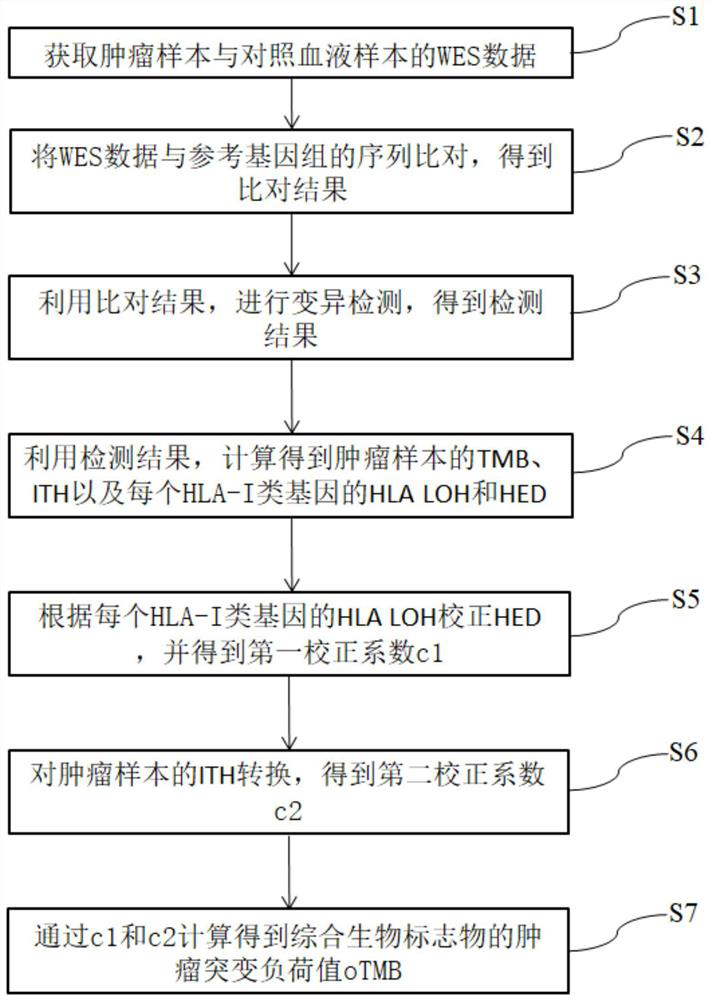
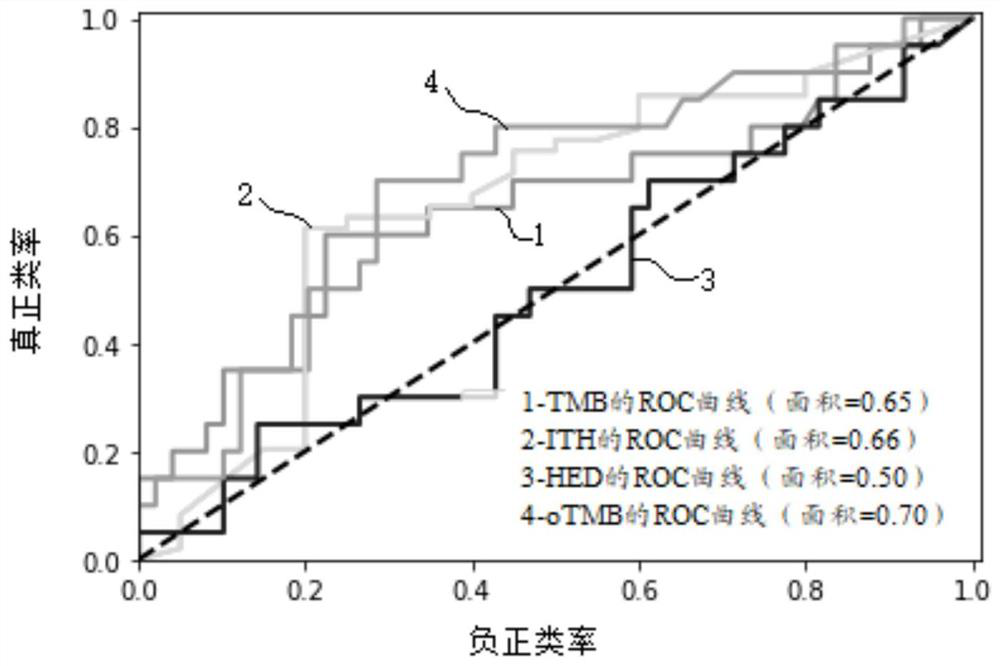
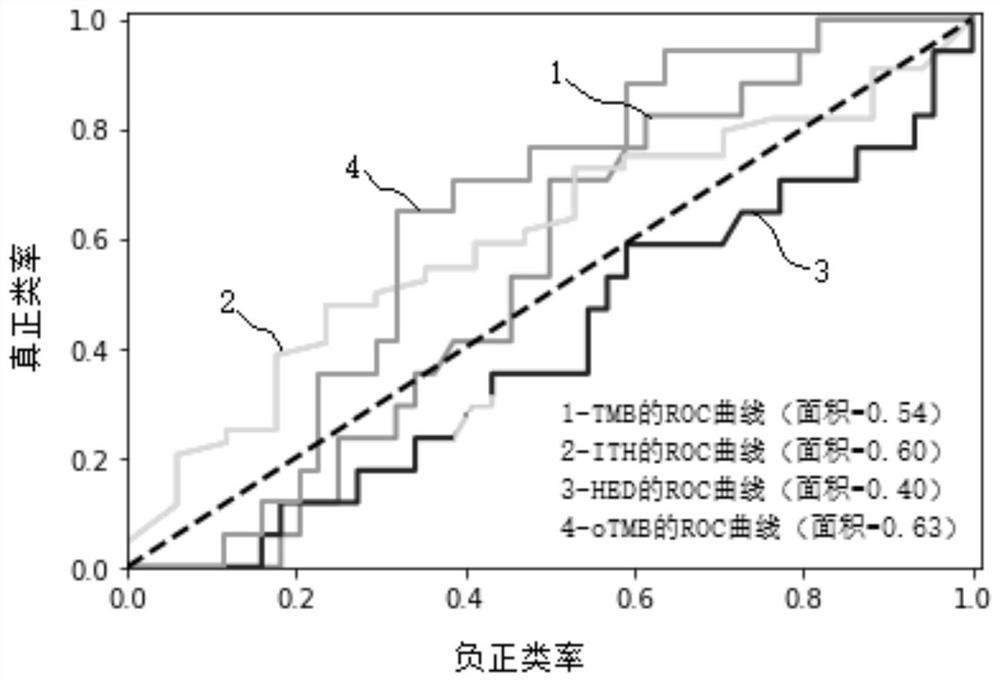
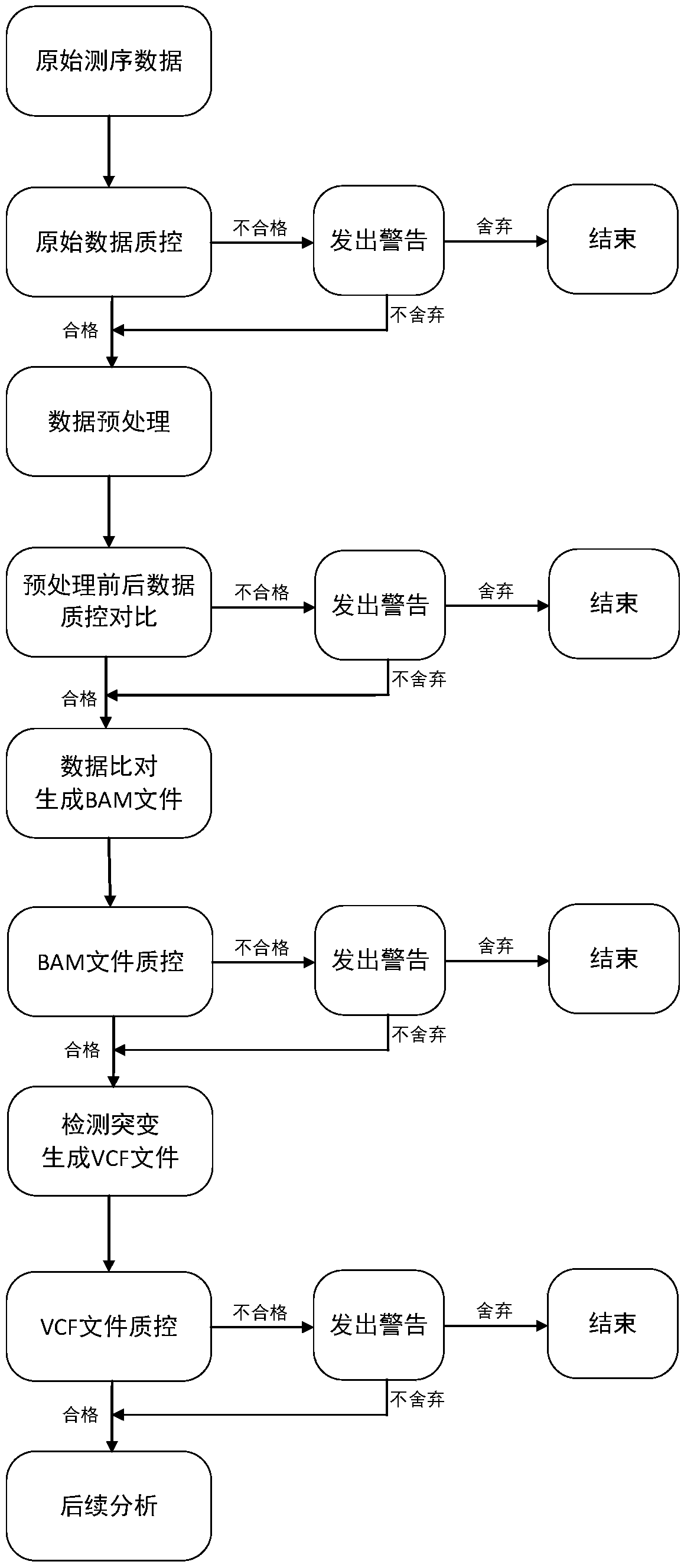
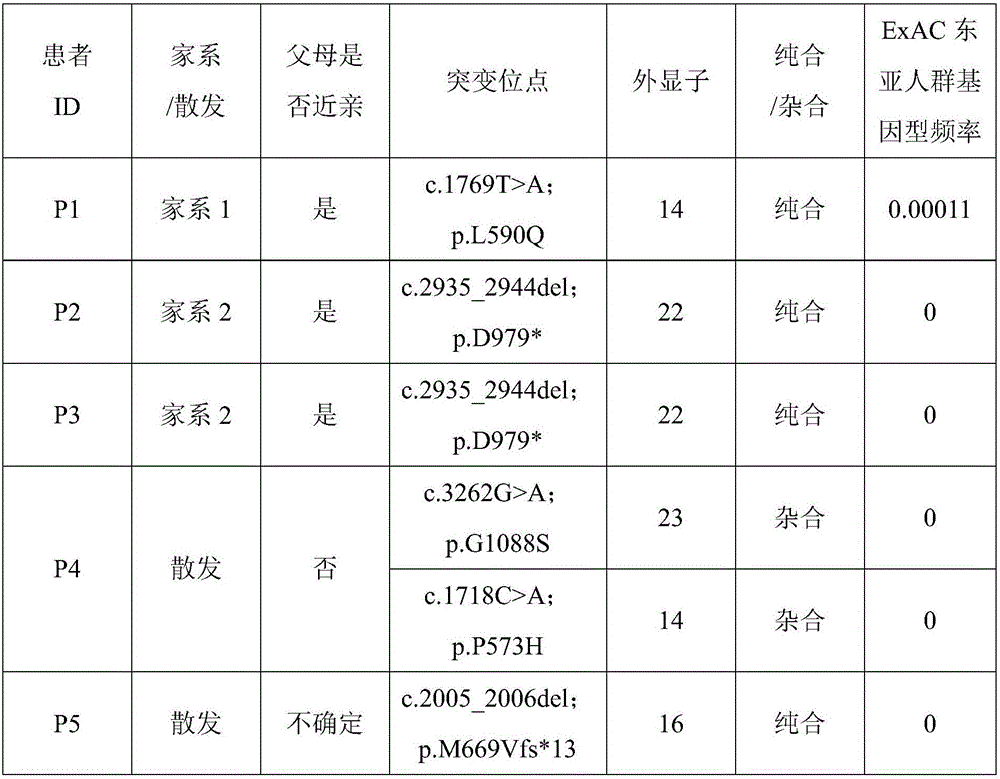
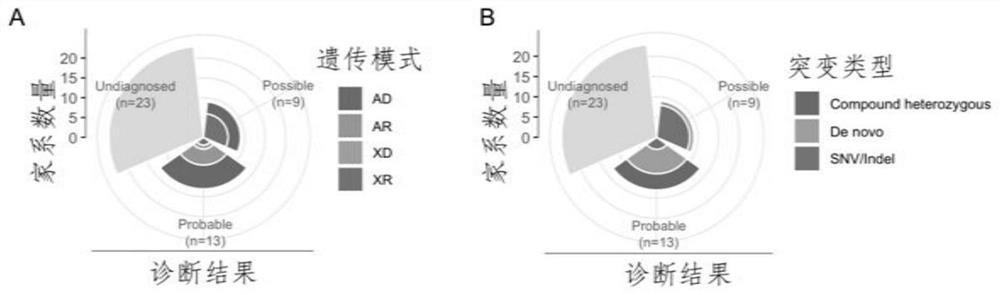
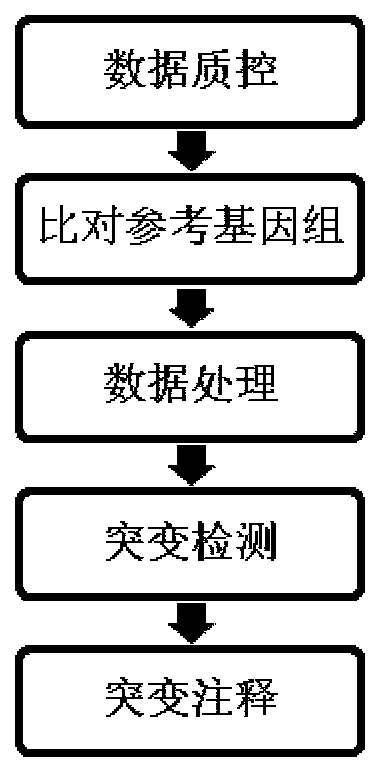
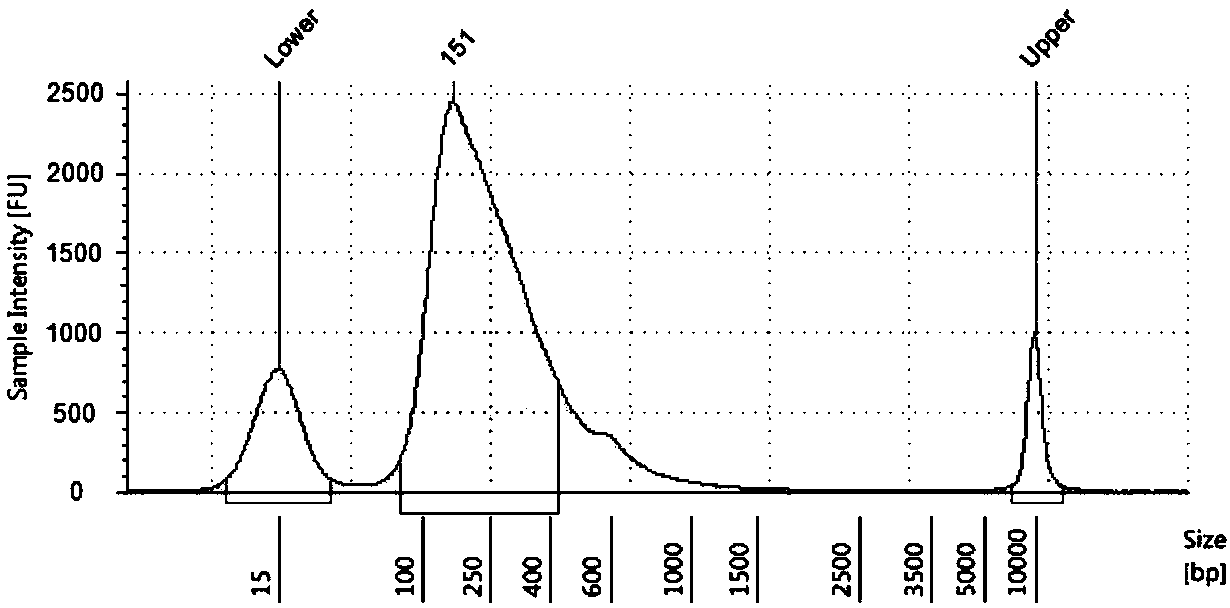
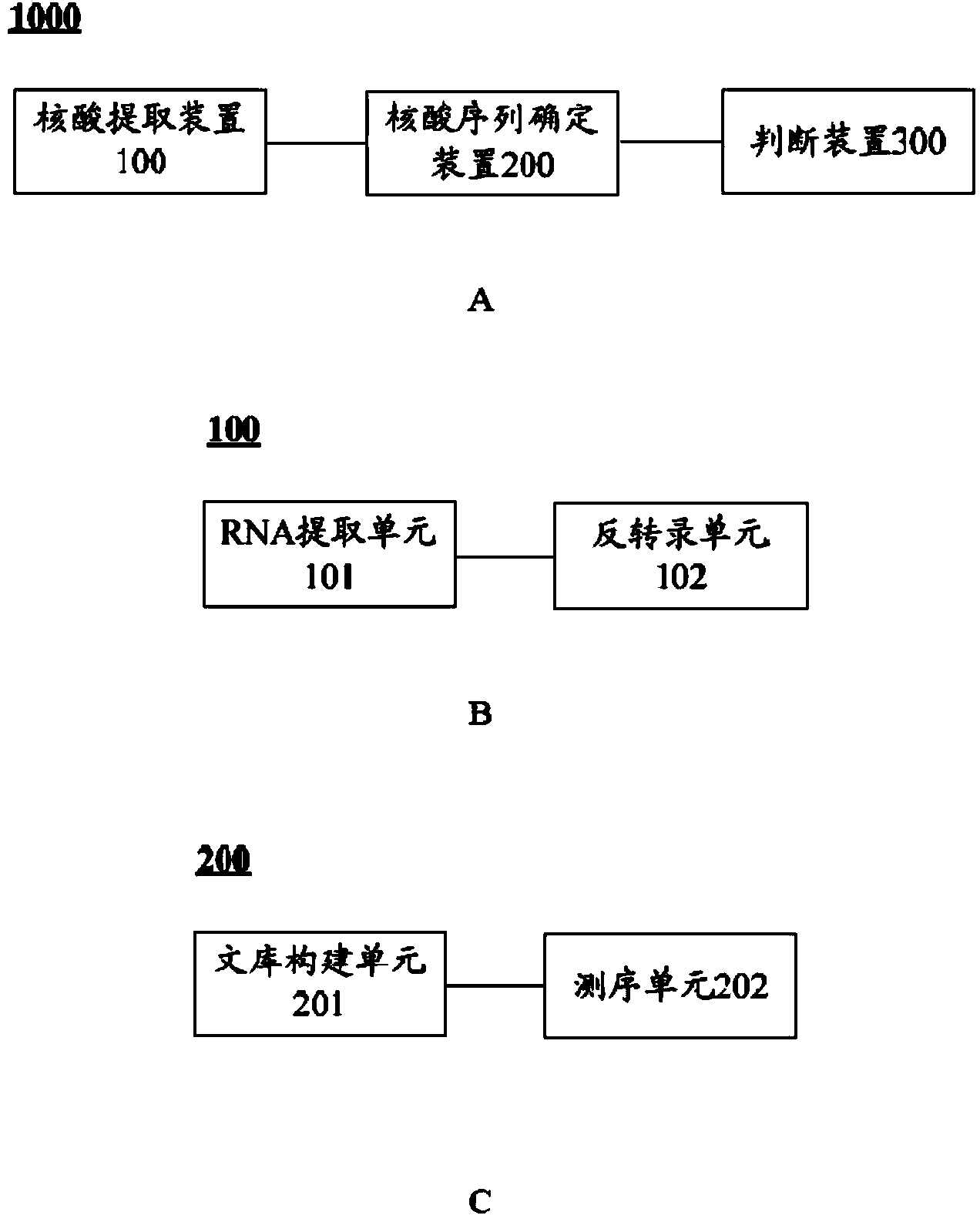
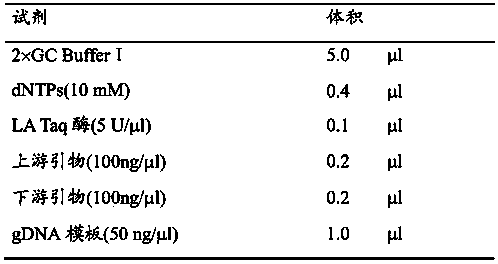
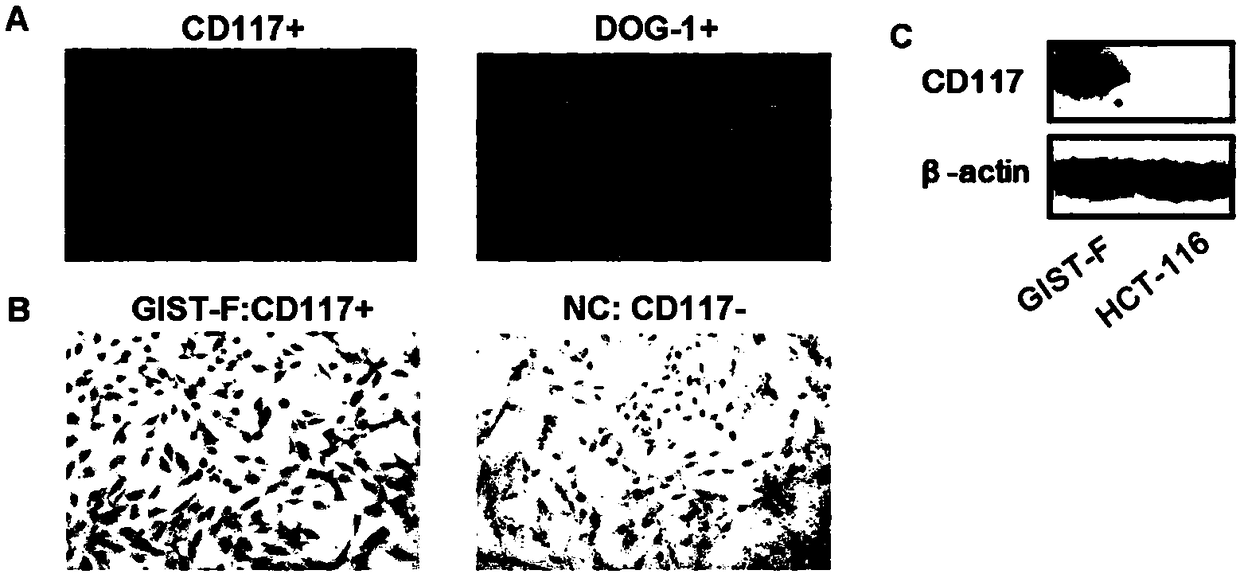
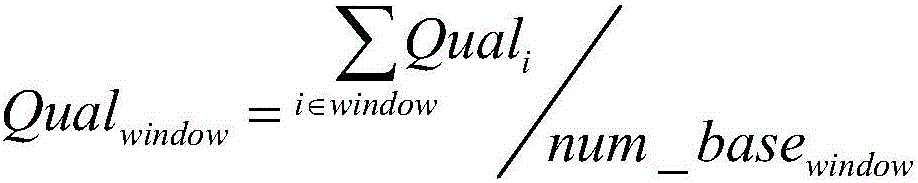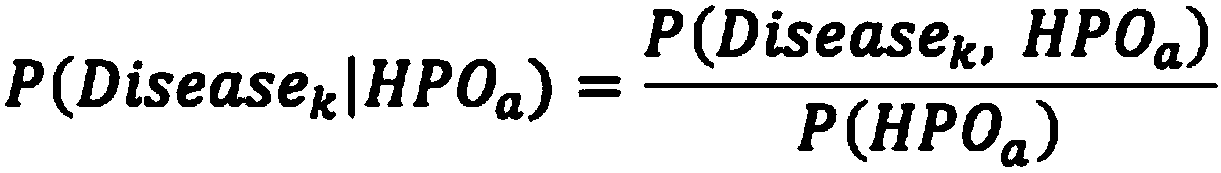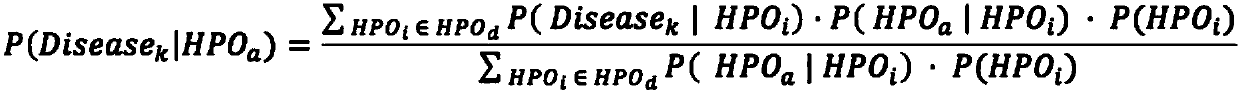Patents
Literature
76 results about "Exome sequencing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exome sequencing, also known as whole exome sequencing (WES), is a genomic technique for sequencing all of the protein-coding region of genes in a genome (known as the exome). It consists of two steps: the first step is to select only the subset of DNA that encodes proteins. These regions are known as exons – humans have about 180,000 exons, constituting about 1% of the human genome, or approximately 30 million base pairs. The second step is to sequence the exonic DNA using any high-throughput DNA sequencing technology.
