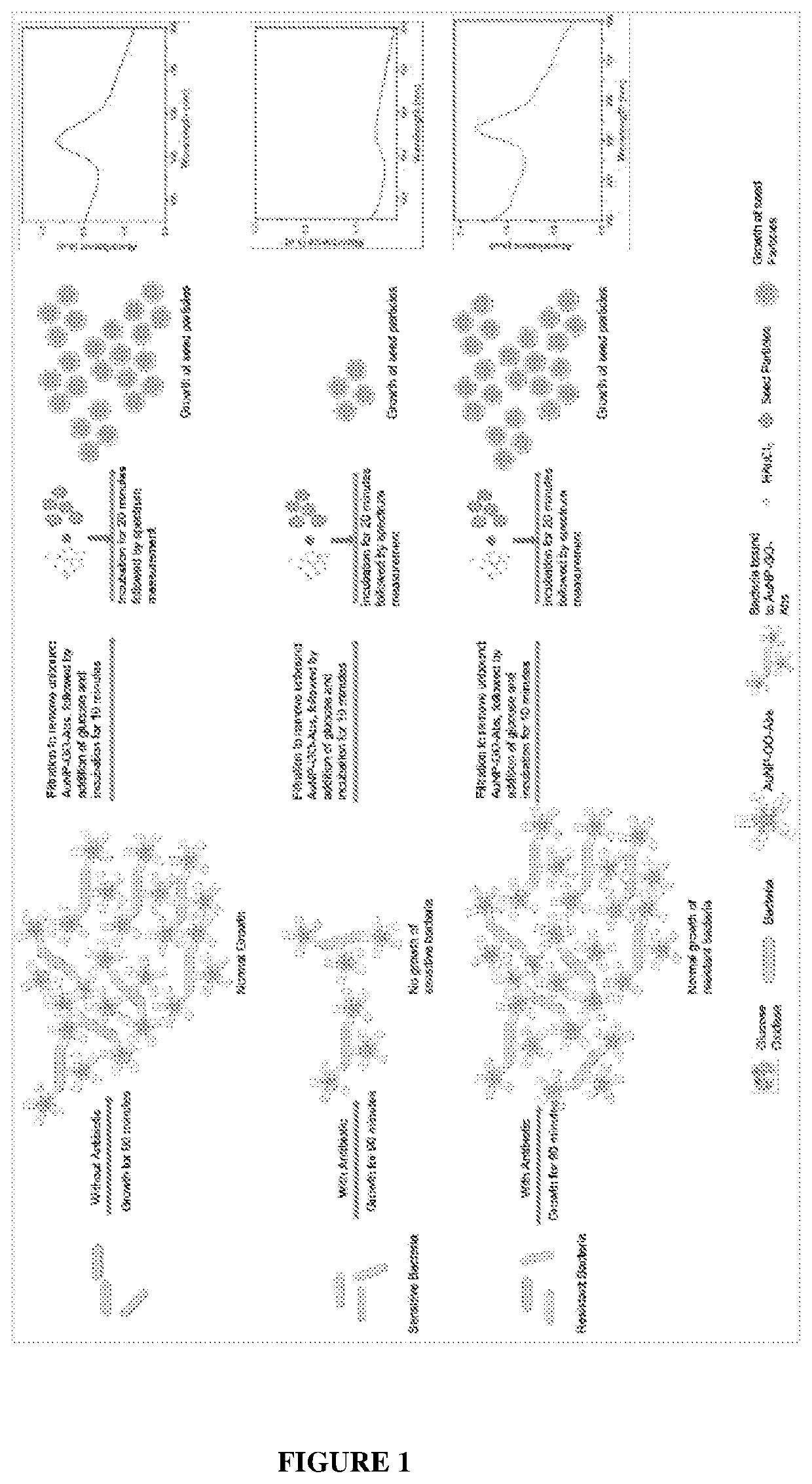
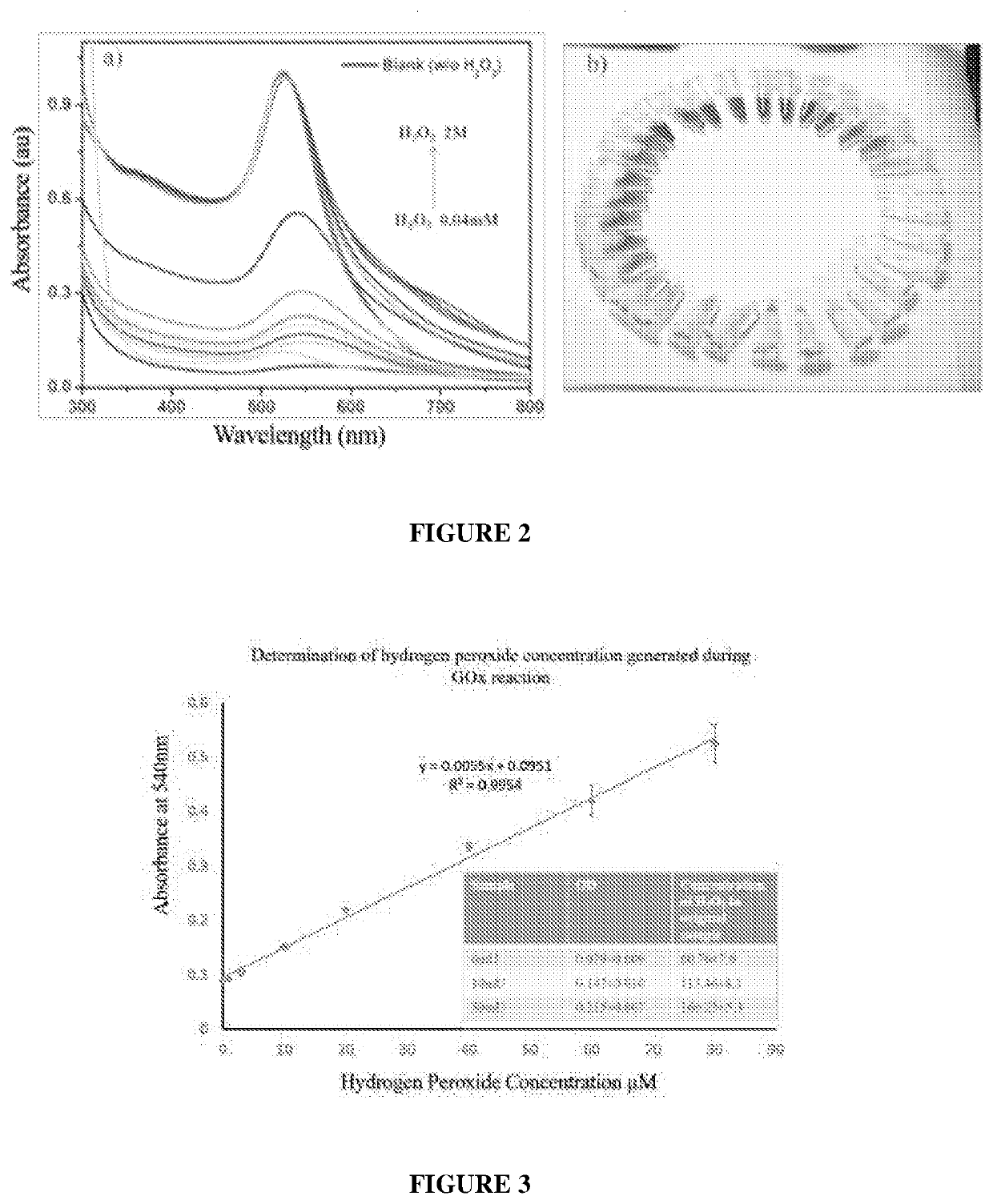
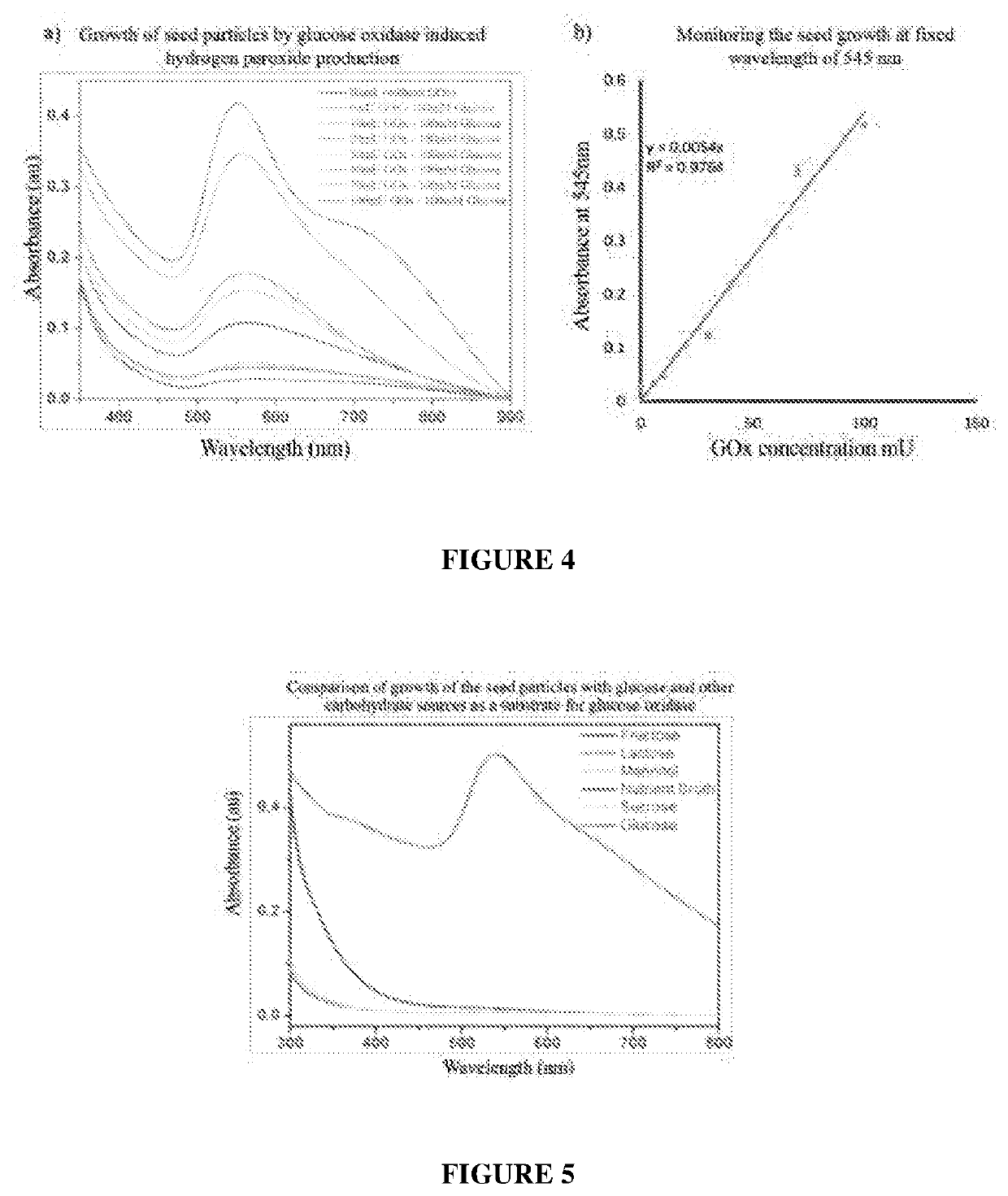
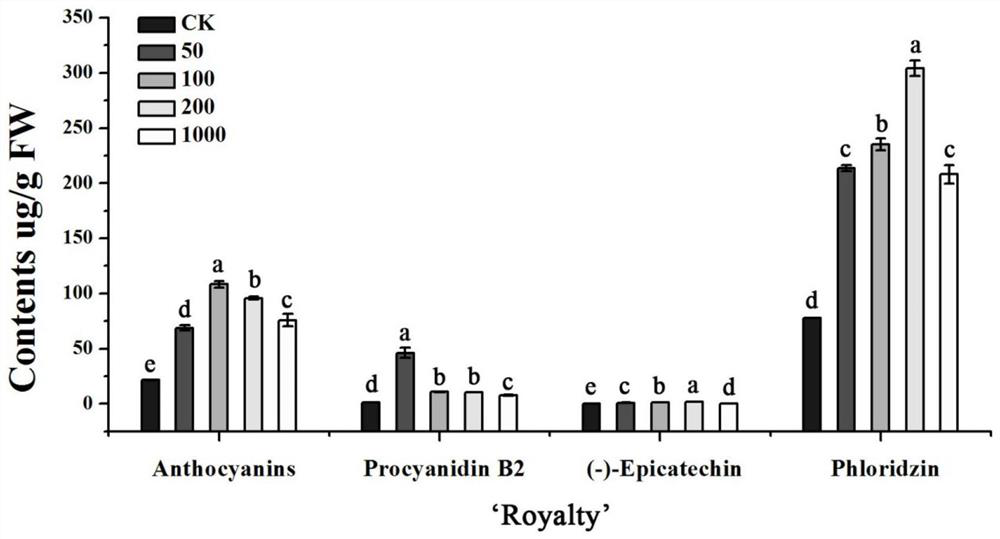
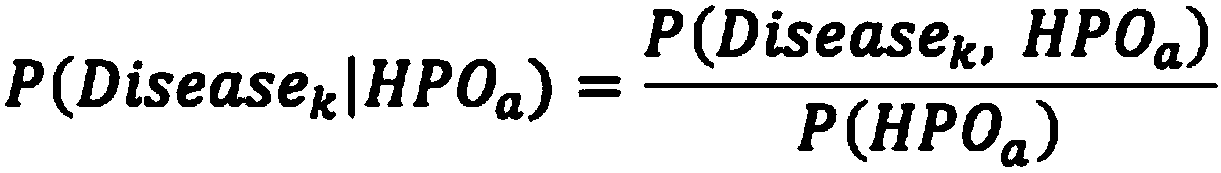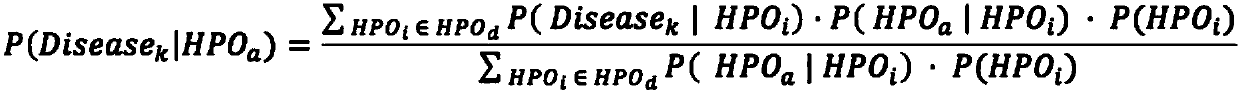Patents
Literature
33 results about "Phenotypic screening" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phenotypic screening is a type of screening used in biological research and drug discovery to identify substances such as small molecules, peptides, or RNAi that alter the phenotype of a cell or an organism in a desired manner.
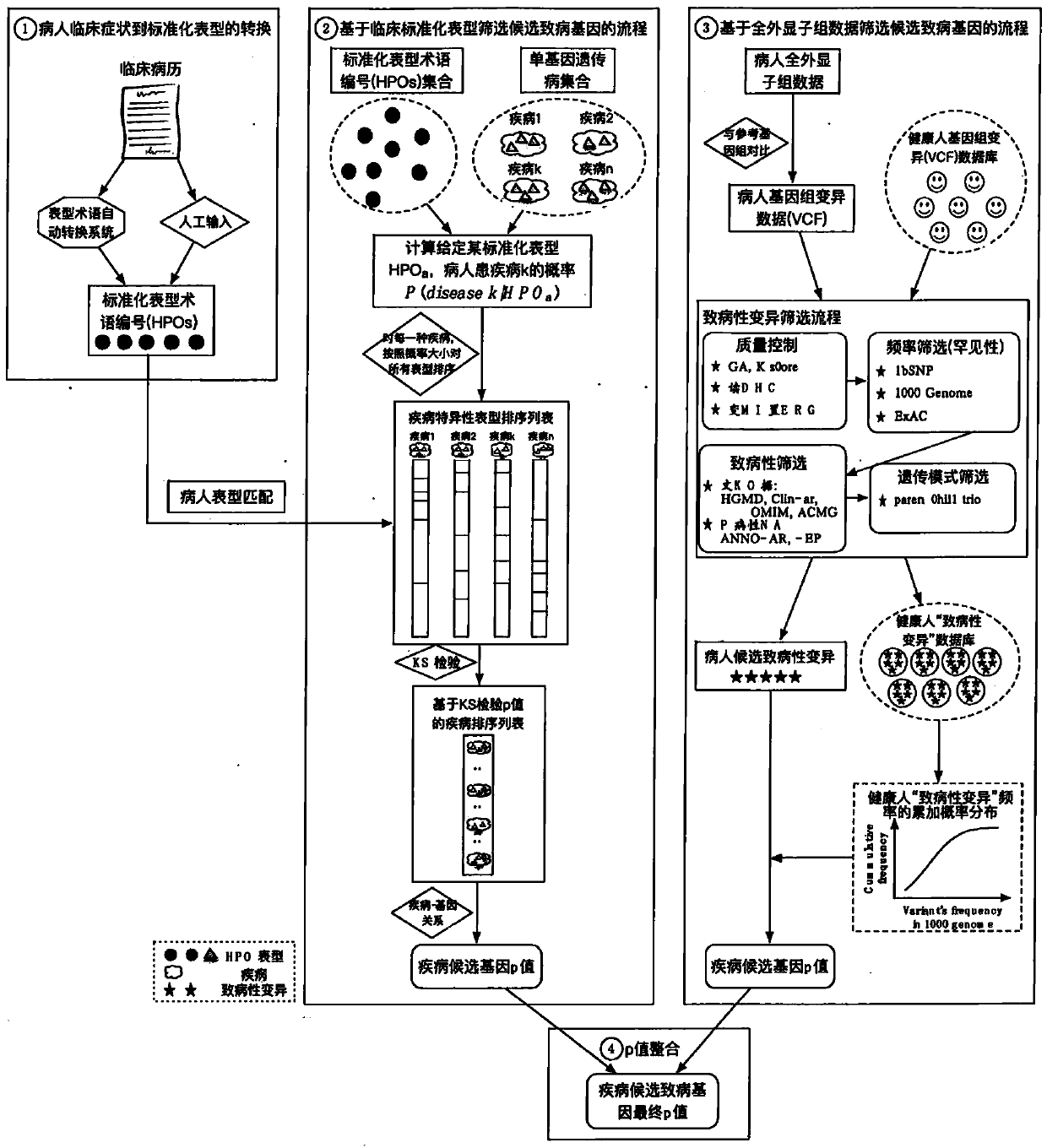
Analysis detection system for screening single gene hereditary disease pathogenic gene based on patient clinical symptom data and whole exome sequencing data
The invention relates to an automated analysis system for automatically screening the single gene disease and hereditary disease pathogenic gene based on patient clinical phenotype information and whole exome sequencing data. The system comprises four automatic analysis modules: (1) an automatic transferring subsystem for automatic transferring from patient clinical report to standardized phenotype term (HPO, human phenotype ontology); (2) an automatic analysis system for screening disease pathogenic gene based on patient standardized phenotype; (3) an automatic analysis system for screening disease pathogenic gene based on patient whole exome sequencing data; and (4) a p value integration system. The system adopts a possibility model to calculate the possibility of developing a certain single gene hereditary disease under the situation that a certain standard phenotype of the patient is provided, and utilizes a computer statistic check method to systematically evaluate the significance level of developing a certain single gene hereditary disease after all standard phenotype of the patient are provided, so as to accordingly achieve the purpose of screening candidate disease pathogenic gene based on clinical standard phenotype.
