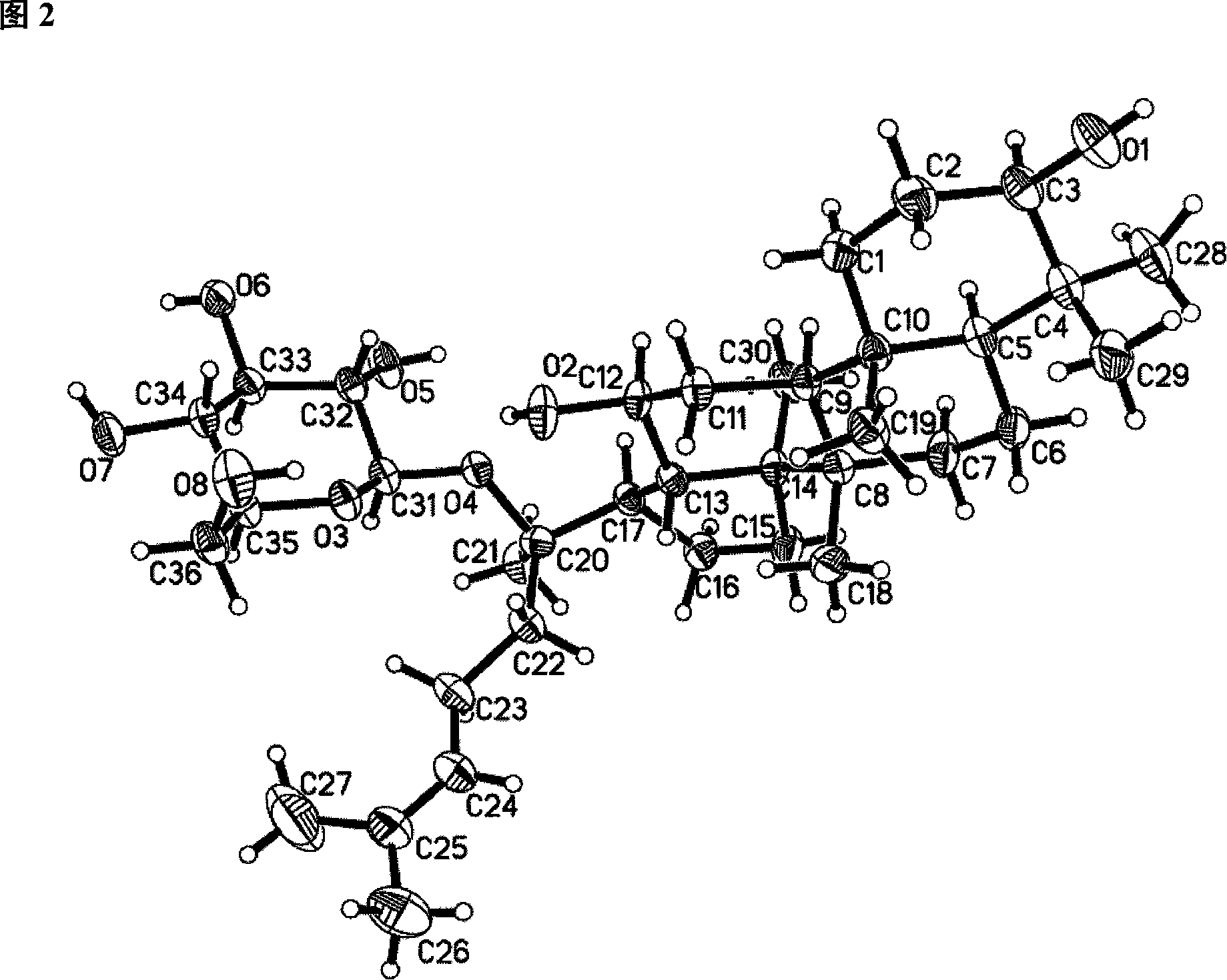
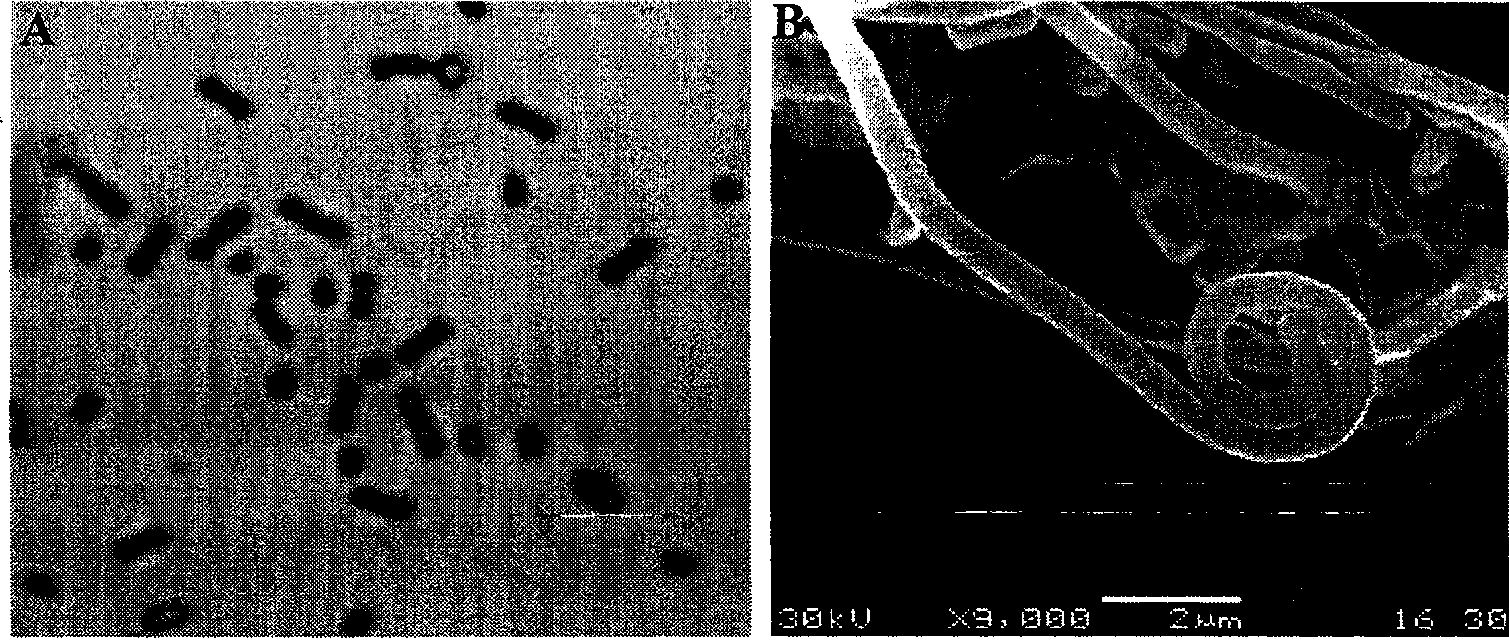
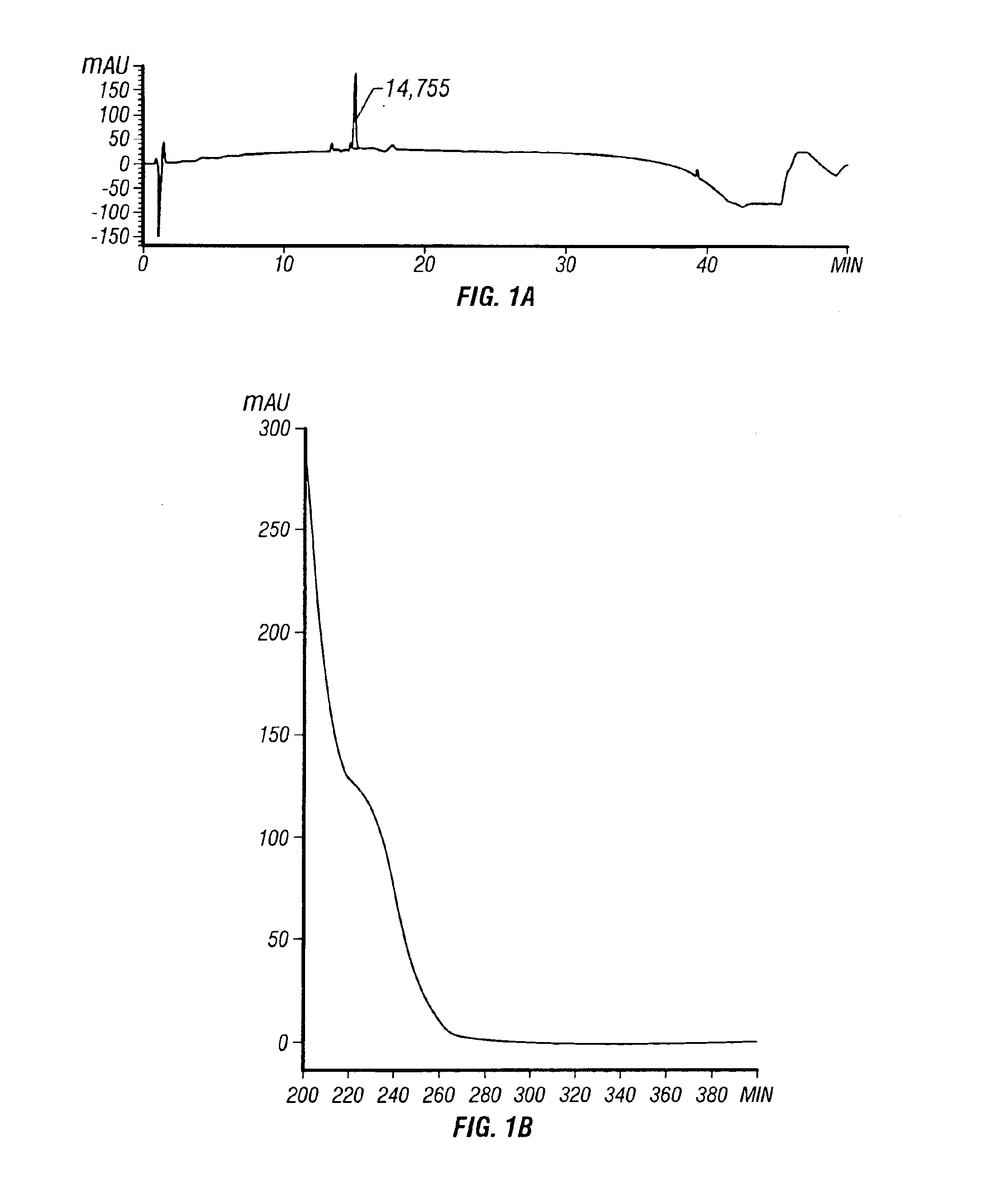
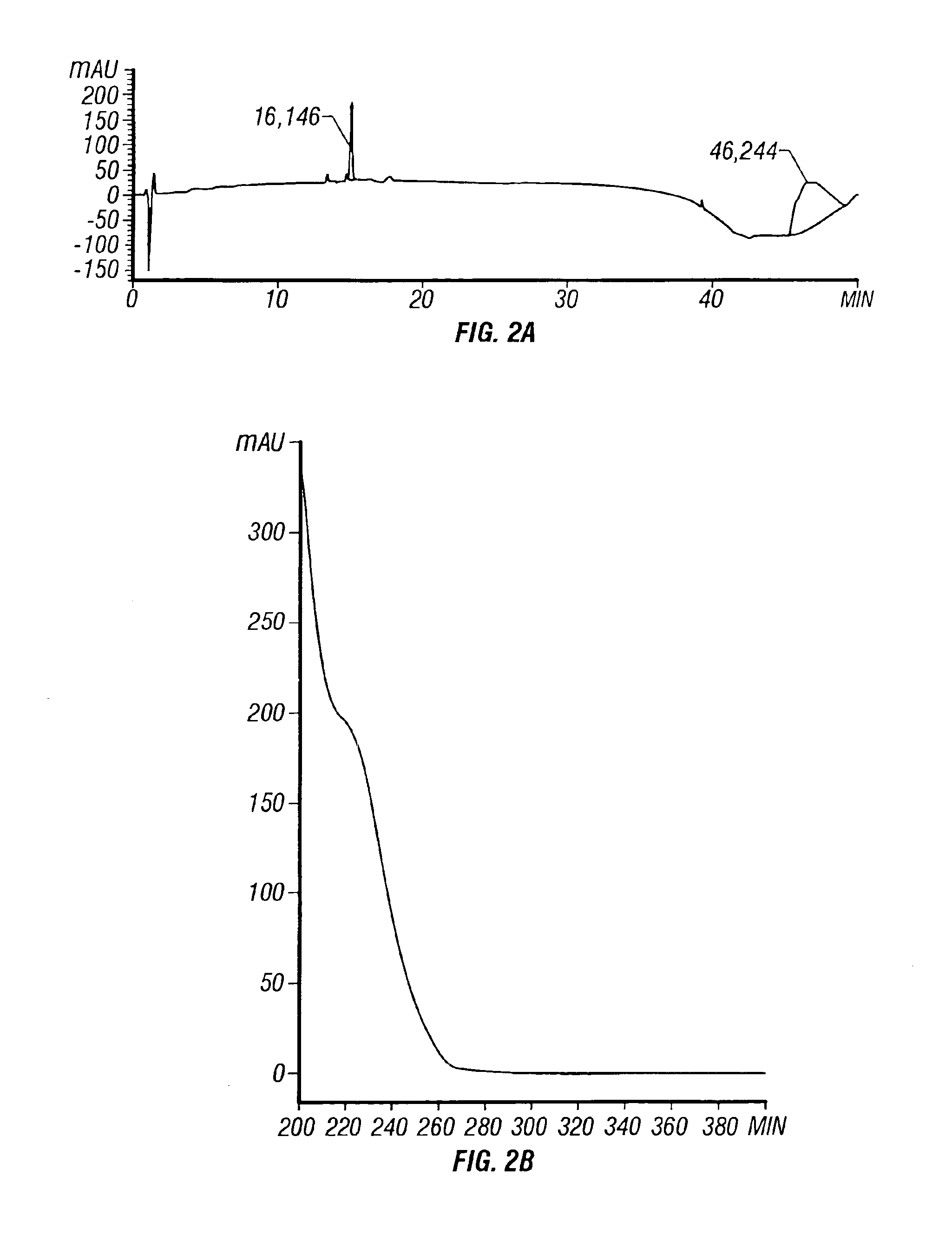
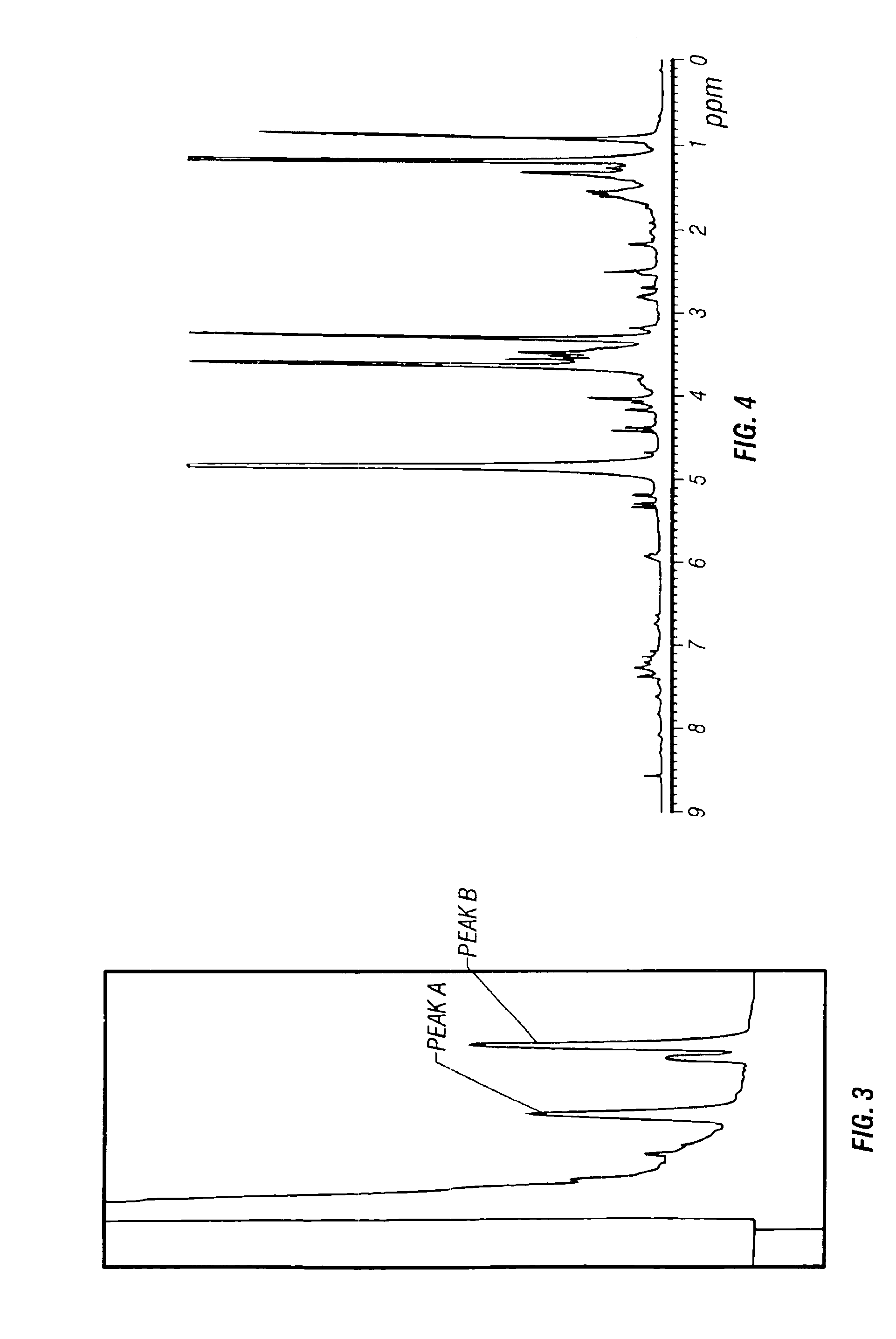
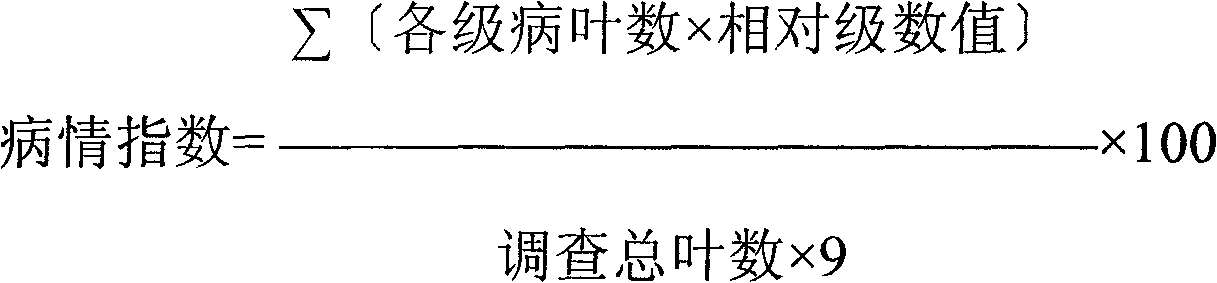
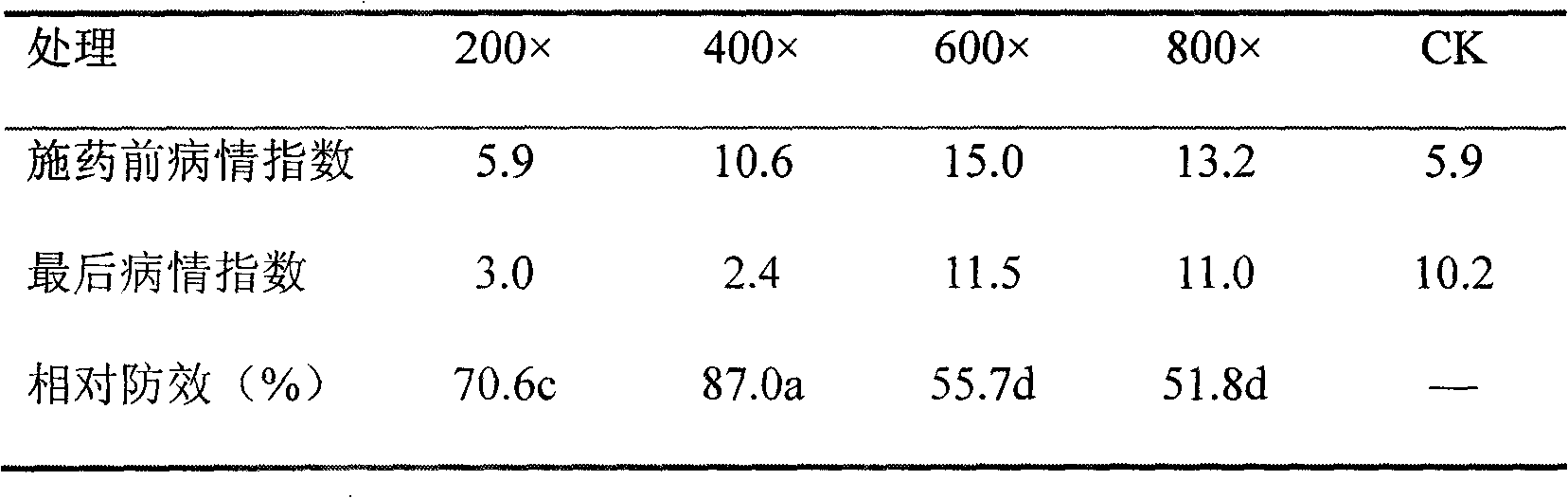
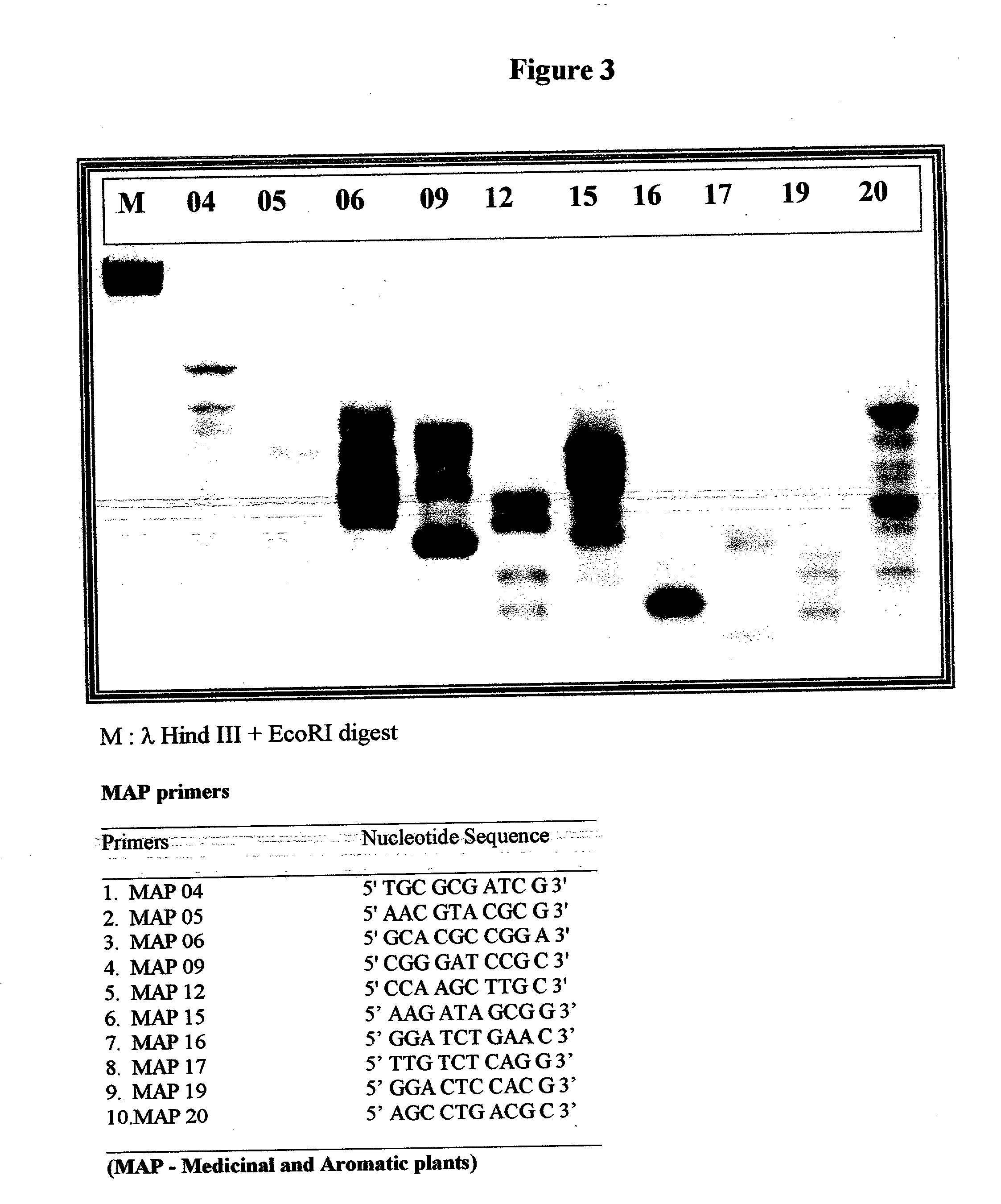
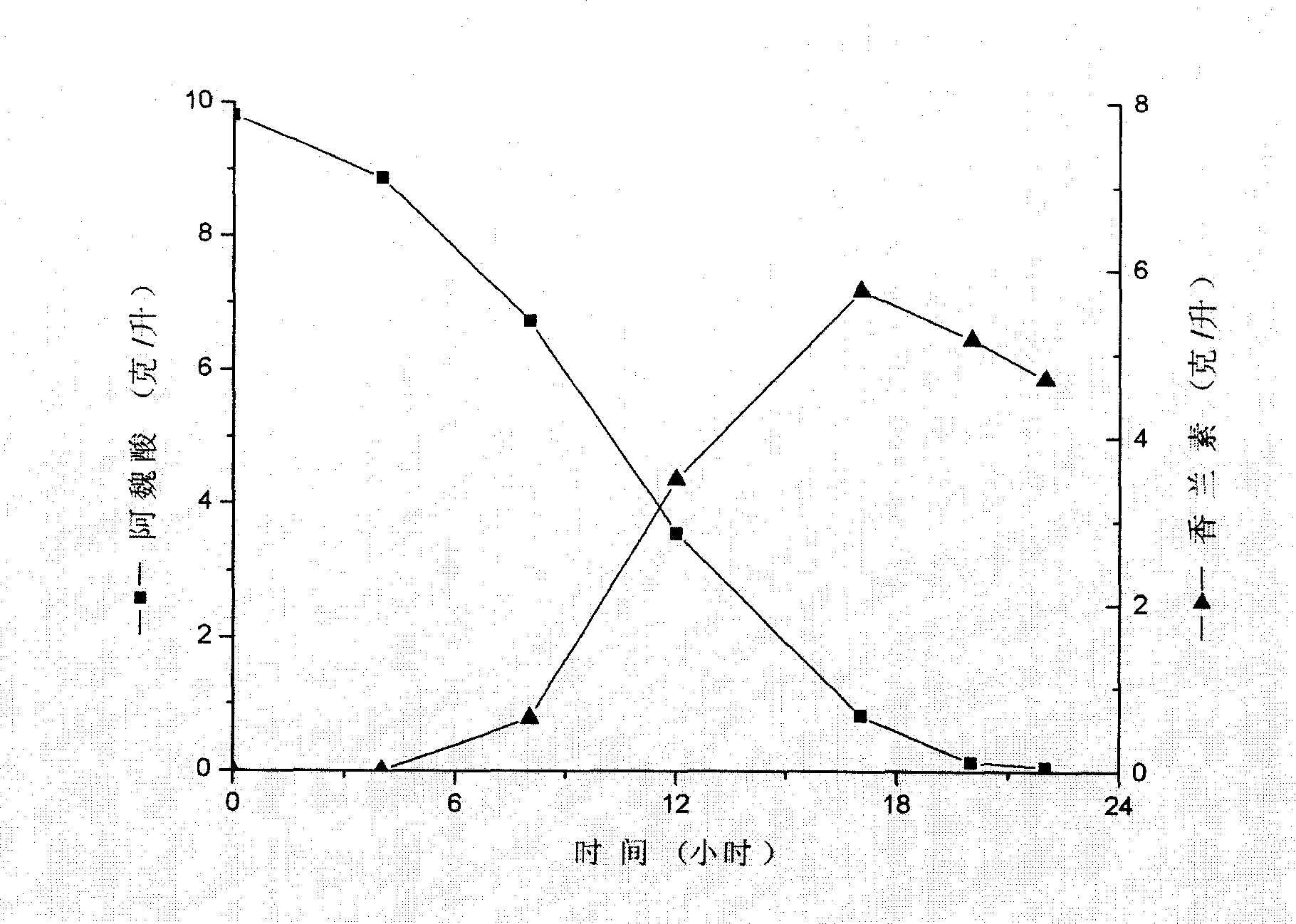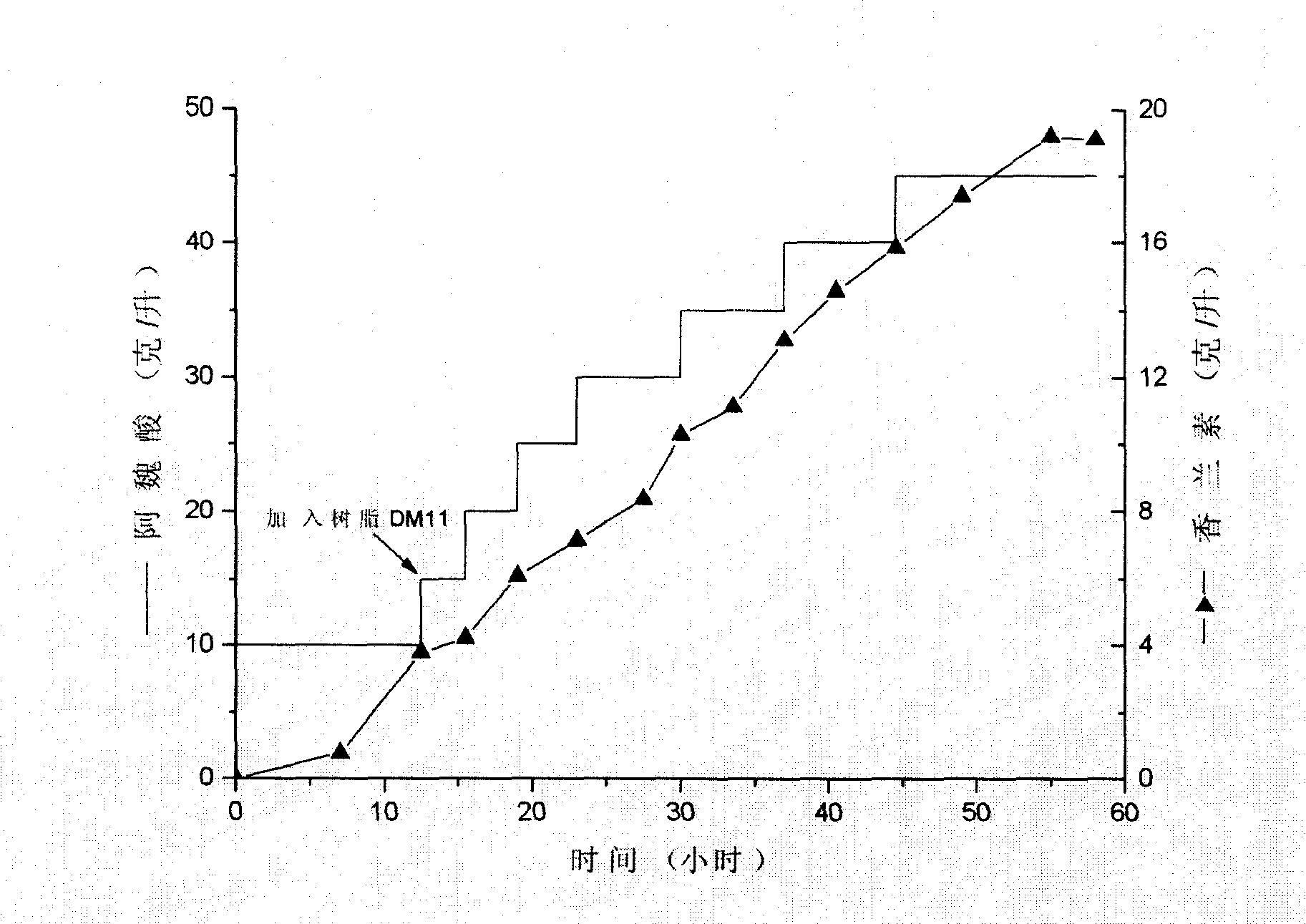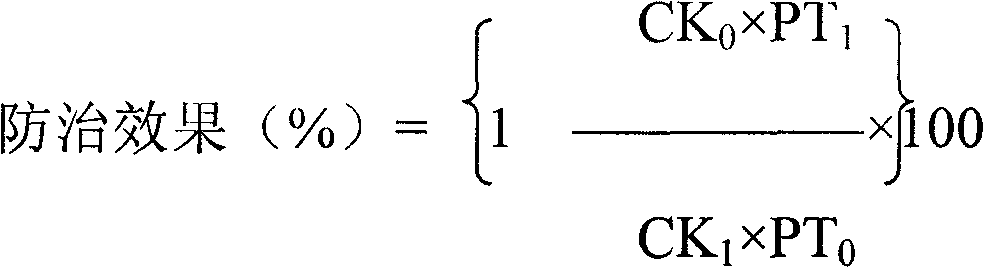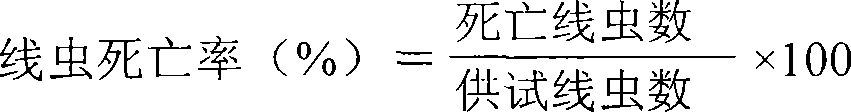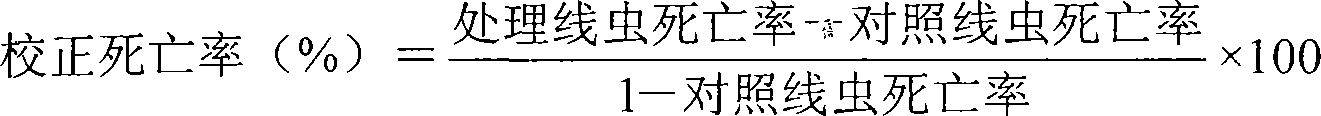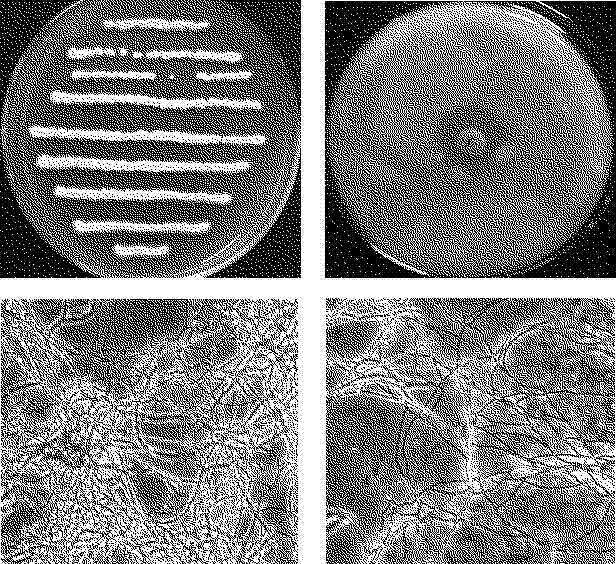Patents
Literature
161 results about "Streptomyces strain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Streptomyces corchorusii strain NF0919, purpose and preparation method of active zymotic fluid thereof
ActiveCN102010835AGood control effectThe fermentation process is simpleBiocideBacteriaDiseasePlant disease
