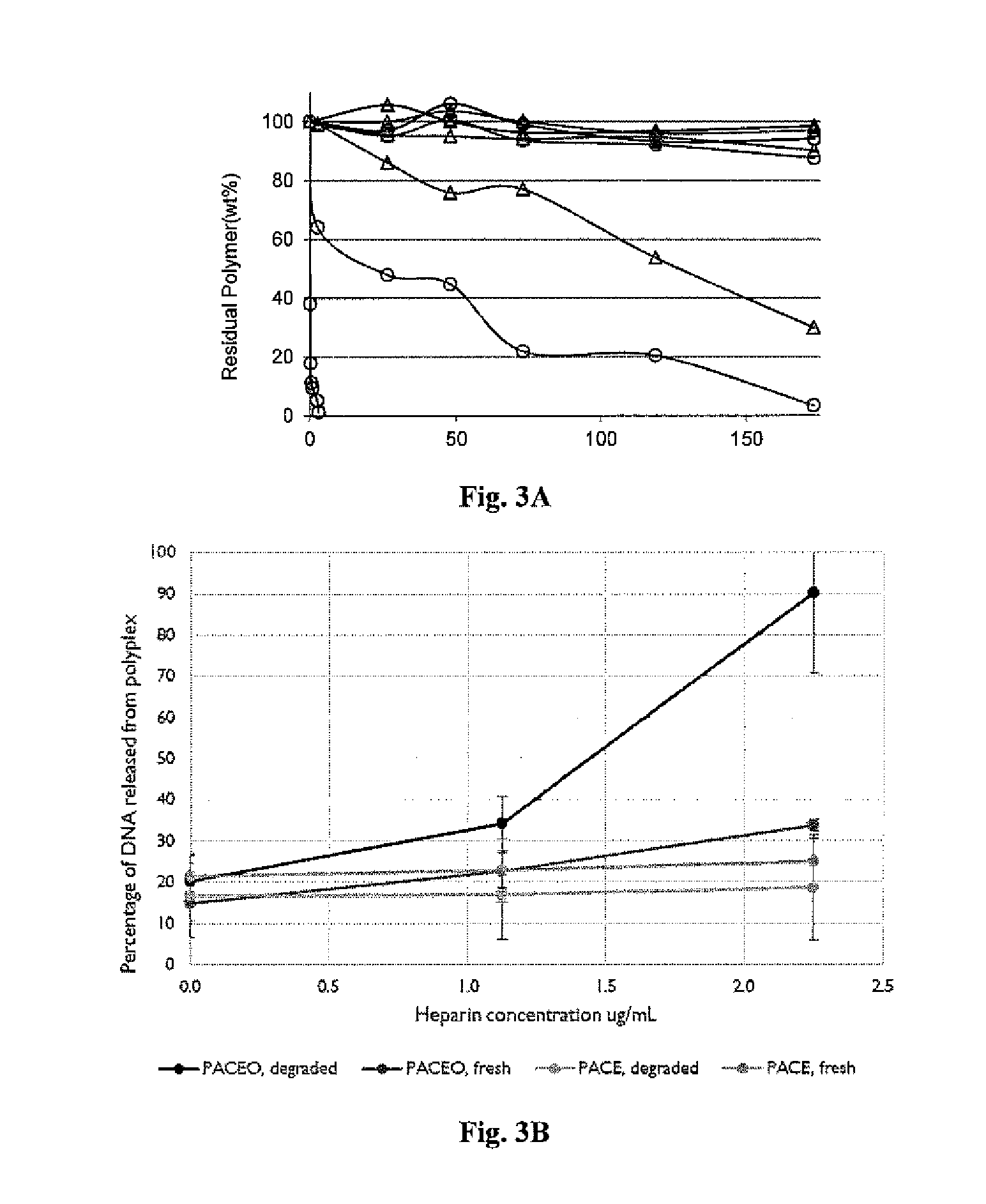
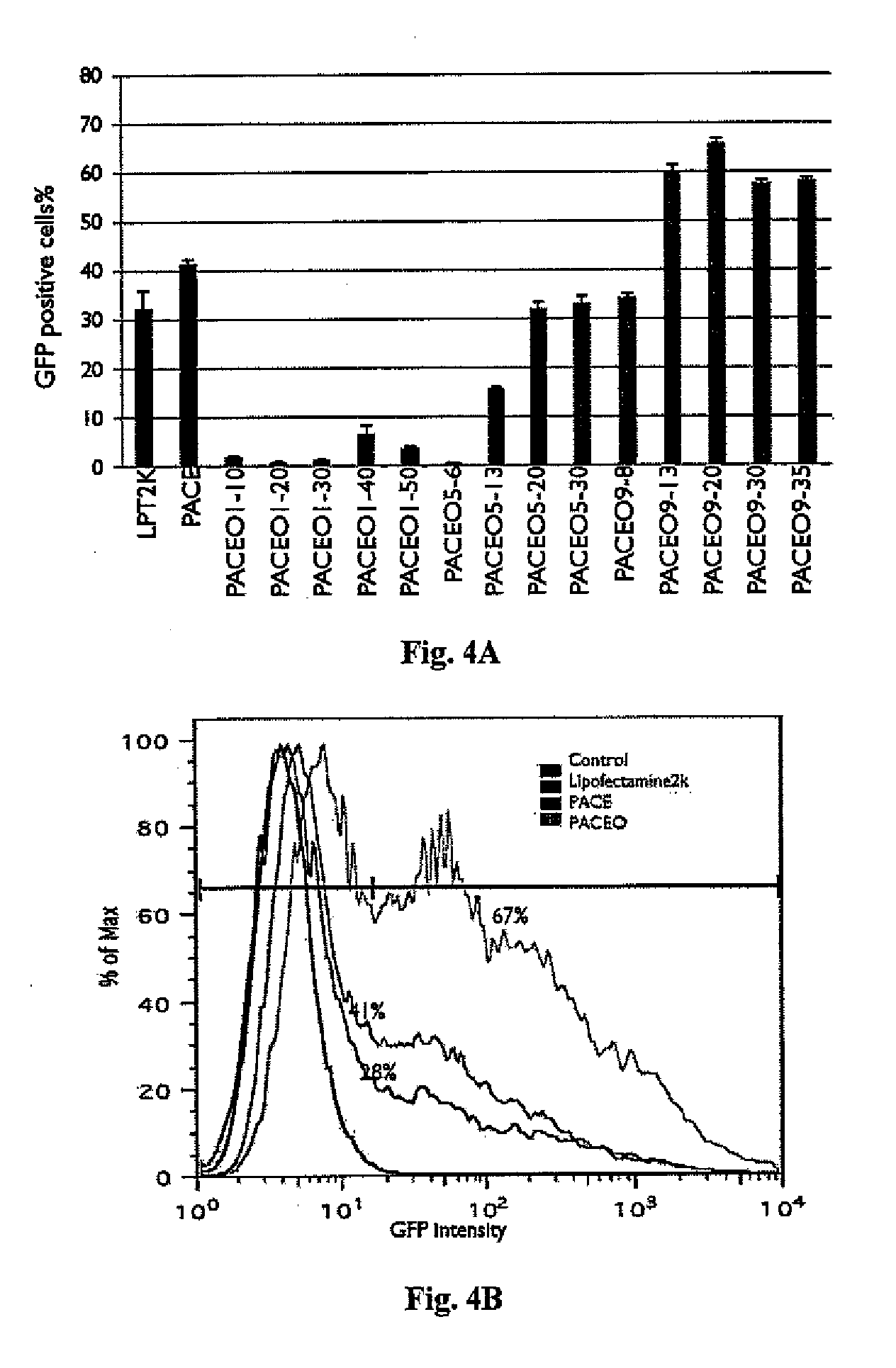
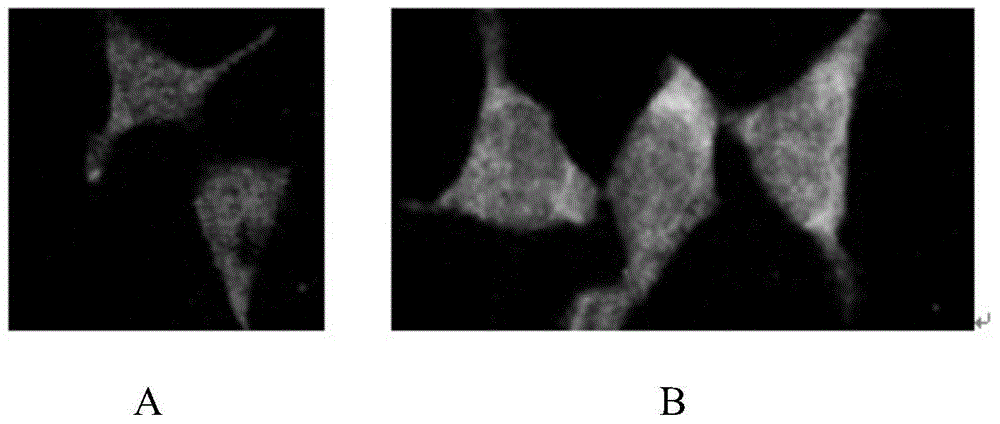
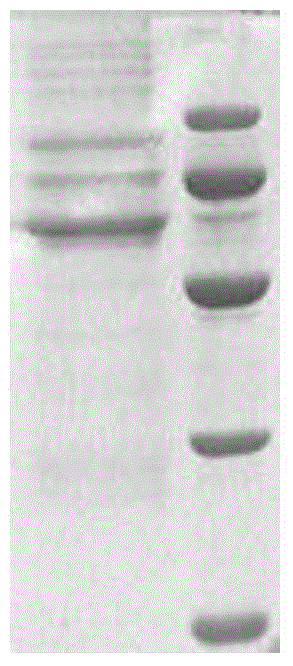
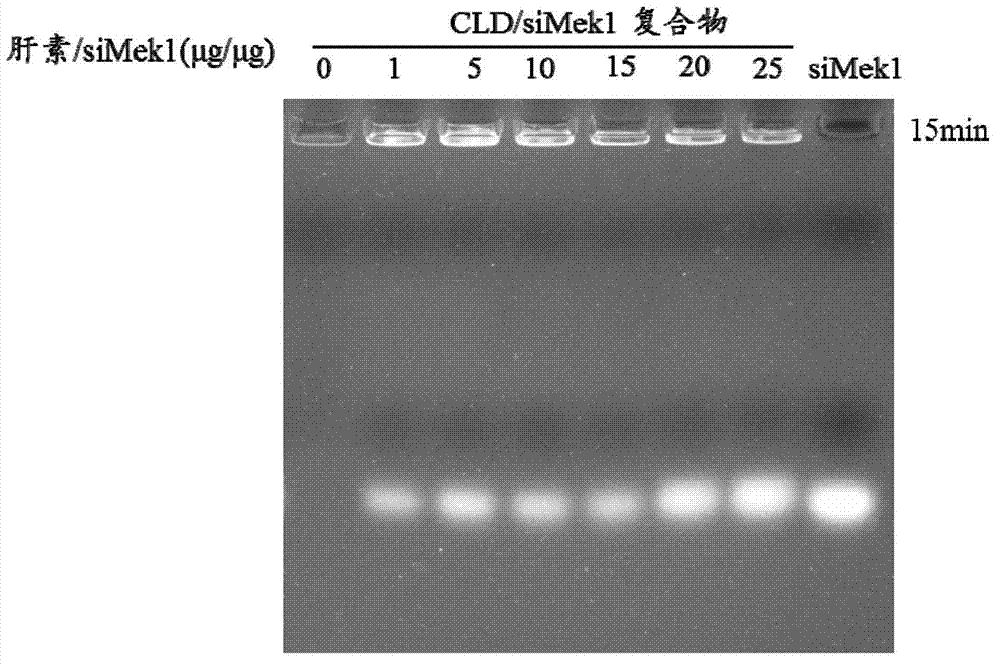
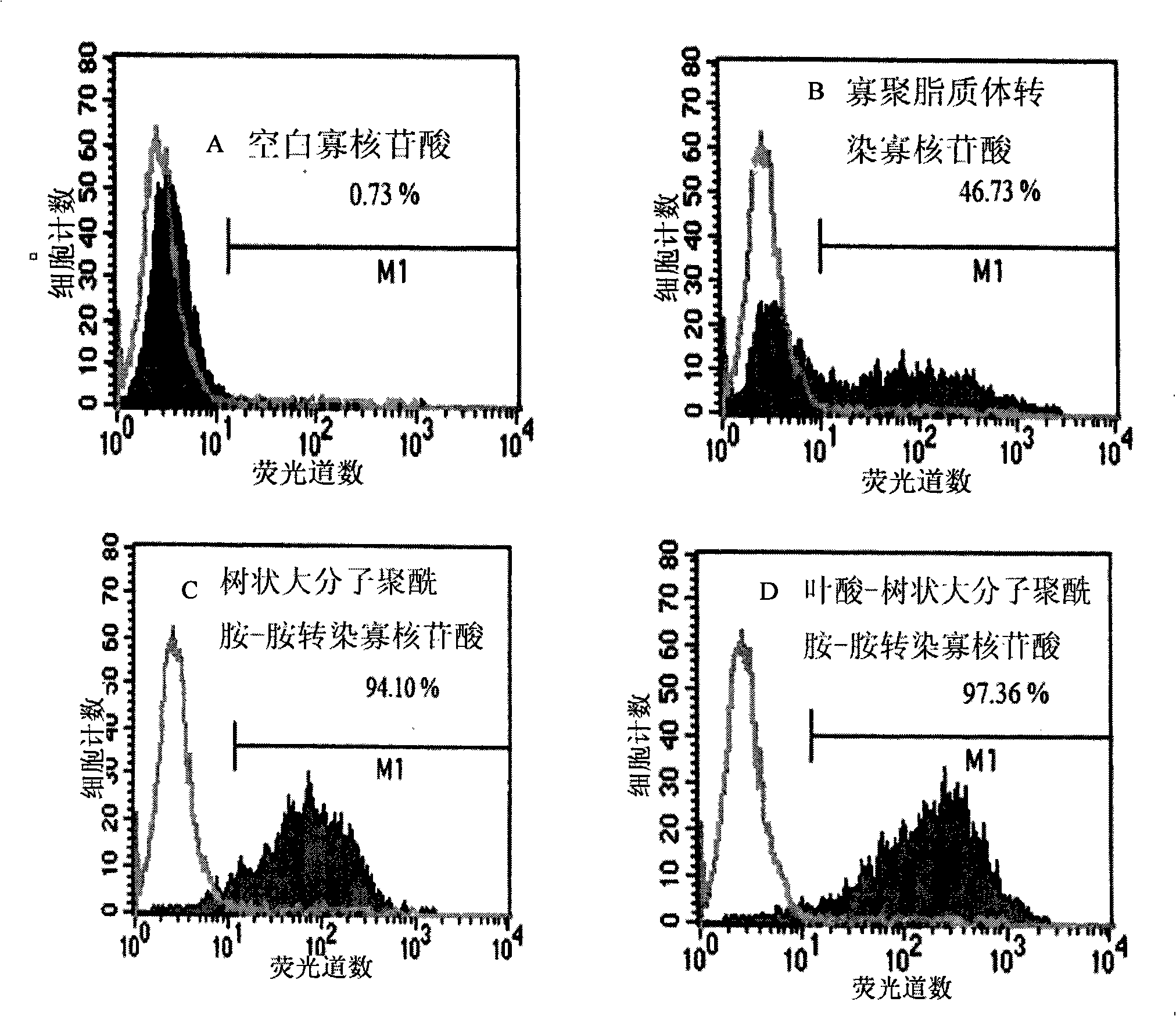
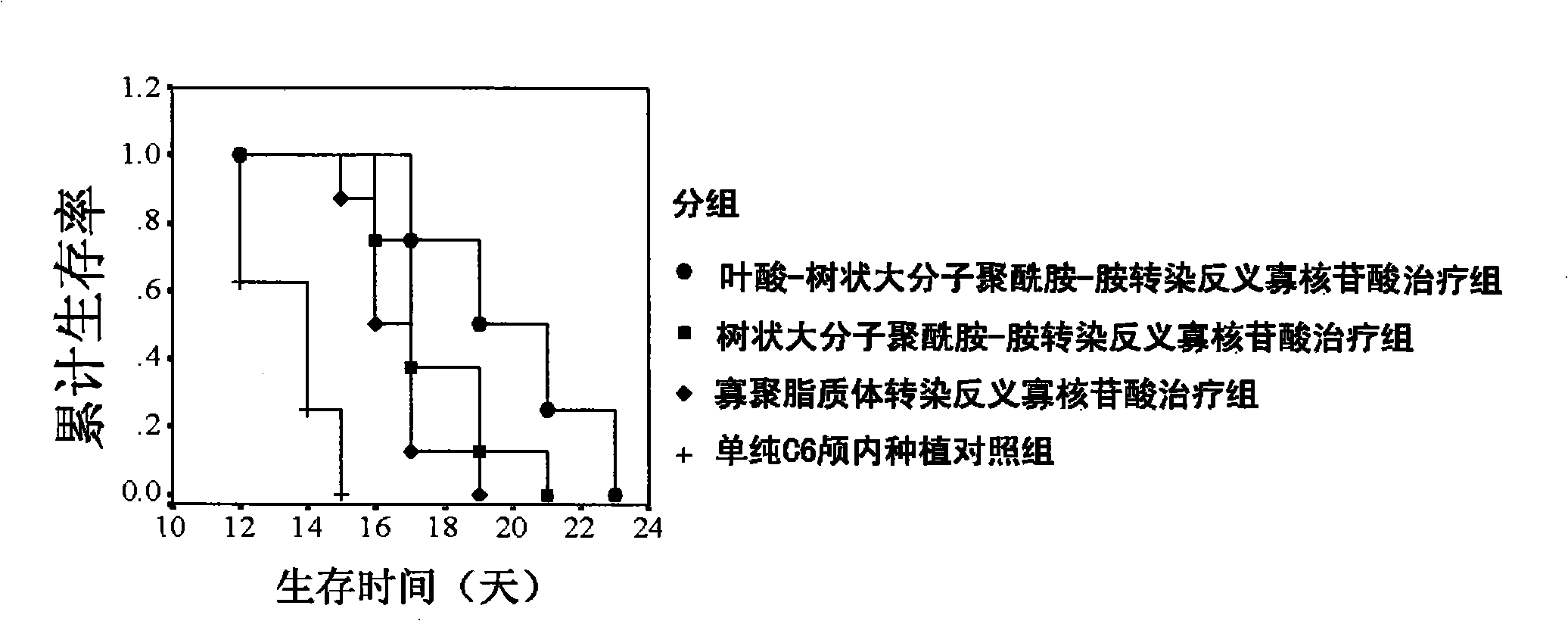
Patents
Literature
134results about How to "Efficient transfection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
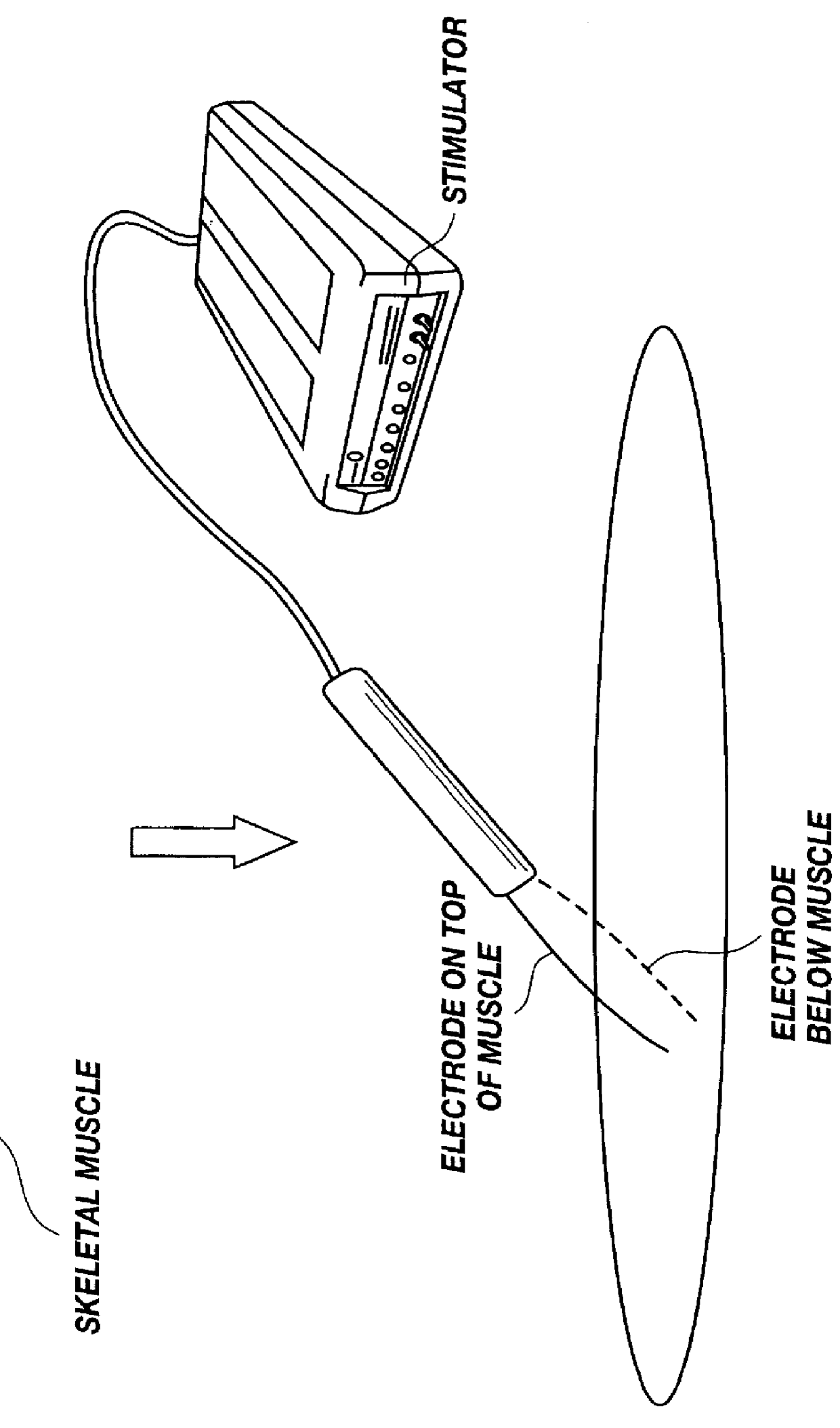
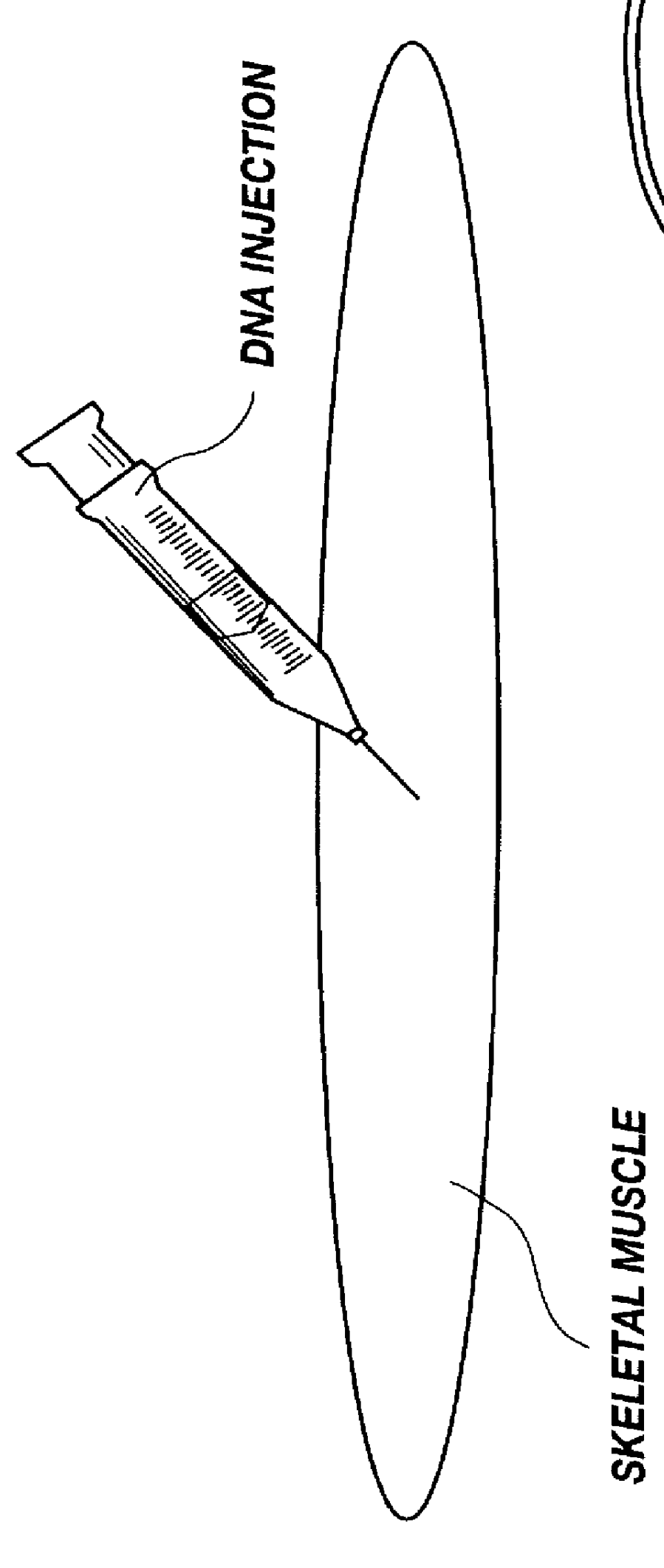
Method for introducing pharmaceutical drugs and nucleic acids into skeletal muscle
InactiveUS6110161ADetermine effectGreat luciferace activityBacterial antigen ingredientsElectrotherapyPower flowSecretory protein
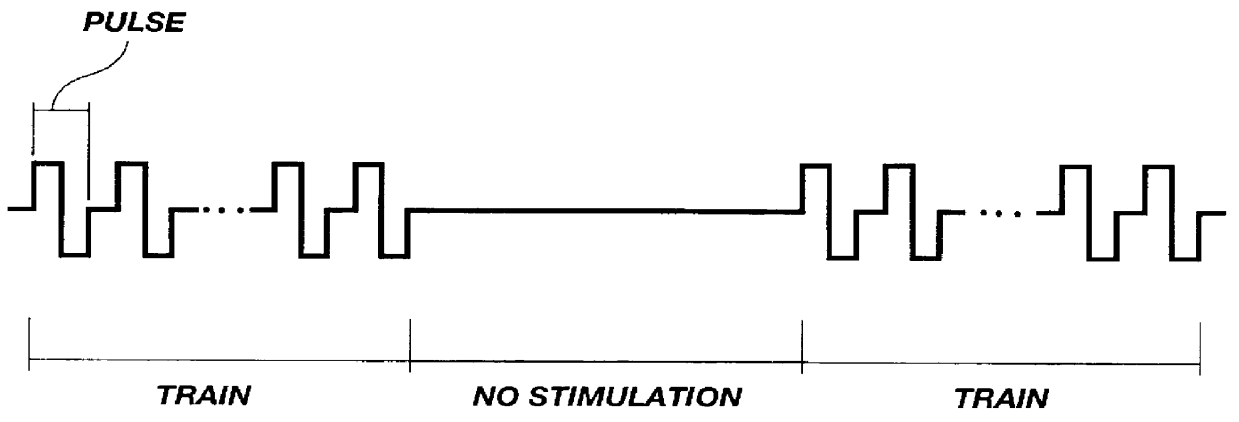
A method is disclosed for delivering molecules such as pharmaceutical drugs and nucleic acids into skeletal muscle in vivo. The pharmaceutical drug or nucleic acid is first injected into the muscle at one or multiple sites. Immediately, or shortly after, injection, electrodes are placed flanking the injection site and a specific amount of electrical current is passed through the muscle. The electrical current makes the muscle permeable, thus allowing the pharmaceutical drug or nucleic acid to enter the cell. The efficiency of transfer permits robust immune responses using DNA vaccines and produces sufficient secreted proteins for systemic biological activity to be observed.