Owner:上海睿视健康科技有限公司
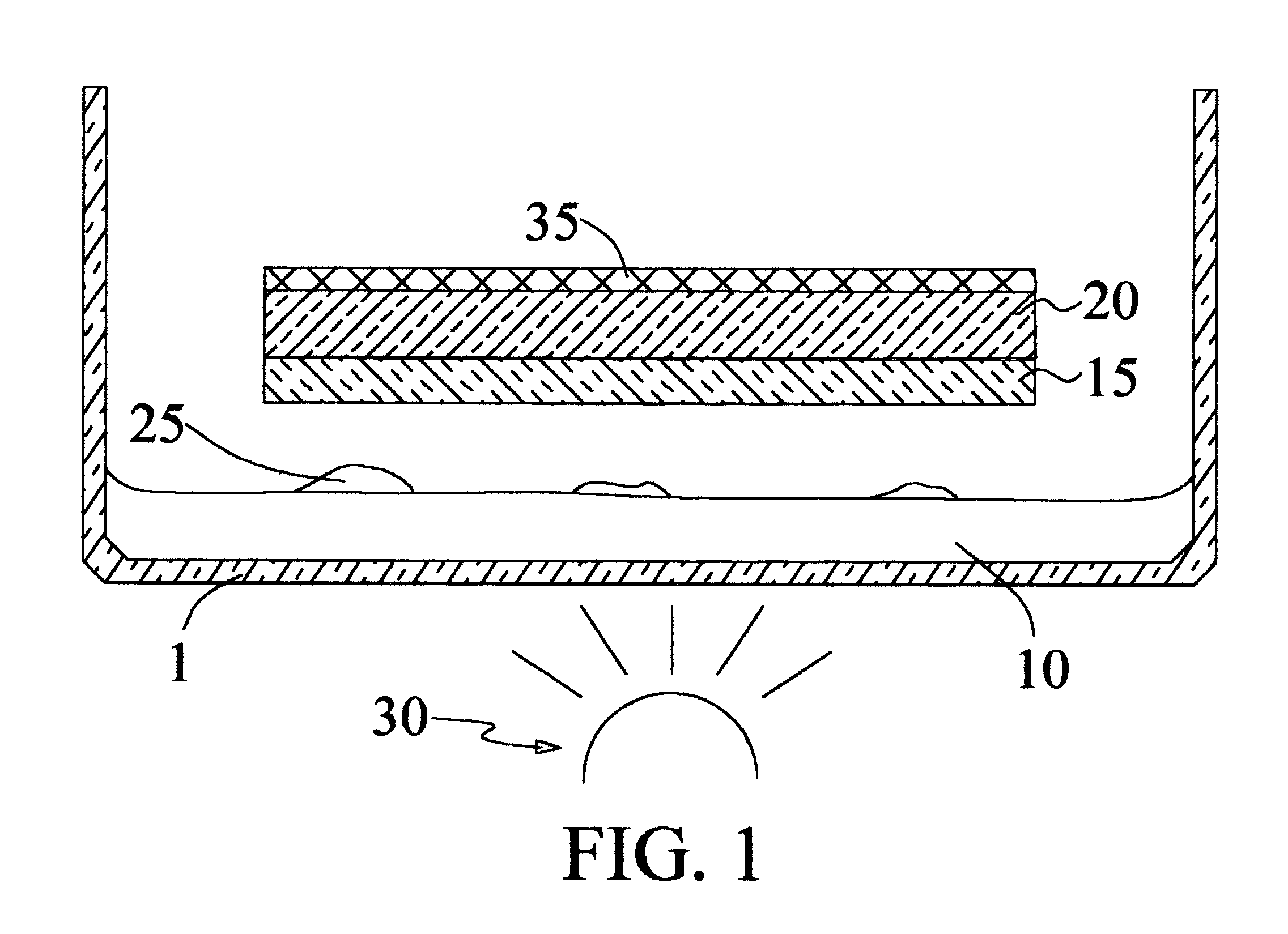
Method and apparatus for rapid biohydrogen phenotypic screening of microorganisms using a chemochromic sensor
InactiveUS6277589B1Microbiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementMicroorganismHydrogen
The invention provides an assay system for identifying a hydrogen-gas-producing organism, including a sensor film having a first layer comprising a transition metal oxide or oxysalt and a second layer comprising hydrogen-dissociative catalyst metal, the first and second layers having an inner and an outer surface wherein the inner surface of the second layer is deposited on the outer surface of the first layer, and a substrate disposed proximally to the outer surface of the second layer, the organism being isolated on the substrate.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
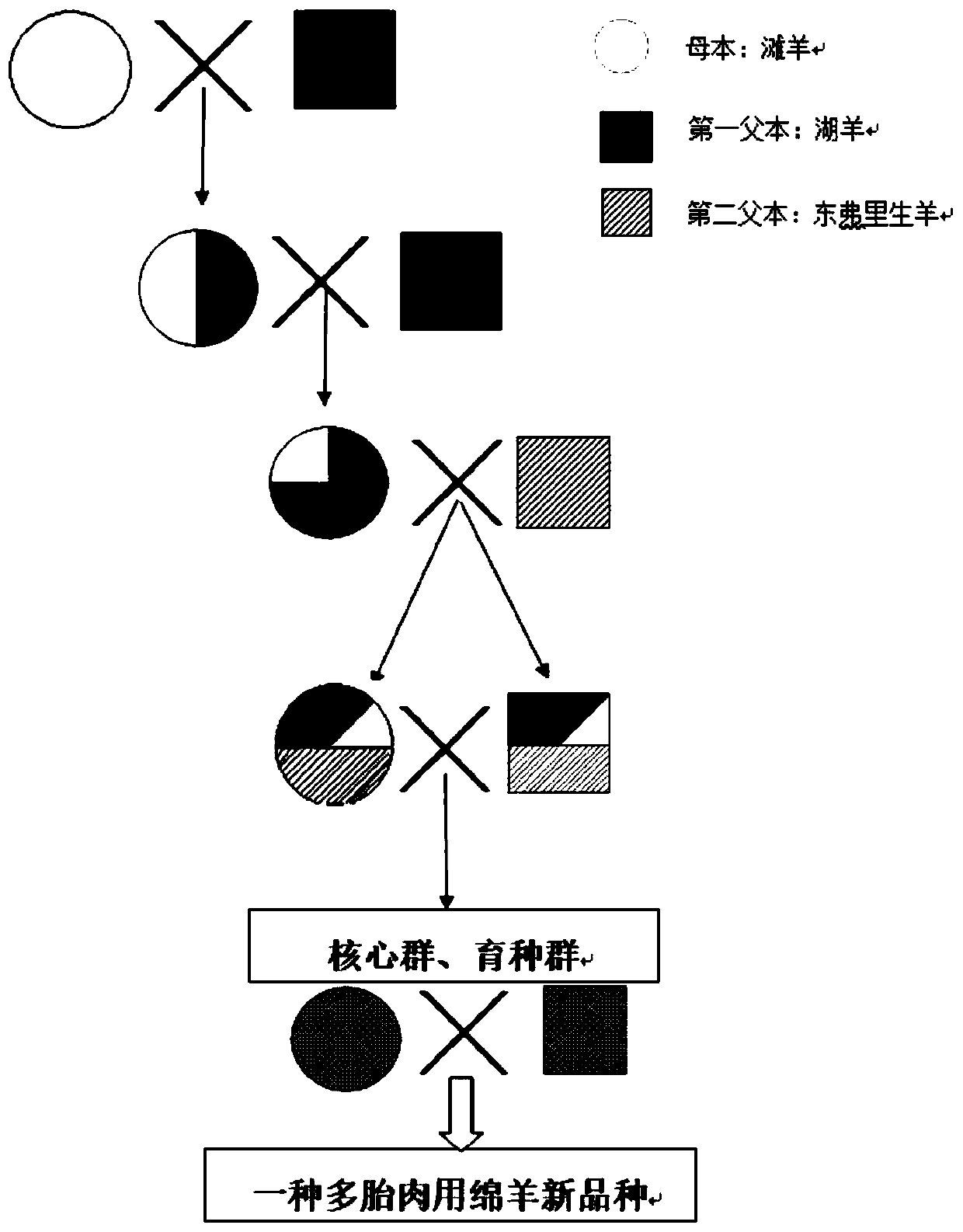
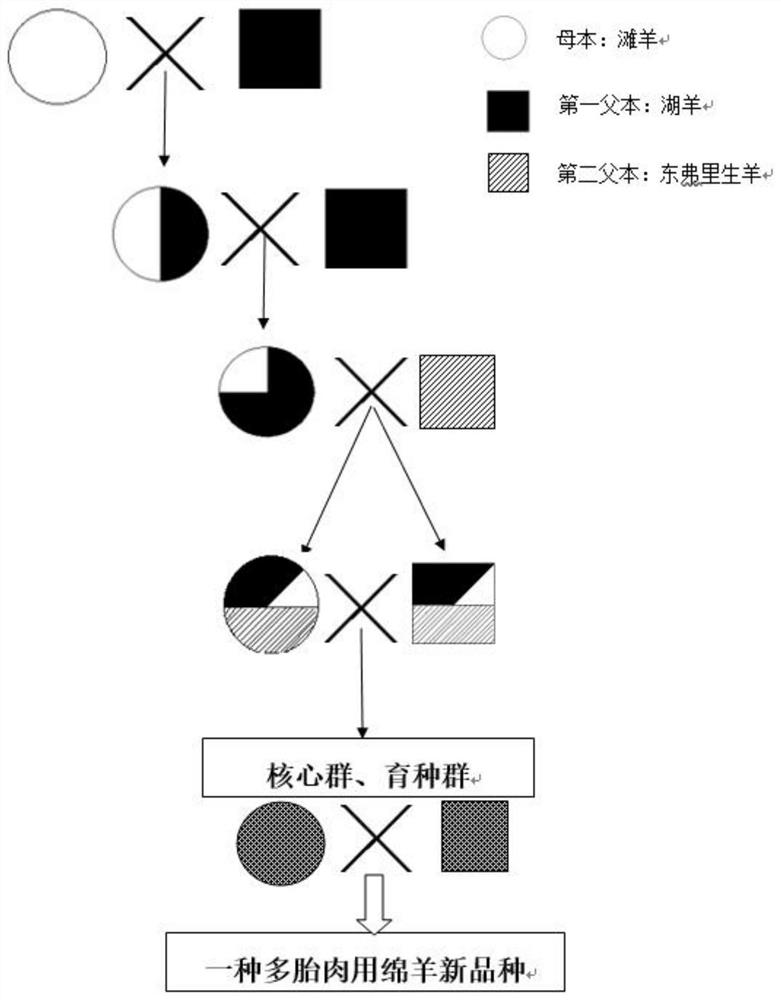
Breeding method of multiple-birth mutton sheep breed
The invention provides a breeding method of a multiple-birth mutton sheep breed and relates to the technical field of animal breeding. The breeding method herein is characterized in that a Hu sheep, as a first male parent, an east eastfrierian sheep as a second female parent and a Tan sheep as a female parent are subjected to three-breed crossing; the novel multiple-birth mutton sheep breed suitable for the ecological conditions of loess plateau is cultivated through phenotypic screening in combination with screening of specific gene carriers; the multiple-birth mutton sheep breed is adaptiveto the natural ecological conditions of the loess plateau ecological region of China and has the advantages of good stress resistance, crude feeding resistance, high propagation rate, good meat tenderness, uniform fat distribution, little odor and the like.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Application of Arabidopis thaliana transcription factor at3g46080 gene
PendingCN110305218AIncrease resistanceAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPlant peptidesDisease phenotypePseudomonas tolaasii
The invention relates to an application of an Arabidopis thaliana transcription factor at3g46080 gene. By constructing a CDS sequence of the Arabidopsis thaliana at3g46080 gene into the upstream of aFLAG protein label by a Gateway technology, Arabidopsis thaliana is conversed, which affects the disease phenotype of Arabidopsis thaliana, screening and identification are carried out, and finally the transgenic plants can be obtained. The analysis of the screened plants carried out so that the plant has enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas lycoposum by Arabidopis thaliana, the gene has the same function for homologous genes in crops, and thus has important significance in production.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
High-yield crossbreeding method of two-line super rice parent GuiKe-2S stock seeds
InactiveCN103609434AHigh purityIncrease productionPlant genotype modificationRice cultivationPhenotypic screeningEcology
The invention provides a high-yield crossbreeding method of two-line super rice parent GuiKe-2S stock seeds. The high-yield crossbreeding method comprises the following steps: A, carrying out phenotypic screening on a GuiKe-2S large group, namely, planting a GuiKe-2S group of a single plant; B, detecting a specificity marker of a GuiKe-2S sterile locus; C, detecting a molecular marker of a GuiKe-2S fingerprint spectrum; D, carrying out low-temperature screening on a GuiKe-2S first-time manual climatic box; E, carrying out low-temperature screening on a GuiKe-2S second-time manual climatic box; and F, breeding a rice root in winter of Hainan, transplanting the GuiKe-2S the root of which is cut again to Sanya of Hainan for breeding in winter, and harvesting seeds when ripening to obtain the two-line super rice parent GuiKe-2S stock seeds. According to the high-yield crossbreeding method, the stock seeds are further bred to obtain high-purity parent seeds applied to seed production, which has a very important significance in developing two-line hybrid rice. Through tests, the purity of the obtained breeder seeds reaches above 99.99 percent, and the purity of the stock seeds obtained through expanding propagation reaches above 99.9 percent.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
Method for accurately and rapidly identifying drug target of active compound obtained by phenotypic screening
ActiveCN104237530AImprove throughputThroughput phenotypic screening facilitatesBiological testingProteomics methodsDisease
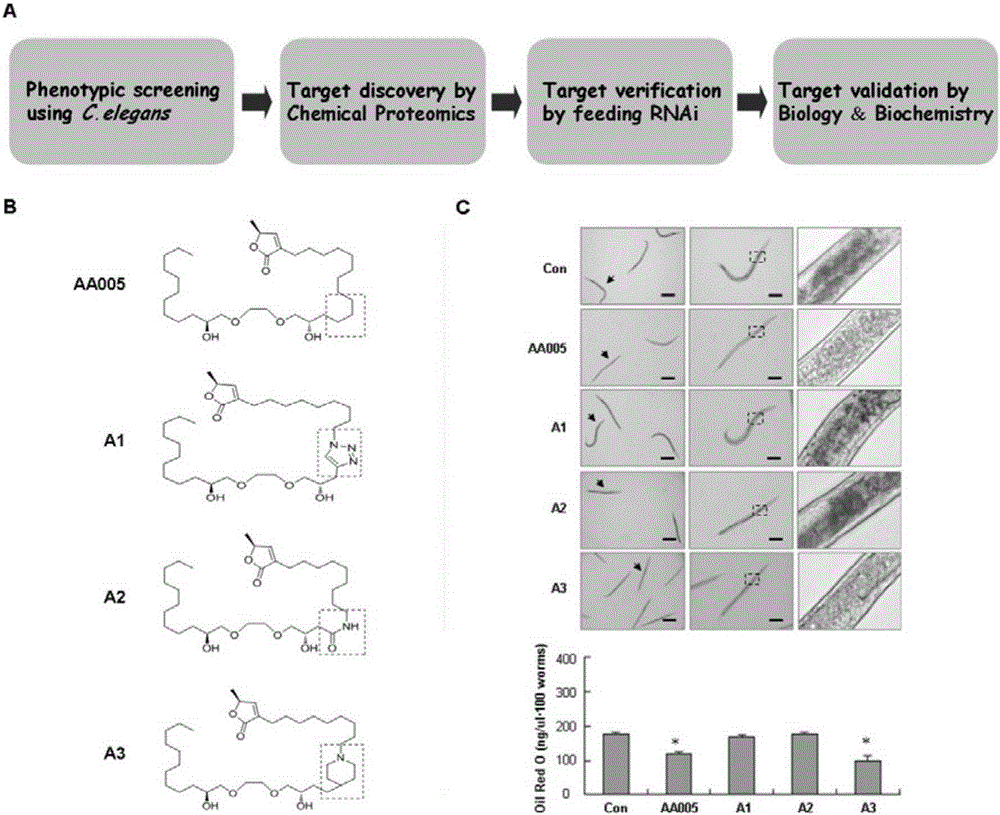
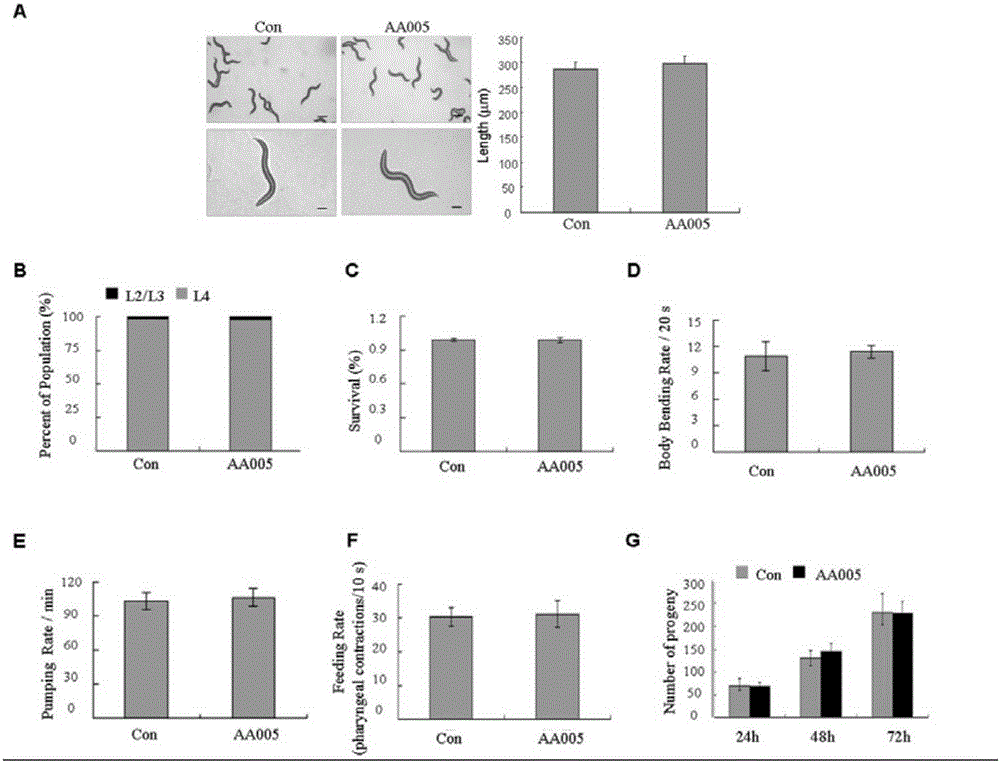
The invention discloses a method for accurately and rapidly identifying a drug target of an active compound obtained by phenotypic screening. The seamless joint of compound phenotypic screening and target identification is established by a chemical proteomics-driven caenorhabditis elegans feeding RNAi technology; the active compound is an active compound with a corresponding phenotype in the elegans; the phenotype includes but is not limited to lipid dysbolism, cell apoptosis, autophagy, senility, neurodegenerative disease and anti-infection. The problem that at present, false positive and false negative are easily produced when the proteomics method is purely used for analyzing the interacting protein of drug can be solved, and the aim of eliminating the false and retaining the true can be realized; furthermore, the method is simple and convenient in operation and rapid and accurate in screening, and provides a feasible scheme for the analysis of the large-flux interacting protein of the drug; a more perfect chemical proteomics technology system is formed, and the possibility of breaking through the choke point of phenotypic screening protein target identification is provided.