The invention discloses a streptomyces corchorusii strain NF0919, which is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and has the collection number CGMCC No. 3968. The strain can be used for preventing and treating rhizoctonia cerealis, rice false smut, rice sheath blight disease and other various plant diseases.
Owner:ZHENJIANG AGRI SCI INST JIANGSU HILLY AREAS
Process for preparing rare ginsenoside Compound K by fermenting panax notoginseng saponins with streptomycete
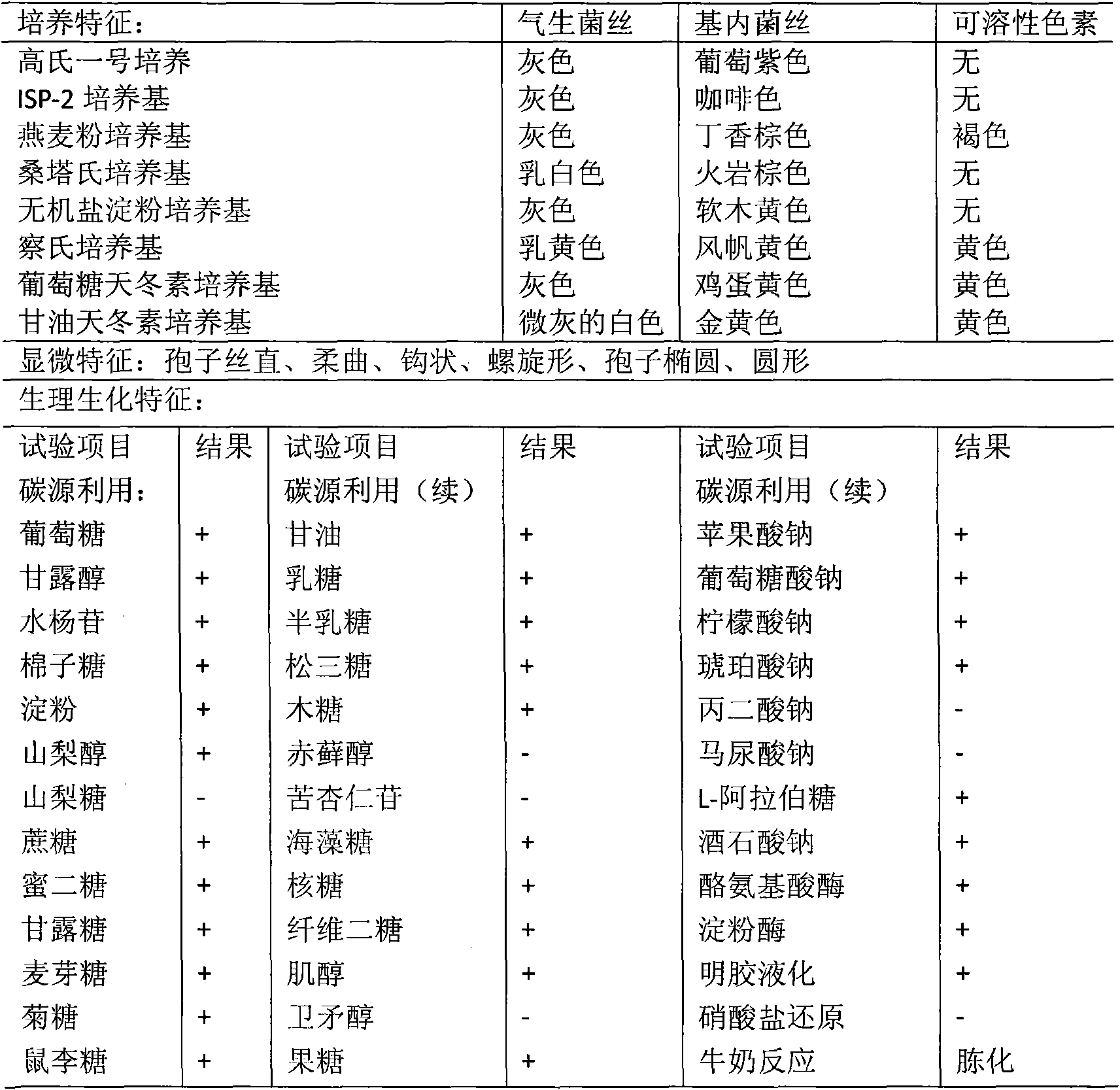
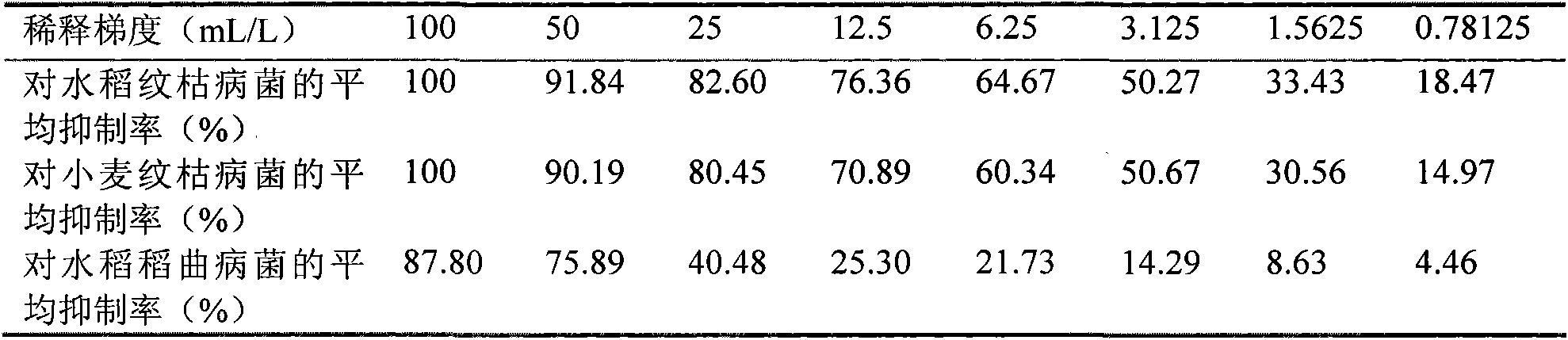
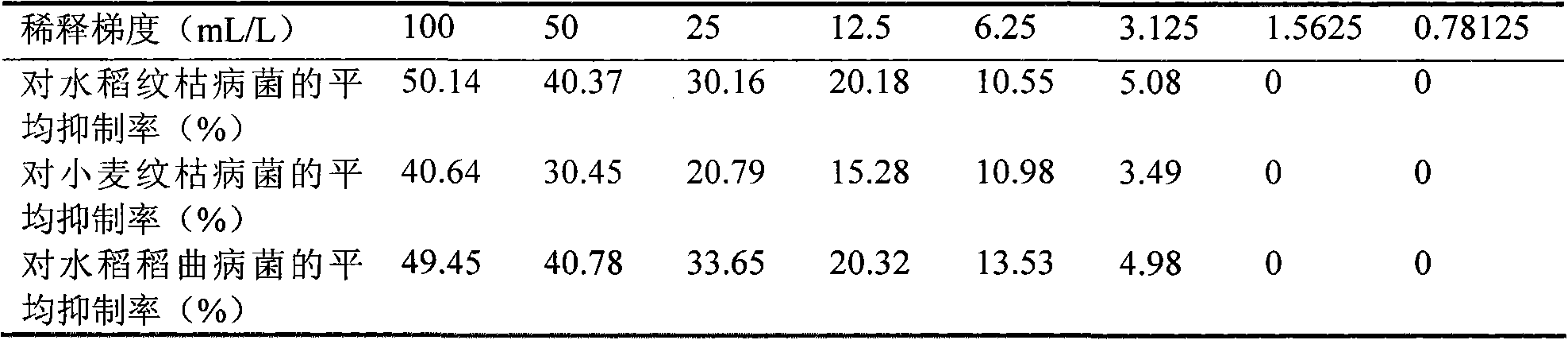
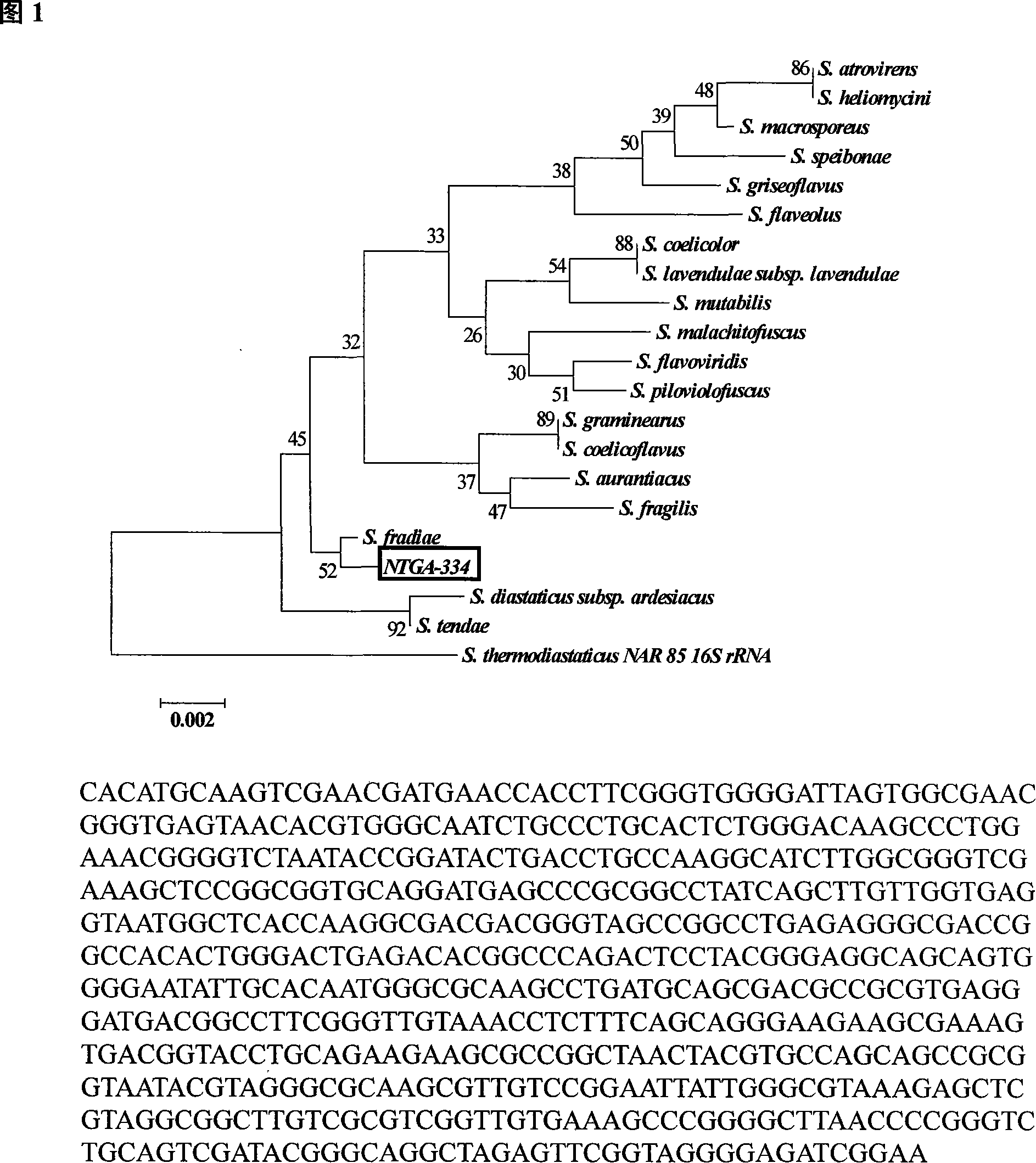
The invention pertains to the technical field of biology and medicine, and relates to a bacterial strain of streptomyces fradiae NTGA-334 with a preseravation no. of CGMCC No.2074, and a process for using the bacterial strain to ferment and transform Compound K in glycol group in various notoginsenosides so as to prepare 20-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside-20 (S)-protopanaxadiol. The culture media are Gause's no.1, ISP2, corroding acid (HSG culture medium) and asparagine culture medium. During the fermentation, the dosing proportions of various notoginsenosides are 0.1-10% (w / v), fermenting temperature is 18-50 DEG C, dynamically adjusted pH value of 0.1-35%(w / v) aqueous ammonia is 0.1-30% (w / v). The invention transforms and ferments in a scaled way various notoginsenosides, prepares Compound K, provides a streptomycete stain that is of steady condition, simple nutrition requirement and good growth, and provides a process for fermenting and separating by a simple and easy fully automatic fermenting tank. Using this bacterial strain and process to produce Compound K, the production cost is low, the foreign matter is less, and the yield rate is high.
