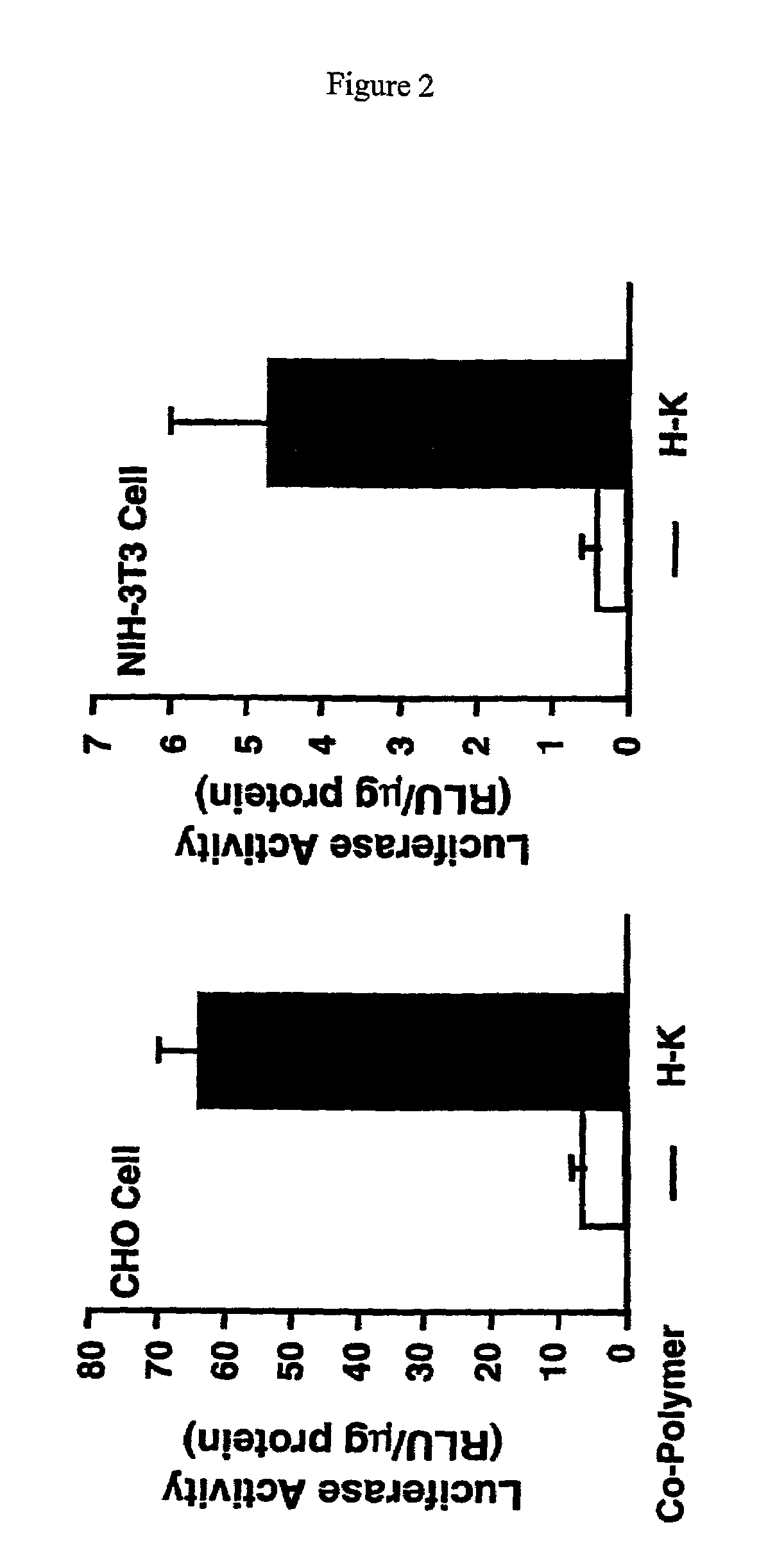
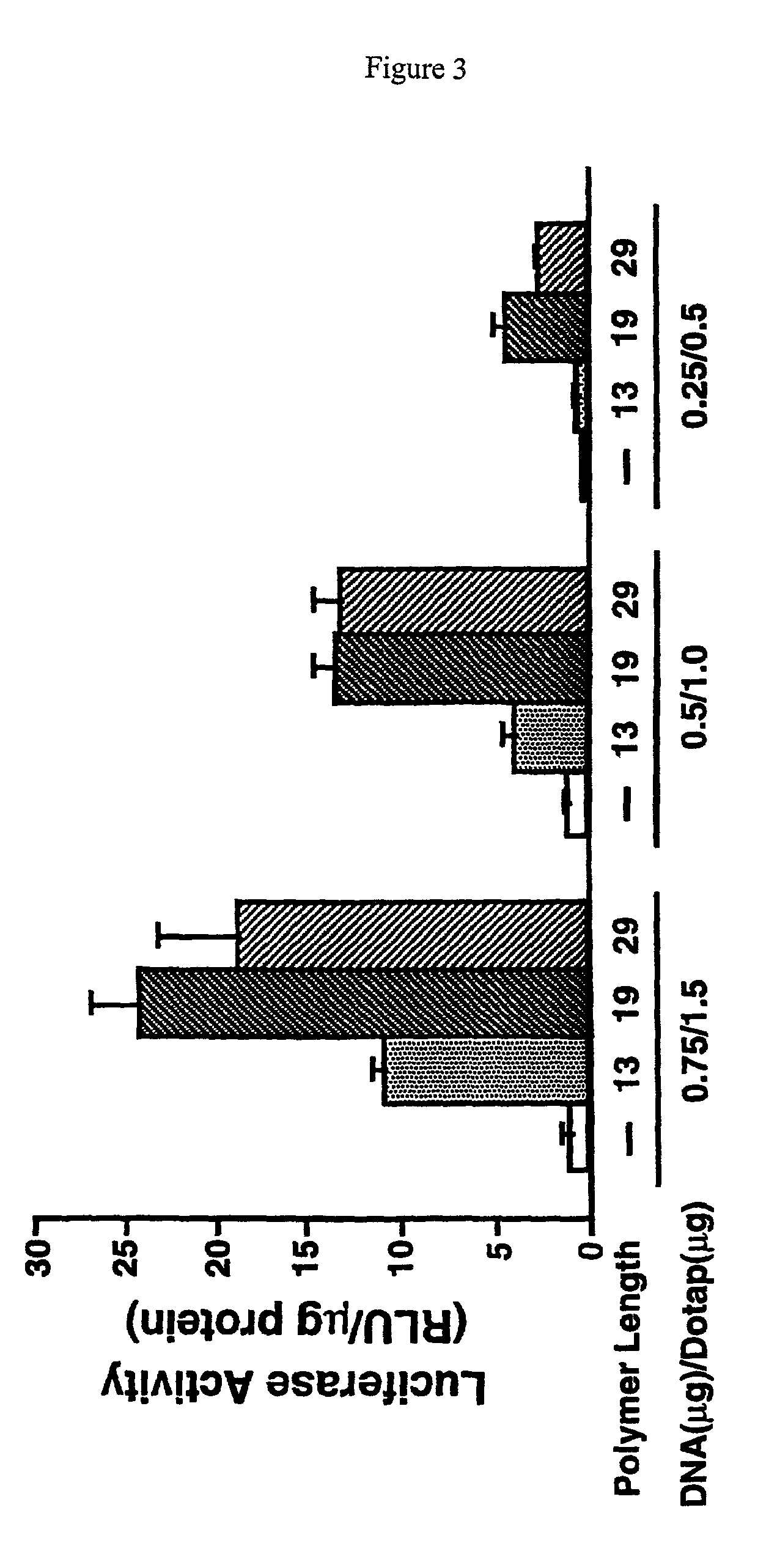
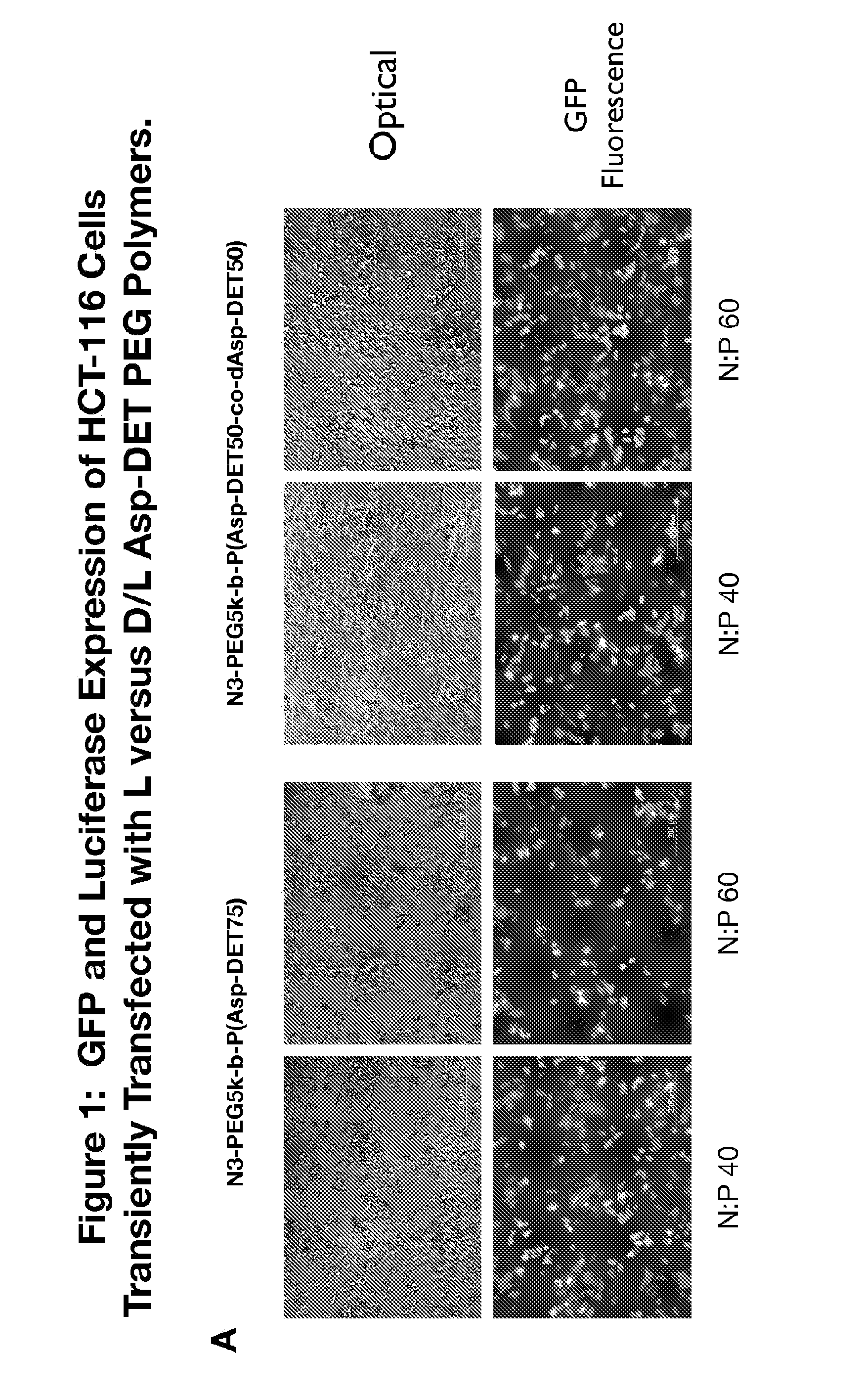
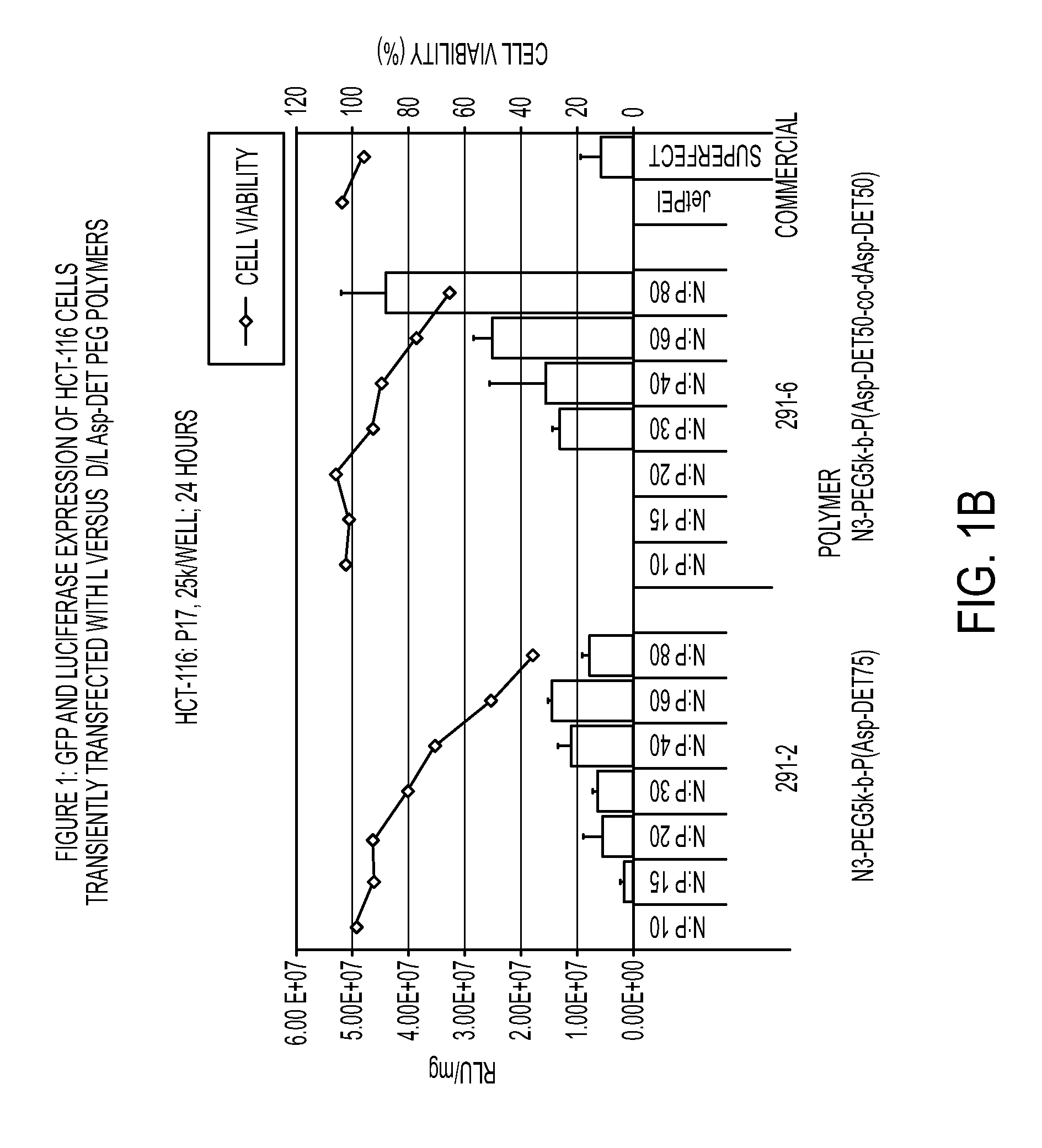
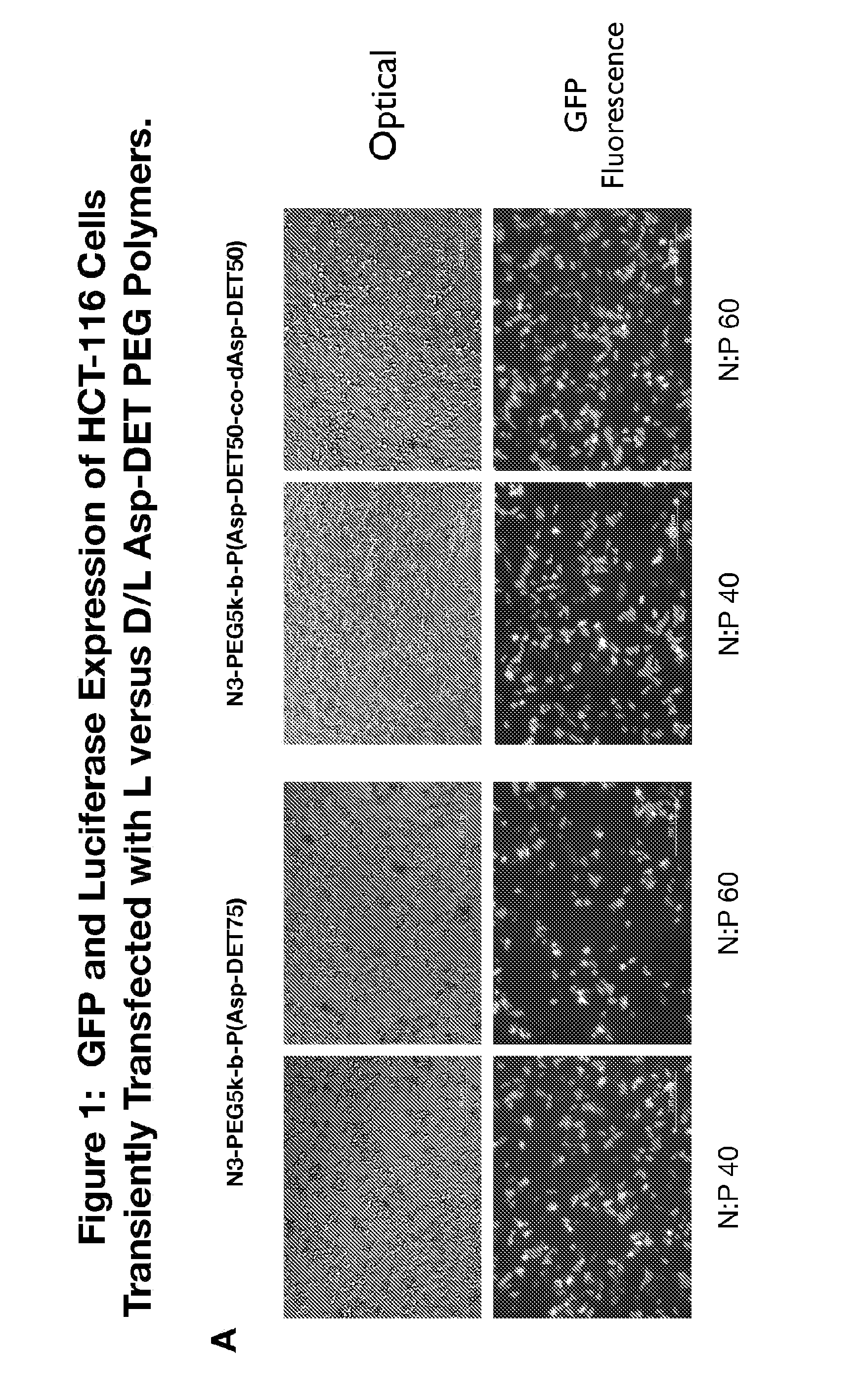
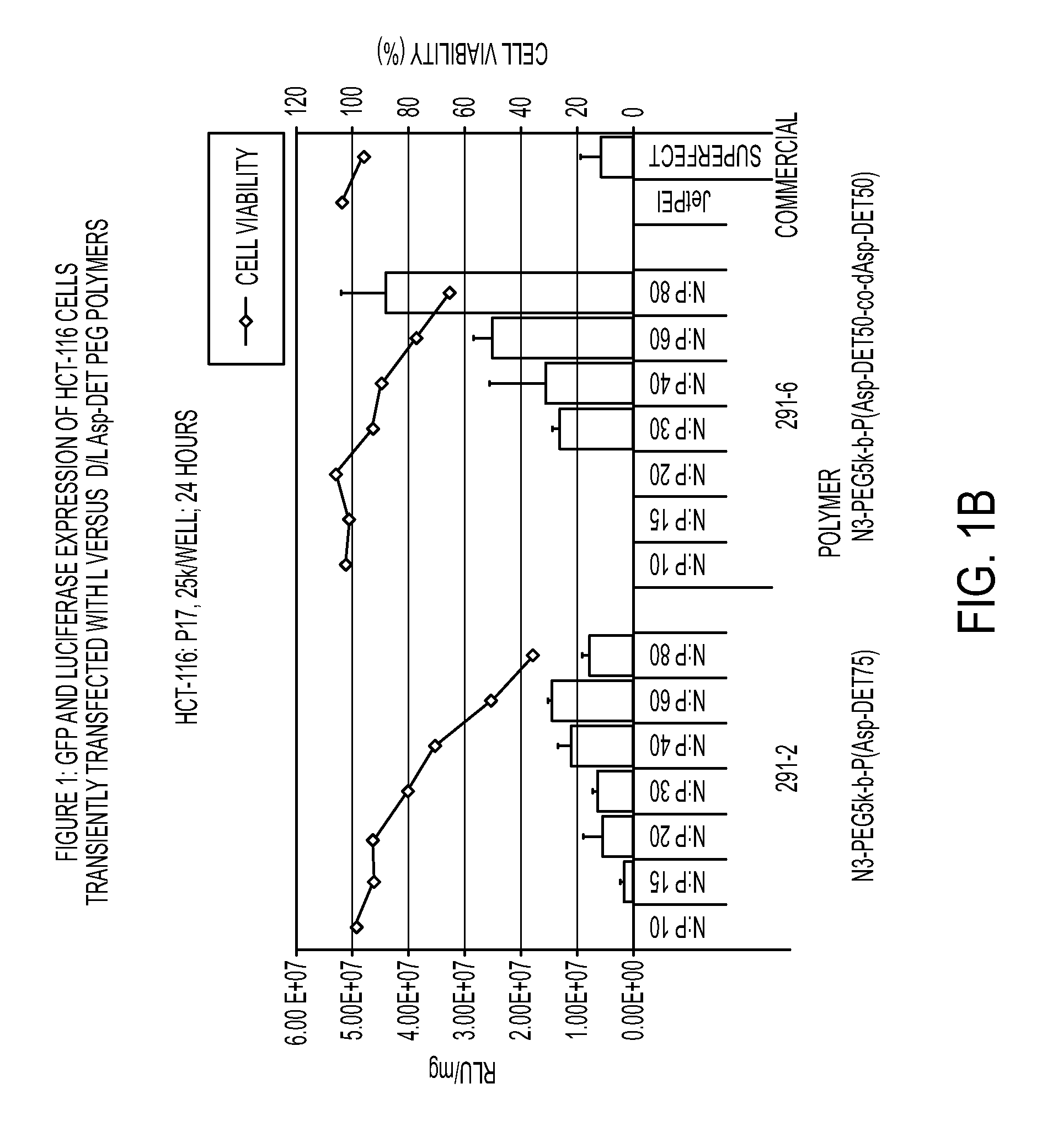
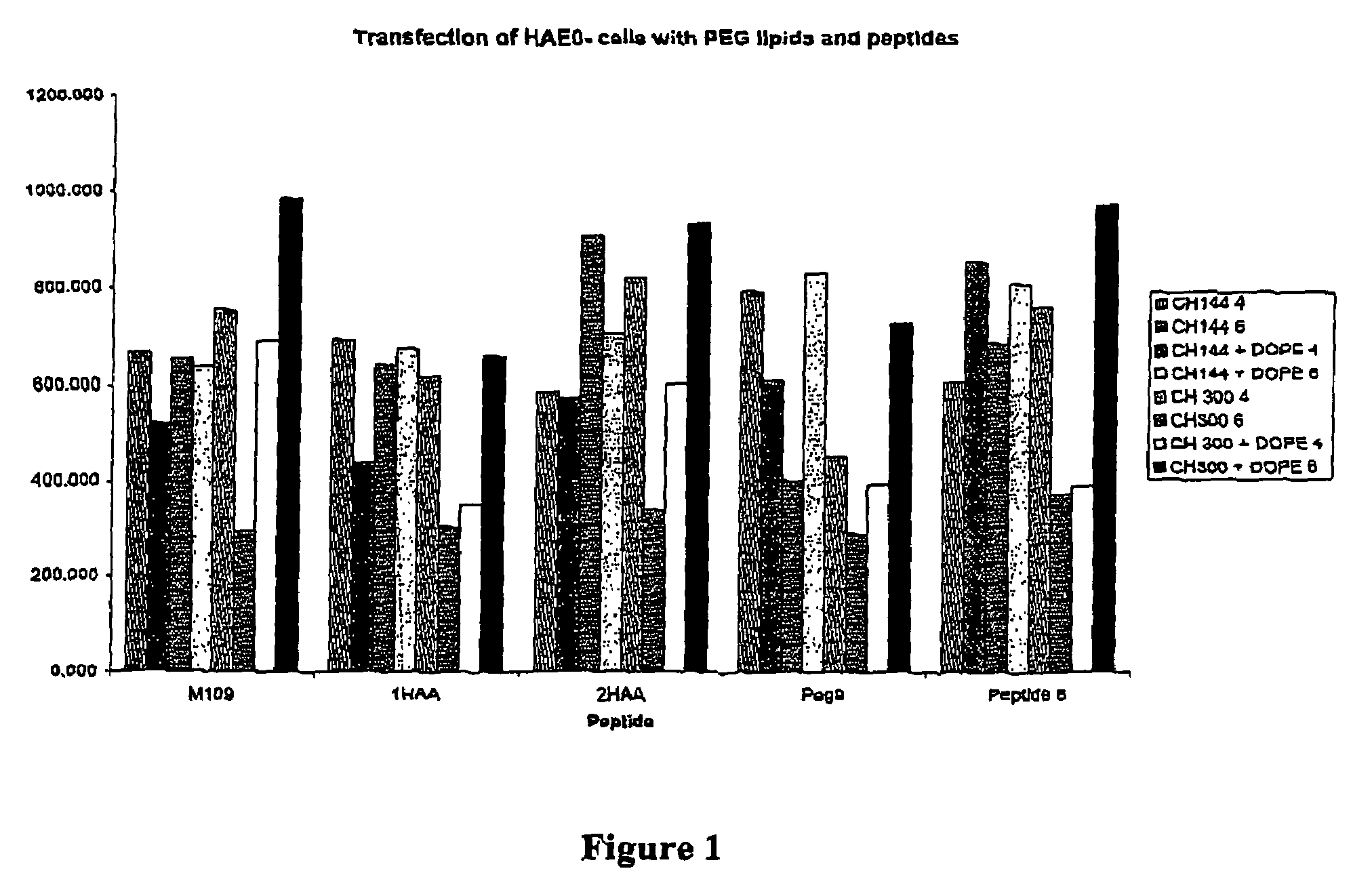
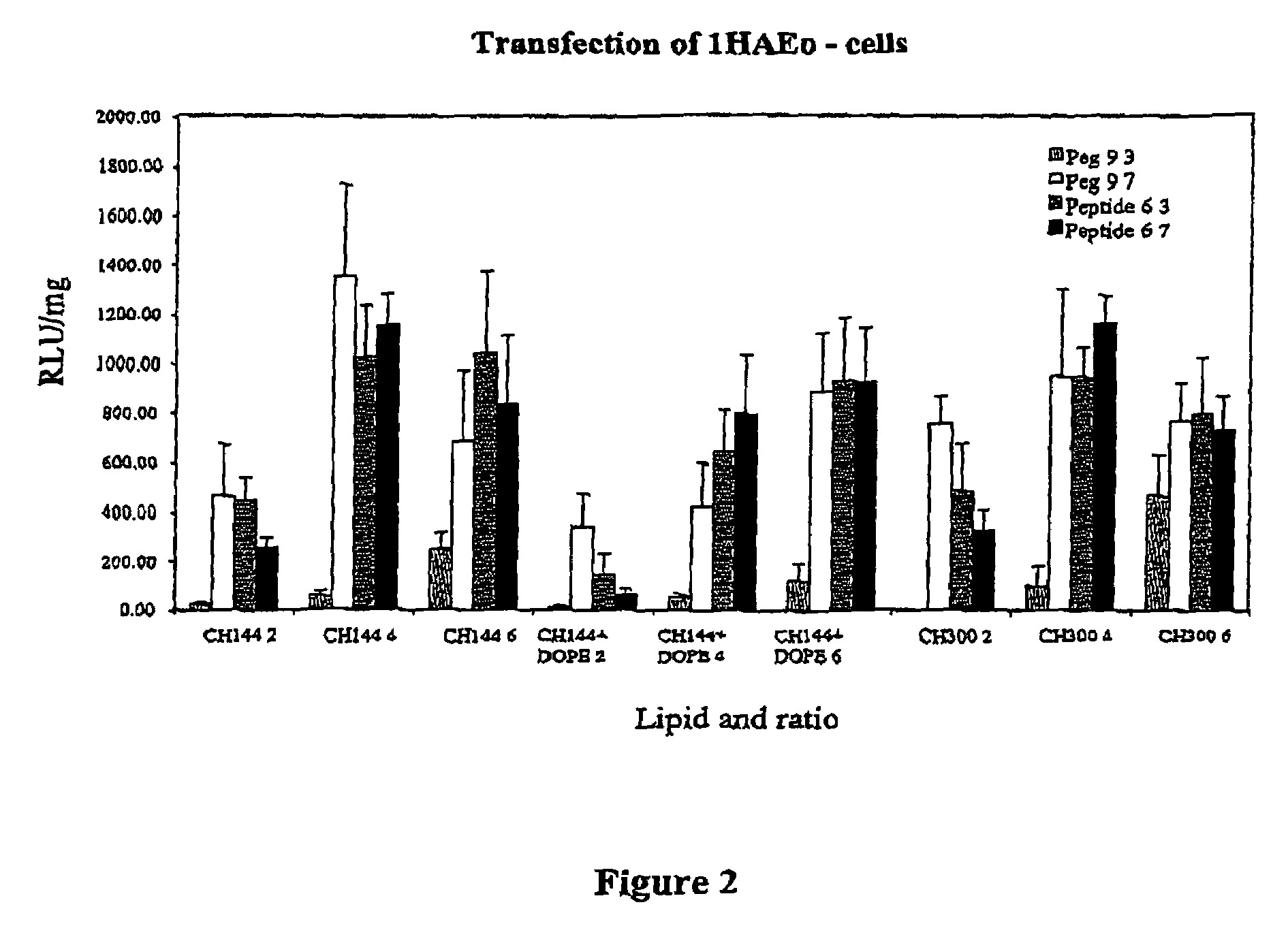
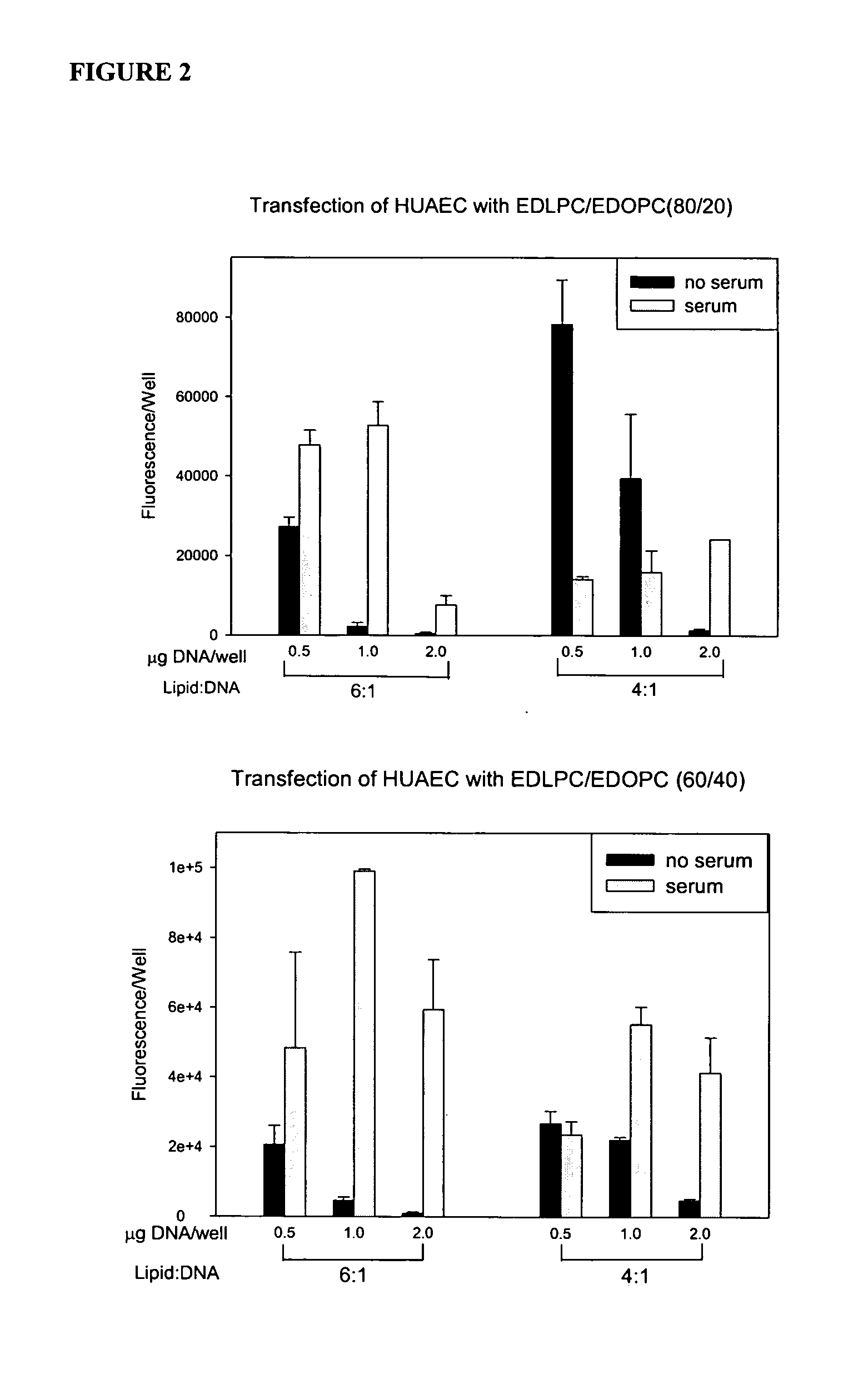
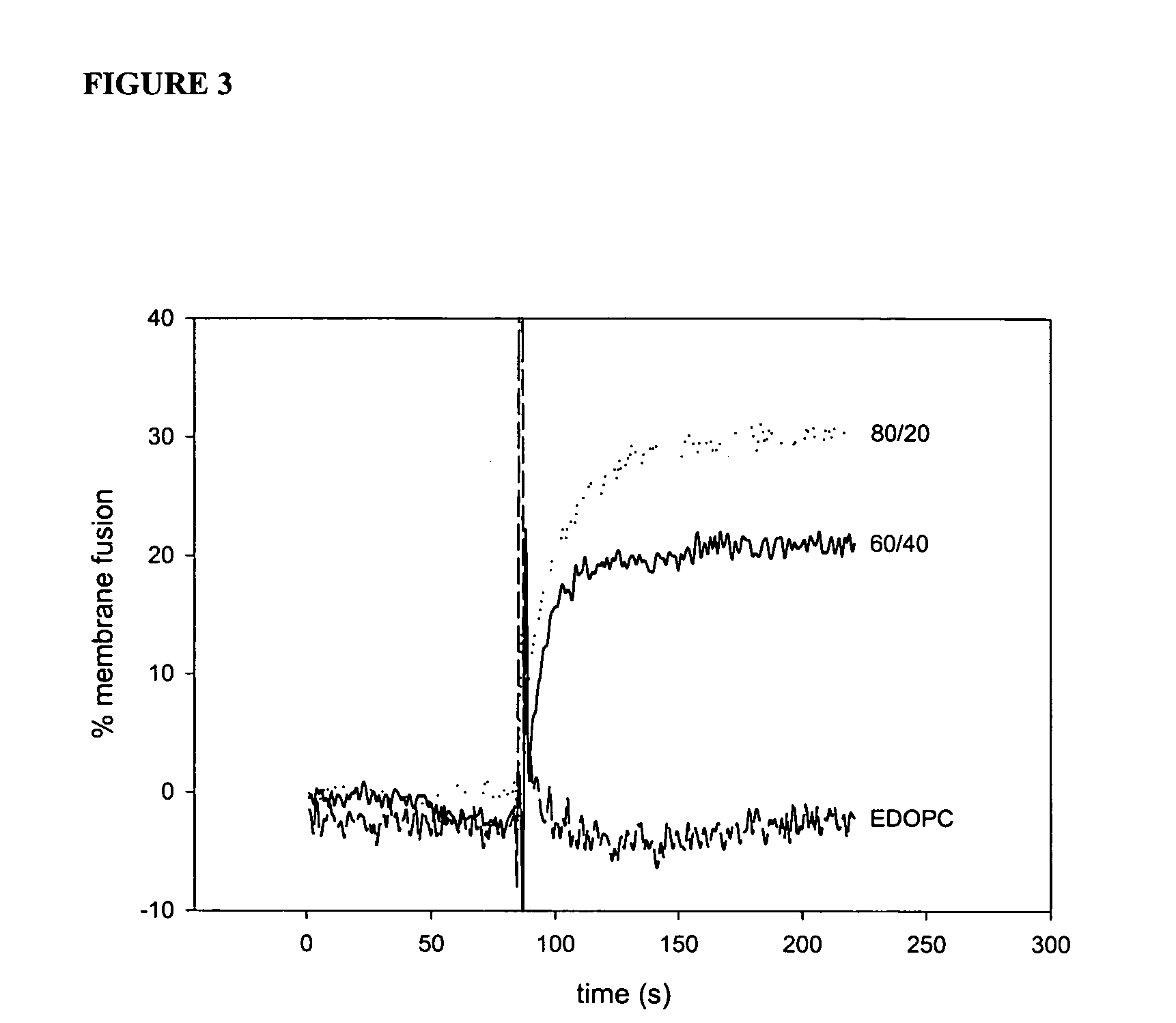
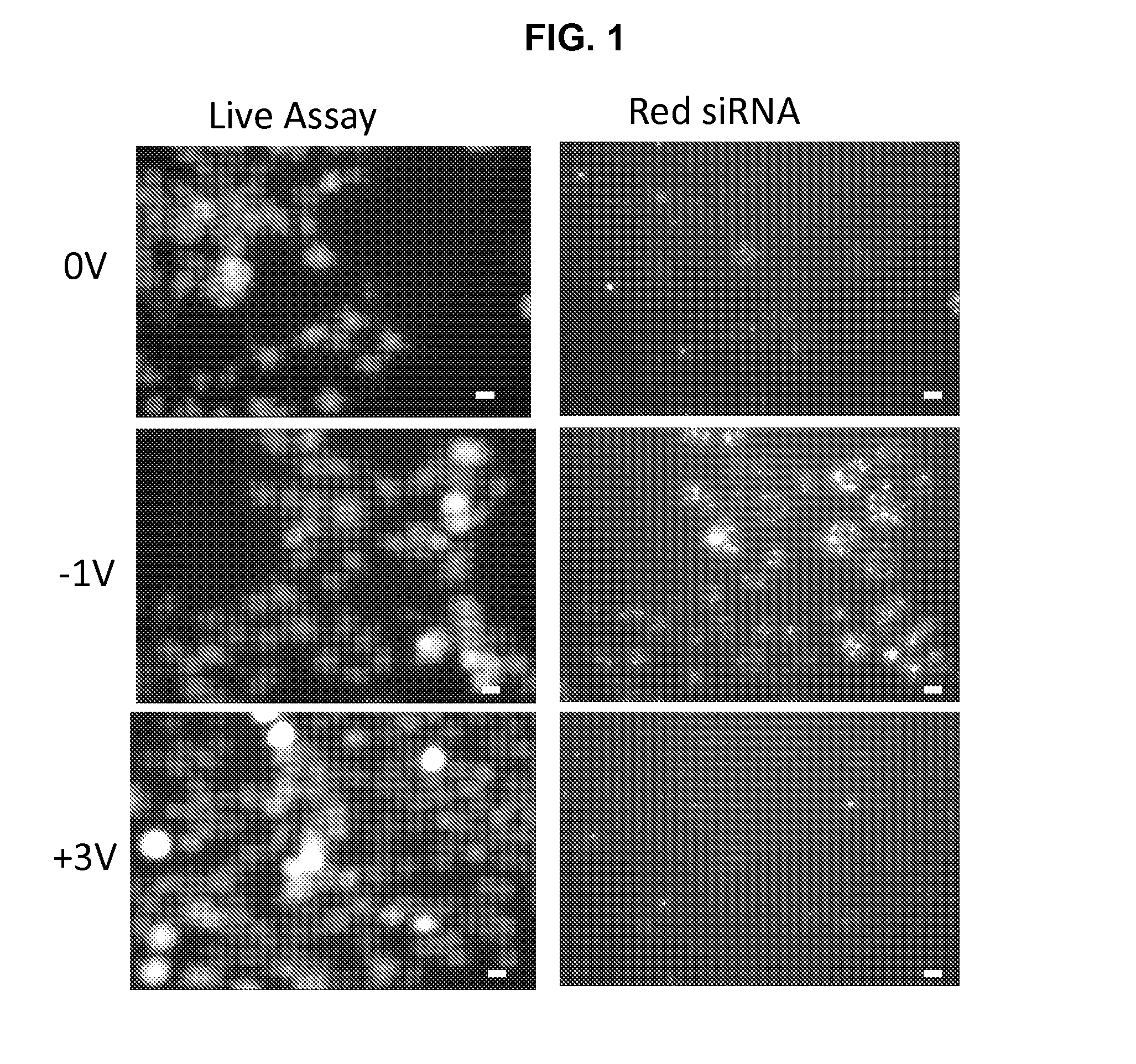
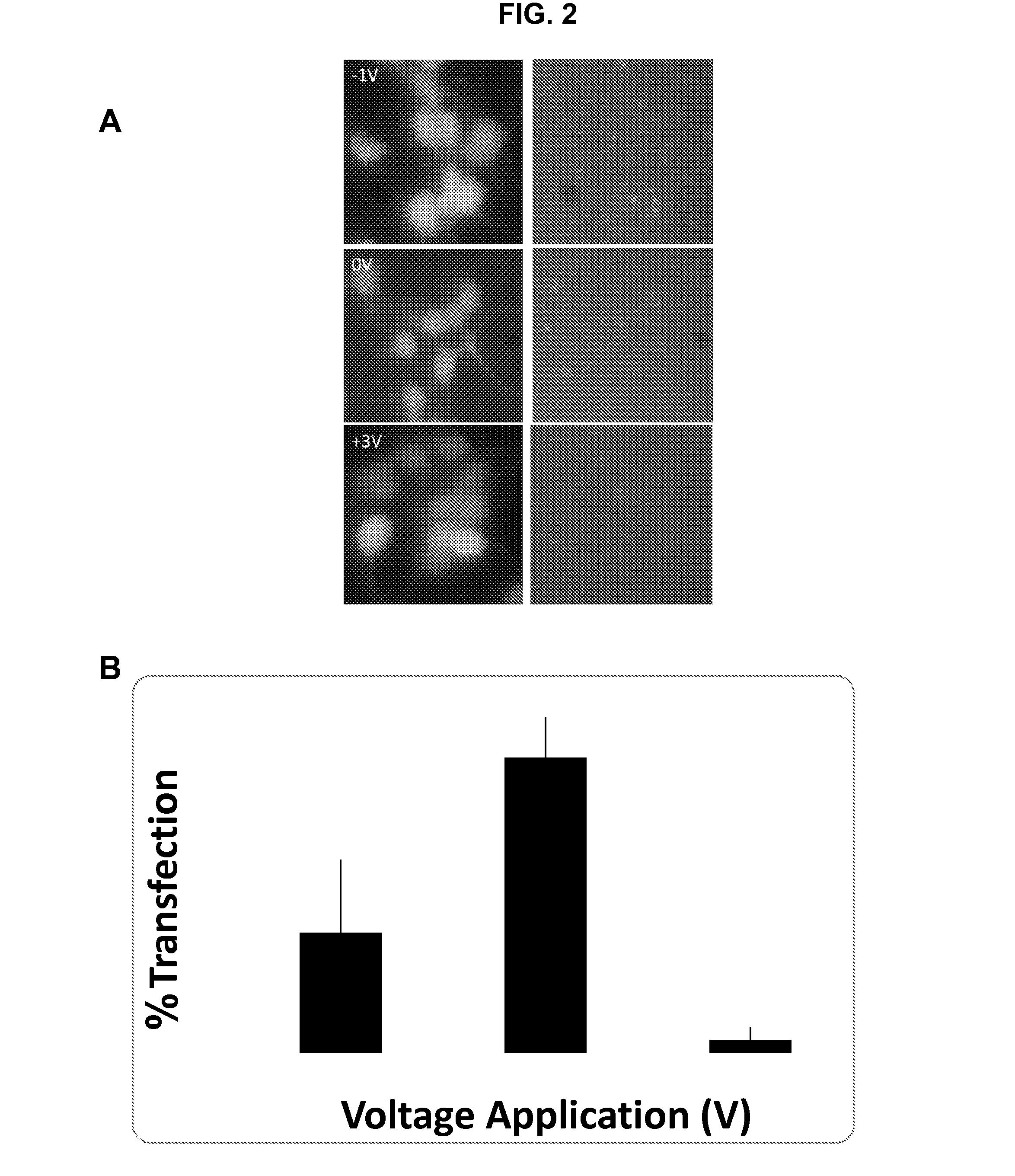
Patents
Literature
