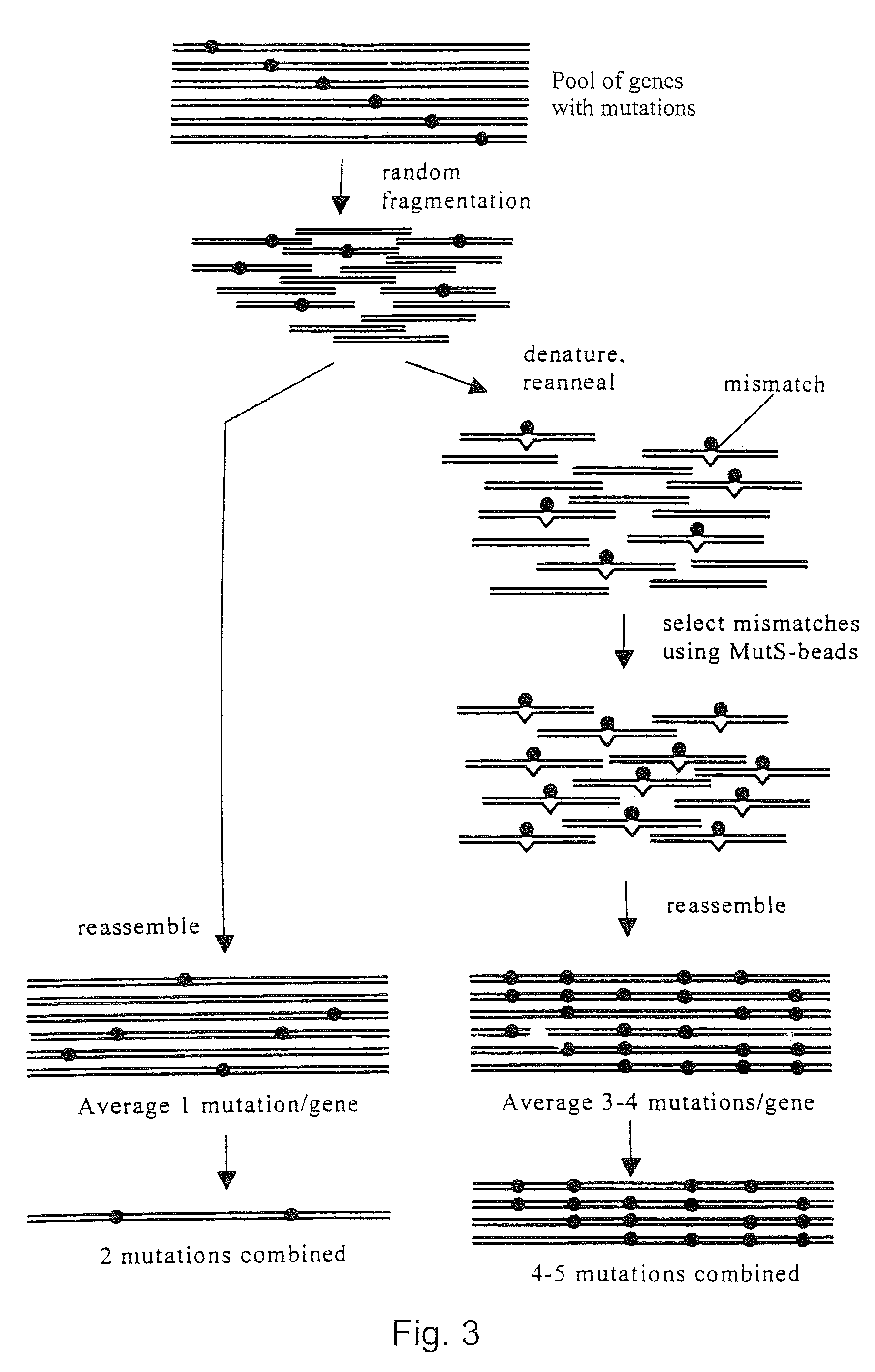
Evolution of whole cells and organisms by recursive sequence recombination
InactiveUS7148054B2Increase diversityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteSecondary metabolite
The invention provides methods employing iterative cycles of recombination and selection / screening for evolution of whole cells and organisms toward acquisition of desired properties Examples of such properties include enhanced recombinogenicity, genome copy number, and capacity for expression and / or secretion of proteins and secondary metabolites.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Evolution of whole cells and organisms by recursive sequence recombination
InactiveUS8377681B2Prediction of efficacyIncrease diversityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteEntire cell
The invention provides methods employing iterative cycles of recombination and selection / screening for evolution of whole cells and organisms toward acquisition of desired properties. Examples of such properties include enhanced recombinogenicity, genome copy number, and capacity for expression and / or secretion of proteins and secondary metabolites.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Bacillus belleus GT11 and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacillus belleus GT11 and application thereof. The bacillus belleus CT11 is collected at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on December 13th, 2016; the collection number is CGMCC No.13446; the bacillus belleus CT11 can be prepared into water agent, wettable powder or coating material and can be used for preventing and controlling the root rot diseases of pseudo-ginseng and plukenetia volubilis and Chinese cabbage clubroot. The invention provides an efficient, nontoxic, safe, non-residual and conveniently used biological agent for preventing and controlling the diseases such as root rot and clubroot; the effective active ingredient is bacillus belleus CT11 strain; the strain can generate the secondary metabolite antimicrobial active matter, is capable of degrading the cell wall of pathogenic bacteria and has an excellent growth-promoting effect for the crops, such as, plukenetia volubilis, pseudo-ginseng and Chinese cabbage; besides, the bacillus belleus CT11 has a better antibacterial effect for pseudo-ginseng phytophthora sojae, pseudo-ginseng fusarium solani, plukenetia volubilis gray mold, paddy bacterial mycosphaerella, and the like.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for supply of starter cultures having a consistent quality
InactiveUS20010049132A1Good reproducibilityUniform qualityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMilk preparationPharmaceutical industrySecondary metabolite
The present invention relates to the field of producing starter cultures. In particular, a method for customers in need of a starter culture with a consistent quality, is provided. Specifically, the method involves the use of subsets of a stock inoculum material, which comprises a concentrate of starter culture organism cells to be propagated for direct inoculation of a cultivation medium, to obtain a starter culture whereby the conventional stepwise preparation of inoculum material for the production of a starter culture can be avoided. This novel method can be used for the manufacturing of starter cultures for the food, feed or pharmaceutical industry. Furthermore, the method is useful in the cultivation of cells expressing desired products, such as primary and secondary metabolites, including e.g. enzymes and flavors.
Owner:CHR HANSEN AS
Methods of increasing production of secondary metabolites by manipulating metabolic pathways that include methylmalonyl-coa
A process of increasing the cellular production of secondary metabolites, such as antibiotics, is provided. The process is particularly useful for increasing antibiotic production by bacterial cells, especially erythromycin. The process includes the step of increasing the activity of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase.
Owner:FERMALOGIC
Method for improving content and aromas of tobacco secondary metabolite products
InactiveCN102986391AImprove qualityIncrease contentBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMetaboliteSecondary metabolite
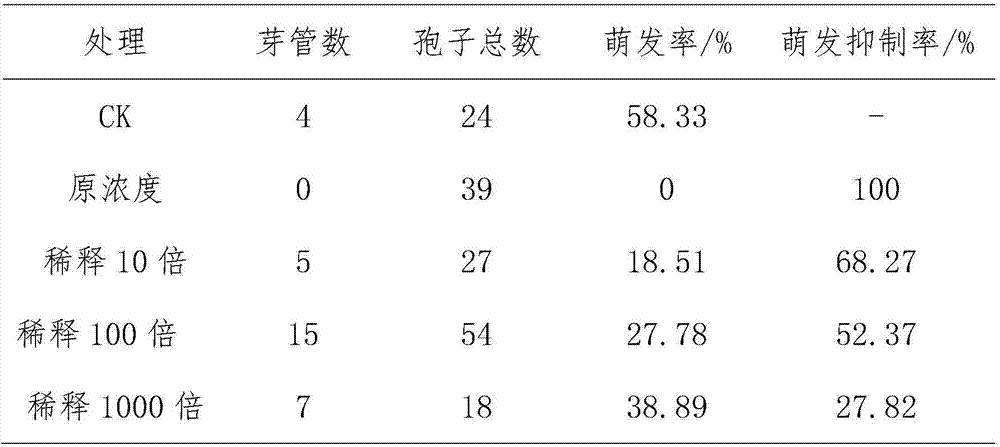
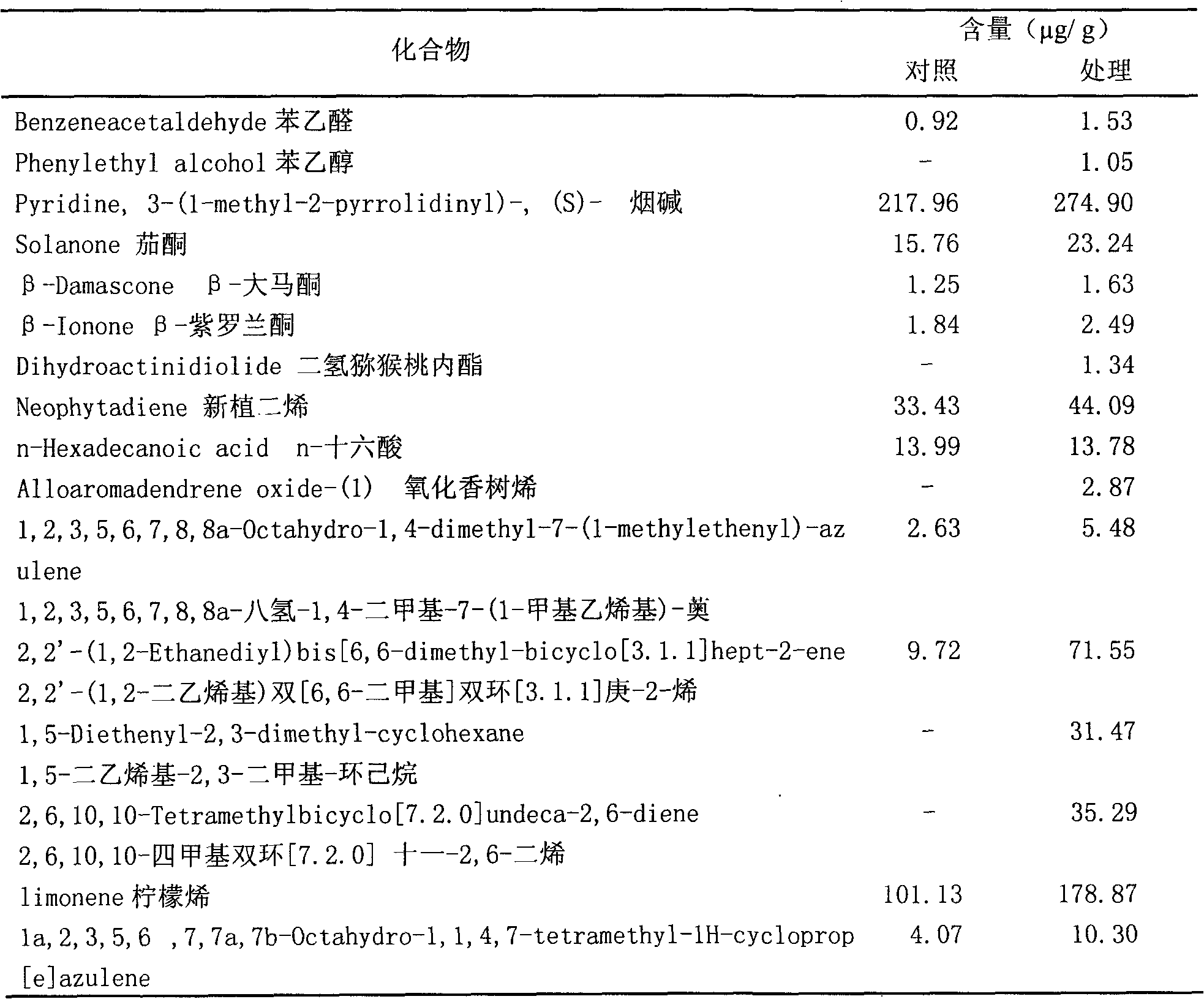
The invention provides a method for improving the content and aromas of tobacco secondary metabolite products. During any tobacco plant growth period or after tobacco harvesting, a leaf surface spraying method, a stem top spraying method or a root-irrigation method is adopted to implement one or more of salicylic acid elicitors and / or jasmonic elicitors on the tobacco plants or the tobaccos so as to induce synthesis of the tobacco secondary metabolite products. The method can not only remarkably increase the content of tobacco essential oil, petroleum ether extract and glandular hair secreta and the like and improve tobacco aroma quality, but also improve yield of some important natural products in the tobacco such as solenesol and provide high-content raw materials for extraction of the natural products. Meanwhile, the method can activate tobacco plant immune system and improve insect resistance, disease resistance and stress resistance of the tobacco plants.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Artificial induction agarwood production method from tree of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg by high-pressure injection
InactiveCN102511329AFast injectionSimple and fast operationHorticulture methodsSecondary metaboliteEconomic benefits
An artificial induction agarwood production method from a tree of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg by high-pressure injection includes: inducer solution is instantly injected into a trunk of the tree of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg, the inducer solution is led to the tip of the tree through conducting tissues of the tree, the tree of tree of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg rejects drugs under stimulation of inducer and starts defense reaction to generate secondary metabolites, and finally agarwood formation is realized in the trunk under induction. The artificial induction agarwood production method is simple in process and convenient in operation, use of a high-pressure truck injector greatly shortens injection time of the inducer solution, and accordingly the operation is complete in one to two minutes and insusceptible to weather and wind force. Agarwood formation is effective, large-scale standard production is facilitated, and important economic benefit and great ecological benefit on protection of tree of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Gilg and development and production of agarwood are achieved.