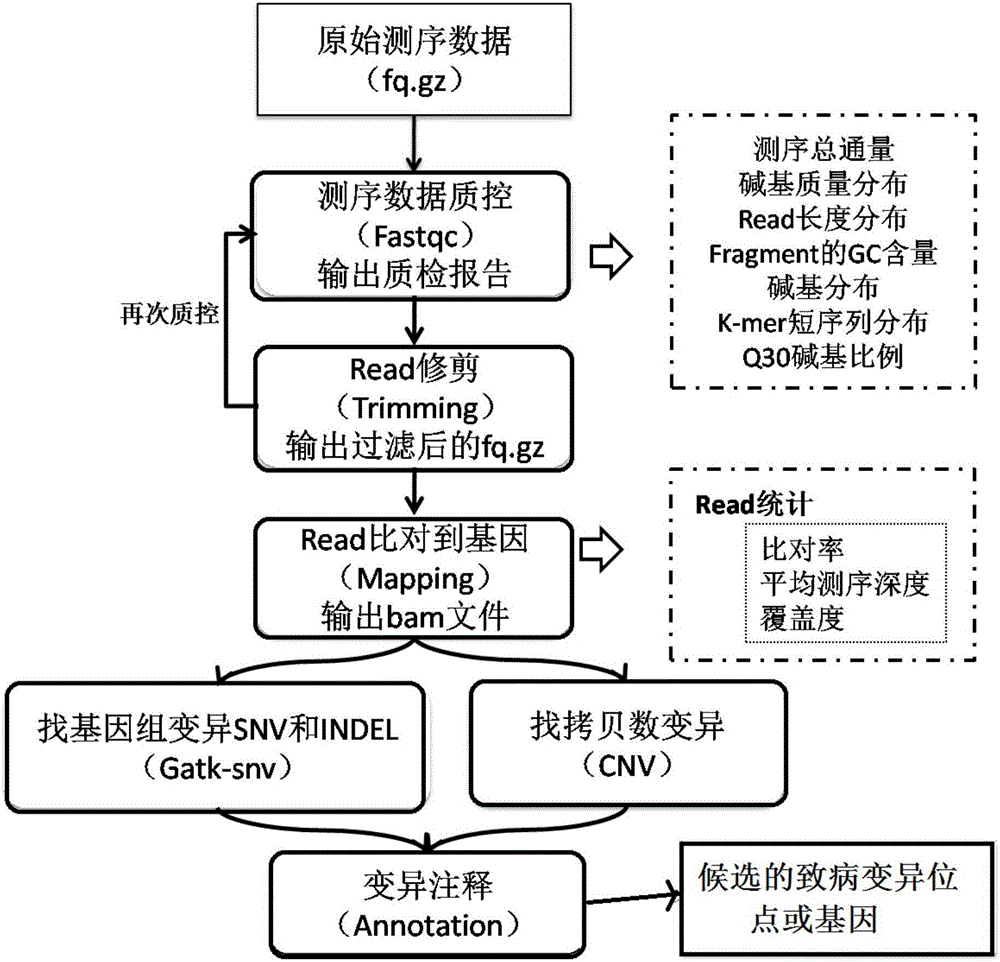
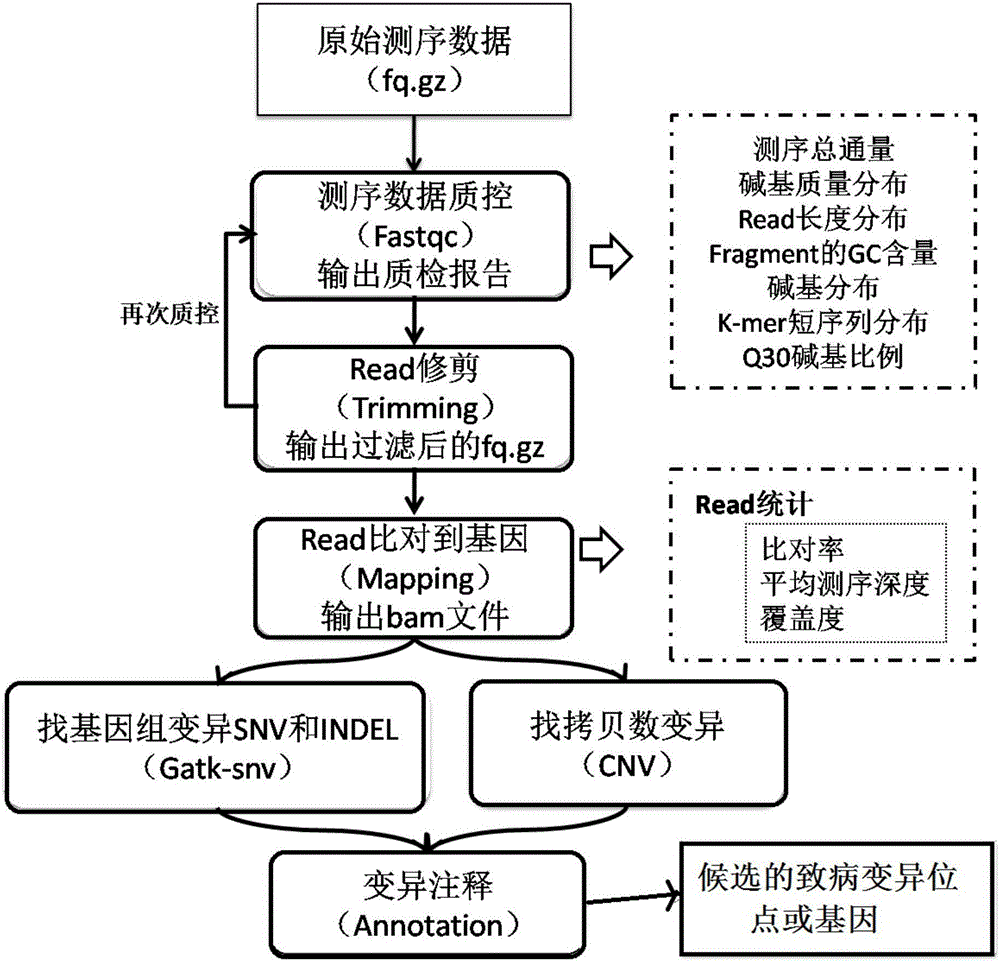
Whole-exome sequencing data analysis system
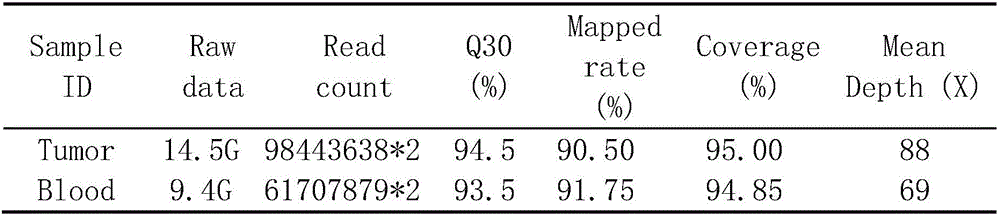
The invention discloses a whole-exome sequencing data analysis system. The system comprises a quality control module which is used for assessing single base quality in an original sequencing data file and read quality; a genome mapping module which is used for finishing a read to genome mapping process by employing an aln algorithm of a BWA; a genome variation module which is used for finding variation sites in a genome by employing a Unified Genotyper method of a GATK packet; and a variation site annotation module which is used for annotating variation candidate sites or a genome interval. According to the system, large-scale data analysis is finished through simple parameter submission; the analysis comprises quality detection of original data, data denoising and sequencing upstream to downstream original sequencing data of genome mapping of the read; the sequencing data is analyzed through a parameter automatic submission and analysis module; the candidate pathogenic mutation sites and related genes are output; and the basis is provided for later experiment verification.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
Identification method for genetic disease-related gene
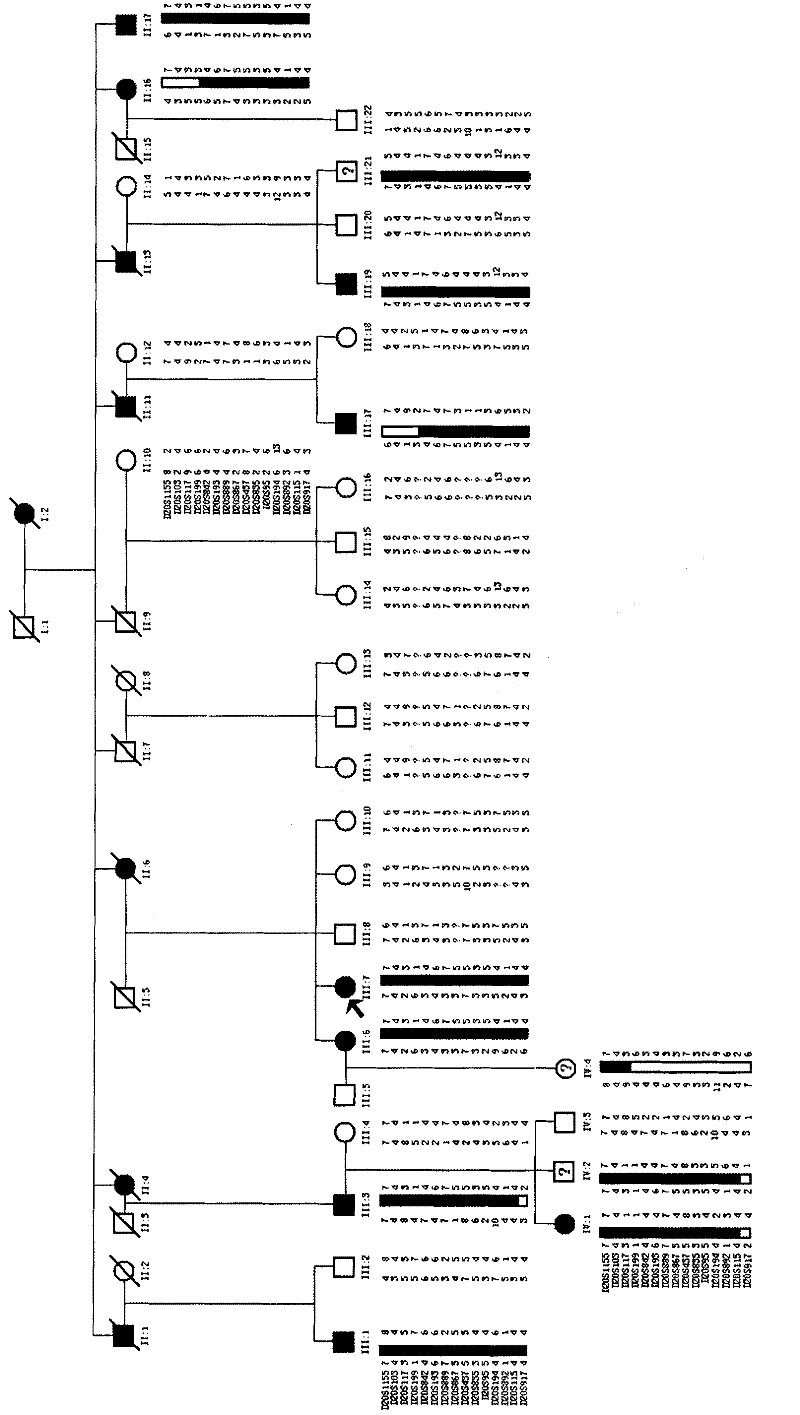
The invention relates to an identification method for a genetic disease-related gene, comprising the following steps: 1) obtaining a sample of DNA in genetic disease gene family; 2) carrying out preliminary positioning of chromosomes of related genes; 3) optionally, further carrying out accurate positioning and haplotype analysis of the chromosomes of the related genes; 4) according to chromosomal localization results, taking a certain amount of DNA samples and identifying the related genes with the technology of human genome exome sequencing. The invention also relates to an identification method for related genes of hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia and a kit for the analysis of the related genes of hereditary spinocerebellar ataxia.
Owner:BGI SHENZHEN CO LTD +1
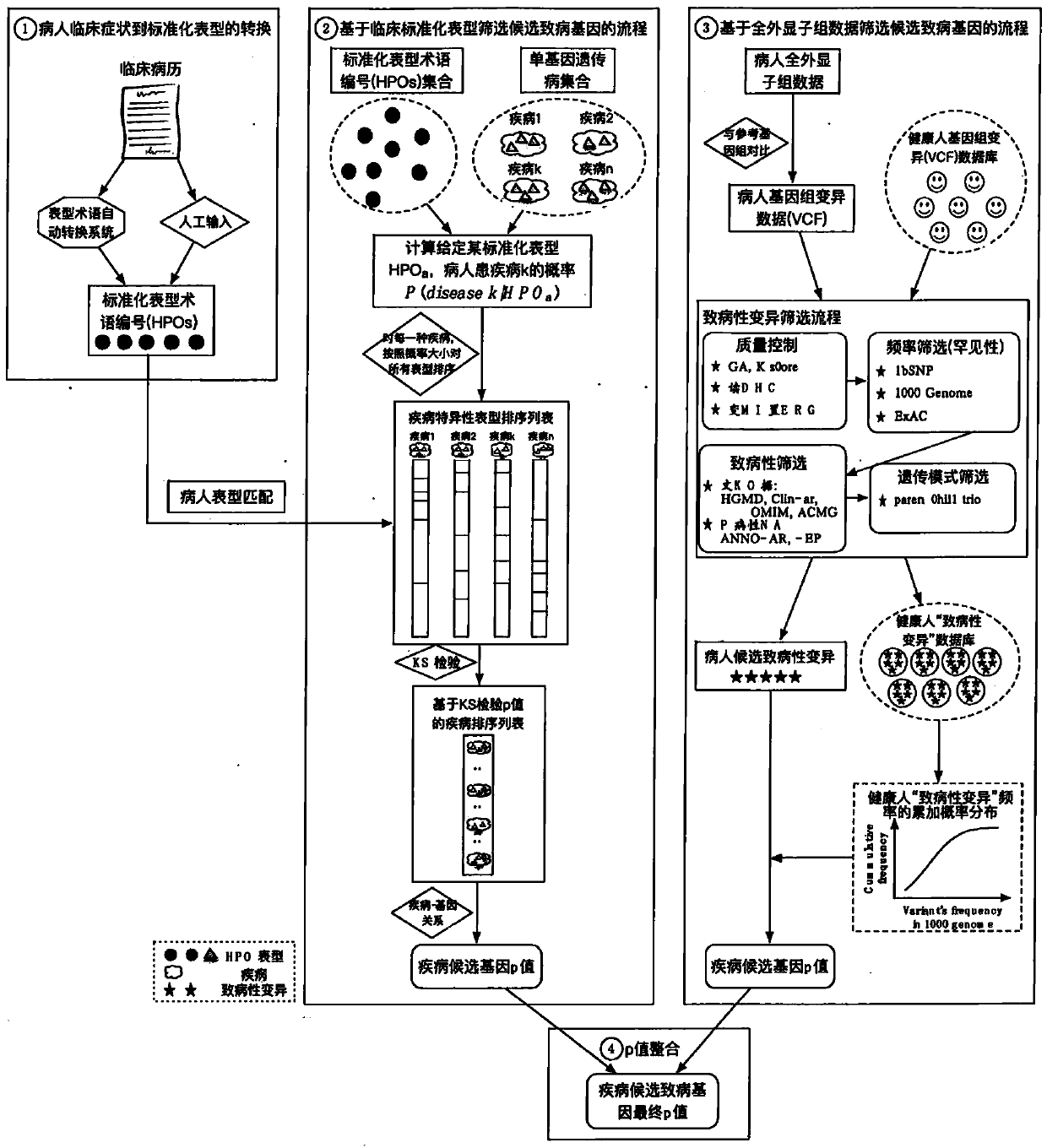
Analysis detection system for screening single gene hereditary disease pathogenic gene based on patient clinical symptom data and whole exome sequencing data
The invention relates to an automated analysis system for automatically screening the single gene disease and hereditary disease pathogenic gene based on patient clinical phenotype information and whole exome sequencing data. The system comprises four automatic analysis modules: (1) an automatic transferring subsystem for automatic transferring from patient clinical report to standardized phenotype term (HPO, human phenotype ontology); (2) an automatic analysis system for screening disease pathogenic gene based on patient standardized phenotype; (3) an automatic analysis system for screening disease pathogenic gene based on patient whole exome sequencing data; and (4) a p value integration system. The system adopts a possibility model to calculate the possibility of developing a certain single gene hereditary disease under the situation that a certain standard phenotype of the patient is provided, and utilizes a computer statistic check method to systematically evaluate the significance level of developing a certain single gene hereditary disease after all standard phenotype of the patient are provided, so as to accordingly achieve the purpose of screening candidate disease pathogenic gene based on clinical standard phenotype.
