Screening device of pathogenic uniparental disomy, storage medium and processor
A diploid, pathogenic technology, applied in the fields of instrumentation, proteomics, medical data mining, etc., can solve the problems of slow speed, low efficiency, small indels, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] A kind of screening of pathogenic uniparental diploid is carried out by using the following device, which includes:
[0047] Data acquisition module: used to acquire whole exome sequencing data;
[0048] Site screening module: used to screen mutations that obtain predetermined conditions;
[0049] LOH judgment module: used for LOH judgment based on the above-mentioned mutation status, if the product of the number of continuous homozygous sites and its coverage is greater than the preset value, then it is judged that the interval is LOH;
[0050] UPD Judgment Module: It is used to judge UPD according to LOH. If the number of chromosomes with LOH exceeds 2, it is judged as a close relative; if the segment with LOH is a single copy, it is judged as a fragment deletion; the rest of the segments with LOH are judged as UPD .
[0051] Run the program according to the following method with the above screening device, including the following steps:
[0052] 1. Data acquisitio...
Embodiment 2
[0077] A kind of screening of pathogenic uniparental diploid is carried out with a sample, using the device of embodiment 1, wherein:
[0078] 1. Data acquisition
[0079] Referring to Example 1.
[0080] 2. Site screening
[0081] Referring to Example 1, 22,210 mutations meeting the predetermined conditions were obtained.
[0082] 3. LOH judgment
[0083] Among the loci obtained above, if the product of the number of consecutive homozygous loci and their coverage is greater than 200, the interval is determined to be LOH, where the number of consecutive homozygous loci is ≥ 20 and the coverage is ≥ 3Mbp.
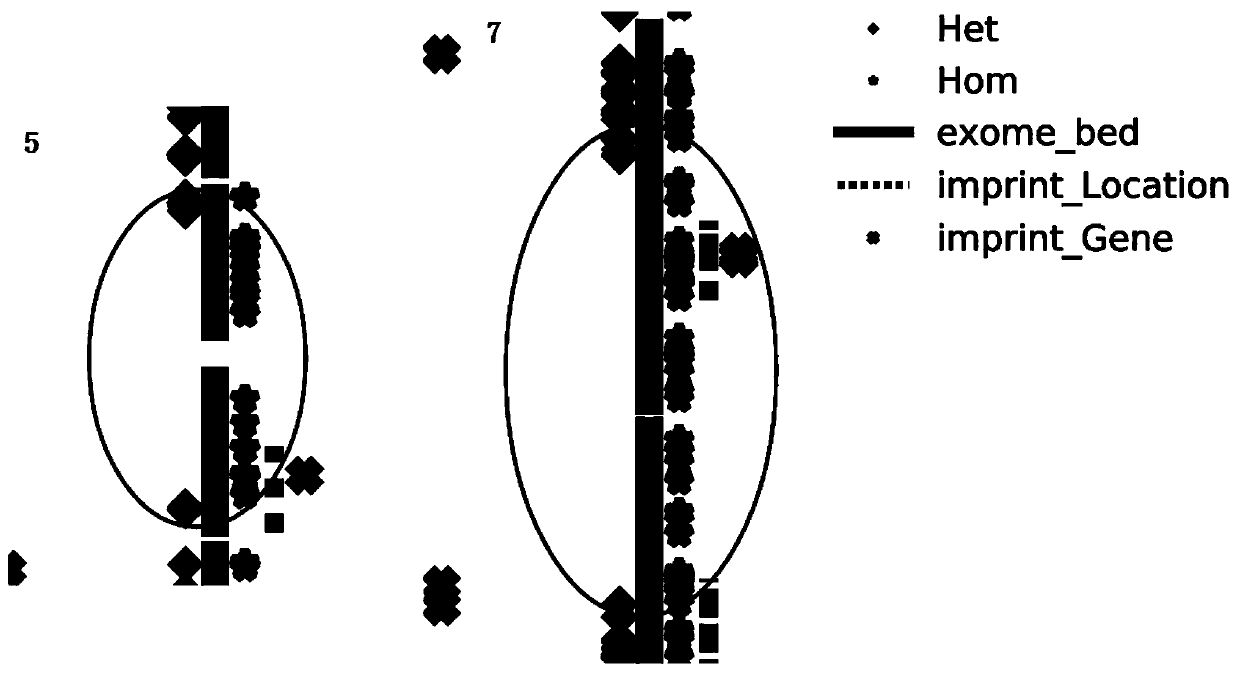
[0084] Judging according to this standard, one segment of LOH was detected in the sample of this embodiment, as shown in the table below.
[0085] Table 2. LOH interval
[0086]
[0087] It can be seen from the above results that the above-mentioned LOH is located on chromosome 15 with a length of 12.28M. Figure 4 This is the distribution of the 12.28M LOH on the c...
