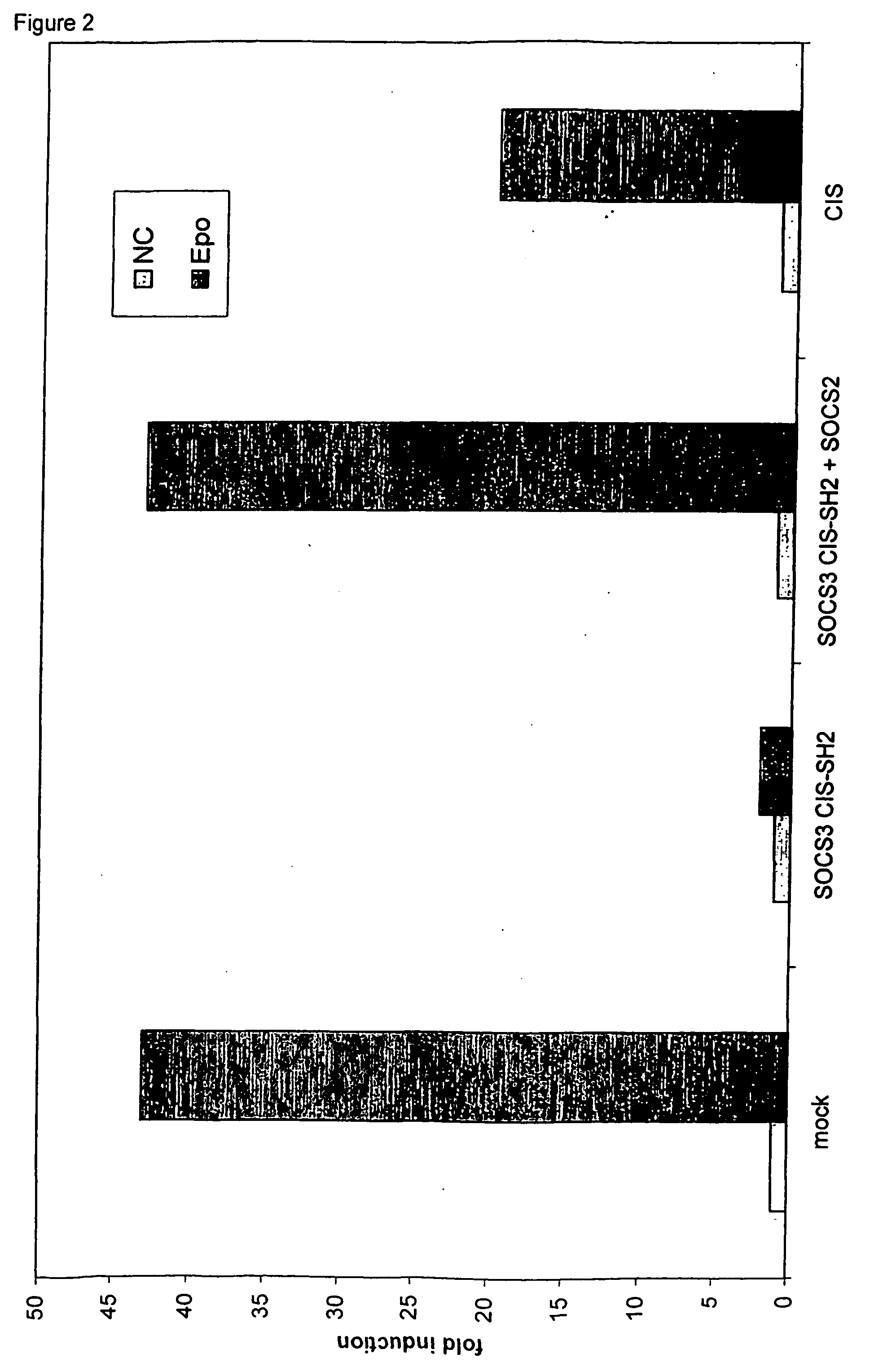
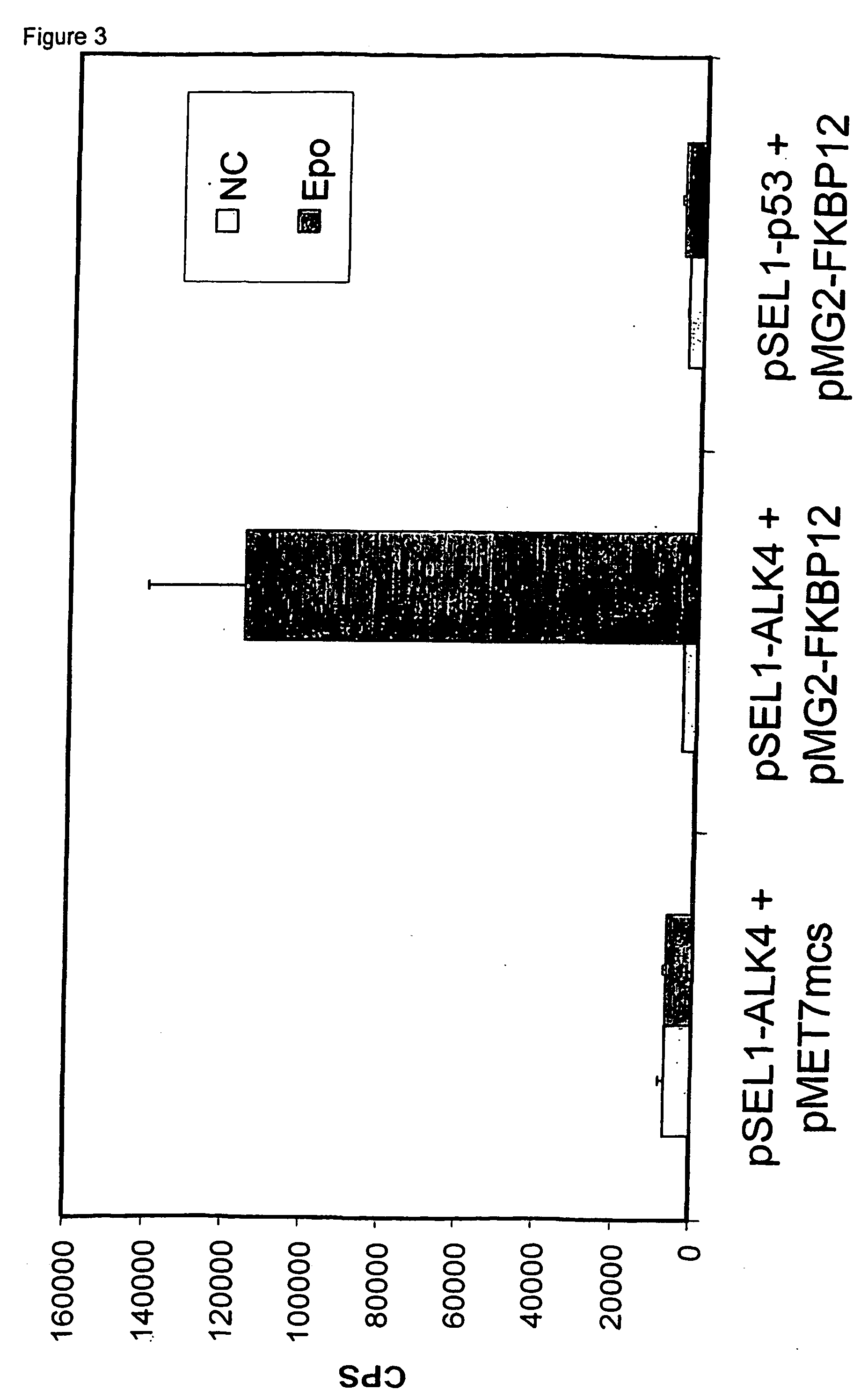
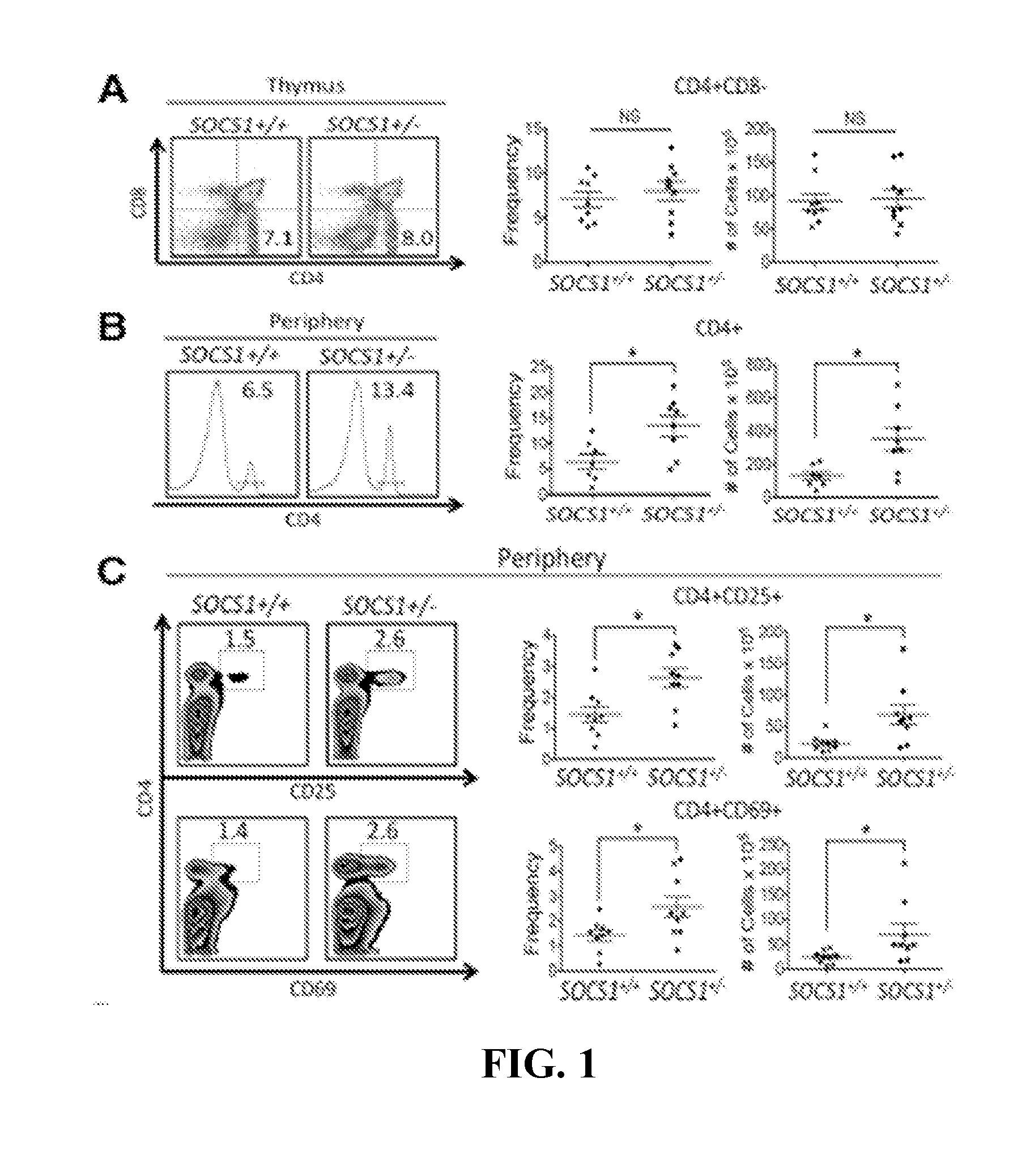
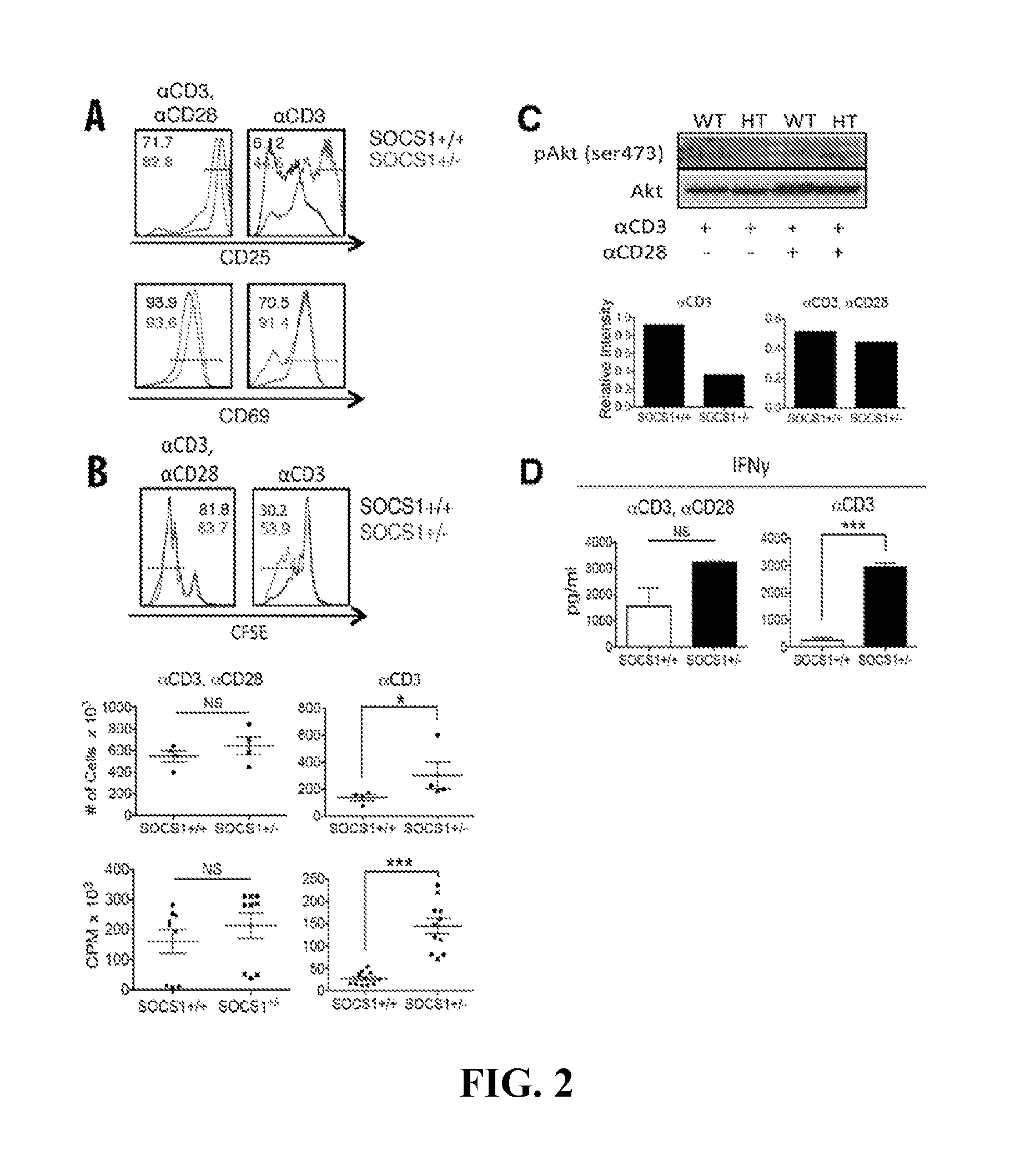
Patents
Literature
38results about "Cytokine-induced proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Antibody to cytokine response gene 2(CR2) polypeptide
InactiveUS6057427AHigh incidenceEliminate the effects ofCytokine-induced proteinsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody fragmentsAmino acid
PCT No. PCT / US96 / 08992 Sec. 371 Date Jun. 5, 1996 Sec. 102(e) Date Jun. 5, 1996 PCT Filed Jun. 5, 1996Disclosed are an isolated antibody or antibody fragment that selectively binds a polypeptide encoded by Cytokine Response gene 2 (CR2), and in particular, selectively binds to a first polypeptide having the sequence of residues 1-60 of SEQ. ID No: 4. Also disclosed is a composition containing the antibody or antibody fragment and a diluent or carrier. Also disclosed are methods, using the present antibody or antibody fragment, of isolating or purifying a peptide comprising an amino acid sequence of residues 1-60 of SEQ. ID No: 4 or an antibody binding fragment thereof that is at least 10 to 30 amino acids long, or a fusion protein comprising any of these.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE
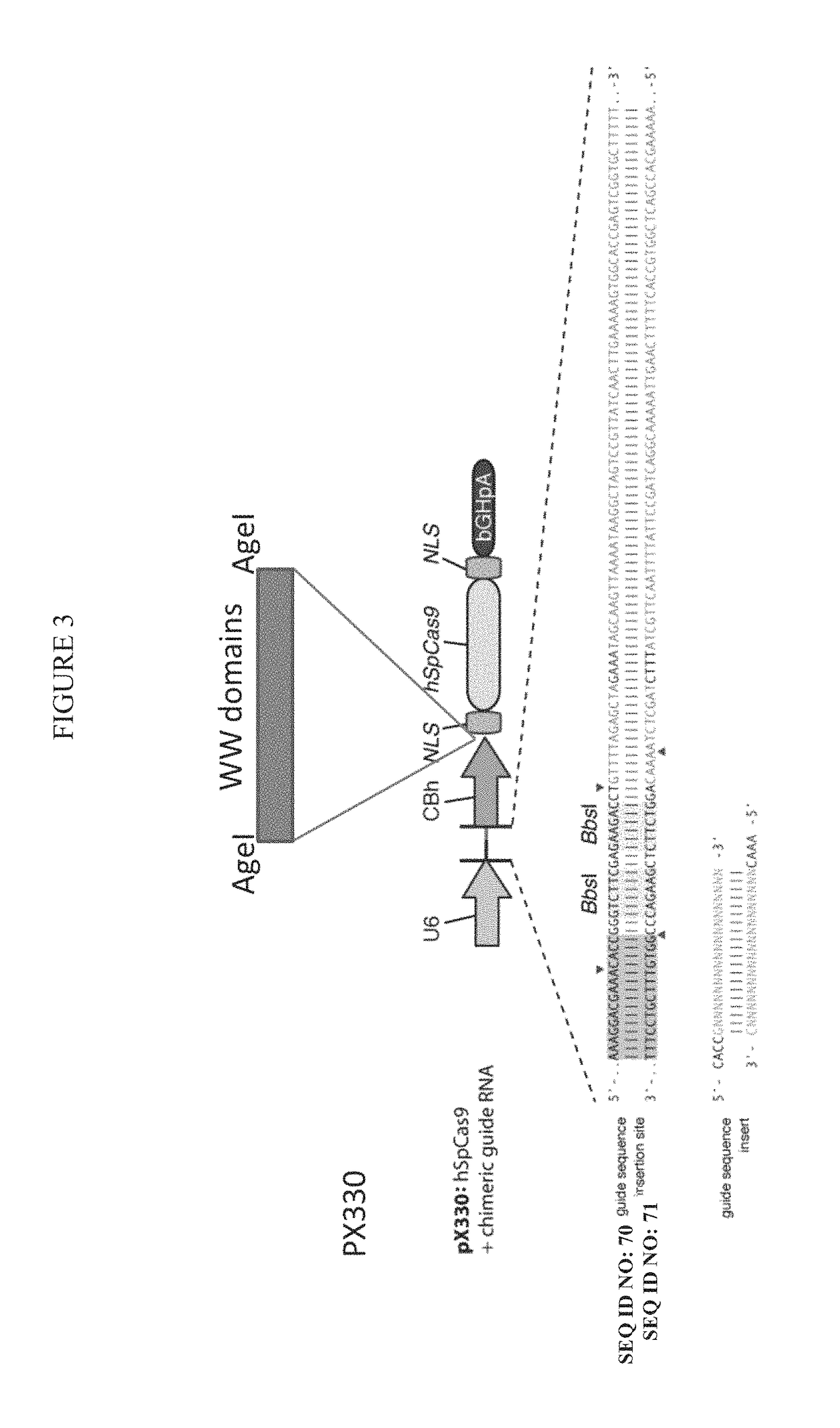
Delivery of cas9 via arrdc1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMS)
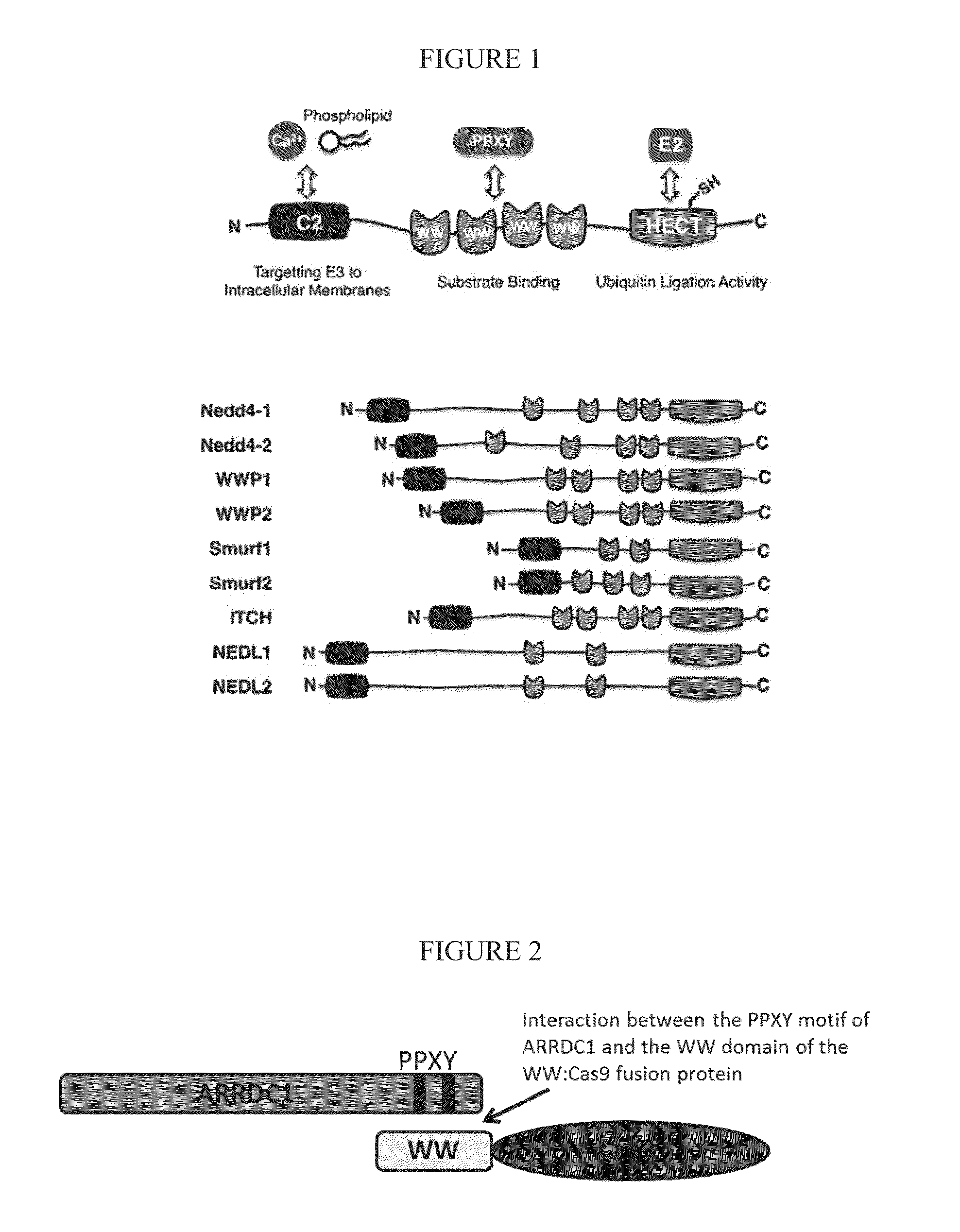
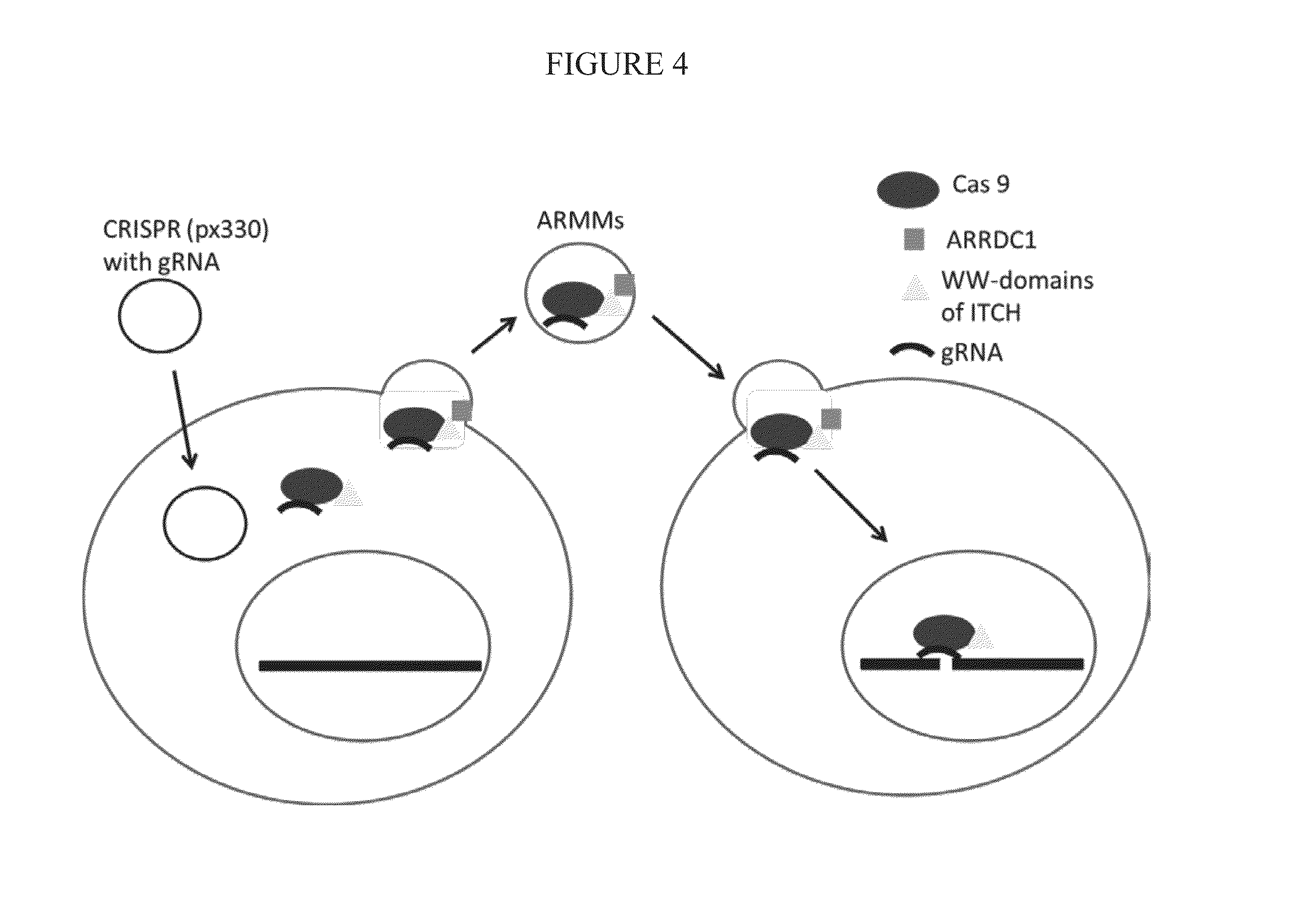
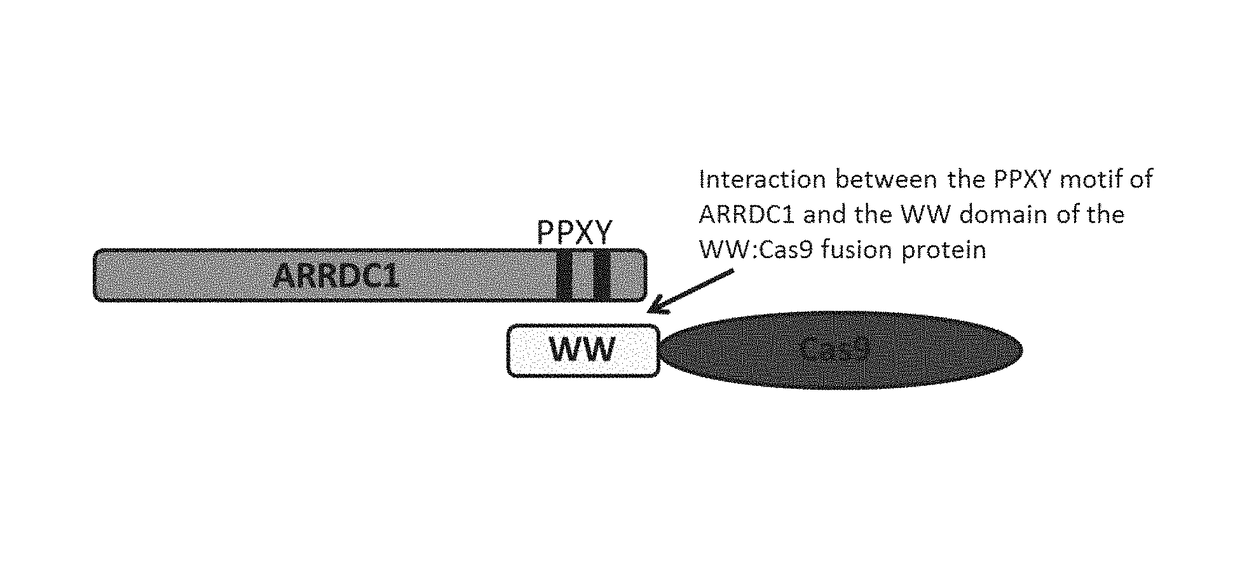