Owner:上海睿视健康科技有限公司
Whole-exome sequencing data analysis method
The invention provides a whole-exome sequencing data analysis method. The method comprises the following steps of 1) quality control of sequencing data; 2) genome mapping of the sequencing data; 3) seeking of high-confidence genome mutation by the sequencing data; and 4) annotation of mutation sites. According to the method, the analysis of large-scale data is finished through simple parameter submitting, wherein the analysis of the large-scale data comprises quality detection of original data, data denoising and genome mapping of sequencing read; an upstream part takes over original sequencing data of a lower machine; the analysis of the sequencing data is finished through a parameter automated submitting and analysis module; and candidate pathogenic mutation sites and related genes are output, thereby providing a basis for later experimental verification.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
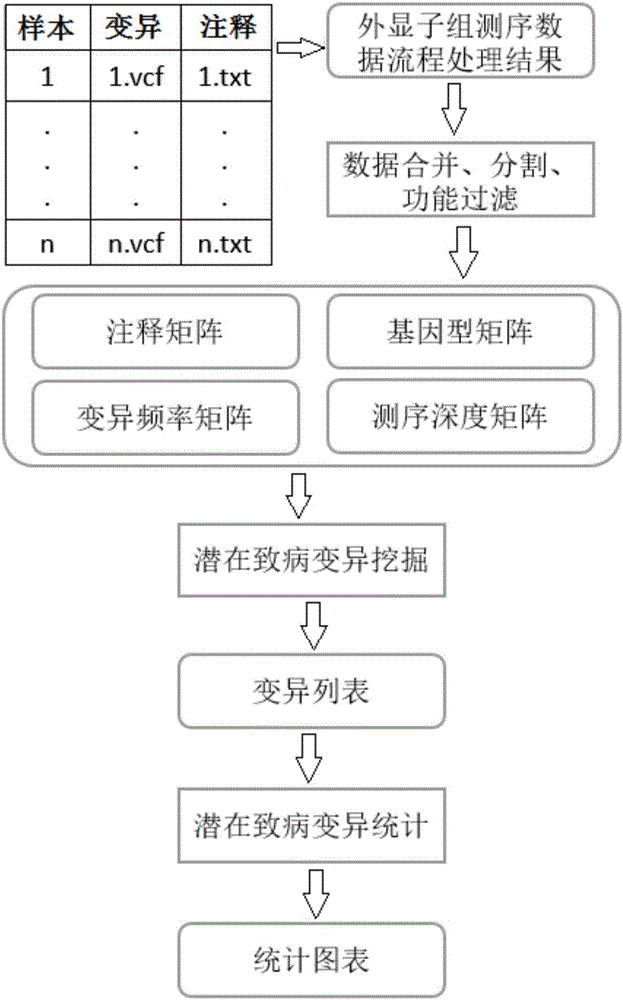
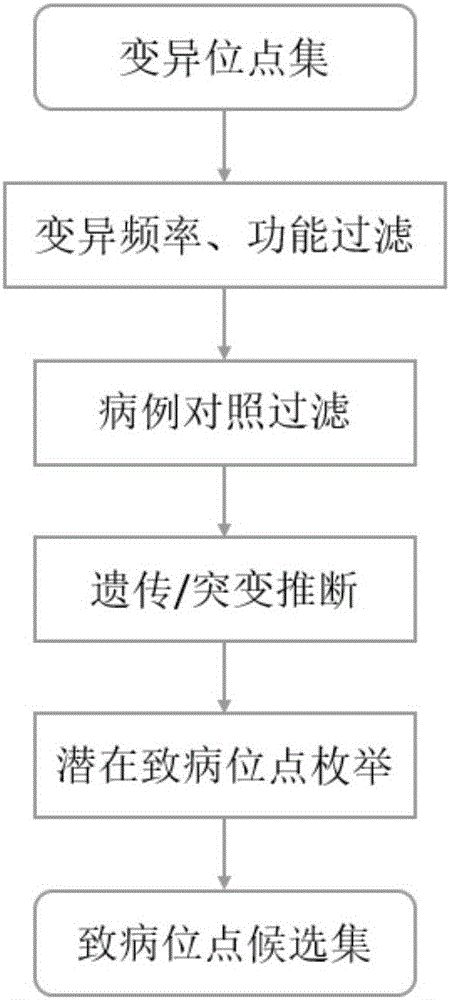
Exome potential pathogenic mutation detection method based on family line
InactiveCN105925685ASolve the problem of mining potential pathogenic variantsImprove heterogeneityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsFiltrationSingle mutation
The invention provides an exome potential pathogenic mutation detection method based on a family line. The detection method comprises the following steps: 1) reading a result file of an exome sequencing data processing flow, and conducting function filtering; 2) reading the file obtained in the last step, extracting mutations in all samples, calculating a union set, and then combining all samples, so that a matrix is constituted; 3) extracting mutation information in the matrix obtained in the last step, enumerating and assessing pathogenicity of single mutation and pathogenicity of combined dual-site mutation, so that a potential pathogenic mutation list is obtained; and 4) in accordance with the list obtained in the last step, calculating the appearance situations of sites in various samples and target genes. According to the method disclosed by the invention, data integration and basic filtration are completed by taking an output result of the common exome sequencing processing flow as an input condition; by virtue of a special mutation screening algorithm, a candidate set of the potential pathogenic mutations is provided; and the method focuses on solving a problem on potential pathogenic mutation mining of sequencing data with high heterogeneity, high mutation rate and high noise.
Owner:WANKANGYUAN TIANJIN GENE TECH CO LTD
Whole genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) extraction kit for blood and method thereof
ActiveCN104017800AReduce the chance of secondary pollutionImprove accuracyDNA preparationLiquid layerLithium chloride
The invention relates to a kit of extracting a whole genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) from blood and a using method thereof. The kit is characterized by comprising a red blood cell lysate, a white blood cell scrubbing solution, digestive juice, proteinase K, a purifying liquid, gDNA salting out liquid, a gDNA scrubbing solution, a gDNA eluant and the like. The using method of the whole genome DNA extraction kit for blood is characterized by comprising the following steps: washing the red blood cell split to obtain the white blood cell; splitting the white blood cell by the digestive juice containing the proteinase K; and further purifying by an improved lithium chloride purifying liquid, salting out the liquid layer, and carrying out chromatography to obtain the high purity whole genome DNA. When the kit provided by the invention is used to extract the whole genome DNA in blood, plasma and serum in blood are not separated in advance but fresh or frozen anti-freezing whole blood is taken, wherein the lowest blood volume required reaches 20 microliters or blood cakes are required. According t the kit provided by the invention, the whole genome DNA with high purity can be fully unlinked and the PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification is efficiently carried out, so that the kit is used for scientific research or clinical diagnostic analysis such as PCR amplification, gene expression, gene sequencing, whole genome sequencing, exome sequencing, gene mutation and single nucleotide polymorphism.
Owner:ZICHENG RUISHENGHUI BEIJING BIOTECH DEV CO LTD
Kit for guiding human mental disease medication and detection method thereof
ActiveCN109777870AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDiseaseHuman DNA sequencing
The invention provides a kit for guiding human mental disease medication and a detection method thereof. The kit can simultaneously type 16 gene loci through one reaction, and comprises 16 pairs of amplification primers for amplifying 16 gene segments; the sequences of 16 pairs of the amplification primers are specifically SEQ ID No.1-SEQ ID No.32; the kit also comprises 16 extension primers, andthe sequences of the 16 extension primers are specifically SEQ ID No.33-SEQ ID No.48. According to the kit and the detection method thereof, through typing based on multiple PCRs and a mass spectrum sequencing technology, human genome mutation related to mental disease medication can be accurately detected; relative to whole genome re-sequencing and whole-exome sequencing, and through the kit andthe detection method of the kit, the experiment cost is also greatly reduced, the period is shortened, and therefore the kit and the detection method of the kit have the all-important practical application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI CONLIGHT MEDICAL LTD
Screening device of pathogenic uniparental disomy, storage medium and processor
Owner:GUANGZHOU KINGMED DIAGNOSTICS GRP CO LTD
Biomarker detection method and system for predicting tumor immune treatment effect
PendingCN111979323AImprove accuracyImprove applicabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsBiologic markerBiology
The invention discloses a biomarker detection method for predicting a tumor immune treatment effect. The method comprises the following steps: detecting a plurality of biomarkers on the basis of second-generation sequencing detection tissue whole exome sequencing (WES) data, and constructing a prediction model for comprehensively predicting a tumor immune treatment effect. Compared with a traditional method capable of only detecting a single biomarker, the method provided by the invention effectively improve the accuracy and applicability of predicting the curative effect of the inhibitor at the immune checkpoint.
Owner:深圳裕策生物科技有限公司
Cloud computing-based method for quality control and management of gene sequence data
InactiveCN109584958AHigh precisionImprove experiment qualityProteomicsGenomicsGenomicsProcess quality
The invention relates to a cloud computing-based method for quality control and management of gene sequence data. The method includes sample clinical information management, experimental data management, data whole process quality control and analysis result management. Testing items of the sample clinical information management includes genomic analysis and transcriptomics analysis, and the genomic analysis includes whole genome sequencing, whole exome sequencing and whole exome sequencing; the transcriptomic analysis includes gene fusion, variable splicing and differential expression analysis. Experimental links are closely connected with analytical links, an analyst can comprehensively understand clinical information, sample information and experimental results, subsequent analysis is facilitated, the accuracy of the analysis result is improved, and the method can help experimenters to understand the quality of sequencing data and thus reflect on shortcomings in the experimental process, the experimental quality is thus improved, and the need of practical use can be applied well.
Owner:江苏医联生物科技有限公司
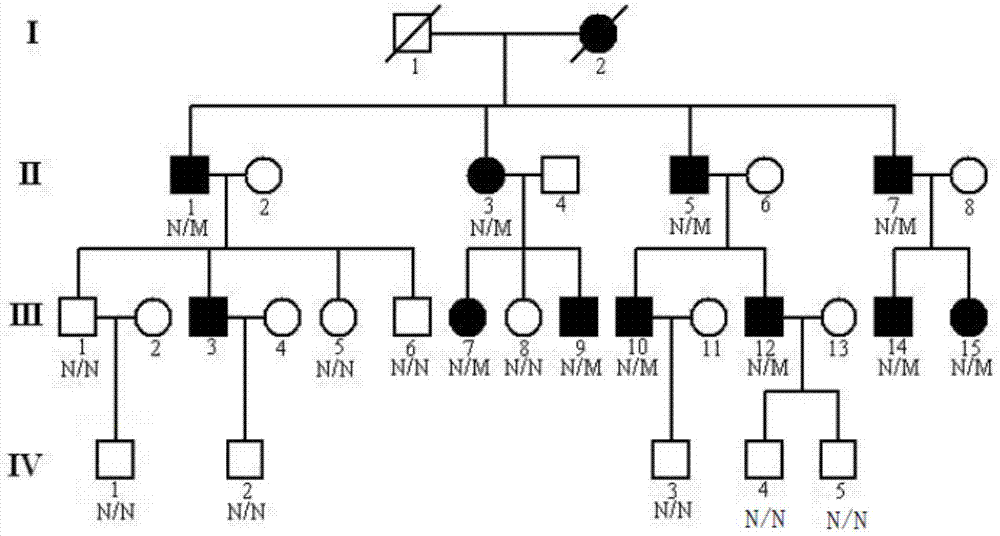
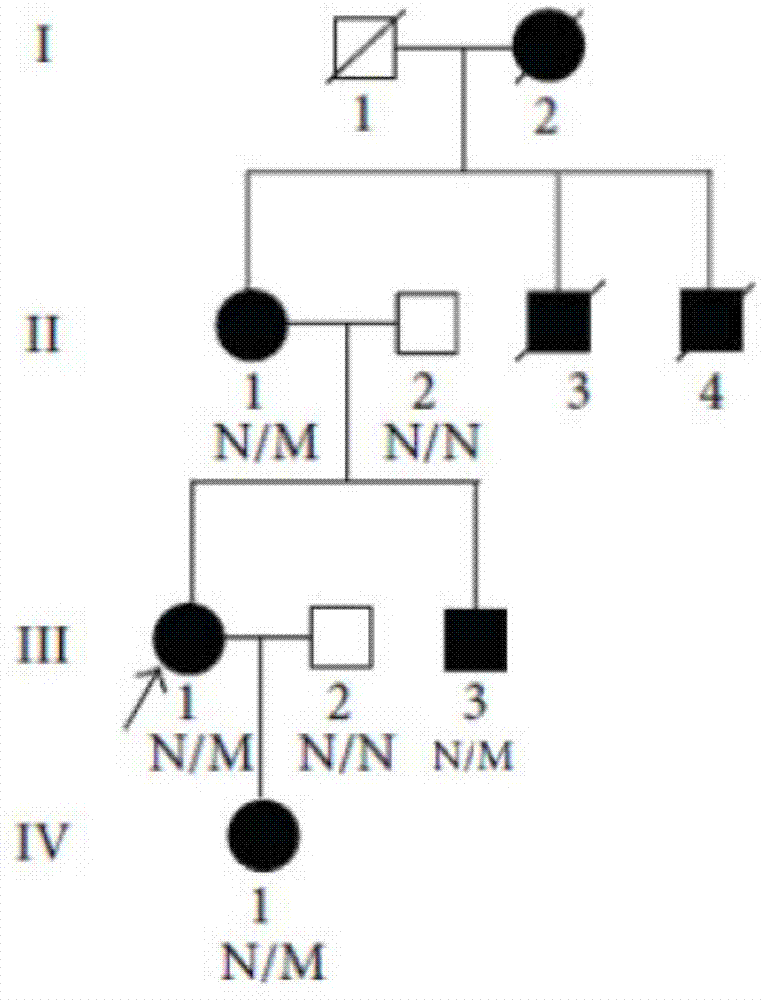
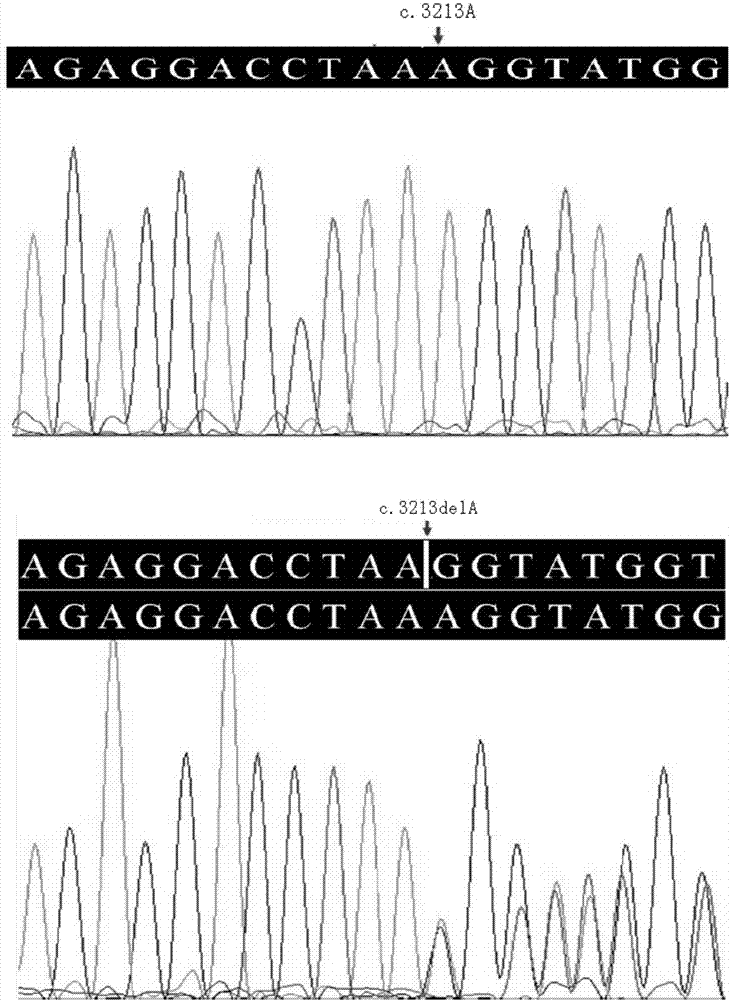
New mutant disease-causing gene of Alport syndrome, encoded protein and application thereof
ActiveCN104212806AQuick forecastRapid diagnosisSenses disorderConnective tissue peptidesDisease riskResearch Object
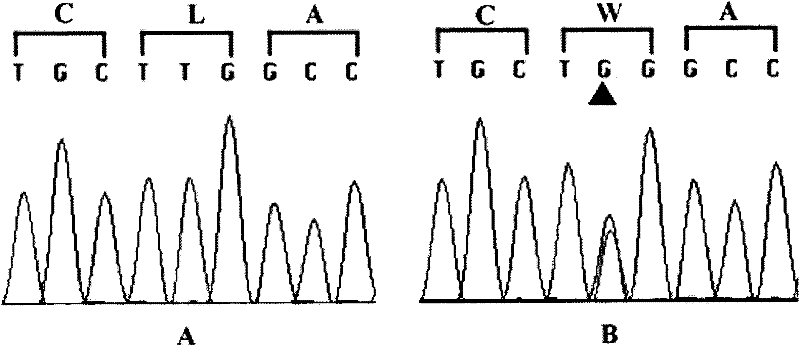
In the invention, two new mutations of two disease-causing genes relative to Alport syndrome are identified through an exon sequencing method. The inventor, by employing two ATS families as research objects, particularly performs exon sequencing and comparison respectively to diseased individuals and non-diseased individuals in the two ATS family and finds a frame shift deletion mutation (c.3213delA,p.Lys1071fs*5) on a COL4A4 gene of one family and a frame shift deletion mutation (c499delC,p.Pro167Glnfs*36) on a COL4A5 gene of the other family, wherein the two frame shift deletion locus are actual disease-causing locus of the two families. On the basis of above, the invention provides a mutant COL4A4 gene and a mutant COL4A5 gene, encoded protein and application thereof and includes carriers, host cells and kits of the mutant COL4A4 gene and / or the mutant COL4A5 gene. By means of the mutant COL4A4 gene and / or the mutant COL4A5 gene, molecular diagnosis and diseasing risk evaluation of the Alport syndrome can be carried out. The two mutant genes and the encoded proteins thereof also can be used as medicine targets for treating the Alport syndrome.
