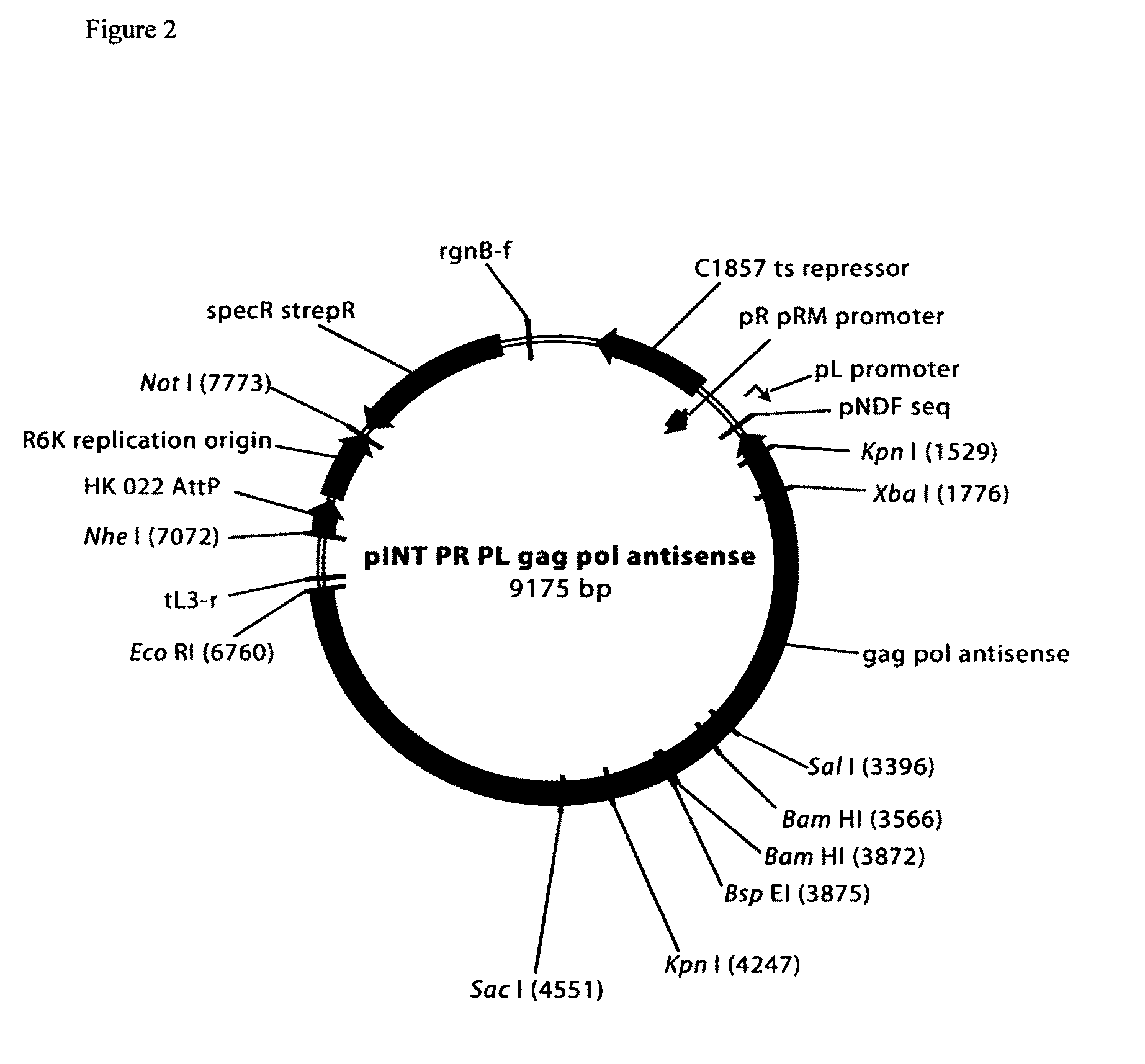
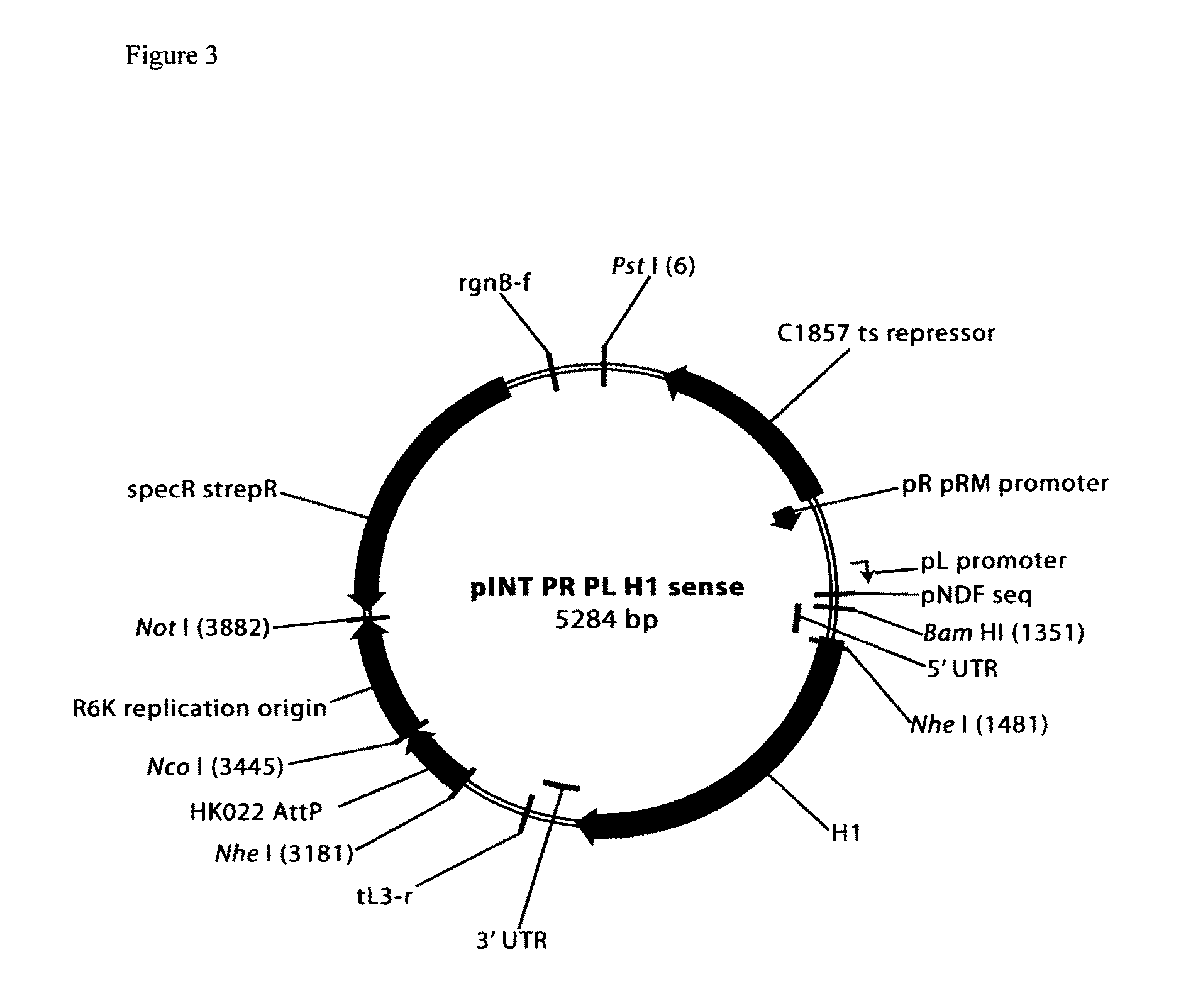
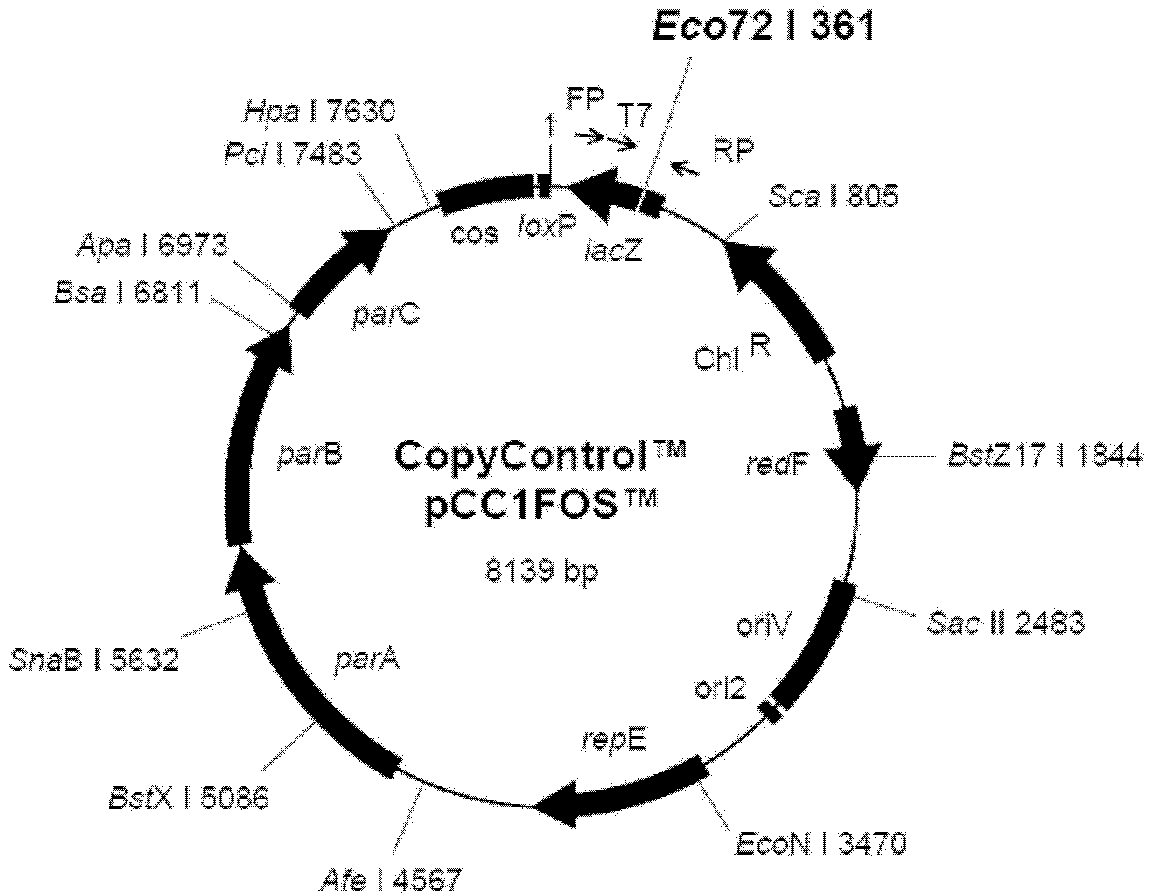
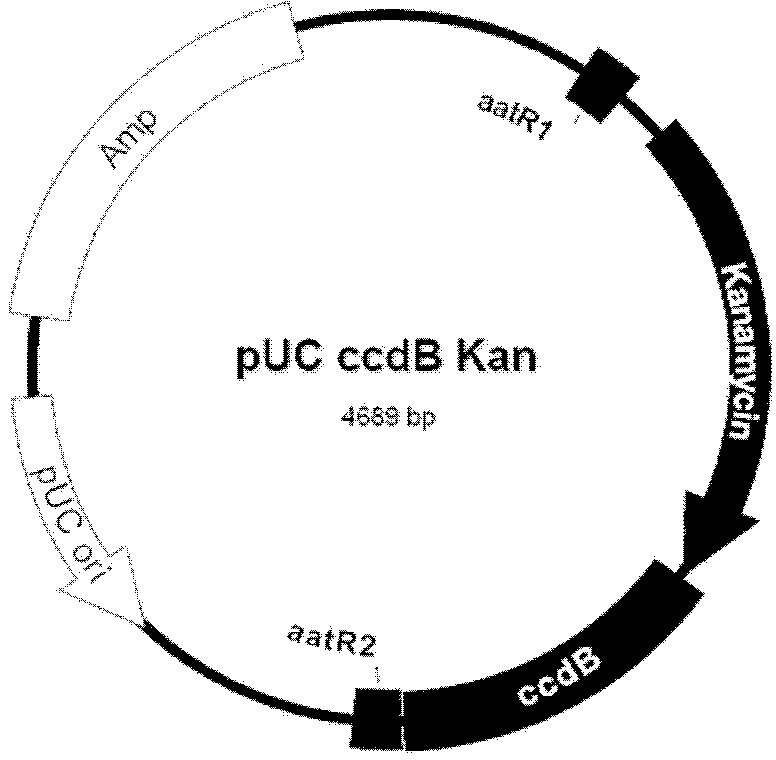
Patents
Literature
44 results about "Cosmid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
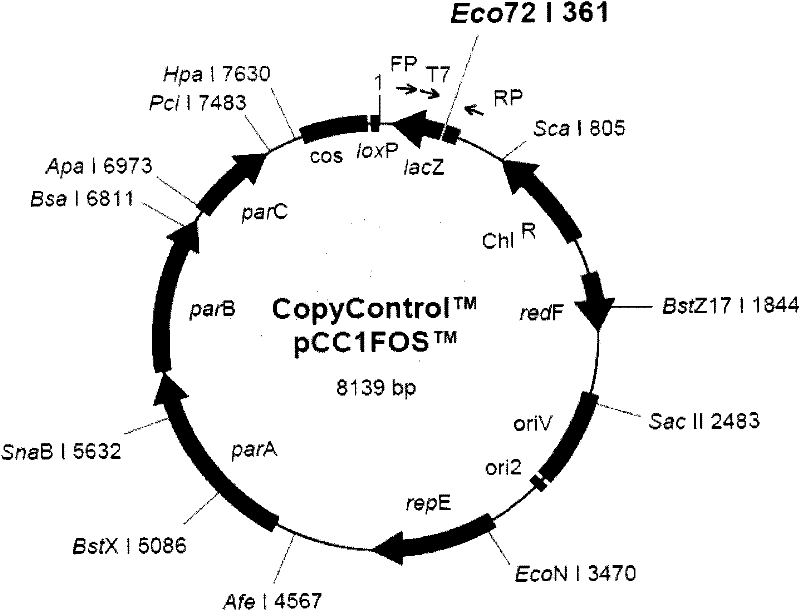
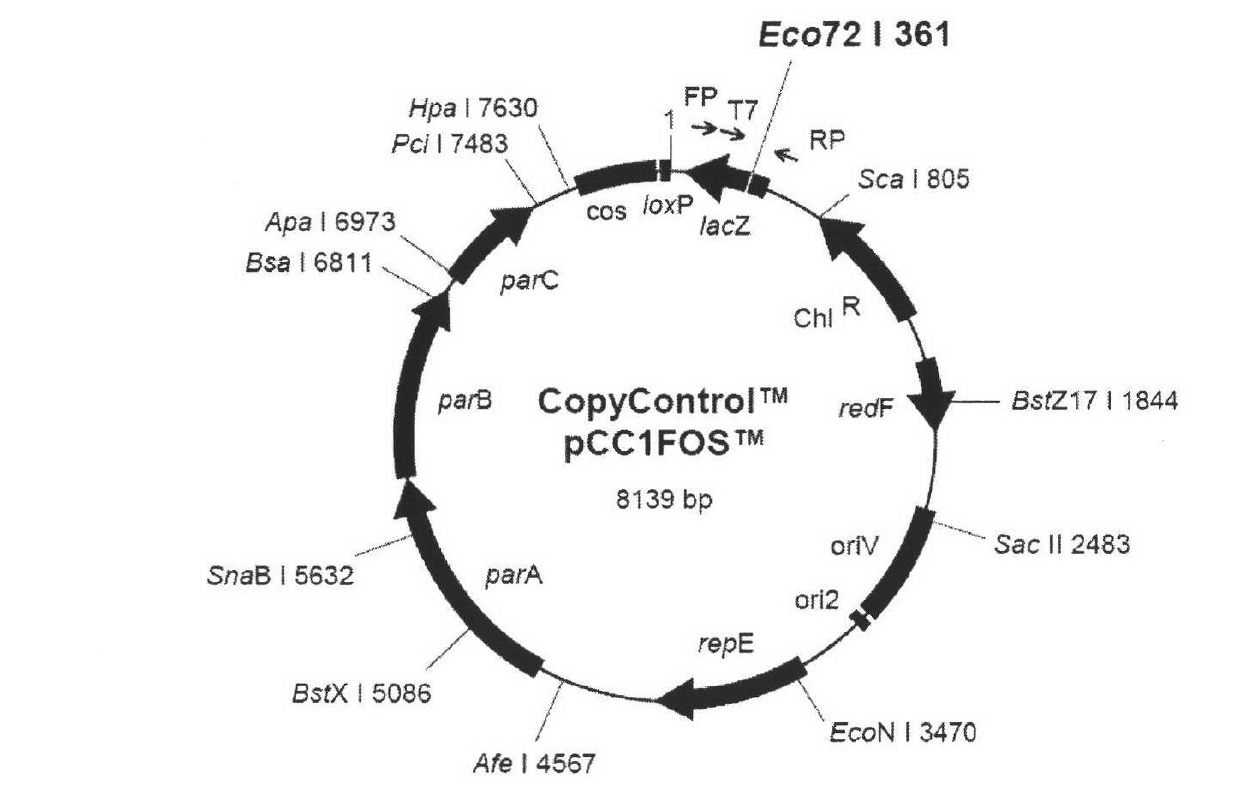
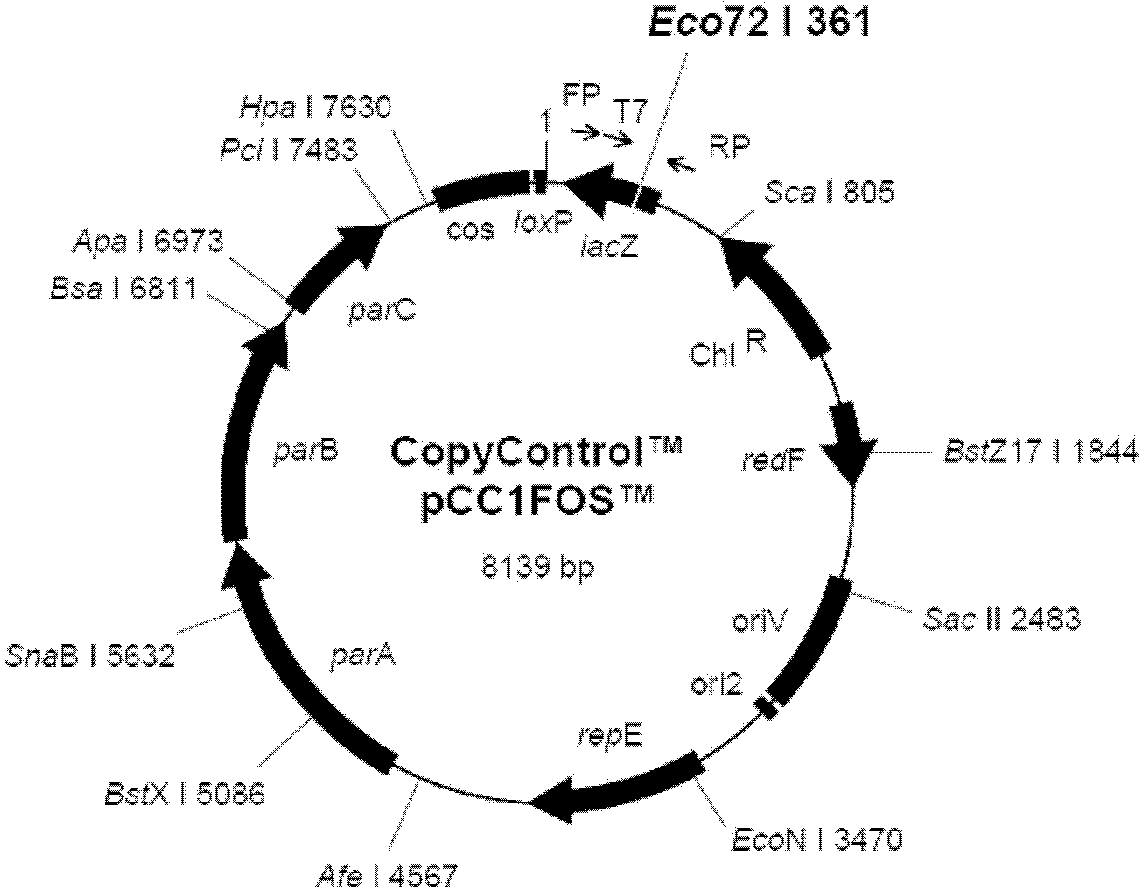
A cosmid is a type of hybrid plasmid that contains a Lambda phage cos sequence . Cosmids (cos sites + plasmid = cosmids) DNA sequences are originally from the lambda phage. They are often used as a cloning vector in genetic engineering. Cosmids can be used to build genomic libraries. They were first described by Collins and Hohn in 1978. Cosmids can contain 37 to 52 (normally 45) kb of DNA, limits based on the normal bacteriophage packaging size. They can replicate as plasmids if they have a suitable origin of replication (ori): for example SV40 