Owner:KUNMING NOVOGINSENG BIOENG
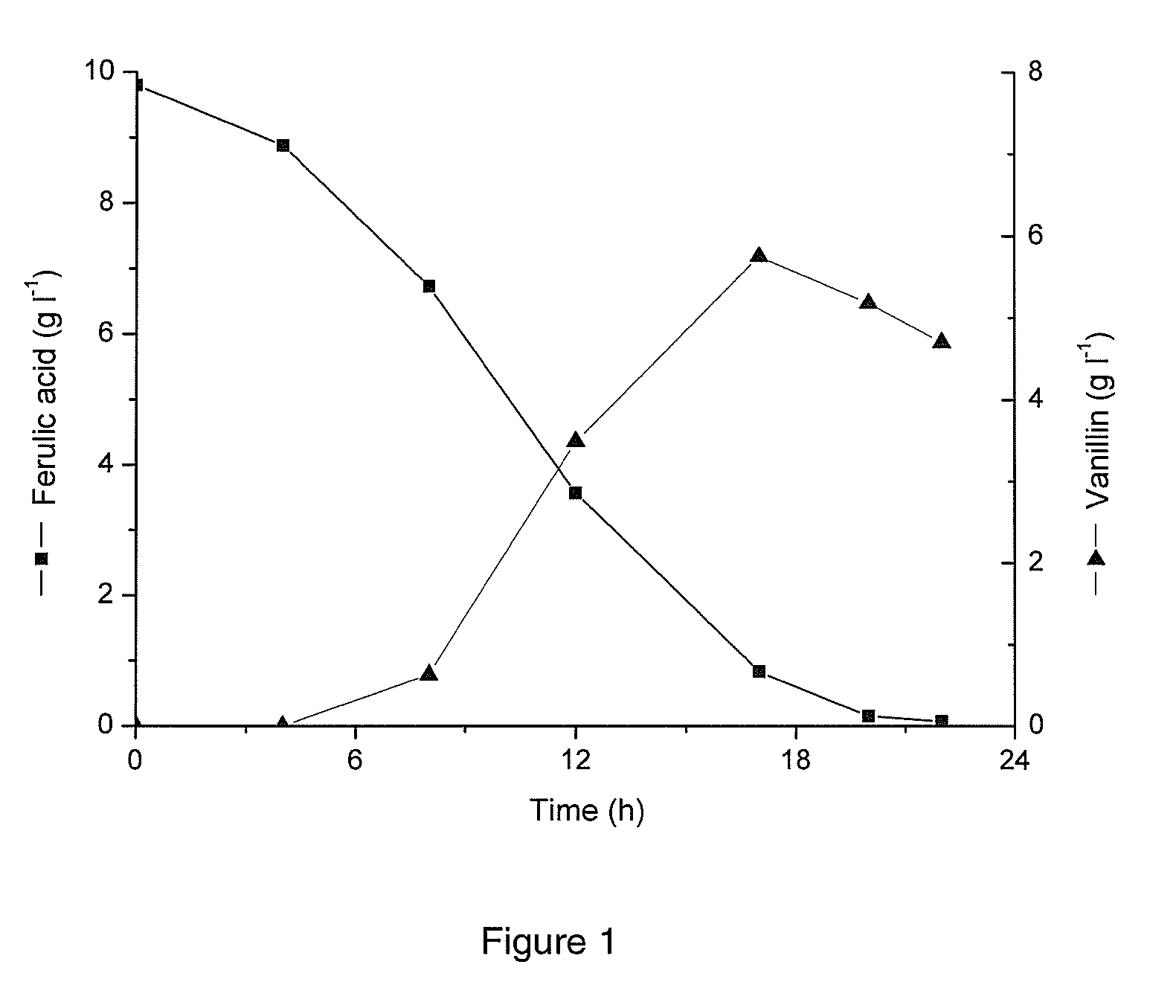
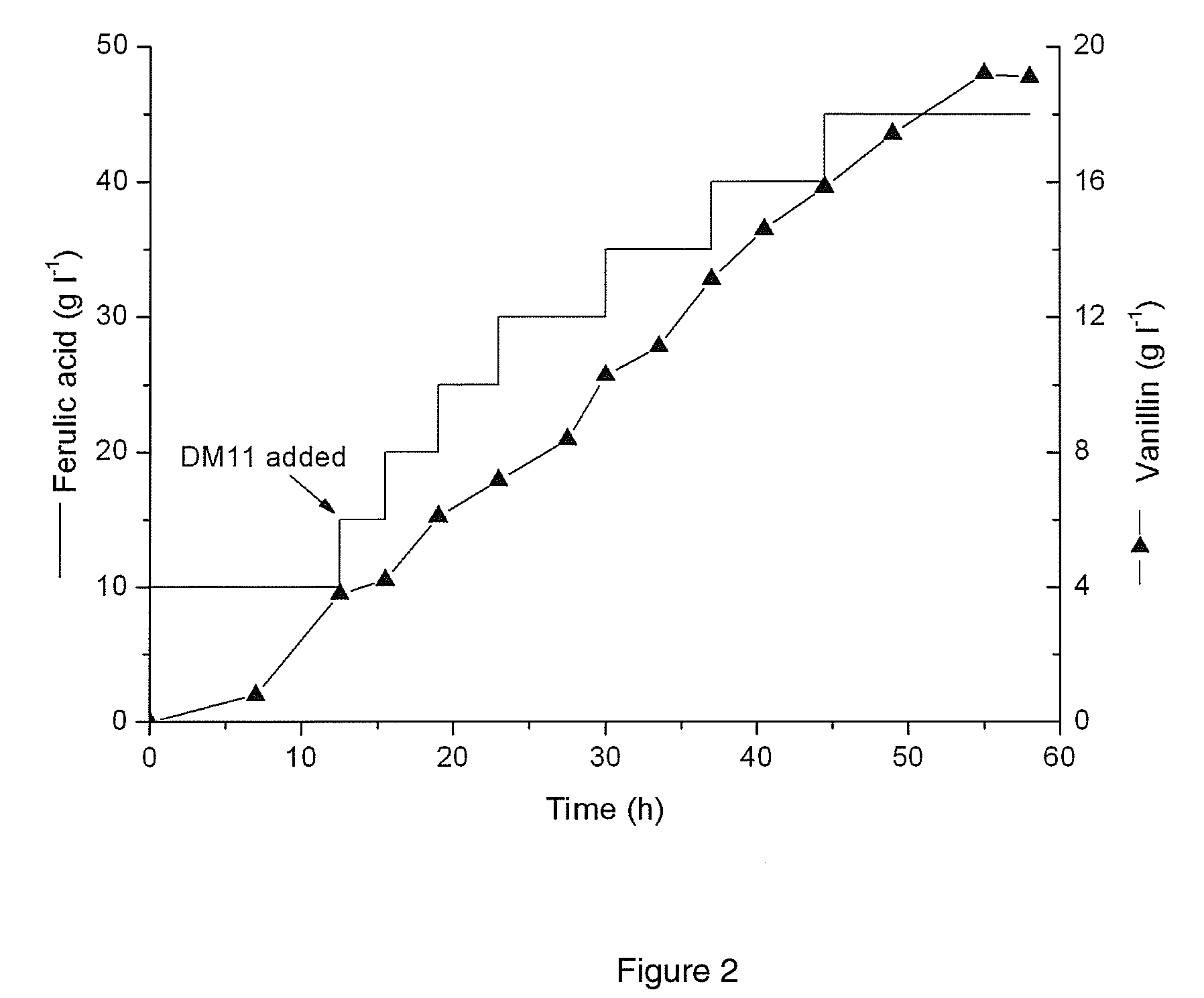
Streptomycete and method for producing vanillin by using the same to biologically transform ferulic acid
ActiveCN101165168AReduce pollutionMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationChemical synthesis
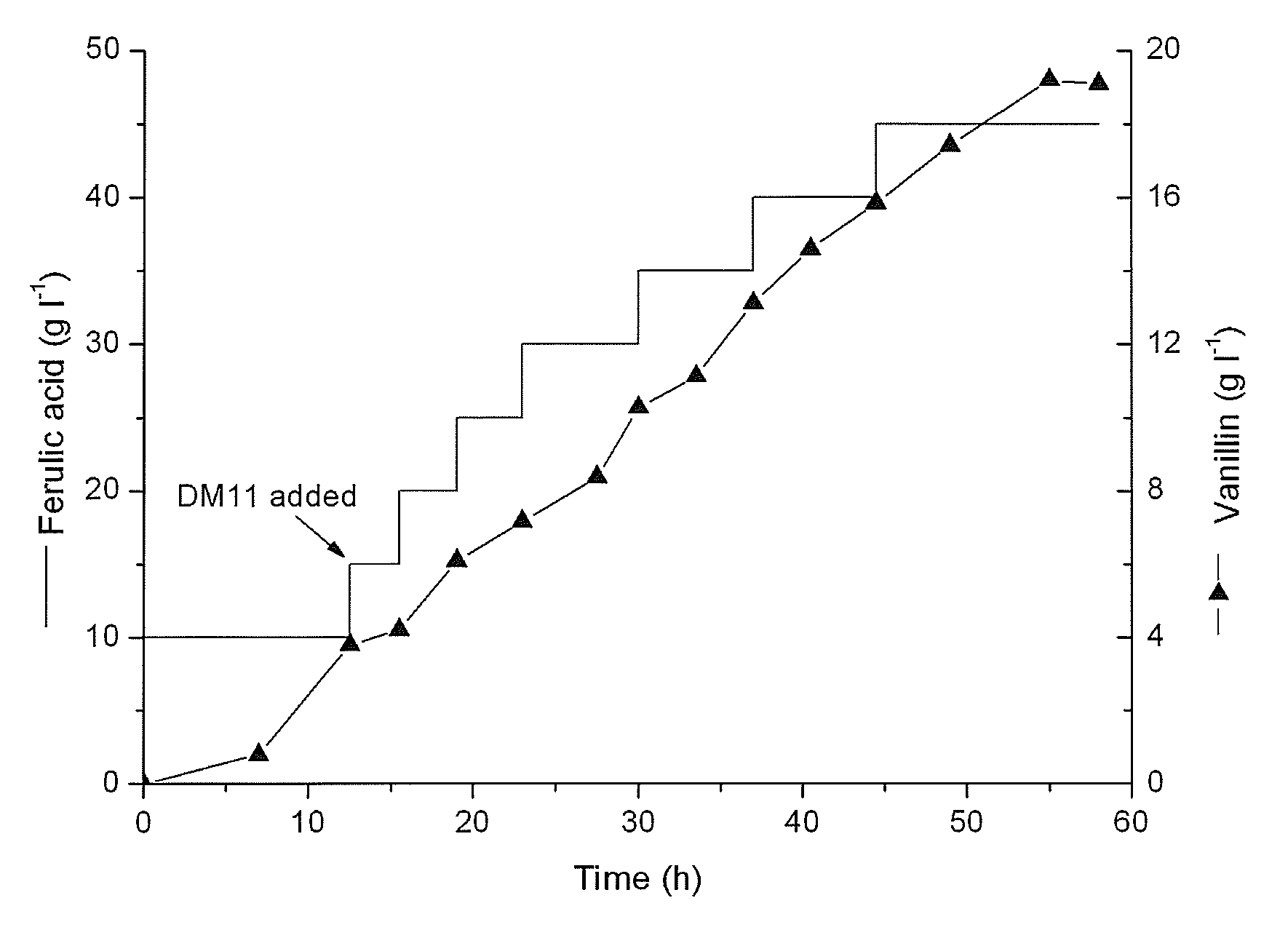
The present invention is one Streptomyces strain and the process of utilizing the Streptomyces strain in converting ferulic acid to produce high concentration vanillin. The Streptomyces strain is Streptomyces sp.V-1 in the preservation number of CCTCC M 206065. In the GY converting culture medium with the Streptomyces strain, ferulic acid may be converted to produce high concentration vanillin fermenting liquid. Adding macroporous adsorption resin DM11 into the converting culture medium can increase the concentration of vanillin fermenting liquid greatly. The present invention has the advantages of less environmental pollution, high product concentration, less side products, short production period, low cost, etc.
Owner:APPLE FLAVOR & FRAGRANCE GRP +2
Streptomyces strain and application thereof
ActiveCN101525587APromote growthImprove the effect of increasing productionBiocideBacteriaDiseaseSocial benefits
The invention discloses a Streptomyces sp. strain and the application thereof. The strain provided by the invention is Streptomyces sp. YL04 CGMCC No.2884. The strain YL04 provided by the invention with ideal biocontrol effect and development value can be popularized in large-area fields and mainly solves the problem that increasingly serious damping-off and blight diseases of crop seedlings like vegetables and melons cause serious output reduction or reduced product quality. The invention has significant scientific meaning and application value in enriching strain resources for biocontrol of our country and provides effective measures for achieving high-output and high-quality modern agriculture. The invention meets the national standards of agricultural goods production safety and the need of constructing a non-polluted, green and organic agricultural production base and has certain economic and social benefits.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Preparation and use of lilac grey streptomycete and active product thereof
InactiveCN101481669AStable sourceStable manufacturingBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDiseasePhytophthora sp.
