Patents
Literature
667 results about "MIDI" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
MIDI (/ˈmɪdi/; short for Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a technical standard that describes a communications protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing and recording music. A single MIDI link through a MIDI cable can carry up to sixteen channels of information, each of which can be routed to a separate device or instrument. This could be sixteen different digital instruments, for example.
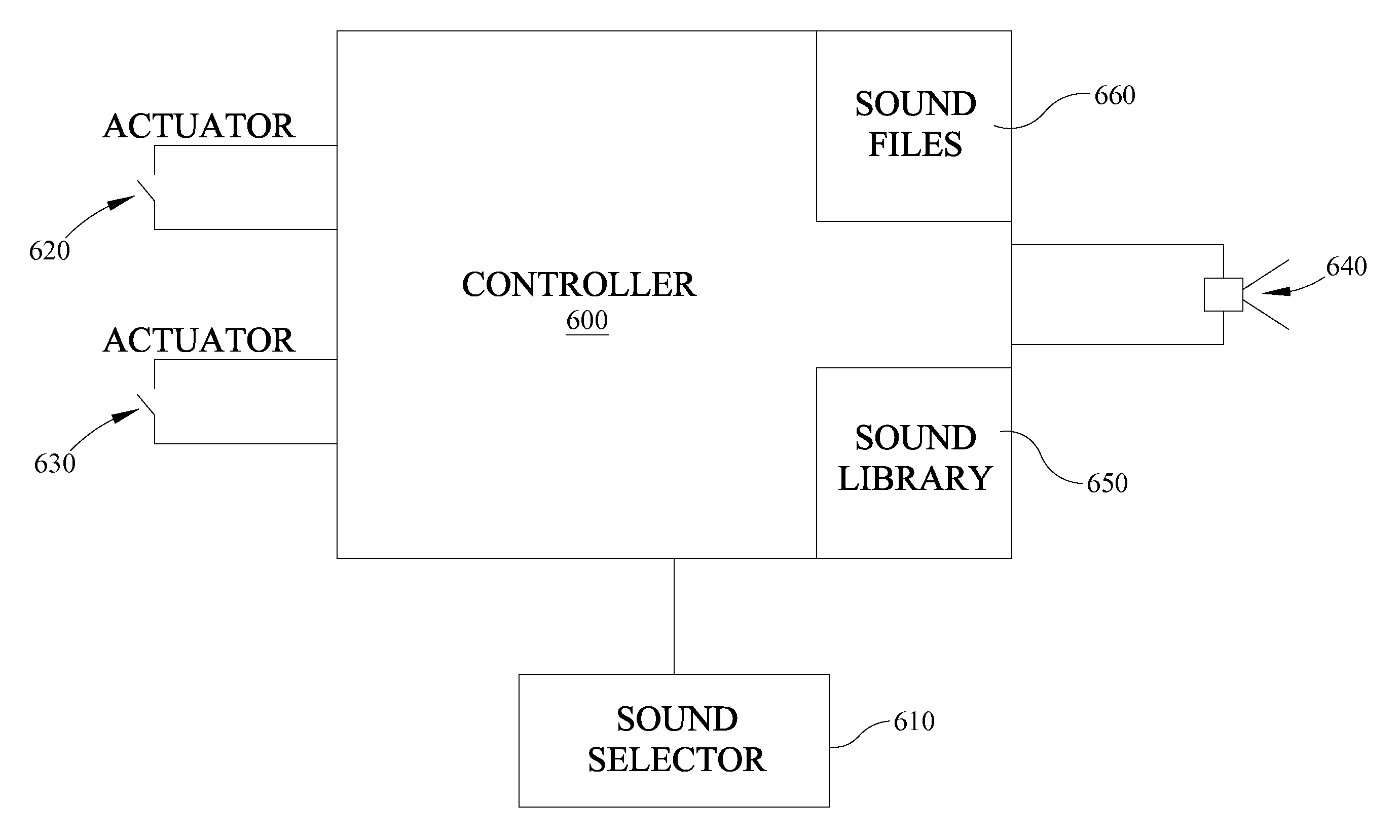
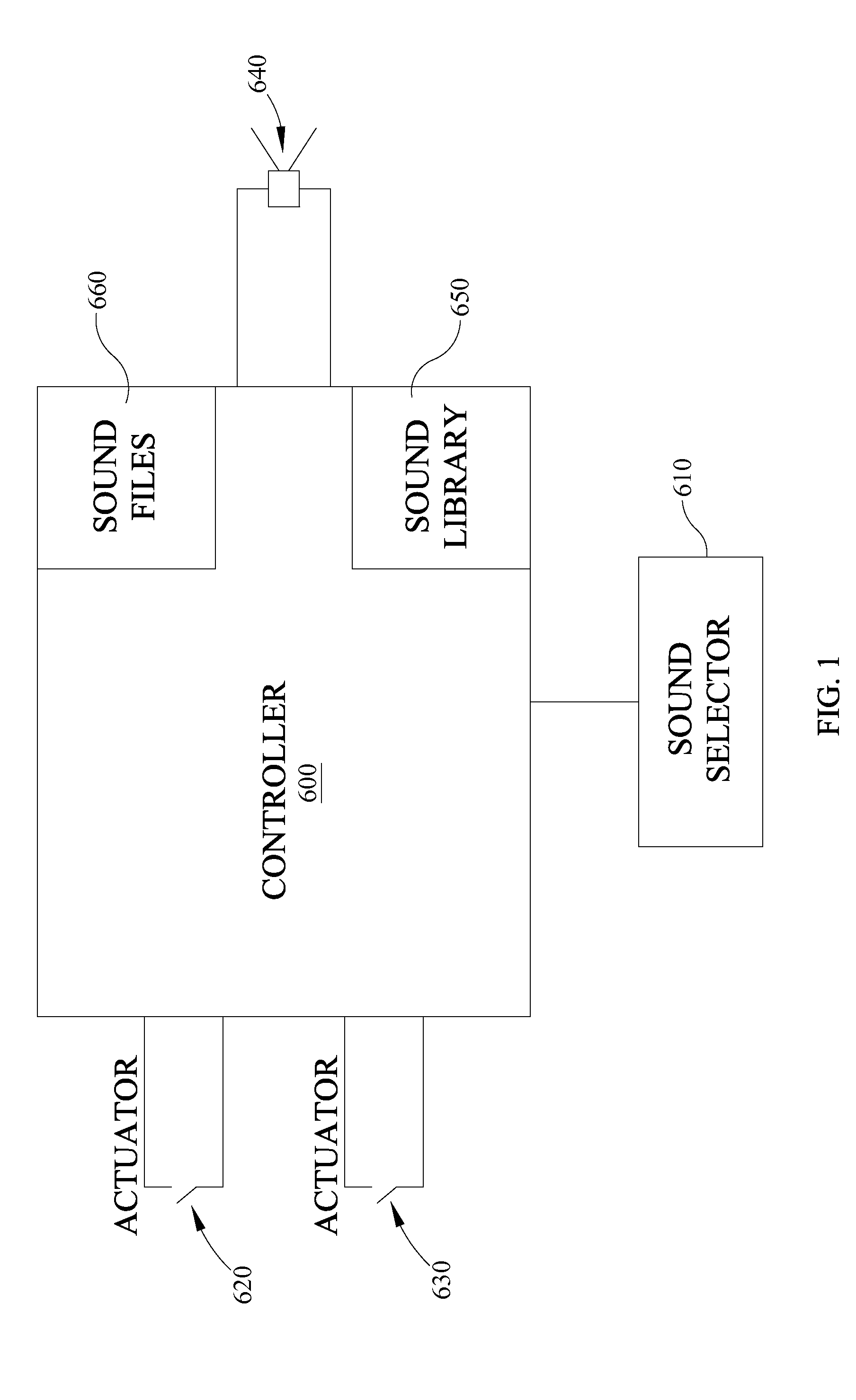
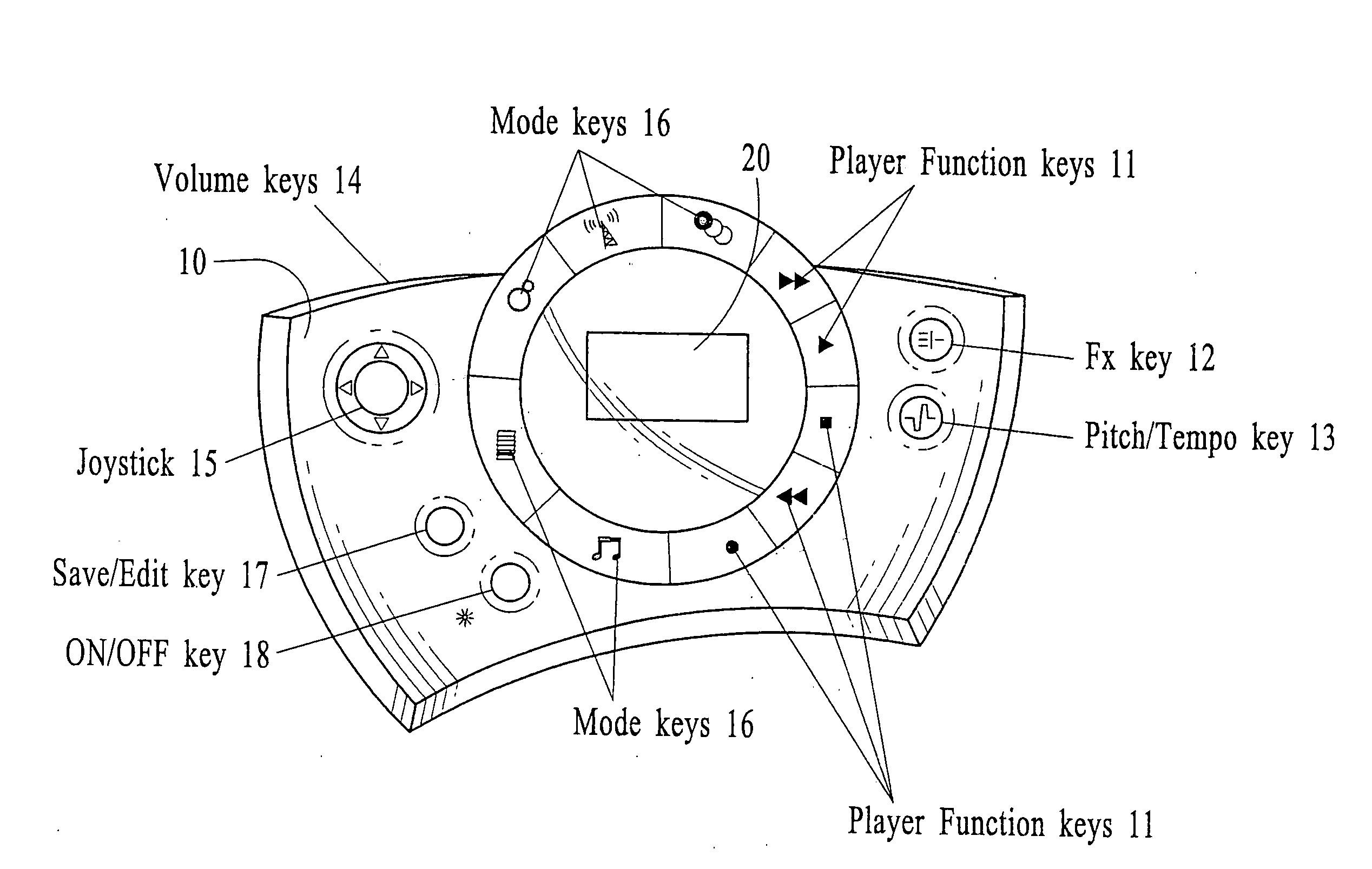
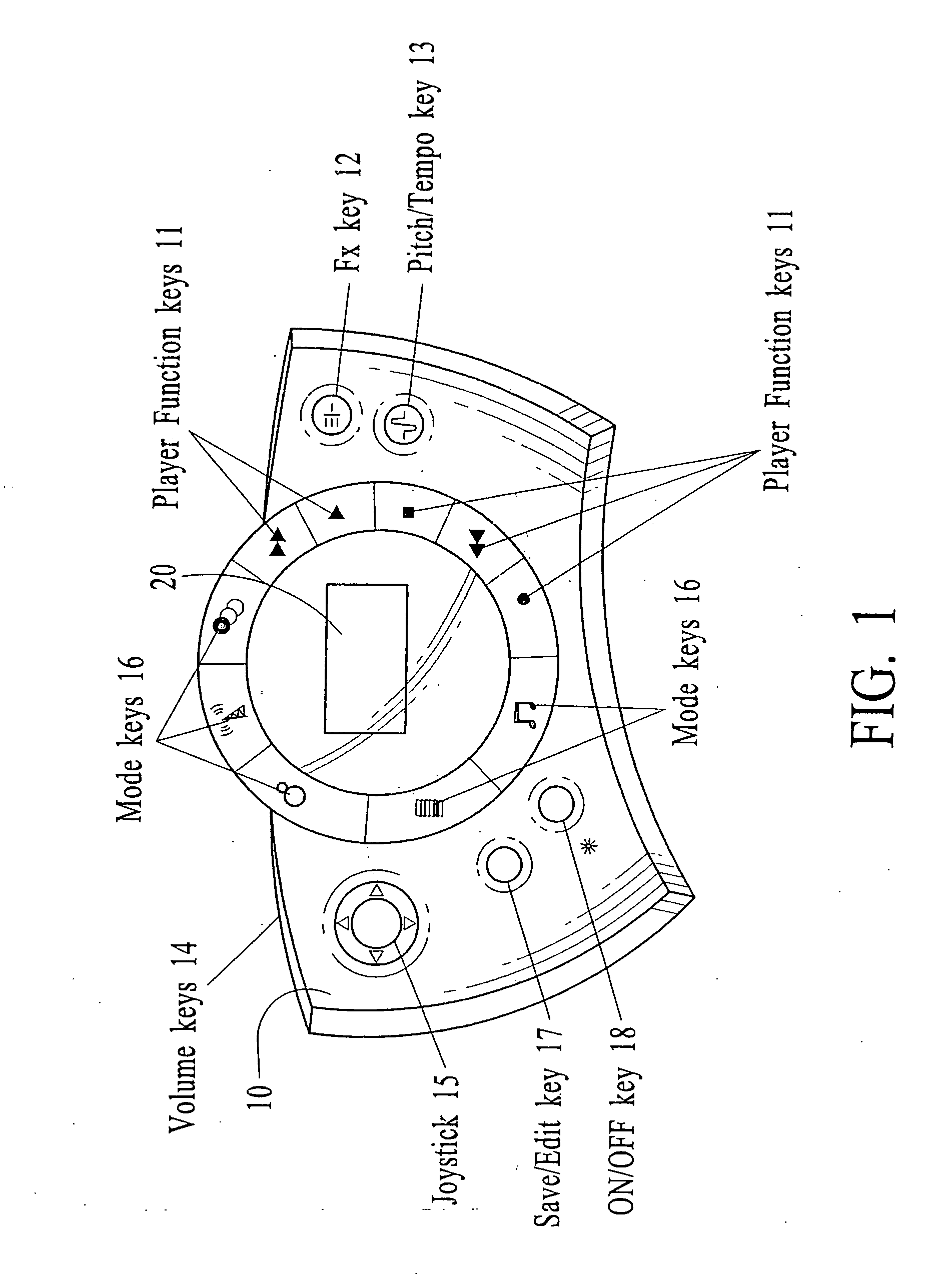
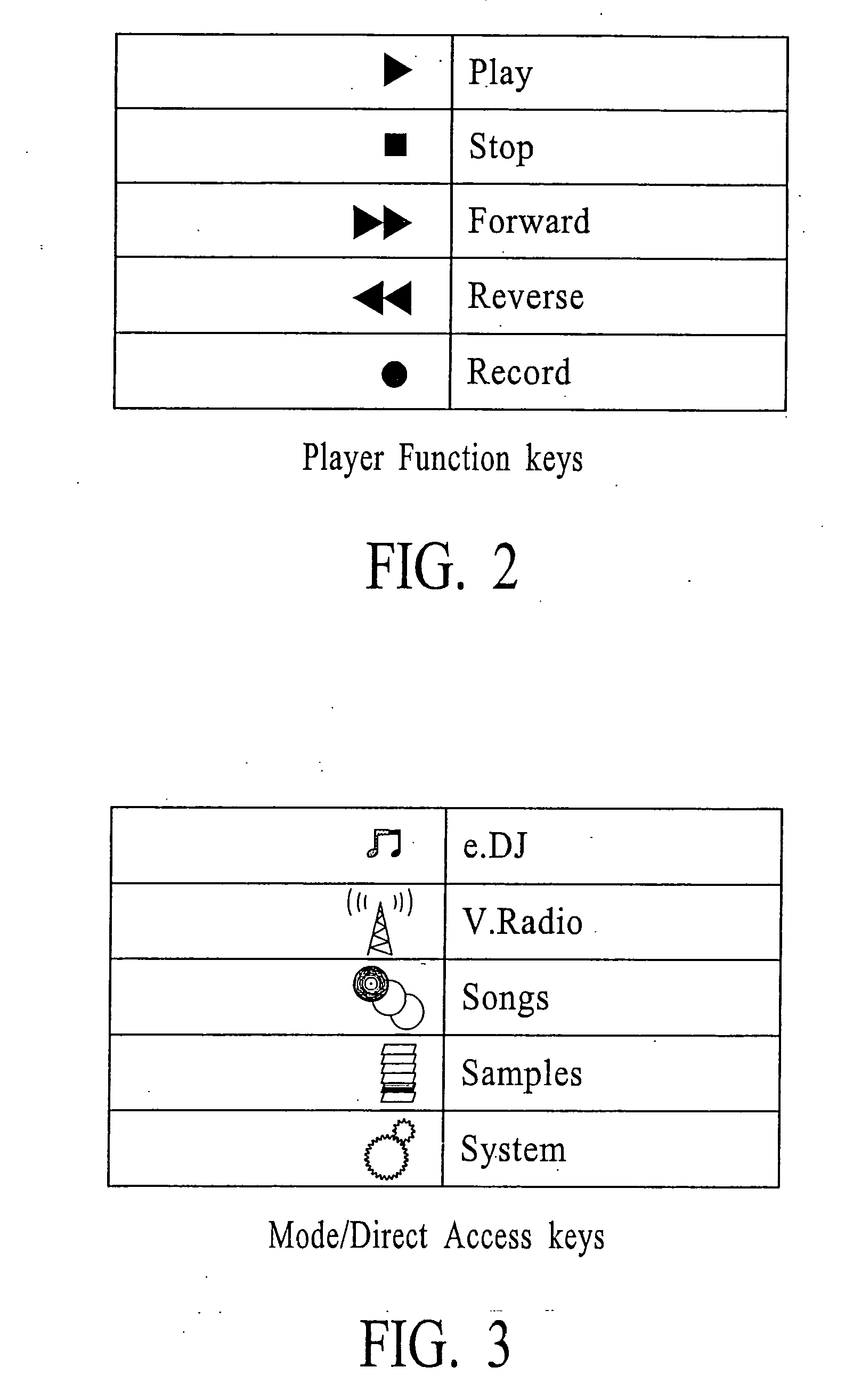
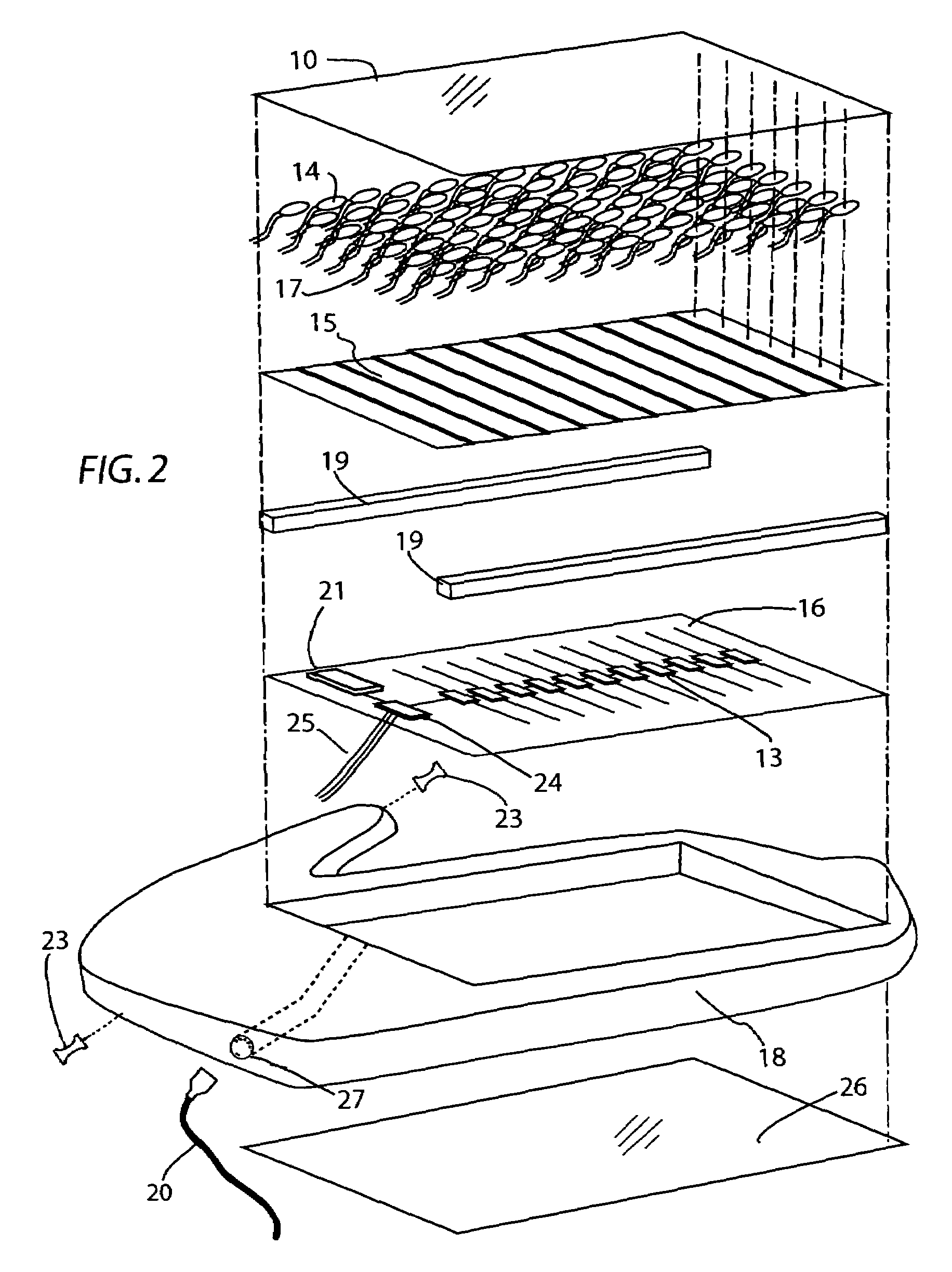
Polyphonic Doorbell Chime System
InactiveUS20100225455A1Increase volumeSmall sizeElectric/electromagnetic audible signallingDoorbellMicrocontroller
A door chime system includes a microcontroller having a polyphonic MIDI music processor and a data memory for storing MIDI format sound files. The microcontroller includes an input for accepting signals from door chime actuators or pushbuttons and an output representative of distinct MIDI sound files.
Owner:HEATH & CO LTD
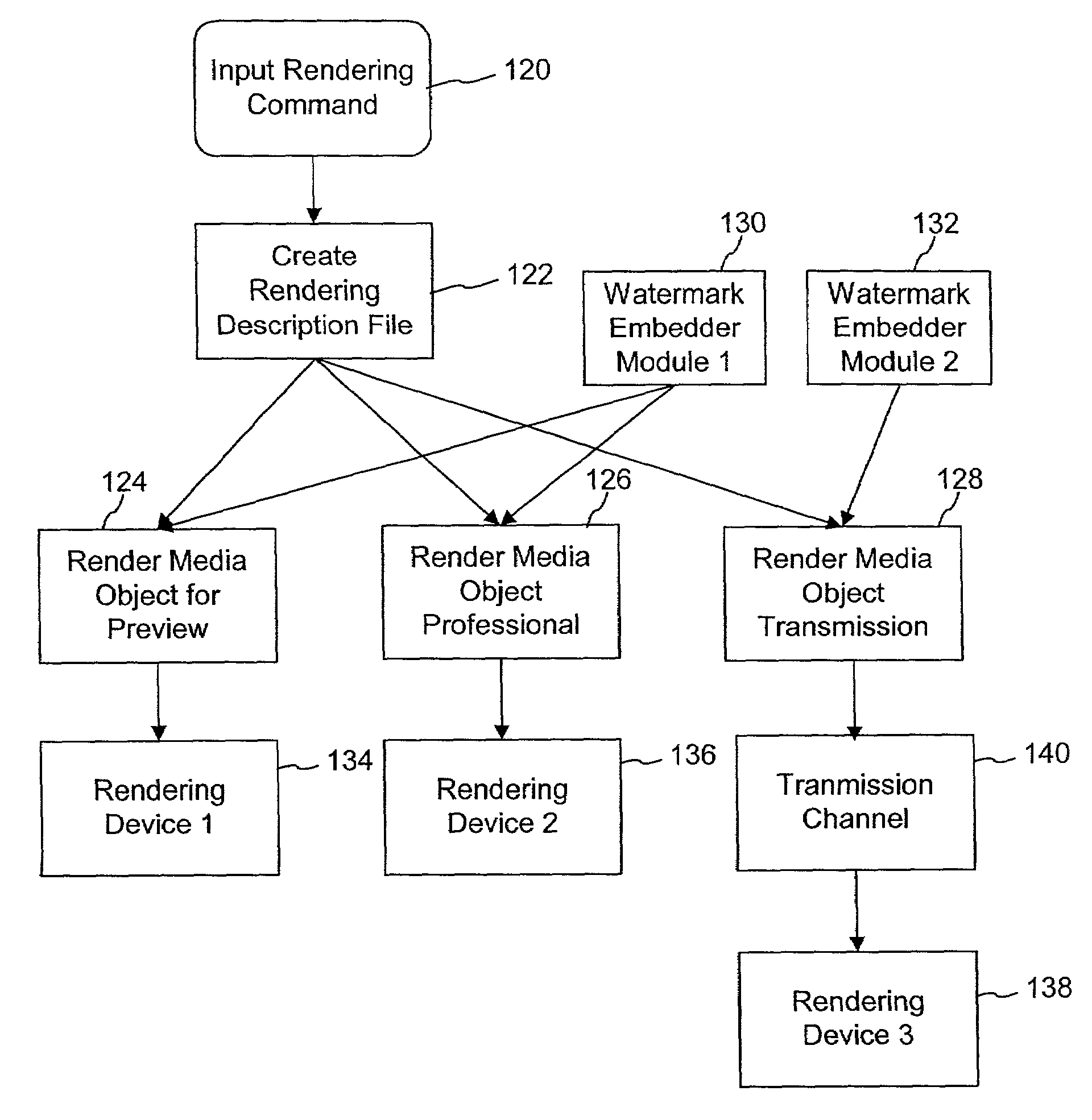
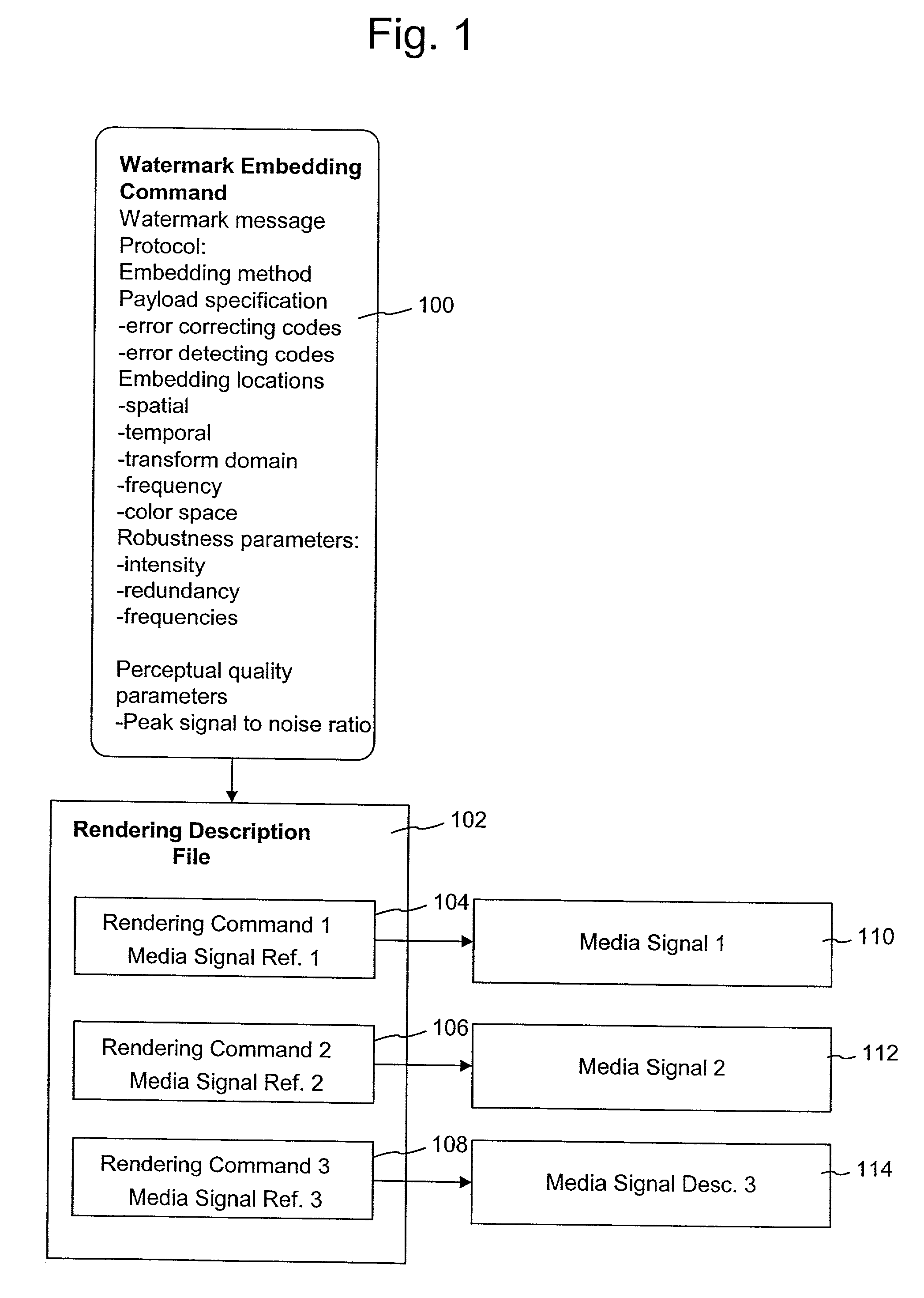
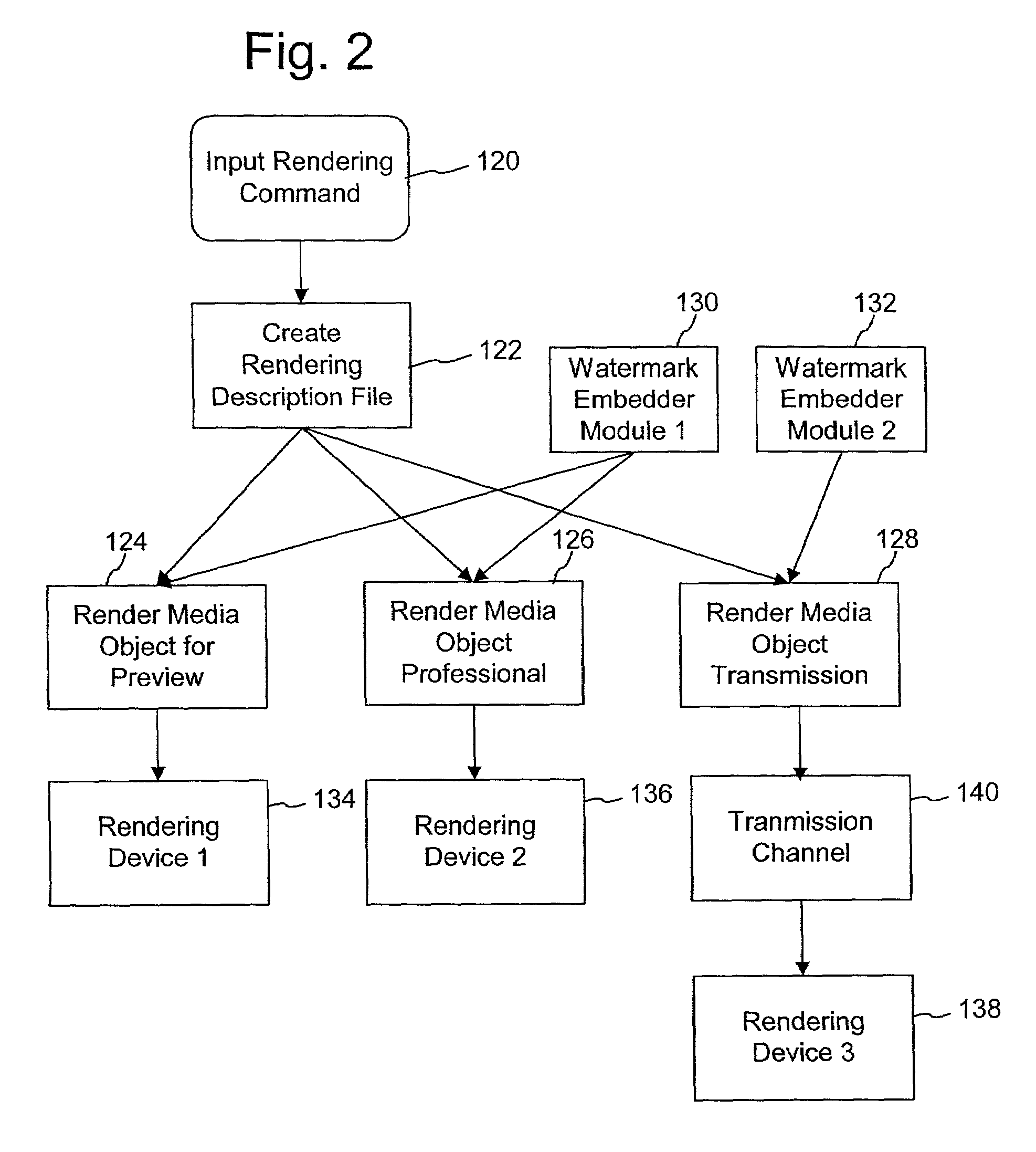
Watermark embedding functions in rendering description files
InactiveUS7142691B2Low costShorten the timeDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationWeb siteMedia type
A method for controlling watermark embedding in a media object through the use of a watermark embedding command. In the process of creating the media object, the method includes a watermark embedding command among a set of one or more rendering commands that specify how the media object is to be rendered. For example, certain media signal formats like PCL, PDF, or postscript for images, MIDI and structured audio for audio signals, and MPEG-4 and MPEG-7 for audio and video signals, include descriptors that control how a particular media signal is to be rendered. The watermark embedding command includes a combination of the following items: an identifier used to link to customer or related content information, the customer's web site, the intensity at which to embed the watermark, areas not to embed, batch processing options, printing preferences for images, watermarking embedding methods to use on different media types, formats, or different parts of the media object, and desired rendering quality.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP +1
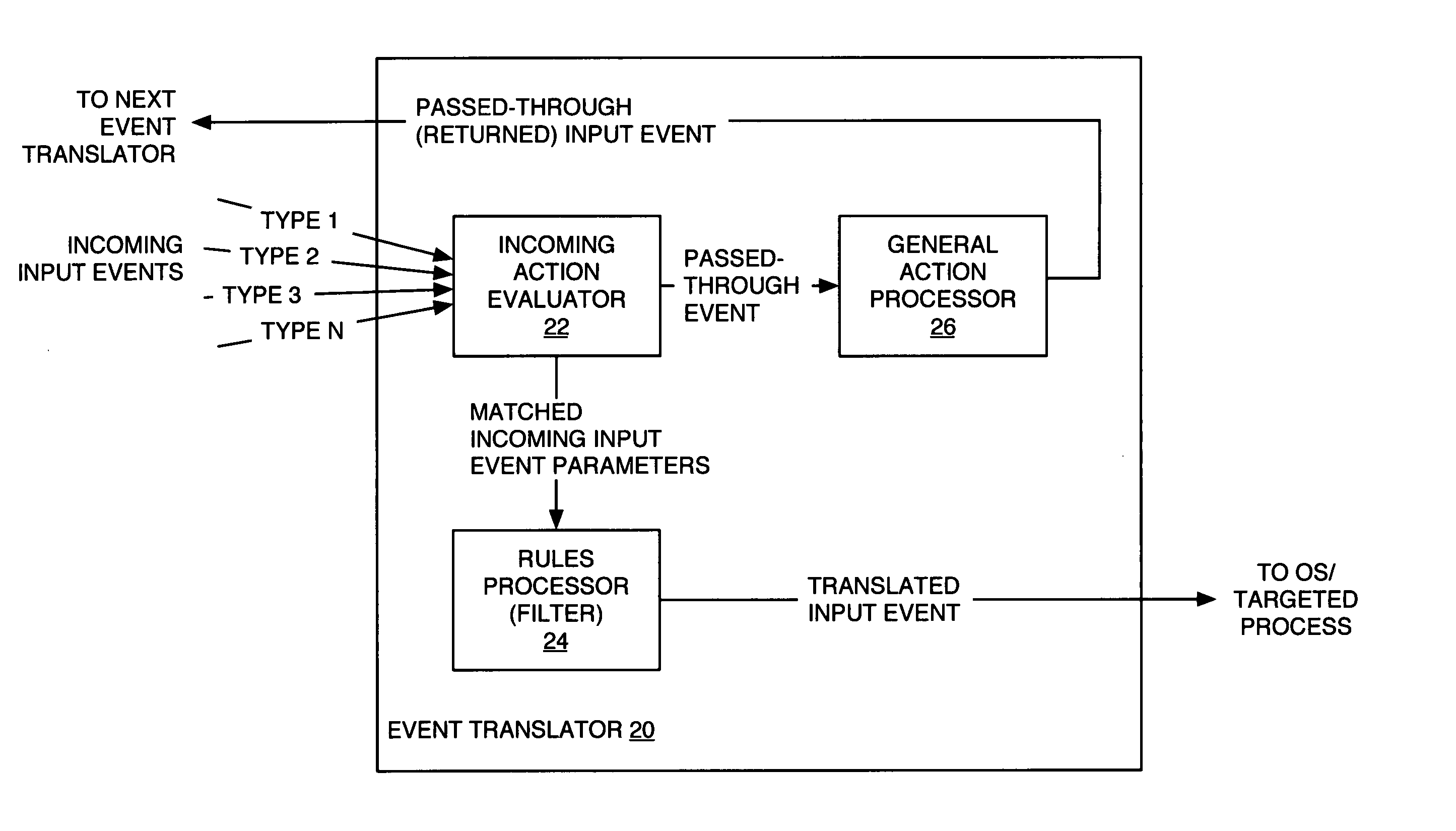
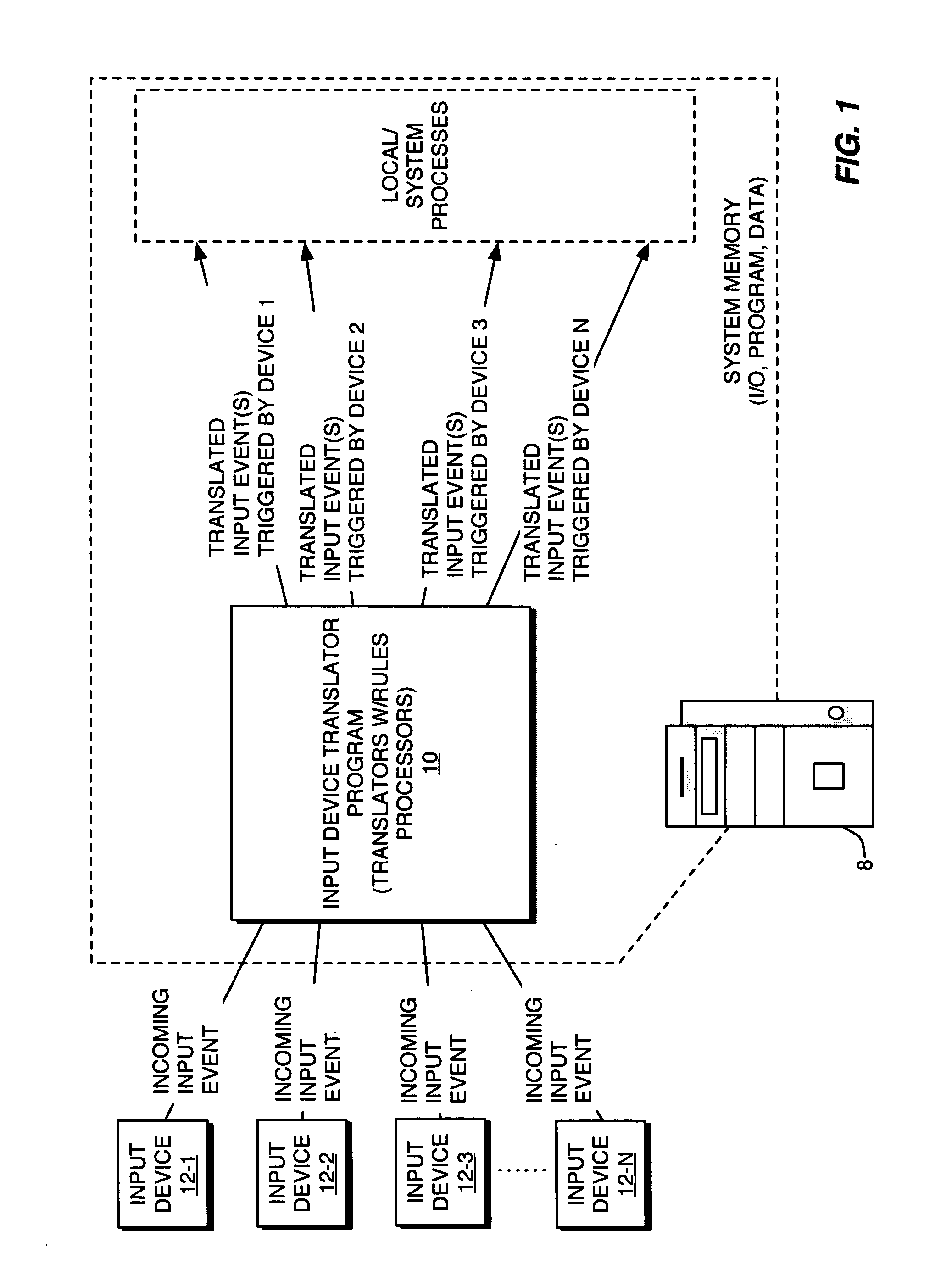
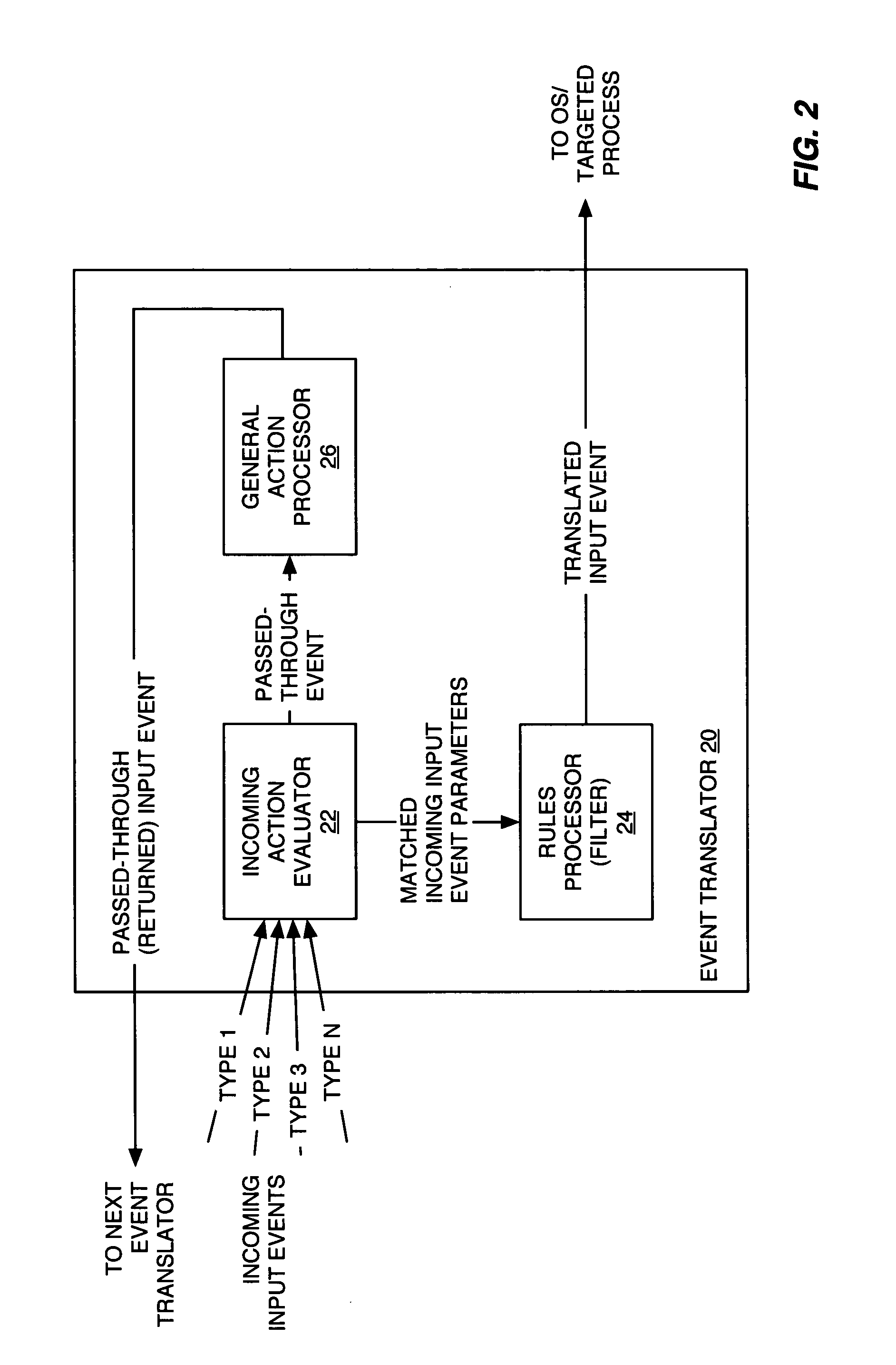
Universal computer input event translator
ActiveUS20050097570A1Input/output for user-computer interactionMultiprogramming arrangementsTheoretical computer scienceGeneral purpose computer
A universal computer event translator, which can be implemented as a computer program for execution on a personal computer, handheld device, or other computer processing platform, provides configurable event translation to map essentially any type of computer input event into essentially any other type(s) of computer input event. The program detects occurrences of desired types of input events, which may be generated via a particular input device, a timer, or another program or processing running on the computer, and provides rules-based translation processing of those events. For example, the program can translate mouse events into keyboard events, MIDI or other port events into mouse or keyboard events, or into custom events. One incoming input event can spawn one or more translated input events of one or more types; conversely, different types of incoming input events can be mapped to a single type or multiple types of translated input events.
Owner:BOMERS FLORIAN U
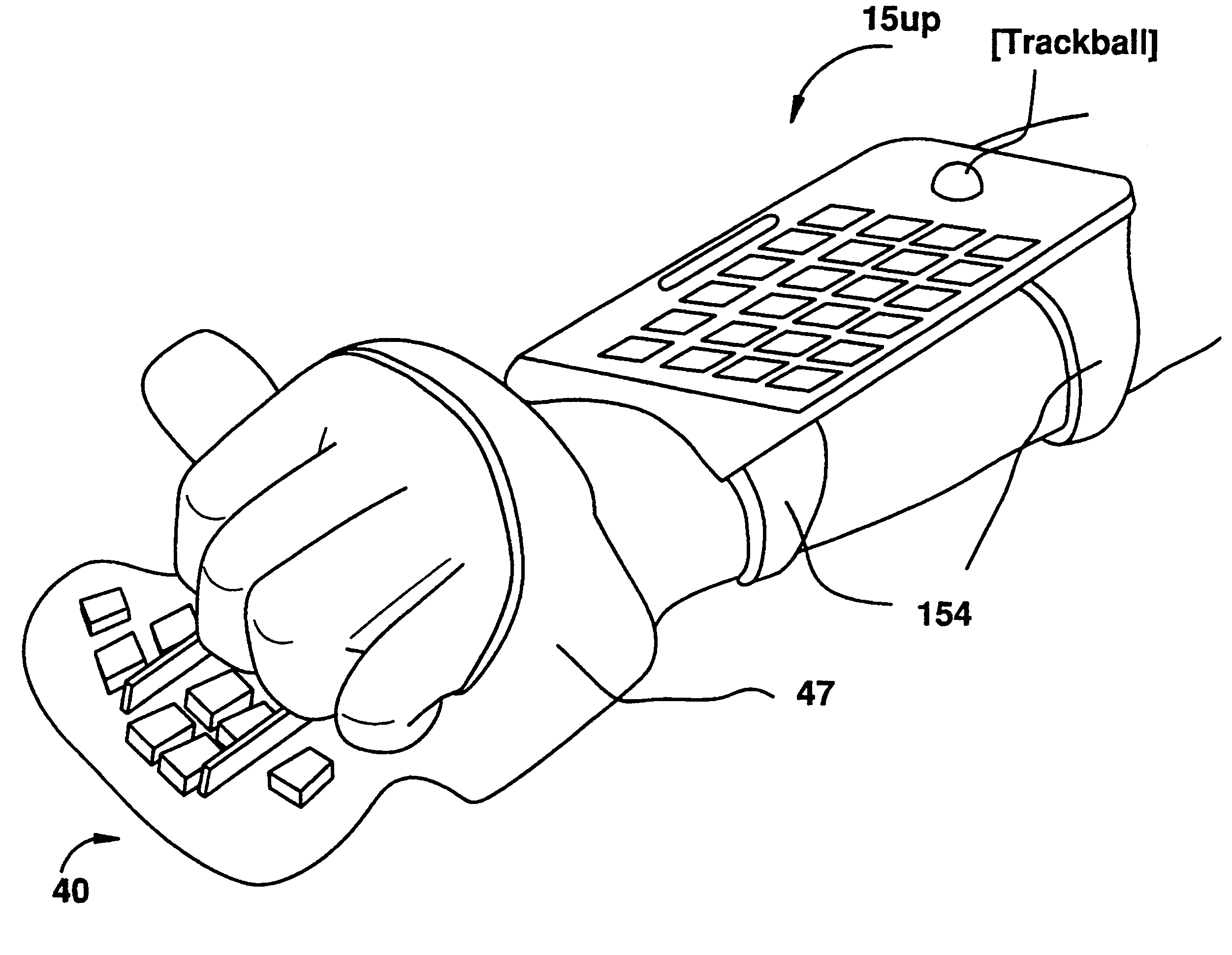
Key palette
InactiveUS6184804B1Increase productivityImprove convenienceInput/output for user-computer interactionCo-operative working arrangementsBarcodePersonal computer
An arm-mounter mechanism affording users almost unlimited mobility, alternately adaptable to personal computers, digital assistants, cellular phones, cameras, audio recorders, barcode scanners, multimedia remote controls, MIDI controllers, gaming devices and others. One embodiment, utilized with speech recognition technology, provides monitor and / or keys on an arm-mounted first element movable attached to allow rotation, swiveling and / or tilting of this element relative to the arm. A second, optional element rests on projections from the arm-mounting mechanism, allowing interface with the hand of the device-bearing arm. Data processing, transmission, reception and storage equipment typically resides within the first element. The second element may be retractable to fit under sleeve. Another embodiment is a laptop PC reconfigurable for arm use. An alternative mechanism arm-mounts pre-existing devices.
Owner:SEARCH & SOCIAL MEDIA PARTNERS
Systems and Methods for Portable Audio Synthesis
InactiveUS20080156178A1Create efficientlyEfficiently stored and/processedGearworksMusical toysAudio synthesisDisplay device