ori in mammalian cells, ColE1 ori for double-stranded DNA replication, or f1 ori for single-stranded DNA replication in prokaryotes. They frequently also contain a gene for selection such as antibiotic resistance, so that the transformed cells can be identified by plating on a medium containing the antibiotic. Those cells which did not take up the cosmid would be unable to grow.
Novel Method for the cheap, efficient, and effective production of pharmaceutical and therapeutic api's intermediates, and final products
InactiveUS20160298151A1Reduce concentrationFermentationDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyPhenylpropanoid
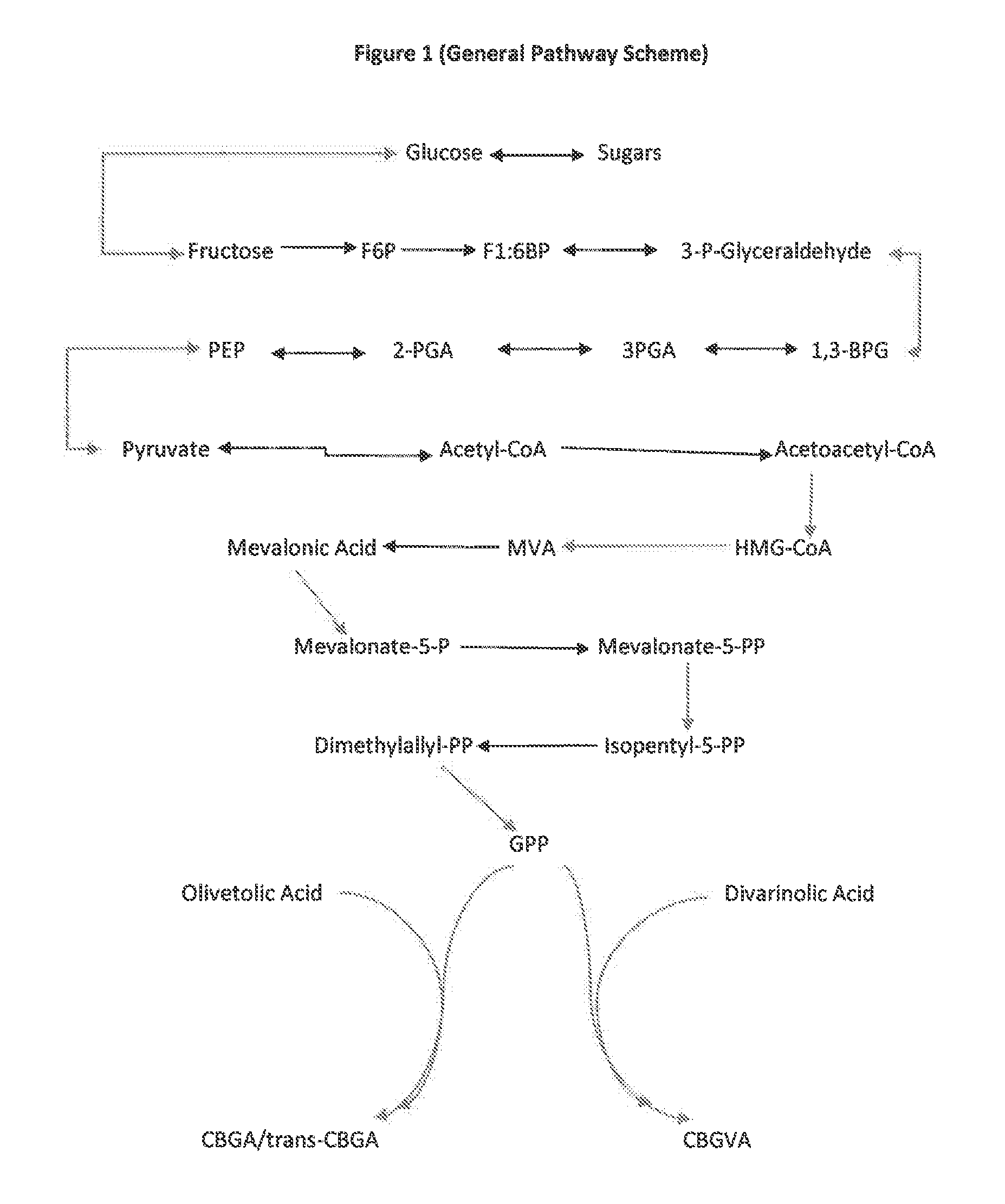
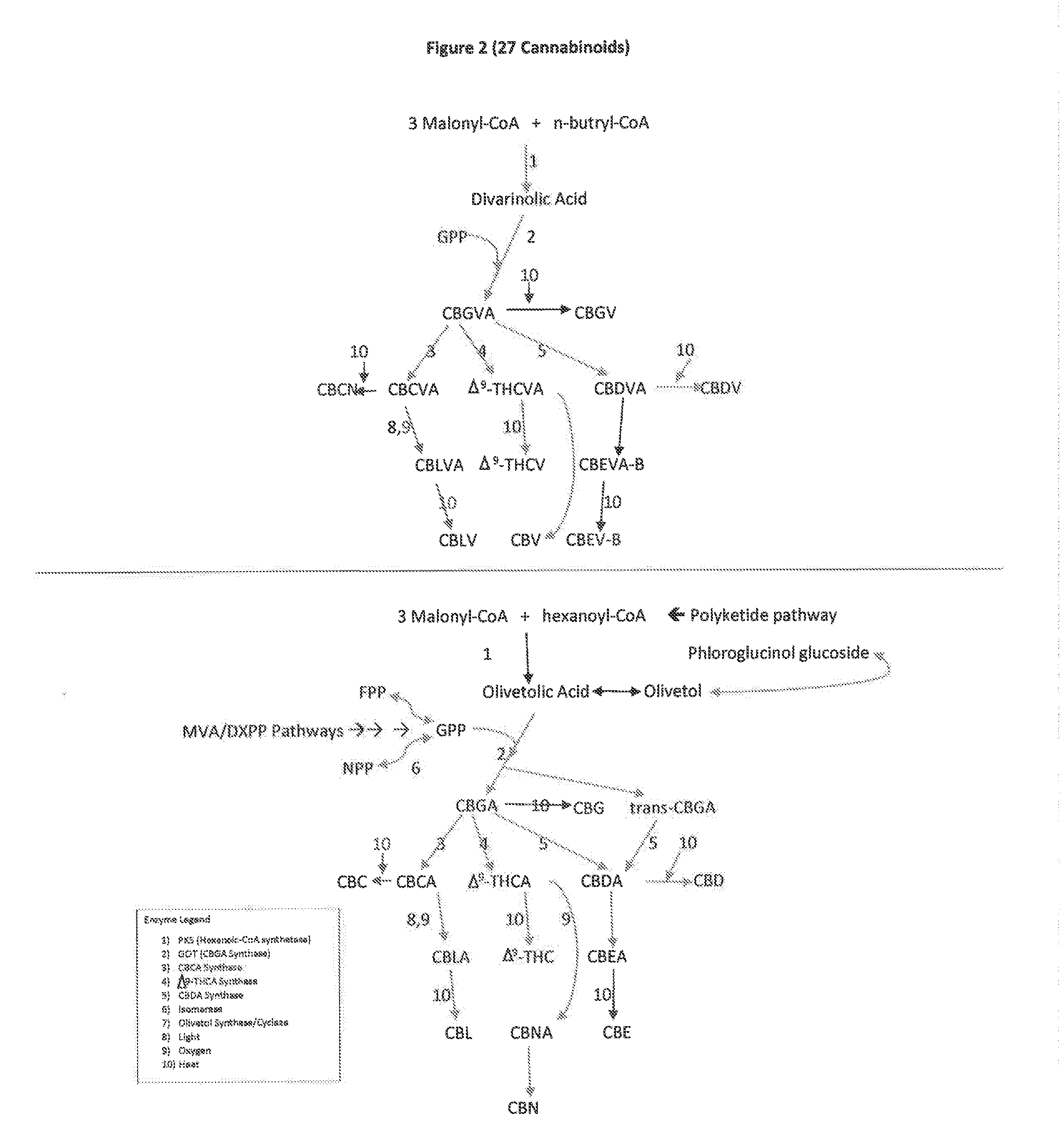
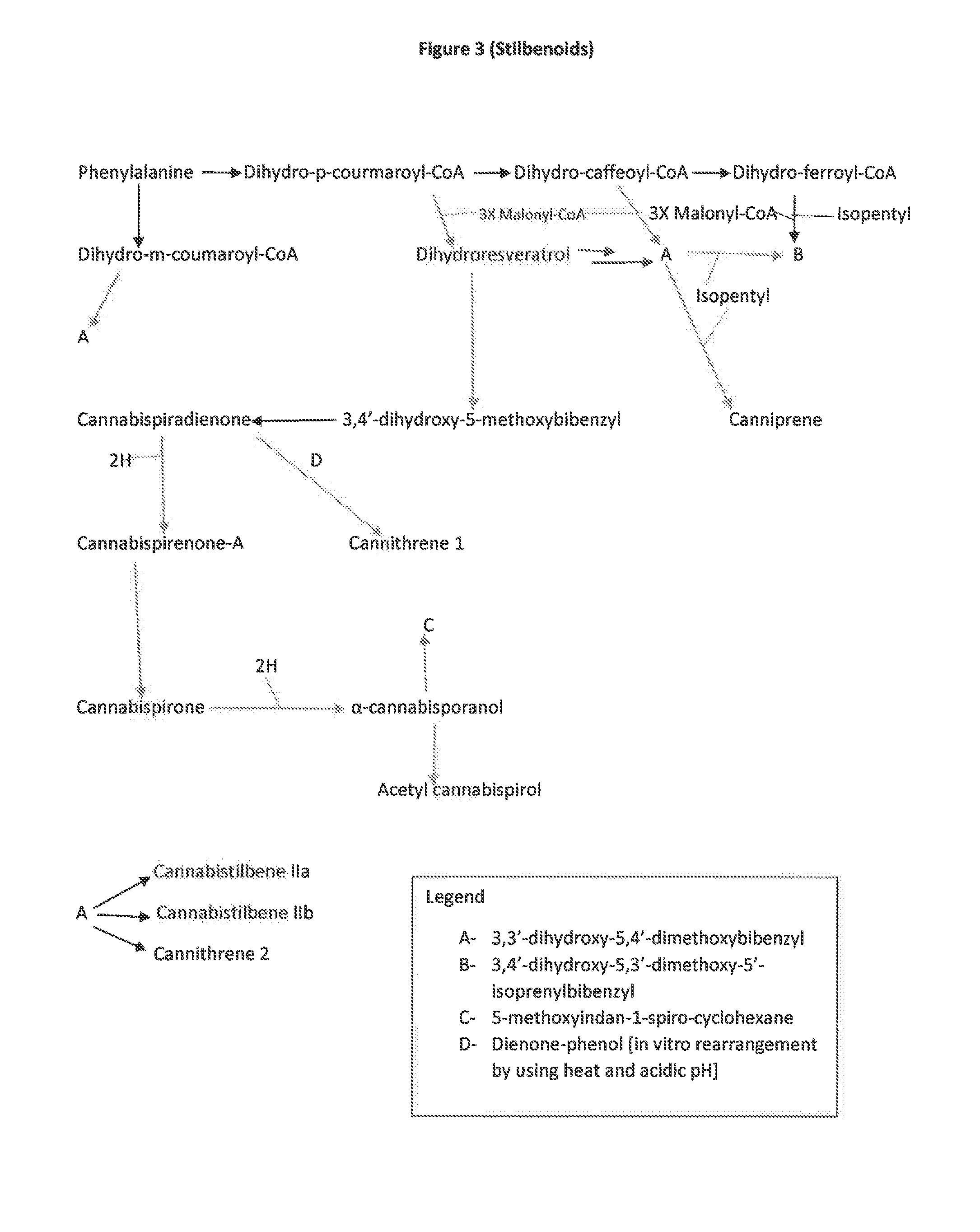
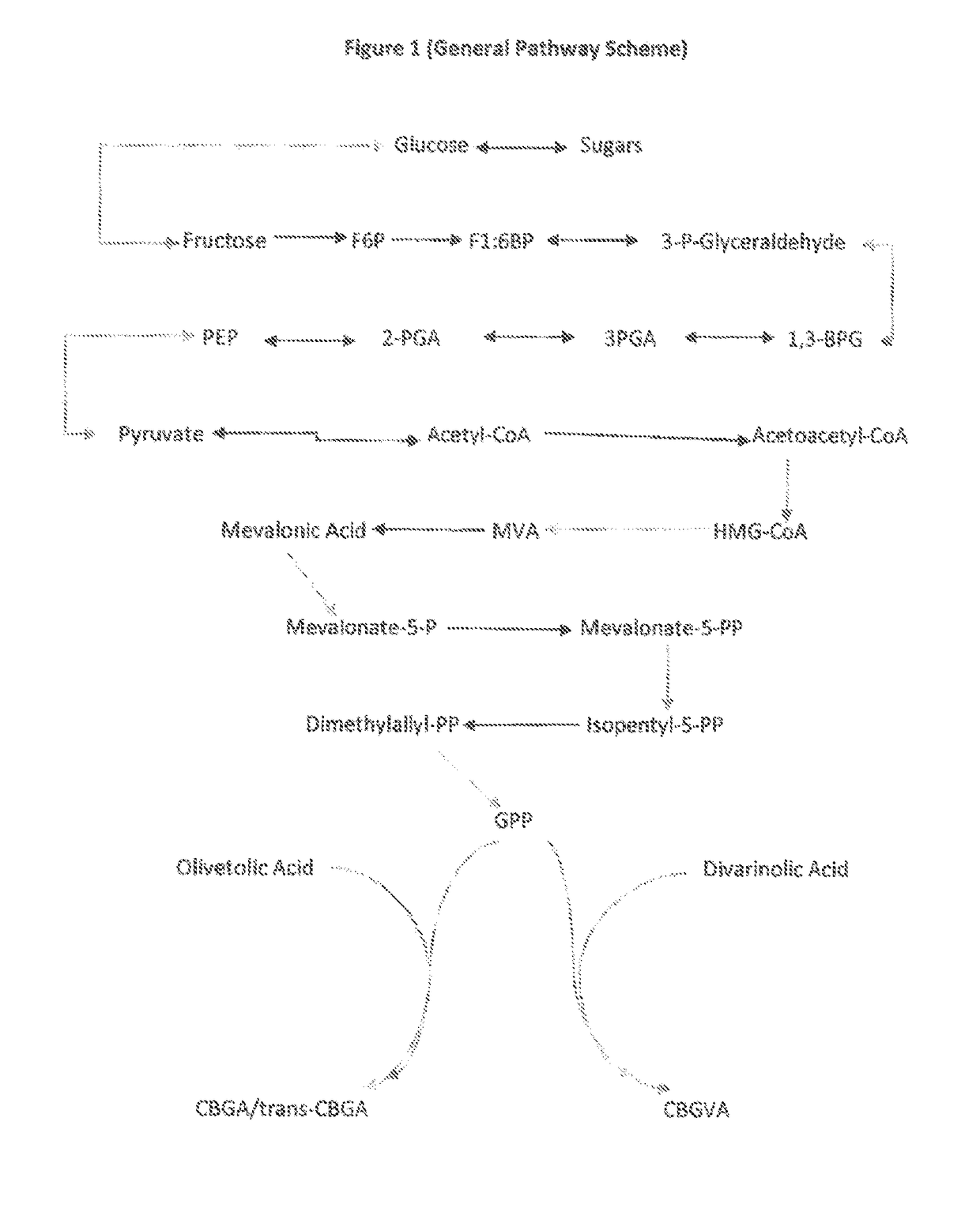
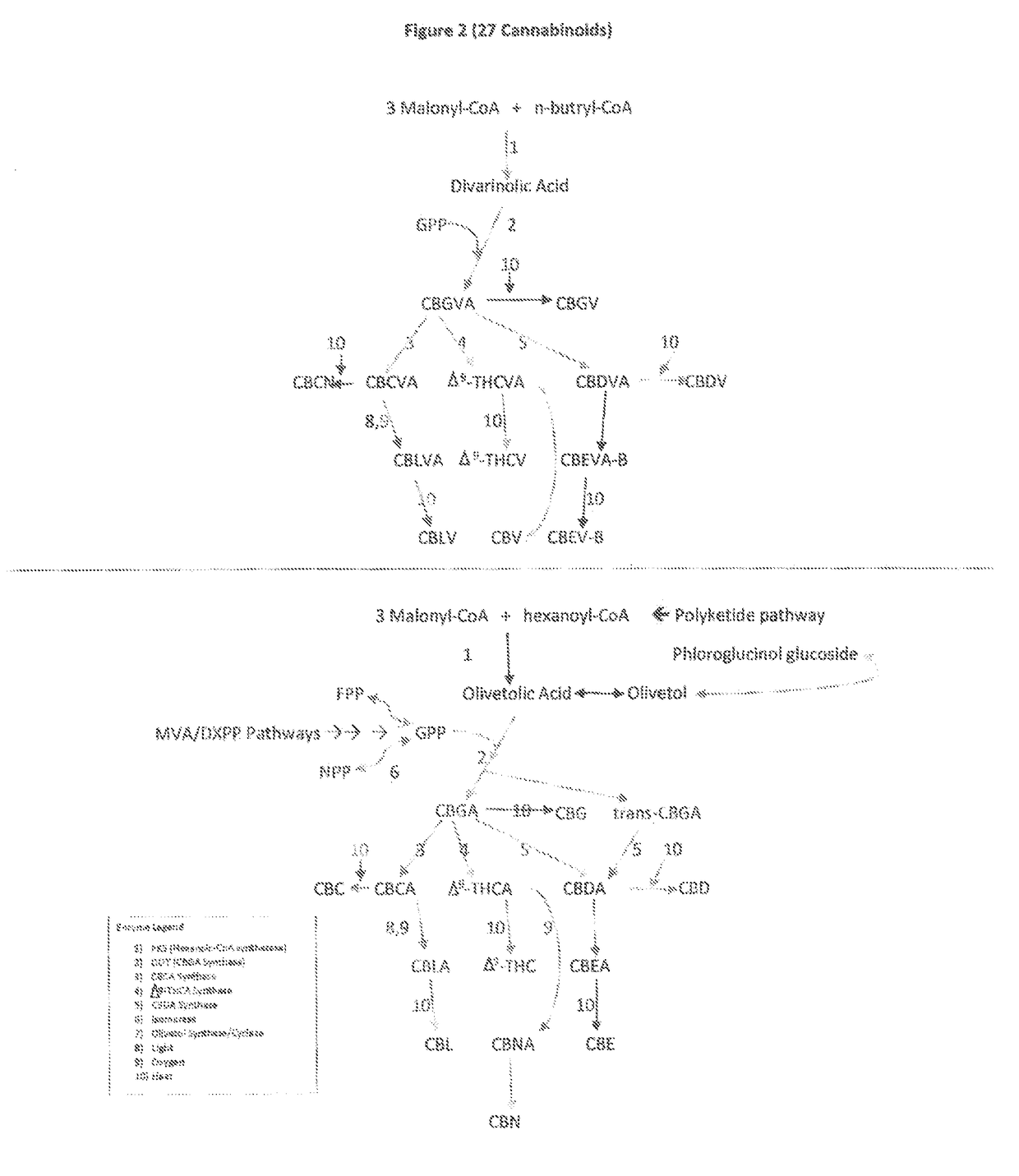
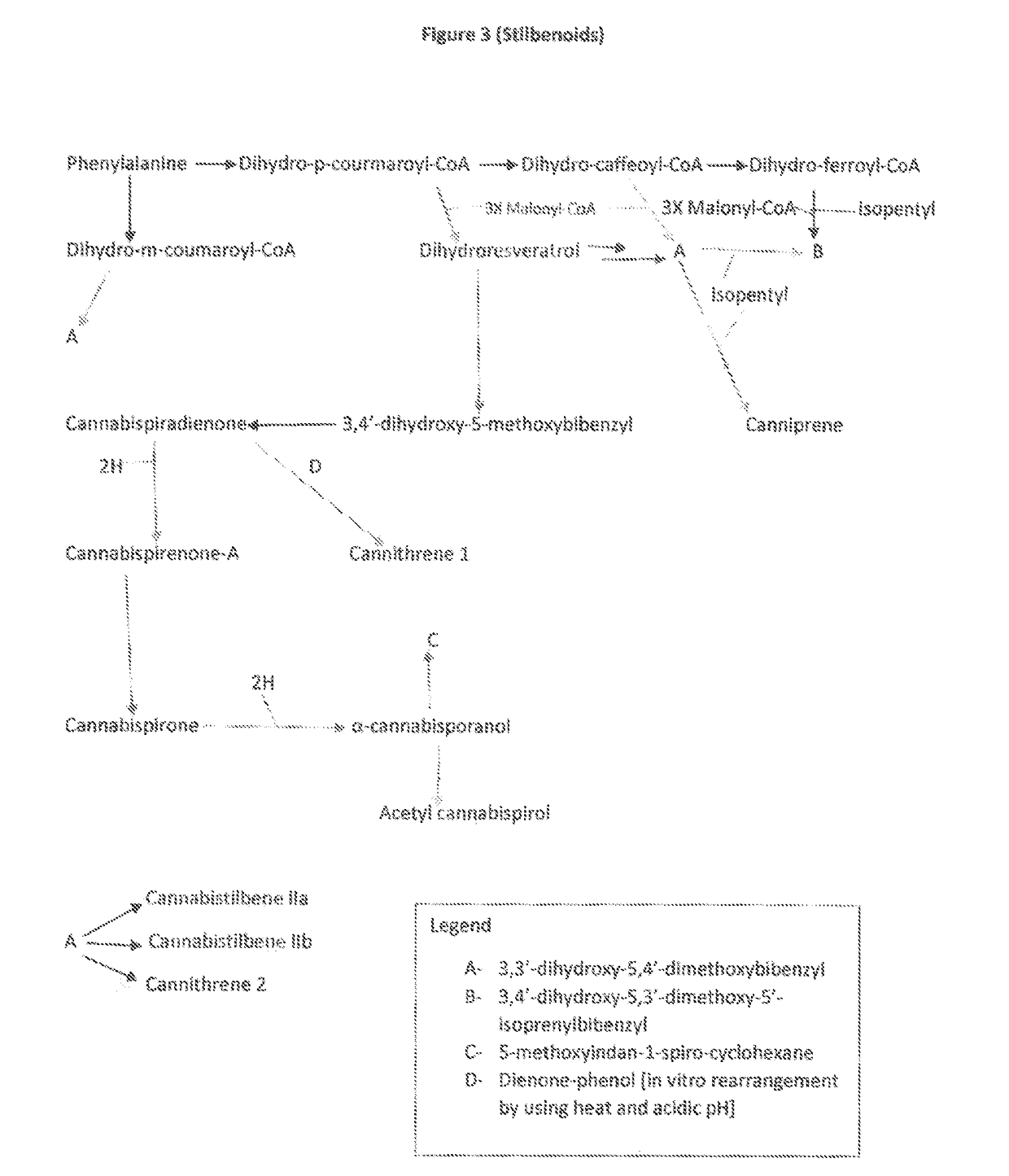
The present invention is a method for the biosynthesis of hundreds of compounds, mainly found in the cannabis plant. The starting material for these compounds can be any biological compound that is used / produced in a biological organism from the sugar family starting materials or other low cost raw materials processed via enzymes or within organisms to give final products. These final products include, but are not limited to: cannabinoids, terpenoids, stilbenoids, flavonoids, phenolic amides, lignanamides, spermidine alkaloids, and phenylpropanoids. Specifically, the present invention relates to the regular / modified / synthetic gene(s) of select enzymes are processed and inserted into an expression system (vector, cosmid, BAC, YAC, phage, etc.) to produce modified hosts. The modified host is then optimized for efficient production and yield via manipulation, silencing, and amplifying inserted or other genes in the host, leading to an efficient system for product.