Owner:徐景辉
Half-dry solid state cultivation method used for industrial production of microalgae
ActiveCN102373156ADecreased mobilityThe growth state is easy to controlImmobilised enzymesUnicellular algaeSecondary metabolitePhotobioreactor
The invention provides a half-dry solid-state cultural method for industrial production of microalgae. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, inoculating microalgae cells on a solid material and allowing cell colony to maintain moist by supplementing liquid; then, adding inorganic carbon sources into the cell colony under the condition of illumination; finally, regulating and controlling and metabolism of microalgae cells by controlling parameters of components in wetting liquid, illumination intensity, the concentration of the carbon source and the like so as to realize accumulation of microalgae biomass and / or secondary metabolites. According to the invention, the practice of using considerable water as a supporting medium in the conventional liquid immersion culture method is abandoned, and the volume and weight of a culture system are reduced, thereby thoroughly solving the problem that a microalgae photobioreactor is difficult to become large-sized and has a low space utilization rate due to limit of material strength and reducing cost for equipment and operation; microalgae has high efficiency in utilizing nutrients, luminous energy and carbon sources and is fast in inducing secondary metabolites, thereby substantially improving output of biomass and secondary metabolites per unit land occupation area.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
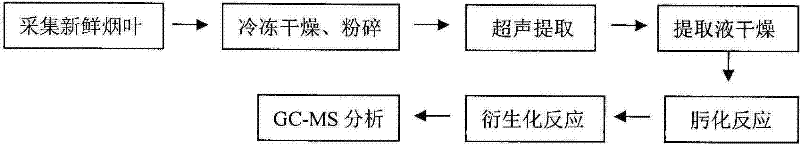
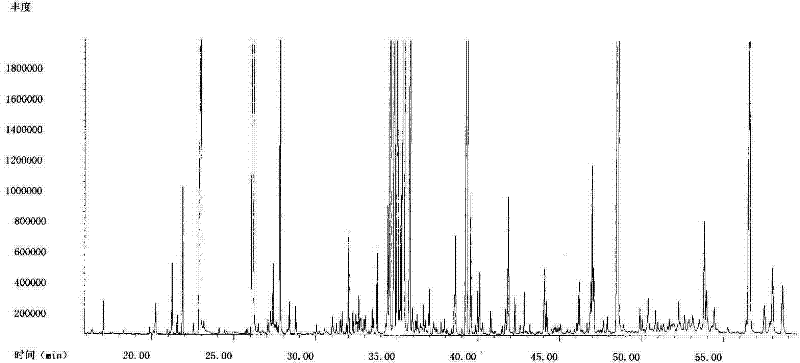
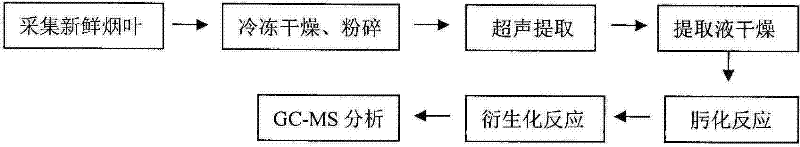
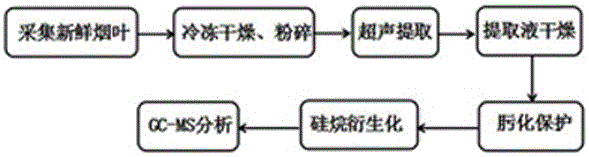
Method for detecting secondary metabolites in fresh tobacco leaves by using derivatization GC-MS
A method for detecting secondary metabolites in fresh tobacco leaves by using a derivatization GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometer) is characterized by comprising the steps: quickly collecting new tobacco leaves and quickly freezing the new tobacco leaves by using liquid nitrogen on the site, crushing the tobacco leaves after removing the moisture in the tobacco leaves by means of freeze drying, extracting the secondary metabolites from tobacco powder by using a solvent, drying the extracted liquid supernatant, then performing oximation reaction and silane derivatization on the dried extractive, and finally performing analysis by the GC-MS. The method has the prominent advantages that firstly, a method suitable for extracting the secondary metabolites in the fresh tobacco leaves is developed. As the area of the tobacco leaves is larger, the secondary metabolites are not uniformly distributed in the whole tobacco leaves, and the tobacco leaves are not applicable to the punching sampling technique. However, according to a tobacco leave collection and extraction method provided by the invention, the collection period and the metabolite composition of the tobacco leaves at the collected part can be truly reflected. Secondly, most of the important metabolites of the tobacco leaves such as saccharides, amino acids, organic acids, terpene alcohols in the fresh tobacco leaves can be simultaneously detected, and the method has the characteristics of high throughput detection.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Method for the isolation of RNA from biological sources
InactiveUS20070015165A1Improve the level ofMethod is fastSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissueMetabolite
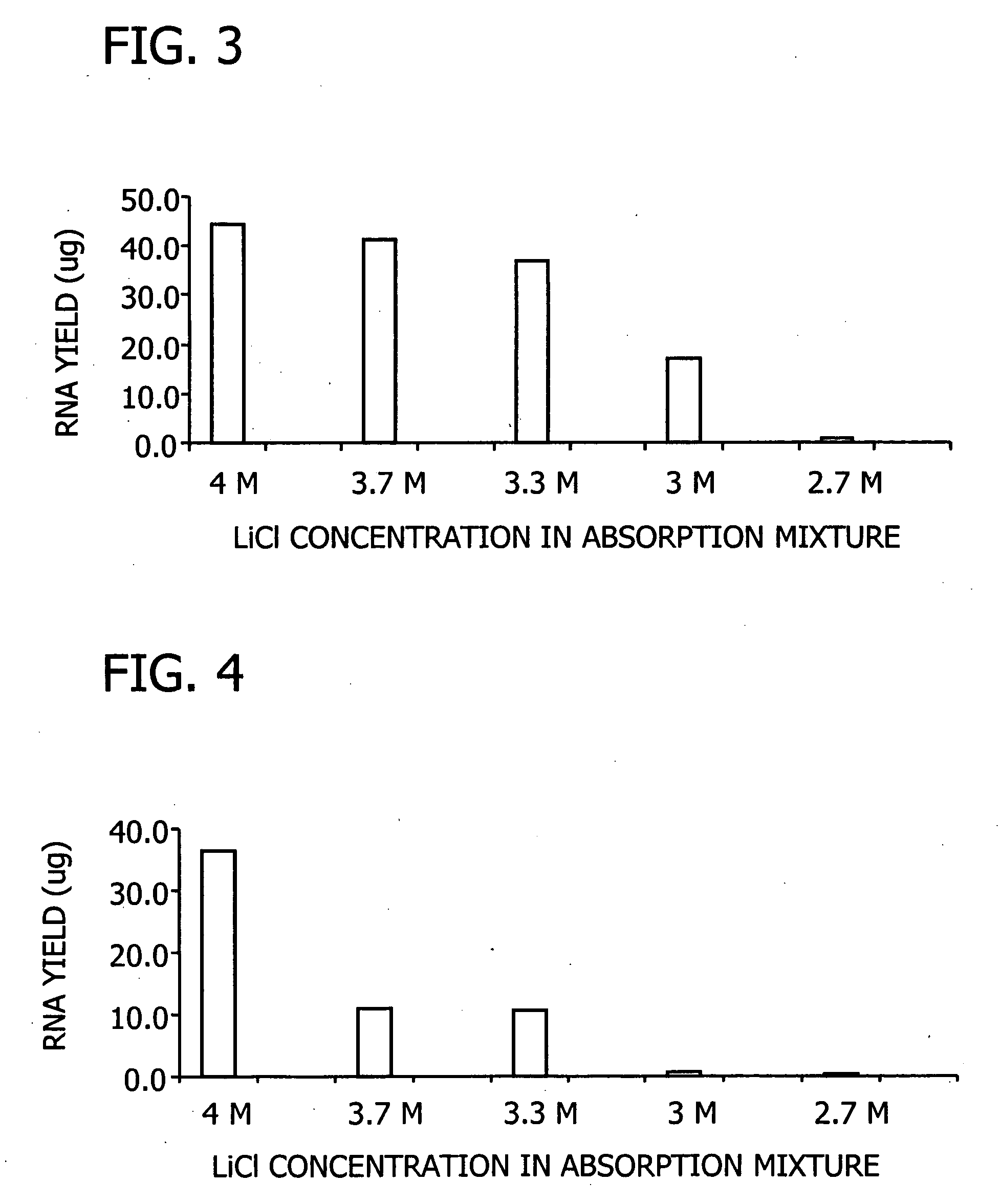
Methods and kits for isolating RNA are provided that enable rapid RNA preparation from biological sources. In one aspect, RNA is isolated from difficult plant tissues and cells that contain high levels of secondary metabolites, without employing organic extraction or salt precipitation procedures. This method employs novel lysing and binding conditions to allow preparation of RNA free from secondary metabolites.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
Preparation method of active seaweed extract
ActiveCN102488253ACompletely killPromote fermentationFood preparationLiquid productAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a preparation method of an active seaweed extract. The method comprises the steps of: seaweed selecting, impurity removing, weak acid washing, mincing and homogenizing, curing and sterilization under high temperature and high pressure as well as polysaccharide component degradation, pH adjustment, probiotic fermentation, and adding of alginate oligosaccharide for blending. The obtained liquid product is an active seaweed extracting solution, or it can be prepared into active seaweed extract powder through drying, and the extracting solution and the extract powder are collectively called an active seaweed extract. The active seaweed extract prepared in the invention reserves algae iodate, mannitol, inorganic salts, trace elements and other components, and the proteinand polysaccharide components in seaweeds are degraded and easy to absorb. Added with probiotics, secondary metabolites, and low molecular weight seaweed polysaccharide, the active seaweed extract ofthe invention has better biological activity, and can remove harmful heavy metals so as to improve the security of the seaweed extract.