39results about How to "Enhanced transfection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
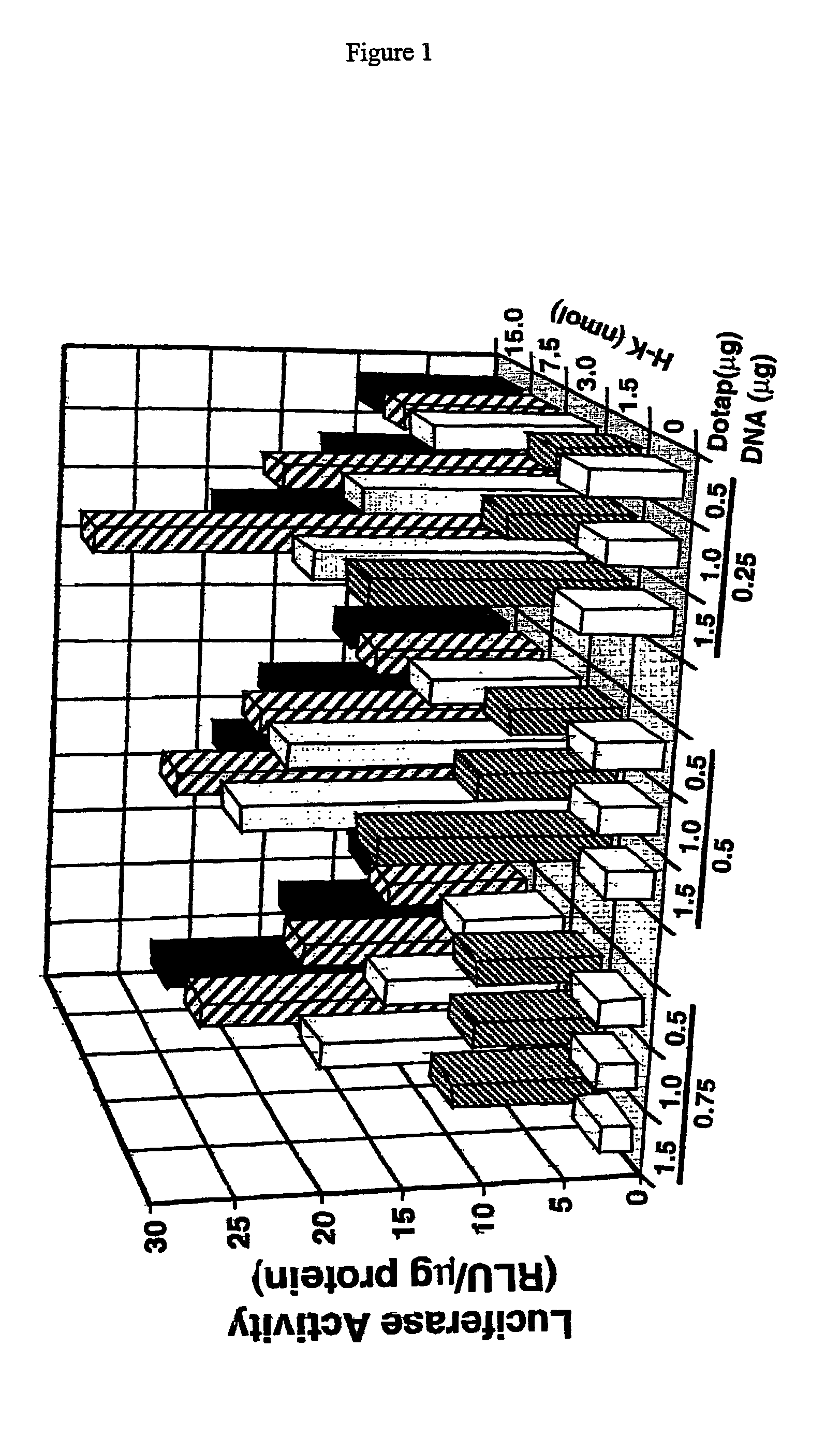
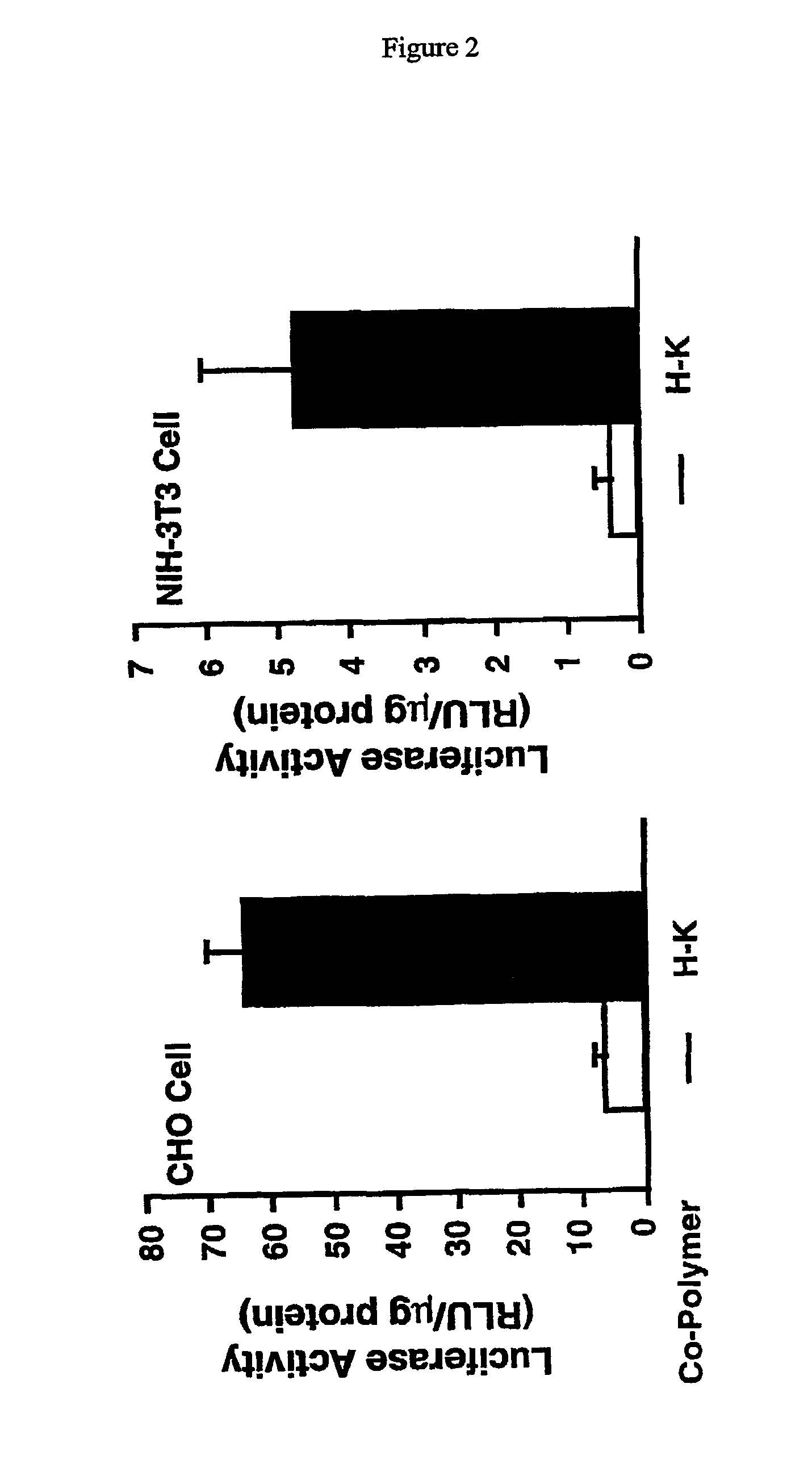
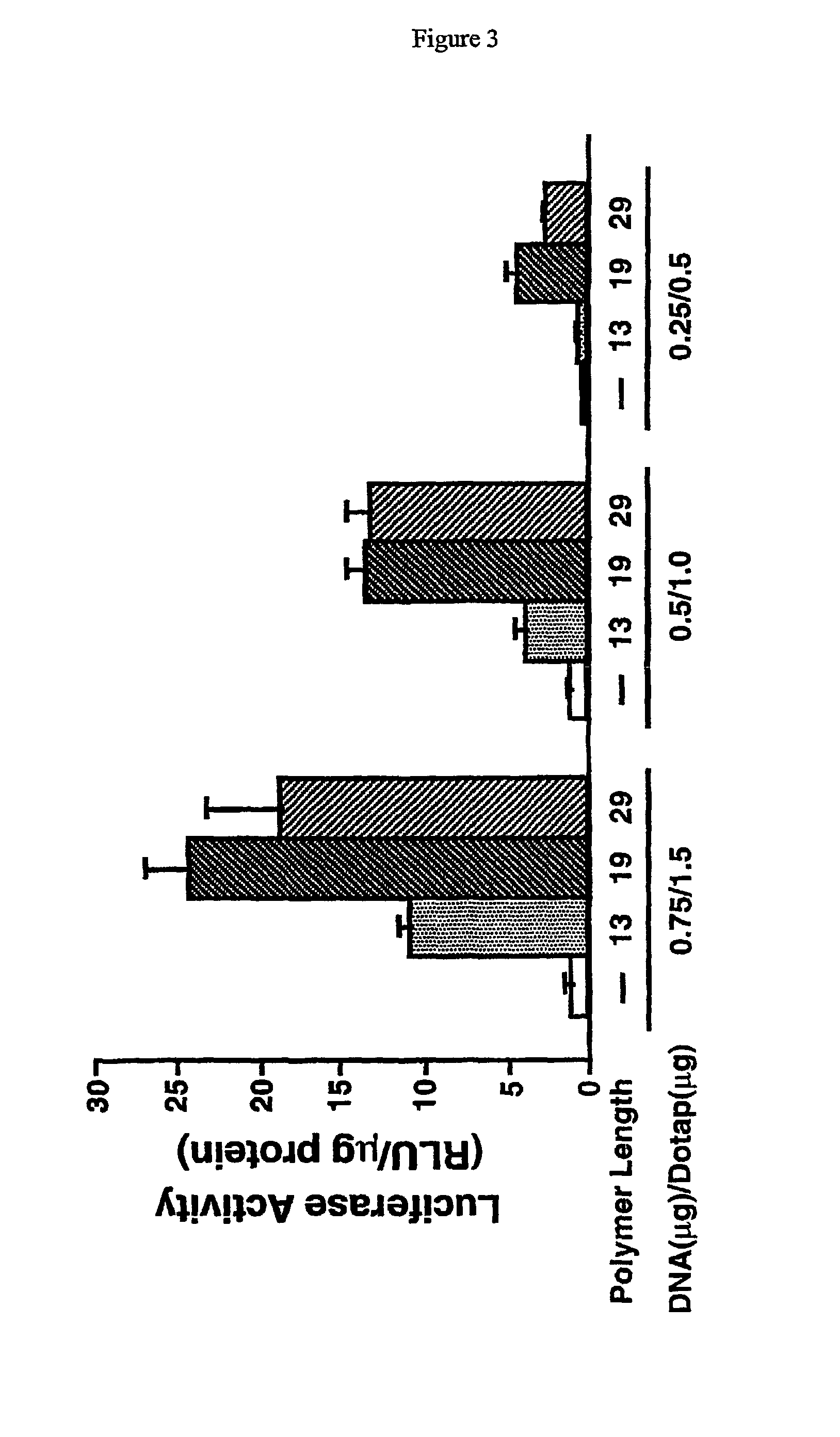
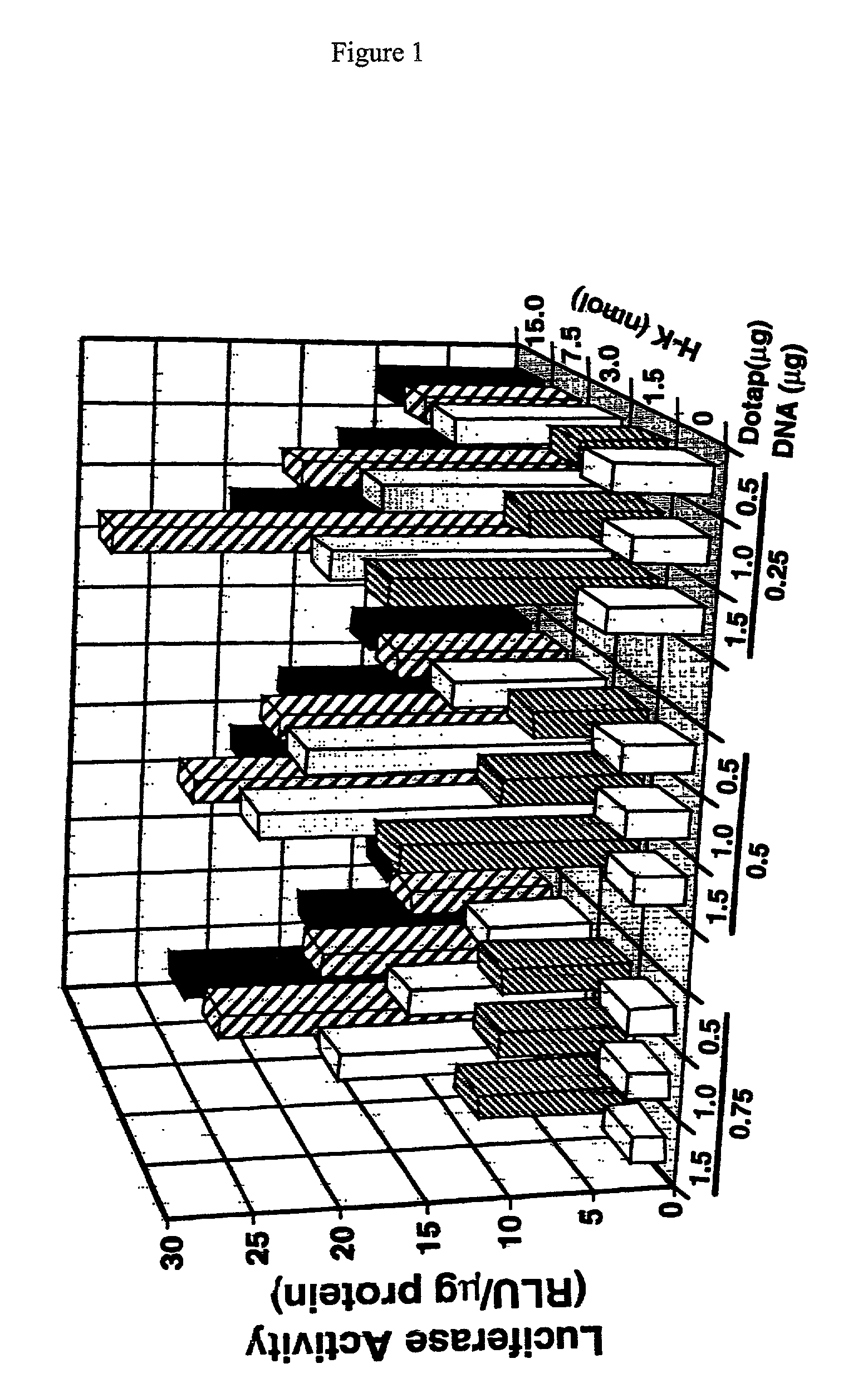
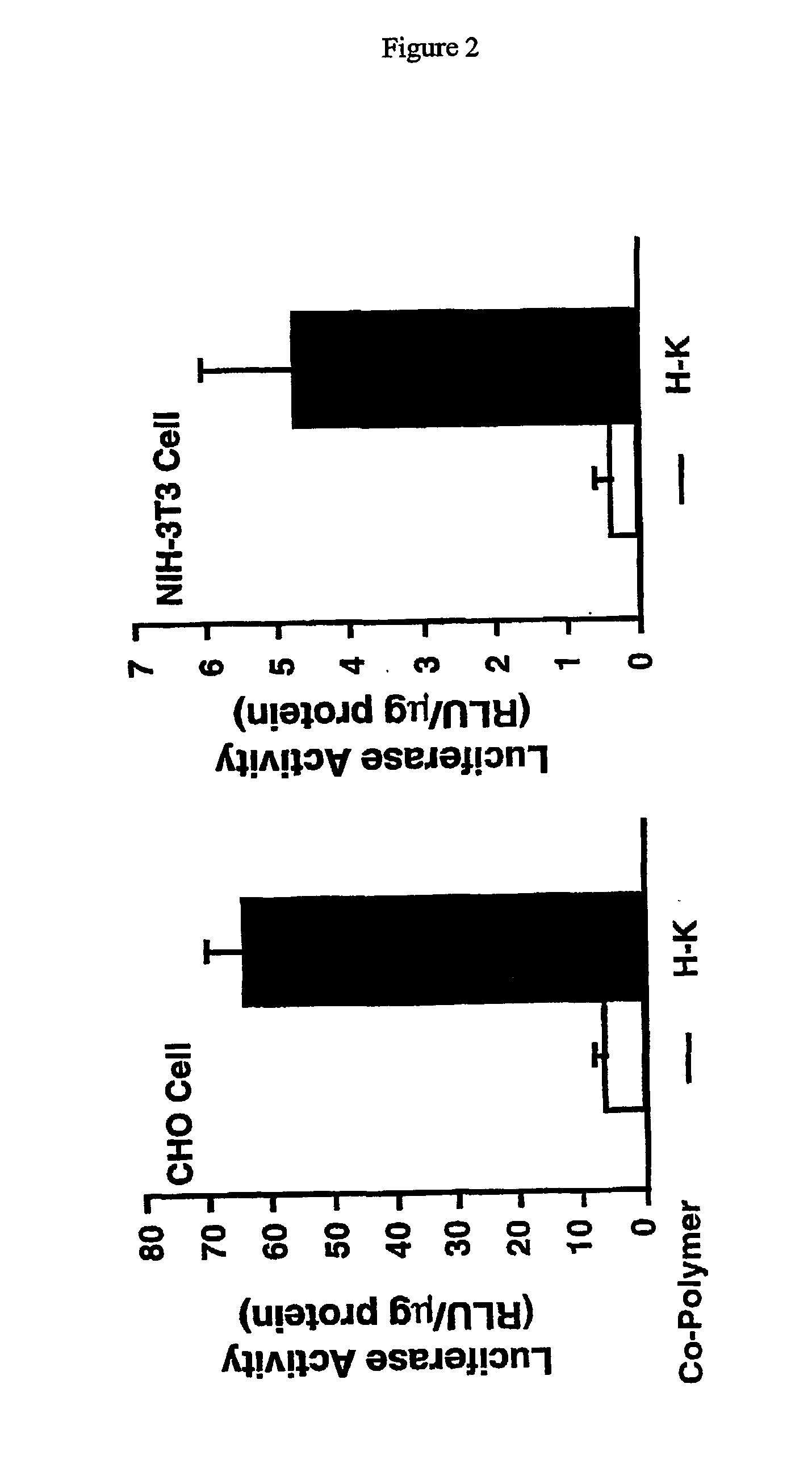
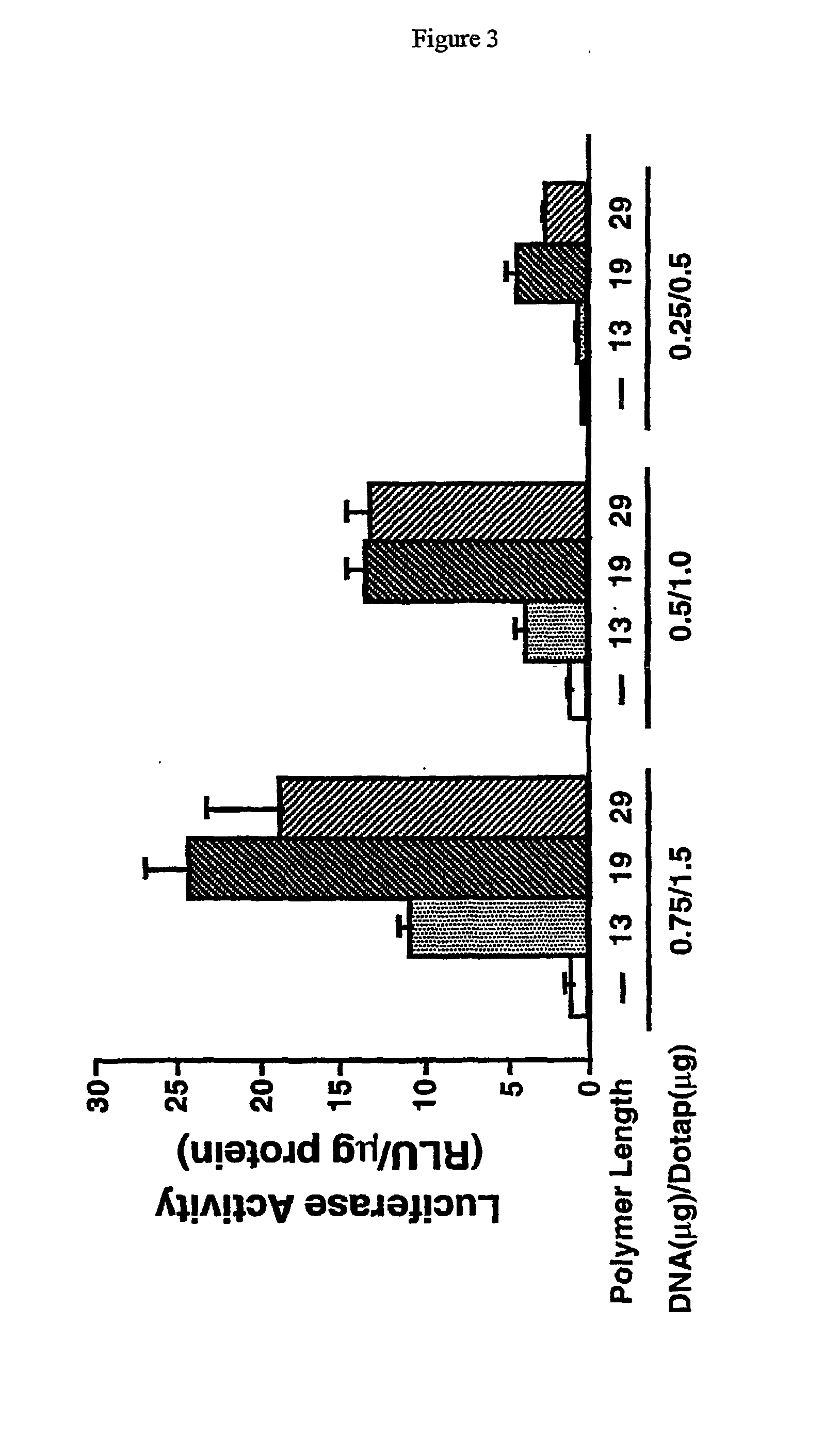
Histidine copolymer and methods for using same
InactiveUS7163695B2Prolong half-life in vivoEnhanced transfectionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsHistidine residueCopolymer
The invention provides a pharmaceutical agent delivery composition comprising: (i) a transport polymer comprising a linear or branched peptide having from about 10 to about 300 amino acid residues, having from about 5 to 100% histidine residues, and optionally having from 0 to about 95% non-histidine amino acid residues; (ii) at least one pharmaceutical agent; and optionally (iii) one or more intracellular delivery components in association with the transport polymer. The invention also provides methods for using such composition to deliver the pharmaceutical agent to the interior of cells.