Embodiment 3
[0095] A kind of screening of pathogenic uniparental diploid is carried out with a sample, using the device of embodiment 1, wherein:
[0096] 1. Data acquisition
[0097] Referring to Example 1.
[0098] 2. Site screening
[0099] Referring to Example 1, 22947 mutations meeting the predetermined conditions were obtained.
[0100] 3. LOH judgment
[0101] Among the loci obtained above, if the product of the number of consecutive homozygous loci and their coverage is greater than 200, the interval is determined to be LOH, where the number of consecutive homozygous loci is ≥ 20 and the coverage is ≥ 3Mbp.
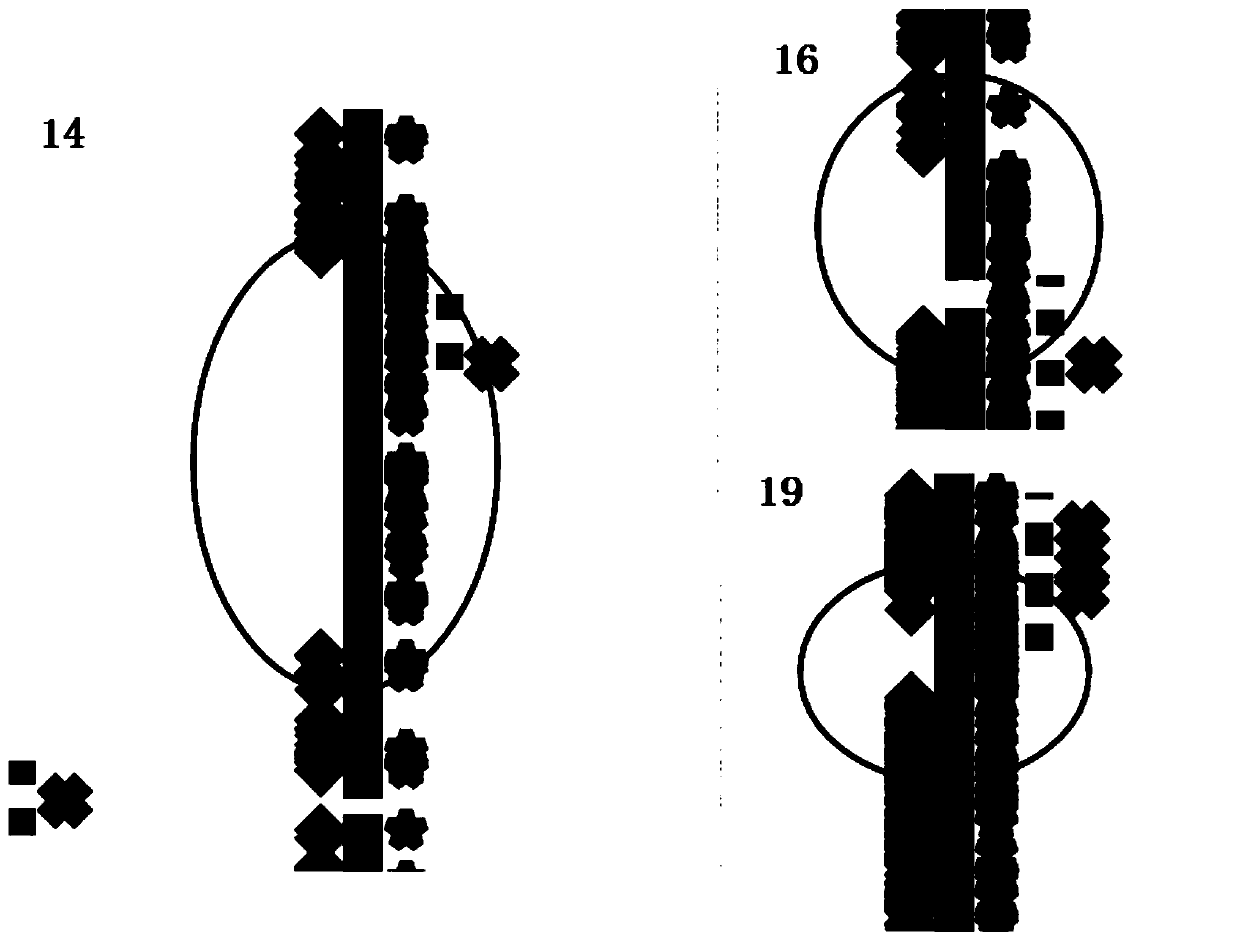
[0102] Judging according to this standard, two segments of LOH were detected in the sample of this embodiment, as shown in the table below.
[0103] Table 3. LOH interval
[0104]
[0105] It can be seen from the above results that the above LOHs are located on chromosome 5, and the lengths are 93.6M and 12.36M, respectively. Image 6 Its distribution on the chromoso...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com