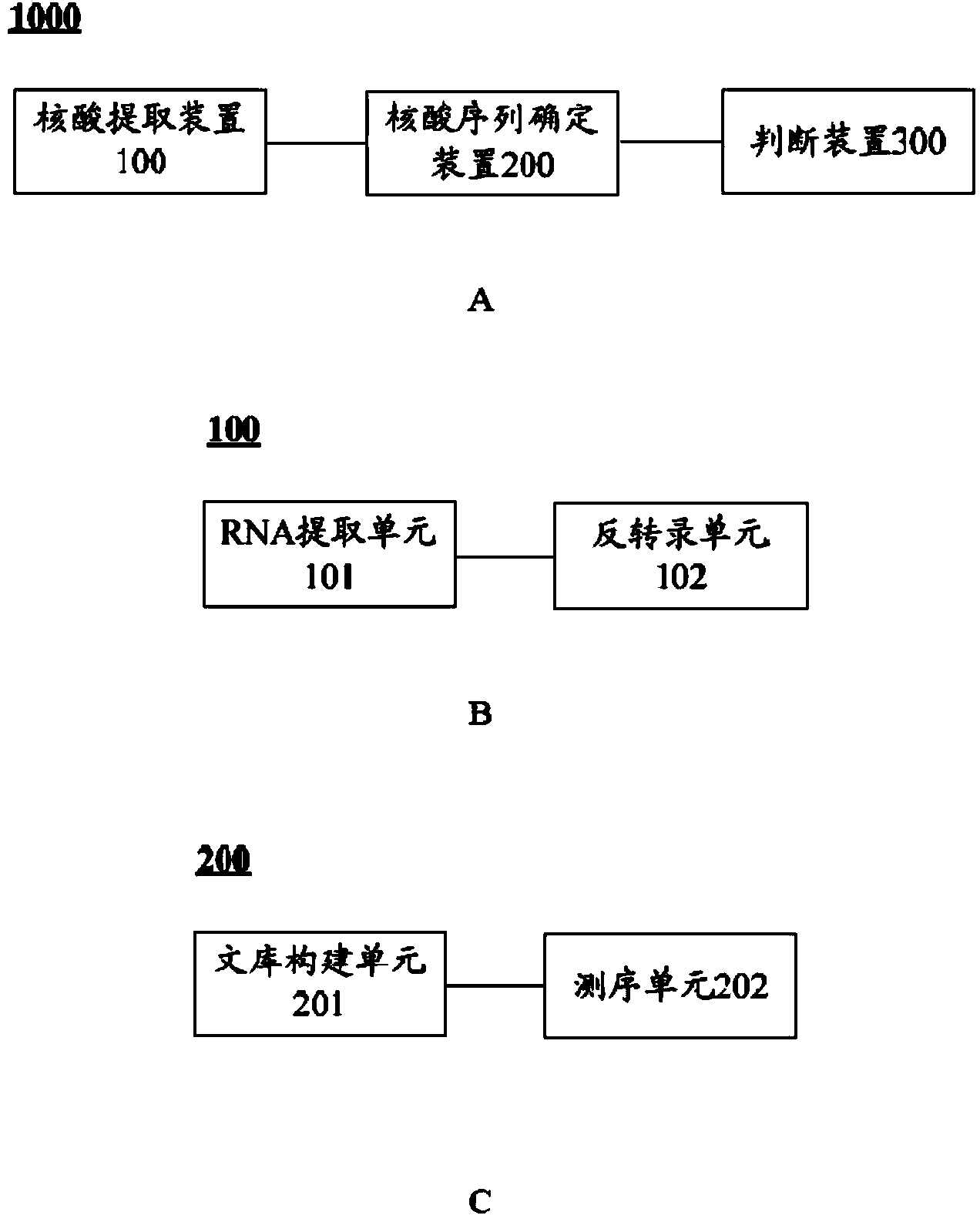
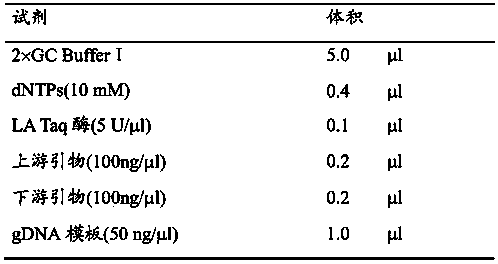
Skin keratinization-less hair-leukonychia syndrome new disease-causing gene and coding protein and application thereof
A syndrome and protein technology, applied in the mutated GJA1 gene and its encoded protein, to screen biological samples susceptible to the disease, the new pathogenic gene of keratinization-hypo-leukonychia syndrome-GJA1 gene field, It can solve problems such as unclear pathogenic genes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1: Sample acquisition
[0048] The inventor has collected a KHLS family in China in recent years. There are three generations in the family, including normal individuals and KHLS patients. In this family, 4 patient samples and 2 normal family samples were selected as research samples. A total of 6 samples were taken as research samples. 2ml of peripheral blood samples were collected from each sample, anticoagulated with EDTA, and stored at -80°C.
[0049] Randomly collect 100 normal individuals unrelated to the family 1 and family 2 as secondary verification samples, collect 2ml of peripheral blood samples from each, add EDTA anticoagulant, and store at -80°C.
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2: sample DNA preparation
[0051] OMEGA Blood DNA Midi Kit whole blood DNA extraction kit was used to extract DNA from peripheral blood samples, and the extraction steps were as follows:
[0052] (1) Take 2ml whole blood sample, add 150ul OB Protease, 2.1ml Buffer BL and 20ul RNase A, vortex at maximum speed for 1 minute, and mix thoroughly.
[0053] (2) 65 degrees Celsius water bath for 15-20 minutes, and vortex 5 times during the water bath.
[0054] (3) Add 2.2ml of absolute ethanol, vortex at maximum speed for 30 seconds, and mix thoroughly.
[0055] (4) Transfer 3.5ml of the lysate into a 15ml centrifuge tube with a filter column, centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 5 minutes, take out the filter column, pour off the filtered liquid, and put it back into the filter column.
[0056] (5) Add the remaining lysate from step 3 into a 15ml centrifuge tube with a filter column, centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 5 minutes, take out the filter column, pour off the filter liqu...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Example 3: Exon capture and sequencing
[0065] The inventor used the Agilent SureSelect Human All Exon Kit (Agilent SureSelect Human All Exon Kit) combined with Solexa high-throughput sequencing technology to sequence the exome sequence of the sample selected in Example 1, as follows:
[0066] 1) Genomic DNA was randomly broken into fragments of about 150-200bp, and then adapters were connected to both ends of the fragments to prepare a hybrid library (see the Illumina / Solexa standard library construction instructions provided by http: / / www.illumina.com / ) .
[0067] 2) After the library is purified, it undergoes ligation-mediated PCR (ligation-mediated PCR (LM-PCR)) linear amplification and SeqCap EZ Oligo pool for hybridization enrichment, and then performs sequencing on the machine after linear amplification of LM-PCR . The sequencing platform is Illumina Hiseq 2000, the read length is 90bp, and the average sequencing depth of each sample is at least 50×.
[0068]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com