Patents
Literature
129 results about "Thiogalactosides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Production method for C8:0/C10:0/C12:0/C14:0 medium-chain fatty acid and ethyl ester thereof
InactiveCN102586350AImprove low temperature performanceSimple extraction processMicroorganism based processesFermentationCupheaThiogalactosides
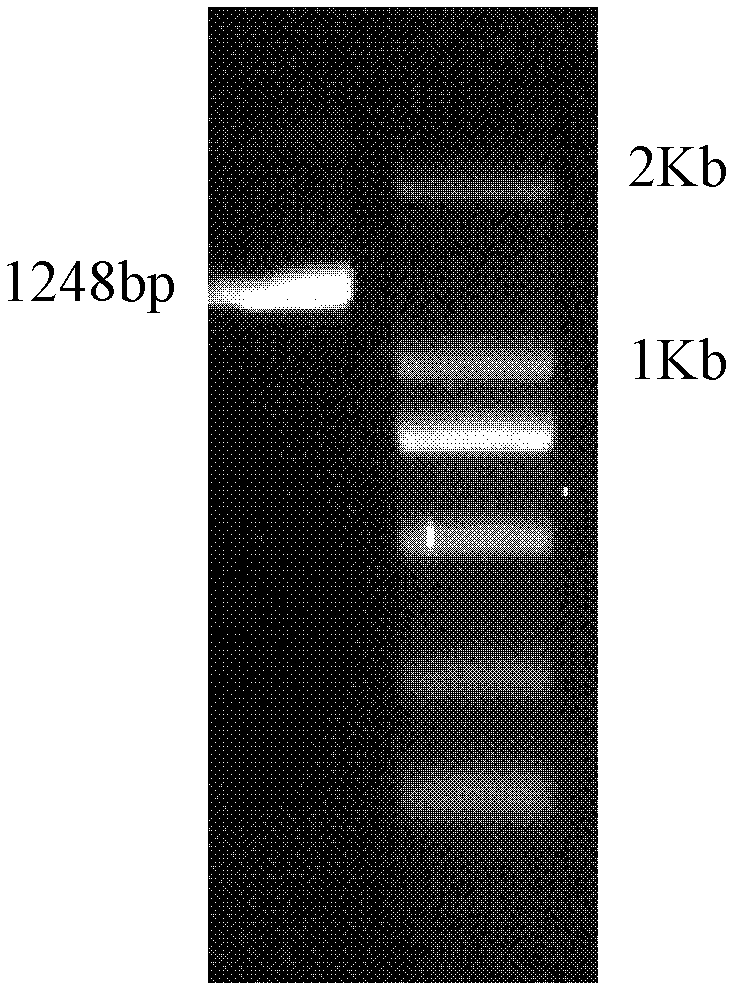
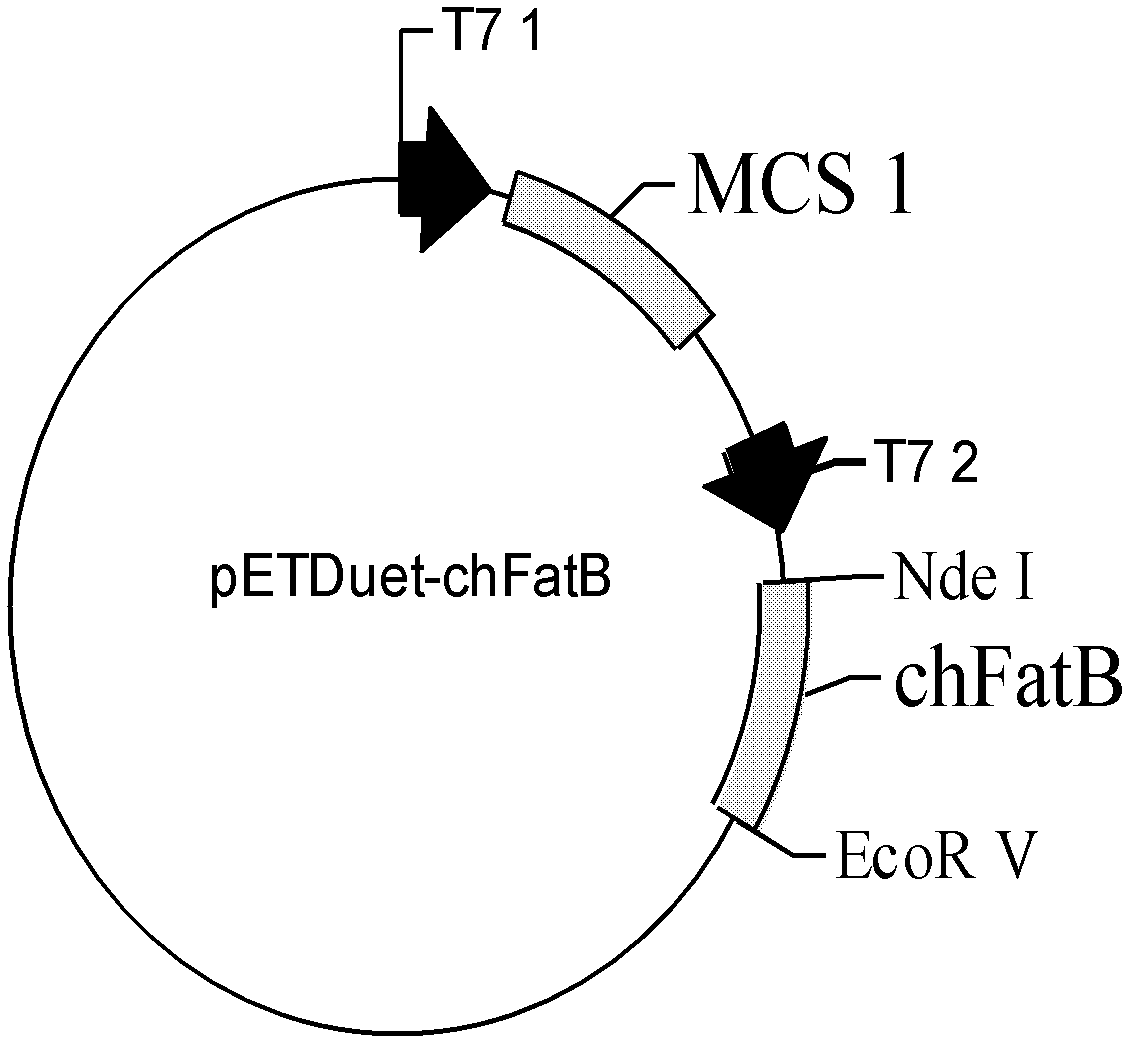
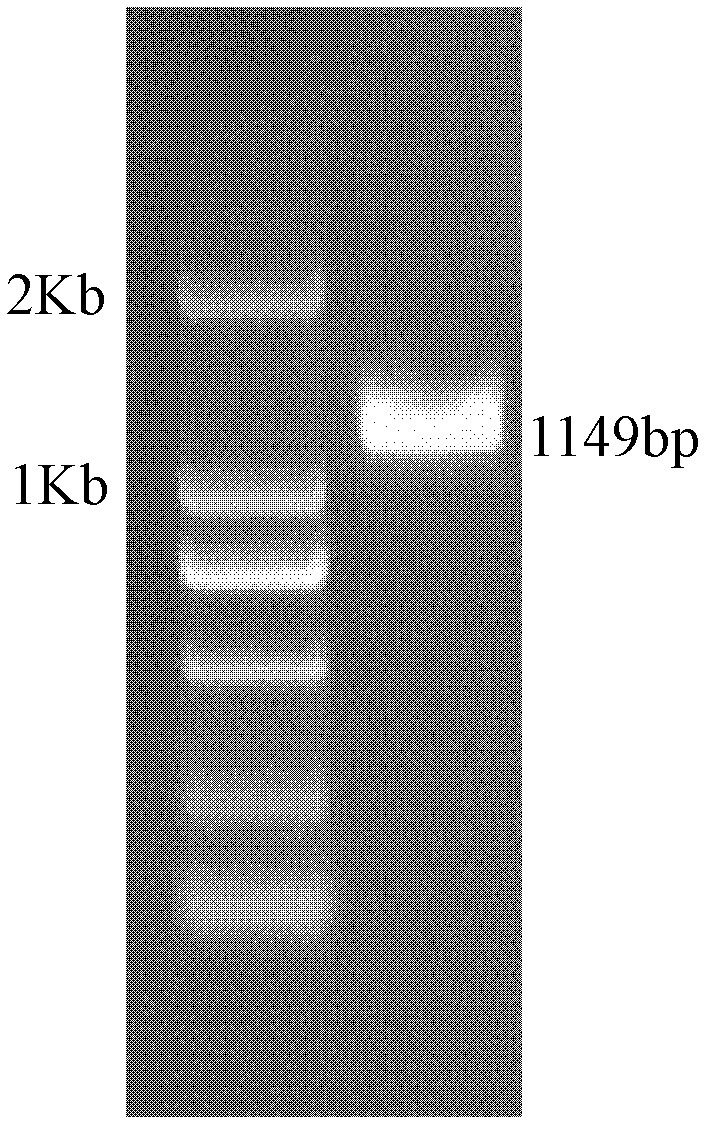
The invention relates to a production method for synthesizing C8:0 / C10:0 / C12:0 / C14:0 medium-chain fatty acid and ethyl ester thereof by using engineering Escherichia coli. The production method comprises the following steps of: cloning thioesterase genes with different specificities chFatB / ucFatB / ccFatB in cuphea / laurel / camphorwood into an expression vector pETDuet-1 to obtain a corresponding recombinant plasmid; transferring the recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli BL21, performing isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside (IPDT) induction expression, and specifically hydrolyzing acyl carrier protein (ACP) with specific chain length by using the expressed thioesterase to obtain medium-chain fatty acid; cloning acyltransferase gene (atfA) in acinetobacter into expression vectors pETDuet-chFatB / pETDuet-ucFatB / pETDuet-ccFatB to obtain corresponding recombinant plasmids; and transferring the recombinant plasmids into the Escherichia coli BL21, performing IPTG induction expression, performing acyl transfer reaction on exogenously fed ethanol and acyl-CoA formed by the medium-chain fatty acid intracellularly by using the co-expressed acyltransferase to obtain fatty acid ethyl ester.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Recombinant antigen protein for diagnosing echinococcosis granulosa as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102863524AIncreased sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingAntigenThiogalactosides
The invention discloses a recombinant antigen protein (of which the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1) for diagnosing echinococcosis granulose. Moreover, the invention further discloses a preparation method of the recombinant antigen protein. The method comprises the following steps of: amplifying an EgENO gene by adopting RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction); cloning the EgENO gene into an expression vector PET28a (+) for constructing a recombined plasmid PET28a-EgENO; converting into escherichia coli BL21(DE3); inducing the expression of a recombinant protein through IPTG (Isopropyl-beta-d-Thiogalactoside); and identifying a purified recombinant antigen by using SDS-PAGE (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis) and Western blotting. In addition, the invention further discloses a diagnosis application of the recombinant antigen protein. As proved by an experiment, the recombinant antigen protein has the advantages of high sensitivity, high specificity and the like for the diagnosis of the echinococcosis granulosa, and has a wide application prospect on the aspect of diagnosis of the echinococcosis granulosa.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
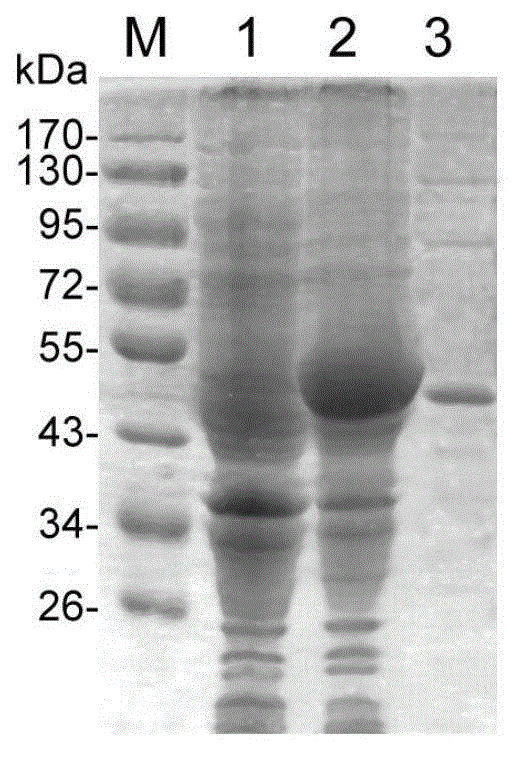
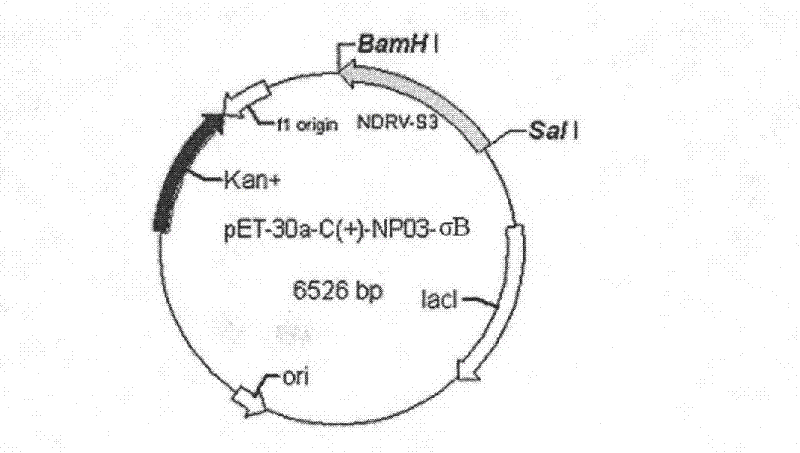
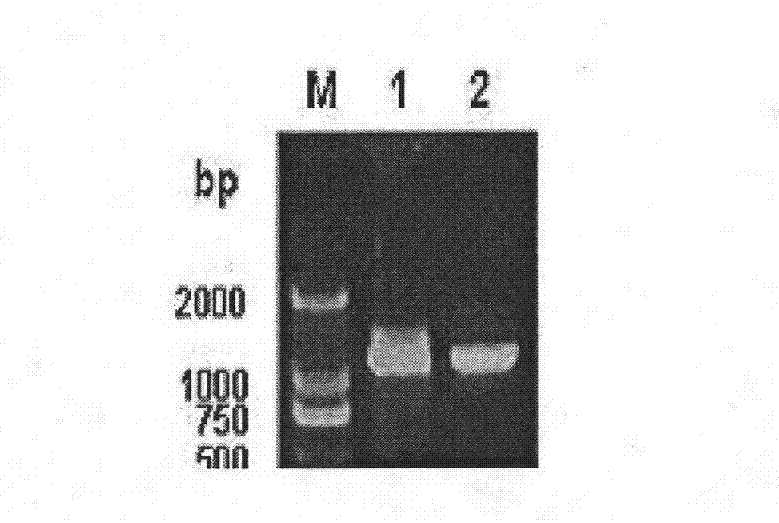
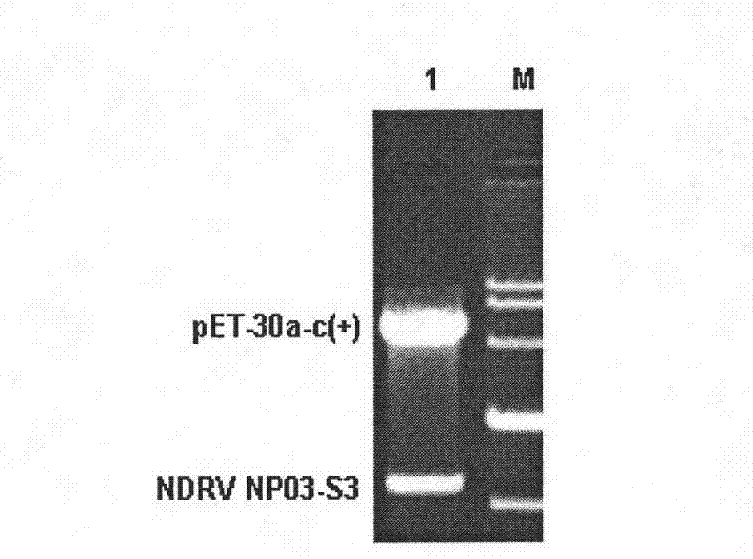
Novel duck reovirus recombinant sigma B protein antigen, preparation method and application
InactiveCN102675469ANo cross reactionHigh detection sensitivityPeptide preparation methodsFermentationInclusion bodiesNucleotide