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Apparatus for rapid biohydrogen phenotypic screening of microorganisms using a chemochromic sensor
InactiveUS20010041351A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismBiological body
Provided is a system for identifying a hydrogen gas producing organism. The system includes a sensor film having a first layer comprising a transition metal oxide or oxysalt and a second layer comprising a hydrogen-dissociative catalyst metal, the first and second layers having an inner and an outer surface wherein the inner surface of the second layer is deposited on the outer surface of the first layer, and a substrate adjacent to the outer surface of the second layer, the organism isolated on the substrate.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
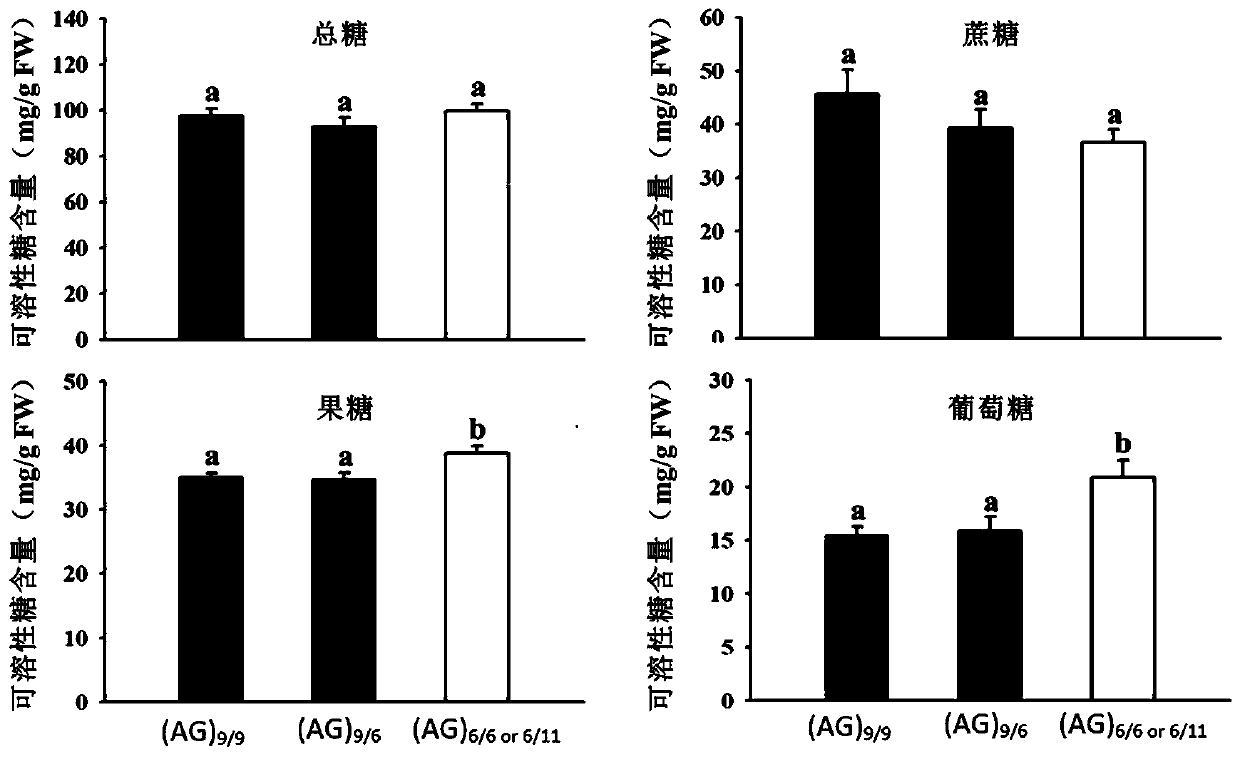
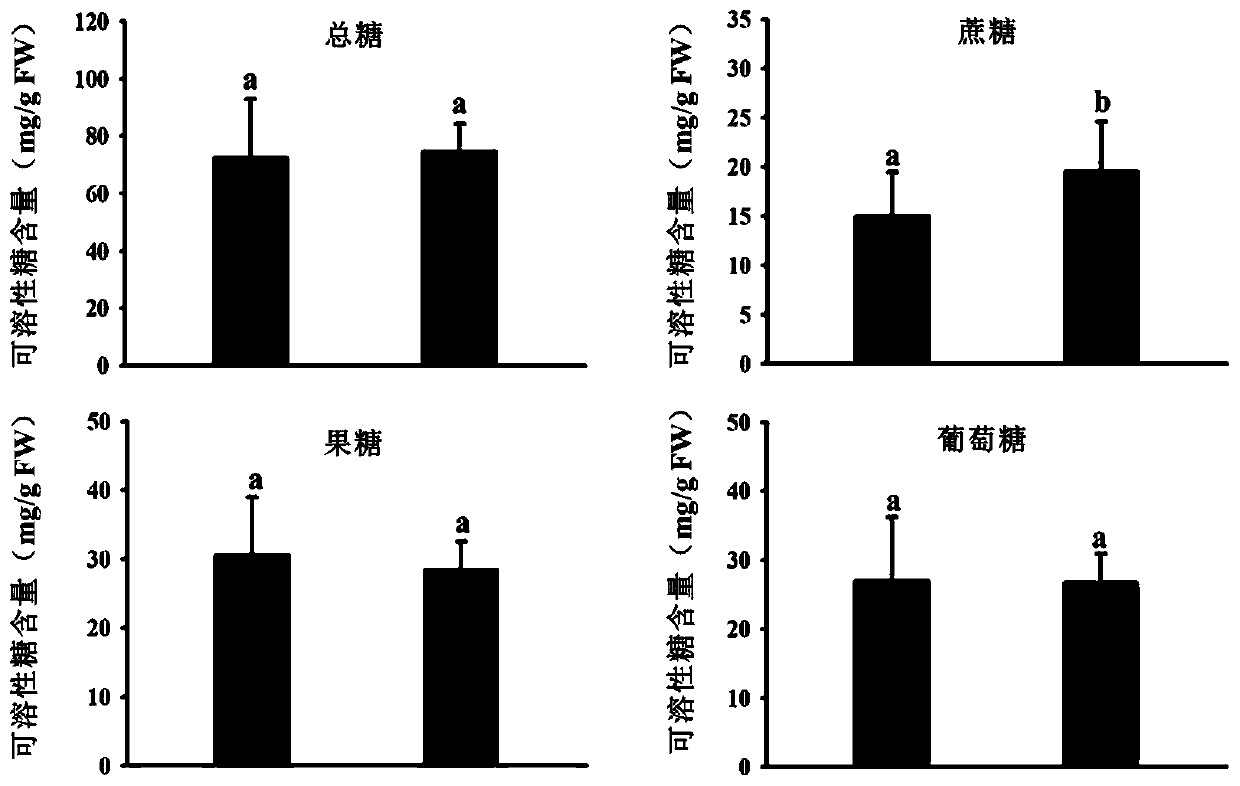
SSR molecular marker for screening content and phenotype of apple fruit sugar and application thereof
ActiveCN110295249AEfficient screeningReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFructoseAgricultural science
The invention discloses an SSR molecular marker for screening the content and phenotype of apple fruit sugar and application thereof. The SSR molecular marker SugarA3 is successfully developed by determining candidate molecular markers through content and phenotype data of genetic typing related sugar. PCR amplification is conducted through the SugarA3, a simple sequence repetitive unit (AG)n is determined in combination with sequencing, and accordingly the content of the fruit sugar is estimated. Three types of genes can be generated through the SugarA3 and include (AG)9 / 9, (AG)6 / 9 and (AG)6 / 6 or 11, wherein one or two (AG)9 sequence motifs indicate that the corresponding content of fruit sugar and glucose in apple fruits is remarkably lower than that of the apple species without (AG)9 sequence motifs. Thus, the sweetness screening of applies in the seedling period can be easily realized by applying the molecular marker SugarA3, the breeding age limit of the excellent species meetingthe market demands is shortened, and the apple quality and breeding efficiency are improved.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
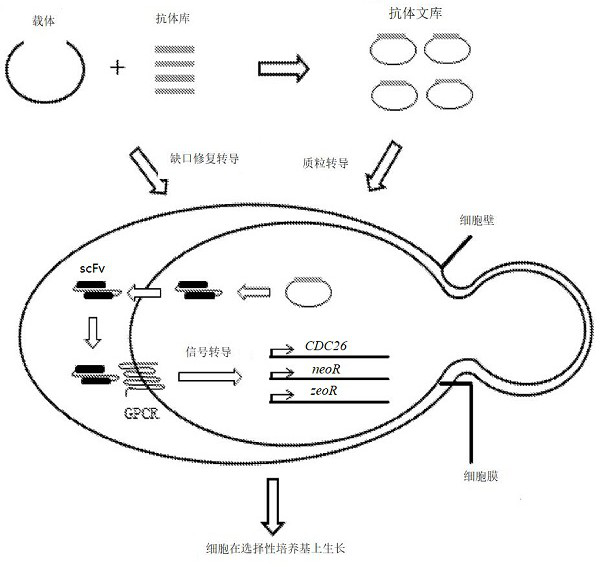
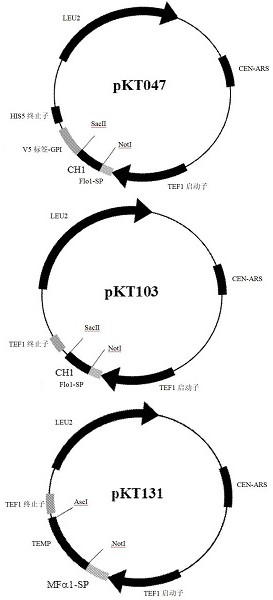
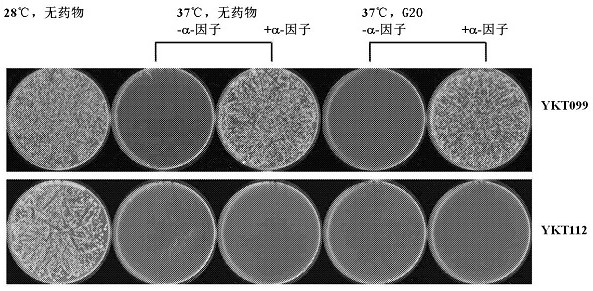
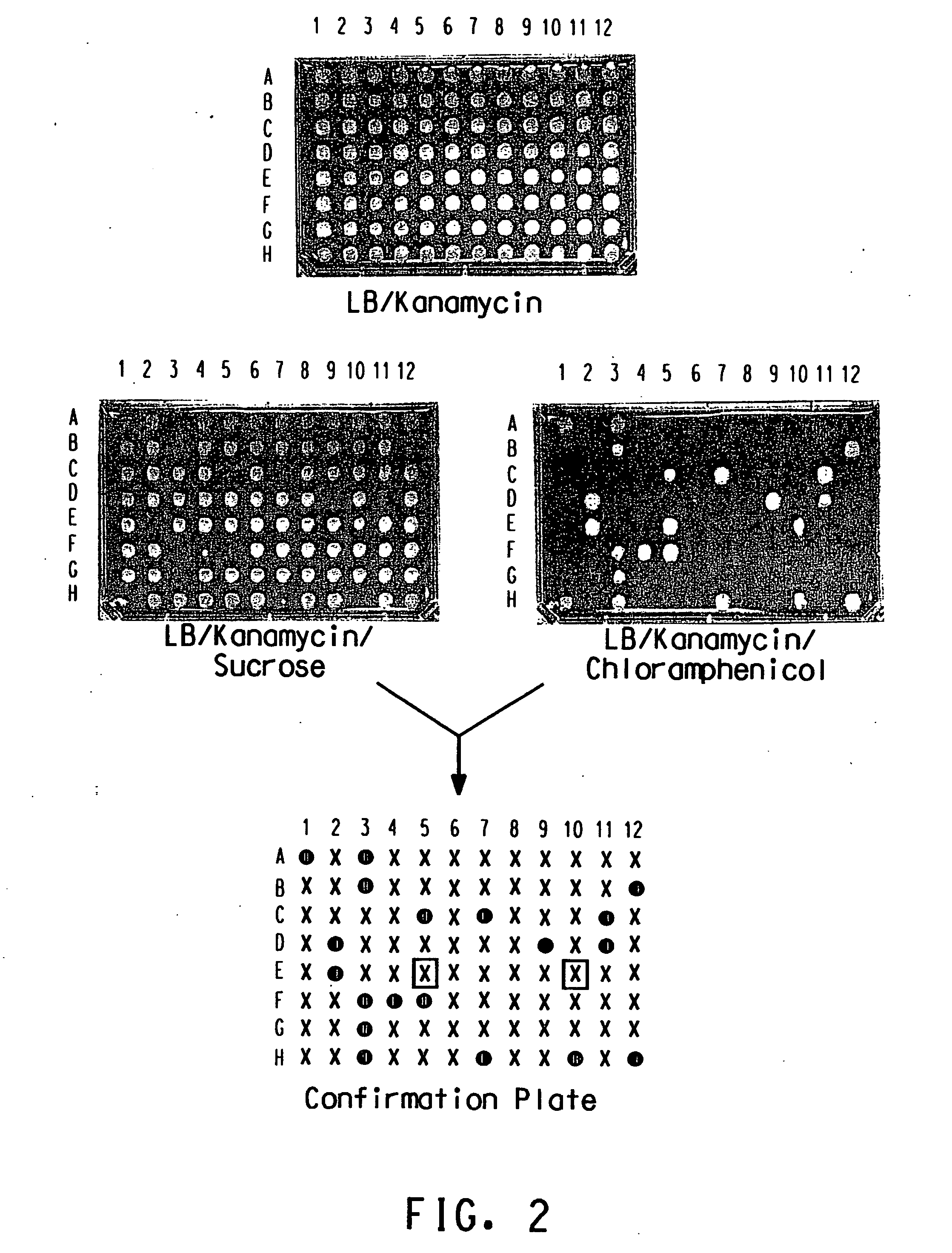
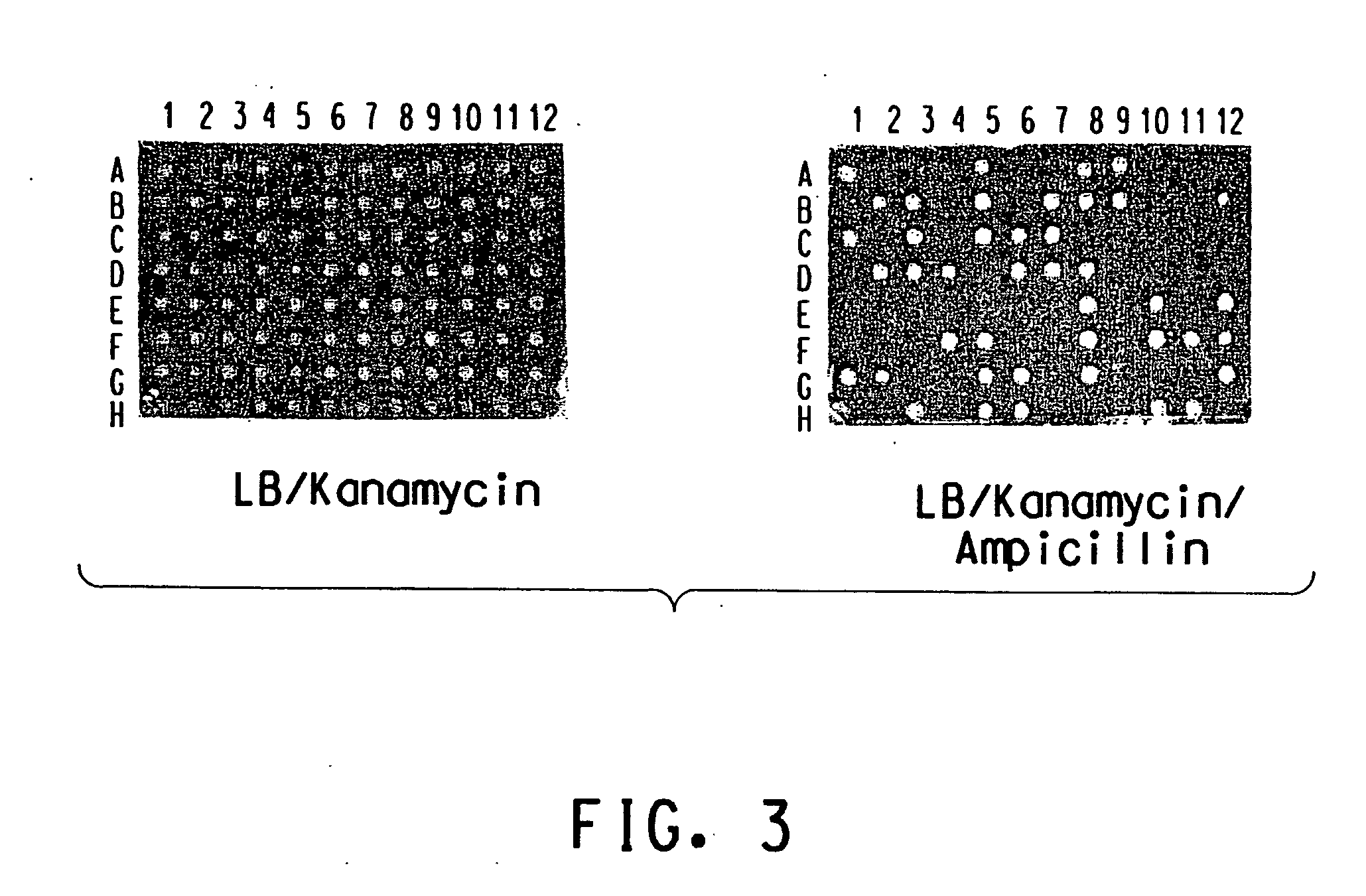
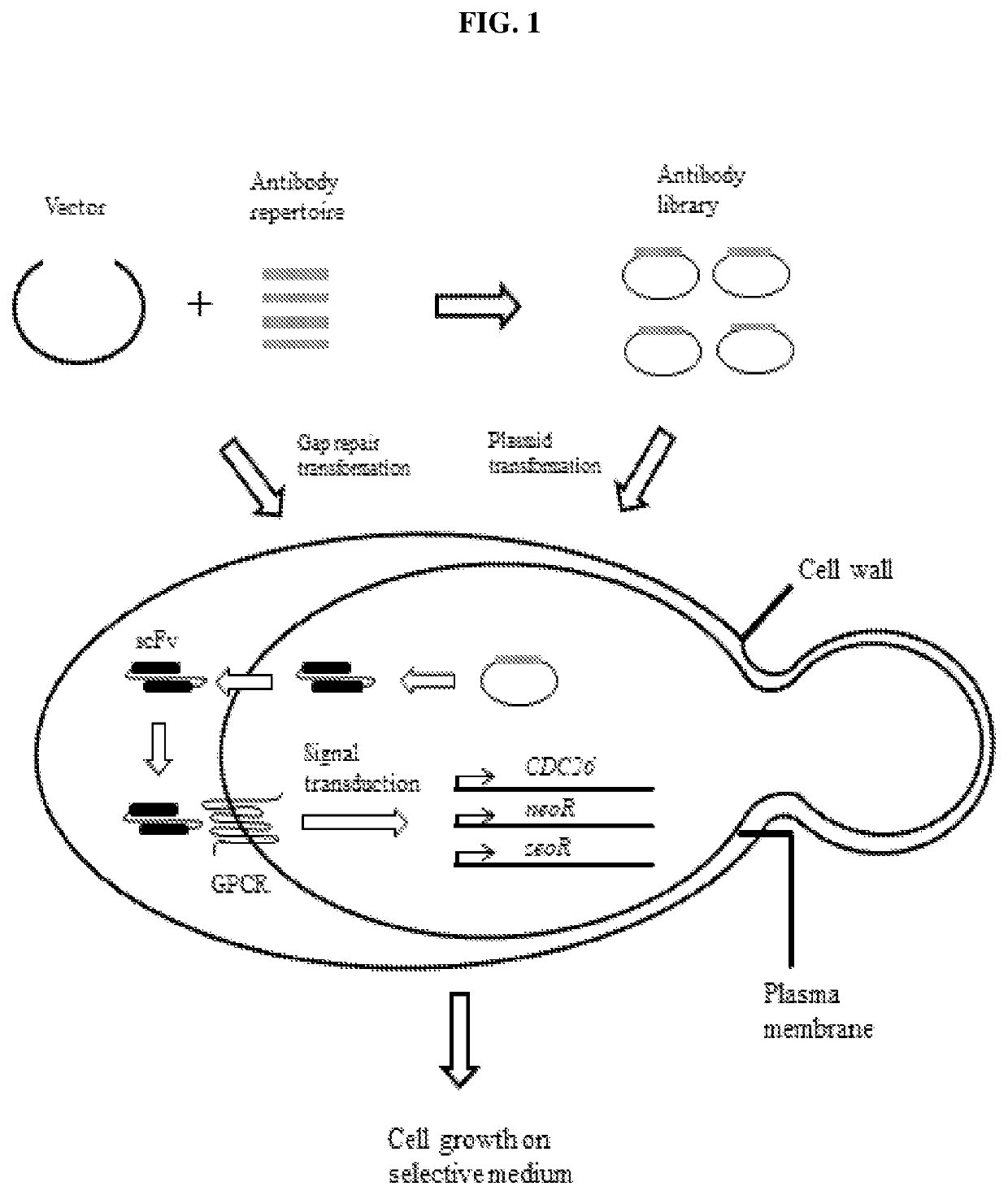
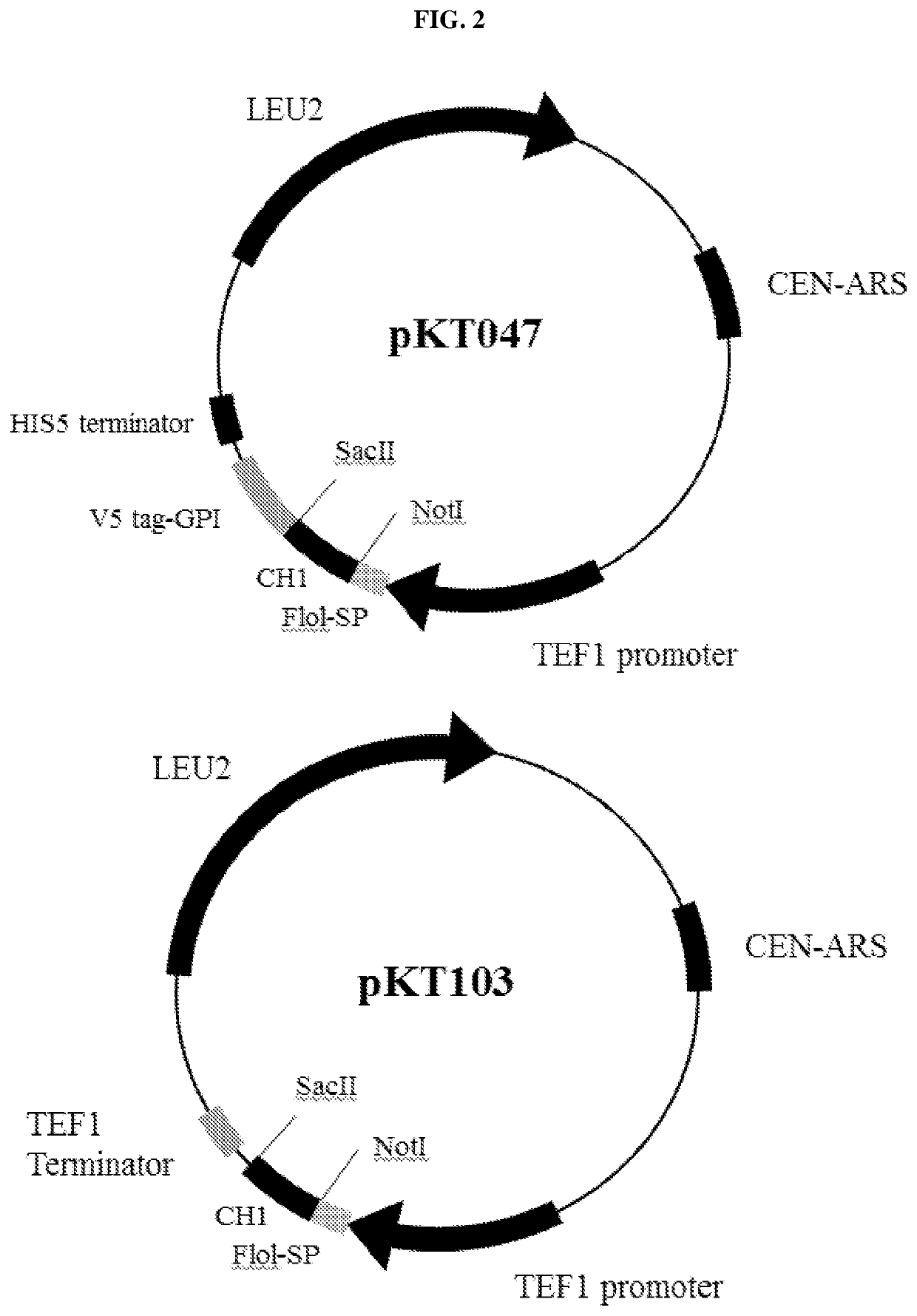
A yeast phenotypic screening method for isolation of functional antibodies against g-protein coupled receptors
The present invention provides a method for identifying a functional antibody or antigen-binding protein or a fragment thereof that is capable of binding to, and stimulating the activity of, a targettransmembrane protein comprising the steps of providing yeast cells transformed with yeast expression vectors encoding a library of antibodies or antigen-binding proteins or fragments thereof, whereinsaid yeast cells express said target transmembrane protein, expressing said library of antibodies or antigen-binding proteins or fragments thereof in the yeast cells, wherein said expressed antibodies or antigen-binding proteins or fragments thereof are secreted into the periplasmic space of said yeast cells, incubating the yeast cells in or on a selective medium or under a restrictive temperature, or a combination thereof, and detecting a predetermined phenotype in the yeast cells, wherein detection or manifestation of the predetermined phenotype is indicative of binding of the functional antibody or antigen-binding protein or a fragment thereof to said target transmembrane protein and stimulation of said target transmembrane protein by the functional antibody or antigen-binding proteinor a fragment thereof. Antibodies or antibody fragments that are agonists of G-protein coupled receptors identified by the method of the invention are also provided.