Owner:INOVIO
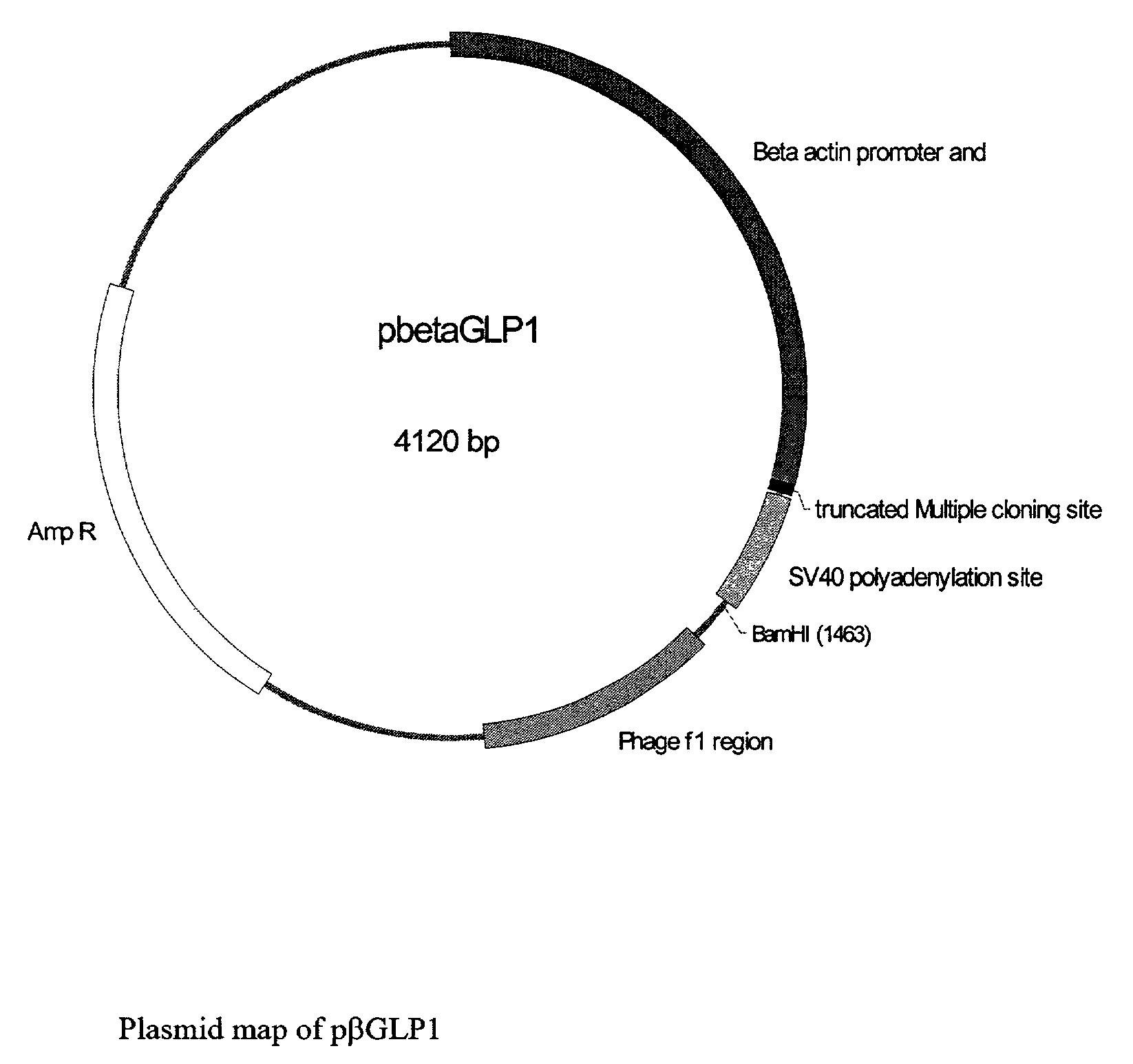
GLP-1 gene delivery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
ActiveUS7374930B2Efficient transfectionEasy to controlSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGene deliveryGlucose polymers
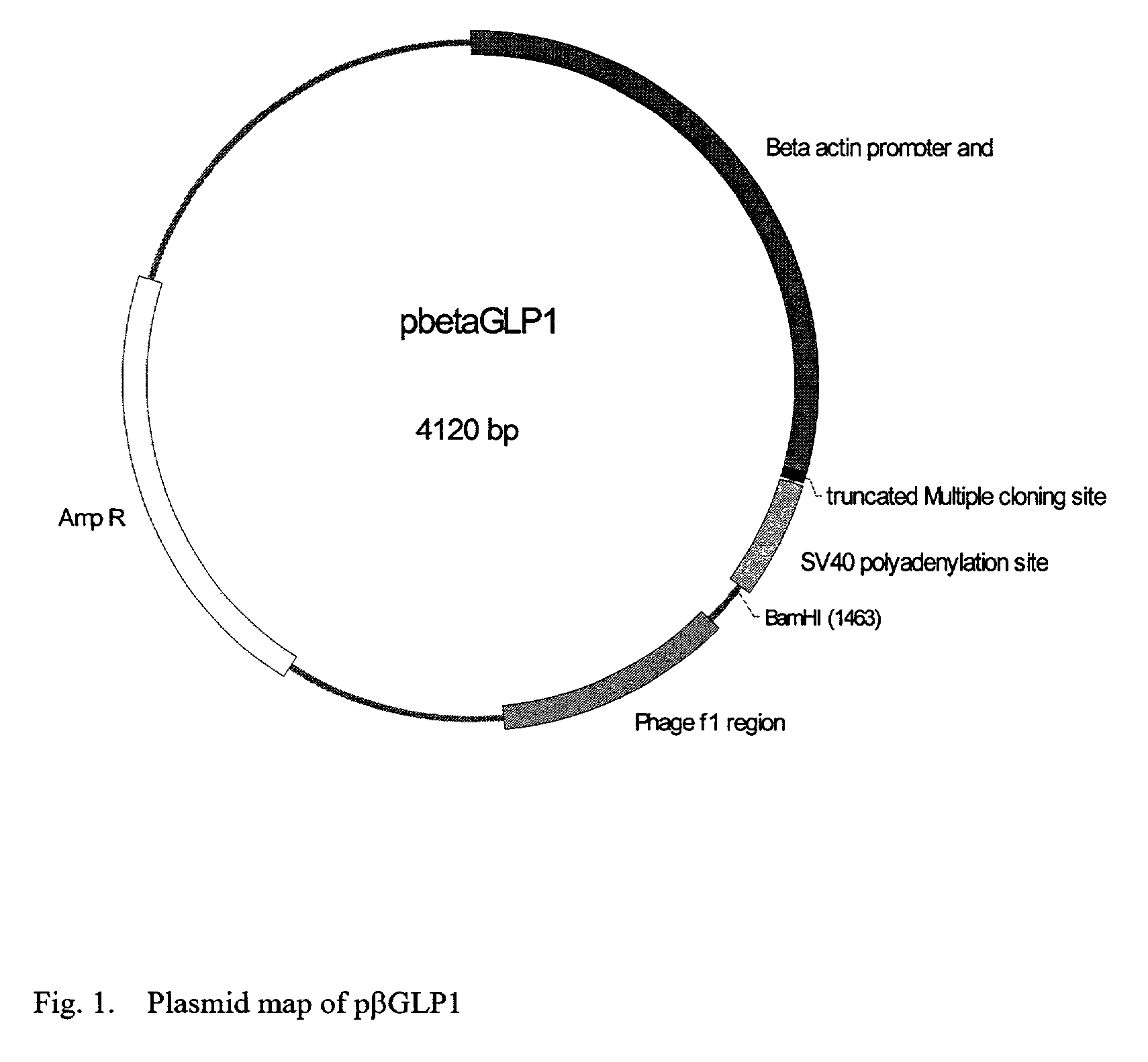
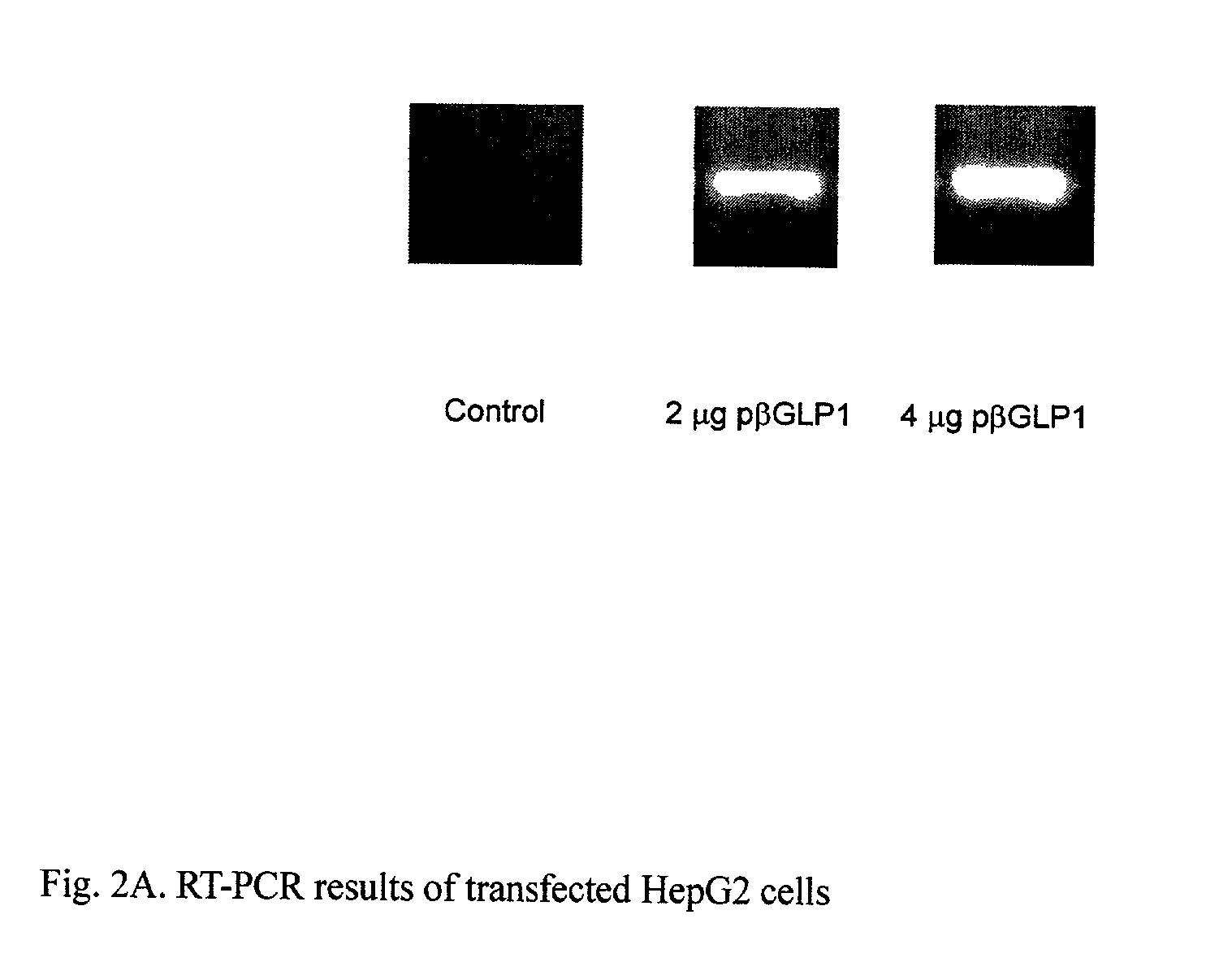
This patent discloses compositions and methods of use thereof to normalize the blood glucose levels of patients with type 2 diabetes. It relates particularly to a plasmid comprising a chicken β actin promoter and enhancer; a modified GLP-1 (7-37) cDNA (pβGLP1), carrying a furin cleavage site, which is constructed and delivered into a cell for the expression of active GLP-1.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Generation of replication competent viruses for therapeutic use
InactiveUS7550296B2Reduced viral genomeImprove effectivenessSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseReplication competent virus
The present invention relates to the generation of replication-competent viruses having therapeutic utility. The replication-competent viruses of the invention can express proteins useful in the treatment of disease.
