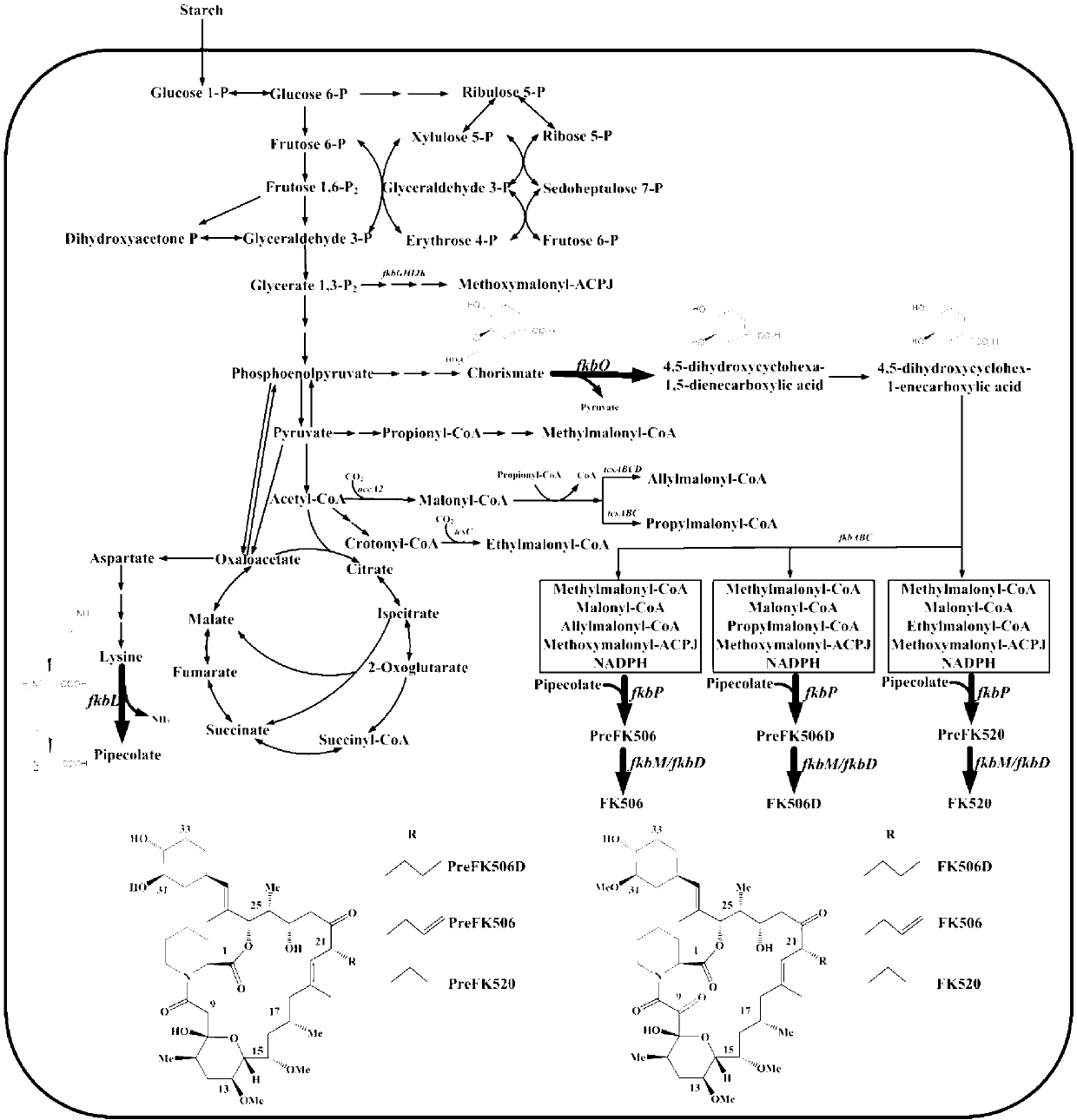
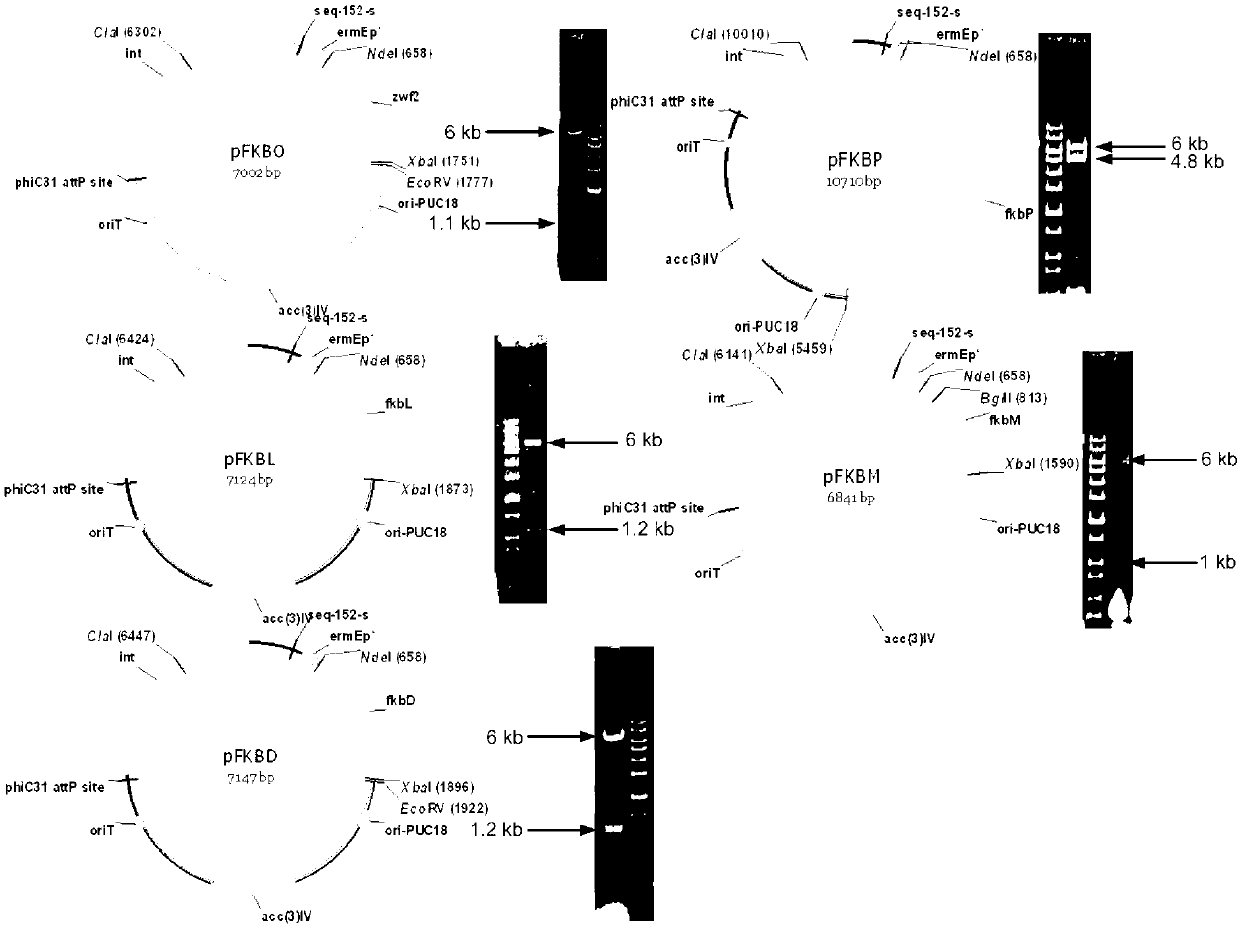
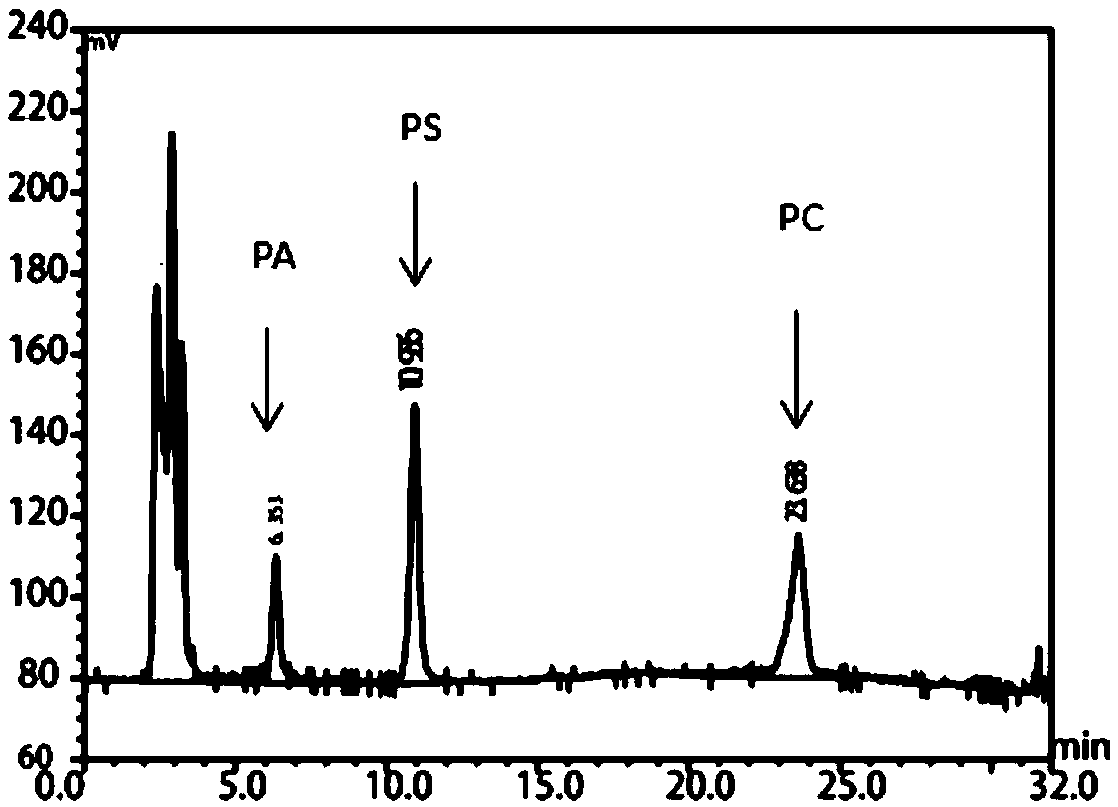
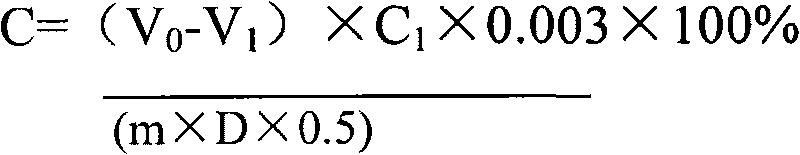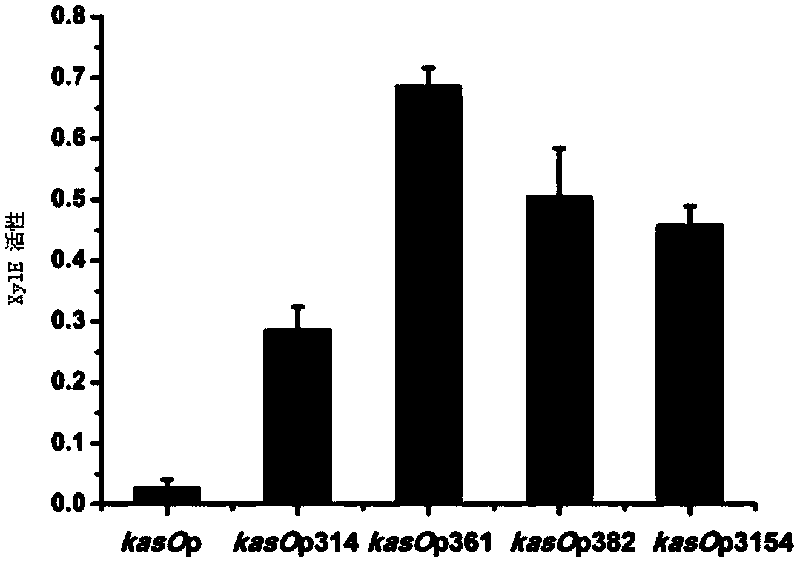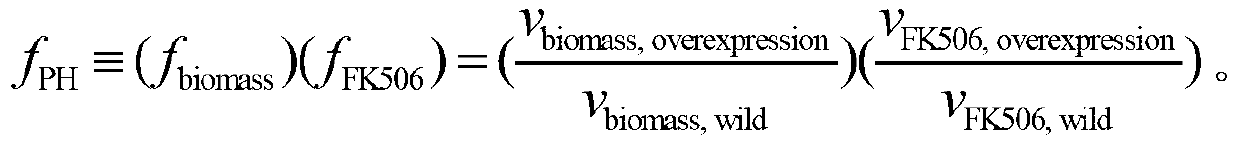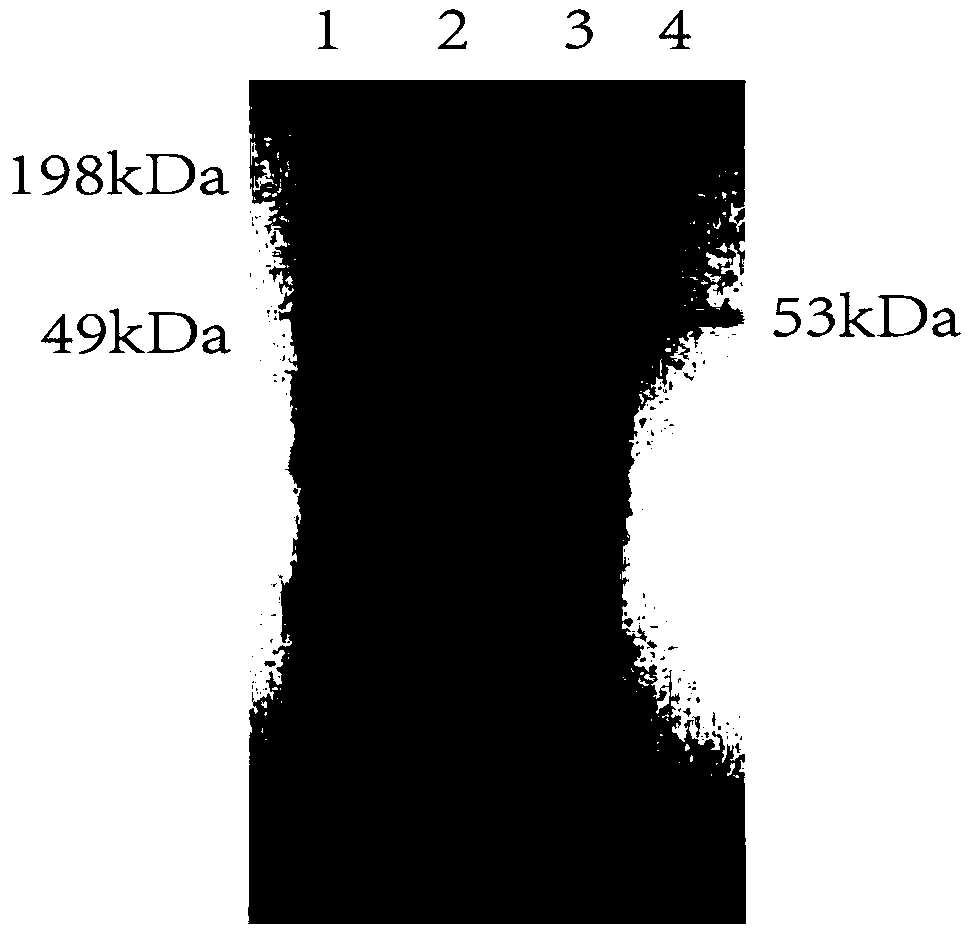Patents
Literature
80 results about "Streptomyces coelicolor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Streptomyces coelicolor is a soil-dwelling Gram-positive bacterium that belongs to the genus Streptomyces.
