Patents
Literature
56 results about "Disease phenotype" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In this context, a phenotype would be any observable characteristic or trait of a disease, such as morphology, development, biochemical or physiological properties, or behavior, without any implication of a mechanism. A clinical phenotype would be the presentation of a disease in a given individual. Some organizations...
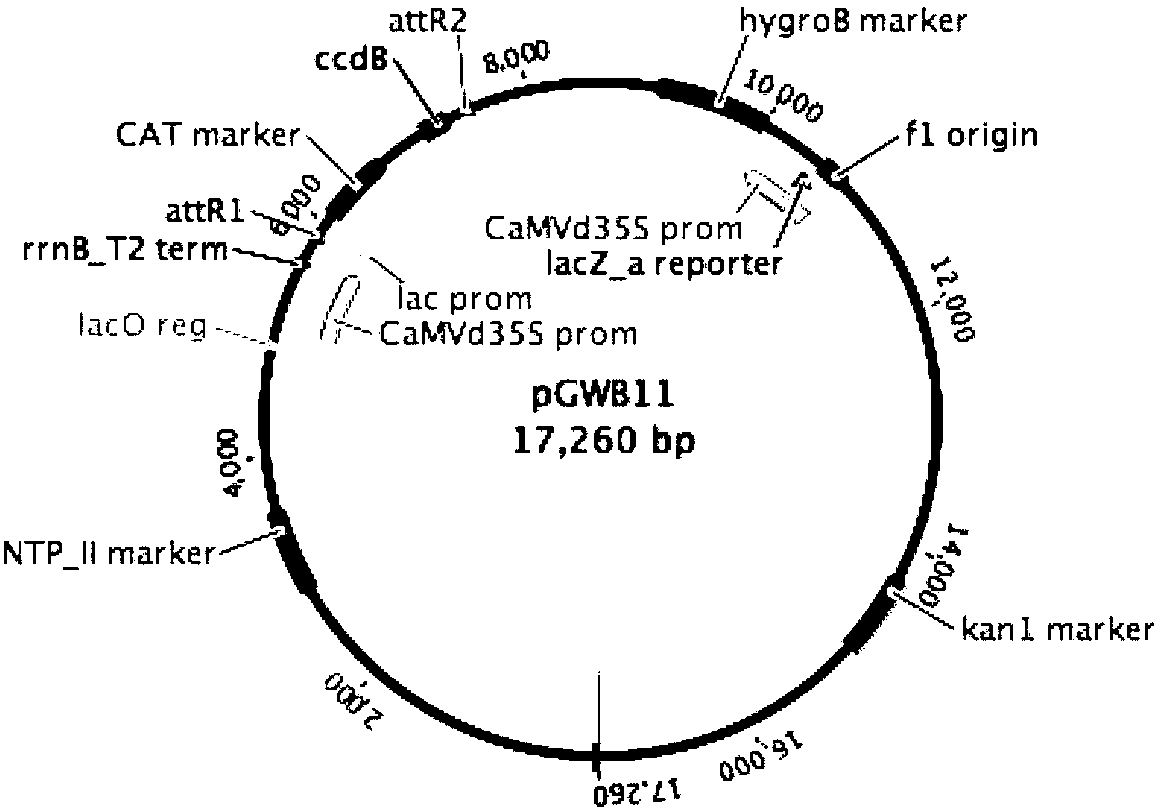
Tissue Phasic Classification Mapping System and Method
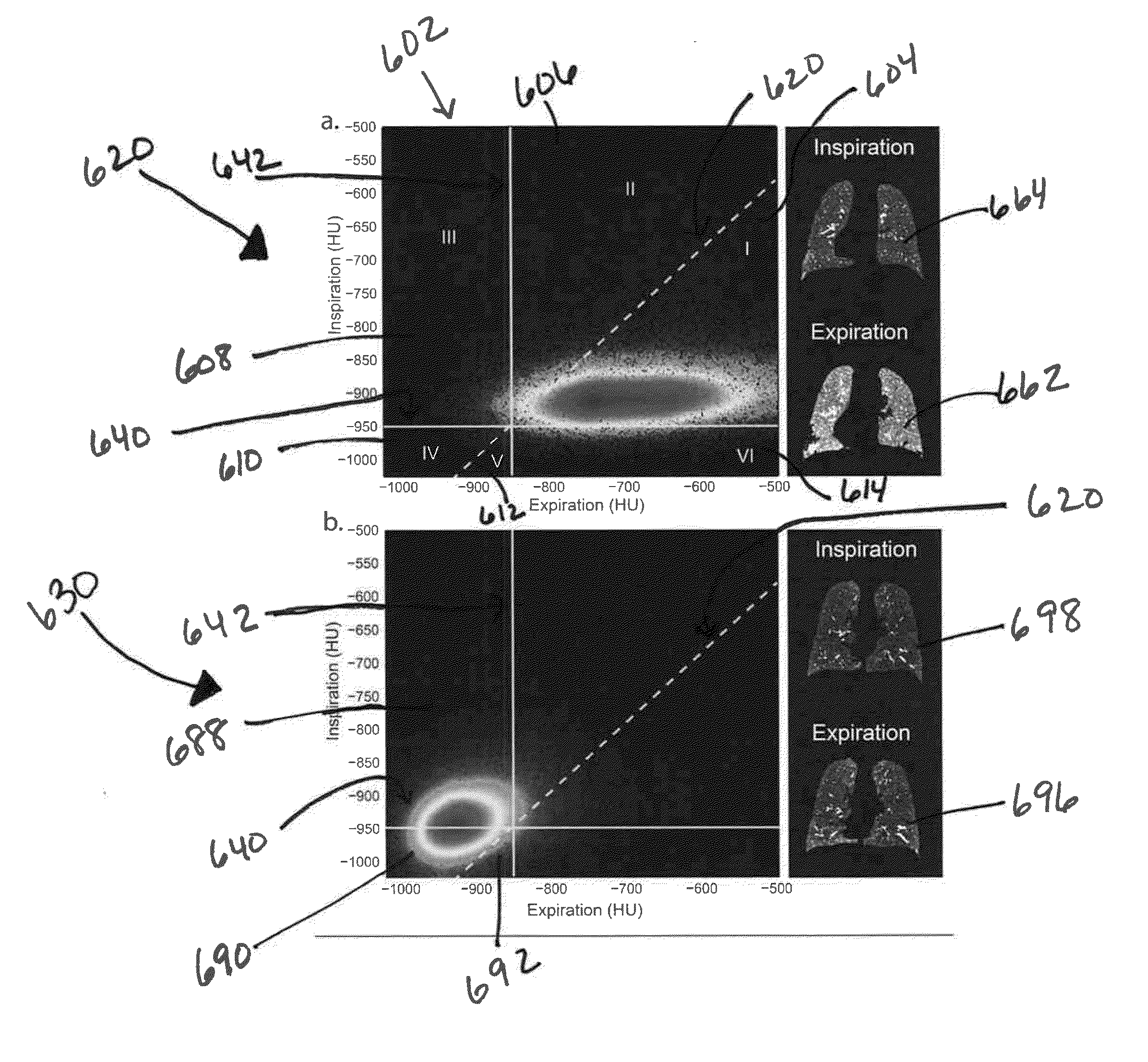
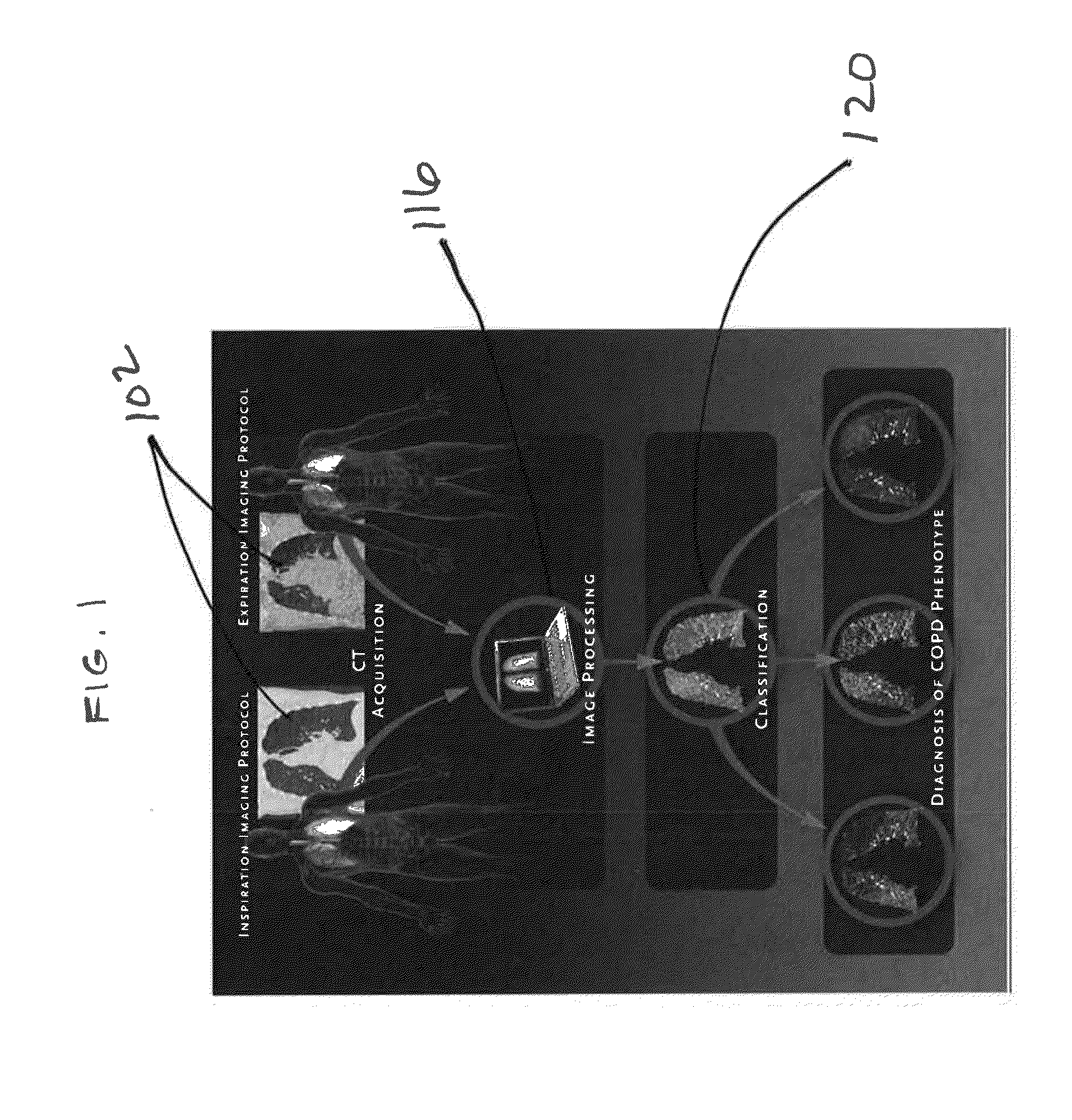
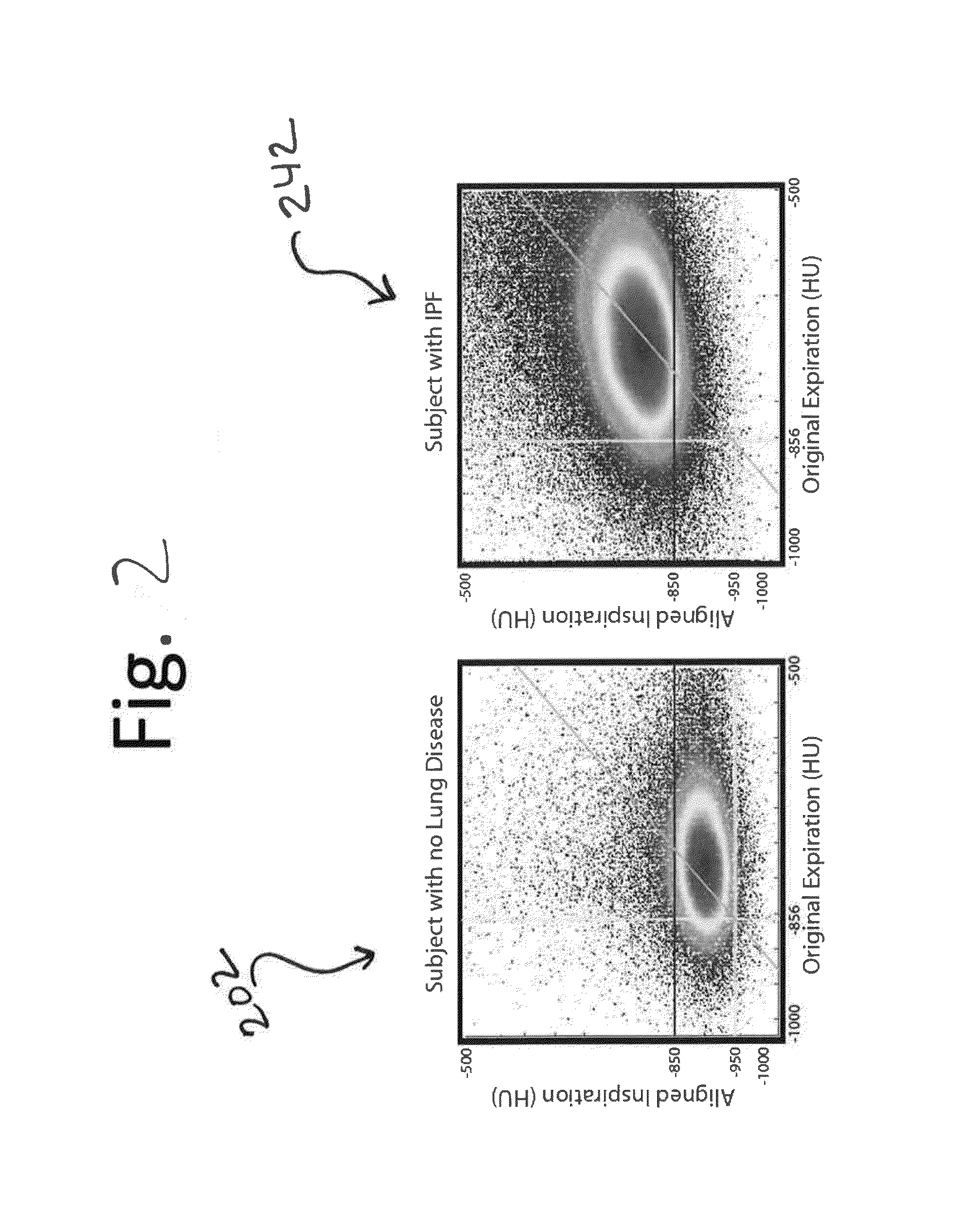
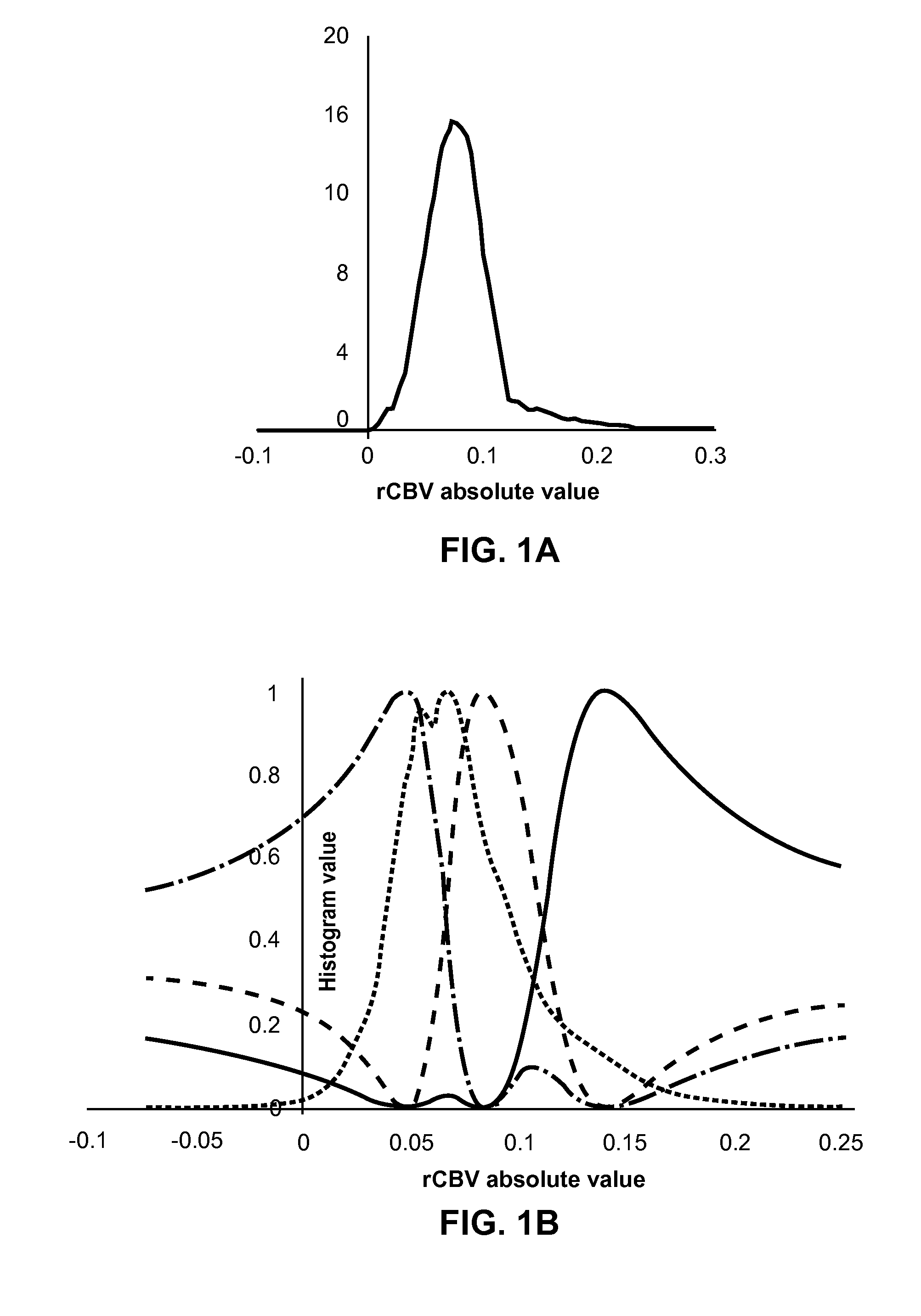
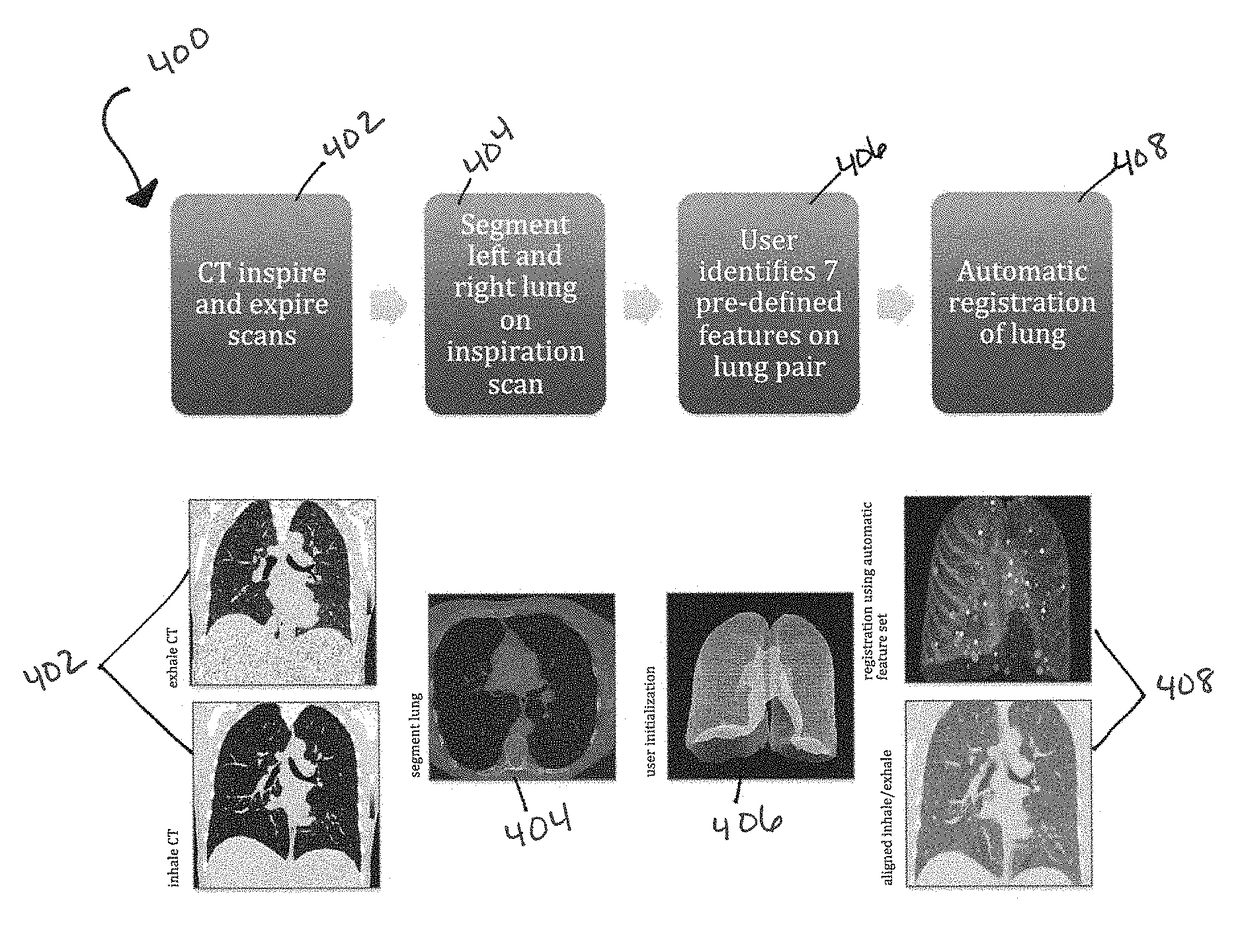
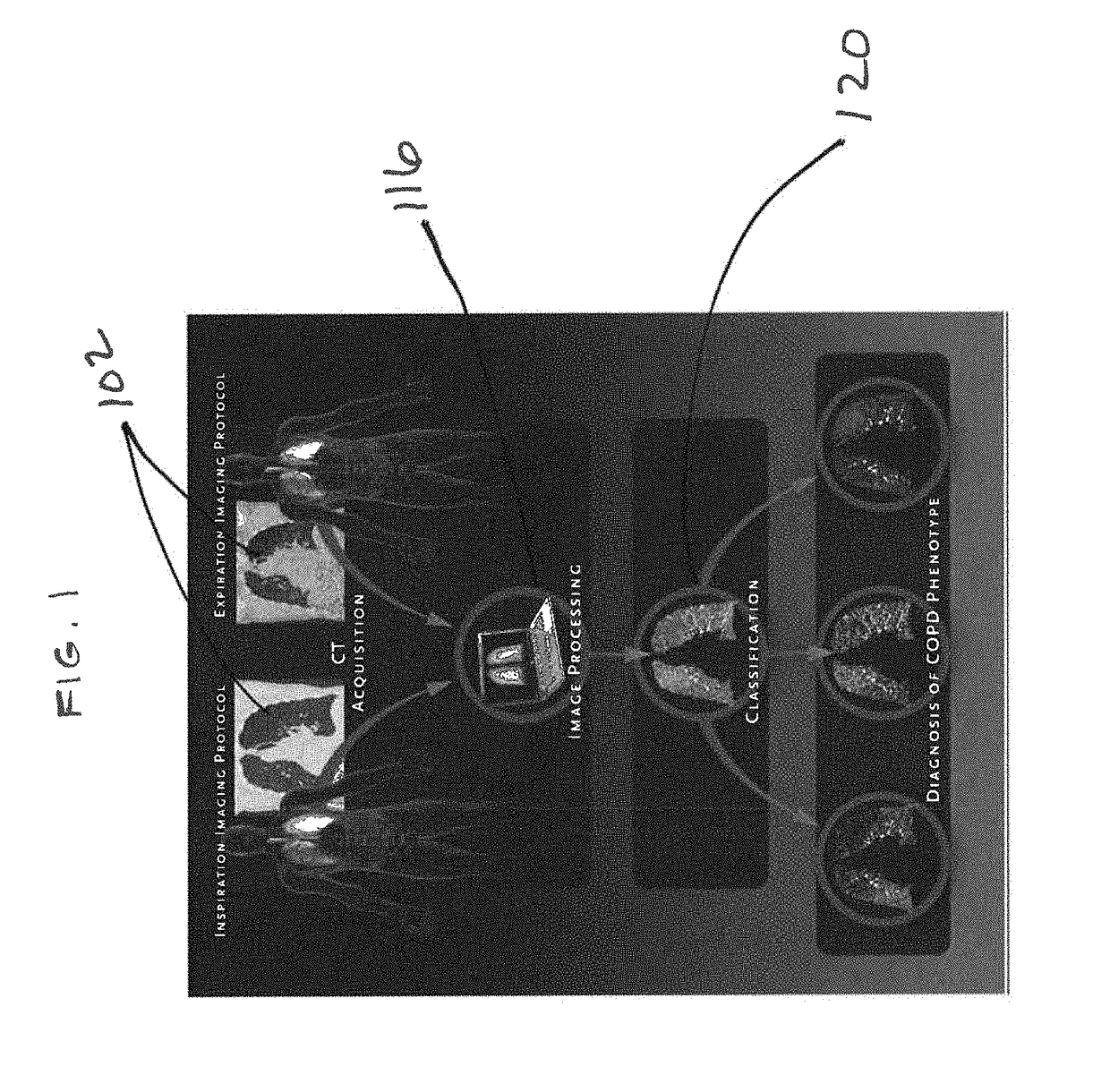
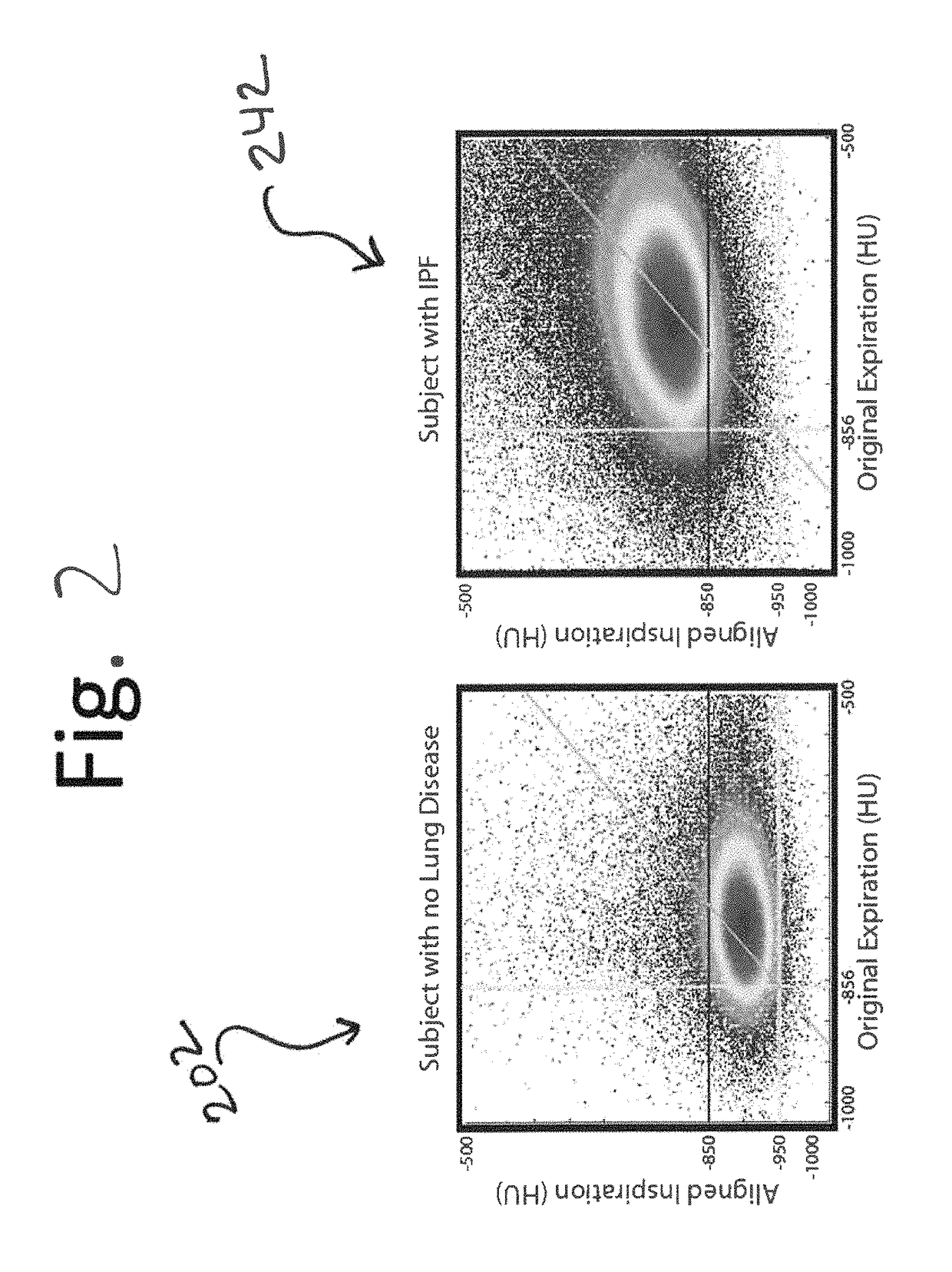
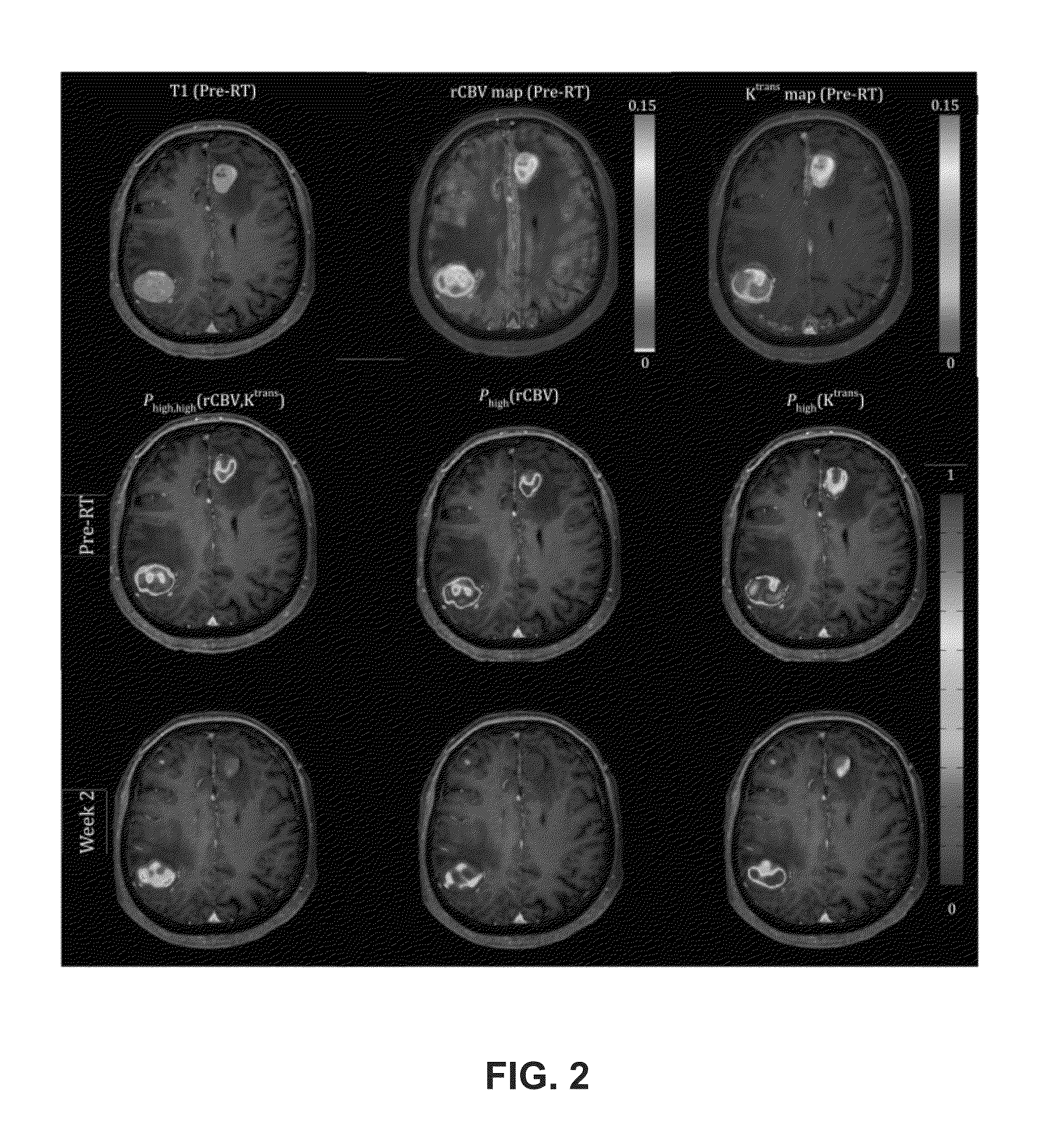
A voxel-based technique is provided for performing quantitative imaging and analysis of tissue image data. Serial image data is collected for tissue of interest at different states of the issue. The collected image data may be deformably registered, after which the registered image data is analyzed on a voxel-by-voxel basis, thereby retaining spatial information for the analysis. Various thresholds are applied to the registered tissue data to identify a tissue condition or state, such as classifying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by disease phenotype in lung tissue, for example.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
High throughput correlation of polymorphic forms with multiple phenotypes within clinical populations