Owner:MIXSON A JAMES
Branched histidine copolymers and methods for using same
InactiveUS7070807B2Prolong half-life in vivoEnhanced transfectionPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsIn vivoLocal injection
The invention provides a branched transport polymer characterized as having at least 10 amino acids and a ratio of histidine to non-histidine amino acids greater than 1.5, said branched transport polymer comprising one or more backbones, one or more terminal branches, and optionally, one or more non-terminal branches. The branched transport polymer may be associated with a pharmaceutical agent to form a pharmaceutical agent delivery composition useful for in vivo therapies based on local injection.
Owner:MIXSON A JAMES
Polymeric micelles for polynucleotide encapsulation
InactiveUS8287910B2Enhance endolysosomal escapePrevent degradationPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolymer sciencePolynucleotide
The present invention provides micelles having a polynucleotide encapsulated therein, the micelle comprising copolymers comprising hydrophobic moieties in a cationic complexing block. The invention further provides methods of preparing and using said micelles, and compositions thereof.
Owner:INTEZYNE TECH INC
Methods of enhancing SPLP-mediated transfection using endosomal membrane destabilizers
InactiveUS7189705B2Increase in transfection efficiencyIncrease transfection efficiencySugar derivativesMicroencapsulation basedBiophysicsPlasmid
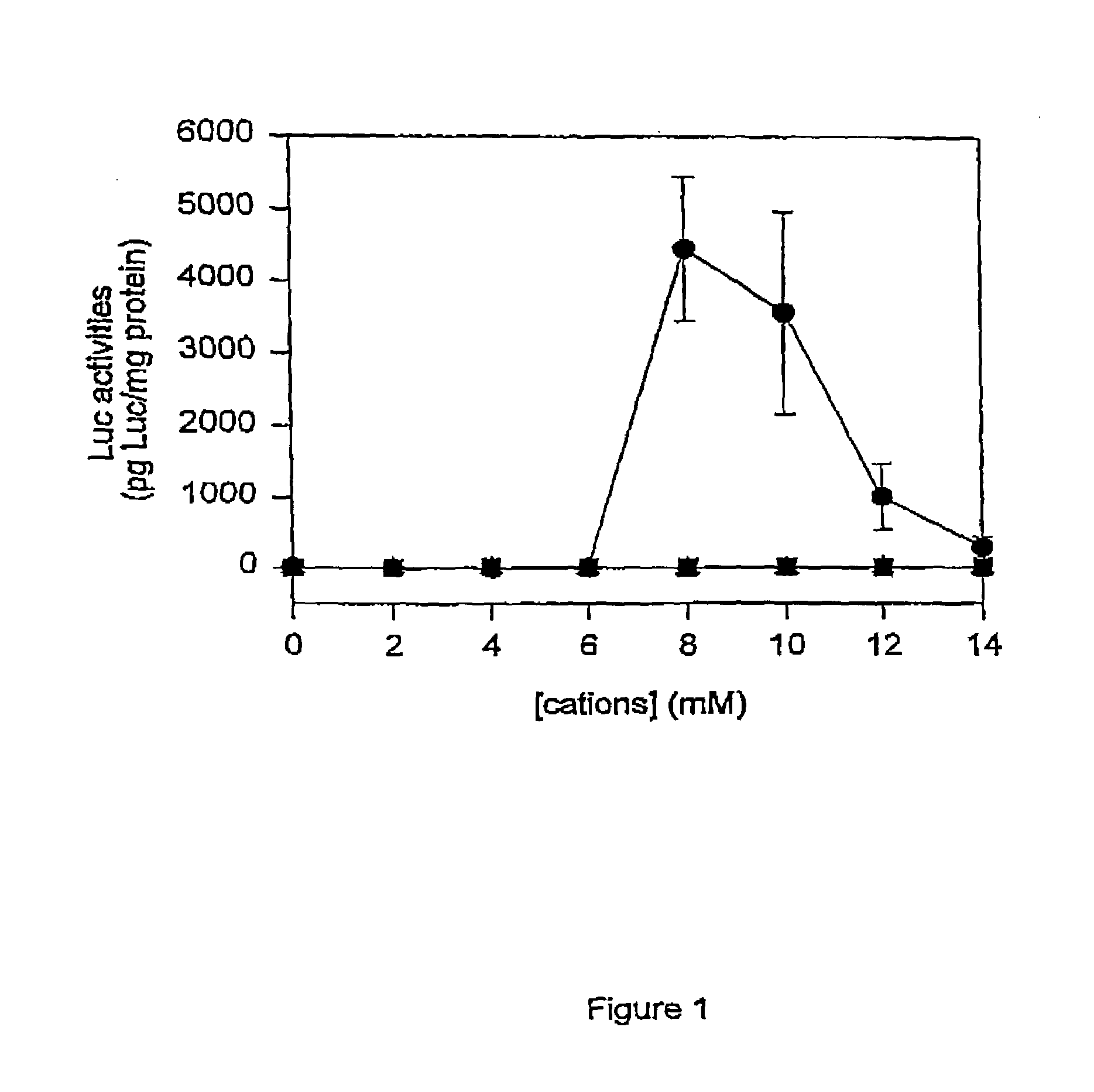
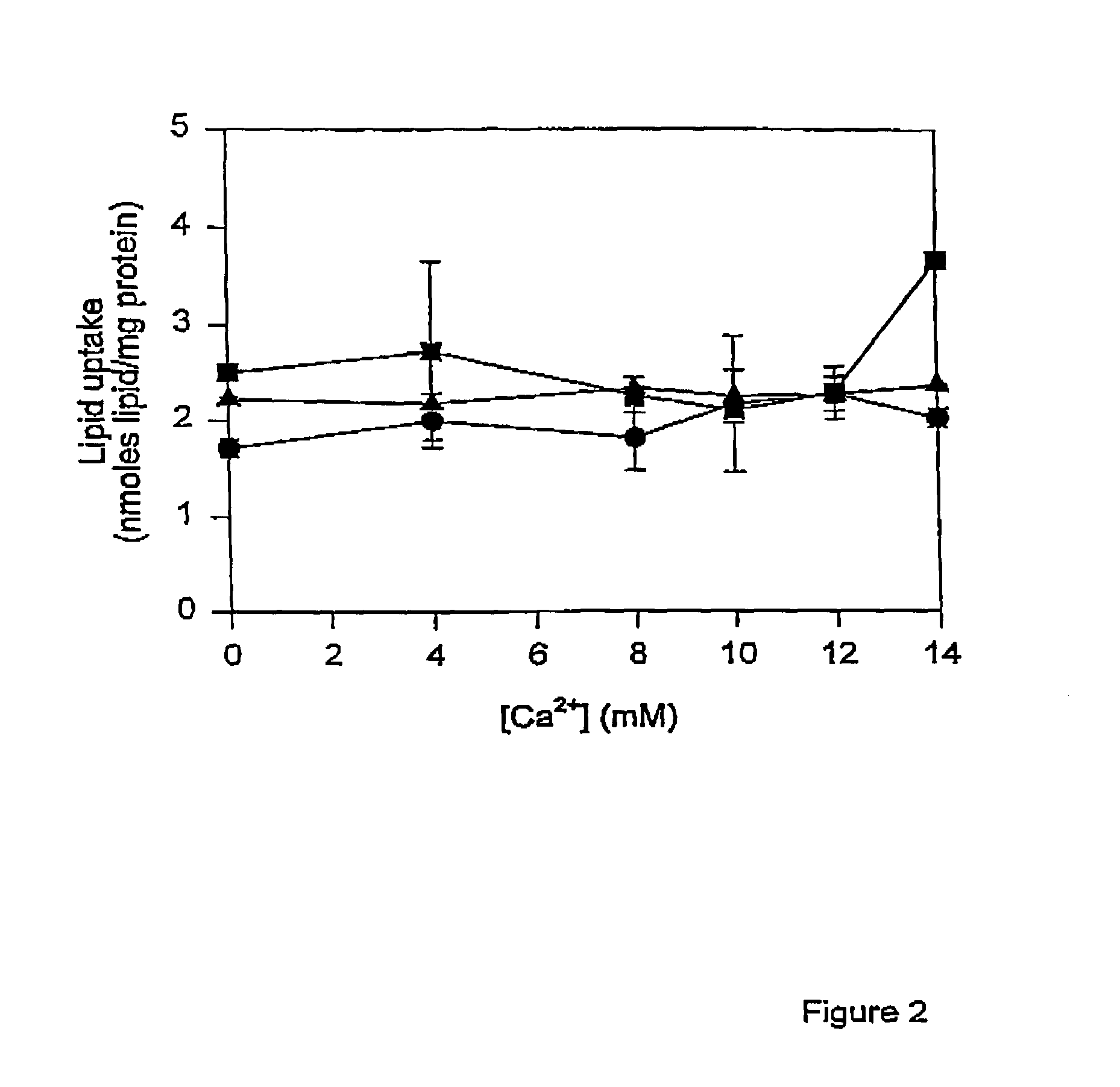
The present invention provides novel and surprisingly effective methods for delivering nucleic acids to cells. These methods are based upon the discovery that the presence of endosomal membrane destabilizers (e.g., calcium) leads to a dramatic increase in the transfection efficiency of plasmids formulated as SPLP, or “stabilized plasmid-lipid particles.”
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Compositions of nucleic acids and cationic aminoglycosides and methods of using and preparing the same
InactiveUS20030096774A1Effectively tranfect complexesHigh transfection efficiencyAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryOrganic chemistryAntibiotic drug
Compositions that include nucleic acid and cationic aminoglycosides and methods for their use are provided. The subject compositions are characterized by having nucleic acid complexed with a cationic aminoglycoside, where the nucleic acid is condensed. In certain embodiments, the cationic aminoglycoside is a cationic aminoglycoside antibiotic. The composition may further include one or more of: functional groups such as targeting moieties, nuclear localization or targeting peptides, endosomolytic peptides and / or one or more lipids and / or polymers, where the lipids may be provided in a manner to encapsulate the nucleic acid. The present invention also provides methods of using and preparing the nucleic acid-aminoglycoside compositions.
Owner:ARADIGM
Methods, systems, and kits for intravascular nucleic acid delivery
InactiveUS6794369B2Transfection of vascular smooth muscle cells with naked DNA is enhancedLow efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsElectrotherapyTransfectionVibrational energy
Nucleic acid transfection of vascular smooth muscle cells is enhanced by the application of vibrational energy to the cells. By applying vibrational energy at frequency in the range from 1 kHz to 10 MHz and at an intensity in the range from 0.01 W / cm.sup.2 to 100 W / cm.sup.2, significant enhancement of the uptake of nucleic acids into vascular smooth muscle cells can be achieved.
Owner:PHARMASONICS
Polymeric micelles for polynucleotide encapsulation
InactiveUS20100278927A1Enhance endolysosomal escapePrevent degradationPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCrystallographyPolynucleotide
The present invention provides micelles having a polynucleotide encapsulated therein, the micelle comprising copolymers comprising hydrophobic moieties in a cationic complexing block. The invention further provides methods of preparing and using said micelles, and compositions thereof.
Owner:INTEZYNE TECH INC
Materials for the delivery of biologically-active material to cells
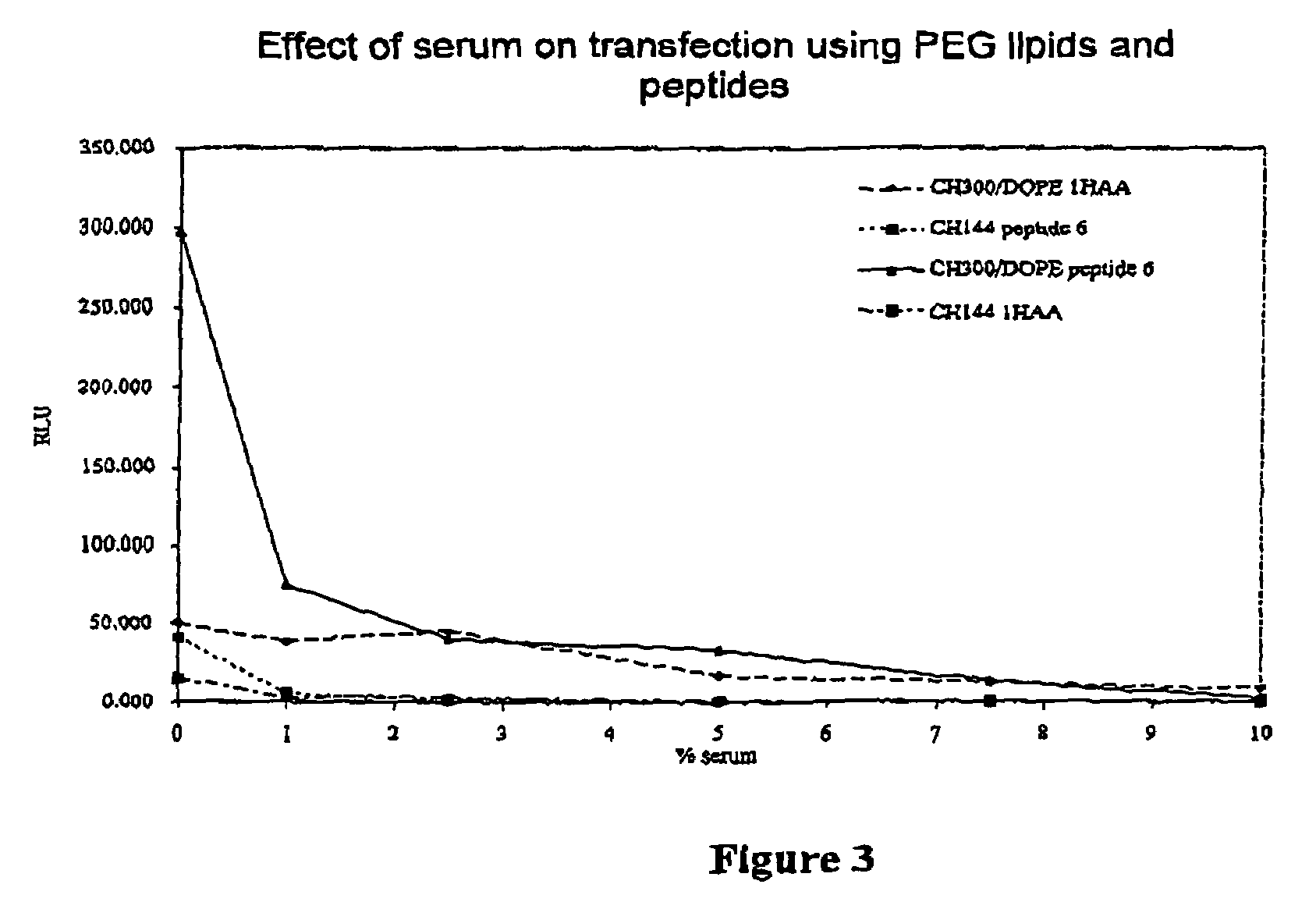
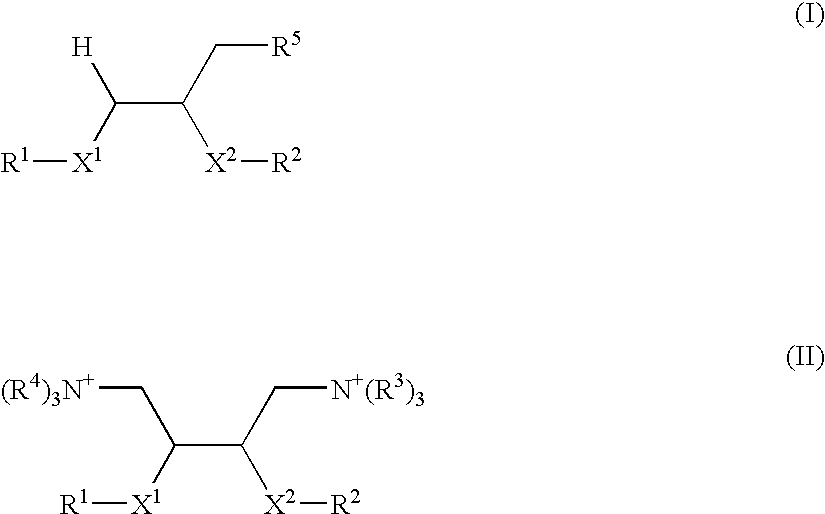
ActiveUS7598421B2Good effectEfficient transfectionCarbamic acid derivatives preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding peptideIntegrin
The invention provides a lipid of general formula (I) or (II):wherein X1, X2 and R1 to R5 are as defined herein. Such lipids are used to form complexes with a biologically-active material such as a nucleic acid, peptide or small molecule for delivering the biologically-active material to cells. The complexes may incorporate an integrin-binding peptide and, when the biologically-active material is DNA, thereby constitute a LID complex.
Owner:RYBOQUIN COMPANY
Materials for the delivery of biologically-active material to cells
ActiveUS20050245446A1Good effectEfficient transfectionCarbamic acid derivatives preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationDrug biological activity
The invention provides a lipid of general formula (I) or (II): wherein X1, X2 and R1 to R5 are as defined herein. Such lipids are used to form complexes with a biologically-active material such as a nucleic acid, peptide or small molecule for delivering the biologically-active material to cells. The complexes may incorporate an integrin-binding peptide and, when the biologically-active material is DNA, thereby constitute a LID complex.
Owner:RYBOQUIN COMPANY
Methods and compositions for delivery of pharmaceutical agents
InactiveUS7320963B2Good effectEnhanced transfectionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCholesterolWhite blood cell
Methods and compositions for delivering pharmaceutical agents into cells, in particular urothelial cells of the bladder, are provided. In the methods and compositions of the invention, a solubilized cholesterol composition is used to facilitate delivery of pharmaceutical agents. Preferably, the cholesterol is solubilized by a cyclodextrin (e.g., methyl-β-cyclodextrin) and the pharmaceutical agent comprises a polynucleotide and either a cationic lipid, a cationic polymer or a dendrimer. Improved methods for transfecting polynucleotides into cells thus are also provided, using cationic lipids, cationic polymers or dendrimers and solubilized cholesterol, wherein the transfection efficiency is enhanced compared to use of cationic lipids, cationic polymers or dendrimers alone. Preferred methods of the invention involve transfecting polynucleotides into urothelial cells, preferably for therapeutic treatment of bladder cancer using, for example, a polynucleotide(s) encoding an interleukin(s), an interferon(s), a colony stimulating factor(s) and / or a tumor suppressor(s).
Owner:GENECURE PTE
Histidine copolymer and methods for using same
InactiveUS20030045465A1Enhance transfectionProlong in vivo half-lifePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptideChemistry
The invention provides a pharmaceutical agent delivery composition comprising: (i) a transport polymer comprising a linear or branched peptide having from about 10 to about 300 amino acid residues, having from about 5 to 100% histidine residues, and optionally having from 0 to about 95% non-histidine amino acid residues; (ii) at least one pharmaceutical agent; and optionally (iii) one or more intracellular delivery components in association with the transport polymer. The invention also provides methods for using such composition to deliver the pharmaceutical agent to the interior of cells.