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological pesticides, discloses a Streptomyces l avendulae xjy strain which has been collected in the general microorganism center of CCCCM in 8.16.2007 with the collection number: CCMCC No.2130. The invention also discloses a separation and authentication method for the strain, a preparation method for antibiotic active substances of the Streptomyces l avendulae xjy strain, authentication for analysis structures of the active substances, prevention and cure experiments for metabolic active substances of the xjy strain against leaf muld of tomato, powdery mildew of cucumber and phytophthora blight of pepper, and growth-promoting experiments for the growth of the strain. The antibiotic active substances secreted by Streptomyces xjy strain is mainly nucleosides antibiotic having the characteristics of persistent effect and no medicinal hazard as well as having the effects of obviously preventing and curing vegetable diseases and promoting the growth to a certain extent.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Metabolite from streptomyces strain NRRL accession No. B-30145 and mutants thereof for controlling plant diseases
A novel antibiotic-producing Streptomyces sp. is provided that exhibits antifungal activity only on certain specific plant pathogens. Also provided is a method of treating or protecting plants from fungal infections comprising applying an effective amount of an antibiotic-producing Streptomyces sp. having all the identifying characteristics of NRRL Accession number B-30145. The invention also relates to fungicidal compositions comprising this novel Streptomyces strain and the antibiotics and metabolites produced by this strain either alone, or in combination with other chemical and biological pesticides.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCI LP
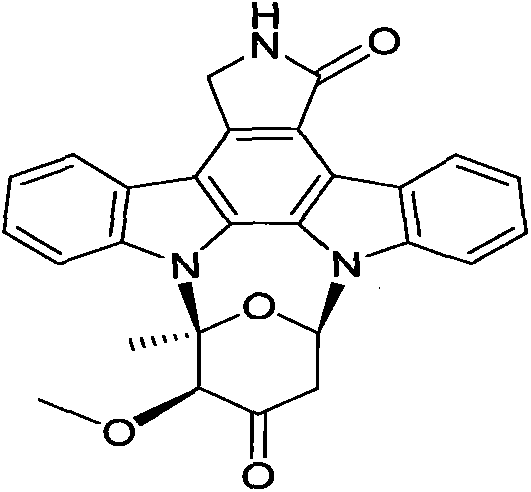
Streptomyces strain and application thereof in production of staurosporine
ActiveCN108676757AIncrease production capacityRealize industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyStreptomyces strain
The invention discloses a novel Streptomyces strain and application thereof. The strain is named as streptomyce sp. HS-HY-153, and the preservation number thereof is CGMCC NO. 14806; the invention also discloses a method for preparing Staurosporine by culturing the strain HS-HY-153.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Marine Streptomyces strain and use thereof
InactiveCN102220271AHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsCandida famataHigh activity
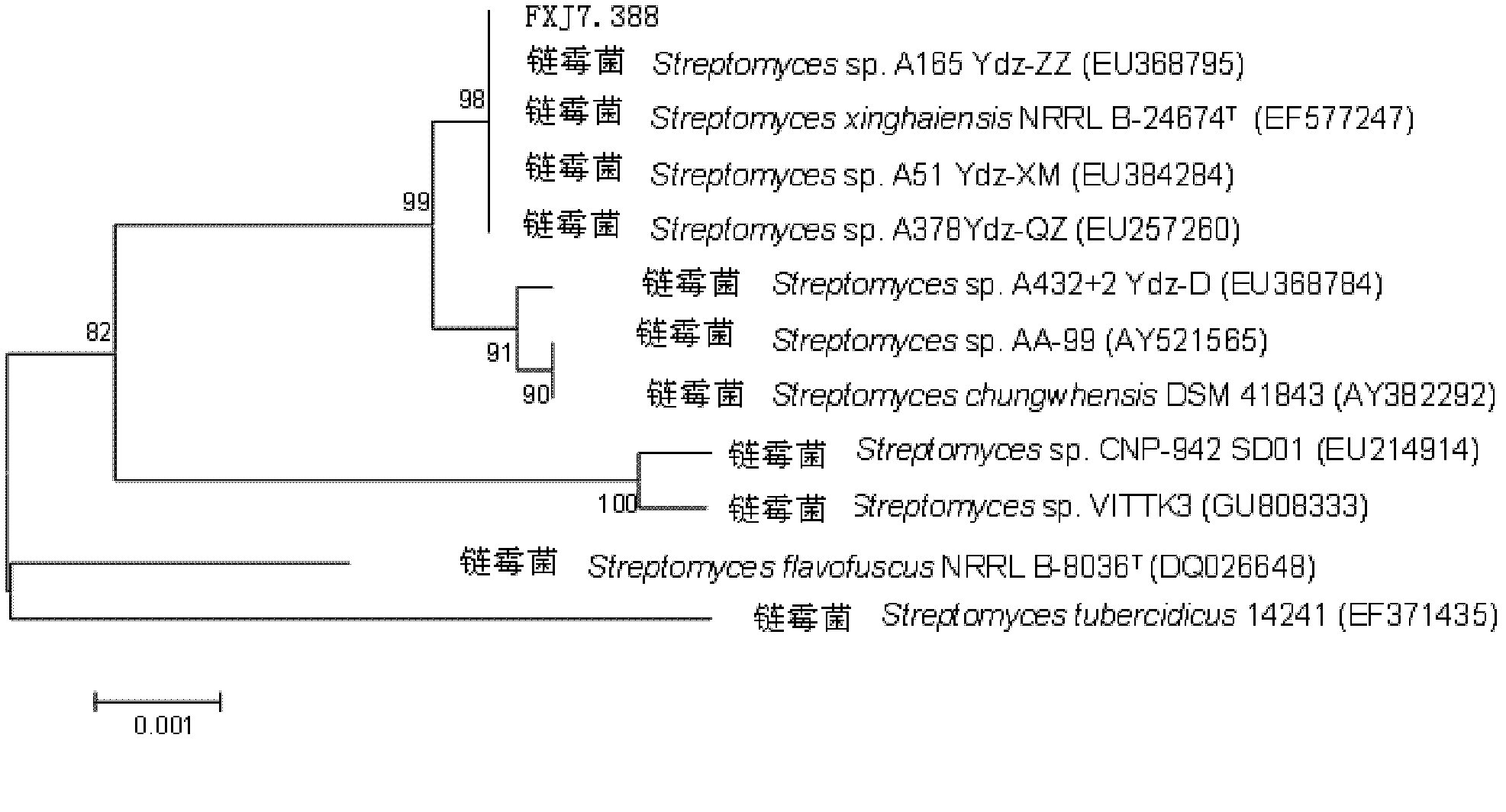
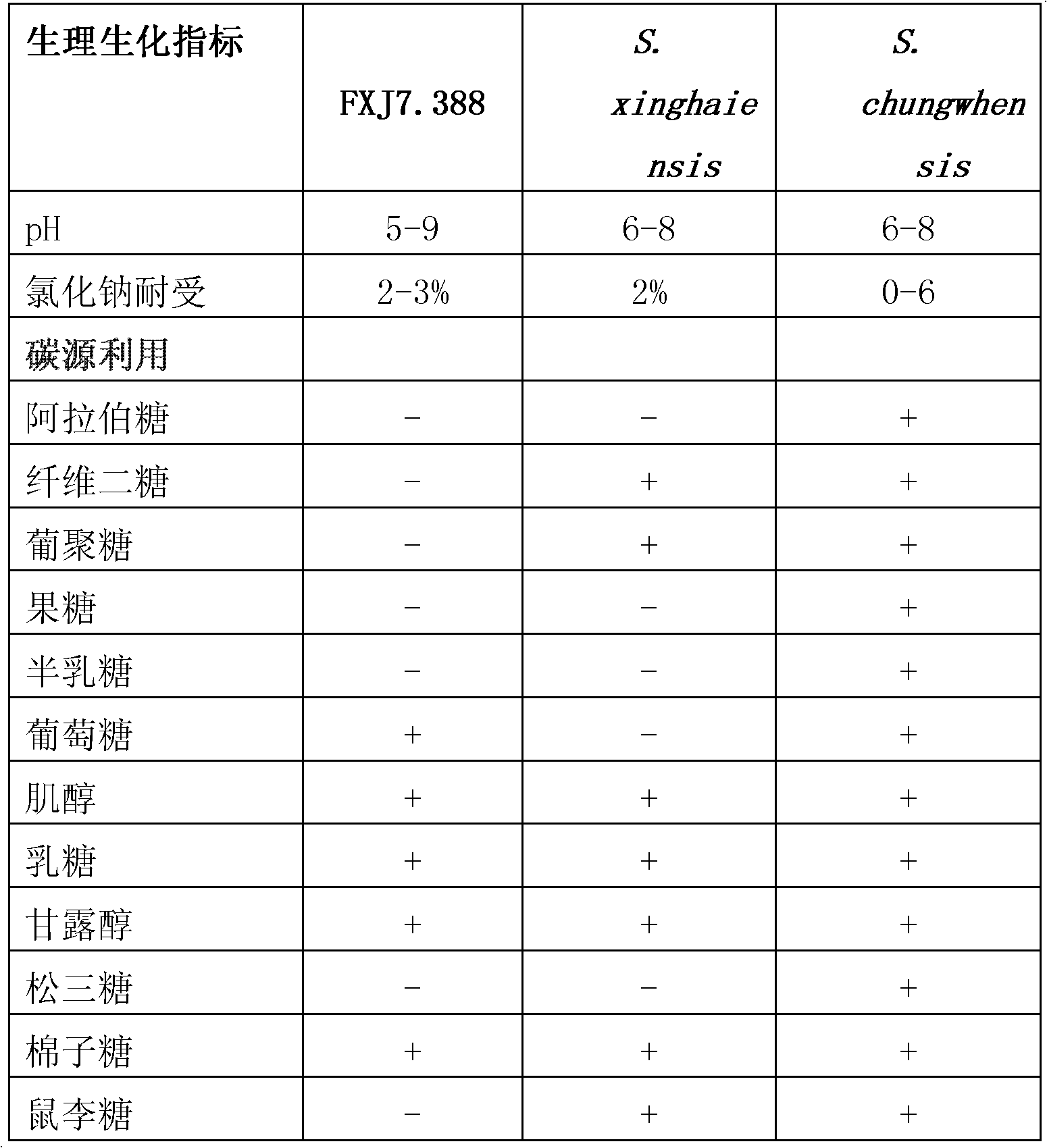
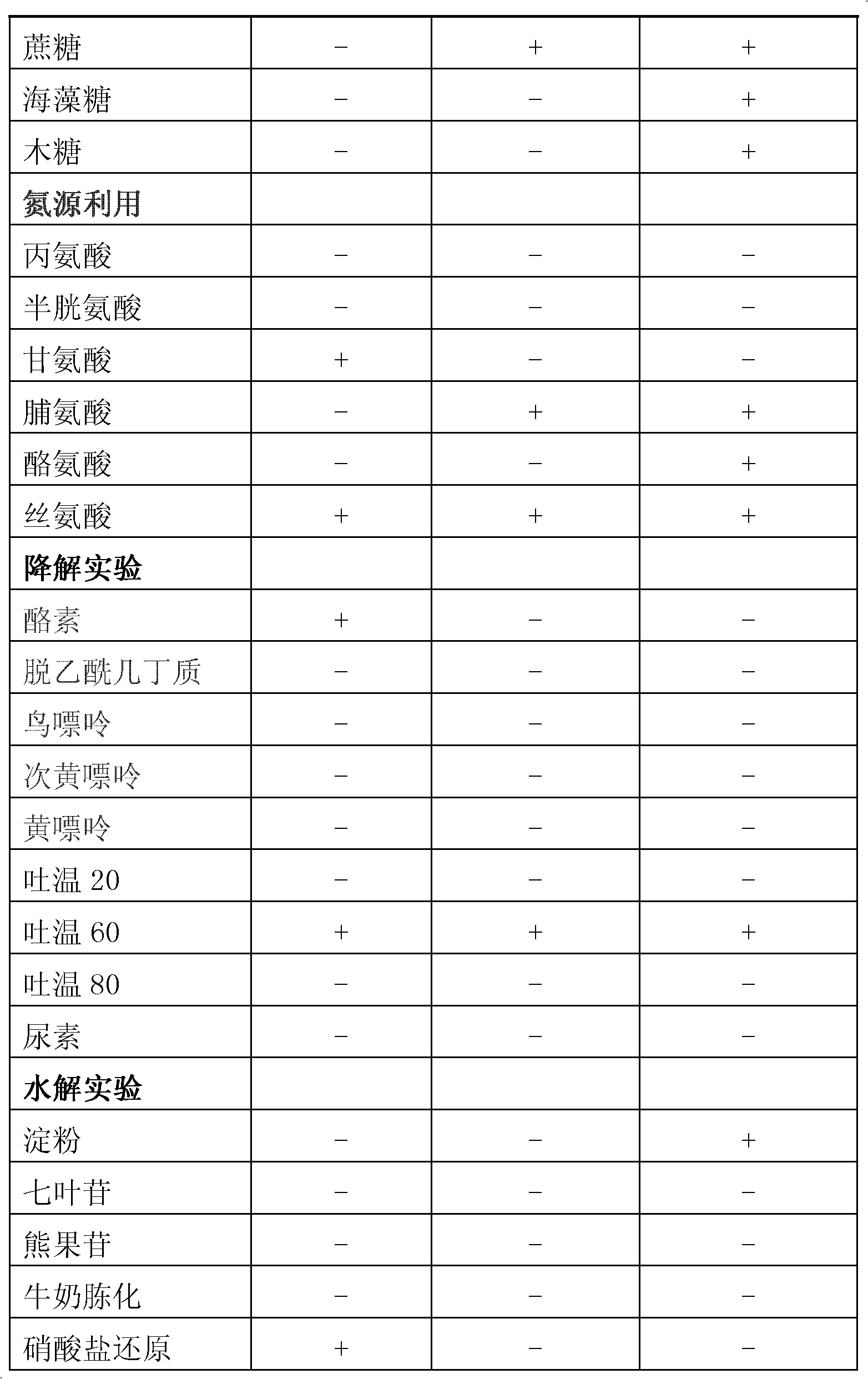
The invention provides a marine Streptomyces strain and use thereof. The strain provided by the invention is Streptomyces sp. FXJ7.388, and the collection number of the strain is CGMCC No.4474. The invention also provides the use of the strain in the preparation of an antibacterial product. The antibacterial effect is to inhibit gram-positive bacteria, including Multi-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA 1-1), staphylococcus aureus CGMCC1.2386, bacillus subtilisGCMCC1.2428 and / or Candida albicans 2.538. Experiments prove that the Streptomyces sp. FXJ7.388 separated by the invention has the advantage of resisting gram-positive bacteria and Candida albicans, namely having high activity for resisting MRSA, staphylococcus aureus AND bacillus subtilis and certain inhibiting effect on Candida albicans.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Wettable powder of streptomyces roseoflavus biological bactericide
InactiveCN103125527AGood inhibitory effectStrong stress resistanceBiocideFungicidesPropaguleSodium lignosulfonate
The invention discloses wettable powder of a streptomyces roseoflavus biological bactericide, which adopts diatomite as a matrix and comprises the following components: not less than 108 propagules of streptomyces roseoflavus strain 0116, and 4% of a wetting dispersant. It is determined that diatomite is used as a carrier and sodium lignosulphonate is used as the wetting dispersant. In addition, the strain wettable powder storage stability is determined by regular detection of the viable bacterial count, and results show that after strain wettable powder storage for 24 months, the viable bacterial count is more than 80%. The invention has the characteristics of short development period, low cost, simple process, and capability of being developed into various dosage forms, and is suitable for large-scale production. Since propagules of streptomyces roseoflavus strain 0116 is used as the main component of the wettable powder, the invention is suitable for large-scale production, and when compared with strain fermentation liquor, the invention greatly shortens the field using amount, and reduces packaging and transport cost.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Strain for generating phospholipase D with high and stable yield by utilizing physical and chemical mutation
InactiveCN101875929AImprove efficiencyEasy to operateMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismLithium chloride
The invention relates to a strain for generating phospholipase D with high and stable yield by utilizing physical and chemical mutation, belonging to the technical field of microbial mutation. The strain is characterized in that the phospholipase D is prepared by fermenting streptomyces chromofuscus of high yield phospholipase D, which is obtained by taking the streptomyces chromofuscus as an original strain and sequentially carrying out composite mutation of ultraviolet rays and lithium chloride and composite mutation of atmosphere cold plasmas and the lithium chloride on a monospore bacterial suspension thereof. The invention has the advantages that the streptomyces chromofuscus of the high yield phospholipase D is obtained through mutation screening, thereby providing a high yield strain with higher application value to industrial production of the phospholipase D, laying a good foundation for fermentation culture and application of the phospholipase D, and also providing a good and feasible method for microbial mutation breeding. The invention adopts a mutation and screening method, has the advantages of simple operation, high efficiency and the like, and has a practical value on screening the strain with an industrial application value.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
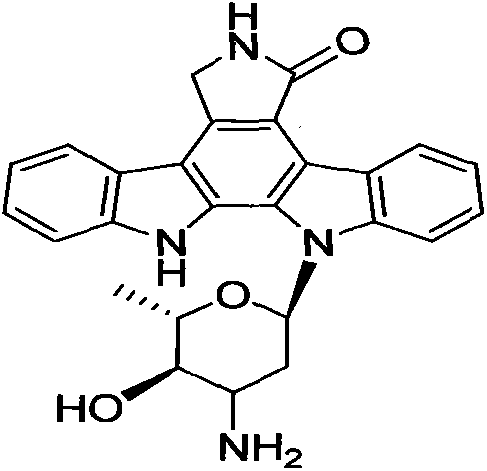
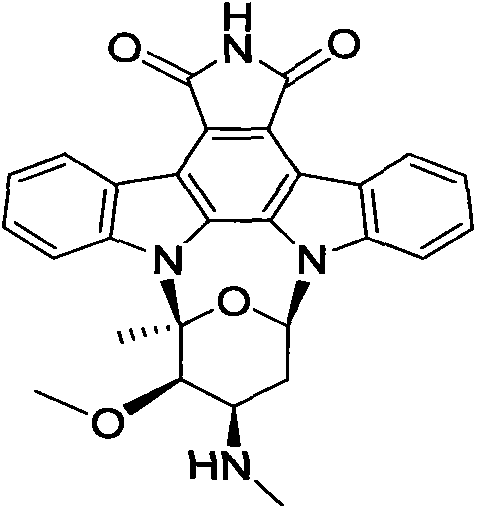
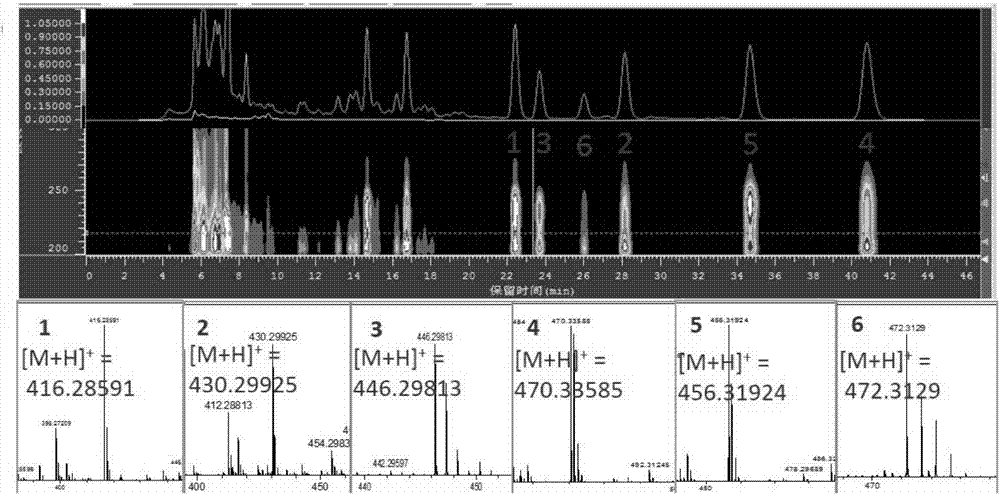
A plurality of indolocarbazole alkaloids having strong insect disinfestation activities, and production strain thereof
InactiveCN104593281AStable characteristicsNo pollution in the processBiocideSugar derivativesArtogeia rapaeMycangium
The present invention discloses a plurality of indolocarbazole alkaloids having strong insect disinfestation activities, and a production strain of the indolocarbazole alkaloids. The indolocarbazole alkaloid compound production strain CQT14-24 is a marine Streptomyces nitrosporeus CQT14-24 strain, wherein the strain is subjected to artificial culture, and the obtained fermentation product is extracted by the conventional chemical method so as to obtain four indolocarbazole alkaloids and an anthraquinone compound. According to the present invention, the indolocarbazole alkaloids and the one anthraquinone compound provide strong killing effects on a variety of cultivated plant pests, particularly the pests having characteristics of spreading in agriculture and forestry production and serious harm and comprising Pieris rapae, Brevicoryne brassicae, Hyphantria cunea, Plutella xyllostella, Mythimna separate and Helicoverpa armigera, wherein the relative mortality rate achieves 81.9-100%, the polypide is seriously reduced, the growth inhibition rate is 100%, and the imago pupation rate is reduced by 70.4-86.7%; and the strain is subjected to acclimation through the artificial culture, and has characteristics of stable feature, easy culture, simple and feasible operation method, no environmental pollution, short period, cheap raw materials, low production cost, good development prospect, and easy industrialization achieving.