Owner:石家庄华大医学检验实验室有限公司 +1
New virulence gene for severe asthenospermia, and application thereof
InactiveCN107164520AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationVirulent characteristicsResearch Object
The invention relates to a virulence gene, and concretely relates to a new virulence gene for severe asthenospermia, and an application thereof. The new virulence gene SPAG17 for severe asthenospermia is found for the first time. A severe asthenospermia affected family and severe asthenospermia affected individuals are researched, and the affected individuals in the family undergo exome sequencing and comparison to find the gene mutation of the SPAG17 gene of the patients. The mutation is used to detect the severe asthenospermia.
Owner:厦门市妇幼保健院 +2
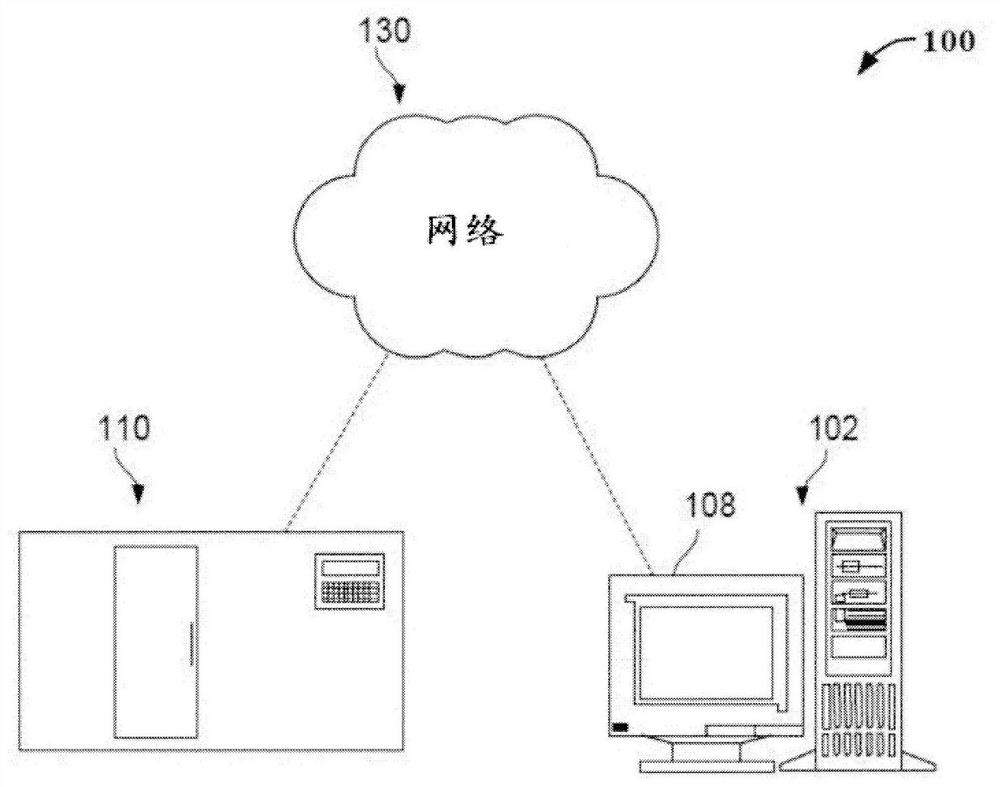
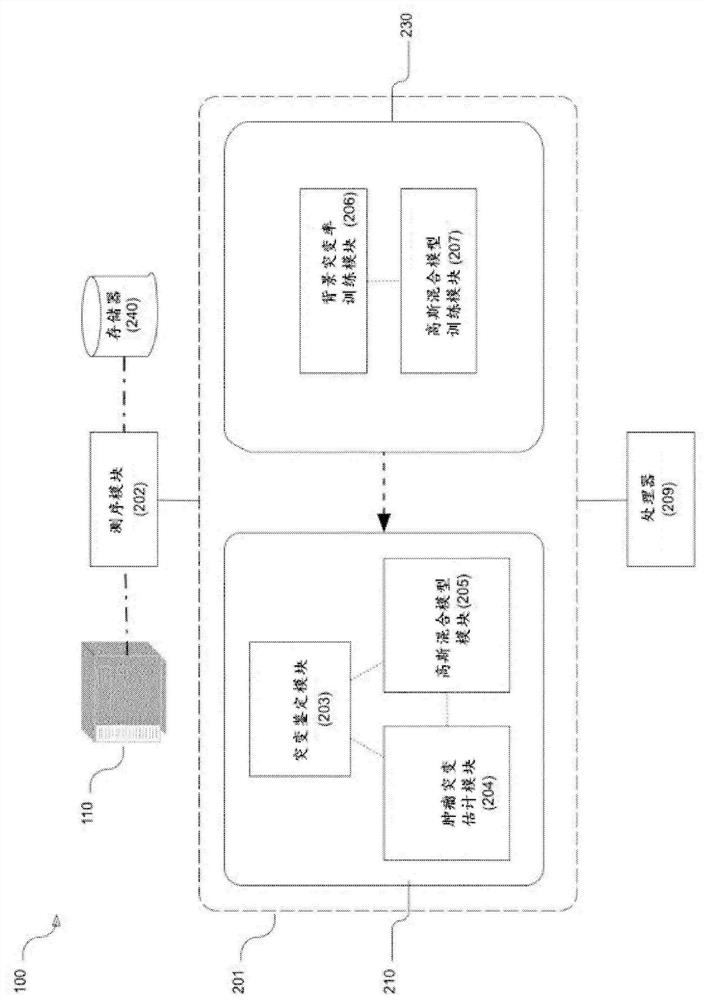
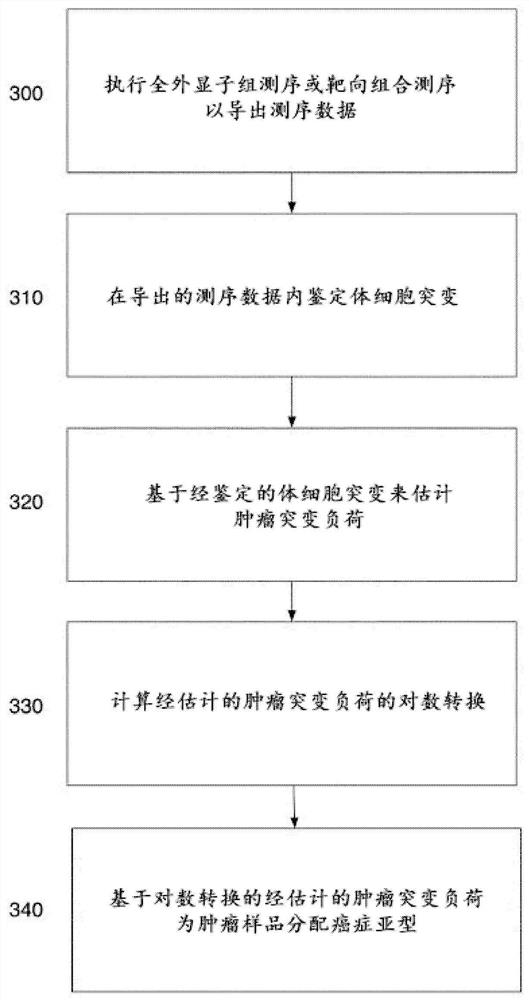
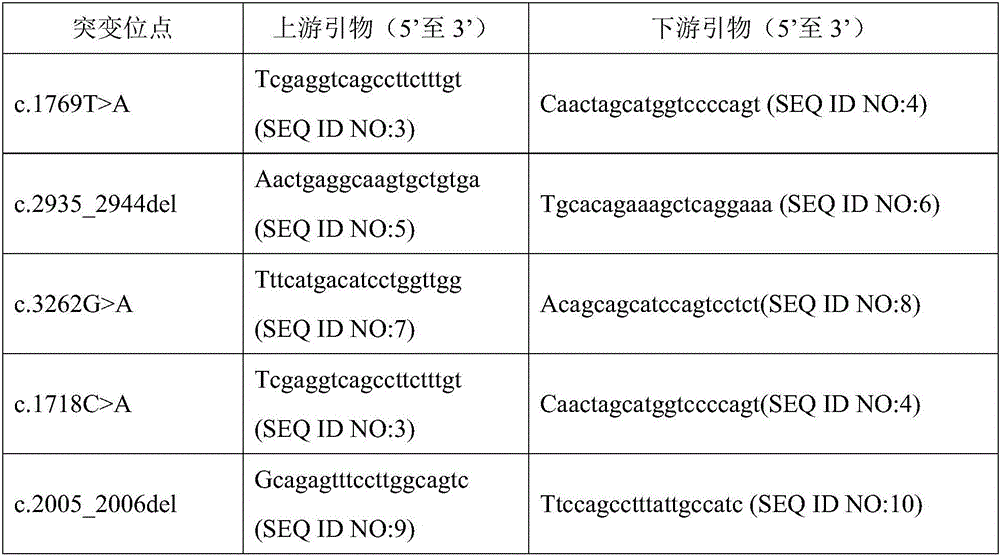
Tumor classification based on predicted tumor mutational burden
The present disclosure provides systems and methods of classifying and / or identifying a cancer subtype. The present disclosure also provides methods of enhancing the prediction of a tumor mutational burden by using both synonymous and non-synonymous somatic mutations in the computation method. It is believed that by increasing the number of mutations in the computation of the tumor mutational burden, a comparatively more consistent tumor mutational burden may be derived, especially for targeted-panel sequencing. It is believed that the consistent computation of the tumor mutational burden from targeted panels allows for computationally quicker and less costly analysis of sequencing data as compared with a tumor mutational burden computed from whole exome sequencing data.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
MMAF novel virulence gene and application thereof
The invention discloses an MMAF novel virulence gene and application thereof, and relates to the virulence genes, and the MMAF novel virulence gene CFAP44 is firstly found. A plurality of affected families and affected individuals of the MMAF are taken as study objects for sequencing and comparing exomes of the affected individuals in the families to find that CFAP44 genes of different patients have different gene mutations which are used for detecting short-tail sperms (MMAF).
