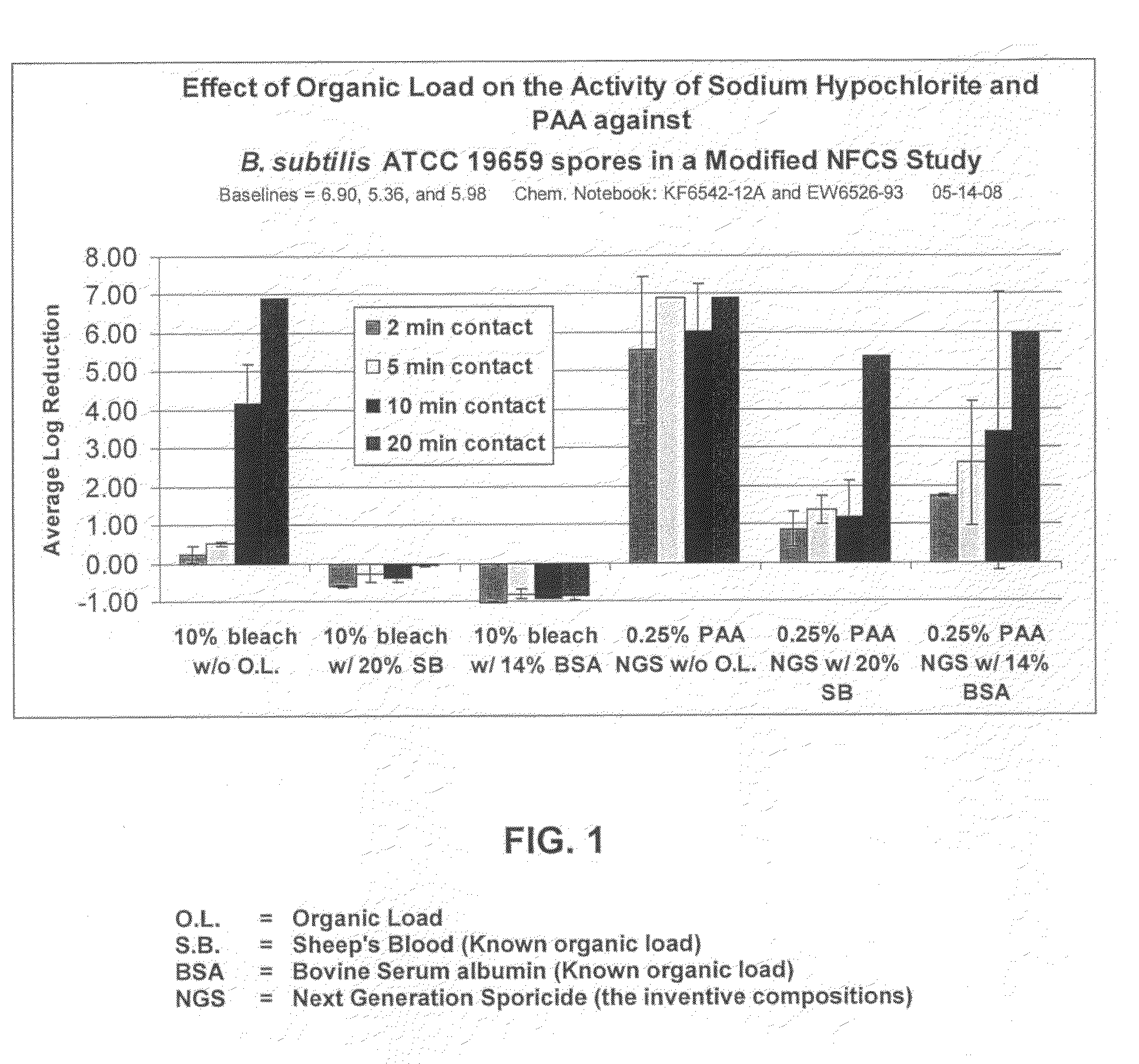
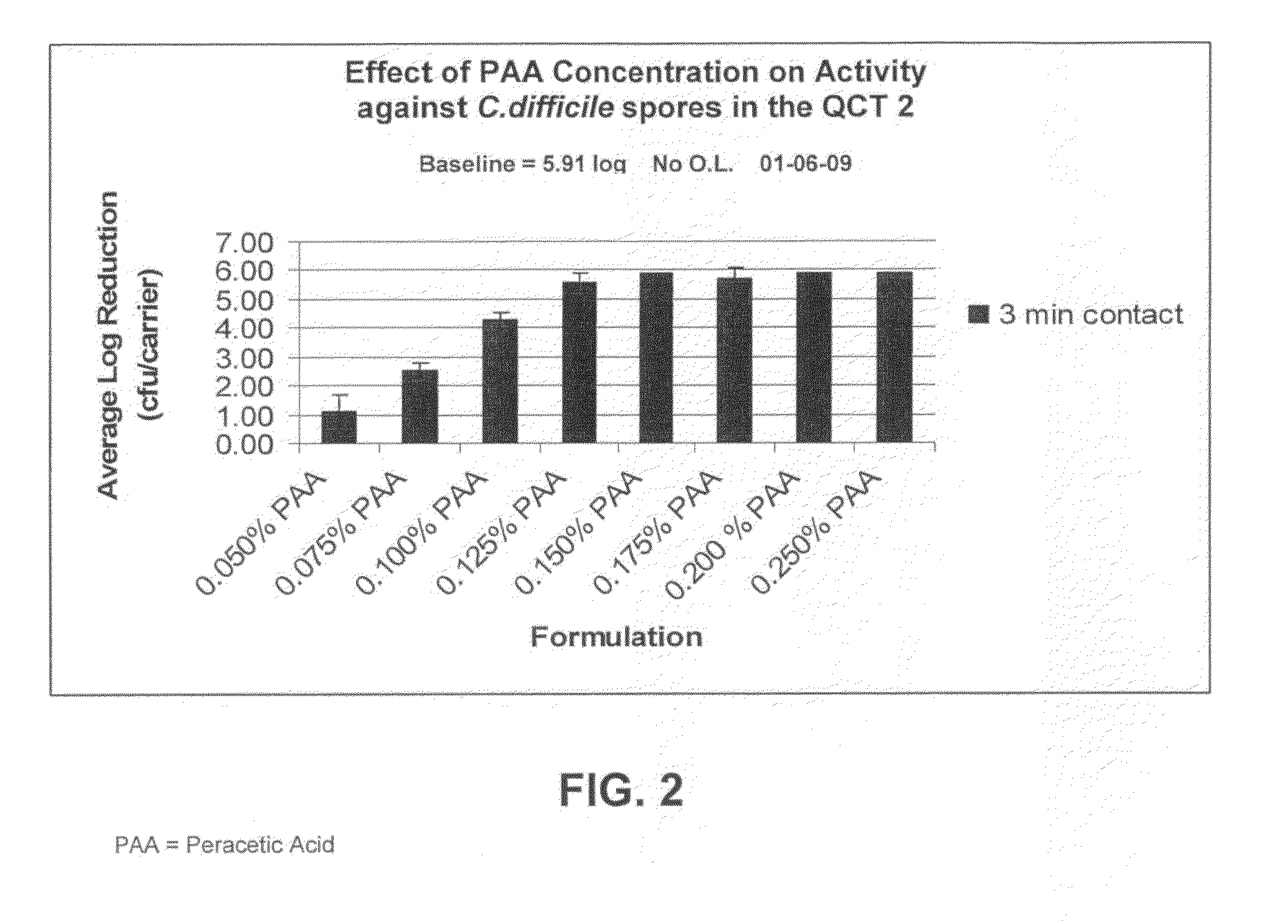
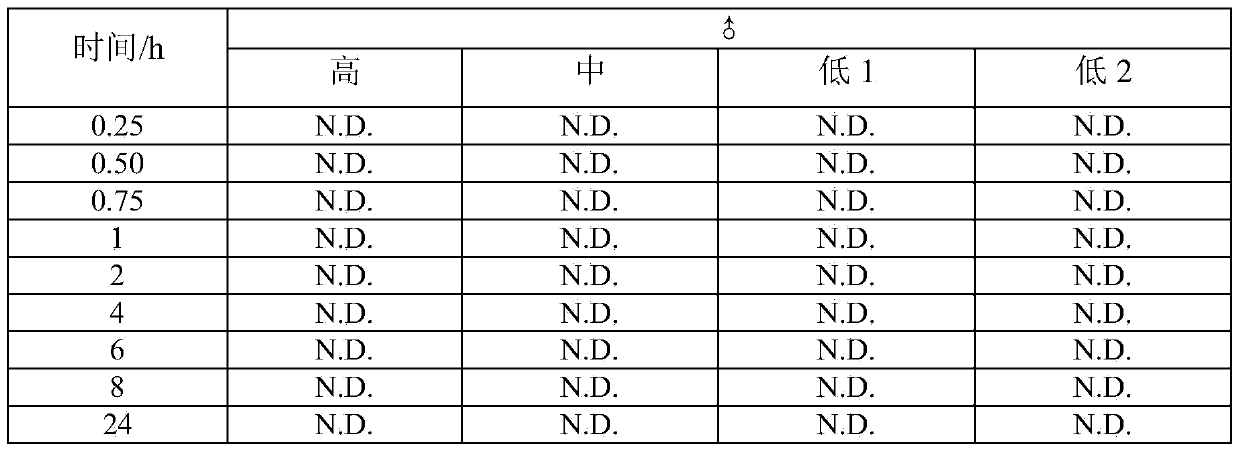
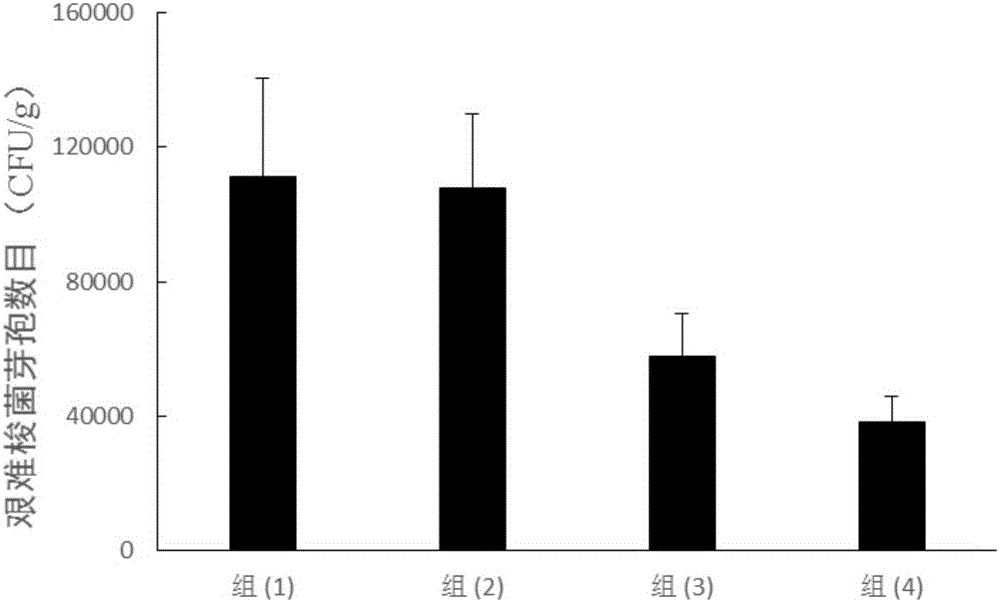
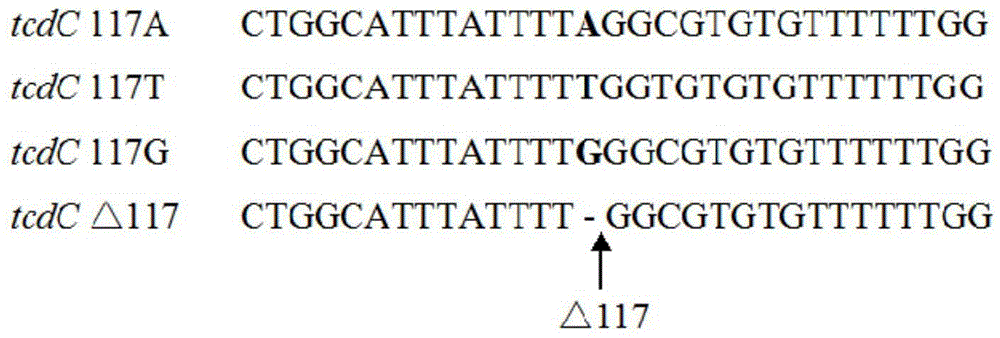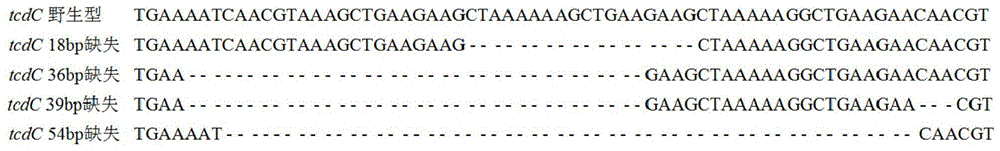Patents
Literature
56 results about "Clostridium difficile toxin B" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clostridium difficile toxin B is a toxin produced by the bacteria Clostridium difficile. C. difficile produces two major kinds of toxins that are very potent and lethal; an enterotoxin (Toxin A) and a cytotoxin (Toxin B, this protein).
Compositions relating to a mutant clostridium difficile toxin and methods thereof
ActiveUS20120269841A1Antibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin BNucleotide
In one aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic composition that includes a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin A and / or a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin B. Each mutant toxin includes a glucosyltransferase domain having at least one mutation and a cysteine protease domain having at least one mutation, relative to the corresponding wild-type C. difficile toxin. The mutant toxins may further include at least one amino acid that is chemically crosslinked. In another aspect, the invention relates to antibodies or binding fragments thereof that binds to said immunogenic compositions. In further aspects, the invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences that encode any of the foregoing, and methods of use of any of the foregoing compositions.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Low odor, hard surface sporicide
ActiveUS20100196503A1Safer and easy to handleSafer and easy to and transportBiocidePeroxide active ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin BNuclear chemistry
A low odor, liquid disinfectant composition comprising multiple components, which, upon mixing, provide an aqueous solution comprising low levels of peracetic acid for use in decontaminating articles and surfaces contaminated with bacteria, viruses, fungi and other biological contaminants such as spores, including, but not limited to, Clostridium difficile (C.diff). The disinfectant composition is prepared just prior to use by combining two or more separately packaged components.
Owner:AMERICAN STERILIZER CO
Compositions relating to a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin and methods thereof
