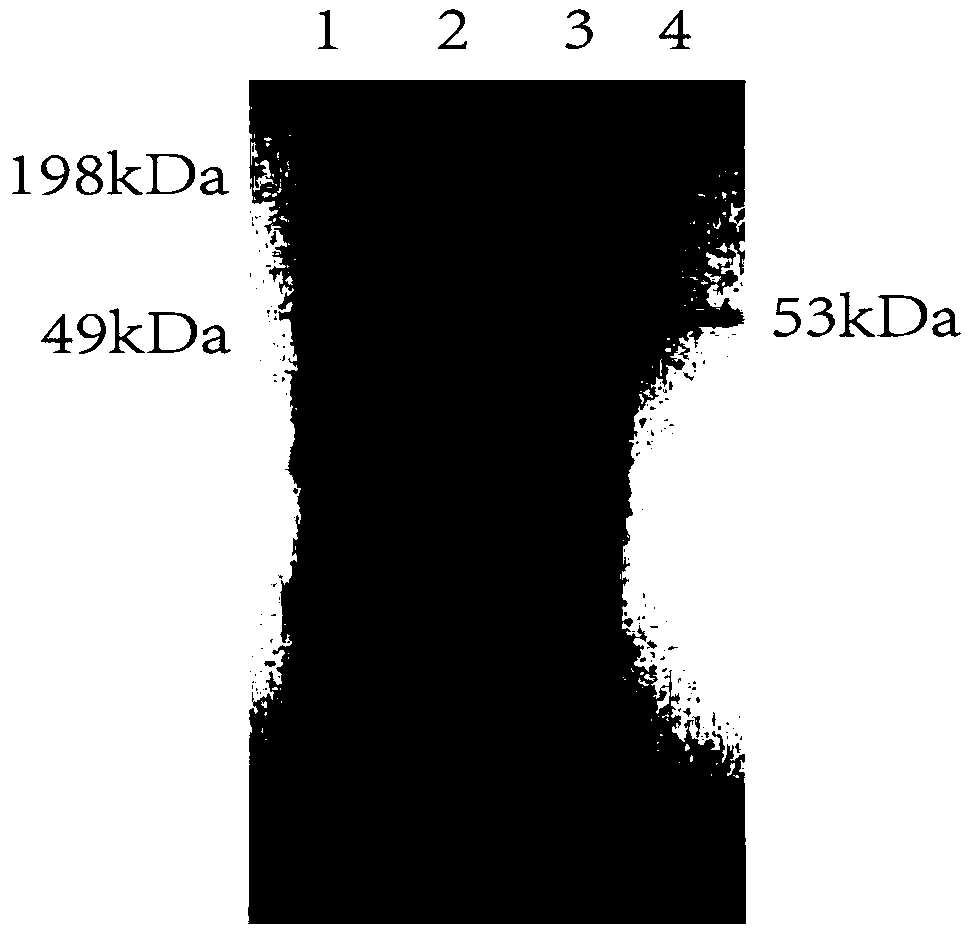Engineering bacillus subtilis capable of expressing phospholipase D
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and phospholipase, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the difficulties of expressing phospholipase D, target gene identification and other problems, and achieve the effect of high reactivity and compact catalytic structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
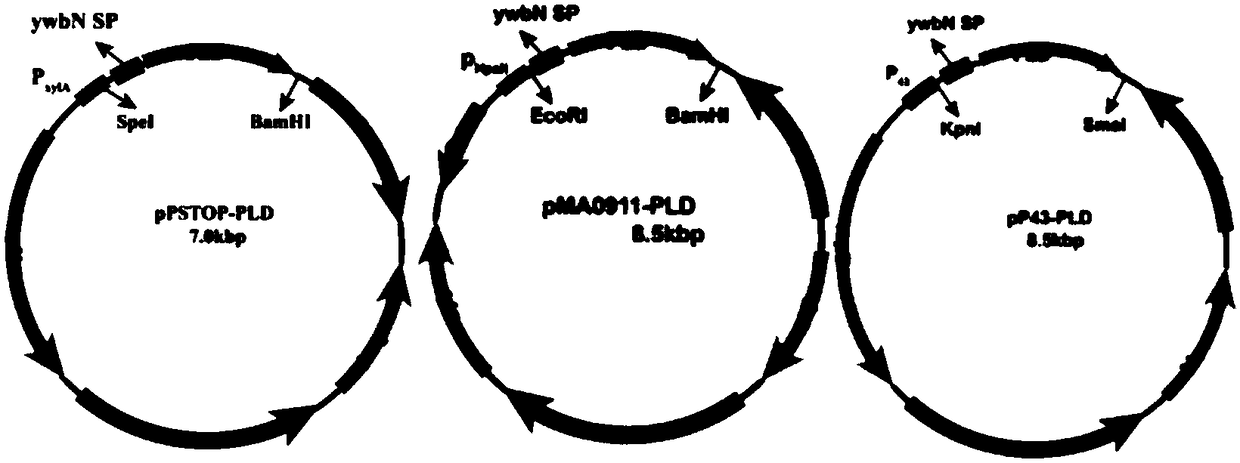
[0051] Embodiment 1: Construction of recombinant plasmid
[0052] According to the codon optimization of the phospholipase D gene (PLD) in Streptomyces racemochromogenes (GenBank: AB573232) published on NCBI, the optimized gene was synthesized and ligated to the plasmid pUC by restriction enzyme ligation, and then according to Plasmid pPUC-PLD sequence information, the designed primer sequence is 2-F of SEQ ID NO.3: 5'-CG GAATTC GAATTCGCATCACCTACACCTCCA-3', with the sequence being 2-R of SEQ ID NO.4: 5'-CG GGATCC GTGGTGGTGGTGGTGGTGTACGCCTGGCAAAGGCCT-3', (where the horizontal lines are the introduced EcoRI and BamHI restriction sites respectively) use the above primers to amplify the phospholipase D coding gene (PLD) using the plasmid pPUC-PLD as a template.