Owner:厦门市妇幼保健院 +1
New mutation of PEB (Phosphatidylethanolamine Binding Protein) virulence gene and application thereof
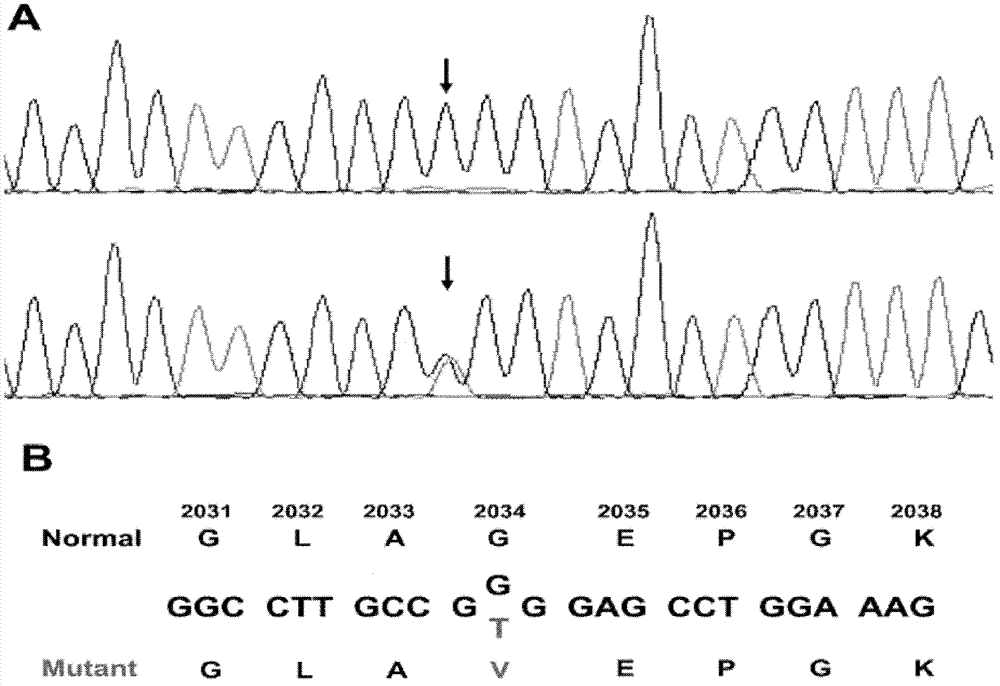
The invention relates to a new mutation of a PEB (Phosphatidylethanolamine Binding Protein) virulence gene and an application thereof. Specifically, a COL7A1 new mutation of a PEB virulence gene is found for the first time by virtue of large-scale screening by the inventor. The inventor takes PEB affected pedigree as a research target, performs exome sequencing and comparison on affected individuals and non-affected individuals in the pedigree and accidently finds a missense mutation (G>T) in the 73rd exon of the COL7A1 gene; due to the mutation, glycocoll Gly of the 2034th of the COLA1 protein is mutated as valine Val; the mutation is highly conservative in the patients; and by applying the mutation, the anterior epidenmoiysis bulbse can be detected.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
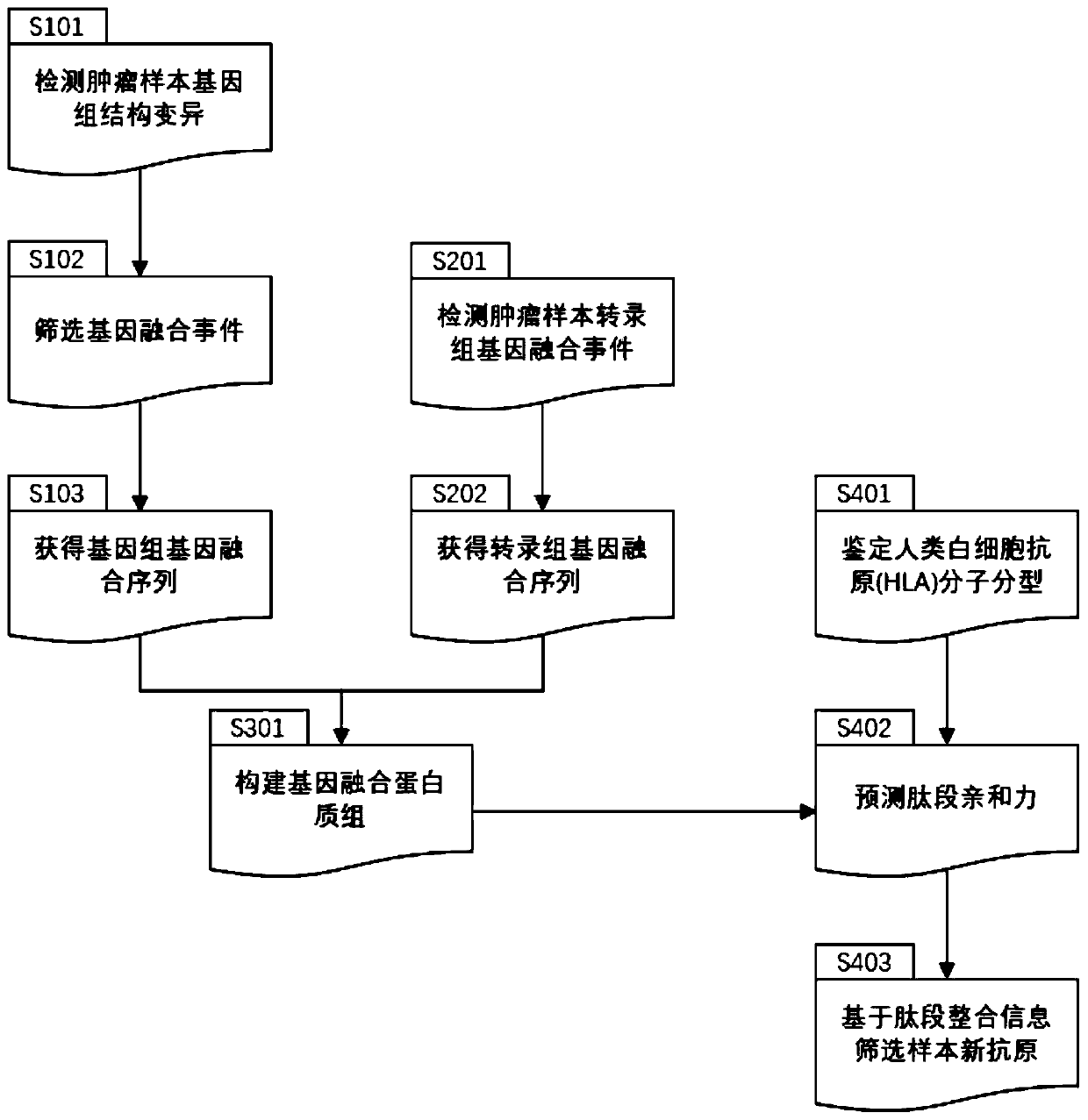
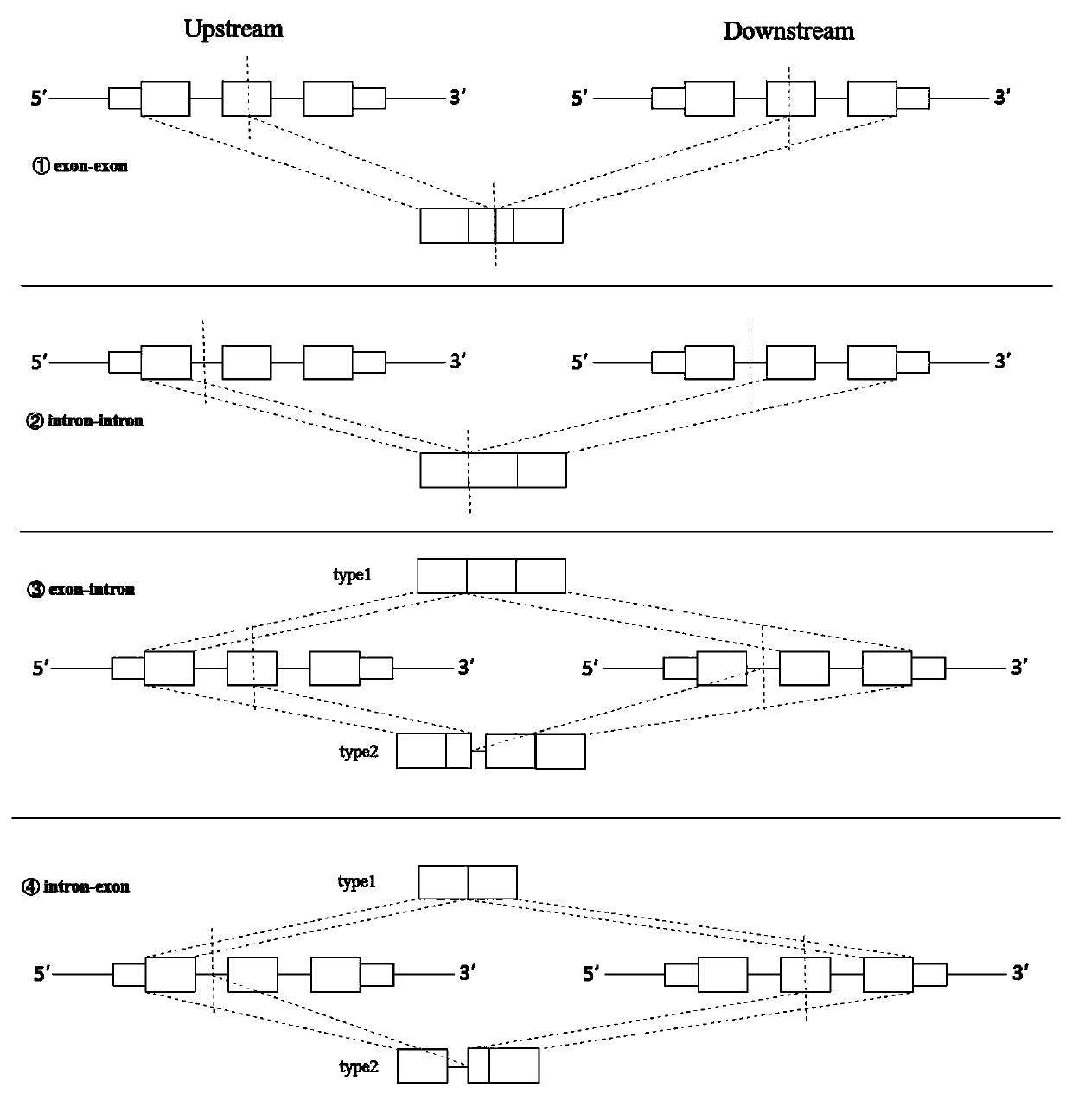
Method and device for extracting gene fusion immune treatment neoantigen by integrating deep sequencing data of DNA and RNA
ActiveCN111192632AExpand the scope of the filterEnrich the "ammunition depot"ProteomicsGenomicsExonTumor specific
The invention discloses a method and a device for extracting a gene fusion immune treatment neoantigen by integrating deep sequencing data of DNA and RNA. The method comprises the following steps: S10, acquiring a genome gene fusion sequence of a sample; S20, acquiring a transcriptome gene fusion sequence of the sample; S30, constructing a gene fusion proteome; and S40, obtaining a sample neoantigen. The tumor specific neoantigens discovered by the scheme of the invention are all from gene fusion, so that the screening range of the neoantigens is expanded, and an ammunition library of an immune treatment method based on the neoantigens is enriched. Through analysis and integration of tumor sample whole exome sequencing data and transcriptome sequencing data, gene fusion events in tumor tissues are comprehensively detected, the false positive rate of neoantigens generated by fusion is reduced, the effectiveness of neoantigen vaccine is improved, and the method is of great significance to improvement of the clinical immune treatment effect.