Owner:BUTT SHER ALI +1
Glucosidase/xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102041251AHigh activityReduce complexityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesChemical industryCellulose
The invention relates to a novel beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The coding sequence of amino acid of the RuGBGX2 contains 18-755th sites of an SEQ ID NO 2 sequence. The RuGBGX2 is sourced from the rumen microorganism of yak from China, a novel coding gene of the beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme RuGBGX2 is obtained by function screening and sequencing analysis on a rumen metagenome cosmid library and a subclone library. The beta glucosidase / xylosidase difunctional cellulose degradation enzyme provided by the invention can be widely applied to the degradation of cellulose and the fields such as cellulose biotransformation, chemical industry, spinning, foods, bioenergy, feed additives, medical industry and the like. By utilizing the difunctional enzyme RuGBGX2 to degrade wood fiber, the varieties of added enzymes can be reduced, and an enzymolysis process can be simplified.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV +1
Recombinant duck enteritis virus (DEV) vaccine strain for expressing avian influenza virus haemagglutinin (HA) gene and constructing method and application thereof
ActiveCN102373180AMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsAvian influenza virusInfluenza virus A hemagglutinin
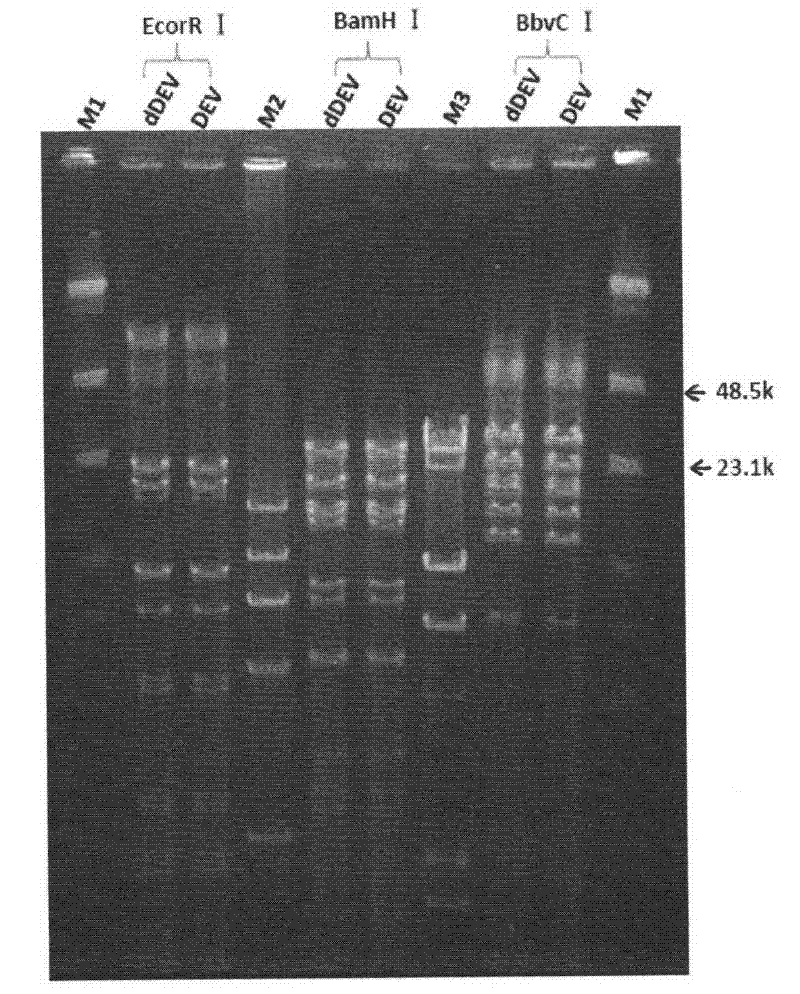
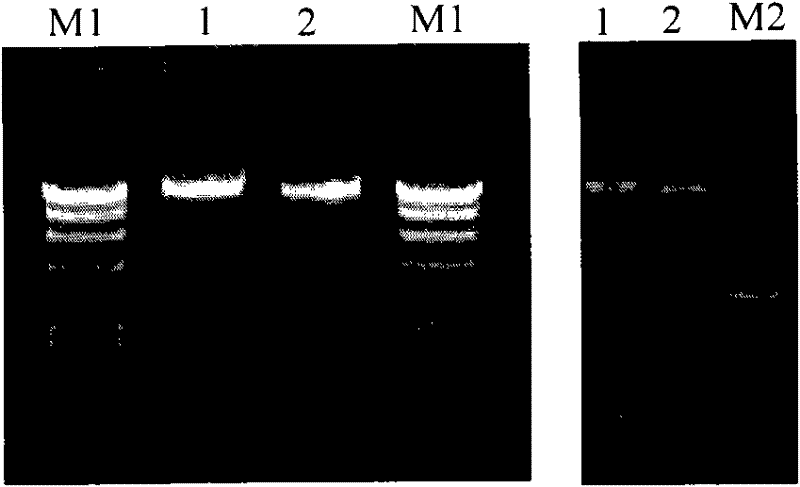
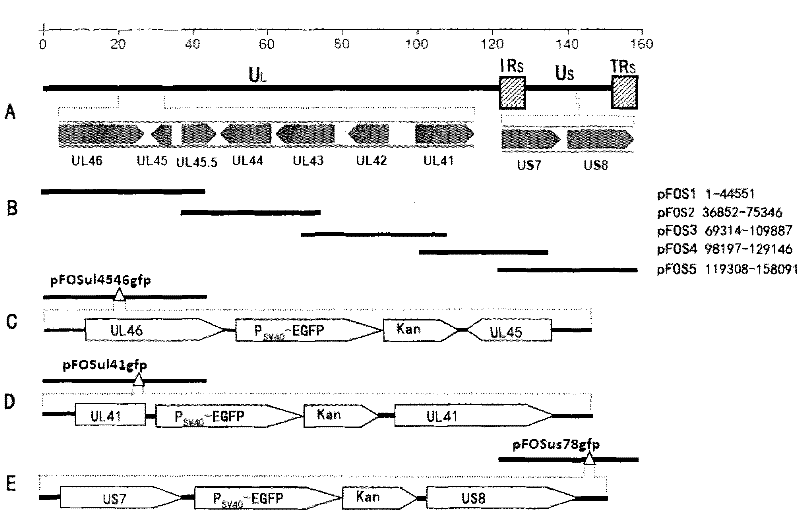
The invention provides a recombinant duck enteritis virus (DEV) vaccine strain CCTCC NO:V201125 named rDEVus78Ha-Re6 for expressing an avian influenza virus haemagglutinin (HA) gene, and a constructing method and application thereof. The vaccine strain is prepared by the following steps of: inserting a genetic fragment SV40-HA comprising the avian influenza virus HA gene and an SV40 promoter sequence into a spacer between a US7 gene and a US8 gene of a DEV by adopting a recombinant cloning technology; constructing a cosmid for inserting an SV40-HA expression frame between the US7 gene and theUS8 gene; and saving to obtain the recombinant DEV vaccine strain CCTCC NO:V201125 for expressing the avian influenza virus HA gene. The invention further relates to a method for constructing the recombinant DEV vaccine strain and application of the recombinant DEV vaccine strain to preparation of a vaccine for preventing duck viral enteritis and avian influenza.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant duck virus enteritis virus vaccine strain (rDEVul41HA) for expressing avian influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) genes and construction method as well as application thereof
The invention provides a recombinant duck virus enteritis virus vaccine strain CCTCC No.V201026, named as rDEVul41HA, for expressing avian influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) genes and a construction method as well as application thereof. Specifically, gene segments SV40-HA containing avian influenza virus hemagglutinin HA genes and a SV40 promoter sequence are inserted into UL41 genes of duck virus enteritis virus to construct cosmids with SV40-HA expression cassette inserted into UL41 genes; and by the cosmids, the recombinant duck virus enteritis virus vaccine strain CCTCC V201026 for expressing the avian influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) genes is saved and obtained. The invention also relates to a method for constructing the recombinant duck virus enteritis virus vaccine strain and application of the recombinant duck virus enteritis virus vaccine strain to preparing vaccines for preventing duck virus enteritis and avian influenza.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Duck viral enteritis virus infectious recombinant cloning system and its construction method and application
The invention relates to a duck enteritis virus infectious recombinant cloning system. The duck enteritis virus infectious recombinant cloning system is characterized by comprising a plurality of cosmids, wherein a duck enteritis virus vaccine strain gene segment is cloned in each cosmid, contains areas which are overlapped with each other, and a duck enteritis virus vaccine strain complete genome is assembled and covered; and an exogenous gene is inserted in a replication nonessential region of at least one cosmid. The invention also relates to a method for constructing the duck enteritis virus infectious recombinant cloning system and application of the duck enteritis virus infectious recombinant cloning system to the construction and recombination of the duck enteritis virus.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Recombined duck virus enteritis viral vaccine strain CCTCC for expressing bird flu virus hemagglutinin (HA) gene (rDEVus78Ha) as well as establishing method and application thereof
The invention provides a recombined duck virus enteritis viral vaccine strain CCTCC for expressing bird flu virus hemagglutinin HA gene with V201025, which is named as rDEVus78Ha, as well as an establishing method and application thereof. Particularly, by utilizing the recombination clone technology, the gene segment SV40-HA including the bird flu virus hemagglutinin HA gene and SV40 promoter sequence is inserted in the spacer between the US7 and US8 genes of the duck virus enteritis virus, so as to establish and obtain the cosmid inserted into the SV40-HA expression cassette between the US7 and US8 genes, as a result, the recombined duck virus enteritis viral vaccine strain CCTCC for expressing bird flu virus hemagglutinin HA gene with V201025 is saved and obtained. The invention also relates to a method for establishing the recombined duck virus enteritis viral vaccine strain and the application of the recombined duck virus enteritis viral vaccine strain to preparing the vaccine for preventing duck virus enteritis and bird flu.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