In one aspect, the invention relates to an immunogenic composition that includes a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin A and / or a mutant Clostridium difficile toxin B. Each mutant toxin includes a glucosyltransferase domain having at least one mutation and a cysteine protease domain having at least one mutation, relative to the corresponding wild-type C. difficile toxin. The mutant toxins may further include at least one amino acid that is chemically crosslinked. In another aspect, the invention relates to antibodies or binding fragments thereof that binds to said immunogenic compositions. In further aspects, the invention relates to isolated nucleotide sequences that encode any of the foregoing, and methods of use of any of the foregoing compositions.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Healthcare facility disinfecting system
ActiveUS8551399B2Effectively eliminating aerosolized pathogensLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsEscherichia coliClostridium difficile toxin B
A system and process for disinfecting rooms such as health care facility rooms with an oxygen / ozone mixture is described, which is effective to combat “superbugs” such as Clostridium difficile (C. difficile); E. coli; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE). In preferred embodiments, hydrogen peroxide is additionally used. The system and process is effective to destroy bacteria deposited on surfaces as biofilm, and, accompanied by physical agitation such as jet nozzle outlets, is effective to disinfect carpet, drapery and similar absorbent and porous surfaces.
Owner:DD STEROZONE LLC +1
Multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and detection method for clostridium difficile toxin genes
ActiveCN103361434AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium difficile infectionsClostridium difficile toxin B
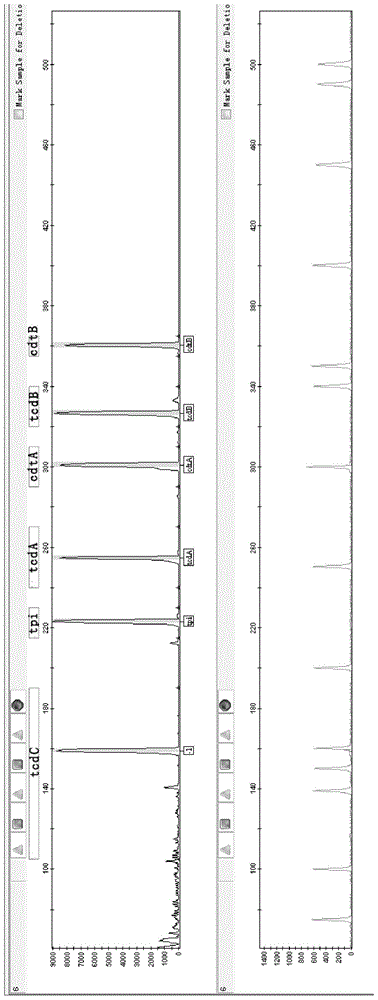
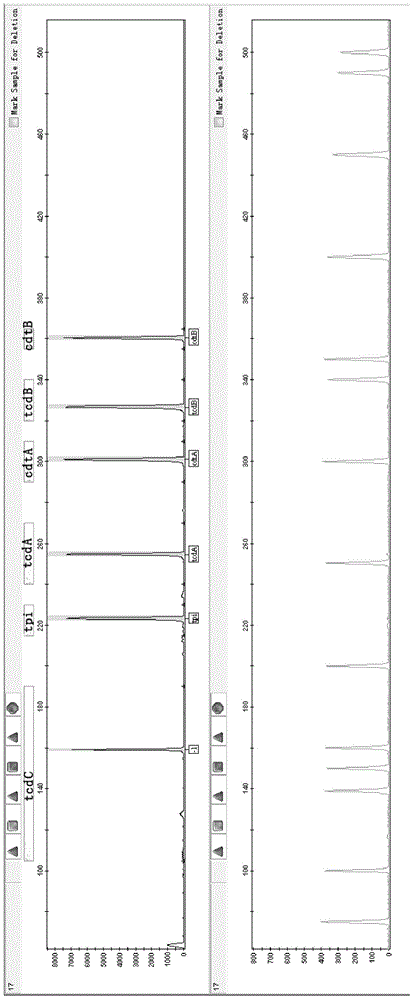
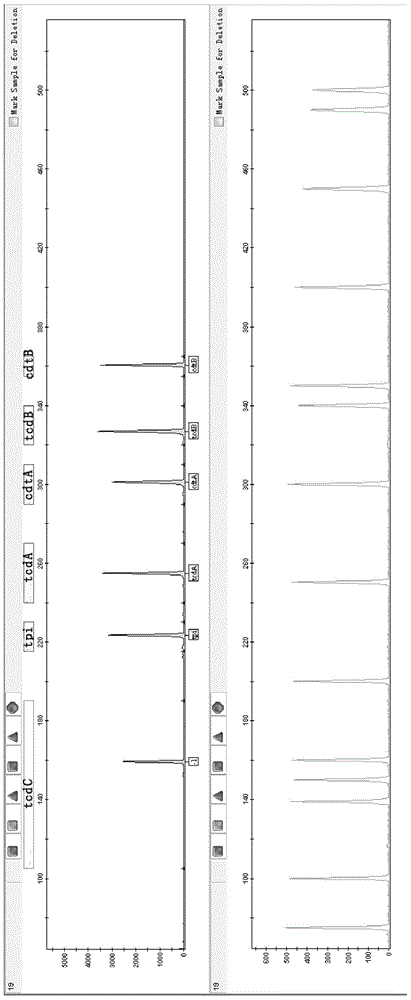
A provided multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit for clostridium difficile toxin genes mainly comprises specific primers, probes and a PCR reaction reagent, and the specific primers and the probes respectively consist of specific primers and probes of clostridium difficile toxin A (tcdA), toxin B (tcdB), binary toxin A (cdtA) and binary toxinB (cdtB). The beneficial effects of the invention comprise: the fast, sensitive and specific multiple fluorescence PCR detection kit and a detection method are provided for the clostridium difficile toxin genes, and a foundation is provided for distinguishing between toxigenic strains and avirulent strains of clostridium difficile, and early diagnosis on infection of clostridium difficile.