A computer-assisted method of looking for pharmacologic targets, in which large numbers of persons are enrolled in drugh clinical trials, they are medically examined and documented, tissue samples are taken, the tissue samples are genotyped, and an examination is made of the genotypes to try to ascertain associations between the genotypes and the documented disease phenotypes of the patients.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
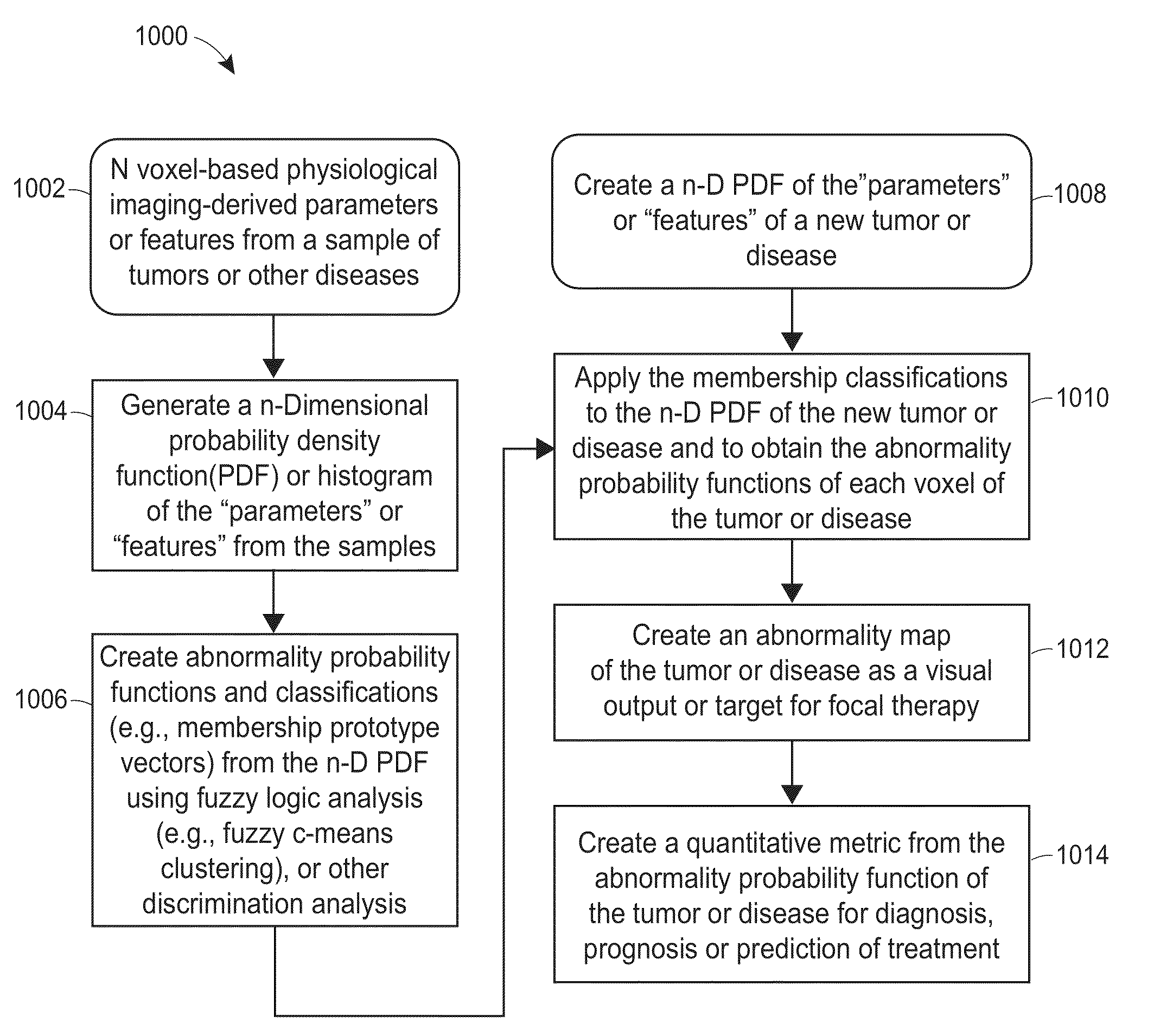
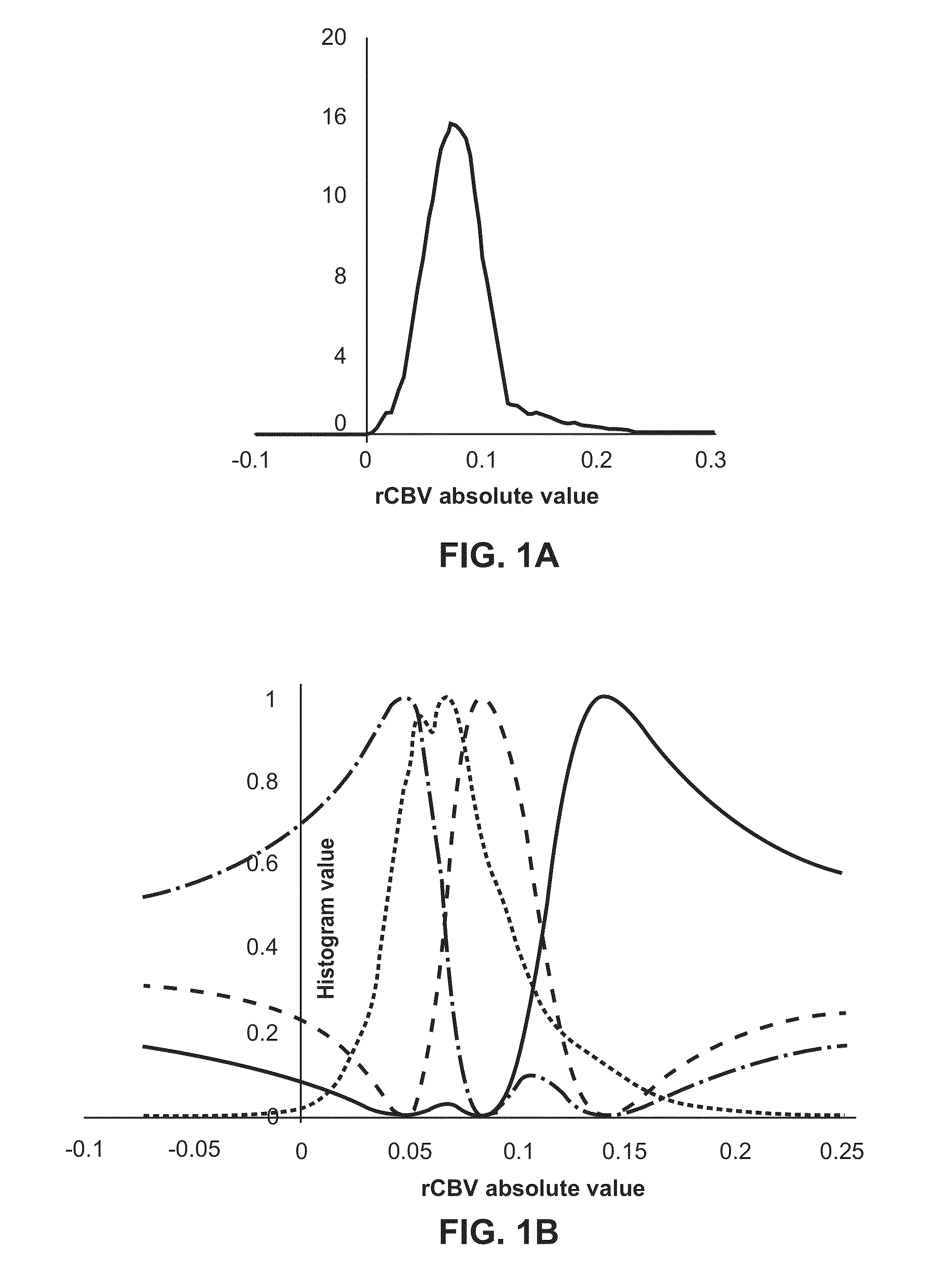
Subvolume identification for prediction of treatment outcome
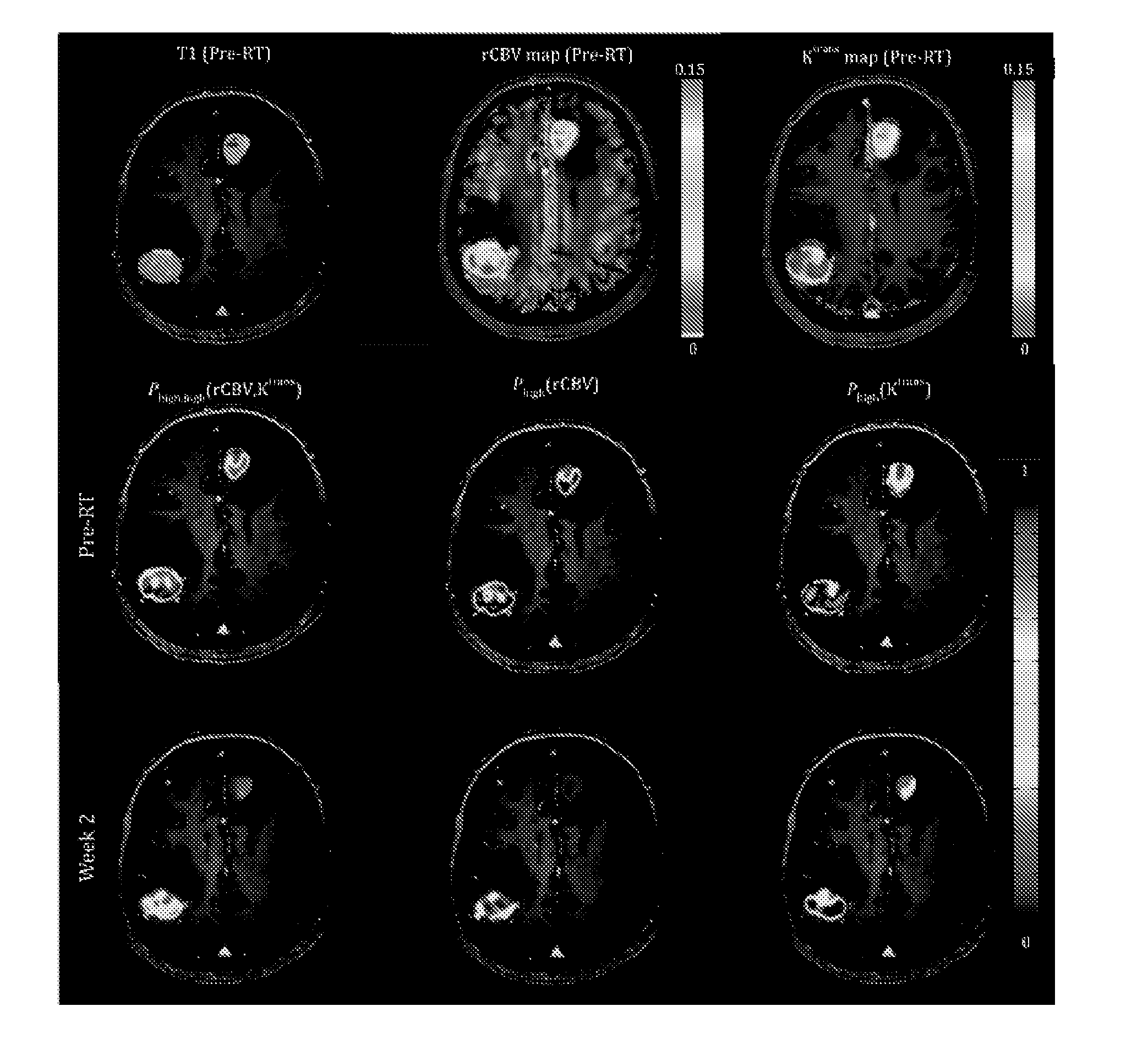
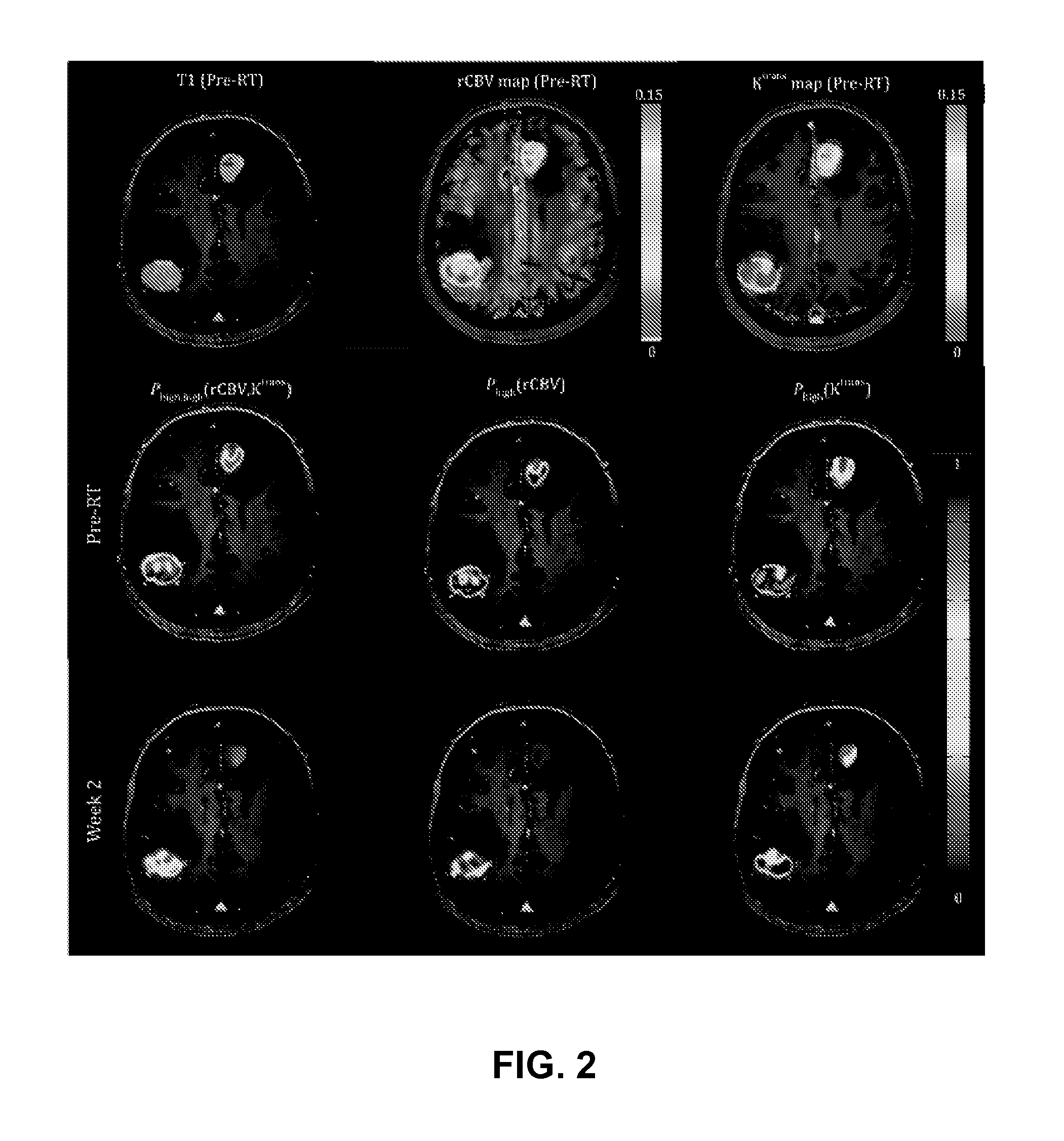
Physiological imaging-defined subvolumes of tissues / disease are identified to yield spatially-defined prognostic and / or predictive indicators and / or focal therapy targets within such tissues, in particular tumors, for evaluation over time, for example, prior to and after a therapy treatment. Medical image data is analyzed to delineate subvolumes of tissue based upon multiple physiological, metabolic, and biological imaging properties, where those subvolumes are extracted and analyzed in a probabilistic manner to associate with one or more abnormal or disease phenotype conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
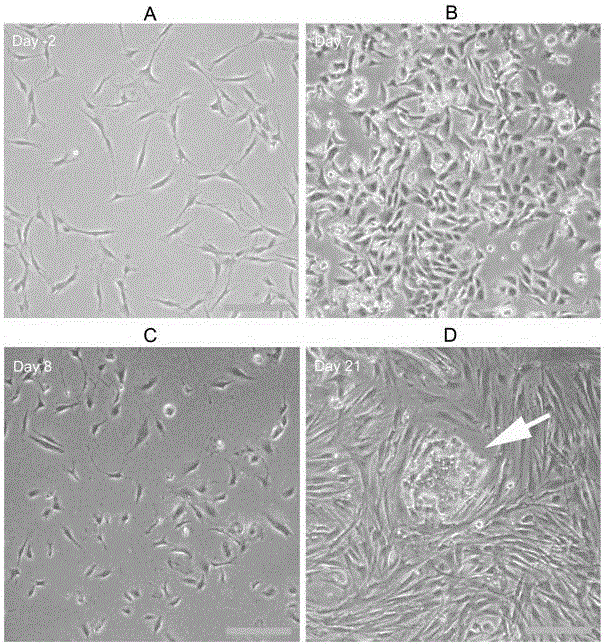
Pluripotent stem cell-hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105039399AWide variety of sourcesLong-term in vitro cultureVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsDiseaseDisease phenotype
The invention belongs to the field of researching and application of biomedicine and particularly relates to human pluripotent stem cell-hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cells and a preparation method thereof. The invention provides a human hereditary cardiomyopathy-pluripotent stem cell, which is constructed by means of TALEN or CRISPR / CAS9 genome editing technology. The human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cell can be combined with any