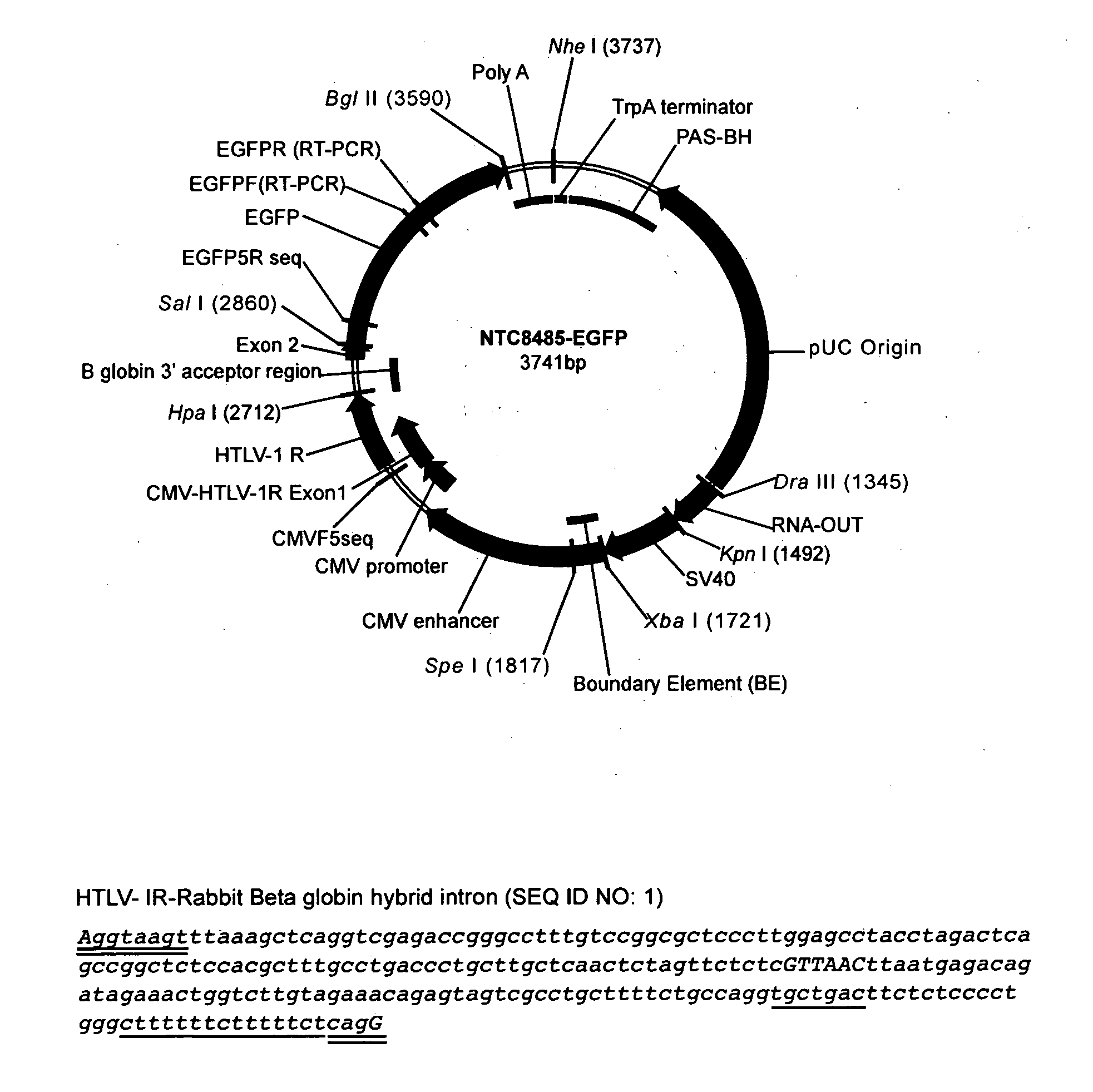
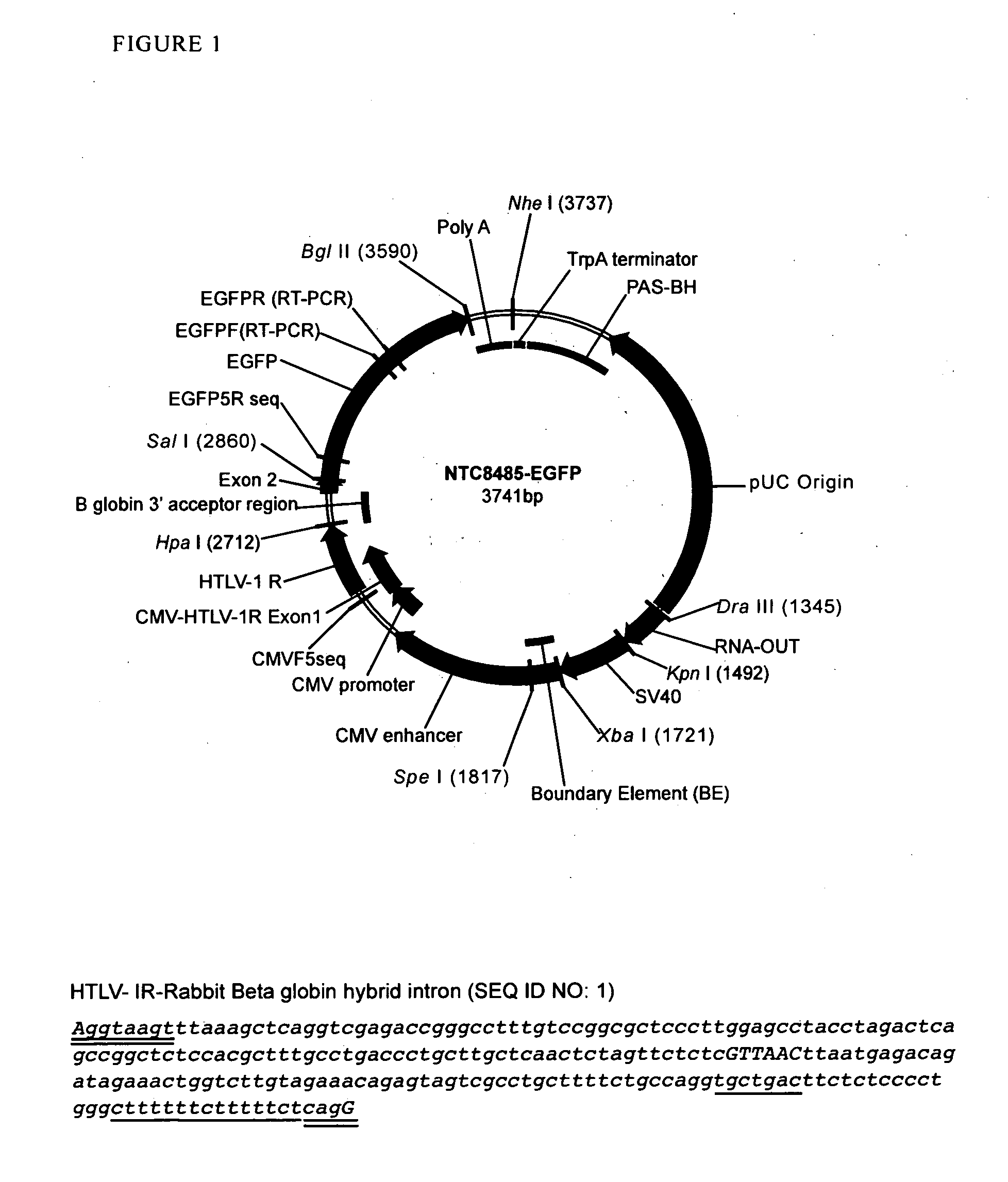
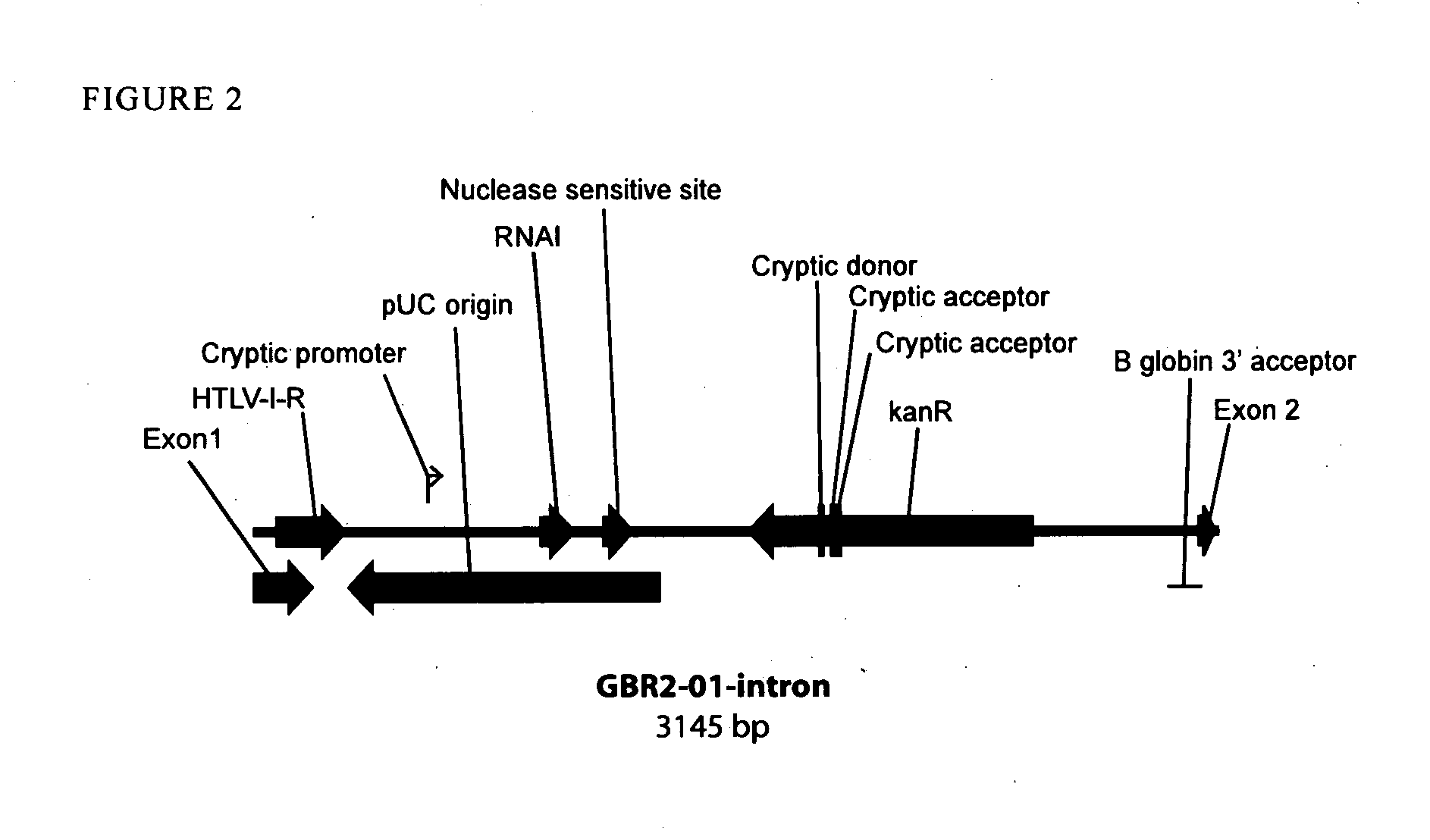
Replicative minicircle vectors with improved expression
ActiveUS20150275221A1Efficient preparationImproved in vivo expressionGenetic material ingredientsNucleic acid vectorBacteriophageViral vector
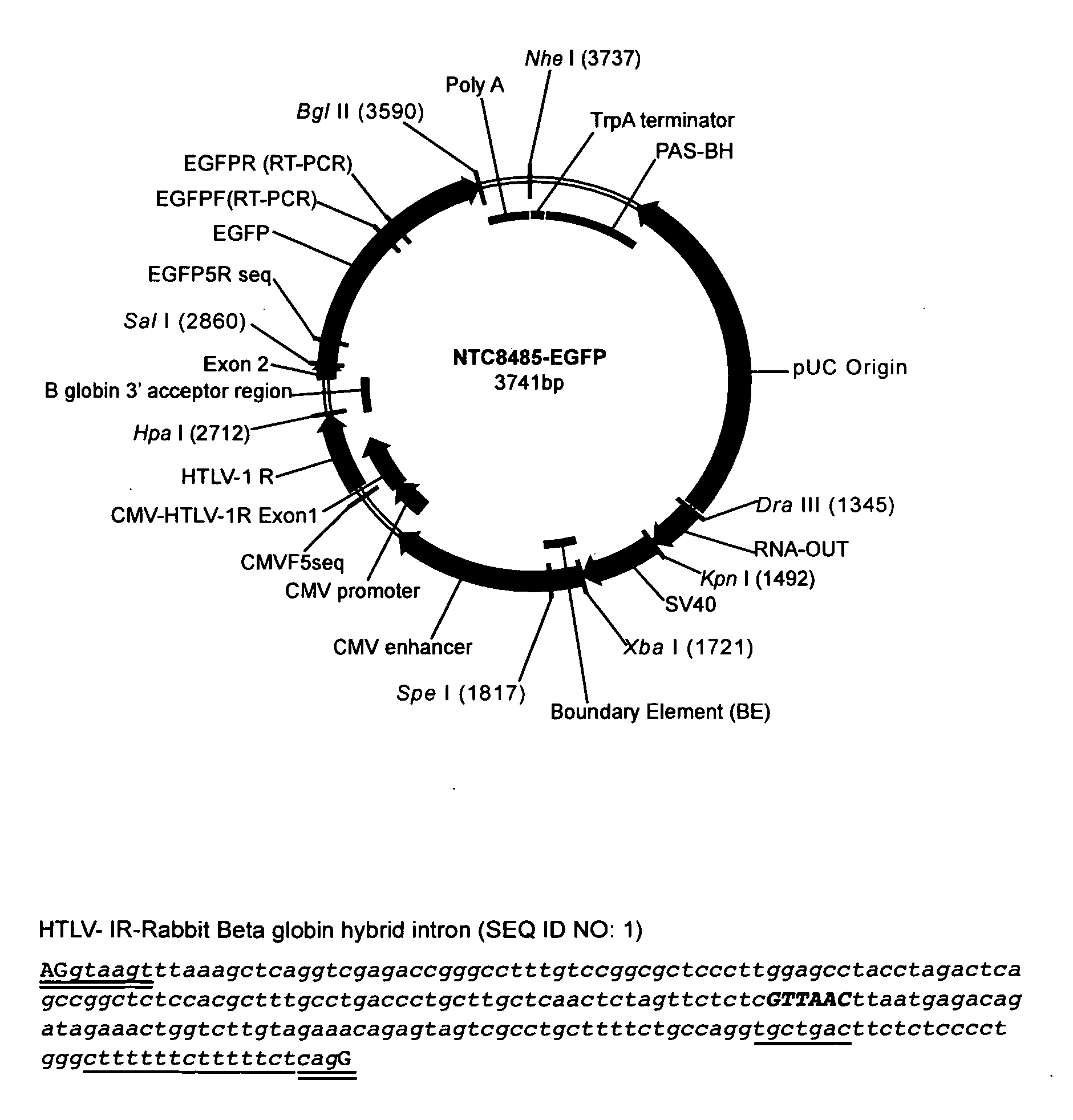
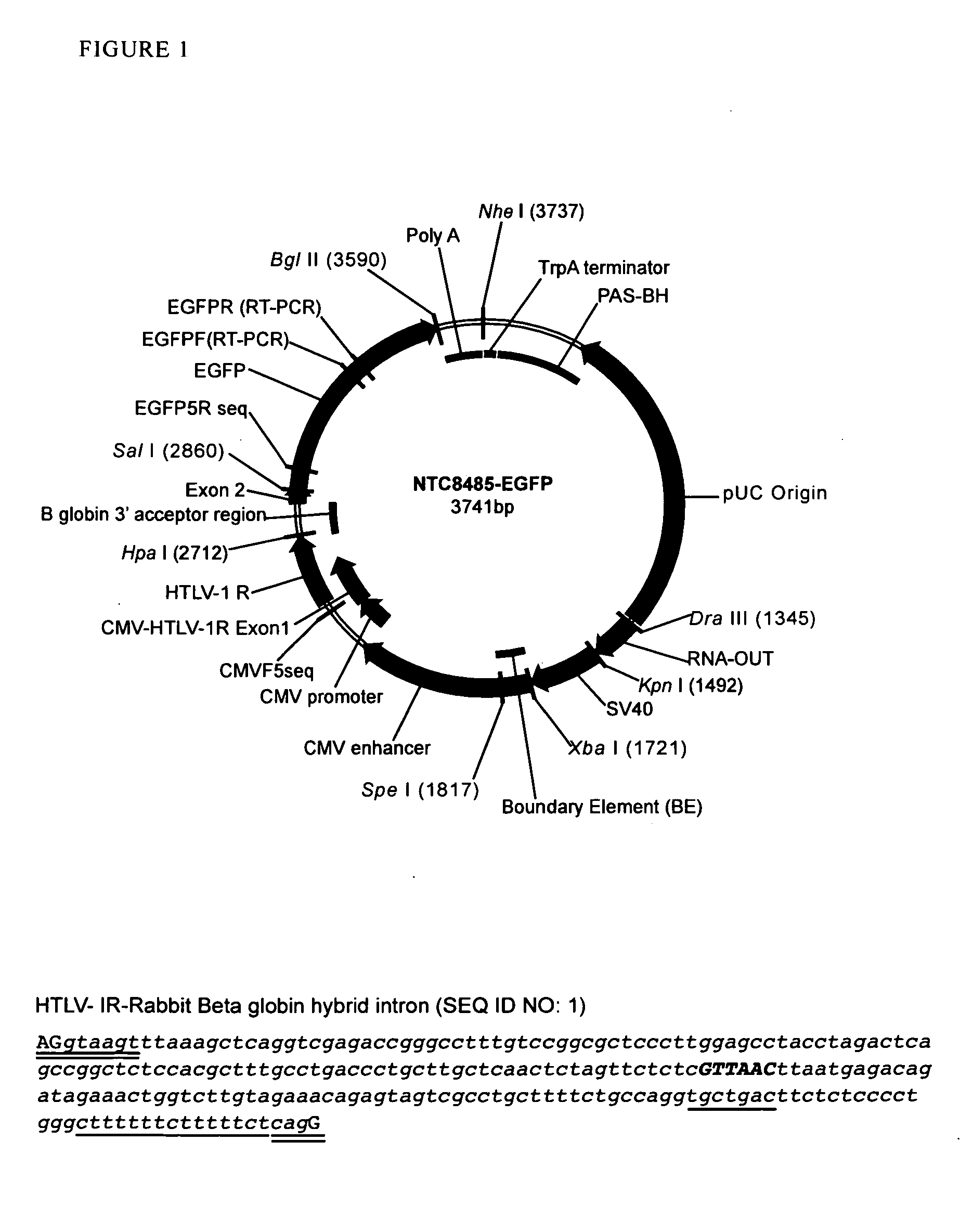
The present invention relates to the production and use of covalently closed circular (ccc) recombinant DNA molecules such as plasmids, cosmids, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), bacteriophages, viral vectors and hybrids thereof, and more particularly to vector modifications that improve expression of said DNA molecules.
Owner:ALDEVRON LLC
Marek's disease virus infectivity recombinant cloning system, and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN104946678AImprove securityEasy to insertMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsMarek's disease virus MDVGenome
The invention discloses a Marek's disease virus (MDV) infectivity recombinant cloning system, and a construction method and application thereof and belongs to the field of biotechnologies. The MDV infectivity recombinant cloning system comprises a plurality of cosmids, wherein an MDV vaccine strain gene segment is cloned in each cosmid; the MDV vaccine strain gene segment contains mutually superposed regions and can be spliced to cover an integral MDV vaccine strain genome; an exogenous gene is inserted into a non-essential region for replication of at least one of the cosmids. The MDV infectivity recombinant cloning system can quickly and efficiently clone an exogenous gene expression cassette into the MDV genome to further realize rescue of the recombinant MDV. The recombinant cloning system can be used for very conveniently inserting different foreign genes into the corresponding regions so as to construct an MDV living-vector multi-vaccine.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
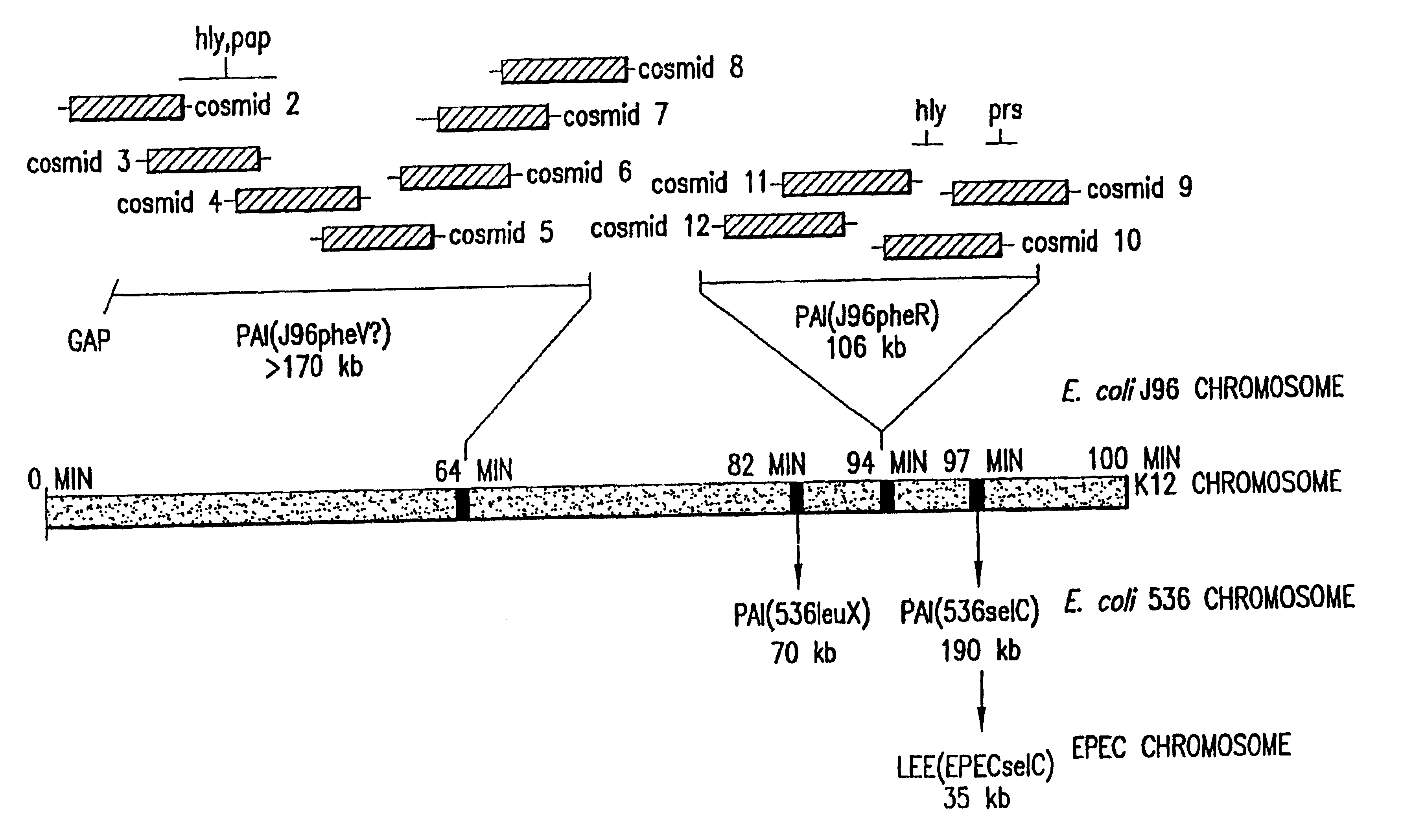
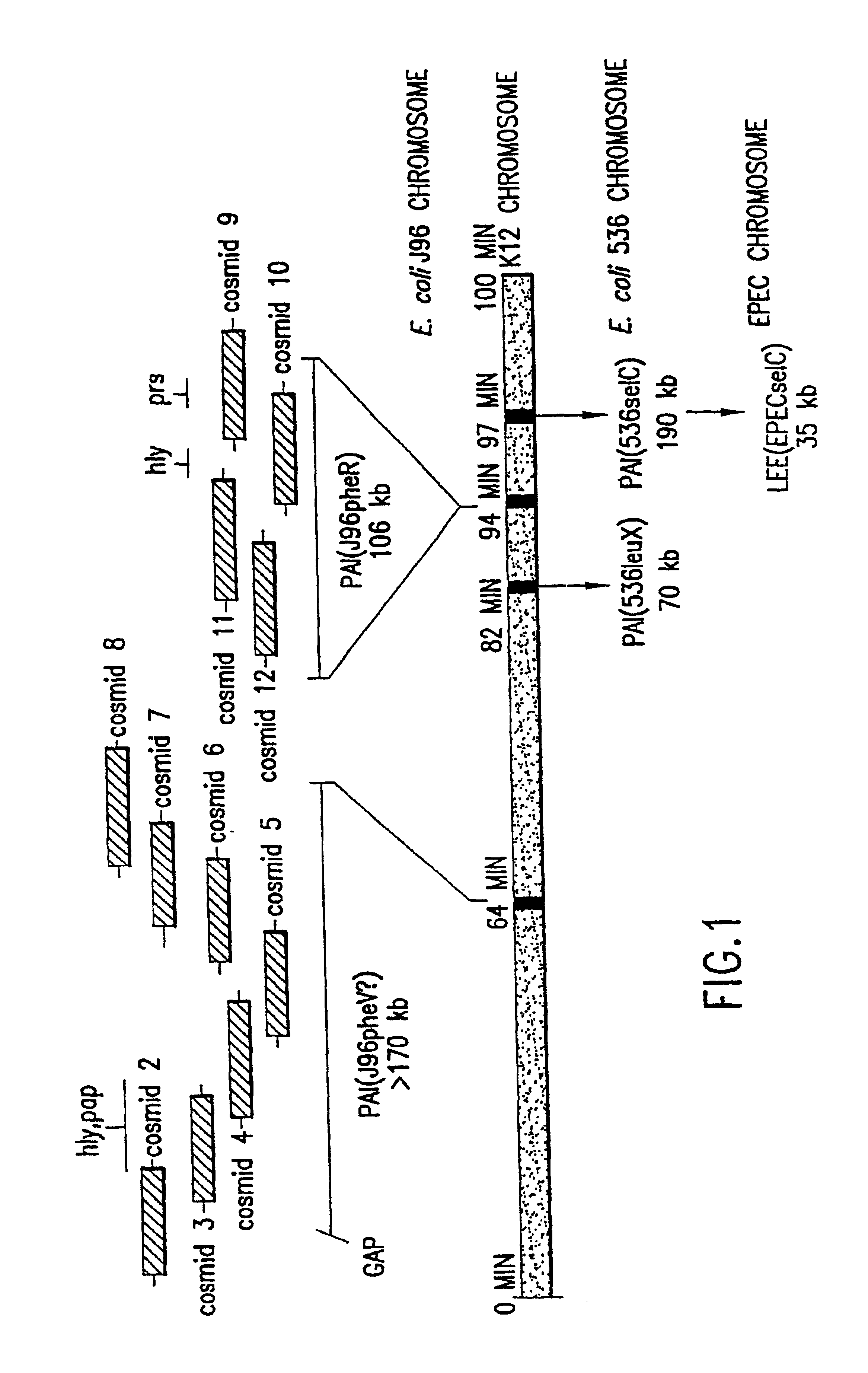
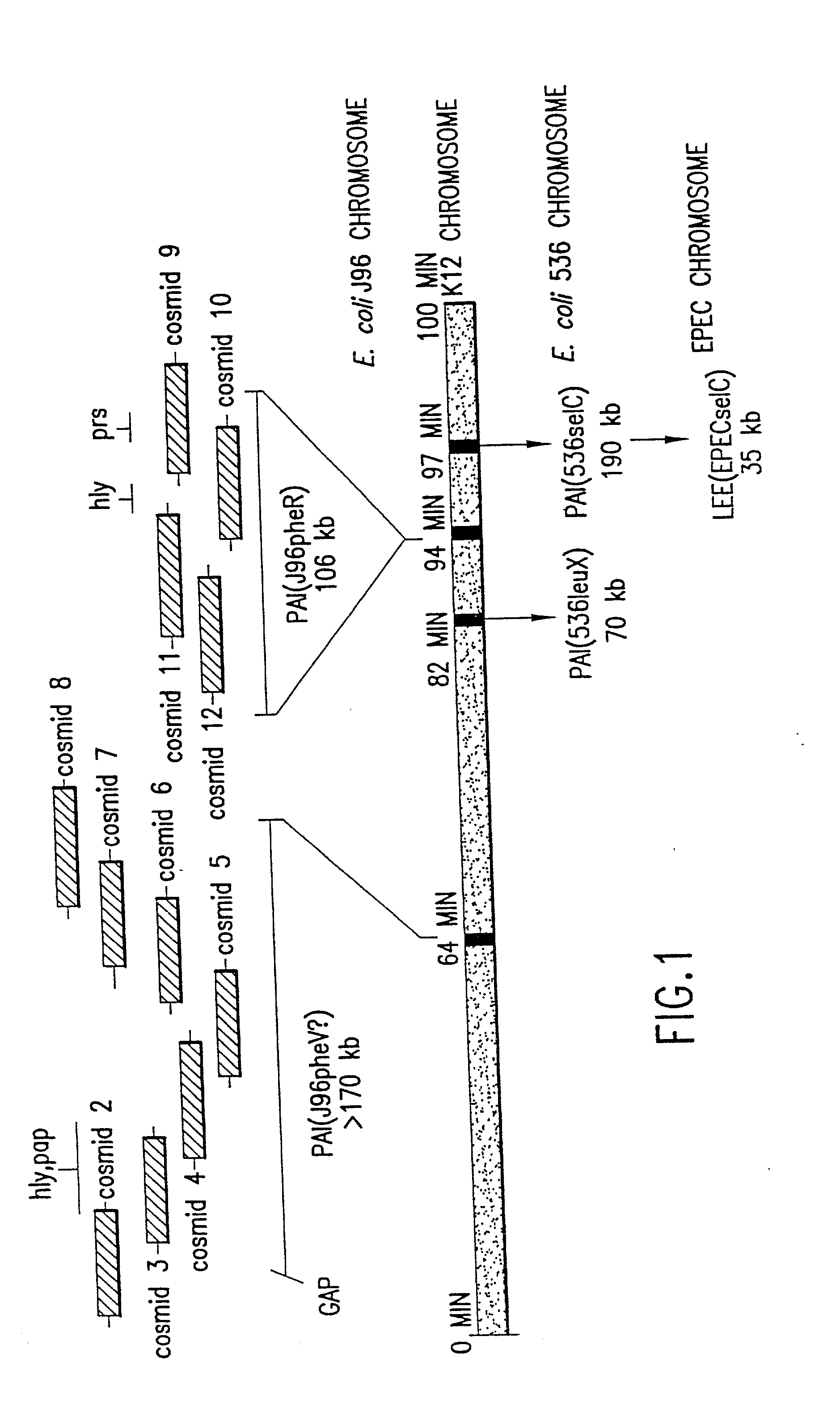
Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli pathogenicity islands
The present invention relates to novel genes located in two chromosomal regions within uropathogenic E. coli that are associated with virulence. These chromosomal regions are known as pathogenicity islands (PAIs). In particular, the present application discloses 142 sequenced fragments (contigs) of DNA from two pools of cosmids covering pathogenicity islands PAI IV and PAI V located on the chromosome of the uropathogenic Escherichia coli J96. Further disclosed are 351 predicted protein-coding open reading frames within the sequenced fragments.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC +1
Fusion proteins useful ln the production of cannabinoids
The present invention is a method for the biosynthesis of hundreds of compounds, mainly found in the cannabis plant. The starting material for these compounds can be any biological compound that is used / produced in a biological organism from the sugar family starting materials or other low cost raw materials processed via enzymes or within organisms to give final products. These final products include, but are not limited to: cannabinoids, terpenoids, stilbenoids, flavonoids, phenolic amides, lignanamides, spermidine alkaloids, and phenylpropanoids. Specifically, the present invention relates to the regular / modified / synthetic gene(s) of select enzymes are processed and inserted into an expression system (vector, cosmid, BAC, YAC, phage, etc.) to produce modified hosts. The modified host is then optimized for efficient production and yield via manipulation, silencing, and amplifying inserted or other genes in the host, leading to an efficient system for product.
Owner:CB THERAPEUTICS INC
Recombined chicken Marek's disease virus vaccine strain for expressing infectious bursaldisease virus VP2 gene and construction method and application of recombined chicken Marek's disease virus vaccine strain
ActiveCN105695423AStrong immune responseStable traitsVirus peptidesDsDNA virusesVp2 geneMarek's disease
The invention discloses a recombined chicken Marek's disease virus vaccine strain for expressing an infectious bursaldisease virus VP2 gene and a construction method and application of the recombined chicken Marek's disease virus vaccine strain, and belongs to the technical field of medicine or veterinary medicine. By means of the recombination and clone technology, a gene segment CAG-VP2 containing the infectious bursaldisease virus VP2 gene and a CAG promoter sequence is inserted in a US2 gene of the strain 814 of the chicken Marek's disease virus, a recombined cosmid with a CAG-VP2 expression frame inserted in a US2 gene is constructed, and the recombined chicken Marek's disease virus vaccine strain for expressing the infectious bursaldisease virus VP2 gene is obtained through salvation of the recombined cosmid. Research shows that the obtained vaccine strain has the same in-vitro replication ability as a parent virulent vaccine strain 814 and good hereditary stability, and can resist attacks of a very virulent MDV strain and a very virulent IBDV strain at the same time. It can be seen that the obtained recombined MDV vaccine strain can be used for preparing medicine for preventing or treating infectious bursaldisease and the chicken Marek's disease.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Retrovirus-based genomic screening