Owner:MIXSON A JAMES
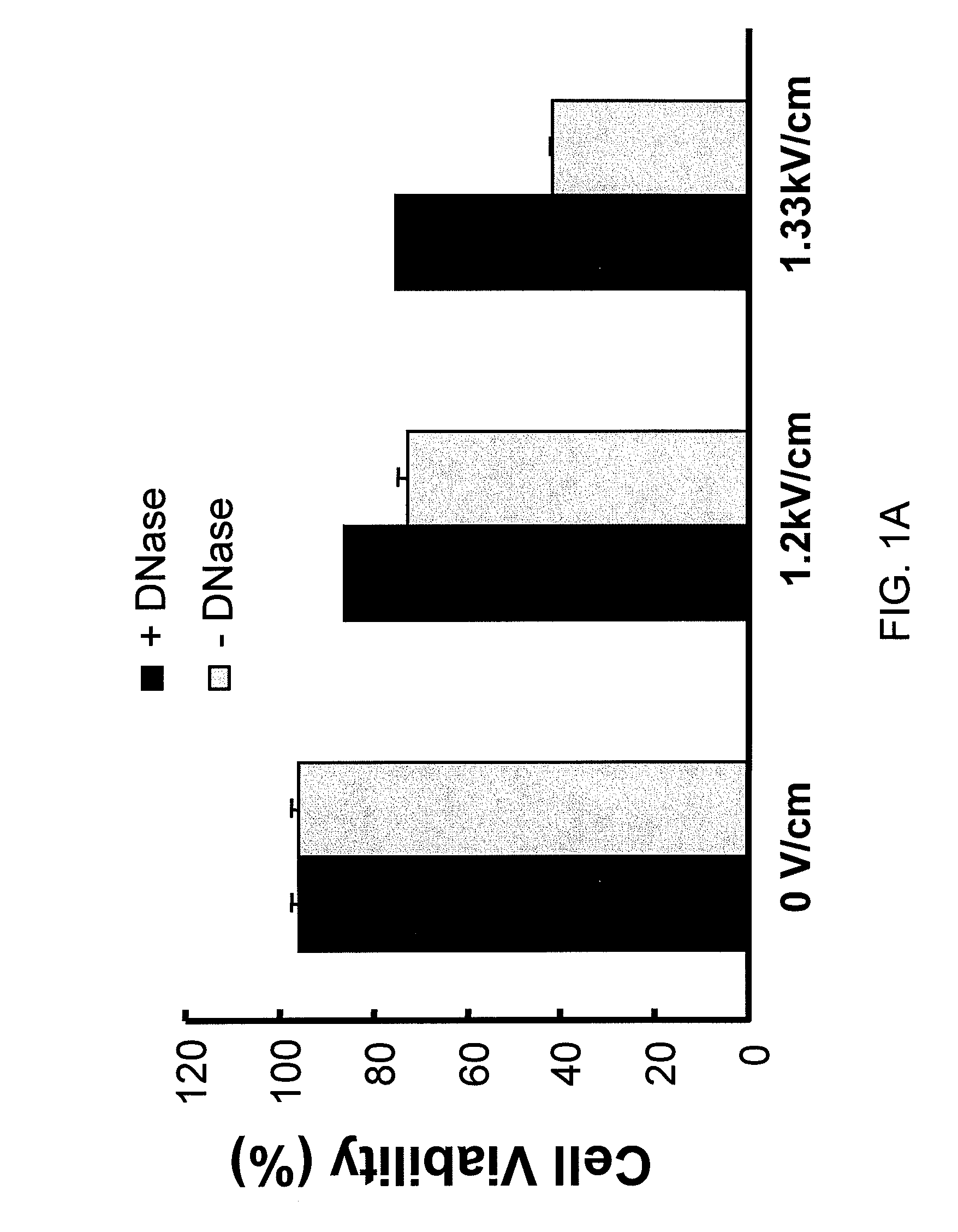
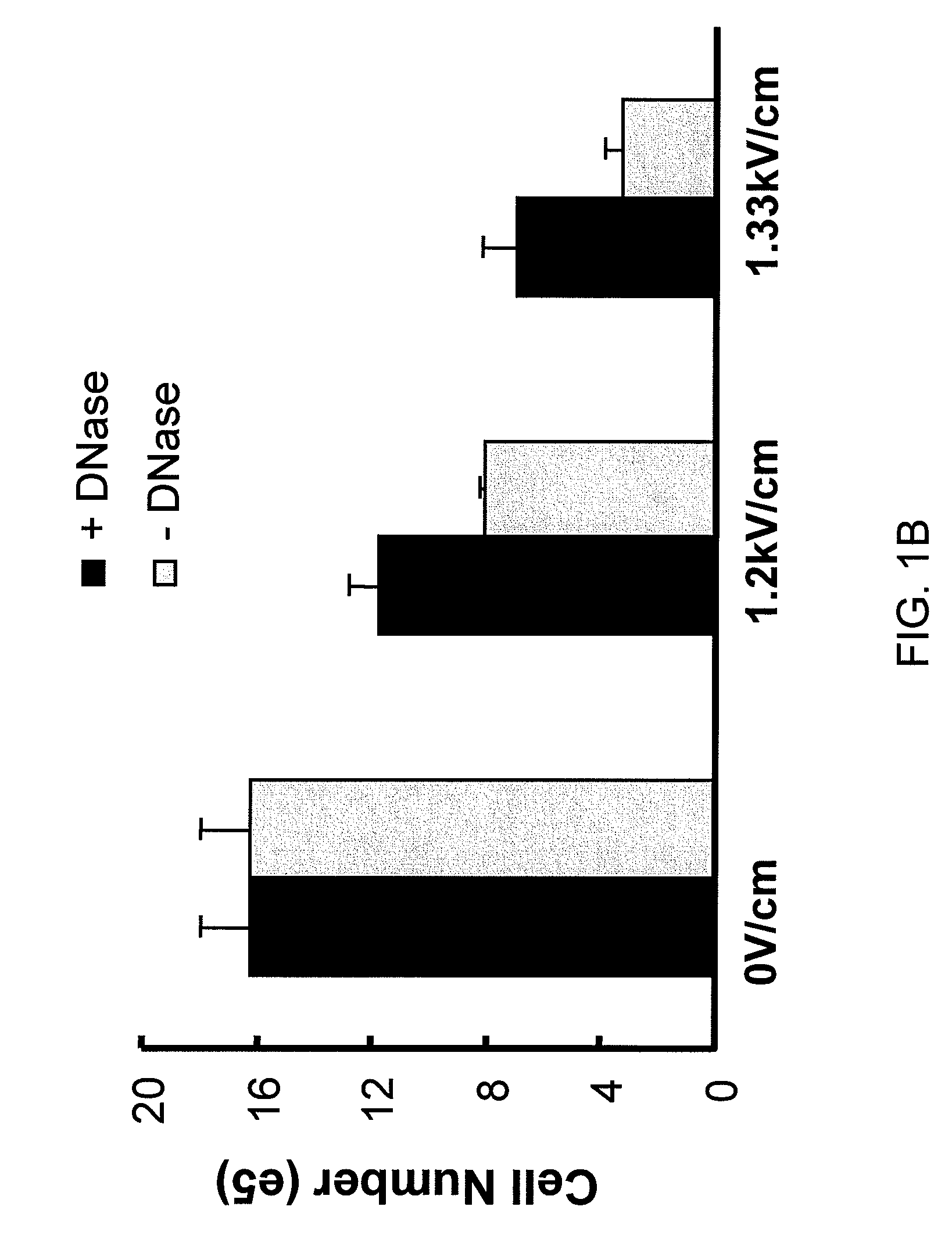
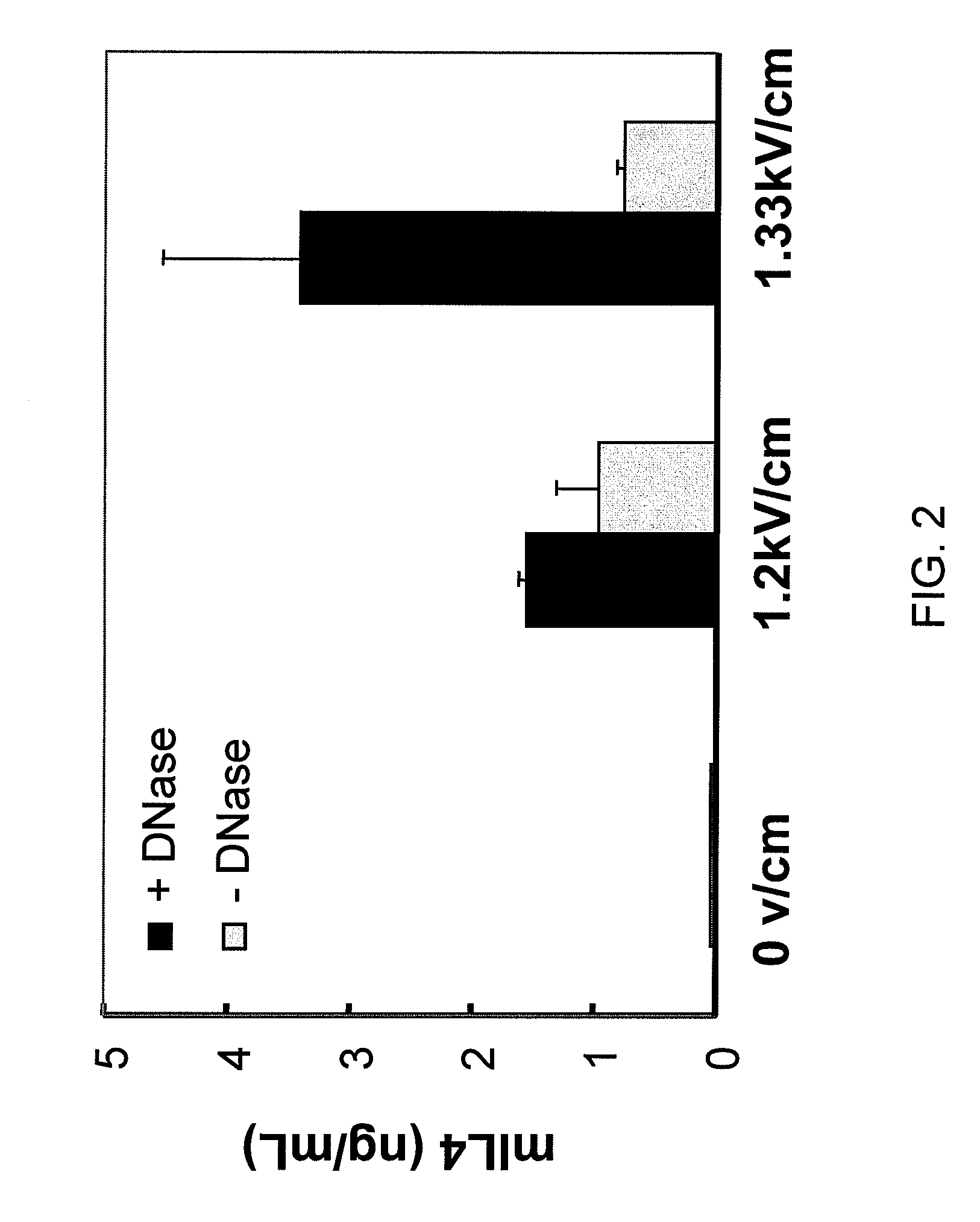
Use of Nucleases to Improve Viability and Enhance Transgene Expression in Transfected Cells
InactiveUS20070059833A1Improve survivabilityHigh transfection efficiencyHydrolasesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleic acid sequencingNuclease
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for improving viability and transgene expression in transfected cells. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a method for increasing the viability of a transfected cell, the method comprising: transfecting a cell with a nucleic acid sequence; and contacting the transfected cell with a nuclease in a manner effective to enhance the viability of the transfected cell.
Owner:MAXCYTE
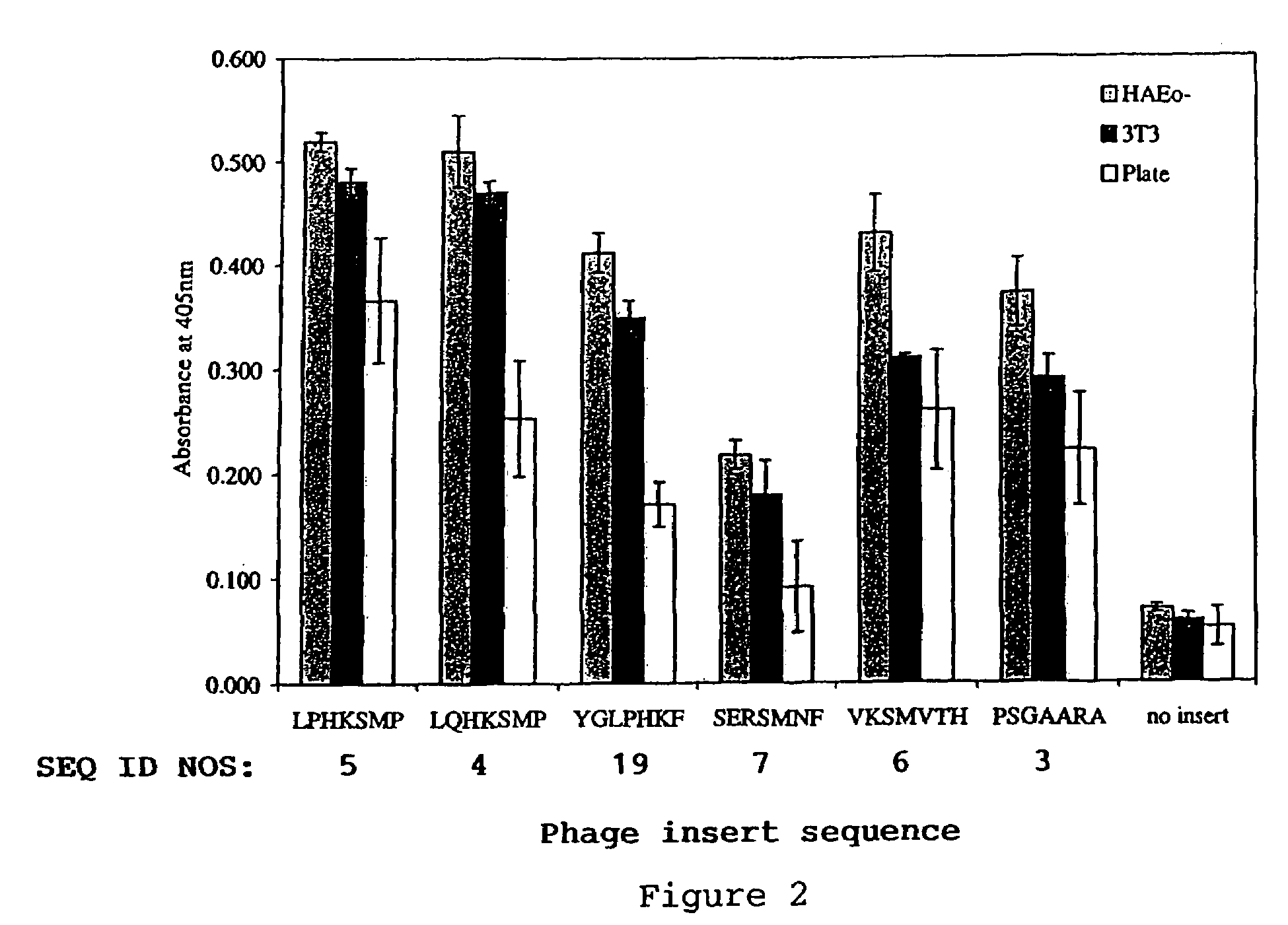
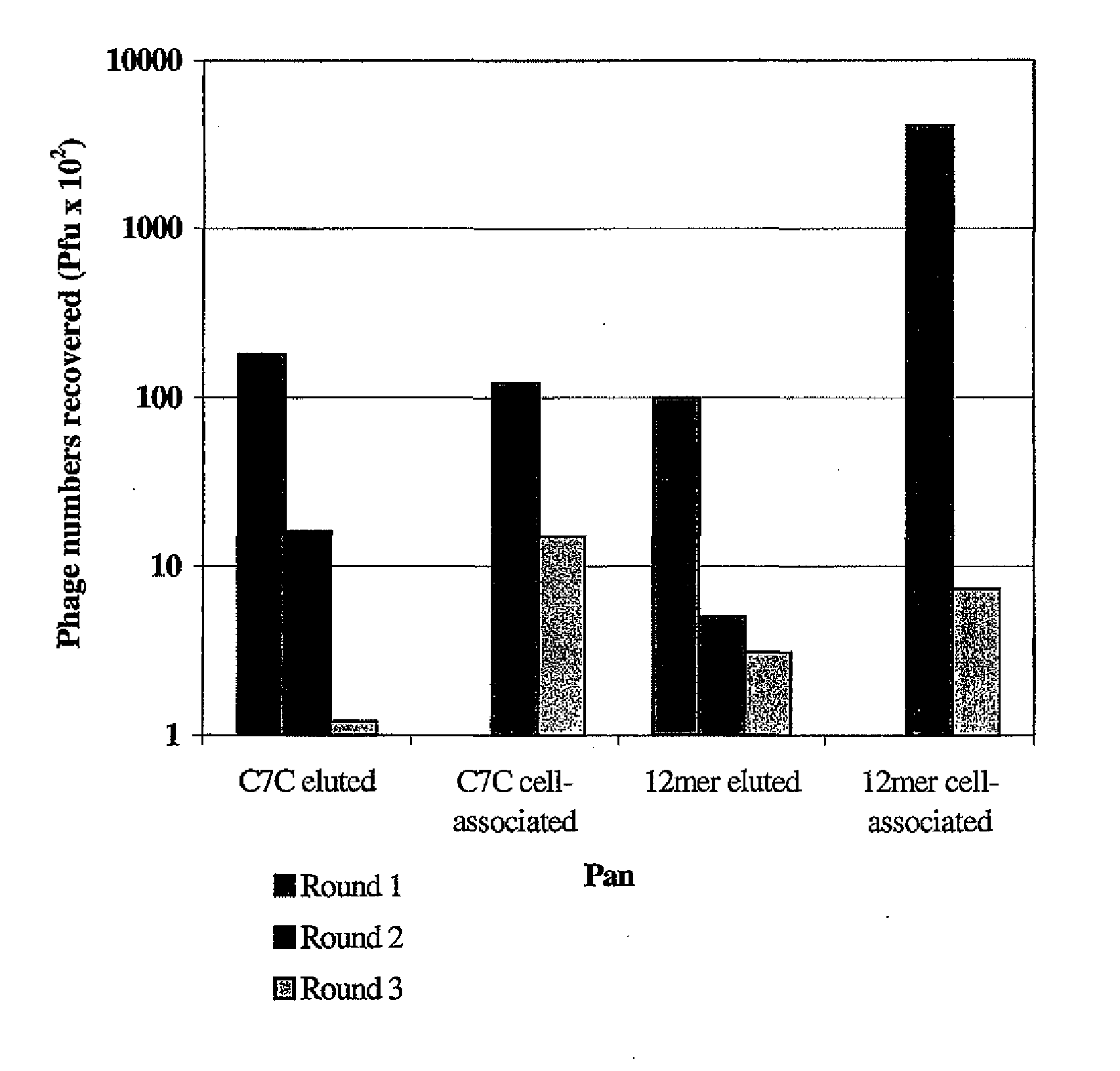
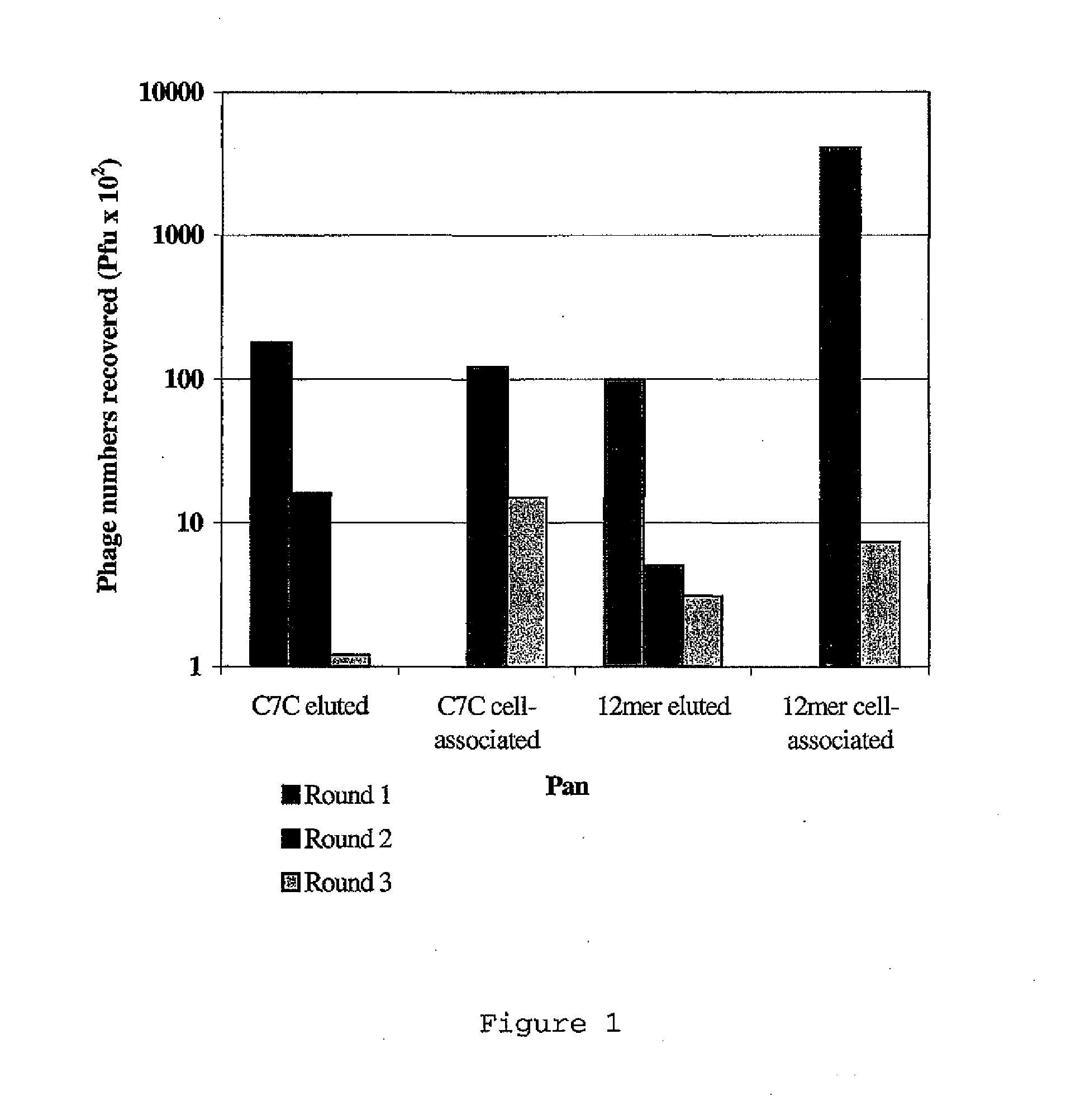
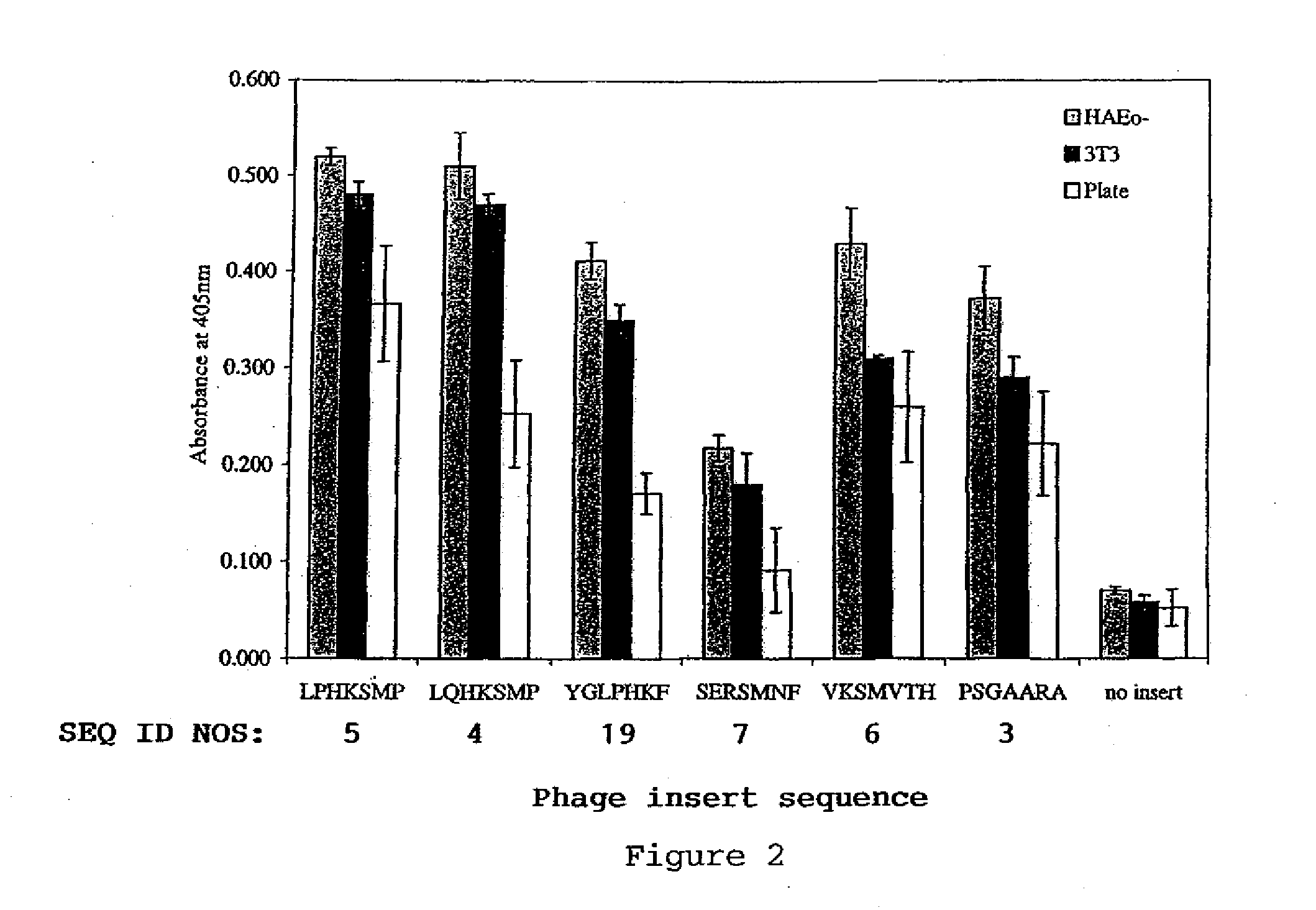
Transfection complexes
InactiveUS7704969B2Improve bindingIncrease the number ofOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAcidic amino acidsTransfection
The invention provides a peptide having at least 3 amino acids comprising an amino acid sequence selected froma)X1SM[SEQ.ID.NO.: 1]b)LX2HK[SEQ.ID.NO.: 2]c)PSGX3ARA[SEQ.ID.NO.: 9]d)SX4RSMNF[SEQ.ID.NO.: 16]e)LX5HKSMP[SEQ.ID.NO.: 18]in which X1 is a basic amino acid residue, X2 is Q or P, X3 is A or T, X4 is an acidic amino acid residue and X5 is P or Q.The invention further provides non-viral cell-targeting vector complexes and methods associated therewith.