scaffold materials to culture various in-vitro human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle tissues. The human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cells in the invention have disease phenotypes and electrophysiology change being similar as the cardiac muscle cells of human hereditary cardiomyopathy patients. The human hereditary cardiomyopathy cardiac muscle cells are wide in sources and can be cultured in-vitro for a long time. The invention provides excellent tools and platforms for researching an effective new therapy means and researching an effective corresponding treatment medicine.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Treatment of disease
ActiveUS20080045456A1Enhance cell viabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease phenotypeNeuronal damage
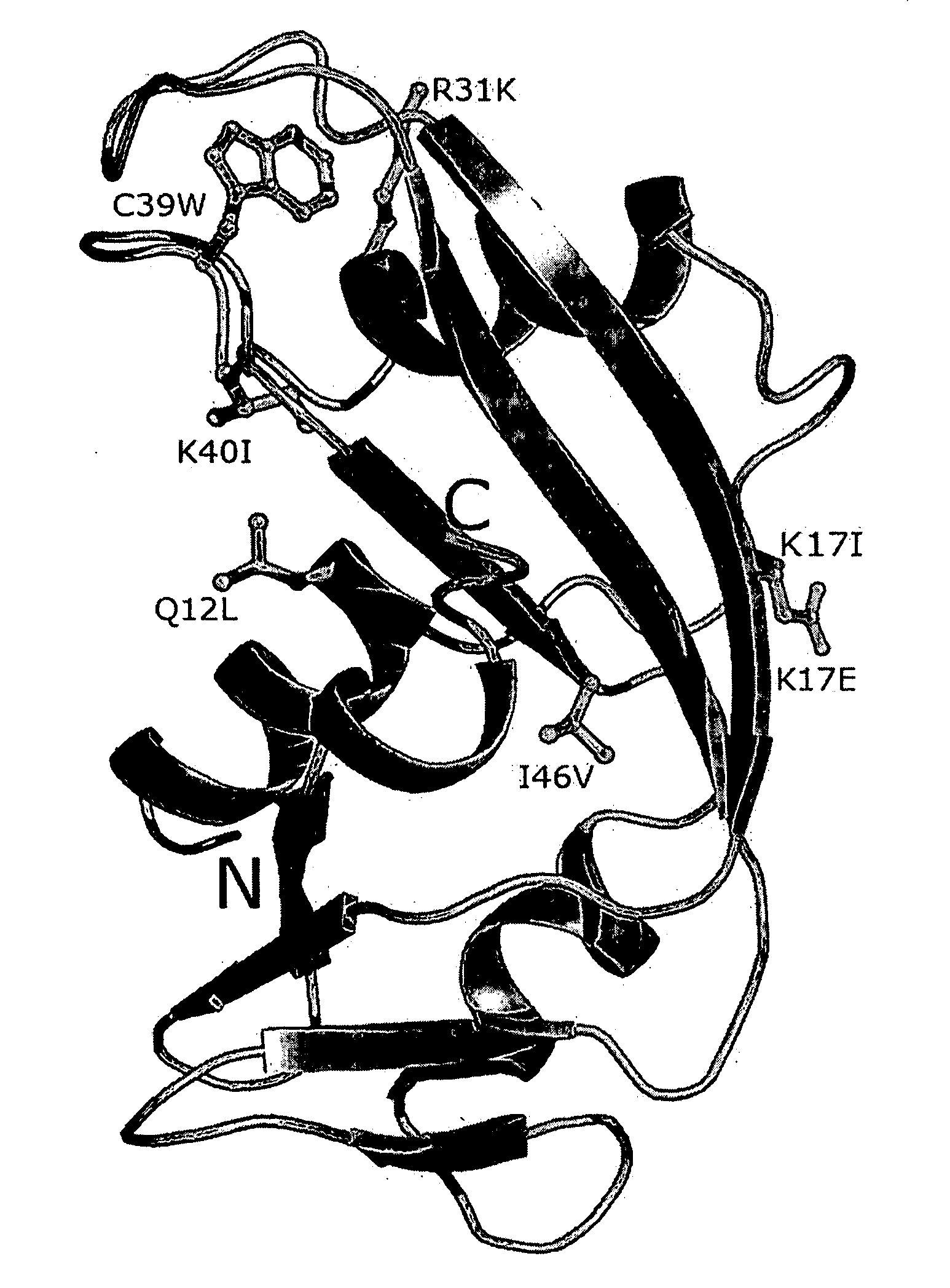
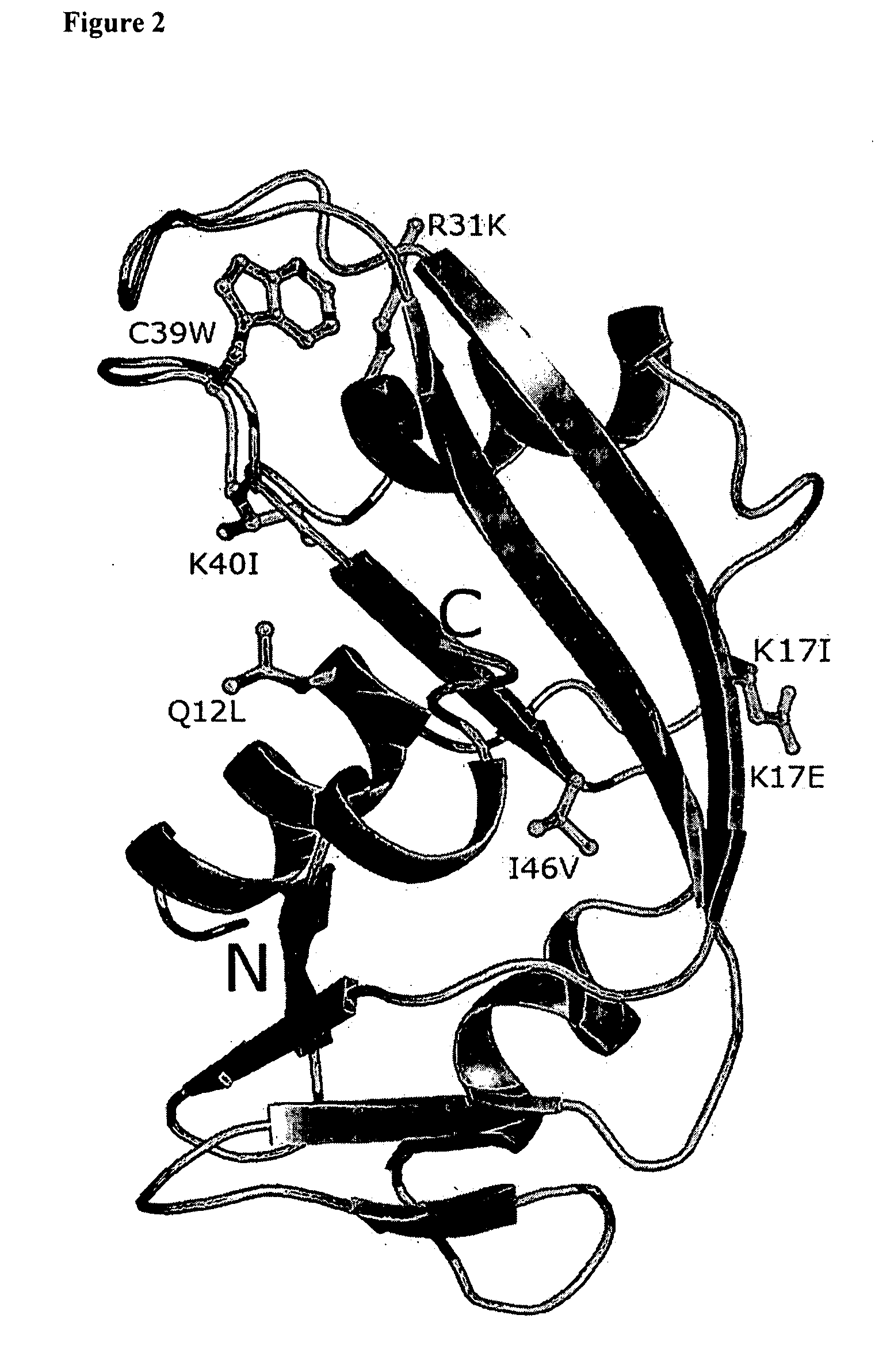
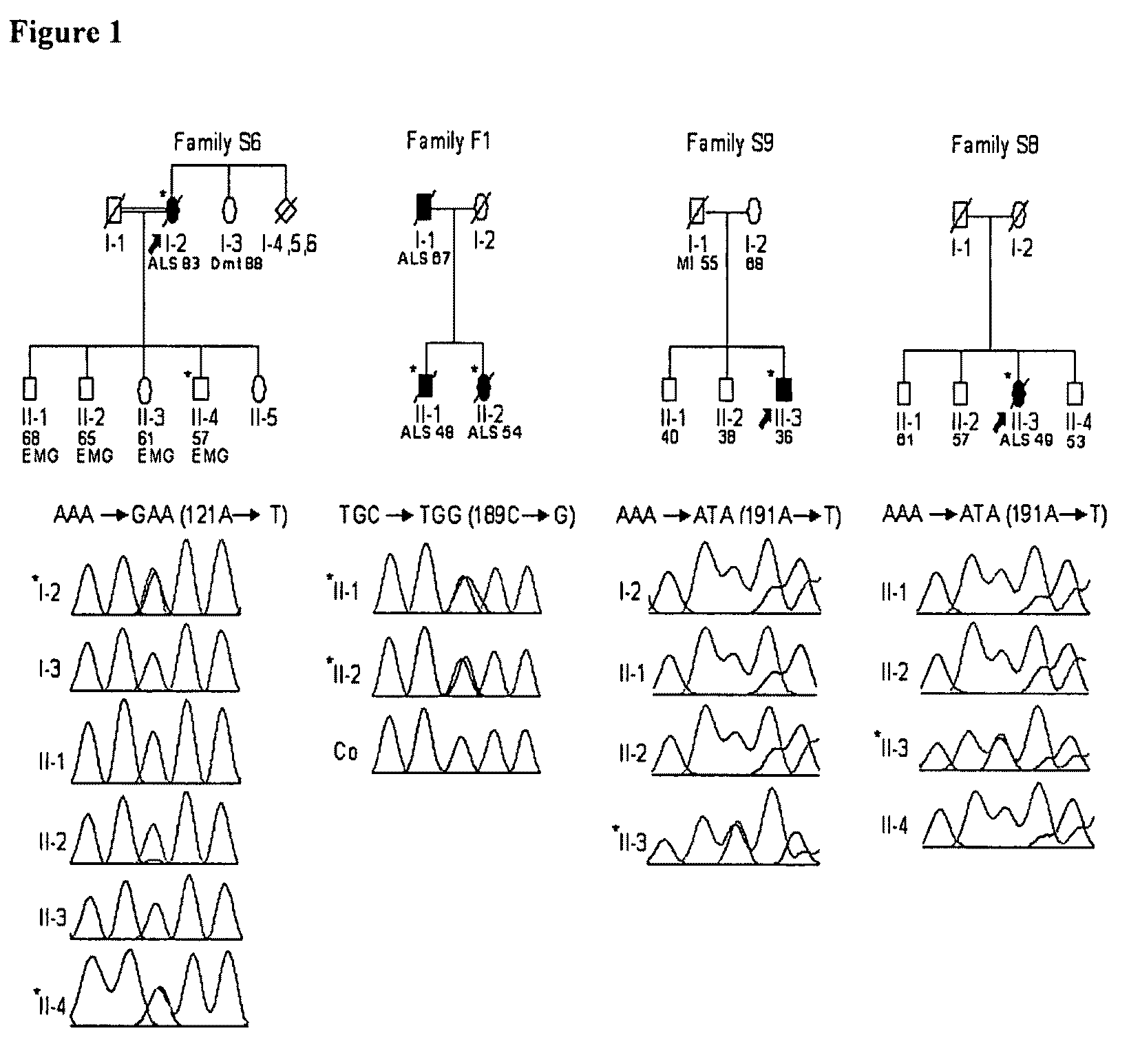
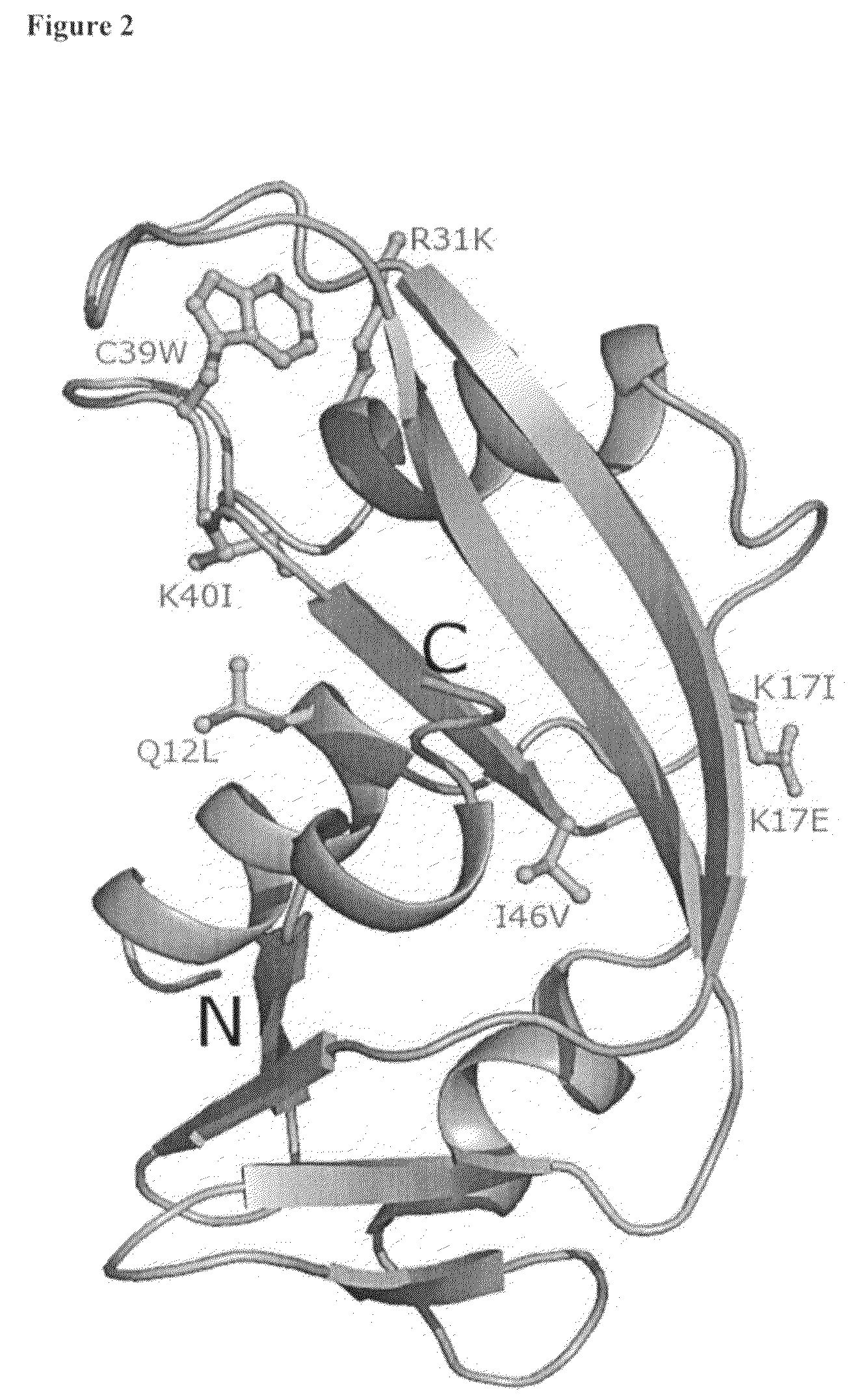
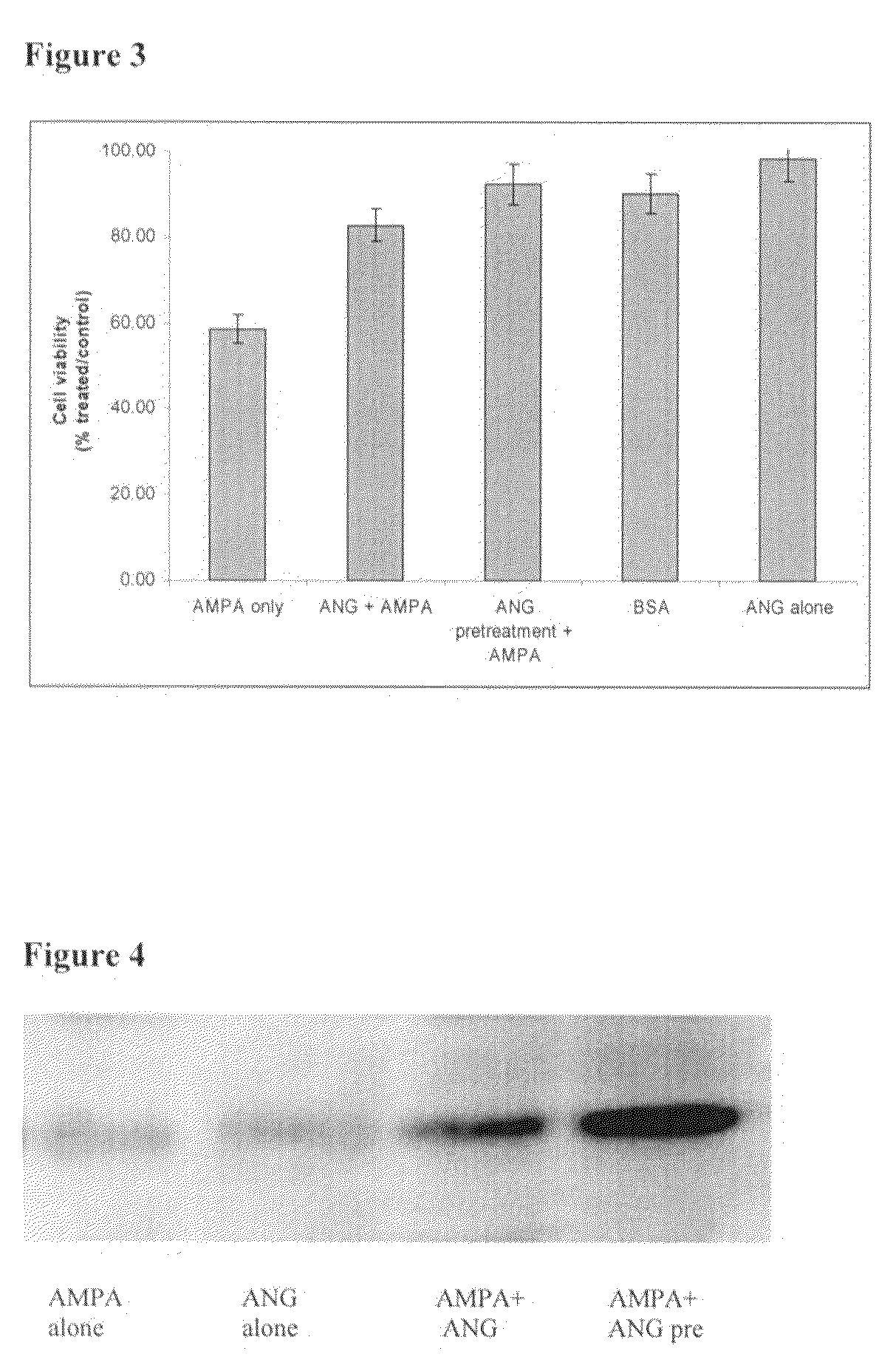
The invention relates to the use of angiogenin, or a fragment or variant thereof, to treat diseases or conditions characterised by neuronal injury or death, or axonal degeneration, especially neurodegenerative diseases such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). The invention also describes a plurality of mutations of the human angiogenin gene which are associated with a neurodegenerative disease phenotype, and particularly a ALS phenotype. Also described is a method of assessing whether an individual is afflicted with, or generically predisposed to develop, a disease or condition characterised by neuronal injury or death, or axonal degeneration.
Owner:ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS & IRELAND
Using Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylases for the Suppression Therapy of Inherited Disease Predisposing Conditions