Owner:杭州海基生物技术有限公司
Mutants of clostridium difficile toxin B and methods of use
InactiveUS20080107673A1Antibacterial agentsAnimal cellsHospitalized patientsClostridium difficile infections
An active, or passive vaccine utilizing purified non-toxic mutant TcdB toxins from Clostridium difficile for humans and animals against infections caused by C. difficile and / or C. sordellii. Persons most potentially affected by C. difficile infections include hospitalized patients, infants, and elderly persons. The TcdB toxin mutant of the vaccine preferably lacks the toxicity of a native C. difficile TcdB toxin. A serum comprising antibodies raised to the TcdB toxin mutant is also available for treating humans or animals against C. difficile infections. The serum may be used in a method for conferring passive immunity against C. difficile. Antibodies to the TcdB toxin mutant may be used in diagnostic tests or in treatments to clear TcdB toxin from bodily fluids. The mutant TcdB toxin may be produced by recombinant methods using cDNA encoding the toxin, the cDNA contained for example in a plasmid or host cell.
Owner:BALLARD JIMMY D +1
Composition, kit and method for detecting high-virulence bacterial strains and/or toxin type of clostridium difficile
ActiveCN104928376AEasy to distinguishIncrease virulenceMicrobiological testing/measurementClostridium difficile toxin BTrue positive rate
The invention discloses a composition, kit and method for detecting high-virulence bacterial strains and / or toxin type of clostridium difficile. The composition and kit comprise primers, probes and standard substances, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the primers is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1-47; the high-virulence bacterial strains and / or toxin type of clostridium difficile can be detected through fluorogenic quantitative PCR by adopting the composition or kit. According to the invention, the sensitivity and specificity are high; the toxin type and virulence of clostridium difficile can be accurately judged through detecting tcdC gene mutation or deletion and coordinating with virulence gene detection, including tcd A / B and binary virulence gene cdt A / B, of clostridium difficile.
Owner:WUHAN AIMISEN LIFE TECH CO LTD
Test paper strip for detecting clostridium difficile toxin A and toxin B colloidal gold, method for making same and applications
ActiveCN101363867ASave manpower and material resourcesThe result is clear and easy to distinguishMaterial analysisCelluloseClostridium difficile infections
The invention provides a test strip for rapid detection of clostridium difficile toxins A and B. A monoclonal antibody or polyclonal antibody of the clostridium difficile toxin A, a monoclonal antibody or polyclonal antibody of the clostridium difficile toxin B, and a quality control double-antibody IgG coat a nitrate cellulose film (NC film), and a membrane chromatography double antibody sandwich method is adopted to detect the clostridium difficile toxins A and B in a specimen in combination with a monoclonal antibody of colloidal gold labeled clostridium difficile toxins A and B. The test strip is simple in operation, convenient, and fast, and has the advantages of no requirements of special instruments and special training, clear and identified result, and easy popularization. The test strip is suitable for base course, site detection and epidemiological investigation, and has auxiliary effect on the diagnosis of clostridium difficile toxin infection.
Owner:辽宁迪浩生物科技有限公司
Healthcare facility disinfecting system
ActiveUS20120100037A1Effective but inexpensive systemReduce the amount requiredLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsEscherichia coliClostridium difficile toxin B
A system and process for disinfecting rooms such as health care facility rooms with an oxygen / ozone mixture is described, which is effective to combat “superbugs” such as Clostridium difficile (C. difficile); E. coli; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE). In preferred embodiments, hydrogen peroxide is additionally used. The system and process is effective to destroy bacteria deposited on surfaces as biofilm, and, accompanied by physical agitation such as jet nozzle outlets, is effective to disinfect carpet, drapery and similar absorbent and porous surfaces.
Owner:DD STEROZONE LLC +1
Method of prevention and treatment of clostridium difficile infection
InactiveUS20140112985A1Improve developmentGrowth inhibitionAntibacterial agentsSurgical needlesClostridial infectionMicroorganism
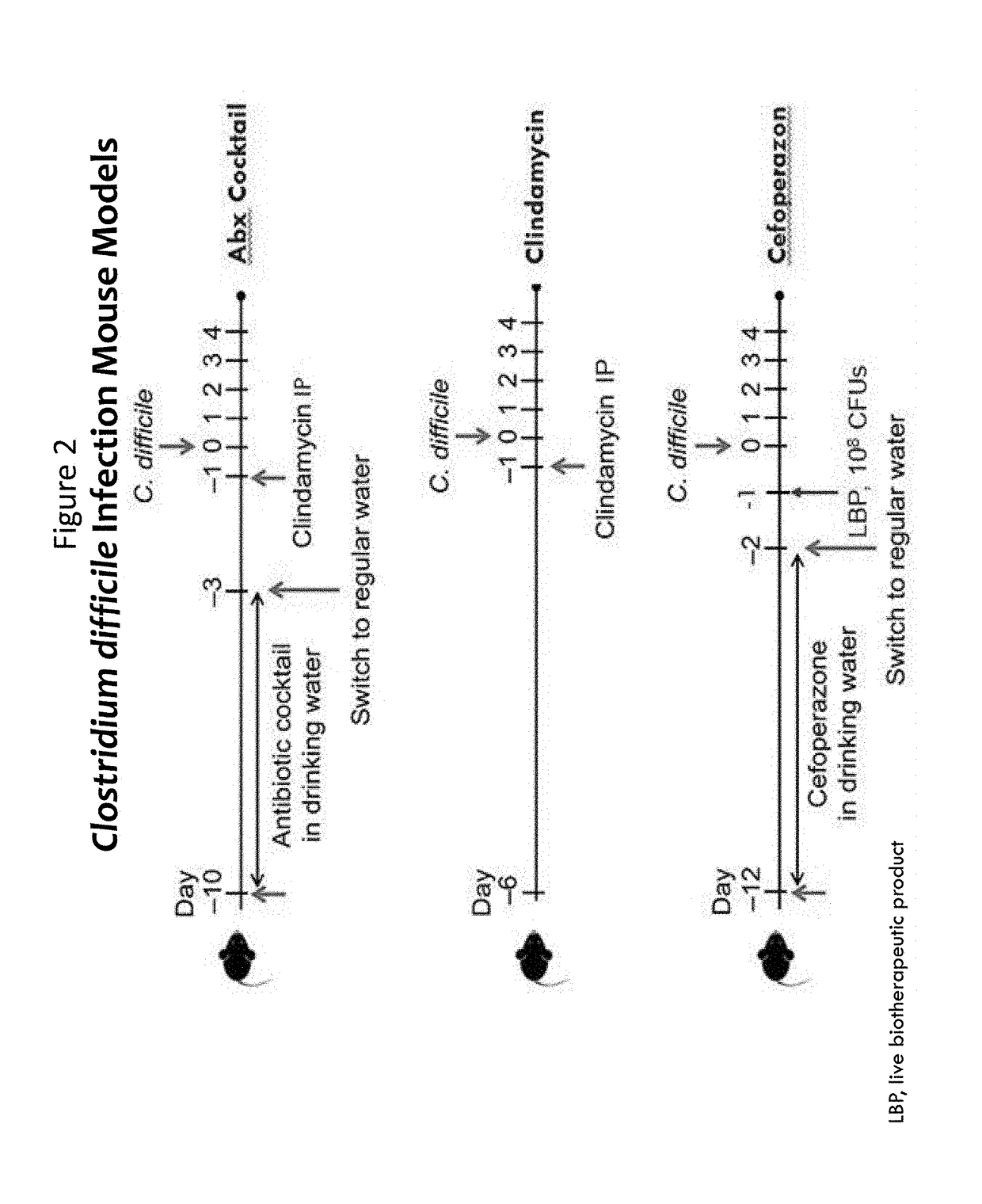
This invention relates to prophylactic and / or therapeutic application of microorganism species that are, for example, administered orally as delayed release formulation designed to release its microbial content to the distal small intestine and / or colon in high quantities and density, which is a “normalized” approach to repopulate the colonic flora as a method of prevention and / or treatment of, for example, Clostridium difficile colitis.
