Patents
Literature
101 results about "Clostridial toxin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clostridium difficile toxin A (TcdA) is a toxin generated by Clostridium difficile. It is similar to Clostridium difficile Toxin B. The toxins are the main virulence factors produced by the gram positive, anaerobic, Clostridium difficile bacteria.
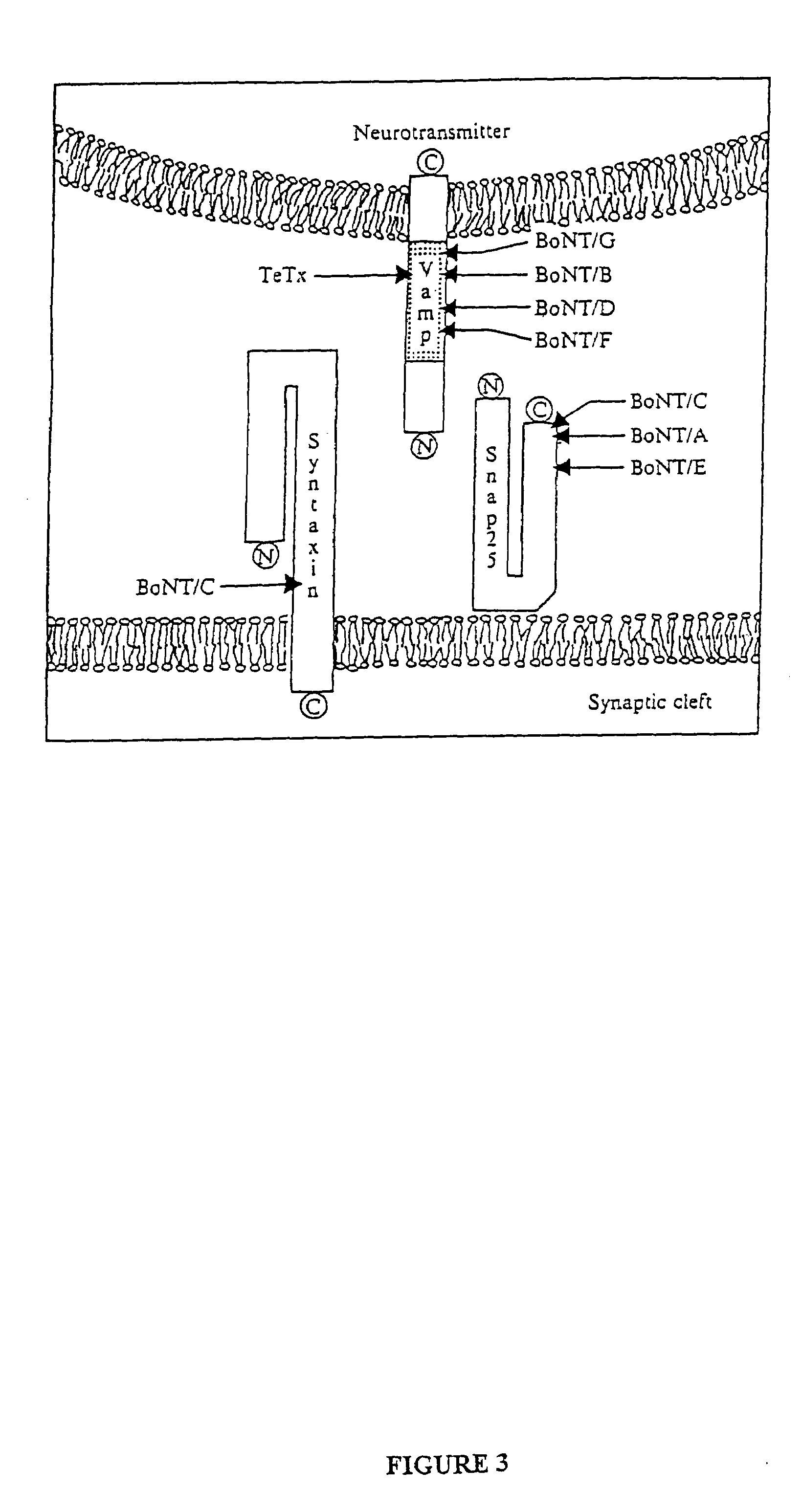
Clostridial toxin derivatives able to modify peripheral sensory afferent functions
InactiveUS6395513B1Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsClostridial toxinProjection neuron
The invention relates to an agent specific for peripheral sensory afferents. The agent may inhibit the transmission of signals between a primary sensory afferent and a projection neuron by controlling the release of at least one neurotransmitter or neuromodulator from the primary sensory afferent. The agent may be used in or as a pharmaceutical for the treatment of pain, particularly chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
Activatable clostridial toxins
InactiveUS20080032931A1Minimize security riskEnhanced efficiency and rateHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsClostridial toxinSaxitoxin
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Fret protease assays for botulinum serotype A/E toxins
InactiveUS7208285B2Used to determineDecreased acceptor fluorescence intensityBacteriaSugar derivativesFluorophoreReceptor for activated C kinase 1
The present invention provides clostridial toxin substrates useful in assaying for the protease activity of any clostridial toxin, including botulinum toxins of all serotypes as well as tetanus toxins. A clostridial toxin substrate of the invention contains a donor fluorophore; an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence that includes a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor and where, under the appropriate conditions, resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Fluorescence polarization assays for determining clostridial toxin activity
The present invention provides a method of determining the presence or activity of a clostridial toxin by (a) treating with a sample, under conditions suitable for clostridial toxin protease activity, a clostridial toxin substrate which includes a fluorophore; a bulking group; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site that intervenes between the fluorophore and the bulking group; (b) exciting the fluorophore with plane polarized light; and (c) determining fluorescence polarization of the treated substrate relative to a control substrate, where a change in fluorescence polarization of the treated substrate as compared to fluorescence polarization of the control substrate is indicative of the presence or activity of the clostridial toxin.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Activatable clostridial toxins
InactiveUS20090018081A1Long duration of therapyOvercome resistanceHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsClostridial toxinNucleic acid
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Clostridial toxin derivatives able to modify peripheral sensory afferent functions
InactiveUS20030049264A1Pain reliefReduce and preferably prevent transmissionNervous disorderHydrolasesClostridial toxinMedicine
The invention relates to an agent specific for peripheral sensory afferents. The agent may inhibit the transmission of signals between a primary sensory afferent and a projection neutron by controlling the release of at least one neurotransmitter or neuromodulator from the primary sensory afferent. The agent may be used in or as a pharmaceutical for the treatment of pain, particularly chronic pain.