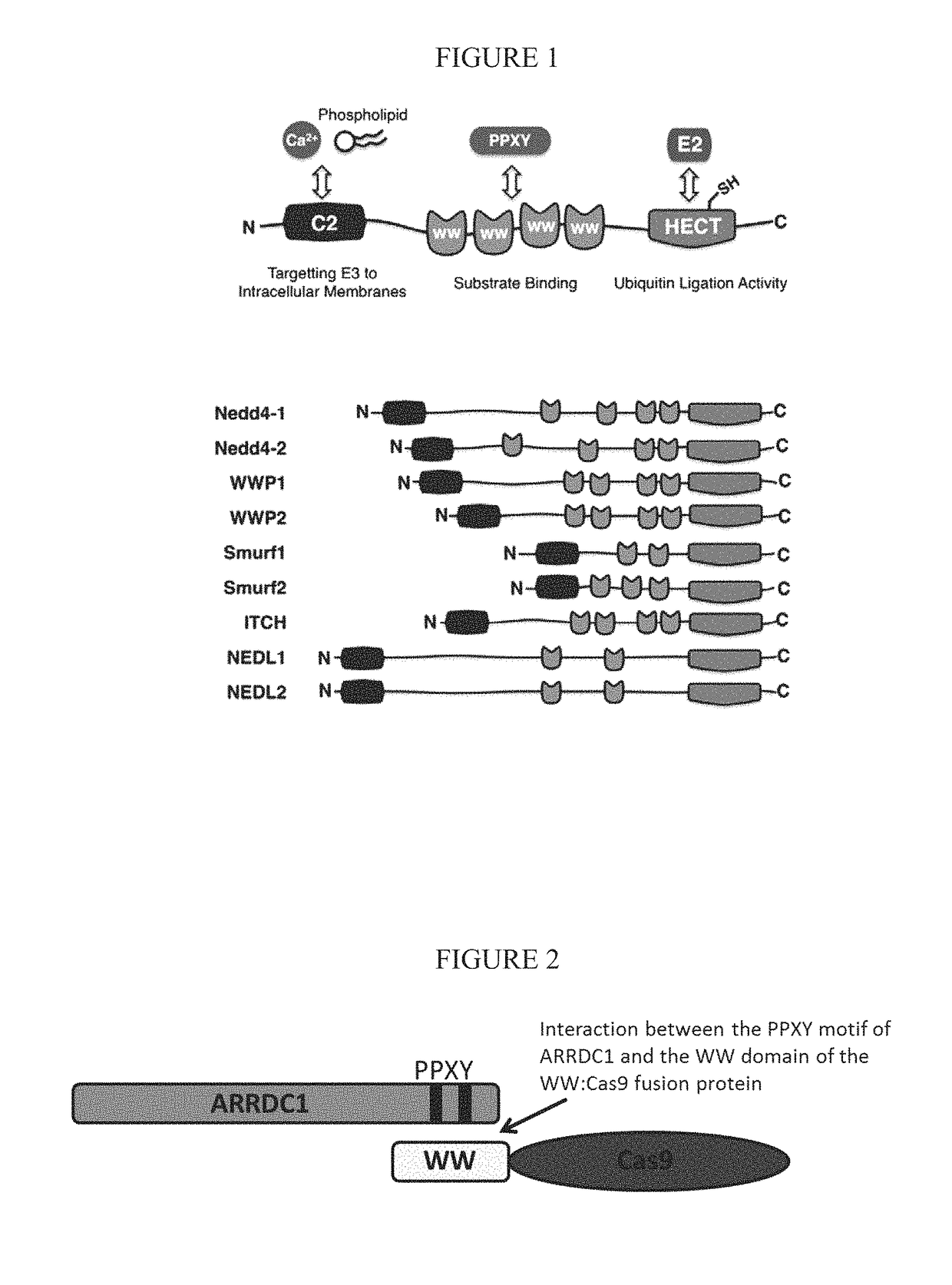
ActiveUS20160206566A1Easy loadingConvenience to mergePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainWW domainTSG101
Methods, systems, compositions and strategies for the delivery of WW domain-containing fusion proteins into cells in vivo, ex vivo, or in vitro via ARMMs are provided. Methods, systems, compositions and strategies for the delivery of Cas9 