Owner:王林
A streptomyces strain, and anti-kidney-cancer applications of piericidin metabolites thereof
A streptomyces strain, and anti-kidney-cancer applications of piericidin metabolites thereof are disclosed. The streptomyces strain is streptomyces sp.HBERC-58855, and is deposited in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, in Wuhan University, Wuhan, China on April 20, 2017. The accession number of the streptomyces sp.HBERC-58855 is CCTCC NO:M 2017186. The 16sRNA nucleotide sequence of the streptomyces sp.HBERC-58855 is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. Piericidin compounds including piericidin A, piericidin A2, piericidin C2, IT-143-A, IT-143-B and piericidin s3a are extracted from the streptomyces sp.HBERC-58855 through fermentation for the first time, and are applied in preparation of anti-kidney-cancer medicines. Candidate compounds are provided for development of novel anti-kidney-cancer medicines. The streptomyces and the piericidin compounds are of great significance for marine microorganism medicine resource development.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
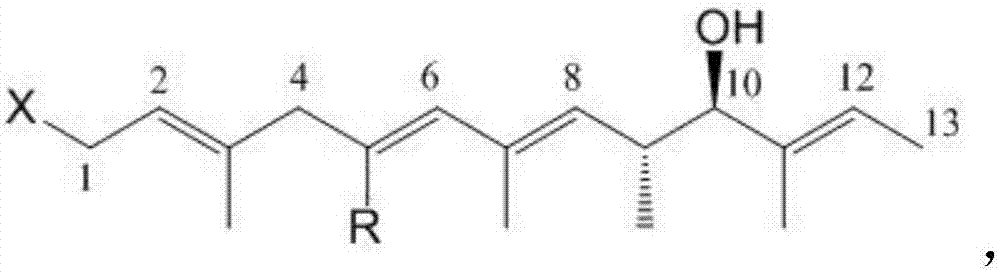
Preparation method of streptomyces having activity for poisoning plant nematodes and uses thereof
The invention relates to a culturing method of streptomyces with the function of poisoning plant menatodes and a preparation method and application of the metabolin, belonging to the technical field of microbial pesticides. The streptomyces bacterial strain Snea253 is Streptomyces venezuelae, stored in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on January 18, 2008 (address: Datun Road, Zhaoyang District, Beijing; post code: 100101) with CGMCC No.2348. The streptomyces bacterial strain Snea253 is classified in species Streptomyces venezuelae, genus streptomyces, order actinomycetales, class actinomycetales, phylum actinomycetales. The culturing method of streptomyces with the function of poisoning plant menatode has the advantages that: through liquid fermentation culture preparation, the metabolites can poison plant parasitic nematodes, in particular Heterodera glycines, Meloidogyne spp. and Aphelenchoides besseyi with distinct effects; the fermentation liquid of the bacterial strain has higher poisonous activity to second instar larva of Heterodera glycines, and can remarkably restrain cyst hatching; the treatment of fermentation liquid with different diluted concentration is significantly different from the treatment of sterile water; the insecticidal effects of stock fermentation solution can reach above 90%, and the effects of greenhouse experiment are obvious; at the same time, the bacterial strain can remarkably poison the Meloidogyne spp. and Aphelenchoides besseyi with good application and development prospects.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Streptomyces griseofuscus strain and method for preparing epsilon-polylysine and salt thereof by utilizing same
ActiveCN102086441ABroad-spectrum antibacterialNo toxicityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEpsilon-PolylysineFiltration
The invention discloses Streptomyces griseofuscus LS-H1, namely CCTCC M 209211, and a method for preparing epsilon-polylysine and salt thereof by utilizing the strain. The Streptomyces griseofuscus LS-H1 is the strain obtained through screening; and the epsilon-polylysine at the concentration of between 0.7 and 20g / L can be accumulated under optimum conditions by culturing the Streptomyces griseofuscus LS-H1 in a culture medium containing a carbon source and a nitrogen source. After thalluses are removed from a zymotic fluid through centrifugation or filtration, the epsilon-polylysine and the salt thereof are obtained through the separation by an ion exchange method. The method is simple in the culture of the thalluses, and is favorable for industrialized mass production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Streptomyces strain for inhibiting harm of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae and application thereof
Aiming at the existing defects in preventing and controlling black shank of tobacco, the invention provides Streptomyces misawanensis D35 for inhibiting Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae. The strain was collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Centre (CGMCC) on August 27, 2009 with the collection number of CGMCC No: 3250. The invention also provides application of the strain in effectively inhibiting diffusion of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae in tobacco, reducing disease incidence, improving the tobacco yield and quality, facilitating the development of biological prevention and control products and further promoting the safe control of Phytophthora parasitica var. nicotianae.
Owner:周倩
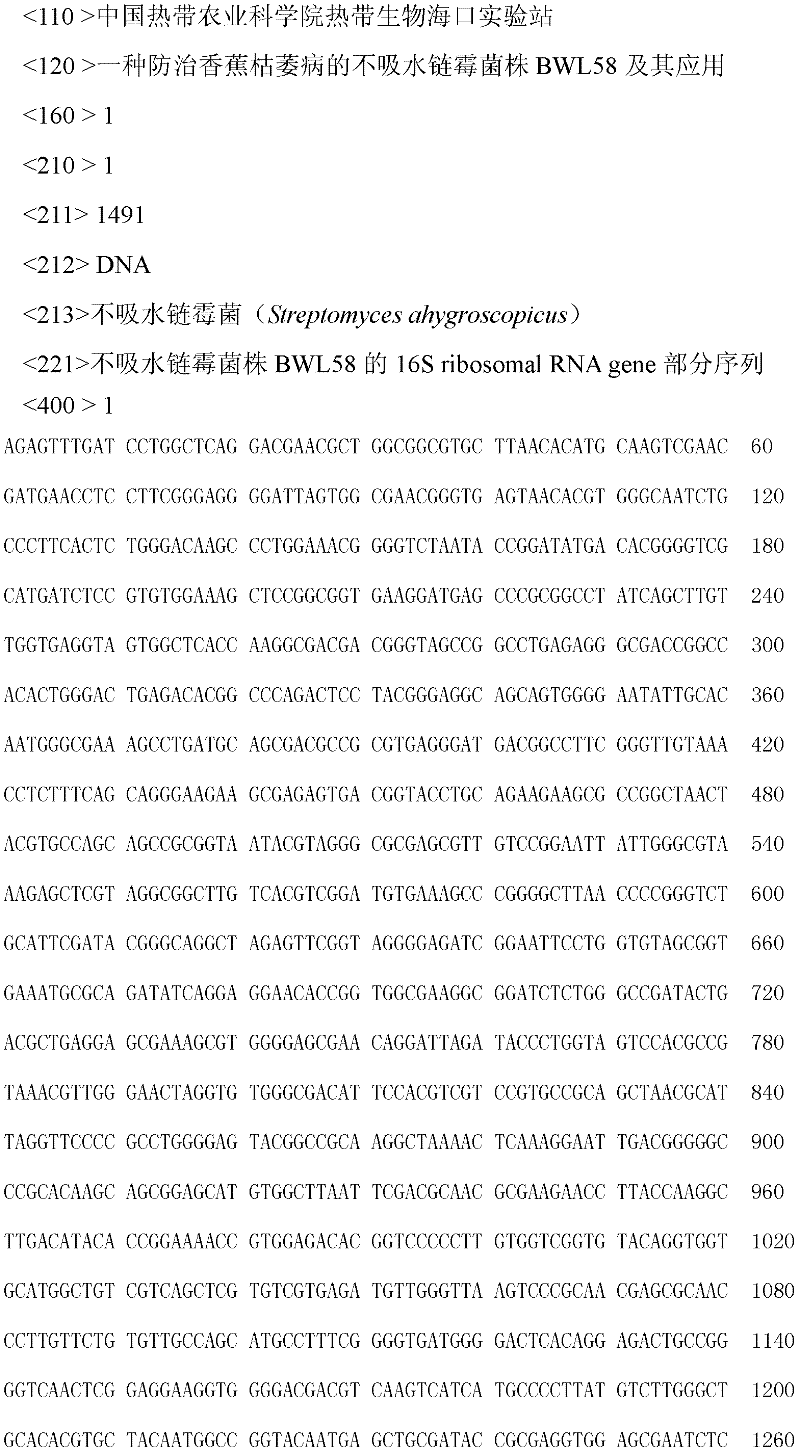
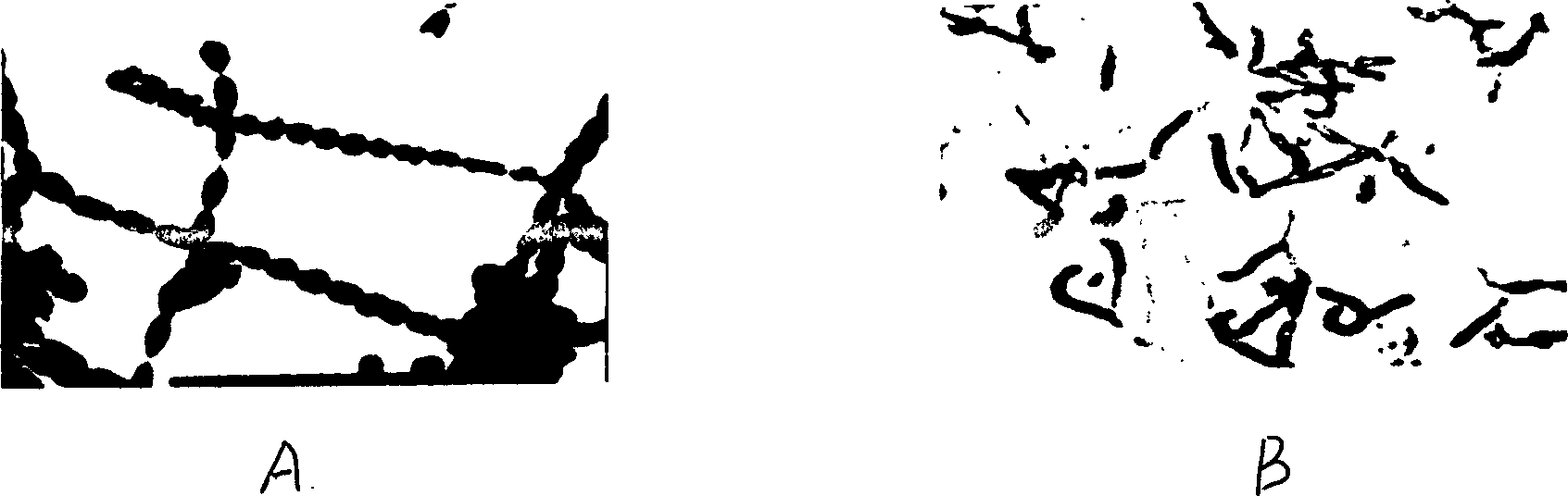
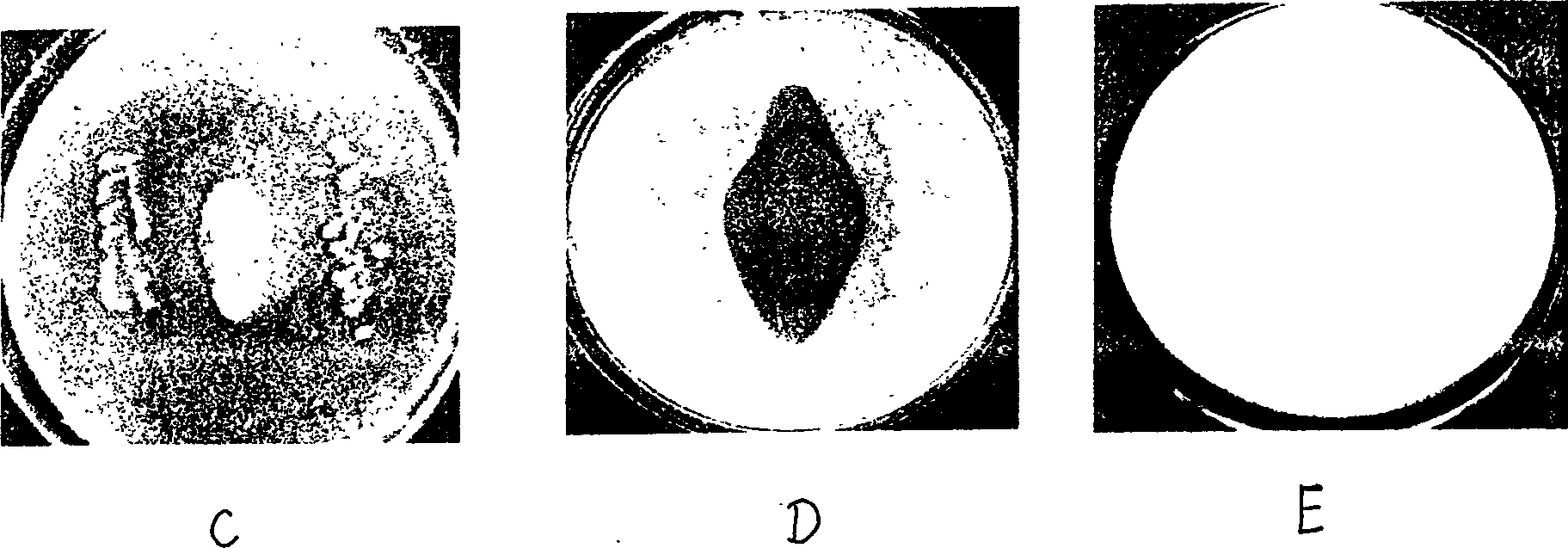
Nonabsorbent streptomyces ahygroscopicus strain BWL58 for preventing and treating banana vascular wilt and application thereof
InactiveCN102329755AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood control effectBiocideBacteriaSnow moldMicroorganism
The invention discloses a nonabsorbent streptomyces strain BWL58 for preventing and treating a banana vascular wilt. The strain BWL58 is classified and named as nonabsorbent streptomyces ahygroscopicus, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May 9, 2011; the preservation number is CGMCC No. 4837; the strain has strong antagonistic capability to the pathogenic bacteria of the banana vascular wilt and can be used for preventing and treating the banana vascular wilt; the invention further discloses a microbial inoculum containing the strain, a preparation method and application thereof; and by using the microbial inoculum, not only can the banana vascular wilt be inhibited, but also the microbial inoculum has a certain growth promotion effect on a plant.