[0053] The plasmid pSTOP and the above amplified gene fragments were respectively digested with SpeI and BamHI and ligated to construct a recombinant plasmid. Double restriction digestion and sequencing confirmed the s...
Embodiment 2
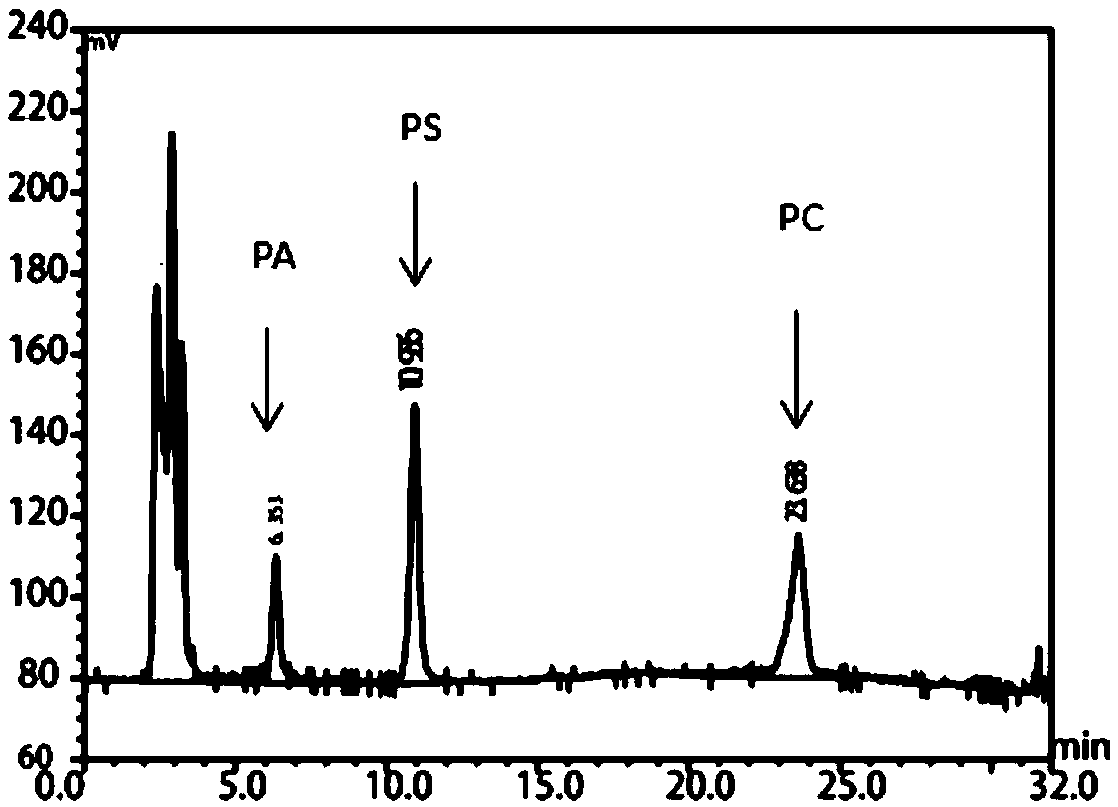
[0056] Embodiment 2: fermentation produces phospholipase D
[0057] The recombinant plasmids pSTOP-PLD, pMA0911-PLD, and pP43-PLD obtained in Example 1 were introduced into Bacillus subtilis WB600, and then the bacteria were inoculated in the seed medium containing kana antibiotic 50 μg / mL, at 37°C, 200rpm Cultivate the logarithmic growth phase as the seed solution; then transfer the seed solution to 20 mL of fermentation medium containing 50 μg / mL of kanamycin at an inoculation amount of 3%, and cultivate at 37 ° C and 200 rpm for 36 h. The fermentation broth was centrifuged at 4°C and 8000r / min for 10min to obtain the supernatant to obtain the crude phospholipase D enzyme solution.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com