A method for producing leucine dehydrogenase by fermentation of Bacillus subtilis
A technology of leucine dehydrogenase, Bacillus subtilis, applied in the field of enzyme engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
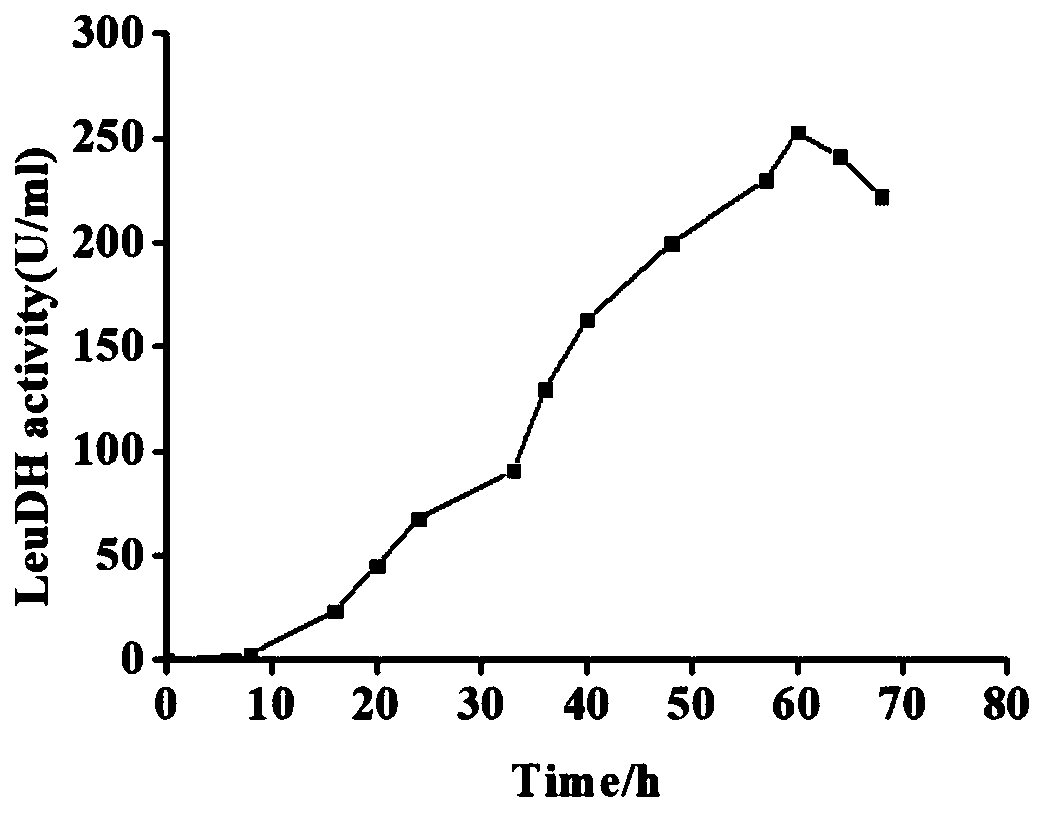
Examples
Embodiment 1
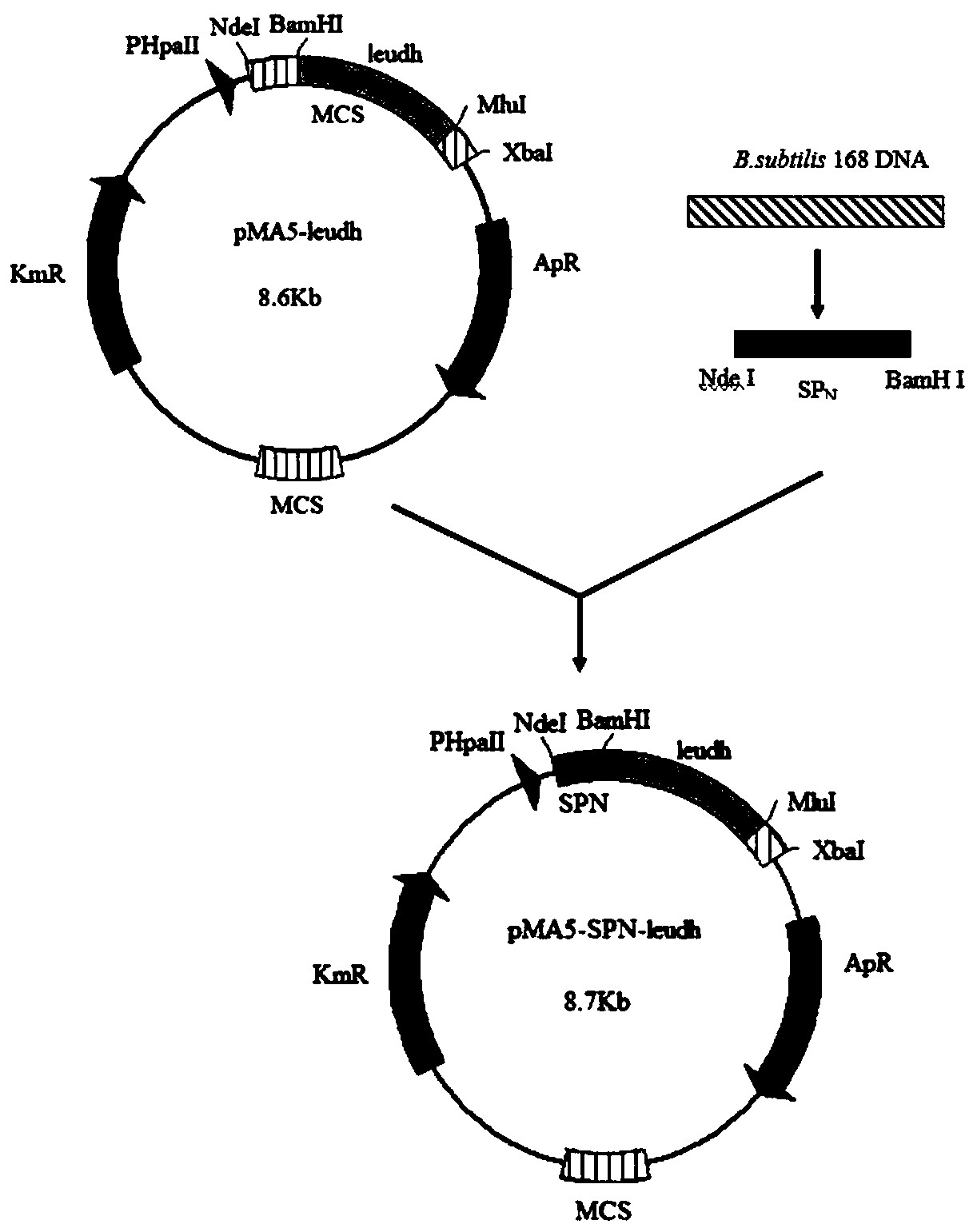
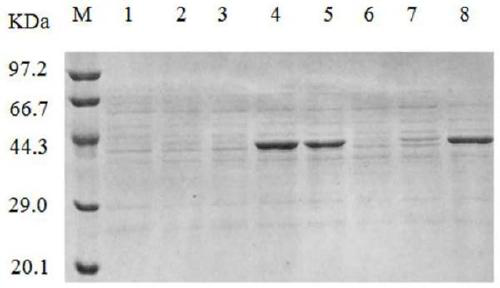
[0037] Example 1: Construction and expression of recombinant plasmid containing recombinant leucine dehydrogenase gene
[0038] Using leudh synthesized from the whole gene as a template, primers F1 / R1 (6×His introduced at the C-terminus) were used for PCR, and restriction site BamH I / Mlu I was introduced. The PCR product and plasmid pMA5 were double-enzymatically digested, and the fragments recovered from the gel were ligated overnight with T4 DNA ligase to obtain the recombinant plasmid pMA5-leudh.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Example 2: Secretion expression plasmid pMA5-SP fused with different signal peptides N - build of leudh
[0040] Extract the genomic DNA of B. subtilis 168, use the genomic DNA as a template, carry out PCR reaction through primers LipA-F / LipA-R, amplify to obtain the signal peptide LipB with sequence such as SEQ ID NO.4, and at the N-terminal of the signal peptide Nde I / BamH I sites were introduced into the C-terminus and the C-terminus, and then the signal peptide fragment and the plasmid pMA5-leudh were double-digested at the same time. After purification, the digested fragments were ligated