Owner:QINGDAO BRIGHT MOON SEAWEED GROUP
Plant cell lines established from the medicinal plant veratrum californicum
The present invention relates to the field of plant secondary metabolites. More particularly plant cell lines are established from the medicinal plant Veratrum californicum. Said plant cell lines can be used for the production of cyclopamine and related steroid alkaloids and their precursors.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Half-dry solid-state adherent culture device for microalgae industrial production
ActiveCN103289887AReduce water consumptionAchieve ultra-high density cultureSolid phase fermentation bioreactorsSecondary metaboliteLiquid storage tank
The invention belongs to the field of microalgae culture, and in particular relates to a half-dry solid-state adherent culture device for microalgae industrial production. The half-dry solid-state adherent culture device comprises a bracket system, adherent culture units, a supporting shaft transmission system, a speed regulating motor, liquid supplementation pipes, collection grooves and a culture medium liquid storage tank, wherein at least one adherent culture unit is arranged on the bracket system and is connected with the speed regulating motor through the supporting shaft transmission system; the liquid supplementation pipes are respectively arranged above the adherent culture unit and are communicated with the culture medium liquid storage tank through pipelines; the collection grooves are respectively formed below the adherent culture unit and are communicated with the culture medium liquid storage tank through liquid collection pipes; a liquid circulating pump and a carbon supplementation device are arranged in the culture medium liquid storage tank. The half-dry solid-state adherent culture device can be used for producing microalgae biomass and secondary metabolites on a large scale; the yield in unit floor area is effectively improved; the culture period is shortened; the culture water consumption is greatly reduced; the cost of the culture device and the operation cost are reduced; the industrial magnification is facilitated.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing gold thread jujube enzyme from jujube paste of gold thread jujube
The invention relates to a method for preparing gold thread jujube enzyme from jujube paste of gold thread jujube, comprising the following steps of: making the jujube paste, carrying out primary enzymolysis and secondary enzymolysis, blending, sterilizing, fermenting, freezing, drying and finally obtaining the enzyme of the jujube paste of the gold thread jujube with the water content of being less than 5%. The gold thread jujube enzyme prepared by the method contains rich protease, lipase, superoxide dismutase, amylase, vitamins, minerals and secondary metabolites such as phenols, flavonoids and the like, and as a novel food and cosmetic additive in the market, the gold thread jujube enzyme has a very wide application prospect.
Owner:山东鼎力枣业食品集团有限公司
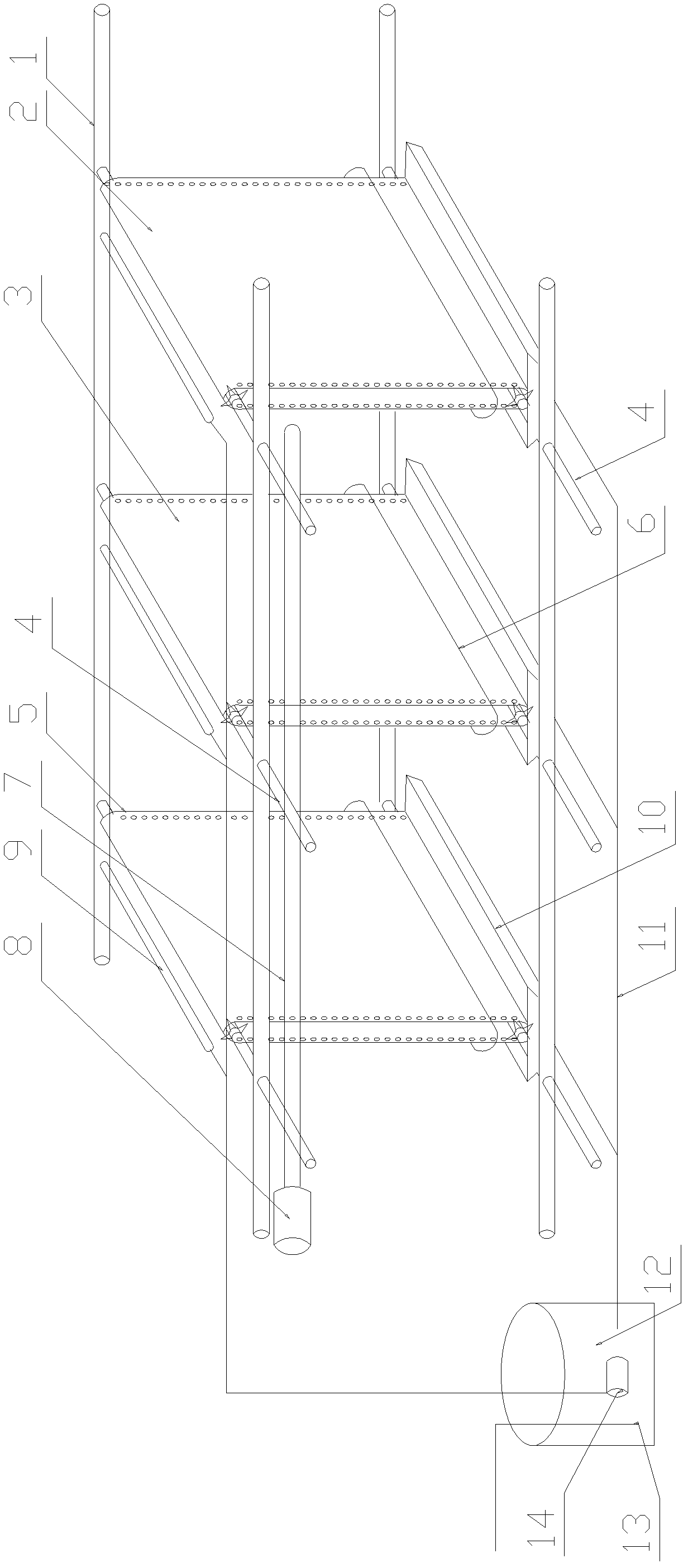
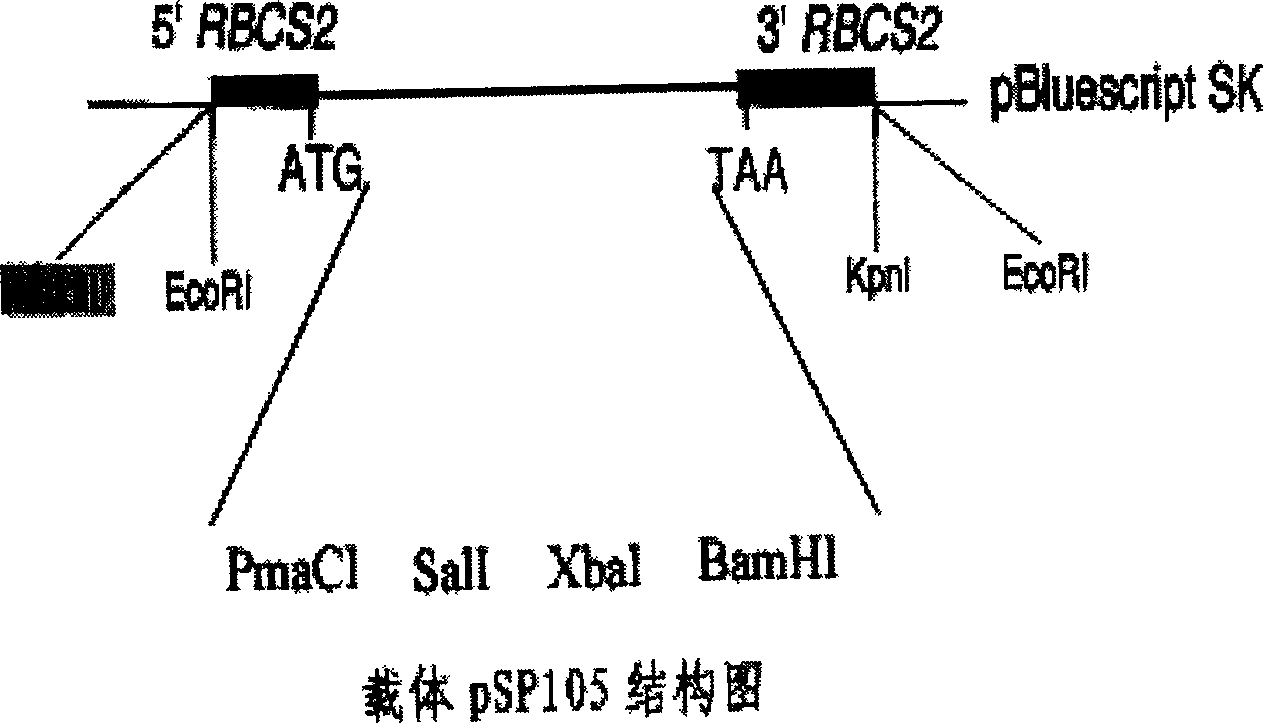
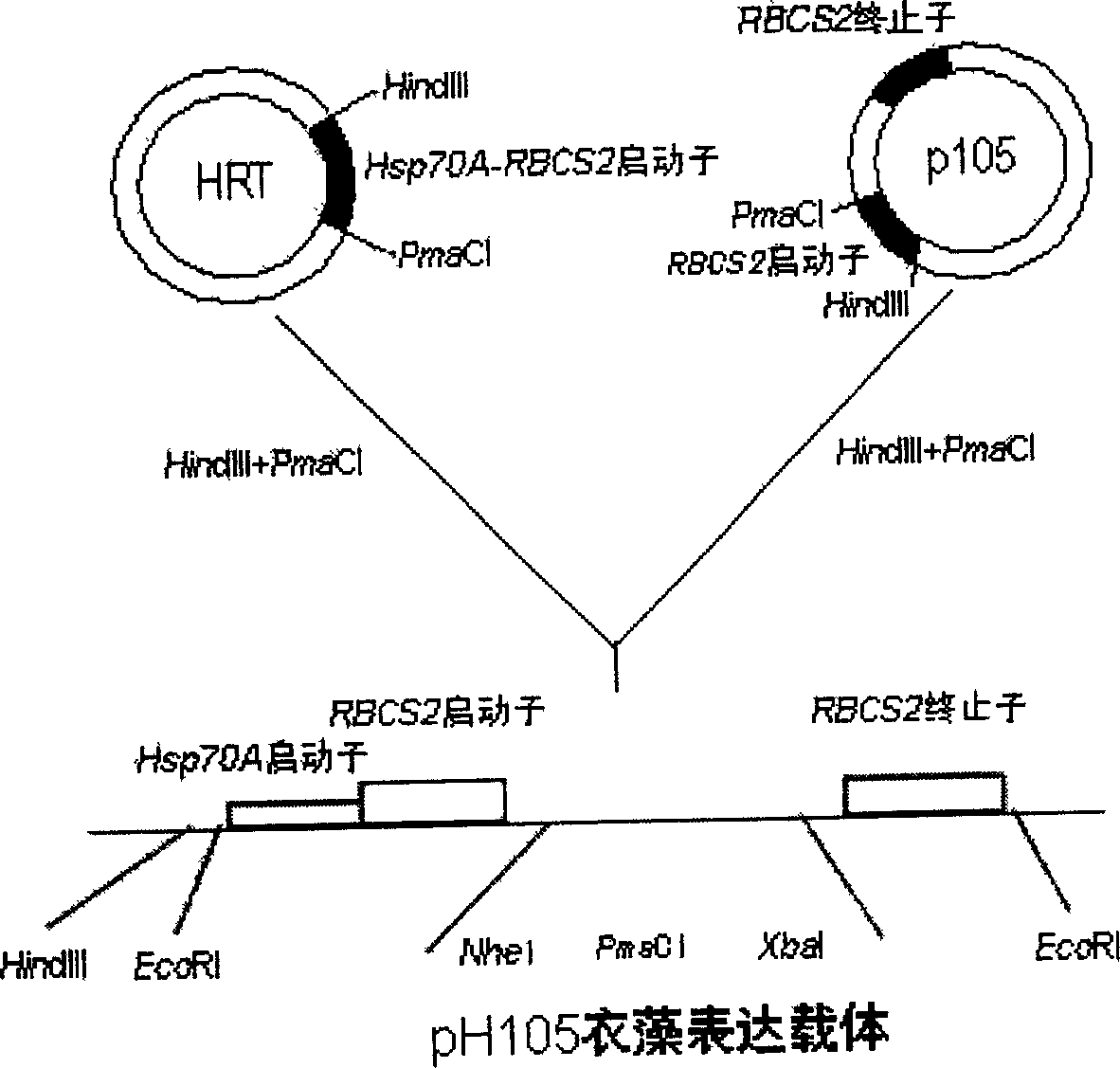
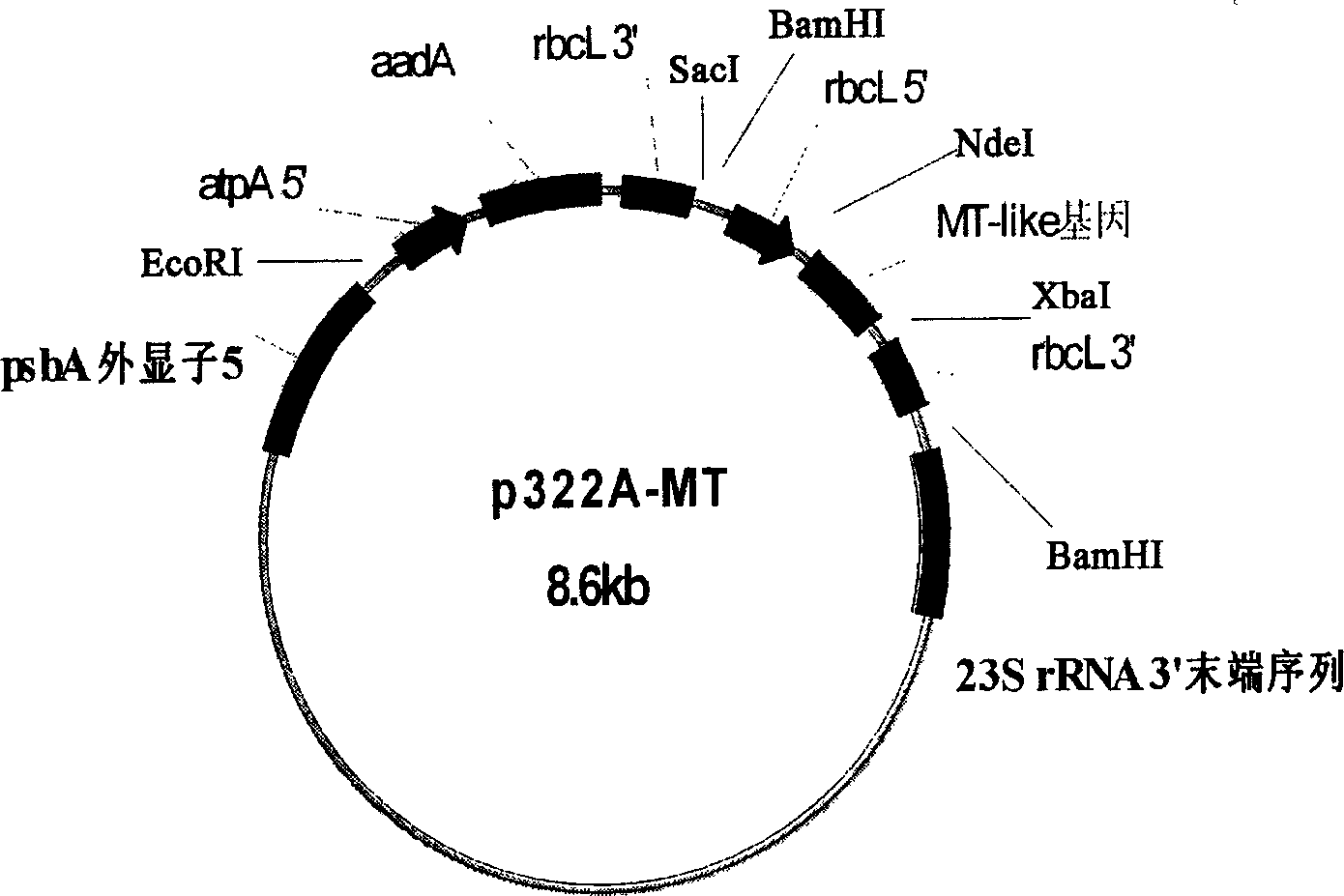
Constructing method for transgene Chlamydomonas reinhardtii bioreactor
InactiveCN1827769AEasy point-to-point integrationSolve training difficultiesUnicellular algaeMicrobiological testing/measurementChlamydomonas reinhardtiiVaccination
The invention relates the construct method for transgenosis rhinestone algae bioreactor. The method comprises the following steps: using the rhinestone algae as transgenosis receptor biology, highly effective expressing the carrier construct by constructing the exogenesis gene containing screening mark expression frame, leading the destination genes in rhinestone algae with bead milling method, electric punching method and other methods, integrating them into nucleus genome or chloroplast genome, and adopting a series of gene expression regulate and control technology to construct the transgenosis rhinestone algae bioreactor. The transgenosis rhinestone algae bioreactor possesses the characters of fast growth rate, short breeding cycle, easy segregation, photoautotroph and large scale culture, fast and cheap producing medicinal protein, industrial raw materials, and feeding vaccination, and possessing the bioactivity secondary metabolite.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Edible mushroom residue feed preparation process