The invention discloses preparation of novel duck reovirus recombinant sigma B protein antigen, and application of the novel duck reovirus recombinant sigma B protein antigen in detection of a novel duck reovirus antibody. With RNA (ribonucleic acid) of the novel duck reovirus (NDRV) as a template, a nucleotide complete sequence of an NDRV S3 gene coding region can be amplified through a reverse-translation polymerase-chain reaction, is directionally subcloned to a fusion expression vector of the prokaryotic expression vector pET-30a-C(+) of escherichia coli, and transformed into the host cell of the Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3), and is subjected to inducible expression with IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside), purification of Ni-NTA Agarose, inclusion body refolding to obtain the expressed NDRV alpha B recombinant protein antigen. The expression mode of the protein is fusion protein (His-alpha B) with molecular weight being about 44kU; and immunoblotting assays prove that the protein has immunoreactivity similar to natural protein..
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
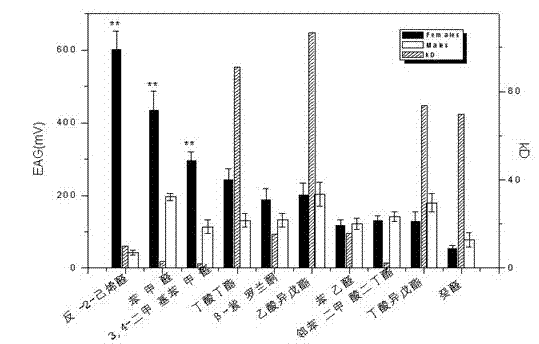
Citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein-based attractant screening method
The invention discloses a citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein-based attractant screening method belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. The citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein-based attractant screening method comprises the following steps of: collecting the total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of antennae of a citrus fruit fly; obtaining the overall length of a citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein through RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction); constructing a prokaryotic expression vector of the citrus fruit fly odorant binding protein; inducing the expression of a citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein through IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside), and purifying the citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein through a nickel sepharose gel affinity column; obtaining a conjugation reaction spectrum of the citrus fruit fly recombinant odorant binding protein and a host fruit odor volatile matter through a competitive fluorescence combing method, wherein a dissociation constant (KD) is lower than below 10 mu mol / L host fruit smell; and the IC 50 value of fluorescence competition is less than 30 mu mol / L, determining a host fruit smell attractant suitable for the citrus fruit fly. The invention provides a new strategy for screening and designing a citrus fruit fly odorant host fruit smell odor information attractant formula.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Genetic engineering bacterial strain for expressing bacillus subtilis laccase in strain cell and method for realizing secreting and expressing laccase in bacterial strain
ActiveCN104593312AGood reference valueImprove abilitiesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThiogalactosidesBacterial strain
The invention discloses a genetic engineering bacterial strain for expressing bacillus subtilis laccase in a strain cell and a method for realizing secreting and expressing laccase in a bacterial strain, and relates to the genetic engineering bacteria strain for expressing bacillus the subtilis laccase in the strain cell and the method for realizing secreting and expressing laccase in the bacterial strain. A preparation method for the genetic engineering bacterial strain comprises the following steps: I, extracting DNA of a bacillus genome and cloning a bacterial laccase gene; and II, constructing a recombinant expression bacterial strain. An inducing method for realizing secreting and expressing recombinant laccase comprises the following steps: I, accessing the engineering bacterial strain into an LB (liquid-phase basicity) culture medium to culture until OD600 is 0.8; and II, adding 0.1 mM of IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside) and 0.1 mM of CuSO4 to culture for 4 hours at 25 DEG C under 120 rpm, and then performing static culture at 30 DEG C. The inducing method provided by the invention can remarkably improve the secretion effects of the recombinant laccase, is simple to operate, and has a high reference value in improving recombinant escherichia coli to secrete laccase.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