The present invention relates to the expression and screening of genomic DNA sequences encoding uncharacterized genes and proteins. The present invention provides systems utilizing unique features of retroviral replication to analyze uncharacterized genes derived from genomic DNA samples. In preferred embodiments, a segment of genomic DNA is inserted between 5′ and 3′ viral long terminal repeats (LTRs) in a vector (e.g., a plasmid, cosmid, or artificial chromosome vector). The resulting vector (or library of vectors containing a plurality of independent genomic sequences) is then introduced into a retroviral packaging cell. The resulting provirus or proteins expression from the provirus are then analyzed.
Owner:CATALENT USA WOODSTOCK INC +3
Bacterial strains with improved plasmid stability
ActiveUS20100233814A1Improve production yieldHigh copy numberFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBacteroidesBacterial strain
The present invention relates to the propagation of covalently closed circular recombinant DNA molecules such as plasmids, cosmids, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), bacteriophages, viral vectors and hybrids thereof, and more particularly is strain modifications that improve strain viability, plasmid stability, plasmid production yield, and plasmid-directed protein production yield, using said DNA molecules in fermentation culture.
Owner:ALDEVRON LLC
Construction and application of recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine for expressing secretory duck Tembusu virus M/E protein
ActiveCN103667197AGenetic material ingredientsMicroorganism based processesTembusu virusSv40 promoter
The invention provides a recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine for expressing secretory duck Tembusu virus M / E protein, and a construction method and application thereof. The collection number is CCTCC NO:V201215, and the name is rDEV-TME-tPAS. By using a recombinant clone technique, a gene segment rDEV-TME-tPAS comprising an SV40 promoter, duck Tembusu virus M and E proteins and a tPA (Tissue plasminogen activator) signal peptide sequence is inserted into a spacer between the US7 and US8 genes of the duck viral enteritis virus to construct a cosmid in which the rDEV-TME-tPAS expression frame is inserted between the US7 and US8 genes, thereby obtaining the recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine CCTCC V201215 for expressing secretory duck Tembusu virus M / E protein. The invention also provides a method for constructing a recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine strain and application of the recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine strain in preparing a vaccine for preventing infectious diseases caused by duck viral enteritis virus and duck Tembusu virus.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Vector system for herpes simplex virus/phiC31 integrase (HSV/phiC31) heterozygosity amplicon and preparation method of vector system
InactiveCN102002514AOvercome the inadequacies that cannot be expressed for a long timeSafer and More Efficient WayFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPurineΦc31 integrase
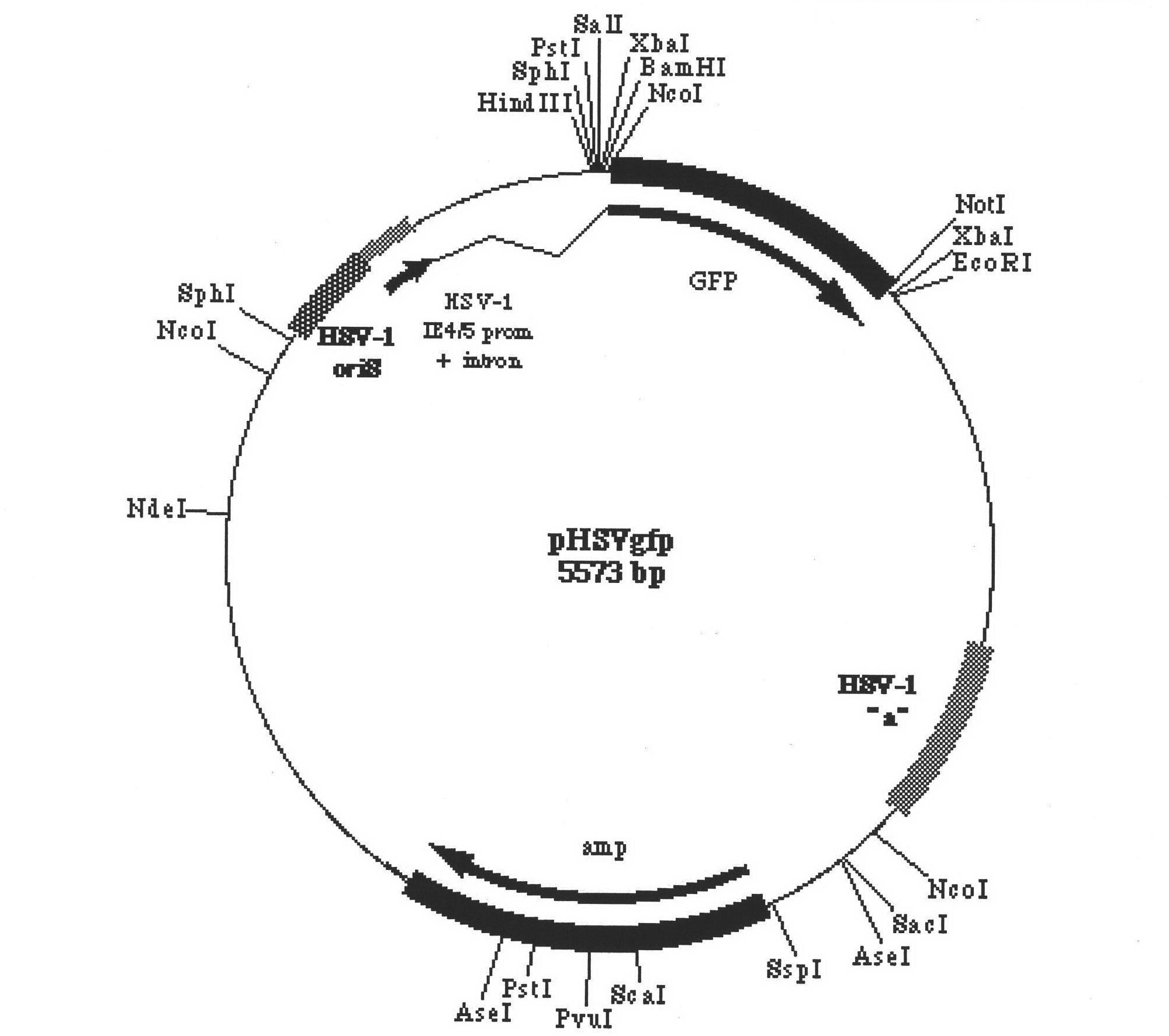
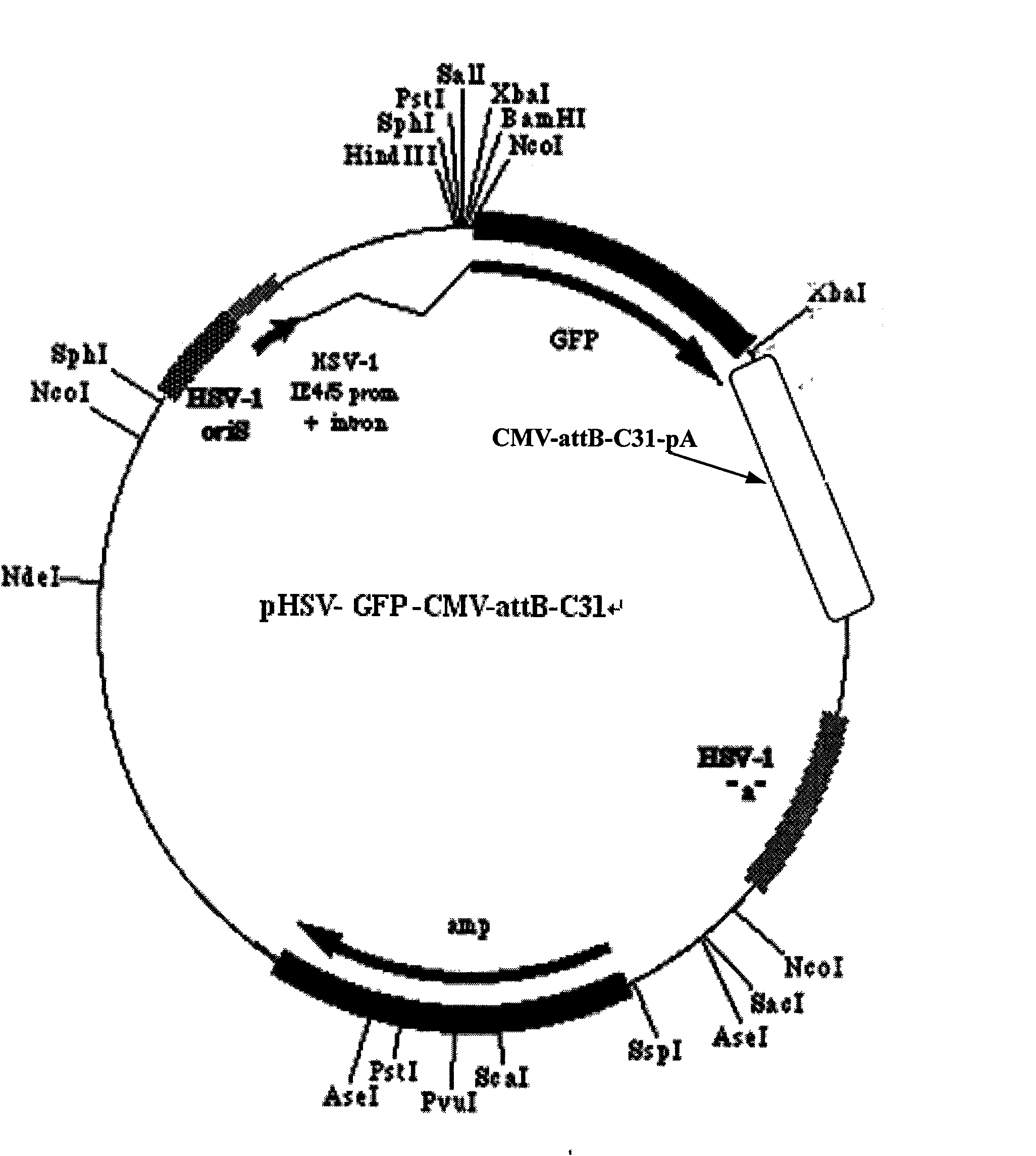
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, relating to a vector system for herpes simplex virus / phiC31 integrase (HSV / phiC31) heterozygosity amplicon and a preparation method of the vector system. The vector system comprises heterozygosity HSV / phi C31 amplicon vector and five helper free virus packaging cosmid, namely COS6 delta a, COS14, COS28, COS56 and COS48 delta a; the heterozygosity HSV / phiC31 amplicon vector plasmid is composed of HSV amplicon vector pHSV-GFP, cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoter, attB locus, a phiC31 intergrase gene coding sequence and poly-adenine, wherein theattB locus is positioned between the CMV promoter and the phiC31 integrase gene coding sequence. The vector system of the invention has function of locus-specific conformability, can express exogenous target gene in various host cells for a long time, and can be used for the research on functions of exogenous genes or gene therapy.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Efficient endoglucanase RuCelB, coded gene, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102041252AImprove thermal stabilityEase of industrial applicationMicroorganism based processesEnzymesCelluloseBio engineering
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering, and relates to a novel endoglucanase RuCelB, a coded gene, a preparation method and an application thereof. The RuCelB contains a 25th-336th amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID NO.2. The preparation method is as follows: obtaining positive cloning capable of hydrolyzing sodium carboxymethylcellulose by active screening rumen microorganism metagenomic cosmid library of a yak, and further obtaining a whole-length cds sequence of the RuCelB by building subcloning, sequencing and homologous comparison; and carrying out recombined expression and obtaining the RuCelB. The specific activity of the RuCelB taking the sodium carboxymethylcellulose as a substrate is up to 158.8U / mg, and the RuCelB also has the degradability for the substrates such as filter paper, cellotriose and the like. The RuCelB can be widely applied in degradation of cellulose, comprising the industries such as cellulose biotransformation, chemical engineering, textile, food, bioenergy, feedstuff adding, pharmaceutical Industry and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Bacterial strains with improved plasmid stability
ActiveUS9012226B2High copy numberImprove production yieldFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBacteroidesBacterial strain
The present invention relates to the propagation of covalently closed circular recombinant DNA molecules such as plasmids, cosmids, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), bacteriophages, viral vectors and hybrids thereof, and more particularly is strain modifications that improve strain viability, plasmid stability, plasmid production yield, and plasmid-directed protein production yield, using said DNA molecules in fermentation culture.