Owner:抗体私人有限公司
Specific DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecular marker of trichiurus punctatus and application thereof
ActiveCN112280871AImprove germplasm purityThe identification result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyGermplasm
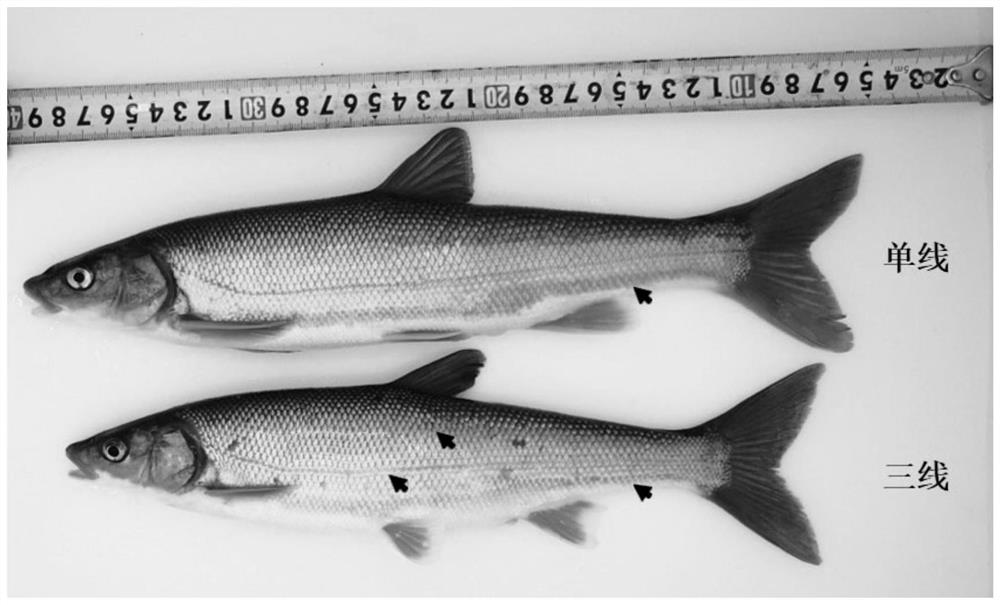
The invention provides a specific DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecular marker and a DNA bar code of trichiurus lepturus and a method for quickly identifying and purifying germplasm of trichiurus lepturus. Aiming at an existing problem of germplasm mixing of the triplophysa zuellii, stable triplophysa zuellii germplasm resources are finally screened out through phenotypic screening, DNA bar code screening and triplophysa zuellii specific DNA molecular marker screening and identification. The method for rapidly purifying the germplasm of the trichiurus punctatus is simple to operate, high in accuracy, short in period, good in stability and high in germplasm purity, and provides technical support for germplasm protection, reasonable utilization and germplasm biodiversity.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
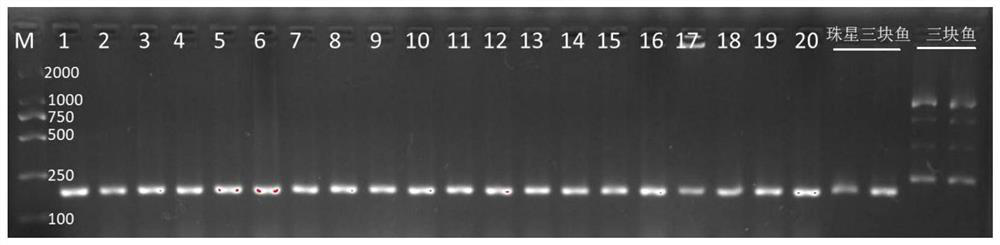
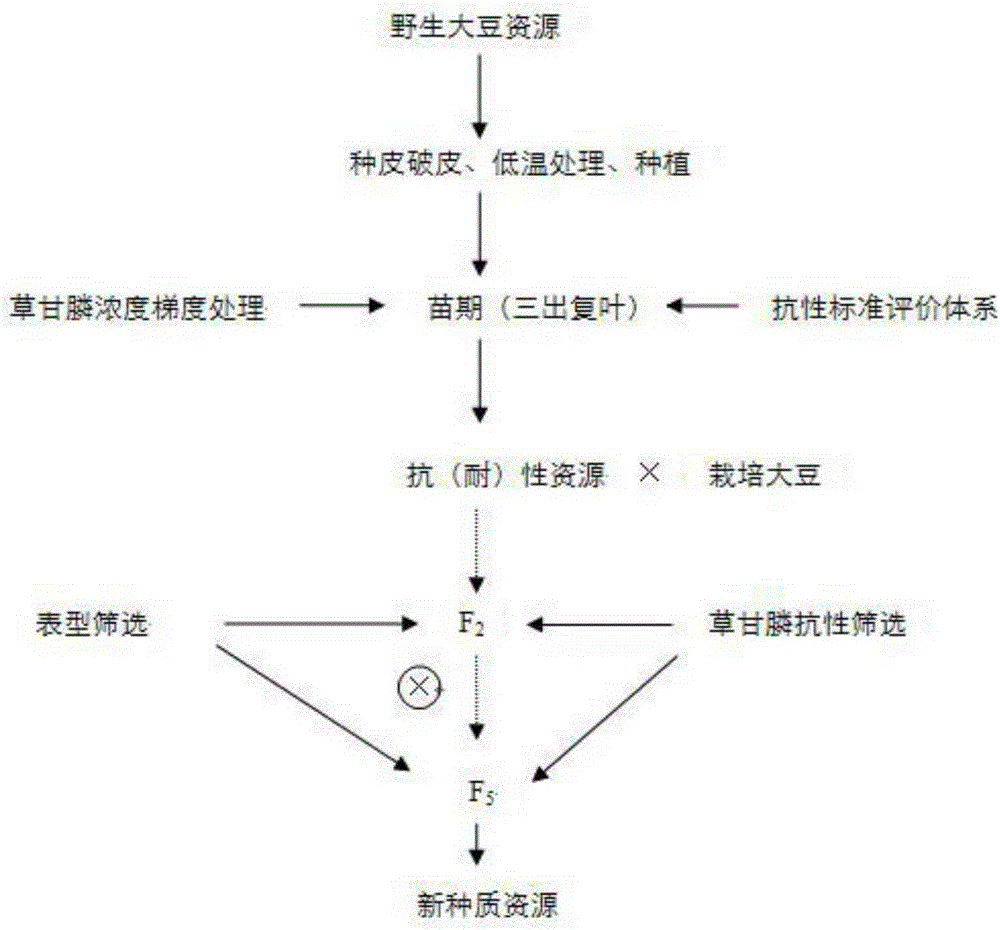
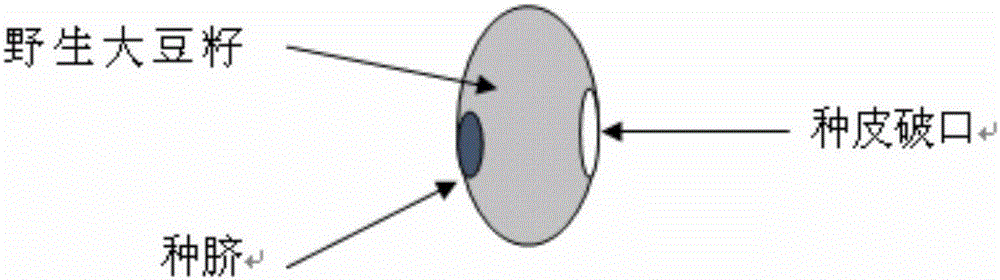
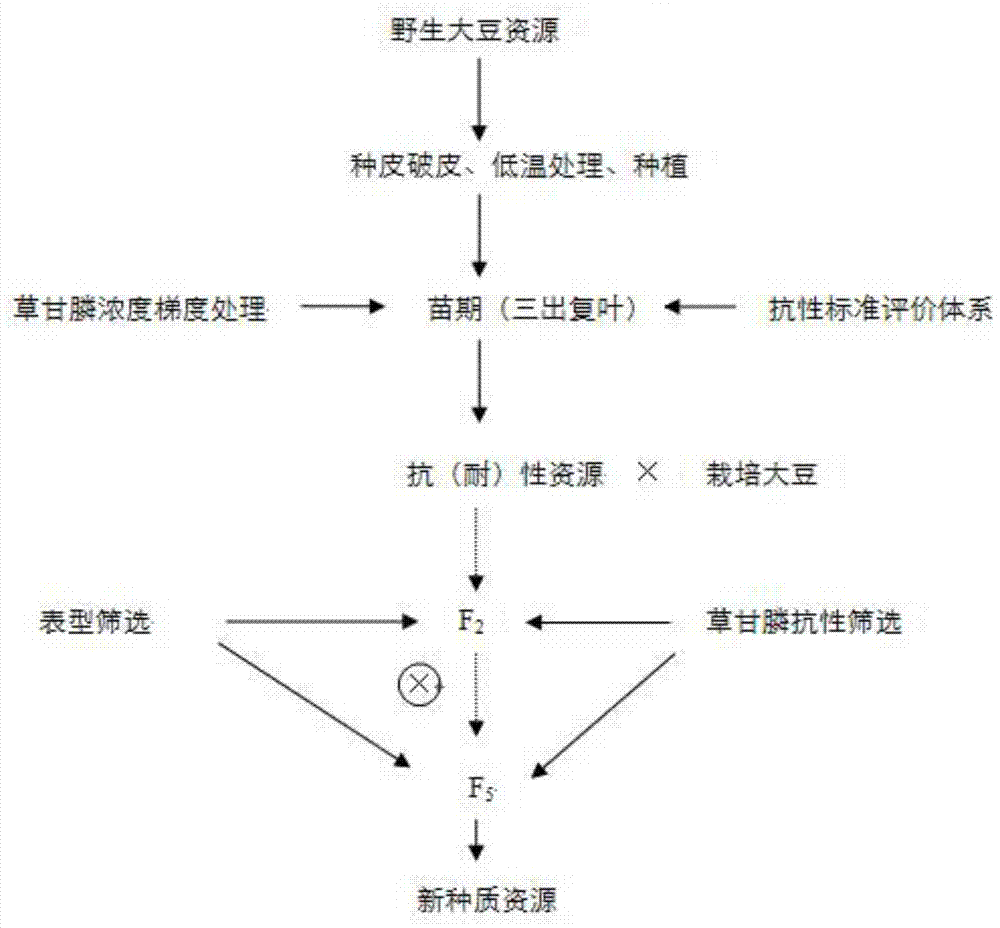
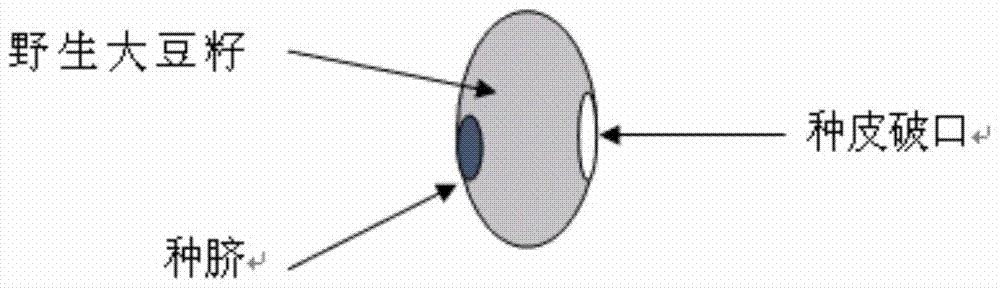
Method for breeding glyphosate-resistant/tolerant novel germplasm by utilizing wild soybeans
ActiveCN105165602AImprove reliabilityIncrease success ratePlant genotype modificationGlyphosateGermplasm
The invention belongs to the field of utilization and research of mild plant resources, and particularly relates to a method for breeding a glyphosate-resistant / tolerant novel germplasm by utilizing wild soybeans. The method for breeding the glyphosate-resistant / tolerant novel germplasm utilizes different concentrations of glyphosate to treat the wild soybeans at the seedling stage to screen out wild soybeans with resistance / tolerance to the glyphosate, and then utilizes the screened wild soybeans with resistance / tolerance to carry out interspecific hybridization with cultivated soybeans, so that an interspecific hybridization generation is obtained, glyphosate resistance / tolerance screening is carried out on the selfing line of the interspecific hybridization generation, and in combination with phenotypic screening, the method breeds out the novel germplasm with resistance / tolerance to the glyphosate. The invention determines a wild soybean resource resistance standard evaluation system, and creates the method for screening the wild soybeans with resistance / tolerance, moreover, by utilizing the wild soybeans with resistance / tolerance to carry out interspecific hybridization, the invention creates the method for breeding the glyphosate-resistant / tolerant novel germplasm, and the method is simple, practical and highly efficient, and is also applicable to the research of the other characters of the wild soybeans.