Owner:HEALTH PROTECTION AGENCY +1
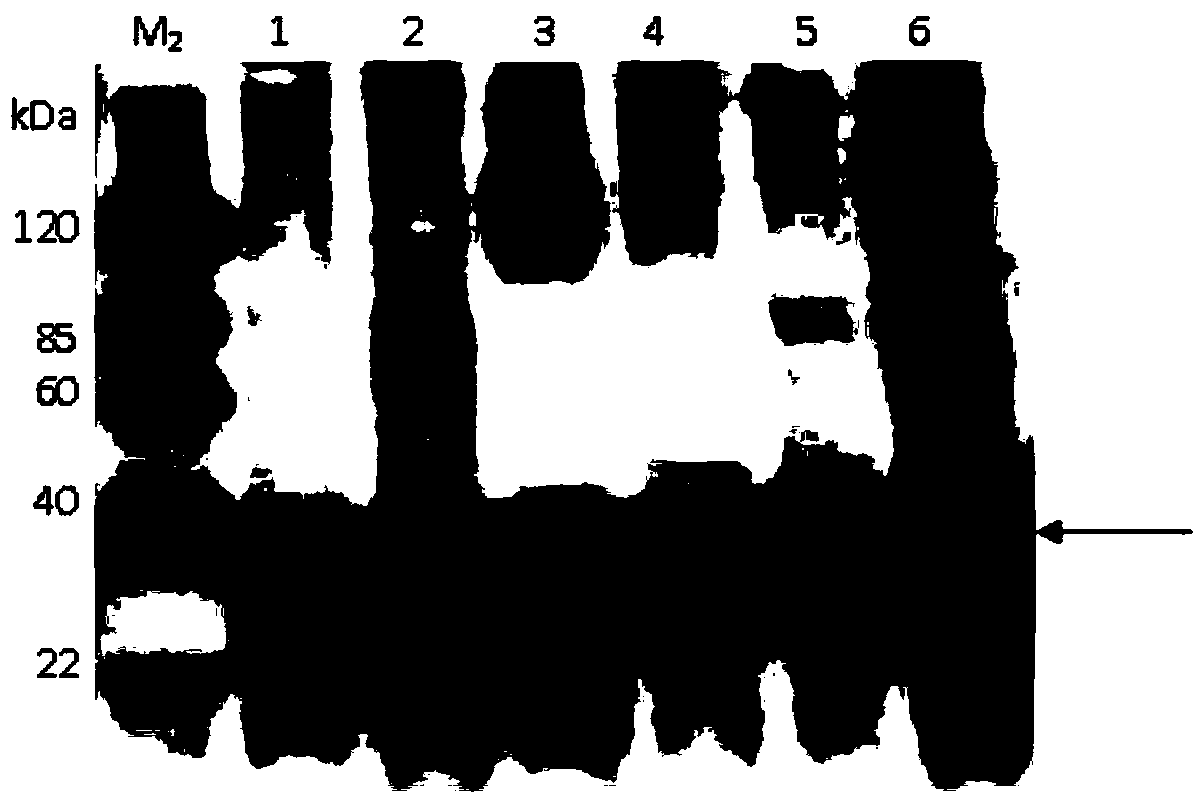
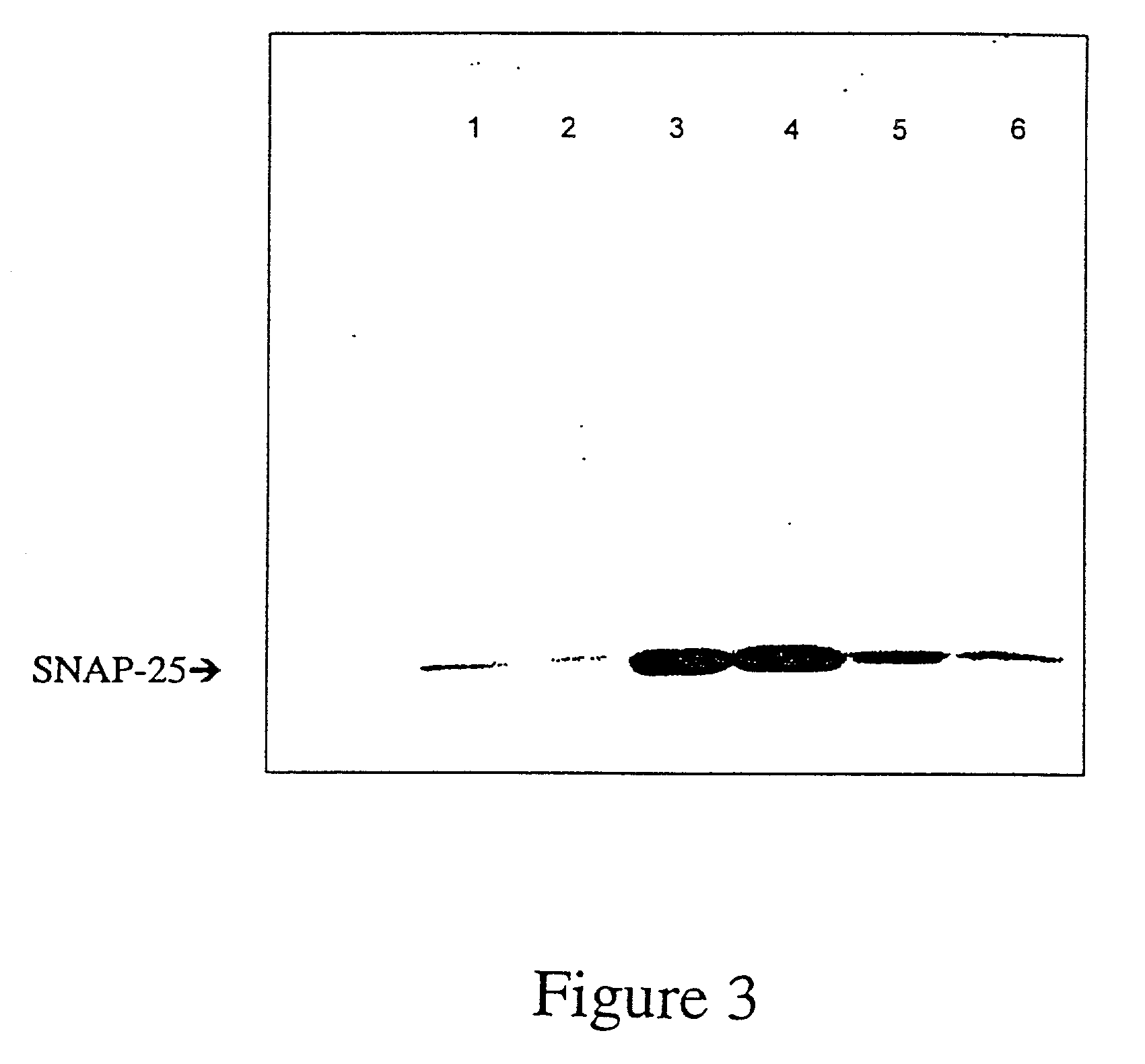
GFP-SNAP25 fluorescence release assay for botulinum neurotoxin protease activity
The present invention provides a nucleic acid molecule which contains a nucleotide sequence encoding a SNAP-25 substrate which includes (i) a green fluorescent protein; (ii) a first partner of an affinity couple; and (iii) a portion of SNAP-25 that includes a BoNT / A, BoNT / C1 or BoNT / E recognition sequence containing a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the green fluorescent protein and the first partner of the affinity couple. Further provided herein is a nucleic acid molecule which contains a nucleotide sequence encoding a tagged toxin substrate which includes (i) a fluorescent protein; (ii) a first partner of an affinity couple; and (iii) a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the fluorescent protein and the first partner of the affinity couple.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Cell-based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assays for clostridial toxins
InactiveUS20070122858A1Decreased acceptor fluorescence intensityHigh fluorescence intensityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaClostridial toxinEnergy transfer
The present invention provides a method of determining clostridial toxin activity by (a) contacting with a sample a cell containing a clostridial toxin substrate that includes a donor fluorophore; an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site that intervenes between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor, where resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor under the appropriate conditions; (b) exciting the donor fluorophore; and (c) determining resonance energy transfer of the contacted cell relative to a control cell, where a difference in resonance energy transfer of the contacted cell as compared to the control cell is indicative of clostridial toxin activity.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Compositions relating to a mutant clostridium difficile toxin and methods thereof