InactiveCN104171759AHigh economic valueSolve UtilizationAnimal feeding stuffNutritive valuesSecondary metabolite
The invention discloses edible mushroom residue feed and a preparation method thereof. The edible mushroom residue feed preparation method comprises the following steps: degrading active ingredients of mushroom residue through a complex enzyme and fermenting a mushroom residue enzymolysis product through food-grade microorganisms, further degrading the active ingredients of the mushroom residue and releasing a functional secondary metabolite, and drying or spray-drying a fermentation product to obtain the edible mushroom residue feed which is intense in edible mushroom-featured flavor and easy in nutrient absorption, and has an antioxidant activity and an antibacterial activity. According to the preparation process disclosed by the invention, active ingredients in the mushroom residue raw material are degraded into polysaccharide, oligosaccharide, protein peptide and the like stronger in specific functional characteristics by the complex enzyme through a green biotechnology, and microorganism mixed fermentation is carried out to further generate beneficial secondary metabolite so as to improve antioxidant activity and antibacterial activity of the fermented product, thus improving the additional value of the product. The preparation process disclosed by the invention, breaking through a conventional mushroom residue feed processing technology, overcomes the shortcomings of the mushroom residue feed processing technology (direct material mixing or conventional simple fermentation), such as low mushroom residue utilization rate, low utilization rate of nutritive value and poor functionality, by organically combining biological enzymolysis and biological fermentation, and the economic value of the edible mushroom residue in the field of animal feed is obviously improved.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for simultaneously extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid) from lily tissue
InactiveCN102776174AResolve interferenceQuality improvementDNA preparationSodium acetateHigh concentration
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA from lily tissue. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining total nucleic acid solution through crude extraction and purification of the same steps from a lily tissue sample; and then sequentially selectively precipitating RNA and DNA, thereby obtaining high-quality DNA and RNA. The method disclosed by the invention is short in time, economic and fast, and good in stability; and the extracted nucleic acid is high in quality. The method has the characteristics that high-concentration potassium acetate is utilized for precipitating polysaccharides twice, so that the polysaccharides in the lily sample can be effectively removed; and in the DNA and RNA separation process, the RNA is selectively precipitated by means of the synergistic effect of lithium chloride and absolute ethyl alcohol and then the DNA is precipitated by using sodium acetate and isopropanol; and therefore, the efficiency of the DNA-RNA separation is high, the loss of the nucleic acid is low and the precipitation time is greatly shortened. The method is suitable for simultaneously extracting the DNA and the RNA from the lily tissue containing rich polysaccharides and other secondary metabolites.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
DNA extraction method for polysaccharide-rich plant dried leaves