Owner:深圳市新合生物医疗科技有限公司
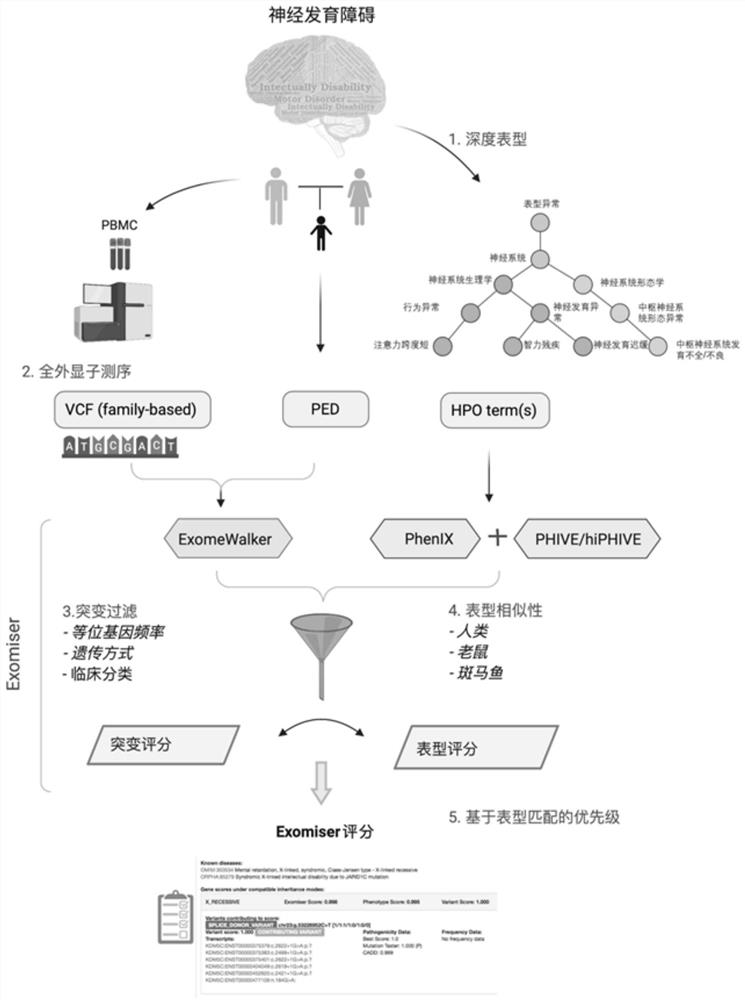
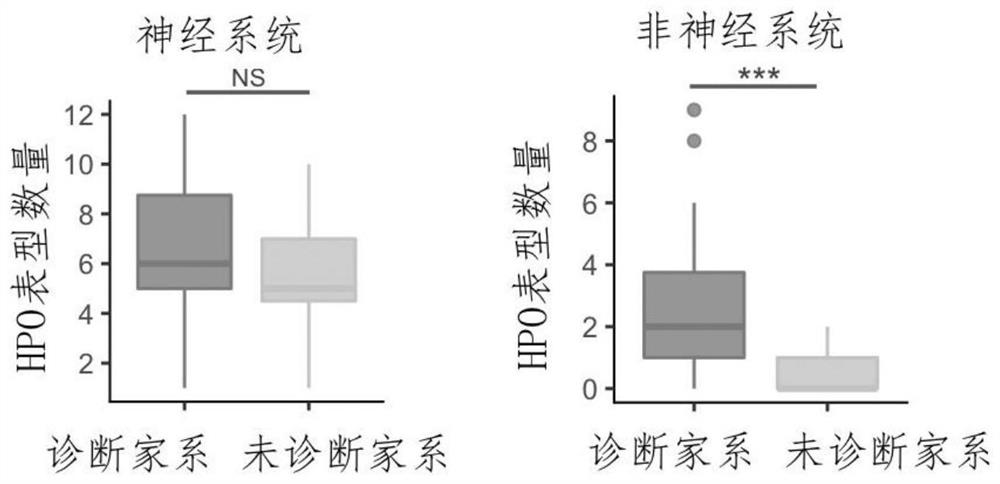
Evaluation method for judging rare hereditary diseases
PendingCN112735599AImprove evaluabilityReduce birthMedical data miningProteomicsDisease phenotypeGenes mutation
The invention discloses an evaluation method for judging rare hereditary diseases, which comprises the steps of deep phenotype analysis, whole exon group sequencing, gene mutation identification and filtration, mutation optimization combined with a genetic pattern and a disease phenotype, whole exon group sequencing and human phenotype ontology. Clinical doctors can be assisted to judge and evaluate pathogenic factors of rare hereditary diseases in time, the evaluable rate of the rare hereditary diseases is increased, a basis is provided for determining appropriate treatment measures and clinical management strategies, genetic counseling and prenatal evaluation are provided for families, birth of similar child patients is reduced, and economic burdens of the families and the society are relieved. Therefore, the method has important significance for judging the hereditary diseases with high phenotypic heterogeneity and low morbidity.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF HENAN PROV
Kit for screening susceptible gene of atrial fibrillation disease
InactiveCN107974498AImprove early detection rateImprove survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementVirulent characteristicsFibrillation
The invention discloses a kit for screening susceptible gene of atrial fibrillation disease, and belongs to the technical fields of medicine and molecular biology. The kit comprises the following detection gene: KCNQ1, SCN5A and KCNJ2, and comprises reagents for performing whole exome sequencing on KCNQ1, SCN5A and KCNJ2. By performing whole exome sequencing on KCNQ1, SCN5A and KCNJ2 of a subject,whether the subject carries mutation sites is found, so that the atrial fibrillation disease is determined. The kit screens sporadic atrial fibrillation virulence gene in a crowd, and effectively improves the early detection rate of fibrillation disease, thereby realizing early treatment, reducing the burden of patients, and providing reference for the medication of patients with atrial fibrillation.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Standard substance for extensive oncogene detection and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111334505AFit closelyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertion deletionCancer genome
The invention provides a standard substance for extensive oncogene detection. The standard substance includes 13 mutation sites verified by Droplet Digital PCR (ddPCR) and 500X high-throughput whole exome sequencing verified site information, has more than 700 variation sites of over 330 genes, also includes common structural variations of cancer genomes, such as common gene SNV, base insertion deletion and the like, has corresponding mutation site frequencies within a range of 1% to 100%, and is wide in application scene and platform. The standard substance can be used for evaluating stability, specificity and sensitivity of the working flow from sample extraction to biological information analysis, evaluating each sample treatment method and detecting performance differences among platforms. The standard substance belongs to a major innovation in the industry, and has wide application prospect and great industrial application value.
Owner:菁良科技(深圳)有限公司
ADCY10 gene mutant and application thereof
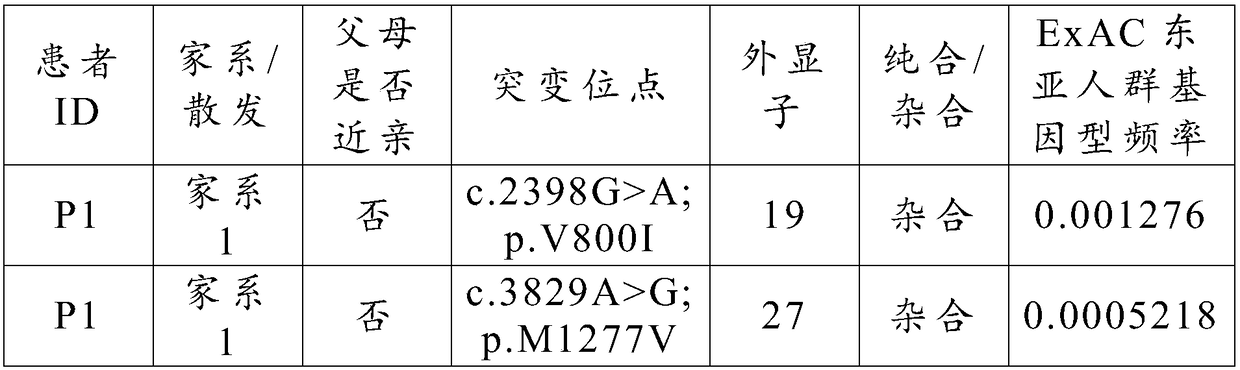
The invention relates to a marker of severe asthenospermia and application of the marker. More specifically, the invention provides an isolated nucleic acid encoding an ADCY10 mutant; compared with SEQ ID NO: 1, the nucleic acid has one or two of the following mutations: c.2398G>A mutation and c.3829A>G mutation; the invention further provides polypeptide encoding the nucleic acid, application anda detection method of the nucleic acid and the polypeptide to detection of the severe asthenospermia, and a primer and a kit which are prepared from the nucleic acid and the polypeptide. According tothe marker provided by the invention, a core family of the severe asthenospermia is used as a research object and whole exome sequencing and comparison are carried out on affected individuals in thefamily to finds out new pathogenic genes and mutation sites, so that the severe asthenospermia is detected by utilizing the new pathogenic genes and the mutation sites.
Owner:BEIJING OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Novel MMAF (multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella) pathogenic gene and application thereof
The invention relates to markers for multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella and their application, in particular to a novel MMAF (multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella) pathogenic gene and application thereof. More particularly, the novel MMAF pathogenic gene CFAP43 is discovered for the first time via large-scale whole-exome sequencing screening. In the case of using multiple families and individuals with MMAF as study subject, the individuals in the families are subjected to exome sequencing and comparing, and it is discovered that the different patients show different gene mutations in the gene CFAP43. By using these mutations, it is possible to detect multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella.
Owner:厦门市妇幼保健院 +4
Application of substance for detecting genetic marker to preparation of kit for risk early warning and early diagnosis of rectal cancer
InactiveCN112592978AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCandidate Gene Association StudyOncology
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedicine, and particularly relates to an application of a substance for detecting a genetic marker to preparation of a kit for risk early warning andearly diagnosis of rectal cancer. Tumor tissue samples of three Chinese Han family sCRC patients are sequenced and analyzed by utilizing an exon group sequencing technology, and specific low-frequency function deletion mutation of screened tumor tissues is determined by genotyping large-sample tumor tissues and normal control tissues of the large-sample tumor tissues. Finally, functional geneticmarkers of new candidate genes BMP5, RASSF6, DDI2 and SARDH which can be used for early-stage sCRC risk early warning.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
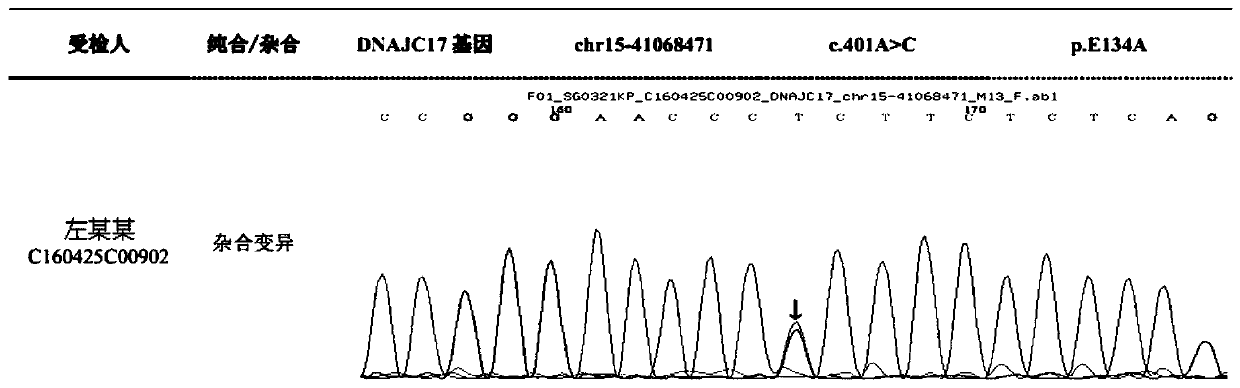
Autosomal dominant Dnajc17 gene mutant as well as application, diagnostic kit and diagnostic gene chip thereof
ActiveCN110904210AHigh clinical application valueMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesDiseaseNucleotide
The invention discloses an autosomal dominant Dnajc17 gene mutant as well as application, a diagnostic kit and a diagnostic gene chip thereof. The mutation site of the autosomal dominant Dnajc17 genemutant is that the 401st nucleotide A of a Dnajc17 gene coding region on the human fifteenth chromosome is mutated into C (c.401A>C), so that the 134th amino acid of the protein sequence is mutated into alanine A (p.E134A) from glutamic acid E. Exome sequencing analysis and animal experiment verification are carried out on deafness family members; the Dnajc17 is found to have obvious correlation with the deafness occurrence, and is an important precipitating factor of hereditary hearing loss. The invention provides the diagnostic kit and the diagnostic gene chip for early diagnosis and early intervention treatment of deafness diseases, the diagnostic kit and the diagnostic gene chip have great clinical application value, and the diagnostic kit and the diagnostic gene chip can be used for screening high-risk groups with deafness diseases.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Novel azoospermia pathogenic gene and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel azoospermia pathogenic gene and an application thereof and relates to a marker for azoospermia disease and the application thereof. The novel azoospermia pathogenic gene BRDT is firstly discovered in the manner of screening in a consanguineous marriage family. After patient individuals in the family are subjected to exome sequencing and comparison on the basis of one azoospermia consanguineous marriage family as a research object, the patients are proved as carrying BRDT gene mutations. These gene mutations can be utilized to detect the azoospermia.