ActiveUS20120269841A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin BNucleotide
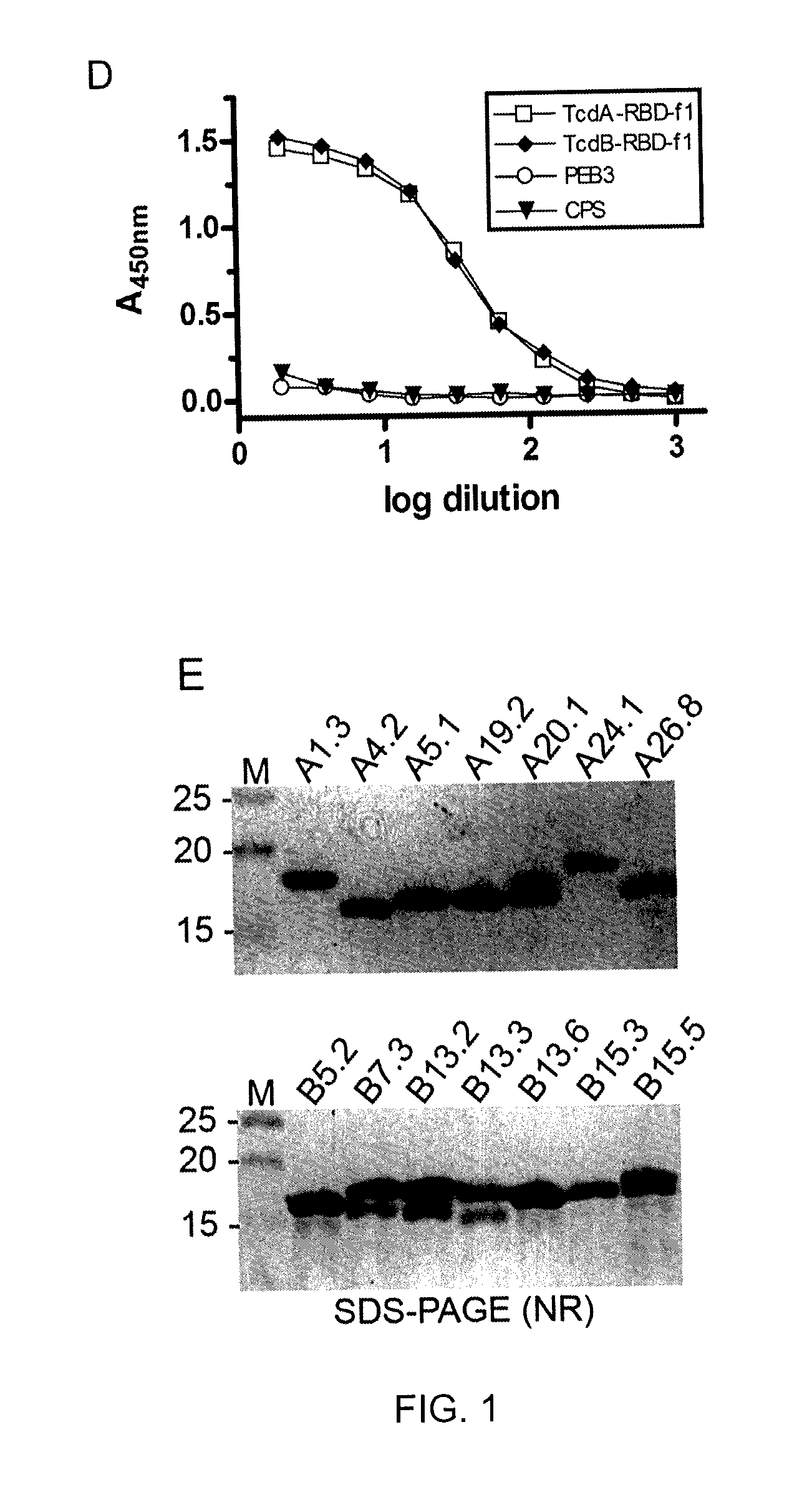
In one aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic composition that includes a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin A and / or a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin B. Each mutant toxin includes a glucosyltransferase domain having at least one mutation and a cysteine protease domain having at least one mutation, relative to the corresponding wild-type C. difficile toxin. The mutant toxins may further include at least one amino acid that is chemically crosslinked. In another aspect, the invention relates to antibodies or binding fragments thereof that binds to said immunogenic compositions. In further aspects, the invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences that encode any of the foregoing, and methods of use of any of the foregoing compositions.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Lanthanide-based substrates and methods for determining clostridial toxin activity
InactiveUS20060063221A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEnergy transferClostridial toxin
The present invention provides a clostridial toxin substrate that contains (a) a lanthanide donor complex; (b) an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the lanthanide donor complex; and (c) a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site that intervenes between the lanthanide donor complex and the acceptor, where, under the appropriate conditions, resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the lanthanide donor complex and the acceptor.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Fluorescence polarization assays for determining clostridial toxin activity
ActiveUS20060063222A1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementClostridial toxinProteinase activity