InactiveUS20070037738A1Improve progressStimulates immunoglobulin secretionBiocideNervous disorderDisease phenotypeHereditary Mutation
Compounds can be used to act as inhibitors of enzymes having histone deacetylase activity for the medical therapy of conditions which predispose a person for the development of a disease, such as but not limited to cancer, inflammatory or metabolic diseases. Such conditions are linked to genetically inherited mutations of crucial genes which predispose a person with this condition to develop the disease phenotype. Thus, such compounds can be used for a suppressive therapeutic approach—the SUPPRESSION THERAPY—in order to inhibit or delay the onset or progression of the genetically predisposed disorder. Furthermore, a clinically used medicament can be manufactured for the SUPPRESSION THERAPY of such inherited predisposing conditions.
Owner:TOPOTARGET GERMANY AG
Methods for Disease Therapy
InactiveUS20100130526A1Improve isolationHigh throughput analysisBiocideBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDisease phenotypeCoronary artery disease
The present invention discloses disease-linked SNPs, microRNAs, and microRNA-targeted mRNAs relevant to the pathogenesis of several major human disorders including, but not limited to, multiple types of cancers, type 2 diabetes, type 1 diabetes, Crohn's disease, coronary artery disease, hypertension, rheumatoid arthritis, bipolar disorder. Also provided are methods for the identification of disease phenotype-defining sets of SNPs, microRNAs, and mRNAs that are defined here as a “consensus disease phenocode” as well as methods of using the information provided by these consensus disease phenocodes for various diagnostic, prognostic, and / or therapeutic applications.