Novel Selectable Marker Genes
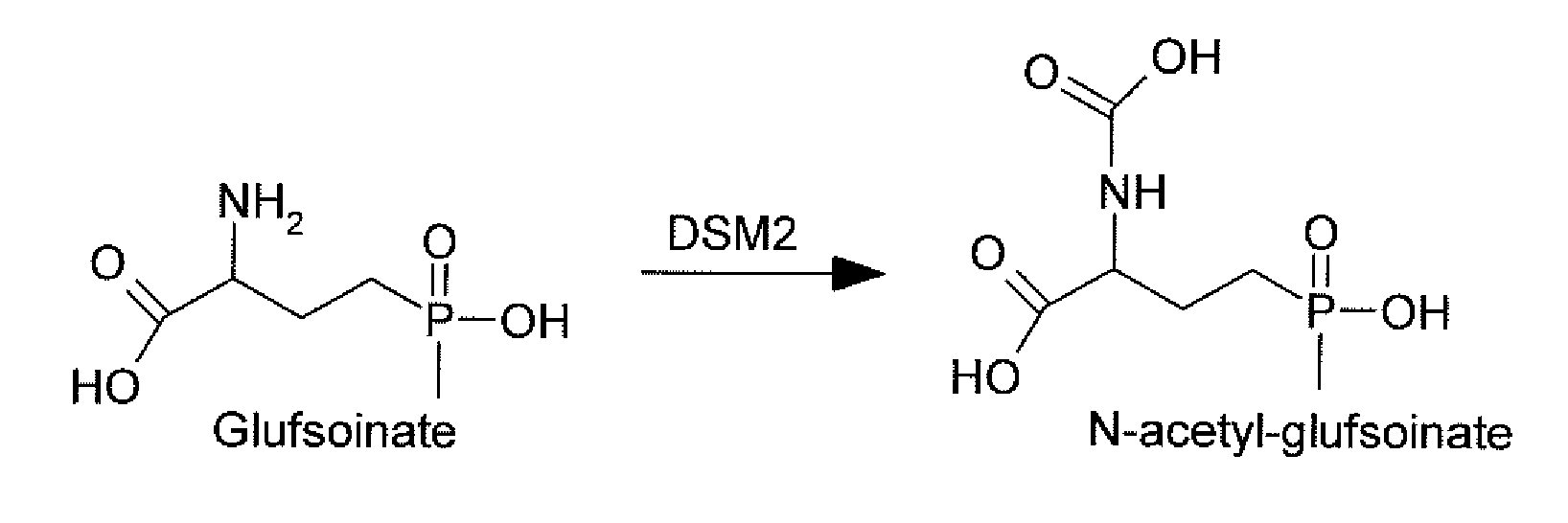
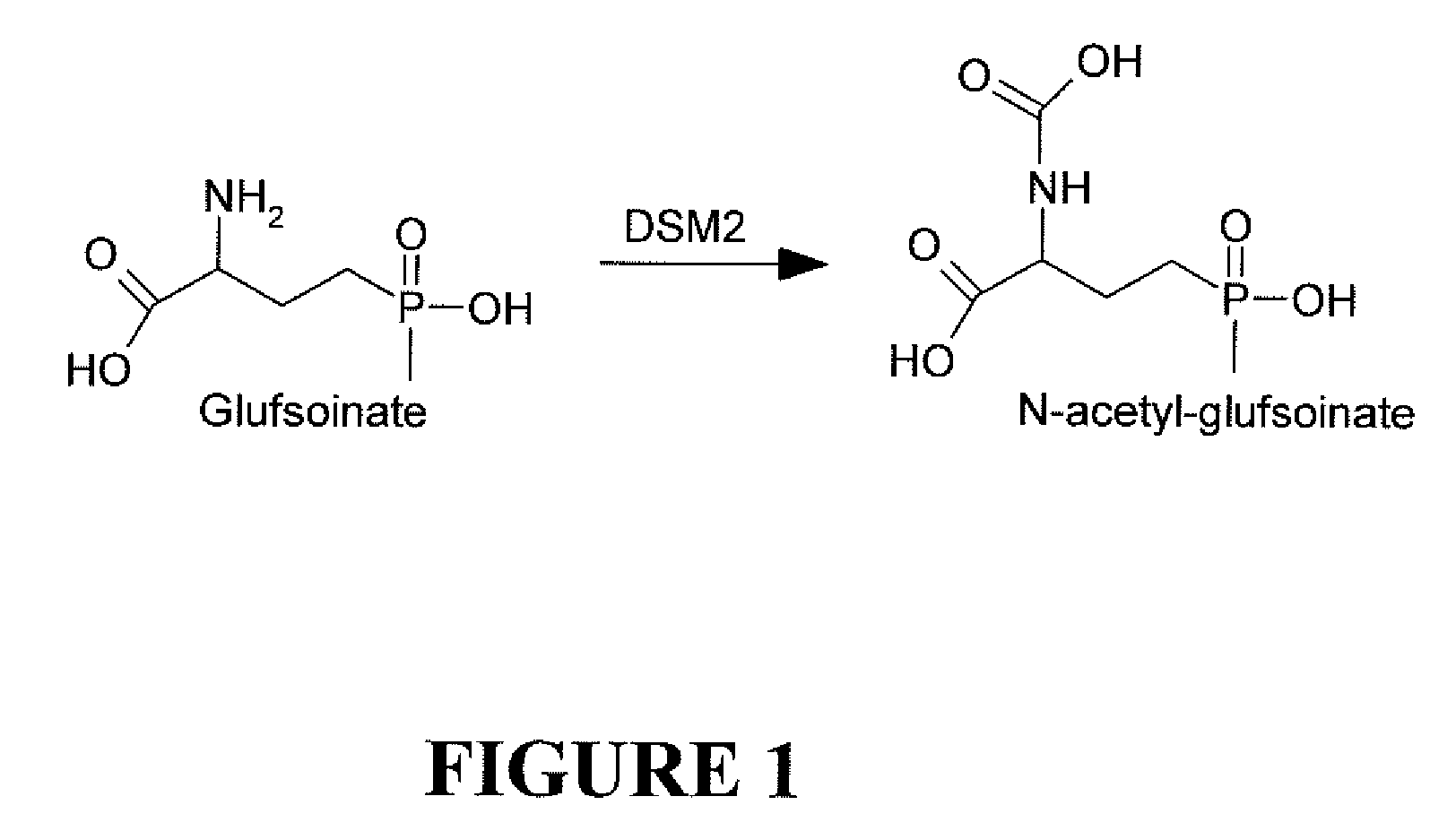
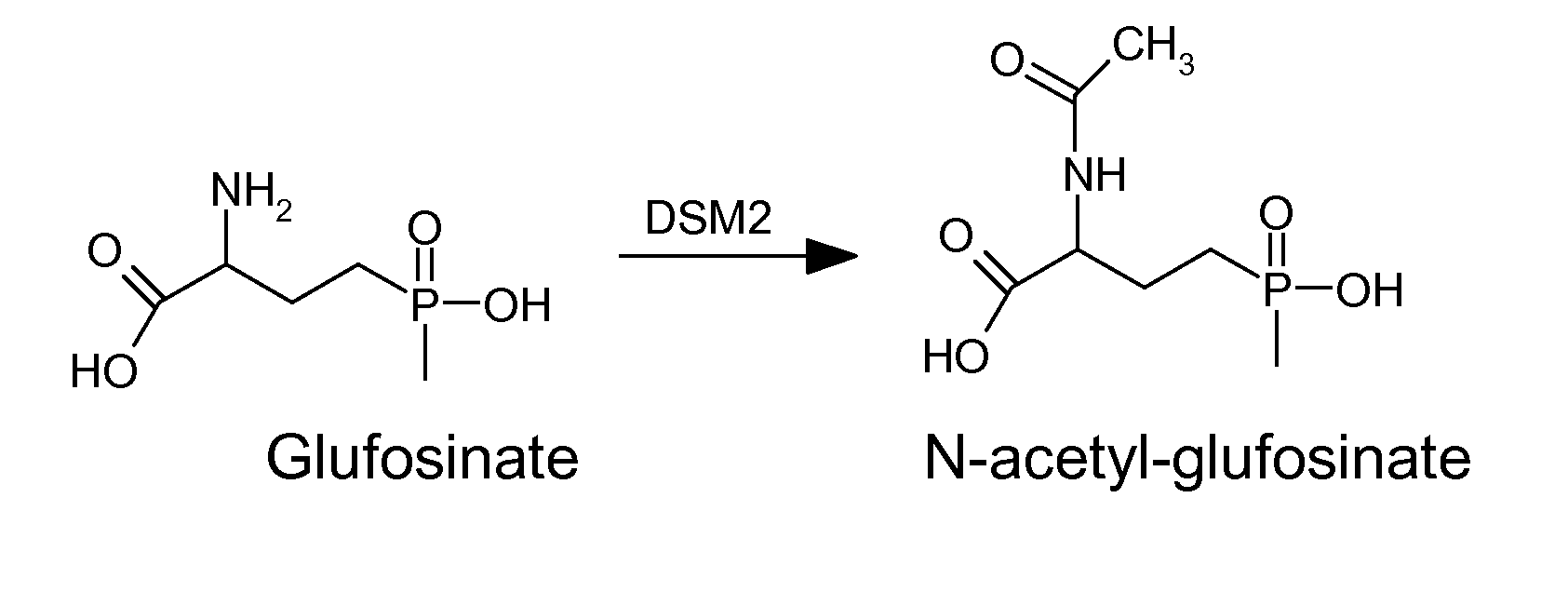
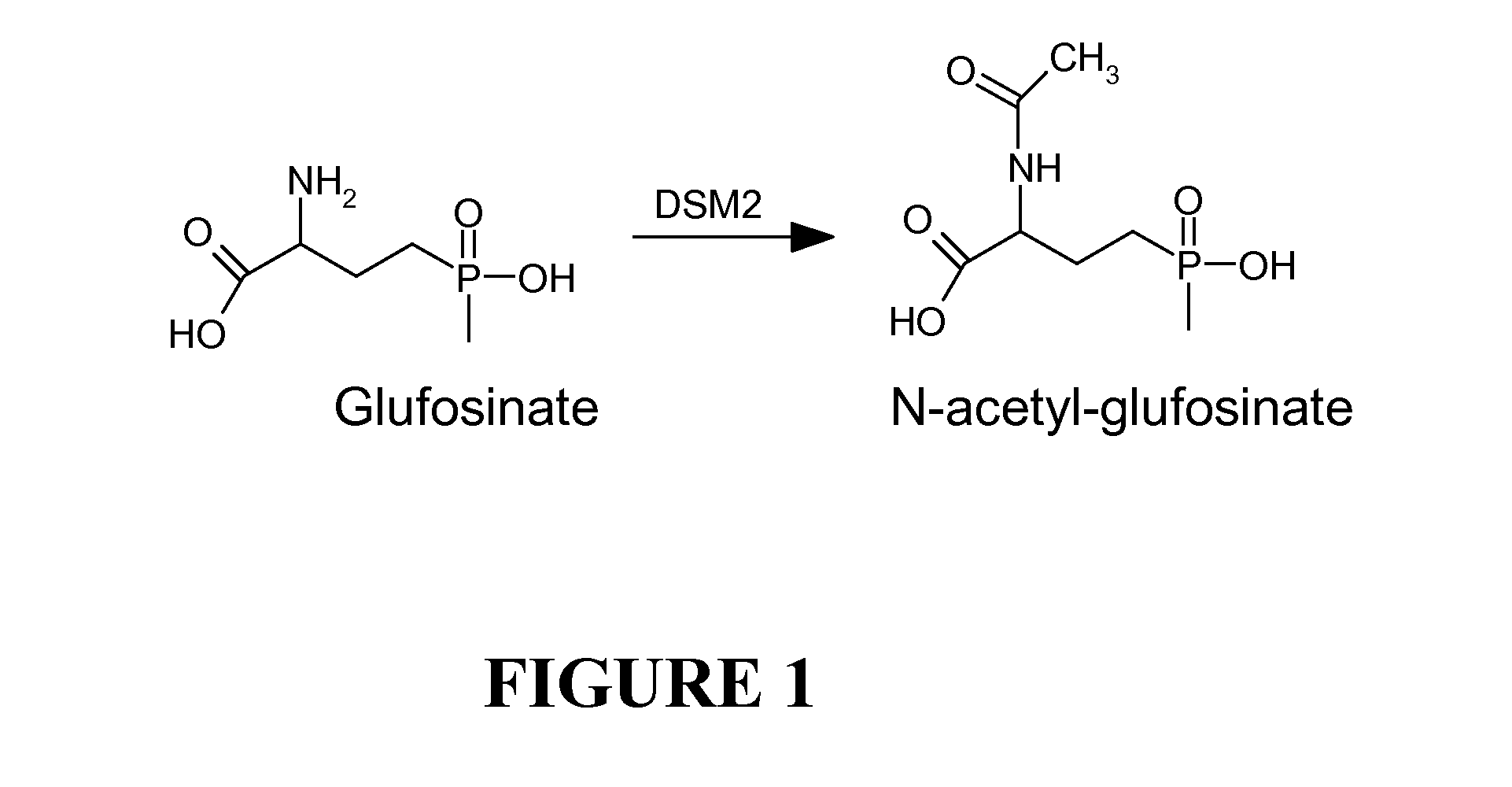
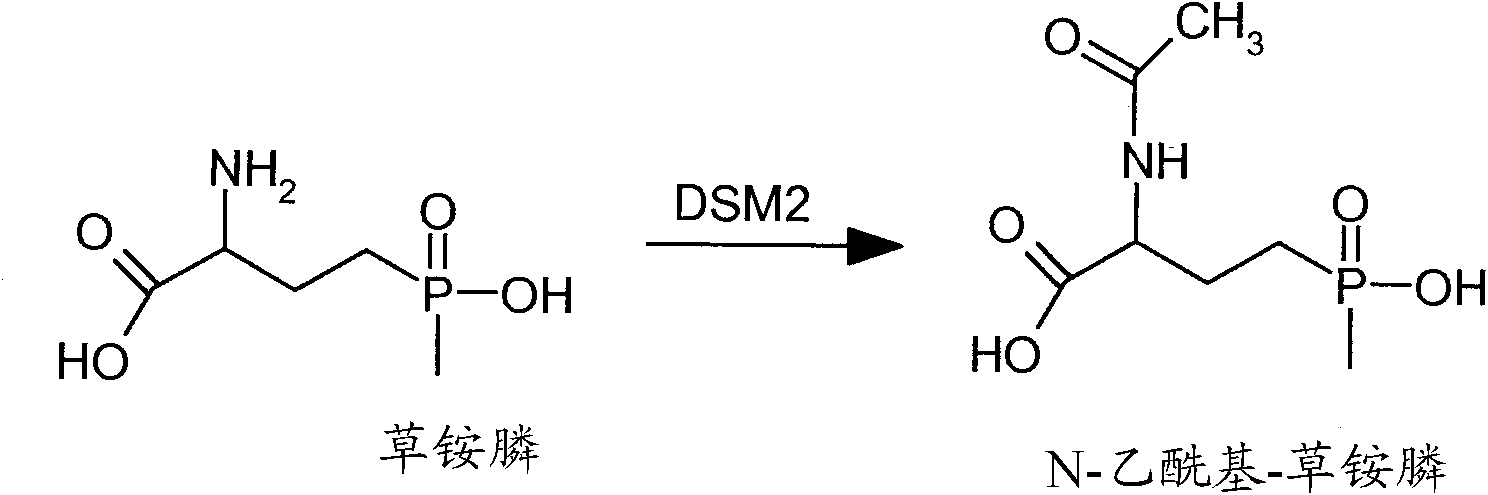
The subject invention relates to a novel gene referred to herein as DSM-2. This gene was identified in Sterptomyces coelicolor A3. The DSM-2 protein is distantly related to PAT and BAR. The subject invention also provides plant-optimized genes encoding DSM-2 proteins, DSM-2 can be used as a transgenic trait to impart tolerance in plants and plant cells to the herbicides glufosinate and bialaphos. One preferred use of the subject genes are as selectable markers. The use of this gene as a selectable marker in a bacterial system can increase efficiency for plant transformations. Use of DSM-2 as the sole selection marker eliminates the need for an additional medicinal antibiotic marker (such as ampicillin resistance) during cloning. Various other uses are also possible according to the subject invention.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Microbial agent capable of reducing leaf vegetable plant diseases and insect pests and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101671212AHigh activityTo promote metabolismPlant growth regulatorsBiocideDiseaseSnow mold
The invention relates to a microbial agent capable of reducing leaf vegetable plant diseases and insect pests and a preparing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of agricultural production application of microorganisms. The microbial agent capable of reducing leaf vegetable plant diseases and insect pests is characterized in that the microbial agent is prepared from the following rawmaterials: beauveria bassiana culture solution, streptomyces coelicolor culture solution, compound strain culture solution, garlic, molasses, Chinese medicinal herb and trace element inorganic salt solution, wherein the compound strain is composed of Bacillus subtilis culture solution, rhodopseudomonas palustris and saccharomycetes. The preparing method is as follows: respectively culturing beauveria bassiana and streptomyces coelicolor alone, culturing Bacillus subtilis, lactobacillus and saccharomycetes in a compound mode; mixing and fermenting three culturing products, Chinese medicinal herb, garlic and the like; and finally, adding trace elements into the compound fermentation product. The invention can obviously strengthen leaf vegetable organism disease resistance and resilience, improves soil and reduces soil-borne diseases.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHUANGBO MODERN NATURAL AGRI GRP
E. coli and Streptomyces host cells that contain MatBC genes or E. coli host cells that contain pcc genes useful for enhanced polyketide production
InactiveUS6939691B1Increase productionImprove the level ofBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliPolyketide
The use of enzymes that catalyze the production of starter and extender units for polyketides in E. coli and Streptomyces is described; these enzymes include malonyl CoA decarboxylase (MatA), malonyl CoA synthetase (MatB), and a malonate transporter (MatC) as well as proprionyl CoA carboxylase (pcc). The matBC gene from Streptomyces coelicolor, the matABC genes from Rhizobium trifoli, and the pccB and accA2 from Streptomyces coelicolor are useful in specific embodiments of the claimed invention. These enzymes may be used to enhance the yield of polyketides that are natively produced or polyketides that are rationally designed. By using these techniques, the synthesis of a complete polyketide has been achieved in E. coli in the presence of a phosphopantetheinyl transferase, such as sfp from Bacillus subtilis. This achievement permits a host organism with desirable characteristics to be used in the production of such polyketides and to assess the results of gene shuffling.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Constructs for Expressing Herbicide Tolerance Genes, Related Plants, and Related Trait Combinations
Constructs for expressing herbicide tolerance genes, related plants, and related trait combinations, said constructs comprise a gene referred to herein as DSM-2 identified in Streptomyces coelicolor (A3). The DSM-2 protein is distantly related to PAT and BAR DSM-2 can be used as a transgenic trait to impart tolerance in plant cells and plants to the herbicidal molecules glufosinate, phosphinothricin, bialaphos, and / or the like. The subject invention also relates to combination of the subject herbicide tolerant crop (HTC) traits along with other HTC traits and / or insect resistance (IR) traits.
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
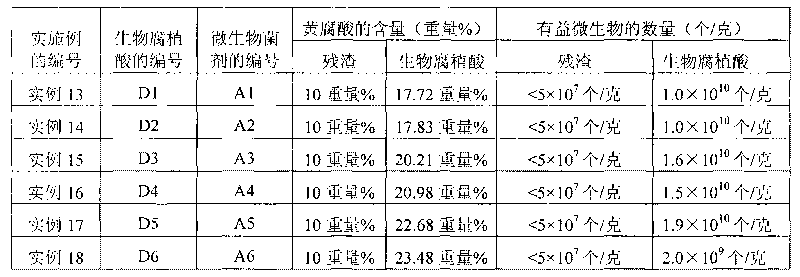
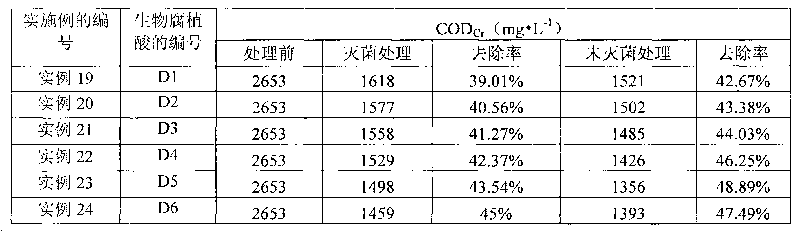
Microbe microbial inoculum, preparation method thereof and method for producing biological humic acid
The invention provides a microbe microbial inoculum and a preparation method thereof as well as a method for producing biological humic acid with sugarcane sugaring residue by the microbe microbial inoculum. The microbe microbial inoculum prepared by the invention comprises a culture medium and thallus, wherein the thallus comprises Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus licheniformis, Streptomyces coelicolor and Aspergillus fumigatus, and each gram of compounded microbe microbial inoculum contains 0.5-1.5*109 total viable bacteria. The microbe microbial inoculum of the invention can quickly ferment sugarcane sugaring residues so as to obtain biological humic acid. Compared with mineral humic acid, the biological humic acid has the advantages of small molecular weight, large amount of active group, favourable water solubility, high bioactivity and the like and is easy to adsorb by the tissues of plants and animals, so that the biological humic acid can serve as the repairing preparation and fertilizer of water body and soil. Thus, the sugarcane sugaring residue can be effectively processed and utilized so as to really change waste material into things of value.