proteins and / or Cas9 variants into cells in vivo, ex vivo, or in vitro via fusion to ARMM associated proteins (e.g., ARRDC1 or TSG101) are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Modified cells and methods of therapy
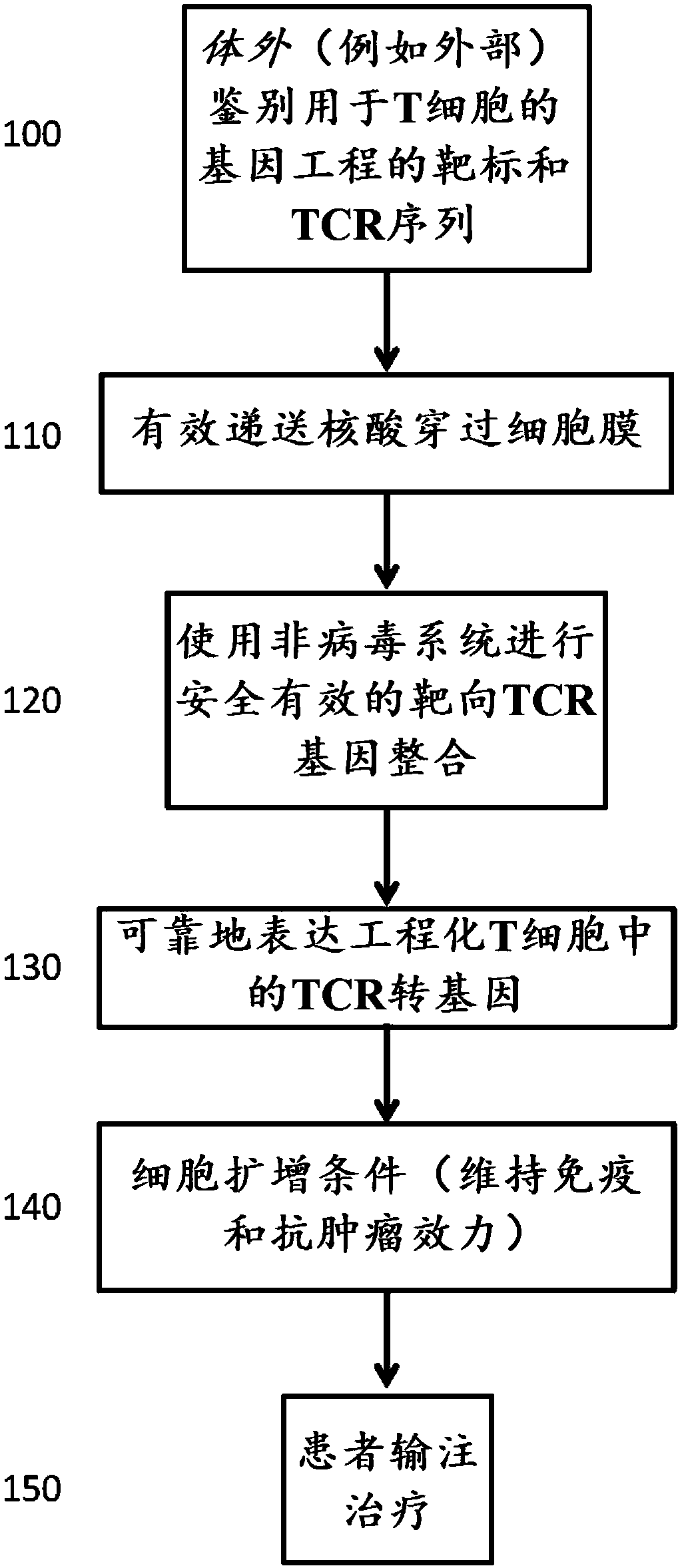
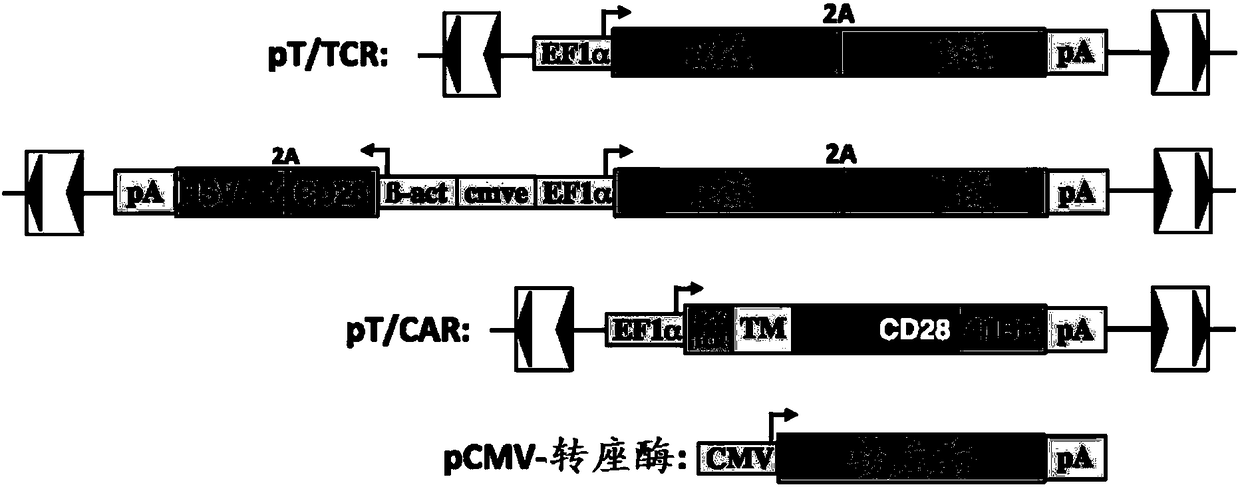
PendingCN108472314AIncrease insertion efficiencyLow toxicityCytokine-induced proteinsFusion with DNA-binding domainOncologyT cell