The present invention discloses a DNA extraction method for polysaccharide plant dried leaves. The DNA extraction method comprises dried leaf grinding, desaccharifying, cracking, extraction, precipitation, washing, detection and other steps, wherein desaccharifying is the key step, a pre-heated desaccharifying buffer solution is added before the nuclear membrane is not cracked and the genome DNA is not released, the leaf tissue solution is suspended under a 65 DEG C water bath condition so as to dissolve polysaccharides and other secondary metabolites in the buffer solution, and low speed centrifugation is adopted to remove the polysaccharides and other impurities, such that the final DNA obtained through precipitation has high concentration and high purity. The DNA extraction method is suitable for dried mature leaves of all cerasus plants and other polysaccharide-rich plants, wherein the concentration of the obtained DNA can be increased if the leaves are the young and tender leaves, and the more DNA with high quality can be obtained from the mature leaves.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Methodologies for improving the quality of meat, health status of animals and impact on environment
InactiveUS20060240077A1Improving odourAdd flavorBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBoar taintSecondary metabolite
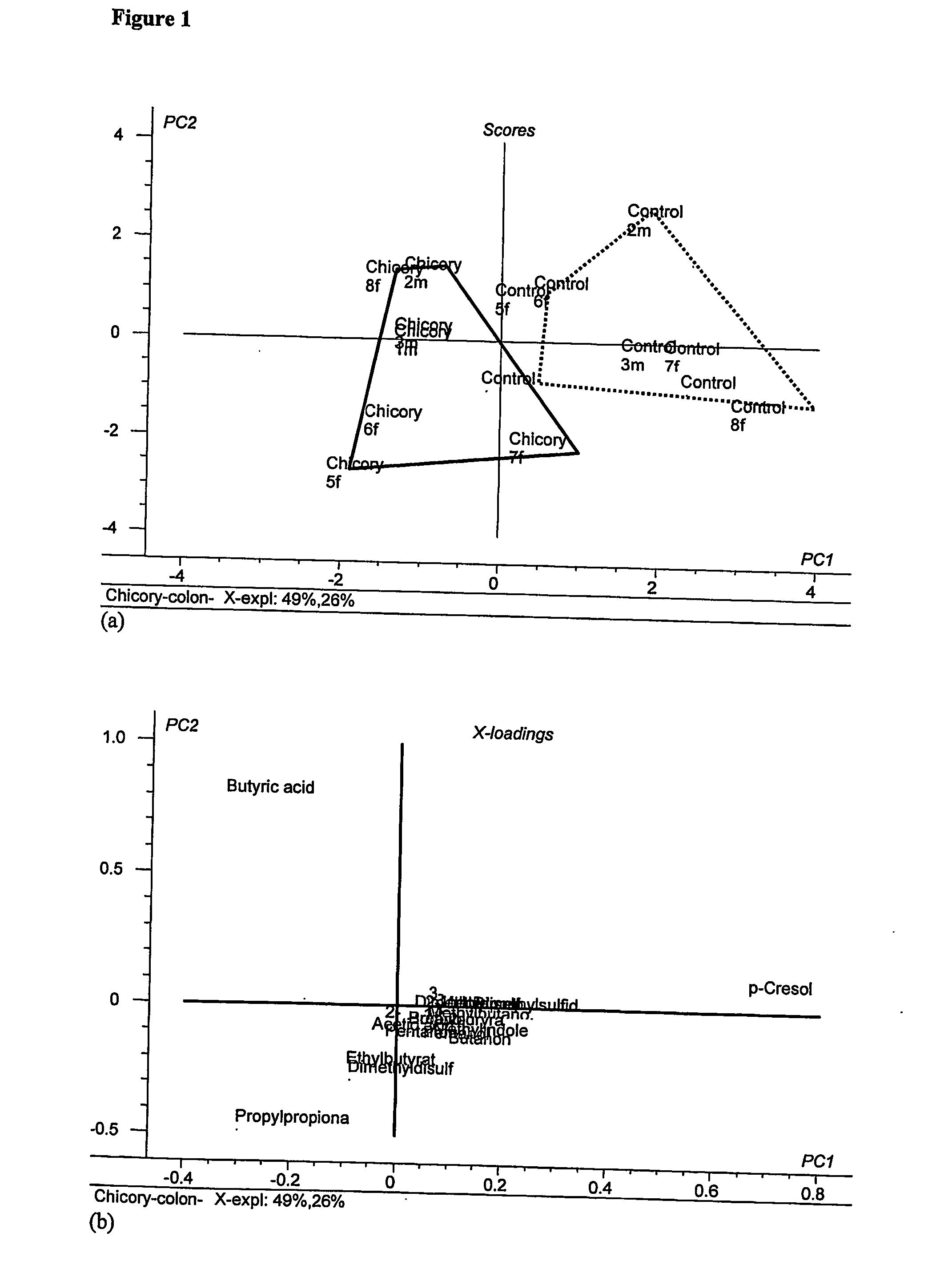
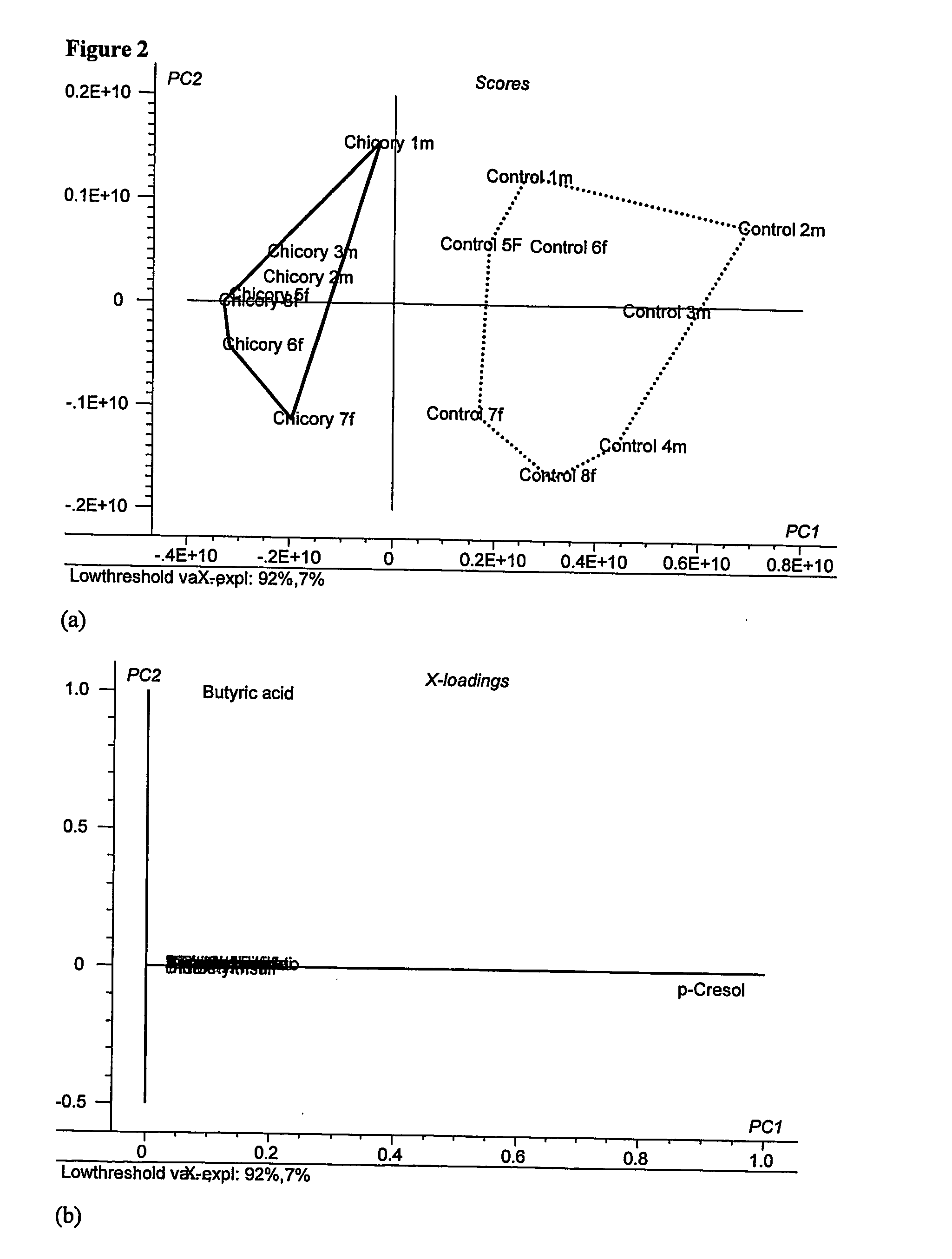
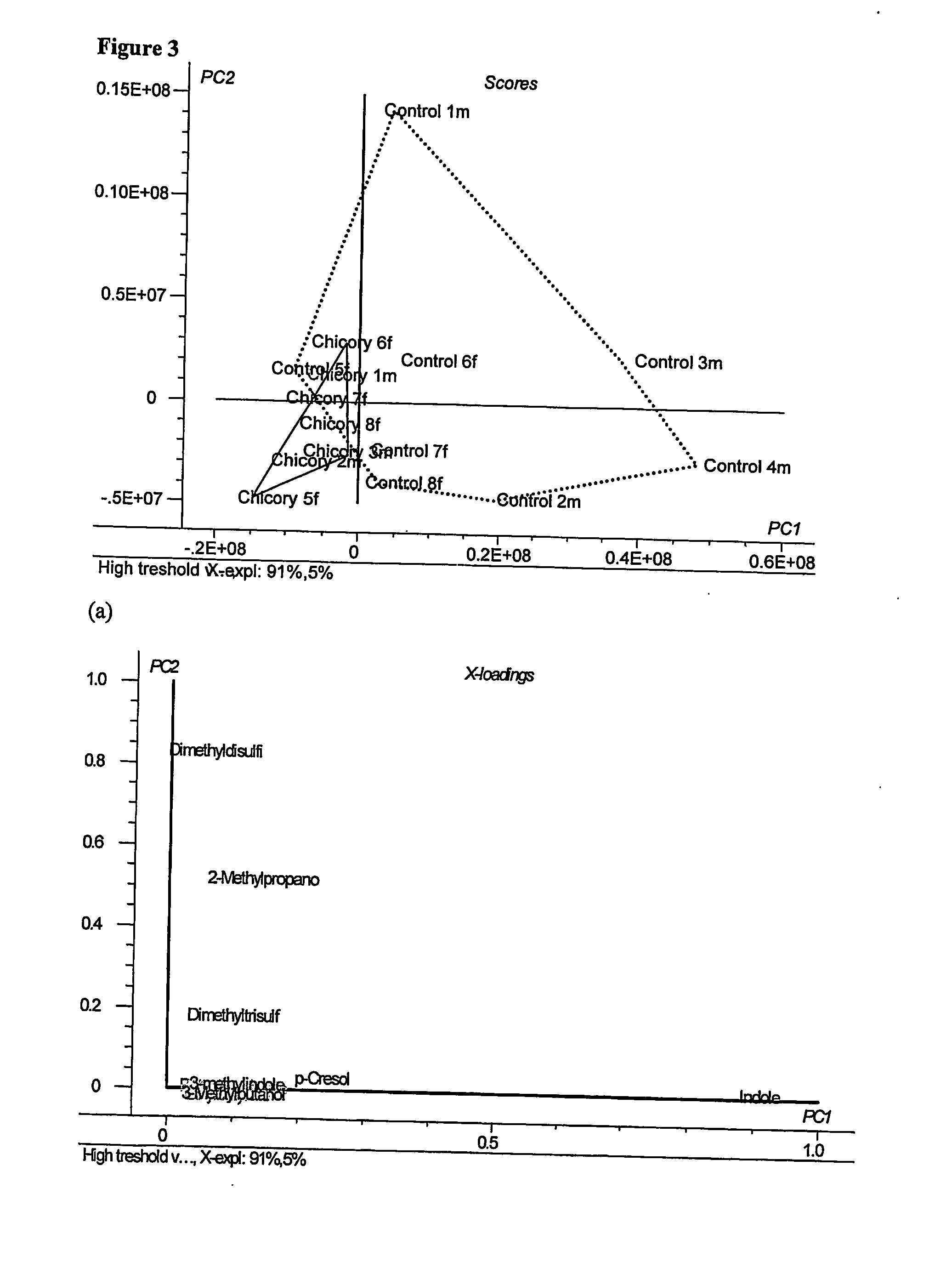
Disclosed is a method and a product of a chicory root product for reducing taint in animals, said method comprising feeding to an animal a chicory root product during at least one day prior to slaughtering the animal. By feeding animals with the chicory root product this improves the quality of meat, prevents or reduces female and male animal taint, primarily boar taint caused by skatole and / or androstenone. The invention also relates to methods for improving the health status of animals e.g. by reducing infections by pathogens in the gastrointestinal tract and to methods for reducing animal caused odors in general. The chicory root product comprises inulin / fructan (fructo-oligosaccharides), other low molecular weight sugars and secondary metabolites.
Owner:DANMARKS JORDBRUGSFORSKNING DANISH INST OF AGRI SCI +3
PDR transport protein gene promoter for controlling ginsenoside accumulation, and its application
InactiveCN103088027AVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsSecondary metaboliteSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a PDR transport protein gene promoter for controlling ginsenoside accumulation, and its application. A promoter ProPDR1 has a DNA sequence represented by SEQIDNo.1 or has a DNA sequence having a homology of above 99% to SEQIDNo.1. A PgPDR1 transport protein gene promoter sequence is obtained through cloning by adopting genome walker in the invention, and includes a TCA element and TCCACCT-Motif. A promoter expression vector pBI121-ProPDR1::GUS is constructed in the invention, and reporter gene GUS is strongly controlled by ginsenoside, salicylic acid, methyl jasmonate and abscisic acid in transgenic tobacco under the driving of the promoter ProPDR1, so the ginseng PgPDR1 gene expression promoted by the promoter is closely related to the ginsenoside accumulation. The promoter provided by the invention has very important application values in the medical plant secondary metabolite synthesis and accumulation control gene engineering.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Preparation method of high-purity fidaxomicin
ActiveCN103275152AEliminate distractionsImprove qualitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChromatographic separationMetabolite
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying fidaxomicin from fidaxomicin fermented mycelia. The method comprises the following steps of first filtering and extracting the fidaxomicin fermentation liquid, diluting the extracted liquor with water, then decoloring, adsorbing and analyzing the extracted liquor through macroporous resin, and concentrating, extracting and drying the analyzed liquor to obtain a fidaxomicin crude product; and dissolving the fidaxomicin crude product in a polarity organic solvent, injecting polymer microsphere columns to carry out the chromatographic separation to obtain the high-purity fidaxomicin fine powder. By adopting the method, the interference of fermented secondary metabolite can be effectively eliminated, and the quality and the yield of the fidaxomicin can be improved. The entire process is simple and easy to operate; the prepared fidaxomicin can be used for drugs; and the purity of the prepared fidaxomicin is more than 95 percent, and the whole-coarse total yield is more than 45 percent. The used solvent is a conventional solvent, small in toxicity and applicable to the industrial production.