Owner:POLONEZ THERAPEUTICS
Bacterial cells, optimized nucleotide sequences and methods for improved expression of recombinant clostridium difficile toxin b
InactiveUS20120070859A1High expressionSugar derivativesBacteriaBacteroidesClostridium difficile toxin B
In some embodiments, the present invention provides isolated nucleotide sequences that encode Clostridium difficile toxin B, wherein the isolated nucleotide sequences have been optimized for improved expression of the toxin B in a bacterial cell. Other embodiments of the present invention pertain to methods of expressing recombinant Clostridium difficile toxin B in a bacterial cell from the isolated nucleotide sequences of the present invention. In other embodiments, the present invention pertains to bacterial cells that comprise the isolated nucleotide sequences of the present invention. In further embodiments, the invention pertains to isolated peptides of recombinant Clostridium difficile toxin B that were derived from the isolated nucleotide sequences of the present invention.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Treatment of Clostridium difficile infection
Owner:VEDANTA BIOSCIENCES INC
Fluorescence labeling multiplex PCR detection kit for Clostridium difficile
ActiveCN103911430AAccurate typingMicrobiological testing/measurementCapillary electrophoresisClostridium difficile toxin B
The invention provides a fluorescence labeling multiplex PCR detection kit for identification of a Clostridium difficile strain and analysis of toxin genes. The kit comprises 6 pairs of fluorescently-labeled primers used for detecting the Clostridium difficile strain. The 6 pairs of fluorescently-labeled primers comprise specific primers of specific triosephosphate-isomerase (tpi) gene, toxin A gene (tcd A), toxin B gene (tcd B), tcd C gene (tcd C), binary toxin A gene (cdt A) and binary toxin B gene (cdt B) of the Clostridium difficile strain. Amplification results are detected through capillary electrophoresis. Thus, existence of Clostridium difficile can be rapidly identified and toxin typing can be rapidly determined.
Owner:江苏安科华捷生物科技有限公司
Antibodies to Clostridium difficile spores and uses thereof
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Healthcare facility disinfecting system
ActiveUS20140037499A1Safe and effective but inexpensive systemReduce the amount requiredLavatory sanitoryDeodrantsEscherichia coliClostridium difficile toxin B
A system and process for disinfecting rooms such as health care facility rooms with an oxygen / ozone mixture is described, which is effective to combat “superbugs” such as Clostridium difficile (C. difficile); E. coli; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); and vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus (VRE). In preferred embodiments, hydrogen peroxide is additionally used. The system and process is effective to destroy bacteria deposited on surfaces as biofilm, and, accompanied by physical agitation such as jet nozzle outlets, is effective to disinfect carpet, drapery and similar absorbent and porous surfaces.
Owner:STERILIZ3 CANADA INC +1
Dual fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method and detection kit for clostridium difficile enterotoxin A and B
InactiveCN102952886AReduce serious infectionsSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClostridium difficile toxin BBiology
The invention discloses a dual fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method and a detection kit for clostridium difficile enterotoxin A and B. The method comprises the steps that 1) the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a sample to be detected is extracted; 2) the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the sample to be detected is used as a template and is subjected to fluorescence quantitative PCR reaction; 3) the fluorescence of each cyclic product in the PCR reaction is subjected to fluorescence detection, and whether the sample to be detected contains clostridium difficile enterotoxin A and B or not is judged according to the lowest Ct value and the highest fluorescence value in the fluorescence detection. The invention also discloses a specific primer, a fluorescence probe and the detection kit. The dual fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method is simple, convenient and quick to operate, can detect the clostridium difficile enterotoxin A and B simultaneously, is high in detection sensitivity and specificity and can be applicable to the laboratory emergency detection of outburst epidemic caused by clostridium difficile.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG EENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
LAMP detection method for clostridium difficile AB toxins and special primer and kit thereof
InactiveCN104328204AEasy identification of resultsEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseClostridium difficile toxin B
The invention discloses an LAMP detection method for clostridium difficile AB toxins and a special primer and a kit thereof. The LAMP detection method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: designing a primer according to the specific conserved genes tcdA and tcdB of clostridium difficile; then, by taking a genomic DNA of an object to be detected as a template, carrying out LAMP amplification under the guide of the obtained primer; and synchronously and qualitatively detecting toxigenic strains of clostridium difficile in a sample to be detected through the color changes and turbidity changes of a reaction liquid. According to the invention, toxigenic strains of clostridium difficile can be detected in a fast, convenient, synchronous, high efficiency, high specificity and high sensitivity mode under isothermal conditions without using complex instruments, so that a new technical platform is provided for the detection and toxin classification of clostridium difficile, therefore, the LAMP detection method disclosed by the invention can be used for screening and detecting clostridium difficile by grassroots medical health units and various disease prevention and control centers, has a broad market prospect and great economic and social benefits, and is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:NANFANG HOSPITAL OF SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Fusion protein with clostridium difficile toxins A/B and encoding gene and application of fusion protein
ActiveCN103772509AImproved Compositing EffectsReduce difficultyAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin BThiogalactosides
The invention provides a fusion protein with clostridium difficile toxins A / B and an encoding gene and application of the fusion protein. The sequence of the fusion protein with the clostridium difficile toxins A / B is represented by SEQ ID NO:2, and the encoding gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:1. According to the fusion protein, a carrier fragment consisting of a clostridium difficile toxin A carboxyl terminal gene and a prokaryotic expression vector pET32b(+) which are modified through a codon and a fusion gene fragment consisting of a clostridium difficile toxin B carboxyl terminal structure and a flexible chain are obtained through PCR (polymerase chain reaction) multiplication segmentation; the obtained fusion fragment and the obtained carrier are respectively connected in an enzyme recycling manner, so that a recombined expression plasmid pET32b(+)-ToxA-ToxB can be obtained; after the recombined plasmid converts a host BL21(DE3) strain, the recombined plasmid can be subjected to induction expression by IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside) to obtain the fusion protein with the clostridium difficile toxins A / B. According to the fusion protein with the clostridium difficile toxins A / B, the fusion protein with the immunogenicity of the toxins A and B can be obtained, and the difficulty and the cost for researching and producing a CDAD (clostridium difficile associated diarrhea) vaccine can be reduced.
Owner:冯东晓
Kit for detecting clostridium difficile and application thereof
ActiveCN106814189AEfficient detectionIncreased sensitivityBiological material analysisClostridium difficile toxin BPhosphate
The invention discloses an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detection kit for clostridium difficile. The kit comprises the following components: a diluent, confining liquid, a clostridium difficile antibody coated ELISA plate, an ELISA second antibody, a positive reference substance, washing liquid, color developing liquid and stop liquid, wherein every 100ml of diluent contains 1ml of NP-40, 0.5-2ml of Triton X-100, 1g of BSA and 0.05ml of Tween20 phosphate buffer. The invention also discloses an application of the kit in clostridium difficile detection. The kit disclosed by the invention can efficiently detect clostridium difficile and has good application prospects.
Owner:嘉兴实践医学科技有限公司
Establishment of methodology for carrying out joint detection on bacterial genus genes and toxin genes of clostridium difficile by using TaqMan-MGB probe real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology
InactiveCN103215362AImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFecesClostridium difficile toxin B
A TaqMan / MGB probe PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology can carry out bacterial genus identification on clostridium difficile in fecal genomes, simultaneously detect the carrying situation of toxin genes, and can judge whether a toxin A has deletion. A fecal specimen is not required to be purely cultured, and the strain identification and the toxin detection are completed in a reaction system. The method has the characteristics of simple operation, good repeatability, high flux detection specimens, short report time, and the like, and is applicable to the screening of pathogenesis of patients with diarrhea caused by clinically unexplained causes. The invention solves the technical problems that fecal specimens can be subjected to strain identification and strain toxin carrying situation screening simultaneously without being purely cultured, and a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) detection method for fecal genomes, which is high in sensibility, is provided. Because traditional anaerobic culture is uneasy to perform, and an enzyme immunoassay has methodology defects, according to the invention, the diagnosis rate of clostridium difficile associated diarrhea is significantly increased. Meanwhile, the invention also can be applied to the monitoring of drug used in the process of treating the diseases.