The present invention provides a method of determining the presence or activity of a clostridial toxin by (a) treating with a sample, under conditions suitable for clostridial toxin protease activity, a clostridial toxin substrate which includes a fluorophore; a bulking group; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site that intervenes between the fluorophore and the bulking group; (b) exciting the fluorophore with plane polarized light; and (c) determining fluorescence polarization of the treated substrate relative to a control substrate, where a change in fluorescence polarization of the treated substrate as compared to fluorescence polarization of the control substrate is indicative of the presence or activity of the clostridial toxin.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Soluble recombinant botulinum toxin proteins
The present invention includes recombinant proteins derived from Clostridium botulinum toxins. In particular, soluble recombinant Clostridium botulinum type A, type B and type E toxin proteins are provided. Methods which allow for the isolation of recombinant proteins free of significant endotoxin contamination are provided. The soluble, endotoxin-free recombinant proteins are used as immunogens for the production of vaccines and antitoxins. These vaccines and antitoxins are useful in the treatment of humans and other animals at risk of intoxication with clostridial toxin.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and detection method for clostridium difficile toxin genes
ActiveCN103361434AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium difficile infectionsClostridium difficile toxin B
A provided multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit for clostridium difficile toxin genes mainly comprises specific primers, probes and a PCR reaction reagent, and the specific primers and the probes respectively consist of specific primers and probes of clostridium difficile toxin A (tcdA), toxin B (tcdB), binary toxin A (cdtA) and binary toxinB (cdtB). The beneficial effects of the invention comprise: the fast, sensitive and specific multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and a detection method are provided for the clostridium difficile toxin genes, and a foundation is provided for distinguishing between toxigenic strains and avirulent strains of clostridium difficile, and early diagnosis on infection of clostridium difficile.