Systems and methods for creating, modifying, interacting with and playing music are provided, particularly systems and methods employing a top-down process, where the user is provided with a musical composition that may be modified and interacted with and played and / or stored (for later play). The system preferably is provided in a handheld form factor, and a graphical display is provided to display status information, graphical representations of musical lanes or components which preferably vary in shape as musical parameters and the like are changed for particular instruments or musical components such as a microphone input or audio samples. An interactive auto-composition process preferably is utilized that employs musical rules and preferably a pseudo random number generator, which may also incorporate randomness introduced by timing of user input or the like, the user may then quickly begin creating desirable music in accordance with one or a variety of musical styles, with the user modifying the auto-composed (or previously created) musical composition, either for a real time performance and / or for storing and subsequent playback. In addition, an analysis process flow is described for using pre-existing music as input(s) to an algorithm to derive music rules that may be used as part of a music style in a subsequent auto-composition process. In addition, the present invention makes use of node-based music generation as part of a system and method to broadcast and receive music data files, which are then used to generate and play music. By incorporating the music generation process into a node-subscriber unit, the bandwidth-intensive systems of conventional techniques can be avoided. Consequently, the bandwidth can preferably be also used of additional features such as node-to-node and node to base music data transmission. The present invention is characterized by the broadcast of relatively small data files that contain various parameters sufficient to describe the music to the node / subscriber music generator. In addition, problems associated with audio synthesis in a portable environment are addressed in the present invention by providing systems and methods for performing audio synthesis in a manner that simplifies design requirements and / or minimizes cost, while still providing quality audio synthesis features targeted for a portable system (e.g., portable telephone). In addition, problems associated with the tradeoff between overall sound quality and memory requirements in a MIDI sound bank are addressed in the present invention by providing systems and methods for a reduced memory size footprint MIDI sound bank.
Owner:MEDIALAB SOLUTIONS
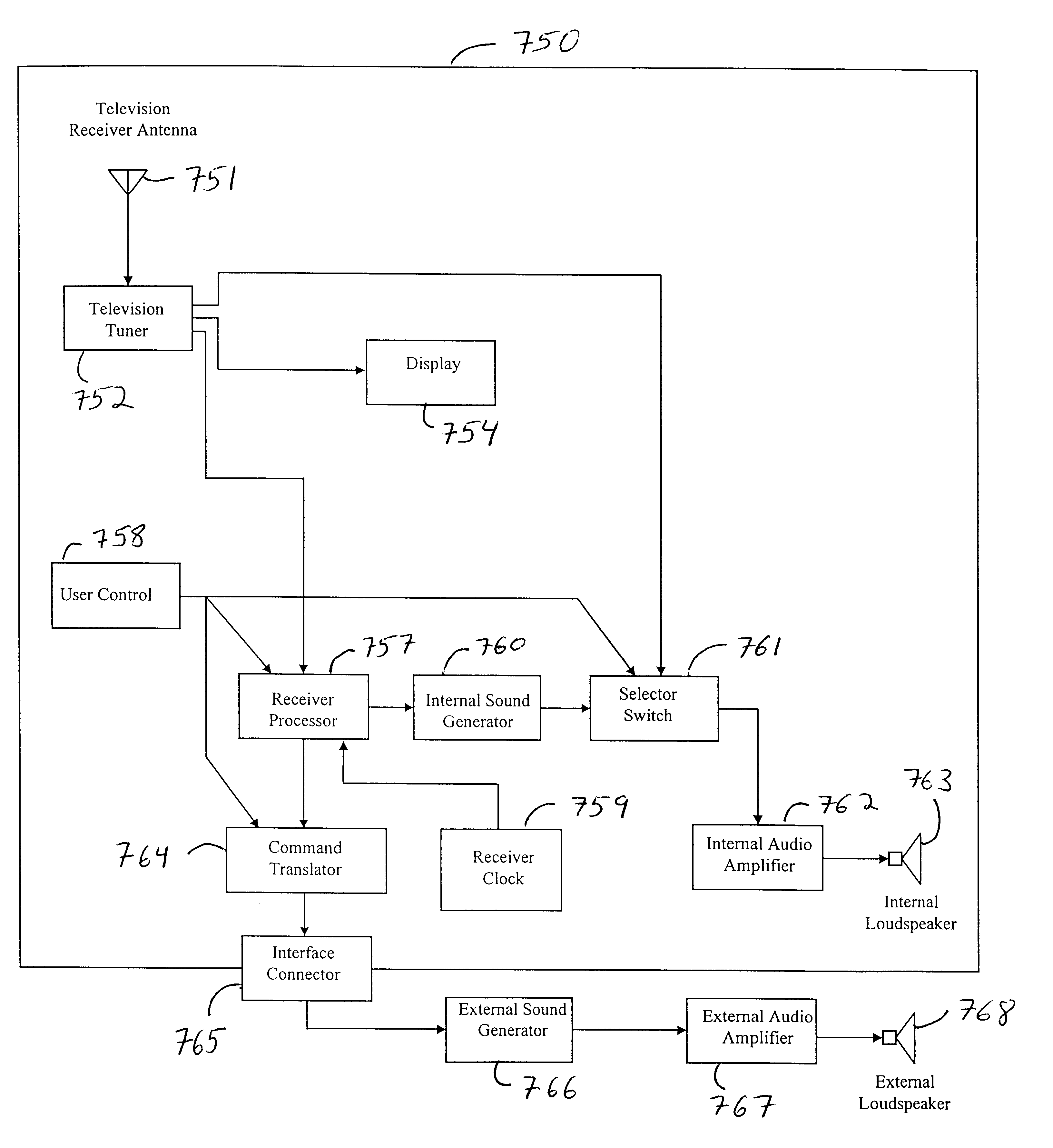
Method and apparatus for audio broadcast of enhanced musical instrument digital interface (MIDI) data formats for control of a sound generator to create music, lyrics, and speech
InactiveUS6462264B1Inhibit outputImprove speech clarityElectrophonic musical instrumentsCode conversionCarrier signalData format
A method and apparatus for the transmission and reception of broadcasted instrumental music, vocal music, and speech using digital techniques. The data is structured in a manner similar to the current standards for MIDI data. Transmitters broadcast the data to receivers which contain internal sound generators or an interface to external sound generators that create sounds in response to the data. The invention includes transmission of multiple audio data signals for several languages on a conventional radio and television carrier through the use of low bandwidth data. Error detection and correction data is included within the transmitted data. The receiver has various error compensating mechanisms to overcome errors in data that cannot be corrected using the error correcting data that the transmitter sent. The data encodes for elemental vocal sounds and music.
Owner:ELAM CARL
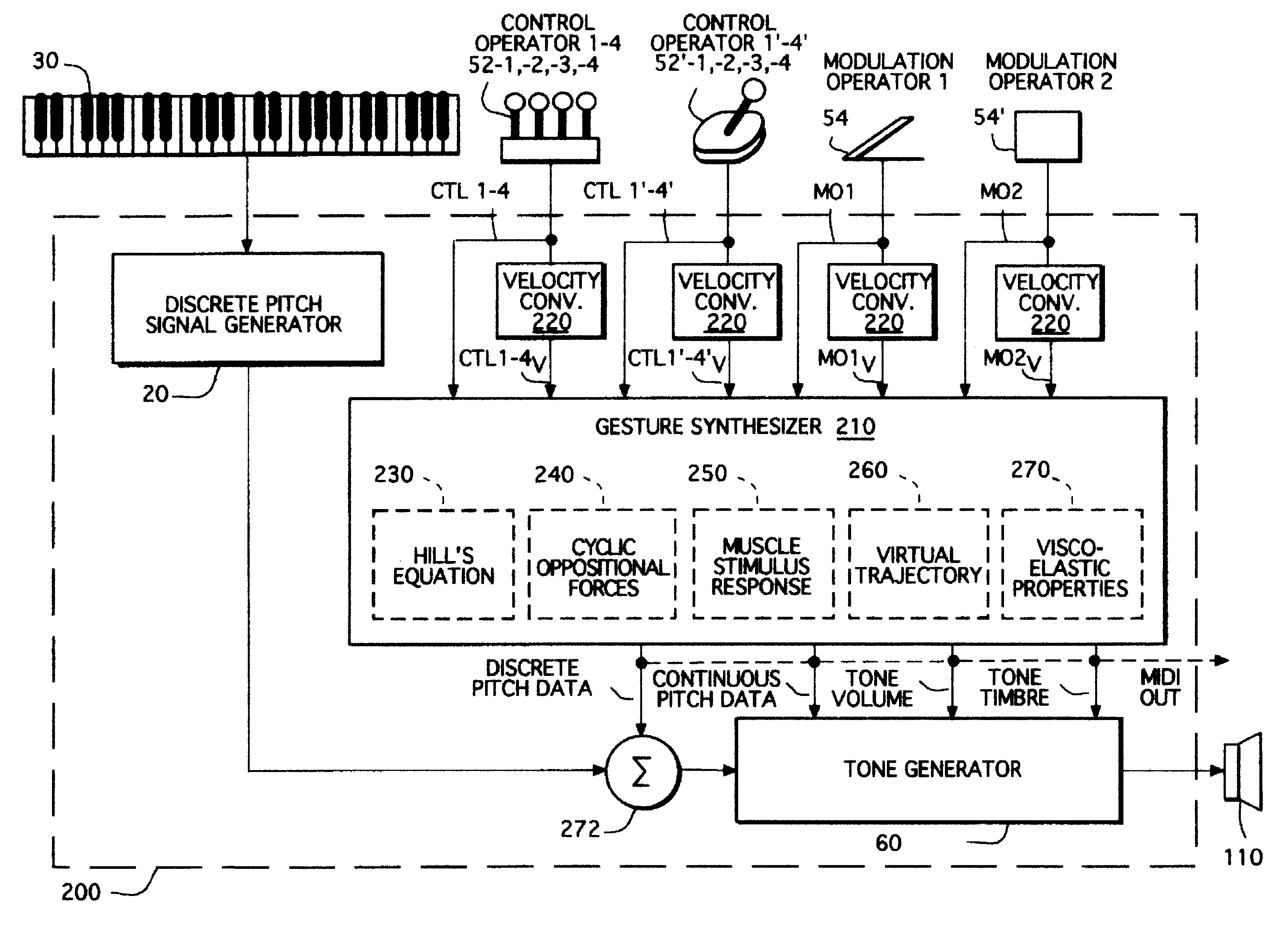
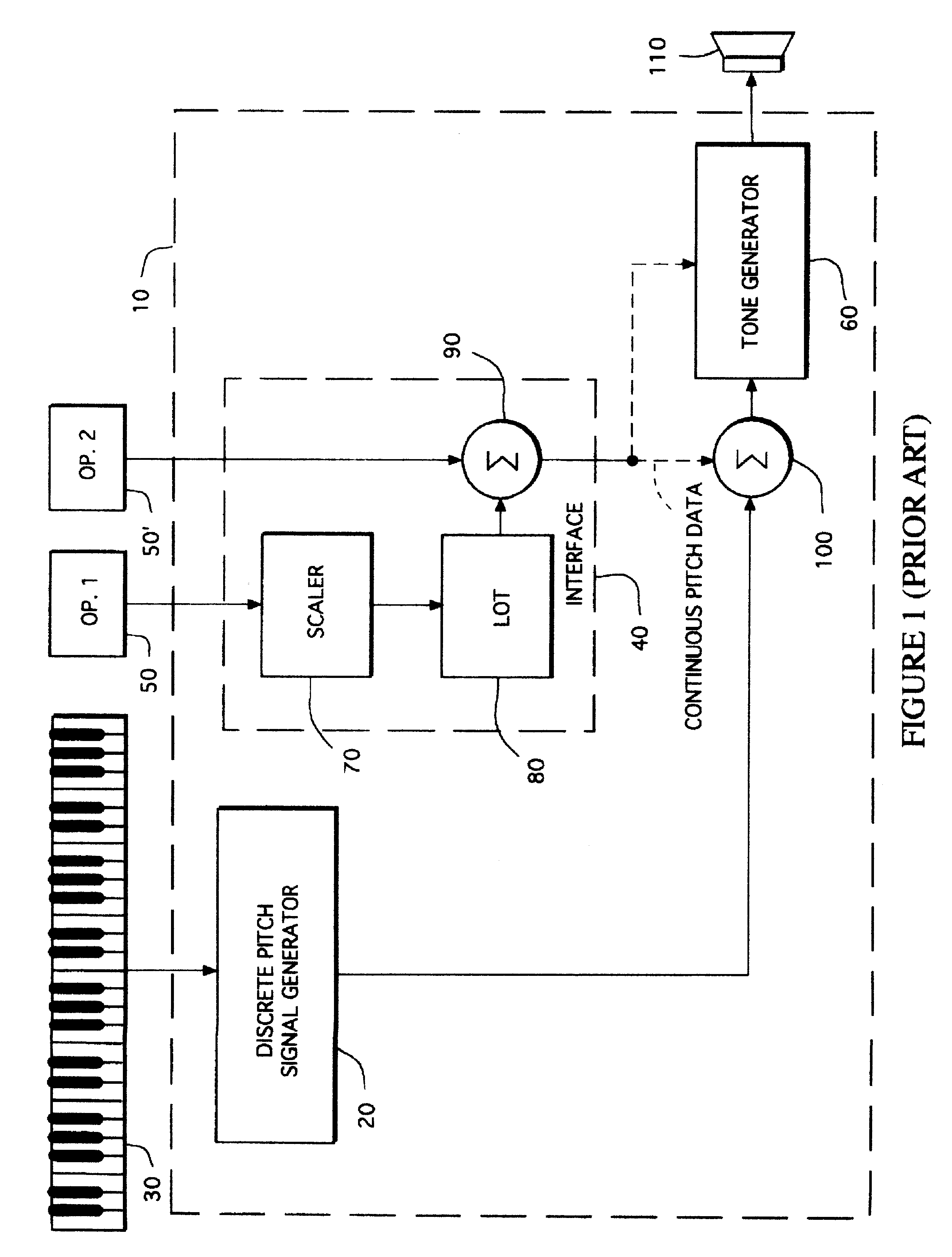
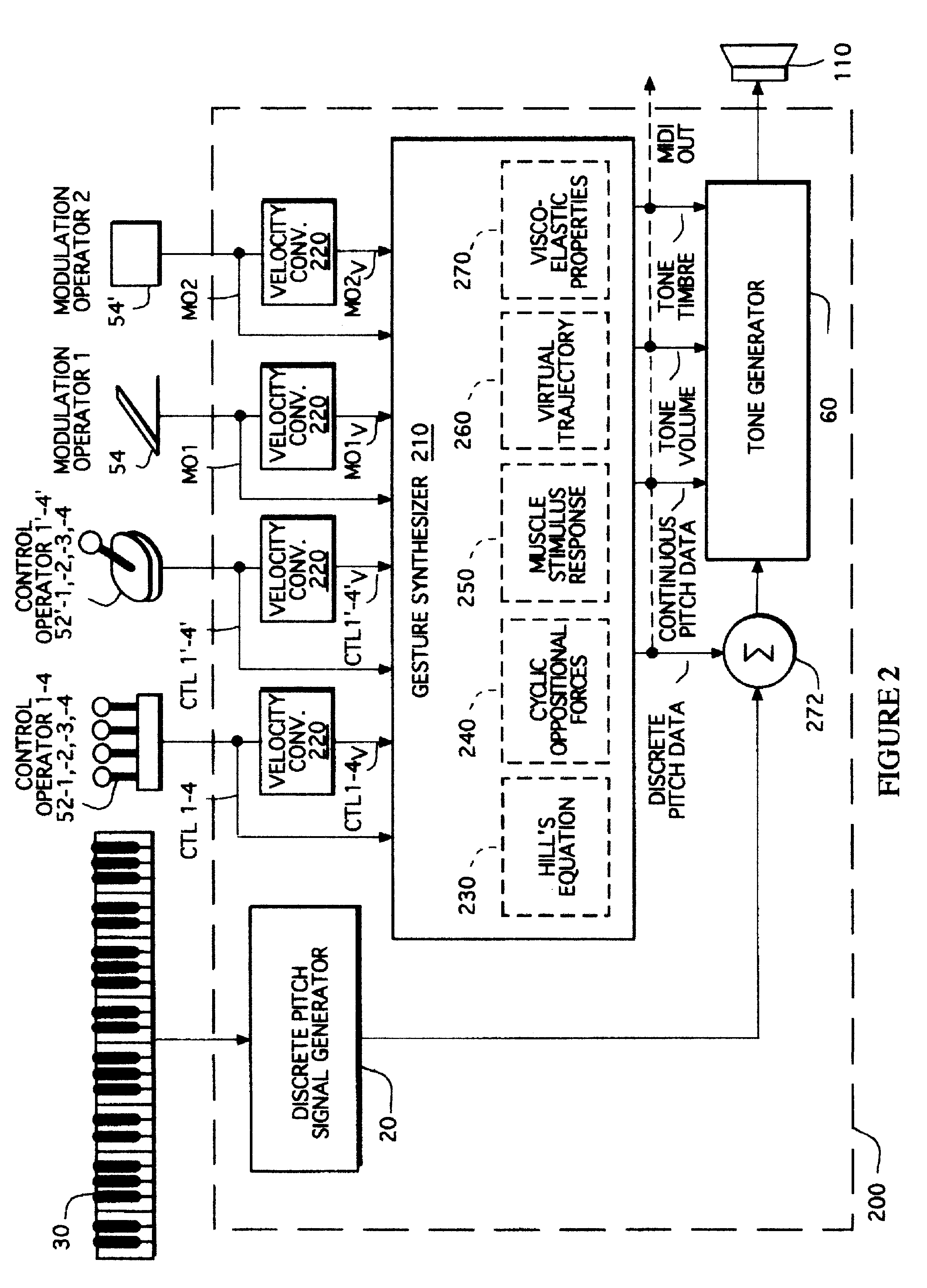
Gesture synthesizer for electronic sound device
InactiveUSRE37654E1Modifies musical gestureElectrophonic musical instrumentsLinear/angular speed measurementMuscle responseElectrical impulse
A MIDI-compatible gesture synthesizer is provided for use with a conventional music synthesizer to create musically realistic<DEL-S DATE="20020416" ID="DEL-S-00001" / >ally<DEL-E ID="DEL-S-00001" / > sounding gestures. The gesture synthesizer is responsive to one or more user controllable input signals, and includes several transfer function models that may be user-selected. One transfer function models properties of muscles using Hill's force-velocity equation to describe the non-linearity of muscle activation. A second transfer function models the cyclic oscillation produced by opposing effects of two force sources representing the cyclic oppositional action of muscle systems. A third transfer function emulates the response of muscles to internal electrical impulses. A fourth transfer function provides a model representing and altering virtual trajectory of gestures. A fifth transfer function models visco-elastic properties of muscle response to simulated loads. The gesture synthesizer outputs <DEL-S DATE="20020416" ID="DEL-S-00002" / >MIDI-compatible<DEL-E ID="DEL-S-00002" / > continuous pitch data, tone volume and tone timbre information. The continuous pitch data is combined with discrete pitch data provided by the discrete pitch generator within the conventional synthesizer, and the combined signal is input to a tone generator, along with the tone volume and tone timbre information. The tone generator outputs tones that are user-controllable in real time during performance of a musical gesture.
