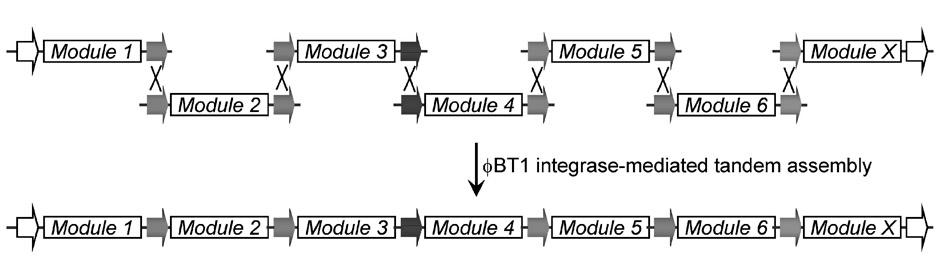
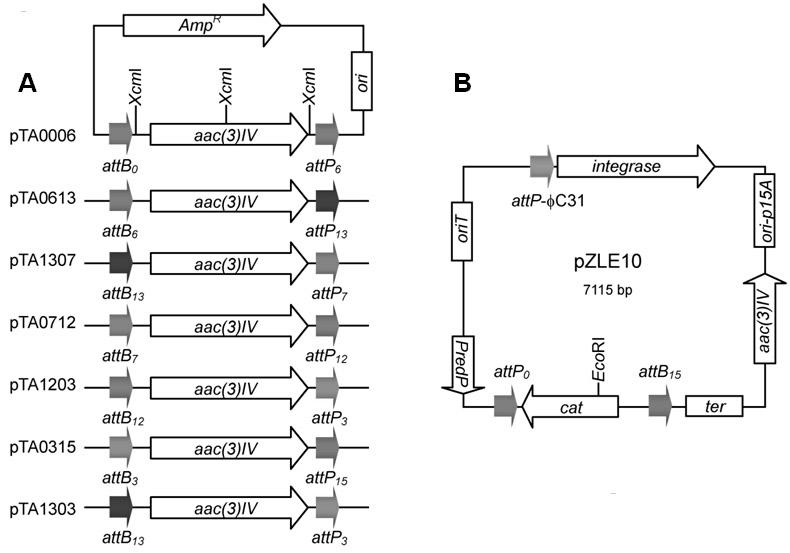
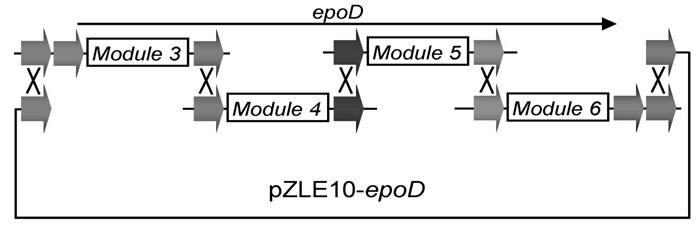
Multi-fragment deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) series connection recombination assembly method based on site-specific recombination
A fragment and site technology, applied in the field of multi-fragment DNA tandem recombination and assembly, can solve problems such as unpredictable results, incompatibility of parts, and variation, and achieve the effect of a simple method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0075] 1. Construction of "entry vector":
[0076] The present invention constructs seven "entry vectors", namely pTA0006, pTA0613, pTA1307, pTA0712, pTA1203, pTA0315 and pTA1303; the first two digits of the plasmid name represent attB Mutation number, the last two digits represent attP For the mutation number, please refer to the corresponding literature [16]. The "entry vector" is constructed as follows: with primer PT1 (containing) attB 0 , SEQ No.1) and PTF (containing attP 6 , SEQ No.2) to amplify the Aparamycin resistance gene ( aac(3)IV ), the obtained PCR fragment was inserted into the pMD19-T (Takara) vector by TA cloning to obtain pTA0006 (such as figure 1 , SEQ No.3).
[0077] By the same method, other "entry vectors" were obtained: with primer PTB6 (containing attB 6 , SEQ No.4) and PTP13 (containing attP 13 , SEQ No.5) to obtain pTA0613 (SEQ No.6); with primer PTB13 (containing attB 13 , SEQ No.7) and PTP7 (containing attP 7 , SEQ No.8) to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com