Owner:NCPC NEW DRUG RES & DEV
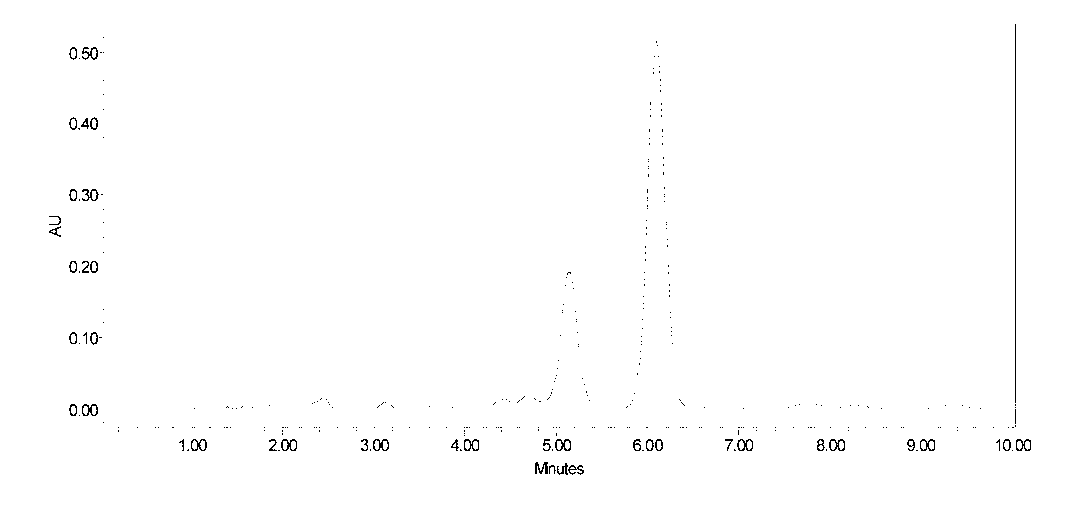
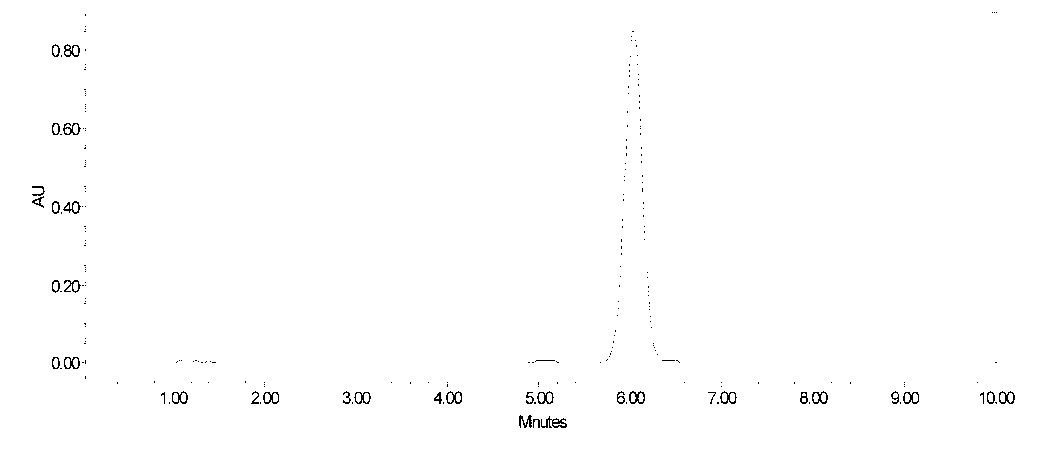
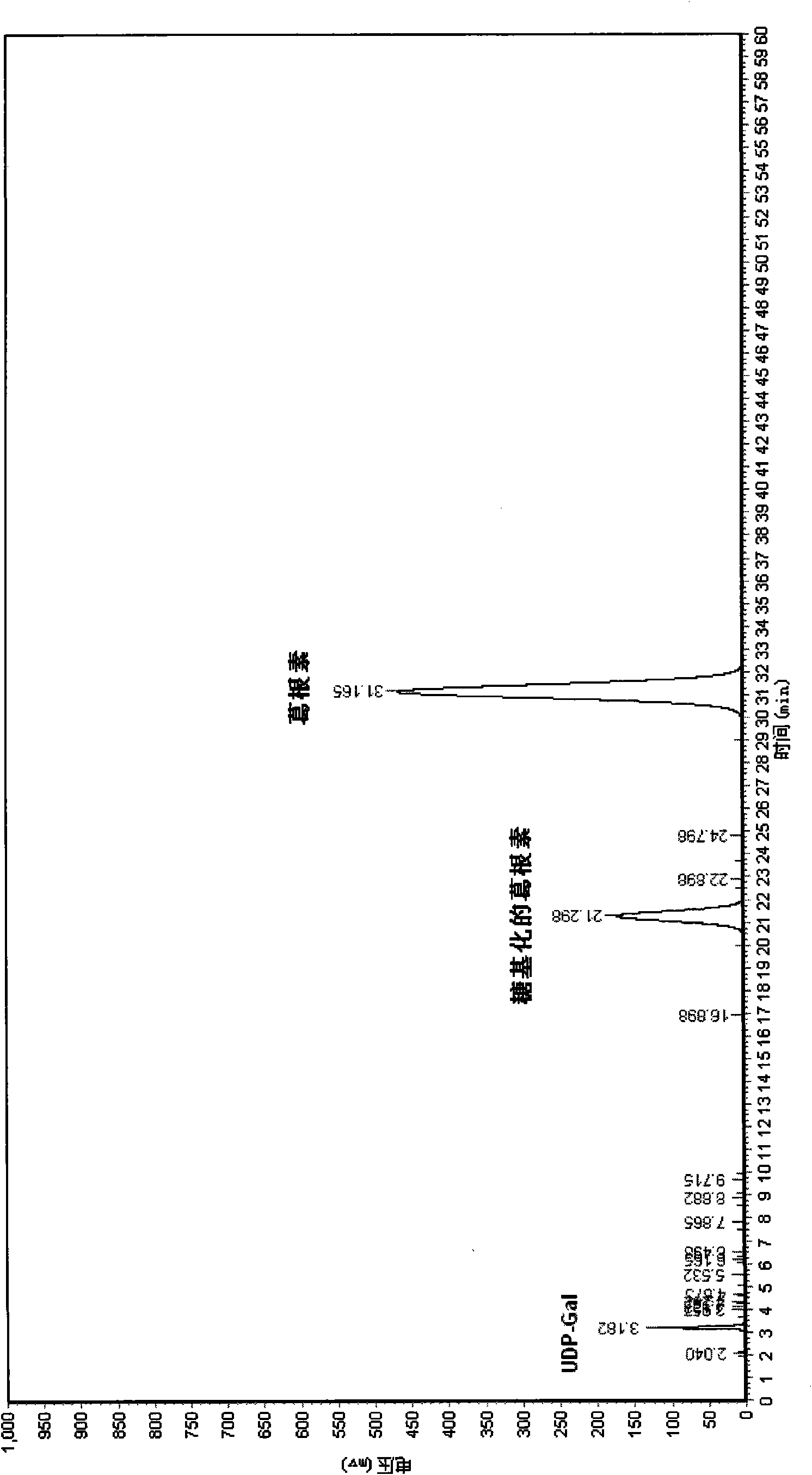
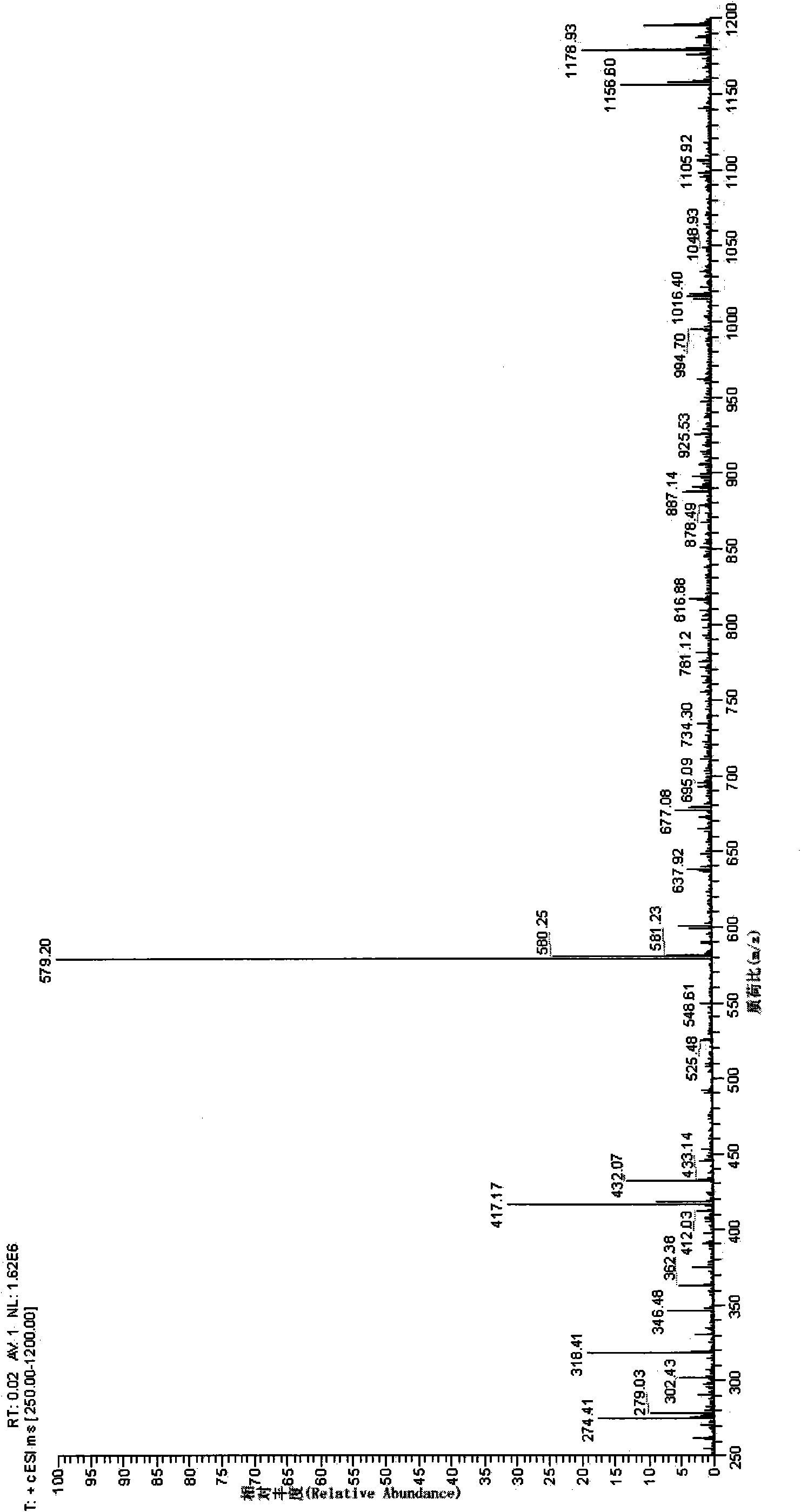
Method for modifying flavonoid glycoside compounds with galactosy transferase
The invention discloses a method for modifying flavonoid glycoside compounds with galactosy transferase. The flavonoid glycoside compounds are ubiquitous secondary metabolites in the nature and one of main active ingredients of medicinal plant, and have physiological activities of antibacterium, cancer resistance, antioxidation and the like. However, natural flavonoid glycoside compounds frequently have the defects of poor water solubility, poor drug effect and the like. The method solves the defects of relatively low solubility of the natural flavonoid glycoside compounds and takes the natural flavonoid glycoside compounds as a forerunner to improve the water solubility thereof by a glycosylation reaction, thereby improving the bioavailability thereof. The technical essential of the method is as follows: an enzymatic reaction is applied to the synthesis of polyglycoside of flavonoid compounds. Compared with chemical synthesis methods, the method has higher synthesis efficiency and lower cost. After glycosylation modification, part of drugs can improve drug effect and reduce toxic side effect; therefore, the method provides a new approach for the development of new drugs of the flavonoid compounds.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Application of trichoderma strains in preparation of biopesticide for preventing and controlling cucumber fusarium wilt
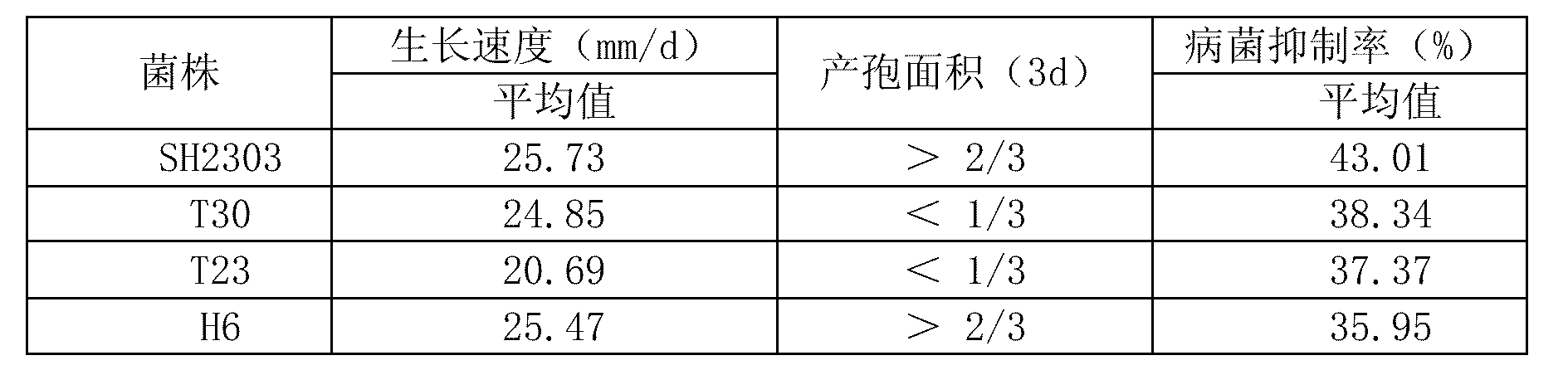
The invention relates to the application of trichoderma strains in preparation of biopesticide for preventing and controlling cucumber fusarium wilt. The trichoderma strains are Trichoderma harzianum SH2303CGMCC NO.4963. The main components for preventing and controlling the cucumber fusarium wilt are conidia of the Trichoderma harzianum SH2303; and the biopesticide can be seed coating agents or granules. The trichoderma strains in the application has high growth speed and high sporulation quantity; the confrontation pathogens inhibition rate in vitro reaches 43.01 percent; the inhibition rate of a non-volatile inhibitor to the cucumber fusarium wilt is 41.33 percent; the inhibition rate of a volatile inhibitor to the cucumber fusarium wilt is 11.49 percent; the chitinase activity is 3.9573U; the beta-1,3-glucanase enzyme activity is 0.5092U; the extracellular protease enzyme activity is 3.0678 U; the prevention effect aiming at the living bodies of the cucumber fusarium wilt is 71.43 percent; the overall proportion of the antibiosis secondary metabolites, having antagonism, in the strains is 30.28 percent; and the trichoderma strains can effectively prevent and treat the disease of the cucumber fusarium wilt.
Owner:侨昌生物科技(上海)有限公司
Method for detecting primary metabolites and secondary metabolites in fresh tobacco leaves with GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometer)
The invention provides a method for detecting primary metabolites and secondary metabolites in fresh tobacco leaves with GC-MS (gas chromatography-mass spectrometer). The method comprises steps as follows: the fresh tobacco leaves are rapidly collected and quick-frozen with liquid nitrogen on site, the quick-frozen tobacco leaves are transferred to dry ice and transported to a laboratory at low temperature, moisture is removed by a freeze dryer with a low-temperature freeze drying method, the tobacco leaves are pulverized by a pulverizer and screened by a 40-mesh sieve, the primary metabolites and the secondary metabolites of the pulverized tobacco leaves are extracted ultrasonically with a solvent, a supernatant of an extracting solution is subjected to nitrogen blow-drying, blow-dried extracts are subjected to an oximation reaction and a silane derivatization reaction, and GC-MS analysis is performed finally. The method has the advantages as follows: a tobacco leaf collecting method can really reflect growth and development periods, collecting parts, varieties and production places of the tobacco leaves; a tobacco leaf extracting and detecting method can cover the primary and secondary metabolites such as sugar, amino acid, organic acid, sterol, alkaloid, polyphenol and the like of the fresh tobacco leaves and has high-flux detection characteristics, and a selective ion monitoring method can realize accurately qualitative and quantitative analysis of 199 primary and secondary metabolites in the fresh tobacco leaves, and 135 metabolites are required to be verified in a standard substance.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