Owner:PSIOXUS THERAPEUTICS LTD
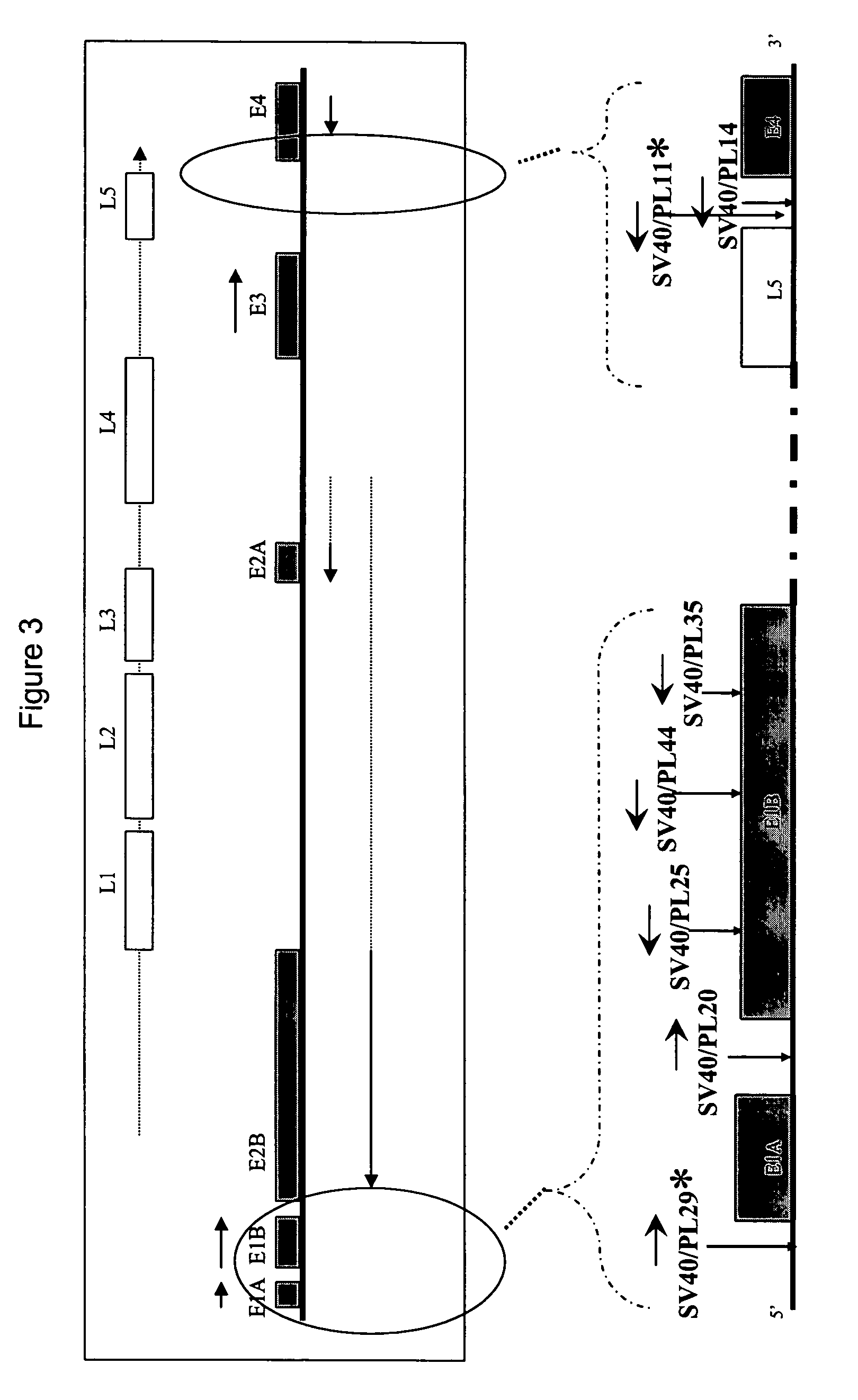
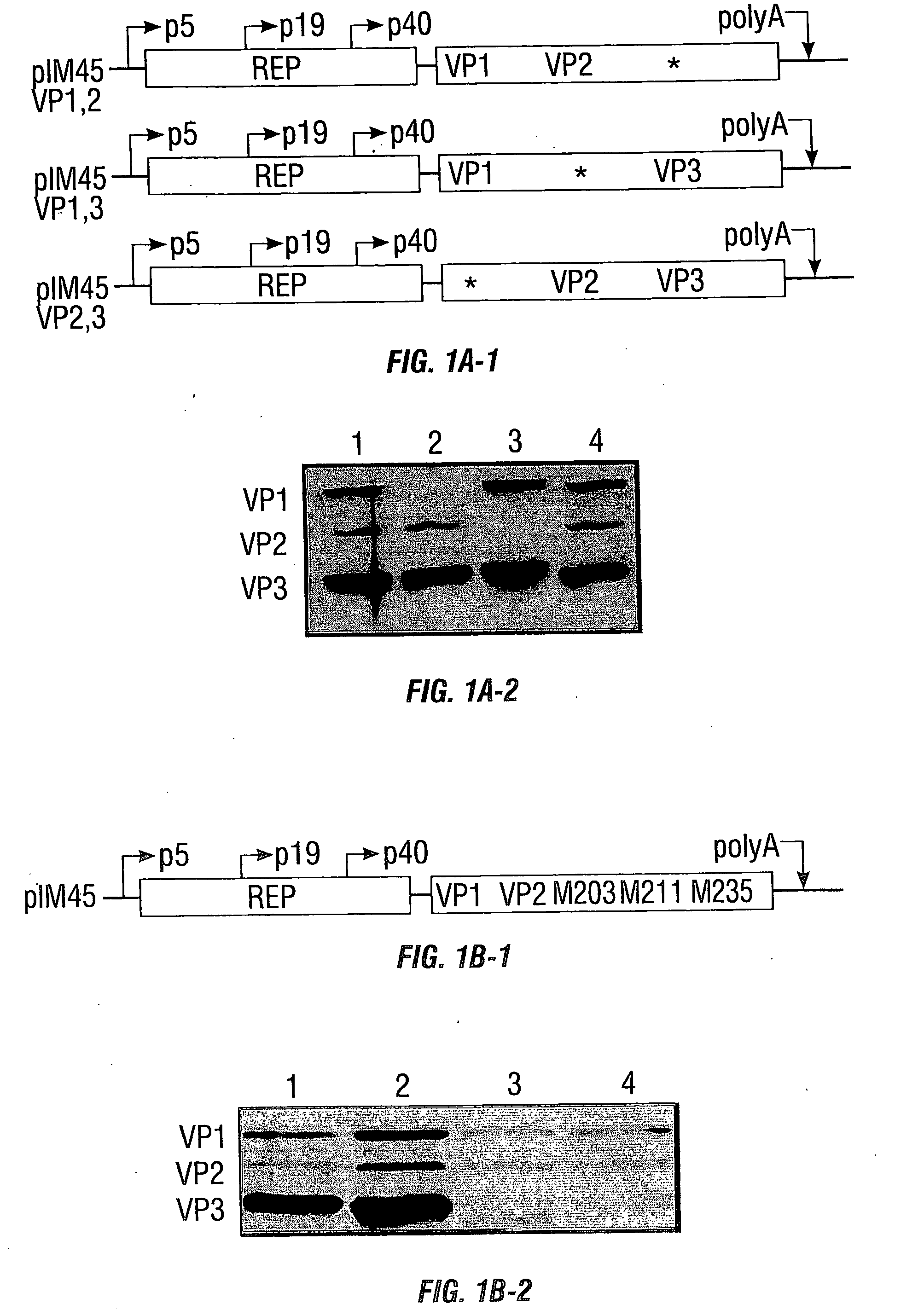
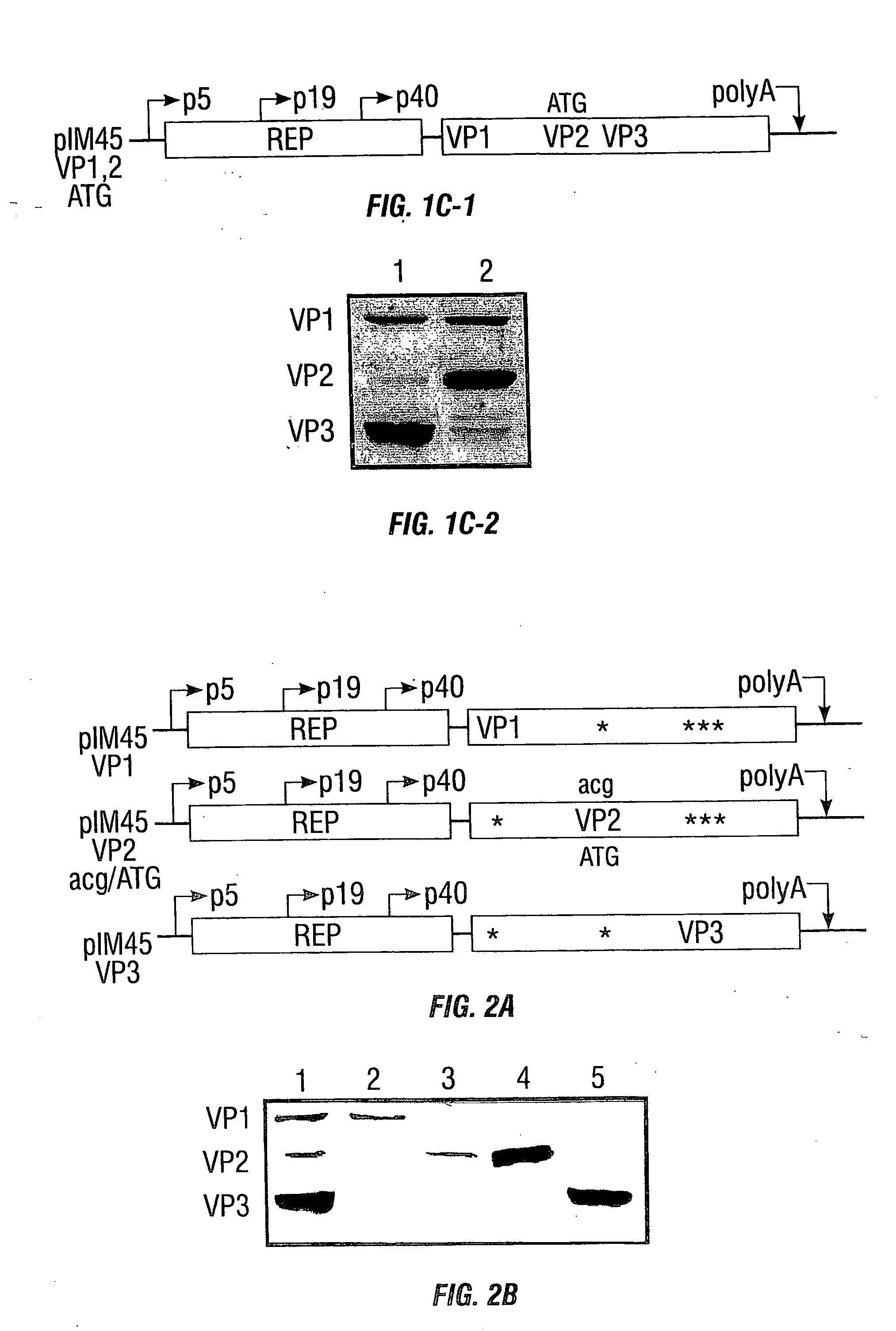
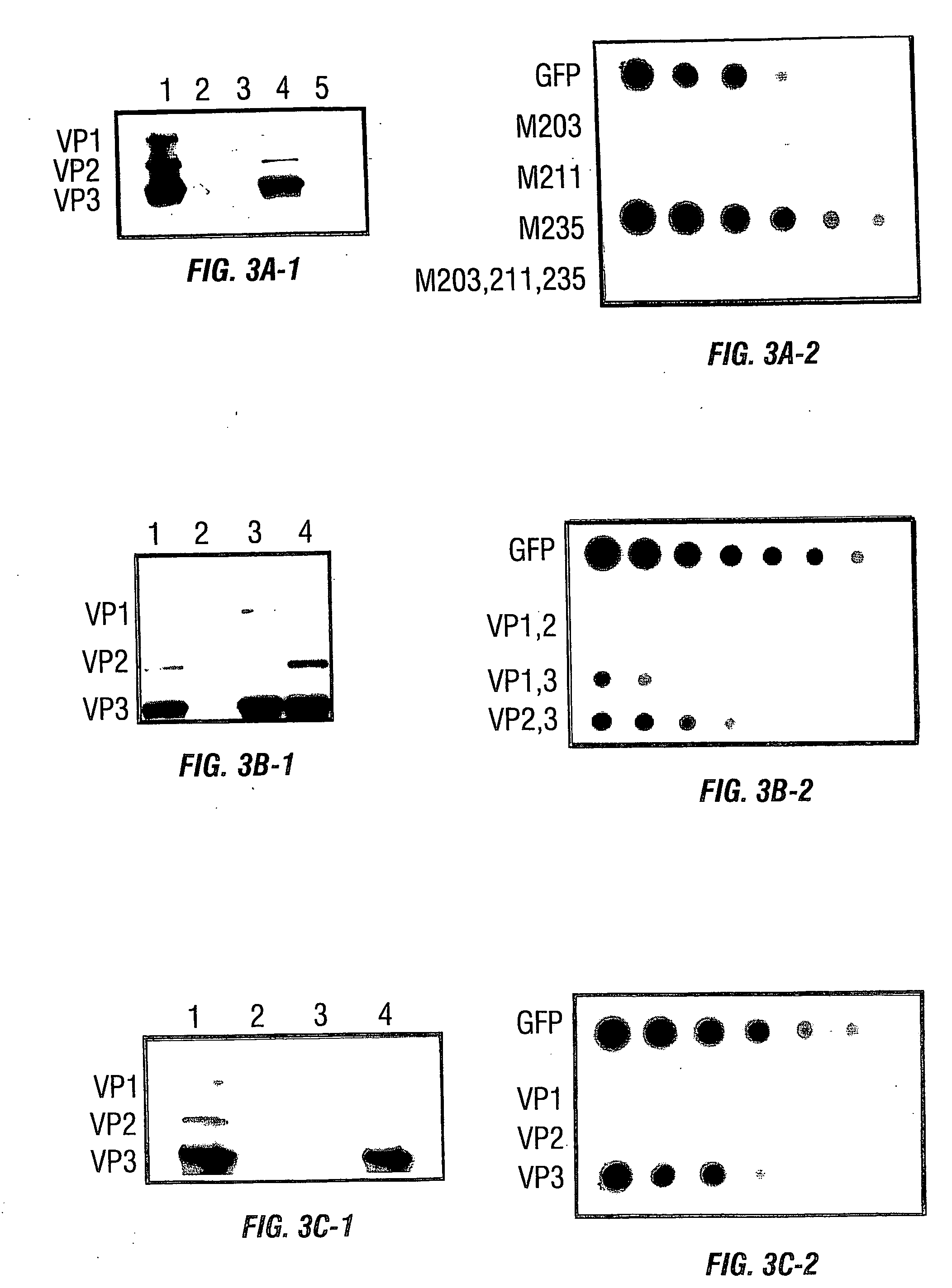
Vp2-modified raav vector compositions and uses therefor
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
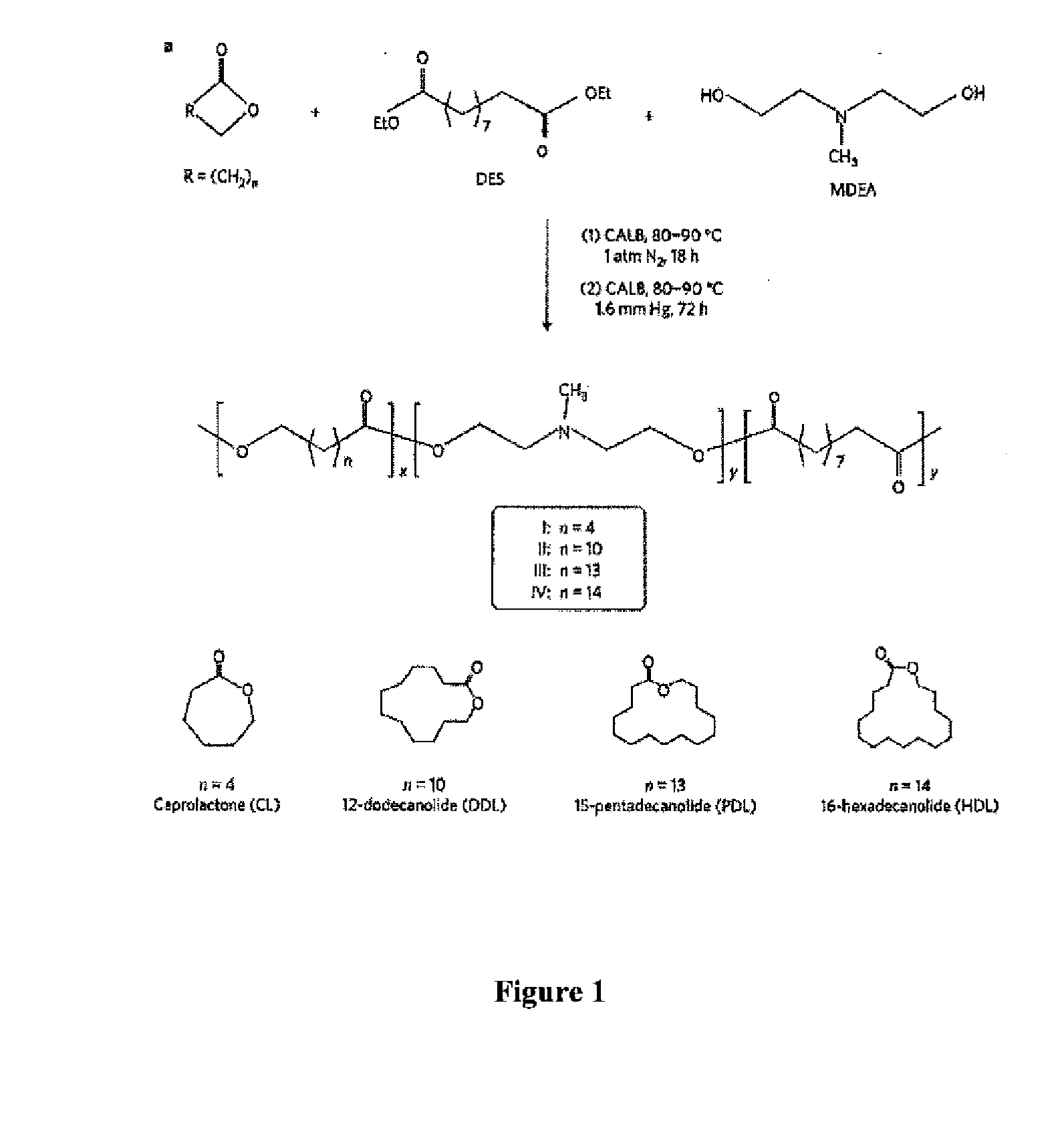
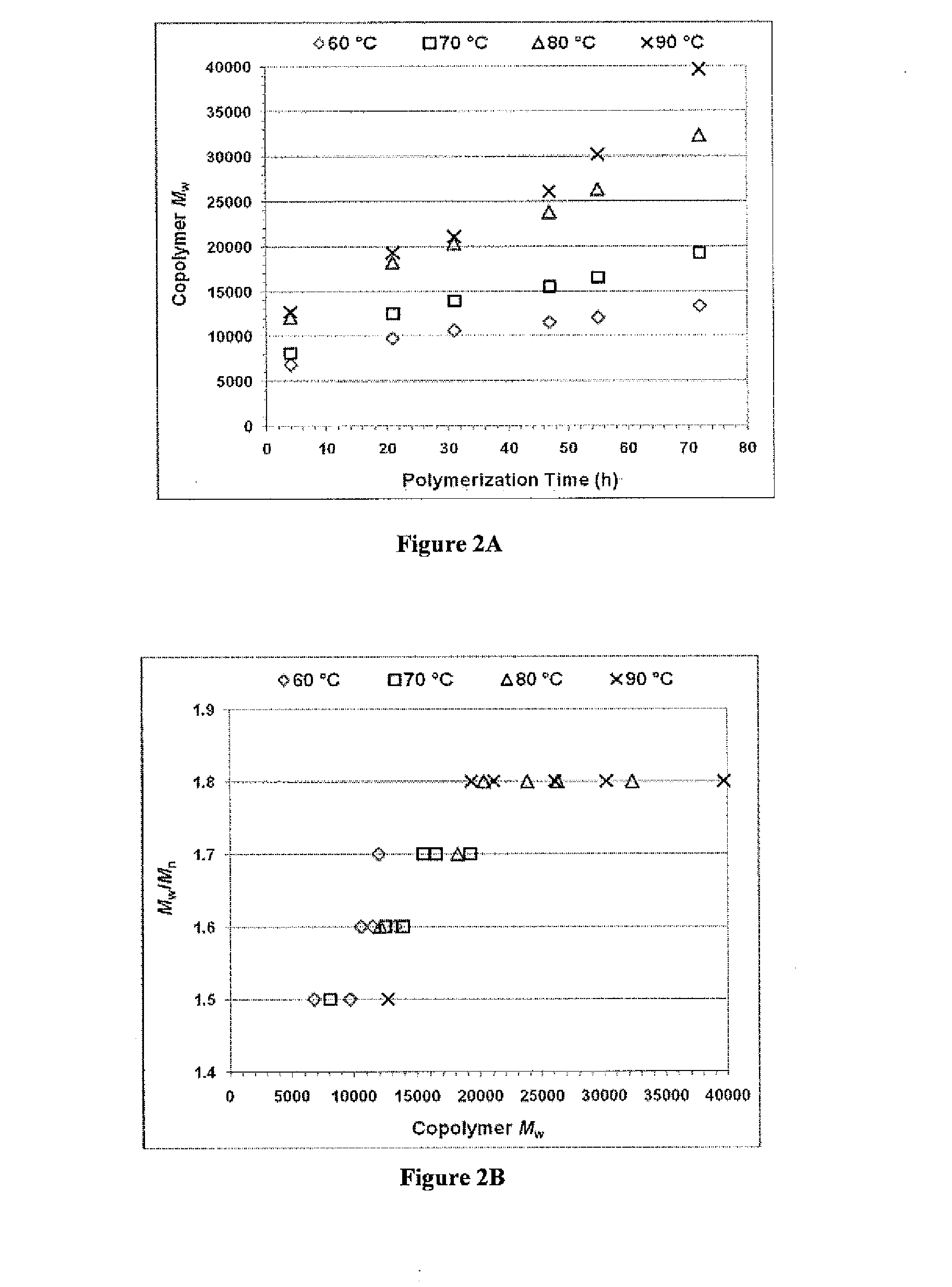
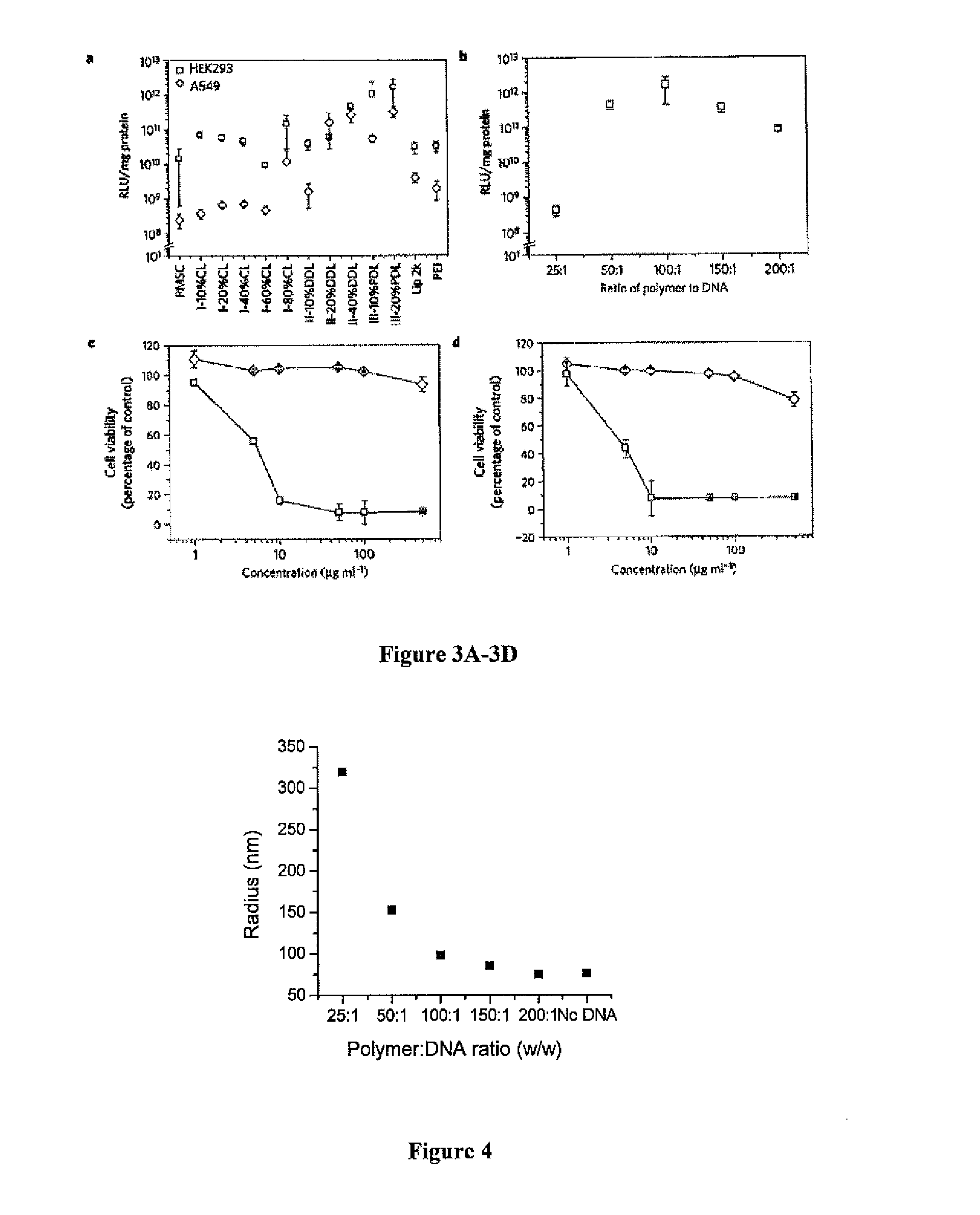
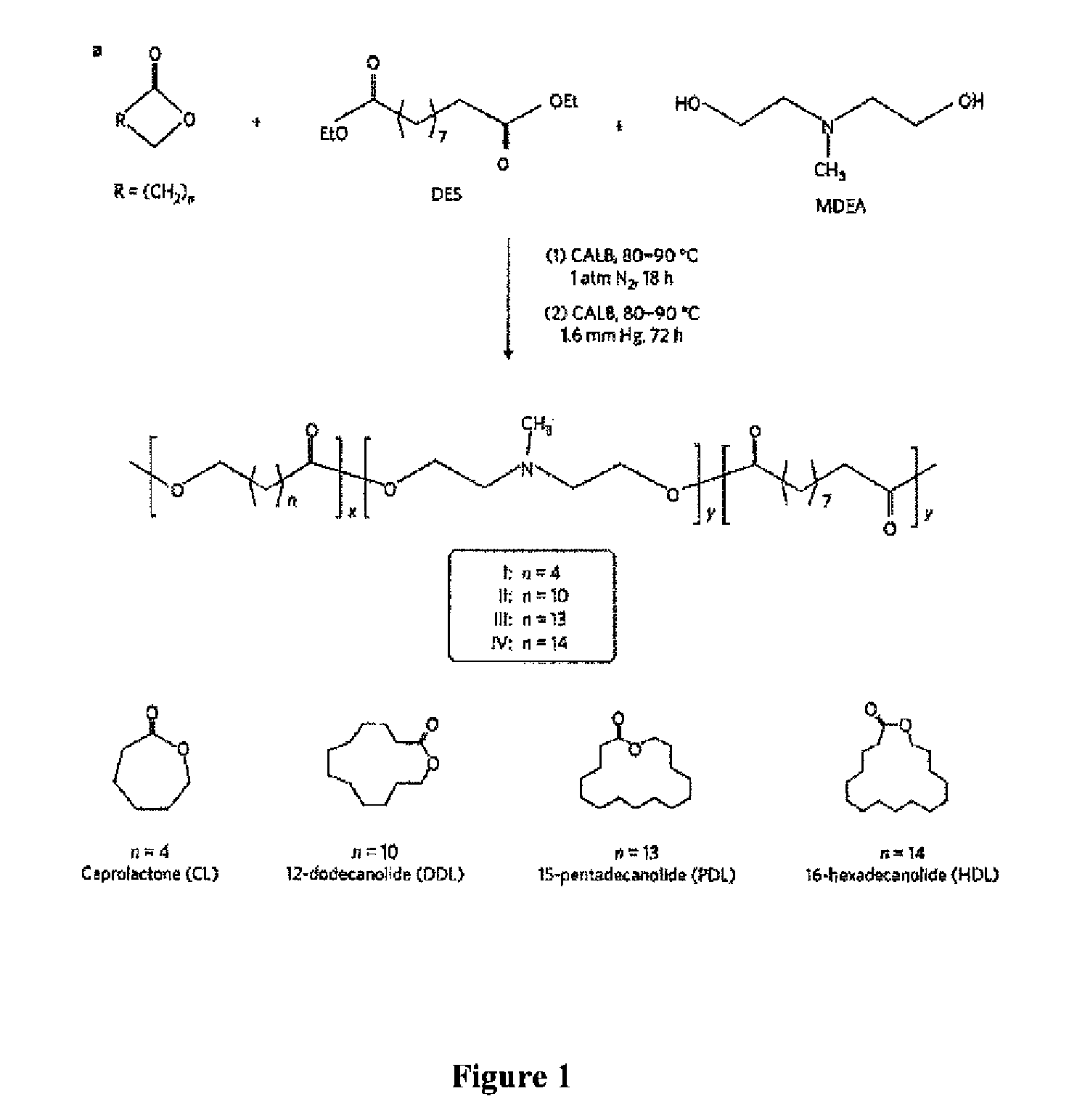
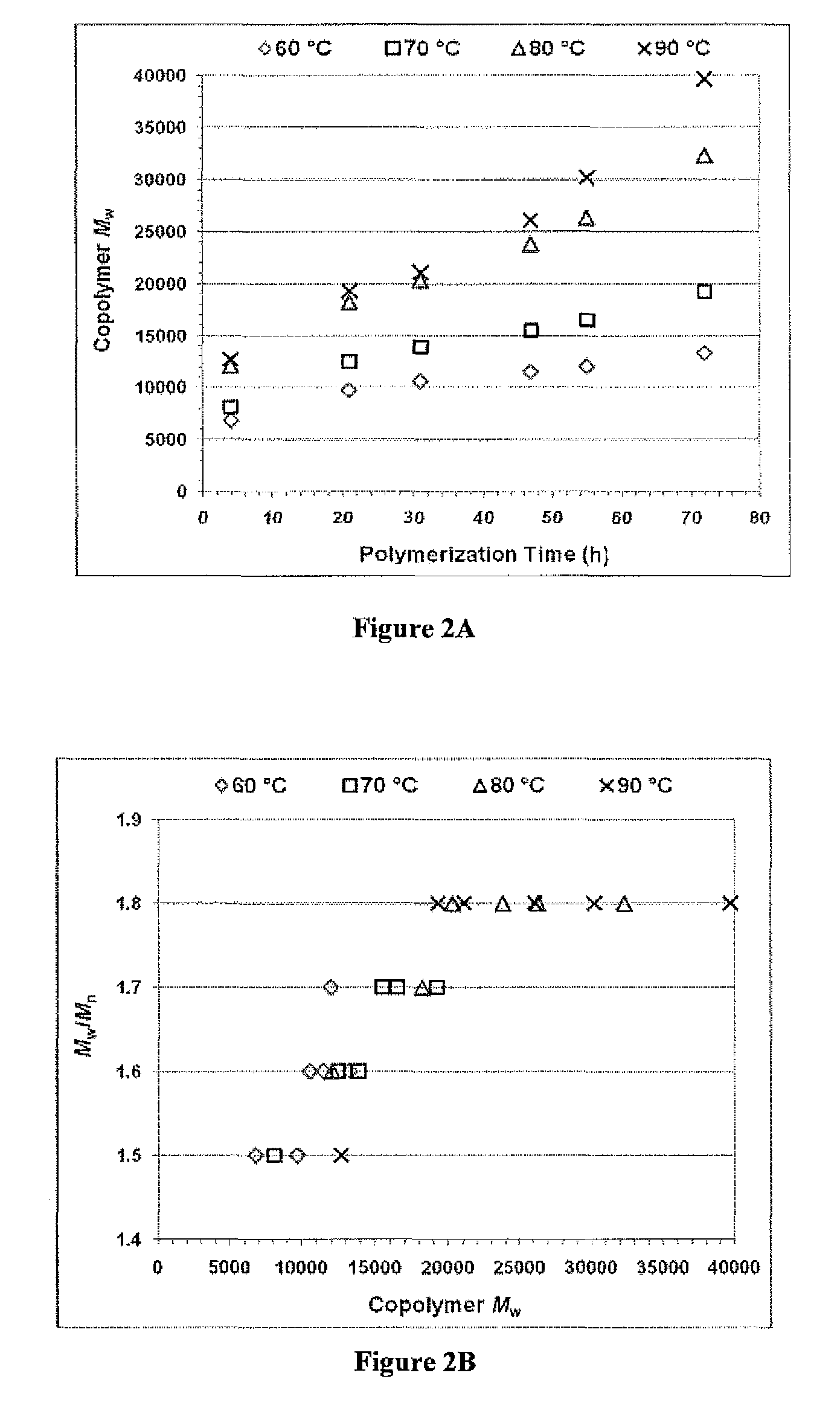
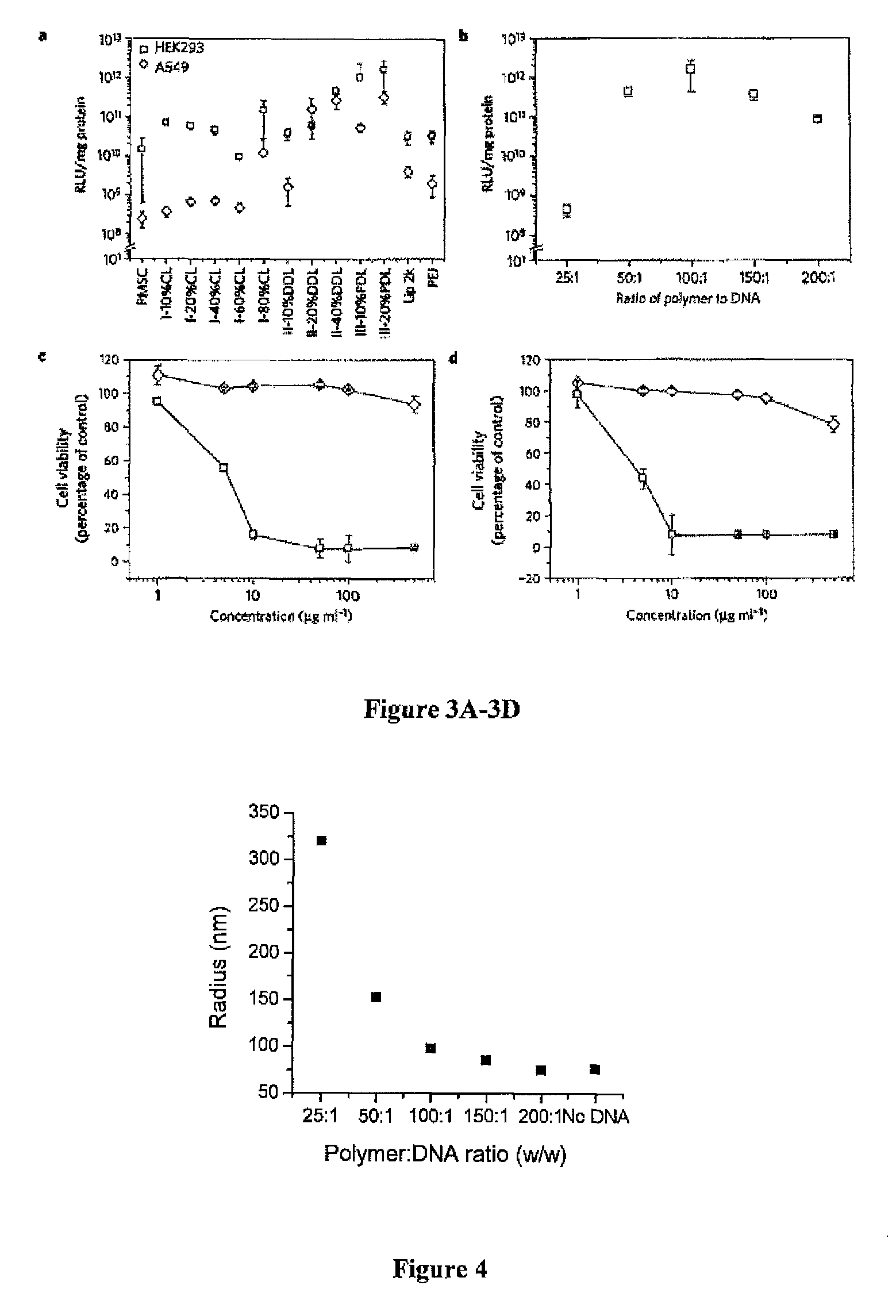
Enzymatic synthesis of poly(amine-co-esters) and methods of use thereof for gene delivery
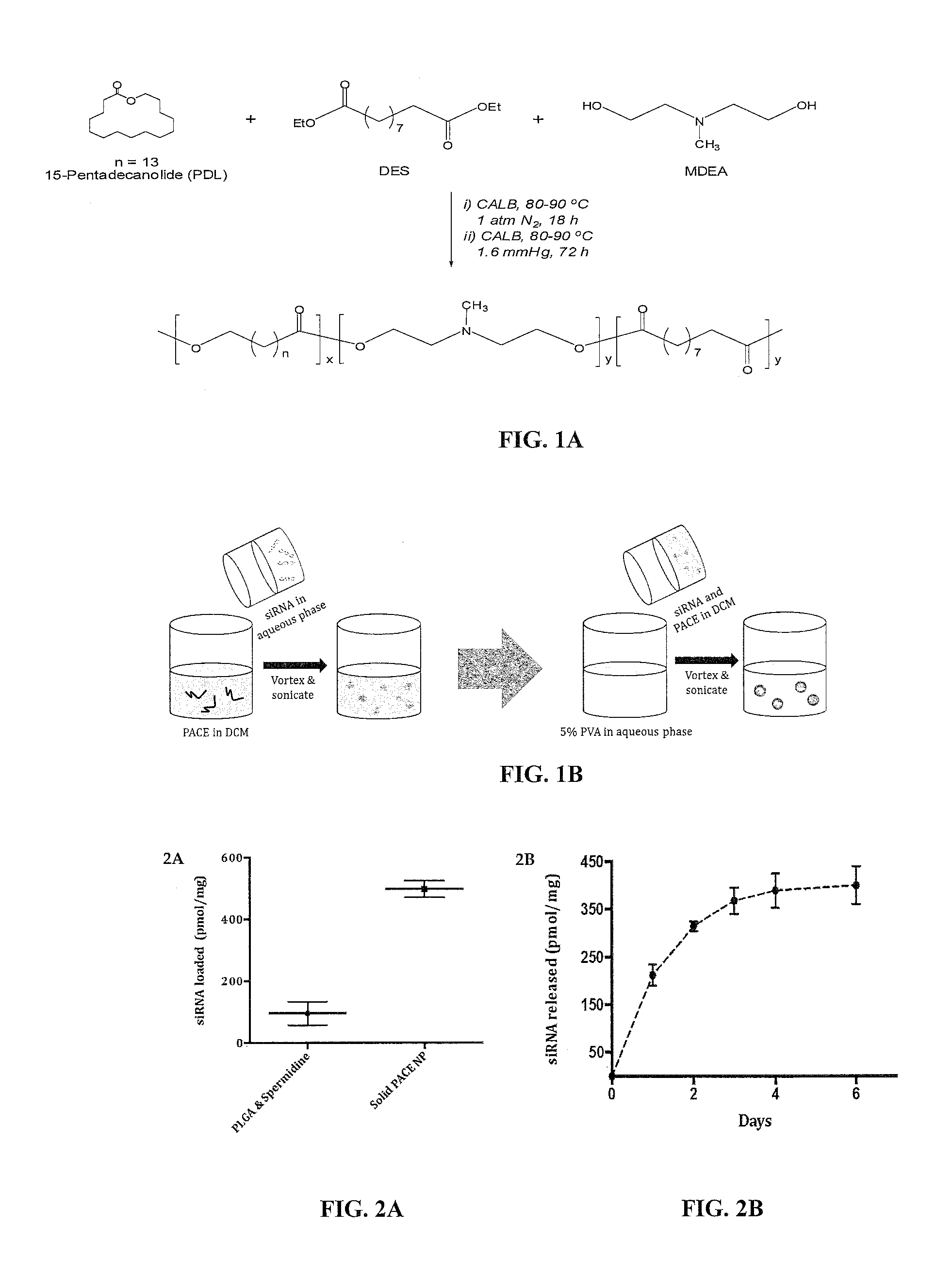
ActiveUS20140342003A1Improve efficiencyMaterial efficiencyPowder deliveryBiocideDiseaseEnzymatic synthesis
Poly(amine-co-ester) polymers, methods of forming active agent-load nanoparticles therefrom, and methods of using the nanoparticles for drug delivery are disclosed. The nanoparticles can be coated with an agent that reduces surface charge, an agent that increases cell-specific targeting, or a combination thereof. Typically, the loaded nanoparticles are less toxic, more efficient at drug delivery, or a combination thereof compared to a control other transfection reagents. In some embodiments, the nanoparticles are suitable for in vivo delivery, and can be administered systemically to a subject to treat a disease or condition.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Formulations for targeted release of agents to low ph tissue environments or cellular compartments and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20150073041A1Easy to optimizeEfficient deliveryOrganic active ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesCell specificActive agent
Polyamine-co-ester-co-ortho ester) polymers, methods of forming active agent-load nanoparticles therefrom, and methods of using the nanoparticles for drug delivery are disclosed. The nanoparticles can be coated with an agent that reduces surface charge, an agent that increases cell-specific targeting, or a combination thereof. Typically, the loaded nanoparticles are less toxic, more efficient at drug delivery, or a combination thereof compared to a control or other transfection reagents.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Recombinant adeno-associated virus-NADH dehydrogenase sigmasubunit 4 gene total length for treating Leber hereditary optic neuropathy and medicament