Owner:RYBOQUIN COMPANY
Methods and compositions for delivery of pharmaceutical agents
InactiveUS7709457B2Good effectEnhanced transfectionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCholesterolCyclodextrin
Methods and compositions for delivering pharmaceutical agents into cells, in particular urothelial cells of the bladder, are provided. In the methods and compositions of the invention, a solubilized cholesterol composition is used to facilitate delivery of pharmaceutical agents. Preferably, the cholesterol is solubilized by a cyclodextrin (e.g., methyl-β-cyclodextrin) and the pharmaceutical agent comprises a polynucleotide and either a cationic lipid, a cationic polymer or a dendrimer. Improved methods for transfecting polynucleotides into cells thus are also provided, using cationic lipids, cationic polymers or dendrimers and solubilized cholesterol, wherein the transfection efficiency is enhanced compared to use of cationic lipids, cationic polymers or dendrimers alone. Preferred methods of the invention involve transfecting polynucleotides into urothelial cells, preferably for therapeutic treatment of bladder cancer using, for example, a polynucleotide(s) encoding an interleukin(s), an interferon(s), a colony stimulating factor(s) and / or a tumor suppressor(s).
Owner:GENECURE PTE
Agent for treating leishmania infections
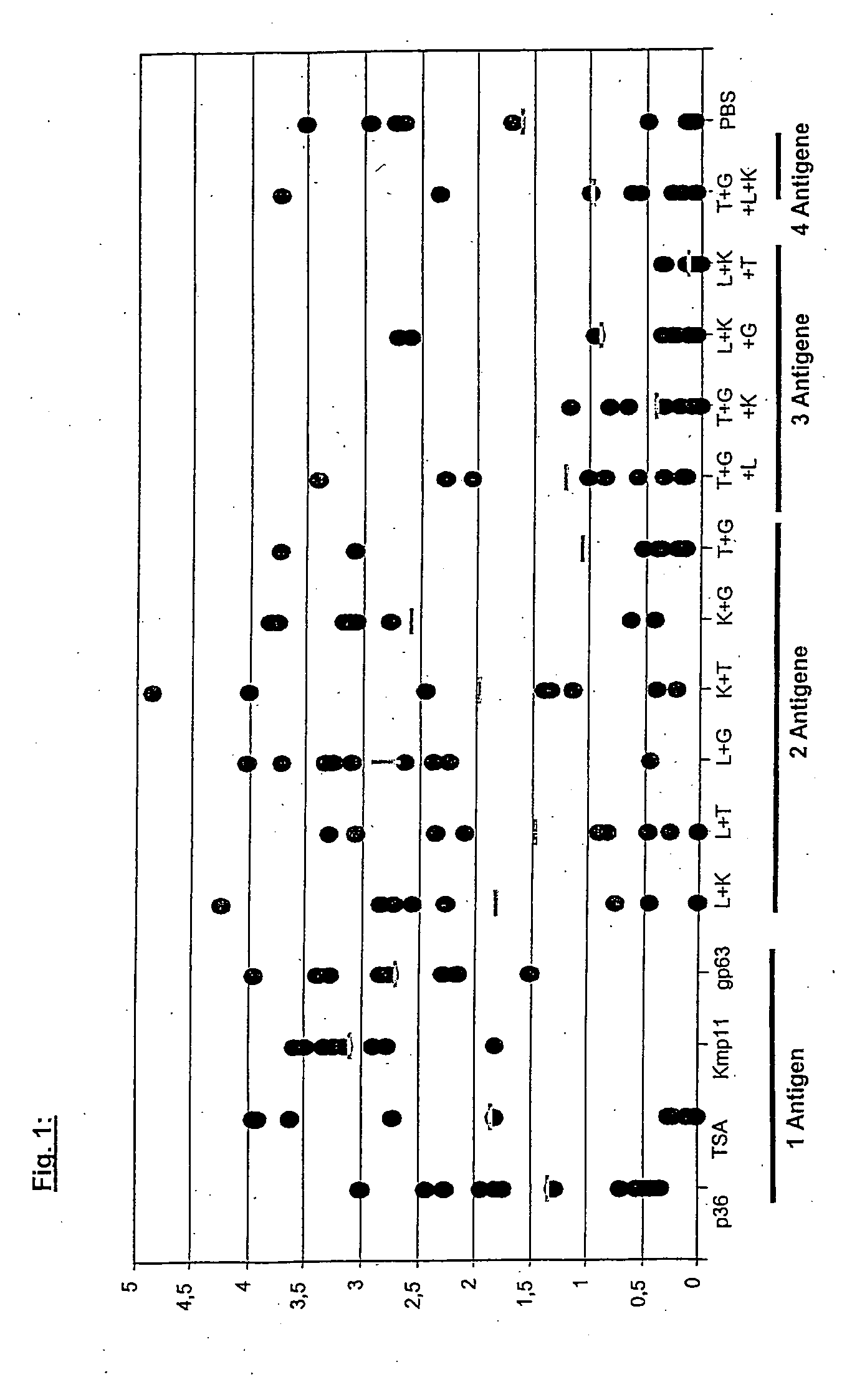
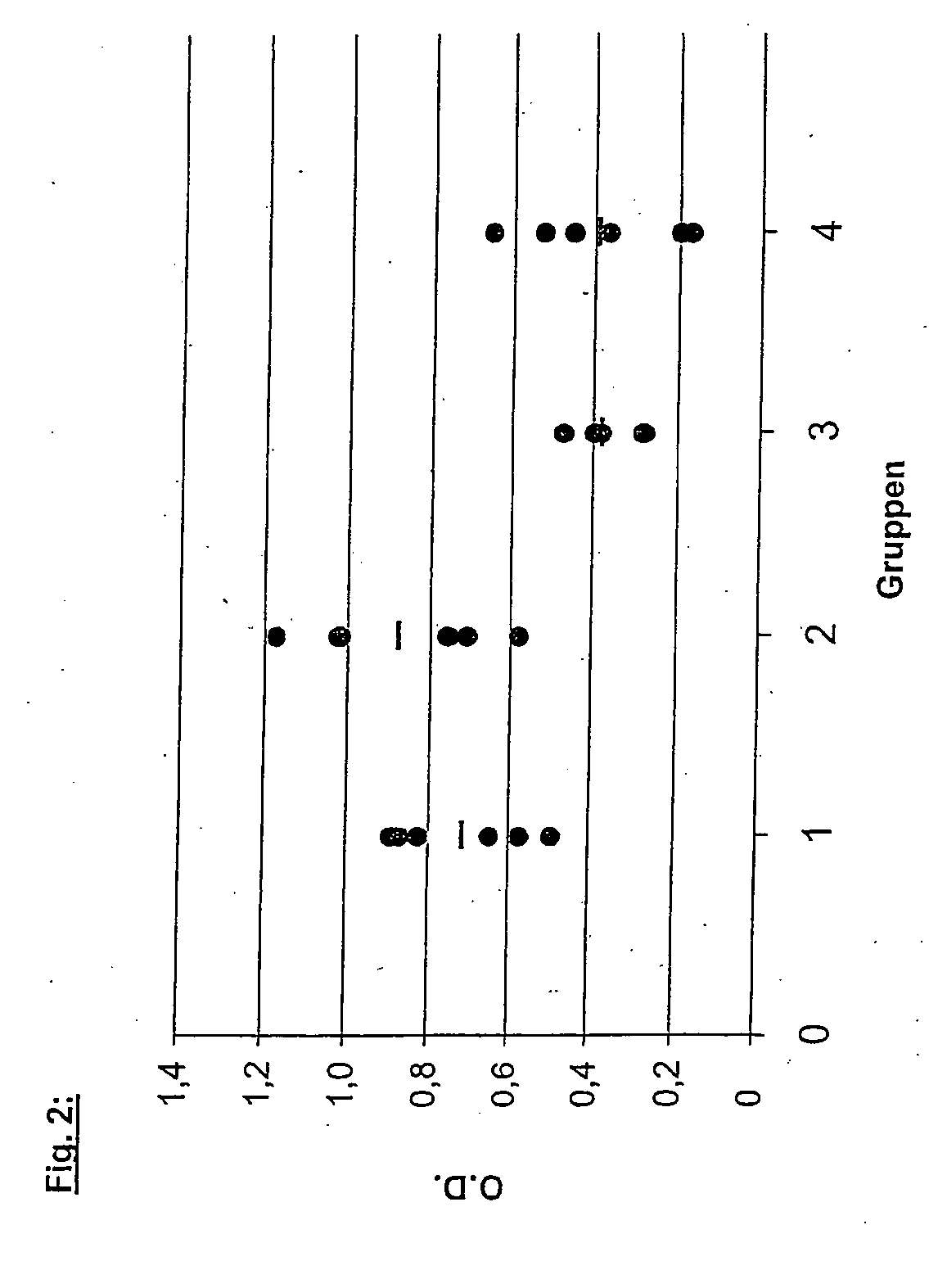
InactiveUS20060194753A1Enhanced transfectionAvoid disadvantagesOrganic active ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsLeishmaniasisTrademark
Use of a combination of DNA expression constructs for the production of a remedy for the immunization against infections with leishmaniasis, as well as a corresponding vaccine. The abstract of the disclosure is submitted herewith as required by 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b). As stated in 37 C.F.R. §1.72(b): A brief abstract of the technical disclosure in the specification must commence on a separate sheet, preferably