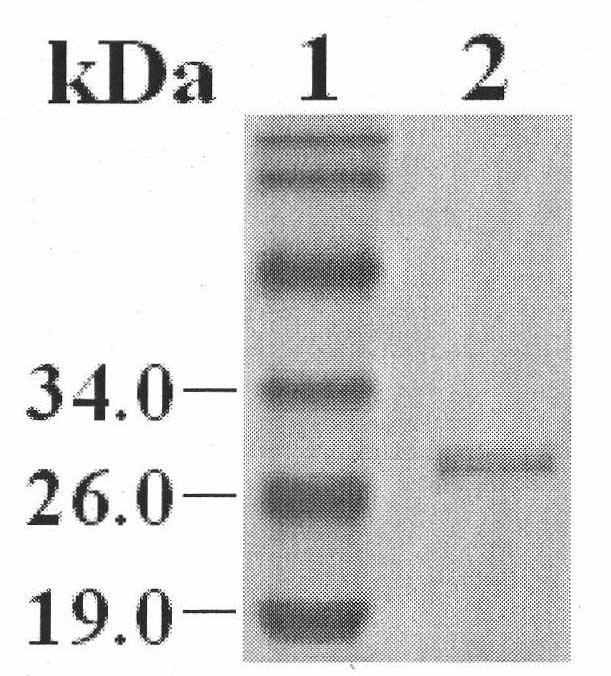
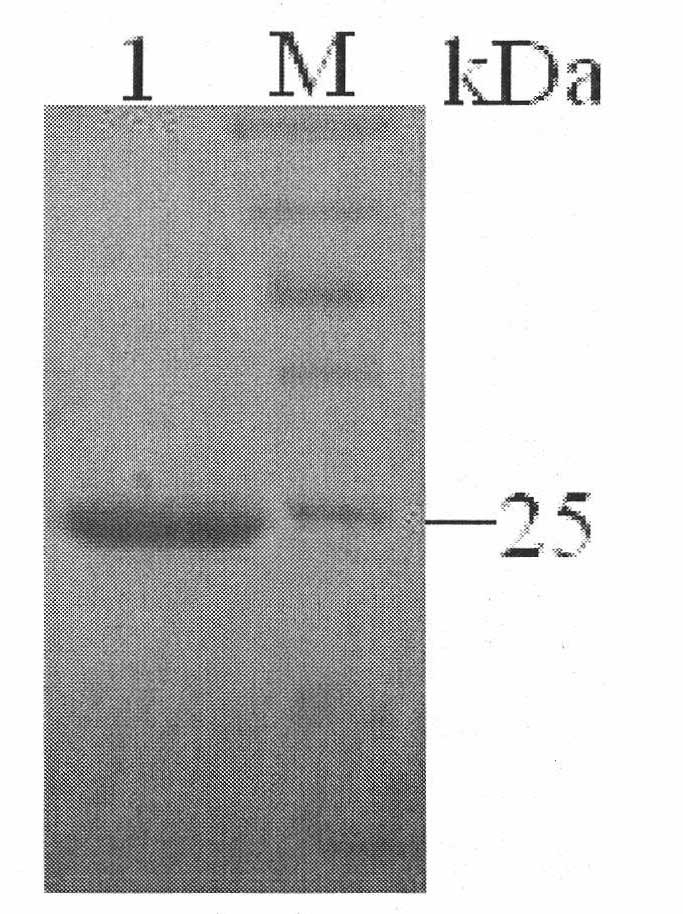
Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli
InactiveCN104212757AEfficient use ofEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThiogalactosidesTheanine
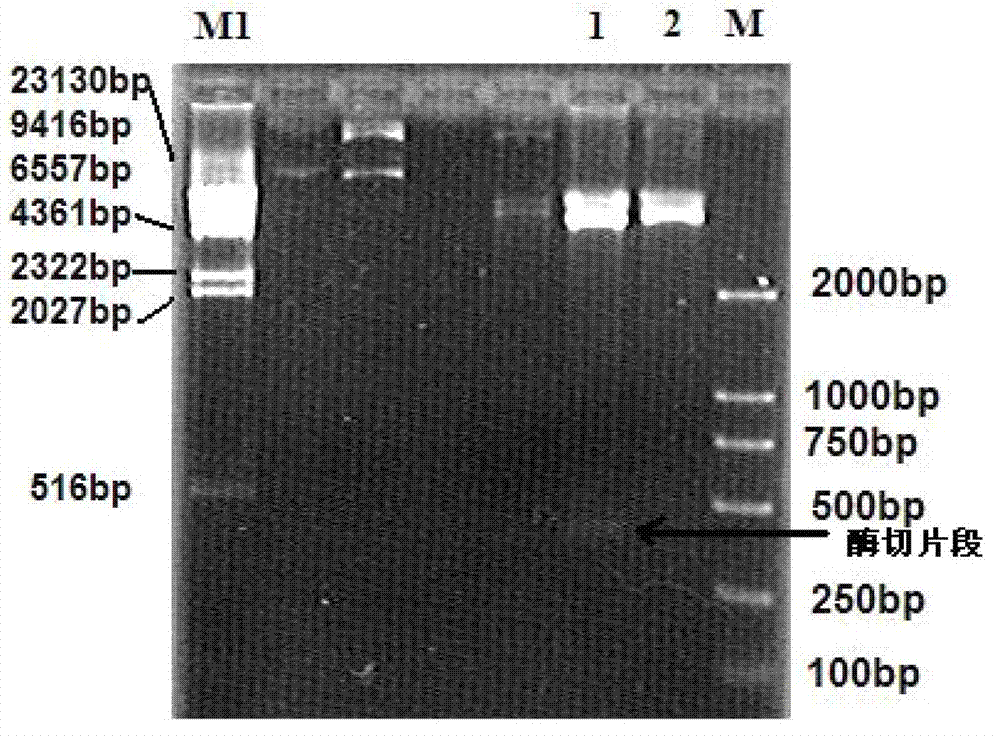
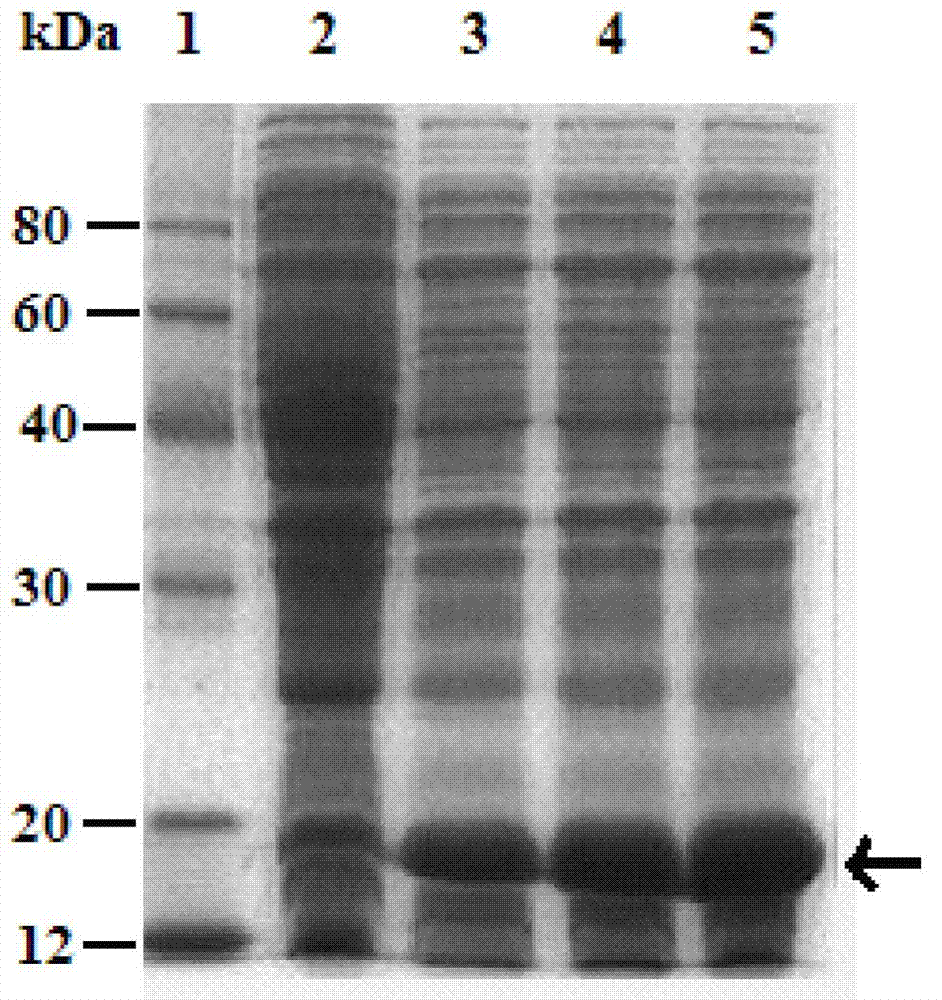
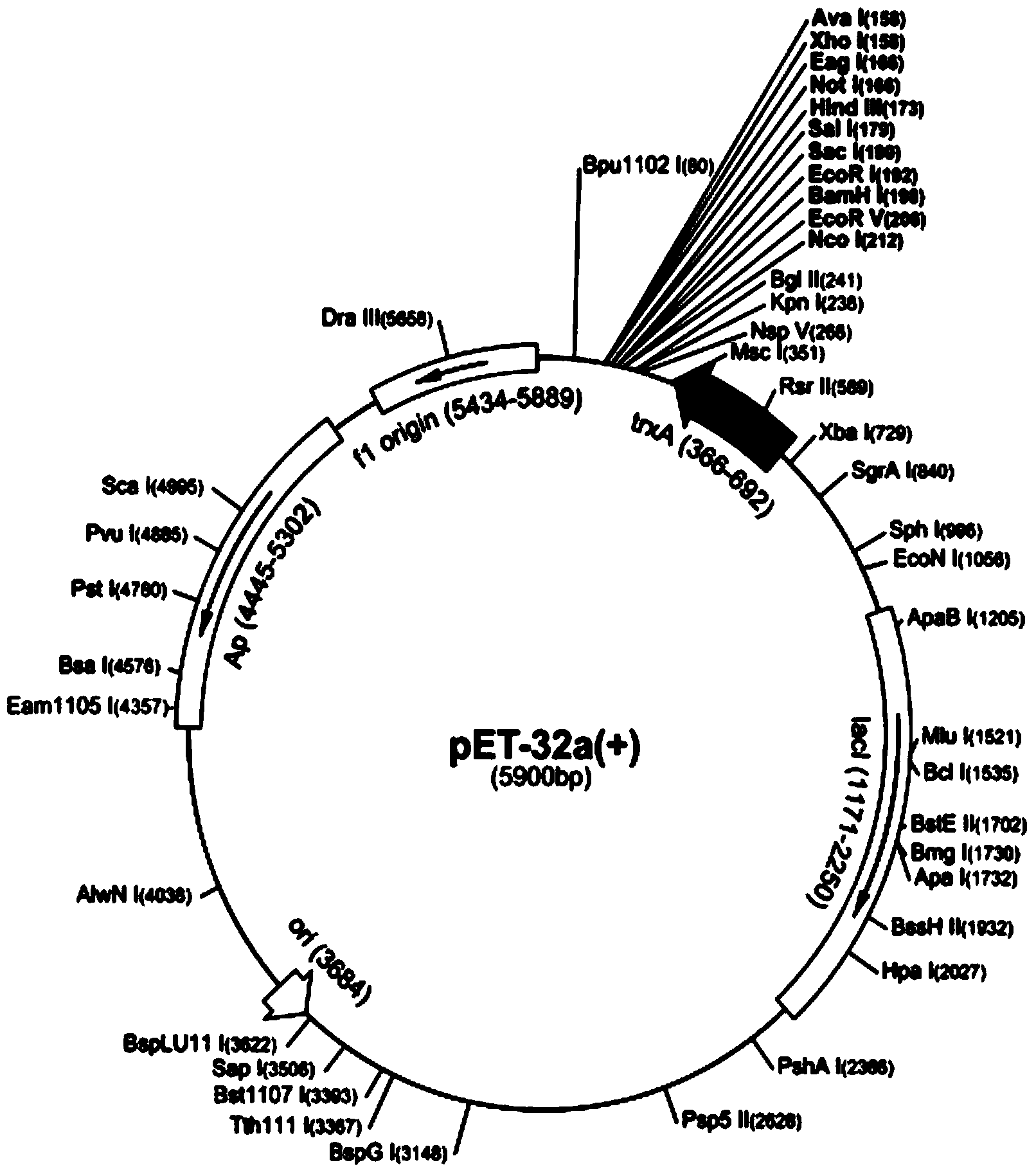
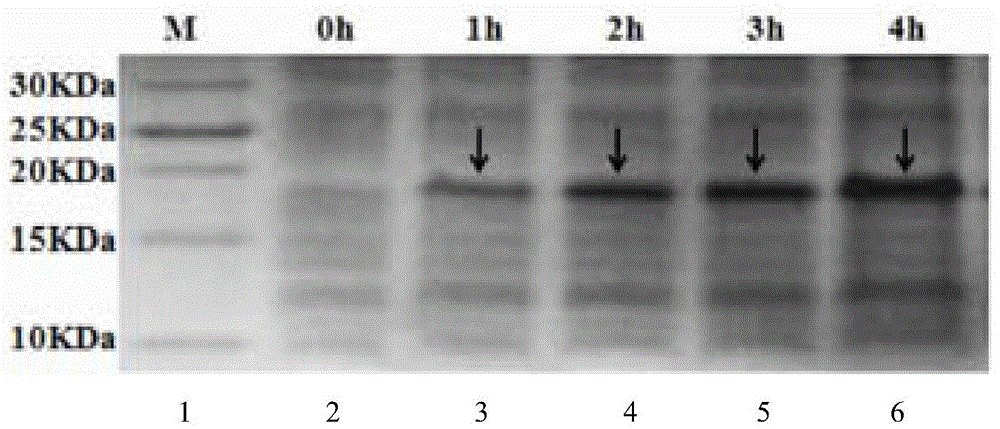
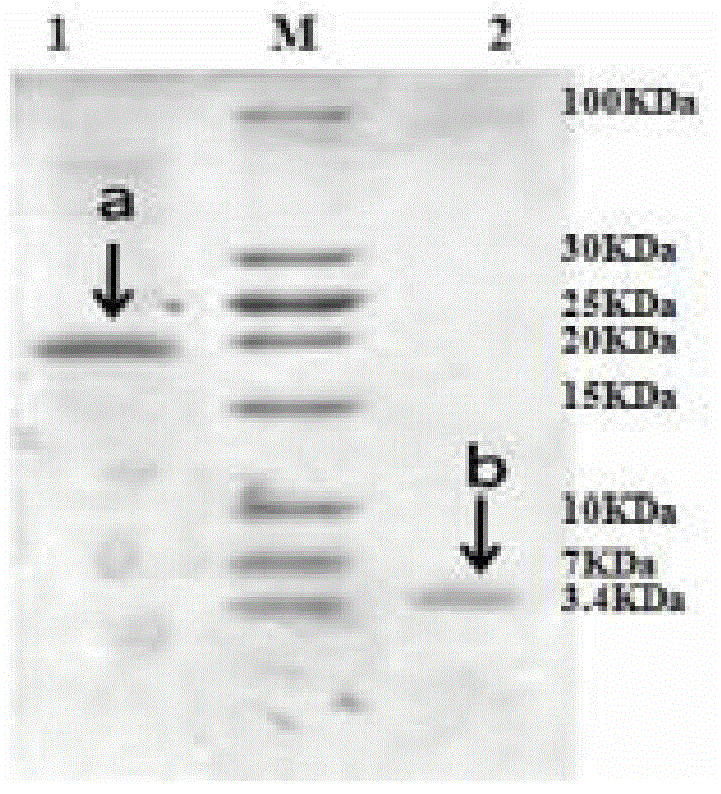
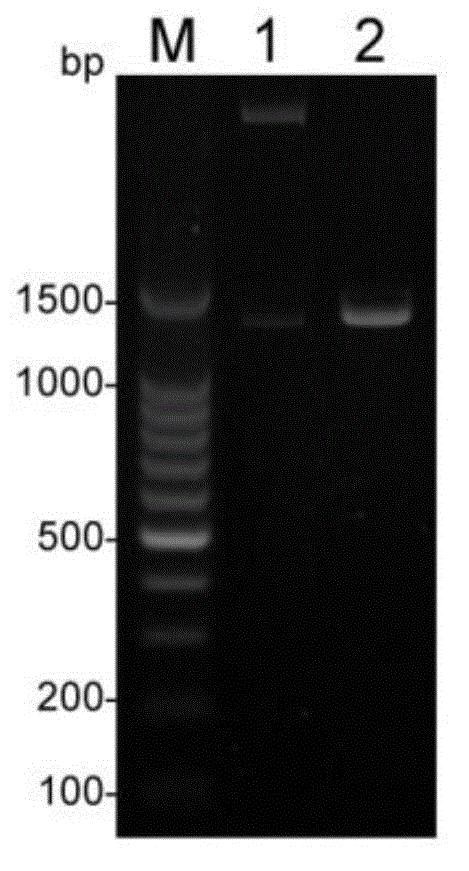
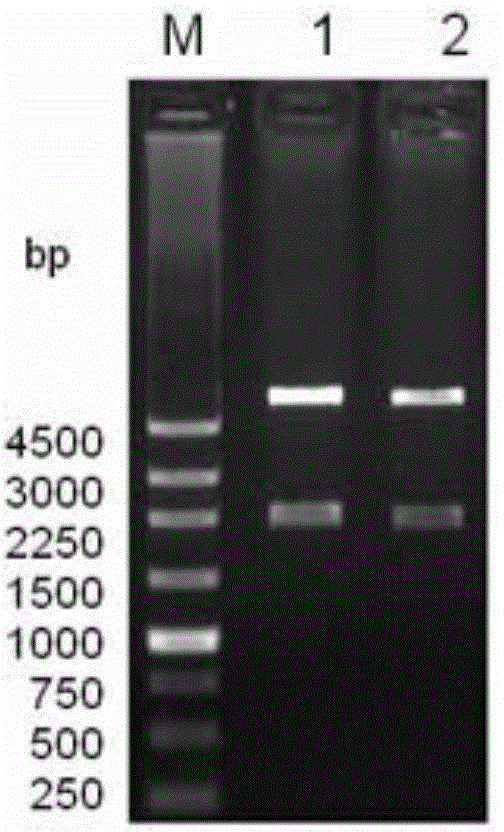
The invention relates to a genetic engineered bacterium which contains a recombinant plasmid pET28a-GMAS, is 6585 bp in a plasmid size, is 1308 bp in a fragment size of a GMAS, is named as Escherichia coli and has a kanapenecilin resistance. Genes of the [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase are inducibly expressed by isopropylsulpho-[beta]-D-galactoside. The genetic engineered bacterium has a capability of biologically synthesizing theanine. By means of glutamic acid and ethylamine as substrates, a method in the invention is simple in operation method, is convenient to control in production, is high in conversion and production efficiency of the theanine and has an excellent industrial application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI KING SHINE BIOLOGY TECH
Method for producing recombinant dermatophagoides farinae allergen Der f1 and Der f2 fusion protein
InactiveCN102676568ARemove completelyHigh purityMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionTotal rnaThiogalactosides
The invention discloses a method for producing recombinant dermatophagoides farinae allergen Der f1 and Der f2 fusion protein and relates to the technical field of construction of dermatophagoides farinae allergen gene by a biological technology. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining a coding gene by extracting the total RNA of the dermatophagoides farinae and adopting PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, cutting glue to recover a product, named as Der fm, cloning to pMD19-T vectors, subcloning to expression vectors pET-28a(+), converting the vectors to escherichia coli, carrying out inducible expression by using IPTG (isopropyl-Beta-d-thiogalactoside). The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the consumed time is short, the process is simple, the cost is lower, the components such as a solvent can be thoroughly removed, the purity of the allergen can be increased fundamentally, the occurrence of side reaction in immunological therapy is avoided, the purity is high, the classification is clear, the accuracy of diagnosis can be increased, and a standard product is expected to be provided for novel immunological therapy.
Owner:崔玉宝 +3
I-group 4-type aviadenovirus genetic engineering subunit vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106344919AGood prospects for commercial developmentLow costViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesSequence analysisInclusion bodies
