Genetic engineering bacterium capable of promoting biological synthesis of medermycin and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and medamycin, applied in the field of genetic breeding, can solve the problems of low antibiotics, high antibiotic-producing bacteria breeding bottlenecks, and restrict antibiotic development, etc., and achieve the effect of high-efficiency expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
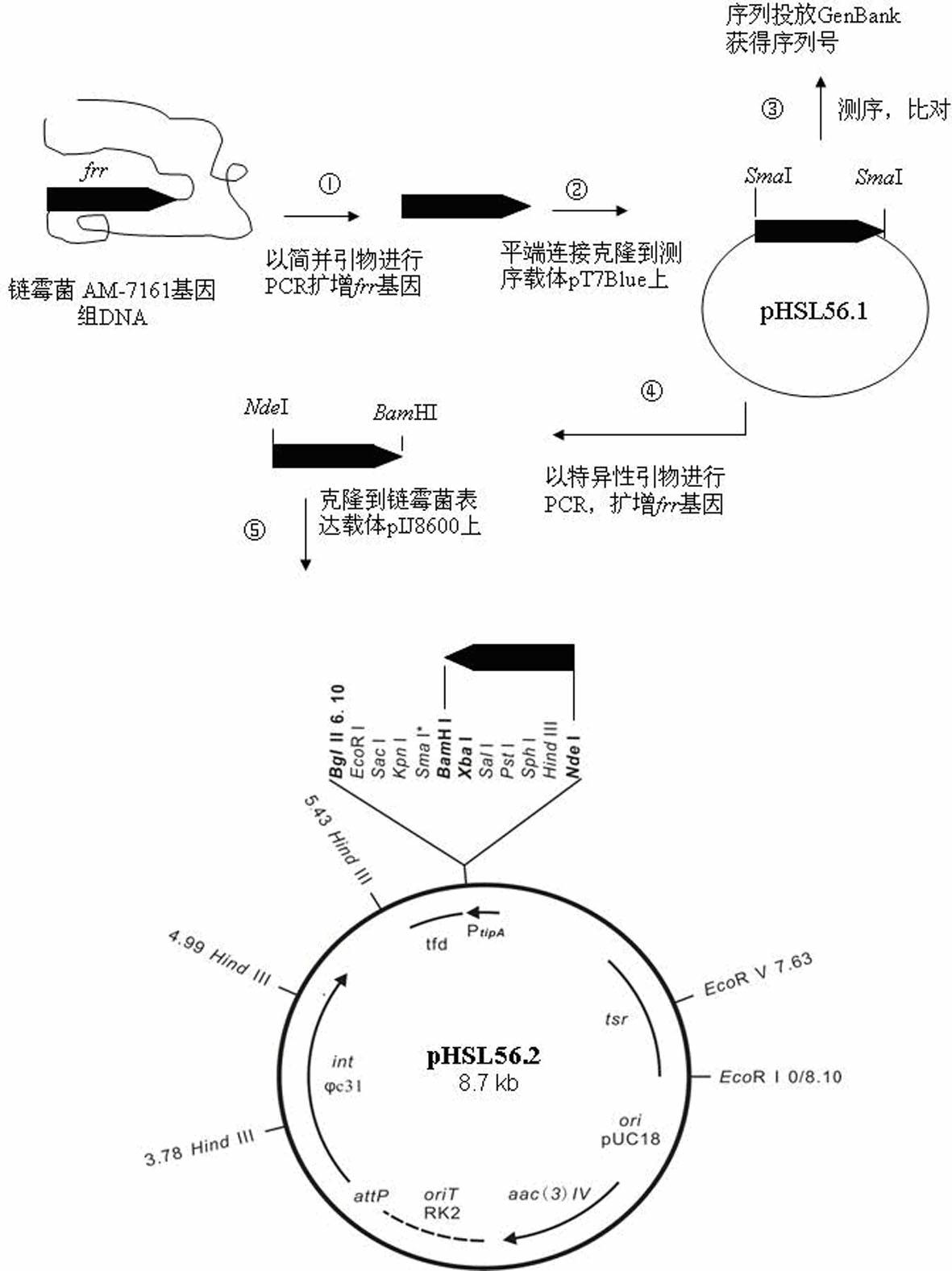
[0044] Solid fermentation of engineering bacteria AM-7161 / pHSL56.2:
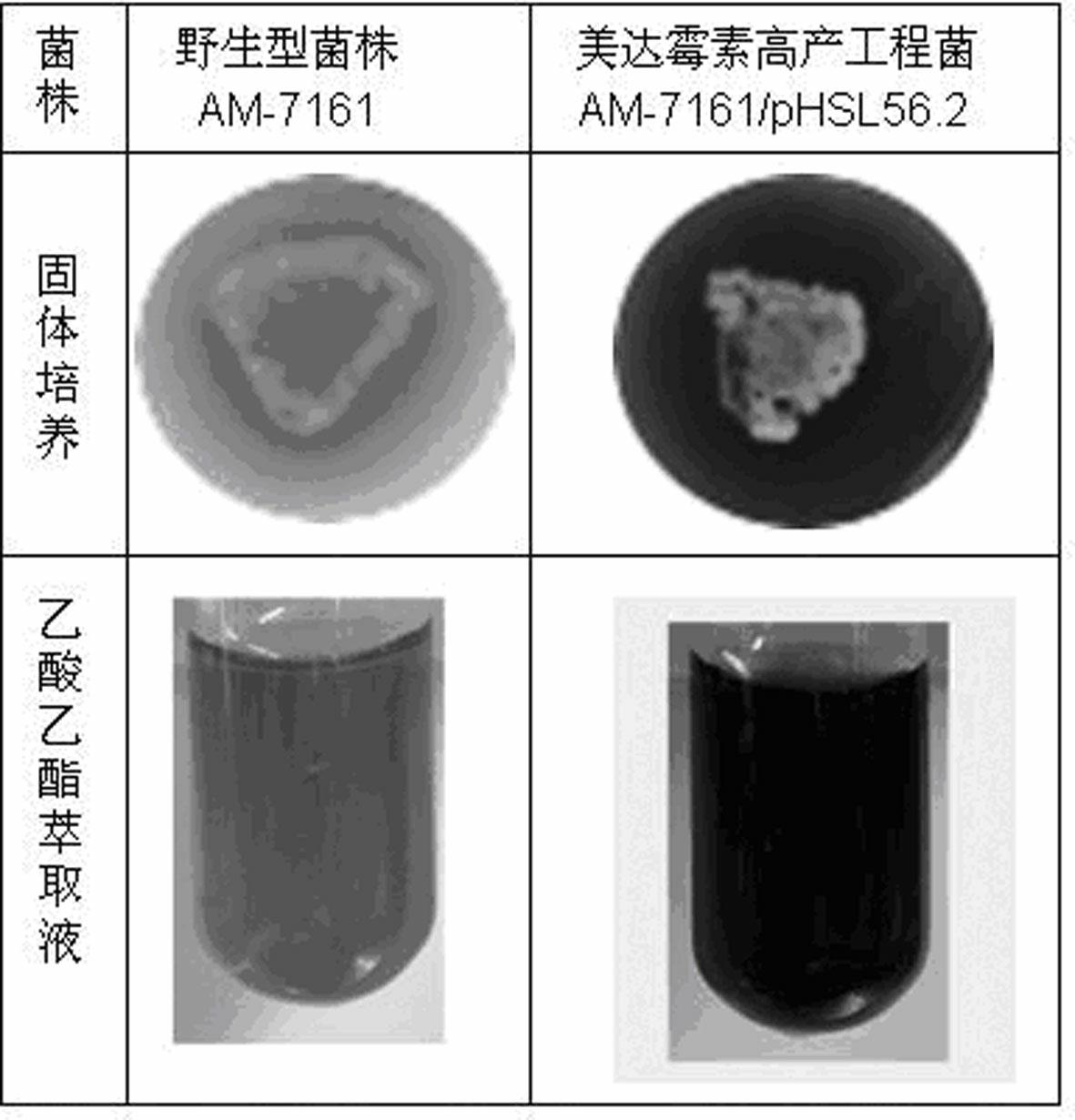
[0045] Eight recombinant strains AM-7161 / pHSL56.2 that may contain the plasmid pHSL56.2 were identified. They were cultured on solid R4 medium at 30°C for 5 days until sporulation. The spores were collected and stored in 20% glycerol for cryopreservation. Get engineering bacterium AM-7161 / pHSL56.2 and wild bacterium AM-7161 spore suspension and spread on 20ml solid R4 medium respectively (R4 medium formula sees content of the invention, do not add in the medium when cultivating wild bacterium AM-7161 thiostrepton, because the wild bacteria AM-7161 has no thiostrepton resistance); placed in static culture at 30°C for 3-5 days, it can be seen that due to the high expression of ribosome recycling factors, the U.S. The production of daxamycin was significantly increased (secreted into the culture medium, showing reddish brown) ( image 3 ); collect the solid culture (together with the culture medium), cut into ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Liquid fermentation of engineering bacteria AM-7161 / pHSL56.2:
[0048] Draw 50 μl of spore suspension of engineering bacteria AM-7161 / pHSL56.2 and inoculate it in 5mL seed medium (see the contents of the invention for the medium formulation), cultivate it for 2 days at 200 rpm and 30°C, and then press 1:100 Ratio Transfer the seed culture into the liquid R4 hormone-producing medium (see the content of the invention for the medium formula, add 12.5 μg / ml thiostrepton as an inducer), and cultivate 5- 6 days. Transfer the fermentation broth into a 50ml centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 3000rpm at room temperature for 10min, and collect the supernatant. Adjust the pH of the supernatant to neutral, extract three times with ethyl acetate, mix the extracts, add water to extract once (wash), filter with anhydrous sodium sulfate powder to remove water, filter with filter paper, remove ethyl acetate by rotary evaporation, and finally in dissolved in ethyl acetate.
[0049]The col...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com