by T4 DNA ligase and transformed into E.coli JM109. Recombinant bacteria were picked for cultivation, and plasmids were extracted for double-enzyme digestion verification. Since the signal peptide fragments are relatively short and generally about 100 bp in size, the extracted plasmids were subjected to double-enzyme digestion verification with Nde I and Mlu I. Digest for intact ...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Embodiment 3: preparation and transformation of Bacillus subtilis competent
[0042] SPI-A: 0.2g (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 , 1.4g K 2 HPO 4 .3H 2 O, 0.6g KH 2 PO 4 , 0.1g Trisodium Citrate Dihydrate, add water to 50ml, sterilize at 121°C for 20min.
[0043] SPI-B: 0.02g MgSO 4 .7H 2 O, add water to make up to 50ml, and sterilize at 121°C for 20min.
[0044] 100×CAYE: 2g Casamino acid, 10g Yeast Extract, sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
[0045] 100×EGTA: 10mmol / l EGTA solution (add NaOH to adjust the pH to 8.0), sterilize at 121°C for 20min.
[0046] 50mM CaCl 2 : Weigh 0.5549g CaCl 2 Add water to dissolve to a volume of 100ml, and sterilize at 121°C for 20min.
[0047] 250mM MgCl 2 ·6H 2 O: weigh 2.38g MgCl 2 ·6H 2 O was dissolved in water to make up to 100ml, and sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
[0048] SPI Medium (20ml): 9.8ml SPI-A, 9.8ml SPI-B, 200ul (1% V) Glucose, 200ul (1% V) 100×CAYE
[0049] SPII Medium (6ml): 5.88ml SPI Medium, 60ul (1% V) 50mM CaCl 2 , ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com