Owner:杭州海基生物技术有限公司
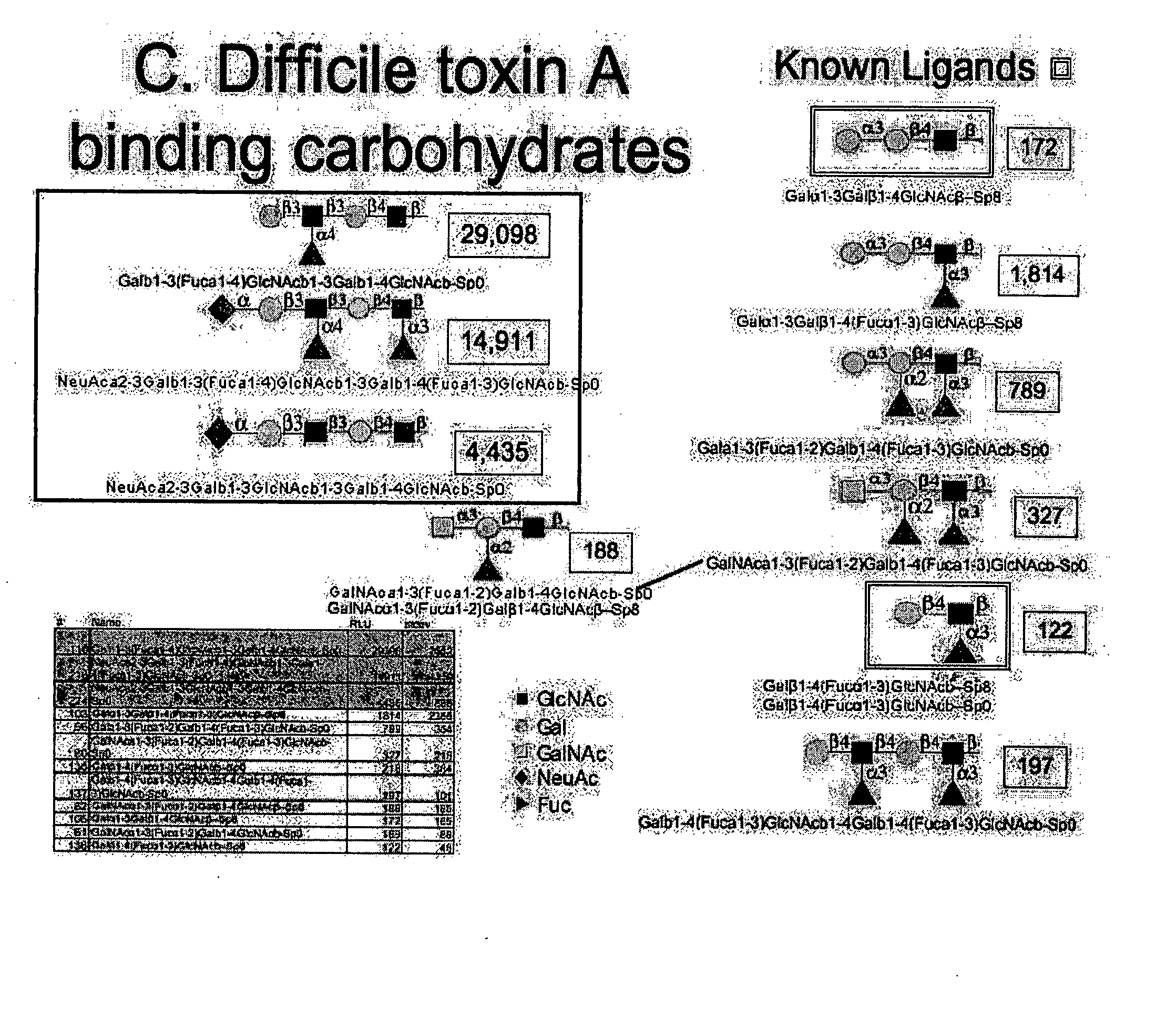
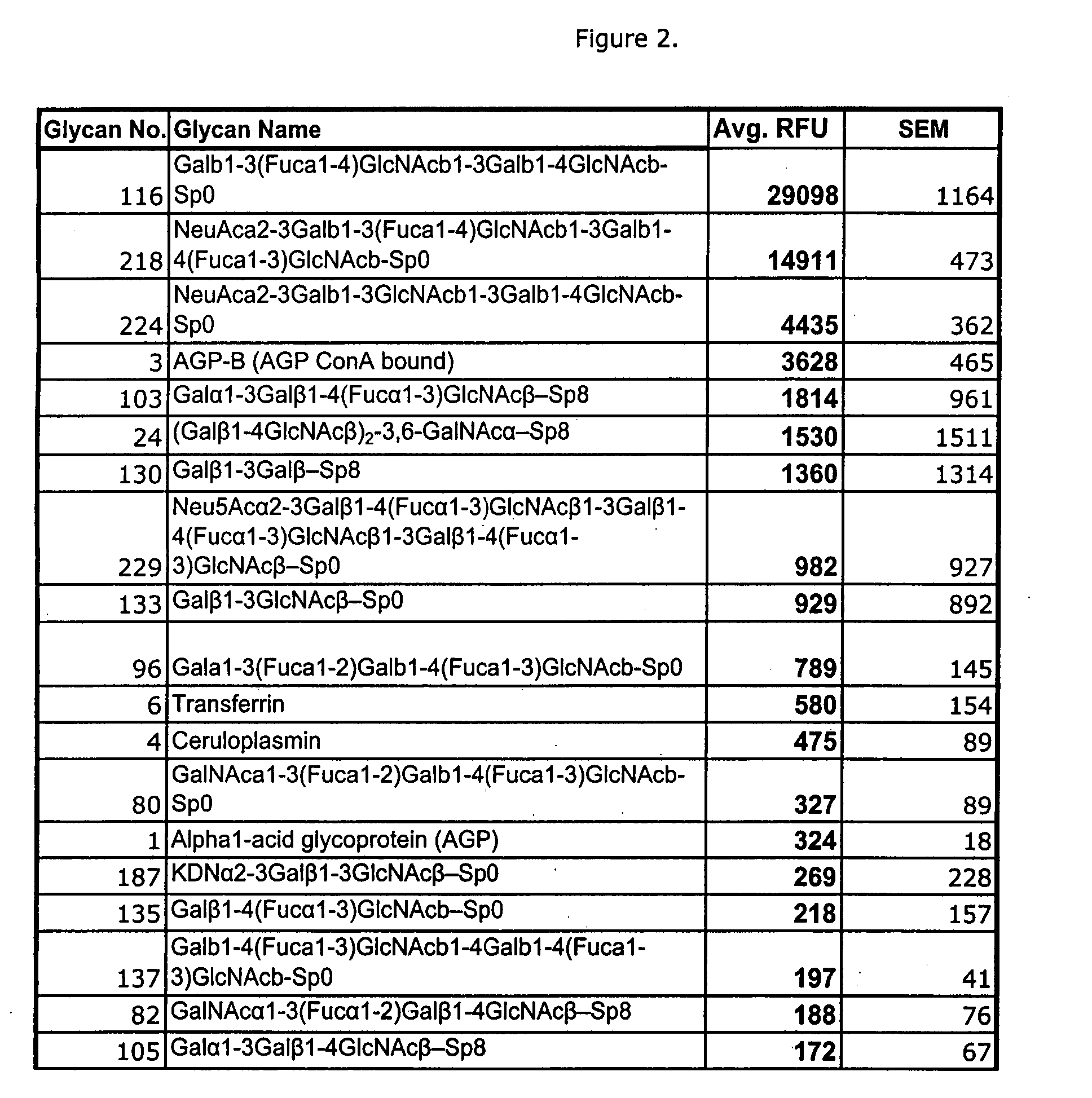
High affinity ligands bind to clostridium difficile toxin A
Glycans are identified which have high affinity for C. difficile toxin A. They share one of two saccharide backbones and may have additional side chains. The backbones are galactose-β1-3 N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-β-1-3-galactose-β-1-4-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and galactose-α-1-3-galactose-β-1-4-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. The ligands may be used therapeutically, prophylactically, and diagnostically.
Owner:DIECKGRAEFE BRIAN
GFP-SNAP25 fluorescence release assay for botulinum neurotoxin protease activity
InactiveUS20060154314A9BacteriaMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFluorescenceNucleotide
The present invention provides a nucleic acid molecule which contains a nucleotide sequence encoding a SNAP-25 substrate which includes (i) a green fluorescent protein; (ii) a first partner of an affinity couple; and (iii) a portion of SNAP-25 that includes a BoNT / A, BoNT / C1 or BoNT / E recognition sequence containing a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the green fluorescent protein and the first partner of the affinity couple. Further provided herein is a nucleic acid molecule which contains a nucleotide sequence encoding a tagged toxin substrate which includes (i) a fluorescent protein; (ii) a first partner of an affinity couple; and (iii) a clostridial toxin recognition sequence containing a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the fluorescent protein and the first partner of the affinity couple.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Treatment of fine wrinkles with clostridia neurotoxins
InactiveUS20080081049A1Reduce the numberReduced activityCosmetic preparationsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridial toxinWrinkle skin
Methods of using clostridial toxins and other biological agents to thin skin and control fine wrinkles in humans are provided. In preferred embodiments the methods provide beneficial effects in humans.