Owner:ORDWAY RES INST
Multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma microrna expression patterns and uses thereof
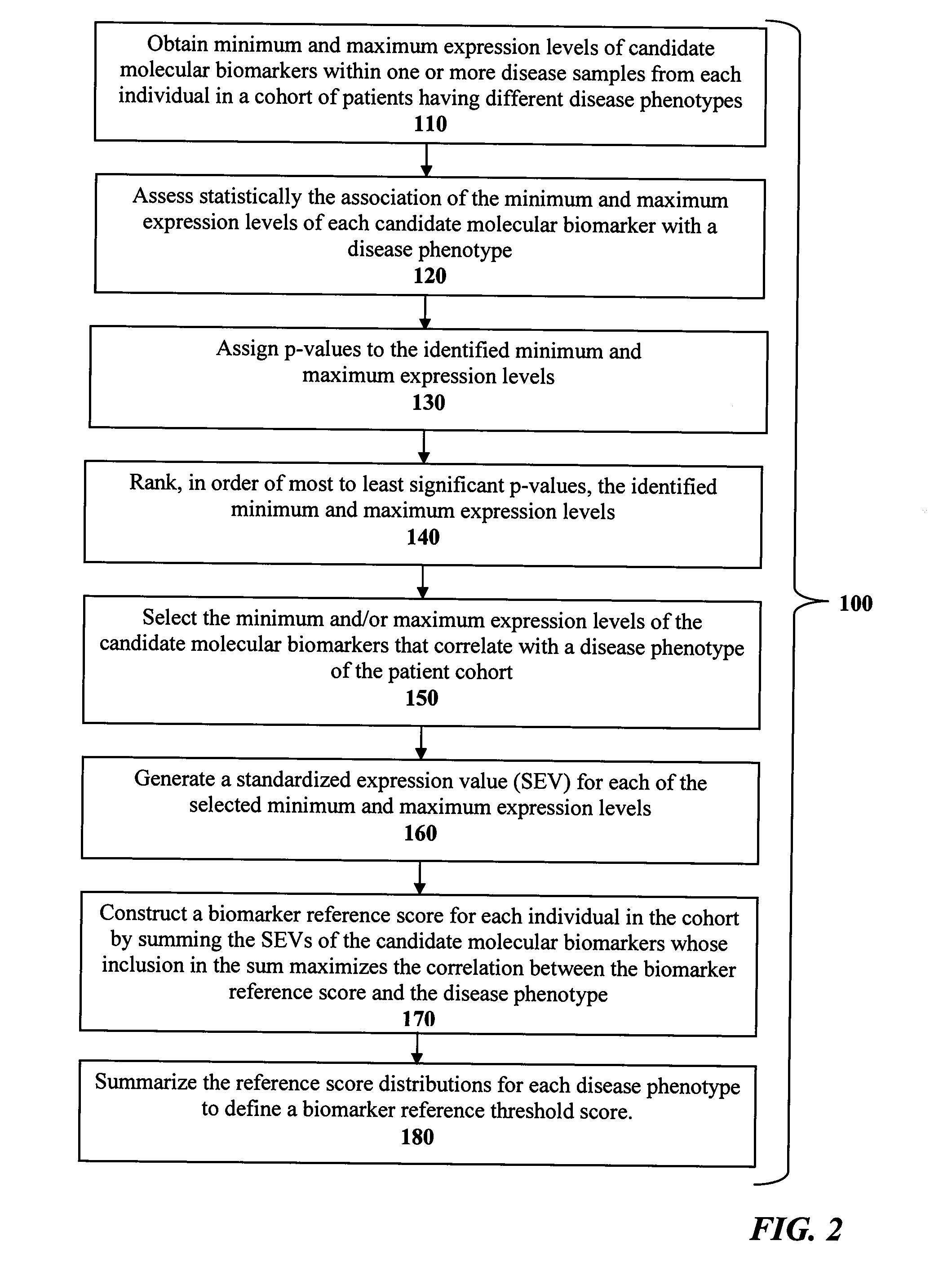
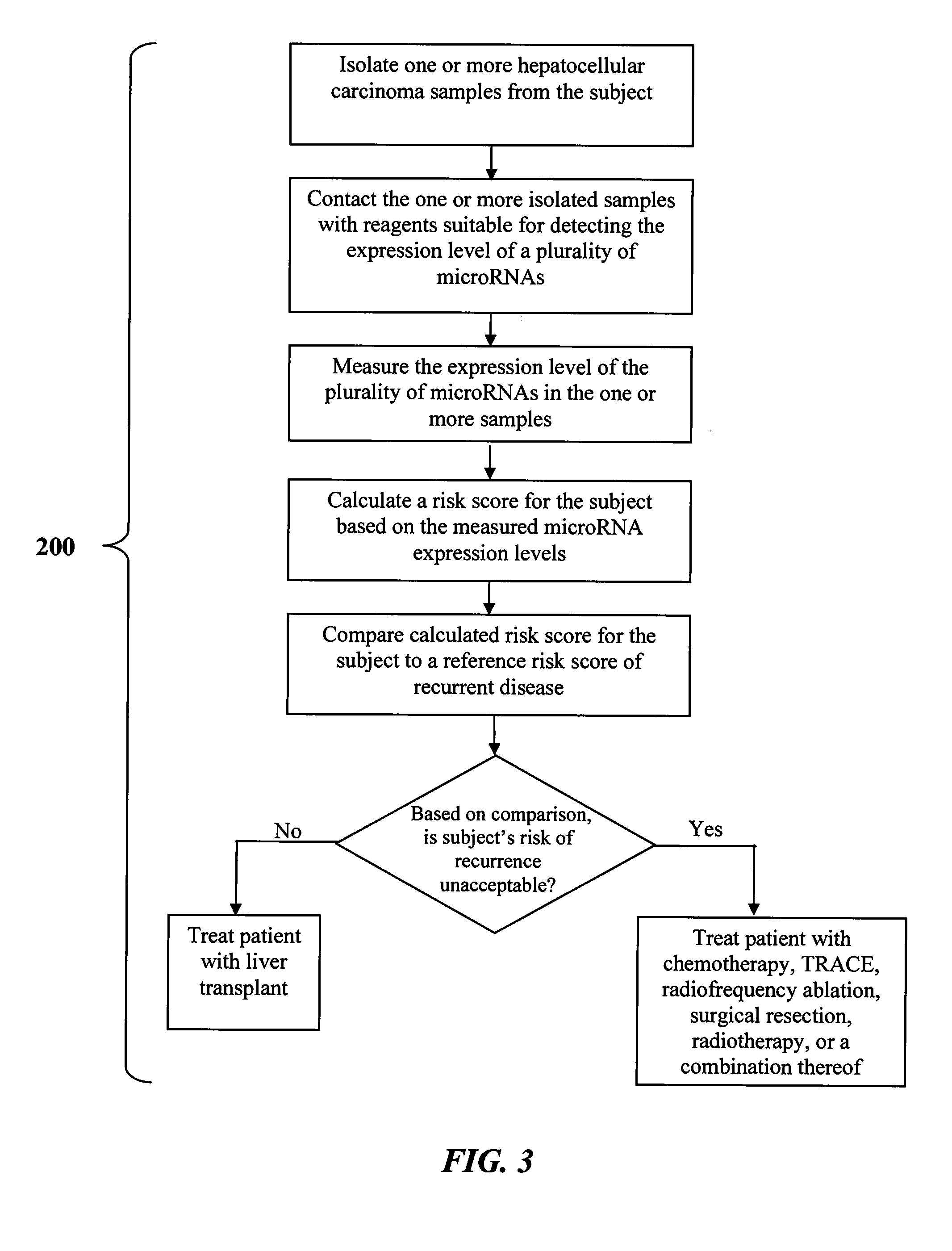
InactiveUS20140113978A1Maximize correlationBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease phenotypeHepatocellular carcinoma
The present invention is directed to methods and products for defining a biomarker of disease phenotype. The present invention further relates to methods and kits for determining a subject's risk of developing recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma based on a defined microRNA biomarker that reliably distinguishes hepatocellular carcinoma disease recurrence from non-recurrence. The invention also relates to methods of treating a patient having heptocellular carcinoma based on their risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma disease recurrence.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Method for obtaining spinal motoneurons and functional cells thereof based on human iPS (induced pluripotent stem) cells
ActiveCN106701824APromote directed differentiationRapid directed differentiationGenetically modified cellsNervous system cellsDisease phenotypeCells transplantation
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, and relates to a safe and reliable reprogrammed method for obtaining human iPS (induced pluripotent stem) cells, a method for simply, rapidly and efficiently inducing and differentiating iPS cells into spinal motoneurons, and a method for economically and efficiently obtaining functional spinal motoneurons and application of the method. Human fibroblasts are infected with Sendai virus carrying a reprogramming factor by using vitronectin as the sole growth medium, and are cultured for 3 weeks to obtain human iPS cells without exogenous serum interference; the iPS cells are efficiently induced and differentiated into spinal motoneurons by a combination of multiple small molecule compounds; and further, an astrocyte conditioned culture medium promotes maturation culture and is applied in the formation of neuromuscular junctions. The functional spinal motoneurons obtained by efficient induction can be applied to simulation of disease phenotype and discussion of pathogenesis, and provides a theoretical basis for the screening of effective therapeutic drugs in the future, and even in the future can be applied to the cell transplantation therapy of diseases.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
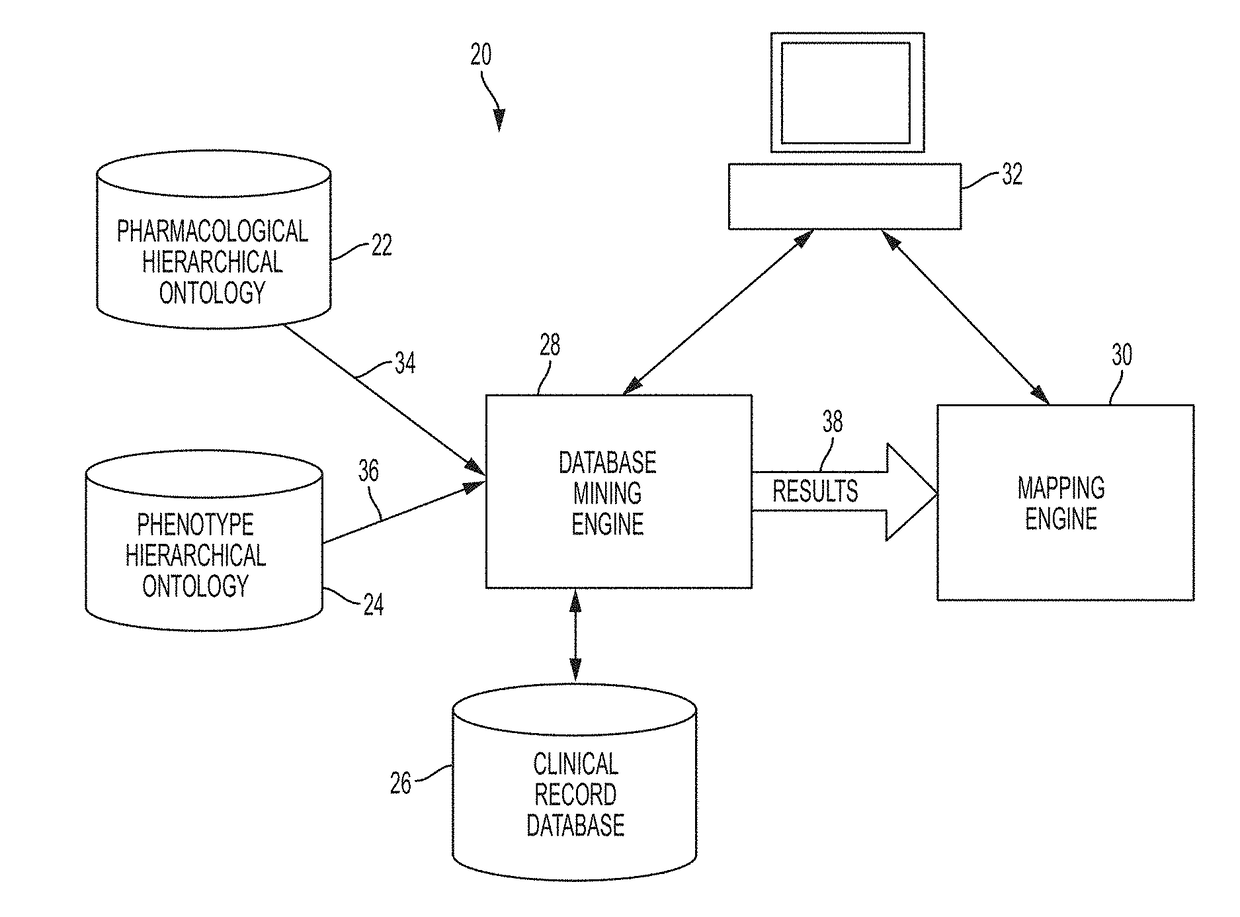
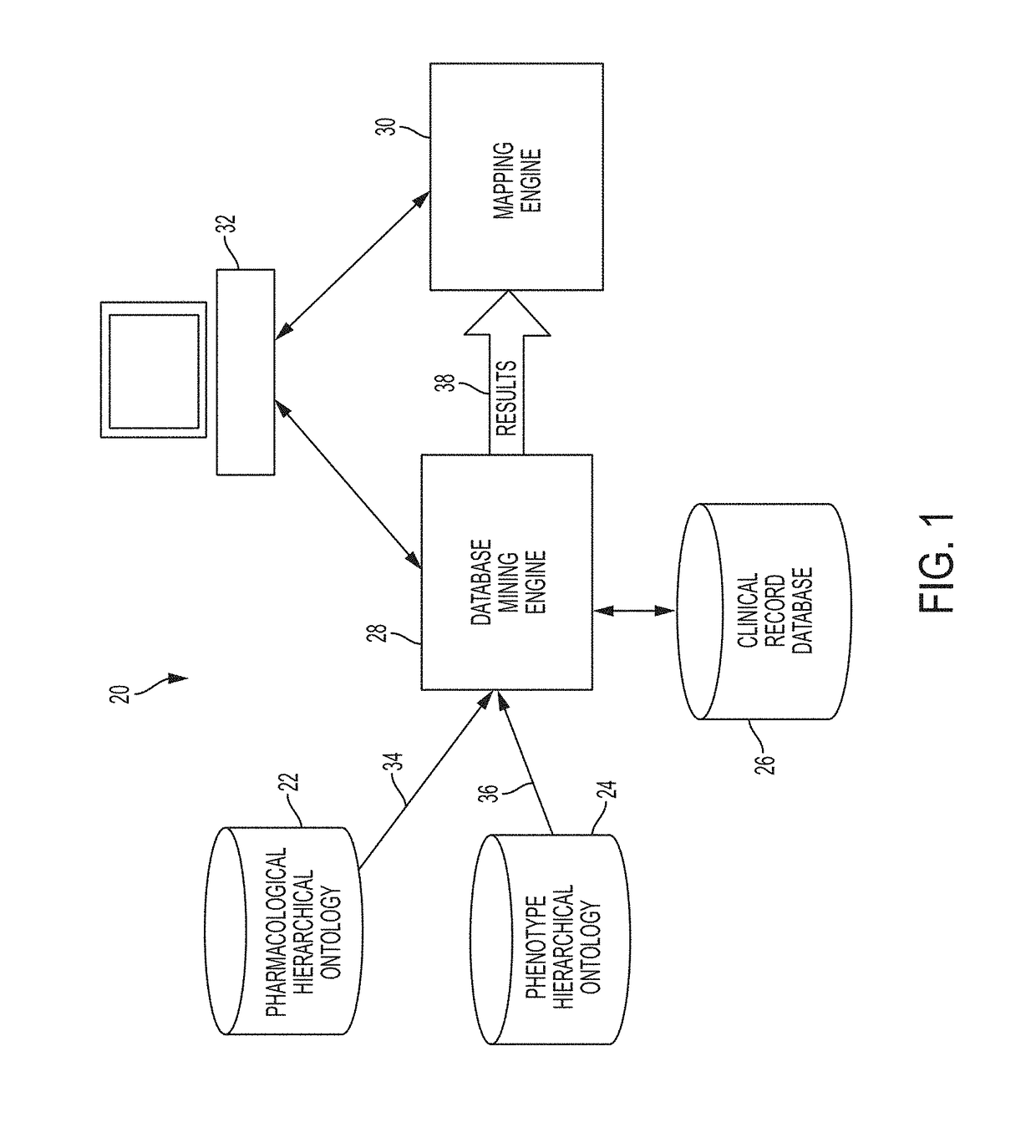
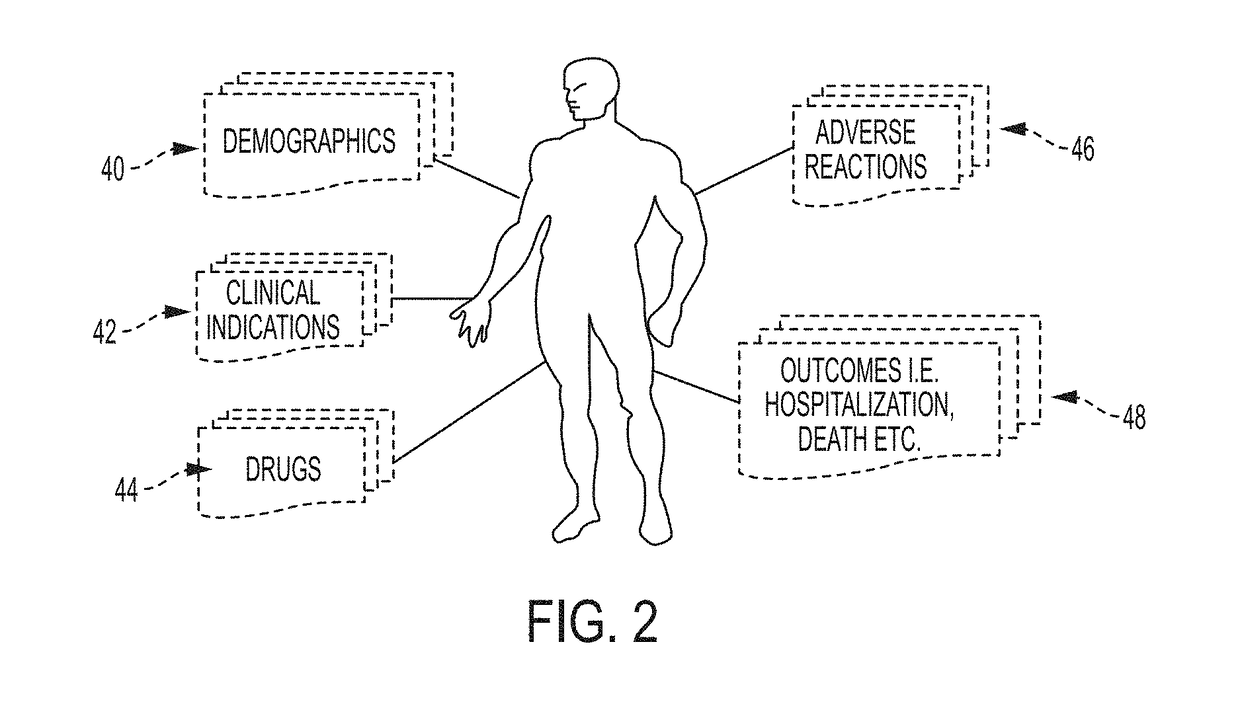
System and Method for Data Mining Very Large Drugs and Clinical Effects Databases
ActiveUS20180004902A1Facilitate high-resolution analysisSimple capabilityMedical data miningDigital data information retrievalDisease phenotypeDisease
A current system allows data-driven hypothesis generation to identify therapeutic candidates for a disease phenotype treatment by identifying drugs and clinical indications associated with lower occurrences of disease-associated phenotype(s) by a drug / drug class. A current system may include a pharmaceutical hierarchical ontology; a phenotype hierarchical ontology; a record database comprising clinical event records; a database mining engine; and a mapping engine. The database mining engine may iteratively progress through a portion of the pharmacological hierarchical ontology and phenotype hierarchical ontology to iteratively select pairs of cohort entries from each ontology; and for each pair of cohort entries, query the clinical record database for matching records. The mapping engine may map each pair of cohort entries into a matrix comprising a drug-event cell for each pair and apply a value thereto representing the number of database records matching items returned by the database mining engine for the corresponding cohort entries.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI
Treatment of ALS and variants thereof consisting of primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) or spinal muscular atrophy (SMA)
ActiveUS7659243B2Enhance cell viabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDisease phenotypeNeuronal damage
The invention relates to the use of angiogenin, or a fragment or variant thereof, to treat diseases or conditions characterised by neuronal injury or death, or axonal degeneration, especially neurodegenerative diseases such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). The invention also describes a plurality of mutations of the human angiogenin gene which are associated with a neurodegenerative disease phenotype, and particularly a ALS phenotype. Also described is a method of assessing whether an individual is afflicted with, or generically predisposed to develop, a disease or condition characterised by neuronal injury or death, or axonal degeneration.