Owner:AEROSPACE CENT HOSPITAL
Fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit for clostridium difficile toxin A/B and detection method
InactiveCN105525023AImprove responseOptimizationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationClostridial toxinClostridium difficile infections
The invention discloses a fluorescent quantitative PCR detection kit for clostridium difficile toxin A / B by adopting a probe method, and a detection method, which can detect clostridium difficile and also can detect and quantify toxin A and B genes. The detection kit mainly comprises specific primers and probes, wherein the specific primers and the probes are composed of primer pairs for detecting clostridium difficile, primer pairs and probes for detecting clostridium difficile toxin A, as well as primer pairs and probes for detecting clostridium difficile toxin B. According to the detection kit and the detection method, the operation is simple, the report time is short, the clostridium difficile strains can be specifically, sensitively and accurately identified for the first time, and the key toxins A and B of clostridium difficile are detected and quantified. A foundation is laid for the early diagnosis for clostridium difficile infection, and the detection kit and the detection method are suitable for screening causes of diarrhea patients with unknown causes clinically.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SAGENE BIOTECH
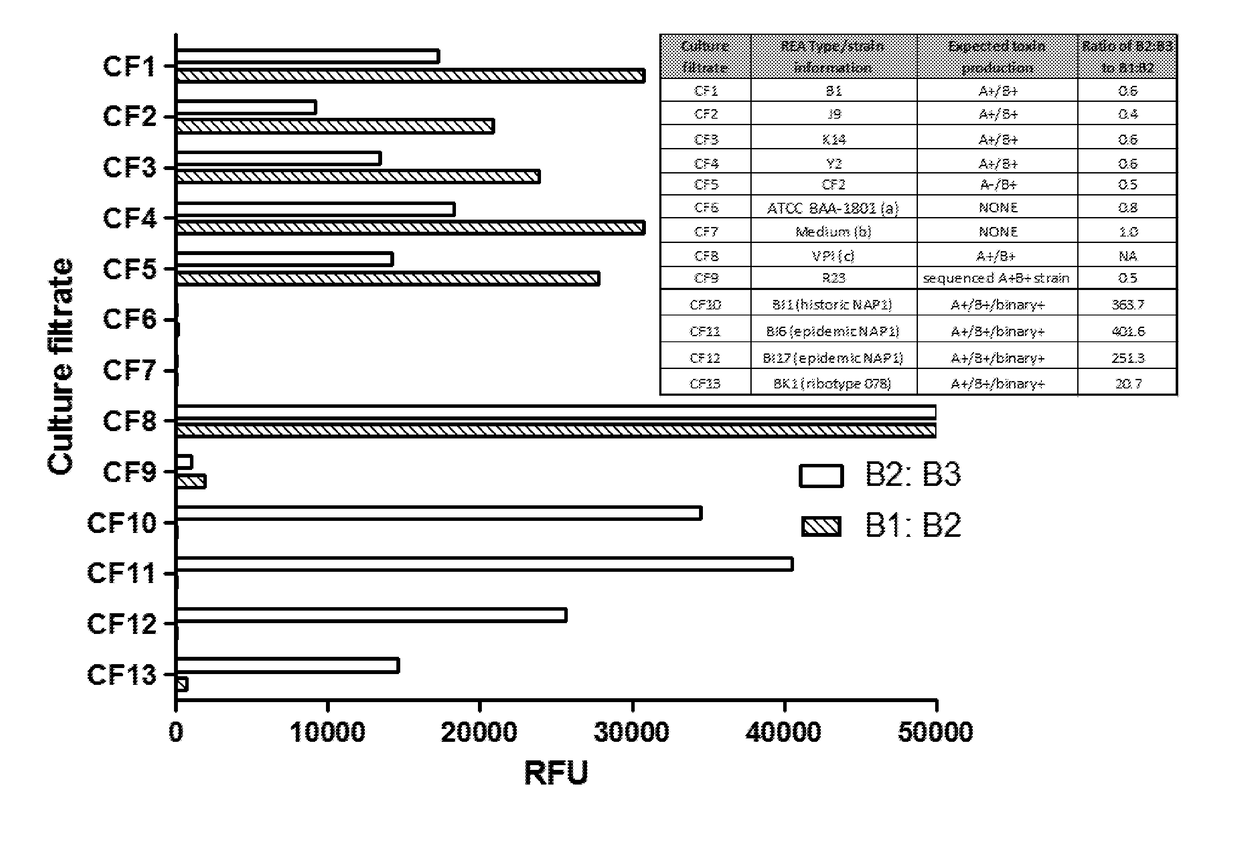
Human Antibodies to Clostridium difficile Toxins
ActiveUS20130230531A1Reduce severityReduce recurrenceAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemClostridium difficile toxin BClostridium difficile infections
The present invention provides fully human antibodies that bind to either toxin A or toxin B of Clostridium difficile, or to both toxin A and toxin B, compositions comprising the antibodies and methods of use. The antibodies of the invention are useful for neutralizing the toxins from C. difficile, thus providing a means of treating the disease and symptoms associated with a C. difficile infection, including the treatment of diarrhea, or pseudomembranous colitis caused by C. difficile. The antibodies may also prevent the severity and / or duration of the primary disease, or may prevent the number, duration, and / or the severity of recurrences, or relapses of the disease attributed to the presence of C. difficile. The antibodies of the invention may also be useful for diagnosis of an infection by C. difficile.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