Owner:ALDEVRON LLC
Construction and application of recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine for expressing secretory duck Tembusu virus E protein
ActiveCN103667198AGenetic material ingredientsMicroorganism based processesTembusu virusSv40 promoter
The invention provides a recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine for expressing secretory duck Tembusu virus E protein, and a construction method and application thereof. The collection number is CCTCC V201214, and the name is rDEV-TE-tPAS. By using a recombinant clone technique, a gene segment SV40-E-tPA comprising an SV40 promoter, a duck Tembusu virus E protein and a tPA (Tissue plasminogen activator) signal peptide sequence is inserted into a spacer between the US7 and US8 genes of the duck viral enteritis virus to construct a cosmid in which the SV40-E-tPA expression frame is inserted between the US7 and US8 genes, thereby obtaining the recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine CCTCC V201214 for expressing secretory duck Tembusu virus E protein. The invention also provides a method for constructing a recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine strain and application of the recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine strain in preparing a vaccine for preventing infectious diseases caused by duck viral enteritis virus and duck Tembusu virus.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Additive for directly reducing nickel laterite ores and application of additive
The invention discloses an additive for directly reducing nickel laterite ores, which is mainly prepared from an NCS additive, sodium sulfate, calcium carbonate, sodium phosphate, soda ash and borax respectively according to proportions of 15 to 25 percent, 5 to 10 percent, 2 to 10 percent, 1 to 5 percent and 2 to 5 percent of mass of the nickel laterite ores. The invention also discloses a method for preparing ferro-nickel alloy powder by the additive. The NCS of the additive is in contact with water in the nickel laterite ores to release more Ca and Al high valence cations and the Ca and Al high valence cations neutralize negative charges of cosmid, so that a diffusion layer is thinned and an enrichment effect of ferro-nickel is improved. In the reducing process, the additive reacts with the nickel laterite ores and breaks the structure of the nickel laterite ores, and a high-enrichment ferro-nickel element is obtained. Compared with other additives, the additive not only has low cost and is environmental-friendly, but also cannot corrode equipment and has wide market popularization prospect.
Owner:TAIZHOU YONGXING ALLOY MATERIAL TECH
Genetic screening method for negative regulatory factor of streptomyces biosynthesis gene cluster
PendingCN108611361AReduce false positivesReduce verification effortMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid vectorMetaboliteBiosynthetic genes
The invention provides a screening method for a negative regulatory factor of a novel biosynthesis gene cluster of streptomyces. The screening method comprises the following steps: constructing a promoter-mediated reporting system of genes of self-interest in a streptomyces cell, then using a random mutation system based on a transposon Himar1 to mutate the streptomyces with the reporting system,intensively screening a mutant streptomyces strain to obtain a streptomyces strain with high expression of target genes, performing bacteriophage packaging on genomes of the streptomyces strain with high expression of target genes and screening out cosmids with randomly inserted fragments, sequencing DNA of the cosmids to determine the location of the randomly inserted fragments in the genomes ofthe streptomyces strain with high expression of target genes. The screening method, provided by the invention, is stable in screening environment, high in screening flux, low in false positive, high in efficiency, accurate and convenient to operate, and can be widely used in the field of high-yield screening and transformation of industrial streptomyces metabolites, and the screened and transformed streptomyces metabolites are high in yield, good in genetic stability and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Recombined chicken Marek's disease virus vaccine strain for expressing Gag and Env genes of avian leukosis virus subgroup J and construction method and application of recombined chicken Marek's disease virus vaccine strain
ActiveCN105695422AReduce distractionsHas a clearing effectViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAvian leukosis virusesEnvelope Gene
The invention discloses a recombined chicken Marek's disease virus vaccine strain for expressing Gag and Env genes of an avian leukosis virus subgroup J (ALV-J) and a construction method and application of the recombined chicken Marek's disease virus vaccine strain, and belongs to the technical field of medicine or veterinary medicine. By means of the recombination and clone technology, a gene segment CAG-ALVGE containing the ALV-J Gag and Env genes and a CAG promoter sequence is inserted in a US2 gene of the strain 814 of the chicken Marek's disease virus, a recombined cosmid with a CAG-ALVGE expression frame inserted in a US2 gene is constructed, and the recombined chicken Marek's disease virus vaccine strain for expressing the Gag and Env genes is obtained through salvation of the recombined cosmid. Research shows that the obtained vaccine strain has the same in-vitro replication ability as a parent virulent vaccine strain 814 and good hereditary stability, and can resist attacks of a very virulent MDV strain and a very virulent ALV-J strain at the same time. It can be seen that the obtained recombined MDV vaccine strain can be used for preparing medicine for preventing or treating avian leukosis and the chicken Marek's disease.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Serum 4 type aviadenovirus reverse genetic vaccine strain rHN20 as well as construction method and application thereof
PendingCN112538464AImproving immunogenicityReduce hidden dangersViral antigen ingredientsDigestive systemSerotypeImmunogenicity
The invention discloses a serum type 4 aviadenovirus reverse genetic vaccine strain rHN20 as well as a construction method and application thereof. According to the invention, infectious cloning cosmid Fos-rFAdV4 with the full length of FAdV-4 recently isolated strain HLJFAd15 genome in China is constructed, and on the basis, the Hexon gene is replaced with the Hexon gene of a foreign attenuated strain ON1 to obtain infectious cloning cosmid Fos-rHN20. The vaccine strain rHN20 is successfully rescued by utilizing the Fos-rHN20. Pathogenicity experiments show that rHN20 does not have pathogenicity on SPF chickens any more (100% of mortality rate exists before mutation). Immune protection experiments prove that the SPF chicken inoculated with the rHN20 can completely resist attacking infection of the FAdV-4 virulent strain, it is proved that the rHN20 has very good immunogenicity and can serve as a vaccine candidate strain, and meanwhile, the attenuated strain greatly reduces the hiddendanger of biosafety of the virulent strain.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli pathogenicity islands
The present invention relates to novel genes located in two chromosomal regions within uropathogenic E. coli that are associated with virulence. These chromosomal regions are known as pathogenicity islands (PAIs). In particular, the present application discloses 142 sequenced fragments (contigs) of DNA from two pools of cosmids covering pathogenicity islands PAI IV and PAI V located on the chromosome of the uropathogenic Escherichia coli J96. Further disclosed are 351 predicted protein-coding open reading frames within the sequenced fragments.
Owner:HUMAN GENOME SCI INC +1
Marek's disease virus infectious recombinant cloning system and its construction method and application