Owner:INST OF ENVIRONMENT & SUSTAINABLE DEV IN AGRI CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
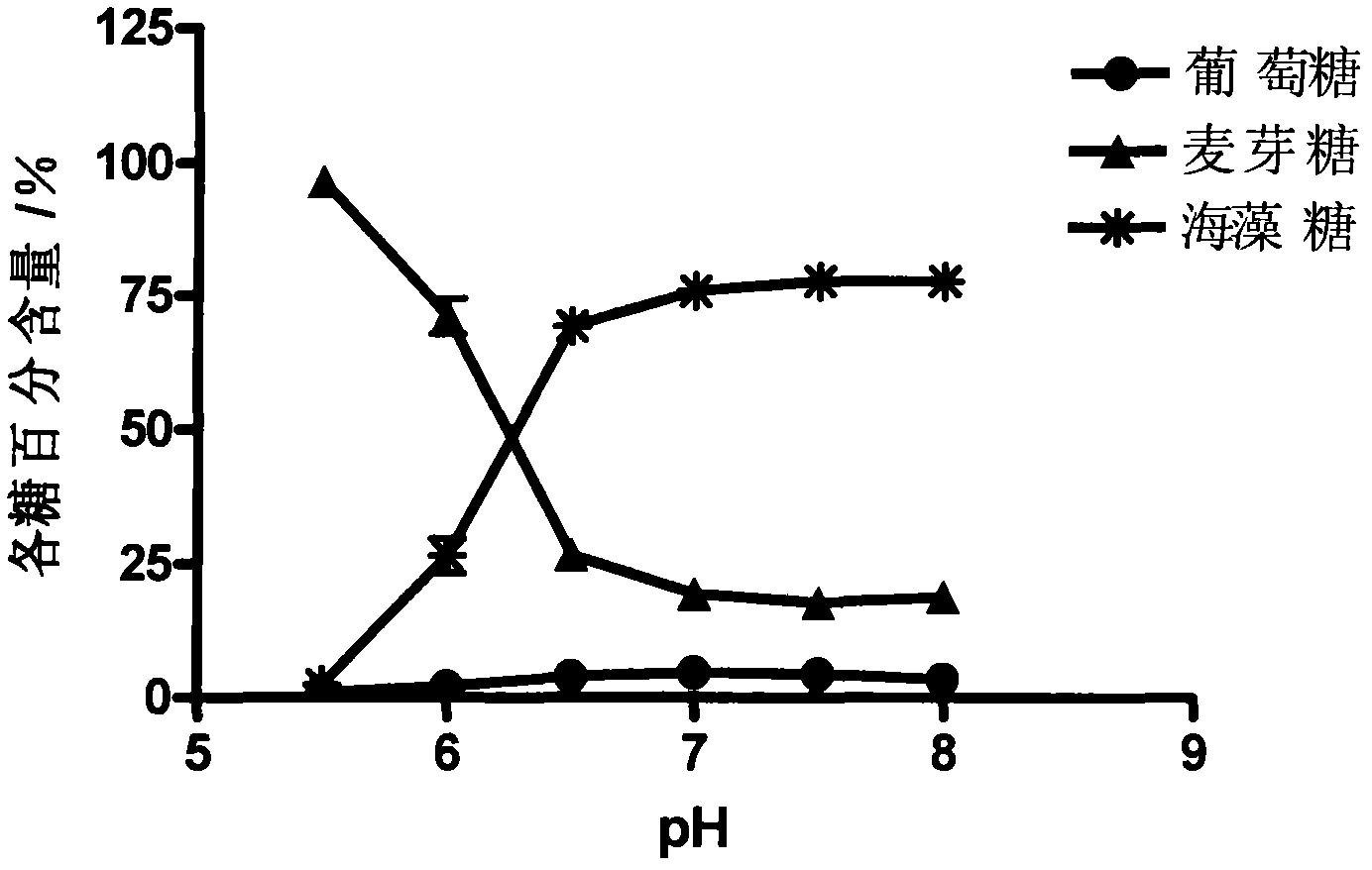
Streptomyces coelicolor trehalose synthase enzyme gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102154326ASmall molecular weightEasy to produceEnzymesFermentationEnzyme GeneTrehalose synthase
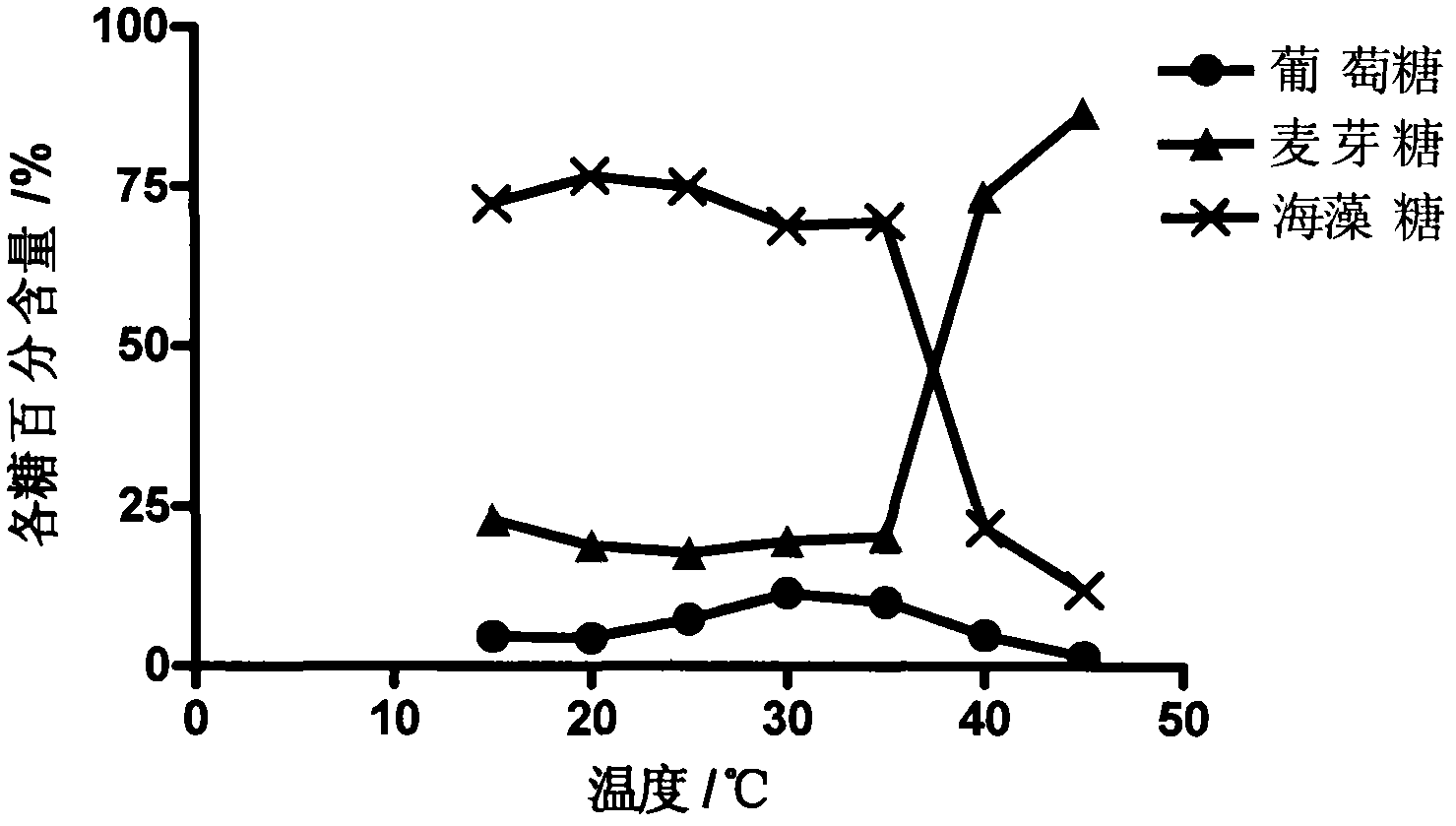
The invention relates to a streptomyces coelicolor trehalose synthase enzyme gene. The gene is cloned from streptomyces coelicolor (Streptomyces coelicolor, AS 4.1061). A trehalose synthase enzyme expressed by the gene can be used for converting maltose into trehalose under the normal biochemical reaction conditions and has the characteristics of high reaction speed, high conversion rate of a substrate and few byproducts. The content of trehalose in a product generated in the process of converting the maltose at a temperature of 25 DEG C can achieve over 75 percent and only little glucose is generated. The streptomyces coelicolor trehalose synthase enzyme gene is beneficial for improving the conversion rate of the substrate and reducing the production cost. The gene can be applied to production of the trehalose. The trehalose can be applied to the fields of food industry, beauty cosmetics, medical biological products and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Phospholipase A2 mutant and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104017786AIncreased specific enzyme activityEasy to produceFungiBacteriaSurface displayPichia pastoris
The invention relates to a phospholipase A2 mutant and a preparation method thereof. The technical scheme is as follows: the preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out site-specific mutagenesis on the amino acid residues of Glu37 and Asp78 of wild type phospholipase A2 derived from streptomyces coelicolor by utilizing a recombinant DNA technology to obtain a phospholipase A2 gene with higher activity; then expressing the phospholipase A2 gene with higher activity in a bacillus subtilis expression system and a pichia pastoris expression system (which comprises a pichia pastoris free expression system and a pichia pastoris cell surface display system) to obtain a recombinant strain capable of generating high-activity phospholipase A2; after the phospholipase A2 gene with higher activity is expressed, detecting that the enzyme activity of the high-activity phospholipase A2 is enhanced by 13.7% compared with that of the wild type phospholipase A2, wherein the enzyme activity of the phospholipase A2 can be up to 53.5 U / ml after the bacillus subtilis high-activity phospholipase A2 recombinant bacteria is fermented, the enzyme activity of pichia pastoris free-expression high-activity phospholipase A2 recombinant bacteria can be up to 106.4 U / ml, and the enzyme activity of a pichia pastoris cell surface display high-activity phospholipase A2 whole-cell catalyst can be up to 260 U / (g.stem cell).
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Streptomycete constitutive promoter and applications thereof
InactiveCN103421778AIncrease productionIncreased transcript levelsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAgricultural scienceStreptomyces venezuelae
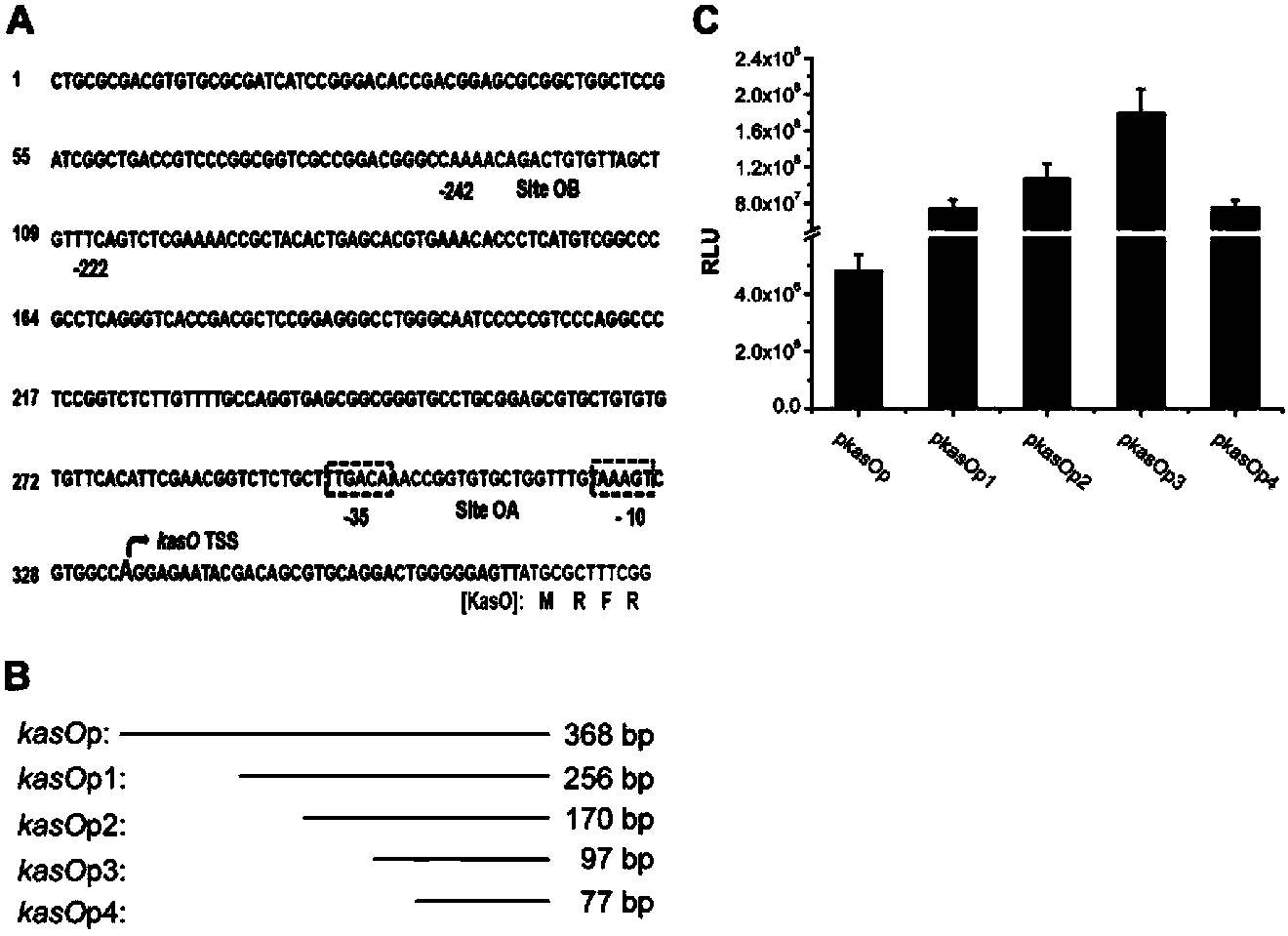
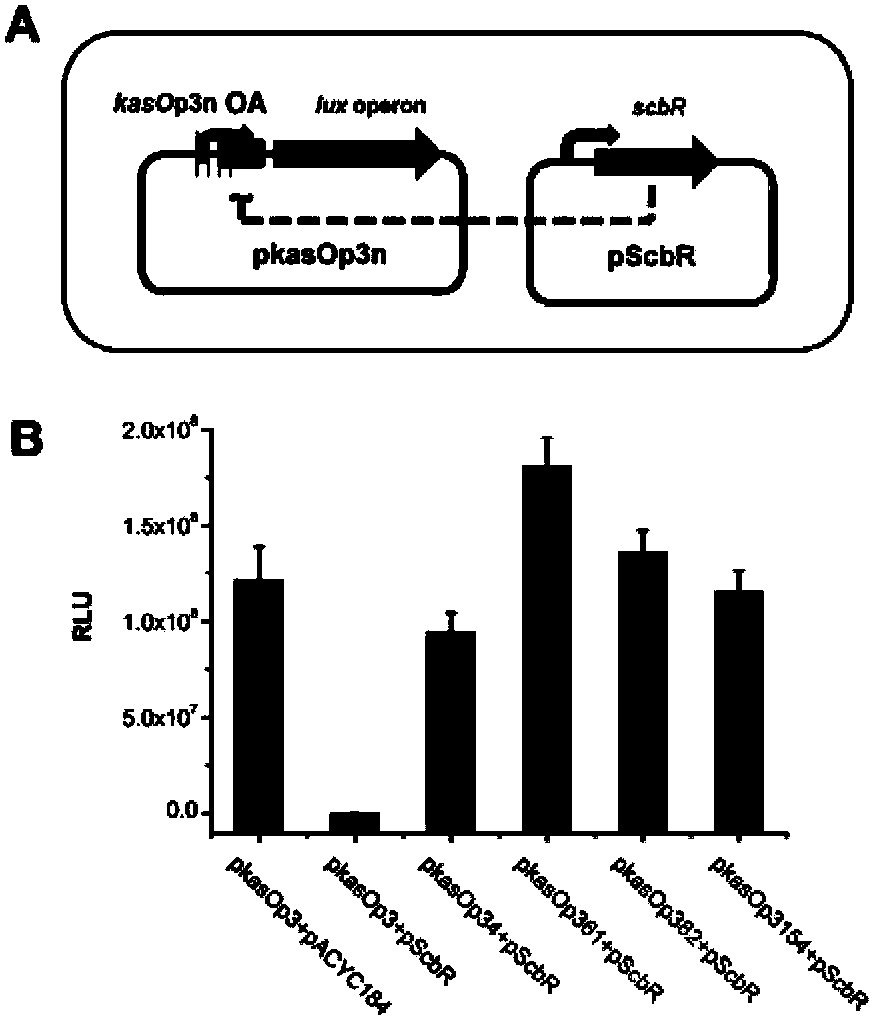
The invention discloses a streptomycete constitutive promoter and applications thereof, and provides an DNA fragment. The DNA fragment is any one selected from the following DNA molecules in 1)-3): 1) an DNA molecule represented by the sequence 1 in a sequence table; 2) an DNA molecule with promoter functions and hybrid with the DNA molecule shown in 1) under strict conditions; 3) an DNA molecule with more than 90% of homology with the DNA molecule shown in 1) and with promoter functions. The experiments shows that a strong constitutive promoter kasO*p is screened out, and the promoter and the erythromycin promoter ermE*p are compared in representation of transcriptional level and expression level in streptomyces coelicolor, streptomyces avermitilis and streptomyces venezuelae, and the results show that the modified promoter kasO*p is better than the the erythromycin promoter ermE*p.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and application thereof
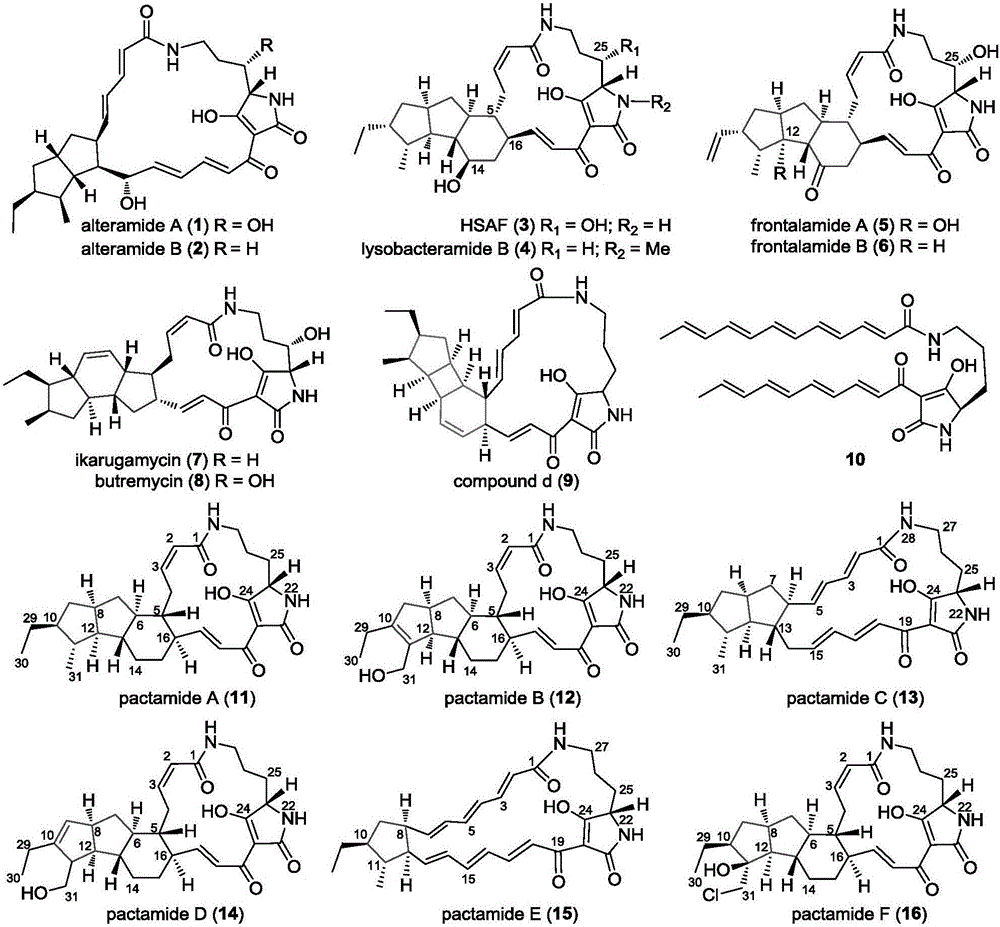
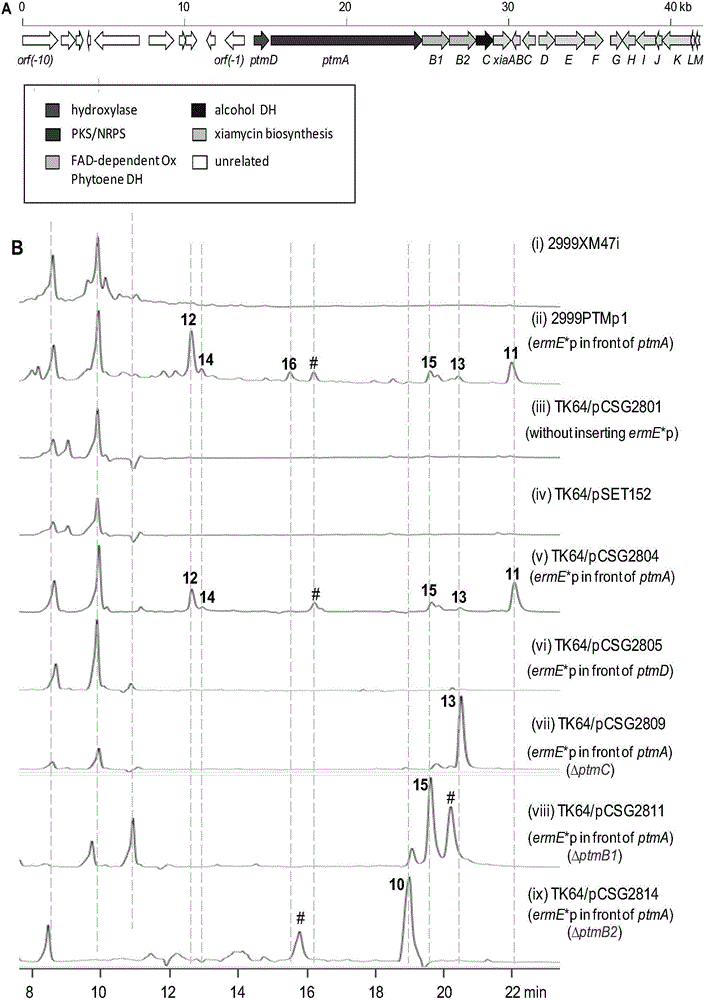