Owner:HAIKOU EXPERIMENTAL STATION CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Strain of streptomycete for preventing sheath blight of rice
A streptomyces globisporus H50 (CCTCC No.M203034) for preventing and eliminating the hypochnus and blast of rice is obtained from soil by screening with PAD and YPTG plate method. Its advantage is high effect (more than 65% for its bacterium inhibiting rate).
Owner:成都川农邑邦农业发展有限公司
Streptomyces termitum ACT-2 strain, its culture and application
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and agricultural production, especially relates to a Streptomyces termitum ACT-2 strain, its culture and application. Streptomyces termitum ACT-2 strain is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC); the address is College of Life Sciences, Wuhan University, Luojia Mountain, Wuchang District, Wuhan, Hubei Province; the collection number is CCTCCCNO: M2011008 and the collection date is Jan. 7, 2010. Streptomyces termitum ACT-2 strain, which has an effect of resisting Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, is obtained by separating and screening from paddy soil. The strain and its fermented products can be used as a biopesticide and also used to control Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Genetic engineering bacterium capable of promoting biological synthesis of medermycin and application thereof
InactiveCN102660488AEfficient expressionEfficient importBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRibosome Recycling FactorPolyketide
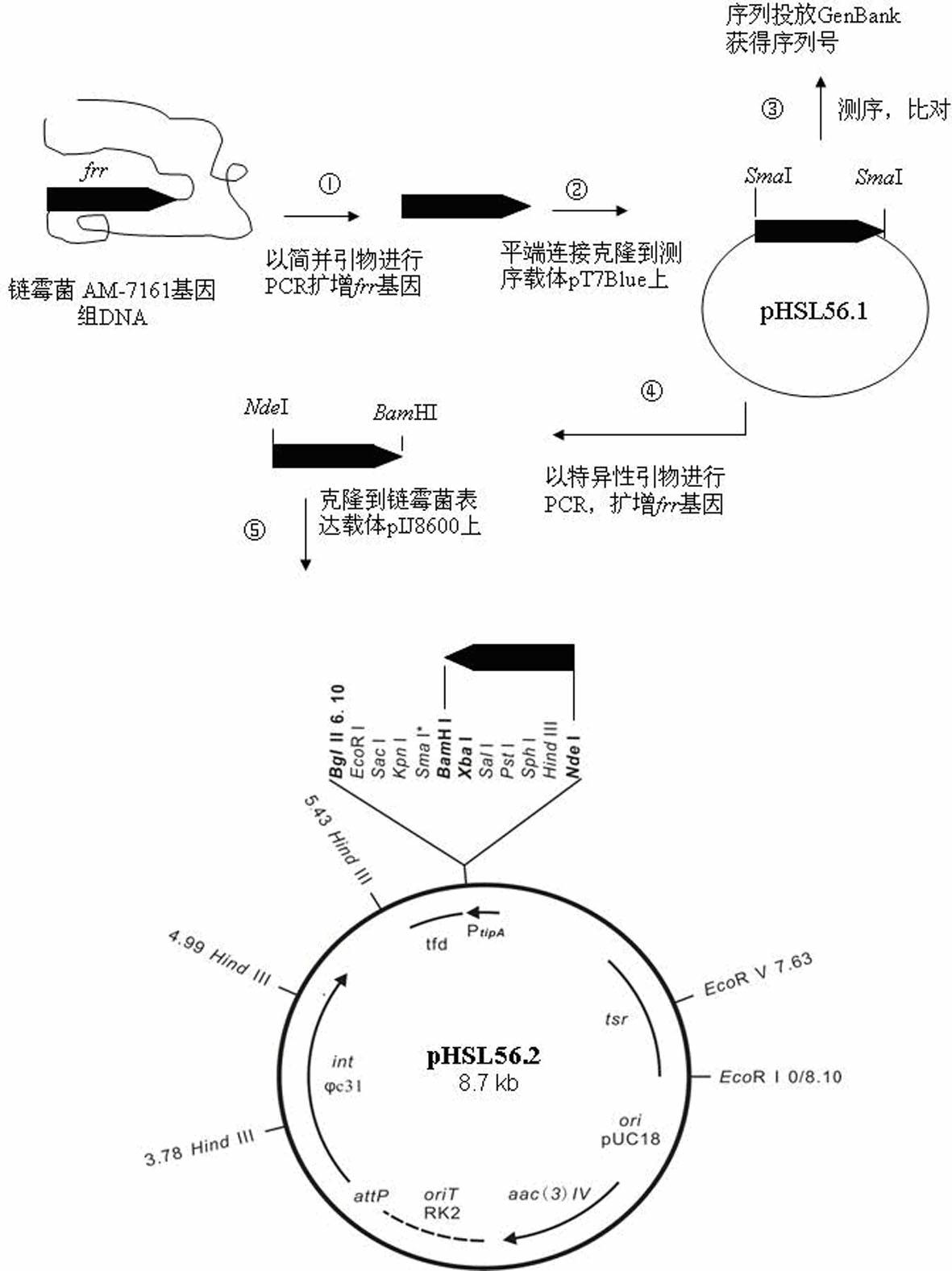
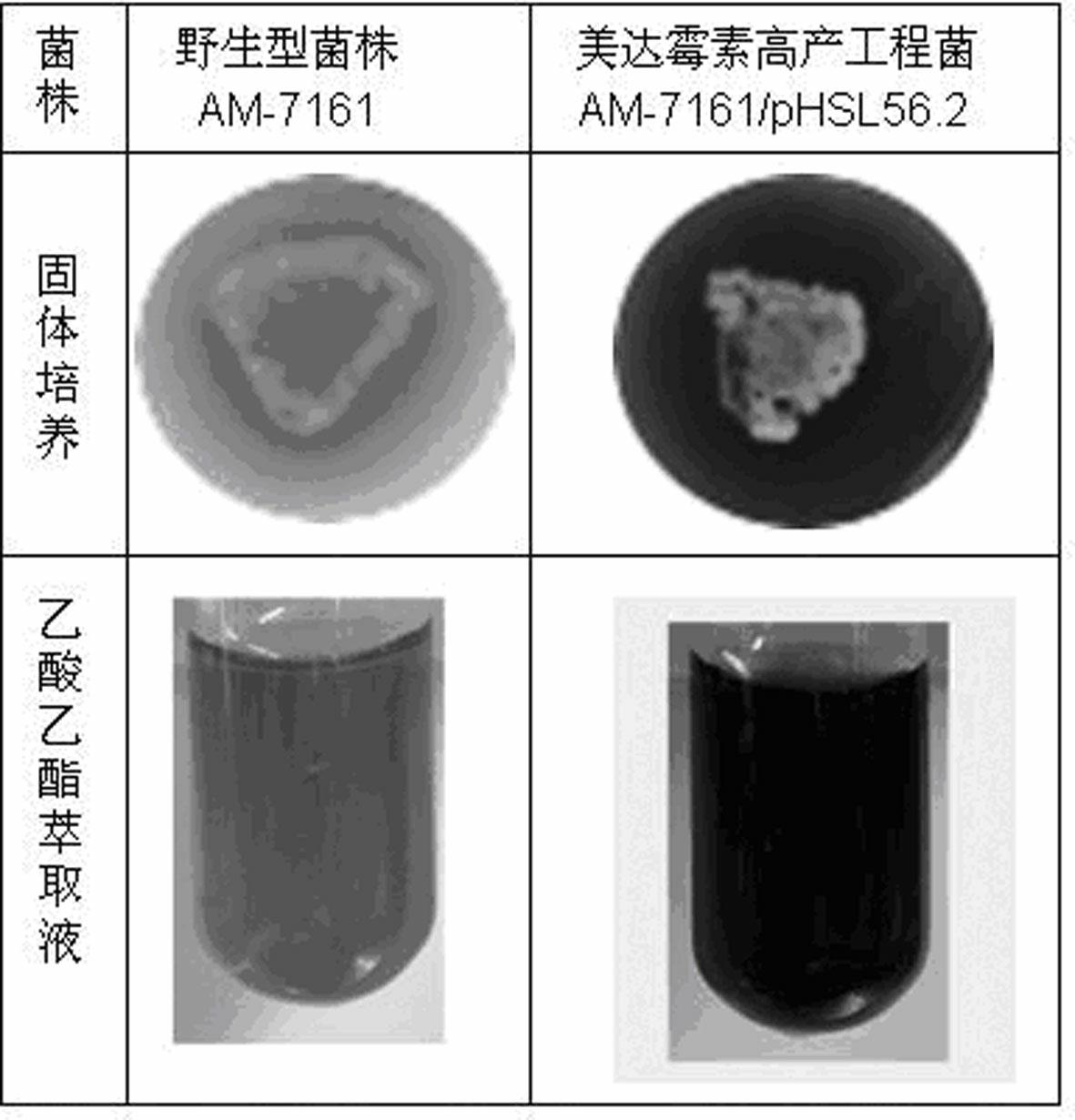
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium capable of promoting the synthesis of antibiotic medermycin and a method for producing the medermycin by using the same. The method comprises the steps that by taking deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a genome of Streptomyces nashvillensis AM-7161 as a formwork and utilizing degenerate primers to conduct polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, a new complete sequence of genes of ribosome recycling factors (RRFs) of the Streptomyces is obtained; the genes are downstream placed on an efficient promoter PtipA of the Streptomyces, so that a plasmid pHSL56.2 capable of efficently expressed in the Streptomyces is constructed; the pHSL56.2 is led into the host cell Streptomyces AM71-61, and then an engineering bacterium AM71-61 / pHSL56.2 (with a preservation number of CCTCCNo:M2012093) is obtained; and when the engineering bacterium AM71-61 / pHSL56.2 is used to conduct solid fermentation and liquid fermentation, the accumulation of the antibiotic medermycin can be effectively promoted. The efficient expression plasmid pHSL56.2 of the genetic engineering bacterium can also be directly led into a Streptomyces strain cell for producing other antibiotics of a benzoisochromanequinones family or other aromatic polyketide antibiotics, so as to obtain corresponding antibiotic high-yield engineering bacteria. By utilizing the method, the antibiotic high-yield bacteria can be genetically bred, so that the synthetic capability of the antibiotics is enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
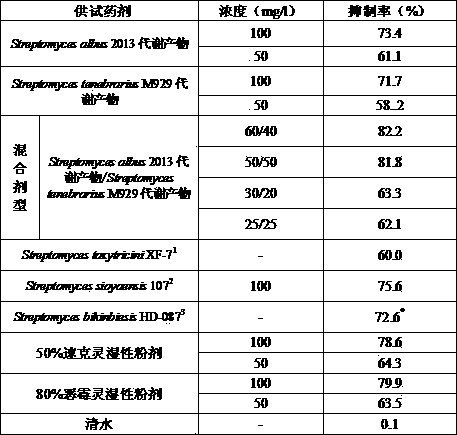
Streptomyces strains and joint application thereof in prevention and treatment of cucumber fusarium wilt
The invention discloses streptomyces strains and joint application thereof in prevention and treatment of cucumber fusarium wilt and relates to the technical field of microbes. Actinomycetes disclosed by the invention are obtained by separation from soil samples collected from rhizospheres of plants in Xixi Wetland, Zhejiang by adopting an actinomycetes separation technology, identified by microbial taxonomy and named as Streptomycesalbus 2013 and Streptomycestenebrarius M929, wherein S. albus 2013 was collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on June 19, 2013 with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M2013269; and S. tenebrarius M929 was collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 25, 2013 with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M2013710. The two strains can be fermented to produce active substances with relatively strong antagonistic effect against the cucumber fusarium wilt (Fusariumoxysporumf. sp. cucumebrium) and can be used for preventing and treating the cucumber fusarium wilt. When fermentation products of the two strains are mixed according to the ratio in percentage by weight of (3:2)-(1:1) to prepare a mixed preparation, the effect of preventing and treating pathogenic bacteria of the cucumber fusarium wilt is more significant than that when each of the two strains is used as a single preparation respectively.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Streptomyces strain and the method of converting ferulic acid to vanillin by using the same
InactiveUS20090186399A1Mild reaction conditionsSimple product extractionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationChemical synthesis
A method of vanillin production from ferulic acid with a high concentration by biotransformation using a Streptomyces sp. strain is claimed in this invention. This strain is named as Streptomyces sp. V-1, which has been deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection on Jul. 12, 2006 with the number of CCTCC M 206065. Using this strain, high concentration of vanillin fermentation broth is obtained from ferulic acid by biotransformation in GY biotransformation medium. With the addition of macroporous adsorbent resin DM11, the concentration of vanillin can be greatly improved. The advantage of this invention is less environmental pollution, high product concentration, less by-product, short processing cycle, low production cost, simple product extraction, clean production process, product environmental friendly, safe and reliable, which solves many difficulties in the vanillin production from botanical raw material extraction or chemical synthesis, and therefore it has good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI APPLE FLAVOR & FRAGRANCE
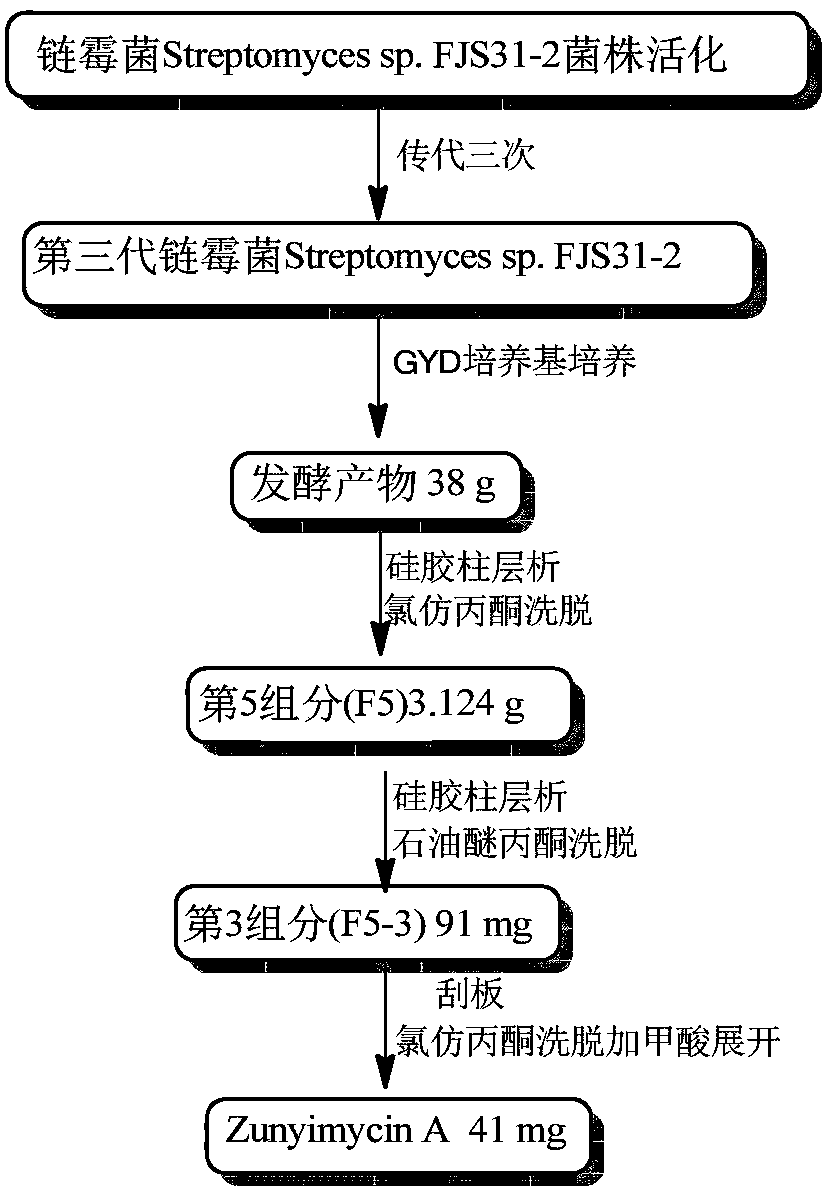
Preparation method for dichloro substituted II-type halogenated polyketone compound and antibacterial activity application
ActiveCN107937453AImprove reproductive performanceTo promote metabolismAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseCandida famata
The invention discloses a preparation method for a dichloro substituted II-type halogenated polyketone compound zunyimycin A, wherein the compound is derived from a secondary metabolite of a streptomyces sp.FJS31-2 strain (with the strain preservation number of CGMCC4.7321), and finally, a structure is identified and determined after strain activation, expansion culture and isolation. The compoundcan be used in treatment of diseases infected by gram-positive bacteria such as staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and drug-resistant bacteria thereof, staphylococcus epidermidis, bacillus subtilis and thelike, is used in treatment of diseases infected by gram-negative bacteria such as super-spectrum beta-lactamase escherichia coli (ESBL), proteusbacillus vulgaris, bacterium burgeri and the like, andis used for treatment of diseases infected by fungi, such as candida albicans.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Application of yingluo mycin in preparing drug resisting plant pathogenic fungi
InactiveCN101701233ASignificant anti-phytopathogenic fungiHighly effective agricultural antibioticsBiocideOrganic chemistryNatural sourceExperimental research
The invention relates to an application of yingluo mycin in preparing drug resisting plant pathogenic fungi, wherein yingluo mycin is natural source antimycin antibiotics (Antimycin) and is obtained by separating Streptomyces albidoflavus I07A-01824 in fermentation liquor. Experiments prove that the compound has obvious function of resisting plant pathogenic fungi, can be further developed and researched into a high-efficient agricultural antibiotics and can be applied to the fields, such as crop cultivation, food refreshment and the like.