ActiveCN104450747AHigh expressionImprove the effect of treatmentSenses disorderNervous disorderNADH dehydrogenaseAdeno associate virus
The invention discloses a recombinant adeno-associated virus-NADH dehydrogenase sigmasubunit 4 gene total length for treating Leber hereditary optic neuropathy and a medicament. The total length of the gene is shown in a nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO:1, wherein the nucleotide sequence, consisting of a CAG starter sequence, a coded sequence of ND4 of a mitochondrial localization sequence with Cox10 and UTR with the length of 625bp, has the total length of 3824bp. The medicament is injected into an eye vitreous chamber and is used for treating Leber hereditary optic neuropathy; because the medicament can be injected into the vitreous chamber, the activity can be kept in the vitreous chamber, and the medicament can be effectively subjected to transfection to optic nerve cells; signal peptide at the front end of the protein N directionally guides the protein to enter mitochondria, and the mature protein ND4 enters the mitochondria to play a function; therefore, the Leber hereditary optic neuropathy can be effectively treated by using the medicine.
Owner:WUHAN NEUROPHTH BIOTECHNOLOGY LTD CO
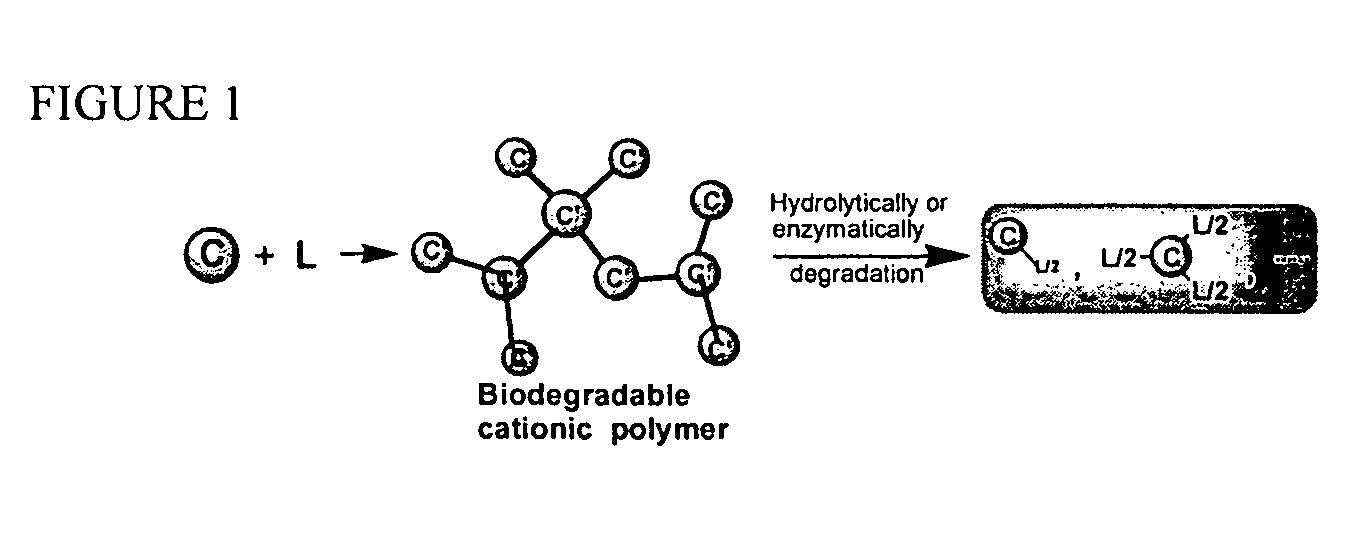
Controllably degradable polymeric biomolecule or drug carrier and method of synthesizing said carrier
InactiveUS20060147376A1Efficient transfectionMinimize cell damagePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptideDrug
The present invention provides a controllably degradable cationic polymer for delivery of biomolecules (nucleic acids, peptides, etc.), drugs, molecules used in medical imaging applications, sensitizing agents used in cancer treatments, and molecules used in tissue engineering. The present invention also provides a method for synthesizing the polymer according to the present invention.