The invention provides an I-group 4-type aviadenovirus genetic engineering subunit vaccine and a preparation method thereof. According to the technical scheme, the preparation method comprises the following steps: cloning an encoding gene of fibrous protein C-terminal from an I-group 4-type aviadenovirus genome according to a PCR technology and performing sequence analysis; cloning the gene to an expression vector pET-32a, transforming escherichia coli, constructing engineering bacteria, and inducing the engineering bacteria by isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside to express the fibrous protein C-terminal; performing lysis on an engineering bacterial cell, performing centrifugal separation on an inclusion body of the engineering bacterial cell, dissolving urea and diluting for renaturation; preparing the vaccine according to the conventional preparation method of a mineral oil adjuvant inactivated vaccine. According to the I-group 4-type aviadenovirus genetic engineering subunit vaccine prepared by the method, the immune effect of the vaccine is evaluated by a serological method and an immunity challenge method, and the result indicates that the aviadenovirus inactivated vaccine prepared by the method can provide effective immunoprotection and has a good commercialized development prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN RINGPU BIO TECH
Recombinant strain capable of expressing fungal immunomodulatory protein from Flammulina velutipes (FIP-fve), construction method, protein expression and purification method, and protein application
ActiveCN102925403AImprove biological activityIncrease productionBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBiotechnologyPurification methods
The invention relates to recombinant strain capable of expressing fungal immunomodulatory protein from Flammulina velutipes (FIP-fve), a construction method, a protein expression and purification method, and protein application. Existing FIP-fve engineered strains have the disadvantages of low expression rate, expression product of insoluble inclusion body, uncertain structure and broken strain, complex purification process, and non-suitability for large-scale production. The invention adopts FIP-fve gene and Transetta (DE3) as host bacteria to construct recombinant strain; induces expression with isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside (IPTG); treats by combining a lysozyme method and ultrasonic method; and desalts by adopting Ni-His.Band column chromatography and Sephadex G25 gel column chromatography, thereby finishing construction of recombinant strain, expression and purification. The invention is used for preparing drug for preventing or treating allergy. The purification process is simple and rapid, and suitable for large-scale fermentation production.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY HEILONGJIANG ACADEMY OF SCI
General type duck hepatitis A virus antibody ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) detection kit
ActiveCN104087609ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateBiological testingHybrid peptidesDuck hepatitis A virusThiogalactosides
The invention discloses a general type duck hepatitis A virus antibody ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay) detection kit which comprises an ELISA plate coated with DHAV (Duck Hepatitis A Virus)-1VP3-3VP1 recombinant protein. The DHAV-1VP3-3VP1 recombinant protein is obtained through a method which comprises the following steps: respectively amplifying and cloning a DHAV-1VP3 gene and a DHAV-1VP1 gene by taking DHAV-1 and DHAV-3 as materials to obtain recombinant plasmids pMD-1VP3 and pMD-3VP1; then directionally inserting into a pET-32a(+) expression vector in series, and screening to obtain a recombinant expression plasmid pET-1VP3-3VP1; and carrying out ITPG (Isopropyl beta-D-thiogalactoside) inducible expression and purification to obtain the DHAV-1VP3-3VP1 recombinant protein. The general type duck hepatitis A virus antibody ELISA detection kit disclosed by the invention can be used for evaluating the levels of DHAV-1 and DHAV-3 antibodies through primary detection and is low in cost, easy, convenient and fast to operate and suitable for the detection of batch samples.