Owner:SANDERS
Fret protease assays for clostridial toxins
InactiveUS20080032318A1Used to determineDecreased acceptor fluorescence intensityPeptide-nucleic acidsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSerotypeFluorophore
The present invention provides clostridial toxin substrates useful in assaying for the protease activity of any clostridial toxin, including botulinum toxins of all serotypes as well as tetanus toxins. A clostridial toxin substrate of the invention contains a donor fluorophore; an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence that includes a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor and where, under the appropriate conditions, resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Test paper strip for detecting clostridium difficile toxin A and toxin B colloidal gold, method for making same and applications
ActiveCN101363867ASave manpower and material resourcesThe result is clear and easy to distinguishMaterial analysisCelluloseClostridium difficile infections
The invention provides a test strip for rapid detection of clostridium difficile toxins A and B. A monoclonal antibody or polyclonal antibody of the clostridium difficile toxin A, a monoclonal antibody or polyclonal antibody of the clostridium difficile toxin B, and a quality control double-antibody IgG coat a nitrate cellulose film (NC film), and a membrane chromatography double antibody sandwich method is adopted to detect the clostridium difficile toxins A and B in a specimen in combination with a monoclonal antibody of colloidal gold labeled clostridium difficile toxins A and B. The test strip is simple in operation, convenient, and fast, and has the advantages of no requirements of special instruments and special training, clear and identified result, and easy popularization. The test strip is suitable for base course, site detection and epidemiological investigation, and has auxiliary effect on the diagnosis of clostridium difficile toxin infection.
Owner:辽宁迪浩生物科技有限公司
Clostridium perfringens alpha toxin double-antibody sandwich ELIS quantitative determination method
ActiveCN103941004AStrong specificityStrong responsivenessMaterial analysisAlpha-toxinClostridium perfringens toxoid
The invention relates to a clostridium perfringens alpha toxin double-antibody sandwich ELIS quantitative determination method. According to the clostridium perfringens alpha toxin double-antibody sandwich ELIS quantitative determination method, alpha toxin protein obtained via prokaryotic expression is taken as an immunogen; monoclonal antibodies obtained via hybridoma technique are taken as detection antibodies and capture antibodies; reaction conditions are optimized via experiments; alpha toxin protein samples with a series of concentration are used for construction of a standard curve; the double-antibody sandwich ELIS method is established; and indexes of the double-antibody sandwich ELIS are verified. The clostridium perfringens alpha toxin double-antibody sandwich ELIS quantitative determination method specifically comprises following steps: (1) prokaryotic expression of alpha toxin; (2) preparation of anti-alpha toxin monoclonal antibodies; (3) establishment of the double-antibody sandwich ELIS method; (4) establishment of the standard curve; and (5) performance evaluation on the double-antibody sandwich ELIS method. The clostridium perfringens alpha toxin double-antibody sandwich ELIS quantitative determination method is excellent in specificity, and high in sensitivity and stability, is fast and convenient, and can be used for effective quantitative determination of alpha toxin in A-E type clostridium perfringens cultural supernatants; and the high-efficient detection method is provided for alpha toxin determination.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Non-protein stabilized clostridial toxin pharmaceutical compositions
InactiveCN101175478APeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismClostridial toxinAlcohol
A Clostridial toxin pharmaceutical composition comprising a Clostridial toxin, such as a botulinum toxin, wherein the Clostridial toxin present in the pharmaceutical composition is stabilized by a non-protein excipient such as a polyvinylpyrrolidone, a disaccharides, a trisaccharide, a polysaccharide, an alcohol, a metal, an amino acid, a surfactant and / or a polyethylene glycol.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Non-protein clostridial toxin compositions
Pharmaceutical compositions that stabilize a Clostridial toxin active ingredient are described. The compositions can be liquid or solid compositions, and comprise a surfactant and an antioxidant. In some embodiments, the compositions comprise a surfactant selected from a poloxamer and a polysorbate; an antioxidant selected from methionine, N-acetyl cysteine, ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and combinations thereof, and, optionally, a tonicity agent and / or a lyoprotector selected from, for example, trehalose, sucrose.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Fret protease assays for botulinum serotype a/e toxins
The present invention provides clostridial toxin substrates useful in assaying for the protease activity of any clostridial toxin, including botulinum toxins of all serotypes as well as tetanus toxins. A clostridial toxin substrate of the invention contains a donor fluorophore; an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence that includes a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor and where, under the appropriate conditions, resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Vaccines against clostridium difficile comprising recombinant toxins
InactiveCN104039816ACan't greatly increase survivalReduce weightAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridial toxinClostridium difficile infections
The present invention relates to recombinant C. difficile toxin A (TcdA) and toxin B (TcdB) and binary toxin A (CDTa) proteins comprising specifically defined mutations relative to the native toxin sequence that substantially reduce or eliminate toxicity. The invention also relates to vaccines and immunogenic compositions comprising these recombinant toxins, as well as combinations of these toxins with binary toxin B (CDTb), which are capable of providing protection against C. difficile infection and / or the effects thereof. The invention also relates to methods of inducing an immune response to C. difficile comprising administering the vaccines and immunogenic compositions described herein to a patient. The invention also encompasses methods of expressing recombinant C. difficile toxin A and toxin B and CDTa mutants and CDTb in recombinant expression systems. In exemplary embodiments, TcdA, TcdB, and CDTa mutant toxins comprising sufficient mutations to substantially reduce or eliminate toxicity are expressed in the baculovirus / insect cell expression system.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC +1
Fret protease assays for clostridial toxins
InactiveUS20080038756A1Peptide-nucleic acidsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorSerotypeFluorophore
The present invention provides clostridial toxin substrates useful in assaying for the protease activity of any clostridial toxin, including botulinum toxins of all serotypes as well as tetanus toxins. A clostridial toxin substrate of the invention contains a donor fluorophore; an acceptor having an absorbance spectrum overlapping the emission spectrum of the donor fluorophore; and a clostridial toxin recognition sequence that includes a cleavage site, where the cleavage site intervenes between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor and where, under the appropriate conditions, resonance energy transfer is exhibited between the donor fluorophore and the acceptor.