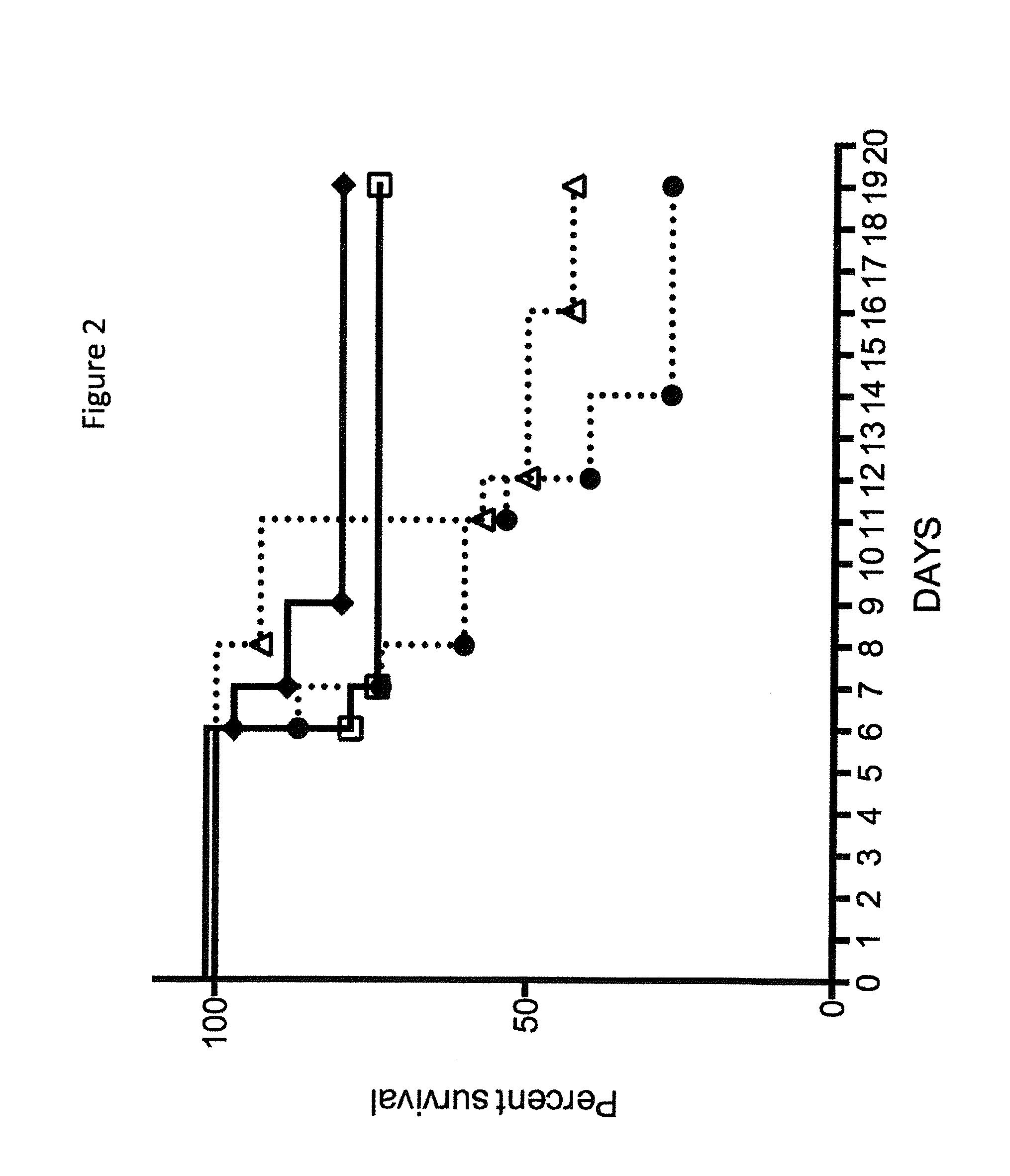
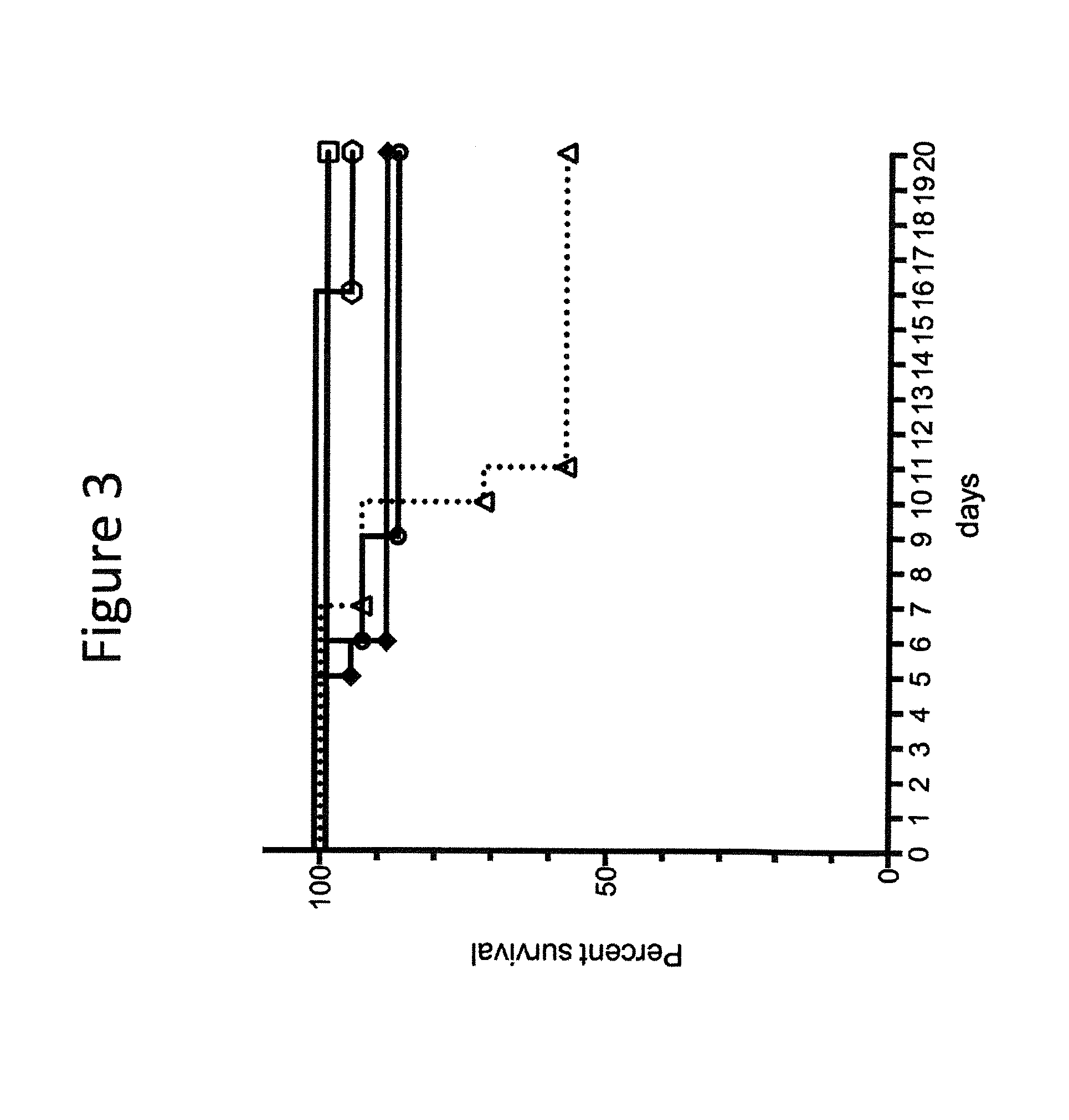
New application of thiopeptcin
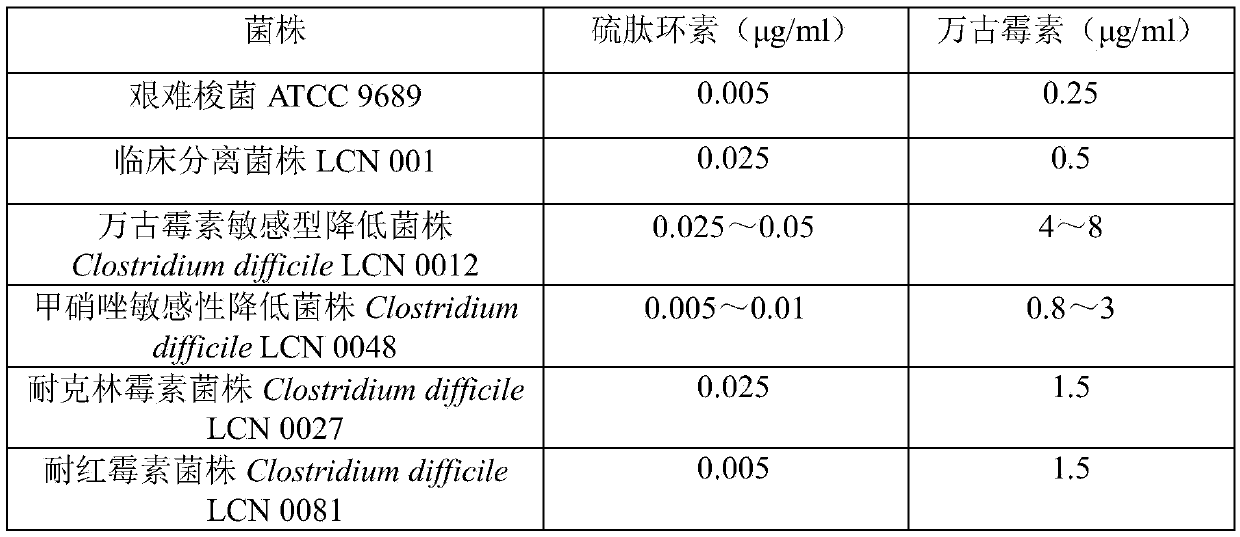
ActiveCN105363018AUnique structureNew mechanism of actionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryClostridial infectionDisease
The invention discloses new application of thiopeptcin to preparation of medicine for treating diseases caused by clostridium difficile infection and complications of the diseases. The thiopeptcin has evident activity on the clostridium difficile and the drug-resistant strains of the clostridium difficile and has great clinical application significance. In-vivo tests prove that the thiopeptcin does not enter blood circulation when a patient takes the thiopeptcin orally. According to the features of intestinal administration, the invention further provides a thiopeptcin orally-taken preparation containing a safe and effective dose and a preparing method of the thiopeptcin orally-taken preparation.
Owner:NANJING BIOTICA PHARMA
Fusion protein and application thereof to treating clostridium difficile related diseases
The invention discloses a fusion protein and application thereof to treating clostridium difficile related diseases. The invention provides a composition composed of clostridium difficile A toxin C-terminal receptor binding domain TcdA, a clostridium difficile B toxin C-terminal receptor binding domain TcdB, a clostridium difficile spore antigen BclA3 and clostridium difficile adhesion molecules CD0873. Experiments prove that the composition immunizes mice and has good immunogenicity, and antiserum of the composition has good neutralization activity on toxin, and the composition can remarkably reduce colonization of clostridium difficile in intestinal tracts and can protect survival of the mice in clostridium difficile infection.
Owner:MICROBE EPIDEMIC DISEASE INST OF PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Method of inhibiting clostridium difficile by administration of oritavancin
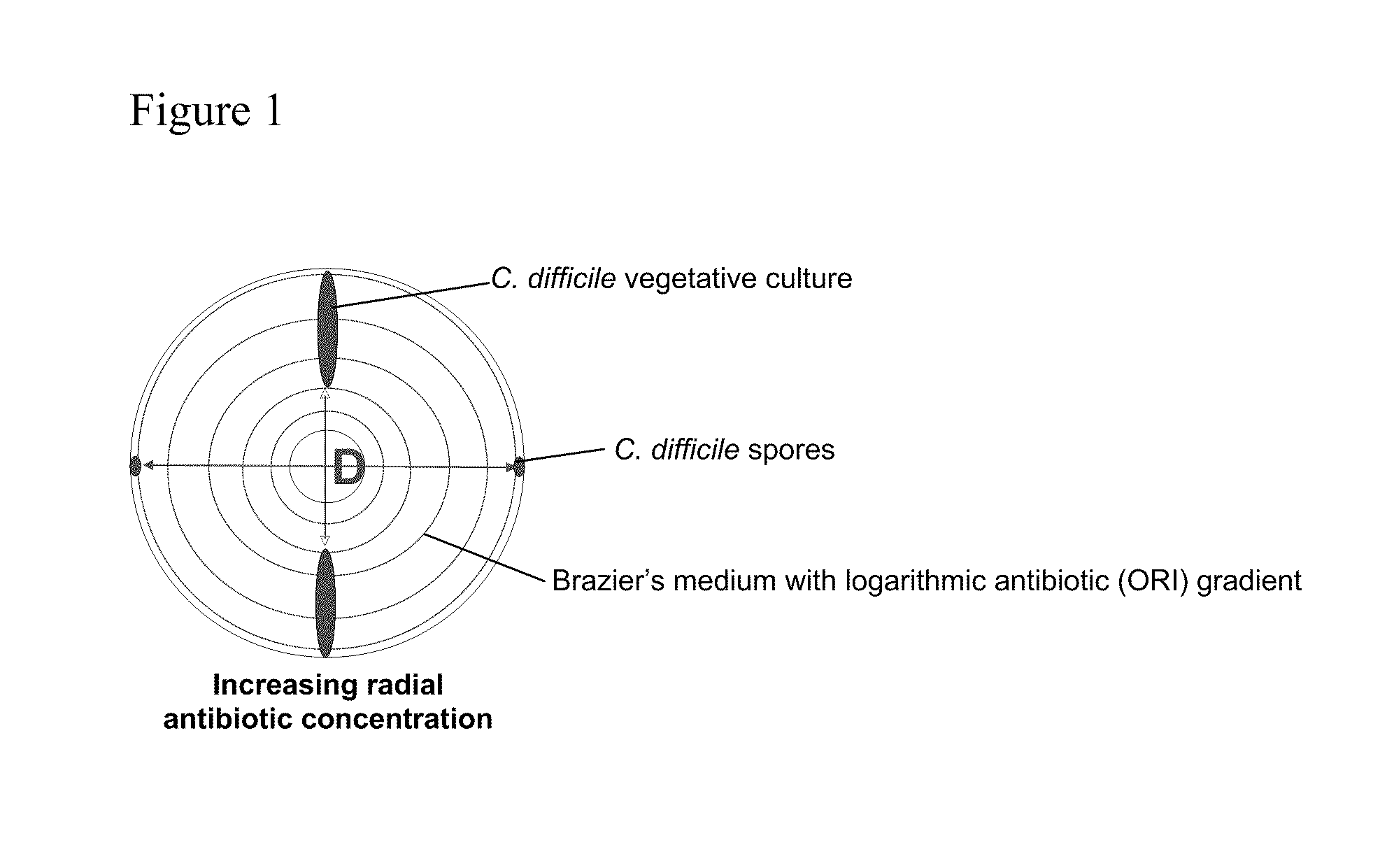
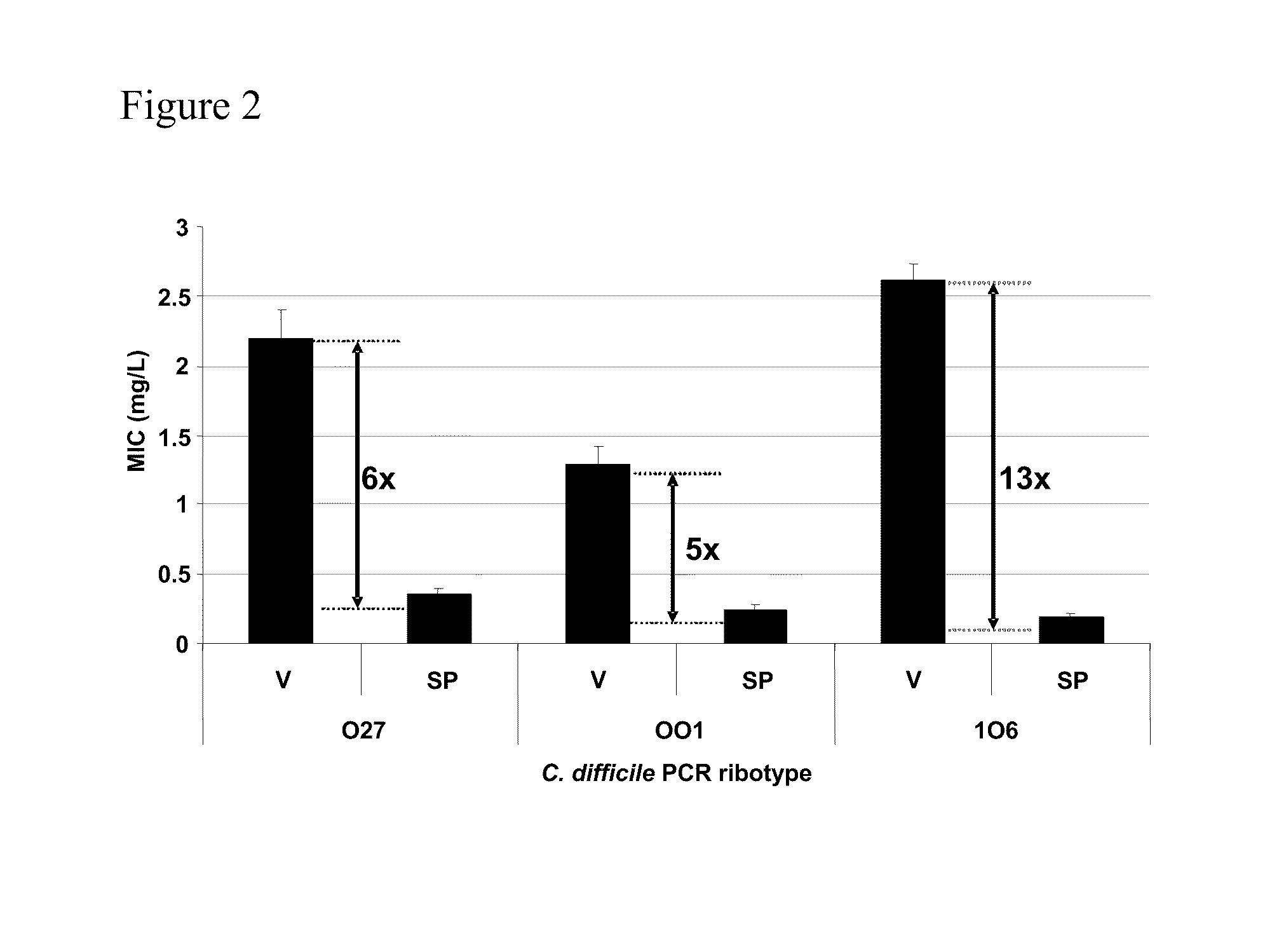
Glycopeptide antibiotics, such as oritavancin, demonstrate significant activity against both a vegetative form of C. difficile and C. difficile spores. Methods for the treatment, prophylaxis and prevention of C. difficile infection and disease in animals, including humans, are described.