Owner:POULTRY INST SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
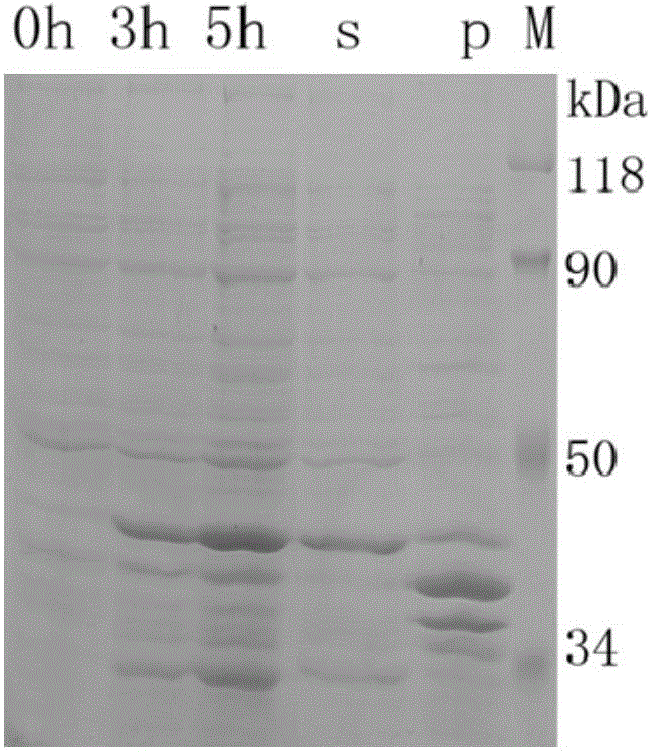
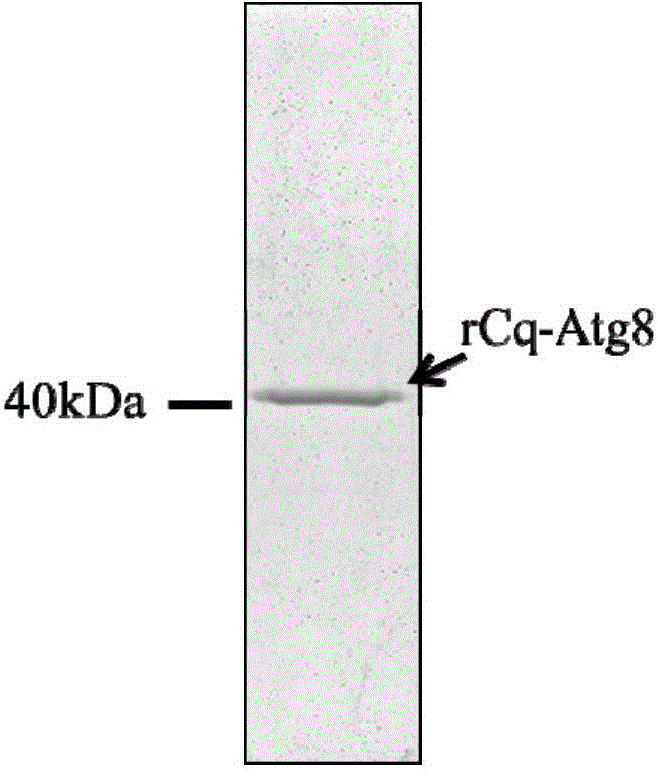
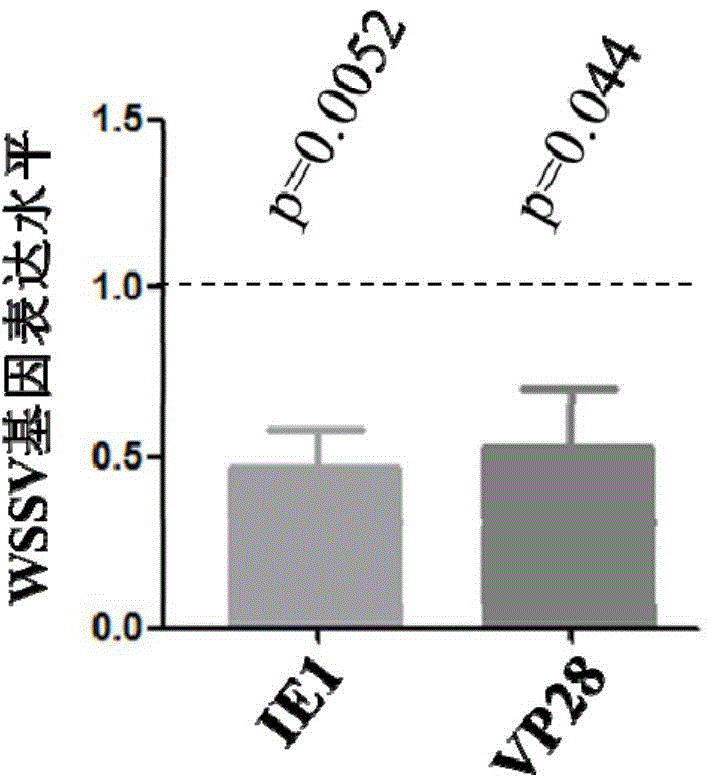
Anti-white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) autophagy associated gene Cq-Atg8 and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104087593AStrong anti-WSSV activityInhibition of infection replicationPeptide/protein ingredientsAnimal feeding stuffThiogalactosidesWhite spot syndrome
The invention relates to an anti-white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) autophagy associated gene Cq-Atg8, and a preparation method and application thereof. The anti-WSSV autophagy associated gene Cq-Atg8 is from C. quadricarinatus and is named Cq-Atg8. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) constructing a Cq-Atg8 pronucleus recombinant expression vector; (2) leading the Cq-Atg8 pronucleus recombinant expression vector obtained in the step (1) into a host cell, and carrying out inducible expression on the host cell by using isopropyl-betad-thiogalactoside (IPTG), so as to obtain an expression product; and (3) separating and purifying the expression product obtained in the step (2) so as to obtain the recombinant protein (rCq-Atg8). The rCq-Atg8 can inhibit infection and duplication of WSSV remarkably, and therefore the rCq-Atg8 can be used in preparation of anti-WSSV medicines and anti-disease feed additives for animals.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for producing 5-glycyl ethylformic acid by using engineering bacterium
InactiveCN101041839AIncrease productionSimple processMicroorganism based processesFermentationAmino-Levulinic AcidThiogalactosides
The invention discloses a method to prepare 5-amino levulinic acid with engineering bacteria, which comprises the following steps: 1) flat-activating engineering bacteria Rosetta(DE3)-pET28a-R.S.hemA with conserve number at CGMCC No.1939 through LB culture medium; 2) seeding the monoclonal on plate into shake flask of LB culture medium; overnight-culturing at 37 deg.c; getting the first grade seed; 3) seeding the first grade seed into shake flask of LB culture medium; getting the second grade seed; 4) seeding the second grade seed into fermentation tank with ferment culture medium; utilizing isopropyl-beta-D-sulfo galactose-glycoside to cool and evoke; culturing effluxion of time continually; proceeding supplement material culture.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Simple and efficient method for preparing and purifying TaqDNA polymerase
InactiveCN102816786ASimple methodReduced Possibility of ContaminationTransferasesFermentationKanamycinCentrifugation
The invention provides a simple and efficient method for preparing and purifying TaqDNA polymerase. The method includes: 1) establishing a TaqDNA polymerase expression vector pET-30aTAQ; 2)converting the TaqDNA polymerase expression vector pET-30aTAQ on a kanamycin low salt LB plate, obtaining a bacterial strain BL21 (DE3) / pEP-30aTAQ; 3) inoculating in a kanamycin low salt LB fluid nutrient medium, and performing shake cultivation until OD600=0.4-0.9; 4) performing isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside (IPTG) induction for 2-24 hours; 5) collecting supernatant of the medium in centrifugal mode; 6) heating the supernatant for 10 minutes at the temperature of 80-100 DEG C, and performing ice-bath for 1 minute at the temperature from 0 DEG C to -20 DEG C; 7) collecting supernatant in centrifugal mode; and 8) freezing enzyme liquid after detection so as to obtain finished enzyme. The simple and efficient method has the advantage that purification is finished through two-step centrifugation and one-step thermal circulation, and the method is simple. The simple and efficient method for preparing and purifying the TaqDNA polymerase omits a bacteria cracking process and subsequent multifarious purification steps of a traditional method, improves purification of the TaqDNA polymerase, reduces pollution, saves preparation cost, shortens production cycle, and can be applied to continuous online immobilized production of the TaqDNA polymerase.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Galectin-3 binding protein, preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102942624AAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsGalectin 3 binding proteinThiogalactosides
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, and in particular to a galectin-3 binding protein, and preparation and application thereof. The galectin-3 binding protein is shown as an amino acid sequence SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence table. The preparation method is as below: using Cynoglossus semilaevis cDNA as a template; conducting PCR amplification by primers F1 and R1; connecting PCR products to an expression vector to obtain a plasmid pETG3BP; conversing BL21DE3 to obtain a transformant BL21 / pETG3BP; inducting by isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside; and purifying the recombinant protein with affinity chromatography column to obtain the galectin-3 binding protein. The galectin-3 binding protein has significant binding ability to various bacteria.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Bacillus subtilis gene engineering strain, construction method thereof and application in lactulose production
ActiveCN105255805AEasy to operateAvoid loss of enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThiogalactosidesBio engineering
The invention discloses a method for producing lactulose by means of a recombinant bacillus subtilis, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering technology. The recombinant bacillus subtilis is used as the production strain, the recombinant bacillus subtilis includes cellobiose epimerase capable of catalyzing lactose for producing the lactulose, and induction expression is performed through the lactose or isopropyl-beta-D-isopropylthiogalactoside (IPTG) so as to use the lactose or whey as a substrate for a biological catalysis reaction. Bacillus subtilis wet cells or a fermentation solution is used for the catalysis reaction, the method is simple and easy to implement, and enzyme activity losses and cost waste in the enzyme separation and purification process are avoided; the food-grade bacillus subtilis is used as the production strain, the method is safe and reliable, and the effective references are provided for industrial and environment-friendly lactulose production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for constructing IL-33 presentation VLP (Virus-Like Particle) vaccine used in active immunotherapy of chronic asthma