Owner:LONGO NICHOLAS
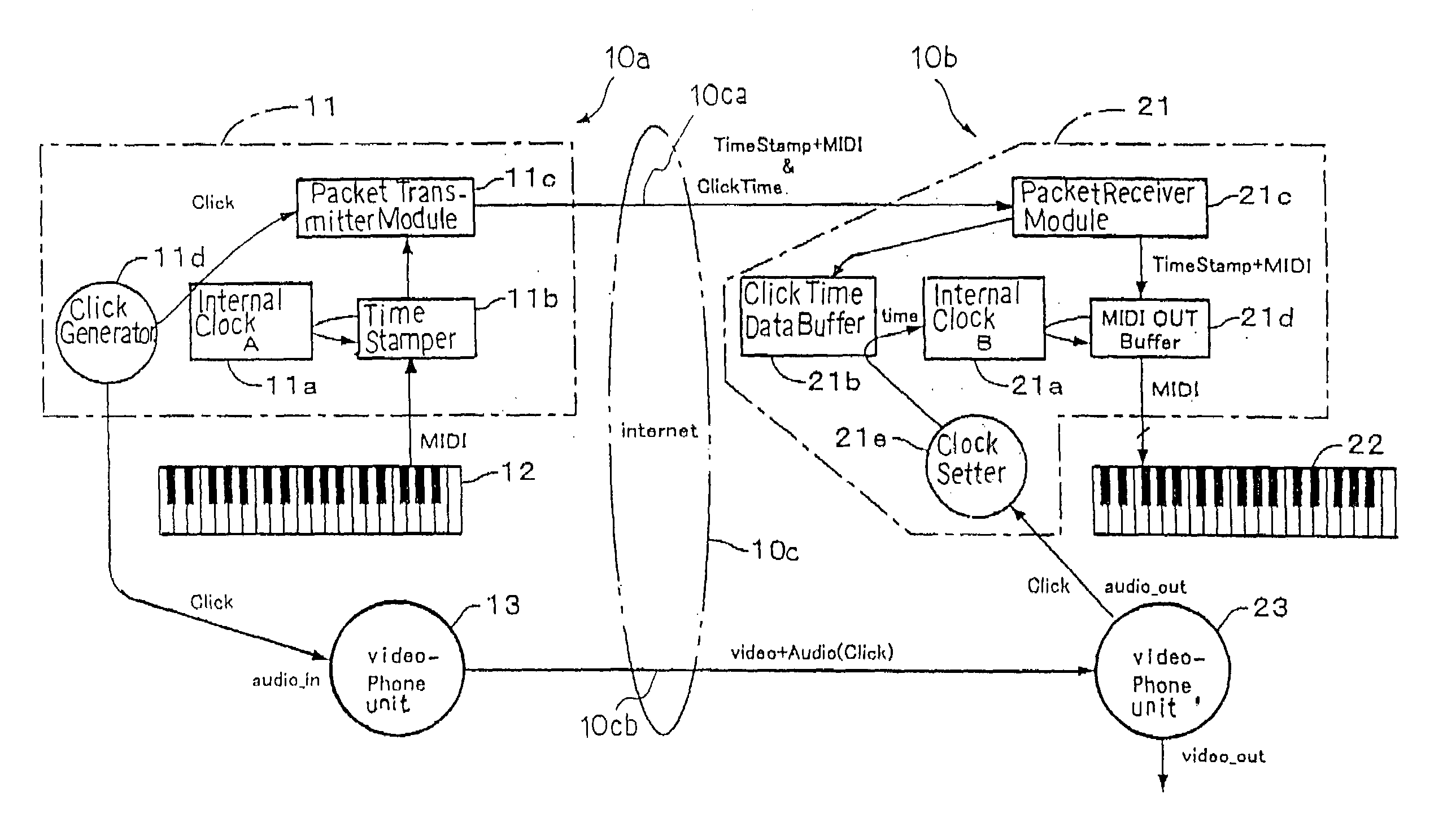
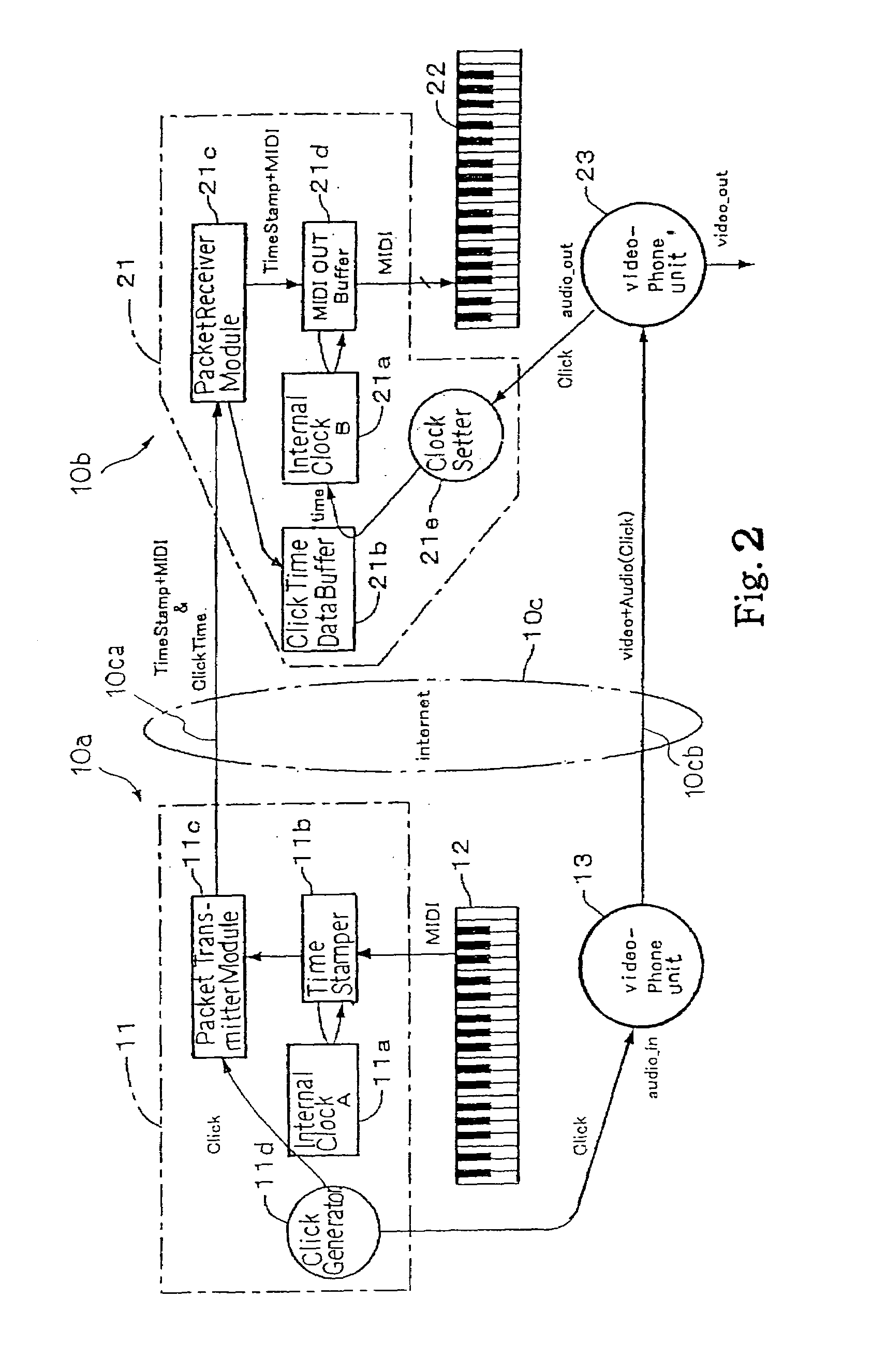
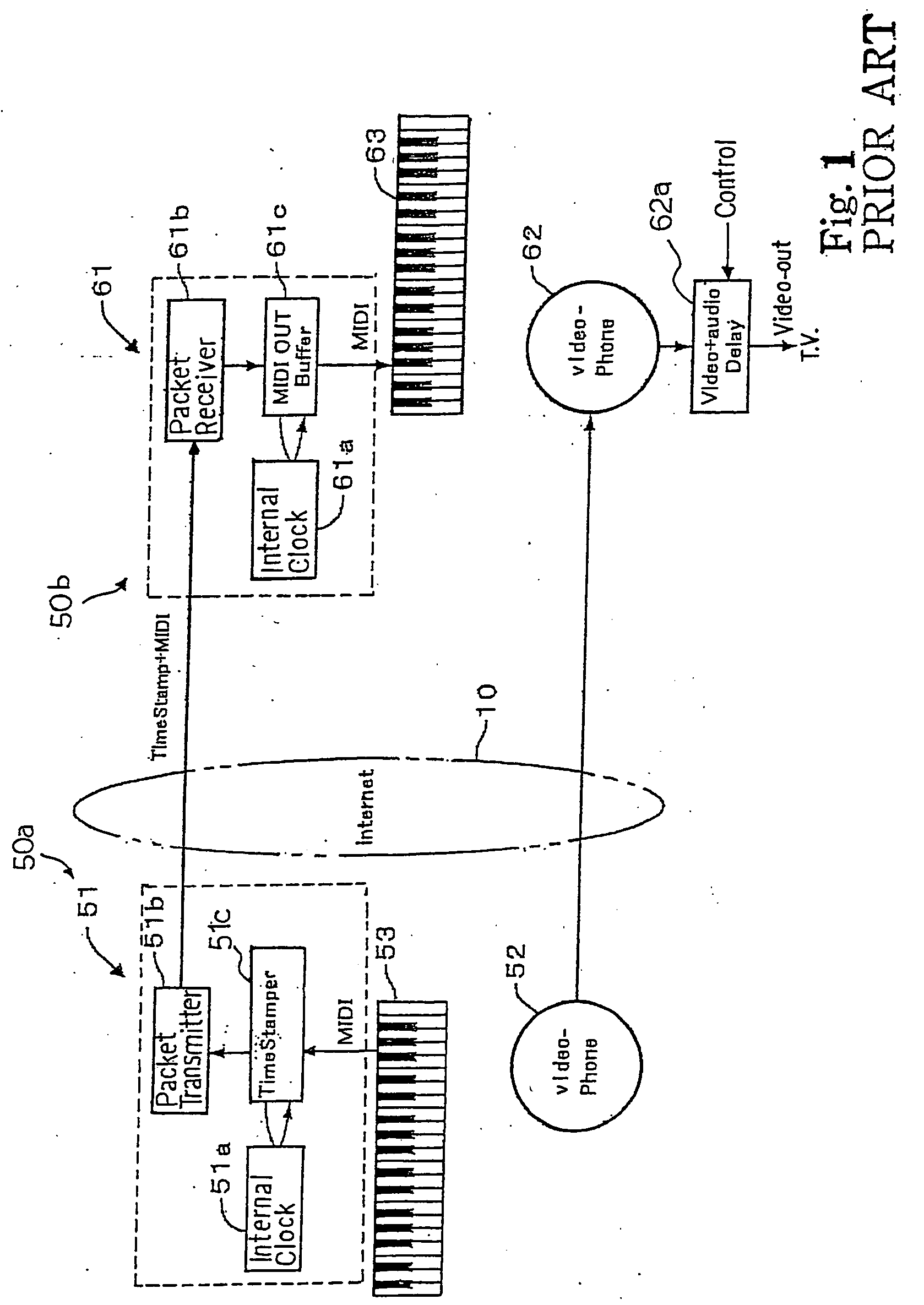
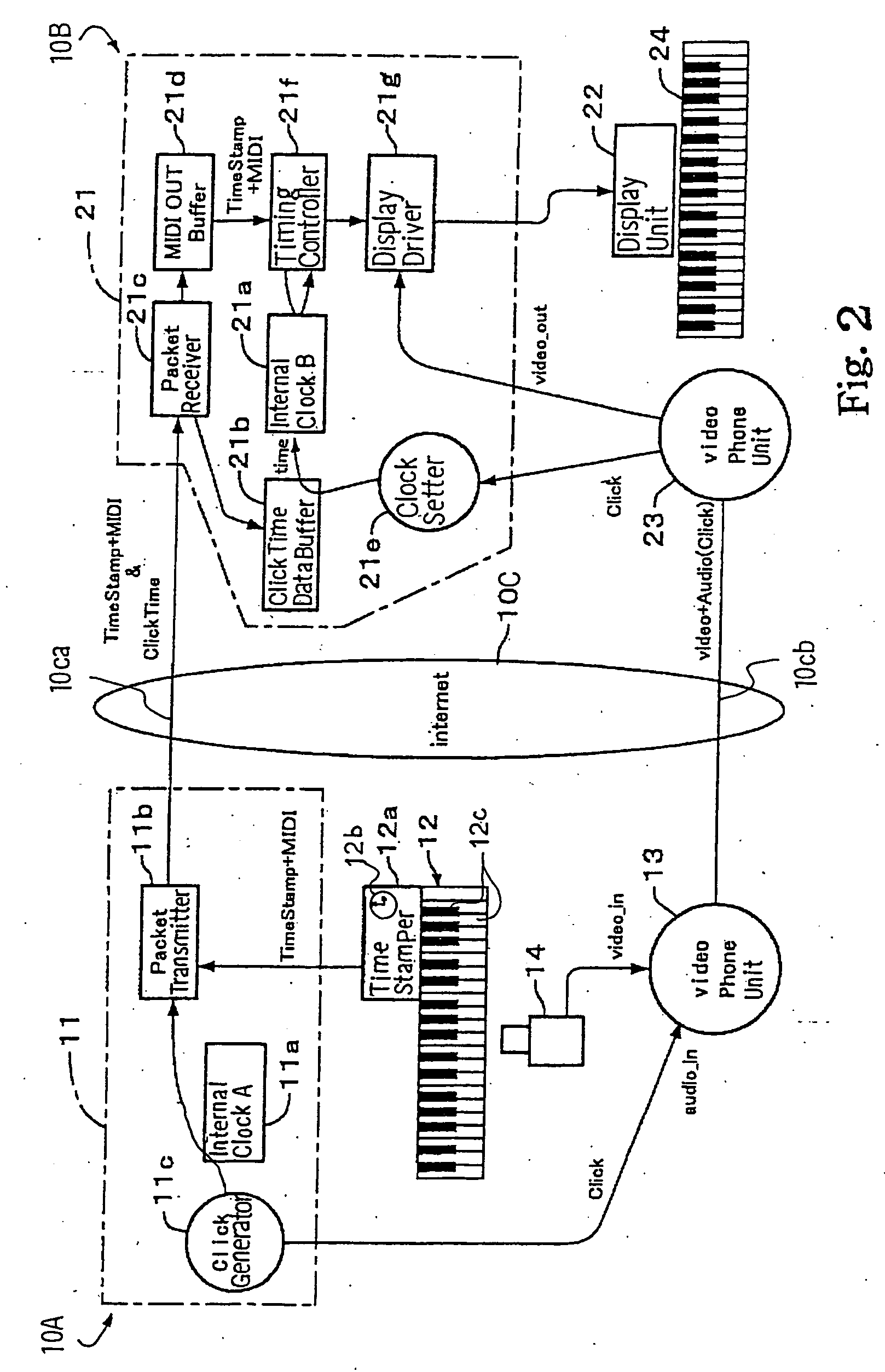
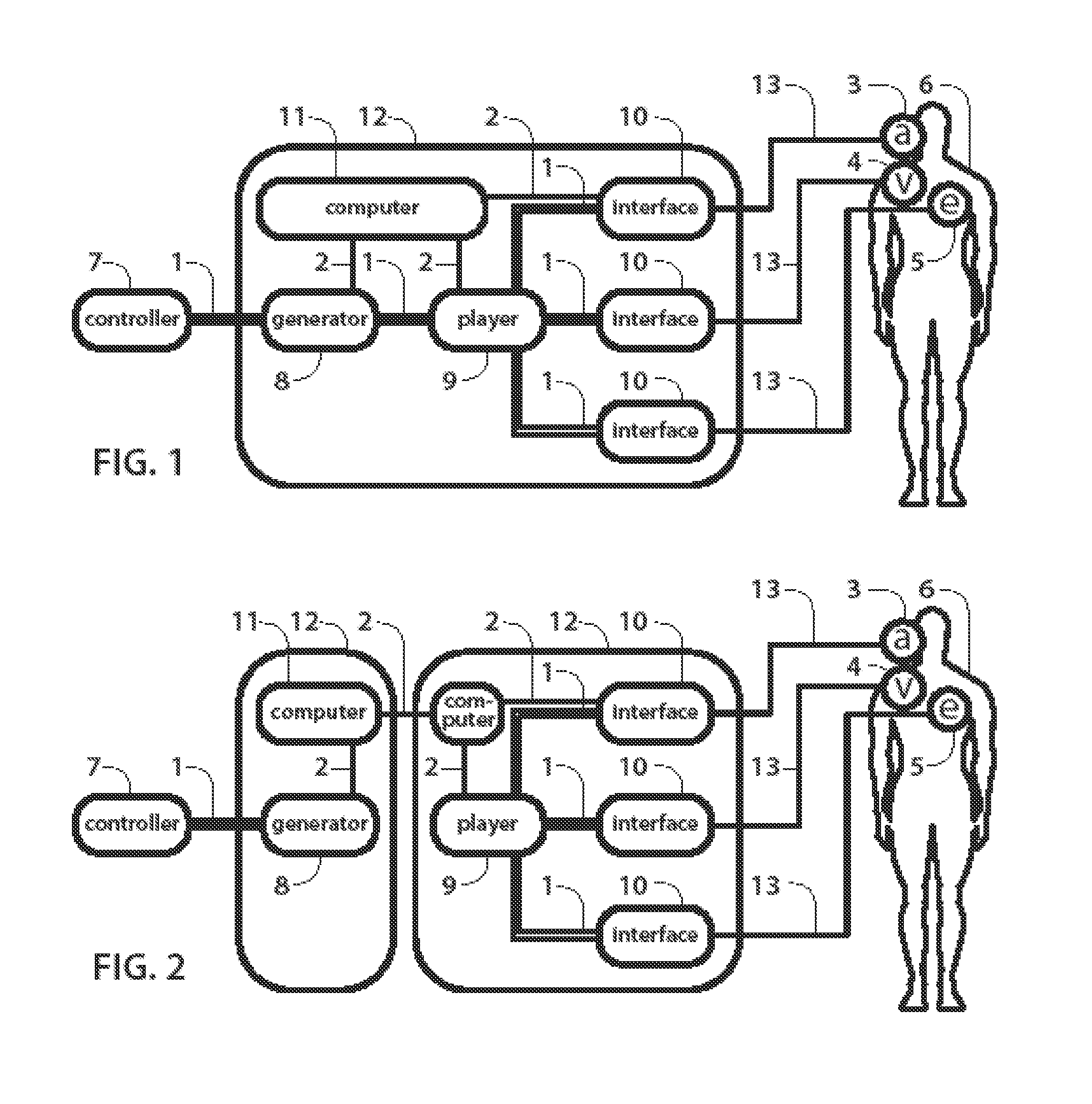
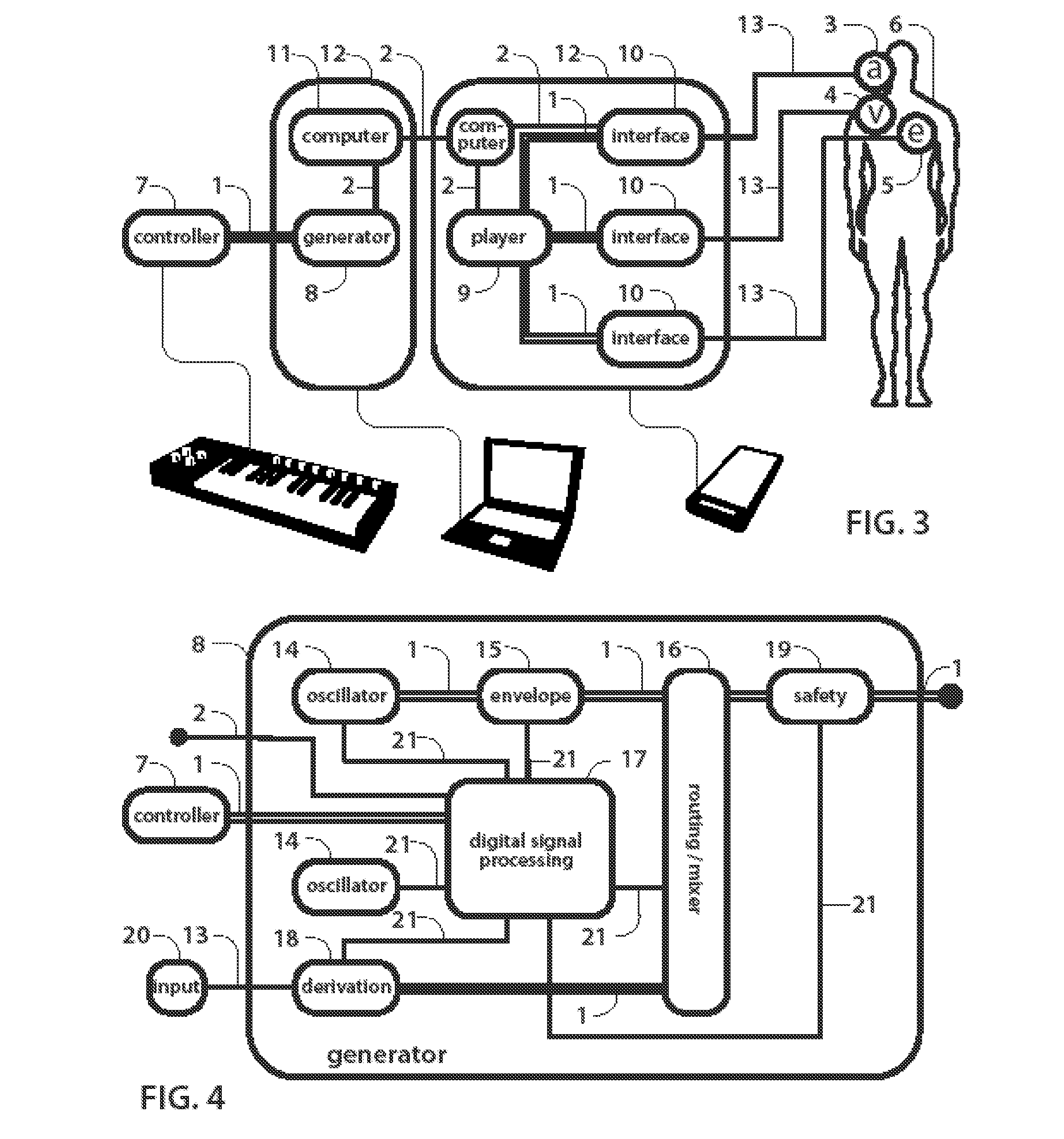
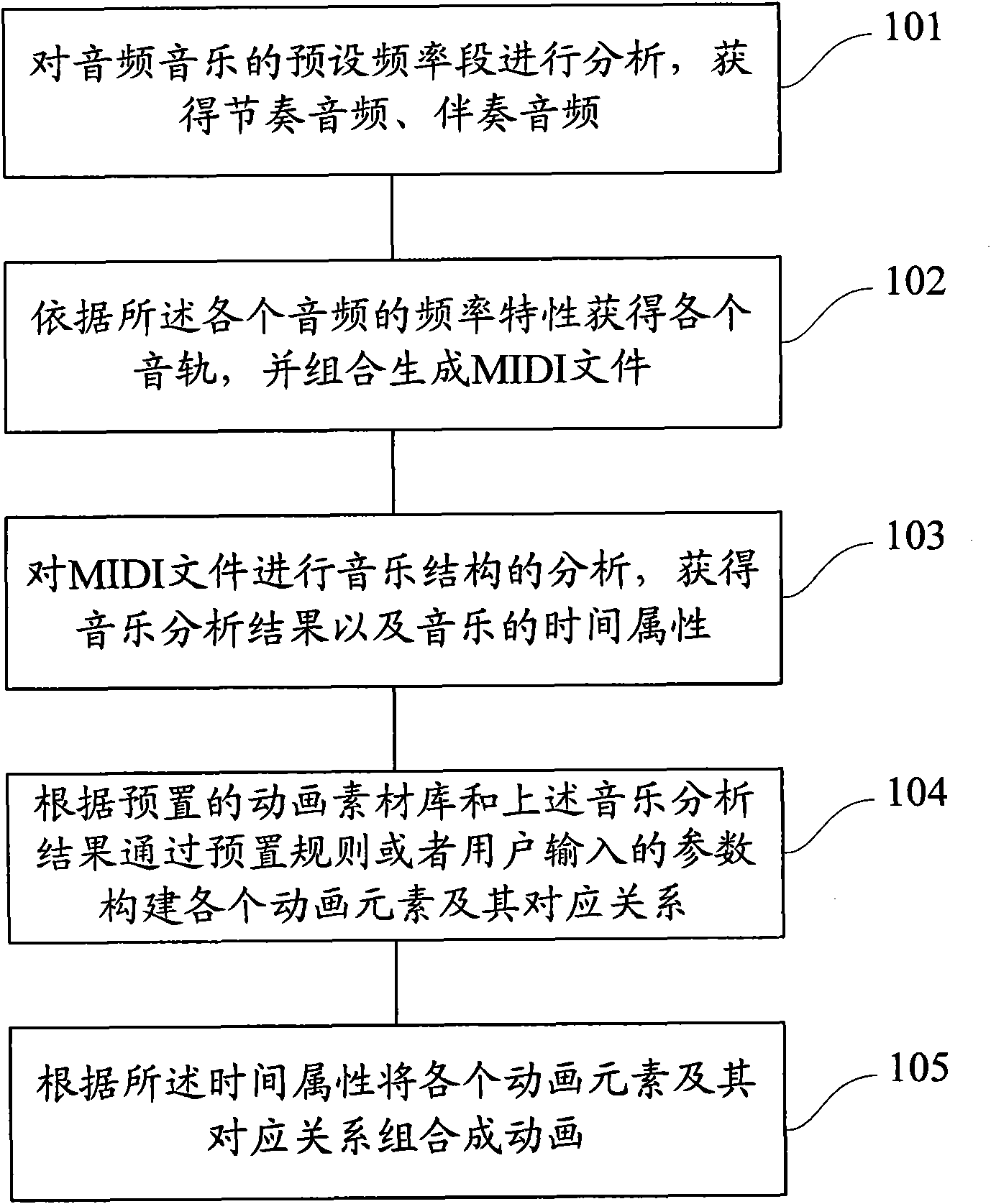
Separate-type musical performance system for synchronously producing sound and visual images and audio-visual station incorporated therein
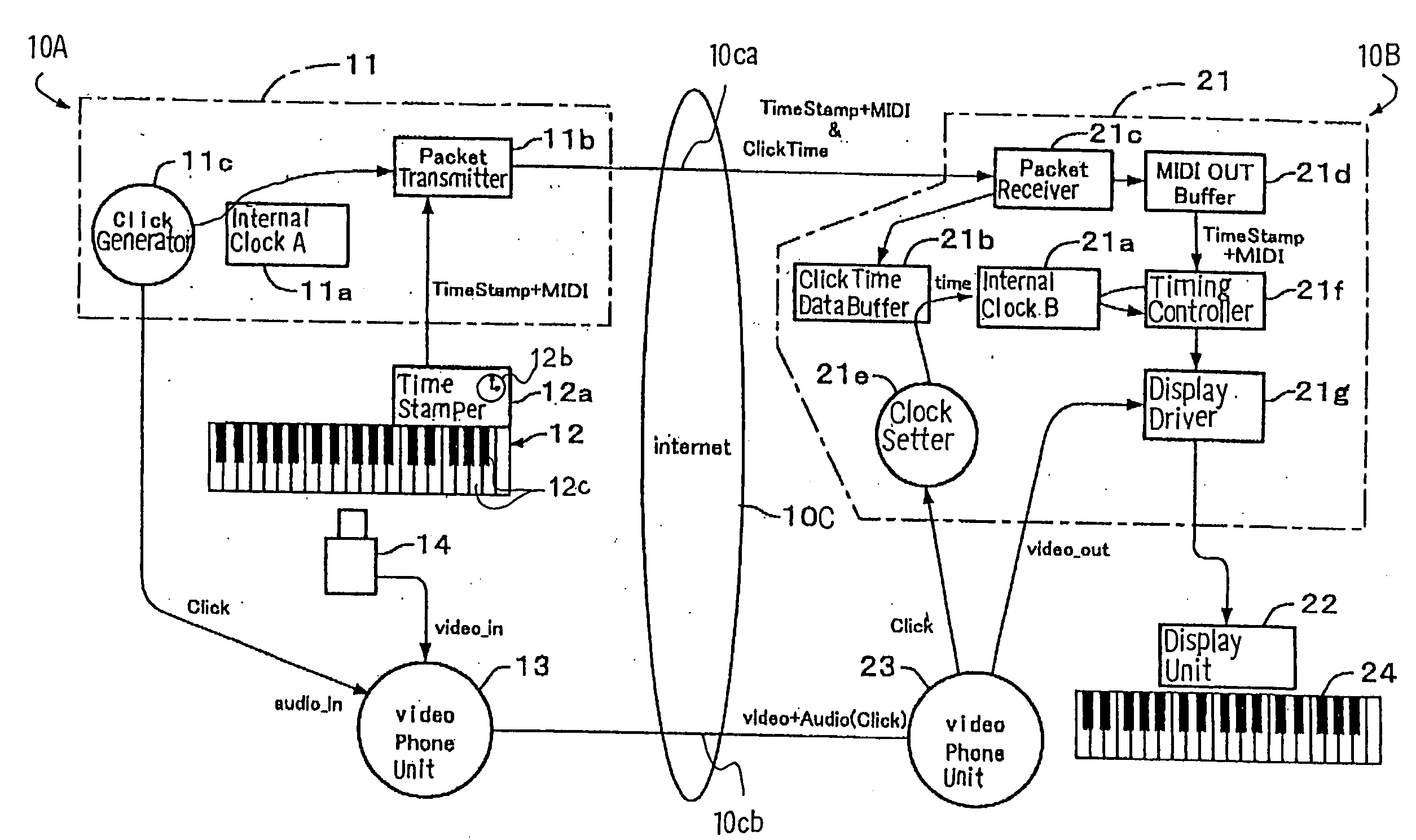
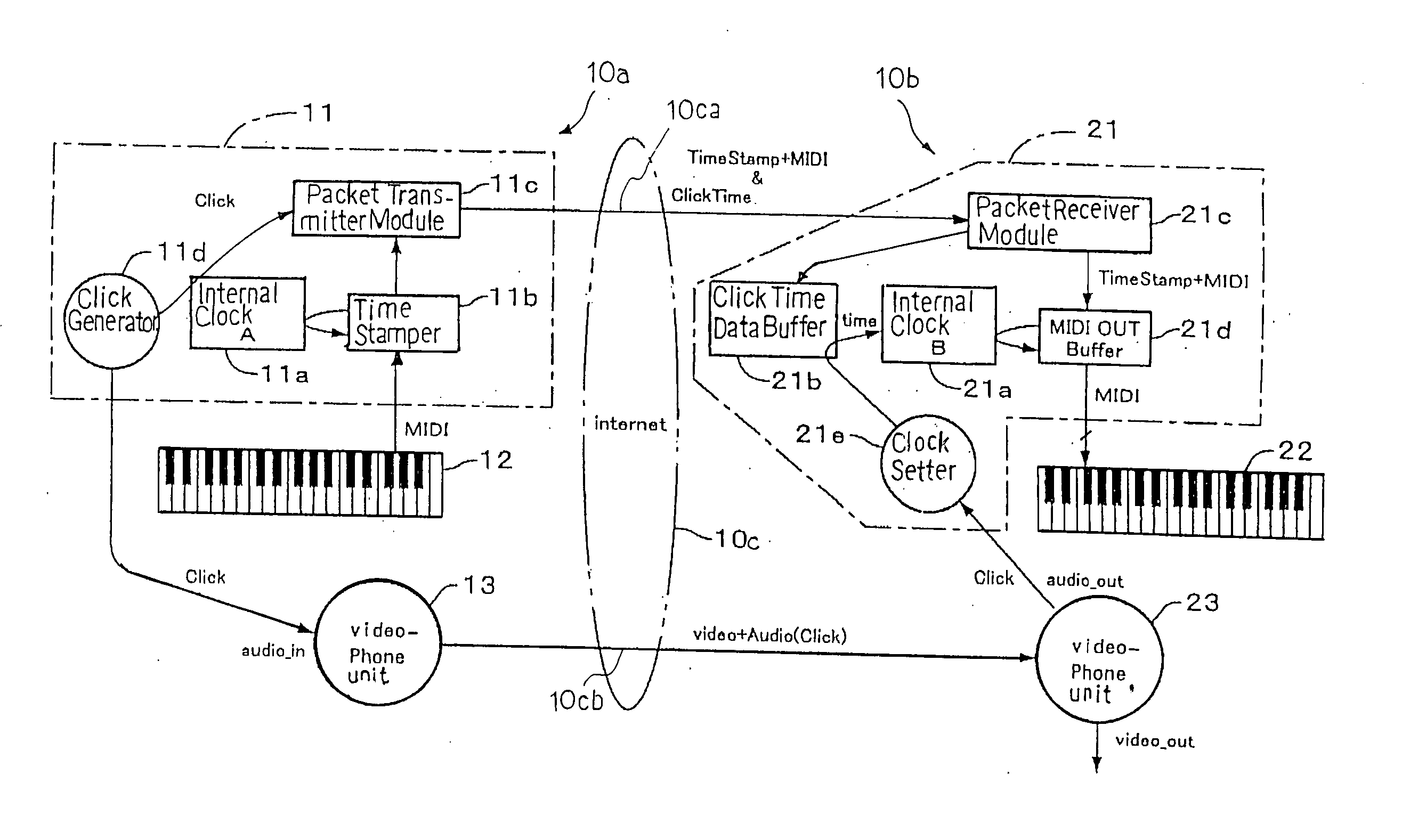
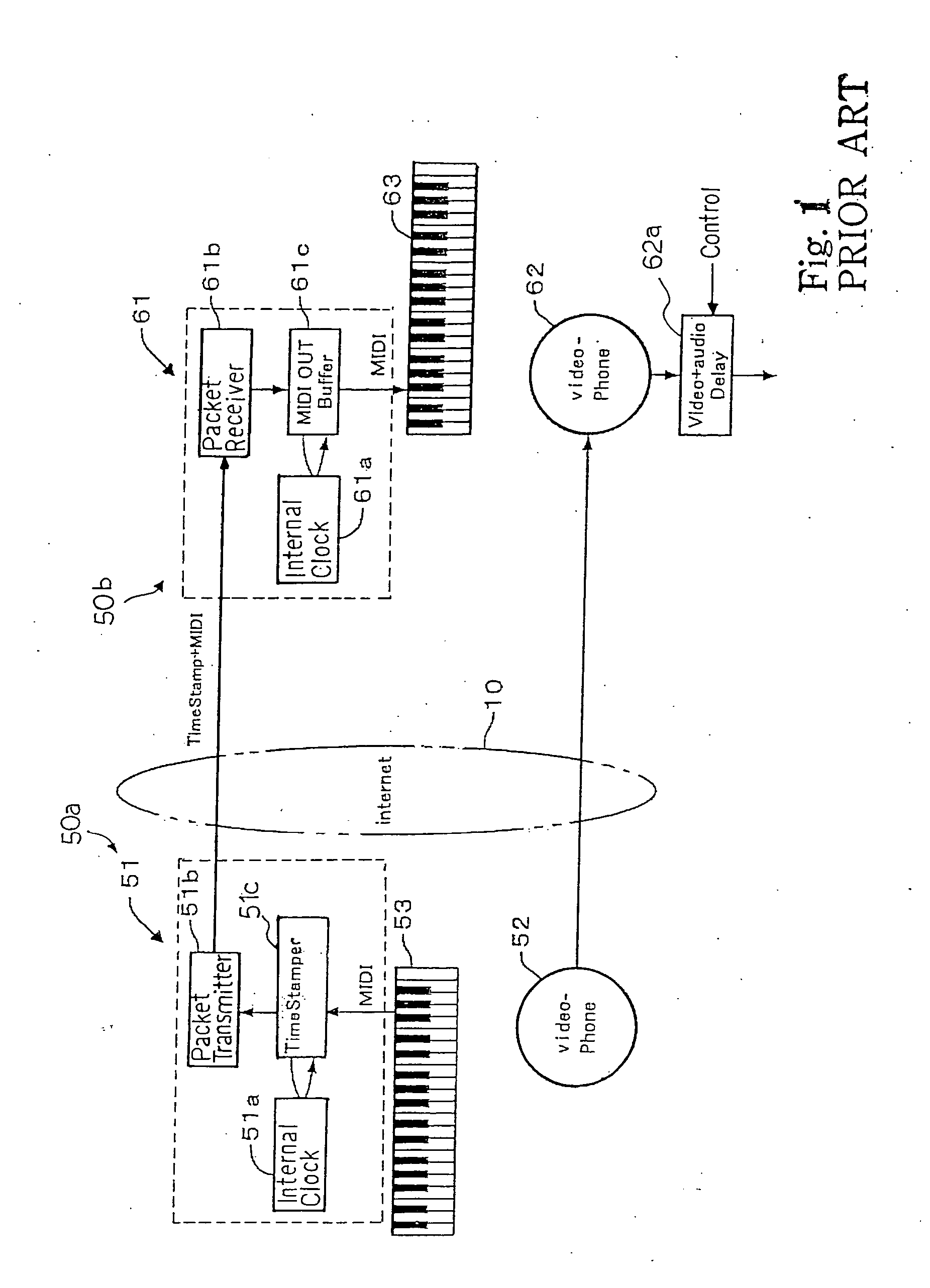
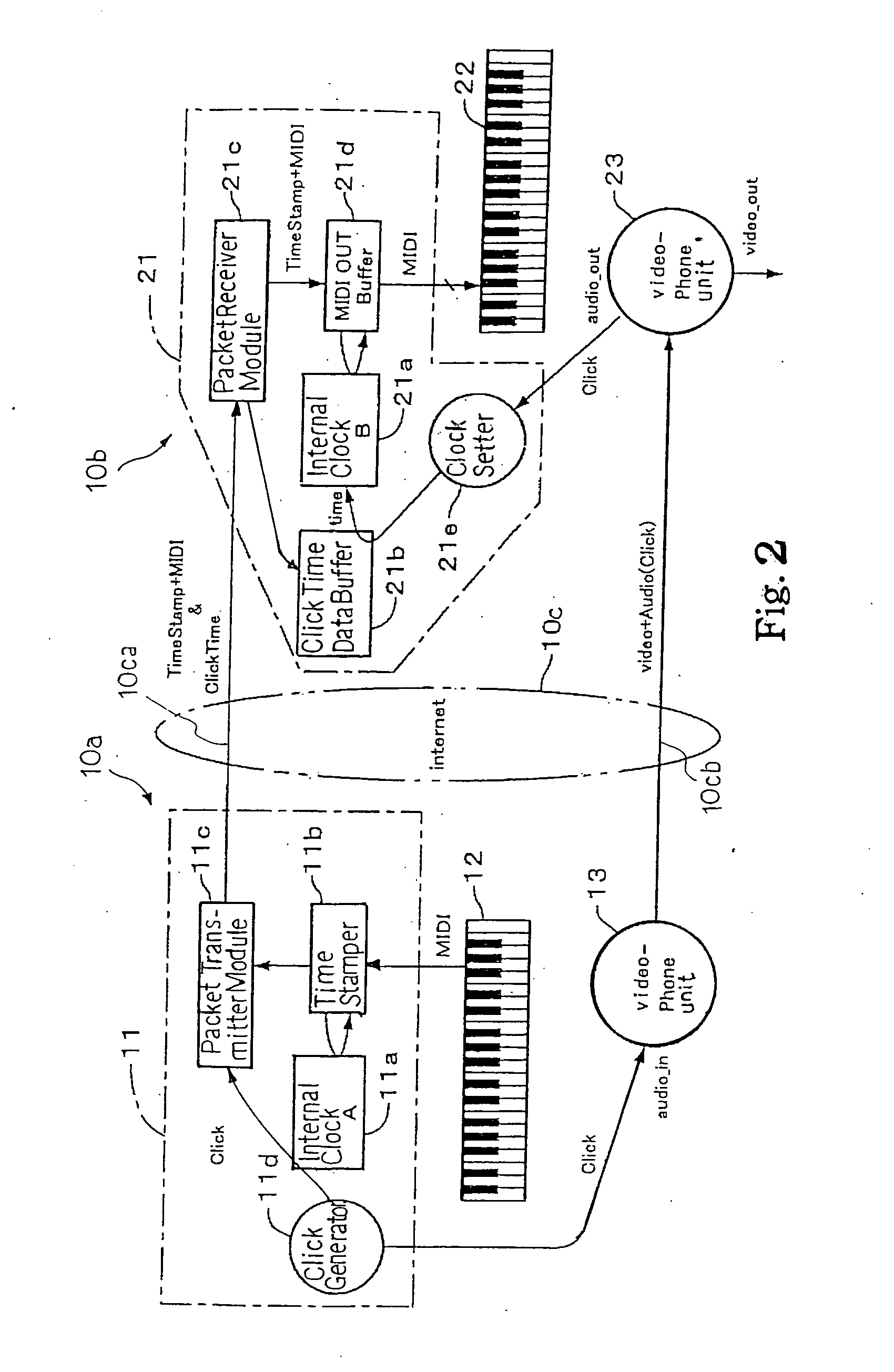
A separate-type music performance system has a master audio-visual station and a slave audio-visual station remote from the mater audio-visual station and connected through two communication channel independently of each other; MIDI music data codes and click time data codes are transmitted through one of the communication channels to the slave audio-visual station, and audio-visual data codes and a click signal are transmitted through the other communication channel; when the click signal and click time data code arrive the slave audio-visual station, the clock setter 21e sets an internal clock with the click time data code paired with the click signal, and the MIDI music data code are transferred to an automatic player piano in comparison with the time data and the internal clock, whereby the tones are produced synchronously with the visual images.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Data reproducing device, data reproducing method, and information terminal
InactiveUS6979769B1Synchronization is simpleEasy to manageElectrophonic musical instrumentsSound producing devicesComputer hardwareComputer terminal
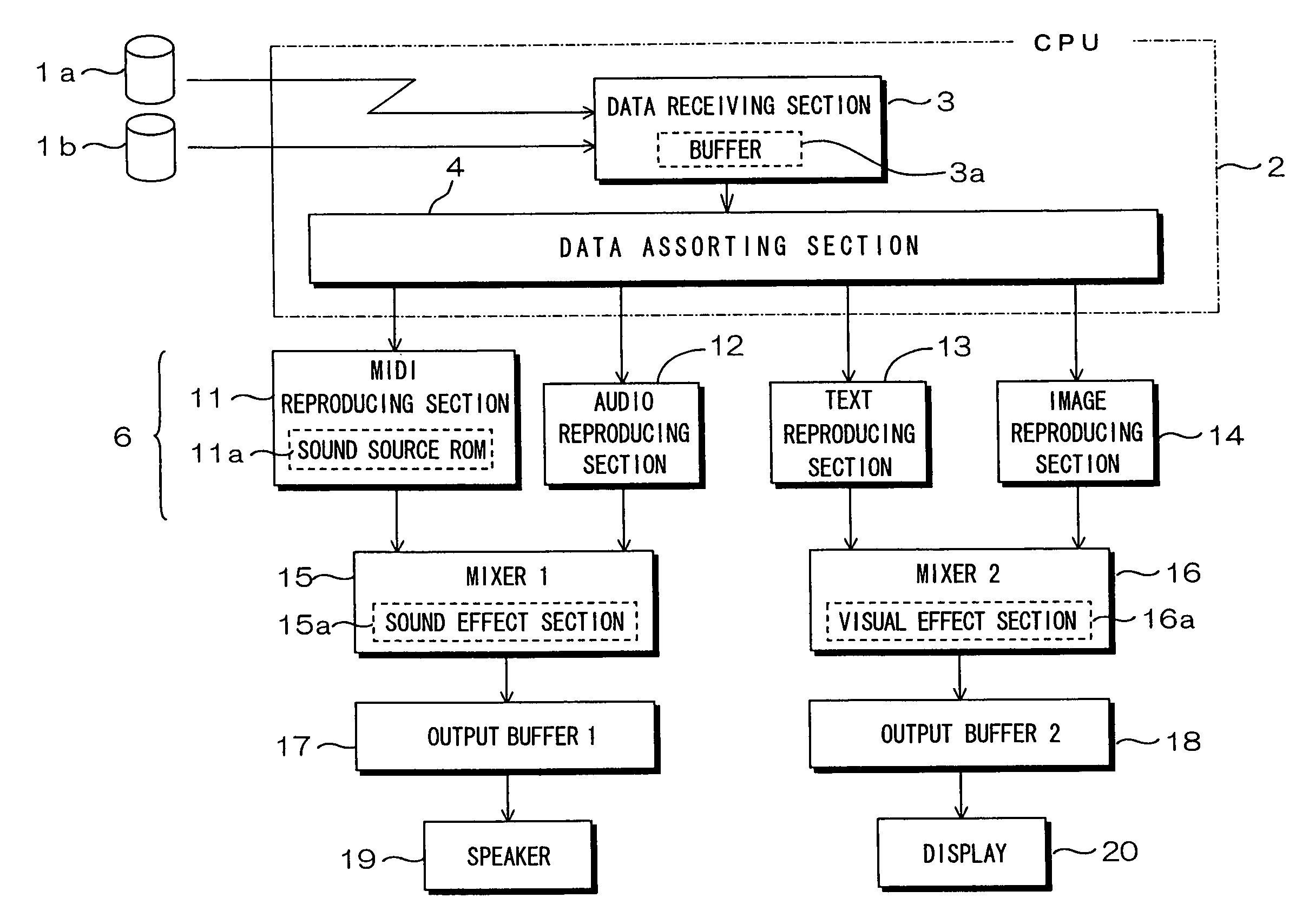
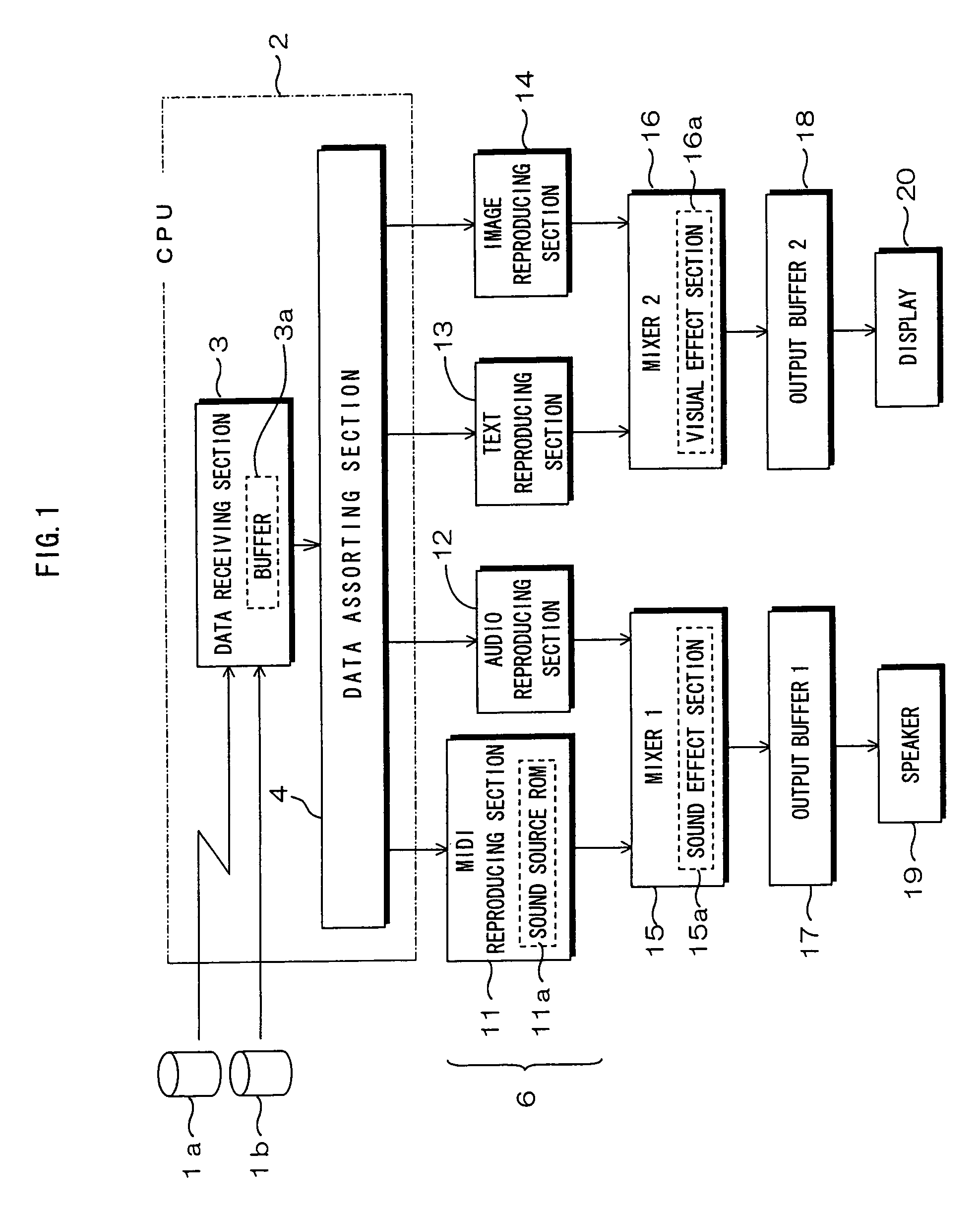
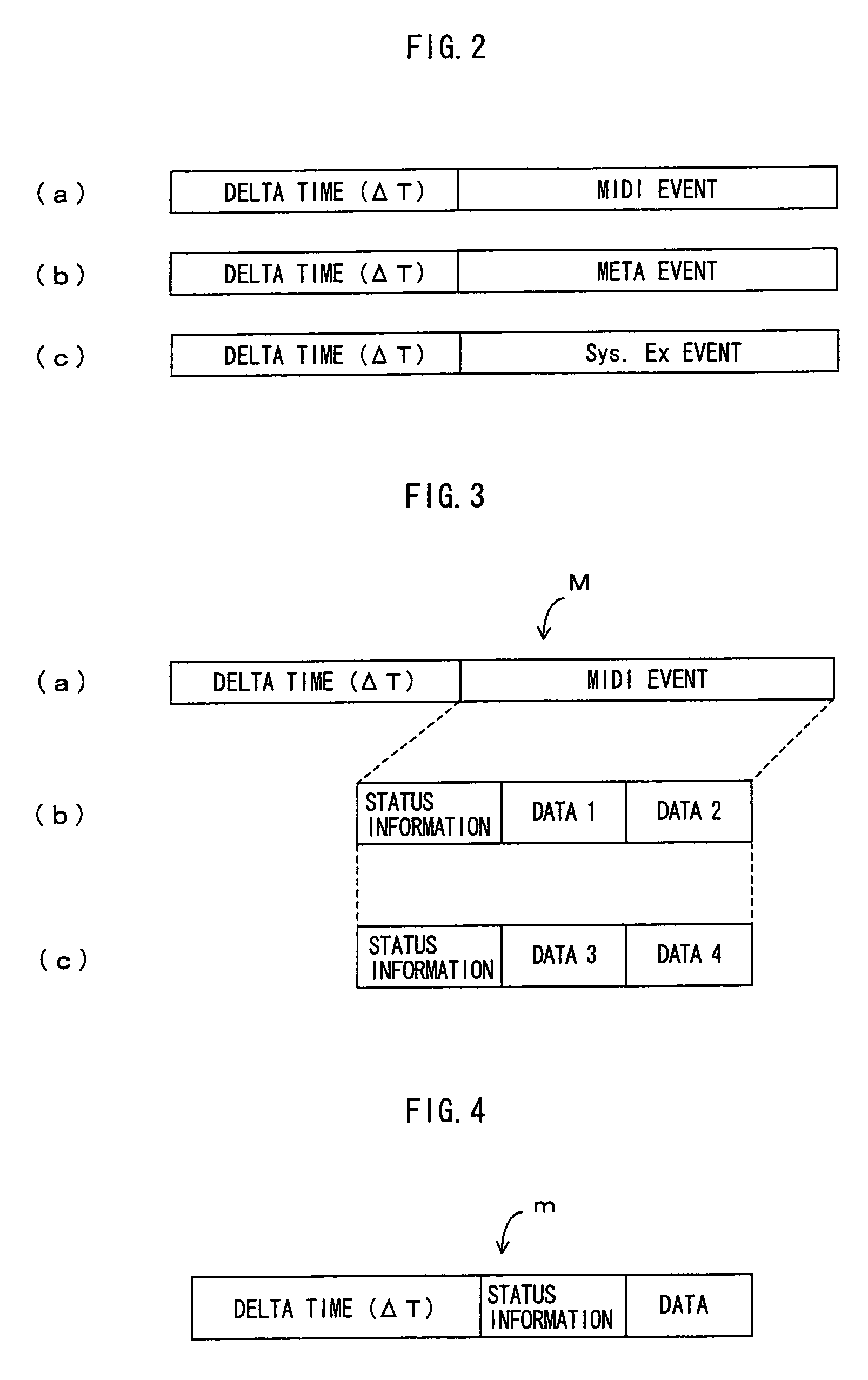
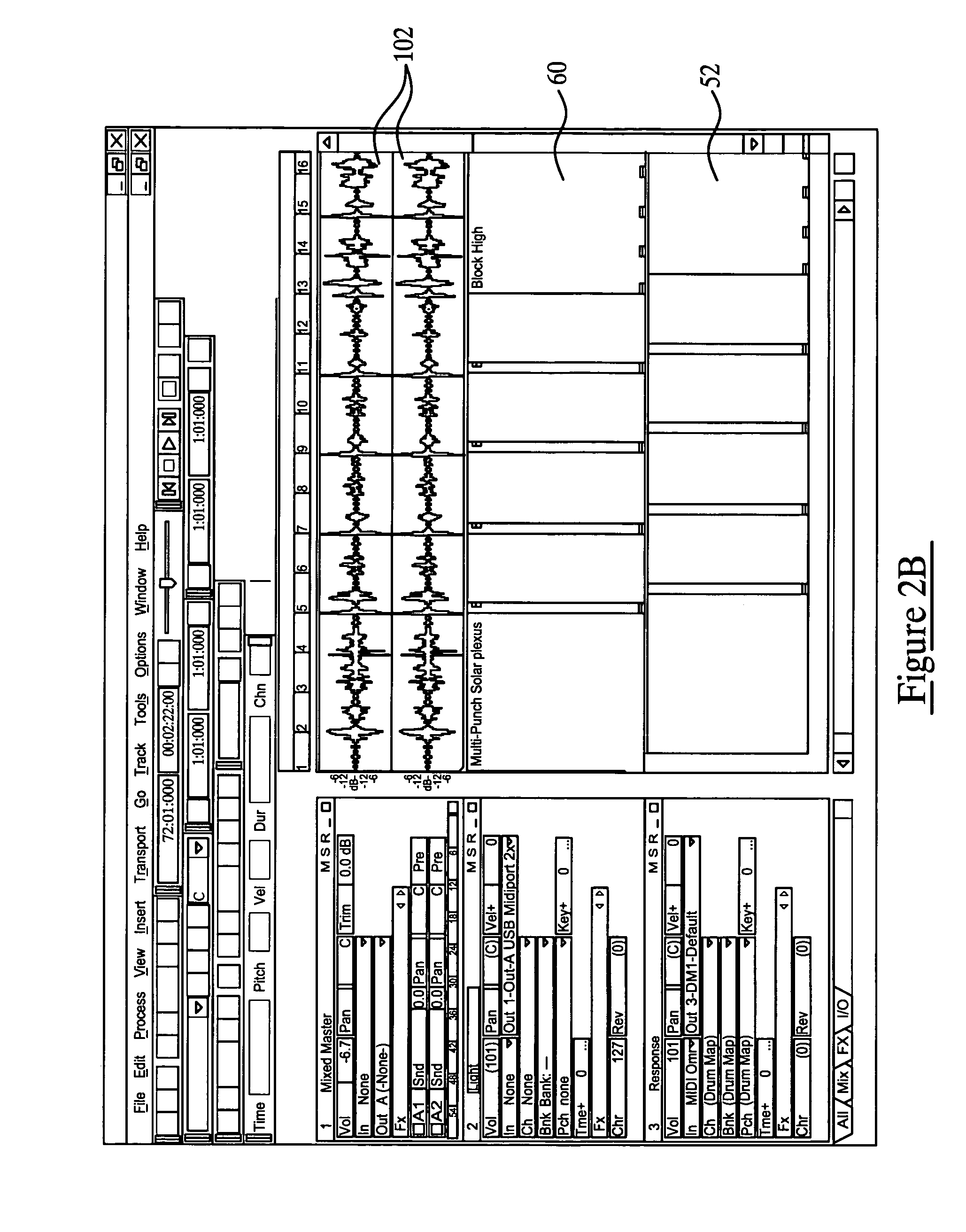
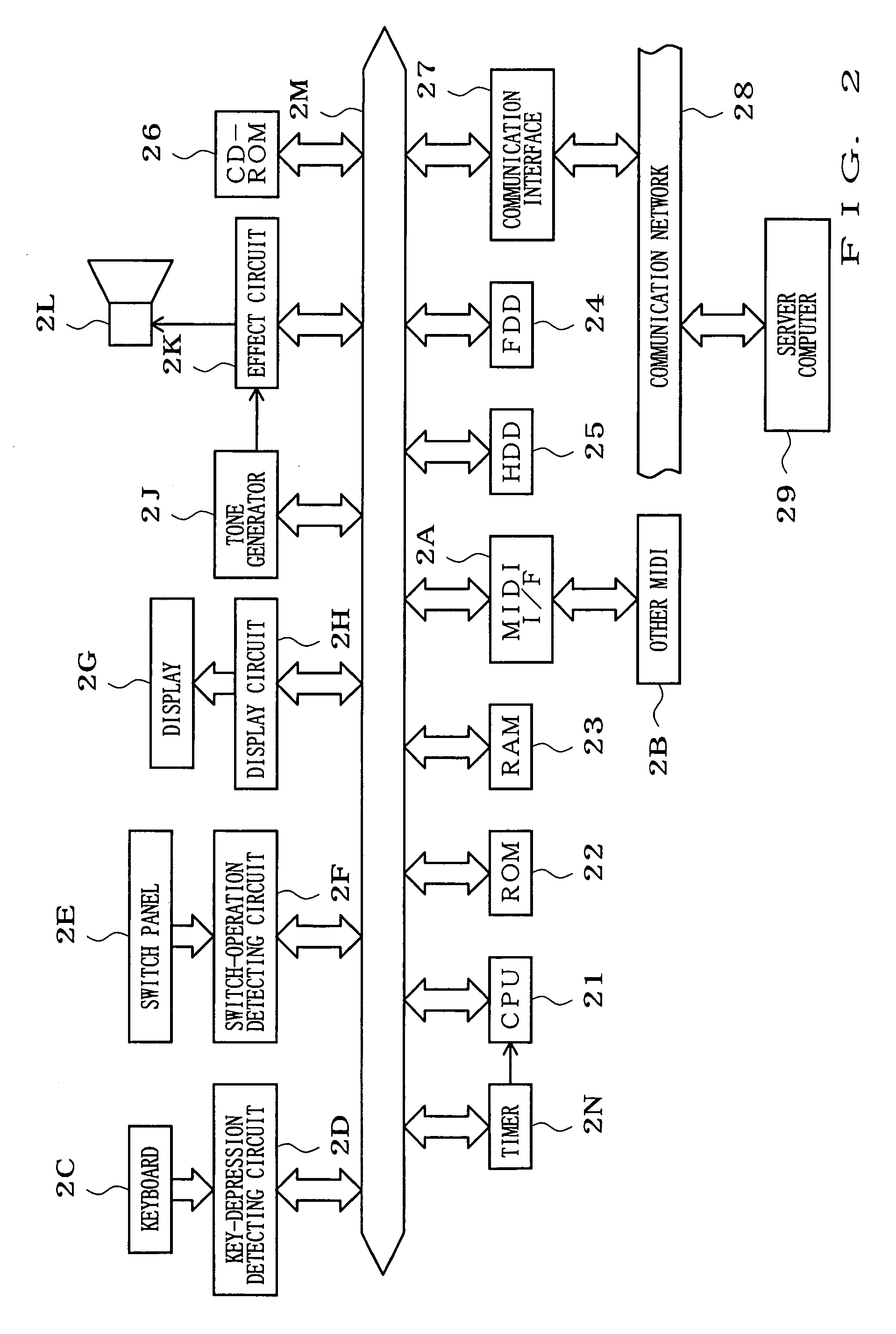
Each of MIDI data, audio data, text data and image data to be received in a data receiving section is SMF-formatted data including event information and event-executing delta time. A data sorting section sorts data based on data type depending upon a delta time of each type of received data. The sorted data are respectively reproduced in a MIDI reproducing section, an audio reproducing section, a text reproducing section and an image reproducing section. The data reproduced in the MIDI reproducing section and audio reproducing section are mixed in a mixer and outputted as sound from a speaker, while the data reproduced in the text reproducing section and image reproducing section are mixed in a mixer and displayed as visual information on a display. Because each type of data is reproduced in the timing according to the delta time, synchronization can be easily provided between different types of data, for example as sound and images.
Owner:FAITH CO LTD