Owner:ROYAL COLLEGE OF SURGEONS & IRELAND
Method for screening bio-control bacteria of cucumber fusarium wilt
InactiveCN103371041AImprove disease resistanceReduce incidenceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDiseaseDisease phenotype
The invention discloses a method for screening bio-control bacteria of cucumber fusarium wilt, and provides a method for identifying the bio-control nature of to-be-identified bacteria to pathogenic bacteria of the cucumber fusarium wilt including experimental treatment. The experiment treatment sequentially includes following steps of 1), accelerating sprouting of sterilized cucumber seeds to obtain the sprouting seeds; 2), subjecting the sprouting seeds to soaking in suspension liquid of the to-be-identified bacteria prior to cultivating the sprouting seeds till radicle length reaches by 1.5-2.0cm; 3), inoculating cucumber seedlings to suspension liquid of the pathogenic bateria of the cucumber fusarium wilt; 4), transferring the cucumber seedlings to MS solid media to cultivate, and identifying the bio-control nature of the to-be-identified bacteria to the patheogenic bacteria of the cucumber fusarium wilt by surveying disease indexes and / or observing disease phenotypes. The method is applicable to screening the bio-control bacteria of the cucumber fusarium wilt. In the method, the cucumber seedlings used as samples can truly reflect disease prevention effect of the bio-control bacteria, and can screen bacterial strains of various bio-control mechanisms.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
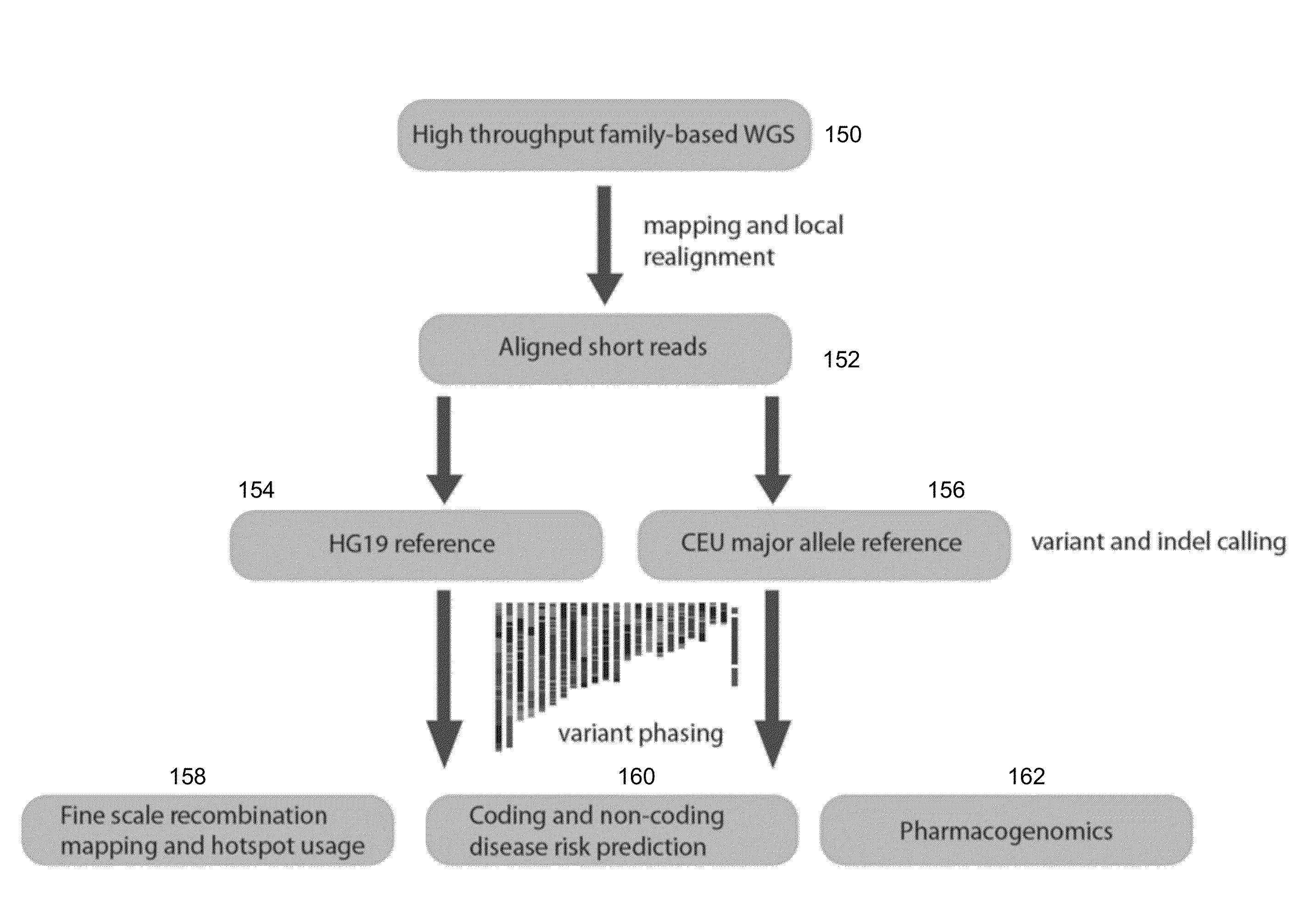
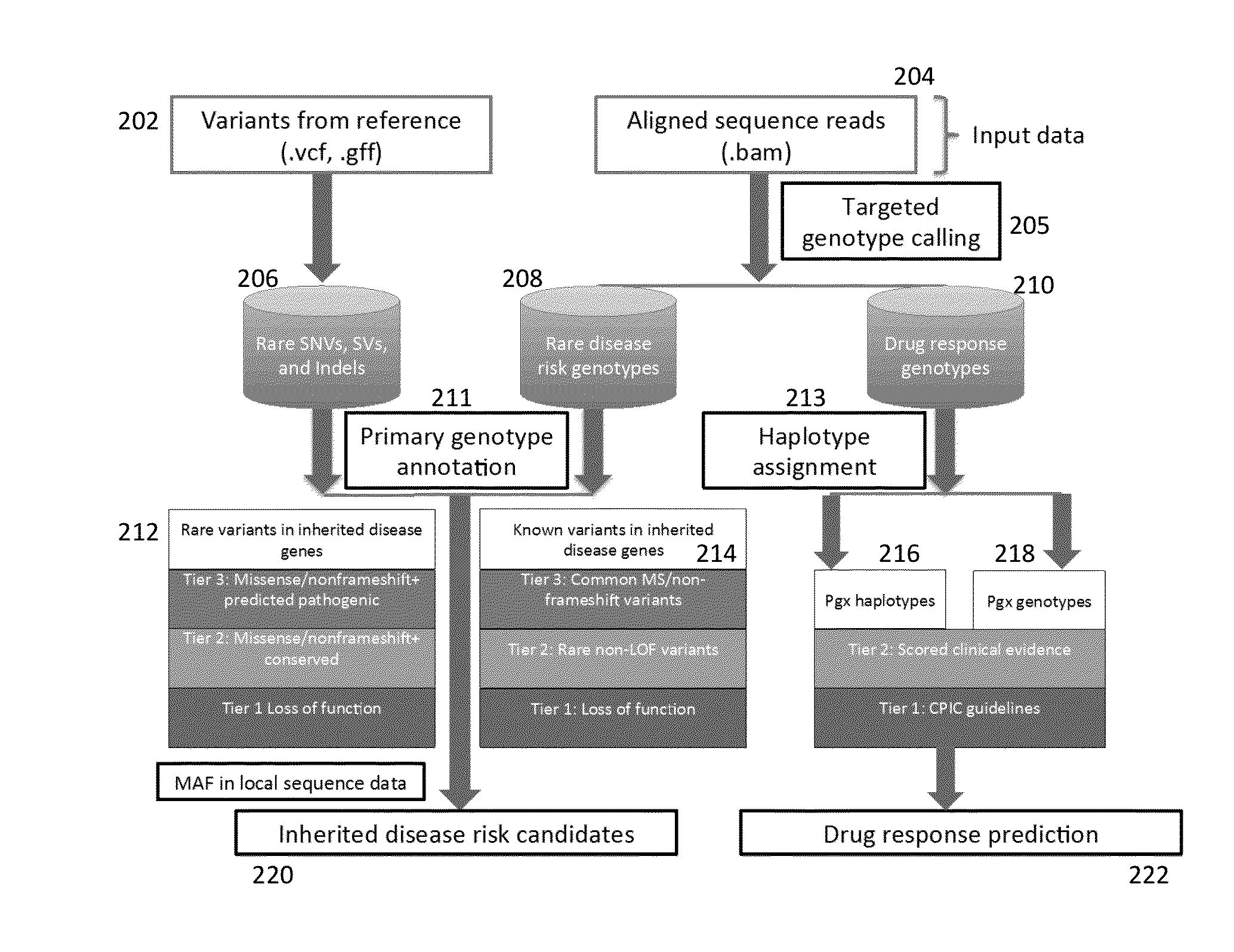
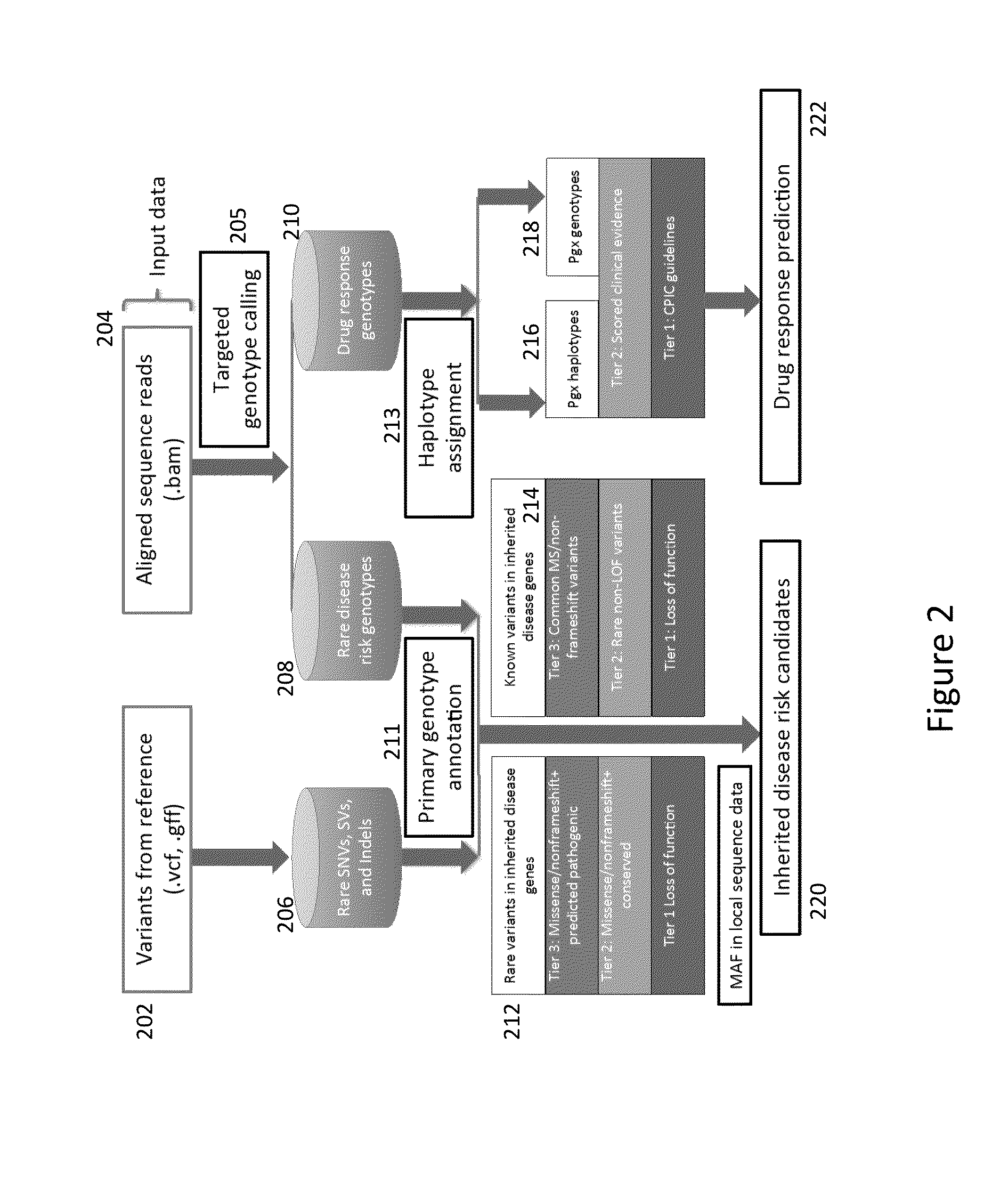
Phased Whole Genome Genetic Risk In A Family Quartet
An embodiment of the present invention is a methodology for prioritizing variants relevant to inherited Mendelian (“single gene”) disease syndromes according to disease phenotype, gene, and variant level information.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
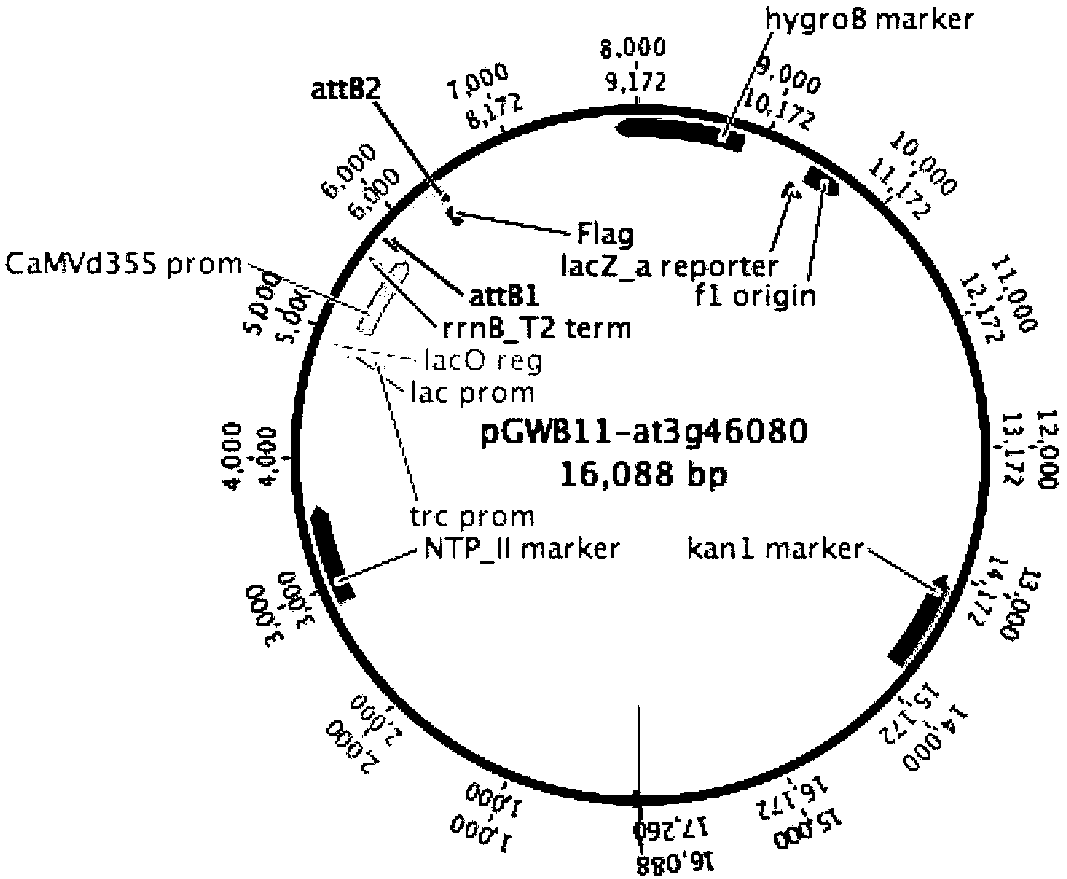
Application of Arabidopis thaliana transcription factor at3g46080 gene
PendingCN110305218AIncrease resistanceAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPlant peptidesDisease phenotypePseudomonas tolaasii
The invention relates to an application of an Arabidopis thaliana transcription factor at3g46080 gene. By constructing a CDS sequence of the Arabidopsis thaliana at3g46080 gene into the upstream of aFLAG protein label by a Gateway technology, Arabidopsis thaliana is conversed, which affects the disease phenotype of Arabidopsis thaliana, screening and identification are carried out, and finally the transgenic plants can be obtained. The analysis of the screened plants carried out so that the plant has enhanced resistance to Pseudomonas lycoposum by Arabidopis thaliana, the gene has the same function for homologous genes in crops, and thus has important significance in production.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
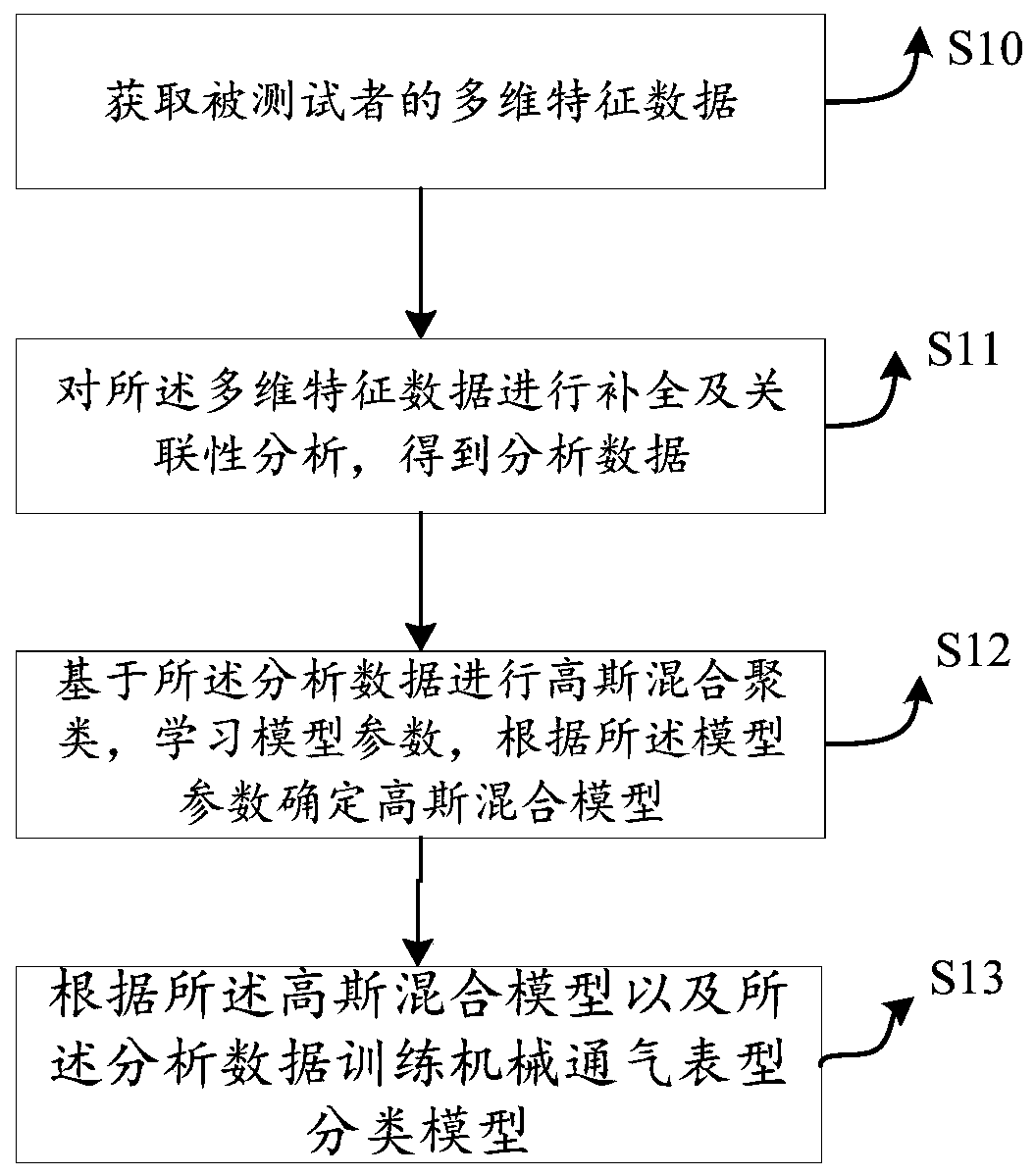
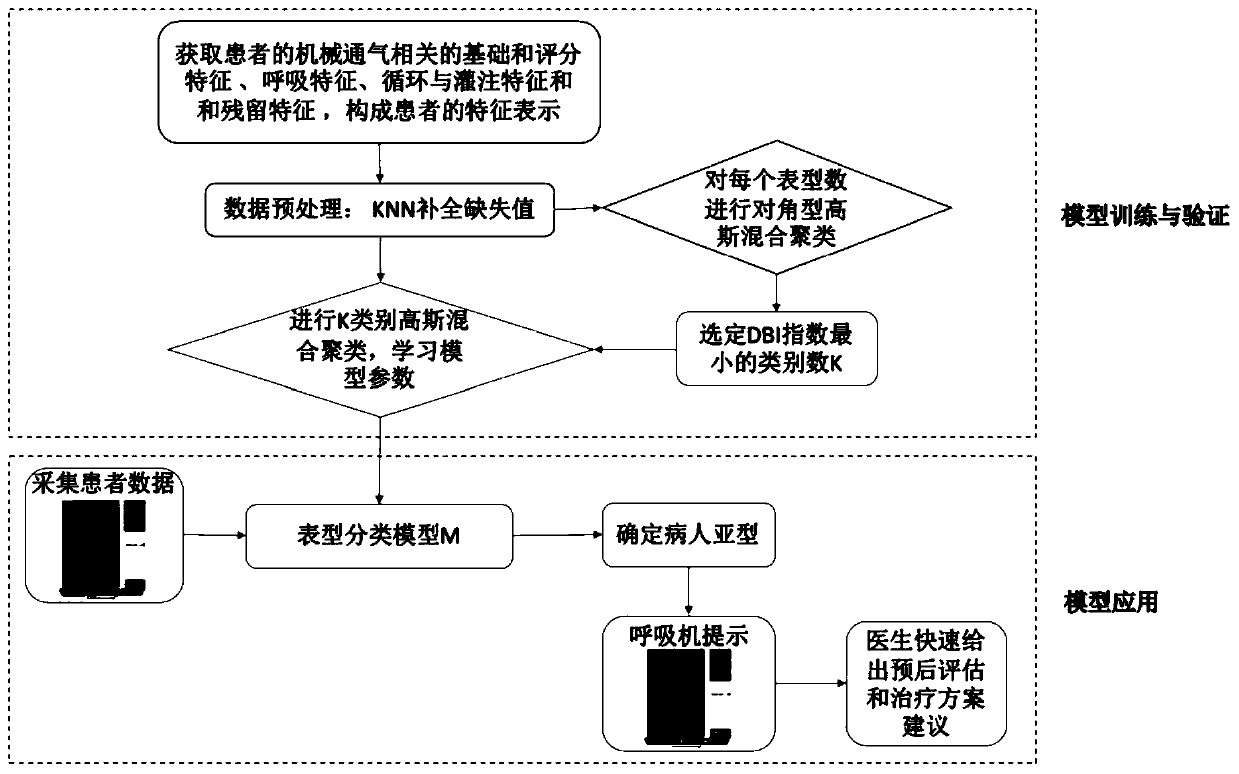
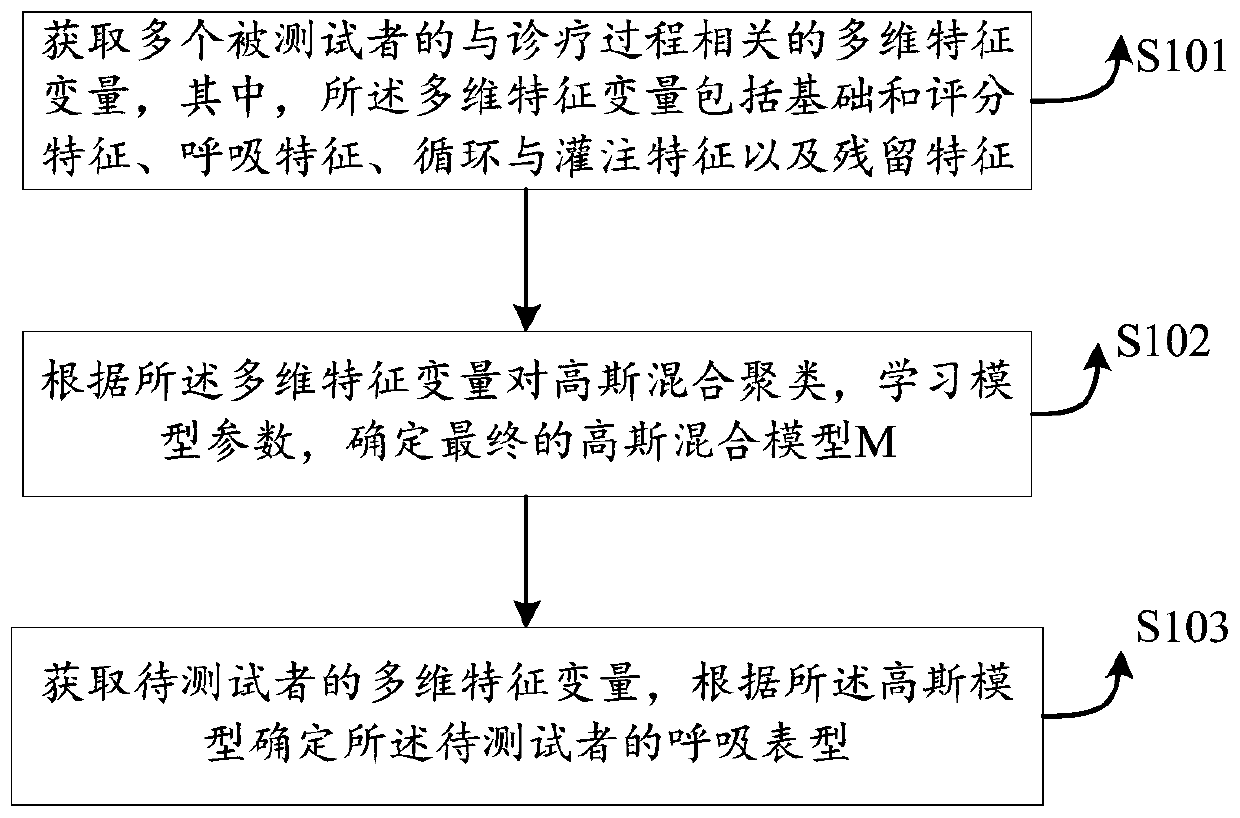
Model training method, mechanical ventilation phenotype recognition method and respirator
The embodiment of the invention provides a model training method, a mechanical ventilation phenotype recognition method and a respirator. The model training method comprises the steps that multi-dimensional feature data of a testee are acquired, and the multi-dimensional feature data at least comprise basic and scoring features, breathing features, circulation and perfusion features and residual feature in-out quantity balance of the testee; complementation and correlation analysis are performed on the multi-dimensional feature data, so that analysis data can be obtained; and Gaussian mixtureclustering is carried out based on the analysis data, model parameters are learned, and a Gaussian mixture model is determined according to the model parameters. According to the embodiment of the invention, the phenotype of the corresponding disease is determined by collecting the characteristic parameters related to the certain disease treatment equipment, and subsequent doctors can perform classified treatment and nursing on different patients according to the combination of the phenotype type of the disease and the related observation data of the certain disease treatment equipment of thepatients.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Tissue phasic classification mapping system and method
A voxel-based technique is provided for performing quantitative imaging and analysis of tissue image data. Serial image data is collected for tissue of interest at different states of the issue. The collected image data may be deformably registered, after which the registered image data is analyzed on a voxel-by-voxel basis, thereby retaining spatial information for the analysis. Various thresholds are applied to the registered tissue data to identify a tissue condition or state, such as classifying chronic obstructive pulmonary disease by disease phenotype in lung tissue, for example.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Gene module analysis method
The invention discloses a gene module analysis method. The gene module analysis method comprises the following steps: inputting a gene phenotype double-layer network, a gene function similarity network and a known disease gene set s0 related to a disease phenotype; increasing the connection relationship between genes and phenotypes in the gene phenotype double-layer network; taking genes which arein edge connection with disease genes in s0 and are not in s0 in the gene phenotypic double-layer network as candidate genes; calculating and selecting a candidate gene with the maximum sum of semantic similarity, topological similarity and phenotypic relevance, and adding the candidate gene into s0; and when the expanded candidate gene set does not significantly enrich the GO ontology function annotation and the biological pathway gene related to the disease phenotype at the same time and express the differential gene in the disease phenotype sample and the normal sample any more, recordingthe current algebra as m, and outputting m-1 as candidate genes expanded in the first generation s0 and known disease genes connected with the edges of the expanded candidate genes.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Methods and compositions for screening for modulators of parkinson's disease
InactiveUS20060101527A1Enhancing Parkinson 's disease phenotypeSuppressing Parkinson 's disease phenotypeGenetic engineeringMaterial analysisDisease phenotypeMammal