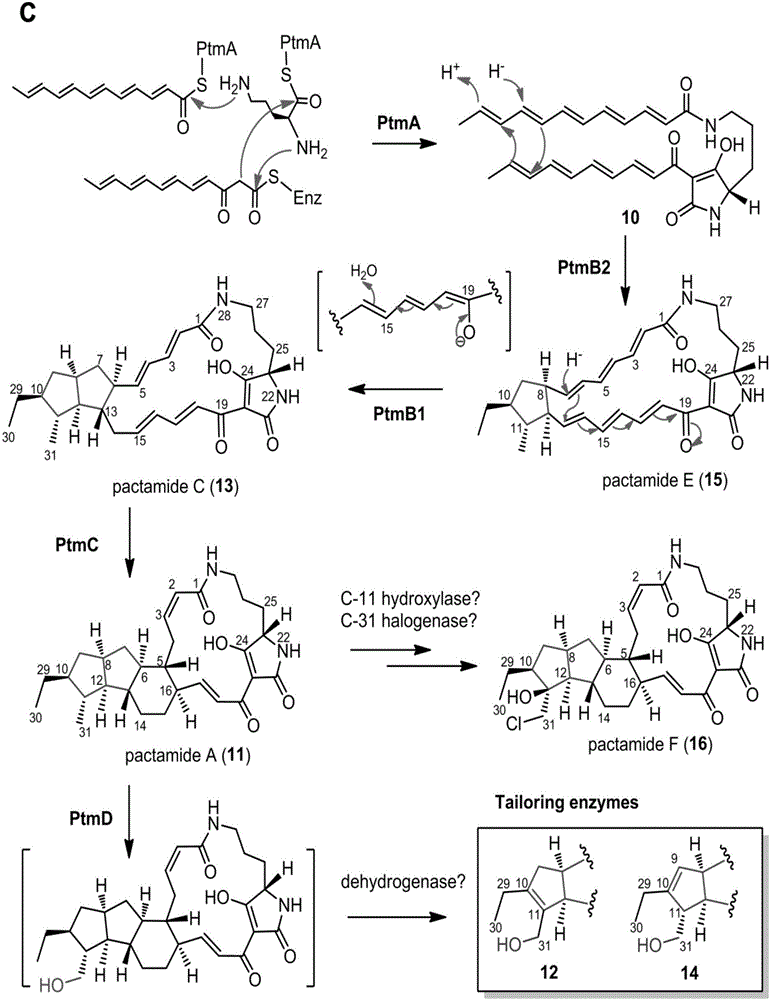
ActiveCN106434702ABiosynthetic gene cluster activationHas antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCyclasePolyketide
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and an application thereof. The biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide comes from (Streptomyces pactum)SCSIO 02999, and the cluster comprises five genes including heterozygous polyketone / nonribosomal peptide synthetases genes ptmA, FAD dependent redox enzyme genes ptmB1, phytoene dehydrogenase genes ptmB2, cyclase genes ptmC and hydroxylase genes ptmD. According to the biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and the application thereof, information in genes and proteins related to biosynthesis of the paquete amide provides theoretical foundations and materials for conducting genetic modification on the biosynthesis of multi-ring tetramate macrocylic lactam family. By conducting genetic modifications on the biological synthetic genes, 6 new structures antineoplastic paquete amide compounds pactamide A-F are obtained, and thus effective compound entities are provided for research and development of antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Streptomyces minitype transposable mutation system as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102154268AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic engineeringStreptomyces thermodiastaticus
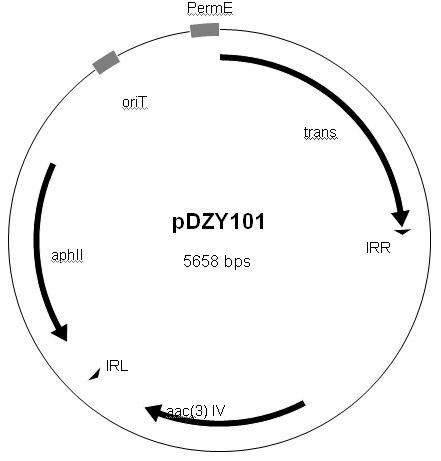
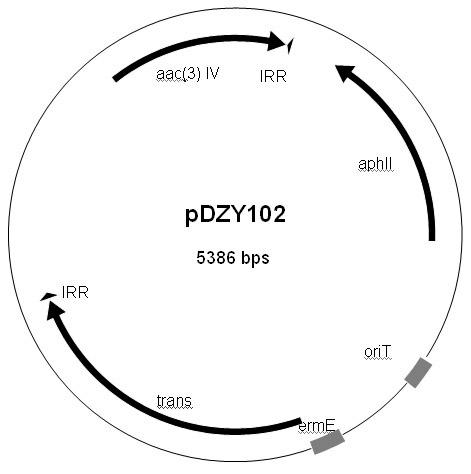
The invention belongs to the fields of biotechnology and genetic engineering, in particular relates to a high-efficiency streptomyces minitype transposable mutation system as well as a construction method and application thereof. Based on a transposable element sourcing from Norcardia aseteroids YP21, the invention constructs the characteristics of action sites of IS204 transposase in streptomyces coelicolor, and the transposable system is proved to have good genetic stability and good transposable randomness. Transposable mutation is carried out on S. coelicolor M145 by utilizing pDZY101 and derivatives thereof to obtain a great quantity of phenotype mutant strains, in addition, similar characteristics are also found in streptomyces lividans and other streptomyces members, and the characteristics endow the transposable system with good application prospect in aspect of researching type streptomyces functional genes.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
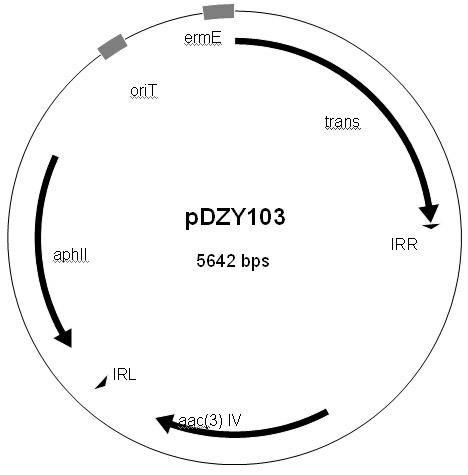
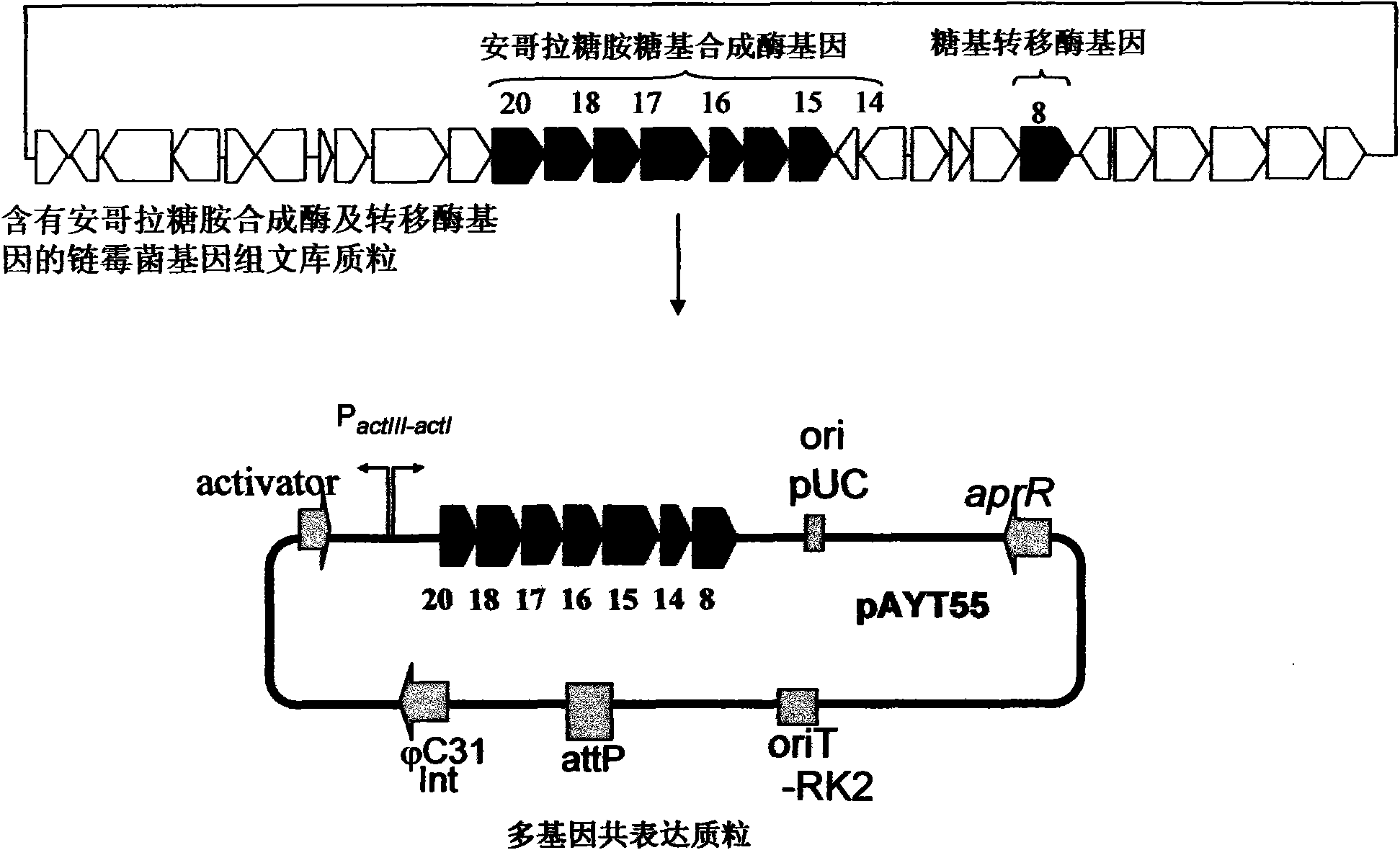
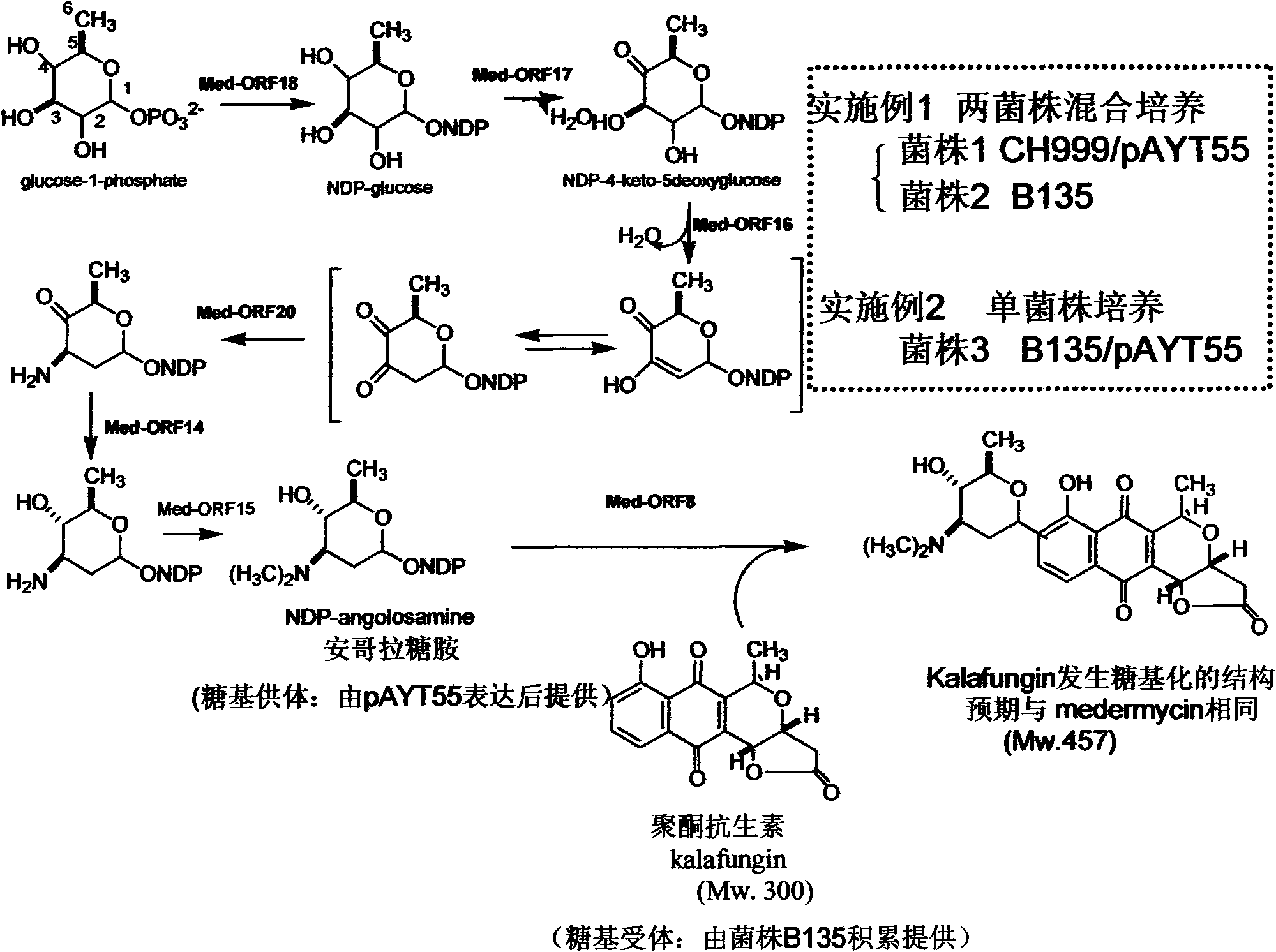
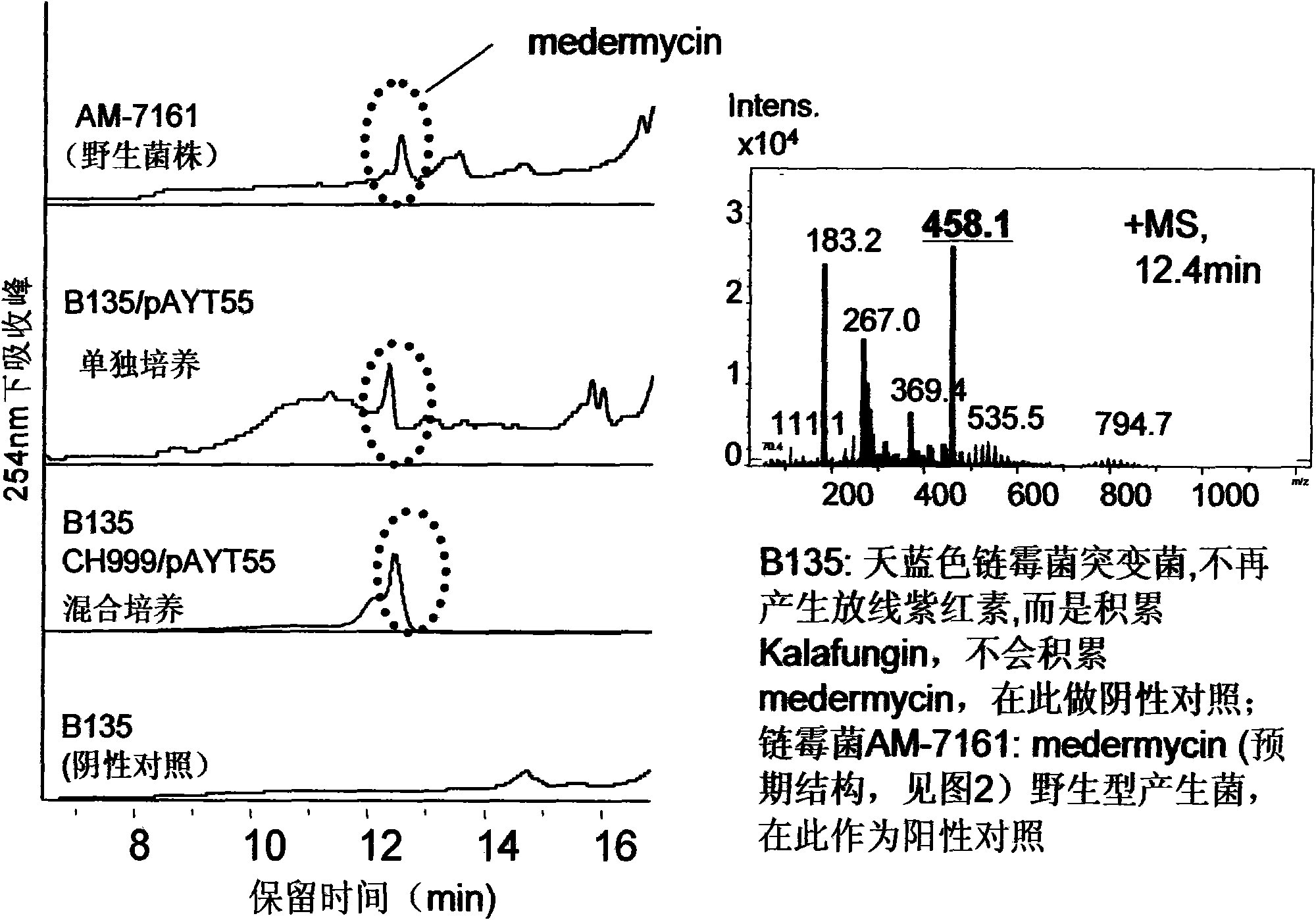
Construction and application of multiple gene coexpression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase
InactiveCN101613711ASimplify the screening processGuaranteed normal expressionMicroorganism based processesFermentationPolyketideGene coexpression
The invention provides construction and application of a multiple gene co-expression system containing angolosamine glycosylsynthetase and glycosyltransferase. The invention is characterized by taking a streptomyces genome bank plasmid as a template; amplifying six angolosamine synthetase genes and a glycosyltransferase gene through PCR and connecting the genes in sequence and placing the genes in the lower reaches of a streptomyces promoter PactIII-actI to form a transcription unit; transferring the transcription unit to a streptomyces plasmid carrier pSET152, thus constructing a streptomyces expression plasmid pAYT55 co-expressed by multiple genes; leading the pAYT55 into a host cell streptomyces coelicolor CH999, mixedly culturing obtained engineering bacteria and streptomyces B135 of accumulated polyketide kalafungin, thus realizing bioconversion of kalafungin into a novel antibiotic with angolosamine; or directly leading pAYT55 into the streptomyces B135 and carrying out single culture to realize glycosylation of kalafungin. Therefore, by adopting the system, rare angolosamine can be synthesized in the cell and angolosamine modification can be carried out on polyketide by adopting the low substrate recognition specificity of antibiotic glycosyltransferases.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Streptomyces coelicolor and application thereof
ActiveCN101792722AImprove fermentation effectIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPentostatinMicrobiology
