Non-therapeutic-purpose gene editing method based on PINK1 and PARK7 through injection of virus into specific brain regions of animals
A technology of gene editing and viruses, applied in the direction of single-stranded DNA viruses, other methods of inserting foreign genetic materials, plant gene improvement, etc., can solve the problems of not being an etiological model, the cause of disease, and the powerlessness of disease mechanism, so as to avoid embryonic The problem of mosaicism in transgenic technology, long molding time, and the effect of avoiding genetic differences
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
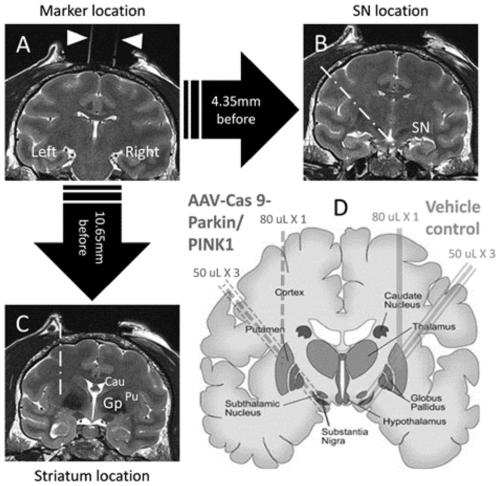
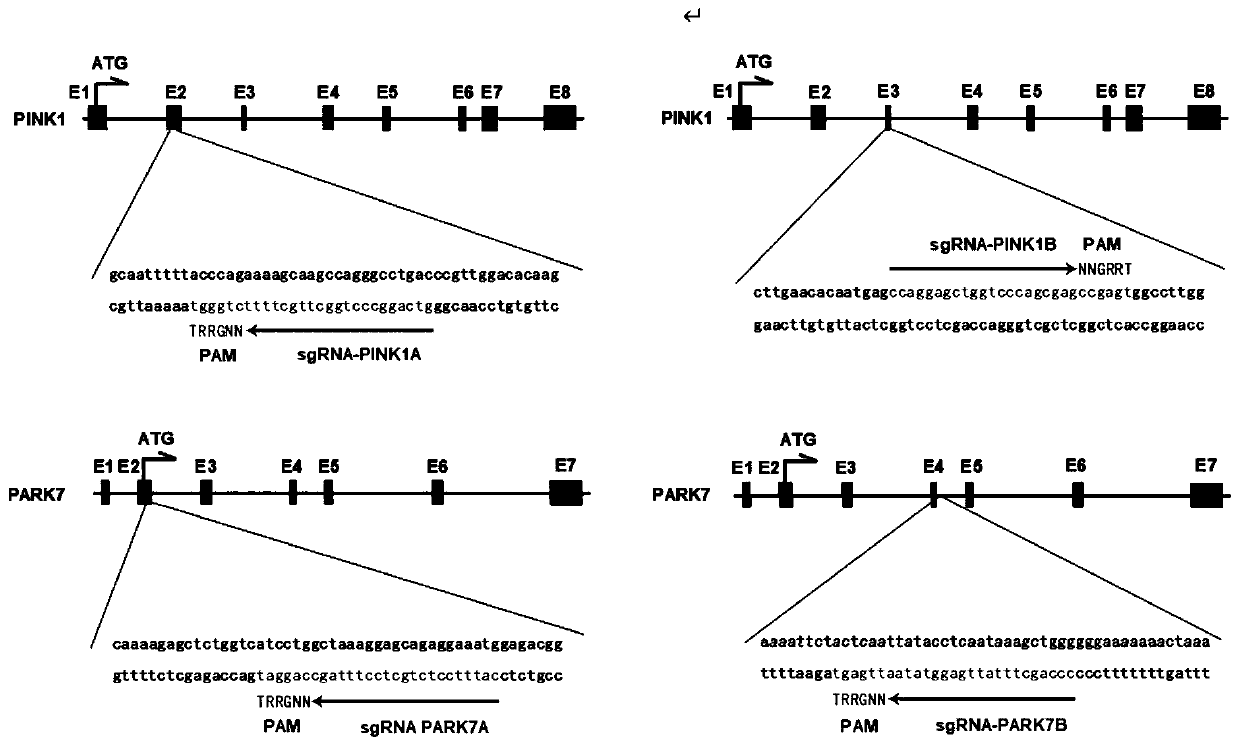
[0011] Rhesus macaques have good kinship with humans, have very similar brain structures, and their genes are as high as 93% similar to human genes (Huang, Zhang and Chen 1993). In addition, macaques have advanced brain functions such as reasoning, analysis, decision-making, and memory, and can complete the most complex behavioral tasks other than humans. Compared with other animals, it is easier to perform complex and accurate behavioral tests. Based on this, we plan to use AAV virus as a vector to mutate the PINK1 and PARK7 genes of rhesus monkeys using CRISPR / CAS9 technology, and use MRI imaging as a precise guide to specifically inject the virus into the unilateral or bilateral substantia nigra of rhesus monkeys to establish the virus. Transgenic PD macaque model. Then use the recognized macaque PD behavior scale (Kurlan scale) and apomorphine-induced rotation behavior to evaluate the PD behavior symptoms of model animals, and perform immunohistochemical pathological verif...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com