ActiveCN104001168AEasy to makeEfficient purificationPeptide/protein ingredientsCarrier-bound antigen/hapten ingredientsDiseaseHepatitis B virus core Antigen
The invention provides a method for constructing an IL-33 presentation VLP (Virus-Like Particle) vaccine used in active immunotherapy of chronic asthma. The method comprises the following steps: extracting IL-33 total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) from a mouse; performing reverse transcription to obtain IL33 total cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid); performing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the obtained total cDNA with a designed specific primer to obtain a coded IL-33 mature segment gene; inserting the gene between 78-bit amino acid and 79-bit amino acid of a hepatitis B virus core antigen HBcAg to obtain a recombinant plasmid pHBcAg33; transferring the plasmid onto escherichia coli DH5alpha or a BL21 competent cell; inducing by using IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside) and purifying to obtain the IL-33 presentation VLP vaccine. A strong neutralizing antibody which is specific to own molecules and has a durable action can be induced by inoculating the vaccine repeatedly in order to regulate and control immune response, thereby fulfilling the aim of regulating and controlling the progress of asthma.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
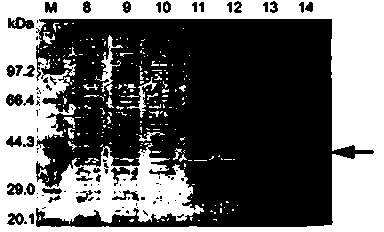
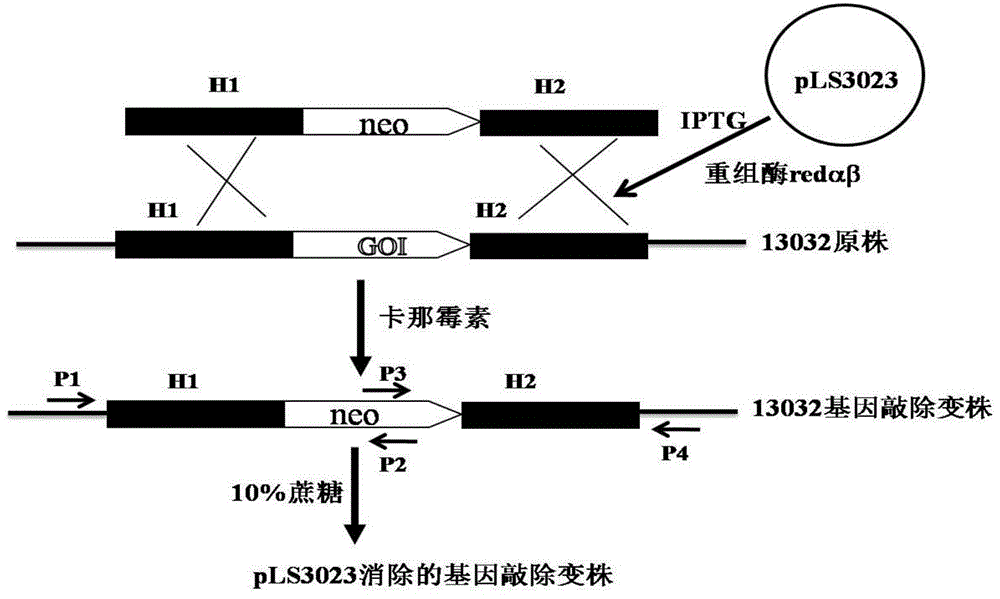
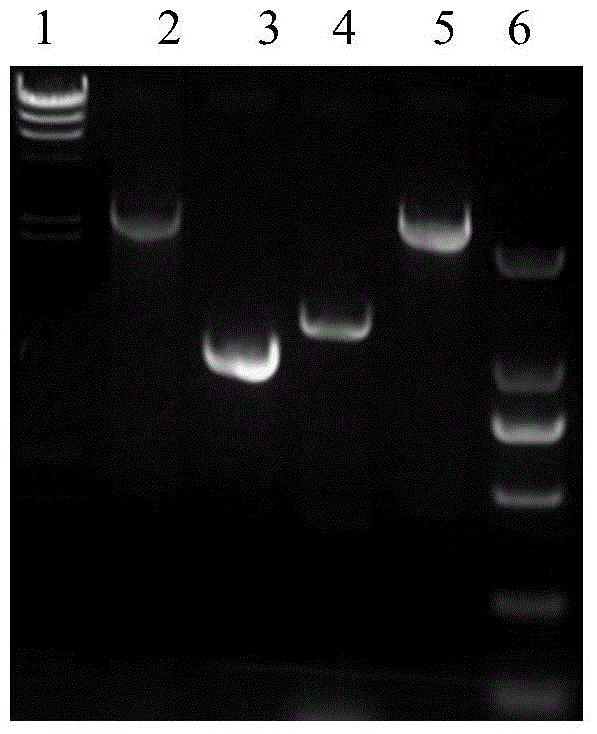
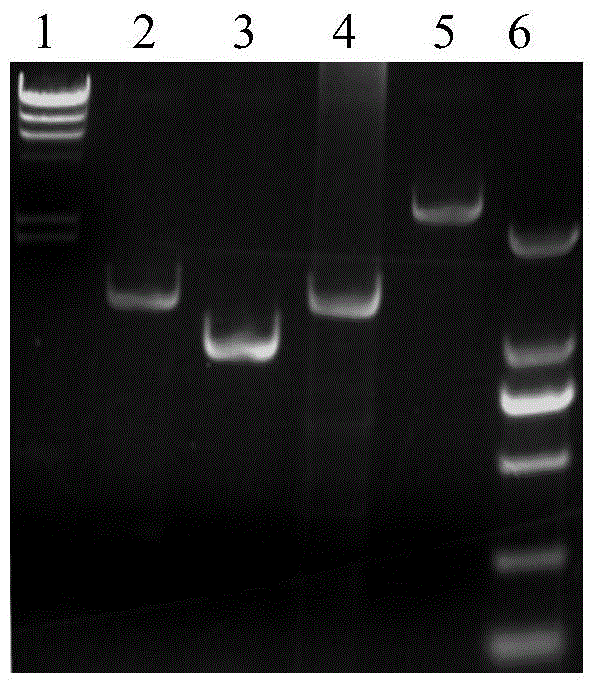
Recombineering-mediated gene knockout method of corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032
InactiveCN104561077AMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionSaccharumThiogalactosides
The invention relates to a recombineering-mediated gene knockout method of corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. The gene knockout method comprises the following specific implementation steps: obtaining a DNA fragment which is provided with 500-bp homologous sequences on two sides aiming at genes to be knocked out and a kanamycin resistance gene in the middle through a polymerase chain reaction amplification; carrying out electrotransformation on the DNA fragment into a corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 cell in which recombinase is induced to express by isopropyl-Beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside, and enabling the kanamycin resistance gene to replace the target gene through the resistance selection of kanamycin to obtain gene knockout strains; finally, cultivating mutant strains in a solid medium containing cane sugar to eliminate plasmids containing recombinase genes. The gene knockout method adopts simple PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and electrotransformation supplemented by the resistance selection of kanamycin, is free of operating steps, such as gene cloning in molecular biology and other certain operating steps, and simple and rapid, and has important application in the aspects of researching gene functions and producing amino acid.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing swine-original interferon-gamma 3 and application
ActiveCN103757041AHigh anti-PEDV activityImprove expression efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsBiotechnologySequence signal
The invention discloses a method for preparing swine-original interferon-gamma 3 (IFN-gamma 3) protein and application, belonging to the field of preparation of a genetic engineered product. The method comprises the steps of: cloning a swine-original interferon-gamma 3 coding gene, building a prokaryotic expression vector which contains the swine-original interferon-gamma 3 gene having no signal peptide sequence, and transforming escherichia coli and carrying out induced expression by using the recombined prokaryotic expression vector containing the swine-original interferon-gamma 3 gene, wherein the optimal induction temperature is 20 degrees centigrade, the optimal induction time is 16 hours, and the optimal IPTG (Isopropyl-beta-d-Thiogalactoside) concentration is 0.4mM. A product prepared by the method disclosed by the invention provides basis for researching the biological activity and the action mechanism of the swine-original interferon-gamma 3, and also can be applied to preparation of swine porcine epidemic diarrhea virus prevention drugs.
Owner:GUANGDONG MAIKETE BIOLOGICAL TECH
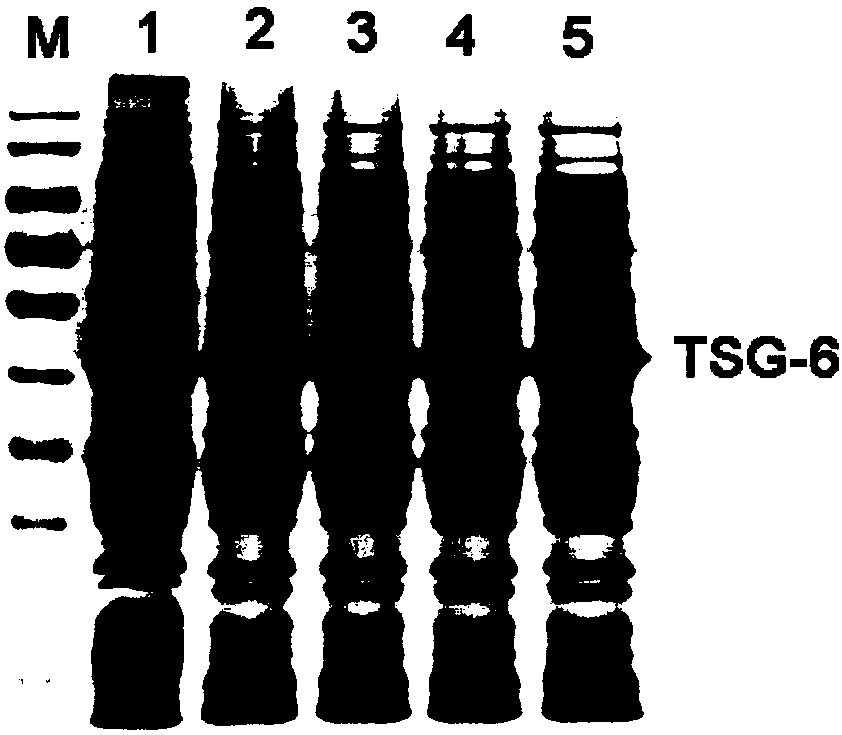
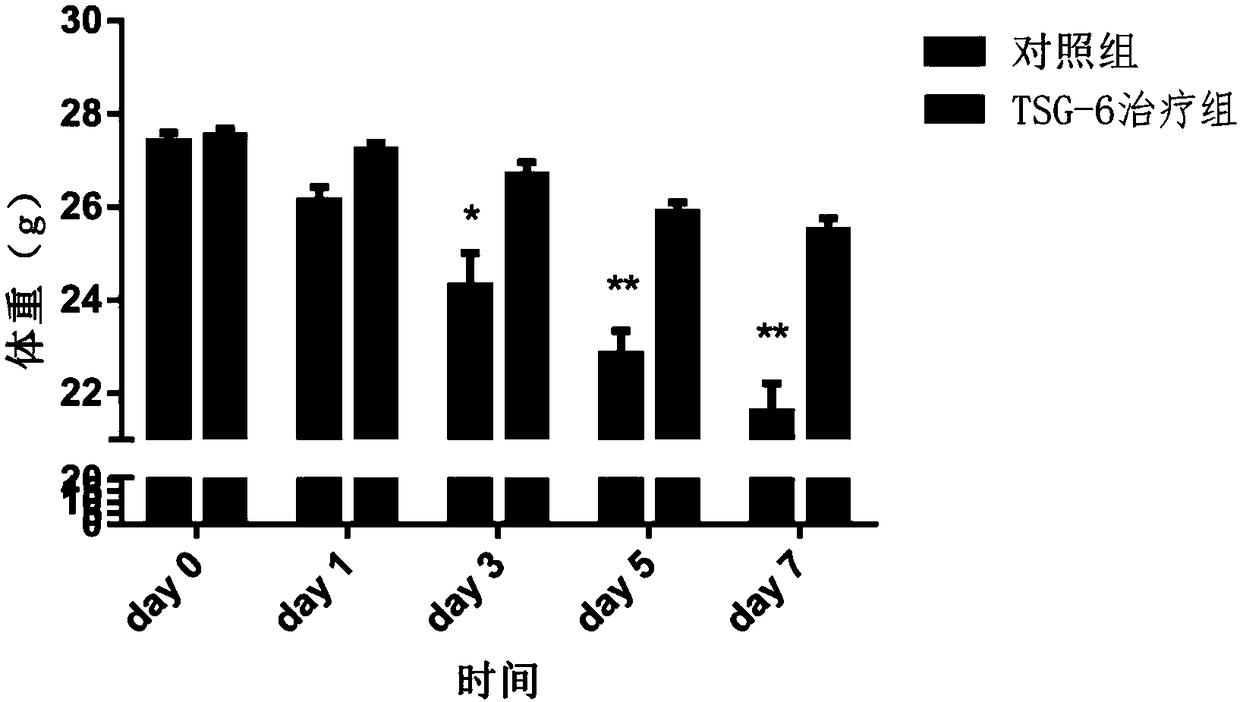
Recombinant human TSG-6 protein, preparation method thereof and application of recombinant human TSG-6 protein in treatment of acute inflammatory diseases
InactiveCN108530528AGood treatment effectCytokine-induced proteinsPeptide/protein ingredientsTSG-6Inclusion bodies
The invention discloses recombinant human TSG-6 protein, a preparation method thereof and application of the recombinant human TSG-6 protein in the treatment of acute inflammatory diseases. The aminoacid sequence of the recombinant human TSG-6 protein is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the encoding gene nucleotide sequence of the recombinant human TSG-6 protein is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The recombinant human TSG-6 protein and the preparation method and application thereof have the advantages that a prokaryotic expression vector pET30a is utilized to build an Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) host strain capable of expressing the recombinant human TSG-6 protein, the strain is subjected to multiplication culture, isopropyl-beta-D-isopropylthiogalactoside induced expression and centrifuging are performed to obtain a thallus, the thallus is split and then inclusion body precipitate is collected centrifugally, and denaturation, renaturation and molecular-sieve purification are performed to obtain the recombinant human TSG-6 protein; the recombinant human TSG-6 protein has a good curative effect on the acute pneumonia, caused by HCMV virus infection, of mice and provides a new thought for thetreatment of the acute inflammatory diseases caused by virus infection.