Owner:FARMING & CULTIVATION RES INST OF HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Creation method of giant flower pop corn
ActiveCN112056211ASimple technologyReduce concentrationClimate change adaptationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention relates to a creation method of giant flower pop corn. The method comprises the following steps of (1) selecting seeds and accelerating germination, namely selecting pop corn selfing line seeds with the large grain size, the large flower size and the high expansion coefficient, and accelerating germination for the first time; (2) performing doubling treatment, namely enabling a chromosome doubling treatment agent to be any one of amiprophos-methyl, trifluralin and colchicine of herbicide; (3) performing breeding; (4) performing phenotype screening and fructification identification; and (5) performing combination and preparation, namely, adopting doubled selfing line seeds as parents, and performing hybridization and matching to obtain a high-yield and high-expansion-coefficient pop corn hybrid. According to the method, a conventional corn chromosome doubling technology is used for reference, large-grain large-flower pop corn is created through a ploidy breeding approach of autotetraploid, large-flower and high-expansion-coefficient germplasm is used as a test material, namely, on the basis of large flowers, the size of the corn flowers is greatly increased again, a giant flower pop corn new variety is bred, and the yield can be increased.
Owner:SHENYANG TEYIJIA CORN TECH +1
Method for determination of gene function
The present method is useful for the identification of genes, ORF's and other nucleic acid molecules which are essential for the expression of a specific phenotype in microorganisms. The method employs in vitro transposition in conjunction with an chromosomal integration vector containing a specific gene or genetic element whose function is unknown. Subsequent transformation of a recombination proficient host with the vector and growth first under non-integrating conditions and then under integrating conditions, followed by a selection screen for either single or double crossover events results in transformation that may be subjected to phenotypic screens to determine gene function.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
A yeast phenotypic screening method for isolation of functional antibodies against g-protein coupled receptors
PendingUS20210214719A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsYeastAntibody fragments
The present invention provides a method for identifying a functional antibody or antigen-binding protein or a fragment thereof that is capable of binding to, and stimulating the activity of, a target transmembrane protein comprising the steps of providing yeast cells transformed with yeast expression vectors encoding a library of antibodies or antigen-binding proteins or fragments thereof, wherein said yeast cells express said target transmembrane protein, expressing said library of antibodies or antigen-binding proteins or fragments thereof in the yeast cells, wherein said expressed antibodies or antigen-binding proteins or fragments thereof are secreted into the periplasmic space of said yeast cells, incubating the yeast cells in or on a selective medium or under a restrictive temperature, or a combination thereof, and detecting a predetermined phenotype in the yeast cells, wherein detection or manifestation of the predetermined phenotype is indicative of binding of the functional antibody or antigen-binding protein or a fragment thereof to said target transmembrane protein and stimulation of said target transmembrane protein by the functional antibody or antigen-binding protein or a fragment thereof. Antibodies or antibody fragments that are agonists of G-protein coupled receptors identified by the method of the invention are also provided.
Owner:KANGTI PTE LTD
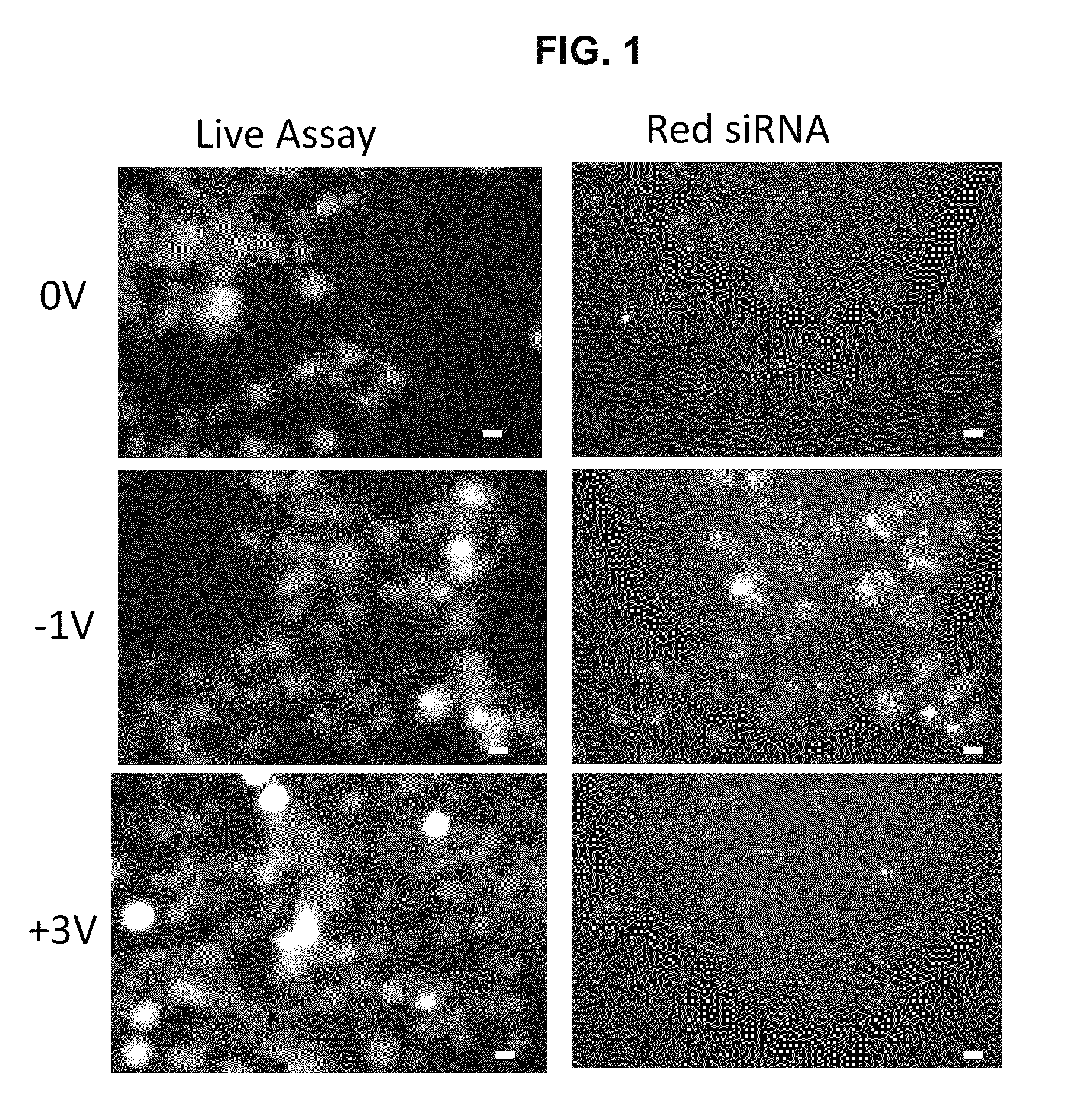
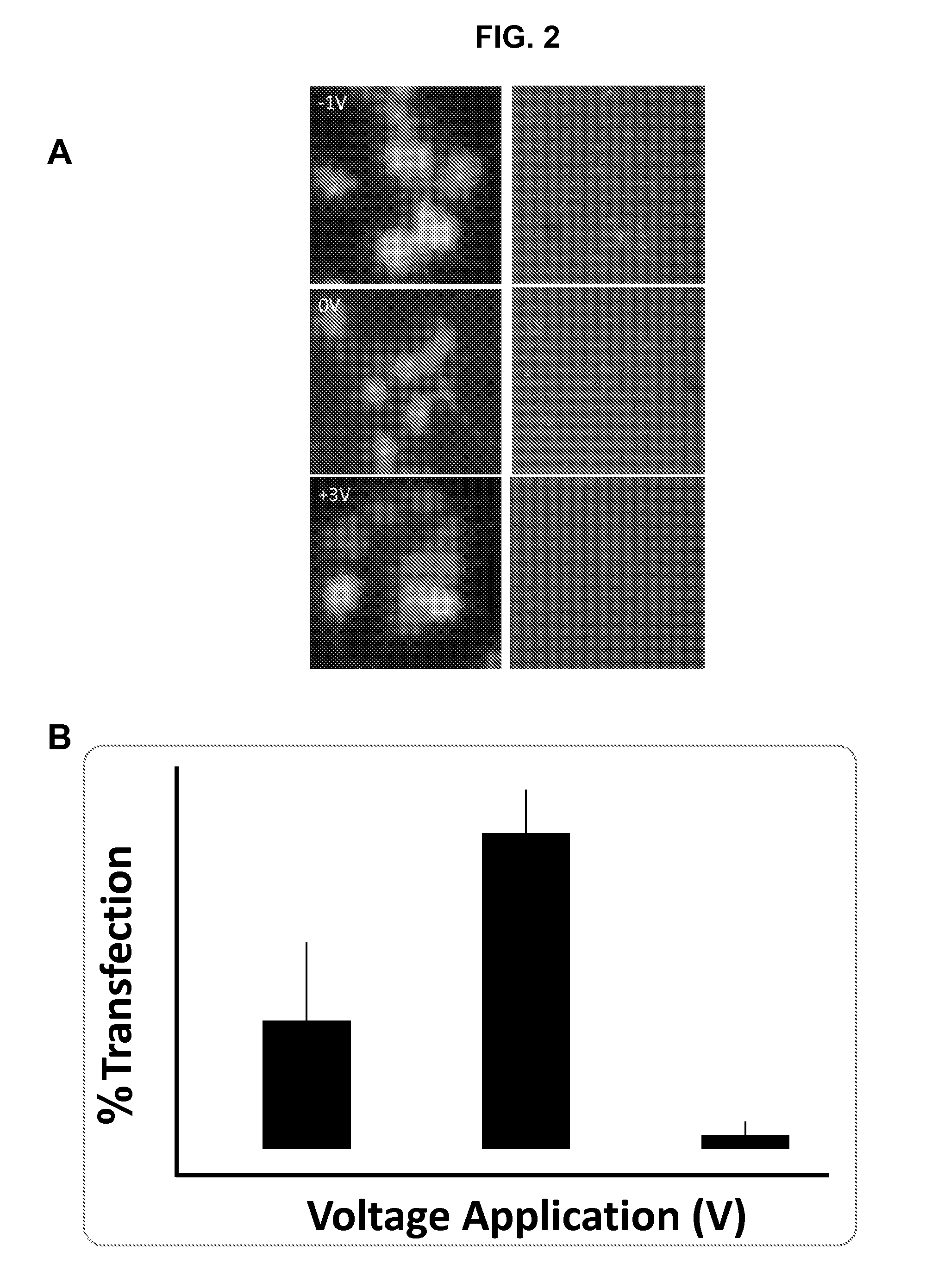
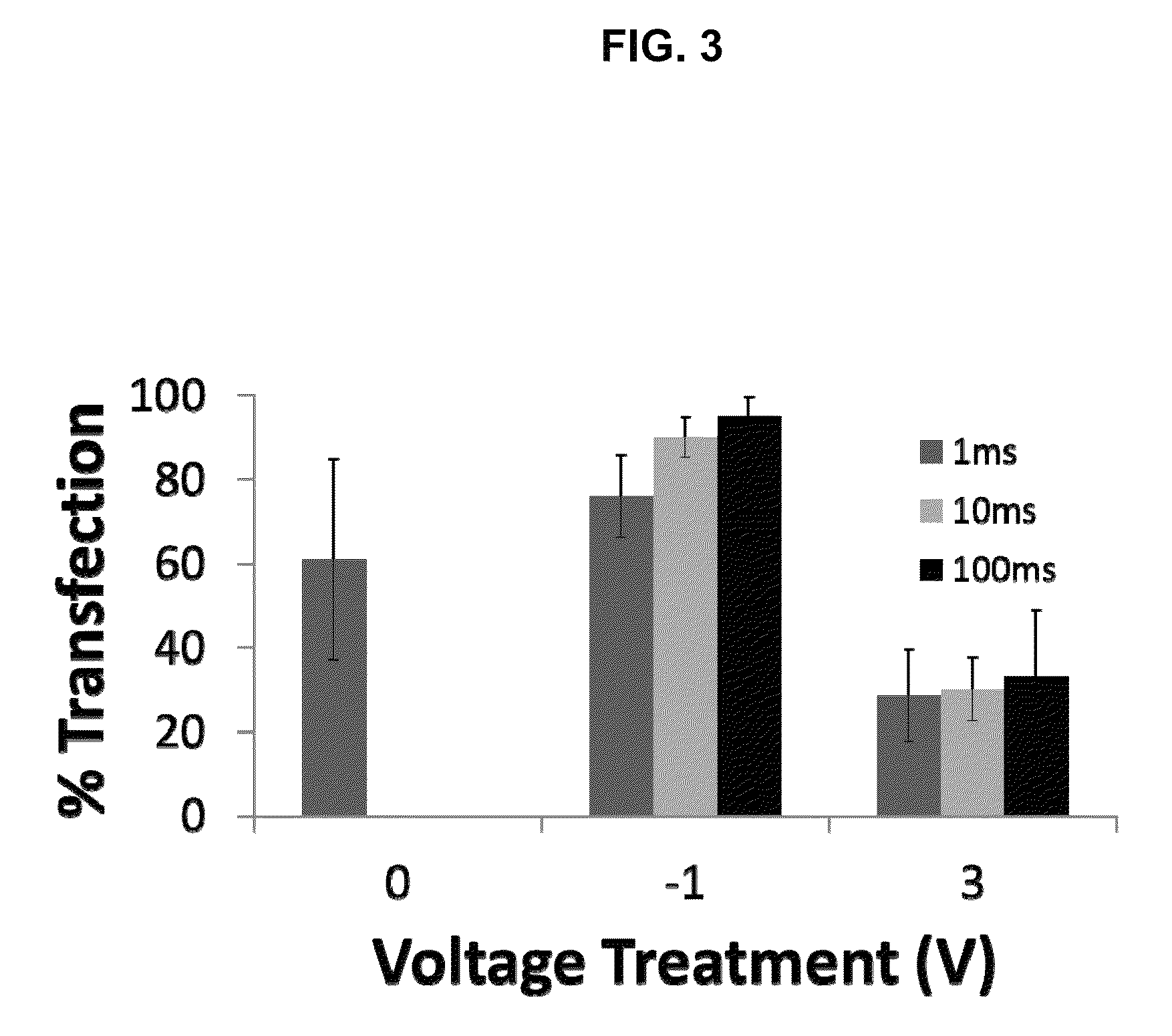
METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR HIGH EFFICIENCY TRANSFECTION OF siRNA
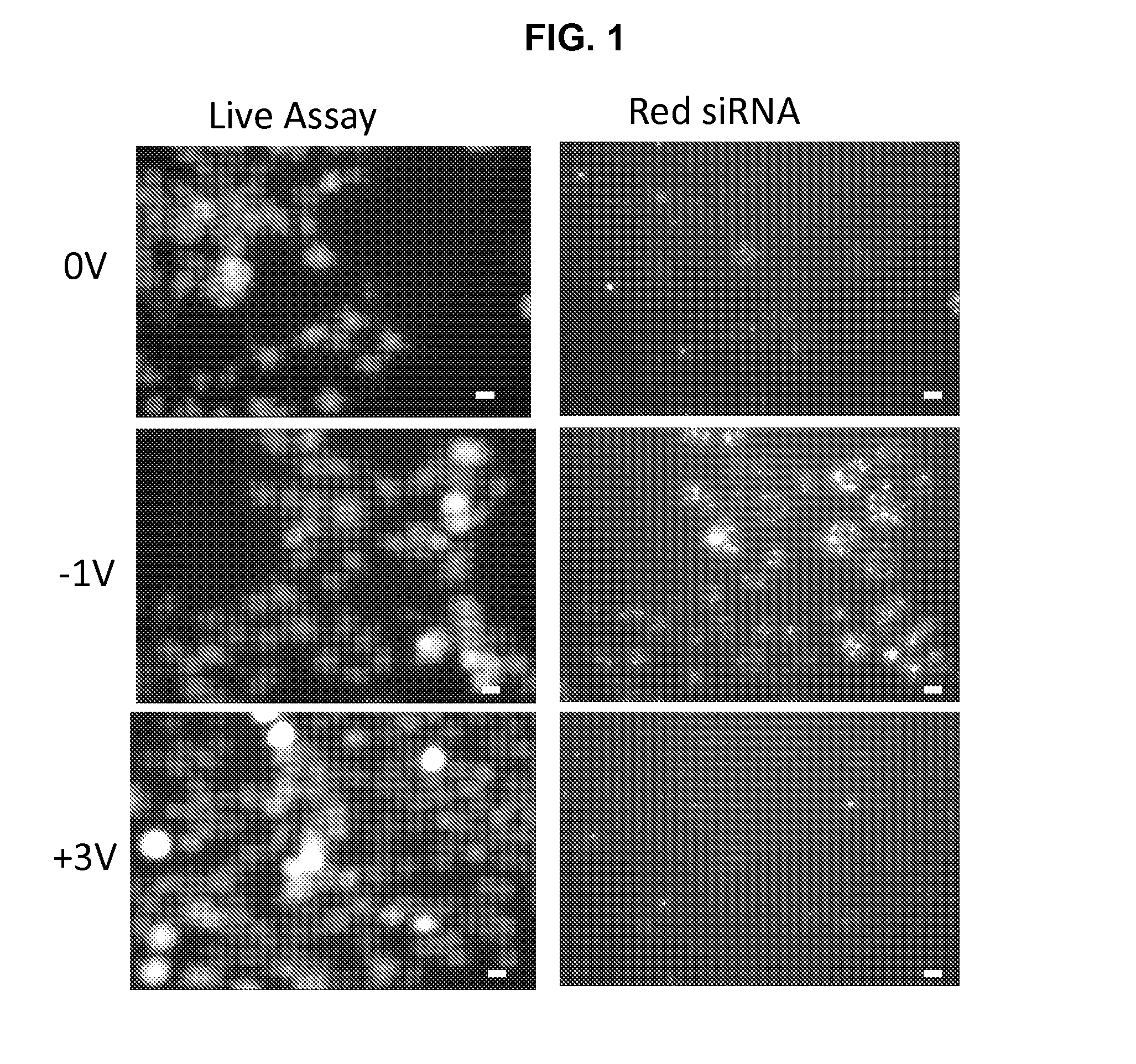
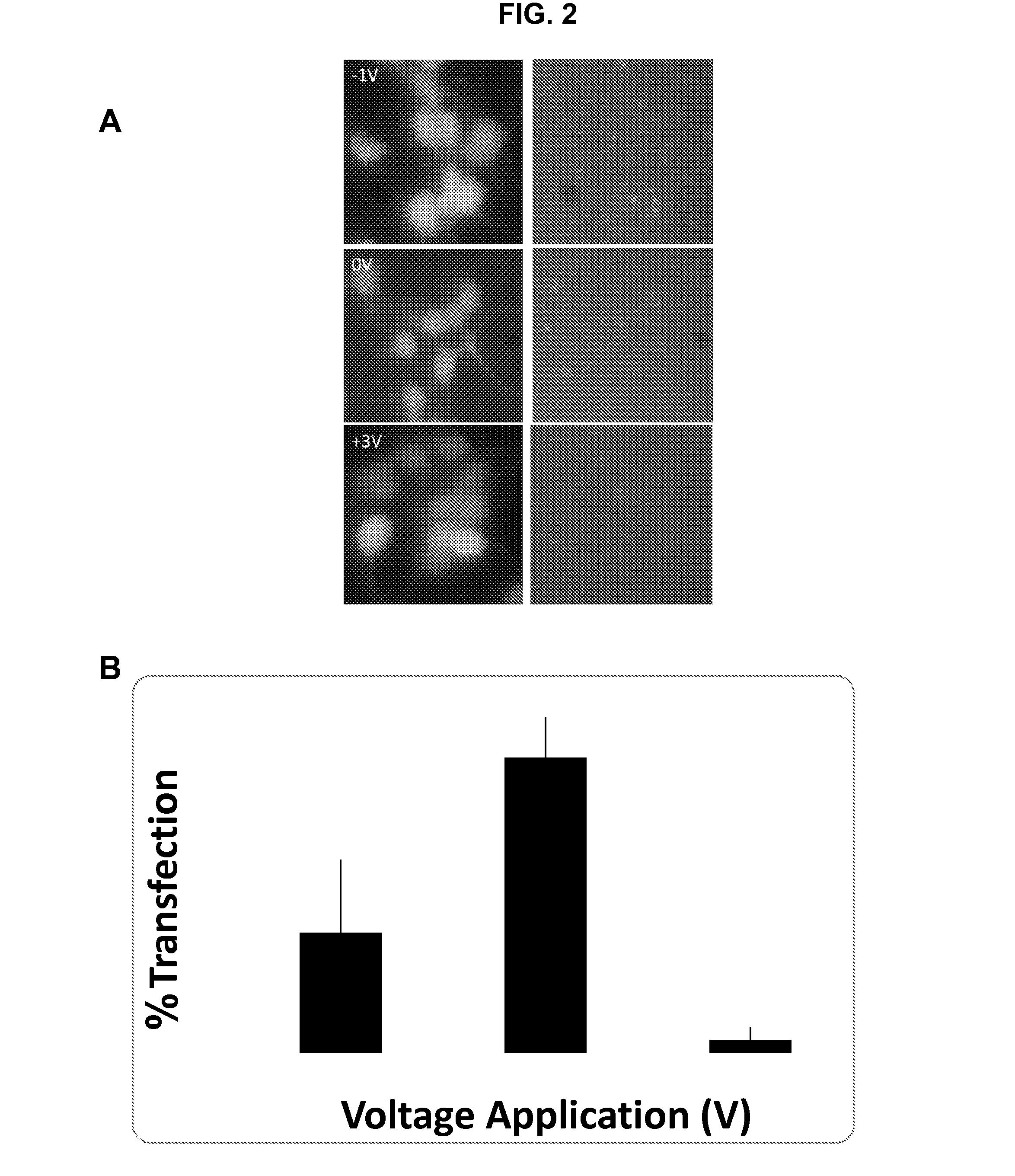
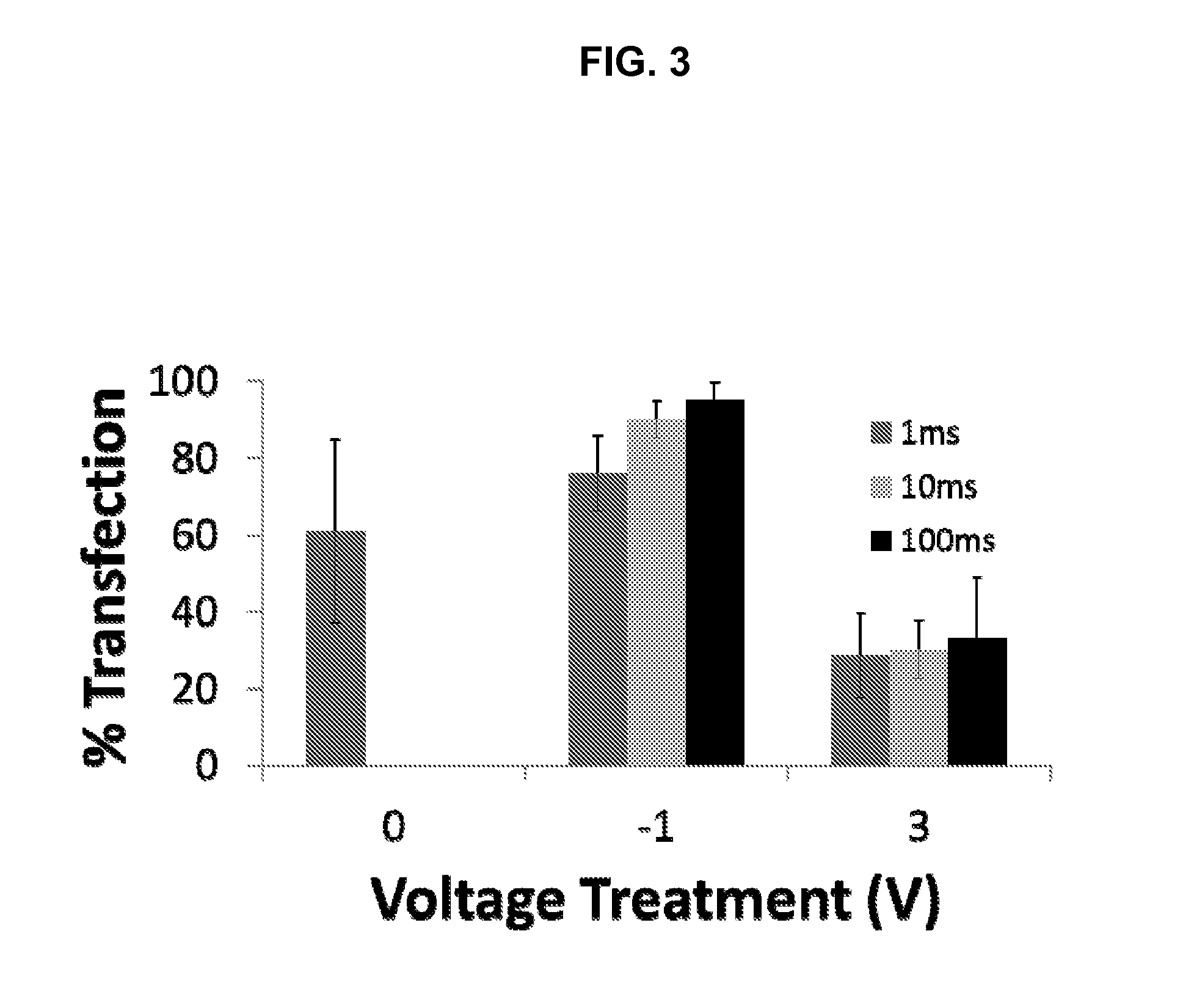
ActiveUS20140106429A1Enhances siRNA transfectionImprove efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLow voltageTransfection
Described herein are methods and compositions for high efficiency transfection of siRNA into a cell population. Such methods and compositions utilize a low voltage pre-conditioning pulse to modulate the efficiency of siRNA transfection. In some embodiments, the methods and compositions permit spatial and temporal control of siRNA transfection efficiency within a population of cells. The disclosed methods and compositions, in some embodiments, are amenable to high throughput applications such as siRNA library-based phenotypic screening.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method for obtaining mutant strains with prolonged growth period through compound mutation of dwarf Phaseolus vulgaris L. through physical method
ActiveCN112470922AReduce the total investment in plantingIncrease productionPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyGermplasm
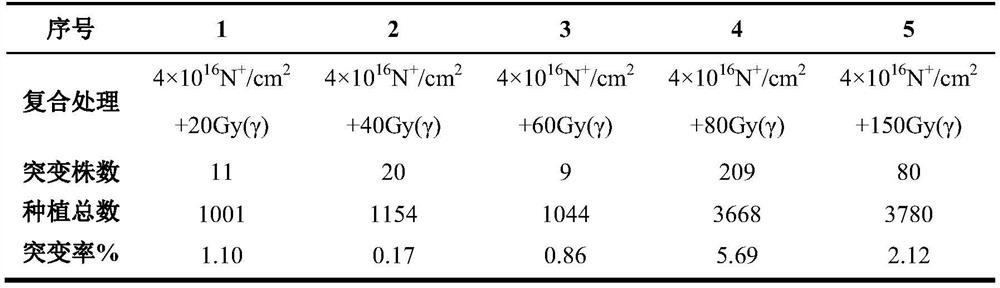