following the claims, under the heading “Abstract of the Disclosure.” The purpose of the abstract is to enable the Patent and Trademark Office and the public generally to determine quickly from a cursory inspection the nature and gist of the technical disclosure. The abstract shall not be used for interpreting the scope of the claims. Therefore, any statements made relating to the abstract are not intended to limit the claims in any manner and should not be interpreted as limiting the claims in any manner.
Owner:MOLOGEN AG
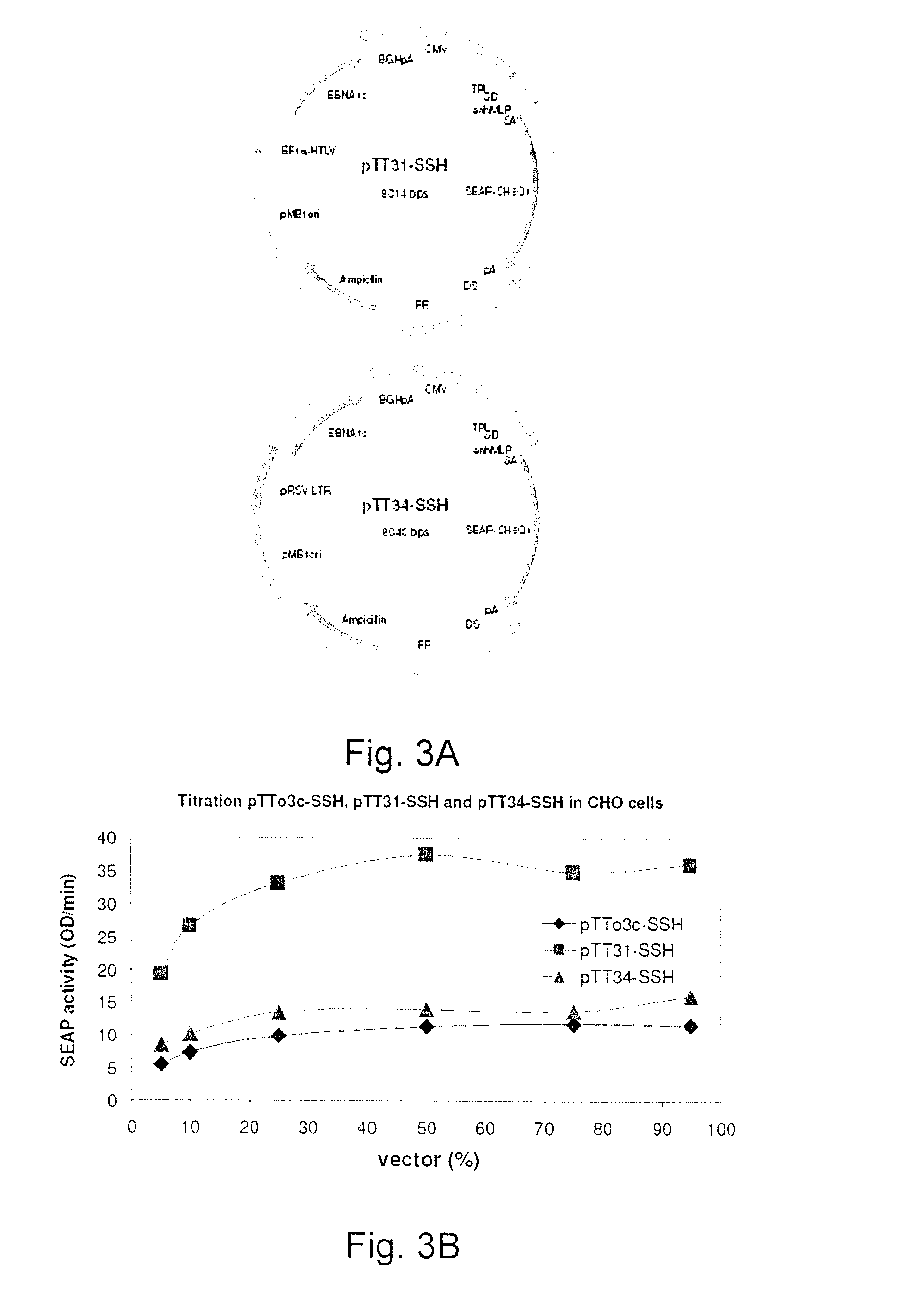
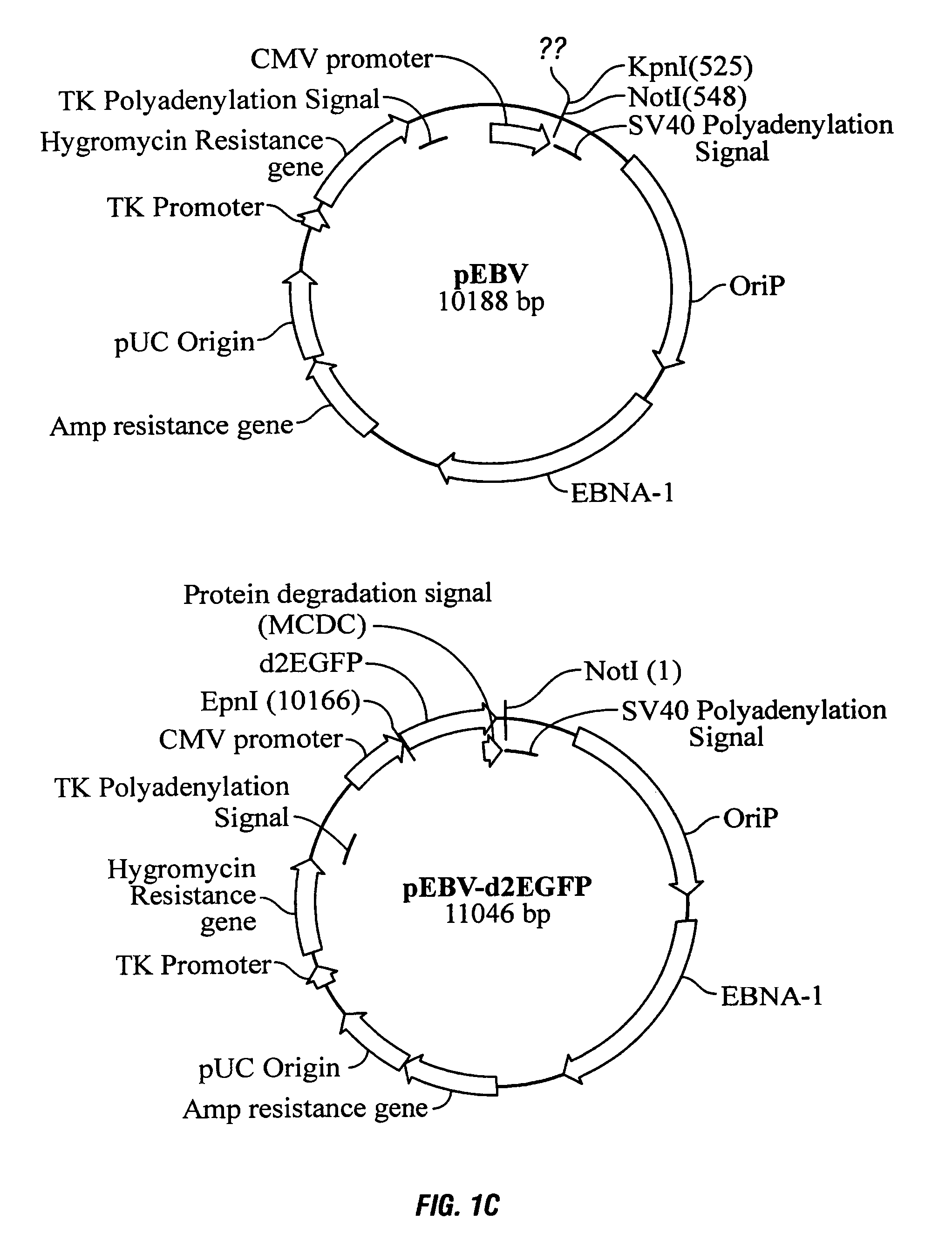
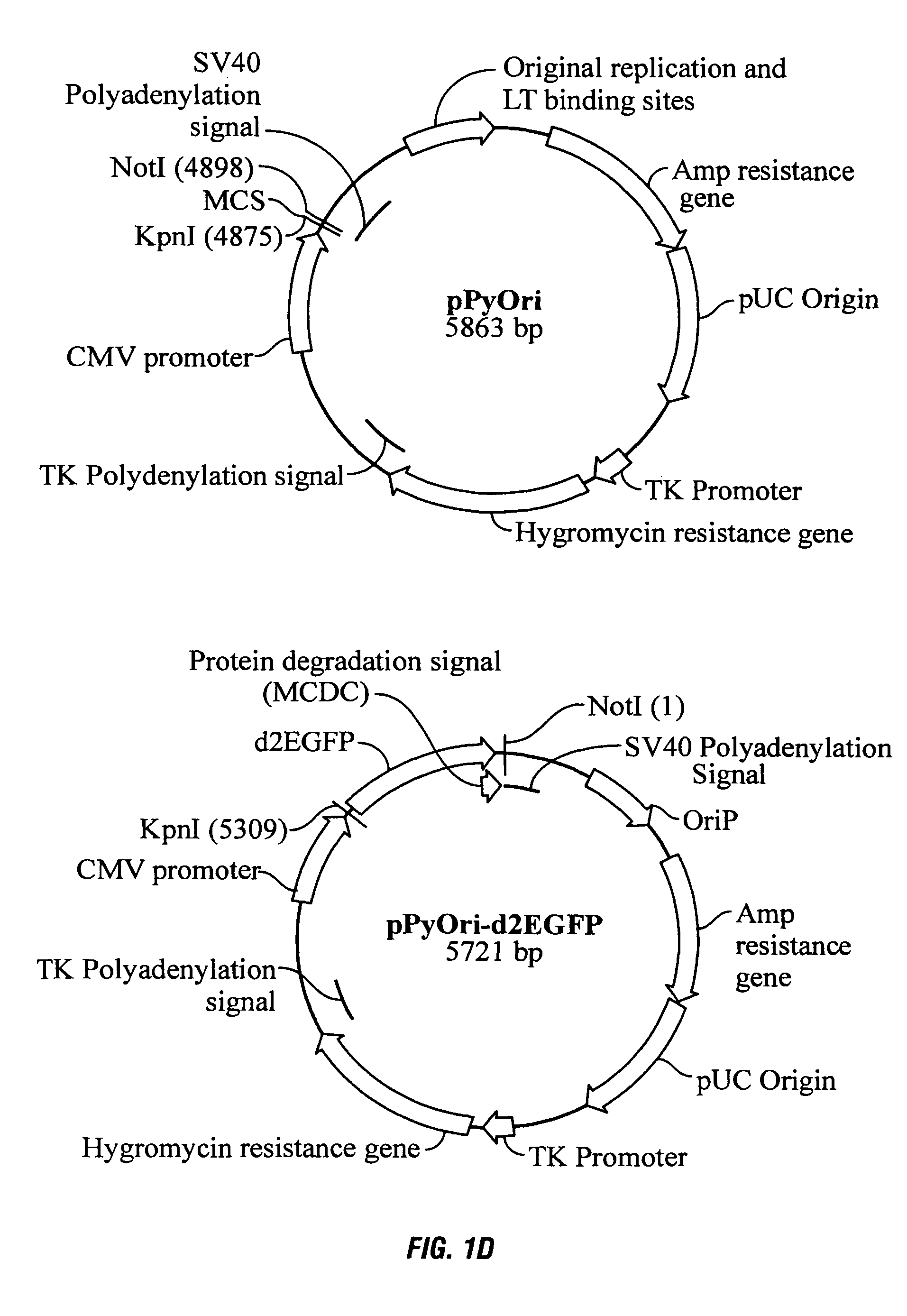
Process, vectors and engineered cell lines for enhanced large-scale transfection
ActiveUS8637315B2Enhanced transfectionHigh expressionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesValproic AcidHamster
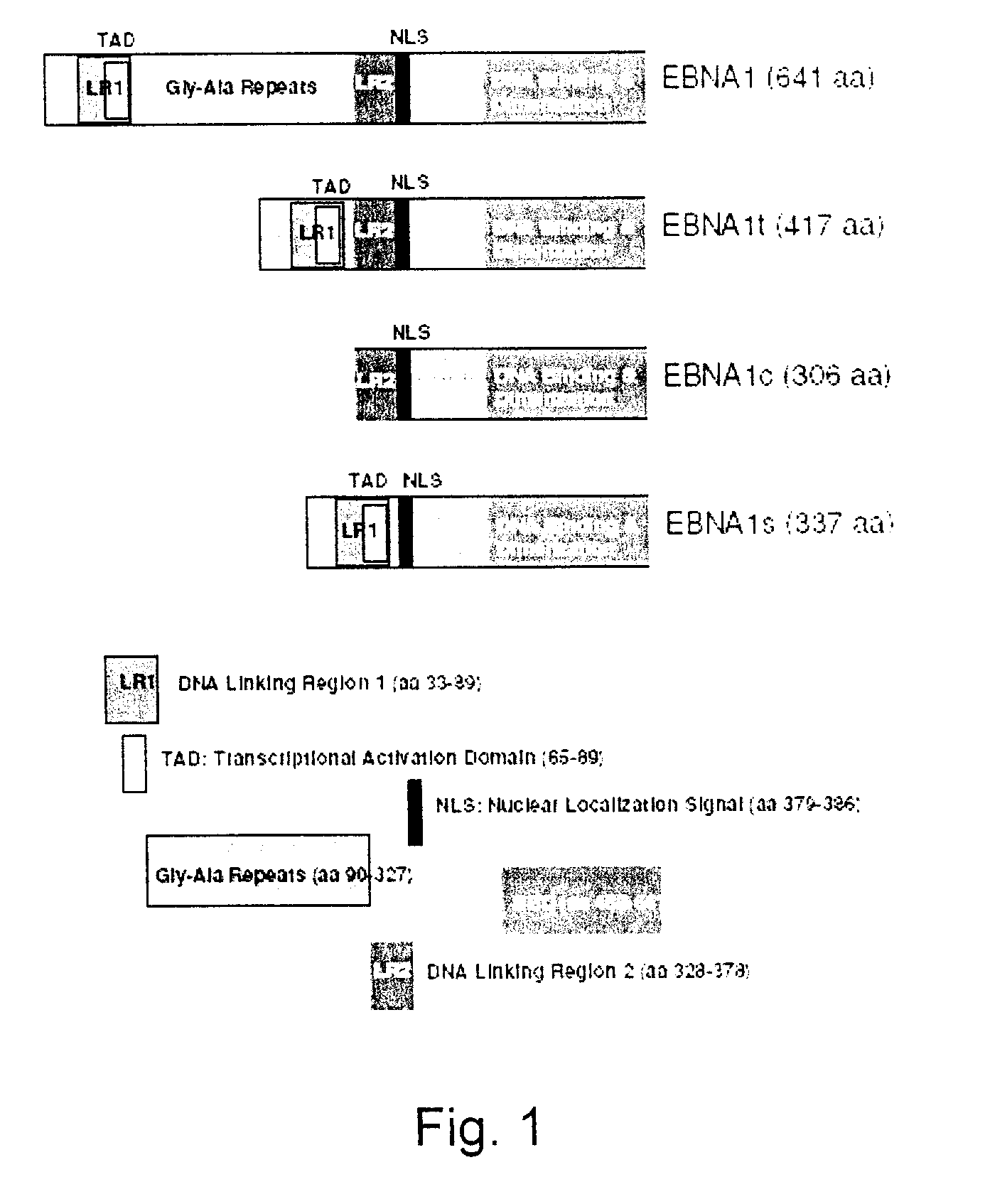
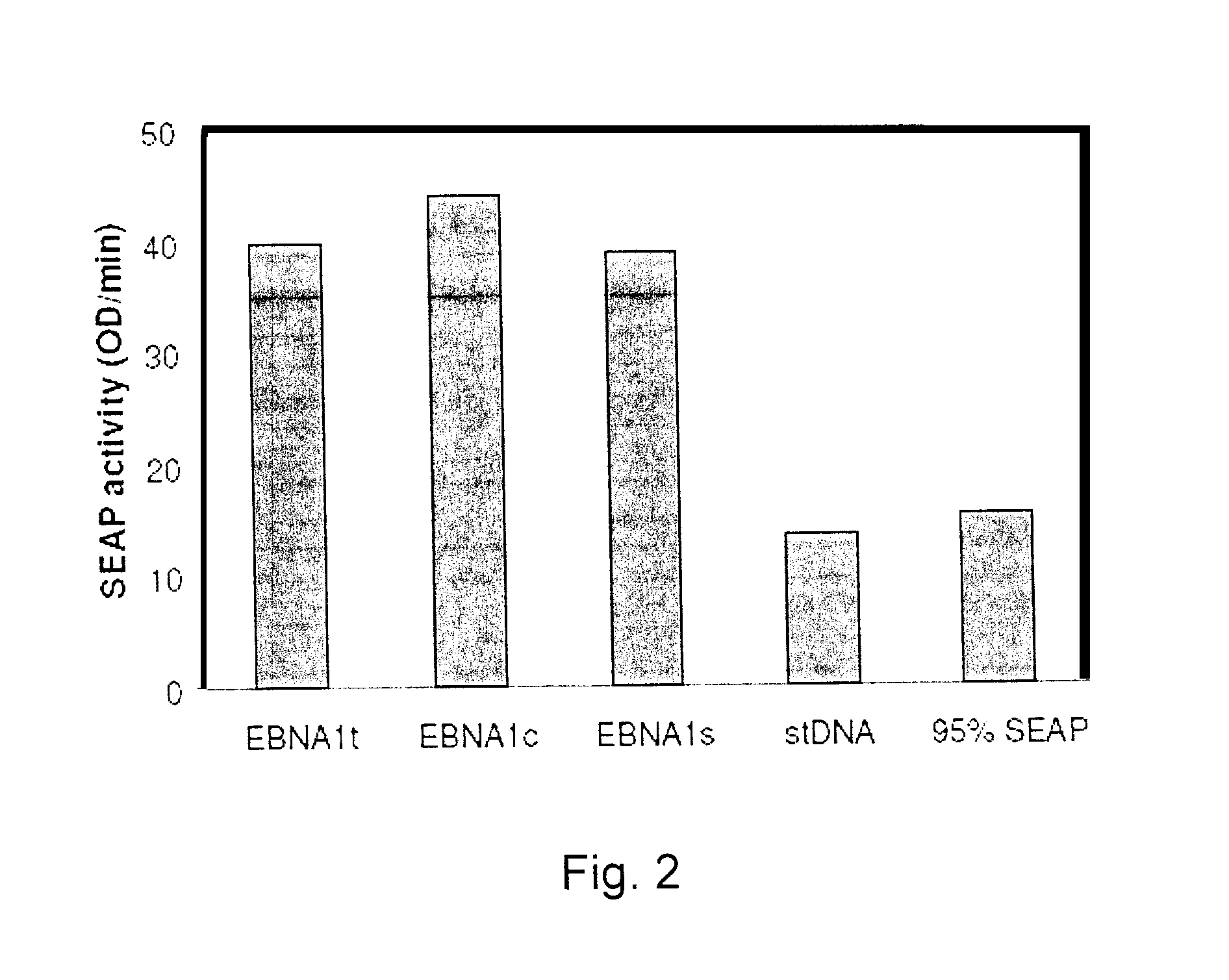
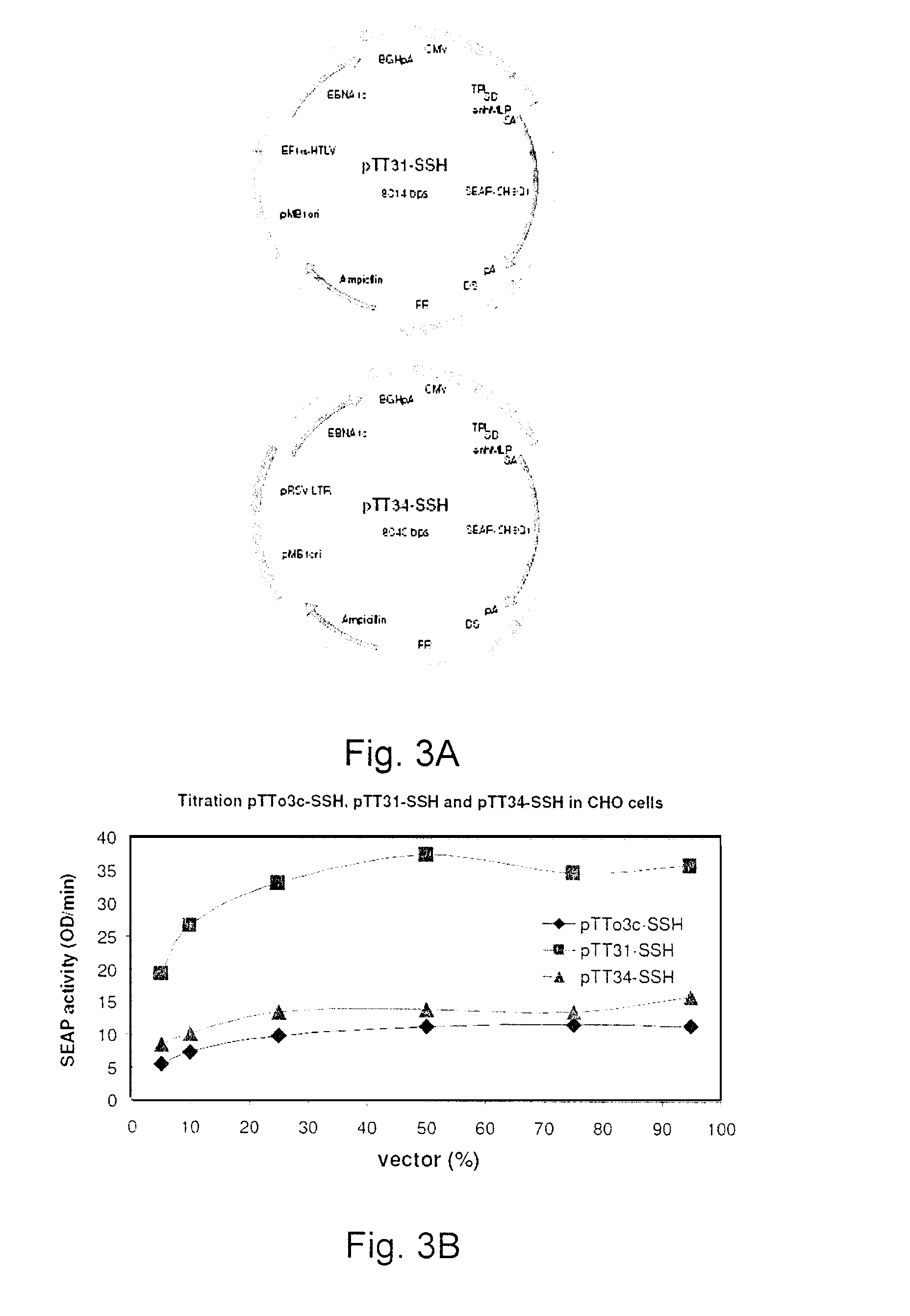
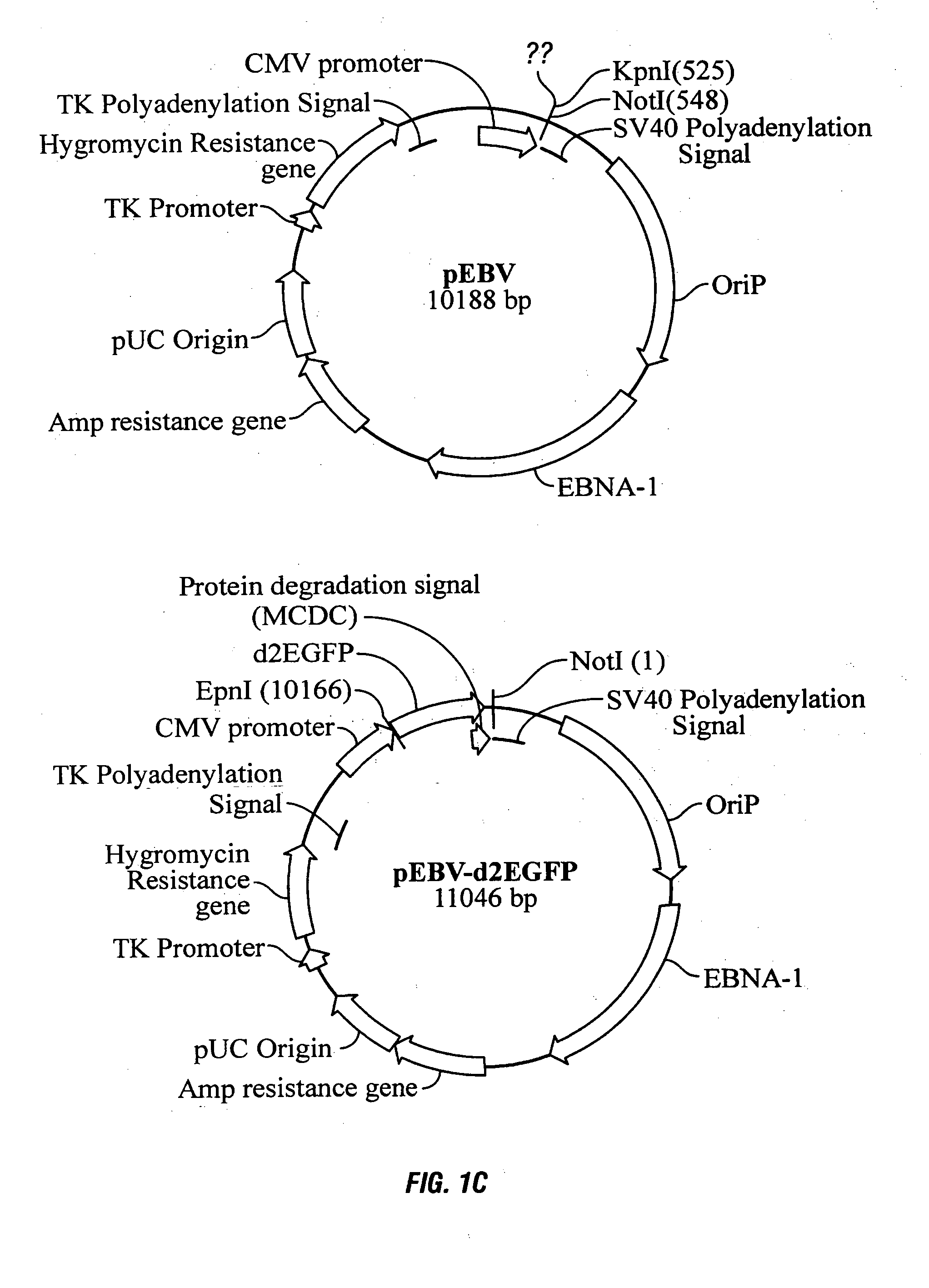
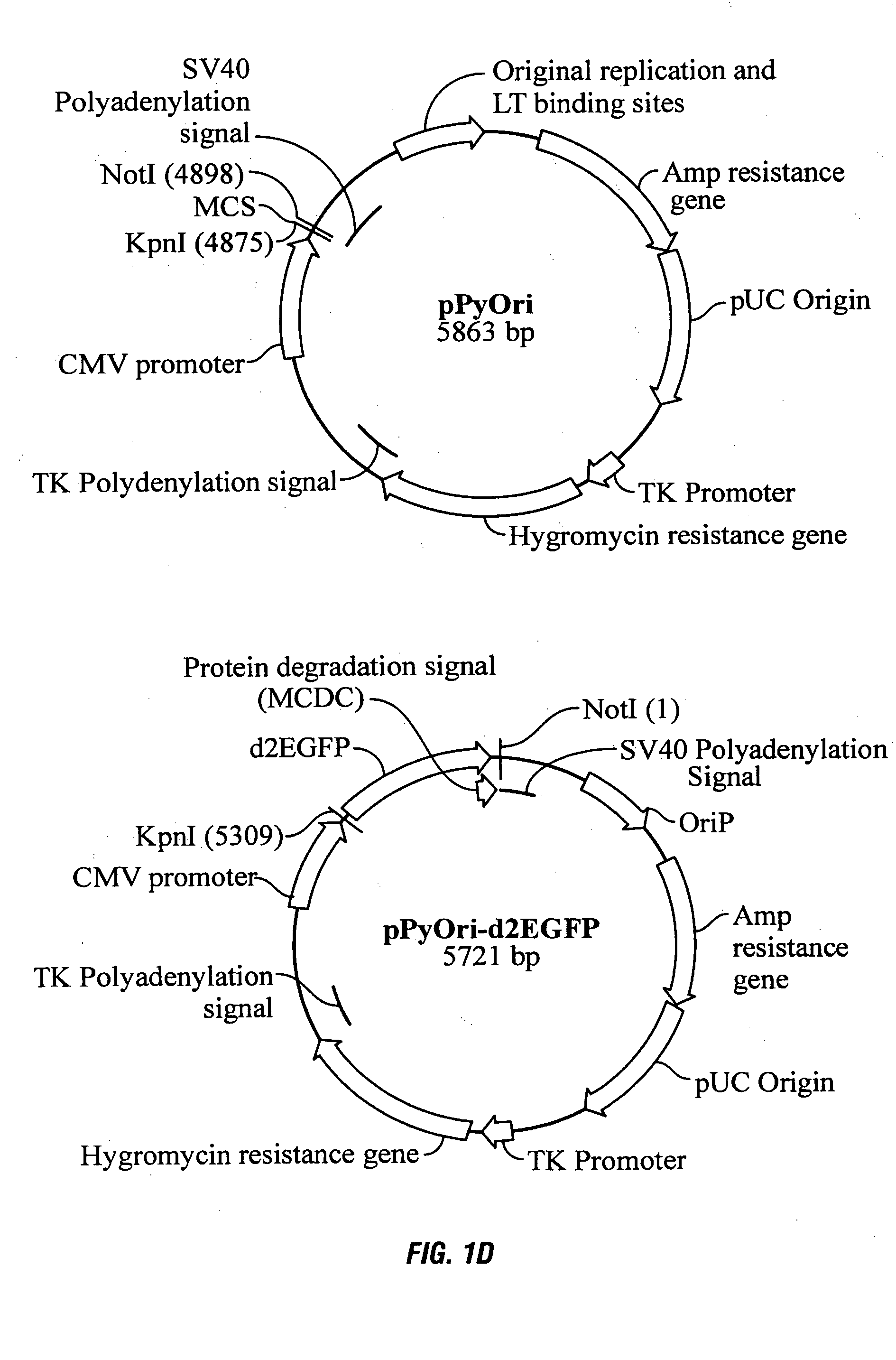
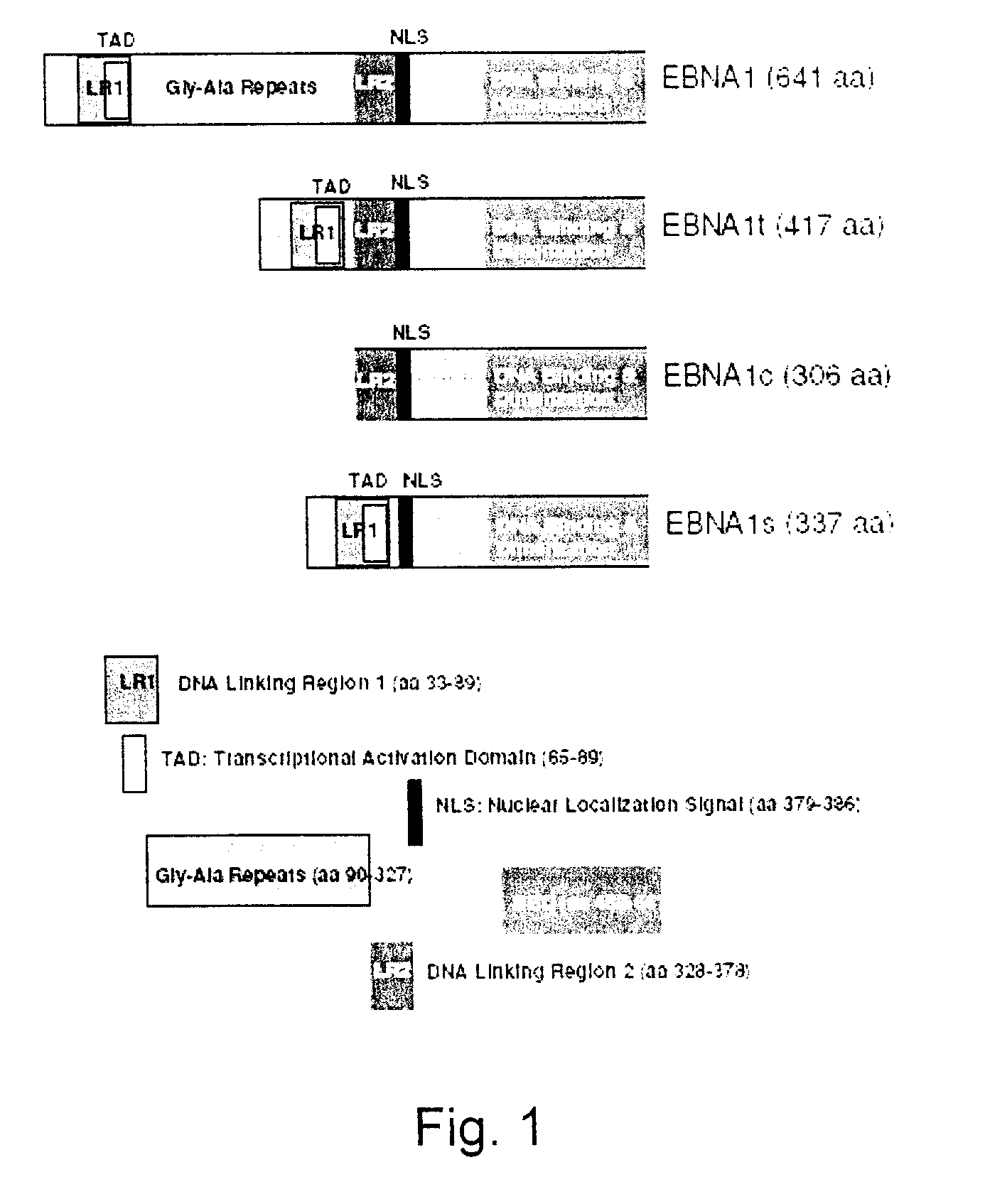
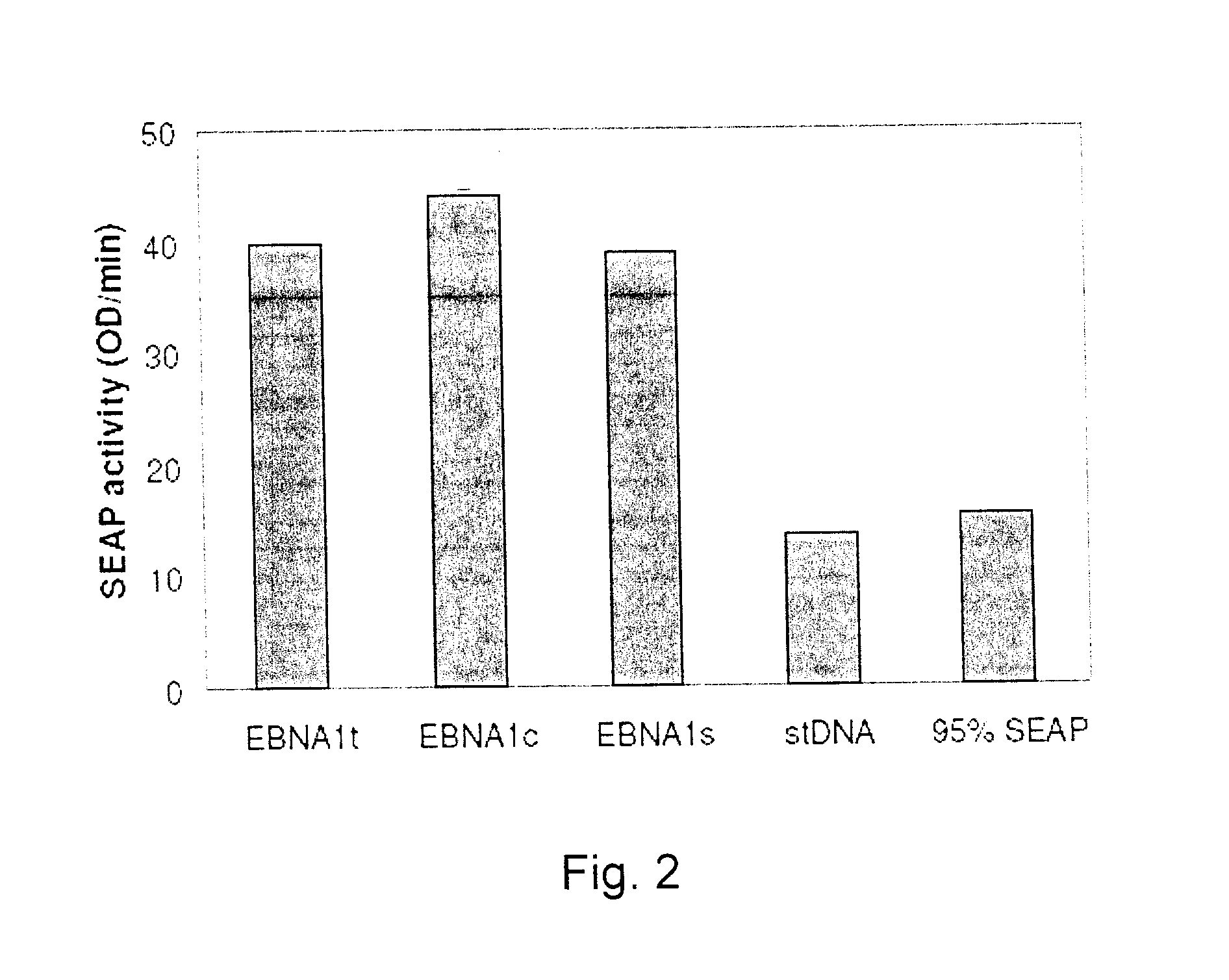
Processes vectors and engineered cell lines for large-scale transfection and protein production in mammalian cells, especially Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells are described in which transfection efficiencies are realized through the use of a single vector system, the use of functional oriP sequences in all plasmids, the use of codon-optimized Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA1) constructs the use of a fusion protein between a truncated Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigenen-1c (EBNA1c) protein and a herpes simplex virus protein VP16, the use of a 40 kDa fully deacetylated poly(ethylenimine) as a transfection reagent, the use of co-expression of a fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and / or the use of protein kinase B to potentiate heterologous gene expression enhancement by valproic acid (VPA).