Owner:ALLERGAN INC
Triple and four-prevention subunit vaccine for sheep and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107308445ASufficient space to expandImprove biological activityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEuropean rabbitAdjuvant
The invention discloses triple and four-prevention subunit vaccine for sheep and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of prevention and control of animal epidemic diseases. The triple and four-prevention subunit vaccine is prepared from clostridium perfringens beta-epsilon fusion protein, clostridium septicum alpha toxin recombinant protein and an adjuvant. After beta-epsilon (beta and epsilon fusion proteins) of a clostridium perfringens C58-1 strain and alpha toxin protein of a clostridium septicum C55-2 strain, which are cloned and expressed, are purified and then are mixed with the adjuvant to prepare vaccine for immunizing white mice and domestic rabbits; the triple and four-prevention subunit vaccine for the sheep is checked to be qualified by utilizing inspection standards related to the triple and four-prevention subunit vaccine for the sheep in the third volume of 2015 version of China Veterinary Pharmacopoeia; an attacking toxin protection test result shows that animals immunized with the proteins have 100 percent protection efficiency on type B, type C and type D of clostridium perfringen and clostridium septicum. Therefore, the triple and four-prevention subunit vaccine can be used for replacing traditional triple and four-prevention vaccine.
Owner:SHANDONG BINZHOU ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY MEDICINE ACADEMY
Clostridium septicum alpha toxin recombinant subunit vaccine and production method thereof
ActiveCN107812183AReduce Biosecurity RisksEasy to purifyAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenAlpha-toxin
The invention relates to a clostridium septicum alpha toxin recombinant subunit vaccine and a production method thereof. According to the production method, 54-site cysteine of wild clostridium septicum alpha mature toxin is mutated into leucine, 264-site asparaginate is mutated into alanine, 269-site histidine is mutated into alanine, and 310-site tryptophan is mutated into alanine, so that an alpha toxin mutant which is nontoxic to animals is obtained; and 6 groups of histidine tags are added to a C end of a mutant protein so as to obtain an antigen for preparing vaccines. The invention simultaneously discloses a recombinant expression vector and a recombinant host cell which contain an encoding gene of a nontoxic alpha toxin mutant of clostridium septicum. The efficacies of the preparedclostridium septicum alpha toxin recombinant subunit vaccine are far higher than the efficacies of existing vaccines, and the bio-safety risk in the production process of the vaccine is greatly reduced. Besides, by virtue of the superiority that a semi-finished product of the vaccine is high in protein concentration, a mixed vaccine can be prepared without increasing the dosage of the vaccine.
Owner:CHINA INST OF VETERINARY DRUG CONTROL
Clostridium difficile-specific antibodies and uses thereof
InactiveUS20130230537A1Improve heat resistanceReduced thermal stabilityAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesClostridial toxinAntiendomysial antibodies
The present invention is directed to Clostridium difficile toxin-specific antibodies, compositions, and uses thereof. The anti-toxin antibodies may be specific for either TcdA or TcdB. The invention also includes methods of treating a Clostridium difficile infection, methods of capturing Clostridium difficile toxins, and methods of detecting Clostridium difficile toxins.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Clostridial toxin netb
ActiveUS20100291131A1Reduce infectionReduce colonizationAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDiseaseClostridial toxin
The present invention relates to a polypeptide based toxin that originates from Clostridium perfringens. The invention further relates to immunogenic compositions comprising the toxin and methods to vaccinate animals, for example chickens, such that they are less susceptible to clostridial diseases. Methods to determine whether an animal has been exposed to the toxin, polynucleotides encoding the toxin and attenuated bacteria that express a reduced or less active form of the toxin are also disclosed.
Owner:AUSTRALIAN POULTRY CRC
Soluble recombinant botulinum toxin proteins
The present invention includes recombinant proteins derived from Clostridium botulinum toxins. In particular, soluble recombinant Clostridium botulinum type A, type B and type E toxin proteins are provided. Methods which allow for the isolation of recombinant proteins free of significant endotoxin contamination are provided. The soluble, endotoxin-free recombinant proteins are used as immunogens for the production of vaccines and antitoxins. These vaccines and antitoxins are useful in the treatment of humans and other animals at risk of intoxication with clostridial toxin.
Owner:ALLERGAN SALES ALLERGAN BOTOX
Clostridial neurotoxins with altered persistency
The invention relates to a polypeptide comprising: (a) a HC-domain or fragment thereof of the neurotoxic component of a clostridial toxin; and (b) a first LC domain or fragment thereof of the neurotoxic component of a clostridial toxin; and (c) at least one further LC domain or fragment thereof of the neurotoxic component of a clostridial toxin wherein the first and the at least one further LC domain may be the same or different from each other, and wherein each of said fragments of said first and of said at least one further LC domain still exhibits proteolytic activity.
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com