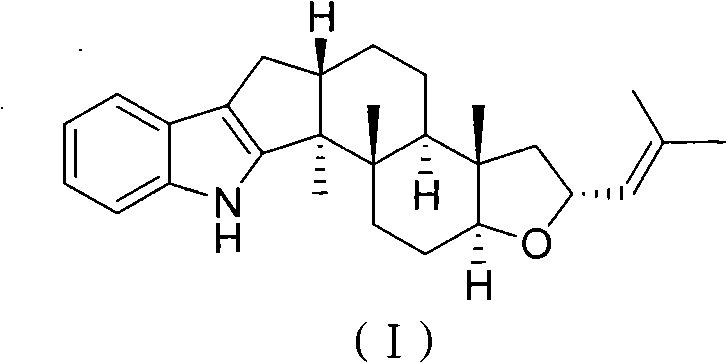
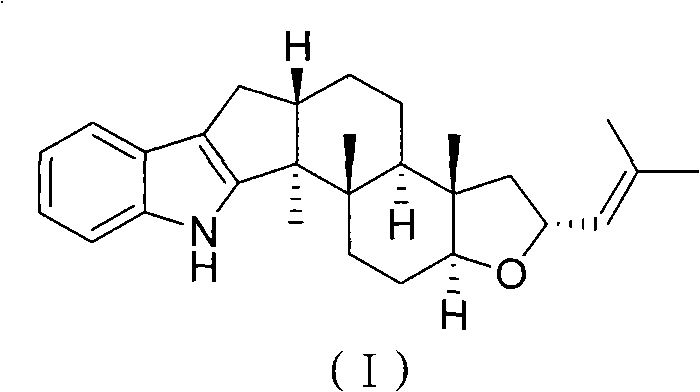
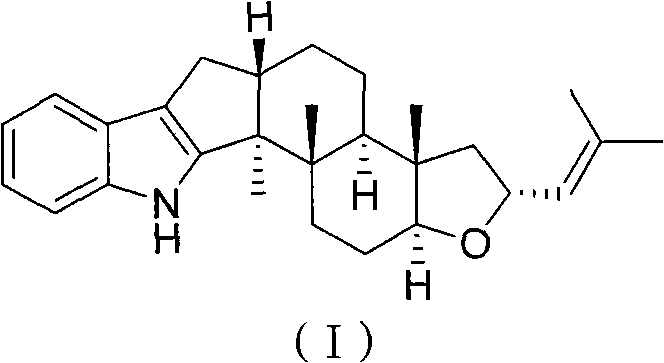
Application of diterpene alkaloid compound serving as secondary metabolite of seaweed endophytic fungus
The invention relates to the field of pesticides, in particular to application of a diterpene alkaloid compound serving as a secondary metabolite of a seaweed endophytic fungus. The diterpene alkaloid compound serving as the secondary metabolite of the seaweed endophytic fungus has insecticidal effect and is shown as a formula (I). The natural diterpene alkaloid compound is obtained by extractingand separating yeast of Aspergillus oryzae cf-2 fungus separated from ocean red alga heterosiphonia; and by insecticidal activity experiments, the fatality rate of artemia is 74.2 percent when the diterpene alkaloid compound is 100 micrograms per milliliter.
Owner:北海南方海洋生态养殖有限公司
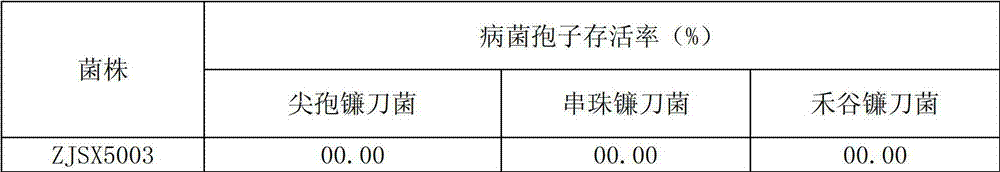
Trichoderma strain for antagonizing soil-borne disease
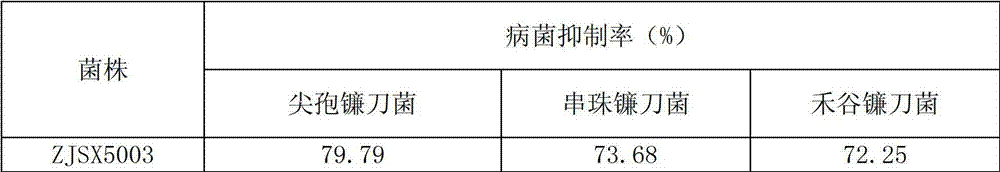
The invention relates to a Trichoderma strain for antagonizing soil-borne disease, belonging to the field of biological control. The Trichoderma strain is Trichoderma asperellum ZJSX5003 CGMCC No.6480. The Trichoderma strain provided by the invention has the characteristics of high growth speed and high spore production amount; the in-vitro standoff pathogen inhibition rates are respectively up to 79.79%, 73.68% and 72.25%, the pathogen spore survival rates are respectively 0.00%, the in-vivo preventive effects for cucumber fusarium wilt and maize stem rot are respectively 85.08% and 66.67%, the enzyme activity of chitinase is 4.0783U, the enzyme activity of beta-1,3-glucanase is 0.8050U, the enzyme activity of extracellular proteinase is 4.8503U, and the content of silicone, terpene and carboxylic acid having antagonistic actions in antibiotic secondary metabolites is 44.44%. The Trichoderma strain provided by the invention has the advantages of high antagonism and high specificity. The biological pesticide produced from the strain can effectively control the soil-borne disease, thereby ensuring the stable increase of crop and vegetable yields.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Azaphilones compounds in marine fungus HK1-6 and application of azaphilones compounds as MRSA-resistant drug
ActiveCN108101878AAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsResistant bacteriaSecondary metabolite
The invention relates to azaphilones compounds in marine fungus HK1-6 and an application of the azaphilones compounds as an MRSA-resistant drug, in particular to secondary metabolites 1-4 produced bymarine fungus Penicillium sp.HK1-6 or pharmaceutically acceptable salt. The compounds 1-4 show very high antibacterial activity for MRSA (such as S. aureus ATCC4330 and S. aureus ATCC33591) and VER (such as E. faecalis ATCC51299), MIC is smaller than or equal to 12.5 mu g / mL, the MIC of a compound 2 for E. faecalis ATCC51299 is one times higher than that of positive drug vancomycin, and the compounds have good prospects to be developed into drugs resisting drug-resistant bacteria, lead compounds of drugs and candidate drugs.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Antifungal compositions containing the endophyte fungus alternaria alternata and/or its metabolites, as antagonist agents of plasmopara viticola
The present invention relates to compositions containing the fungus Alternaria alternata and, or the secondary metabolites thereof, belonging to the family of the diketopiperazines (DKPs), for controlling the pathogen fungus Plasmopara viticola.