Owner:YU LEI +3
Raav expression systems for genetic modification of specific capsid proteins
ActiveUS8802080B2Control of numberControl of positionBiocideVirus peptidesTherapeutic proteinPharmaceutical formulation
Disclosed are improved recombinant adeno-associated viral (rAAV) vectors having mutations in one or more capsid proteins. Exemplary vectors are provided that have altered affinity for heparin or heparin sulfate, as well as vectors, expression systems, and rAAV virions that lack functional VP2 protein expression, but are nevertheless, fully virulent. Also provided by the invention are rAAV vector-based compositions, virus particles, host cells, and pharmaceutical formulations that comprise them useful in the expression of selected therapeutic proteins, polypeptides, peptides, antisense oligonucleotides and / or ribozymes in selected mammals, including organs, tissues, and human host cells.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
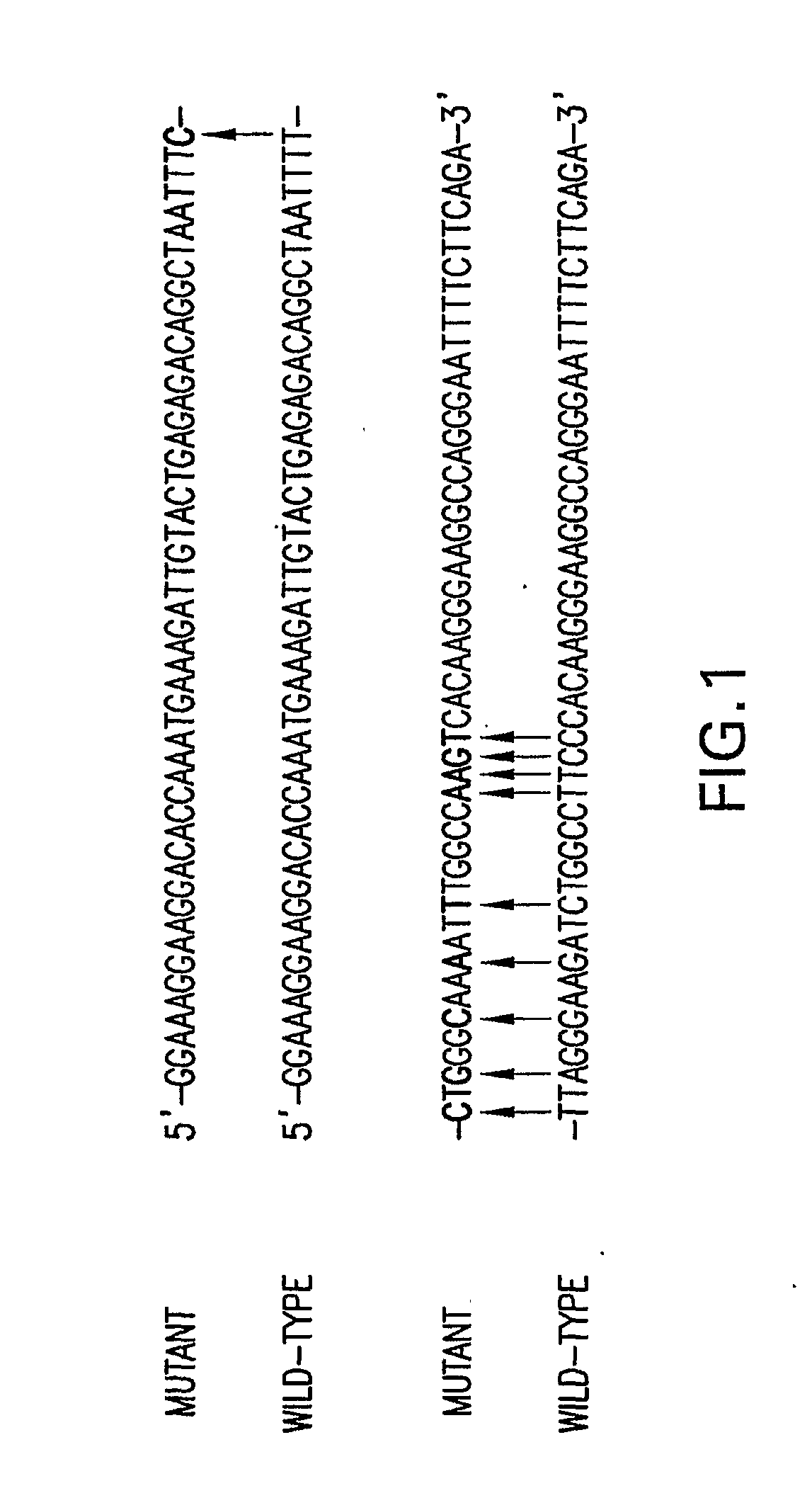
Construction and application of farnesyl pyrophosphoric acid synthetase RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference recombinant lentivirus vector
InactiveCN101805750AOvercoming No Commercial AntibodyOvercoming low transfection efficiencyMetabolism disorderGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseFhit gene
The invention provides the construction for a farnesyl pyrophosphoric acid synthetase RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) interference recombinant lentivirus vector, which comprises the following steps of: sieving the most effective target sequence of an FDS (farnesyl diphosphate synthase) gene RNAi (RNA interference) in a tool cell 293T cell, synthesizing the double-stranded DNA of the most effective target sequence, connecting to a pGCSIL-GFP vector and successfully constructing the recombinant vector through enzyme cutting, sequencing and identification. Researches indicate that the constructed RNA interference vector LV-sh-FDS can downwards modulate the expression of an FDS mRNA (Messenger RNA) level in a neonatal rat cardiac myocyte, simultaneously can downwards modulate the expression of myocardial hypertrophy markers such as cell areas and marker genes beta-MHC (Myosin Heavy Chain) and BNP (Brain Natriuretic Peptide), additionally can effectively inhabit the activity of RhoA while downwards modulating the FDS, can be applied in preparing medicaments for treating myocardial hypertrophy diseases and also can be applied in preparing medicaments for cholesterol metabolic control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
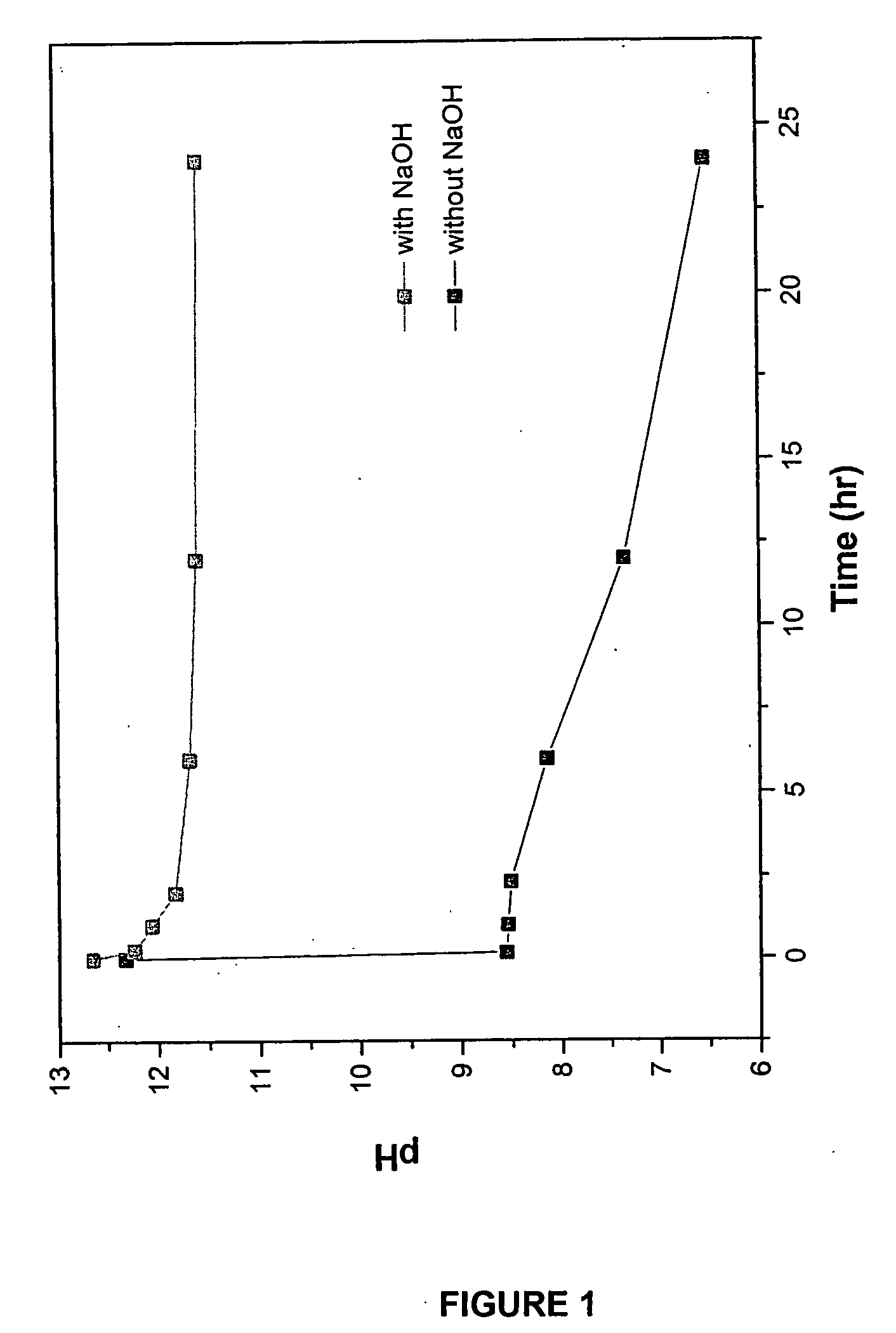
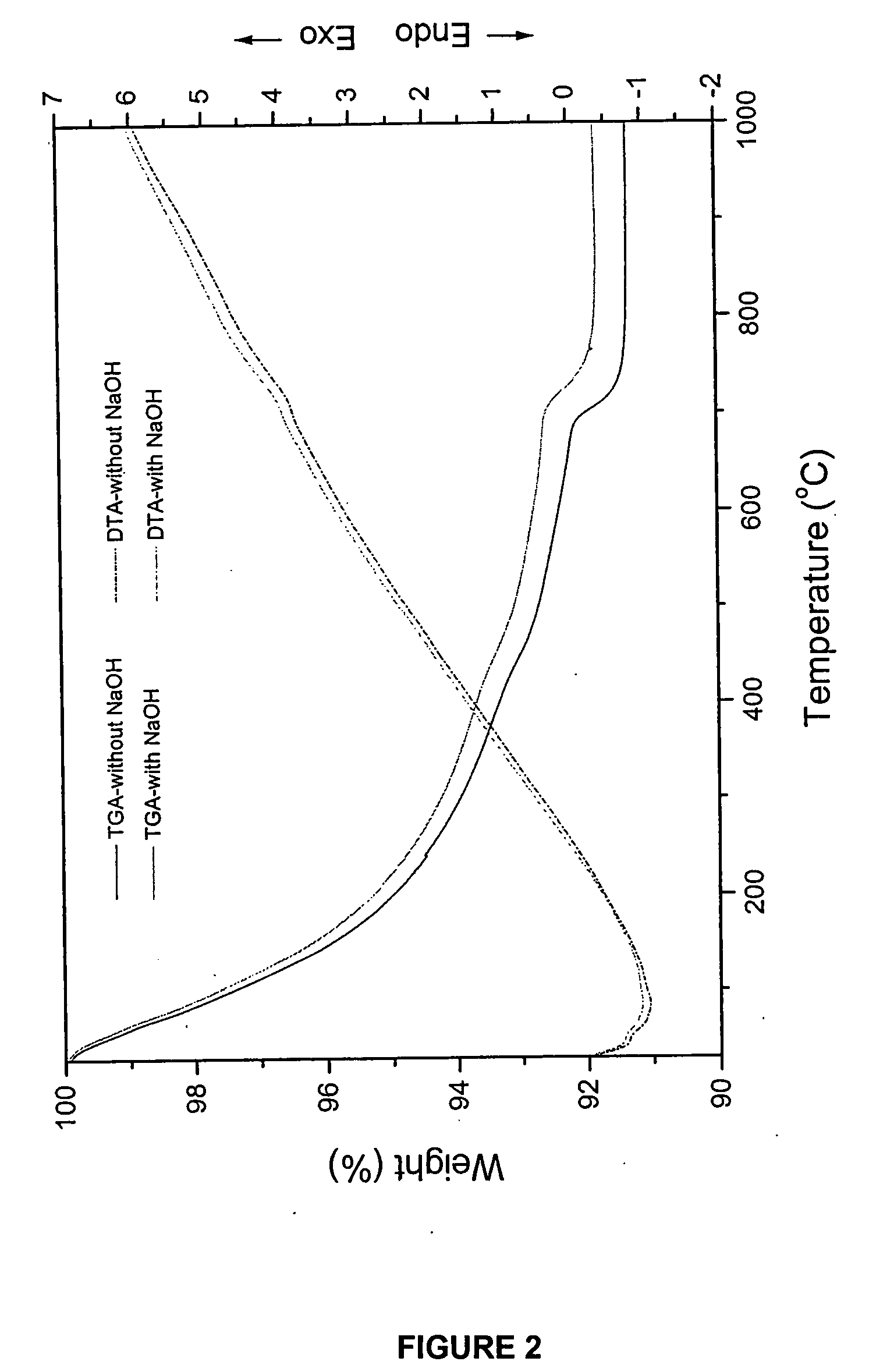
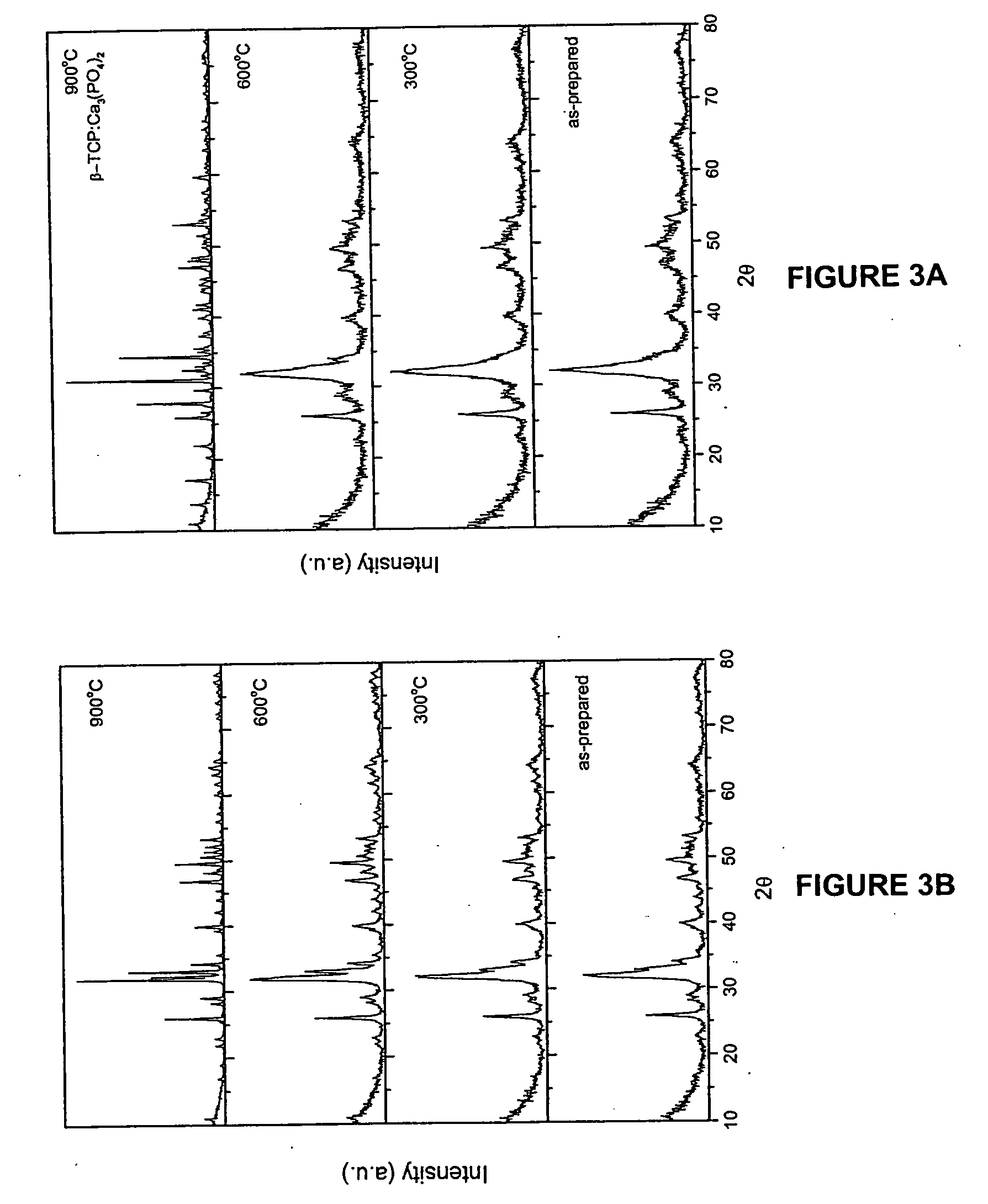
Method of manufacturing hydroxyapatite and uses therefor in delivery of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20080095820A1High transfection efficiencyEfficient transfectionBiocidePhosphatesCalcium biphosphateCalcium hydroxylapatite
Provided is a method for production of nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite particles, and nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite particles produced according to the method. The nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite particles exhibit substantially superior cell transformation abilities as compared to known and commercially-available calcium phosphate kits. The nanocrystalline hydroxyapatite particles also find use in tissue engineering applications, for example bone and tooth engineering and repair applications.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Compositions and Methods Related to Controlled Gene Expression Using Viral Vectors
InactiveUS20090210952A1Significant advanceEfficient delivery and controlled expression of geneAntiviralsNucleic acid vectorViral vectorGenetically modified mouse
Provided herein are methods and compositions related to viral vectors. Also provided herein are methods and compositions for the efficient transfection of a host, for example through the highly efficient lentivector delivery system, and for the exquisite control of the timing and level of expression of the transferred sequence of interest by the simple administration of a modulator to the host harboring the transferred sequence of interest. Also disclosed are methods of making transgenic mice and transgenic mice made using compositions and methods relating to viral vectors.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Phenyloboricacid-modified cationic polymer and composite method and application thereof
InactiveCN101597349AEffective combinationFree from degradationVector-based foreign material introductionPolymer scienceCationic polymerization
The invention discloses a phenyloboricacid-modified cationic polymer, the structural formula is that (see lower right): wherein R is H or alkyl group containing one to ten carbons or substitution alkyl group containing nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, chlorine, bromine or iodine; P is cationic polymer, the molecular weight Mw of P is from 400 to 500000, and n is more than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 20. The preparation method is that: the phenyloboricacid with active groups and the cationic polymer are dissolved in methyl alcohol in N, N-dimethyl fomamide, and are reacted for 2-48 hours at the temperature of 20-60 DEG C for obtaining the phenyloboricacid-modified cationic polymer. The cationic polymer utilizes functional groups such as hydroxide radical and amino-group and the like in biomacromolecules such as phenyloboricacid group energy, protein, amylase, nucleic acid and the like to form reversible covalent-binding property, and improves the capacity of gene combination and cell carrying of carrier materials, so as to realize high-efficiency transfection of genes.
Owner:常熟紫金知识产权服务有限公司
Compounds and Methods for Reversible Modification of Biologically Active Molecules
InactiveUS20080281074A1Reduce aggregationEfficient transfectionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsIn vivoTransfection
The present invention is directed compounds for reversibly modification of biologically active molecules. Described are polyconjugates systems that incorporate targeting, anti-opsonization, anti-aggregation, and transfection activities into small biocompatible in vivo delivery conjugates. The use of reversible modification provides for physiologically responsive activity modulation.
Owner:ARROWHEAD MADISON
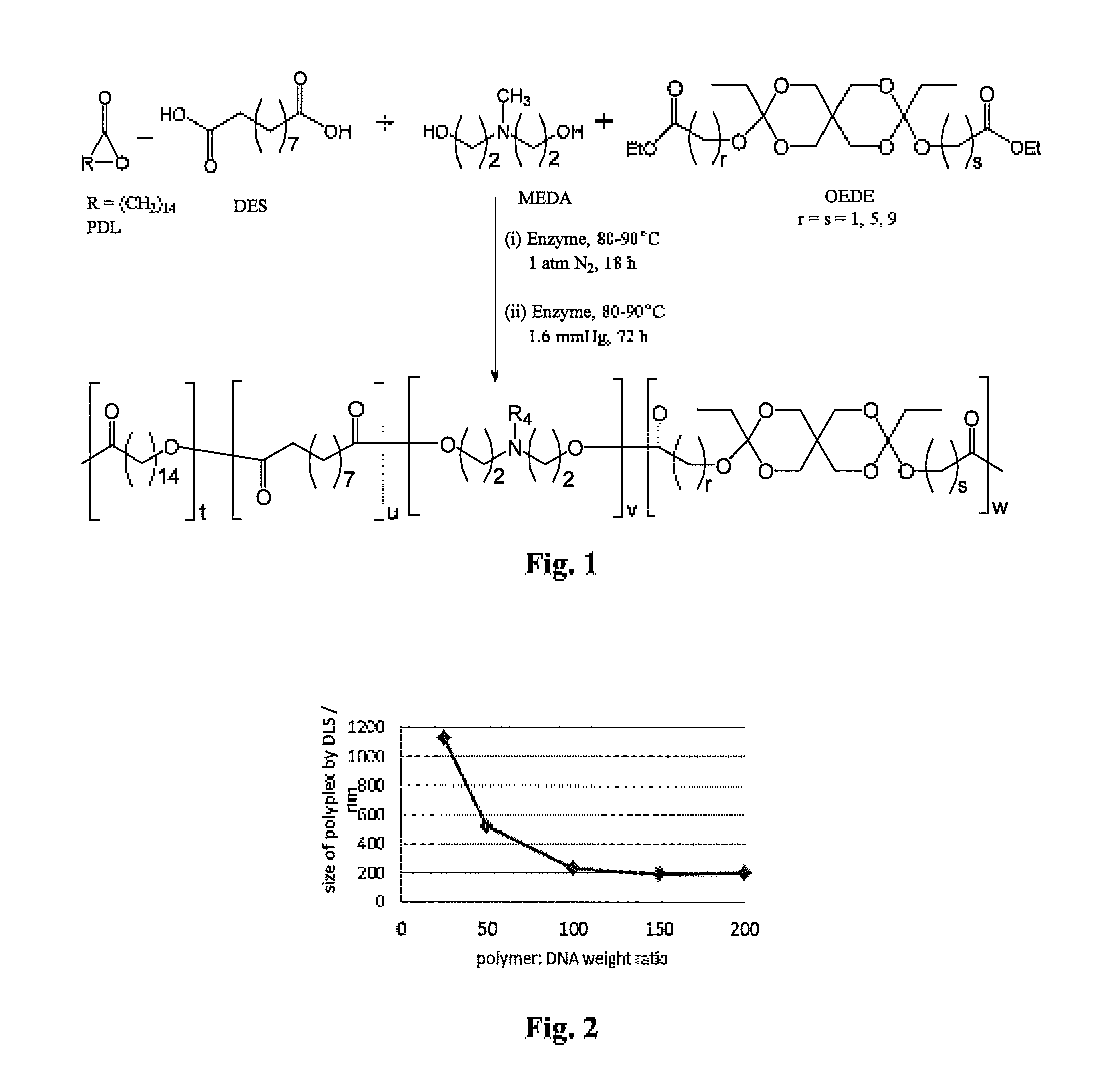
Enzymatic synthesis of poly(amine-co-esters) and methods of use thereof for gene delivery
ActiveUS9272043B2Increase stability and half-lifeImprove targetingOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryDiseaseEnzymatic synthesis
Poly(amine-co-ester) polymers, methods of forming active agent-load nanoparticles therefrom, and methods of using the nanoparticles for drug delivery are disclosed. The nanoparticles can be coated with an agent that reduces surface charge, an agent that increases cell-specific targeting, or a combination thereof. Typically, the loaded nanoparticles are less toxic, more efficient at drug delivery, or a combination thereof compared to a control other transfection reagents. In some embodiments, the nanoparticles are suitable for in vivo delivery, and can be administered systemically to a subject to treat a disease or condition.