The invention discloses a streptomyces coelicolor and an application thereof. The bacterial strain thereof is collected by China Center for Type Culture Collection with the collection number of CCTCC No. M 208263 and the collection date is 26th December, 2008. The invention also discloses a method for preparing pentostatin by fermenting the bacterial strain. The fermentation process provided by the invention is tested by a 10 ton fermentation tank, has stable production capacity, high fermentation unit and fewer fermentation by-products, thus lowering the difficulty for follow-up extraction and being suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:HANGZHOU HUADONG MEDICINE GRP PHARMA RES INST
Genetic engineering bacterium capable of promoting biological synthesis of medermycin and application thereof
InactiveCN102660488AEfficient expressionEfficient importBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRibosome Recycling FactorPolyketide
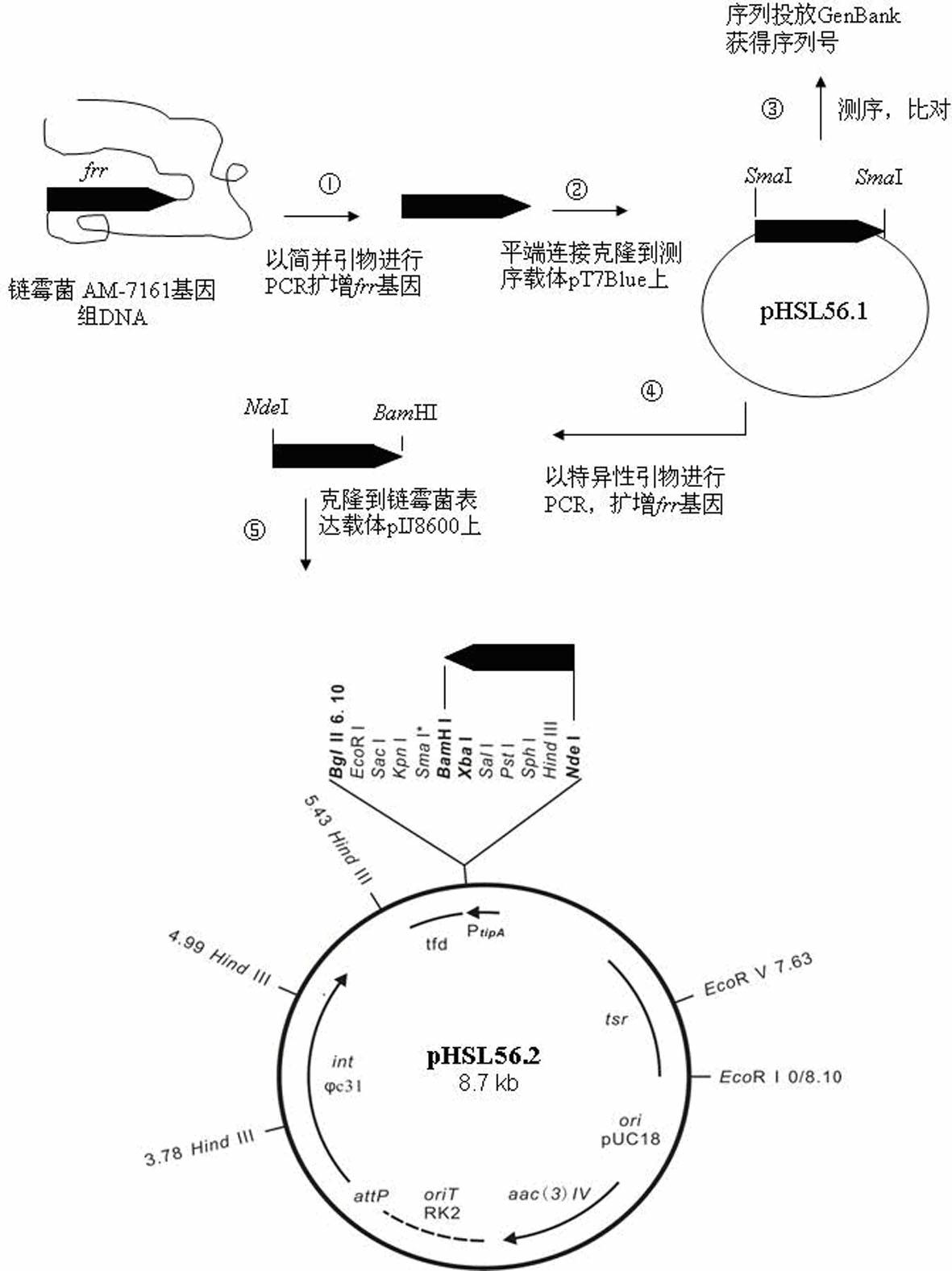
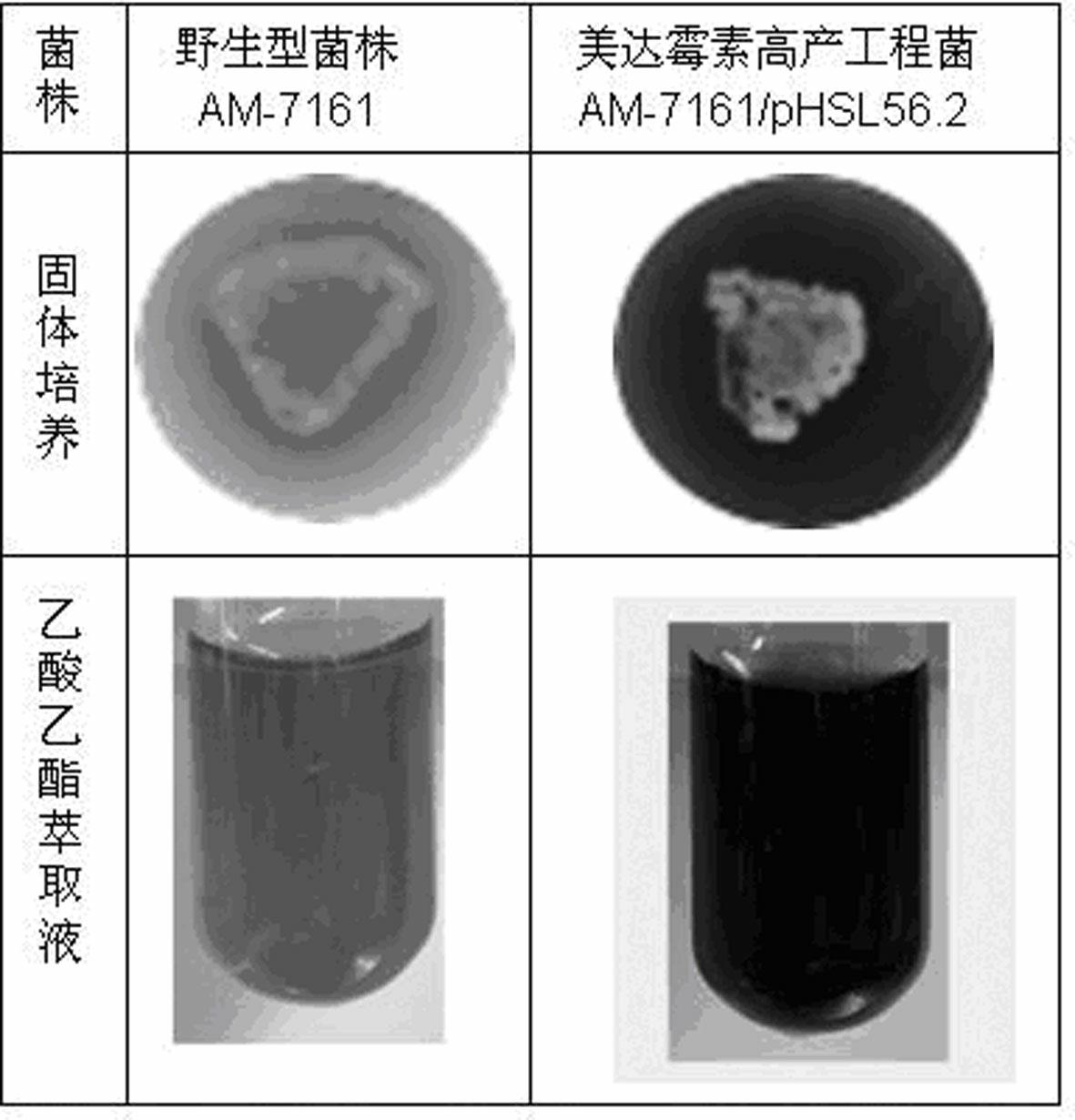
The invention provides a genetic engineering bacterium capable of promoting the synthesis of antibiotic medermycin and a method for producing the medermycin by using the same. The method comprises the steps that by taking deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a genome of Streptomyces nashvillensis AM-7161 as a formwork and utilizing degenerate primers to conduct polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, a new complete sequence of genes of ribosome recycling factors (RRFs) of the Streptomyces is obtained; the genes are downstream placed on an efficient promoter PtipA of the Streptomyces, so that a plasmid pHSL56.2 capable of efficently expressed in the Streptomyces is constructed; the pHSL56.2 is led into the host cell Streptomyces AM71-61, and then an engineering bacterium AM71-61 / pHSL56.2 (with a preservation number of CCTCCNo:M2012093) is obtained; and when the engineering bacterium AM71-61 / pHSL56.2 is used to conduct solid fermentation and liquid fermentation, the accumulation of the antibiotic medermycin can be effectively promoted. The efficient expression plasmid pHSL56.2 of the genetic engineering bacterium can also be directly led into a Streptomyces strain cell for producing other antibiotics of a benzoisochromanequinones family or other aromatic polyketide antibiotics, so as to obtain corresponding antibiotic high-yield engineering bacteria. By utilizing the method, the antibiotic high-yield bacteria can be genetically bred, so that the synthetic capability of the antibiotics is enhanced.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
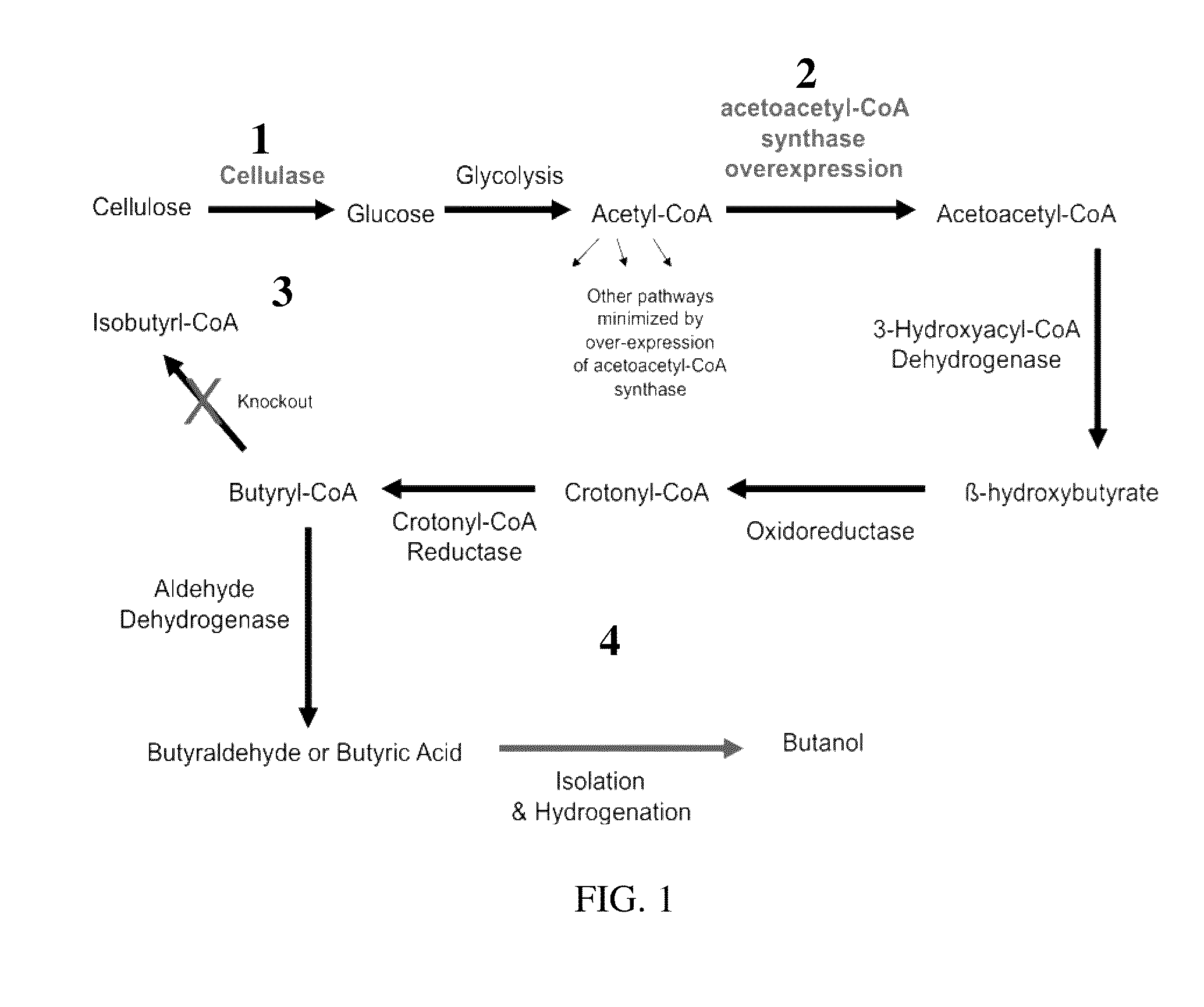
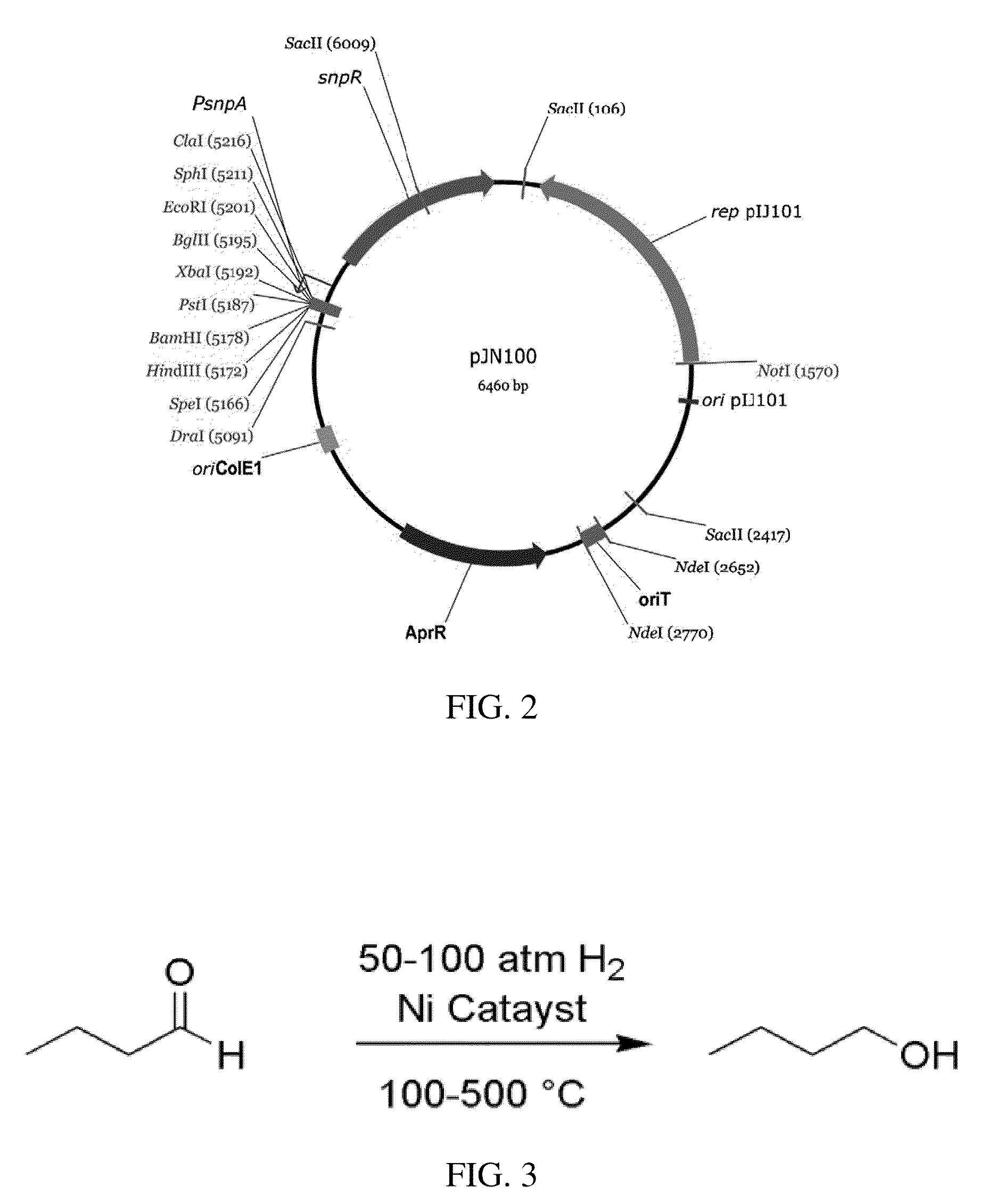
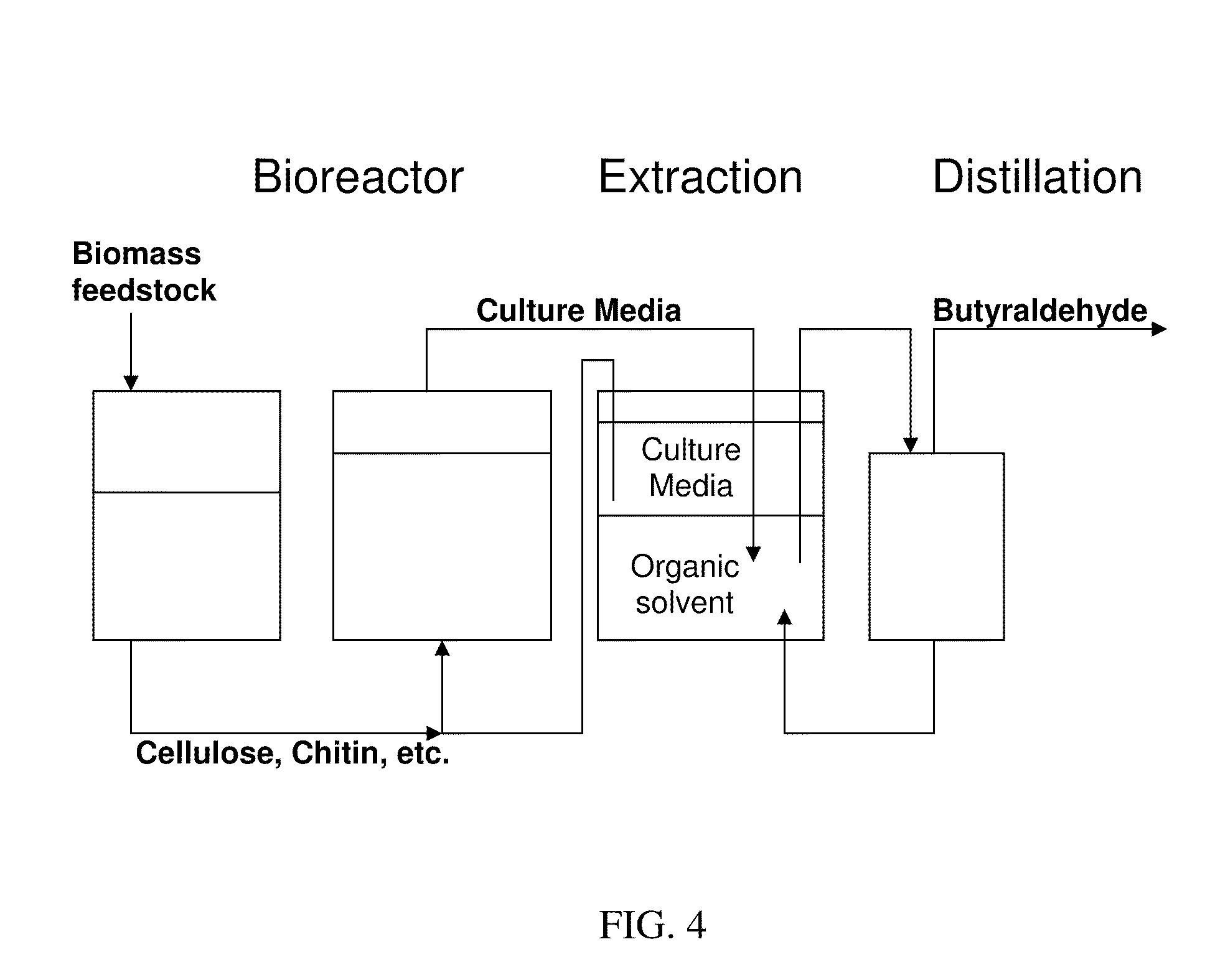
Butanal Production Using Engineered Streptomyces Coelicolor
A method of producing butanal by optimizing the growth of Streptomyces using cellulose as food source, overexpressing a key ‘gate’ enzyme in butyric acid / butyraldehyde production, and knocking out the isobutyryl-CoA synthase gene to shunt the pathway. Optionally, the produced butanal can be isolated and converted into butanol.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
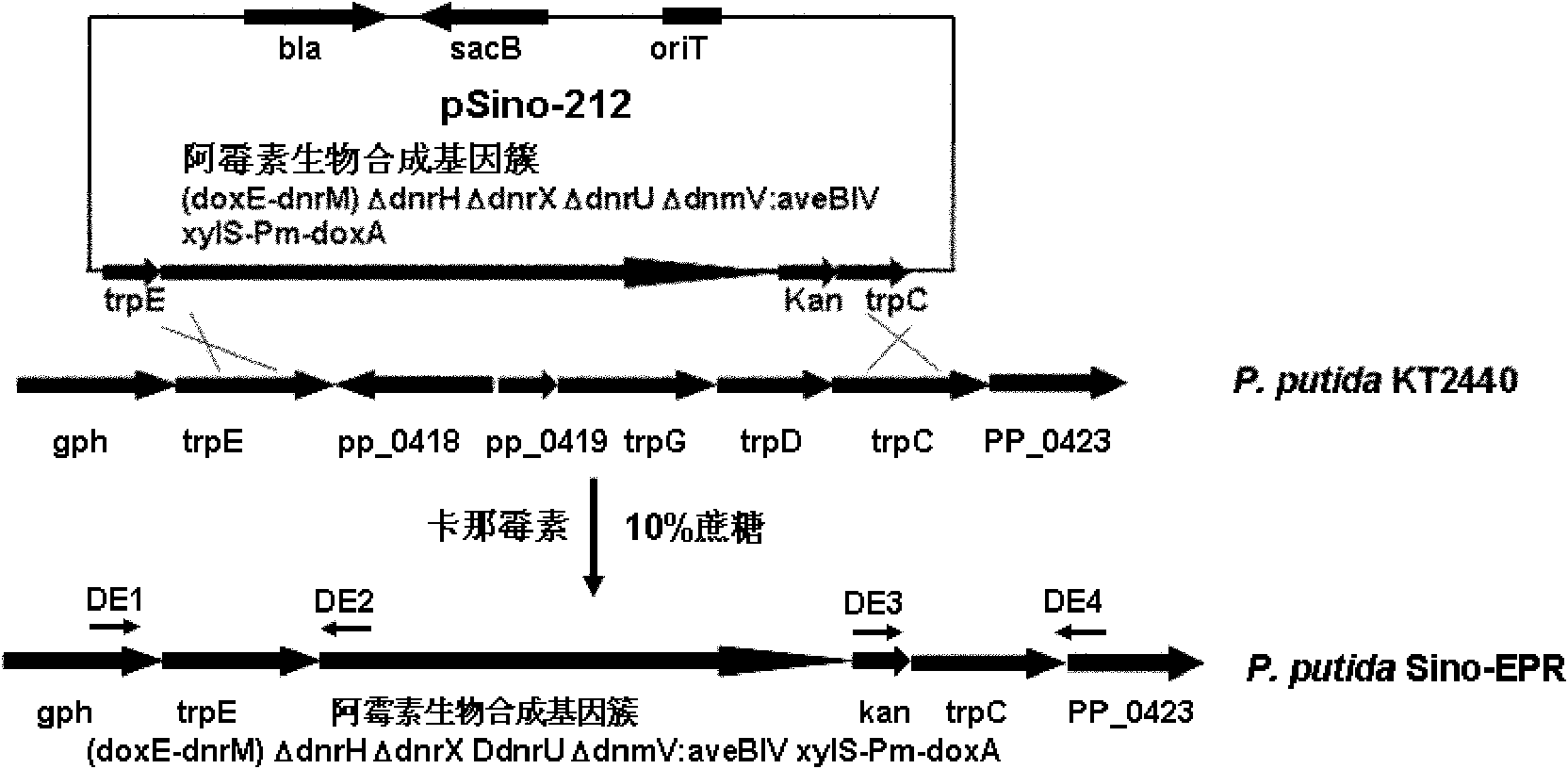
Pseudomonas engineering bacteria for producing epirubicin
InactiveCN102154192AIncrease productionTo achieve the purpose of large-scale industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousStreptomyces peucetius
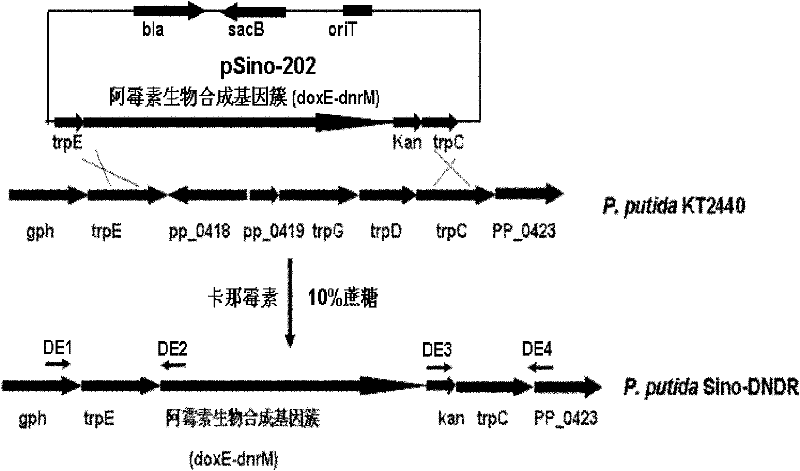
The invention provides a pseudomonas engineering bacteria for producing an epirubicin. The preparation method of the pseudomonas engineering bacteria comprises the following steps: eliminating dnrH gene, dnrX gene and dnrU gene in an adriamycin biosynthesis gene cluster from streptomyces peucetius ATCC 29050; permuting dnmV gene to be aveBIV gene from an abamectin biosynthesis gene cluster; inserting a Pm promoter from pseudomonas before coding doxA gene of oxidation-reduction enzyme; and integrating the modified gene cluster and the screening marker gene into the genome of the pseudomonas putida KT2440 to obtain the pseudomonas engineering bacteria. The pseudomonas engineering bacteria lays a foundation for the heterologous expression and the large-scale industrial production of the epirubicin, thereby being wide in application value.