The invention discloses a method for obtaining mutant strains with the prolonged growth period through compound mutation of dwarf Phaseolus vulgaris L. through a physical method, and belongs to the field of nuclear agricultural science. The method aims to solve the problem that the fresh pod yield of the dwarf Phaseolus vulgaris L. is relatively low. The method for obtaining the mutant strains with the prolonged growth period comprises the following steps that 1, dry seeds of the dwarf edible pod Phaseolus vulgaris L. are placed into ion implantation equipment for nitrogen ion implantation, and the seeds subjected to nitrogen ion implantation are cultivated in a field so as to obtain M1-generation seeds; 2, <60>Co-gamma ray irradiation treatment is carried out on the M1-generation seeds, and the seeds subjected to irradiation treatment are cultivated in the field so as to obtain M2-generation seeds; and 3, the M2-generation seeds are continuously cultivated, and phenotypic screening iscarried out so as to obtain the mutant strains with the prolonged growth period, and therefore the Phaseolus vulgaris L. mutant strains with the prolonged growth period are obtained. According to thecompound mutation method, Phaseolus vulgaris L. mutant germplasm with prolonged growth period can be obtained; and N<+> ion implantation and <60>Co-gamma ray irradiation compound treatment are carried out on the dwarf Phaseolus vulgaris L., 209 mutant strains with the prolonged growth period are obtained, and the growth period can be prolonged by 10-50 days.
Owner:TECHN PHYSICS INST HEILONGJIANG ACADOF SCI
Phenotypic Screen For Plants
ActiveUS20080057511A1Improved and altered seed compositionEfficiency of germinationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringPhenotypic screeningAgronomy
The present invention is directed to a method of identifying plants with enhanced agronomic traits within a larger population of plants grown from a randomly planted set of seeds.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Cultivation method of polyploidy of triptonia macranthum
ActiveCN113475394ANormal growth and developmentGood biological propertiesBryophytesMoss cultivationBiotechnologyColchicine
The invention relates to a cultivation method of polyploidy of triptonium nigrum, and belongs to the technical field of polyploidy induction. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of soaking the leucotinum leucotinoides protonemata by using a colchicine solution to obtain mutagenized leucotinum leucotinoides protonemata; carrying out continuous subculture on the mutagenized hypnum macranthum protonemata for three times to obtain subcultured protonemata; carrying out ploidy identification on gametophytes differentiated from the subcultured protonemata to obtain genomic doubled mutants; carrying out subculture on the genome doubled mutant for five times, and screening out a genome doubled and stably inherited mutant; and observing the phenotype of the mutant with doubled genome and stable inheritance, and screening the triptonia melanoides mutant with a brand new phenotype as a new triptonia melanoides strain. The cultivation method is simple to operate, the occurrence rate of chimeras can be reduced, and the obtained polyploidy is stable in heredity.
Owner:丽水市润生苔藓科技有限公司
Application of PsPIWI-RE protein derived from pseudomonas stutzeri in mediated homologous recombination
The invention relates to an application of PsPIWI-RE (Pseudomonas stutzeri-derived PsPIWI-RE protein) in mediating homologous recombination. The research finds that the PsPIWI-RE protein derived from the pseudomonas stutzeri affects DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) replication and a DNA damage repair way; the invention discloses construction and application of a PsPIWI-RE protein mediated escherichia coli gene knockout technology derived from Pseudomonas stutzeri. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, constructing PsPIWI-RE protein expression plasmids from pseudomonas stutzeri and recombinant plasmids with left and right homologous arm sequences of gene sequences to be knocked out; and then transforming escherichia coli by using two plasmids, inducing double-exchange recombination, and obtaining a strain of which a target gene is knocked out through phenotypic screening or PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) identification. According to the operating system, the gene editing system based on the PsPIWI-RE protein and the homologous sequence is constructed for the first time. And a new excellent tool is provided for gene editing of microorganisms such as escherichia coli.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for breeding drought-enduring male parent germplasm based on corn PB group
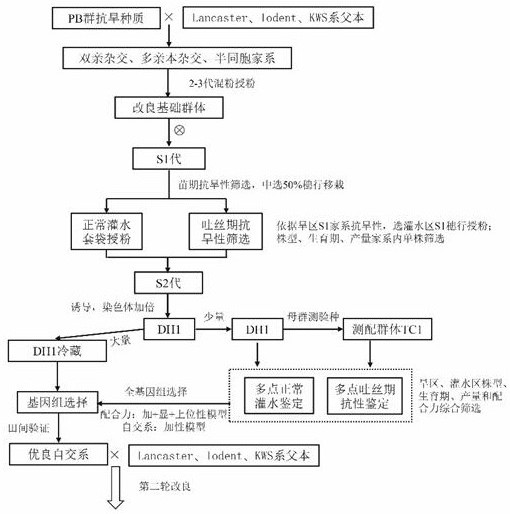
ActiveCN114793886ADehydration fastImprove adaptabilityBiostatisticsHybridisationBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention relates to the technical field of corn breeding, in particular to a method for breeding drought-enduring male parent germplasm based on a corn PB group. The method comprises the following steps: mixing PB group drought-resistant corn germplasm with a male parent material to construct a germplasm improvement basic group, and selfing to generate an S1 generation; performing inter-ear-row drought resistance screening on the S1 generation in the seedling stage, dividing the screened drought-resistant ear rows into two parts, respectively transplanting the two parts, selecting ear rows correspondingly planted in a normal irrigation area according to the identification result of the drought resistance of the ear rows after planting in an arid area, and performing selfing to obtain an S2 generation and form a DH1 line; taking a small amount of DH1 lines to form a test mating group TC1, performing multi-environment drought resistance phenotype identification on the test mating group TC1 and parent DH1 lines thereof, and respectively establishing whole genome selection models; a whole genome selection model is utilized to predict phenotypes of a large number of DH1 lines, and a screened excellent inbred line is a drought-resistant corn male parent germplasm. The invention aims to solve the problems of long breeding period, low selection efficiency and difficulty in balance of yield and drought tolerance of the existing corn male parent germplasm.