Owner:YALE UNIV
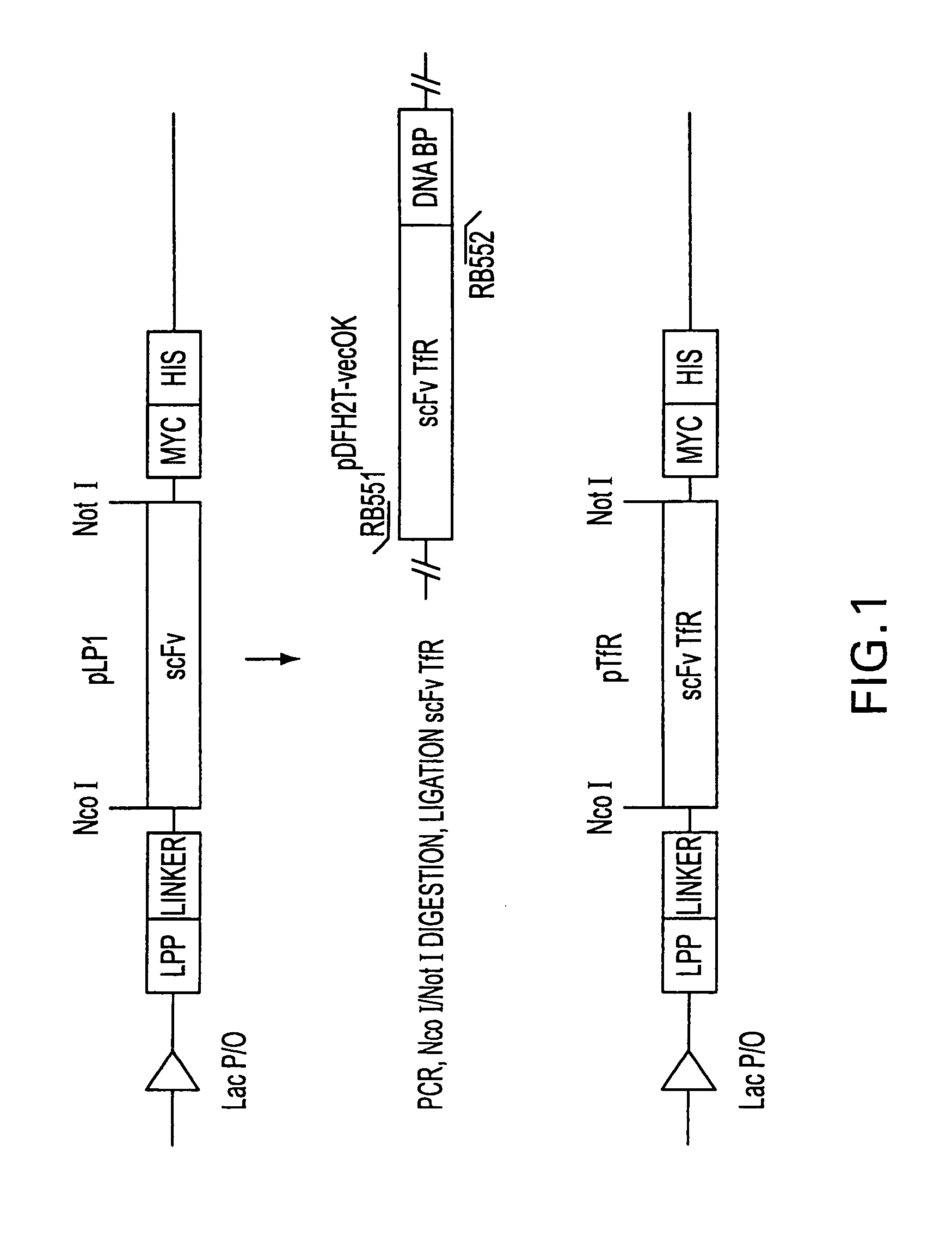
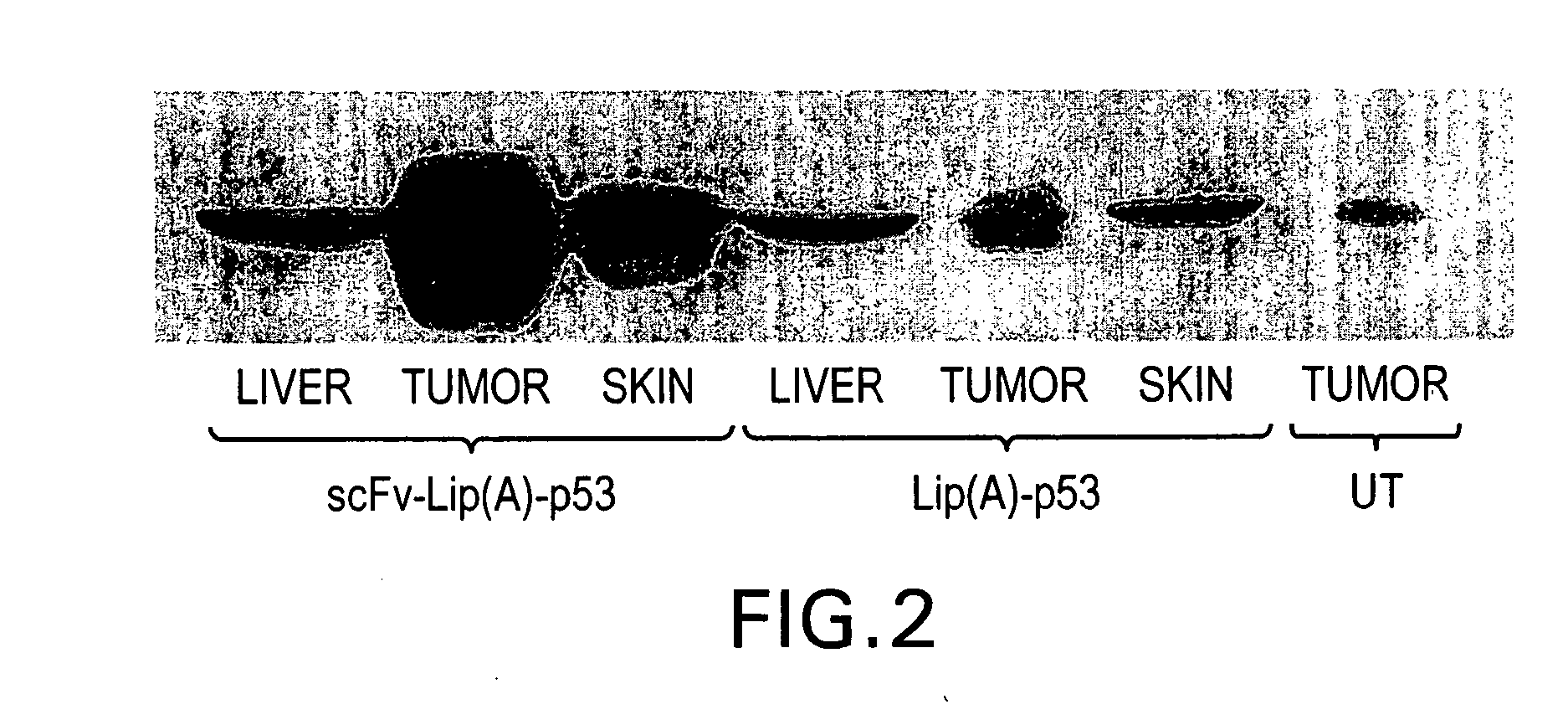
Antibody fragment-targeted immunoliposomes for systemic gene delivery
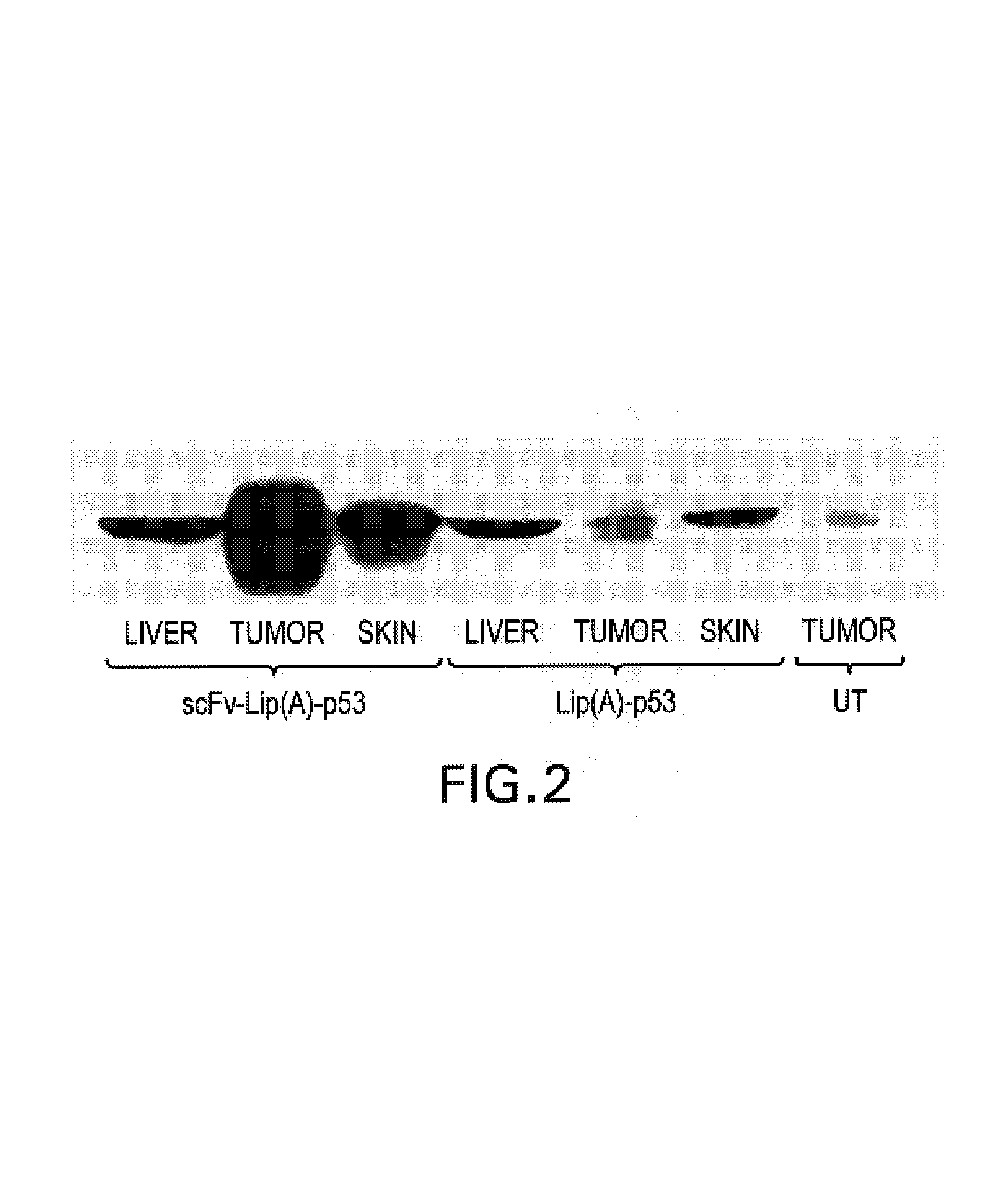
InactiveUS7479276B1Improve the level ofEfficient transfectionVectorsAntibody ingredientsGene deliveryAntiendomysial antibodies
Nucleic acid-immunoliposome compositions useful as therapeutic agents are disclosed. These compositions preferably comprise (i) cationic liposomes, (ii) a single chain antibody fragment which binds to a transferrin receptor, and (iii) a nucleic acid encoding a wild type p53. These compositions target cells which express transferrin receptors, e.g., cancer cells. These compositions can be used therapeutically to treat persons or animals who have cancer, e.g., head and neck cancer, breast cancer or prostate cancer.
Owner:SYNERGENE THERAPEUTICS +1
Materials for the delivery of biologically-active material to cells
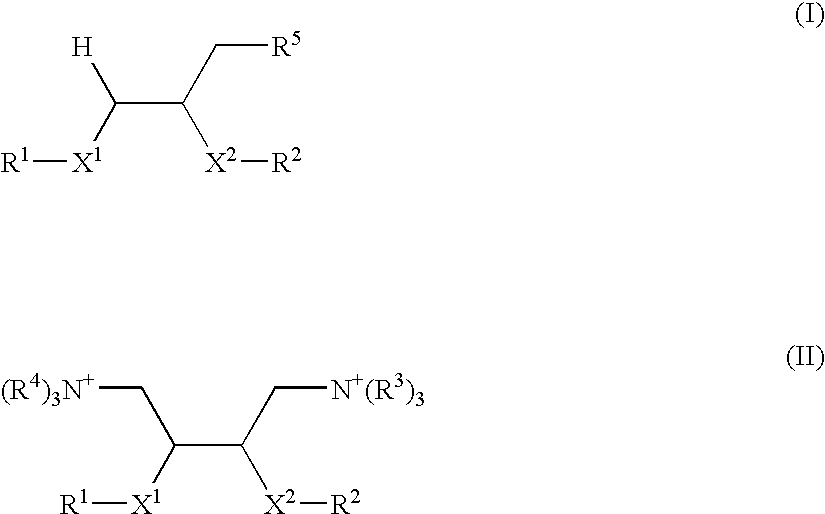
ActiveUS7598421B2Good effectEfficient transfectionCarbamic acid derivatives preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsBinding peptideIntegrin
The invention provides a lipid of general formula (I) or (II):wherein X1, X2 and R1 to R5 are as defined herein. Such lipids are used to form complexes with a biologically-active material such as a nucleic acid, peptide or small molecule for delivering the biologically-active material to cells. The complexes may incorporate an integrin-binding peptide and, when the biologically-active material is DNA, thereby constitute a LID complex.
Owner:RYBOQUIN COMPANY
Nanospearing for molecular transportation into cells
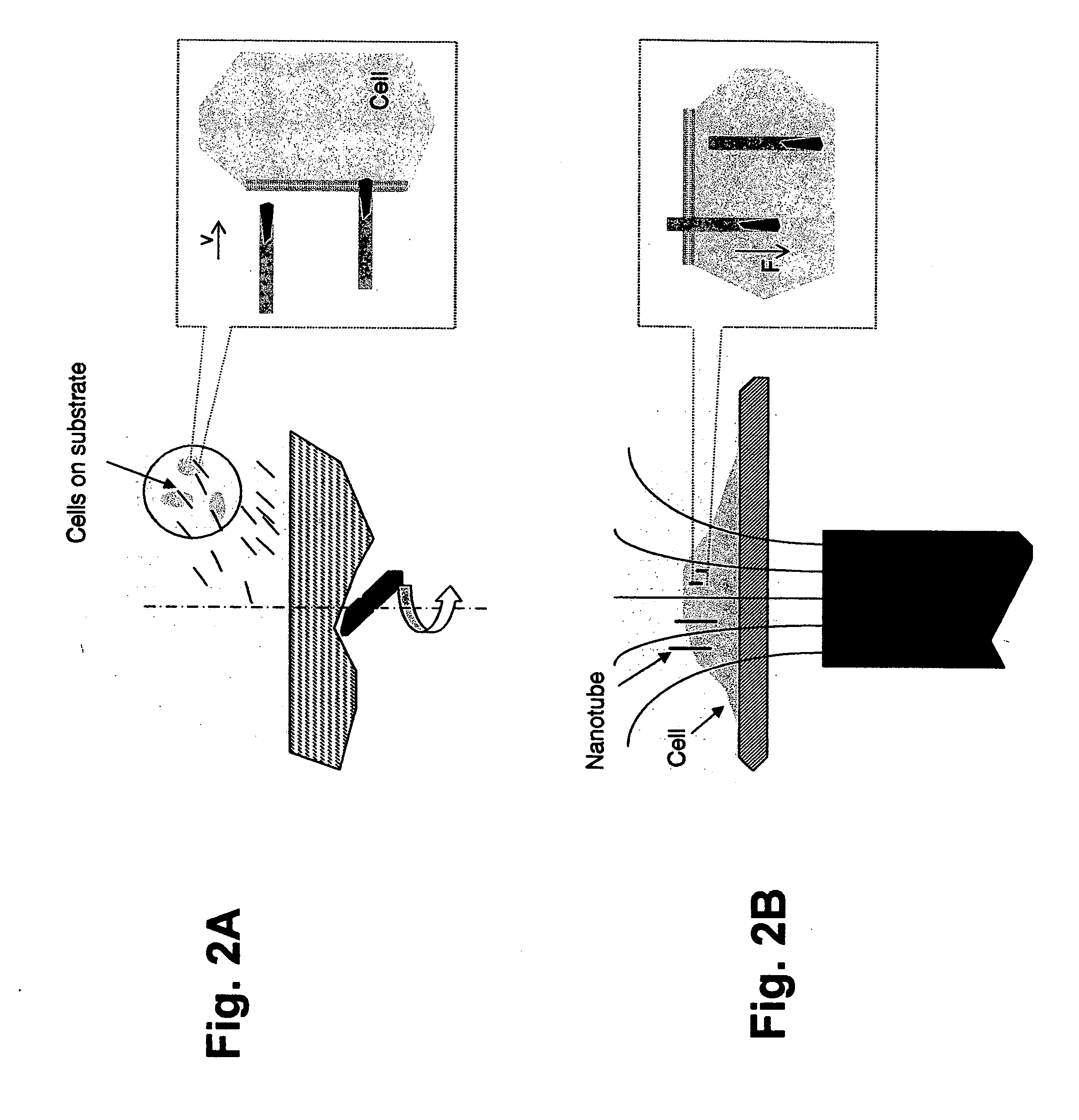
InactiveUS20070231908A1Facilitate easyFacilitate reliable attachmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNanotechVaccinationDelivery vehicle
A nanostructured molecular delivery vehicle comprising magnetic materials and configured to receive passenger biomolecules. The application of a an appropriate magnetic field having a gradient orients and drives the vehicle into a biological target, which may comprise cells, cell masses, tissue slices, tissues, etc. Under the control of the magnetic field, these vehicles can penetrate cell membranes. Then, the biomolecules carried by the vehicle can be released into the cells to perform their functions. Using this “nanospearing” technique, unprecendented high transfection efficiency has been achieved in several difficult-to-transfect cells. These include, but are not limited to, Bal 17 cells, ex vivo B cells, primary cultured cortical neurons, etc. This method advances the state of the art, providing an improved technique for the introduction of exogenous molecules to cells, with the clinical applications including, but not being limited to, drug delivery, gene therapy, vaccination, etc.
Owner:NANOLAB
Poly(amine-co-ester) nanoparticles and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20160251477A1Improve packaging efficiencyIncrease in nucleic acid loadingOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryCrystallographyNanoparticle
Polymers including poly(amine-co-ester), poly(amine-co-amide), or a combination thereof, and nanoparticles, particularly solid core nanoparticles, formed therefrom are provided. Solid core nanoparticles fabricated from hydrophobic polymers often require the presence of cationic complexing agents to stabilize negatively charged active agents such as siRNA. However, complexing agents are optional in the disclosed formulations because the nanoparticles contain cationic amines to stabilize negatively charged nucleic acids and hydrophobic domains to condense the nucleic acid into the core of the formed nanoparticles, thus improving encapsulation efficiency. This increase in nucleic acid loading allows the disclosed solid core nanoparticles to deliver more nucleic acid per cell without increasing total polymer delivered, further reducing cytotoxicity. Pharmaceutical compositions including an effective amount of the nanoparticles are also provided, and be used, for example, for in vitro and in vivo delivery of nucleic acids.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Genetic medicine for preventing and treating cancer of colon and rectum, preparation process and use thereof
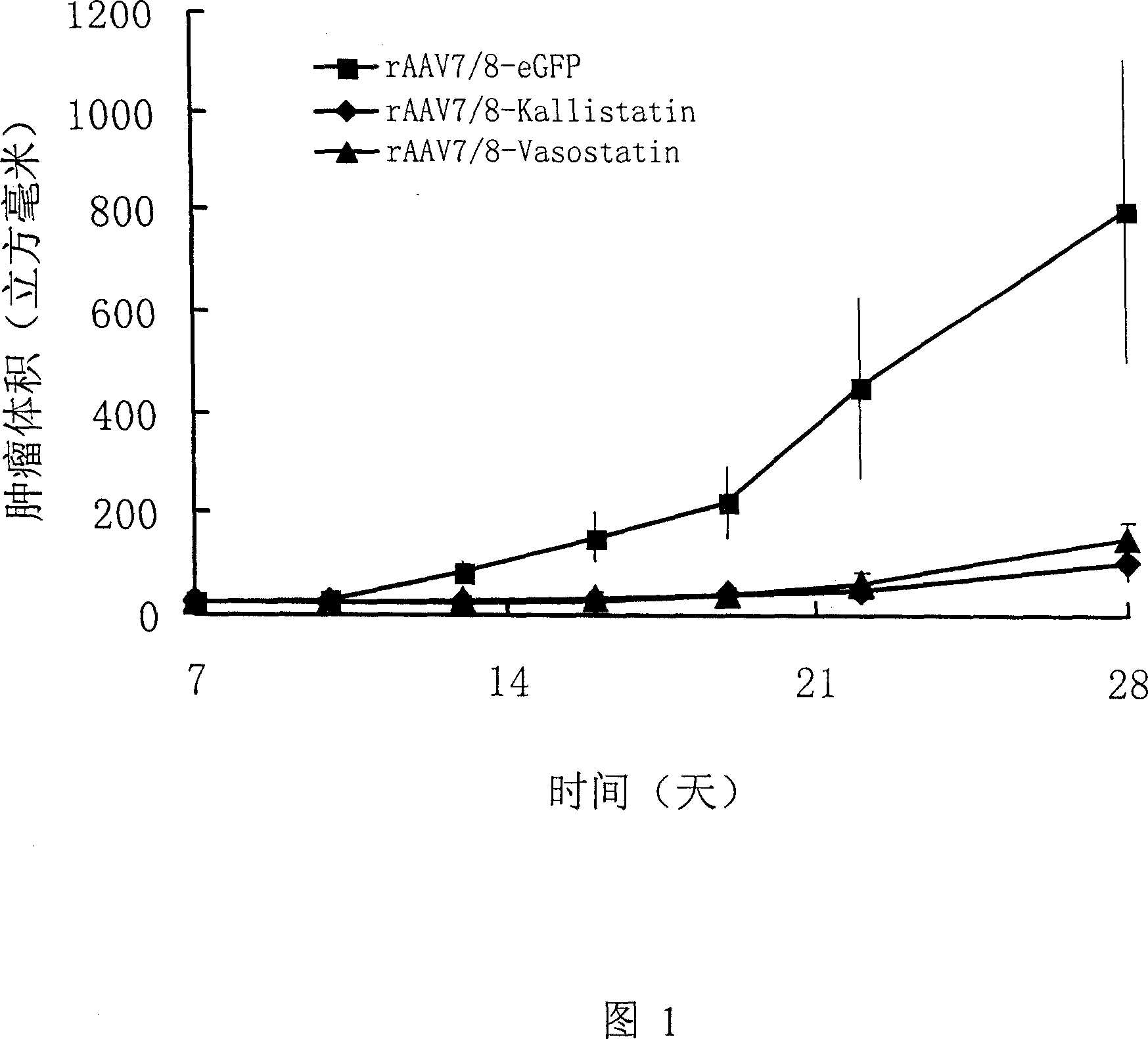
InactiveCN1966082AEfficient transfectionConvenient route of administrationGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsKallistatinOncology
The invention relates to a gene drug based on genes as kallistatin and vasostatin, to treat carcinoma of colon, wherein it also provides relative application to improve treatmene effect. The carrier of genes is adenovirus (AAV), while the best one is AAV7 / 8. The inventive drug can be made into injection or dried powder, and it can be injected into muscle.