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Mammalian expression system
InactiveUS20050227317A1High transfection efficiencyHigh expressionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHigh level expressionMammal
The present invention relates to protein expression systems and in particular to a mammalian protein expression system. Specifically, the present invention provides a rodent cell line with enhanced protein production capabilities. The invention also relates to eukaryotic cloning and expression vectors and related methods, and in particular to DNA vectors capable of high level expression of a protein of interest. The invention allows for long-term episomal maintenance of expression vectors in mammalian cells.
Owner:ACYTE BIOTEC
Process, Vectors and Engineered Cell Lines for Enhanced Large-Scale Transfection
ActiveUS20110039339A1Heterologous gene expression can be improvedEnhanced transfectionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesValproic AcidHamster
Processes vectors and engineered cell lines for large-scale transfection and protein production in mammalian cells, especially Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cells are described in which transfection efficiencies are realized through the use of a single vector system, the use of functional oriP sequences in all plasmids, the use of codon-optimized Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA1) constructs the use of a fusion protein between a truncated Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigenen-1c (EBNA1c) protein and a herpes simplex virus protein VP16, the use of a 40 kDa fully deacetylated poly(ethylenimine) as a transfection reagent, the use of co-expression of a fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and / or the use of protein kinase B to potentiate heterologous gene expression enhancement by valproic acid (VPA).
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Nucleic acid complex
InactiveUS20150024488A1Improve protectionEnhanced transfectionSsRNA viruses negative-sensePowder deliveryBlock structureNucleic acid
The present invention relates to a complex comprising a cationic block copolymer and a nucleic acid, the cationic block copolymer having at least a tri-block structure comprising a cationic block and two hydrophilic blocks, or a hydrophilic block and two cationic blocks.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
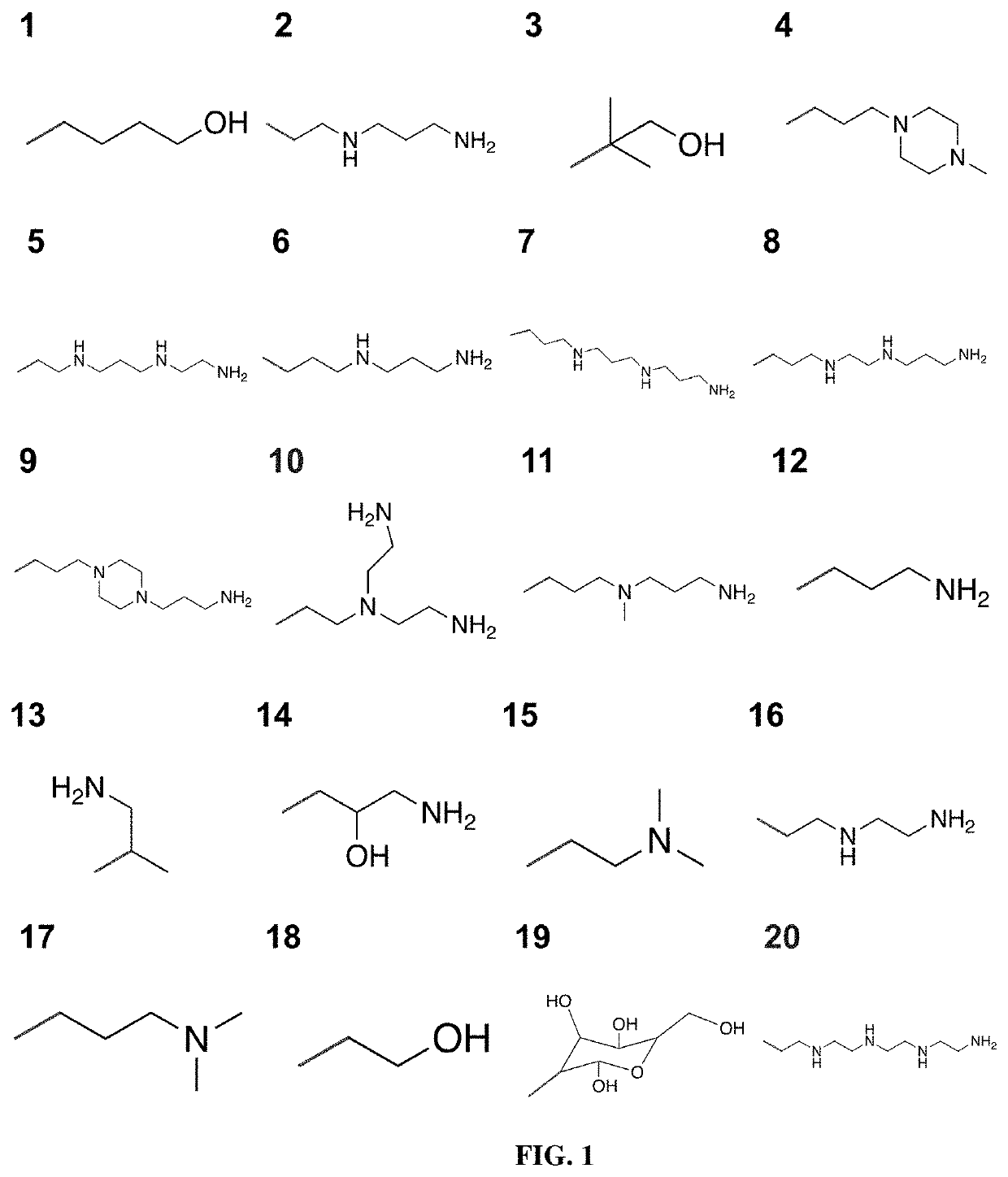
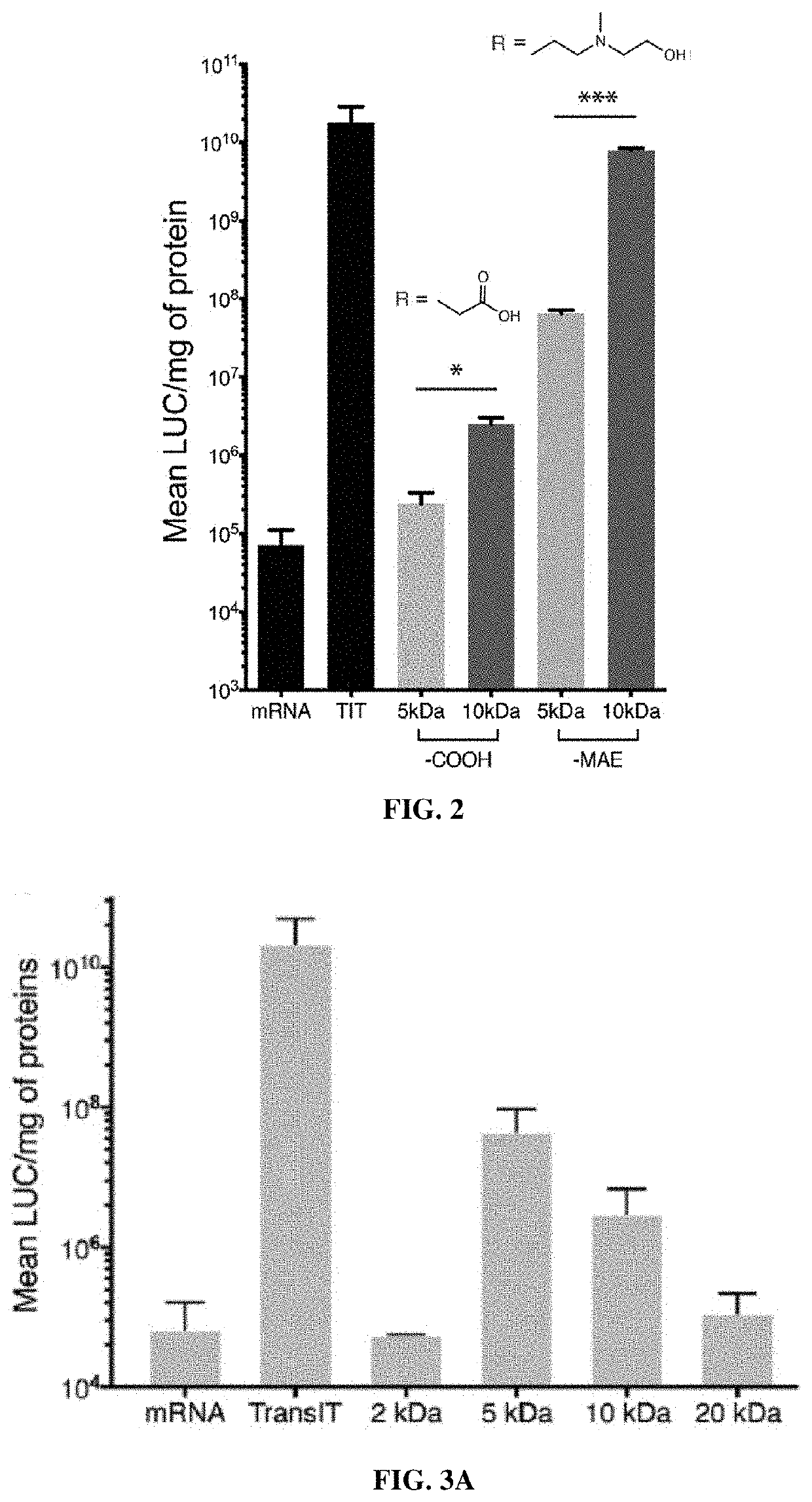
Poly(amine-co-ester) polymers and polyplexes with modified end groups and methods of use thereof
PendingUS20200399424A1High efficiencyMaterial efficiencyMicroencapsulation basedGenetic material ingredientsDrug deliveryActive agent
Poly(amine-co-ester) polymers, methods of forming active agent-load polyplexes and particles therefrom, and methods of using them for delivery of nucleic acid agents with optimal uptake have been developed. Examples demonstrate critical molecular weights in combination with exposed carboxylic and / or hydroxyl groups, and methods of making Typically, the compositions are less toxic, more efficient at drug delivery, or a combination thereof compared to a control other transfection reagents. In some embodiments, the compositions are suitable for in vivo delivery, and can be administered systemically to a subject to treat a disease or condition.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Mammalian expression system
InactiveUS7919270B2High expressionEnhanced transfectionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesBiotechnologyHigh level expression
The present invention relates to protein expression systems and in particular to a mammalian protein expression system. Specifically, the present invention provides a rodent cell line with enhanced protein production capabilities.The invention also relates to eukaryotic cloning and expression vectors and related methods, and in particular to DNA vectors capable of high level expression of a protein of interest. The invention allows for long-term episomal maintenance of expression vectors in mammalian cells.
Owner:ACYTE BIOTEC
Agent for treating leishmania infections
InactiveUS7795406B2Enhanced transfectionAvoid disadvantagesOrganic active ingredientsProtozoa antigen ingredientsLeishmaniasisImmunotherapy
Owner:MOLOGEN AG
Polymers for polynucleotide encapsulation
InactiveUS20100292432A1Enhance endolysosomal escapePrevent degradationPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryPolymer sciencePolynucleotide
The present invention provides block copolymers comprising hydrophobic moieties in a cationic complexing block, methods of preparing the same, and intermediates thereto. The compounds are useful in a variety of applications such as the assembly of micellar polyion complexes. The invention further provides methods of using said compounds and compositions thereof.
Owner:INTEZYNE TECH INC
Transfection reagents
InactiveUS20060257464A9High activitySufficient hydrophobicityMicroencapsulation basedTissue cultureDna deliveryPhospholipid
The present invention provides optimized transfection reagents comprising mixtures of cationiclipoids. In particular, the present invention provides DNA delivery vehicles based on identifying the optimal hydrophobicity of novel cationic phospholipid derivatives that, alone or in combination, form complexes with DNA (lipoplexes) and exhibit enhanced transfection activity.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR HIGH EFFICIENCY TRANSFECTION OF siRNA
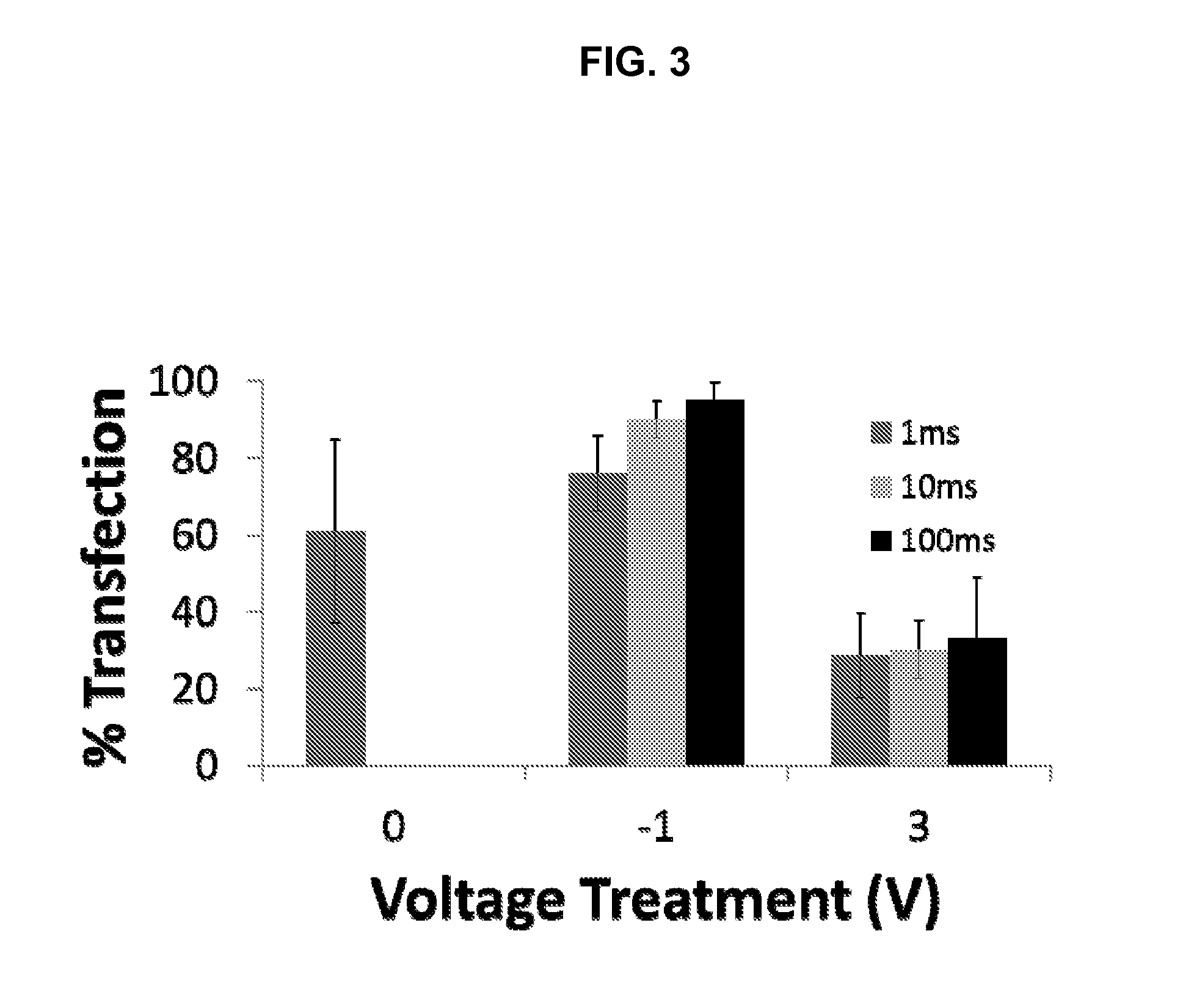
ActiveUS20140106429A1Enhances siRNA transfectionImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLow voltageTransfection
Described herein are methods and compositions for high efficiency transfection of siRNA into a cell population. Such methods and compositions utilize a low voltage pre-conditioning pulse to modulate the efficiency of siRNA transfection. In some embodiments, the methods and compositions permit spatial and temporal control of siRNA transfection efficiency within a population of cells. The disclosed methods and compositions, in some embodiments, are amenable to high throughput applications such as siRNA library-based phenotypic screening.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Transfection complexes
InactiveUS20100172930A1High affinityImprove bindingOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAcidic amino acidsTransfection
The invention provides a peptide having at least 3 amino acids comprising an amino acid sequence selected froma) X1SM[SEQ.ID.NO.: 1]b) LX2HK[SEQ.ID.NO.: 2]c) PSGX3ARA[SEQ.ID.NO.: 9]d) SX4RSMNF[SEQ.ID.NO.: 16]e) LX5HKSMP[SEQ.ID.NO.: 18]in which X1 is a basic amino acid residue, X2 is Q or P, X3 is A or T, X4 is an acidic amino acid residue and X5 is P or Q.The invention further provides non-viral cell-targeting vector complexes and methods associated therewith.
Owner:RYBOQUIN COMPANY
NOVEL VEHICLES FOR THE TRANSFECTION OF miRNAS
ActiveUS20190111002A1Improve stabilityImprove in vivo transportOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderOncologyBiochemistry
The invention relates to a nanoparticle comprising: (i) between 60 wt.-% and 99 wt.-% sorbitan ester, relative to the total weight of the nanoparticle; (ii) a positively charged substance; and (iii) a miRNA. The invention also relates to the methods for producing same and to the uses thereof, particularly for therapeutic uses, such as cancer treatment.
Owner:UNIV DEL PAIS VASCO EUSKAL HERRIKO UNIBERTSITATEA
Transfection reagents
InactiveUS20050142179A1Reduce hydrophobicityImprove abilitiesMicroencapsulation basedTissue cultureDna deliveryPhospholipid
The present invention provides optimized transfection reagents comprising mixtures of cationiclipoids. In particular, the present invention provides DNA delivery vehicles based on identifying the optimal hydrophobicity of novel cationic phospholipid derivatives that, alone or in combination, form complexes with DNA (lipoplexes) and exhibit enhanced transfection activity.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Genetic modification of the lung as a portal for gene delivery
InactiveUS20070238693A1Reduce the amount requiredEasy accessPowder deliveryNervous disorderGene deliveryWhole body
The present invention relates to methods for treatment of systemic disorders using the lung as a depot organ for transgene delivery. Transfection of the pulmonary epithelium, particularly the deep alveolar cells, or pulmonary endothelial cells, is achieved via local administration of a transgene delivery vector to the lung. The transfected cells express the transgene, and the protein thereby expressed is communicated into the circulatory system. Once entering into the circulatory system, the protein is able to achieve a systemic therapeutic effect.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method for transfecting nucleic acid to cell and nucleic acid complex
InactiveUS9057067B2Low cytotoxicityHigh transfection efficiencySpecial deliveryGenetic material ingredientsSide chainPhosphate
A method for transfecting nucleic acid to cell comprising a step for forming a nucleic acid complex by bringing a double-stranded nucleic acid molecule into contact with a nucleic acid carrier having an amino acid sequence of alternating a basic amino acid and a hydrophobic amino acid, which has a peptide chain that forms a β-sheet structure in which a side chain of a positively charged basic amino acid is disposed on one surface side and a side chain of a hydrophobic amino acid is disposed on the opposite surface side in the presence of the double-stranded nucleic acid molecule having a double helix structure, and by binding the double-stranded nucleic acid molecule and the peptide chain through either one or both of the electrostatic interaction between the side chains of the basic amino acid and phosphate groups and hydrogen bonds between the double stranded-nucleic acid molecule and the peptide chain and a nucleic acid complex used for the same are disclosed.
Owner:KINKI UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com