Owner:北京赛诺百奥生物技术有限公司
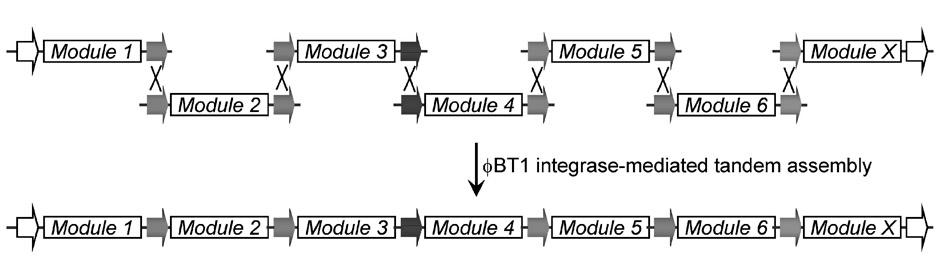
Multi-fragment deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) series connection recombination assembly method based on site-specific recombination
InactiveCN102286512AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationEscherichia coliSite-specific recombination
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering and synthetic biology, and particularly relates to a multi-fragment deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) series connection recombination assembly method based on BT1 integrase and mutation recognition sites thereof. In the method, sixteen pairs of mutational integrase recognition sequences are provided through mutation screening and verification, on the basis, a complete set of related carriers is constructed and comprises a framework carrier and seven TA cloning vectors, the framework carrier can realize escherichia coli-streptomyces coelicolor shuttle, the seven TA cloning vectors comprise mutation substrates and are used for DNA element construction and screening, and a concrete method for multi-fragment external series connection recombination reaction is provided. The method of the invention is simple, fast and efficient and can be used for the multi-fragment fast series connection recombination assembly, and the amplification of series connection products is realized through escherichia coli transformation. The method can be widely used for combination and assembly of standard modules and elements in the synthetic biology.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent and isothermal nucleic acid amplification method
ActiveCN105543402ASimplify the amplification reaction processLower requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LHelicase
The invention provides an isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent. The isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent is characterized by comprising components as follows: 100-800 mM of a Tris-HCl buffer solution, 10-150 mM of sodium chloride, 10-150 mM of potassium chloride, 10-50 mM of magnesium chloride, 5-15 mM of dithiothreitol, 5%-20% of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 10-20 mM of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), 1-5 mM of dNPTs, 10-50 mM of phosphoenolpyruvate, 500-1,500 ng / mu l of pyruvate kinase, 10-500 ng / mu l of BSA (bovine serum albumin), 25-200 pmol of each primer in a primer group, 50-200 ng / mu l of T4 bacteriophage DNA helicase gp41 protein, 100-500 ng / mu l of streptomyces coelicolor recA protein, 200-1,000 ng / mu l of single-strand binding protein and 50-200 ng / mu l of escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. The invention further provides an isothermal nucleic acid amplification method. According to the isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent and the isothermal nucleic acid amplification method, nucleic acid amplification under the isothermal condition at the lower temperature is realized, and a traditional nucleic acid amplification reaction process is greatly simplified.
Owner:刘国宪
Secondary approach transformation method based on instruction of FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model
InactiveCN103279689AIncrease production levelsImprove the experimental effectSpecial data processing applicationsMicroorganismGene cluster
The invention discloses a secondary approach transformation method based on an instruction of an FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model. The model is based on annotation genes and physiology and biochemistry information. By comparing and analyzing the model with a streptomyces coelicolor genome, metabolic genes are found being highly conservative. Metabolic flux analysis is performed on a genome scale metabolic network, and therefore the model predicts a mutation bacterium secondary approach gene cluster transformation strategy for improving a production level. According to the secondary approach transformation method based on the instruction of the FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model, the transformation method utilizes the genome scale metabolic network model to predict special structural genes in an FK506 bacterial strain secondary approach gene cluster, the production level of bacterial strains after transformation is improved by 20 percent to 90 percent, the special structural genes in the gene cluster are augmented to improve production capacity, and large application value is achieved in secondary approach rational transformation of microorganism immunosuppressor production bacterial strains. The high-efficiency and systematic method is provided for optimizing of the bacterial strains.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Negative regulator gene of streptomyces roseofulvus as well as preparation method and application thereof
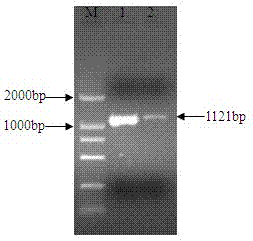
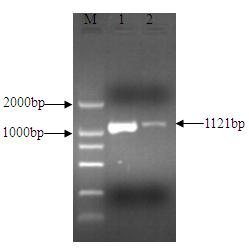
The invention relates to an nsdBmgh gene of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63 as well as a preparation method and application thereof. In the invention, primers Ns8F and Ns8R are designed by utilizing an important negative regulator gene nsdB sequence in a Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) antibiotic metabolic pathway, and genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63 is amplified to obtain a 1121bp segment; and two ends of a target sequence are extended by utilizing a primer anchoring polymerase chain reaction) (NPA-PCR ) method by a non-specific primer, thus obtaining the nsdBmgh gene of Streptomyces roseoflavus Men-myco-93-63. The preparation of the nsdBmgh gene provides an important basis for further researching and verifying the Streptomyces roseoflavus antibiotic metabolic pathway and regulatory mechanism, and establishes an important base for obtaining high-yield antibiotic gene engineering strains.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Engineering bacillus subtilis capable of expressing phospholipase D