Owner:ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
Fusion protein with clostridium difficile toxins A/B and encoding gene and application of fusion protein
ActiveCN103772509AImproved Compositing EffectsReduce difficultyAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsClostridium difficile toxin BThiogalactosides
The invention provides a fusion protein with clostridium difficile toxins A / B and an encoding gene and application of the fusion protein. The sequence of the fusion protein with the clostridium difficile toxins A / B is represented by SEQ ID NO:2, and the encoding gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:1. According to the fusion protein, a carrier fragment consisting of a clostridium difficile toxin A carboxyl terminal gene and a prokaryotic expression vector pET32b(+) which are modified through a codon and a fusion gene fragment consisting of a clostridium difficile toxin B carboxyl terminal structure and a flexible chain are obtained through PCR (polymerase chain reaction) multiplication segmentation; the obtained fusion fragment and the obtained carrier are respectively connected in an enzyme recycling manner, so that a recombined expression plasmid pET32b(+)-ToxA-ToxB can be obtained; after the recombined plasmid converts a host BL21(DE3) strain, the recombined plasmid can be subjected to induction expression by IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside) to obtain the fusion protein with the clostridium difficile toxins A / B. According to the fusion protein with the clostridium difficile toxins A / B, the fusion protein with the immunogenicity of the toxins A and B can be obtained, and the difficulty and the cost for researching and producing a CDAD (clostridium difficile associated diarrhea) vaccine can be reduced.
Owner:冯东晓
Method for counting colibacillus in water body rapidly
InactiveCN101003830AShorten the timeEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrochemical detectorAmpere
This invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting E. coli concentration in water body. The method comprises: utilizing IrO2 / Pd decorative electrode as the electrochemical detector for flow injection-Ampere analysis, adding inducer isopropyl beta-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG), penetrant polymixin B nonapeptide and lysozyme into E. coli solution, releasing beta-D-galactosidase from E. coli cells induced by IPTG and catalytically hydrolyzing substrate 4-aminophenol-beta-D-galactopyranose in E. coli solution to obtain 4-aminophenol. Since the E. coli concentration in E. coli solution is in linear relationship with the amount of 4-aminophenol, rapidly detecting the amount of 4-aminophenol can realize rapid detection of E. coli concentration. The method has such advantages as short detection time, easy operation and high detection accuracy.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Method for preparing xylitol by utilizing whole-cell catalysis
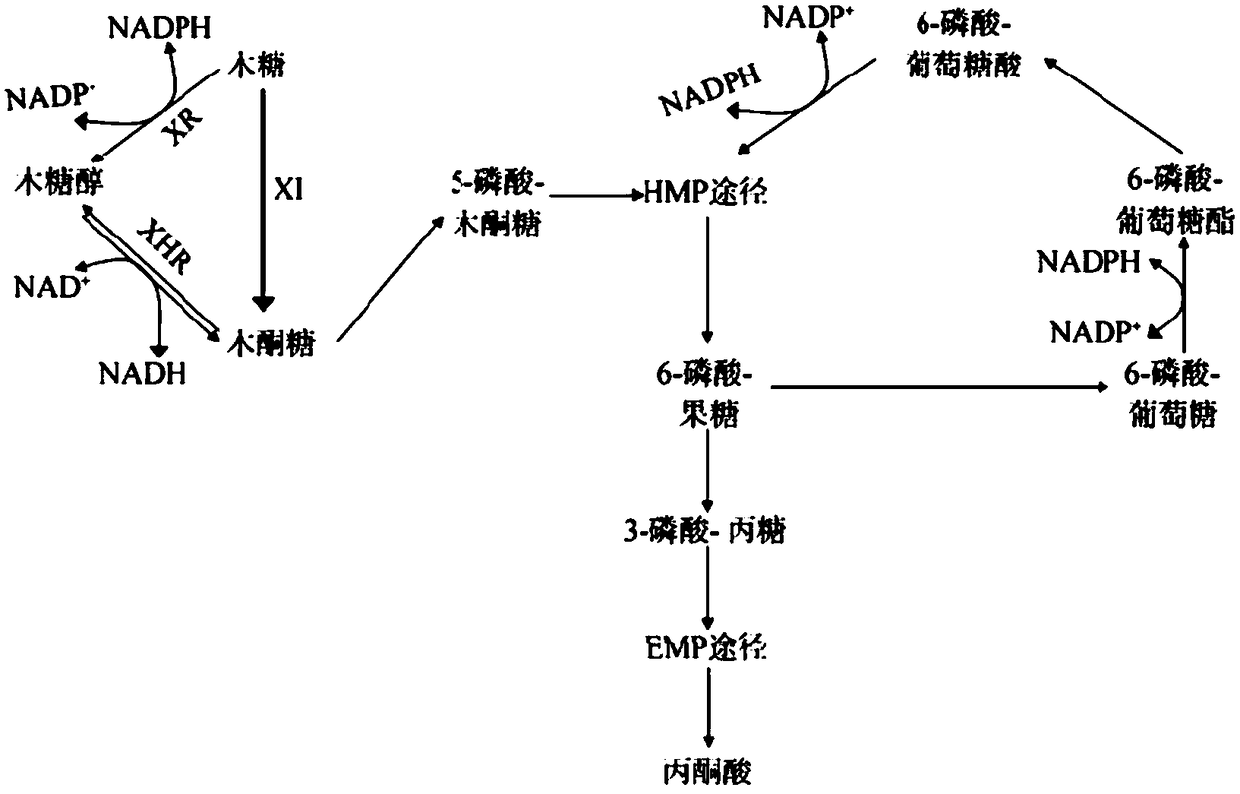
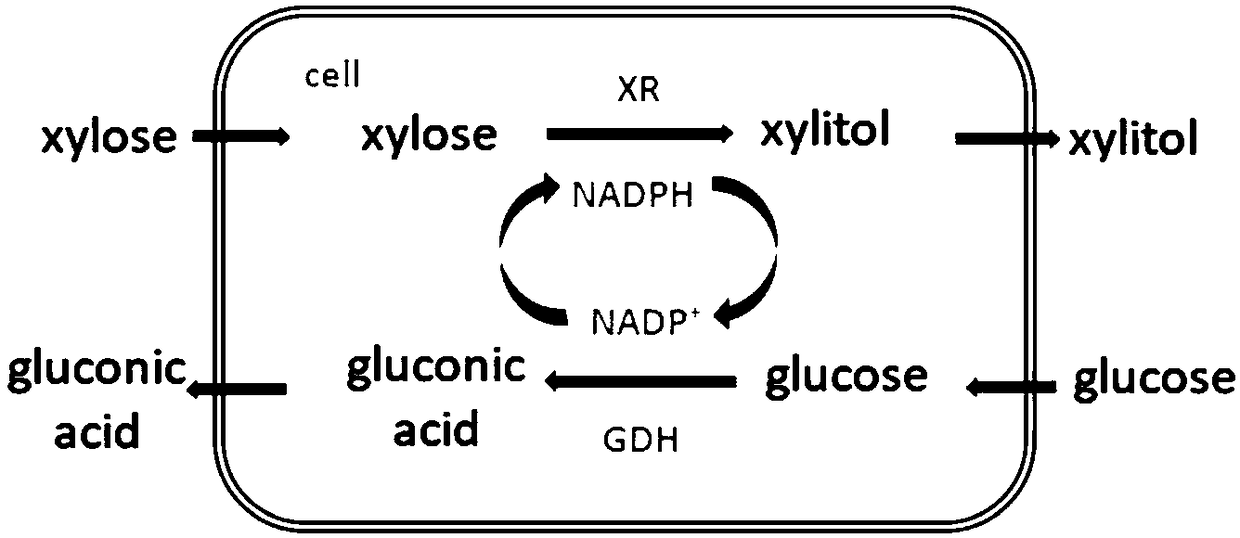
ActiveCN108949852AEliminate the extraction processReduce addBacteriaMicroorganism based processesThiogalactosidesCulture mediums
The invention discloses a method for preparing xylitol by utilizing whole-cell catalysis. The method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing recombinant Escherichia coli containing xylose reductase genes XR and glucose dehydrogenase genes GDH in an LB culture medium until the OD is 0.6-0.8, adding IPTG (Isopropyl-beta-d-Thiogalactoside) to induce expressions of the xylose reductase and glucose dehydrogenase, and centrifuging to obtain whole cells; and (2) enabling an aqueous solution containing xylose and glucose, the whole cells obtained in the step (1) and CaCO3 to form a biological catalysis system, and catalyzing the xylose to carry out a reduction reaction so as to produce the xylitol. The method disclosed by the invention can be effectively applied to comprehensive utilization of straws, the reaction system is applied to treating crop straw hydrolyte, and the substrate of the hydrolyte can be completely consumed within 20 hours. According to the method disclosed by the invention, extraction of enzymes in cells and addition of exogenous cofactors can be saved, and the process and cost for producing the xylitol by biological catalysis can be greatly simplified.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Heterozygous antibacterial and antiviral polypeptide as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104017084AGood antibacterial effectLow toxicityAntibacterial agentsBiocideBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
The invention provides a heterozygous antibacterial and antiviral polypeptide, the amino acid sequence and the nucleotide sequence of which are respectively shown as SEQ ID No.1 and SEQ ID No.2. The preparation method comprises the following steps: cloning a gene which encodes the polypeptide to an expression vector pETSUMO to obtain a recombinant expression vector; then, converting the vector into escherichia coli BL21 though a hot stress method; inducing expression by IPTG (Isopropyl-beta-d-Thiogalactoside); carrying out enzyme digestion on an expression product through SUMO enzyme digestion and purifying through a Ni-NTA Sepharose chromatographic column; separating to obtain the targeted polypeptide. The polypeptide has inhibiting and killing effects to various bacteria and viruses in vitro and is less in possibility of generating resistance, so that the polypeptide can be used as an ideal antibiotic substituent, a human and animal biological medicine, a feed additive, a preservative or a killing agent and the like.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for preparing virus analogs of nervous necrosis viruses
ActiveCN101942496AHigh expressionLow costMicroorganism based processesPeptide preparation methodsNecrovirusPlasmid Vector
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a method for preparing virus analogs of nervous necrosis viruses. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) performing expression of the virus analogs of the nervous necrosis viruses on escherichia coli of pQE30 plasmid vectors coded with nervous necrosis virus capsid protein genes under the pronucleus condition, wherein the expression is performed under the following conditions of: inoculating 1 mass percent of escherichia coli solution of which OD600 is equal to 1.5 into a culture medium, culturing the escherichia coli at 37 DEG C under 250rpm till the OD600 is 0.3 to 0.5, adding isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside into the escherichia coli solution till the final concentration of the isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside is 900muM, transferring the solution, and continuously culturing the escherichia coli for 3 to 4 hours at the temperature of between 25 and 30 DEG C at the rotational speed of 200rpm to finish the expression; and (2) after the expression is finished, breaking, separating and purifying the strains to obtain the virus analogs of the nervous necrosis viruses, wherein the plasmid coded genes also can be nervous necrosis virus capsid protein genes containing histidine tags, and the expression product of the genes can be purified by affinity chromatography. The method provided by the invention can obtain high virus analog expression amount; and the chromatography and purification method is simple and convenient and has low costs in required apparatuses and reagents.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), preparation method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN102070711AStable expressionEfficient and stable expressionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseThiogalactosides
The invention relates to the field of microbiology, in particular to a tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), a preparation method thereof and application thereof. A TFPI-1 is represented by the amino acid sequence SEQ ID No.1 in the sequence list; and a TFPI-2 is represented by the amino acid sequence SEQ ID No.2 in the sequence list. The preparation method comprises: converting colibacillus BL21 (DE3) by plasmids pE15TFPI1 and pE15TFP2 to obtain BL21 / pE15TFPI1 and BL21 / pE15TFPI2 respectively; inducing the obtained products with isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside; and purifying recombinant proteins through affinity chromatography to obtain TFPI-1 and TFPI-2. The TFPI has a high-efficiency sterilization effect and therefore can resist to bacterial infection and be used for disease prevention and treatment. The TFPI provided by the invention can effectively crack many pathogenic bacteria so as to inhibit bacterial infection.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
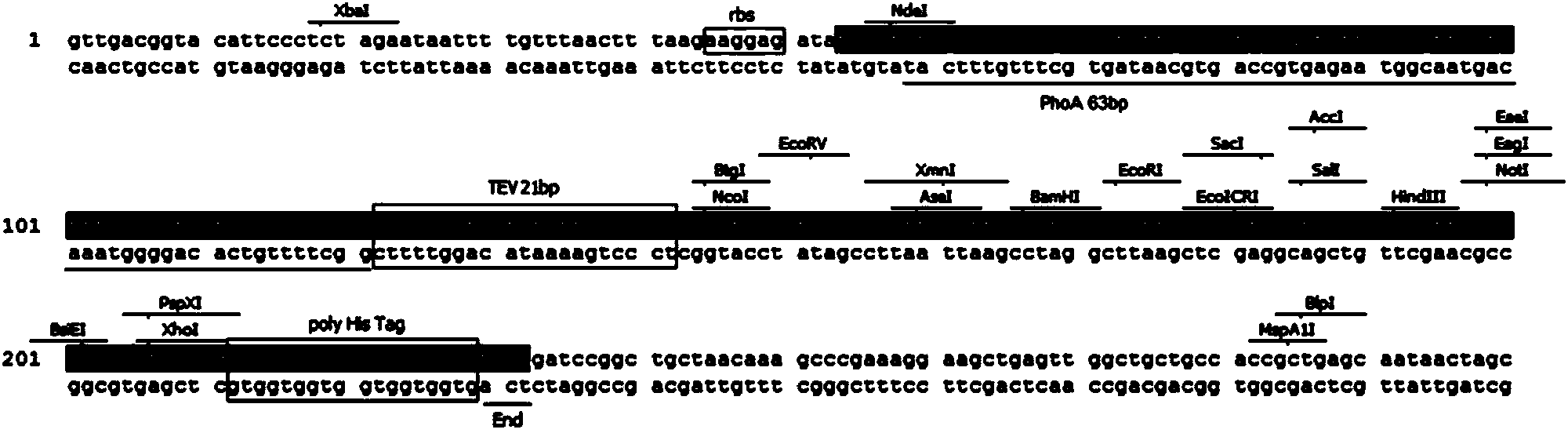
Plasmid vector of escherichia coli secretory expression heterologous protein and establishment method of plasmid vector
ActiveCN103834676ABacteriaMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFusion Protein ExpressionThiogalactosides
The invention discloses a plasmid vector of escherichia coli secretory expression heterologous protein and an establishment method of the plasmid vector, and in particular discloses a recombinant secreting type expression vector. The vector comprises an alkaline phosphatase PhoA secretory signal peptide and multi-poly histidine sequence, and can express the heterologous recombinant protein through IPTG (Psopropyl-beta-d-Thiogalactoside) induction in escherichia coli BL21. The invention further discloses techniques for establishment of the vector, PhoA induced peptide-heterologous protein fusion gene clone and fusion protein expression and detection. As the heterologous protein is enabled to be stably expressed in an extracellular manner, the vector can be applied to secretory expression of ordinary protein.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing lactulose through whole-cell catalysis
InactiveCN104004699AAvoid loss of enzyme activityReduce dosageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFreeze-dryingThiogalactosides
The invention discloses a method for producing lactulose through whole-cell catalysis, and belongs to the field of the food biotechnology. According to the method, recombinant escherichia coli E. coli BL 21 (DE3) for producing cellobiose epimerase is taken as production bacterial strains, lactose is used for replacing isopropyl-beta-D-sulfo-galactoside (IPTG) and taken as an inductive agent for fermental cultivation, and thalluses obtained through centrifugation are subjected to ethyl alcohol permeabilization and vacuum freeze drying to serve as a cell biocatalyst for directly converting the lactose to produce the lactulose. The maximum percent conversion of the lactulose can reach 65.1%, the concentration of the lactulose reaches 390.6 g / L, the production rate of the lactulose reaches 195.3 g / (L*h), and the production quantity of by-product epidepride lactulose is smaller than 2%(w / w). According to the method, microbial cells are directly used for converting the lactose to produce the lactulose, and the method is simple and easy to implement, avoids the loss of enzyme activity in the separation and purification process, greatly reduces the cost of producing the lactulose through an enzymic method and is beneficial for achieving industrialization of lactulose production through the enzymic method early.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
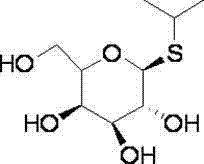
Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside preparation method
ActiveCN103709209AImprove the safety factor and productionEasy to operateSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSodium methoxideAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to the field of sugar compounds, and concretely relates to an isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside preparation method. The method comprises the following steps: adding acetic anhydride and a catalyst at room temperature, adding galactose, adding isopropyl mercaptan after the above reaction, and post-processing to obtain isopropyl thioacetylgalactosamine; and adding isopropyl thioacetylgalactosamine into methanol for dissolving, adding sodium methoxide, adding acetic acid after the above reaction to neutralize, and post-processing to obtain isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside. The method allows isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactoside to be synthesized through a two-step reaction process, and has the advantages of simple operation, easily available raw materials, and saving of the operation cost and materials.
Owner:济南尚博医药股份有限公司
Preparation method and application of sarcosine oxidase
InactiveCN103013941AEasy to operateReduce manufacturing costMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesSarcosine oxidaseThiogalactosides
The invention discloses a preparation method of sarcosine oxidase. The method comprises the following steps: transforming a whole-gene synthesis humanization sarcosine oxidase coding deoxyribonucleic acid sequence, and removing escherichia coli rare codon; inserting the transformed sarcosine oxidase coding deoxyribonucleic acid sequence into an expression carrier, and carrying out transformation and expression by using an escherichia coli strain; inoculating the strain subjected to transformation and expression into a luria-bertani (LB) culture medium, and carrying out isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside (IPTG) induction; and breaking the obtained thallus, centrifugally separating and purifying through an Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid (NTA) column. The method is simple in sarcosine oxidase preparation operation, low in preparation cost, high in finished product yield, high in purity and high in biological activity, and can be used as a diagnostic reagent for sarcosine assay kit research.
Owner:BEIJING HOSPITAL
Thioredoxin and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102586202AEasy to makeApparent reductase activityAntinoxious agentsOxidoreductasesThiogalactosidesThioredoxin
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, in particular to Cynoglossus semilaevis thioredoxin and a preparation method and application thereof. The thioredoxin is shown as an amino acid sequence in a sequence table SEQ ID No.1. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: constructing a plasmid pETrx, transforming the plasmid pETrx by using BL21(DE3) to obtain BL21(DE3) / pETrx, inducing by using isopropyl-beta-D-isopropylthiogalactoside, and purifying recombinant protein by using an affinity chromatography column to obtain the thioredoxin. The thioredoxin has remarkable reductase activity, a remarkable antioxidation effect and a remarkable cell growth promotion effect.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


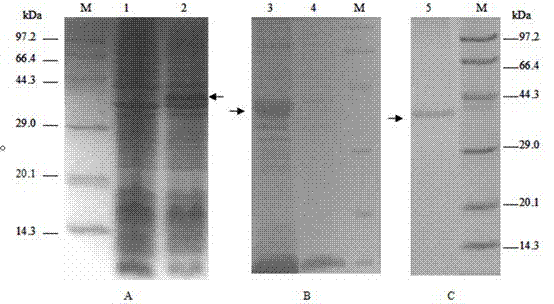
![Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d07e9897-9b5a-4b04-af13-722aec5a2368/140704155216.PNG)
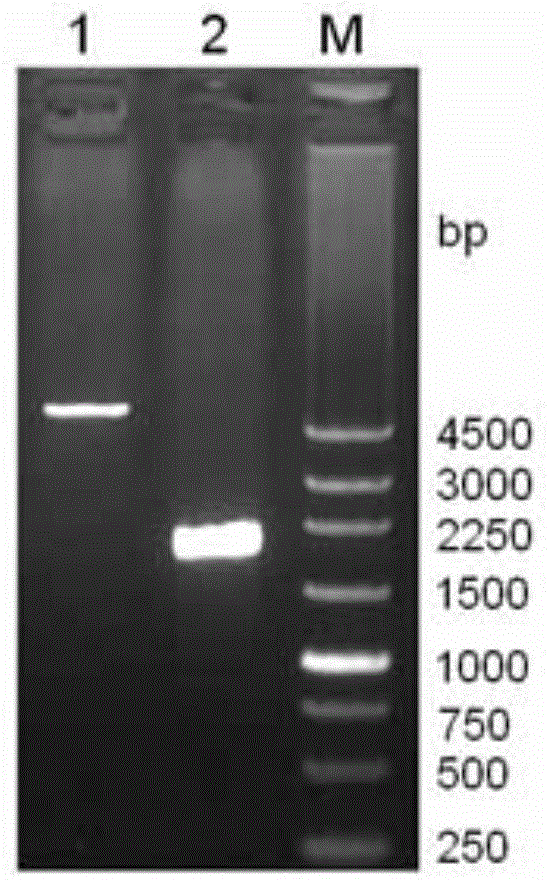
![Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d07e9897-9b5a-4b04-af13-722aec5a2368/140704155227.PNG)
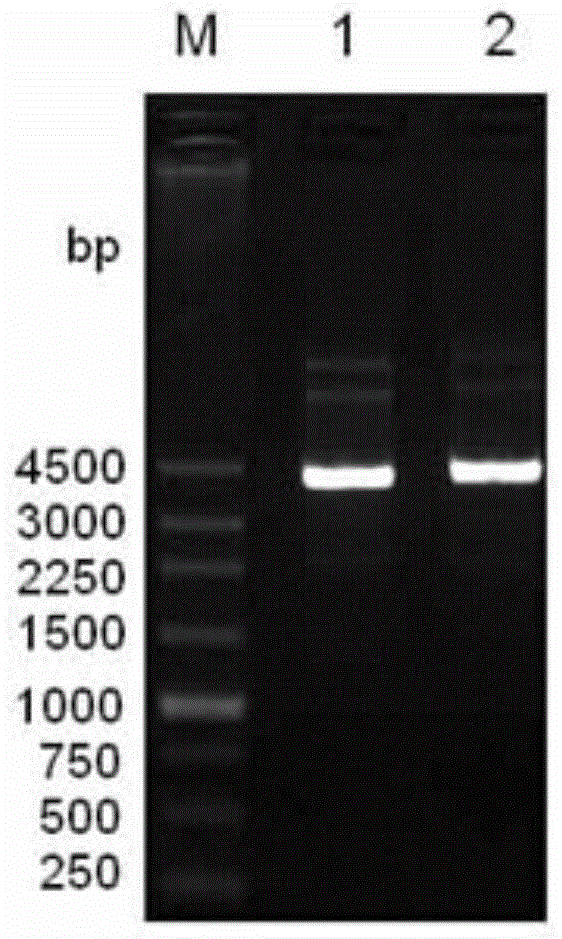
![Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli Method for high-efficiently producing L-theanine through production of coli [gamma]-glutamylmethylamine synthetase with escherichia coli](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/d07e9897-9b5a-4b04-af13-722aec5a2368/93258DEST_PATH_IMAGE002.PNG)