Owner:XINJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI & RECLAMATION SCI
Method for testing of antibiotic susceptibility in microorganisms
PendingUS20210278402A1Overcome deficienciesReduce evolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMicroorganismMedicine
The present invention relates to novel diagnostic tools including system, method and kit for determining antibiotic susceptibility in microorganisms directly in a clinical sample. Specifically, the present invention relates to a diagnostic system and method for testing antibiotic susceptibility based on a phenotypic screening of the microorganisms in the presence of major antibiotics being used currently. The present invention can be used directly on the clinical samples and obliterates the need for prior culturing. The present invention is convenient, rapid, cost-effective, does not need prior expertise to handle, has excellent selectivity and sensitivity. The present invention has the potential to improve patient outcomes and help reduce further evolution of antimicrobial resistant microorganisms.
Owner:MODULE INNOVATIONS PTE LTD
High-yield crossbreeding method of two-line super rice parent GuiKe-2S stock seeds
InactiveCN103609434BHigh purityIncrease productionPlant genotype modificationRice cultivationPhenotypic screeningEcology
The invention provides a high-yield crossbreeding method of two-line super rice parent GuiKe-2S stock seeds. The high-yield crossbreeding method comprises the following steps: A, carrying out phenotypic screening on a GuiKe-2S large group, namely, planting a GuiKe-2S group of a single plant; B, detecting a specificity marker of a GuiKe-2S sterile locus; C, detecting a molecular marker of a GuiKe-2S fingerprint spectrum; D, carrying out low-temperature screening on a GuiKe-2S first-time manual climatic box; E, carrying out low-temperature screening on a GuiKe-2S second-time manual climatic box; and F, breeding a rice root in winter of Hainan, transplanting the GuiKe-2S the root of which is cut again to Sanya of Hainan for breeding in winter, and harvesting seeds when ripening to obtain the two-line super rice parent GuiKe-2S stock seeds. According to the high-yield crossbreeding method, the stock seeds are further bred to obtain high-purity parent seeds applied to seed production, which has a very important significance in developing two-line hybrid rice. Through tests, the purity of the obtained breeder seeds reaches above 99.99 percent, and the purity of the stock seeds obtained through expanding propagation reaches above 99.9 percent.
Owner:广西壮族自治区农业科学院水稻研究所
A method for promoting the accumulation of flavonoids in leaves of ornamental crabapple
ActiveCN108849498BImproved color degradation defectsIncrease contentHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureBiotechnologyFlavonoid metabolism
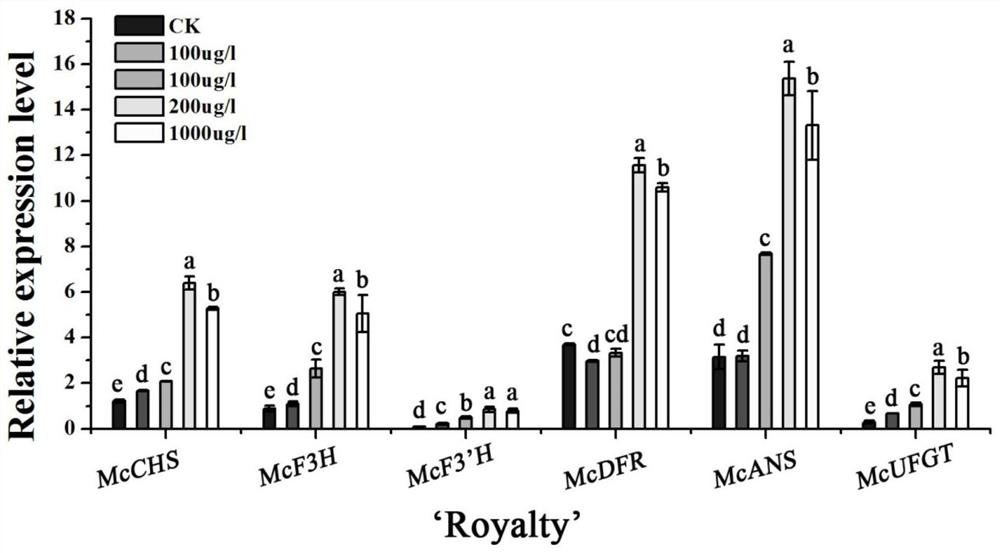
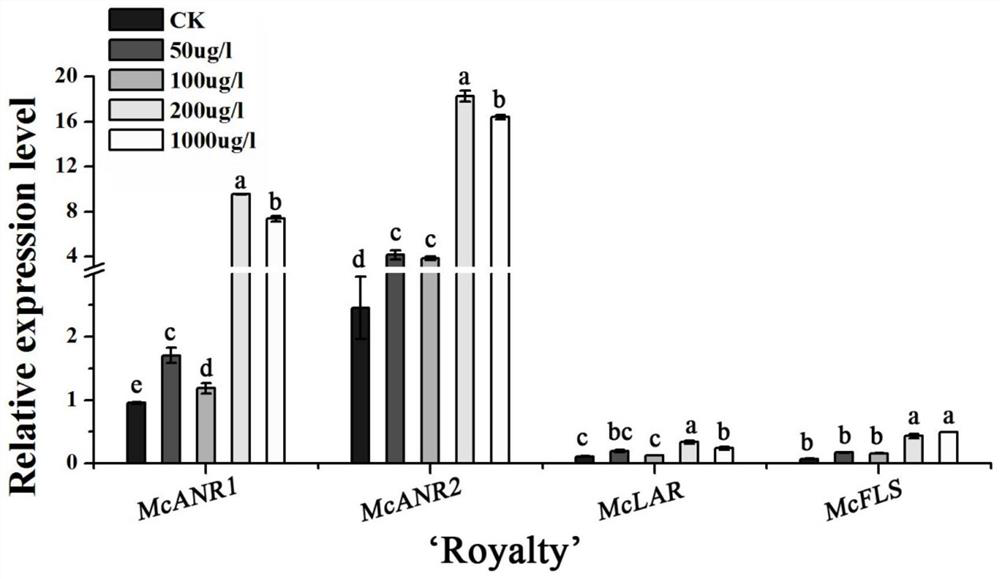
The invention discloses a method for promoting the accumulation of flavonoid substances in the leaf tissue of the ornamental crabapple of the ever-colored purple-leaved species, comprising: using the ornamental crabapple leaf species as materials, designing melatonin with different concentration gradients to treat the ornamental crabapple tissue culture seedlings, The leaves treated with 200μg / l melatonin were selected according to the phenotype, and the color of the leaves was very obvious, and there was no obvious change in the color of leaves at high or low concentrations. Subsequent detection of ornamental crabapple treated with 200μg / l melatonin The content of flavonoids in the leaves, the transcription levels of key genes in the flavonoid metabolism pathway, and the transcription levels of genes related to the melatonin pathway, the results showed that the anthocyanin content was the highest in the ornamental crabapple treated with 200 μg / l melatonin . The invention provides a method for improving the atavism phenomenon of the ornamental crabapple due to the increase in the number of generations, and further provides a good theoretical basis for the genetic improvement of the color-leaved plants in the future.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
A method for accurate and rapid identification of drug targets of active compounds obtained by phenotypic screening
Owner:RUIJIN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
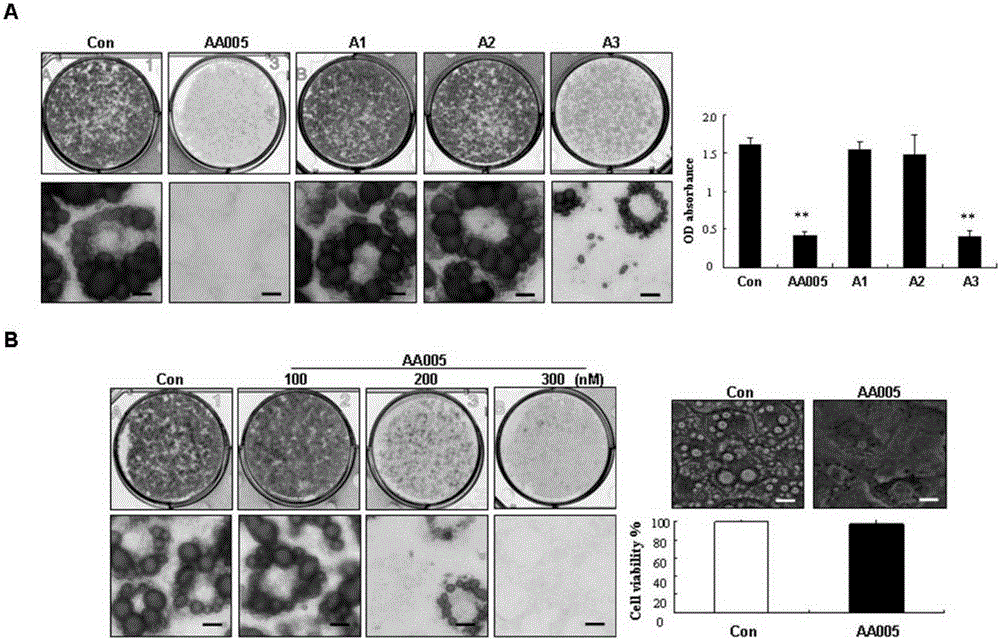
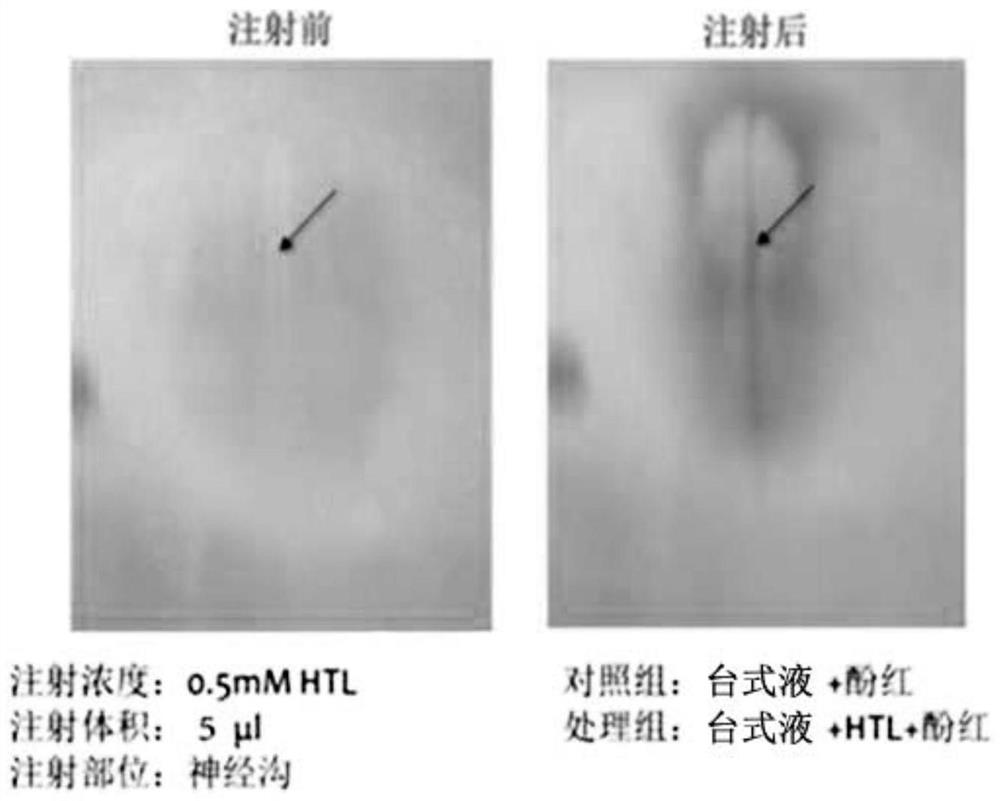
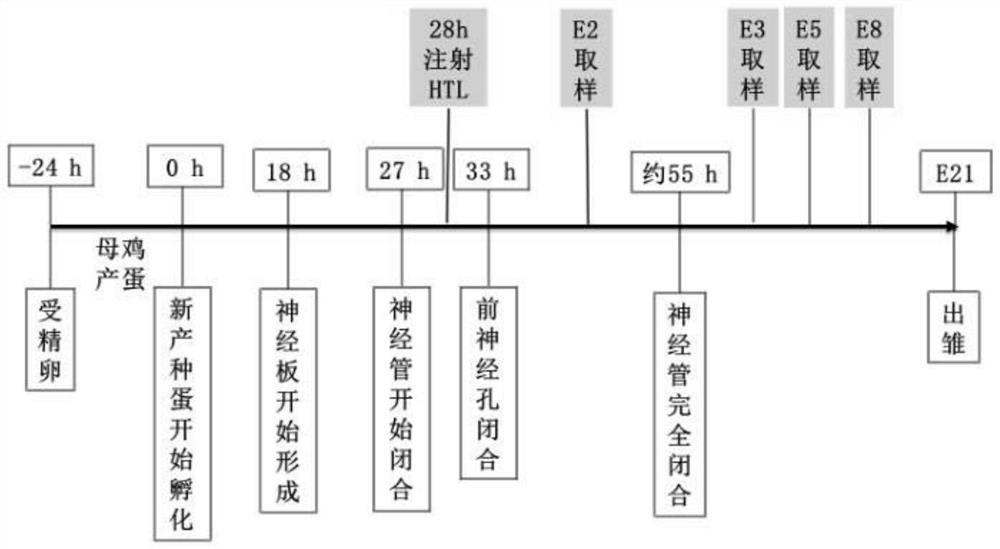
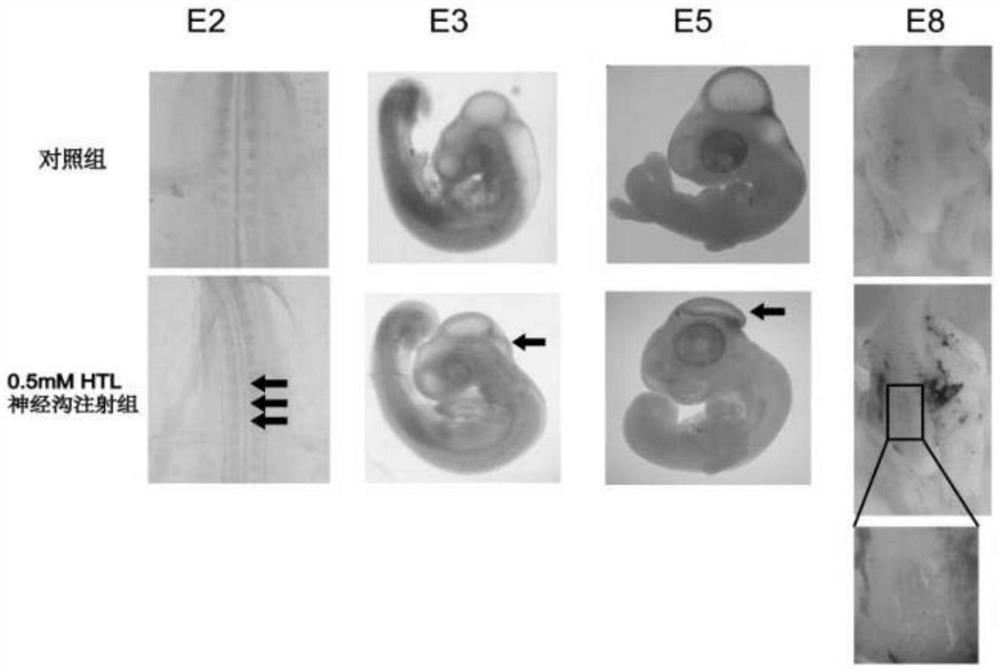
A method of constructing a neural tube defect model and its application
ActiveCN108853092BImprove survival rateEasy to observeOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAnimal scienceNervous system
The invention discloses a method for constructing a neural tube defect model, which comprises the following steps: step 1, collecting artificially inseminated eggs, cleaning them and placing them in an incubator for incubation; step 2, incubating the eggs to the neural plate of chicken embryos After the start of closure, inject homocysteine thiolactone into the eggs using the chicken embryo neural groove injection method; step 3, continue to incubate the treated eggs, observe the phenotype of the chicken embryos, and screen out successful neural tube defects Model. Another aspect of the present invention also discloses the application of the above construction method in the study of the pathogenesis of neural tube defects caused by high homocysteine. By adopting the neural tube defect model construction method provided by the invention, the deformity rate of the nervous system reaches 50%, and the embryo survival rate reaches 87.5%, which is currently the best modeling method for observing neural tube defects.