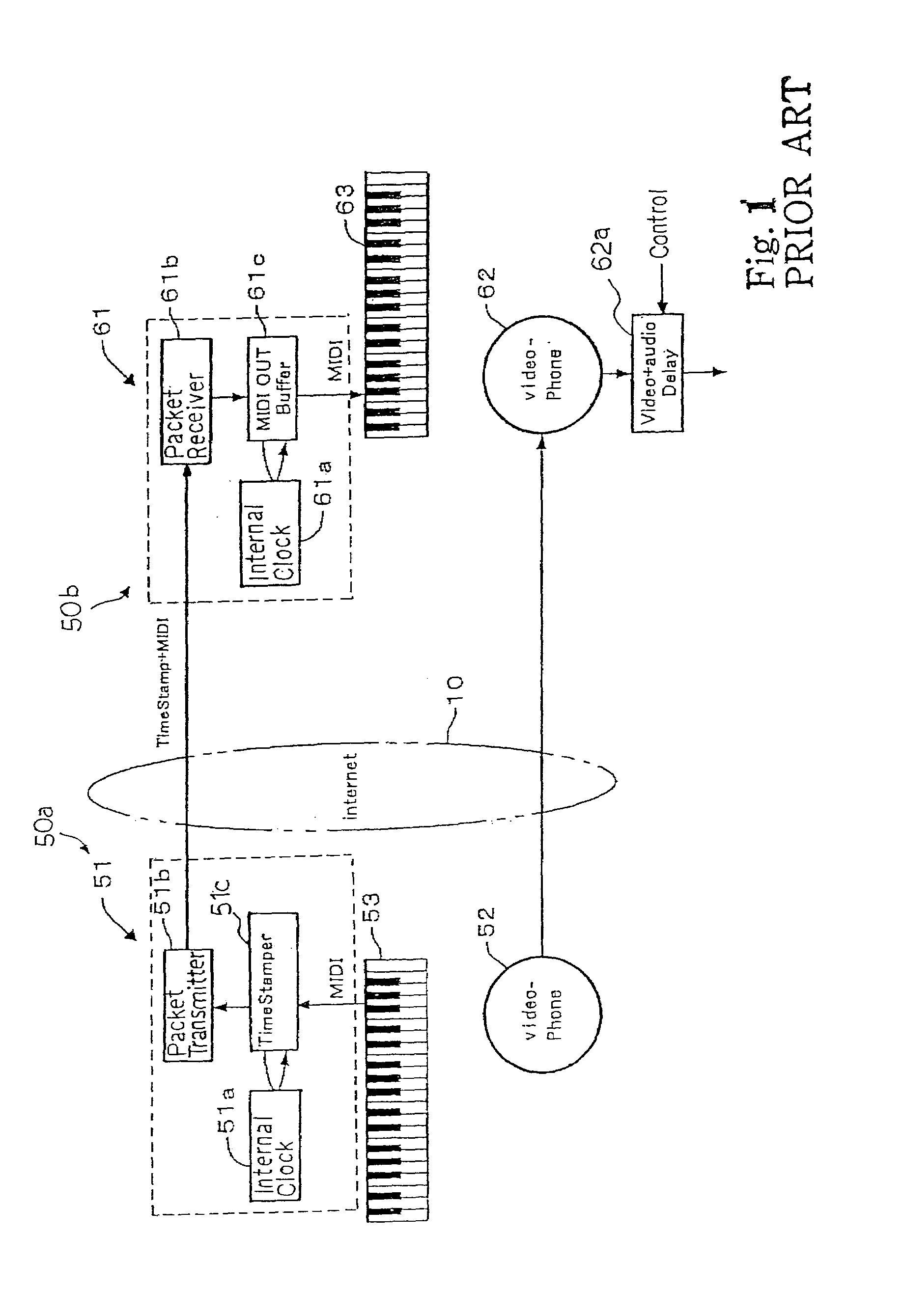
Music station for producing visual images synchronously with music data codes
In order to make a tutor give a remote music lesson to a trainee, the audio-visual station transmits MIDI music data codes / time stamp data codes and click time data codes through a packet switching network and an audio-visual signal, which expresses real images of tutor's hands on the keyboard, and click signal through a teleconference system to another audio-visual station; the controller for the trainee makes the internal clock synchronous with the internal clock for the tutor through the pairing work between the click time data codes and the click signals so that the images of note bars and real images are synchronously produced on a display unit in front of the trainee's keyboard; moreover, while the tutor's exhibition is being carried out, any oral direction does not reach the trainee so that the trainee concentrate himself to the exhibition.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
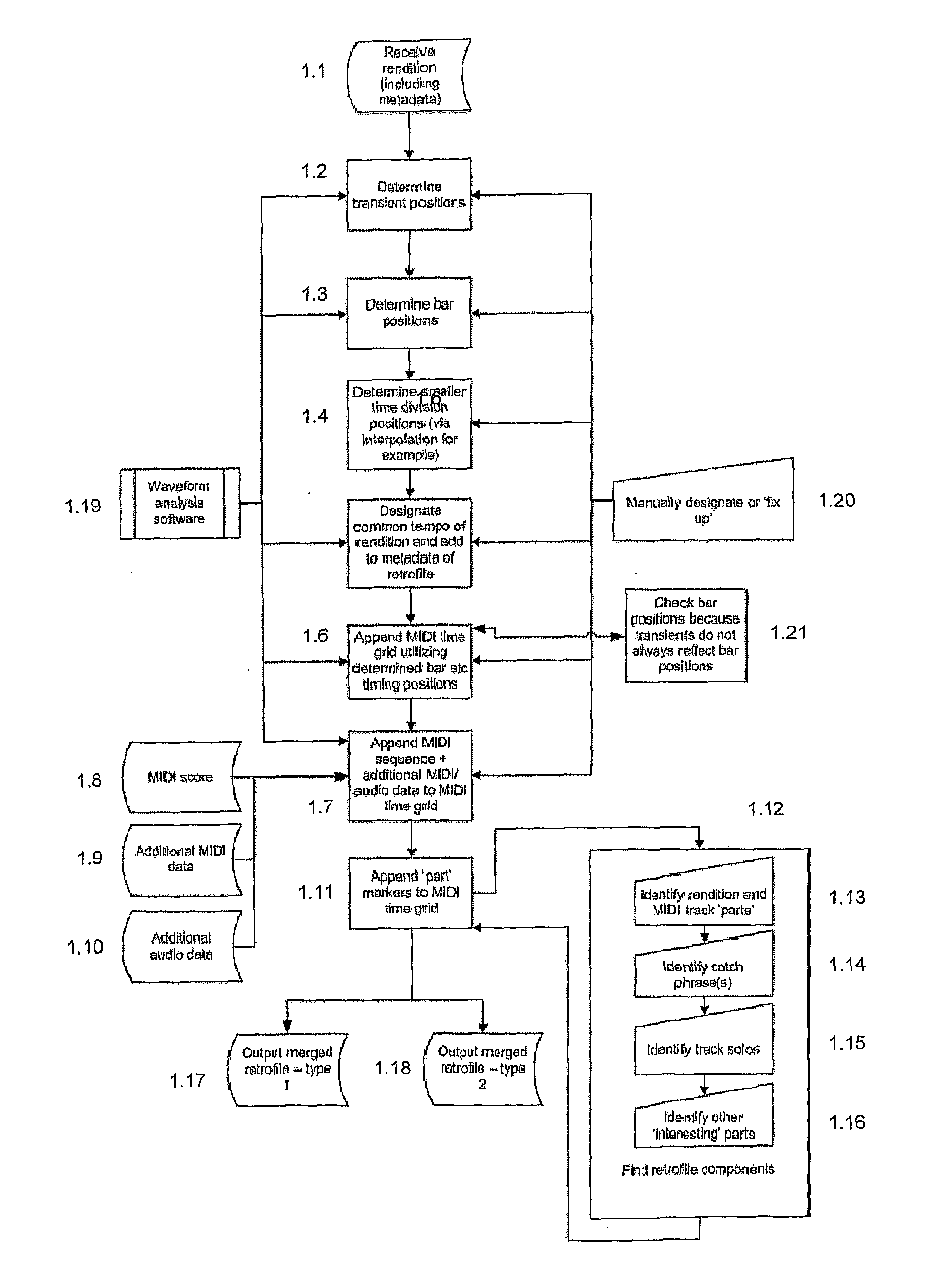
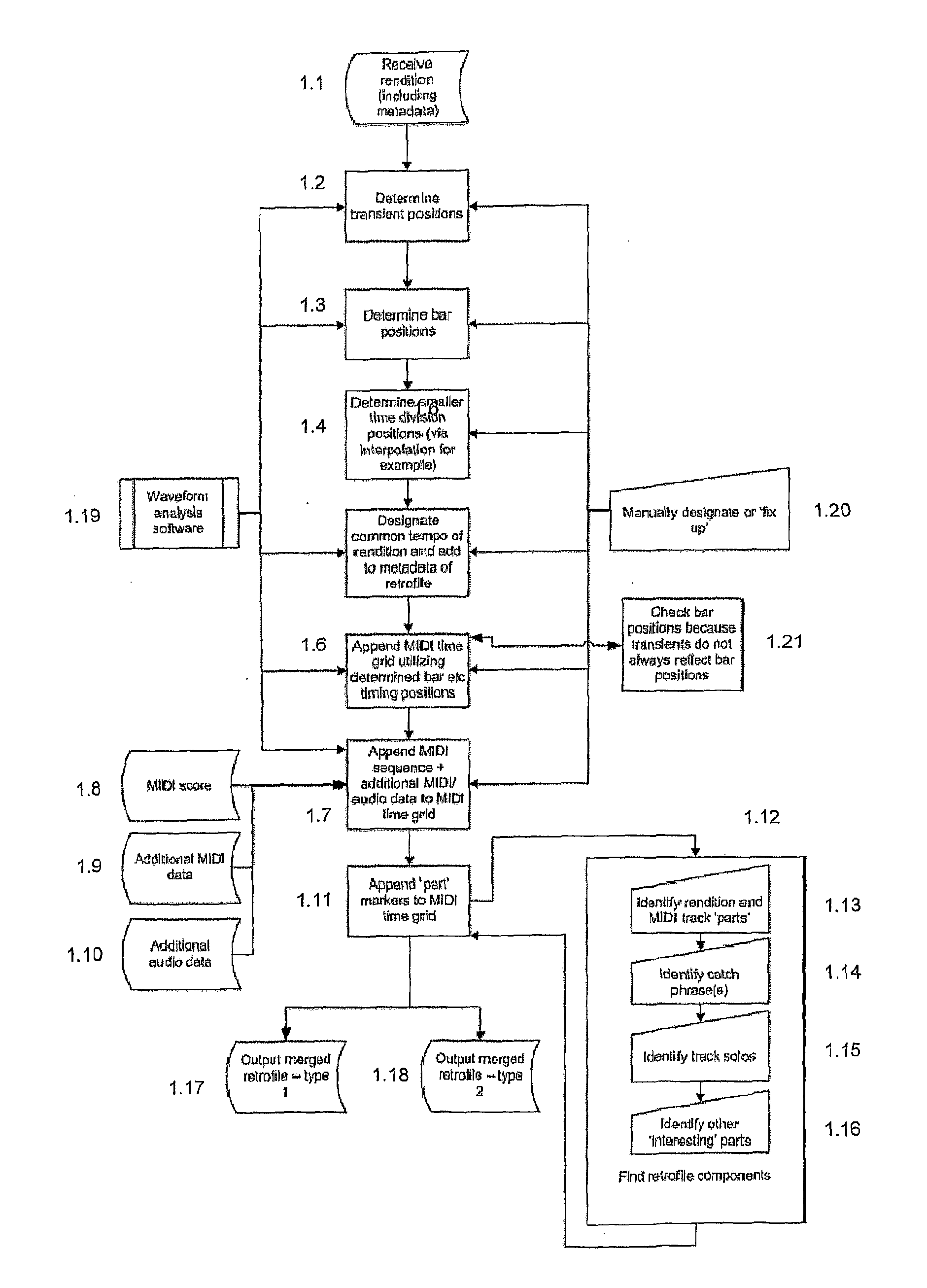
File creation process, file format and file playback apparatus enabling advanced audio interaction and collaboration capabilities
A file creation process, file format and playback device are provided that enables an interactive and if desired collaborative music playback experience for the user(s) by combining or retro-fitting an ‘original song’ with a MIDI time grid, the MIDI score of the song and other data in a synchronized fashion. The invention enables a music interaction platform that requires a small amount of time to learn and very little skill, knowledge or talent to use and is designed to bring ‘mixing music’ to the average person. The premiere capability that the file format provides, is the capability for any two bars, multiples of bars or pre-designated ‘parts’ from any two songs to be mixed in both tempo and bar by bar synchronization in a non-linear drag and drop fashion (and therefore almost instantaneously). The file format provides many further interaction capabilities however such a remixing MIDI tracks from the original song back in with the song. In the preferable embodiment the playback means is a software application on a handheld portable device which utilizes a multitouch-screen user interface, such as an iPhone. A single user can musically interact with the device and associated ‘original songs’ etc or interactively collaborate with other users in like fashion, either whilst in the same room or over the Internet. The advanced inter-active functionality the file format enables in combination with the unique features of the iPhone (as a playback device), such as the multitouch-screen and accelerometer, enable furthered intuitive and enhanced music interaction capabilities. The object of the invention is to make music interaction (mixing for example) a regular activity for the average person.