Owner:厦门市妇幼保健院 +3
New mutant pathogenic gene of febrile convulsion as well as coding protein and application thereof
InactiveCN104372010AQuick forecastRapid diagnosisNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementResearch ObjectFebrile convulsions
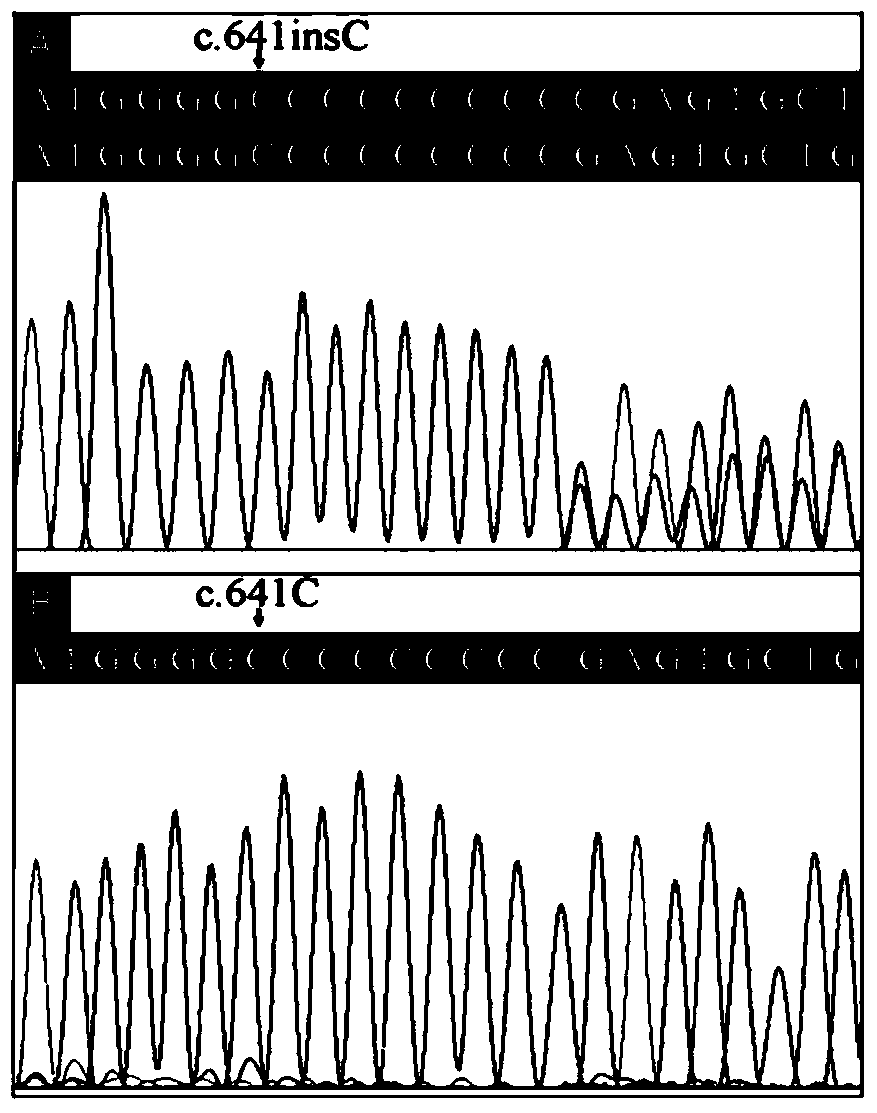
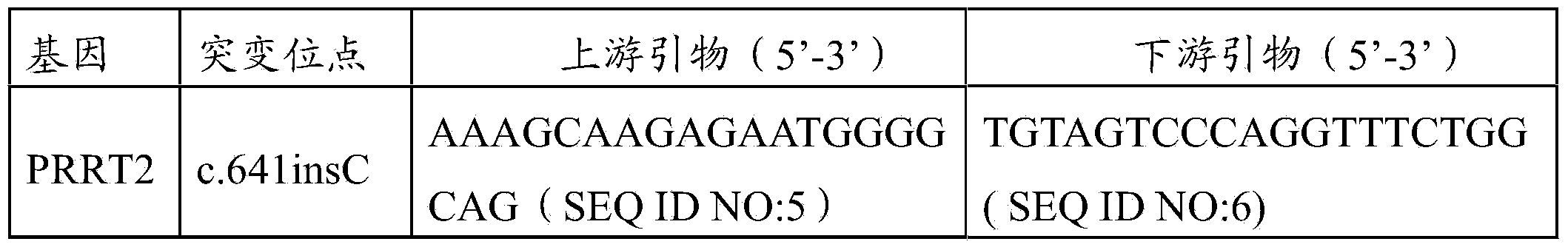
The invention authenticates a new pathogenic gene-PRRT2 related with febrile convulsion. Specifically, a four-generation Chinese family of febrile convulsion dominant inheritance is used as a research object, sick individuals and non-sick individuals in the family are subjected to exome sequencing and comparison, a frame-shift insertion mutant c.641insC(p.R217Pfs*8) is discovered in the PRRT2 gene, and the mutant causes the change of a PRRT2 protein. Based on condition, the invention provides a mutant PRRT2 gene as well as a coding protein and application thereof, including a vector of the mutant PRRT2 gene, a host cell and a kit. The febrile convulsion can be subjected to molecular diagnosis and sickening risk evaluation by using the mutant PRRT2 gene. The mutant gene and the coding protein thereof can also be used as medicament targets for treating febrile convulsion.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
A kit and method for extracting whole genome dna from blood
ActiveCN104017800BNo pollution in the processReduce the chance of secondary pollutionDNA preparationWhite blood cellNucleotide
Owner:ZICHENG RUISHENGHUI BEIJING BIOTECH DEV CO LTD
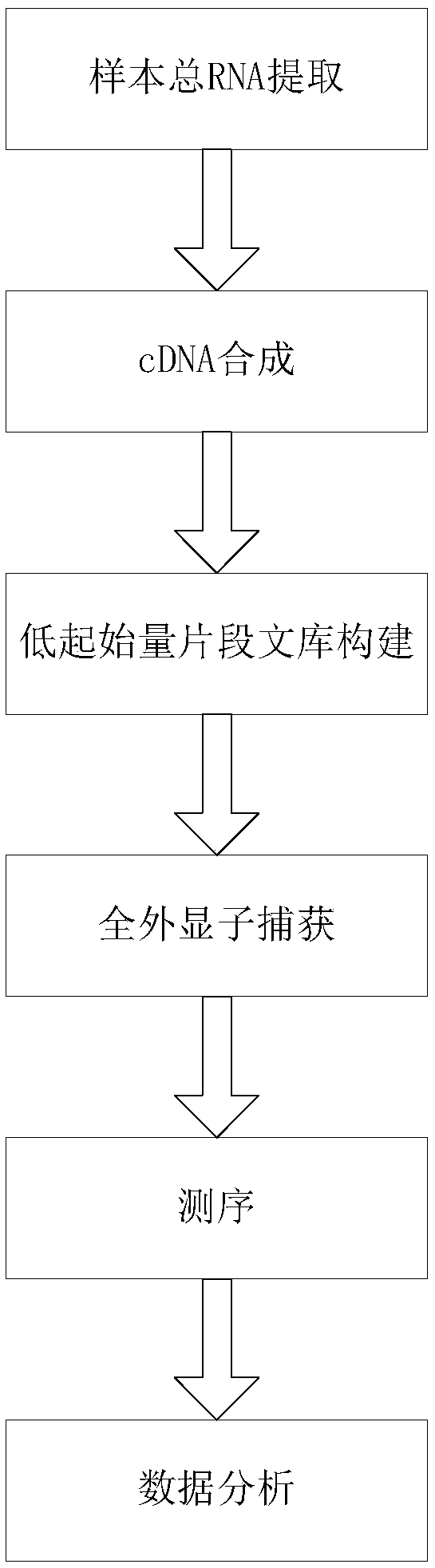
Transcriptome sequencing method based on RT-WES (reverse transcription-whole exome sequencing) technology
InactiveCN108823297AReduce distractionsReduce quality problemsMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseTotal rna
The invention discloses a transcriptome sequencing method based on RT-WES (reverse transcription-whole exome sequencing) technology. The method comprises the following steps: 1) extracting total RNA of a sample; 2) synthesizing cDNA with total RNA as template; 3) constructing a cDNA fragment library; 4) capturing whole exons of the fragment library and enriching transcriptome fragments of functional genes; 5) sequencing the transcriptome fragments and analyzing sequencing data. The RT-WES technology is adopted, RNA is first converted into DNA through cDNA synthesis process, and then exon information is enriched through whole exon capture, transcriptome sequencing data with less interference between rRNA and genomic DNA, high expression enrichment of functional genes and low background is obtained, accordingly, requirements on RNA quality and initial amount are reduced, the step of removing rRNA interference is eliminated, and a more accurate and efficient way is provided for expressionchange analysis of mutant gene transcripts.
Owner:GENOMICARE BIOTECH SHANGHAI CO LTD +2
Skin keratinization-less hair-leukonychia syndrome new disease-causing gene and coding protein and application thereof
ActiveCN104250649AQuick forecastRapid diagnosisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDisease riskLeukonychia
The present invention identifies skin keratinization-less hair-leukonychia syndrome new disease-causing gene-GJA1 gene. Specifically, skin keratinization-less hair-leukonychia syndrome diseased family is taken as a study object, by exon group sequencing and comparison of a diseased individual and a non-diseased individual in the family, the GJA1 gene is found to be the skin keratinization-less hair-leukonychia syndrome disease-causing gene, the following a plurality of pathogenic mutations of c.23Ggt; T (p.Gly8Val), c.412Ggt; C (p.Gly138Arg) and C.689-690delAT (p.Tyr230Cysfs * 7) are found in the GJA1 gene, and the pathogenic mutations cause GJA1 protein translation errors or early interrupts. On the basis, the invention provides mutant GJA1 gene and a coding protein thereof, a carrier containing the mutant GJA1 gene, host cells, and a system, a kit and a method for screening biological samples which are susceptible to the disease. Through use of the mutant GJA1 gene, molecular diagnosis and disease risk evaluation of the skin keratinization-less hair-leukonychia syndrome can be performed, and the mutant GJA1 gene and the coding protein can be used as drug targets for treatment of the skin keratinization-less hair-leukonychia syndrome.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
Imatinib-drug-resistance KIT and PDGFRA wild type GIST cell strain and establishment method and application thereof
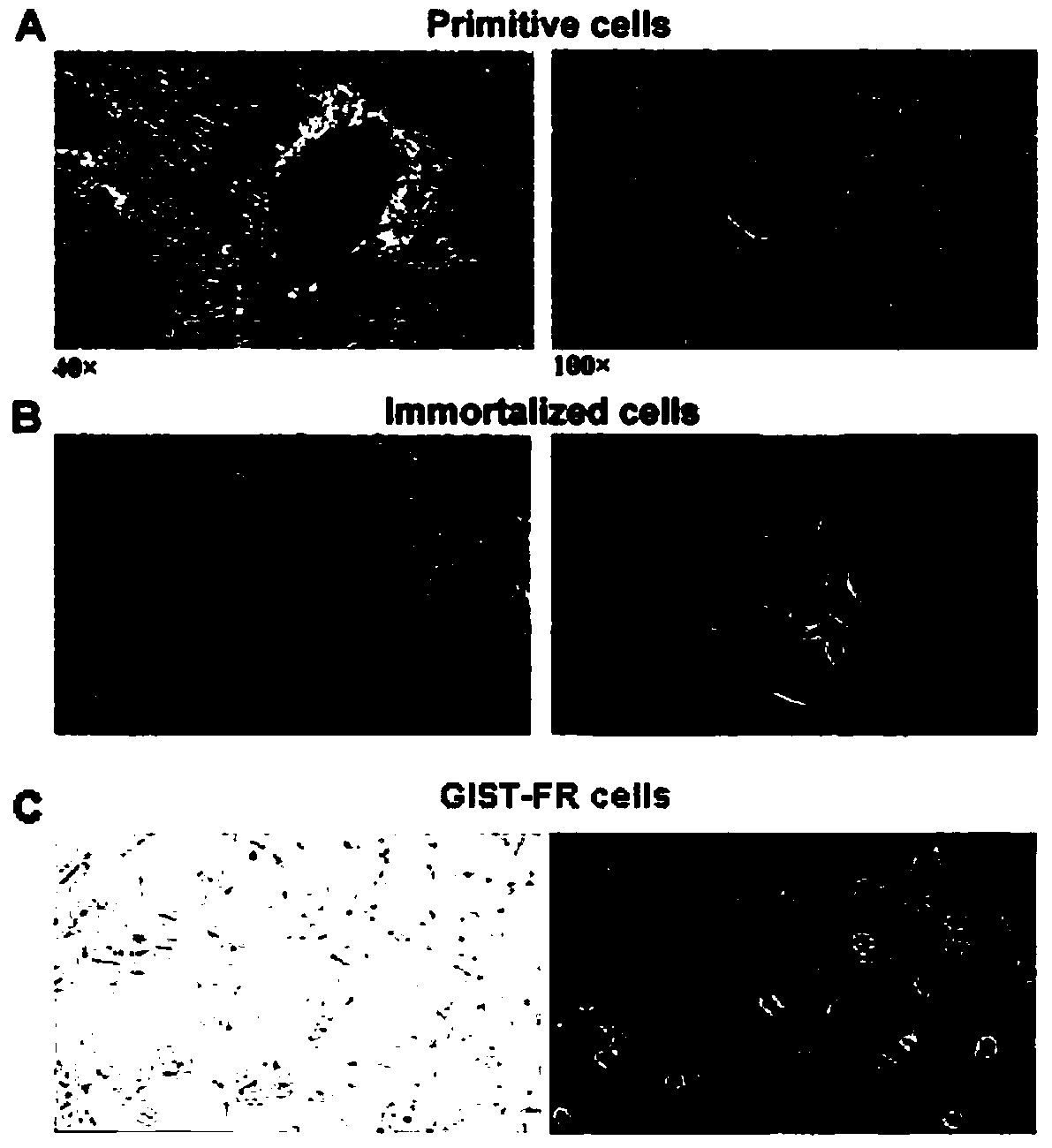
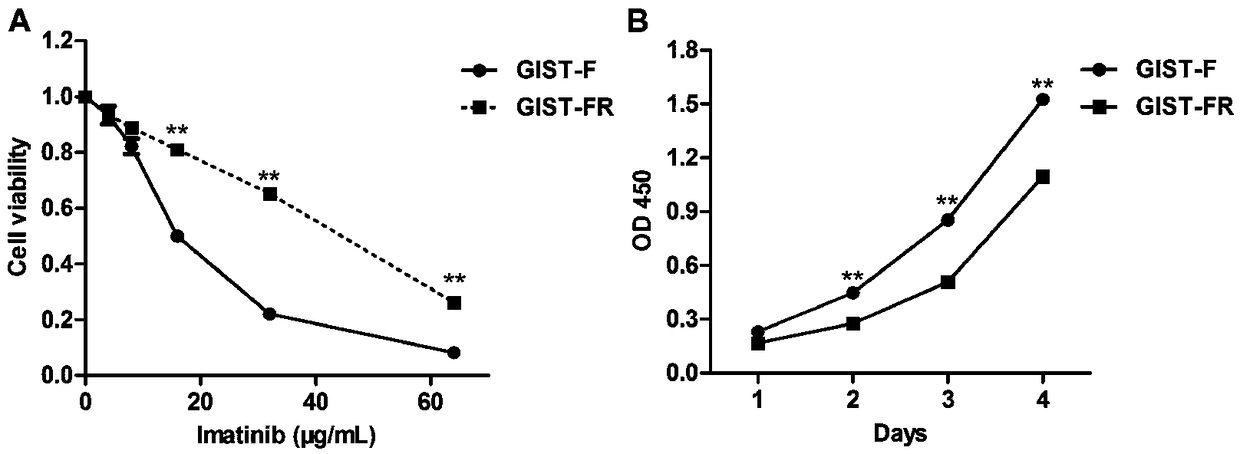
The invention provides an Imatinib-drug-resistance KIT and PDGFRA wild type GIST cell strain which is named as GIST-FR and preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection with the preservation number being CCTC NO:C2017111. The invention further provides an establishment method of the cell strain and application of the cell strain as a cell model for discussing the human GIST drug resistance mechanism and researching relevant signal channels thereof. A tissue block culture method is adopted to obtain GIST primary cells, immortalization is carried out, and a GIST-F cell line is established; then Imatinib drug resistance induction is carried out on the GIST-F cell line, and the Imatinib-drug-resistance GIST cell strain GIST-FR is established. The GIST-FR cells are subjected to in-vitro passage for more than 40 generations, growth is slow compared with GIST-F cells, IC50 of Imatinib is remarkably increased, and the drug resistance index is 3.52 (P is less than 0.01); and a wholeexon group sequencing result shows that KIT and PDGFRA of the GIST-FR cells are negative. The GIST cell line is successfully built from human GIST primary tissue, and further induction is carried outto obtain the Imatinib-drug-resistance cells thereof, so that a foundation is laid for the GIST pathogenesis and drug resistance related research.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF JIANGNAN UNIV
Novel azoospermia pathogenic gene and application thereof
The invention relates to a novel azoospermia pathogenic gene and an application thereof and relates to a marker for azoospermia disease and the application thereof. The novel azoospermia pathogenic gene TSGA10 is firstly discovered in the manner of screening in large scale. After patient individuals in the family are subjected to exome sequencing and comparison on the basis of multiple azoospermia families and patient individuals as research objects, different patients are proved as carrying TSGA10 gene mutations. These gene mutations can be utilized to detect the azoospermia.
Owner:厦门市妇幼保健院 +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com