Owner:许瑞安 +2
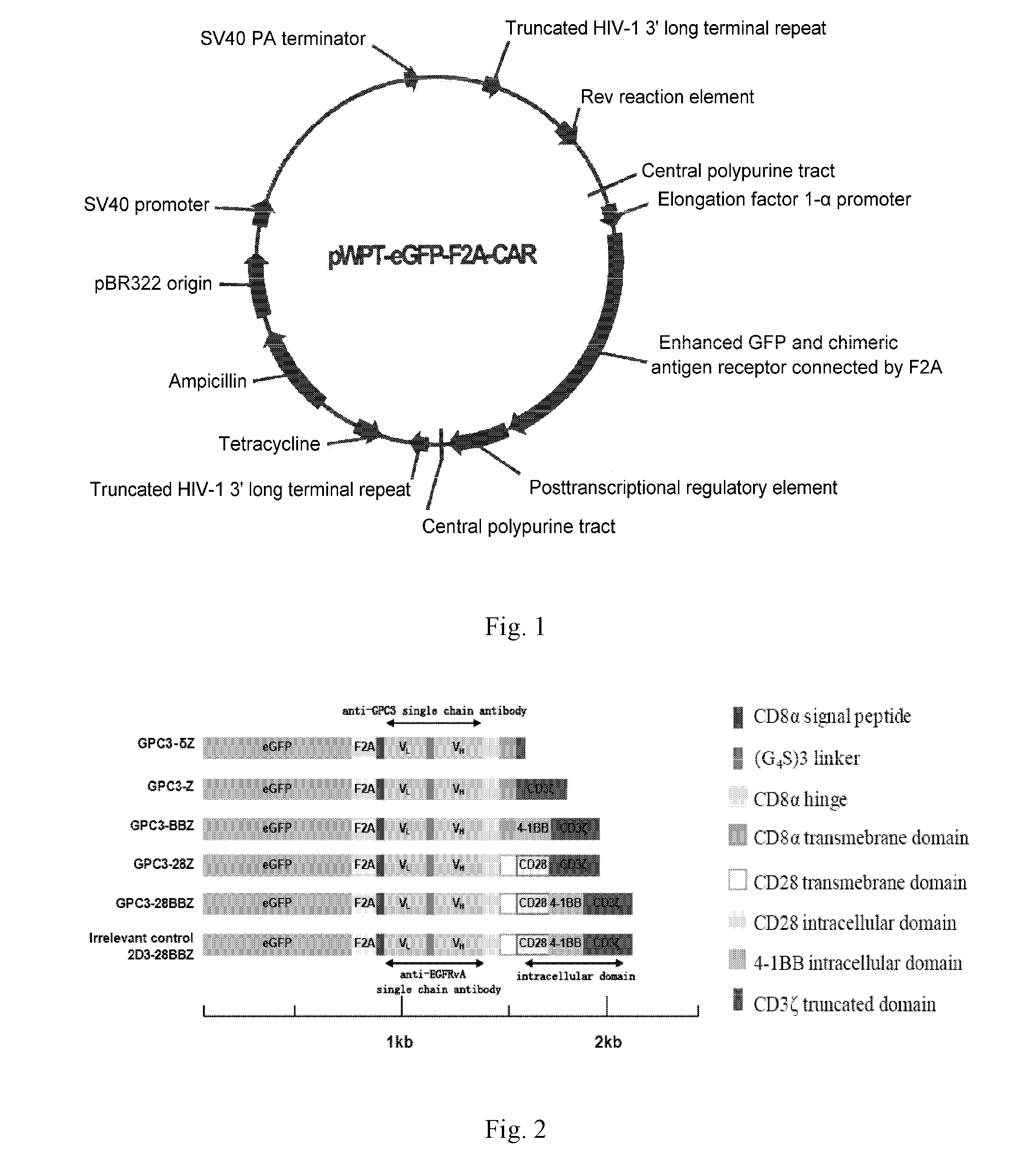
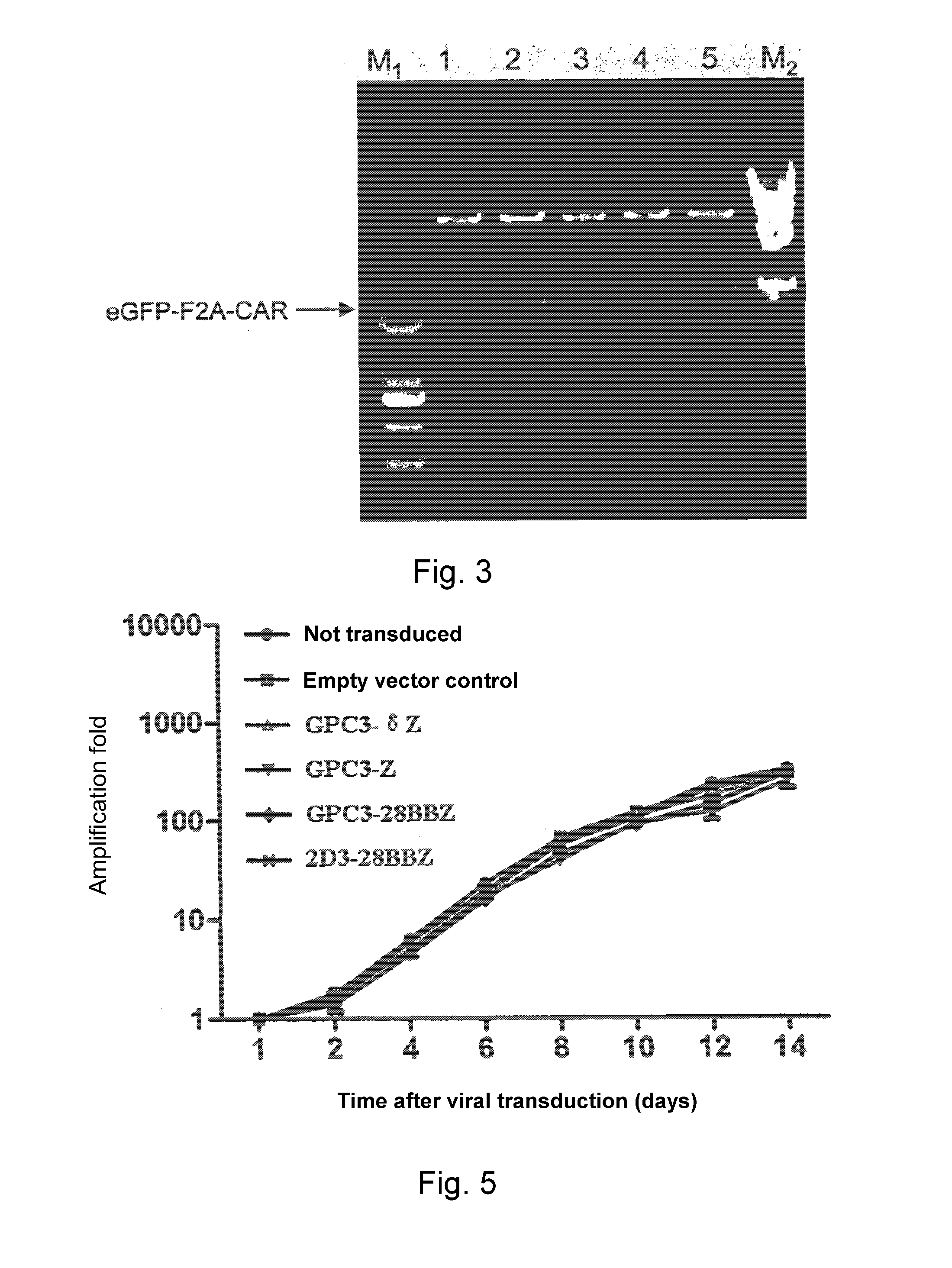
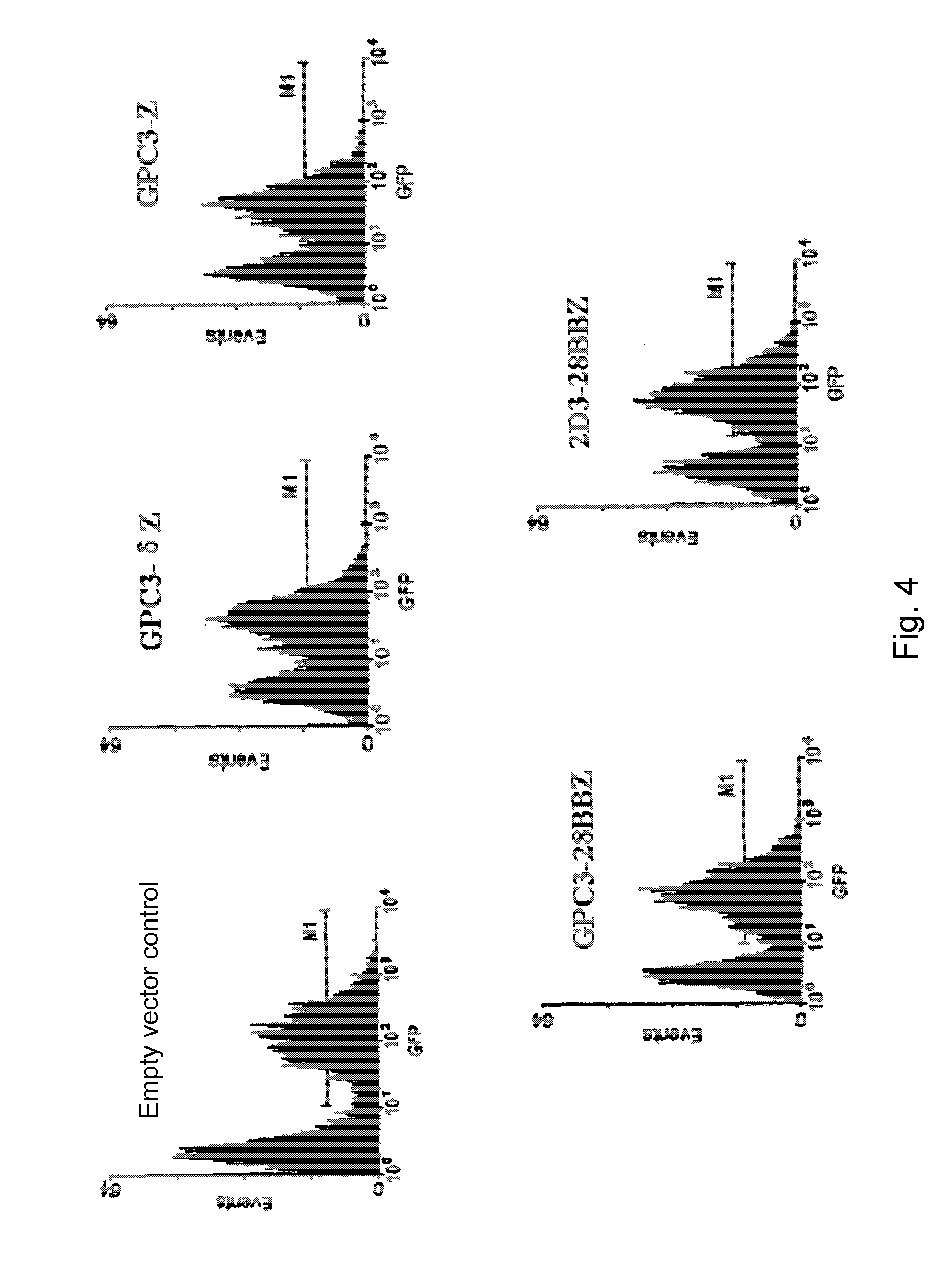
Nucleic Acid Of Coded GPC3 Chimeric Antigen Receptor Protein And T Lymphocyte Expressing GPC3 Chimeric Antigen Receptor Protein
ActiveUS20160215261A1Improve the level ofGood effectPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyIntracellular signallingSingle-Chain Antibodies
A nucleic acid encoding a chimeric antigen receptor expressed at surface of a T lymphocyte, said chimeric antigen receptor comprises, connected in the order of, an extracellular binding domain, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular signaling domain, wherein the extracellular binding domain comprises a single chain antibody, scFv(GPC3), which specifically recognizes the C-terminal epitope of GPC3. A genetically modified T lymphocyte having a chimeric antigen receptor expressed at surface thereof, and the chimeric antigen receptor is expressed by the nucleic acid described above.
Owner:CRAGE MEDICAL CO LTD
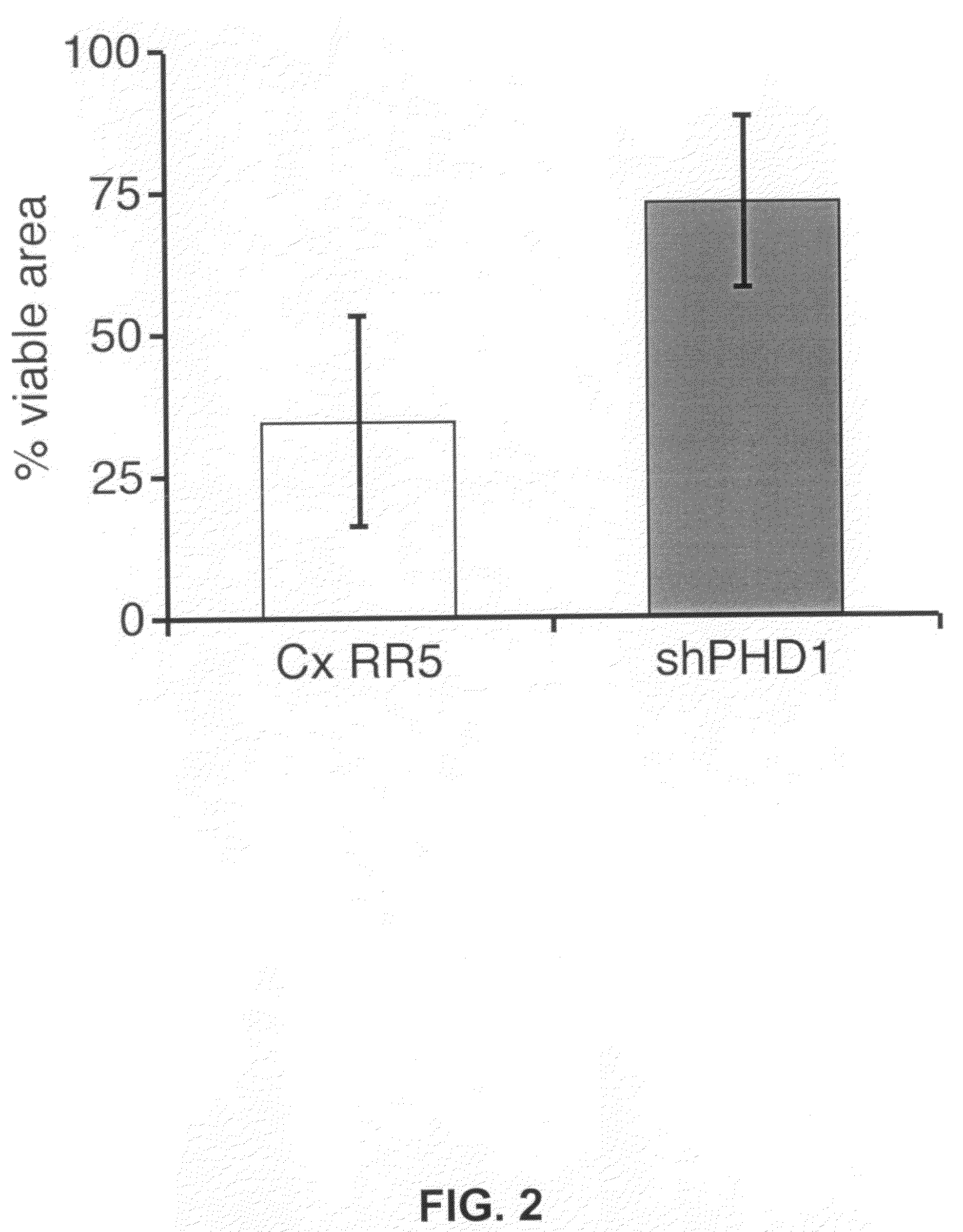
Inhibitors of prolyl-hydroxylase-1 for the treatment of skeletal muscle degeneration
InactiveUS7858593B2Efficient transfectionImprovement in hybridization stabilityBiocideVirusesMuscle involvedSkeletal muscle atrophy
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +1
Materials for the delivery of biologically-active material to cells
ActiveUS20050245446A1Good effectEfficient transfectionCarbamic acid derivatives preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsLipid formationDrug biological activity
The invention provides a lipid of general formula (I) or (II): wherein X1, X2 and R1 to R5 are as defined herein. Such lipids are used to form complexes with a biologically-active material such as a nucleic acid, peptide or small molecule for delivering the biologically-active material to cells. The complexes may incorporate an integrin-binding peptide and, when the biologically-active material is DNA, thereby constitute a LID complex.
Owner:RYBOQUIN COMPANY
Antibody fragment-targeted immunoliposomes for systemic gene delivery
InactiveUS20070065432A1Facilitate conjugationGood useVectorsAntibody ingredientsGene expressionHigh affinity antibody
A targeted vector allowing enhanced gene transfer to human hepato-cellular carcinoma (HCC1) cells in vitro was developed using cationic liposomes covalently conjugated with the mAb AF-20. This high affinity antibody recognizes a rapidly internalized 180 kDa cell surface glycoprotein which is abundantly expressed on the surface of human HCC and other cancer cells. Quantitative binding analysis of liposomes with target cells by flow cytometry showed specific association of mAb-targeted liposomes with human HCC cells. Using mAb-targeted cationic liposomes containing 20% DOTAP, in the presence or absence of serum, gene expression in HuH-7 cells was enhanced up to 40-fold as compared to liposomes conjugated with an isotype-matched non-relevant control antibody. Transfection specificity was not observed in a control cell line that does not express the antigen recognized by mAb AF-20. This study demonstrates that cationic liposome foormulations can be targeted with monclonal antibodies (mAbs) to enhance specific in vitro gene delivery and expression in the presence or absence of serum.