Owner:MELINTA THERAPEUTICS
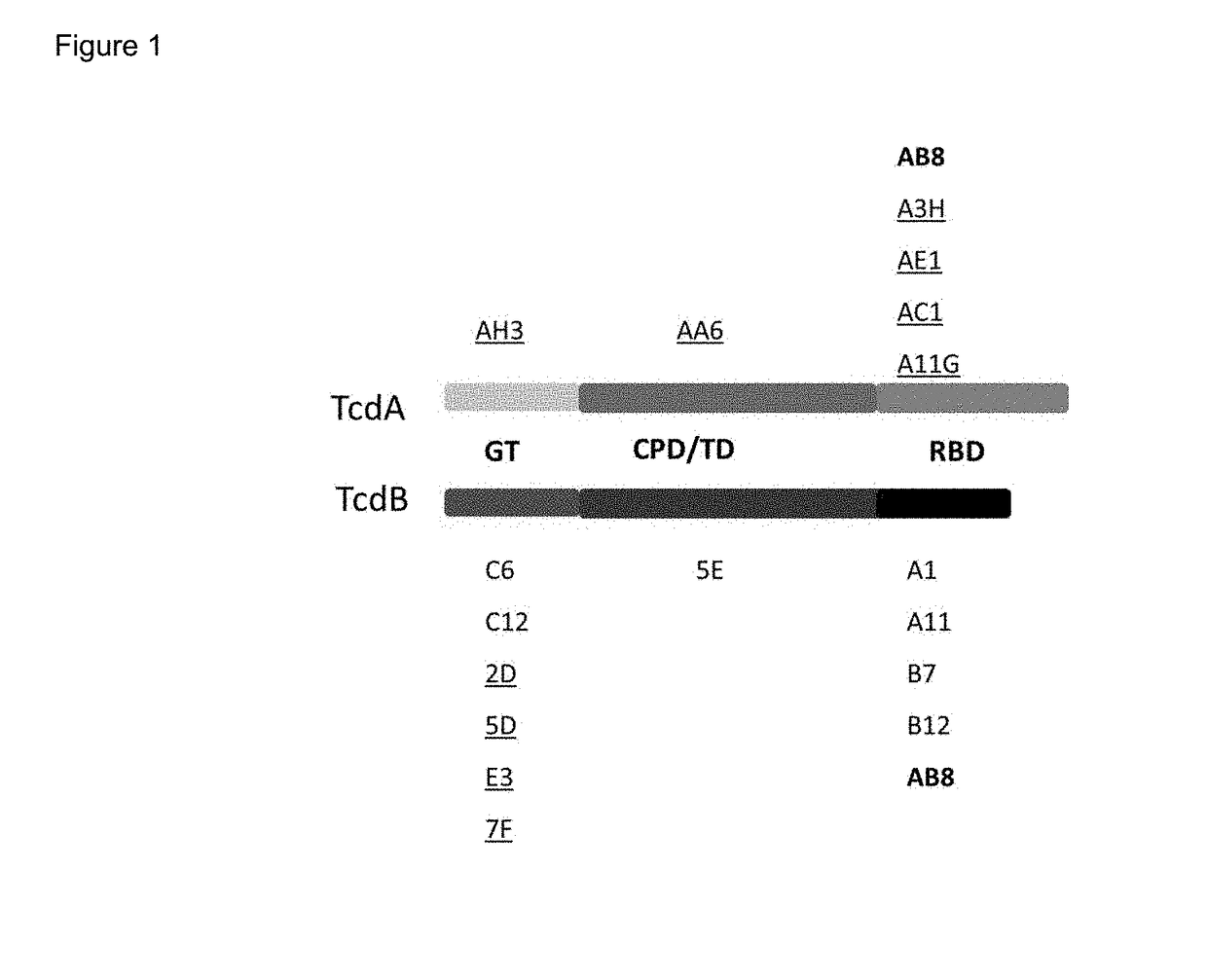
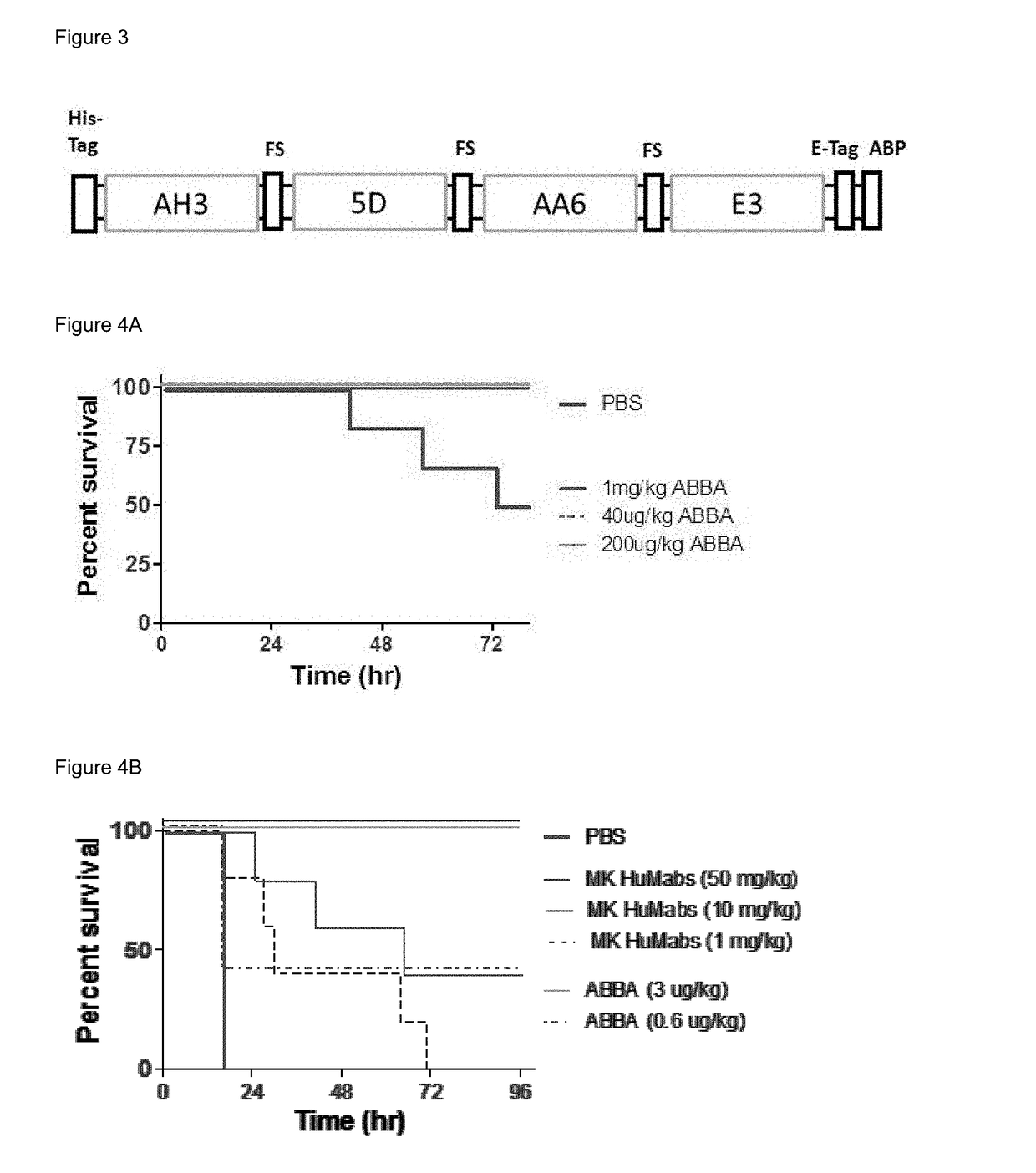
Tetra-specific, octameric binding agents and antibodies against clostridium difficile toxin a and toxin b for treatment of c. difficile infection
ActiveUS20180244760A1Promote cloningEasy to produceAntibacterial agentsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsClostridial toxinClostridium difficile toxin B
Novel, antibody-based binding agents derived from human and camelid immunoglobulins are described. These binding agents recognize and bind with specificity to Clostridium difficile toxin A and / or toxin B and in some cases exhibit toxin neutralizing activity. These binding agents can be used to treat or prevent primary and recurrent CDI. The binding agents include camelid VHH peptide monomers, linked groups of VHH peptide monomers, VHH peptide monomers joined to antibody Fc domains, and VHH peptide monomers joined to IgG antibodies.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Immunoassays for differential detection of clostridium difficile
ActiveUS20180037614A1Immunoglobulins against bacteriaBiological material analysisClostridium difficile toxin BClostridium difficile (bacteria)
Ultrasensitive and quantitative assays for detecting toxins of Clostridium difficile, which may involve digital ELISA, are provided. Also provided herein are differential detection assays that allow for distinguishing toxin B of highly virulent Clostridium difficile strains from toxin B of less virulent strains.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
Identification method of ST37 type clostridium difficile and unit point variation type ST81 thereof
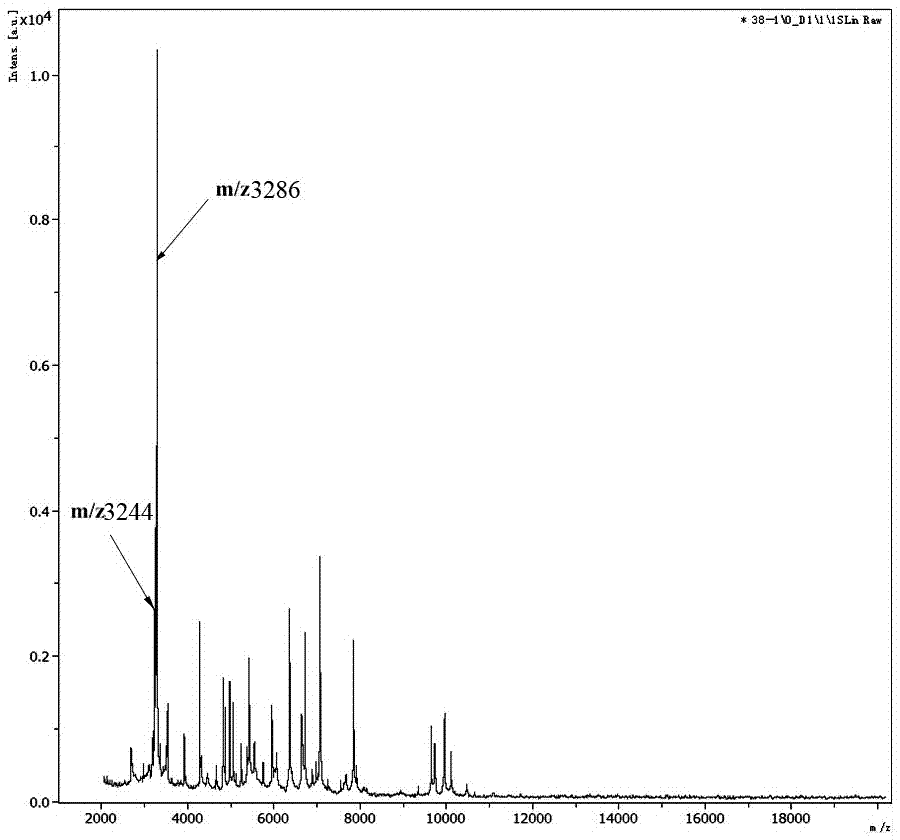
InactiveCN107202834ARapid diagnosisTimely clinical medication guidanceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDiseaseClostridium difficile toxin B
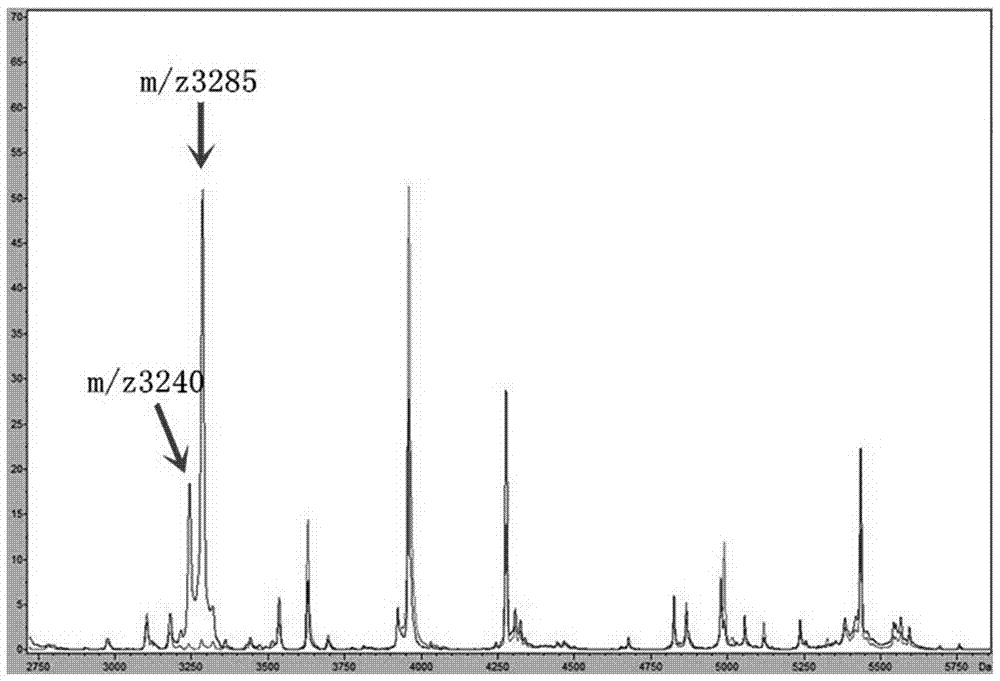
The invention provides an identification method of ST37 type clostridium difficile and unit point variation type ST81 thereof. The identification method comprises the following steps: protein in a clostridium difficile strain to be identified is extracted to obtain a mass spectrometric text sample; and mass spectrometric detection equipment is utilized to detect the sample, and