Methods and compositions for identifying an agent (e.g., a gene product or small molecule compound) that modulates a Parkinson's disease phenotype are provided. In practicing the subject methods, a non-mammalian animal model, such as Drosophila melanogaster, that includes a mutant parkin gene and at least one other mutant gene are evaluated for a Parkinson's disease phenotype. Also provided are kits, and systems for practicing the subject methods, as well as methods of use of agents identified in the screening method of the invention.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Method and System for Identifying Clinical Phenotypes in Whole Genome DNA Sequence Data
High throughput sequencing has facilitated a precipitous drop in the cost of whole genome human DNA sequencing, prompting predictions of a revolution in medicine via personalization of diagnostic and therapeutic strategies to individual genetics. Disclosed is a comprehensive series of methods for identification of genetic variants and medical genotypes, phasing genetic data and using Mendelian inheritance for quality control, and providing predictive genetic information about risk for rare disease phenotypes and response to pharmacological therapy in single individuals and father-mother-child trios.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
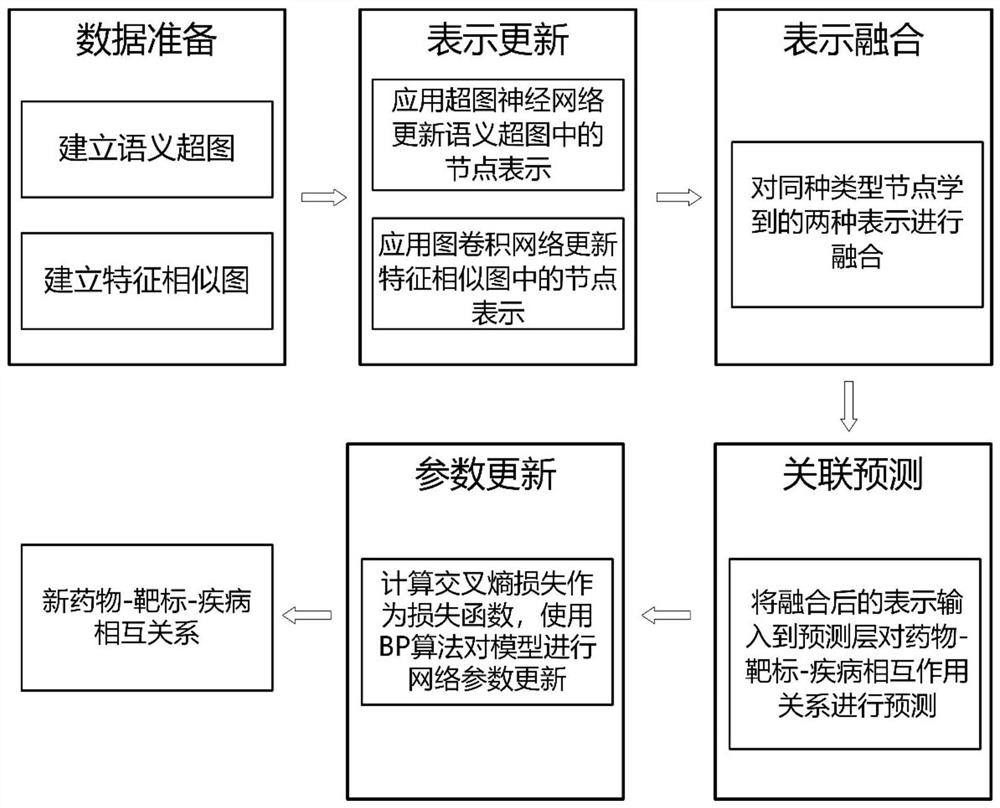
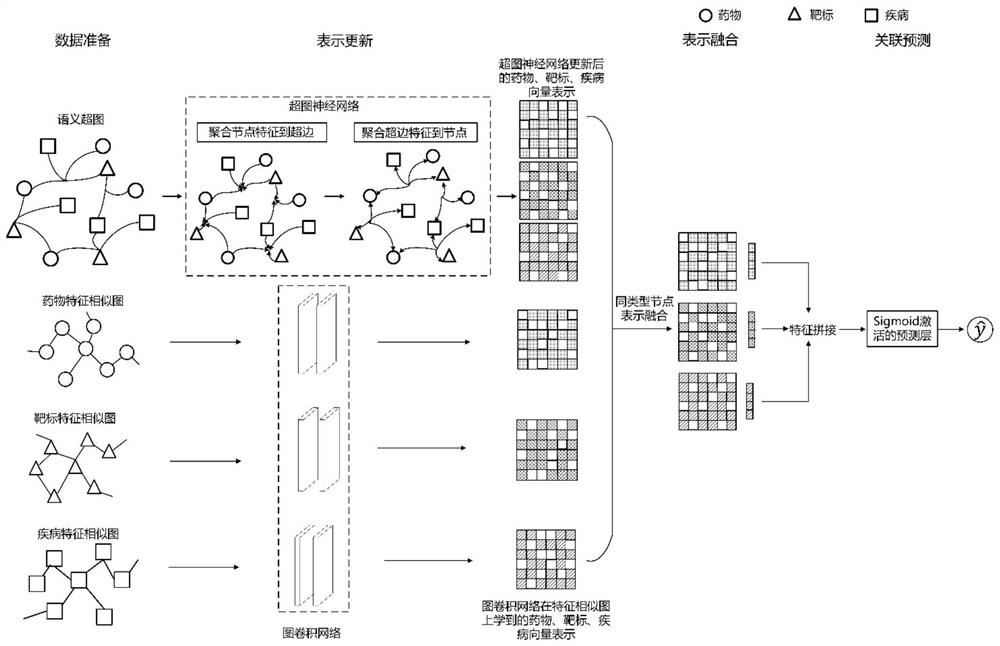
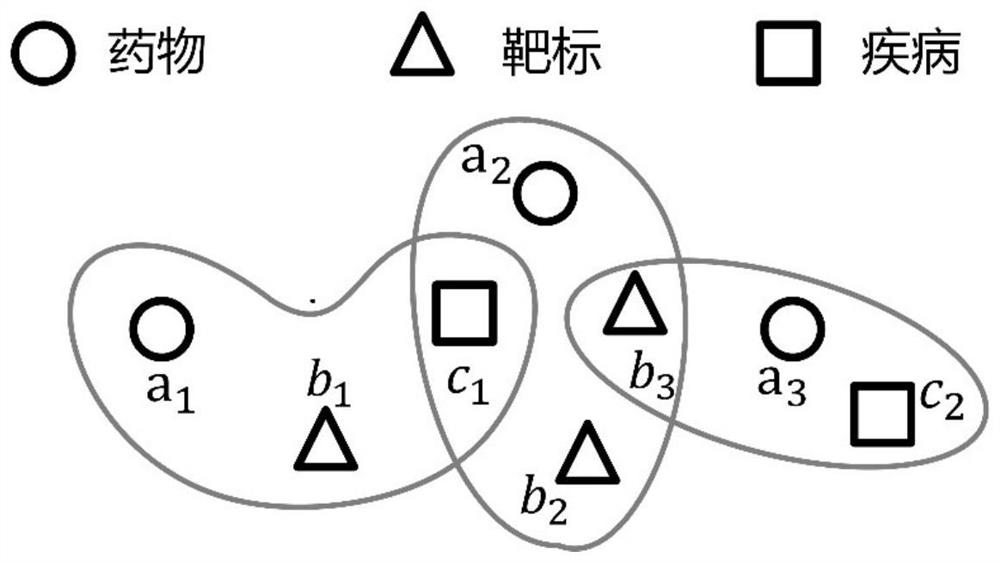
Hypergraph-based drug-target-disease interaction prediction method
ActiveCN113066526AEasy to understandCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesDisease phenotypeDisease
The invention discloses a drug-target-disease interaction prediction method based on a hypergraph. The method comprises the following steps: 1) establishing a semantic hypergraph G according to a binary relationship R between every two drugs, targets and diseases; according to the drug molecule fingerprints, the target sequences and the disease phenotypes, establishing feature similarity graphs of drug nodes, target nodes and disease nodes; 2) applying a hypergraph neural network on the semantic hypergraph G to obtain node representations corresponding to drugs, targets and diseases; respectively applying a graph convolutional network on the feature similarity graphs of the drugs, the targets and the diseases to obtain node representations corresponding to the drugs, the targets and the diseases; 3) fusing the node representations obtained in the step 2); 4) training a prediction model by using the fused node representation corresponding to each hyperedge obtained in the step 3); 5) generating node representations of a to-be-predicted drug a and a to-be-predicted disease c, and inputting the node representations into the trained prediction model for prediction to obtain a prediction probability that the drug a treats the disease c through the target b.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for screening disease phenotype related mutation sites and application thereof
PendingCN112735594ASmall sample sizeAvoid allele frequency effectsMedical data miningProteomicsDisease phenotypeDisease
The invention relates to the technical field of bioinformatics, in particular to a method for screening disease phenotype related mutation sites and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining sequencing data of a plurality of disease samples and normal samples, and carrying out variation detection; performing association rule mining by taking the phenotype of the samples and the mutation type of the detected mutation site as a total project set to obtain a mutation site having a strong association relationship with the phenotype of the disease samples; and performing modeling analysis on the mutation sites obtained through association rule mining and screening to obtain mutation sites related to disease phenotypes. Alleles are converted into classification variables for association rule mining, and then modeling analysis is carried out on sites strongly associated with disease phenotypes, so that the total quantity of analyzed samples can be effectively reduced, and the influence of allele frequency on an analysis result is avoided; and screening and analysis of disease phenotype related sites can be completed only by obtaining mutation genotype information.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL DEVICES CO LTD
Systematic screening and mapping of regulatory elements in non-coding genomic regions, methods, compositions, and applications thereof
PendingUS20200143907A1Health-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease phenotypeRegulator gene
The application relates to methods for identifying putative regulatory elements that regulates a gene, comprising: obtaining a measure of intrinsic activity of a plurality of genomic elements; obtaining a measure of proximity between each of the genomic elements and the gene; scoring a predicted impact of each of the genomic elements on the gene as a function of the measure of intrinsic activity and the measure of proximity, wherein a plurality of predicted impacts scored are ranked to identify at least one genomic element as a putative regulatory element that regulates the gene; and optionally, training, optimizing, and / or validating the scoring of predicted impact using experimental or computational data describing functional interactions between the genomic elements and the gene. The application also relates to methods for identification of transcriptional enhancers and repressors regulating a gene associated with an agricultural trait of interest in plants or a disease phenotype in mammalians.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
Evaluation method for judging rare hereditary diseases
PendingCN112735599AImprove evaluabilityReduce birthMedical data miningProteomicsDisease phenotypeGenes mutation
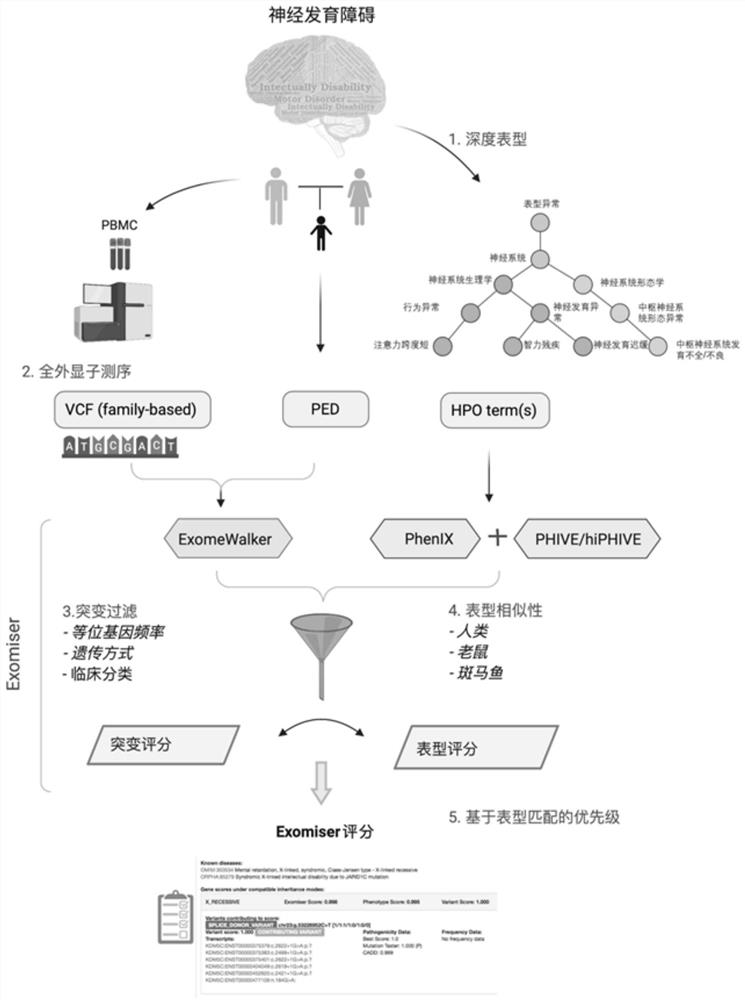
The invention discloses an evaluation method for judging rare hereditary diseases, which comprises the steps of deep phenotype analysis, whole exon group sequencing, gene mutation identification and filtration, mutation optimization combined with a genetic pattern and a disease phenotype, whole exon group sequencing and human phenotype ontology. Clinical doctors can be assisted to judge and evaluate pathogenic factors of rare hereditary diseases in time, the evaluable rate of the rare hereditary diseases is increased, a basis is provided for determining appropriate treatment measures and clinical management strategies, genetic counseling and prenatal evaluation are provided for families, birth of similar child patients is reduced, and economic burdens of the families and the society are relieved. Therefore, the method has important significance for judging the hereditary diseases with high phenotypic heterogeneity and low morbidity.