Owner:乌迪内大学 +1
Apparatus and Method for Controlled Release of Botanical Fumigant Pesticides
A fumigant pesticide composition made up of a base formula and enhancement formula, which include botanical essential oil-based active ingredients and inert materials identified under the United States Environmental Protection Agency's approved list of minimum risk pesticides. The enhancement formula is effective to inhibit or enhance the release of the secondary metabolites of the essential oil-based active ingredients. An apparatus and method for the controlled release of the fumigant pesticide composition is also disclosed.
Owner:SUMATICS
Biologic emulsifier for livestock feed
InactiveCN102696880ADoes not cause residues in the bodyQuality is not affectedAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceSecondary metabolite
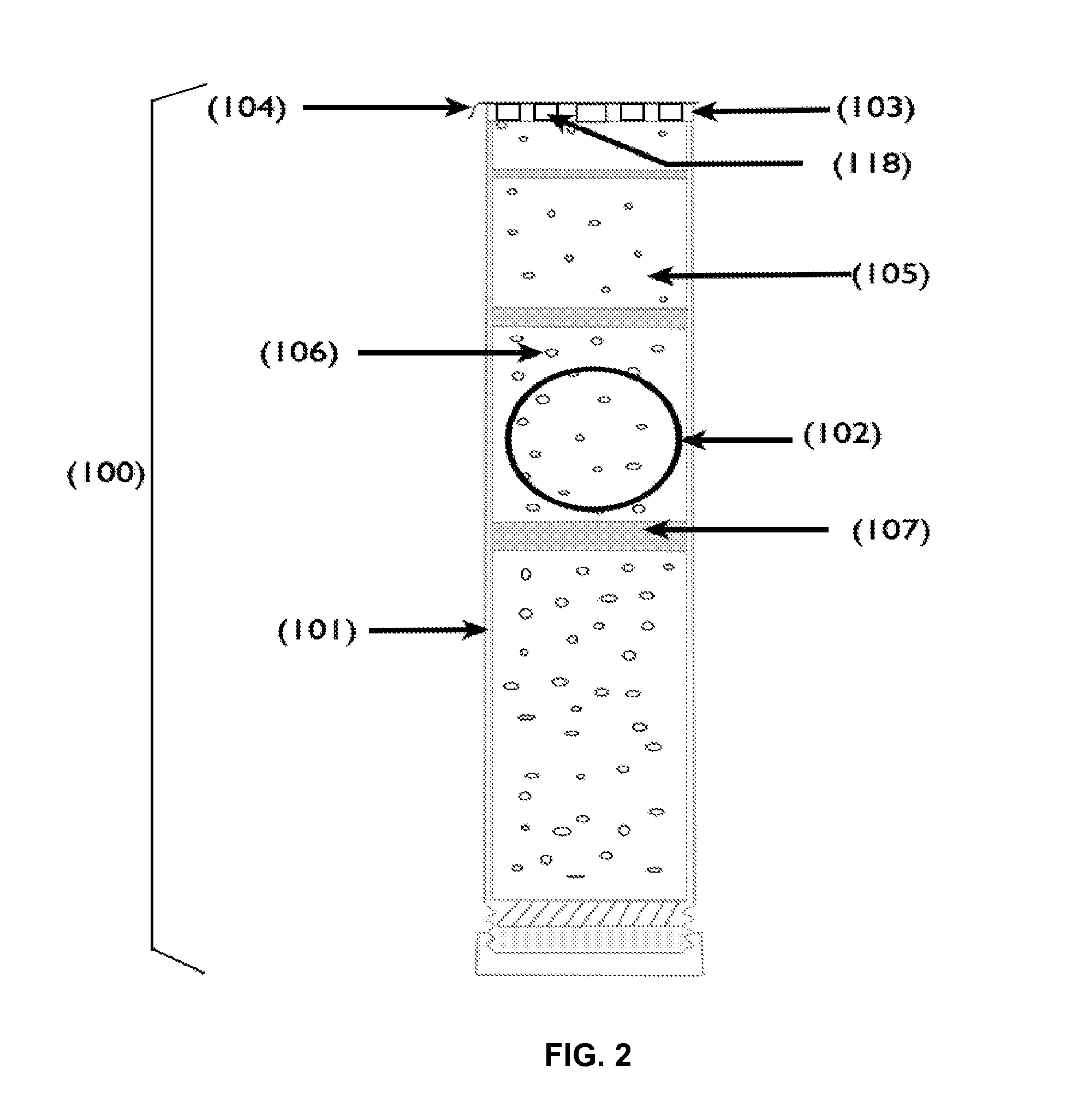
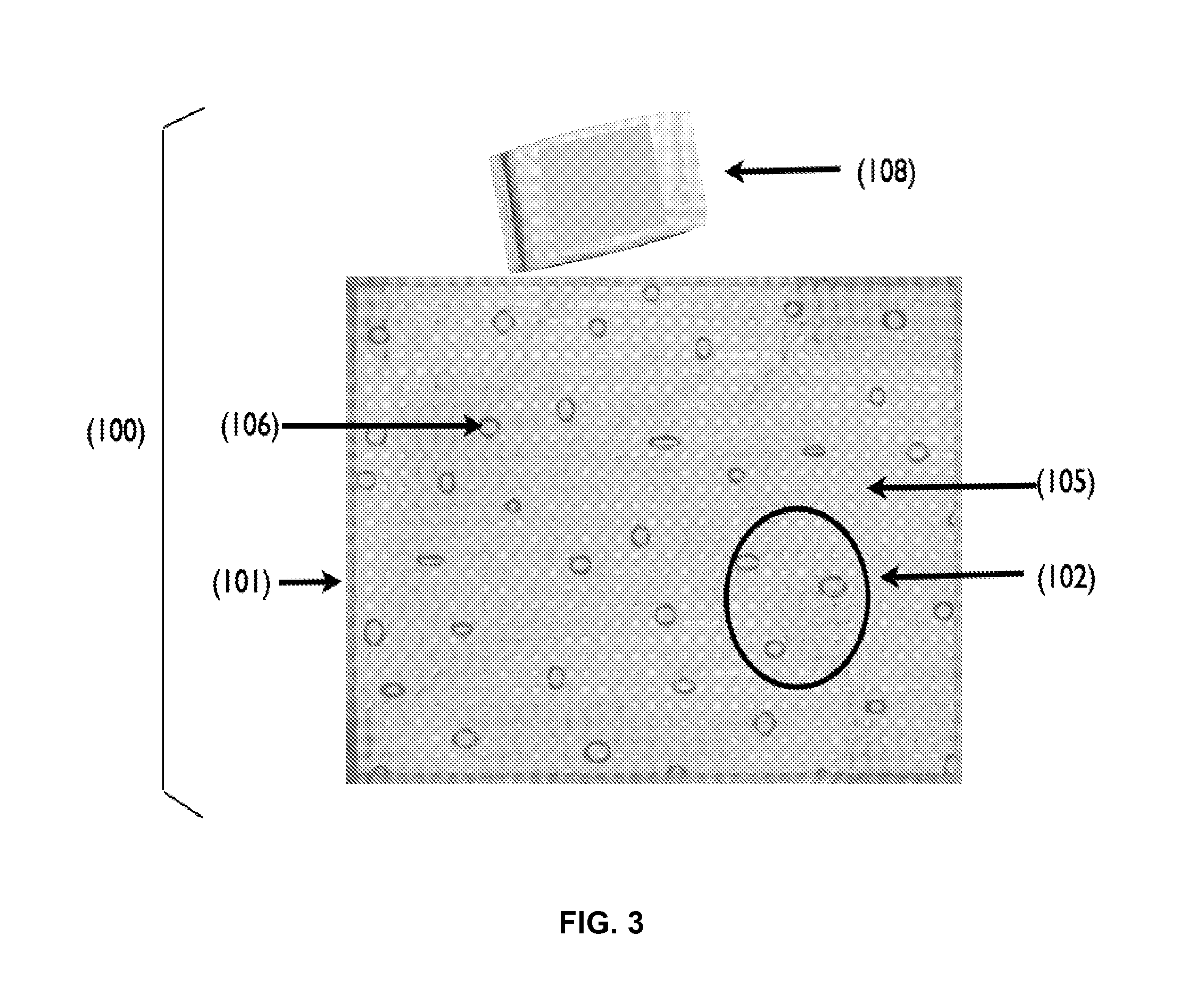
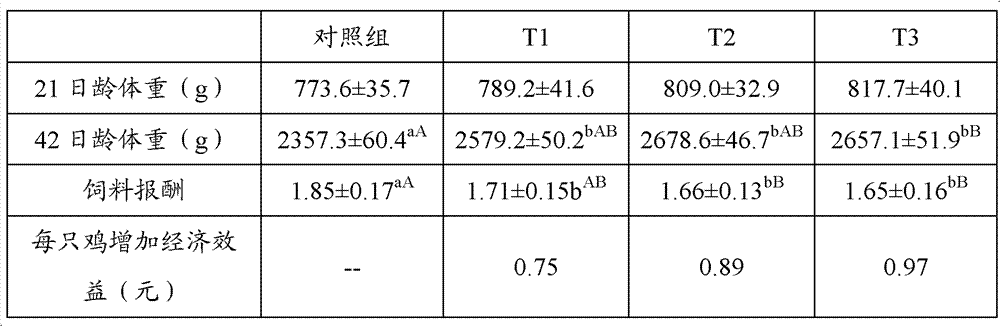
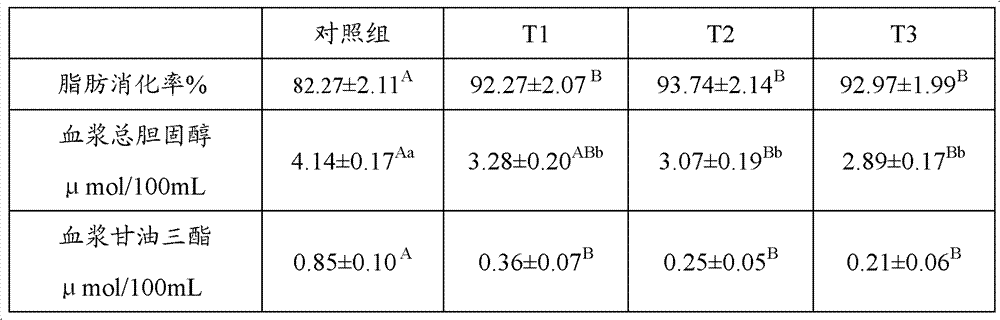
The invention discloses a biologic emulsifier for livestock feed. The biologic emulsifier is characterized by being prepared by two or more than two of sophorolipid, rhamnolipid and trehalose. The sophorolipid, the rhamnolipid and the trehalose and the like in the emulsifier are all secondary metabolites generated by microbial fermentation, can be naturally metabolized and degraded, do not cause residues in animal bodies, and do not influence quality of animal products. The biologic emulsifier can remarkably improve livestock fat digestion utilizing rate, improves feed reward, reduces livestock blood cholesterol and triglyceride, remarkably improves livestock production performances, improves carcass quality, improves body immune function, reduces morbidity and mortality, and remarkably improves economic returns.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com