ActiveCN104946678BImprove securityEasy to insertMicroorganism based processesAntiviralsMareks disease virusMarek's disease
The invention discloses a Marek's disease virus (MDV) infectivity recombinant cloning system, and a construction method and application thereof and belongs to the field of biotechnologies. The MDV infectivity recombinant cloning system comprises a plurality of cosmids, wherein an MDV vaccine strain gene segment is cloned in each cosmid; the MDV vaccine strain gene segment contains mutually superposed regions and can be spliced to cover an integral MDV vaccine strain genome; an exogenous gene is inserted into a non-essential region for replication of at least one of the cosmids. The MDV infectivity recombinant cloning system can quickly and efficiently clone an exogenous gene expression cassette into the MDV genome to further realize rescue of the recombinant MDV. The recombinant cloning system can be used for very conveniently inserting different foreign genes into the corresponding regions so as to construct an MDV living-vector multi-vaccine.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
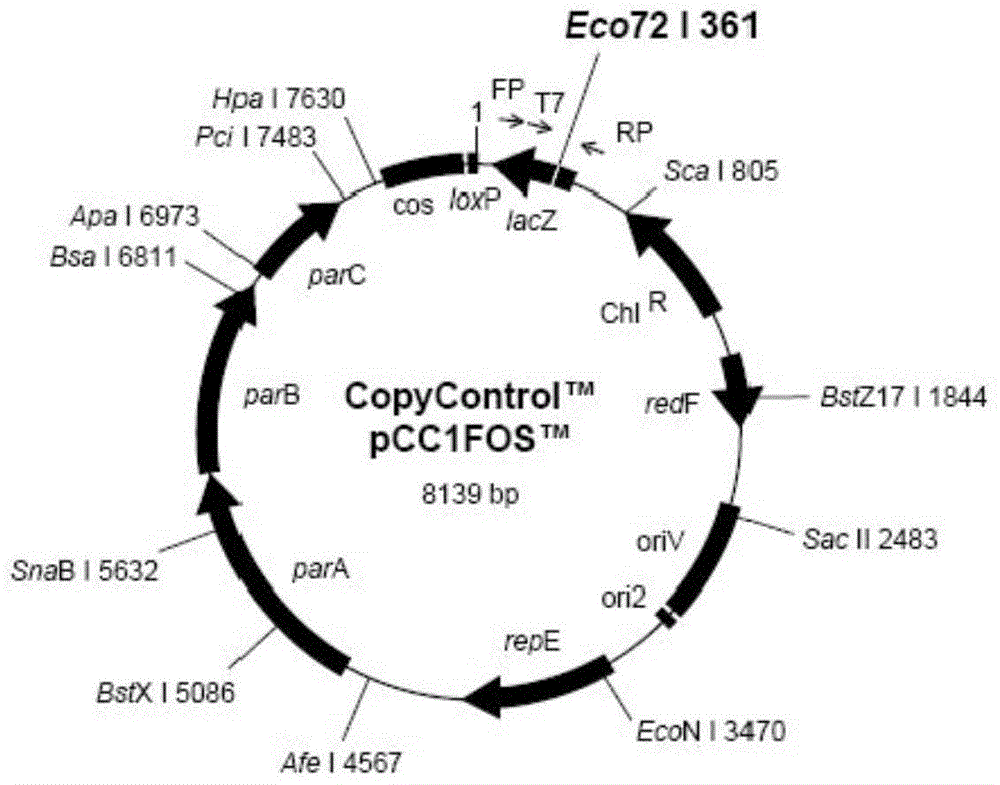
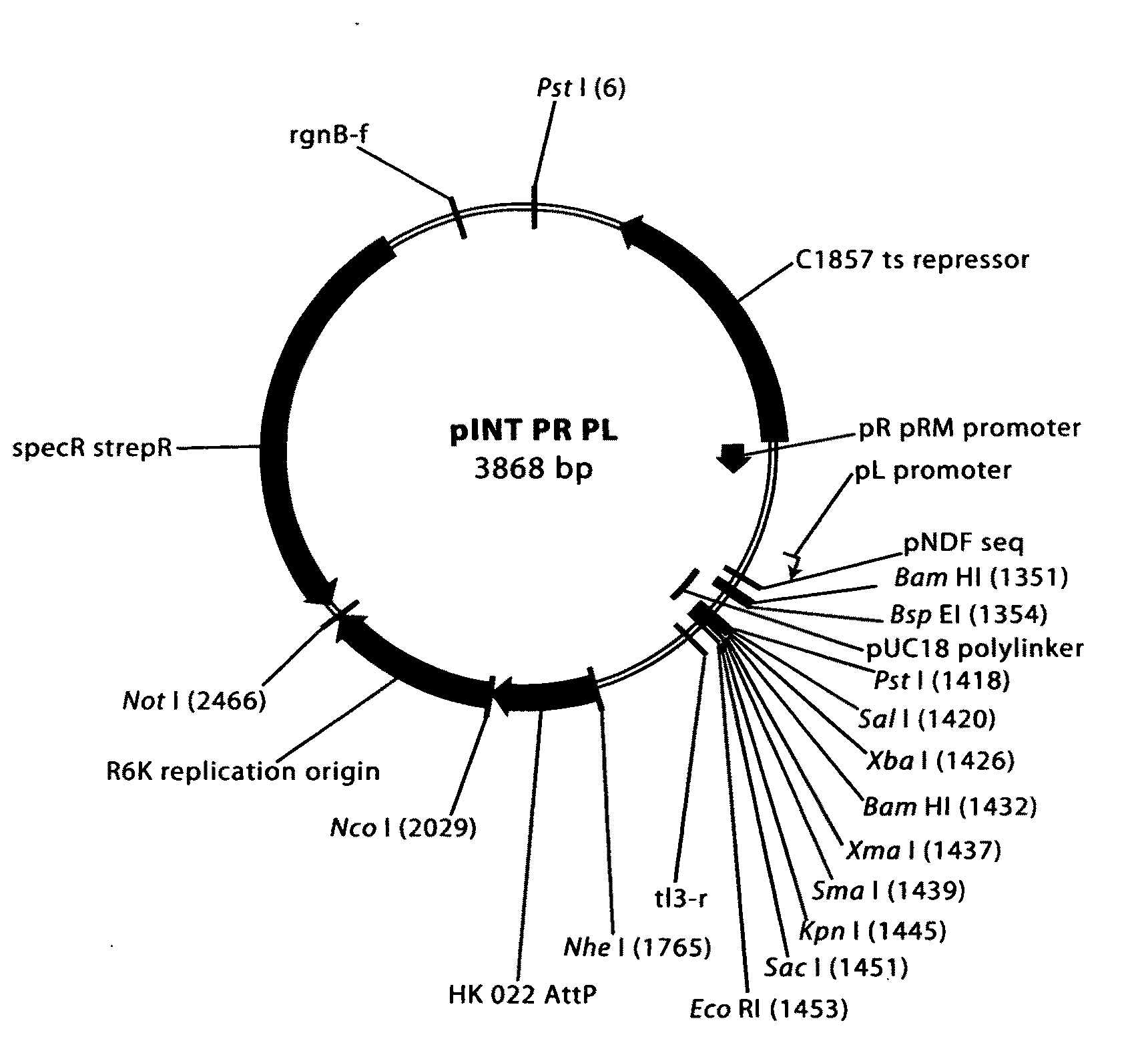
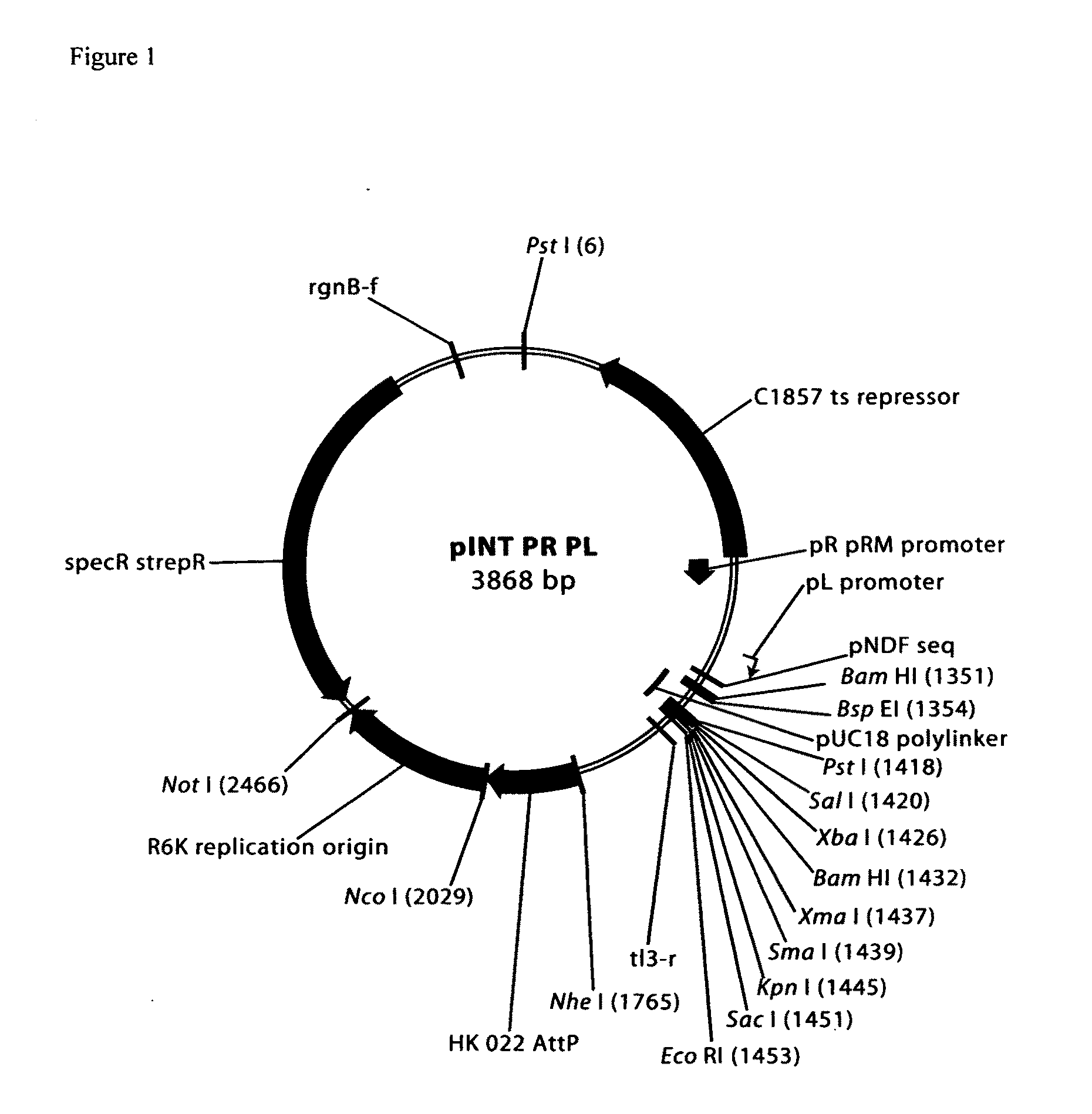
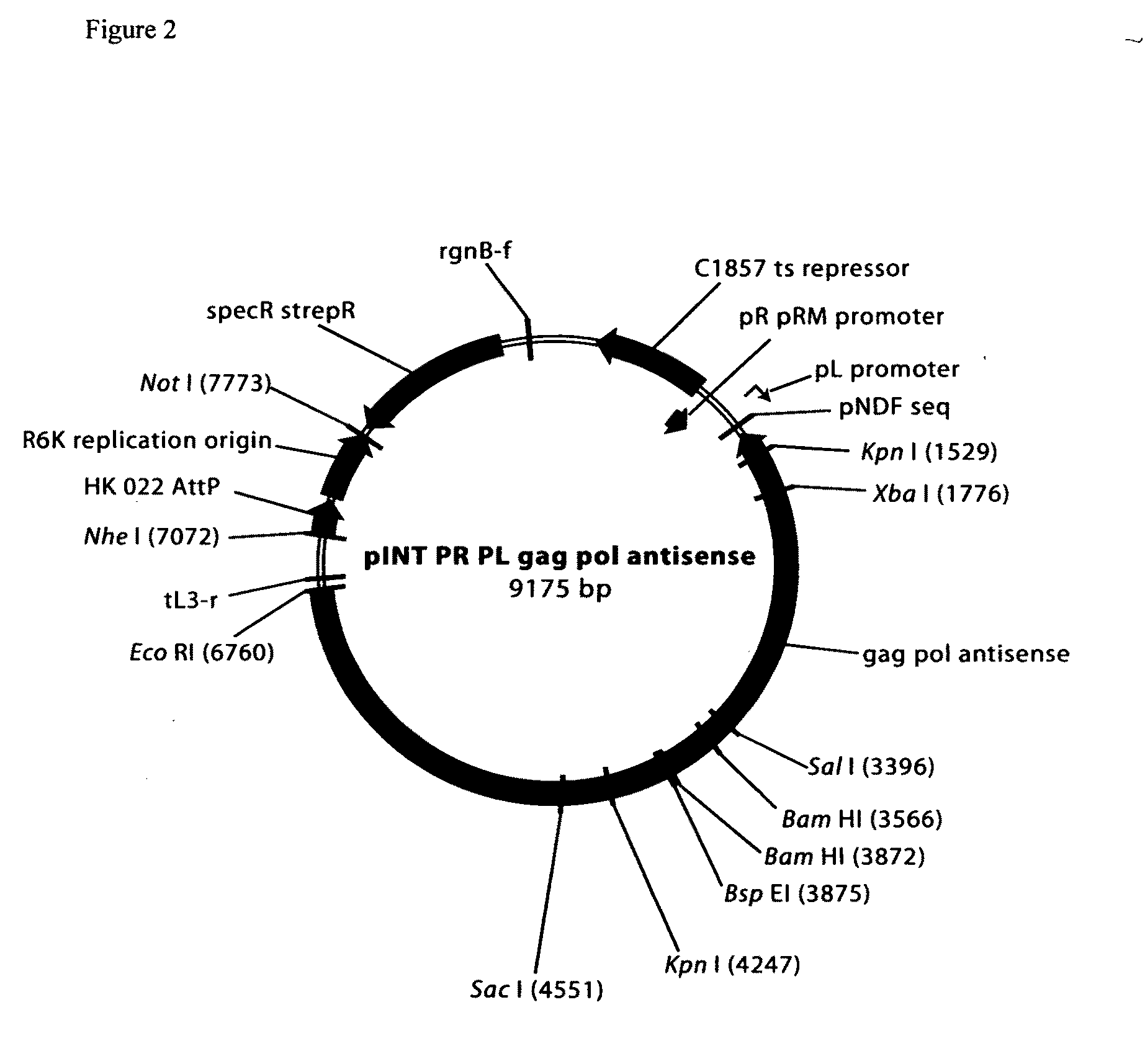
Cosmid DNA constructs and methods of making and using same
Methods of inducing immune responses in individuals against a pathogen are disclosed. Methods of treating individuals susceptible to or suffering from a disease associated with a genetic defect which results in the non-production or under production of a protein or the production of a non-functioning or partially functioning protein are disclosed. Methods of delivering a protein to an individual are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions that comprise cosmids are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Cosmid dna constructs and methods of making and using same
Methods of inducing immune responses in individuals against a pathogen are disclosed. Methods of treating individuals susceptible to or suffering from a disease associated with a genetic defect which results in the non-production or under production of a protein or the production of a non-functioning or partially functioning protein are disclosed. Methods of delivering a protein to an individual are disclosed. Pharmaceutical compositions that comprise cosmids are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Fine mapping and application of dna markers linked to a gall midge resistance gene for marker-aided selection in rice
InactiveUS20050183173A1Resist attackEasy to followMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesYeast artificial chromosomeScarring tissue
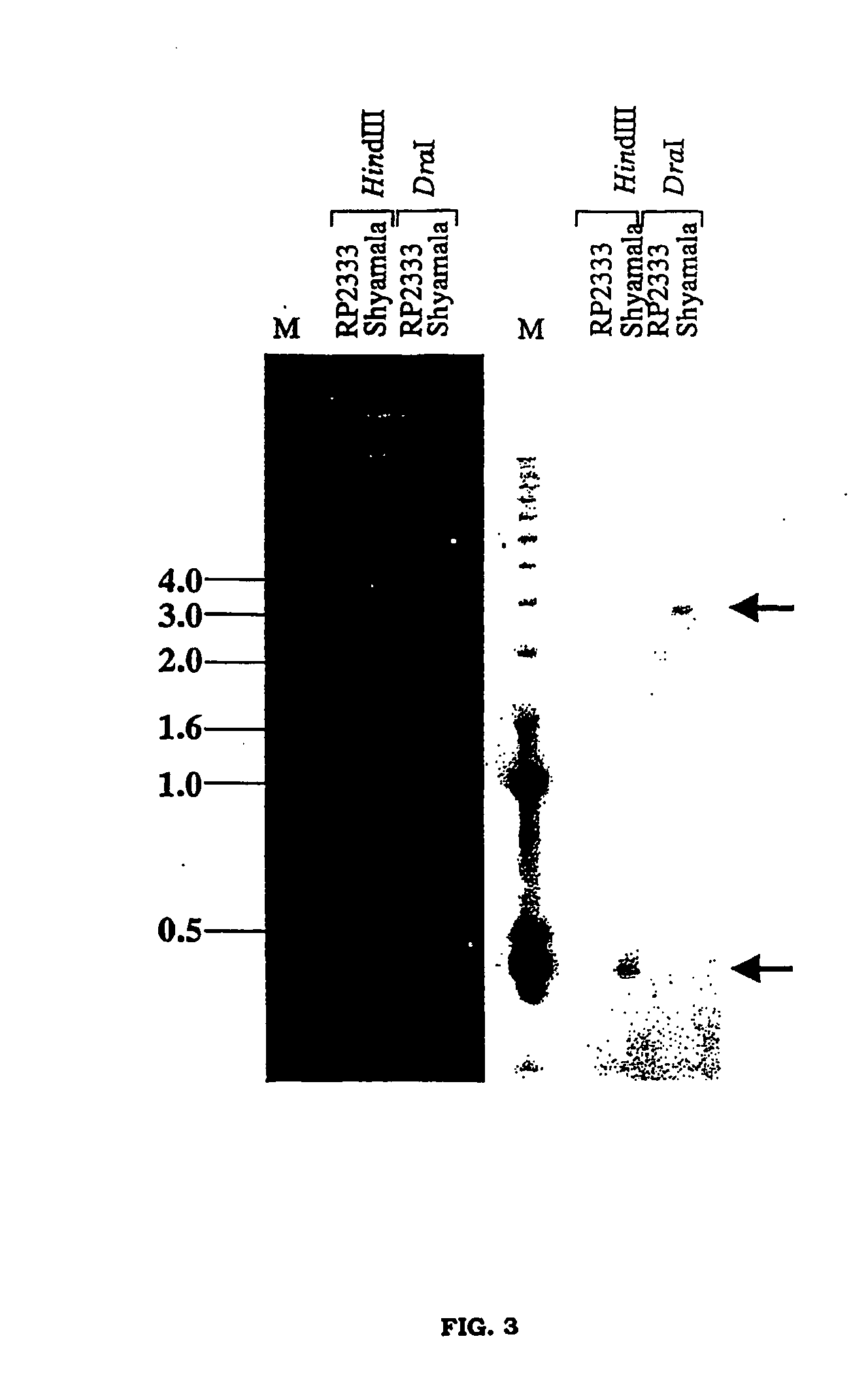
The present invention relates to fine mapping and potential application of dna markers linked to a gall midge resistance gene gm7 for marker-aided selection in rice. Towards this, the present invention discloses a combination of novel sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) primers for use in assay with the DNA of Rice plants in question. A cross between the gall midge resistant parent, RP2333 carrying the Gm7 gene and susceptible parent Shyamala, is developed and a F5 progeny is raised. A polymorphic band is identified from the F5 progeny, using AFLP that cosegregates with the susceptible phenotype. This band is eluted from the gel and cloned. The cloned AFLP fragment is sequenced and primers are developed for selectively amplifying DNA of susceptible phenotypes, thus differentiating them from the resistant phenotypes. This Gm7 gene linked marker is mapped onto chromosome 4 of rice and is also shown to be linked to Gm2 gene and the blight resistance gene, Xal through fine mapping using Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (YACS) and cosmids. This marker is present in a single copy in the susceptible parent, Shyamala. Primers developed from this marker are able to differentiate between the resistant and susceptible phenotypes in different crosses carrying different gall midge resistance genes. A number of screenings of resistant and susceptible varieties of rice with these primers show consistent polymorphism between them. The use of primers for PCR amplification of DNAs from F3 progenies derived from crosses between three different parental lines and the primers also differentiates the resistant phenotypes from the susceptible one. The primers of the present invention therefore have a great use in marker assisted selection as they show polymorphism between resistant and susceptible plants and therefore between plants with or without gall midge resistance genes.
Owner:SARDESAI NAGESH +2
Replicative minicircle vectors with improved expression
InactiveUS20150322439A1Efficient preparationMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsBacteriophageViral vector
The present invention relates to the production and use of covalently closed circular (ccc) recombinant DNA molecules such as plasmids, cosmids, bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs), bacteriophages, viral vectors and hybrids thereof, and more particularly to vector modifications that improve expression of said DNA molecules.
Owner:NATURE TECH CORP (US)
High-efficiency endoglucanase rucelb, its coding gene, preparation method and application
ActiveCN102041252BImprove thermal stabilityEase of industrial applicationMicroorganism based processesEnzymesCelluloseBio engineering
The invention belongs to the field of biological engineering, and relates to a novel endoglucanase RuCelB, a coded gene, a preparation method and an application thereof. The RuCelB contains a 25th-336th amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID NO.2. The preparation method is as follows: obtaining positive cloning capable of hydrolyzing sodium carboxymethylcellulose by active screening rumen microorganism metagenomic cosmid library of a yak, and further obtaining a whole-length cds sequence of the RuCelB by building subcloning, sequencing and homologous comparison; and carrying out recombined expression and obtaining the RuCelB. The specific activity of the RuCelB taking the sodium carboxymethylcellulose as a substrate is up to 158.8U / mg, and the RuCelB also has the degradability for the substrates such as filter paper, cellotriose and the like. The RuCelB can be widely applied in degradation of cellulose, comprising the industries such as cellulose biotransformation, chemical engineering, textile, food, bioenergy, feedstuff adding, pharmaceutical Industry and the like.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Construction and Application of Recombinant Duck Viral Enteritis Virus Vaccine Expressing Secreted Duck Tembusu Virus E Protein
ActiveCN103667198BGenetic material ingredientsMicroorganism based processesTembusu virusSimian Vacuolating Virus 40
The invention provides a recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine for expressing secretory duck Tembusu virus E protein, and a construction method and application thereof. The collection number is CCTCC V201214, and the name is rDEV-TE-tPAS. By using a recombinant clone technique, a gene segment SV40-E-tPA comprising an SV40 promoter, a duck Tembusu virus E protein and a tPA (Tissue plasminogen activator) signal peptide sequence is inserted into a spacer between the US7 and US8 genes of the duck viral enteritis virus to construct a cosmid in which the SV40-E-tPA expression frame is inserted between the US7 and US8 genes, thereby obtaining the recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine CCTCC V201214 for expressing secretory duck Tembusu virus E protein. The invention also provides a method for constructing a recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine strain and application of the recombinant duck viral enteritis virus vaccine strain in preparing a vaccine for preventing infectious diseases caused by duck viral enteritis virus and duck Tembusu virus.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com