Owner:PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF HENAN PROV
Fast assistant positioning method for disease
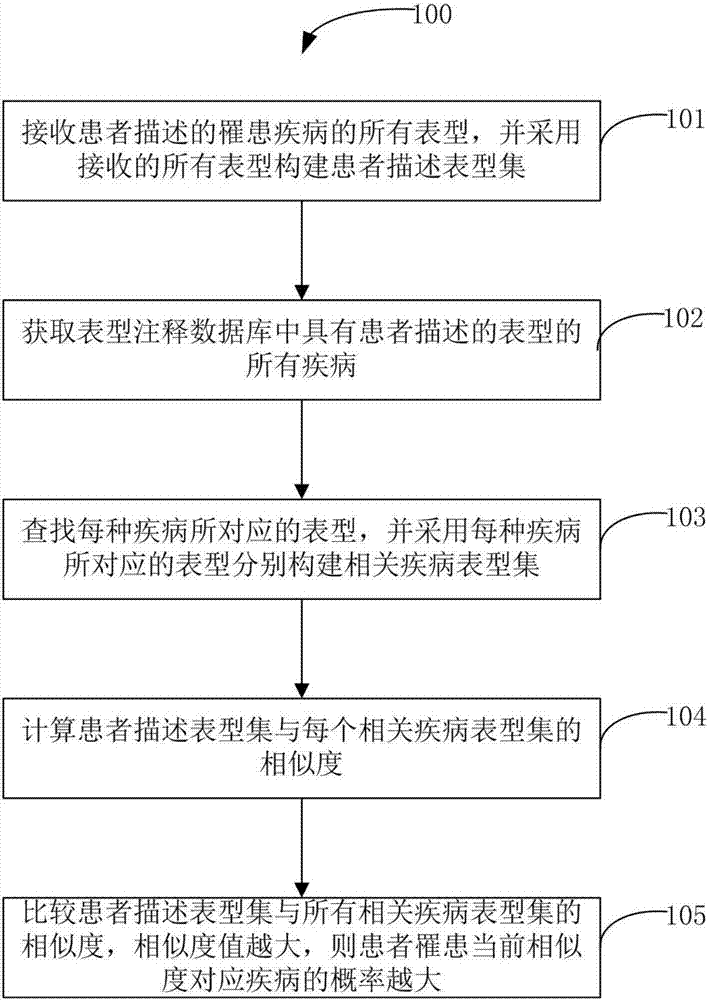
ActiveCN106980749ARemove uncertaintyHigh resistance to external interference factorsMedical automated diagnosisSpecial data processing applicationsDisease phenotypeDisease
The invention discloses a fast assistant positioning method for a disease. The method comprises the steps that all phenotypes, described by a patient, of an affected disease are received, and all the received phenotypes are adopted to construct a patient description phenotype set; all diseases with the phenotypes described by the patient in a phenotype annotation database are acquired; phenotypes corresponding to each disease are searched for, and the phenotypes corresponding to each disease are adopted to construct a relevant disease phenotype set; the similarity between the patient description phenotype set and each relevant disease phenotype set is calculated; and the similarities between the patient description phenotype set and all the relevant disease phenotype sets are compared, wherein the higher a similarity value is, the higher the probability of suffering from the disease corresponding to the current similarity by the patient.
Owner:成都奇恩生物科技有限公司
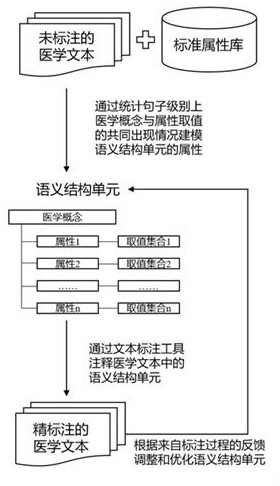
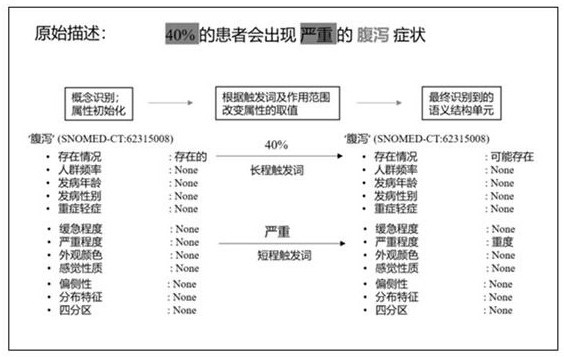
Semantic structuralization processing method for medical text phenotypic information
PendingCN112270965AAccurate Structured RepresentationEasy to understandSemantic analysisPatient-specific dataDisease phenotypeMedicine
The invention discloses a semantic structuralization processing method for the medical text phenotypic information. A finer and more accurate disease phenotypic knowledge database is obtained by constructing a phenotypic semantic structure unit, automatically identifying the phenotypic semantic structure unit and interactively proofreading the phenotypic semantic structure unit. The method is advantaged in that phenotypic knowledge in the medical text can be subjected to more accurate and deeper structured representation on the semantic level, and fine-grained representation on the semantic level is deeper. According to the method, development of the medical informatization and intelligent career of China can be greatly promoted.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF SYST MEDICINE
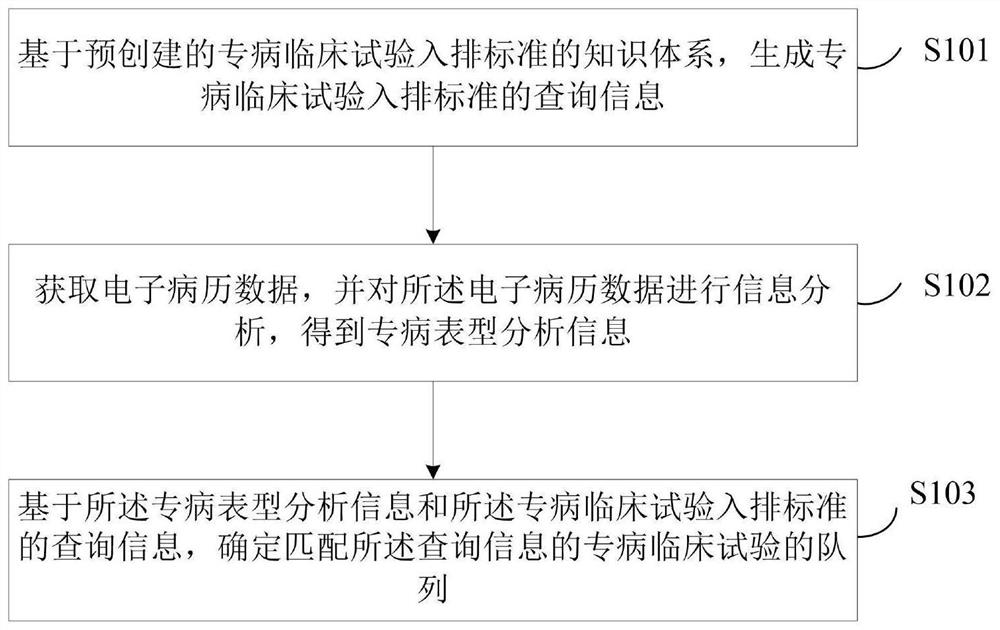
Queue identification method and device applied to special disease clinical test
PendingCN111667891AImprove processing efficiencyImprove accuracyMedical data miningLaboratory analysis dataMedical recordDisease phenotype
The invention discloses a queue identification method and device applied to a special disease clinical test. The method comprises the following steps: based on a pre-established knowledge system of aspecial disease clinical test in-and-out standard, generating query information of the special disease clinical test in-and-out standard; acquiring electronic medical record data, and performing information analysis on the electronic medical record data to obtain special disease phenotype analysis information; and based on the special disease phenotypic analysis information and the query information of the special disease clinical test in-and-out standard, determining a special disease clinical test queue matched with the query information. According to the invention, the knowledge system of the special disease clinical test in-and-out standard is a system for expressing the special disease clinical test in-and-out standard by knowledge of computer recognizable information; the in-and-outstandard is automatically converted into the structured query language, the electronic medical record data can be directly processed, a subject meeting the special disease clinical test is obtained, the information conversion processing efficiency is improved, and the accuracy of the queue identification work of the clinical test is improved.
Owner:中国医学科学院医学信息研究所
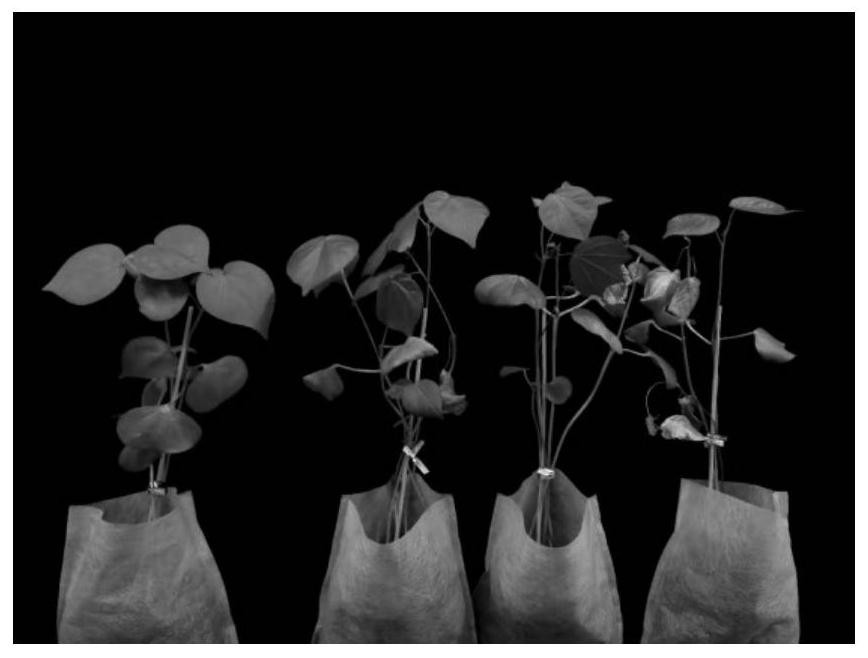
Cotton verticillium wilt disease phenotype identification method
ActiveCN112630184ALess destructivePrecise machine visionMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyDisease phenotype
The invention discloses a cotton verticillium wilt disease phenotype recognition method. The method comprises the following steps of 1, cultivating cotton seedlings in a non-woven fabric seedling raising bag; step 2, acquiring a canopy spectrum curve by utilizing a near-infrared multispectral technology; step 3, analyzing sensitive waveband correlation among different resistant varieties; step 4, establishing an estimation model according to the waveband combination; and step 5, obtaining a sensitive waveband corresponding to the disease grade. The method disclosed by the invention is low in destructiveness, simple to operate, labor-saving, high in inoculation success rate, uniform and consistent in morbidity and suitable for carrying out large-batch material identification work on vast scientific research workers, the bottoms of the nutrition pots do not need to be cut off, and the accuracy is higher than that in the prior art.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
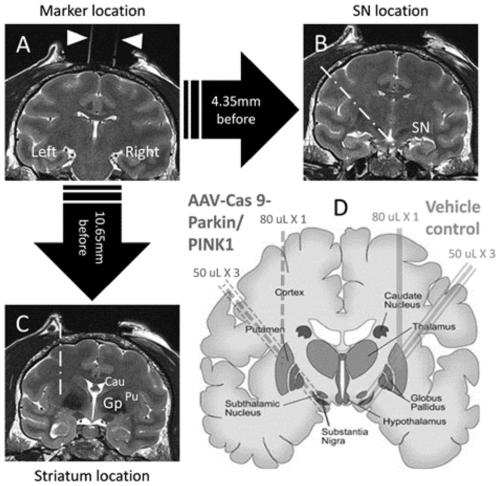
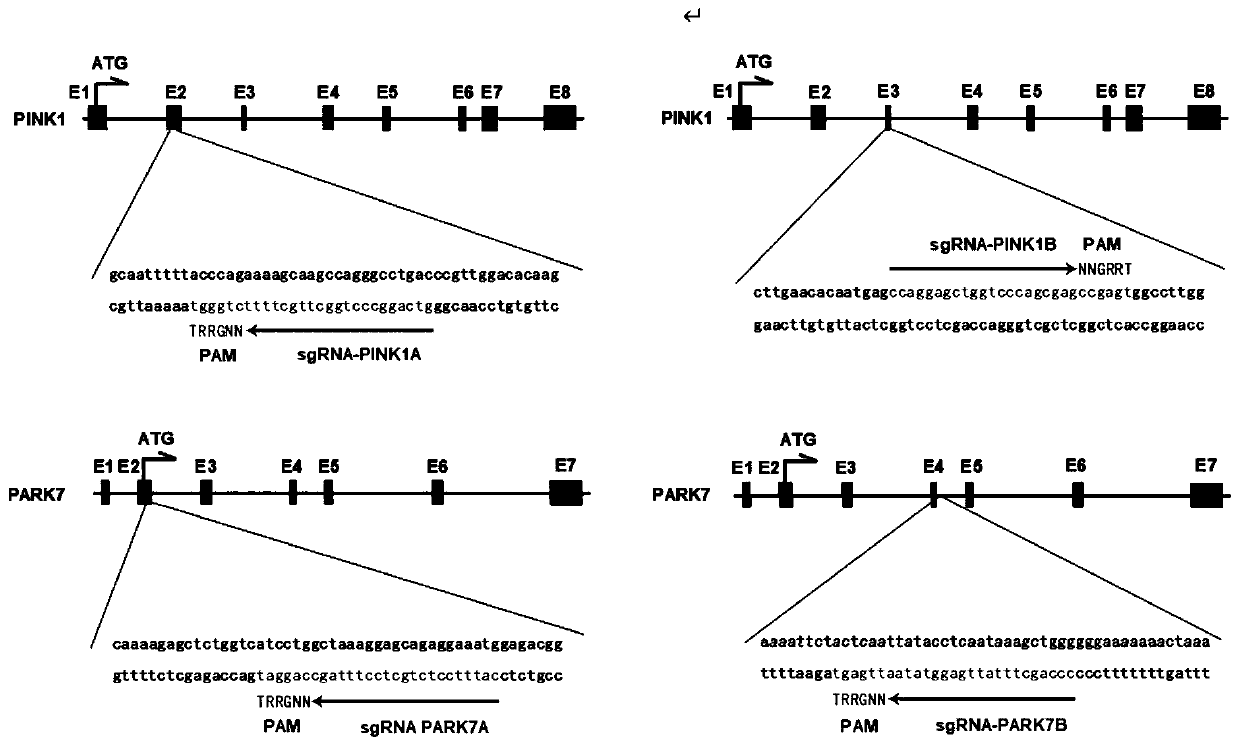
Non-therapeutic-purpose gene editing method based on PINK1 and PARK7 through injection of virus into specific brain regions of animals
PendingCN111304252AAvoid genetic differencesIncreased mortalityHydrolasesTransferasesDisease phenotypeDisease
The invention discloses a non-therapeutic-purpose gene editing method based on PINK1 and PARK7 through injection of a virus into specific brain regions of animals. The virus is directly injected intothe specific brain regions of non-human primates by using a brain stereotaxic injection pump, wherein the injection volume is 1 [mu]L of the injected virus per 1 m<3>, and the titer of the injected virus is 10*10<13>vg / mL. Through the method, gene editing is performed directly on the specific brain regions of the non-human primates, and transgenic monkey models with disease phenotypes can be obtained in a short time, so that urgent research needs of Parkinson's syndromes (PD) at the present stage are met.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Subvolume identification for prediction of treatment outcome
Physiological imaging-defined subvolumes of tissues / disease are identified to yield spatially-defined prognostic and / or predictive indicators and / or focal therapy targets within such tissues, in particular tumors, for evaluation over time, for example, prior to and after a therapy treatment. Medical image data is analyzed to delineate subvolumes of tissue based upon multiple physiological, metabolic, and biological imaging properties, where those subvolumes are extracted and analyzed in a probabilistic manner to associate with one or more abnormal or disease phenotype conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
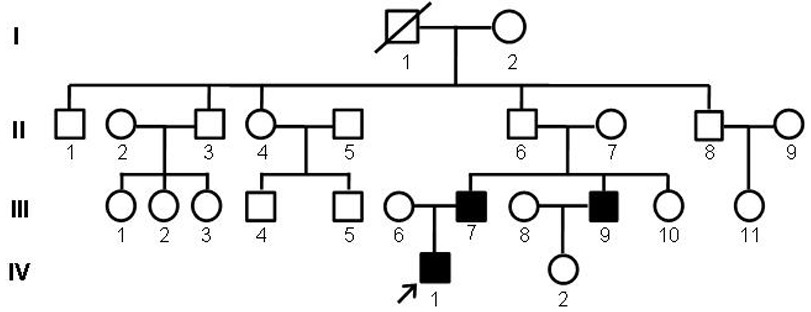
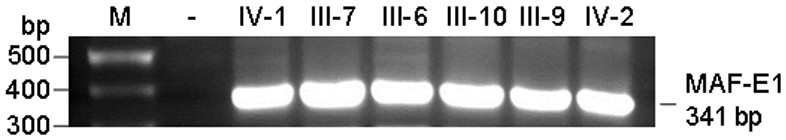
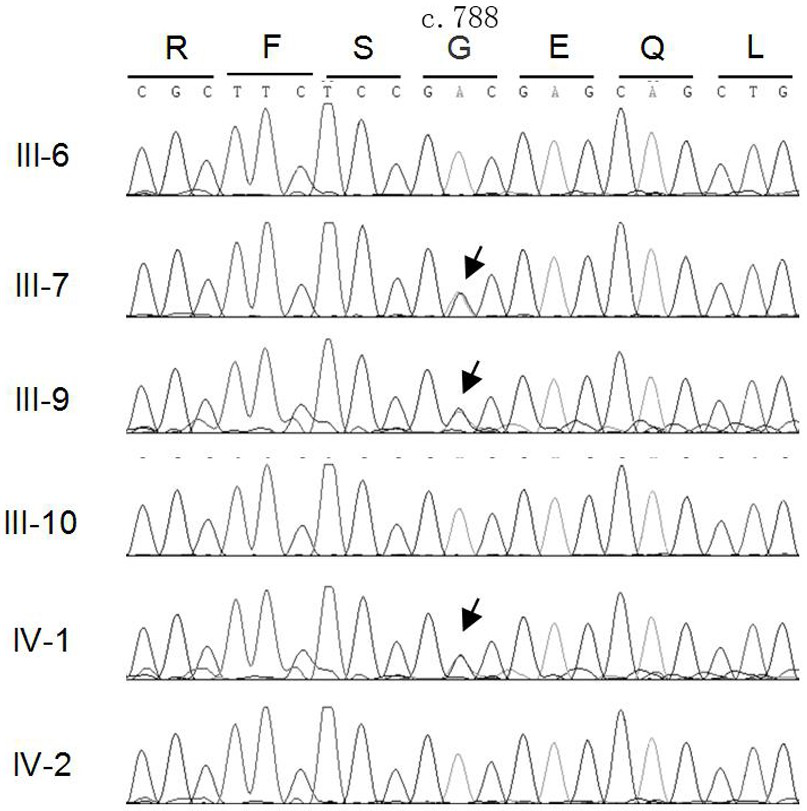
MAF gene mutant causing congenital cataract, polypeptide, kit, construct, recombinant cell and application
ActiveCN114045292AEfficient detectionAvoid reproductive riskMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDisease phenotypeNucleotide
The invention relates to an MAF gene mutant causing congenital cataract disease phenotype, a polypeptide, a kit, a construct, a recombinant cell and application, belonging to to the technical field of biological gene engineering. The MAF gene mutant disclosed by the invention is characterized in that nucleotide at the 788 site of a No. 1 exon of an MAF gene is subjected to A-G mutation. The polypeptide has p.D263G mutation. The kit can be used for screening biological samples susceptible to congenital cataract and contains a reagent for detecting the MAF gene mutant. The nucleic acid construct contains the MAF gene mutant. The recombinant cell is obtained by transfecting recipient cells with the nucleic acid construct containing the MAF gene mutant, and can express the MAF polypeptide with the p.D263G mutation. The method can be used for molecular genetic diagnosis of congenital cataract, and provides a basis for prenatal gene diagnosis of patients with cataract caused by MAF gene mutation.
Owner:AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF WEIFANG MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com