Owner:MEDICINE & BIOENG INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Novel streptomyces strain with potential anti-microbial activity against phytopathogenic fungi
InactiveUS20020076802A1Reduce infectionPotent antifungal activityBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicroorganismMicrobiology
The present invention relates to a new strain of Streptomyces sp., called CIMAP A1 isolated from the soil of geranium (Pelargonium graleoleus) planted in the experimental fields of CIMAP and having the accession No. . . . and capable of inhibiting the growth of phytopathogenic fungi.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
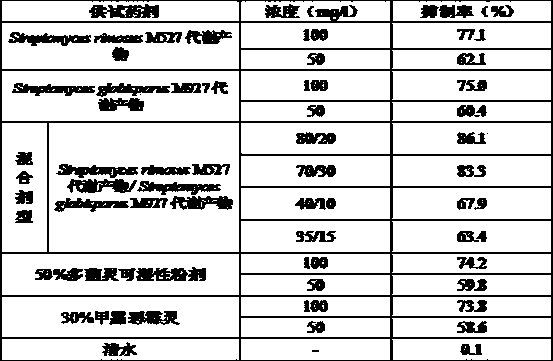
Streptomyces strain and combined application thereof in prevention and treatment of tomato blight
The invention discloses a streptomyces strain and a combined application thereof in the prevention and treatment of tomato blight and relates to the technical field of microbes. According to the streptomyces strain and the combined application thereof, actinomycetes are obtained through collecting 10-15cm deep-layer soil samples from saline-alkaline land of a suburban district of Tai'an in Shandong and separating by adopting an actinomycete separation technology, and are named streptomyces rimosus M527 and streptomyces globisporus M927 through microbial taxonomic identification, S. rimosus M527 has been collected in CCTCC (China Center for Type Culture Collection) on June 19, 2013 and has the collection number of CCTCC NO: M 2013270, and S. globisporus M927 has been collected in CCTCC on December 25, 2013 and has the collection number of CCTCC NO: M 2013709. Both strains can be fermented to generate active substances which have relatively strong antagonism on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Lycopersici Snyder et Hansen and can be used for preventing and treating plant diseases, such as tomato blight. When fermentation products of the two strains are mixed according to the weight percent of (4: 1) to (7: 3), the biological prevention effect is particularly remarkable compared with that when the two kinds of metabolic products are used respectively as single preparations.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
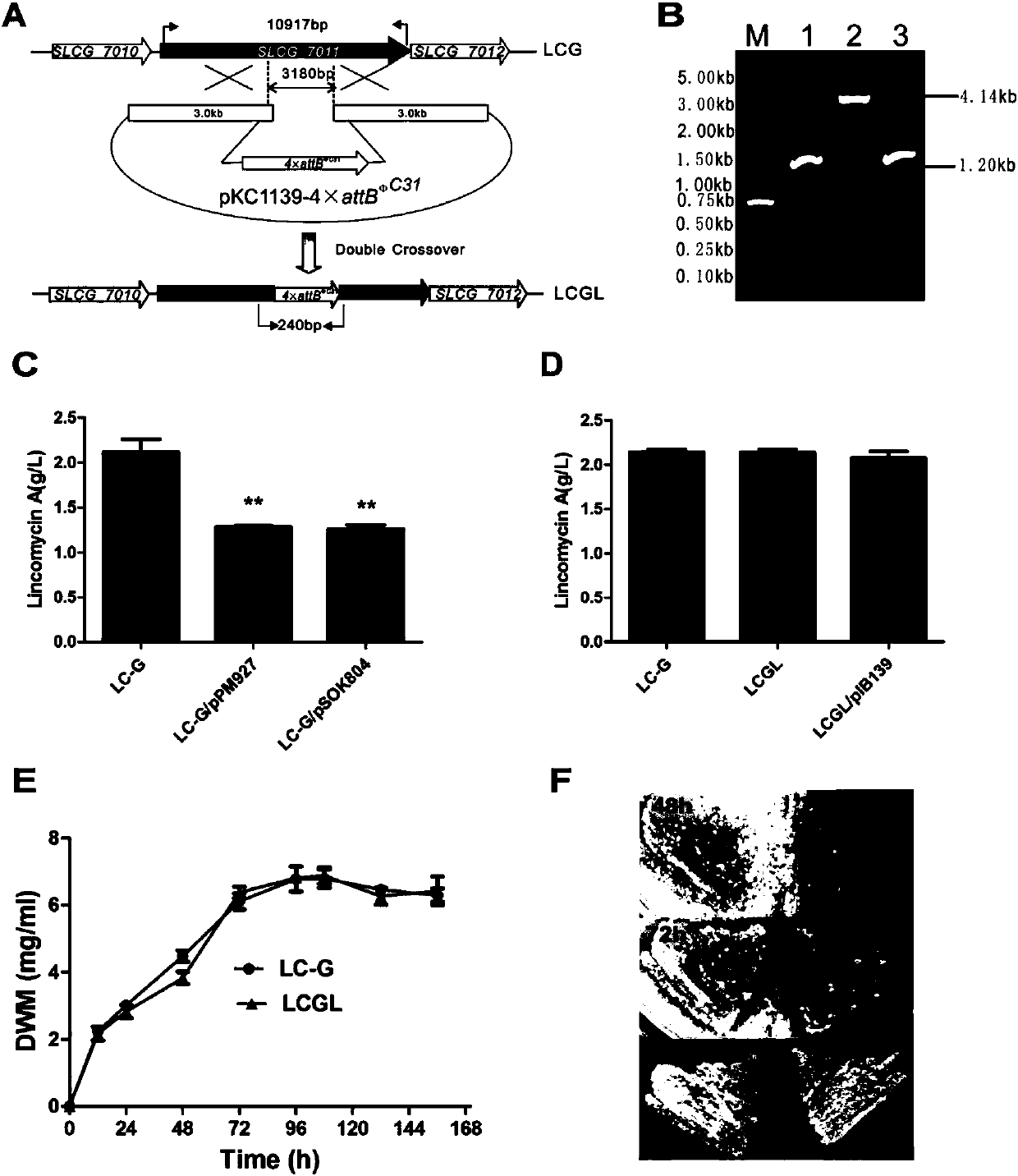
Method for increasing yield of lincomycin by co-expressing metK1 and metK2 genes in streptomyces lincolnensis
InactiveCN107746826AIncrease productionImprove fermentation yieldBacteriaTransferasesMicrobiologyGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of lincomycin by co-expressing metK1 and metK2 genes in streptomyces lincolnensis. The method is characterized in that the metK1 and metK2 genes in the streptomyces lincolnensis are co-expressed through a genetic engineering way, so that an engineering strain with high lincomycin yield of the streptomyces lincolnensis is obtained; and the strain obtained by the technology can be fermented to increase the yield of the lincomycin.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Bacterial-wilt-resistant Streptomyces rochei strain and bio-organic fertilizer thereof
InactiveCN105969686AGood control effectBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaBiotechnologyRalstonia solanacearum
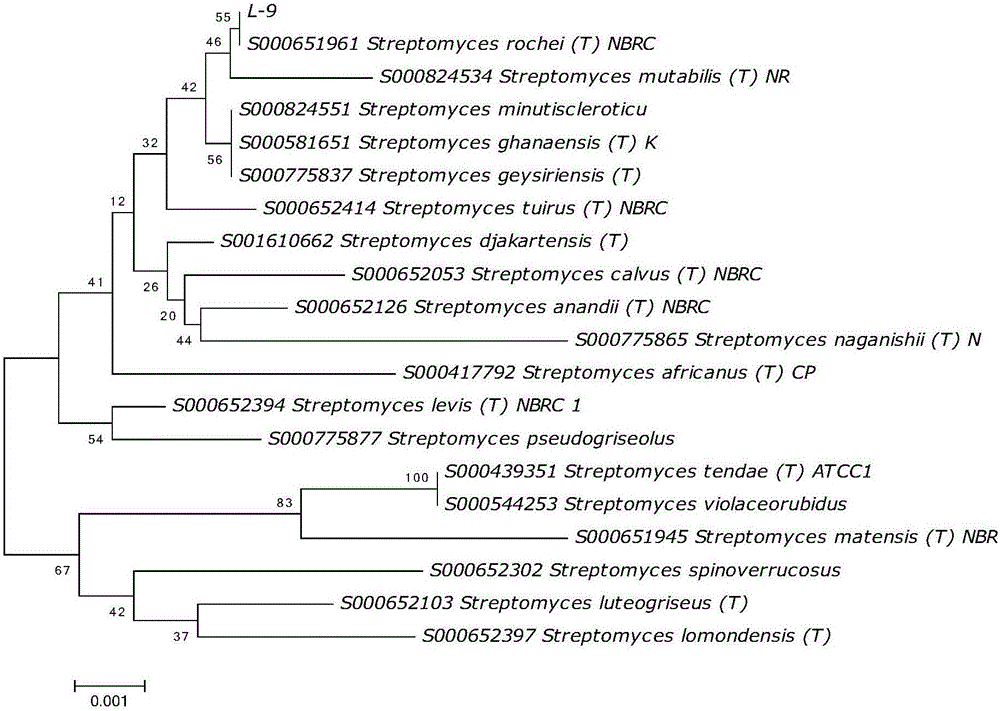
The invention discloses a bacterial-wilt-resistant antagonistic bacterium strain. The strain is named Streptomyces rochei L-9, and was collected by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on September 25th, 2013; and the collection number is CGMCC No.8264. The strain L-9 has high bacterial wilt resistance, and the antagonistic ring radius reaches 15mm. The invention provides a new microbial resource for biological control on bacterial wilt, and overcomes the defects in the prior art.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI RES INST +1
Fermenting method for producing natamycin
The invention relates to the fermenting method for producing natamycin that breeds a streptomycete strain of high yield natamycin, by the method of fermenting metabolizing method to select the fermenting culture medium compounding and fermenting technology condition. The method has the advantages of high yield, low cost, short producing cycle, etc.
Owner:广州市微生物研究所
Streptomyces lunalinharesii ZJNU968 strain and applications thereof
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnological agricultural production, and particularly relates to a Streptomyces lunalinharesii ZJNU968 strain and applications thereof, wherein the strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (the address is Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 3# Court No.1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing.) on November 11, 2013, and has the preservation number of CGMCC No:8465. According to the present invention, the Streptomyces lunalinharesii ZJNU968 strain and the fermentation broth thereof can be used for preventing and controlling tobacco brown spot.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of monensin premix
ActiveCN104313079AHigh yieldReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroscopic examMonensin
The invention discloses a preparation method of a monensin premix. The preparation method comprises the following specific steps: preparing cinnamon streptomyce strain; seed flask culture and seed tank culture are performed; when the age of the seed is 20-24h, the pH of a culture solution is 6.6-7.1, the biomass is above 10%, and microscopic examination shows that mycelia are thick and reticular, are stretched and darkly stained and are free of foreign bacteria, performing fermentation culture is performed; when the residual oil amount is below 0.7%, the biomass is above 40%, the mycelium concentration is 40-50%, and the monensin titer is not lower than 40000U / mL, fermentation is finished; monensin is extracted by a one-step spray drying method, wherein the prepared finished monensin product has the monensin content of above 20% and the grain rate of above 75%. According to the preparation method, the fermentation process is simple, so that the fermentation unit can be effectively increased and the production cost can be reduced; usages of an animal-derived nitrogen source and a chemical organic solvent are avoided.
Owner:金河生物科技股份有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com