Owner:ODWYER SEAN PATRICK
Cybernetic 3D music visualizer
InactiveUS20060181537A1Control inputImprove the level ofElectrophonic musical instrumentsAnimationFrequency spectrumInput control
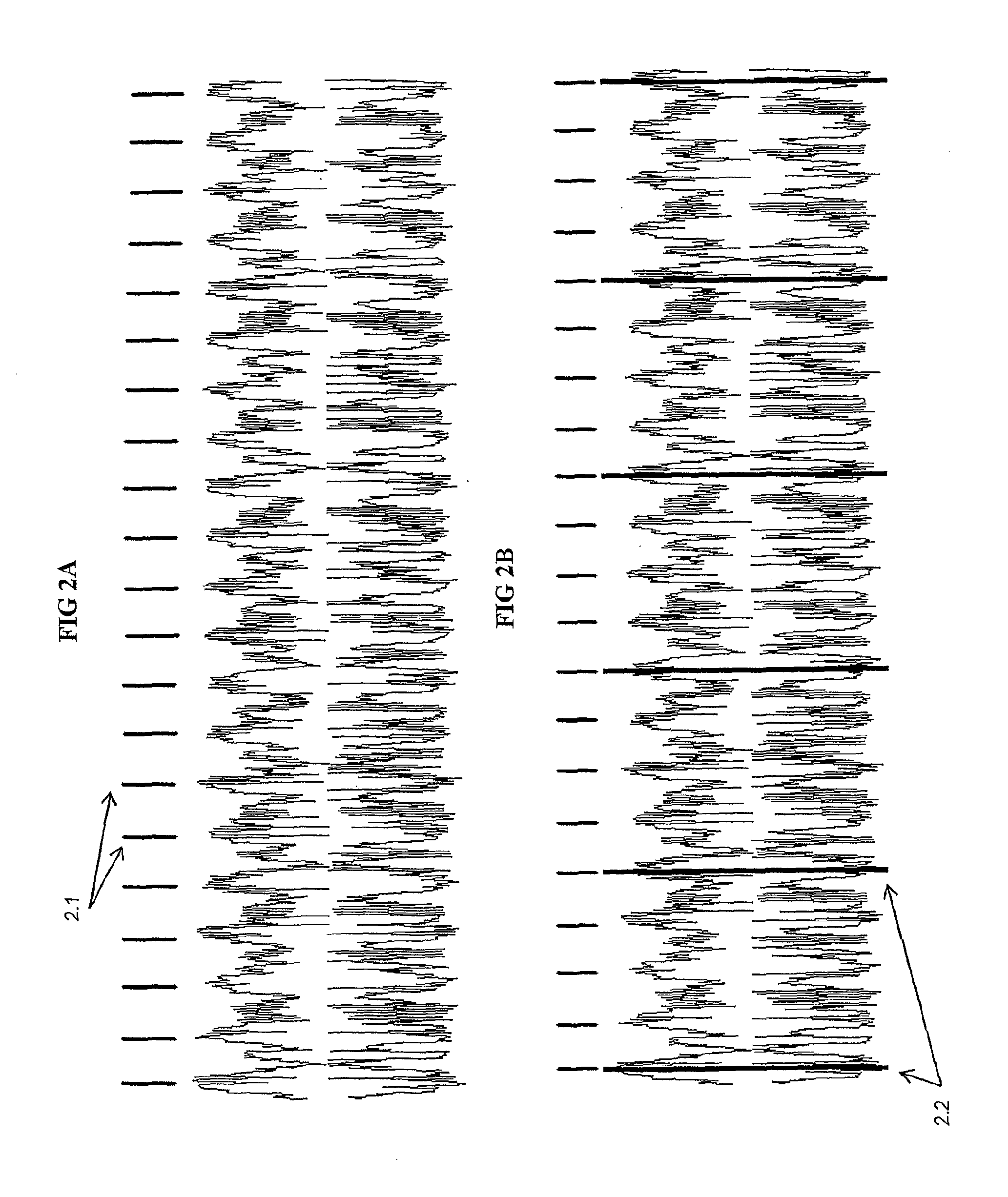
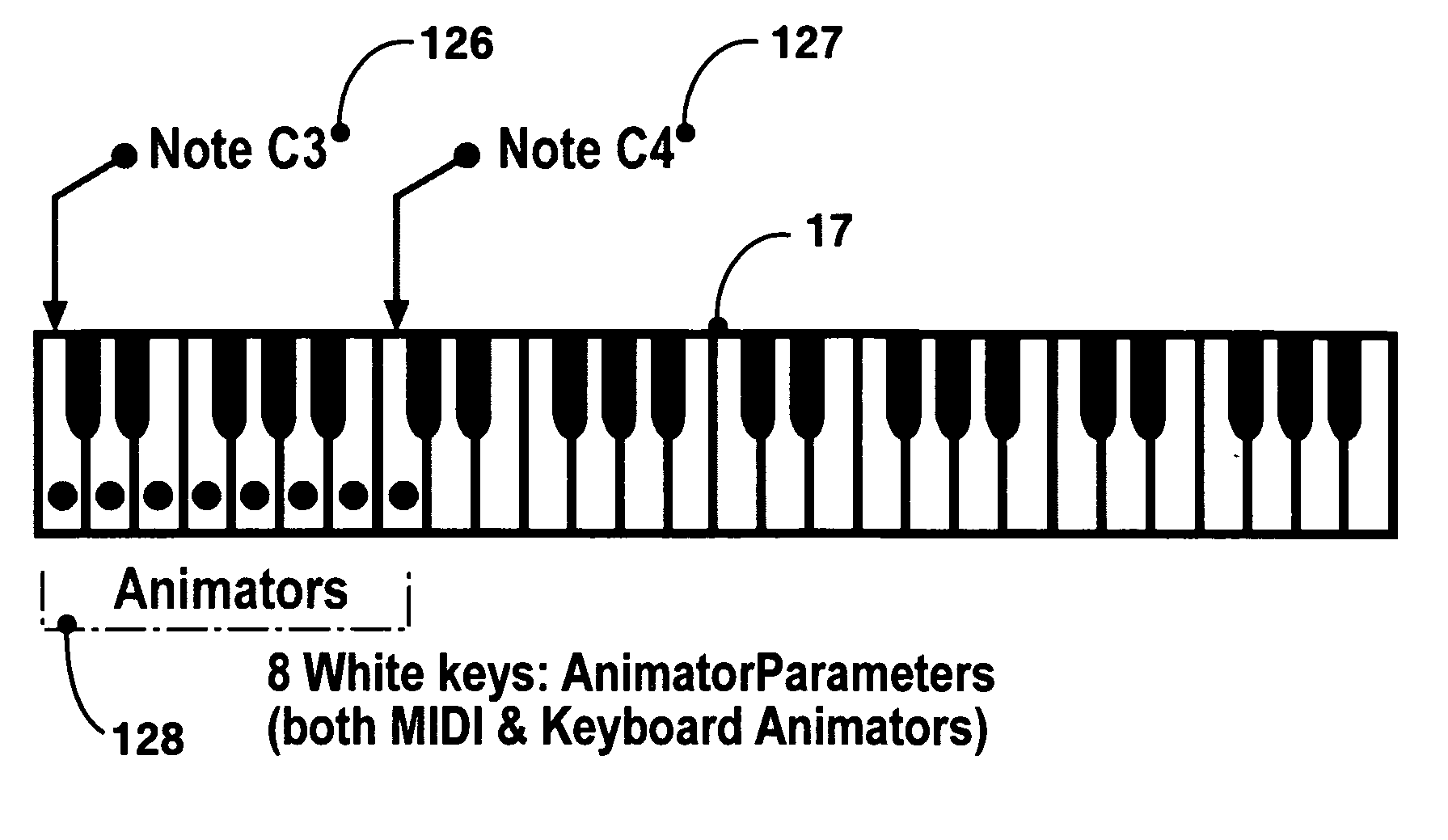
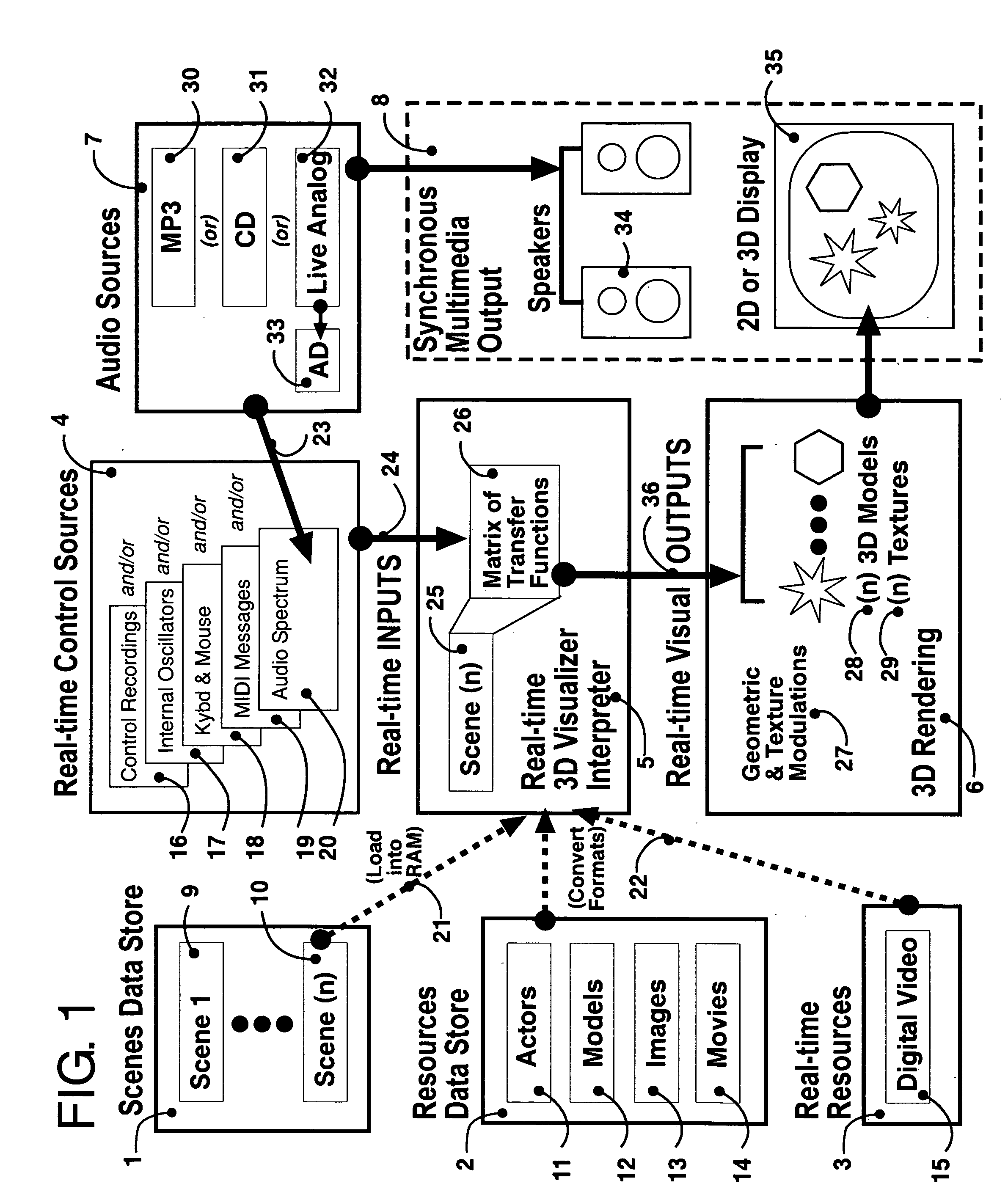
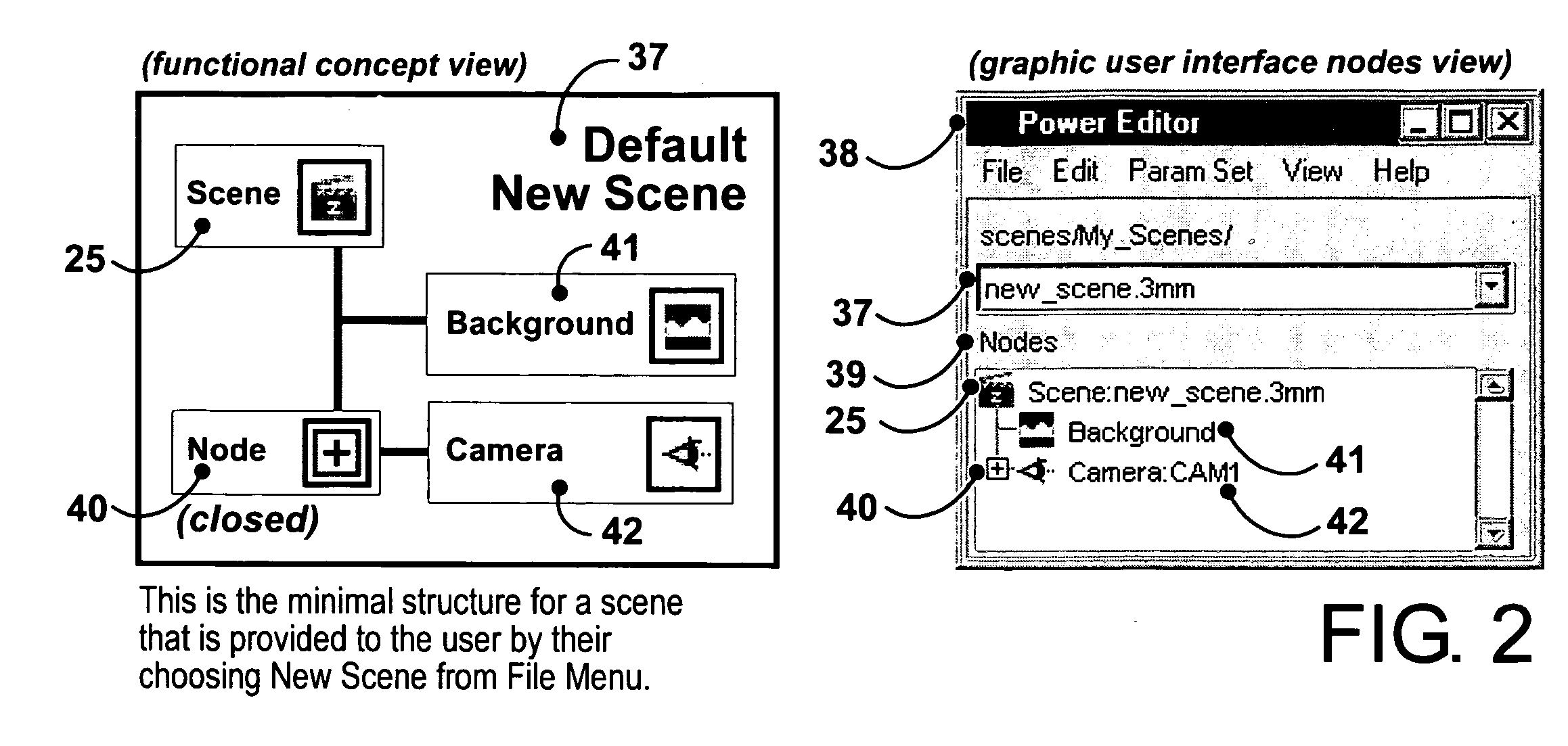
3D music visualization process employing a novel method of real-time reconfigurable control of 3D geometry and texture, employing blended control combinations of software oscillators, computer keyboard and mouse, audio spectrum, control recordings and MIDI protocol. The method includes a programmable visual attack, decay, sustain and release (V-ADSR) transfer function applicable to all degrees of freedom of 3D output parameters, enhancing even binary control inputs with continuous and aesthetic spatio-temporal symmetries of behavior. A “Scene Nodes Graph” for authoring content acts as a hierarchical, object-oriented graphical interpreter for defining 3D models and their textures, as well as flexibly defining how the control source blend(s) are connected or “Routed” to those objects. An “Auto-Builder” simplifies Scene construction by auto-inserting and auto-routing Scene Objects. The Scene Nodes Graph also includes means for real-time modification of the control scheme structure itself, and supports direct real-time keyboard / mouse adjustment to all parameters of all input control sources and all output objects. Dynamic control schemes are also supported such as control sources modifying the Routing and parameters of other control sources. Auto-scene-creator feature allows automatic scene creation by exploiting the maximum threshold of visualizer set of variables to create a nearly infinite set of scenes. A Realtime-Network-Updater feature allows multiple local and / or remote users to simultaneously co-create scenes in real-time and effect the changes in a networked community environment where in universal variables are interactively updated in real-time thus enabling scene co-creation in a global environment. In terms of the human subjective perception, the method creates, enhances and amplifies multiple forms of both passive and interactive synesthesia. The method utilizes transfer functions providing multiple forms of applied symmetry in the control feedback process yielding an increased level of perceived visual harmony and beauty. The method enables a substantially increased number of both passive and human-interactive interpenetrating control / feedback processes that may be simultaneously employed within the same audio-visual perceptual space, while maintaining distinct recognition of each, and reducing the threshold of human ergonomic effort required to distinguish them even when so coexistent. Taken together, these novel features of the invention can be employed (by means of considered Scene content construction) to realize an increased density of “orthogonal features” in cybernetic multimedia content. This furthermore increases the maximum number of human players who can simultaneously participate in shared interactive music visualization content while each still retaining relatively clear perception of their own control / feedback parameters.
Owner:VASAN SRINI +2
Generating music and sound that varies from playback to playback
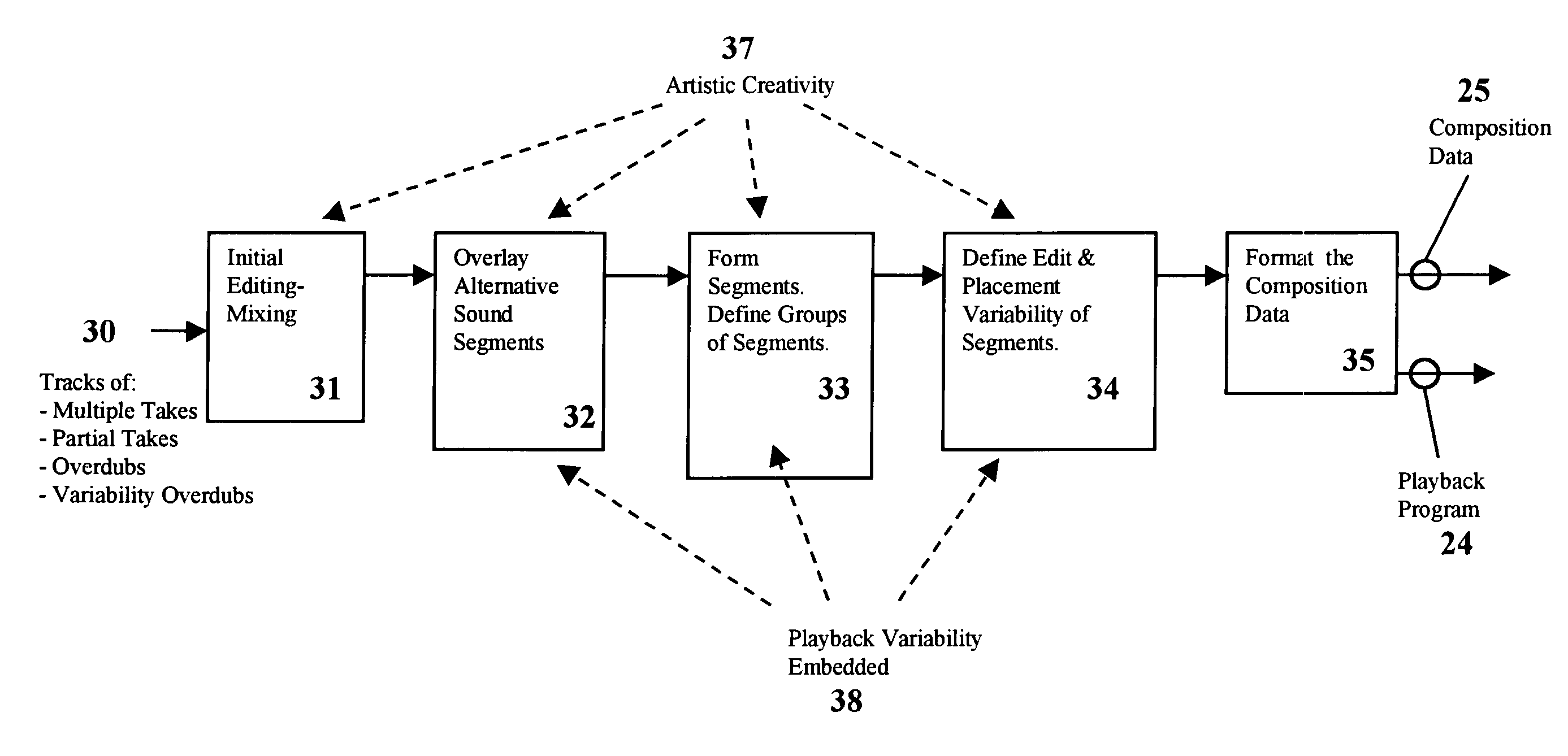
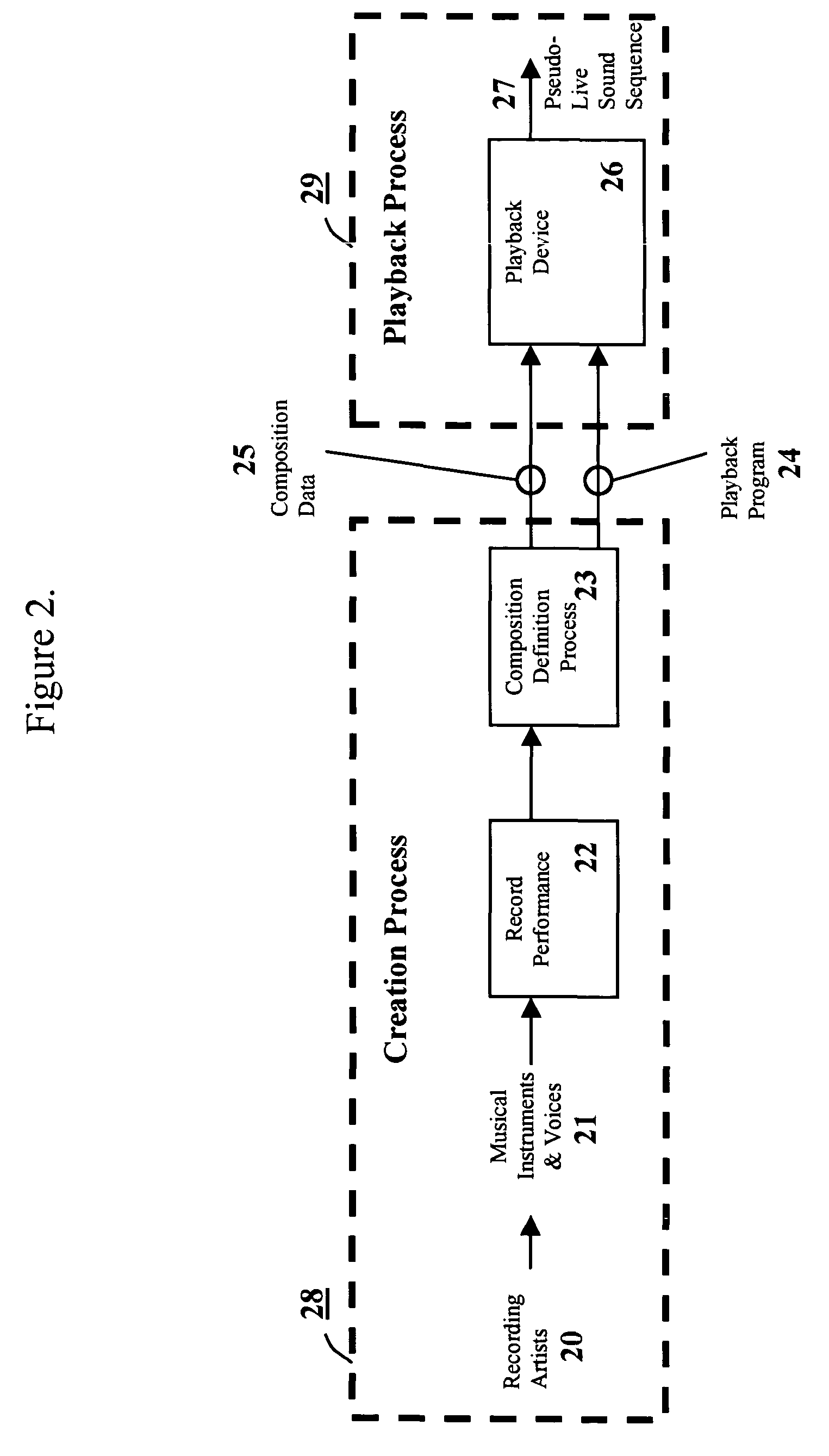
A method and apparatus for the creation and playback of music, audio and sound; such that each time a composition is played back, a different sound sequence is generated in the manner previously defined by the artist. During composition creation, the artist's definition of how the composition will vary from playback to playback is embedded into the composition data set. During playback, the composition data set is processed by a playback device incorporating a playback program, so that each time the composition is played back a unique version is generated. Variability occurs during playback per the artist's composition data set, which specifies: the spawning of group(s) from a snippet; the selection of snippet(s) from each group; editing of snippets; flexible and variable placement of snippets; and the combining and / or mixing of multiple snippets to generate each time sample in one or more channels. MIDI-like variable compositions and the variable use of segments comprised of MIDI-like command sequences are also disclosed.
Owner:SYNERGYZE TECH LLC
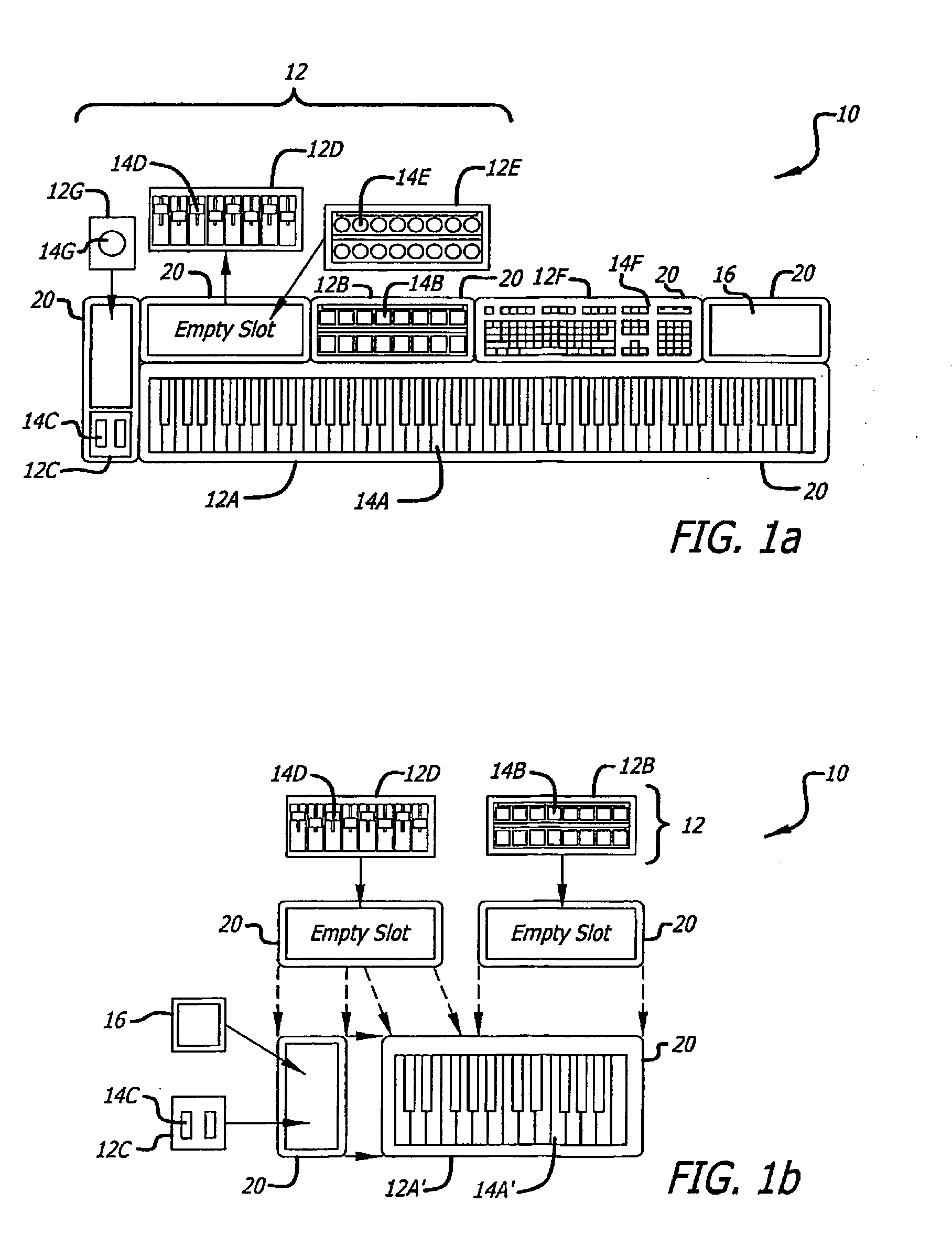
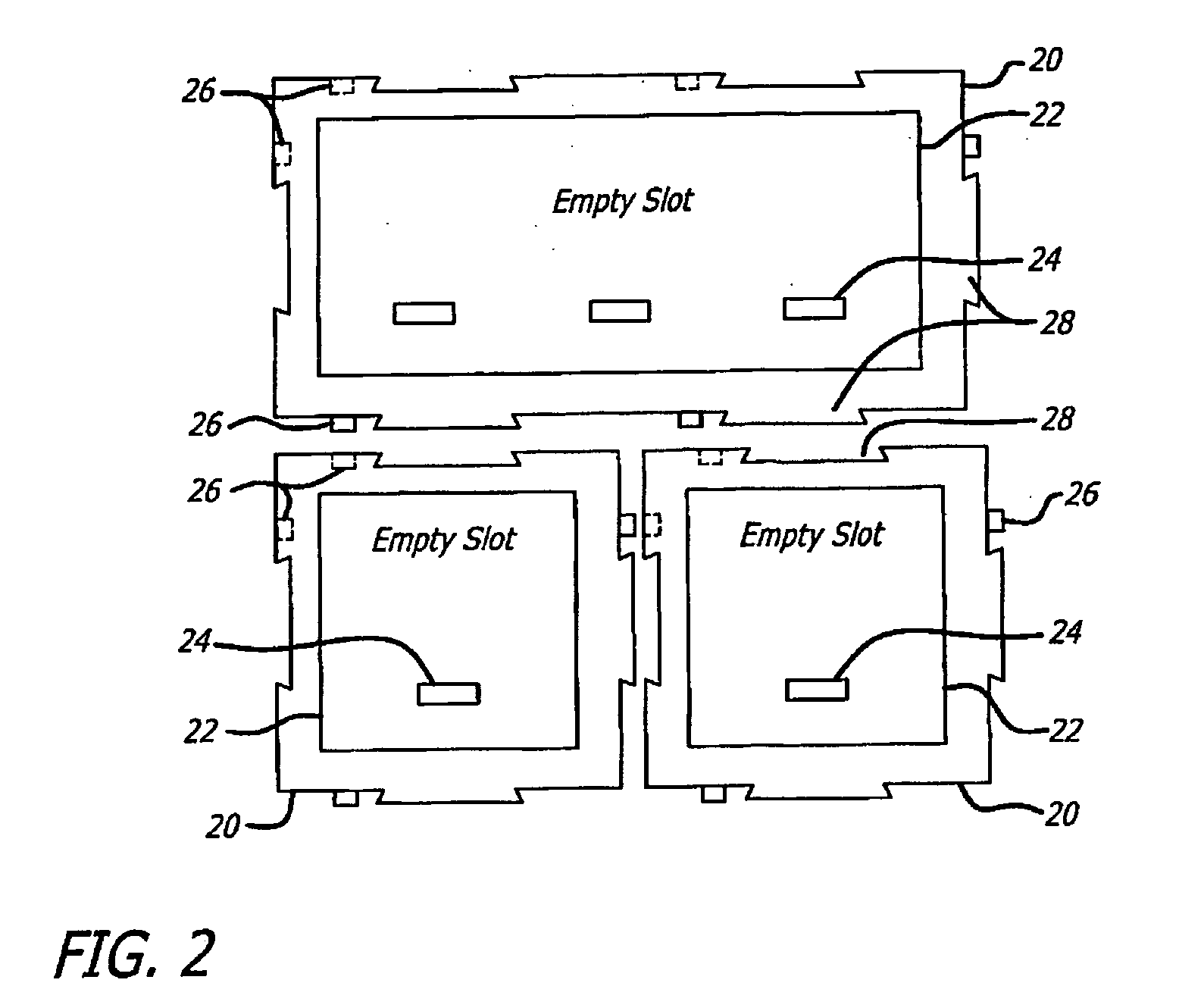
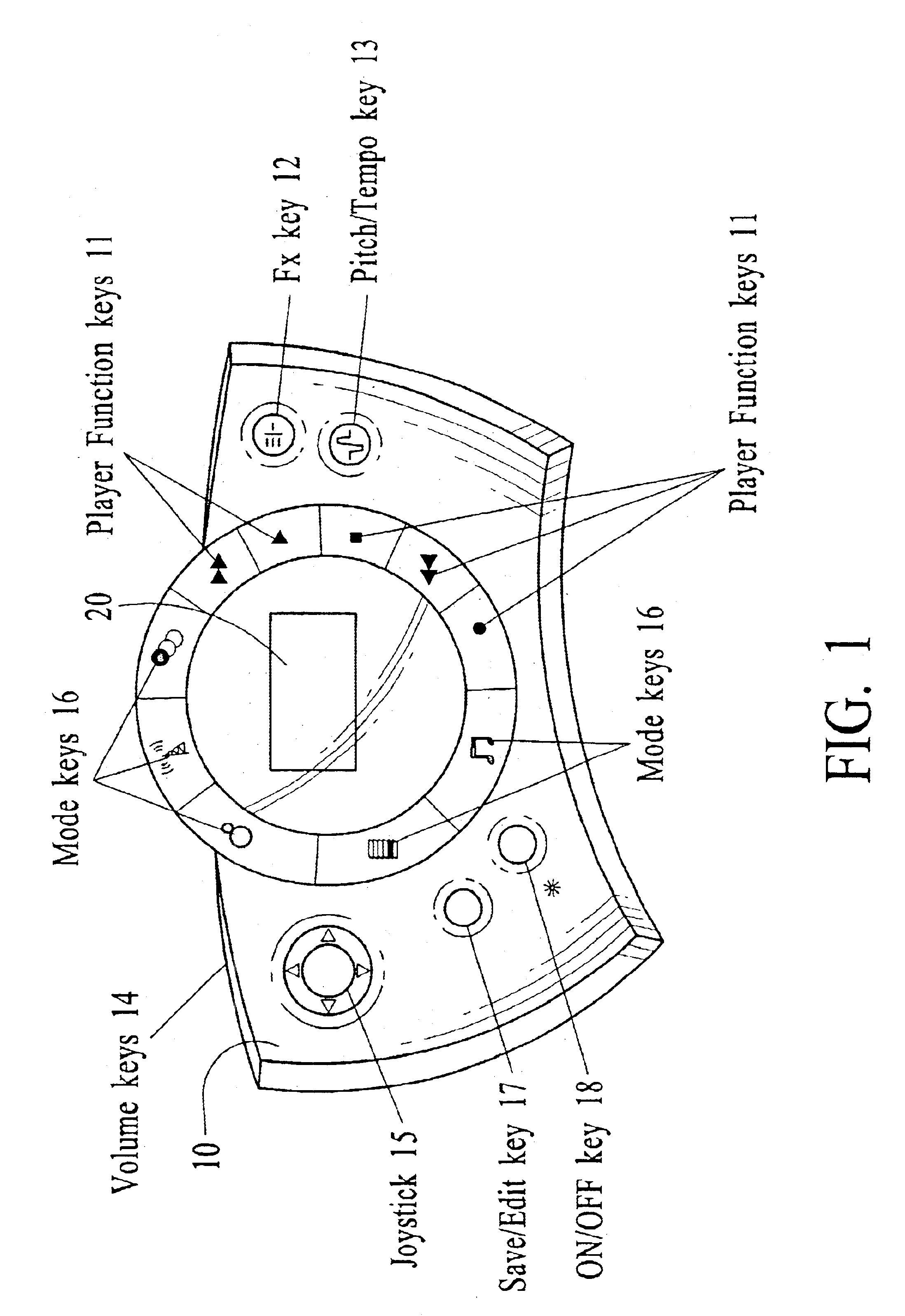
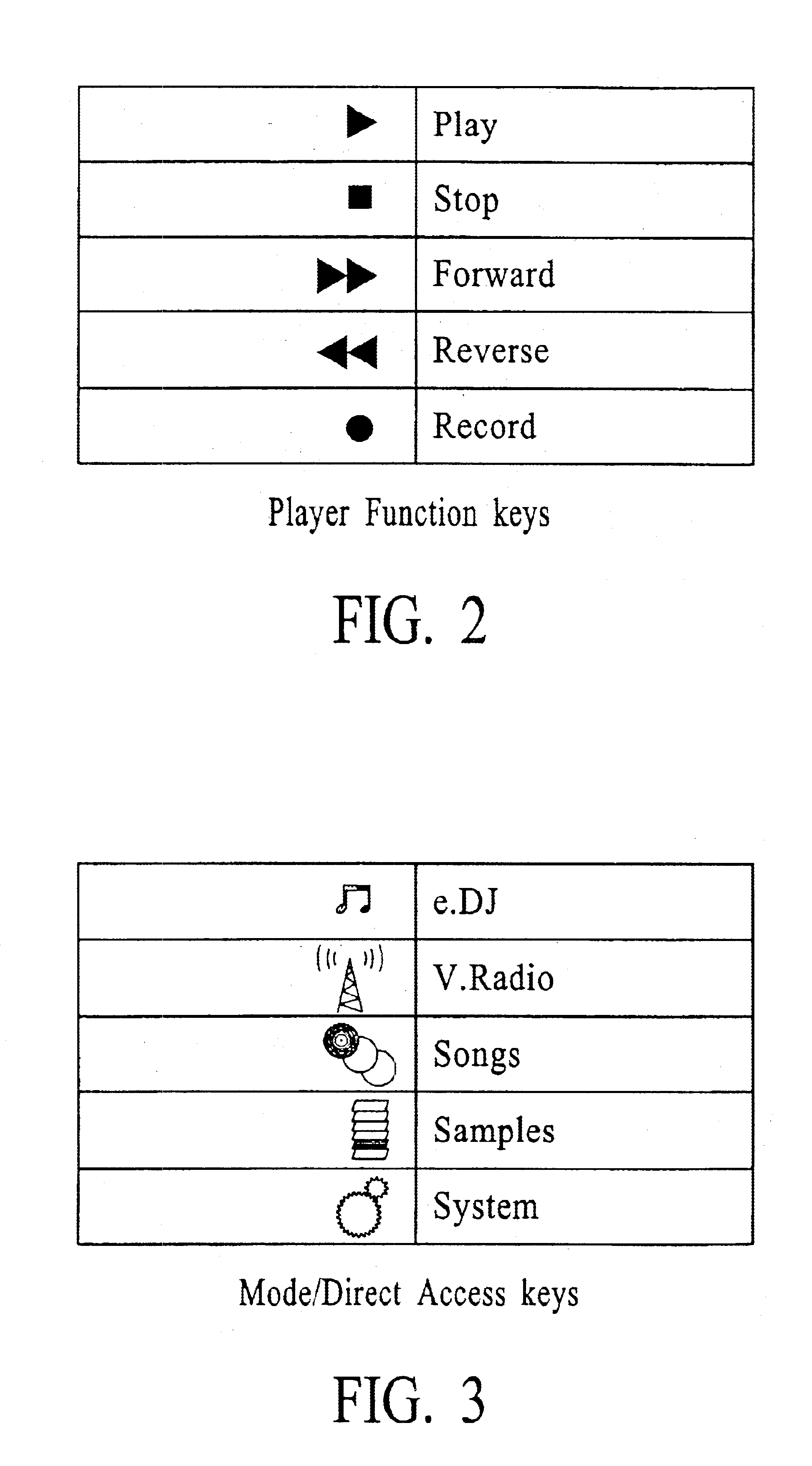
Modular MIDI controller
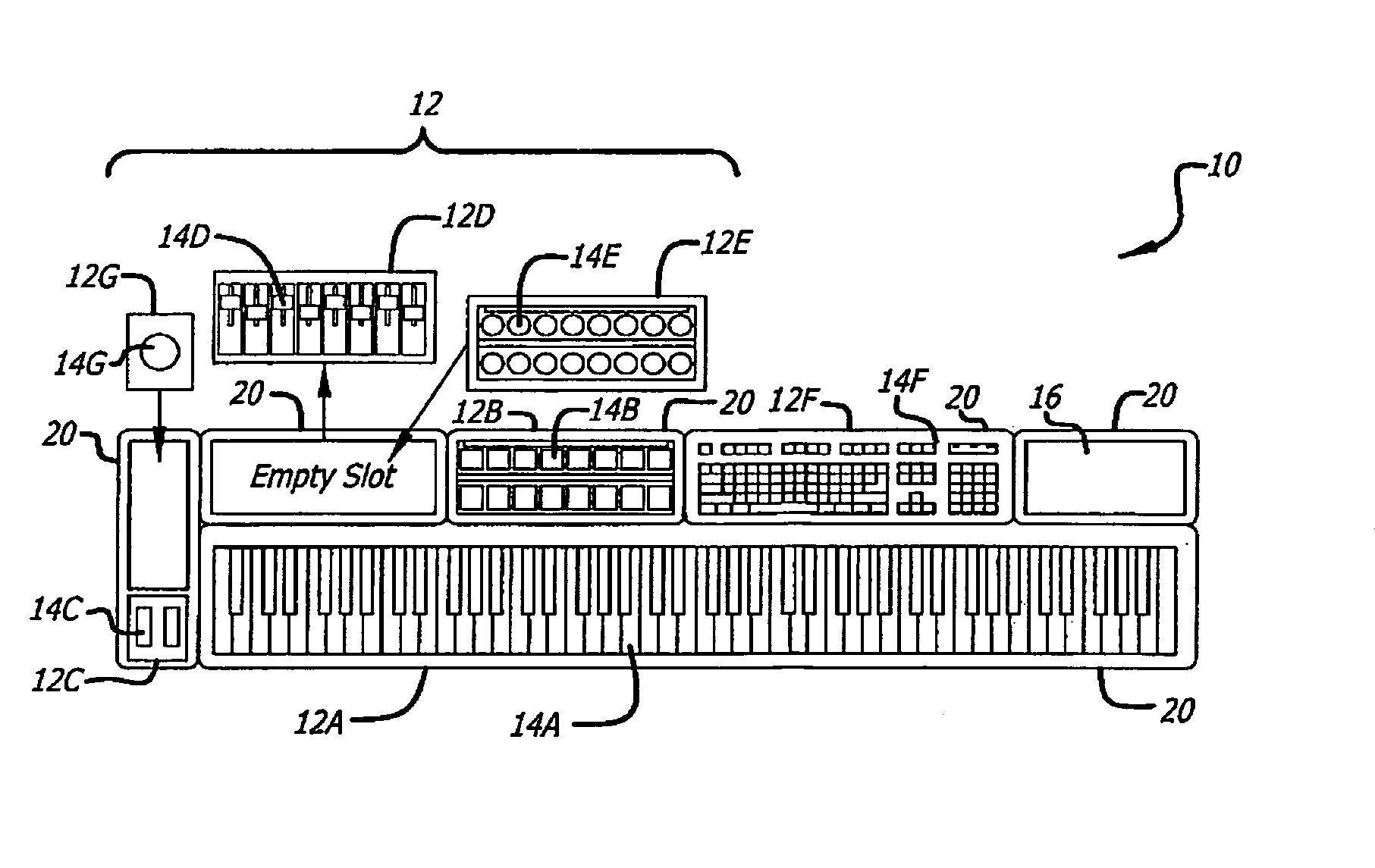
InactiveUS20090301289A1Easy to reconfigureElectrophonic musical instrumentsElectricityComputer module
A modular MIDI controller. The novel controller includes two or more modules, each module including a plurality of controls, and a mechanism for connecting the modules together to form one unit. In an illustrative embodiment, each control is adapted to convert a mechanical action by a user into an electrical signal, and each module includes a processor adapted to convert the electrical signals from the controls into control messages. A system control unit receives the control messages from each module and generates a corresponding MIDI output. In a preferred embodiment, the controller includes a plurality of chassis connected together to form a controller having a desired size and shape. Each chassis is adapted to hold one or more modules and may include a slot for holding one or more removable modules.