strains with specific protein peaks at m / z 3235-3245 and m / z 3280-3290 in an obtained mass spectrogram are the ST37 type clostridium difficile or the unit point variation type ST81 thereof. The invention establishes an MALDI-TOF MS-based rapid identification method of the ST37 type clostridium difficile and the unit point variation type ST81 thereof for the first time. The method has the characteristics of real time and rapidness, can screen the ST37 type clostridium difficile and the unit point variation type ST81 thereof in real time while identifying the strains, only needs to add 1min for the detection process of ST37 or ST81 type on the basis of strain identification without other special instruments or equipment or additional operation steps and has important significance on rapidly diagnosing diseases and timely providing clinical medication guidance.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF HEBEI MEDICAL UNIV
Bacterial cells, optimized nucleotide sequences and methods for improved expression of recombinant Clostridium difficile toxin B
In some embodiments, the present invention provides isolated nucleotide sequences that encode Clostridium difficile toxin B, wherein the isolated nucleotide sequences have been optimized for improved expression of the toxin B in a bacterial cell. Other embodiments of the present invention pertain to methods of expressing recombinant Clostridium difficile toxin B in a bacterial cell from the isolated nucleotide sequences of the present invention. In other embodiments, the present invention pertains to bacterial cells that comprise the isolated nucleotide sequences of the present invention. In further embodiments, the invention pertains to isolated peptides of recombinant Clostridium difficile toxin B that were derived from the isolated nucleotide sequences of the present invention.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Immunogenic proteins against clostridium difficile
ActiveUS20180344834A1Antibacterial agentsPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifClostridial infectionClostridium difficile toxin B
Described are immunogenic proteins against Clostridium difficile. Also described are compositions comprising the immunogenic proteins. Further described are methods of preventing or treating a Clostridium difficile infection in a subject in need thereof.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com