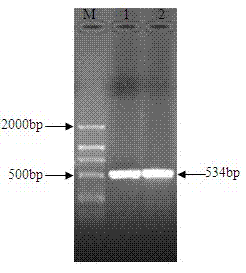
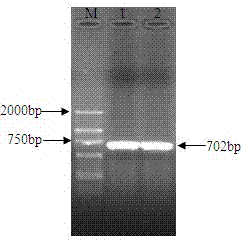
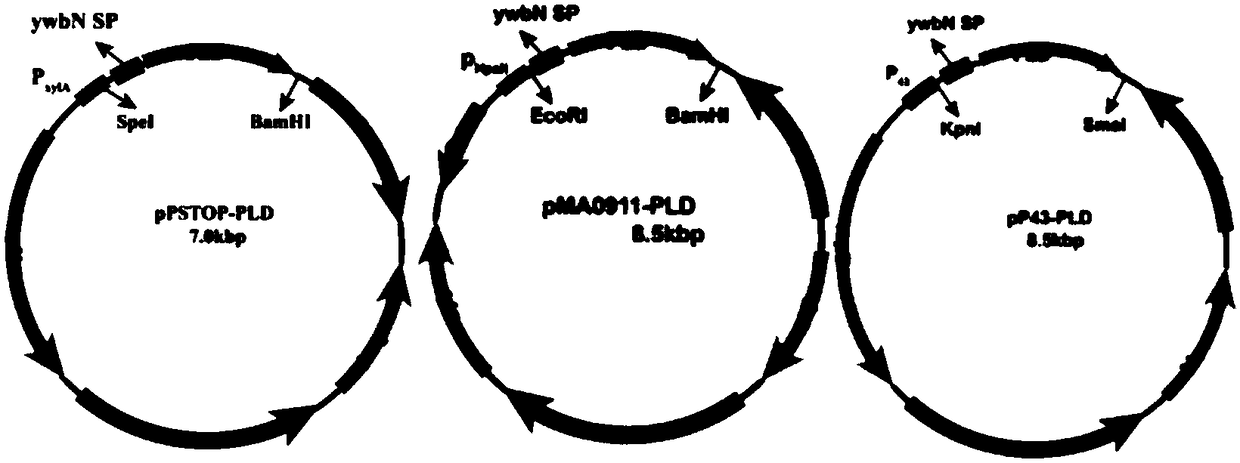
InactiveCN108841770AAchieve secretory expressionHigh selectivityBacteriaHydrolasesPhospholipidStreptomyces peucetius
The invention discloses engineering bacillus subtilis capable of expressing phospholipase D, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The engineering bacillus subtilis capable of expressing the phospholipase D is constructed by taking bacillus subtilis (WB600) as an expression host and taking a phospholipase D encoding gene (PLD) from streptomyces racemochromogenes as a target gene.The activity of the phospholipase D produced by the engineering bacteria can be up to 5.916 U / mL and has an extremely high application value in the field of medicines, food and health care products;meanwhile, the phospholipase D adopted by the engineering bacteria is actinomyces-derived endogenous phospholipase D, which has high reaction activity, high phosphatidyl substrate selectivity and highorganic matter stability; furthermore, a catalysis structure is the most compact; the phospholipase D is more suitable for efficient synthesis of phospholipid and a phospholipid derivative in the industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Constructs for expressing herbicide tolerance genes, related plants, and related trait combinations
InactiveCN102118966AClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellGene
Owner:DOW AGROSCIENCES LLC
ADP-ribosylating bacterial toxins
InactiveUS7928192B2Diminishing the ADP-ribosylating enzymatic activityAntibacterial agentsVirusesEscherichia coliStreptococcus pyogenes
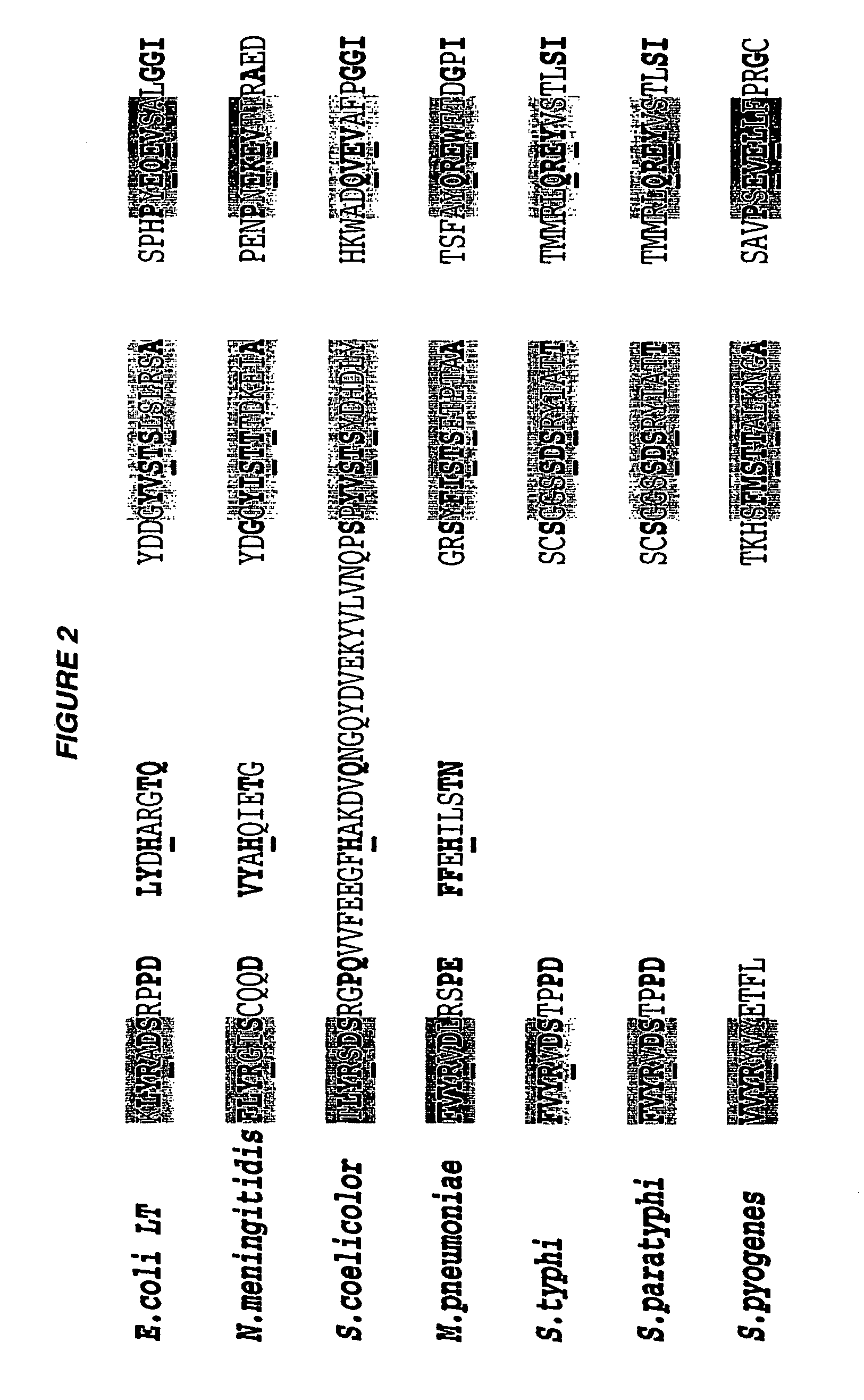
ADP-ribosylating toxins from Neisseria meningitidis, Streptomyces coelicolor, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Salmonella typhimurium, Salmonella paratyphi, and Streptococcus pyogenes are disclosed, together with mutant toxins and uses therefor. There is only a low level of sequence identity between these toxins and toxins such as cholera toxin and E. coli heat labile toxin.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method for improving fermentation level of salinomycin by increasing supply of precursors
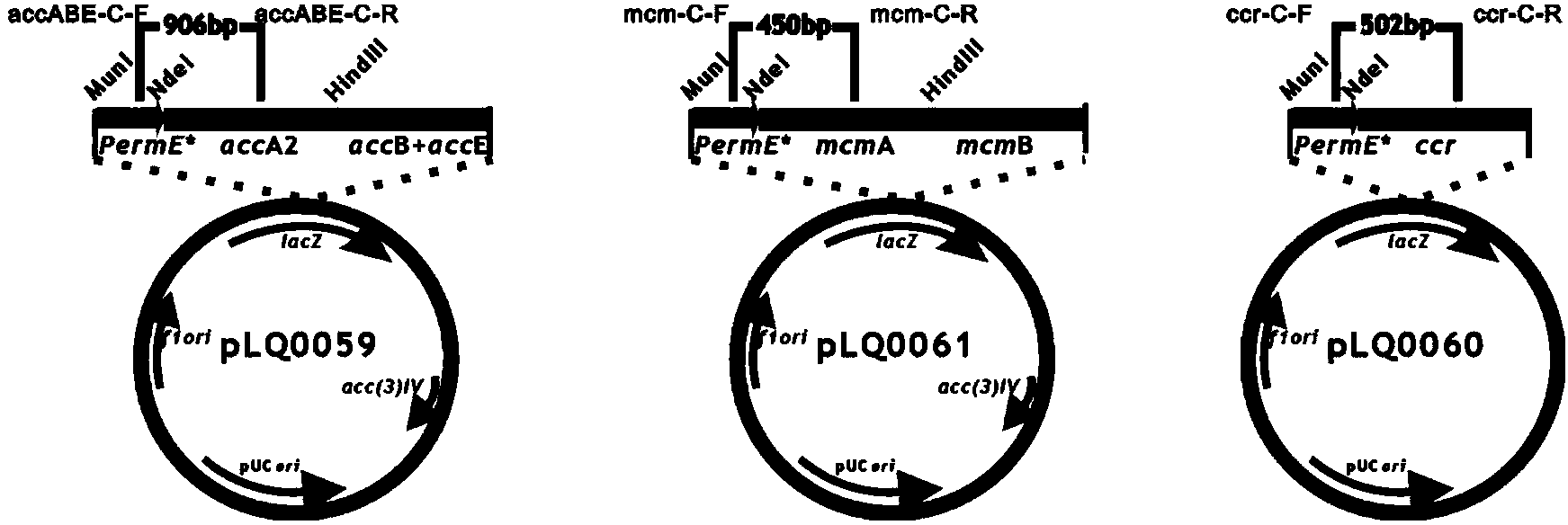
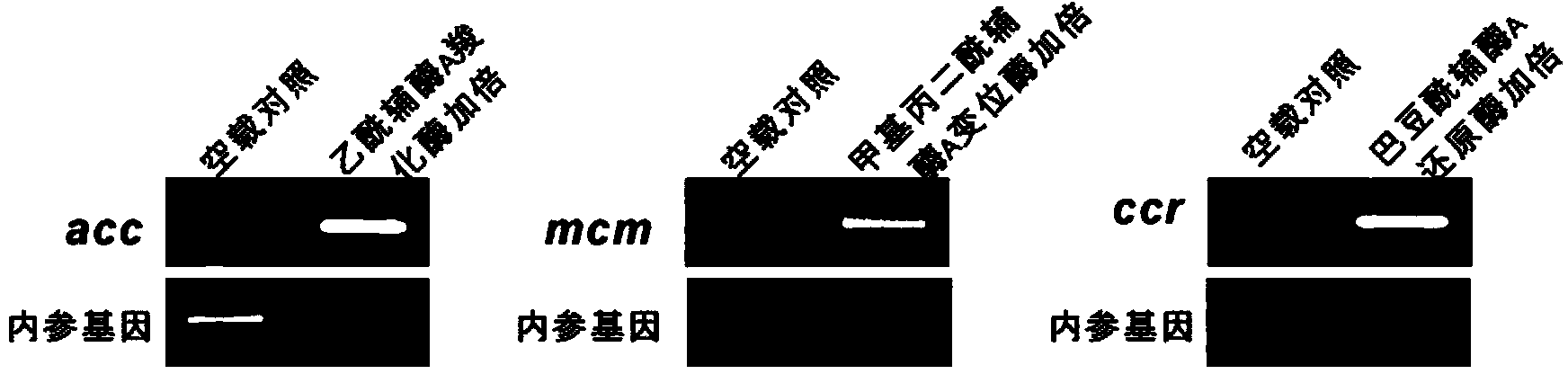
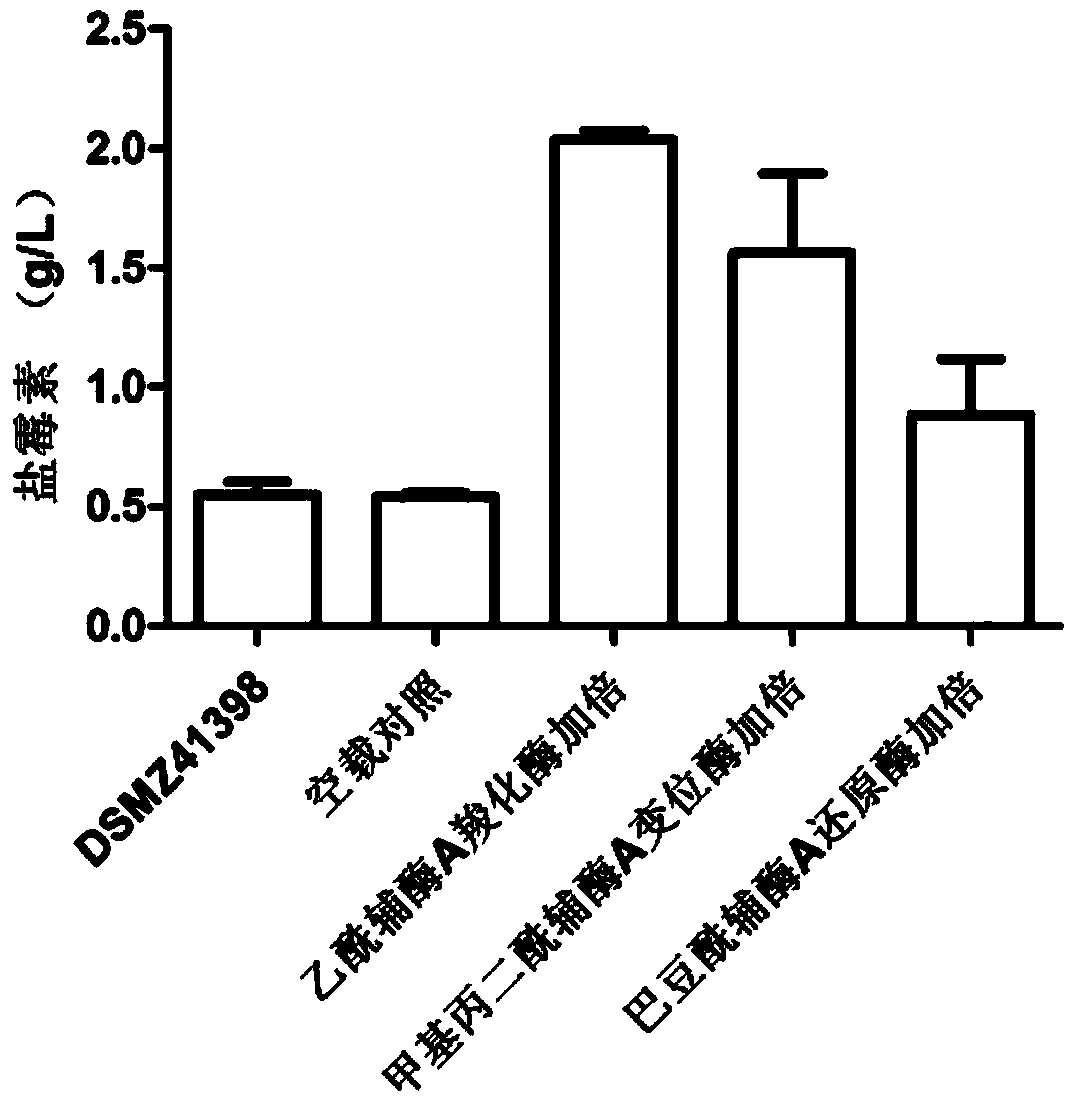
ActiveCN104357506AIncrease supplyImprove fermentation yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAcyl-CoA carboxylase
The invention discloses a method for improving the fermentation level of salinomycin by increasing supply of precursors. The method comprises the following steps: doubling acetyl coA carboxylase genes from streptomyces coelicolor, methyl malonyl coA mutase genes from streptomyces albus DSMZ41398 and crotonoyl coA reductase genes from the streptomyces albus DSMZ41398 on the chromosomes of the streptomyces albus DSMZ41398 through an integrating vector pSET152 respectively to increase supply of three precursors required for synthesizing salinomycin so as to increase the salinomycin yield. According to the method, the final fermentation yield of engineering strain salinomycin is increased by 260% and the shake flask level of a lab reaches 2 g / L.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
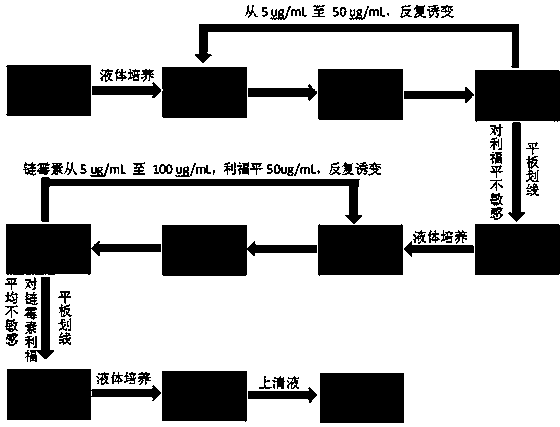
Mutation screening method and application of streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1
The invention discloses a mutation screening method of a streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1. The mutation screening method comprises the steps of inducing mutation of streptomyces coelicolor and streptomyces Lzsg6 through nitrosoguanidine to obtain a streptomyces mutant library, and screening the mutant library through rifampicin and streptomycin to obtain a strain with a transcription system and a translation system in mutation. The invention also discloses a streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1 and application thereof. The streptomyces strain SPC6-50-1 disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that the strain contains substances having bacteriostatic activities, and the method of nitrosoguanidine (NTG) inducing as well as rifampicin and streptomycin screening can activate silent genes of the streptomyces to obtain a new metabolite, thus obtaining a new antibiotic; meanwhile, the mutation screening method has the advantages of simple operation, short cycle and high efficiency, and is not only applicable to streptomyces but also suitable for such microorganisms as myxobacteria rich in secondary metabolites; the mutation screening method has good popularization and application values.
Owner:COLD & ARID REGIONS ENVIRONMENTAL & ENG RES INST CHINESE
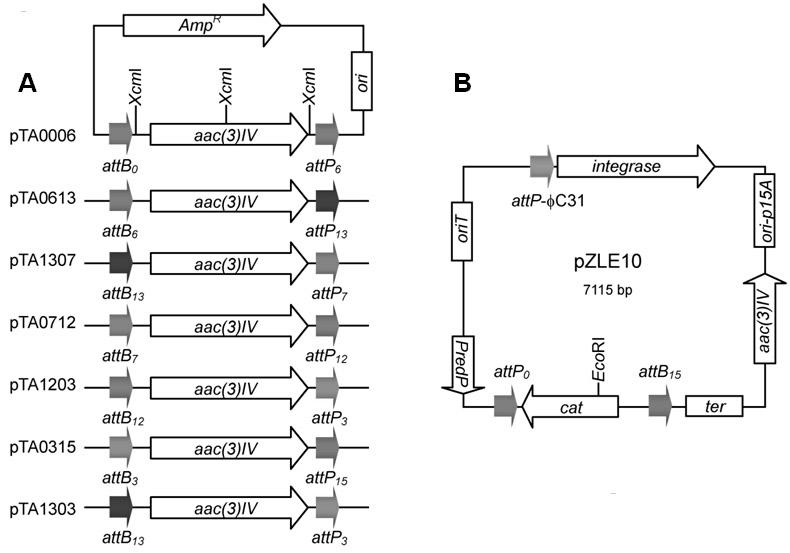
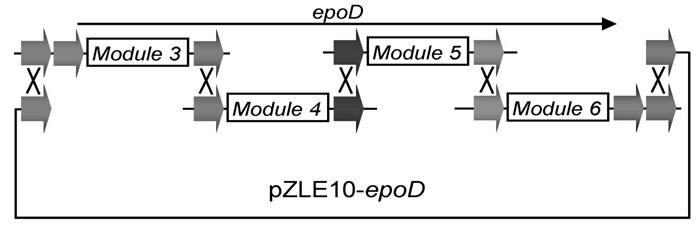
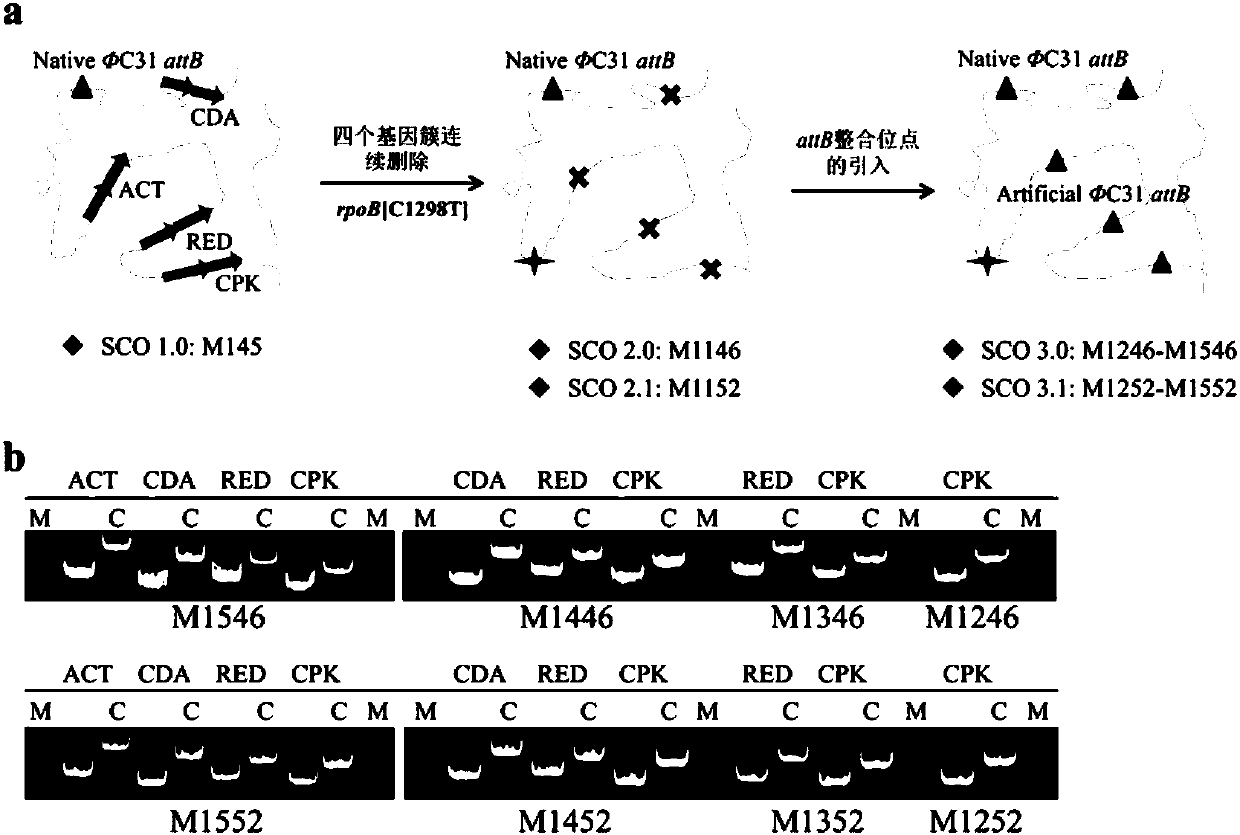
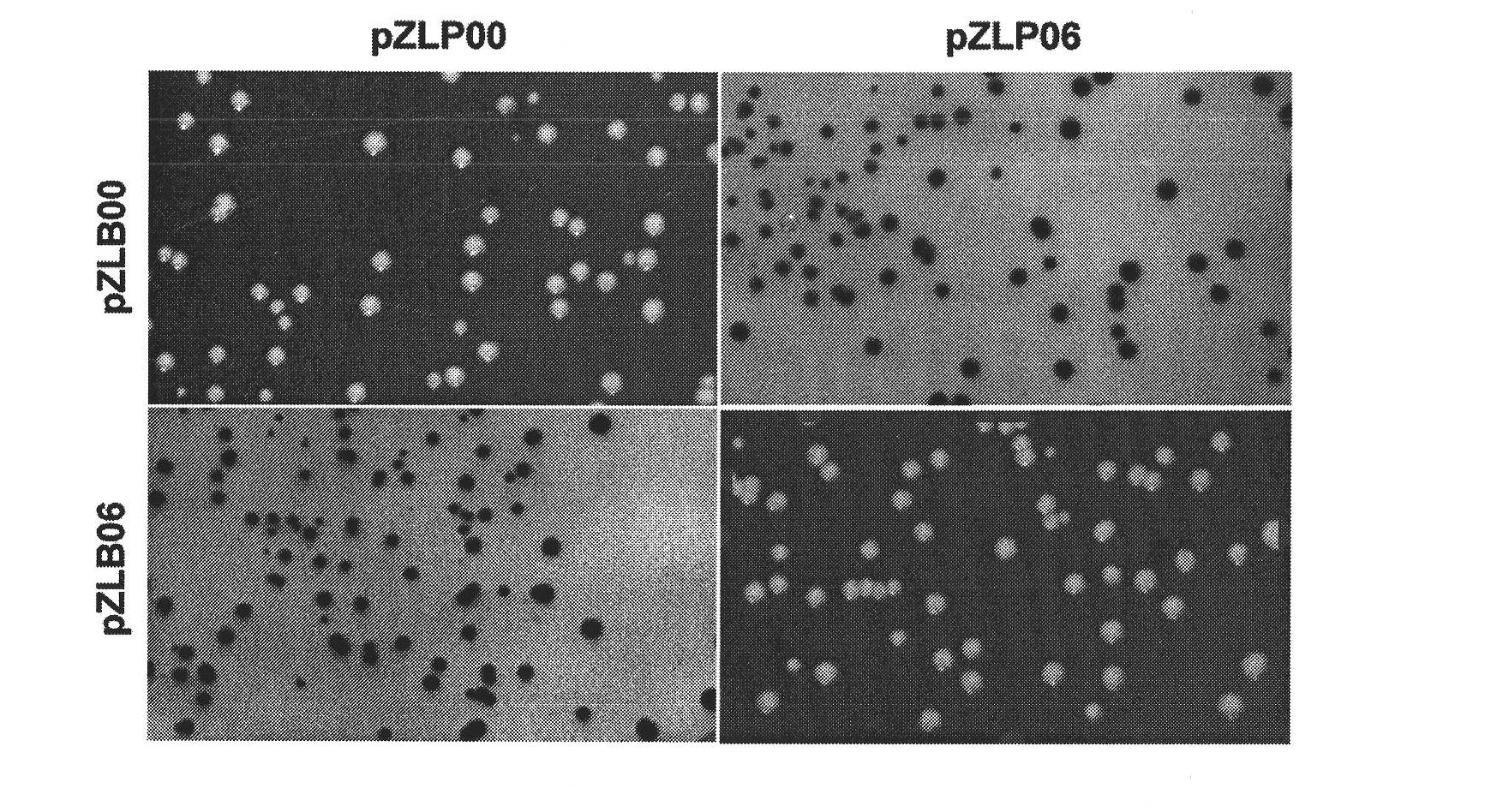
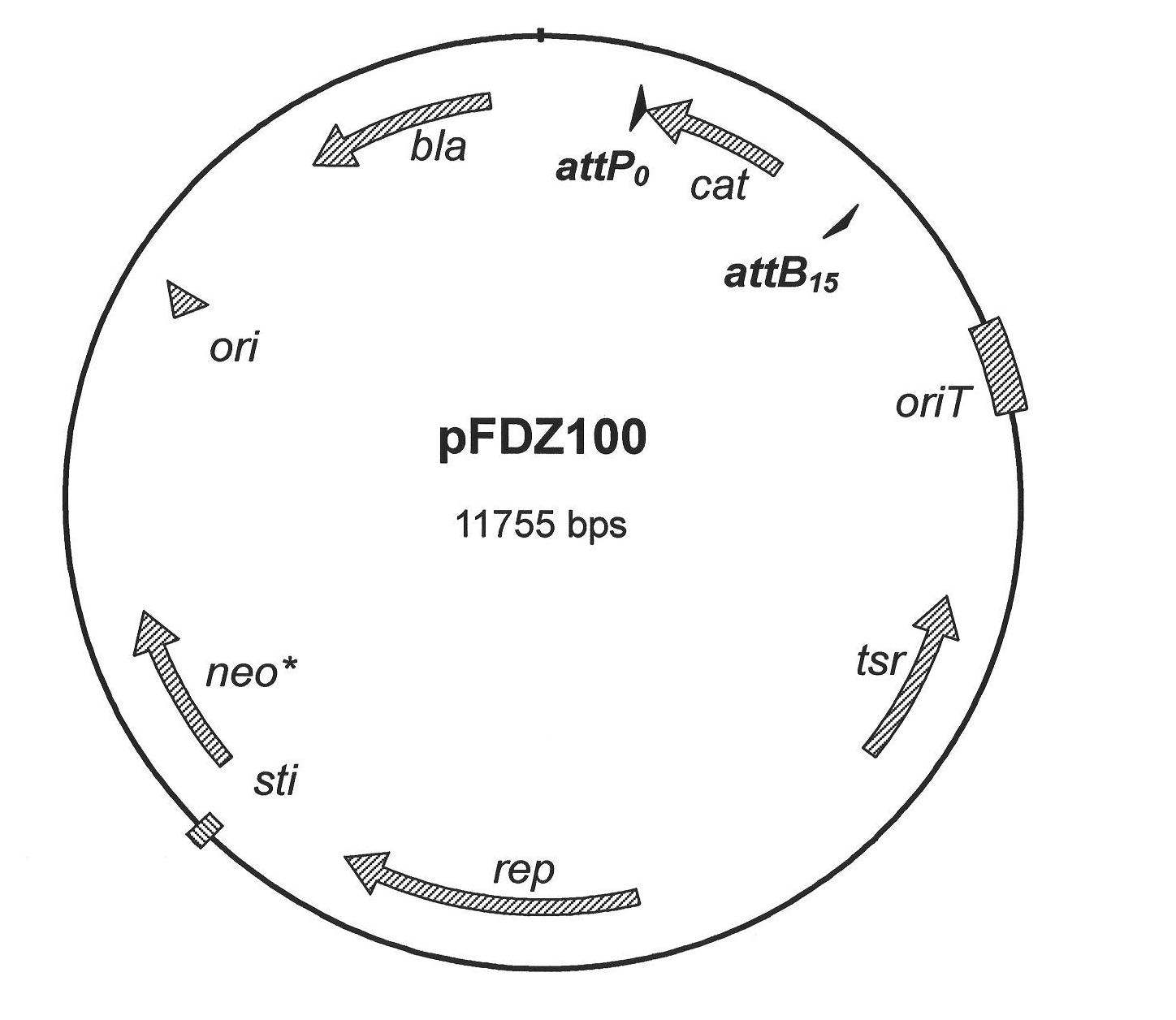
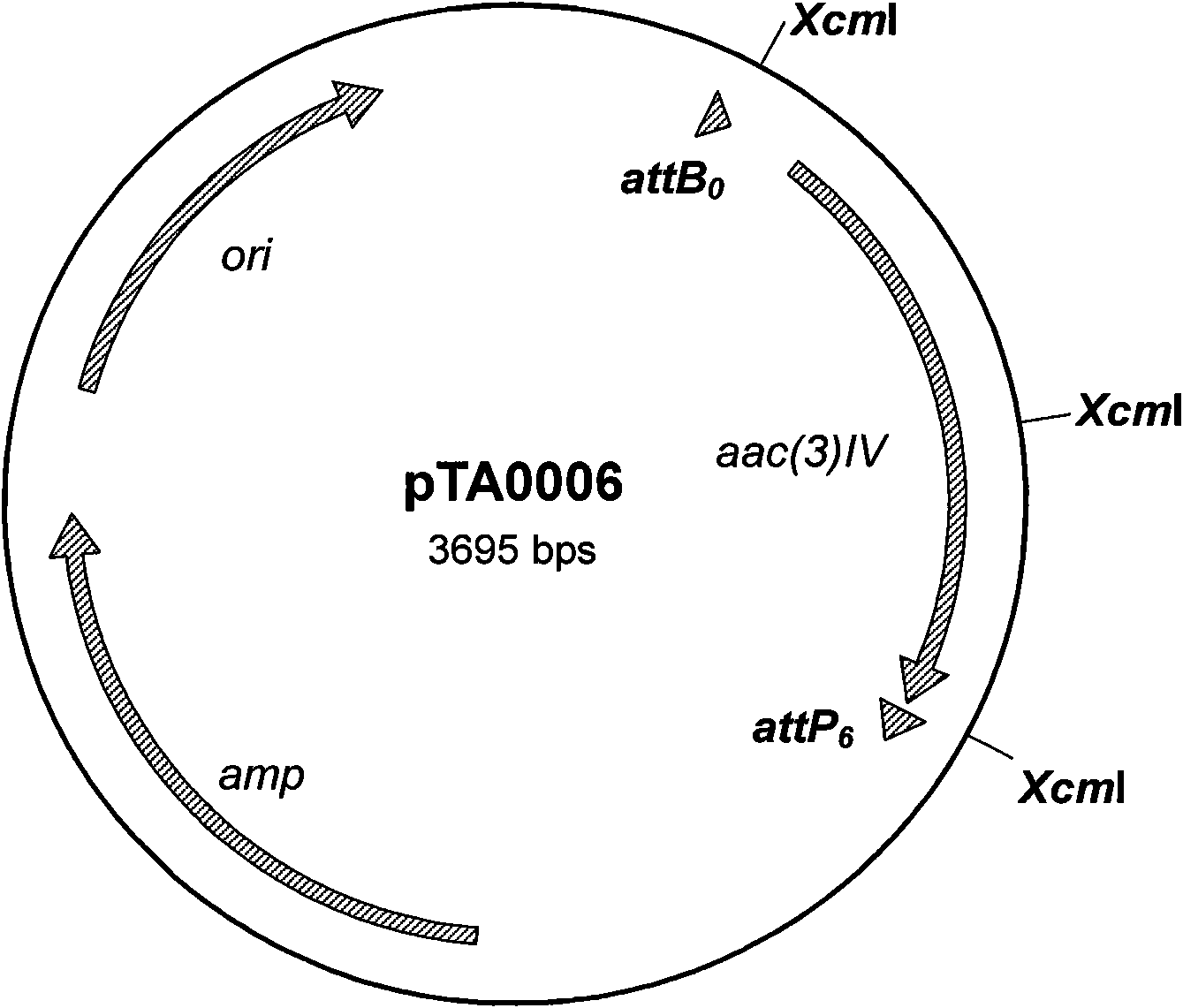
Construction and applications of a series of efficient heterologous expression hosts of Streptomyces coelicolor
The invention relates to construction and applications of a series of efficient heterologous expression hosts of Streptomyces coelicolor, and specifically provides genetically engineered Streptomycescoelicolor, wherein the genome of the genetically engineered Streptomyces coelicolor contains more than two attB sites. The invention further provides a method for improving the efficiency of the transformation of a multi-copy gene cluster into Streptomyces coelicolor, a method for preparing a natural product or improving the yield of a natural product, and corresponding uses thereof. According tothe present invention, a series of Streptomyces coelicolor capable of achieving the multi-copy amplification of the target gene cluster at one time are constructed by introducing a plurality of the attB sites in Streptomyces coelicolor, such that the yield of the target product is increased by increasing the number of the copies of the gene cluster.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Method for quickly constructing gene targeting vector based on site specificity recombination