Owner:首都儿科研究所
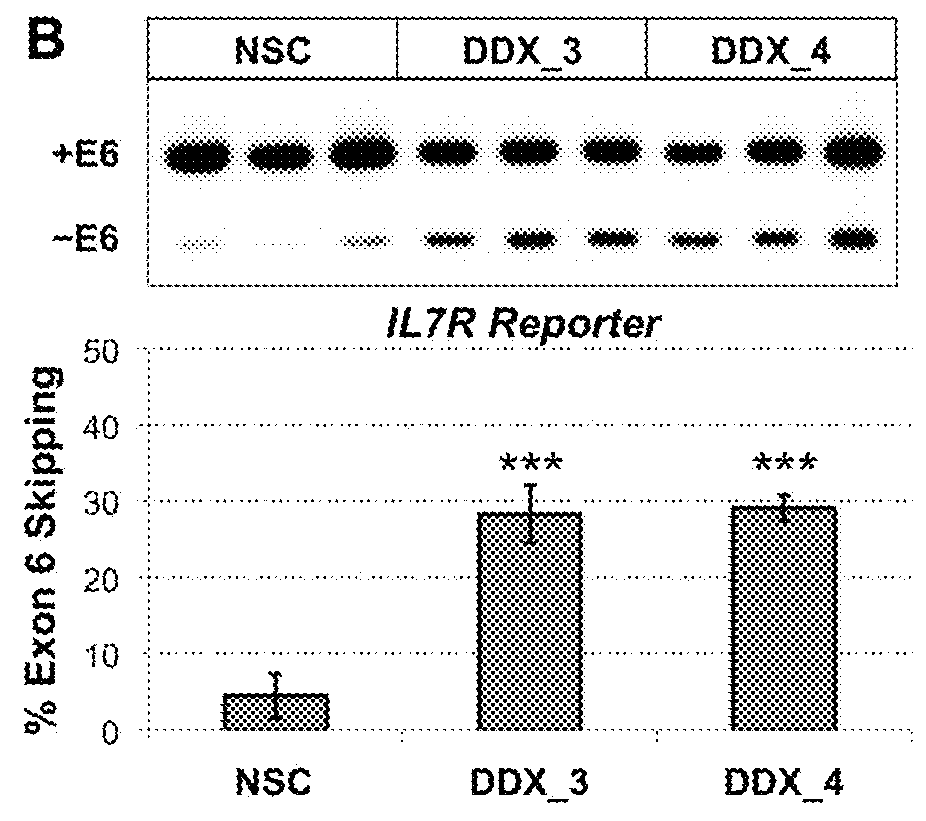
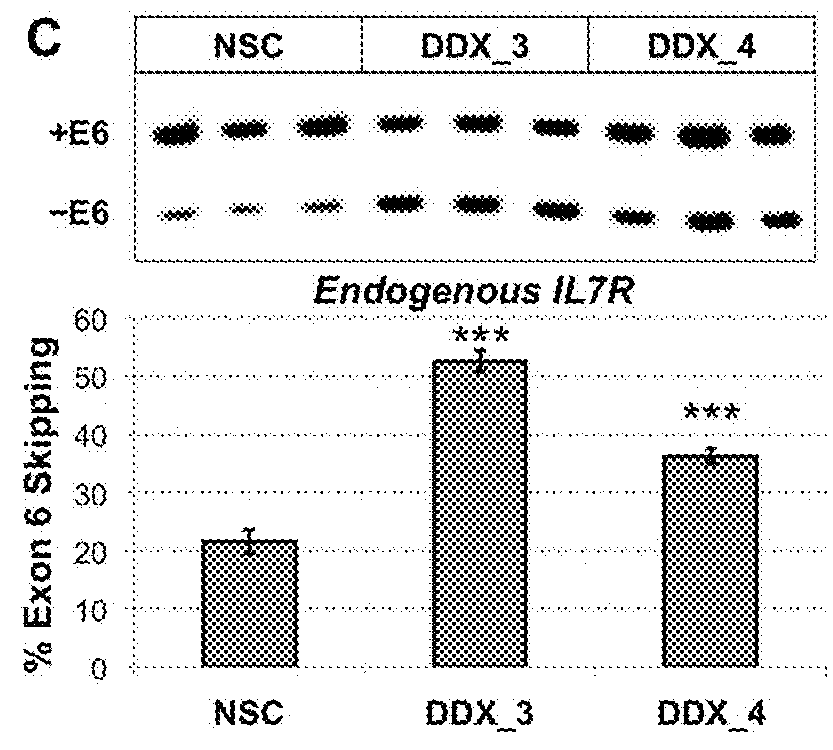
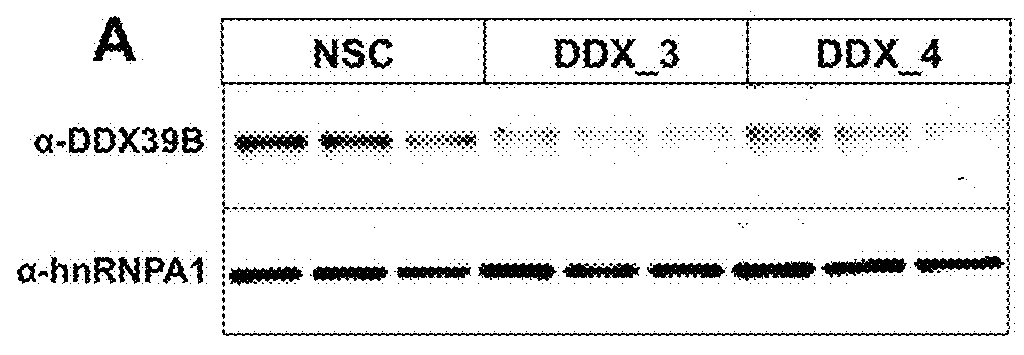
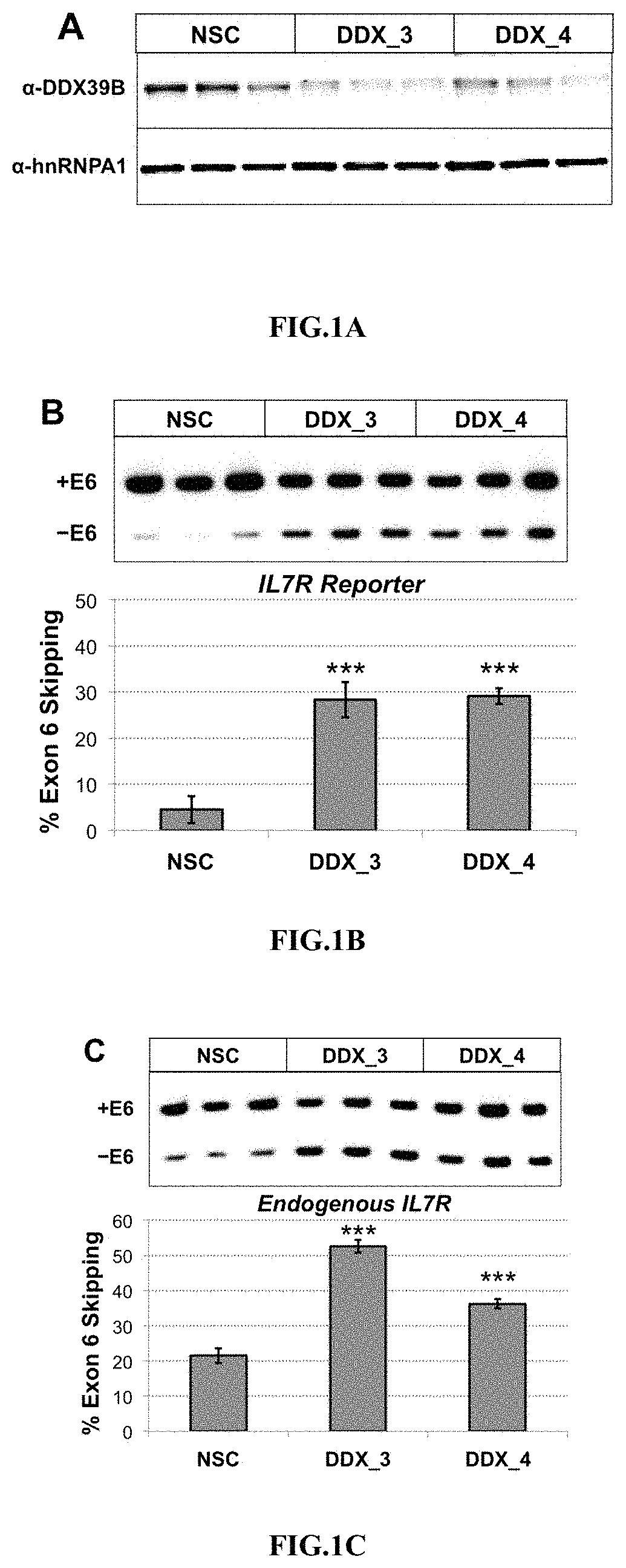
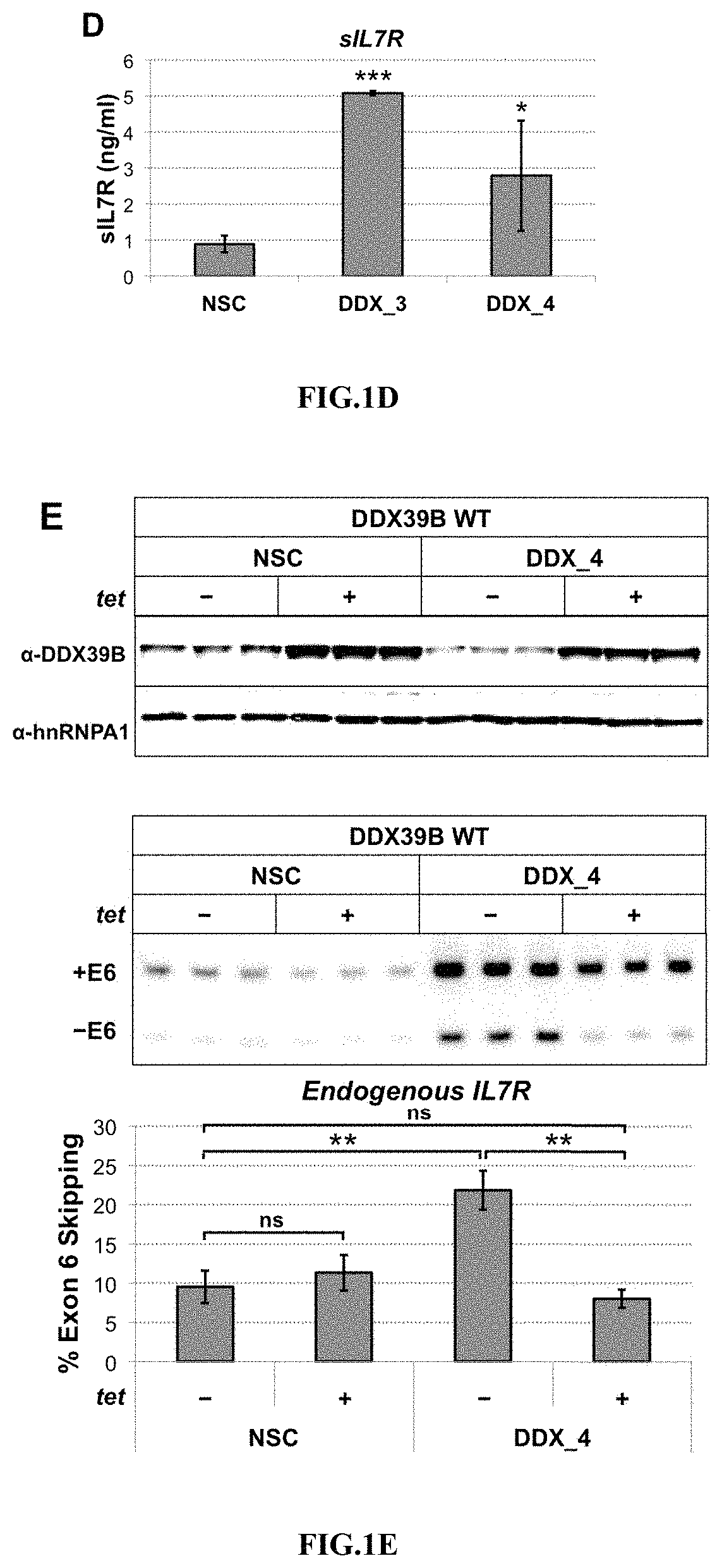
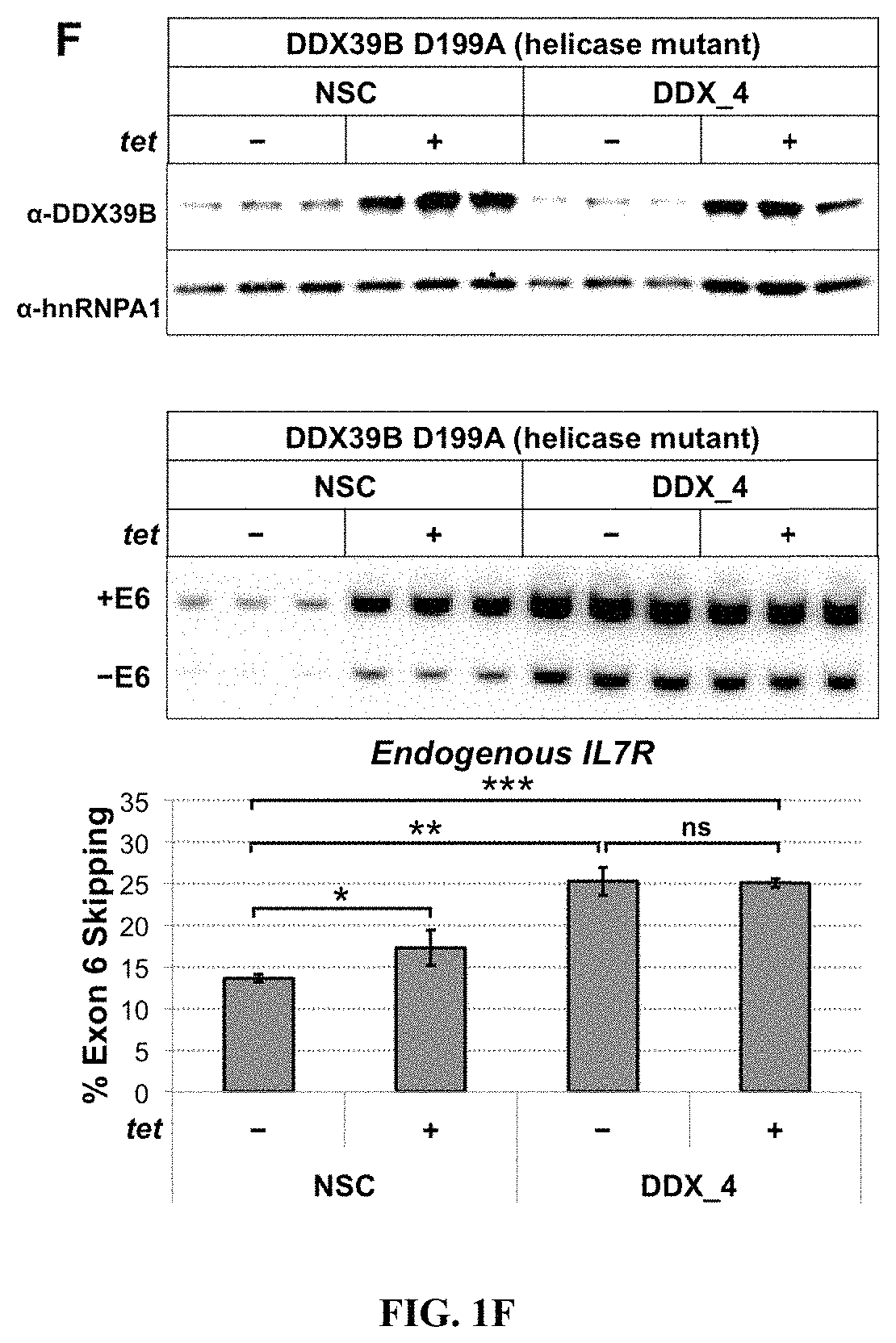
Method to identify subjects at higher risk to develop an autoimmune disease based on genetic and/or phenotypic screening for epistatic variants in ddx39b (rs2523506) and il7r (rs6897932)
ActiveUS20180274033A1Increased riskFacilitates inclusionHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementAutoimmune diseaseHelicase
The present invention includes a method, kits, and assays for identifying a human subject as having an increased risk of developing an autoimmune disease, or a human subject with multiple sclerosis caused by elevated soluble Interleukin 7 receptor (sIL7R), by obtaining a biological sample and detecting or measuring in the biological sample an amount of a soluble Interleukin-7 receptor (sIL7R) and an amount of an RNA Helicase DDX39B, whereby a lower expression of DDX39B and a higher secretion of sIL7R identifies the subject from which the biological sample was obtained as having an increased risk of developing an autoimmune disease, when compared to a human subject not having an autoimmune disease. The present invention also includes a method of modifying a treating of subjects based on the lower expression of RNA Helicase DDX39B alone or in combination with an increase in sIL7R.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +2
Breeding method of a breed of sheep for multiple litter meat
The invention provides a breeding method of a multiple-birth mutton sheep breed and relates to the technical field of animal breeding. The breeding method herein is characterized in that a Hu sheep, as a first male parent, an east eastfrierian sheep as a second female parent and a Tan sheep as a female parent are subjected to three-breed crossing; the novel multiple-birth mutton sheep breed suitable for the ecological conditions of loess plateau is cultivated through phenotypic screening in combination with screening of specific gene carriers; the multiple-birth mutton sheep breed is adaptiveto the natural ecological conditions of the loess plateau ecological region of China and has the advantages of good stress resistance, crude feeding resistance, high propagation rate, good meat tenderness, uniform fat distribution, little odor and the like.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY PHARMA OF CAAS
Methods and compositions for high efficiency transfection of siRNA
ActiveUS9399771B2Improve efficiencyEnhanced transfectionSpecial deliveryElectrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentLow voltagePre conditioning
Described herein are methods and compositions for high efficiency transfection of siRNA into a cell population. Such methods and compositions utilize a low voltage pre-conditioning pulse to modulate the efficiency of siRNA transfection. In some embodiments, the methods and compositions permit spatial and temporal control of siRNA transfection efficiency within a population of cells. The disclosed methods and compositions, in some embodiments, are amenable to high throughput applications such as siRNA library-based phenotypic screening.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Method to identify subjects at higher risk to develop an autoimmune disease based on genetic and/or phenotypic screening for epistatic variants in DDX39B (RS2523506) and IL7R (RS6897932)
ActiveUS10961581B2HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunologic disordersAutoimmune condition
The present invention includes a method, kits, and assays for identifying a human subject as having an increased risk of developing an autoimmune disease, or a human subject with multiple sclerosis caused by elevated soluble Interleukin 7 receptor (sIL7R), by obtaining a biological sample and detecting or measuring in the biological sample an amount of a soluble Interleukin-7 receptor (sIL7R) and an amount of an RNA Helicase DDX39B, whereby a lower expression of DDX39B and a higher secretion of sIL7R identifies the subject from which the biological sample was obtained as having an increased risk of developing an autoimmune disease, when compared to a human subject not having an autoimmune disease. The present invention also includes a method of modifying a treating of subjects based on the lower expression of RNA Helicase DDX39B alone or in combination with an increase in sIL7R.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +2
A method for breeding new germplasm with resistance/resistance to glyphosate using wild soybean
ActiveCN105165602BImprove reliabilityIncrease success ratePlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceResource utilization
Owner:FARMING & CULTIVATION RES INST OF HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com