Owner:SYNERGENE THERAPEUTICS +1
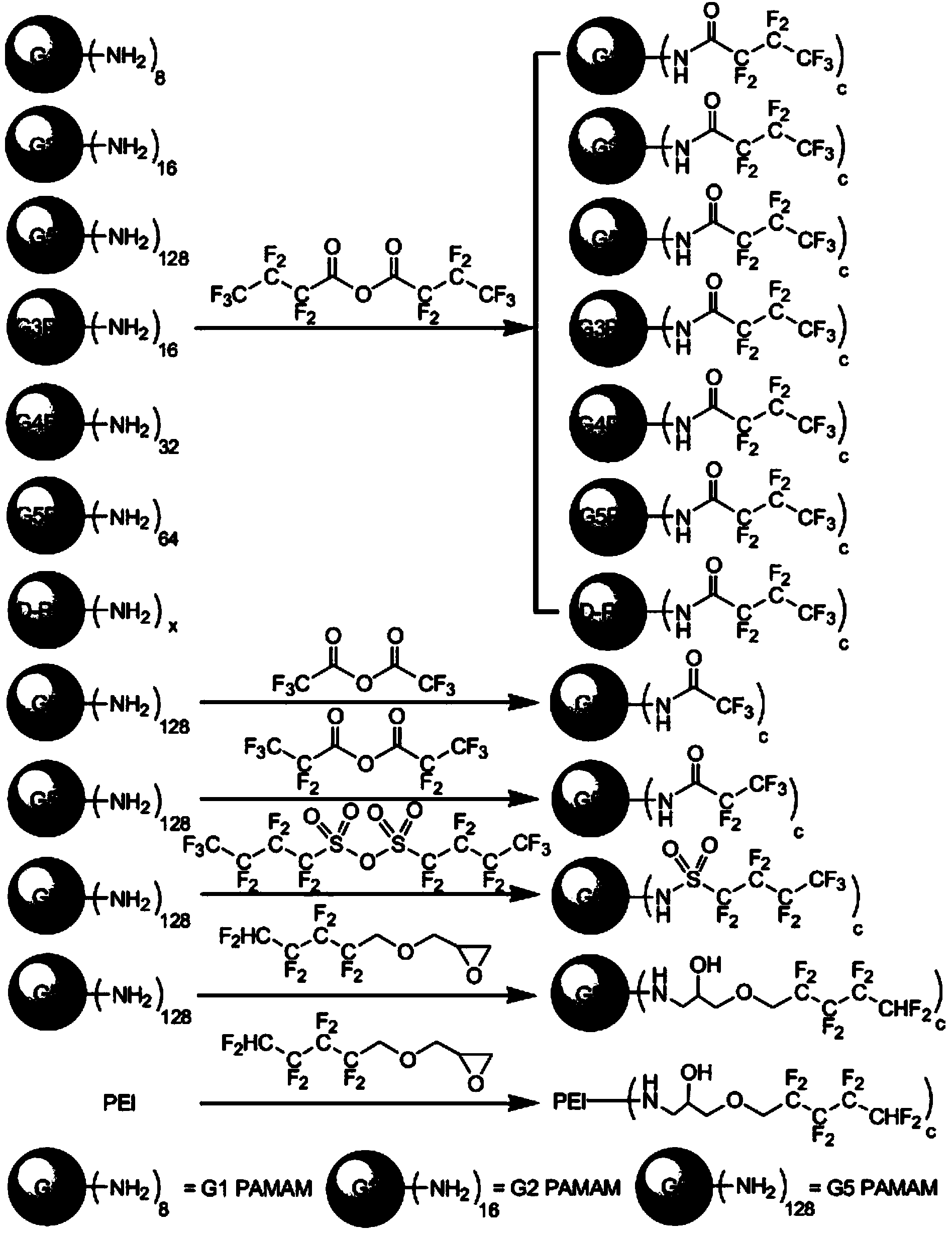
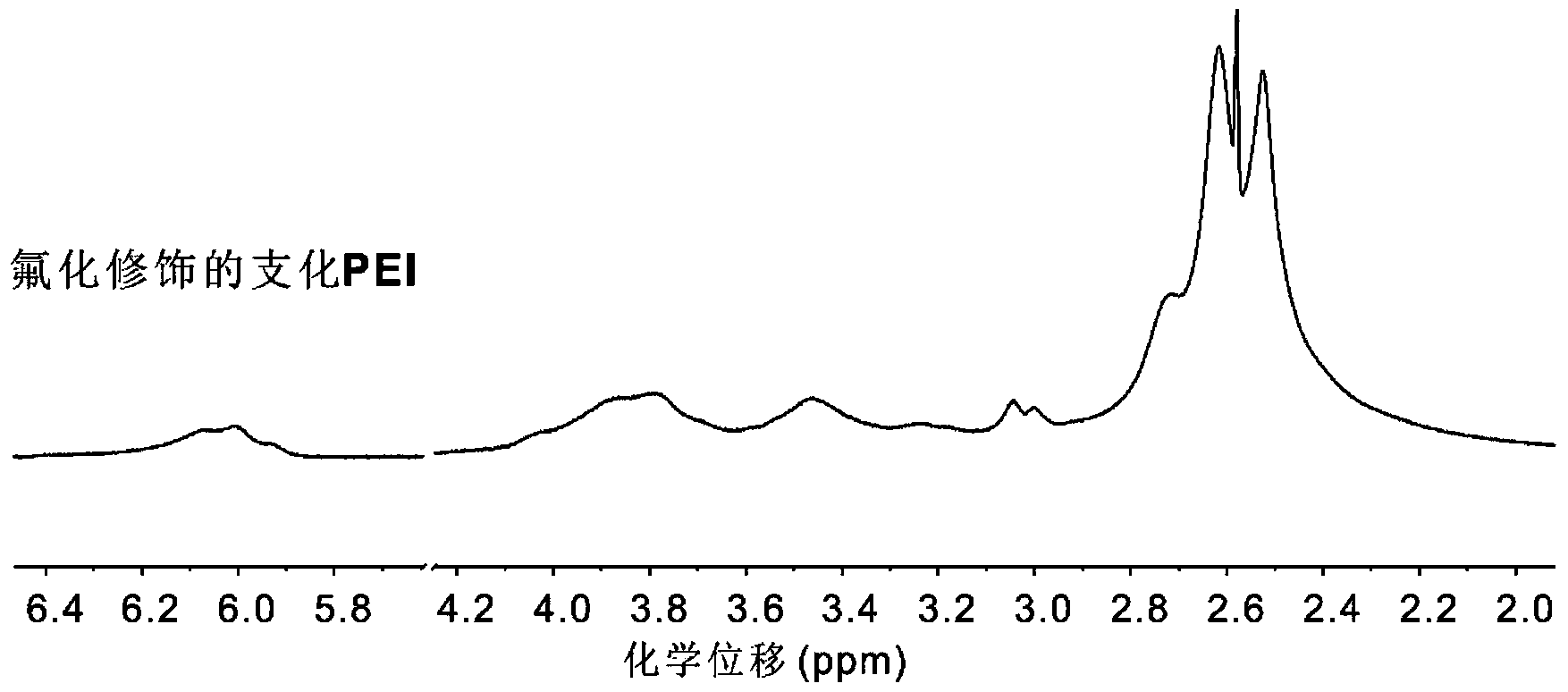
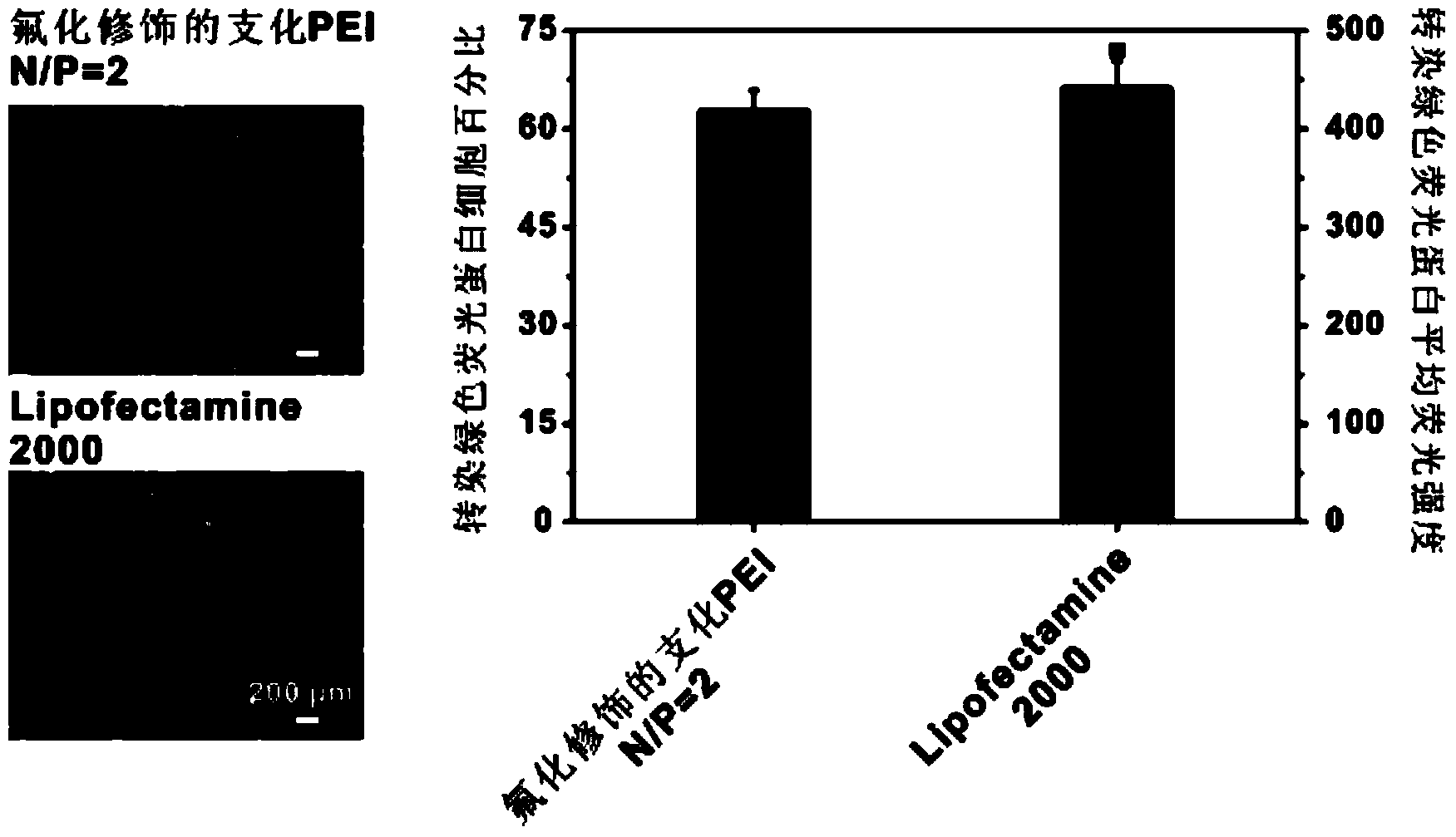
Fluorine-containing aliphatic chain-modified cationic polymer and application of fluorine-containing aliphatic chain-modified cationic polymer as gene carrier
ActiveCN104017828ALow priceEasy to synthesizeOther foreign material introduction processesVector-based foreign material introductionCationic polymerizationPolyamide
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
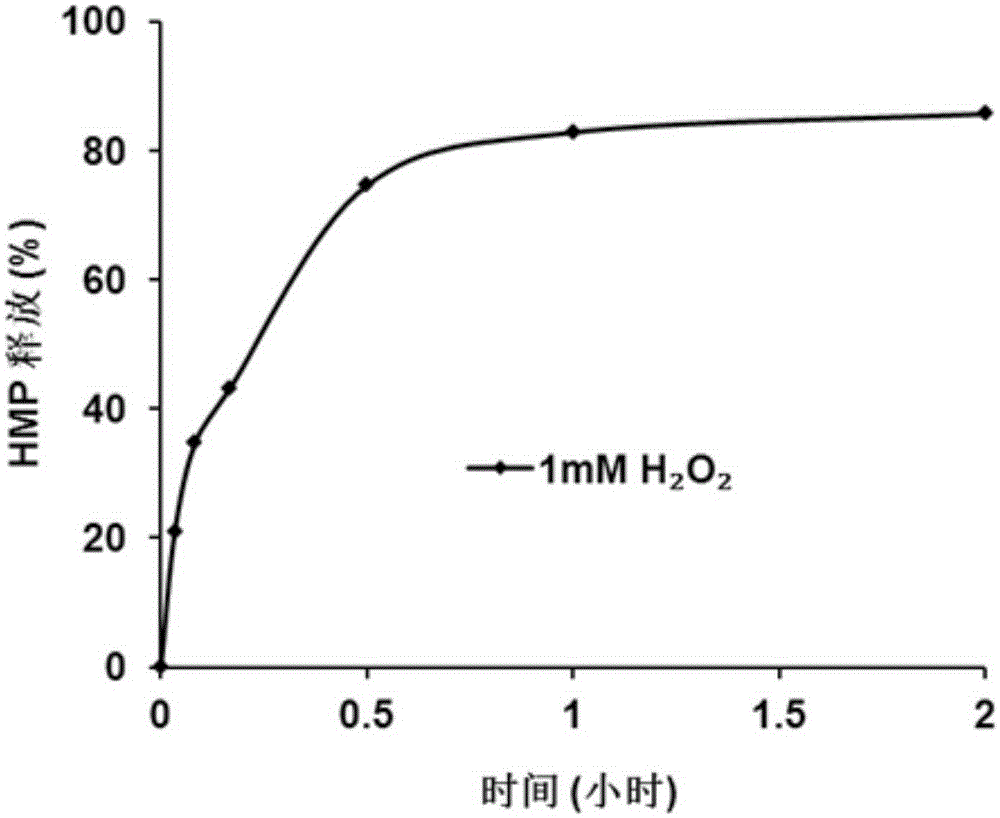
Cation polymer capable of removing positive charges through oxidative response, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105153339ASimple structureEasy to synthesizeGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGene deliveryPhenylboronic acid
The invention discloses a cation polymer capable of removing positive charges through oxidative response, a preparation method and application. The cation polymer is a charge reversal type gene delivery carrier synthesized from 4-(bromomethyl)phenylboronic acid and ethyl (E)-3-diethylaminoprop-2-enoate through quaternary amination. Compared with the prior art, the cation polymer is different from the common quaternary amination carrier; the synthesized charge reversal type gene delivery carrier for oxidative response has a large quantity of positive charges and can well coat a DNA, but the positive charges can be removed under the condition of intracellular oxidation when the charge reversal type gene delivery carrier enters a cell, a charge reverse is triggered (the positive charges turn to negative charges), and the DNA is quickly released for transfection. The charge reversal type gene delivery carrier is efficient, low in toxicity, and good in application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing glutathione response shell disulfide bond crosslinking non-virogene vector
InactiveCN101265477ASimple methodDifferent transfection efficienciesVector-based foreign material introductionHigh concentrationPlasmid dna
The invention discloses a method for preparing a glutathione-response shell disulfide bond crosslinking non-virus gene carrier. The method comprises the following steps: (1) synthesizing sulfhydrylation polyethyleneimine; (2) preparing sulfhydrylation polyethyleneimine aqueous solution with concentration of 0.1-1mg / ml; (3) preparing plasmid DNA solution with concentration of 50-250Mu g / ml; and (4) adding the solution prepared in step (2) to the solution of the same volume prepared in step (3), whirling to mix, standing to obtain sulfhydrylation gene carrier solution, stirring in air, and obtaining the glutathione-response shell disulfide bond crosslinking non-virus gene carrier. Through the preparation of the shell disulfide bond bionic crosslinking non-virus gene carrier, the stability of the gene carrier in physiological salt solution can be improved. The degradation of high concentration reduced glutathione in cells on disulfide bond can release associated DNA molecule so as to realize effective gene transfection.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Positive ion nanostructure lipid carrier, manufacturing method and application thereof
ActiveCN102925487ALow toxicityHigh transfection efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesChemical compoundChain structure
The invention discloses a positive ion nanostructure lipid carrier, a manufacturing method and the application of the positive ion nanostructure lipid carrier. A positive ion nanostructure lipid carrier compound has a structure in a general formula VI, wherein, 3A and A4 are hydrophilic head parts, 3A or A4 is a hydrophilic molecule formed by one or multiple same or different amino acids, and 3A and A4 are the same or different; R is a linking arm between the head part and a tail part and is of a chain-shaped or branched-chain structure; and 3B and B4 are hydrophobic tail parts, 3B or B4 is a chain-shaped hydrophobic molecule, and 3B and B4 are the same or different. The positive ion nanostructure lipid carrier compound disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of simple structure, convenient composition and the like; the positive ion nanostructure lipid carrier compound also has the characteristics of low toxicity and high transfection efficiency, the complicated process in composition is avoided, auxiliary lipidosome in other types is not needed to be used in a transfection process, the operation and the use are easy, thus the positive ion nanostructure lipid carrier compound disclosed by the invention has a potential development prospect of commercial transfection reagent.
Owner:BEIJING INTELLIGENE BIOTECH LTD CO
Functional dendritic polymer gene vector system of targeted malignant cerebroma
InactiveCN101337076AGrowth inhibitionEfficient transfectionGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsCyclic peptidePolyamide
The invention relates to a functionalized arborescent macro radical carrier system for targeting malignant cerebroma. The functionalized arborescent macro radical carrier system is obtained by taking one or more of the following combinations as the targeting functional factor: transferrin and transferrin monoclonal antibody, or polyclonal antibody, folic acid (FA) and epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody, or polyclonal antibody and RGD cyclic peptide, chemically connecting the combinations to arborescent macro radical polyamide-amine (PAMAM) carrier system, and then compounding the combinations with treatment factor oligonucleotide, siRNA molecule or plasmid DNA. Through intra-tumor stereotactic injection, carotid injection or tail vein, the distribution of genes in the malignant cerebroma can be improved, high expression can be realized, and the effective cerebroma inhibition can be realized. Compared with the commercialized gene carrier Oligofectamin and unmodified PAMAM, the FA-PAMAM can remarkably improve the targeting delivery ability of the in vitro and in vivo genes.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Method for preparing cells carrying exogenous molecules in photoinduced perforating mode, base material for preparing cells and cells
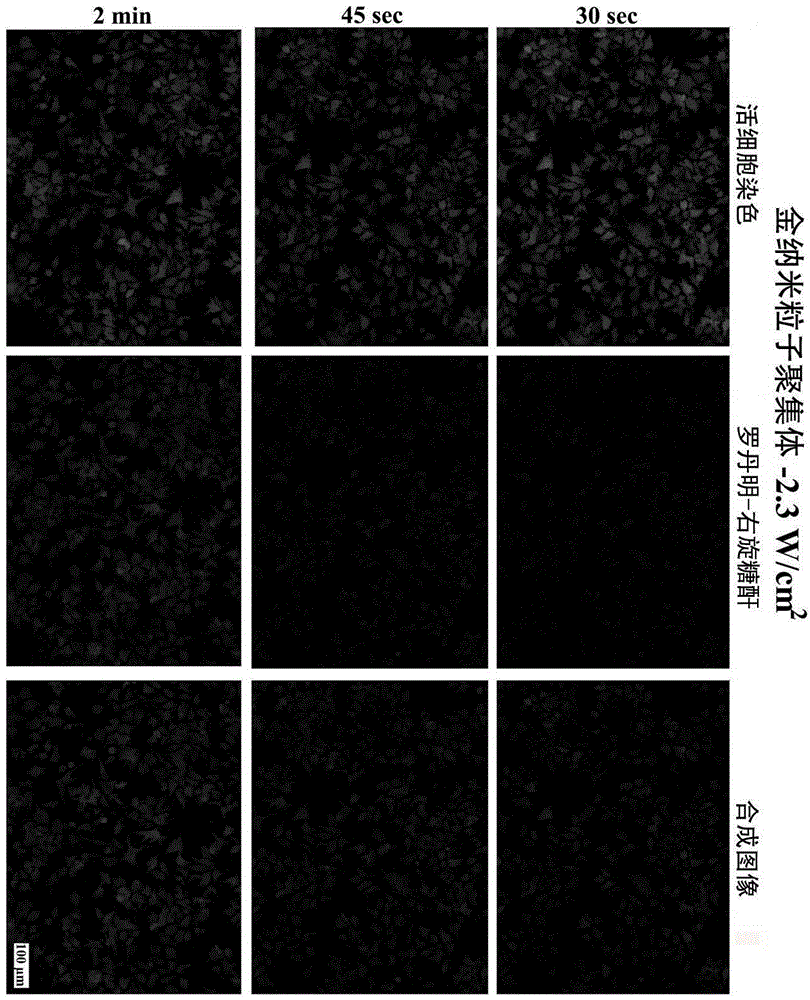
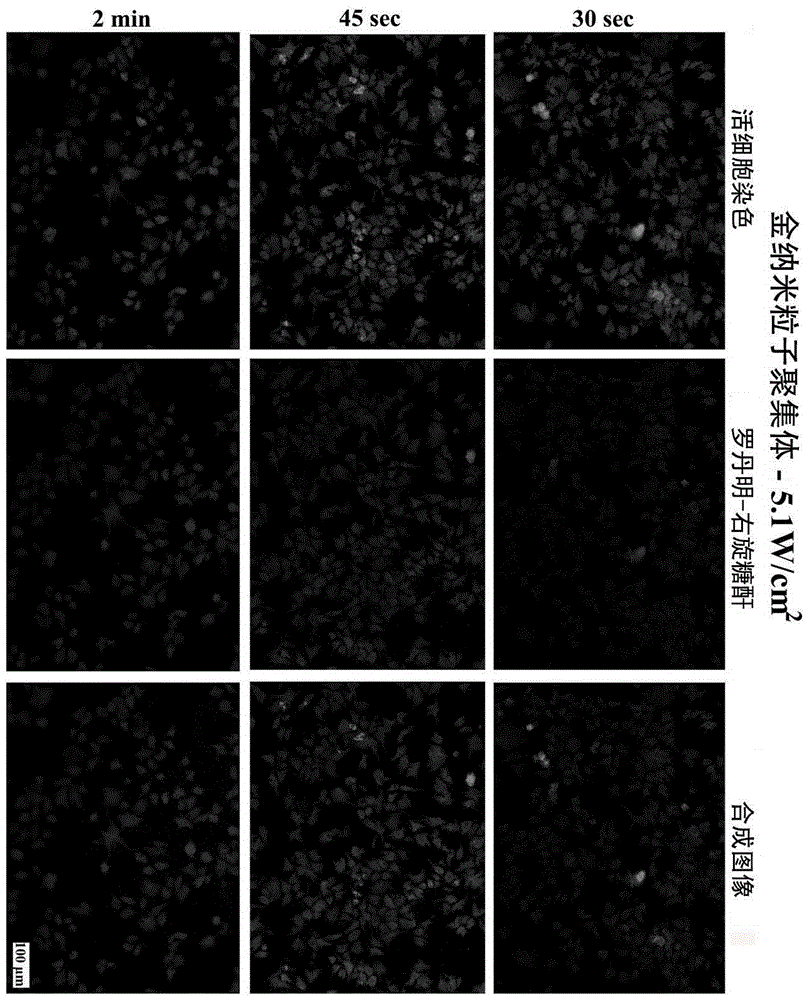
InactiveCN105420278AAvoid the disadvantage of not being fully released by the carrierGuaranteed normal transmissionTissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesCell culture mediaCell membrane
The invention discloses a method for preparing cells carrying exogenous molecules in a photoinduced perforating mode, a base material for preparing the cells and the cells, belongs to the field of medical instrument modification and the field of nanometer materials, and particularly relates to a reagent kit for modifying the surface of a cell culture base material (including a cell culture plate and other base materials capable of being used for culturing cells) with gold nano-materials (including gold nano particle aggregation, gold nano rods, gold nano cones and the like). The purpose of carrying out exogenous macromolecular transfer on cells cultured on the reagent kit is achieved through near-infrared band laser assistance. According to the system, gold nano particles are used for absorbing a large amount of laser energy at the near-infrared band so as to improve the membrane permeability of the cells cultured on the system; the activity of the cells can be well maintained by optimizing the laser power and the irradiation time; the reagent kit has the advantages of being simple, direct, fast and efficient, and can be applied to different cell lines for transfer of exogenous macromolecules of different types.
Owner:JIANGSU BIOSURF BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com