InactiveCN101967475AEasy to buildBuild methods are fast and efficientMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliSite-specific recombination
The invention belongs to the technical fields of biotechnology and gene engineering, and in particular relates to a method for quickly constructing a gene targeting vector based on phi BT1 integrase and a mutation recognition site thereof. The invention provides three pairs of mutative intergrase recognition sequences by strict mutation screening and verification, and the mutative substrate pair has equal reaction efficiency to that of a wild type, and appears as incompatible in the same system. On the basis, the method constructs a set of related vectors comprising a backbone vector capable of realizing Escherichia coli-streptomyces coelicolor shuttle, and three TA clone vectors containing mutative substrate pairs for constructing and screening homology arms, and provides a concrete method of series recombination and reaction of four DNA fragments in vitro. The method of the invention is simple, quick and high-efficiency, can be used for constructing the gene targeting vector of streptomyces, and can be widely used for quickly constructing gene targeting vectors of different species by corresponding original substitution.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Negative control gene of streptomyces roseoflavus as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102634523AIncreased ability to produce antibioticsIncrease productionBiocideBacteriaGenomic DNAGenetic engineering
The invention relates to a nsdBmgh gene of streptomyces roseoflavus (Men-myco-93-63) as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the nsdBmgh gene of streptomyces roseoflavus comprises the following steps: automatically designing a primer Ns8F and Ns8R through the sequence of a negative control gene nsdB in the metabolic pathway of sky blue streptomycete A3(2) antibiotic, amplifying genomic DNA of the streptomyces roseoflavus (Men-myco-93-63) to obtain fragments of 1121bp, and then extending the two ends of a target sequence by utilizing a nonspecific primer anchoring PCR(NPA-PCR) method so as to obtain the nsdBmgh gene of the streptomyces roseoflavus (Men-myco-93-63). The functions of the nsdBmgh gene are verified through the gene disruption, and the bacteriostatic activity of the gene disruption mutant strain is obviously enhanced as compared with that of metabolin of original strains. The preparation and the application of the nsdBmgh gene provide an important basis for further researching and verifying the synthetic and metabolic pathway and the adjusting and controlling mechanism of the streptomyces roseoflavus, and lay the foundation for the application of high-yield genetic engineering strains of antibiotics for preventing plant diseases.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
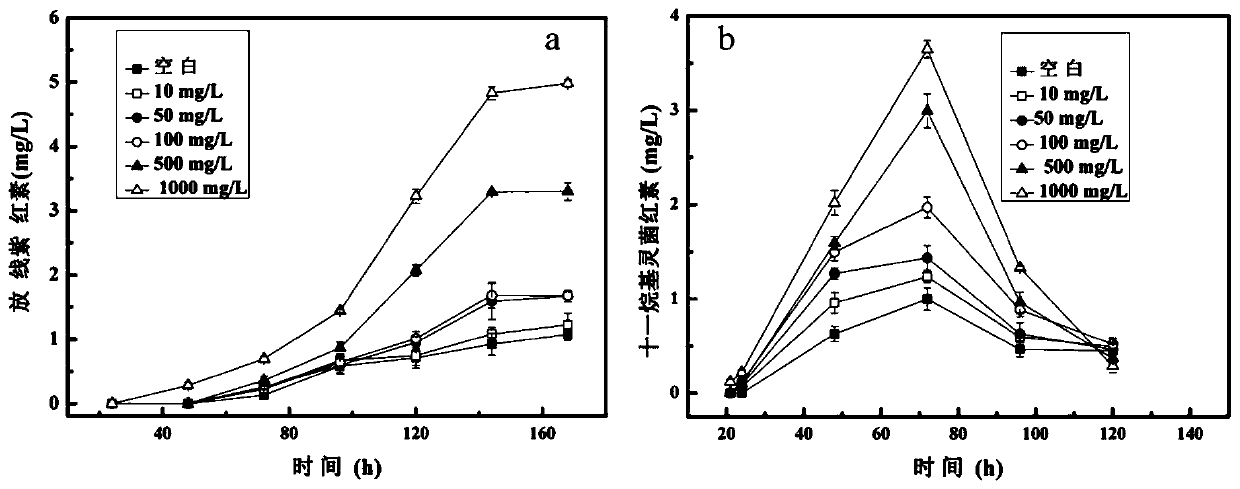
Method for improving production of Streptomyces antibiotics by using nanomaterial as additive
ActiveCN109880863AIncrease productionThe method is simpleMicroorganism based processesFermentationSporeLiquid medium
The invention relates to a method for firstly using a nanomaterial as an additive to increase the production of Streptomyces antibiotics. Compared with a traditional method of increasing the production of antibiotics, the method is simple and easy to operate, and has high operability. The method adds Streptomyces spores to a well-prepared YBP liquid medium containing different concentrations of nanoparticles, and ferments the materials for about one week, and during the period, the condition of the strain is regularly determined to produce two colored pigments, actinorhodin and undecylamine. For the first time, the method is applied to the antibiotic fermentation of Streptomyces as the additive, and the method is used to culture Streptomyces coelicolor, and the method found that the addition of 1000 mg / L of nano-alumina increases the yield of actinorhodin by 4.6 times and the yield of undecylprodigiosin by 3.7 times. The method found that the addition of 10 mg / L of nano copper increases the yield of actinorhodin by 2.1 times and the yield of undecylprodigiosin by 1.8 times.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
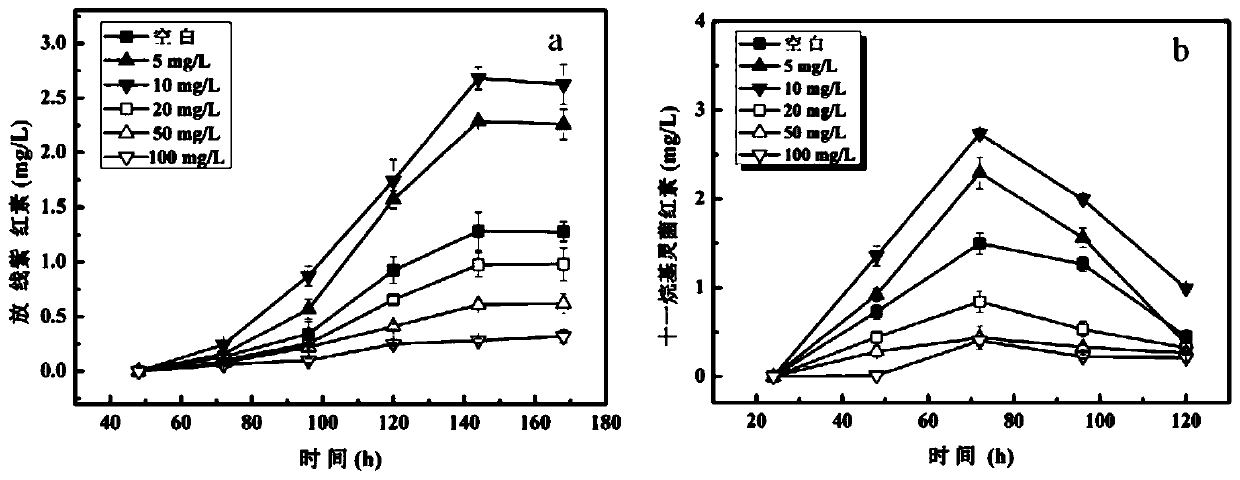
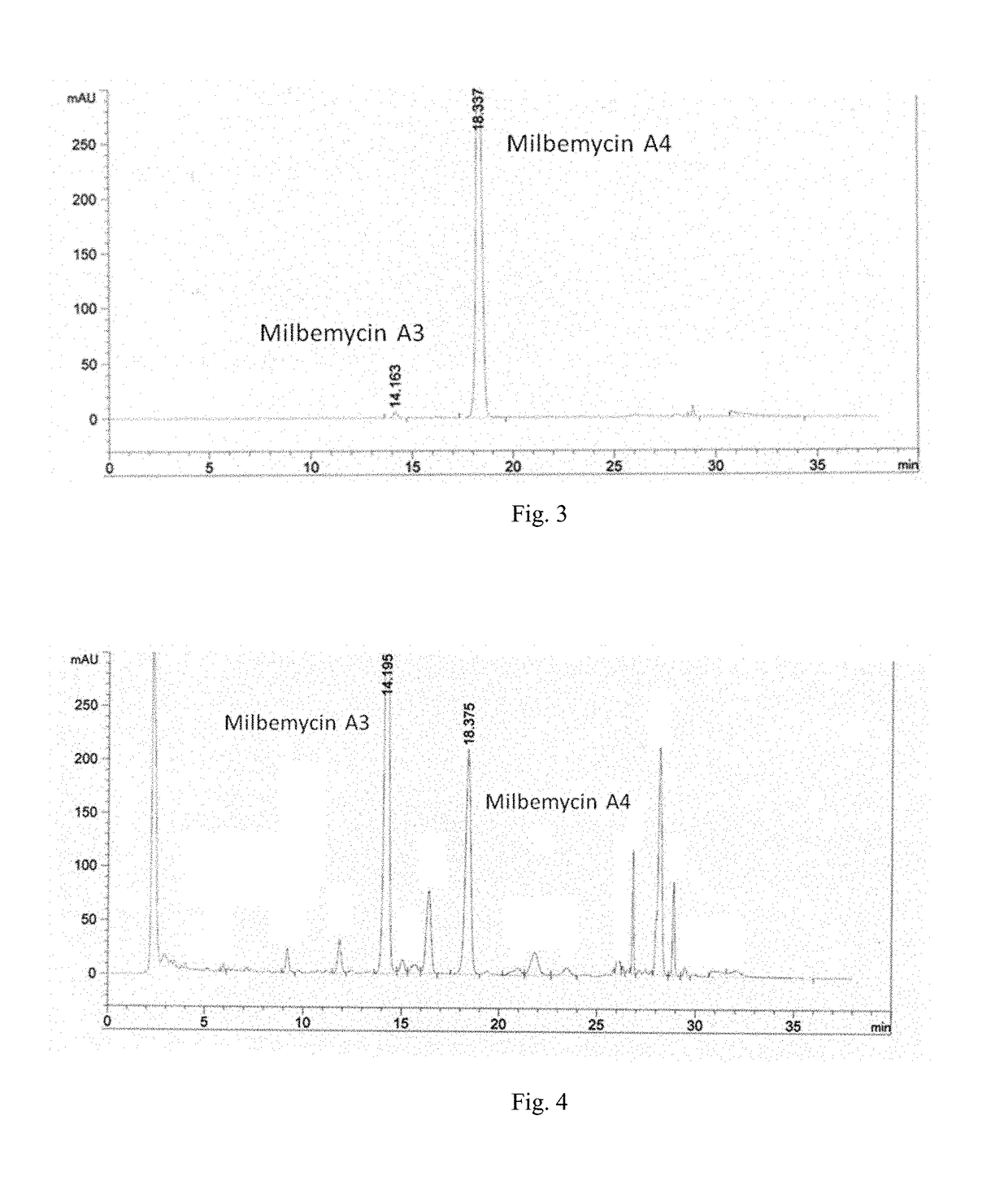
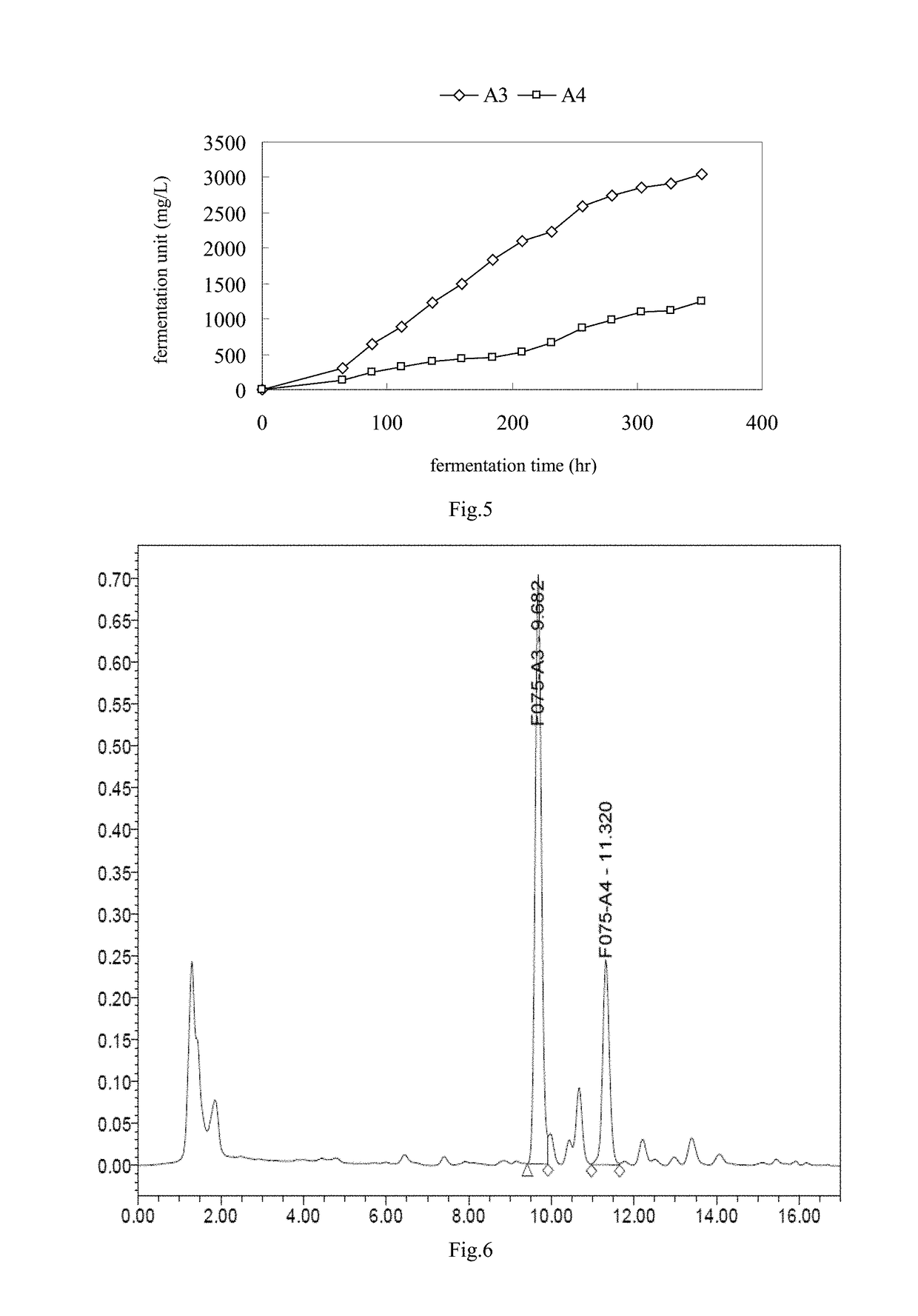
Streptomyces and method for producing milbemycin a3 using same
ActiveUS20180171283A1Increase unit outputLow impurity contentBacteriaFermentationStreptomyces hygroscopicusStreptomyces ambofaciens
Provided are a Streptomyces (Streptomyces hygroscopicus) HS7523 and a method for preparing milbemycin A3 by culturing the Streptomyces. The Streptomyces (Streptomyces hygroscopicus) HS7523 is deposited in “China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center” with an accession number of CGMCC No. 9672 on Sep. 16, 2014.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Daunorubicin and adriamycin producing engineered pseudomonas
InactiveCN102229906AIncrease productionTo achieve the purpose of large-scale industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHeterologousPseudomonas
The invention provides daunorubicin and adriamycin producing engineered pseudomonas, which is constructed by substituting doxE for dnrM in a TDP-D-glucose 4,6-dehydratase gene lacking frame shift from adriamycin biological synthesis gene cluster of Streptomyces peucetius ATCC 29050, and integrating the TDP-D-glucose 4,6-dehydratase gene and a screened marker gene into genome of Pseudomonasputida KT2440. The daunorubicin and adriamycin producing engineered pseudomonas provides a basis for the heterologous expression and large-scale industrial production of daunorubicin and adriamycin and has high wide application value.
Owner:北京赛诺百奥生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com