Owner:GYNES DESHKO
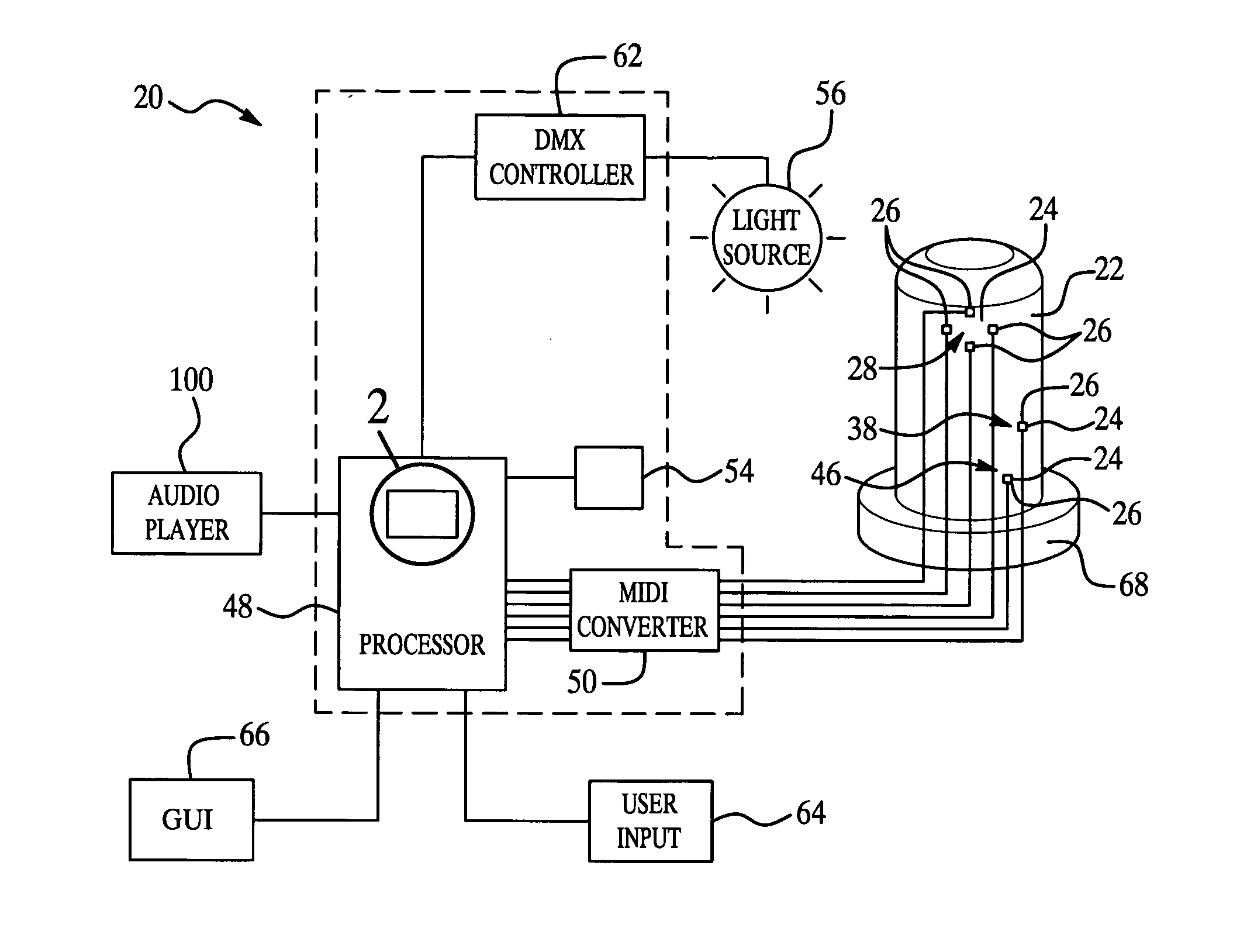
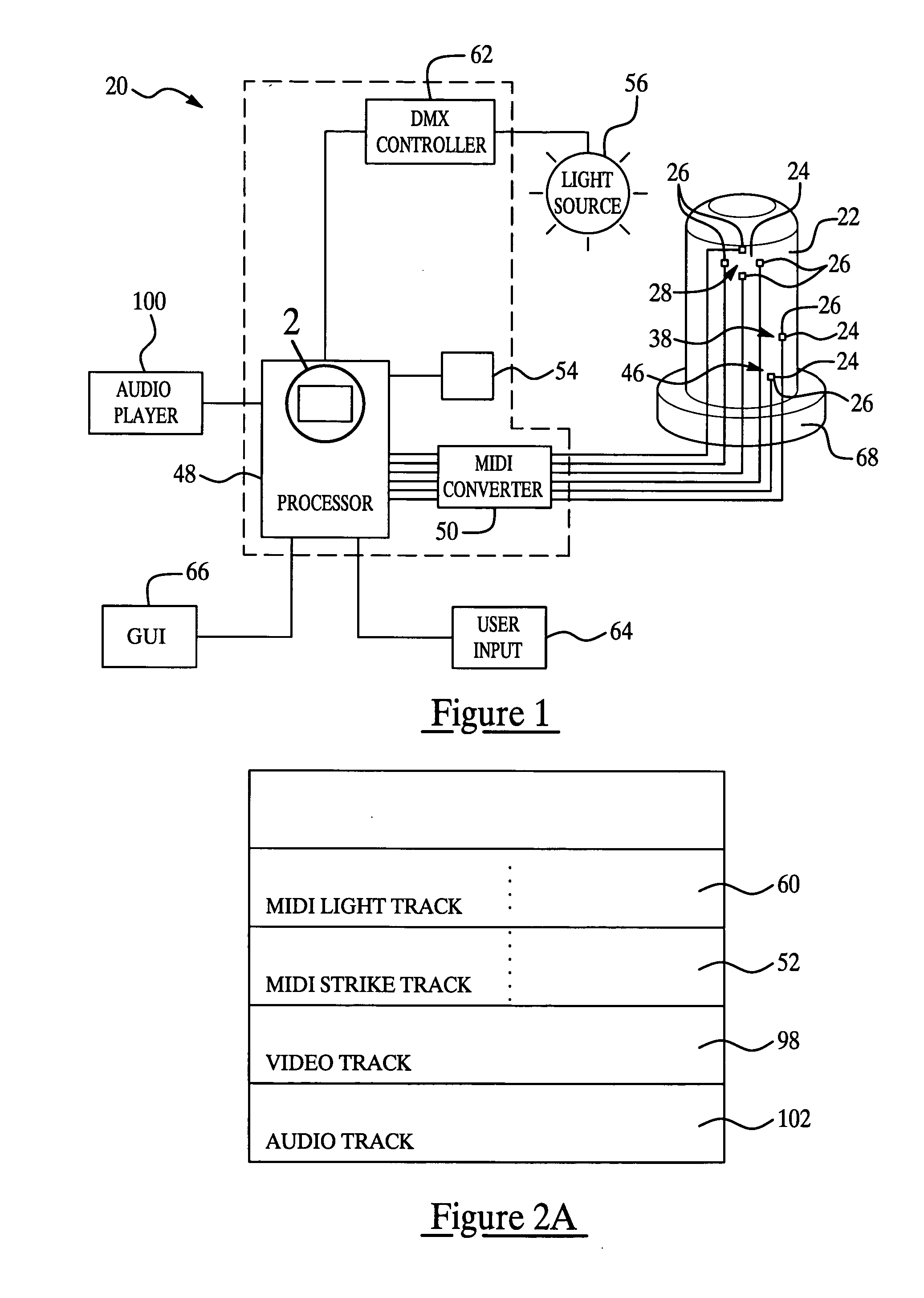
Exercise unit and system utilizing MIDI signals
InactiveUS20050288159A1High level of interactionHigh level of feedbackCombat sportsMuscle exercising devicesDigital interfaceEngineering
An exercise unit (20) and system (104) comprising a target (22) having at least one area (24) to be stuck by a user and at least one sensor (26) located at the area (24) is disclosed. The sensor (26) generates an electrical signal in response to being struck by the user. A processor (48) is in operative communication with the sensor (26) and a musical instrument digital interface (MIDI) converter (50) is disposed between the sensor (26) and the processor (48). The MIDI converter (50) converts the electrical signal from the sensor (26) to a MIDI signal and transmits the MIDI signal to the processor (48) for generating a MIDI strike track (52). The MIDI strike track (52) is used to determine an accuracy and a force of the strike by the user to provide interaction and feedback to the user to continue to help motivate the user.
Owner:TACKETT JOSEPH A
Method and device for incorporating additional information into main information through electronic watermaking technique
InactiveUS6959383B1Small sizeEffective informationElectrophonic musical instrumentsUser identity/authority verificationData segmentComputer science
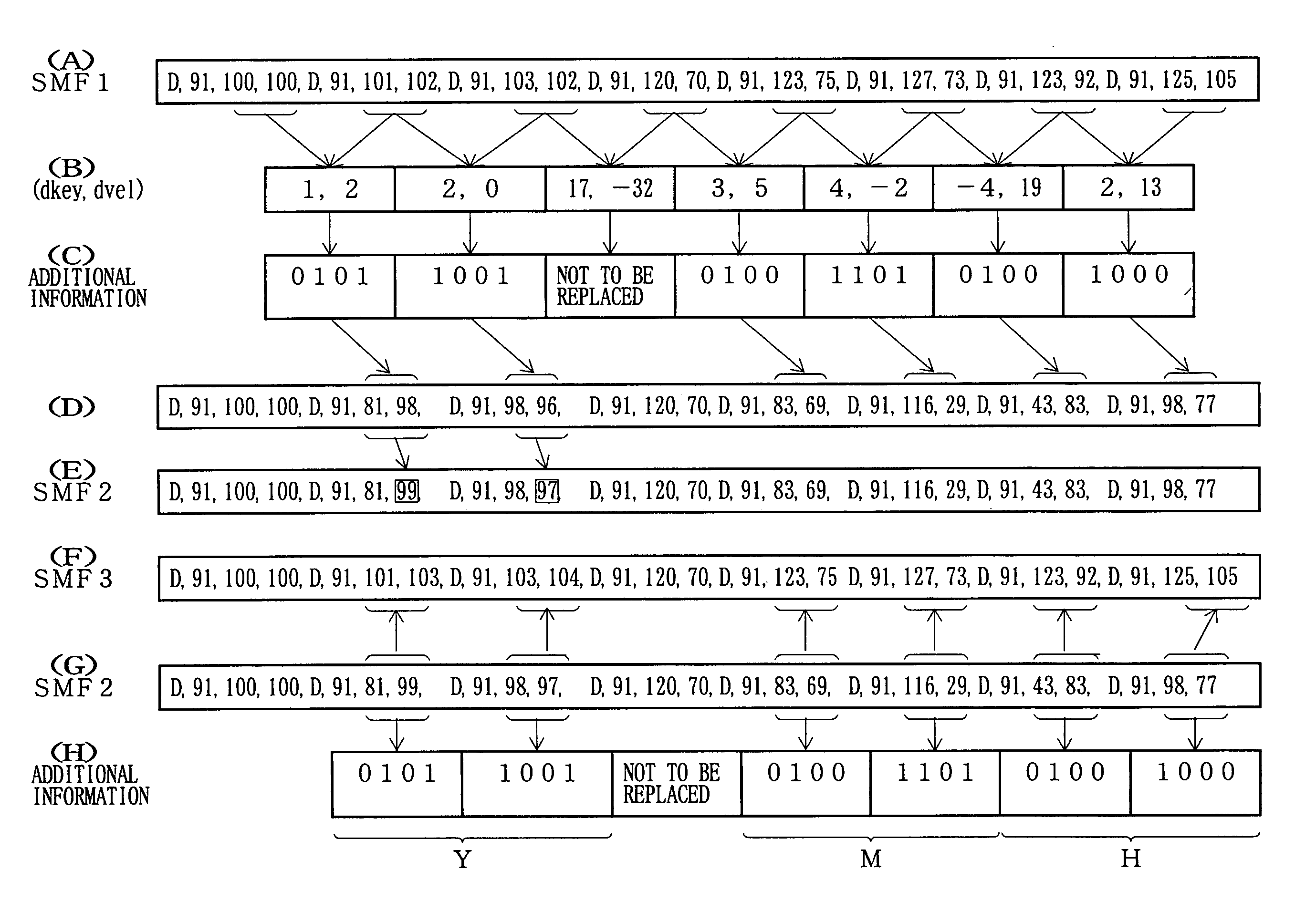
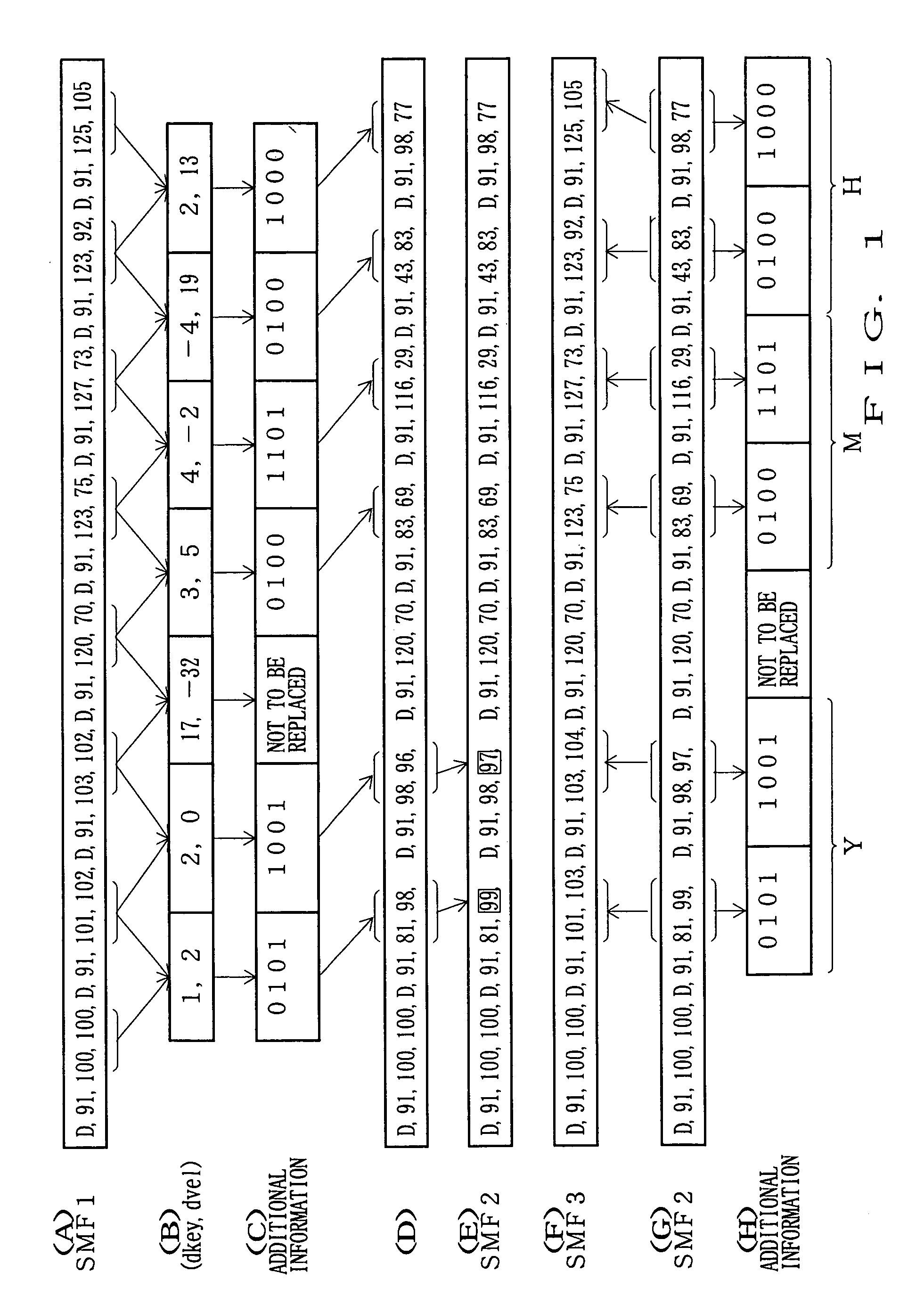
Two data units are selected from main information, such as MIDI data, into which additional information is to be incorporated, to calculate a difference between respective values of the two data units. A particular data segment to be incorporated into one of the MIDI data units is selected from a group of data of additional information. The size of the data segment to be incorporated into one of the data units may be either one bit or two or more bits. Substitute data to replace the content of one MIDI data unit is generated on the basis of a predetermined function using, as variables, the data-related value and a value of the particular data segment, and the content of the data unit corresponding to a predetermined one of the two MIDI data units is replaced by the generated substitute data. Thus, through such an electronic watermarking technique, any desired additional information can be incorporated into the MIDI data without changing the MIDI data format. In another implementation, data of encoding information, representative of an encoding procedure, are incorporated dispersedly into particular data units belonging to a predetermined first data group of the main information, and data belonging to a predetermined second data group of the main information are encoded by the encoding procedure represented by the encoding information.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Separate-type musical performance system for synchronously producing sound and visual images and audio-visual station incorporated therein
A separate-type music performance system has a master audio-visual station and a slave audio-visual station remote from the mater audio-visual station and connected through two communication channel independently of each other; MIDI music data codes and click time data codes are transmitted through one of the communication channels to the slave audio-visual station, and audio-visual data codes and a click signal are transmitted through the other communication channel; when the click signal and click time data code arrive the slave audio-visual station, the clock setter 21e sets an internal clock with the click time data code paired with the click signal, and the MIDI music data code are transferred to an automatic player piano in comparison with the time data and the internal clock, whereby the tones are produced synchronously with the visual images.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Systems and methods for creating, modifying, interacting with and playing musical compositions
InactiveUS6897368B2Easy to createEasy to modifyGearworksMusical toysDisplay deviceComposition process
Systems and methods for creating, modifying, interacting with and playing music are provided, particularly systems and methods employing a top-down process, where the user is provided with a musical composition that may be modified and interacted with and played and / or stored (for later play). The system preferably is provided in a handheld form factor, and a graphical display is provided to display status information, graphical representations of musical lanes or components which preferably vary in shape as musical parameters and the like are changed for particular instruments or musical components such as a microphone input or audio samples. An interactive auto-composition process preferably is utilized that employs musical rules and preferably a pseudo random number generator, which may also incorporate randomness introduced by timing of user input or the like, the user may then quickly begin creating desirable music in accordance with one or a variety of musical styles, with the user modifying the auto-composed (or previously created) musical composition, either for a real time performance and / or for storing and subsequent playback. The graphic information preferably is customizable by a user, such as by way of a companion software program, which preferably runs on a PC and is coupled to the system via an interface such as a USB port. A modified MIDI representation of music is employed, preferably, for example, in which musical rule information is embedded in MIDI pitch data, and in which sound samples may be synchronized with MIDI events in a desirable and more optimum manner. The system architecture preferably includes a microprocessor for controlling the overall system operation. A synthesizer / DSP preferably is provided in order to generate audio streams. Non-volatile memory preferably is provided for storing sound banks. Preferably removable non-volatile storage / memory is provided to store configuration files, song lists and samples, and optionally sound bank optimization or sound bank data. A codec preferably is provided for receiving microphone input and for providing audio output. A radio tuner preferably is provided so that output from the radio tuner may be mixed, for example, with auto-composed songs created by the system, which preferably includes a virtual radio mode of operation.
Owner:MEDIALAB SOLUTIONS
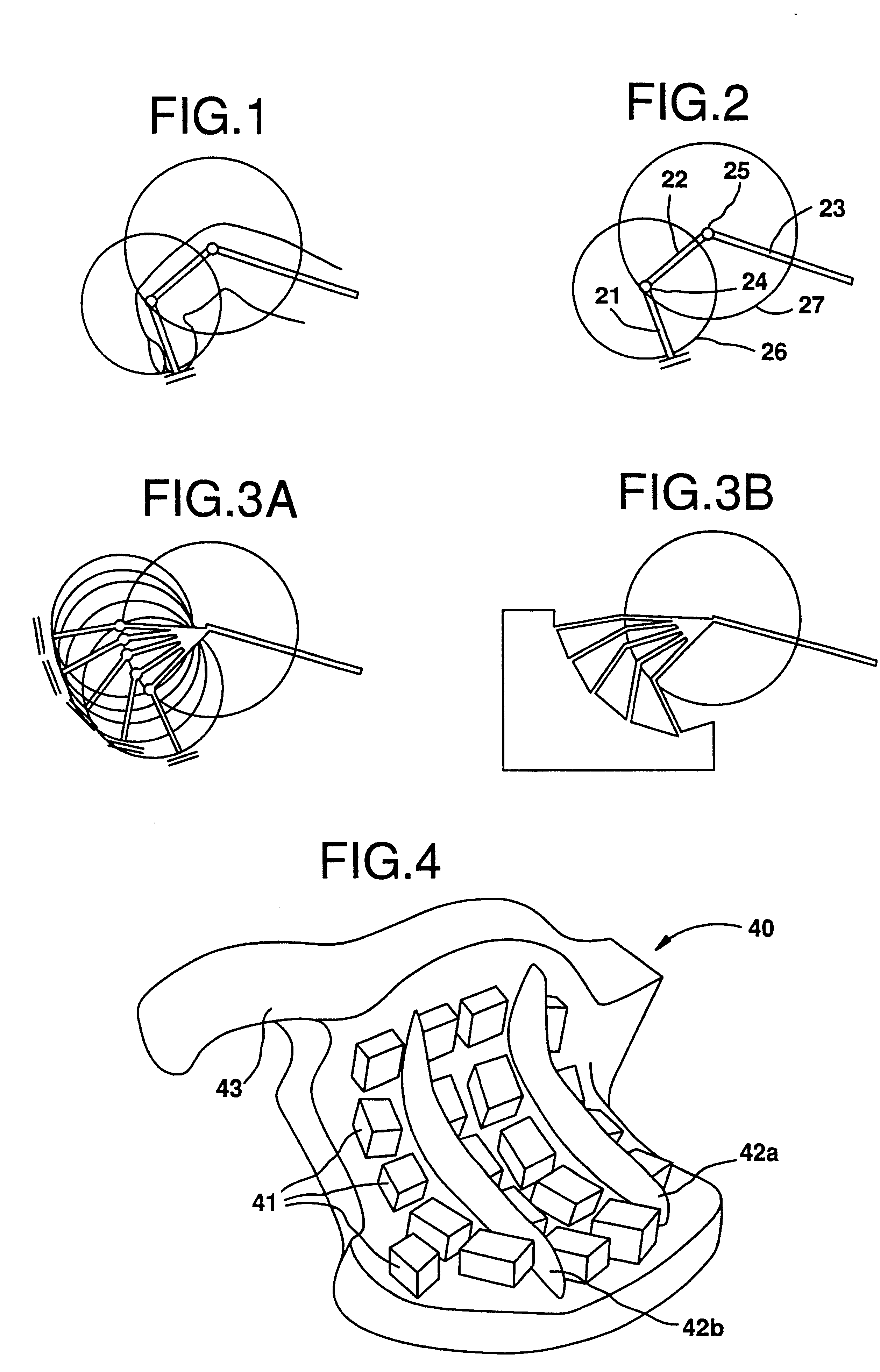
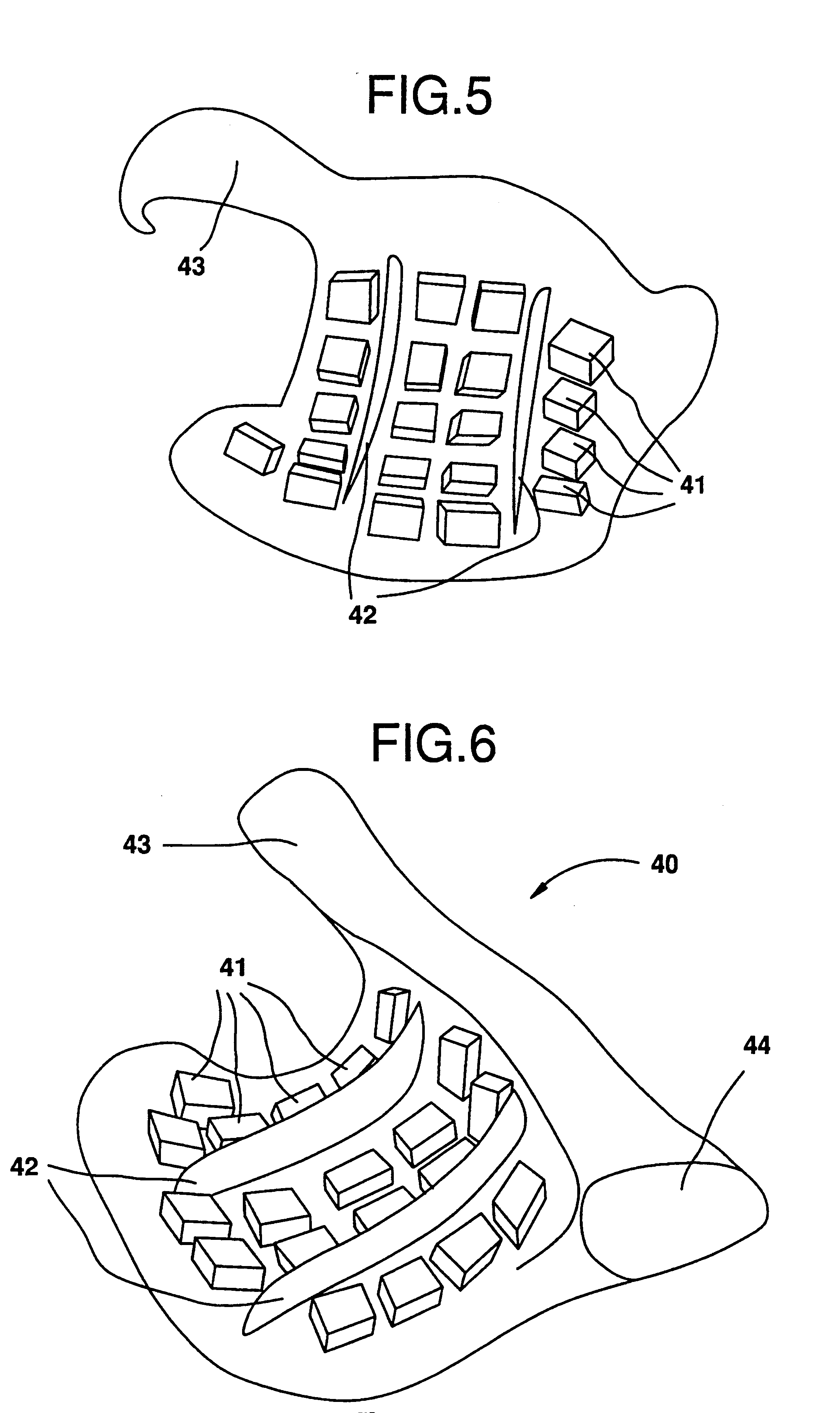
Wearable sensor matrix system for machine control
InactiveUS7273979B2Easy to controlHigh degreeElectrophonic musical instrumentsContact surface shape/structureSensor arrayMachine control
Owner:CHRISTENSEN EDWARD LEE
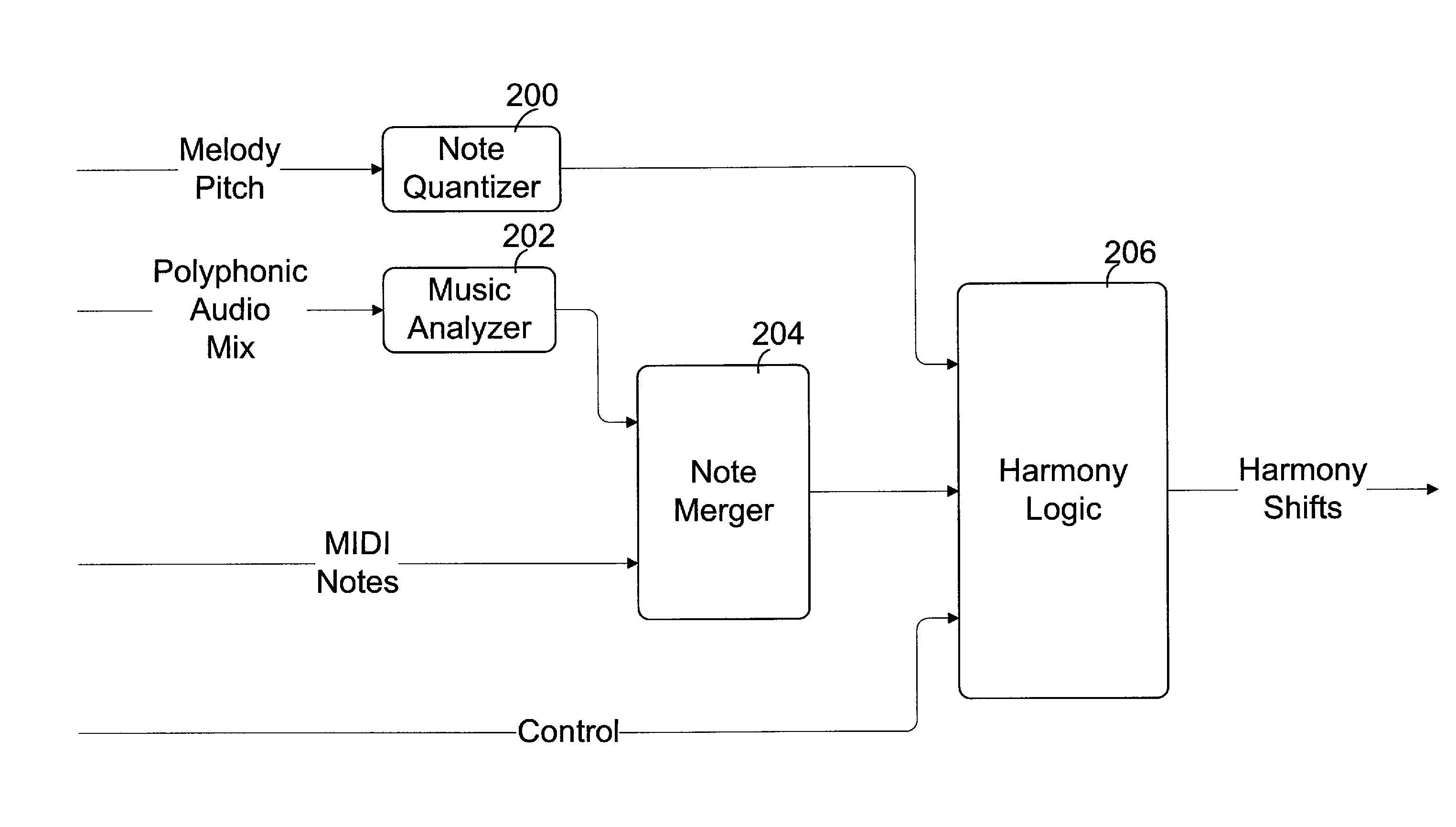
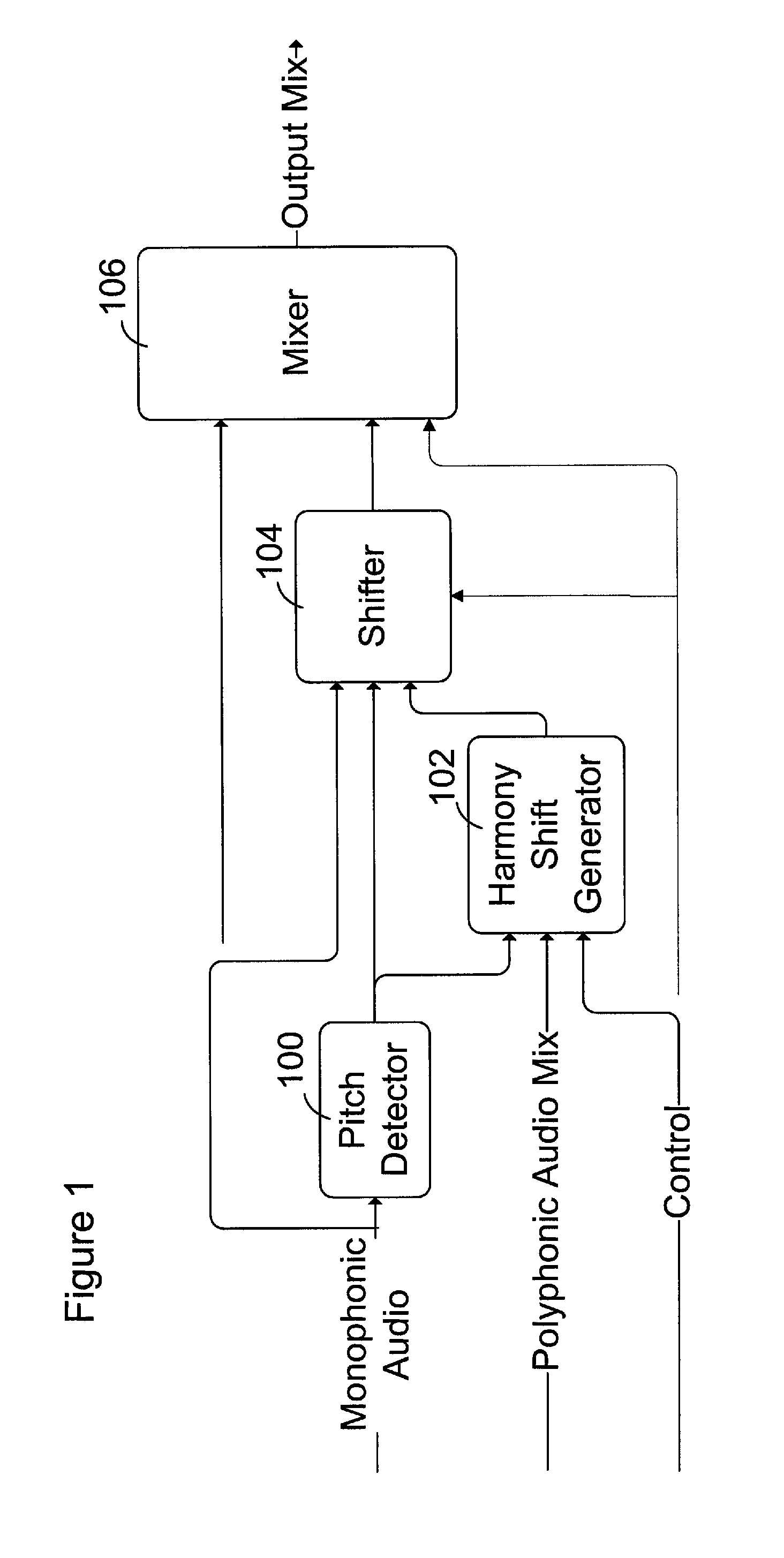
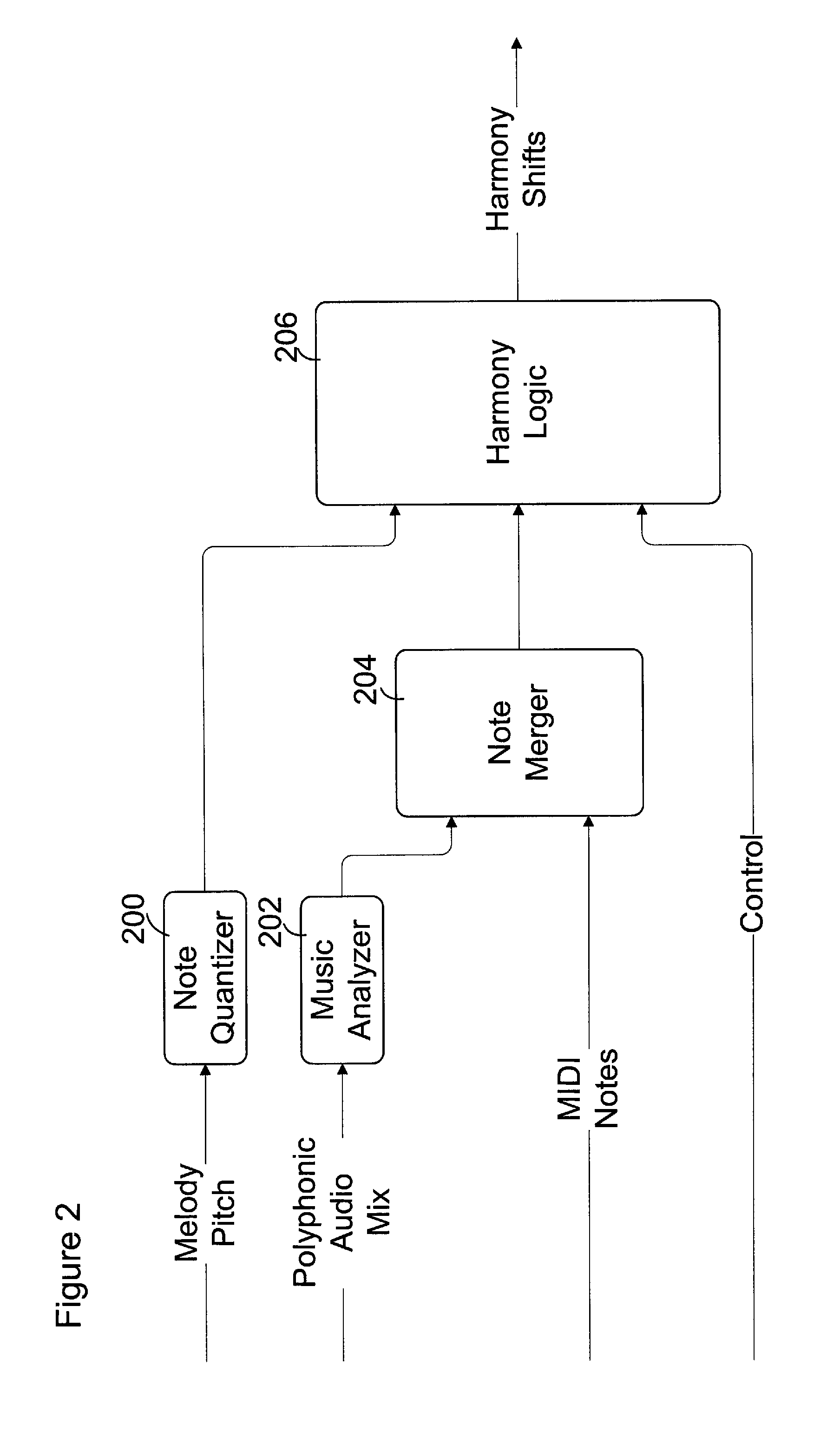
Musical harmony generation from polyphonic audio signals
Melody and accompaniment audio signals are received and processed to identify one or more harmony notes and a harmony signal is produced based on the one or more harmony notes. Typically the melody note is identified and a spectrum of the accompaniment audio signal and is obtained, and one or more harmony notes are identified based on the melody note and the accompaniment spectrum. The melody, and accompaniment signals can be processed in real-time for combination with the harmony signal in an audio performance. In some examples, audio signals are processed and harmonies generated for subsequent performance based on, for example, MIDI files generated from the audio signals.
Owner:COR TEK
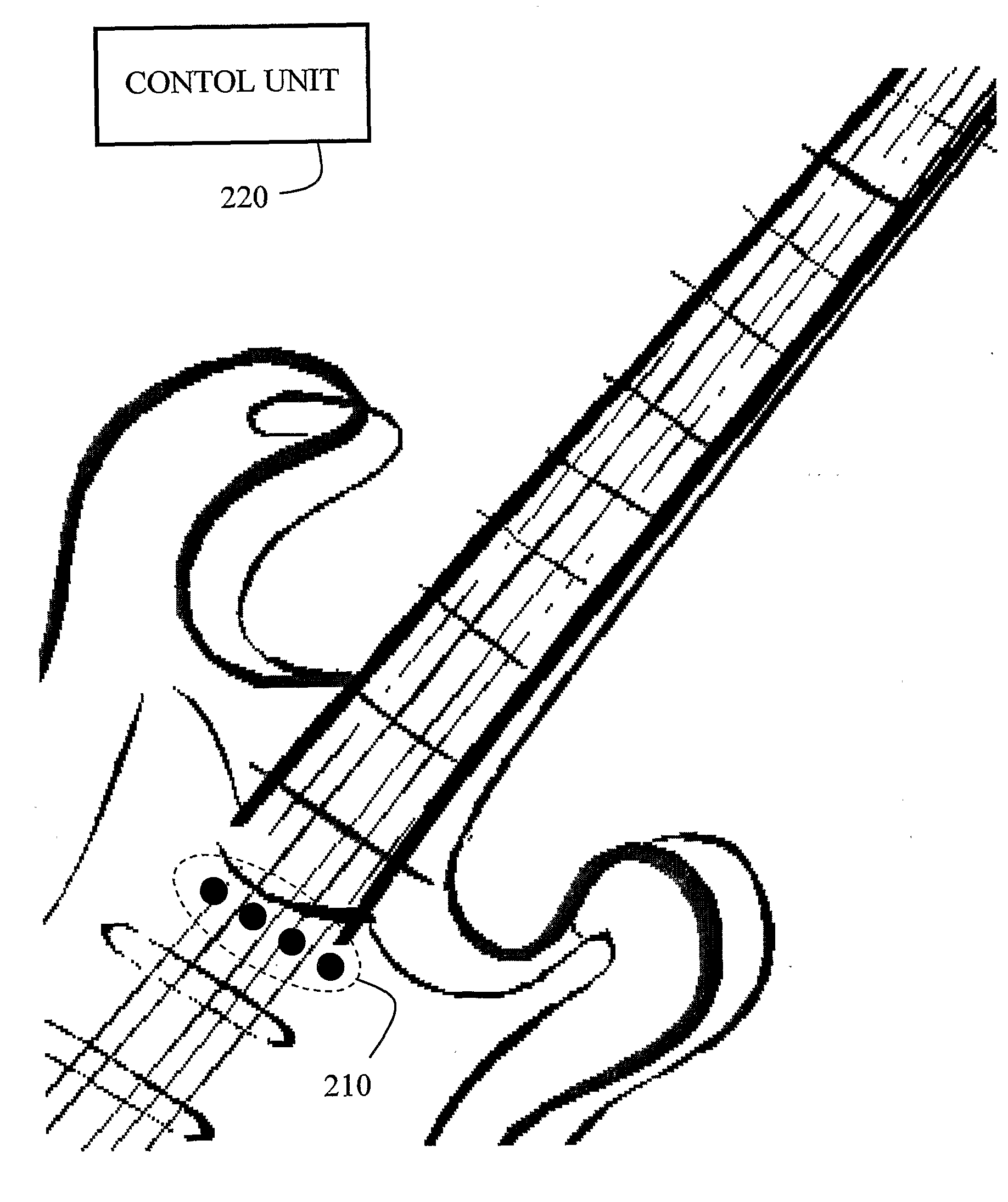
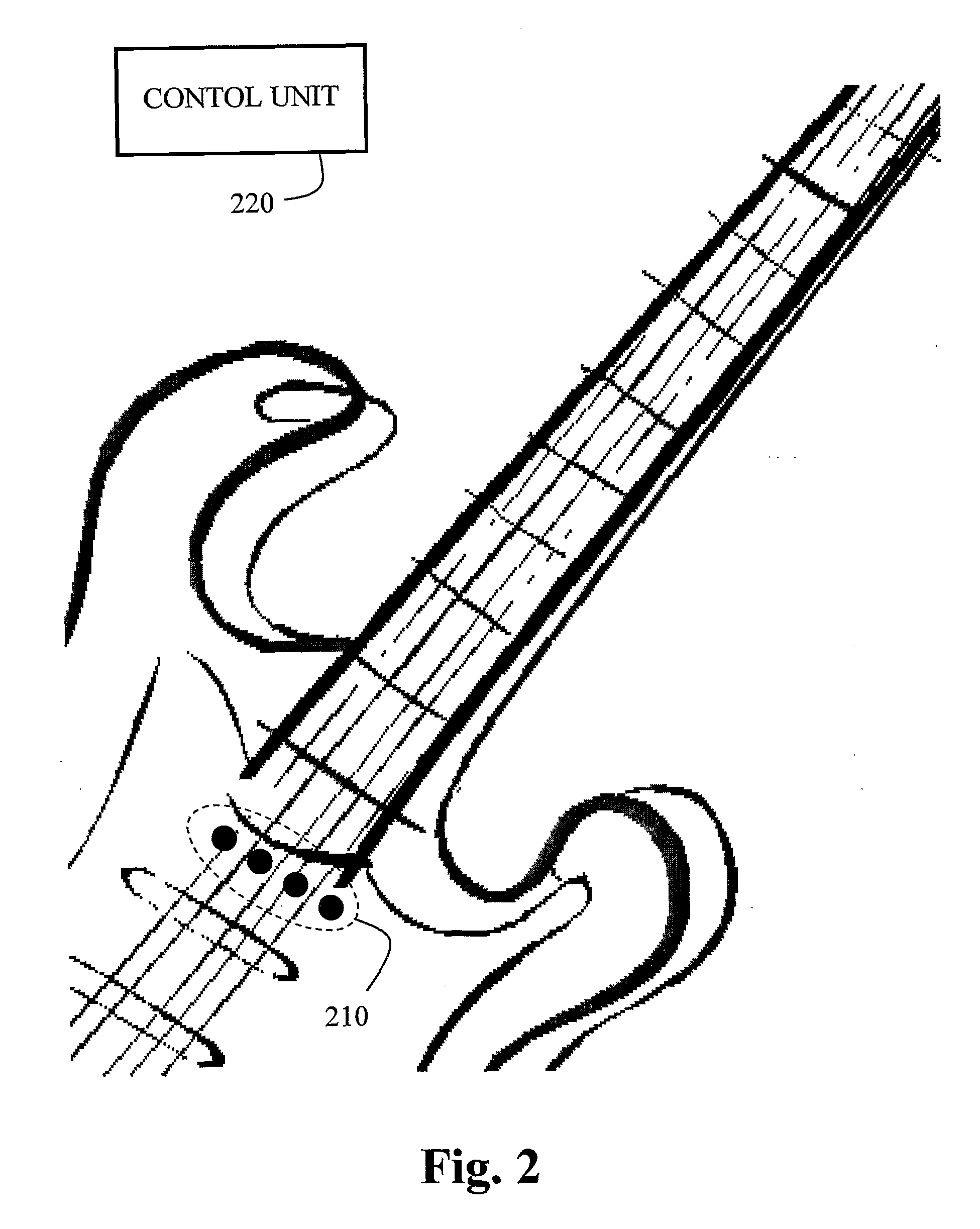
Method and System for Reproducing Sound and Producing Synthesizer Control Data from Data Collected by Sensors Coupled to a String Instrument
InactiveUS20080282873A1Mean of controlAccurate predictionElectrophonic musical instrumentsSound generationControl data
A method and system for producing synthesizer and MIDI control data and for reconstructing and reproducing a signal from data collected by sensors coupled to a string instrument comprising a plurality of sensors coupled to the string instrument and a control unit that is associated with the plurality of sensors. The sensors are adapted to collect temporal and spatial data referring to performer's actions and to the sound generation process of the string instrument, specifically as to string deflection along time, while the control unit is adapted to process the data and generate a signal corresponding to the sound characteristics of the performer's playing and actions on the string instrument.
Owner:KOTTON GIL +2
System and method for the creation and playback of animated, interpretive, musical notation and audio synchronized with the recorded performance of an original artist
InactiveUS20060032362A1Promote enjoymentEasy to appreciateGearworksMusical toysAnimationComputer science
Owner:FIVER LLC
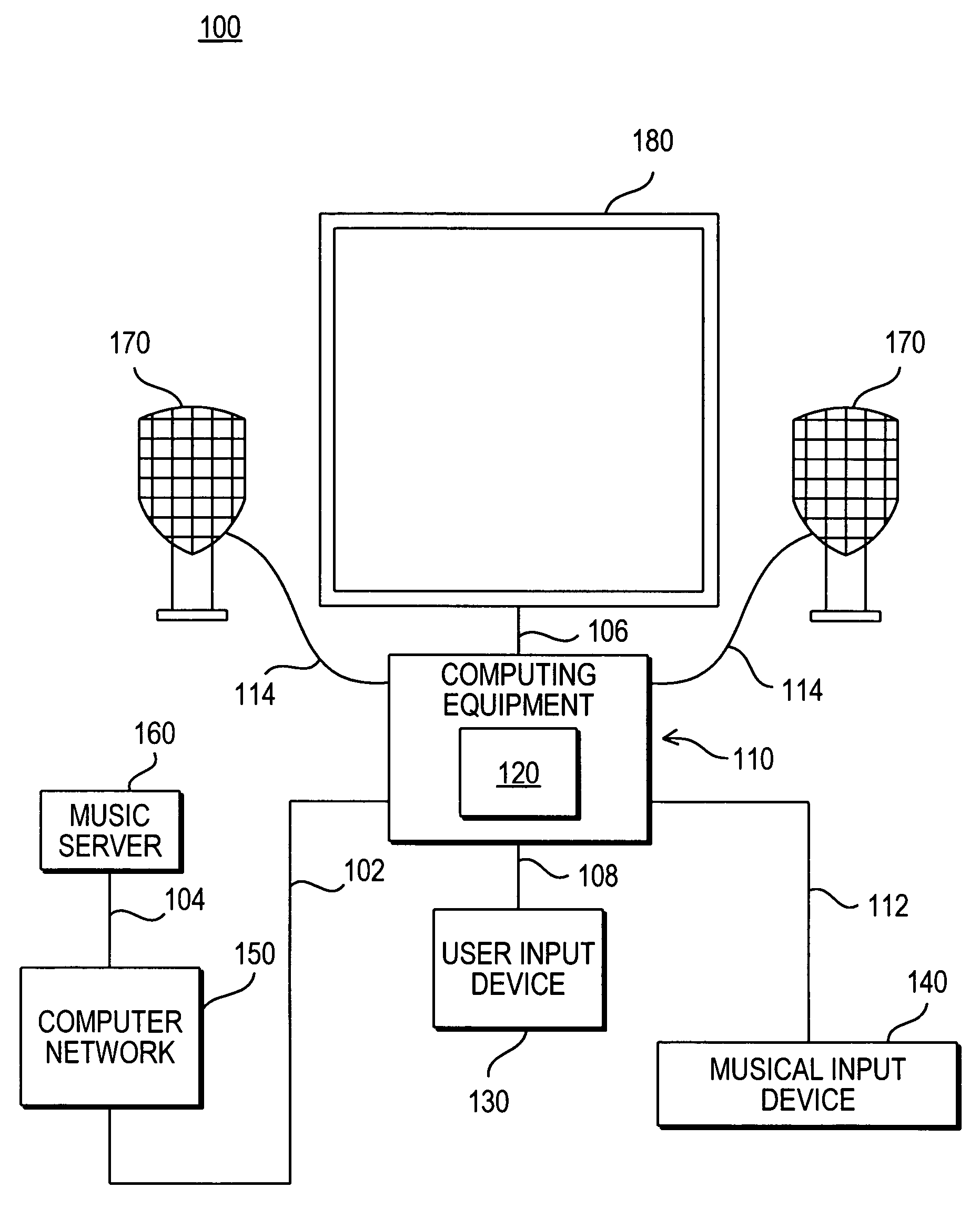
Method and Apparatus for Enabling a User to Amend an Audio FIle
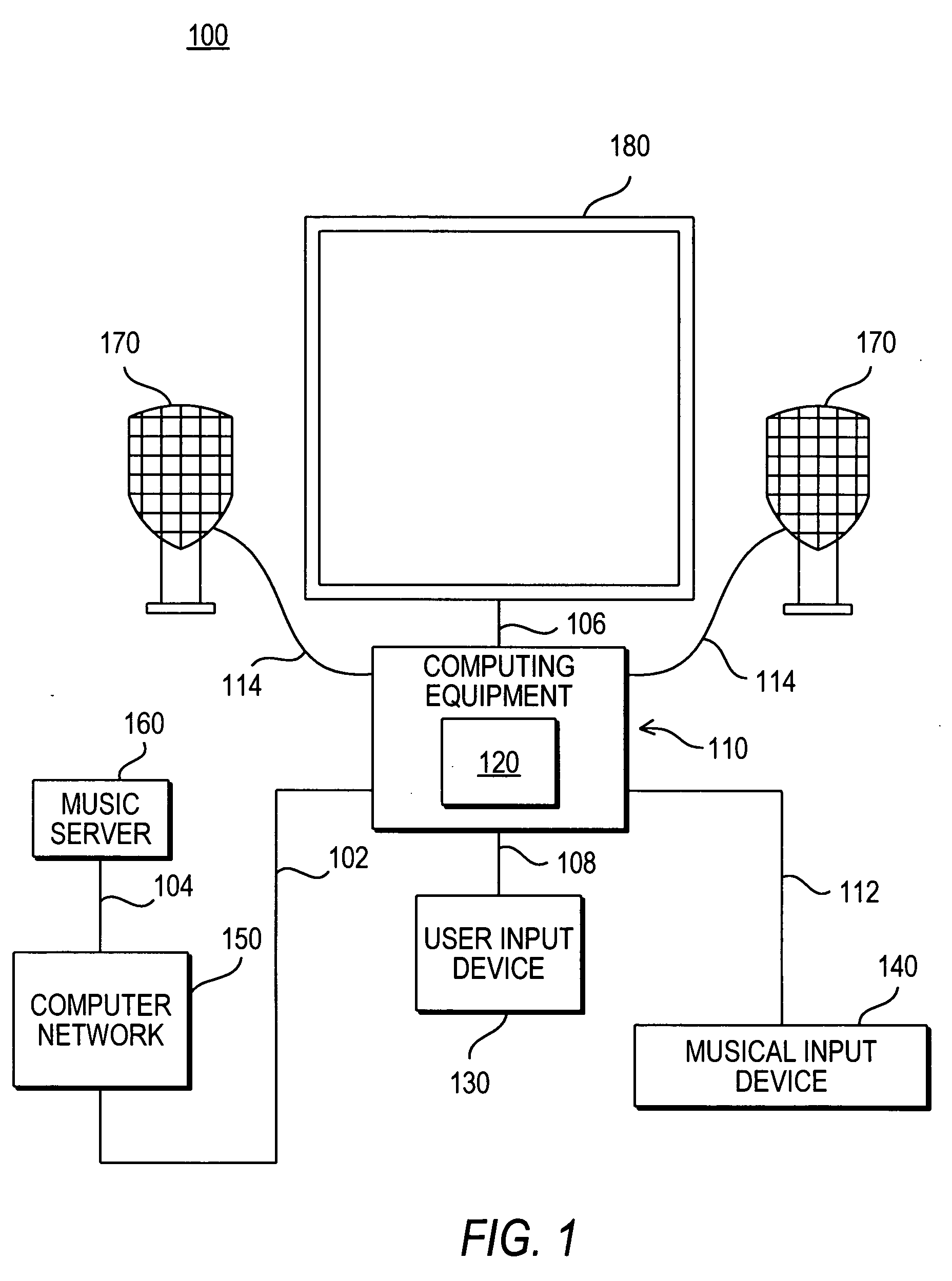
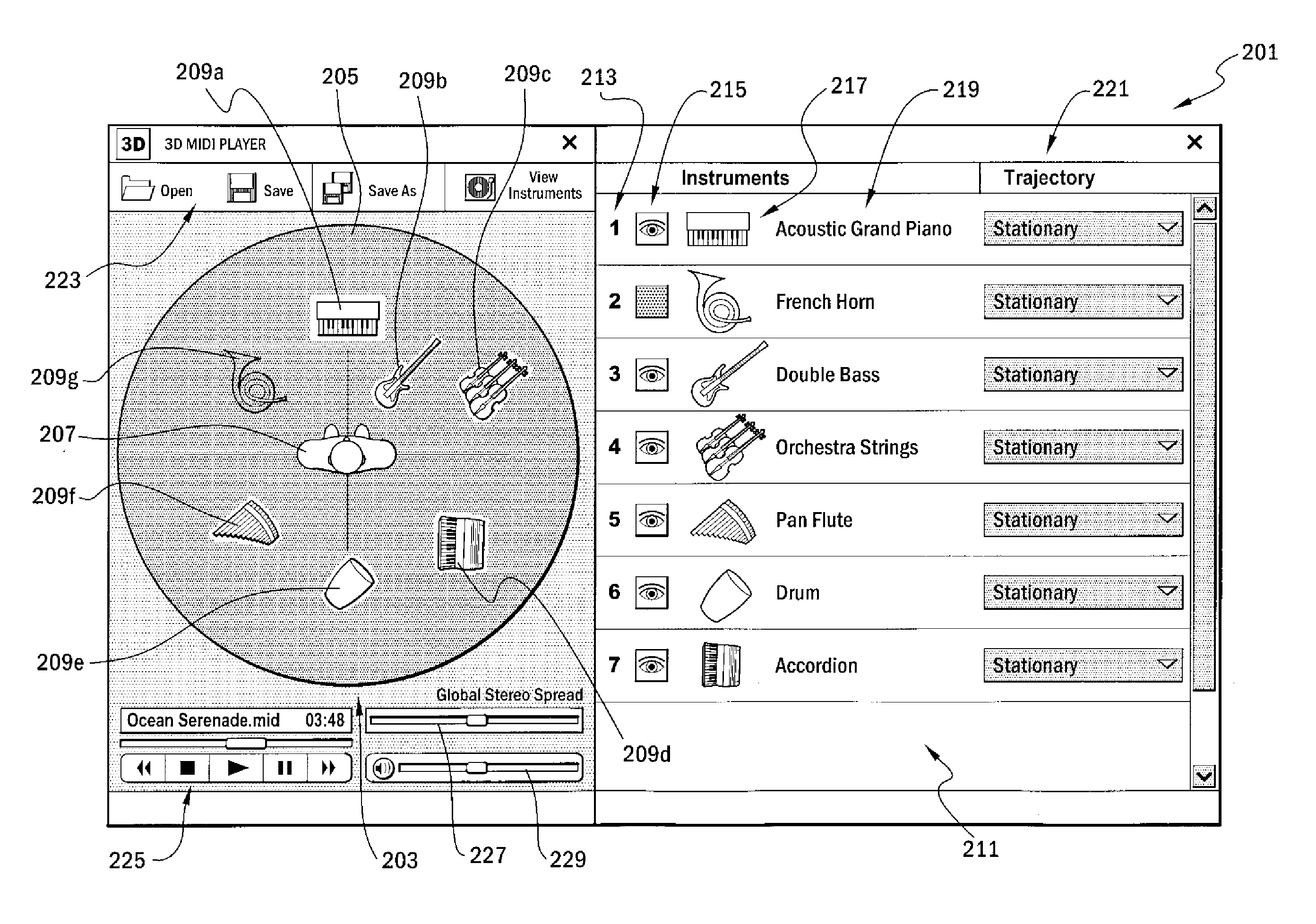
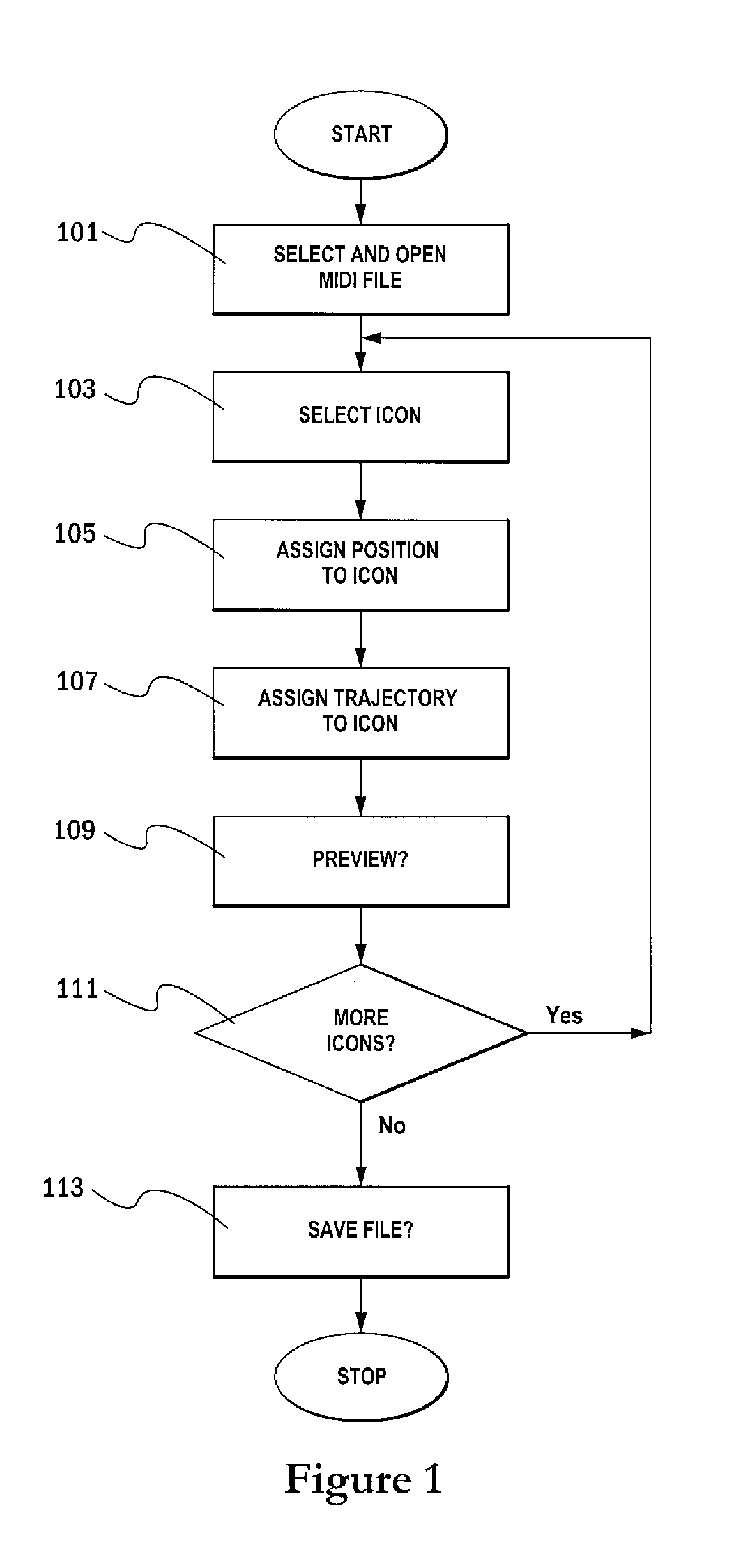
InactiveUS20060117261A1Electrophonic musical instrumentsSound input/outputVirtual positionDisplay device
There is a provided a method and apparatus for enabling a user to amend an audio file, via a user interface for controlling a driver for re-authoring the audio file. The method comprises the following steps: a) associating an icon on said user interface with one or more instruments or sets of instruments in said audio file; b) providing a selection of possible trajectories for each said icon, each trajectory defining the virtual path, relative to said user, of the associated instrument or set of instruments; c) providing a display on said user interface for showing the position of each said icon, each position defining the virtual position, relative to said user, of the associated instrument or set of instruments; d) the user selecting an icon; e) the user assigning a position and / or a trajectory from the selection, to the selected icon; and g) indicating, on said display, the position of the selected icon and whether a trajectory has been assigned to the selected icon. The invention relates in particular to a method for enabling a user to amend a MIDI file, via a user interface for controlling a driver for applying three-dimensional audio data to the MIDI file.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
Interactive game providing instruction in musical notation and in learning an instrument
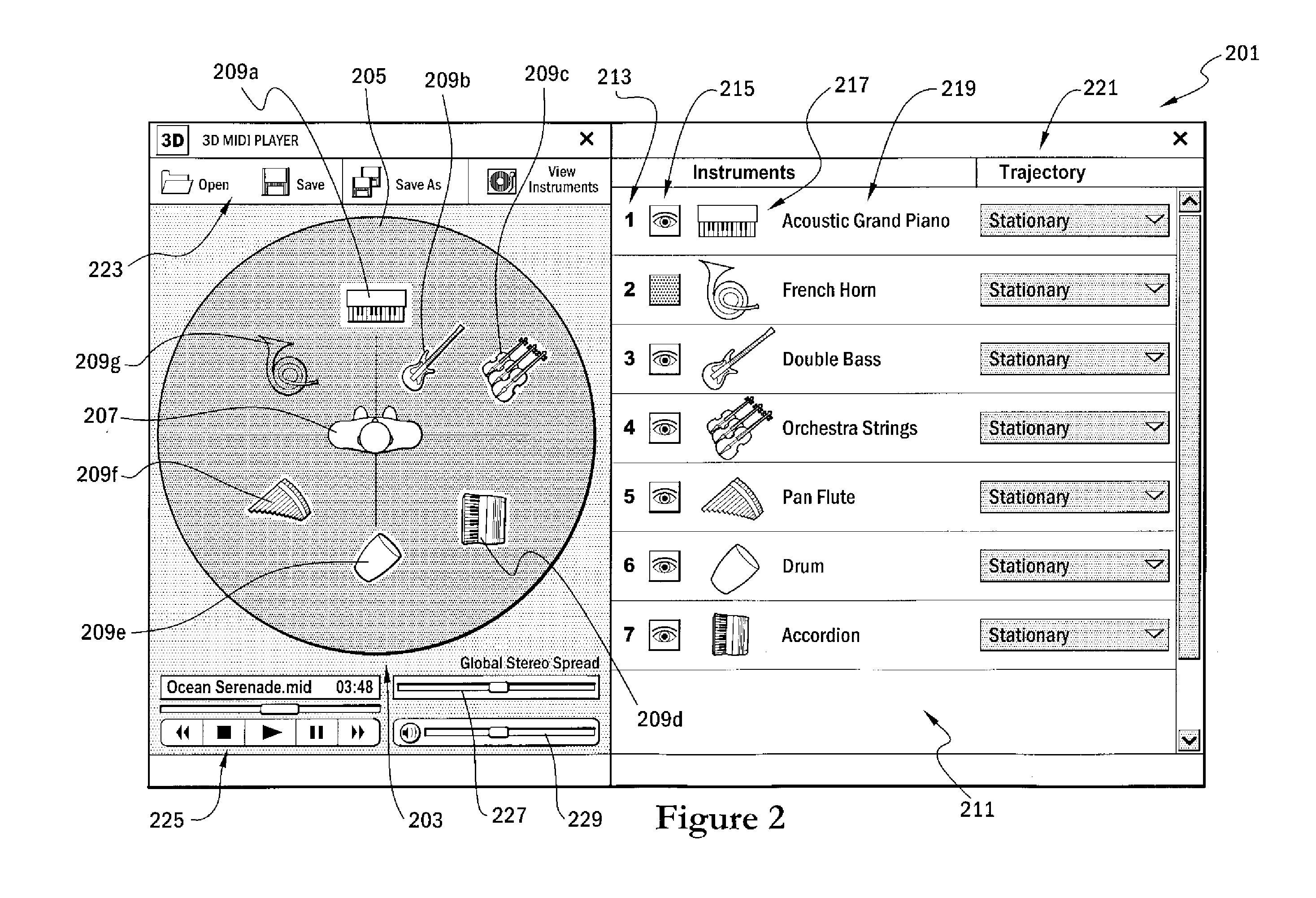
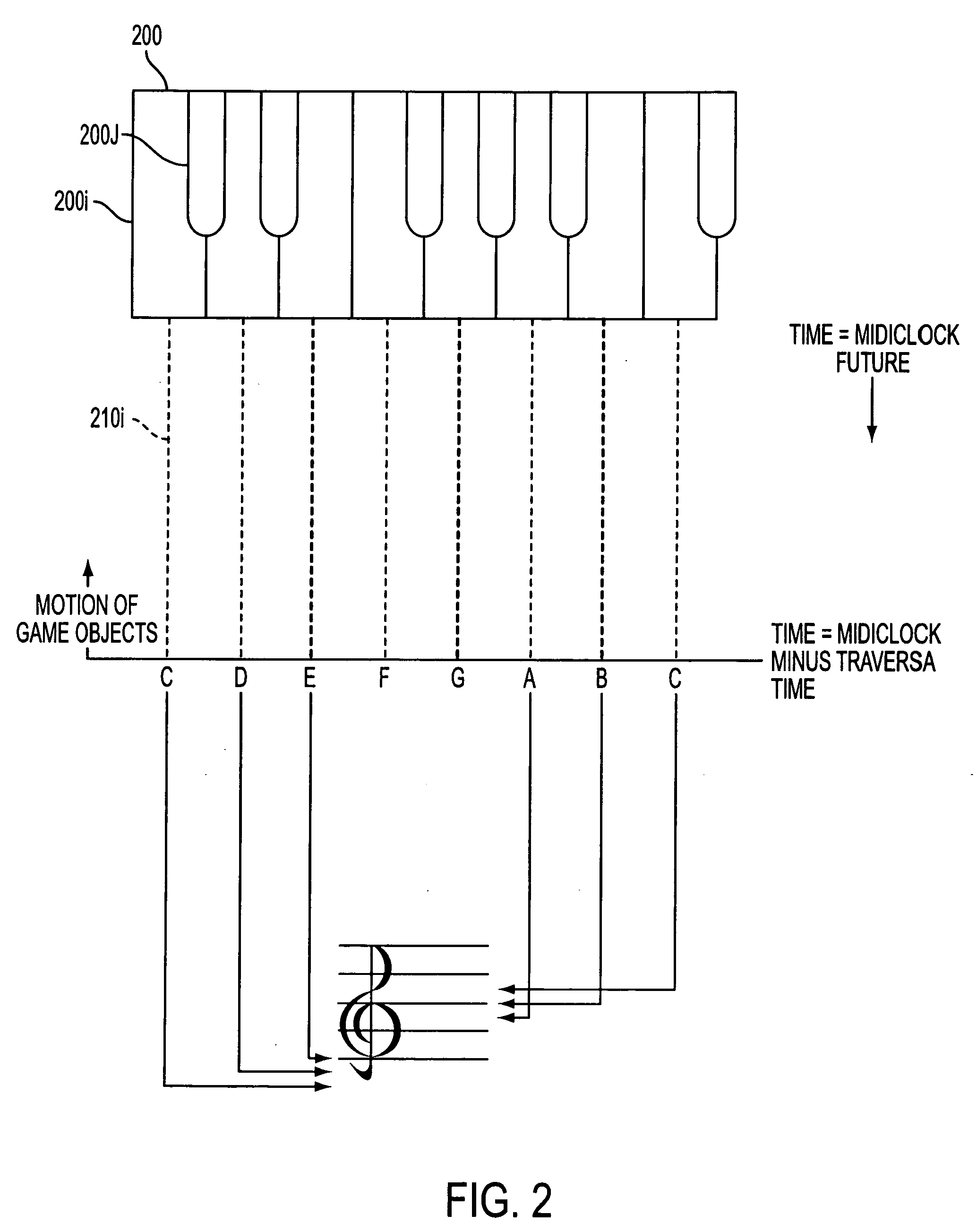
A musical keyboard is connected to a computer. The computer implements a graphical user interface for teaching users to play the musical instrument. A computer readable music file, such as a MIDI file, is used to drive the creation of game objects that travel from a point of origination along a path toward a key of a virtual keyboard. In one form, when a user presses a key of the musical keyboard within a certain time window of arrival of the game object at the corresponding key of the virtual keyboard, the user is awarded with an audio presentation, a visual presentation and / or with game points. In a more structured learning mode, the game can be played with selectable, progressively more difficult challenges that the user masters on the road to proficiency.
Owner:ALLEGRO MULTIMEDIA
Method and apparatus for measuring timing characteristics of message-oriented transports
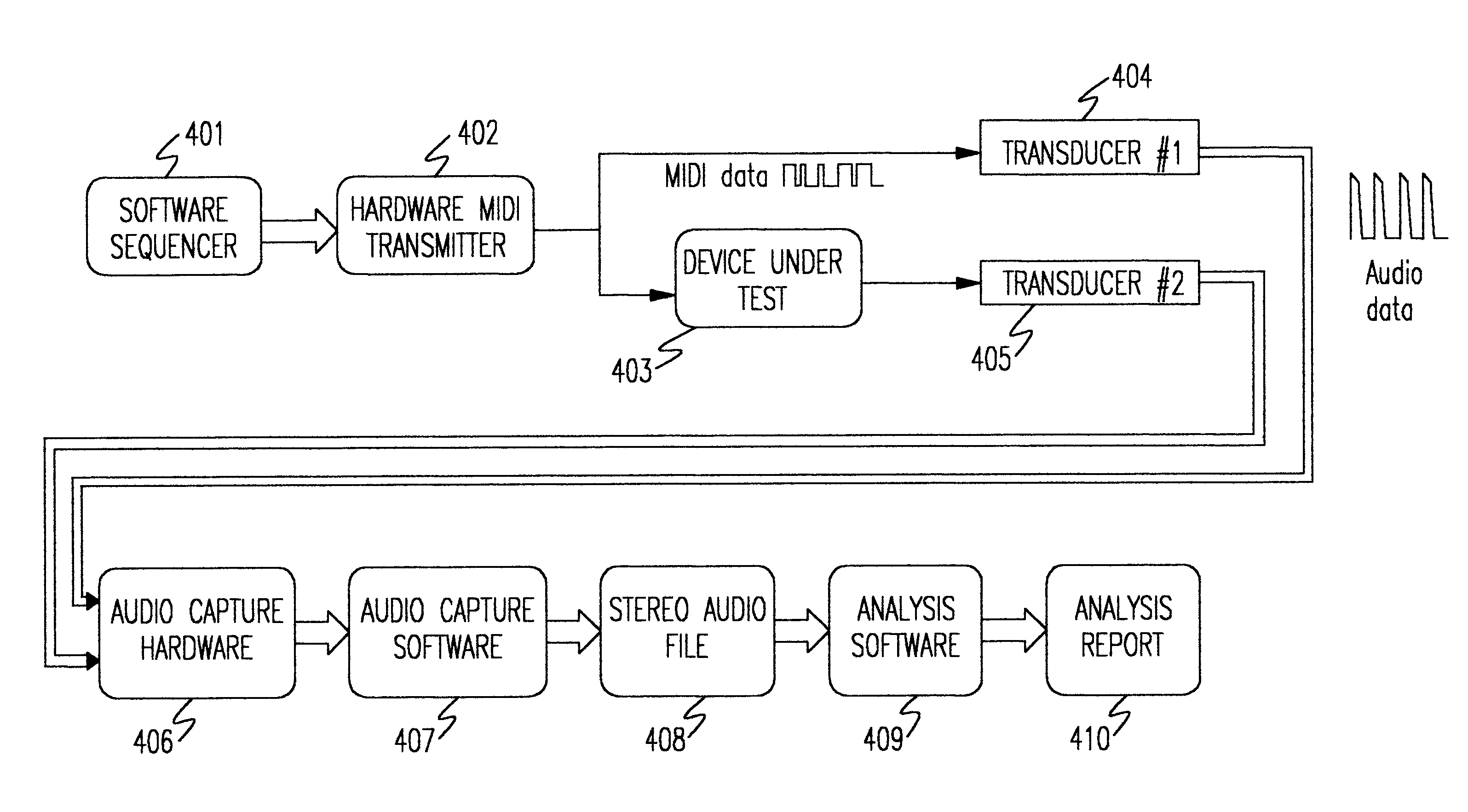
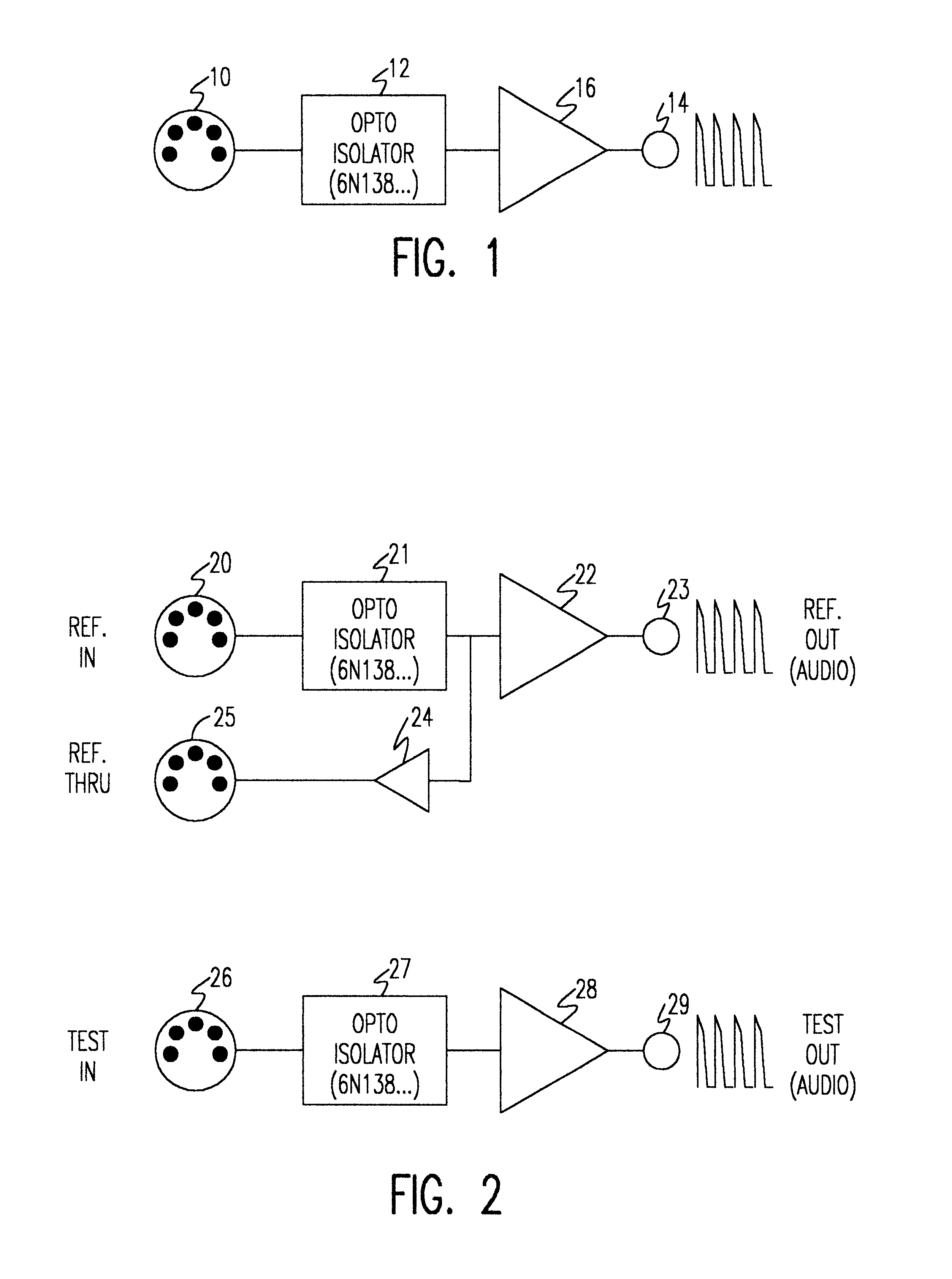
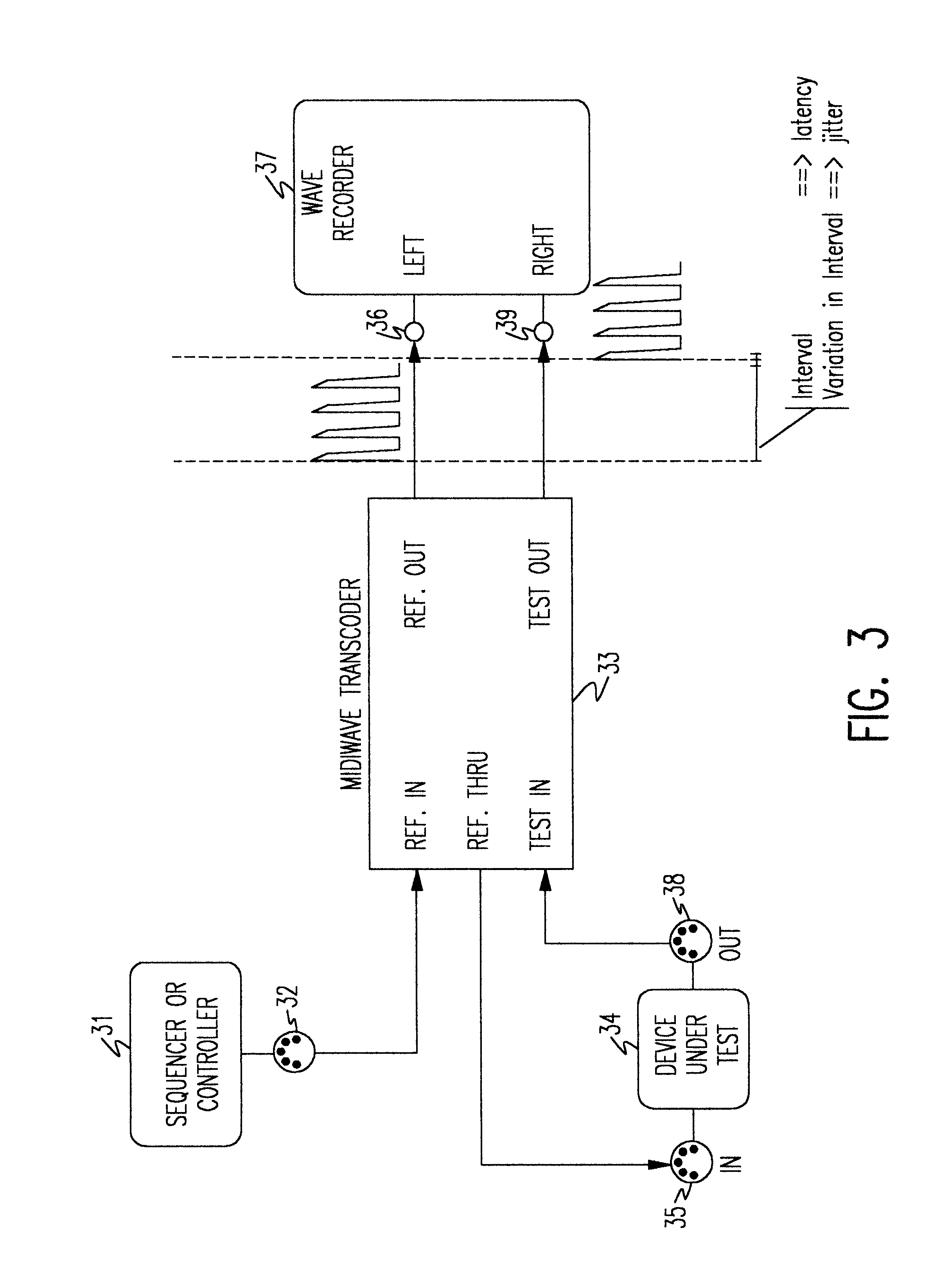
Timing characteristics of message-oriented transports are measured using common personal computers which easily support a wide variety of analytical tools. The apparatus measures timing characteristics of bursty message traffic over relatively low-speed digital transports such as the Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI). The apparatus includes means for generating a reference pulse stream, such as a sequencer. A transcoder device receives the reference pulse stream and routes the pulse stream to a device under test and, in analog form, to a first channel input of a digital recording device, such as a sound card installed in a personal computer. The transcoder also receives an output pulse stream from the device under test and routes the output pulse stream, in analog form, to a second channel input of the digital recording device. A differential technique allows timing errors in the reference pulse stream to be eliminated from measurements. The apparatus can also be used for measuring propagation characteristics of a particular transmission medium.
Owner:IBM CORP
Automatic song creation method via computer
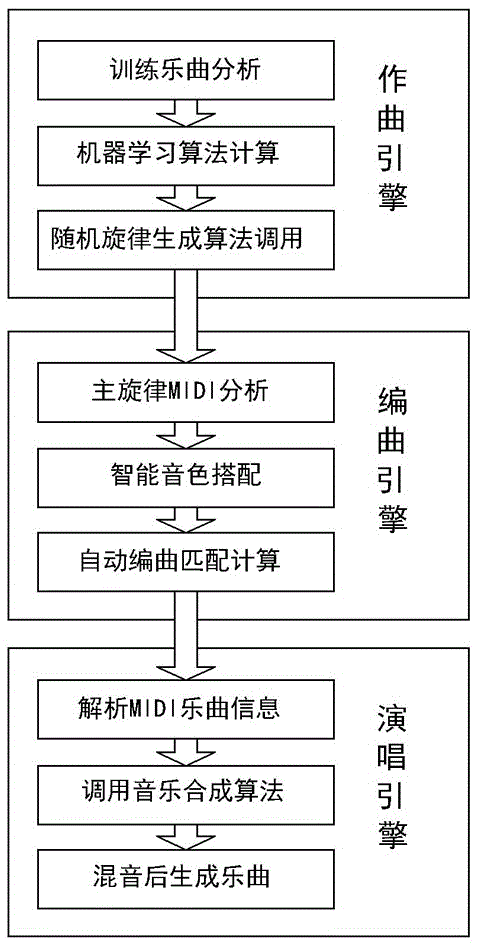
The invention discloses an automatic song creation method via a computer. The method comprises the steps of computer composing, computer arranging and computer singing concretely, and is realized via computer composing software by that a user inputs random rows of lyrics, the rows of lyrics are separated by separators respectively, and an algorithm operation composing module generates a melody MIDI music score file; the operation composing module adds an accompaniment audio track to the corresponding MIDI music score file, and renders an accompaniment file into a high-quality WAVE audio accompaniment file via a sound source library; the MIDI music score file is combined with a specific human sound source file via a music synthesis algorithm to generate a theme; and the theme is combined with the accompaniment file to form a final song. The method is a great innovation in the field of computer music, and through the method, an ordinary person can convert words of himself / herself into the song which includes melody and customized accompaniment and can be sung.
Owner:张文铂
Wearable sensor matrix system for machine control
InactiveUS20060123982A1High degree of accuracyGood repeatabilityElectrophonic musical instrumentsContact surface shape/structureSensor arrayMusical tone
A real-time controller of devices such as computers, synthesizers, and processors. It consists of a portable ergonomic body housing a configurable pressure sensitive array of sensors. Ideally suited as a MIDI controller, it may be used to control musical sounds, lighting systems, media viewers, or video games in a real-time or performance environment.
Owner:CHRISTENSEN EDWARD LEE
Live combined stimulation of auditory, sensory and motor functions and enhanced therapeutic and communicative applications based on advanced generation of complex electrical signals
InactiveUS20110046687A1Lack of flexibiltyFlexible signal processingElectrotherapyLocal control/monitoringPattern perceptionEngineering
A stimulator device is disclosed that is capable to produce and apply synchronized complex electrical stimulation signals very responsive and user friendly with interactive ability to change and derivate multiple signals or processing parameters immediately and simultaneously. The stimulator processes signals e.g. music and is typically controlled in real-time by a communication protocol e.g MIDI data or live by a MIDI controller. Immediate patient response and adoption facilitates the development of more efficient, diversified and enjoyable stimulation content for the majority of therapies based on electrical activated transducers. Special scope is combined auditory, electrical and vibration stimulation of the sensory and motor functions. One disclosed embodiment is enhanced audio perception for deaf and hearing impaired patient. Another typical application is combined music, electrical and vibration stimulation e.g. for neck and back muscle relaxation or thrombosis prophylaxis provided by a PC based stimulation content generator and a protable player.
Owner:NASCHBERGER RAIMUND
Method and system for generating animation according to audio music
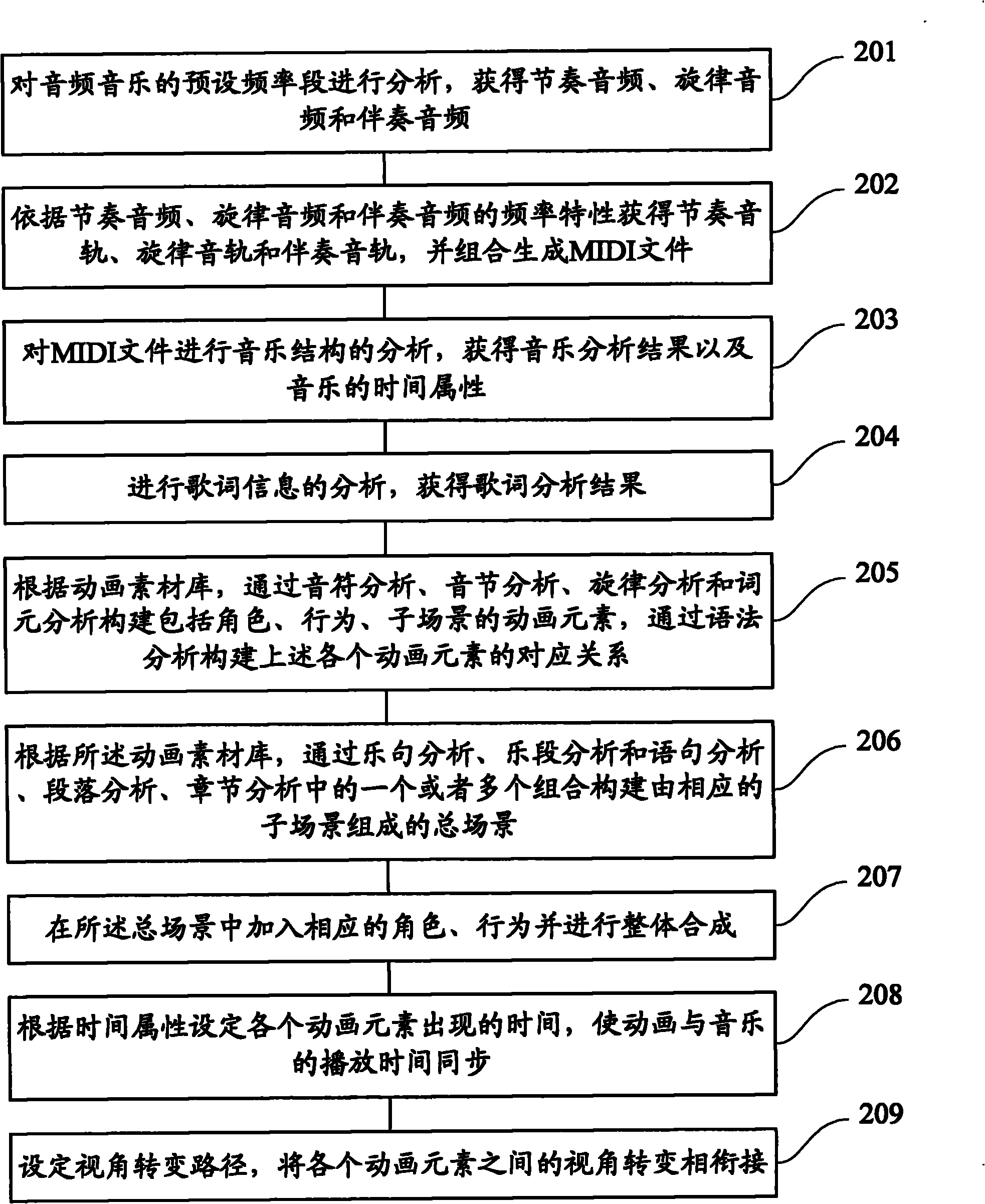
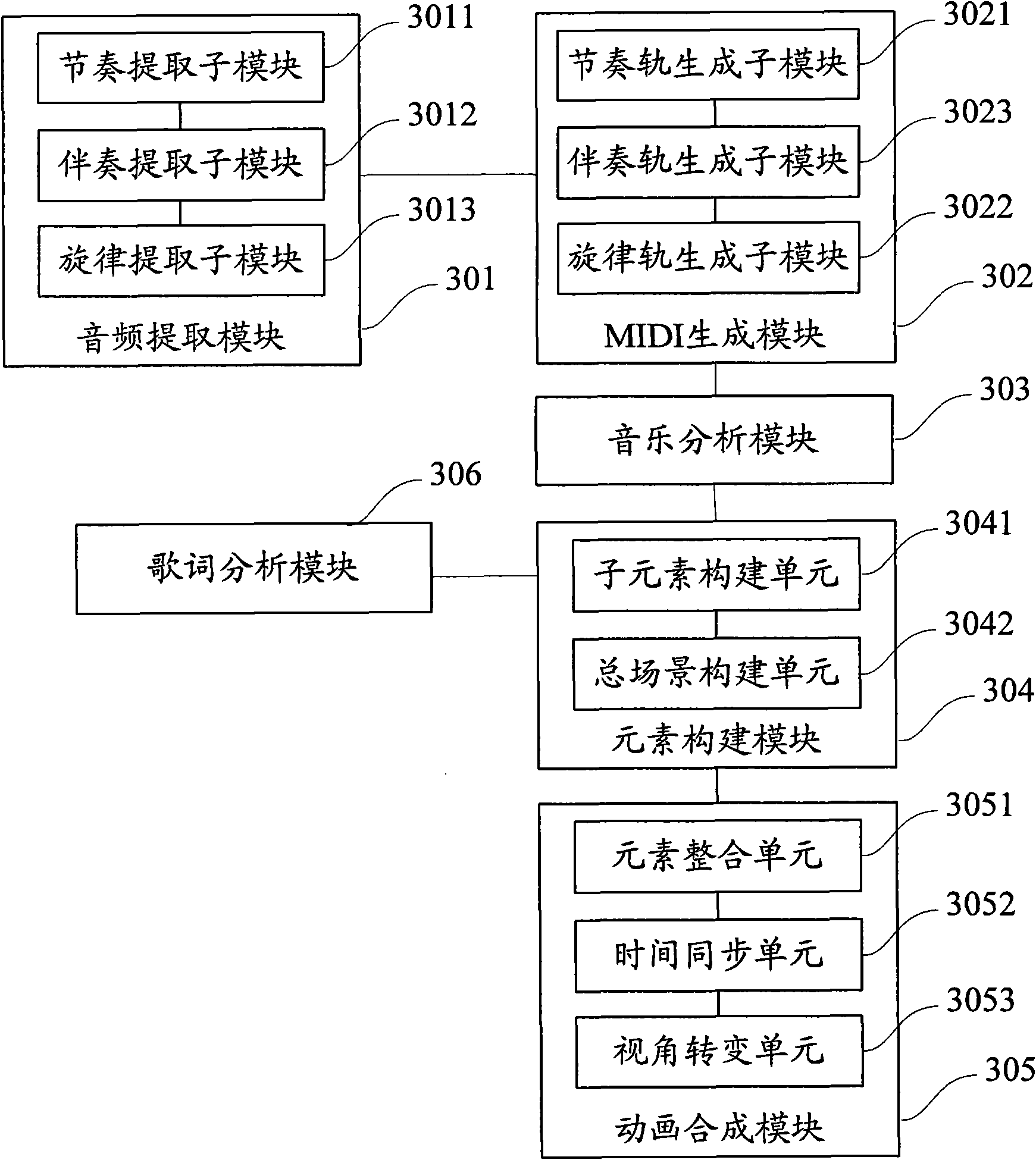
ActiveCN101901595ARealize audio-visual bindingSatisfy and enjoyElectrophonic musical instrumentsAnimationAnimationInformative content
The invention provides a method and a system for generating animation according to audio music. The method comprises the following steps of: analyzing the preset frequency band of the audio music to acquire rhythm audio and accompaniment audio; acquiring each audio track according to the frequency characteristic of each audio, and combining to generate an MIDI file; analyzing the music structure of the MIDI file to acquire a music analysis result and the time attribute of the music; establishing each animation element and the corresponding relationship thereof through the preset rule or parameters input by a user according to the preset animation material library and the music analysis result; and combining each animation element and the corresponding relationship thereof into the animation according to the time attribute. The method and the system can automatically generate visual information which has rich contents and corresponds to the contents expressed by the music according to the audio music.
Owner:GUANGDONG VIMICRO
System and method for video assisted music instrument collaboration over distance
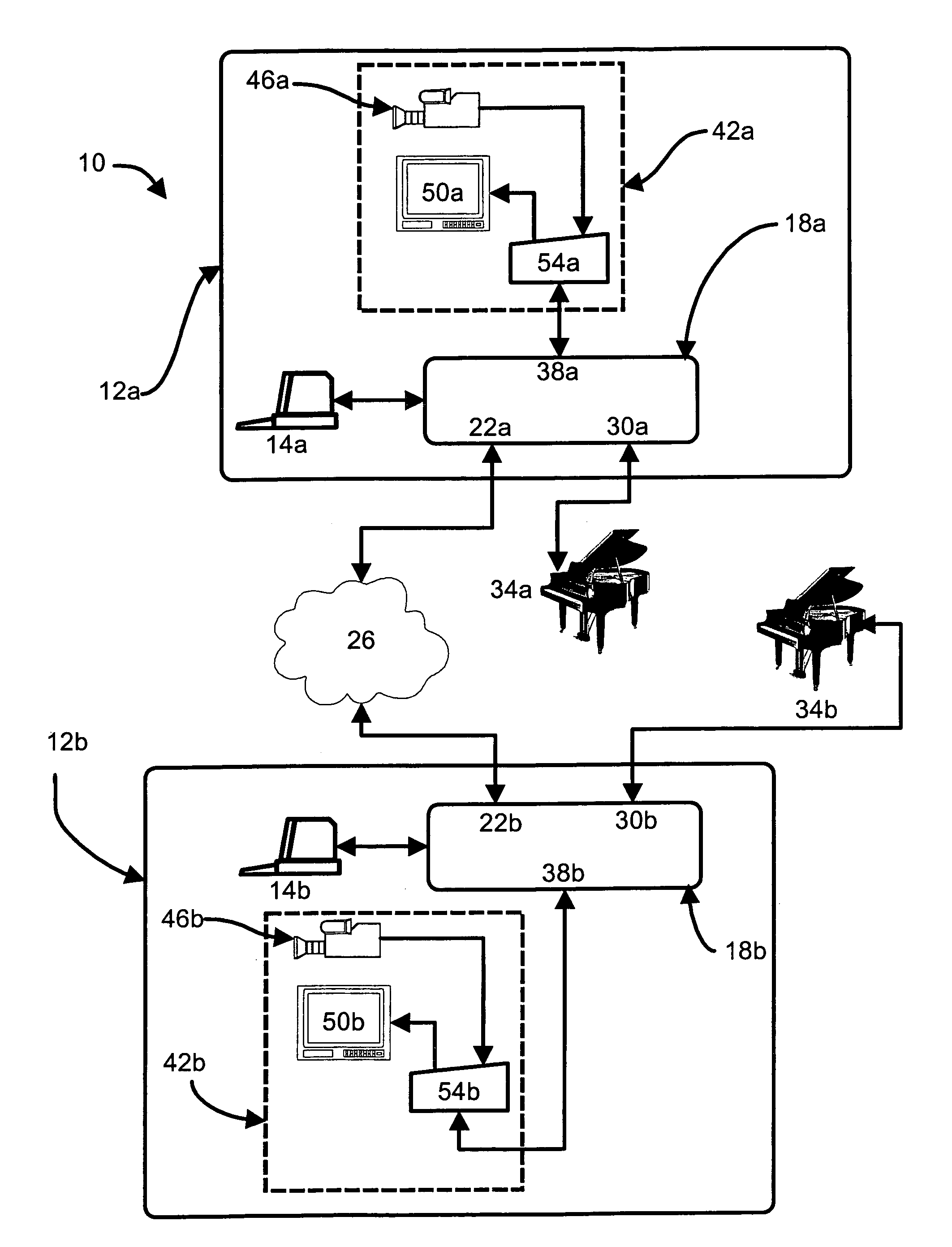
InactiveUS7405355B2Easy to disassembleAvoid damageElectrophonic musical instrumentsData switching networksThe InternetInstrumentation
A novel system and method of video assisted music instrument collaboration over distance. The system and method enable a musician to play a music instrument at one location and have the played music recreated by a music instrument at another location is provided. The system and method can be used to provide distance education for musical instrument instruction and, in this case, each student and instructor of the system has an end point which can connect to other end points in the system to exchange music data, preferably MIDI data, and videoconferencing data through a data network such as the Internet. The system and method can also be used for performances wherein a musician at a first end point plays an instrument and music data, representing the music played, is transferred to a second end point where the music played at the first end point is reproduced and one or more other musicians at the second end point play with the reproduced music in a musical performance. Preferably, each end point includes a music processing engine which buffers data received from another end point to remove the effects of transmission delays and jitter and to discard overly delayed data and to prevent damage to the music instrument at the end point due to undue network delays. Further, the music processing engine can inform the users when network performance is responsible for improper and / or undesired music playback by the instrument at the end point. This buffering by the music processing engine can also allow the synchronization of a video conferencing system between the end points with the playing of music by the instruments at the end points.
Owner:DIAMOND JAMES DR +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com