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA +2
Delivery of CAS9 via ARRDC1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs)
ActiveUS9816080B2Easy loadingConvenience to mergePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainWW domainProtein C
Methods, systems, compositions and strategies for the delivery of WW domain-containing fusion proteins into cells in vivo, ex vivo, or in vitro via ARMMs are provided. Methods, systems, compositions and strategies for the delivery of Cas9 proteins and / or Cas9 variants into cells in vivo, ex vivo, or in vitro via fusion to ARMM associated proteins (e.g., ARRDC1 or TSG101) are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
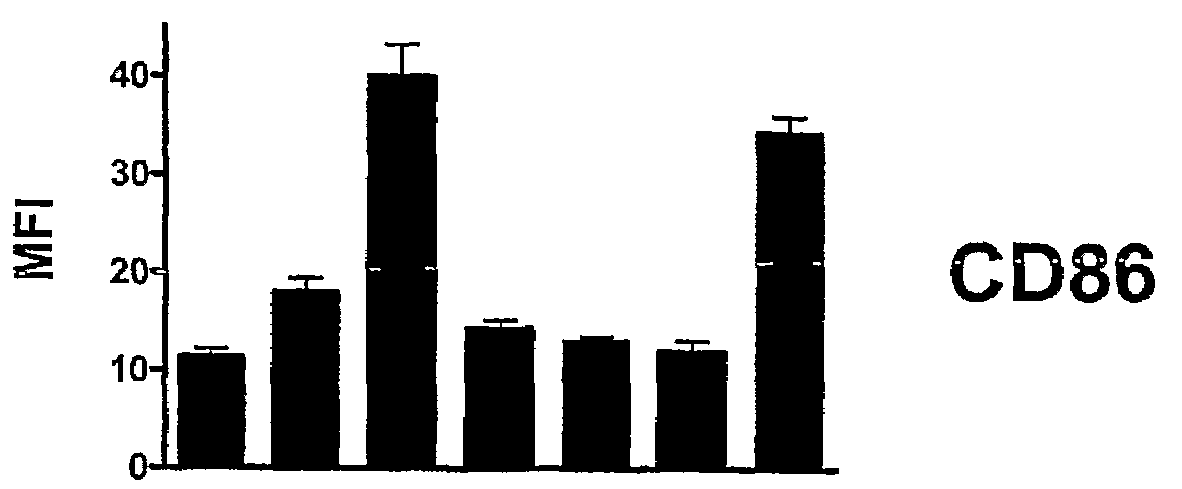
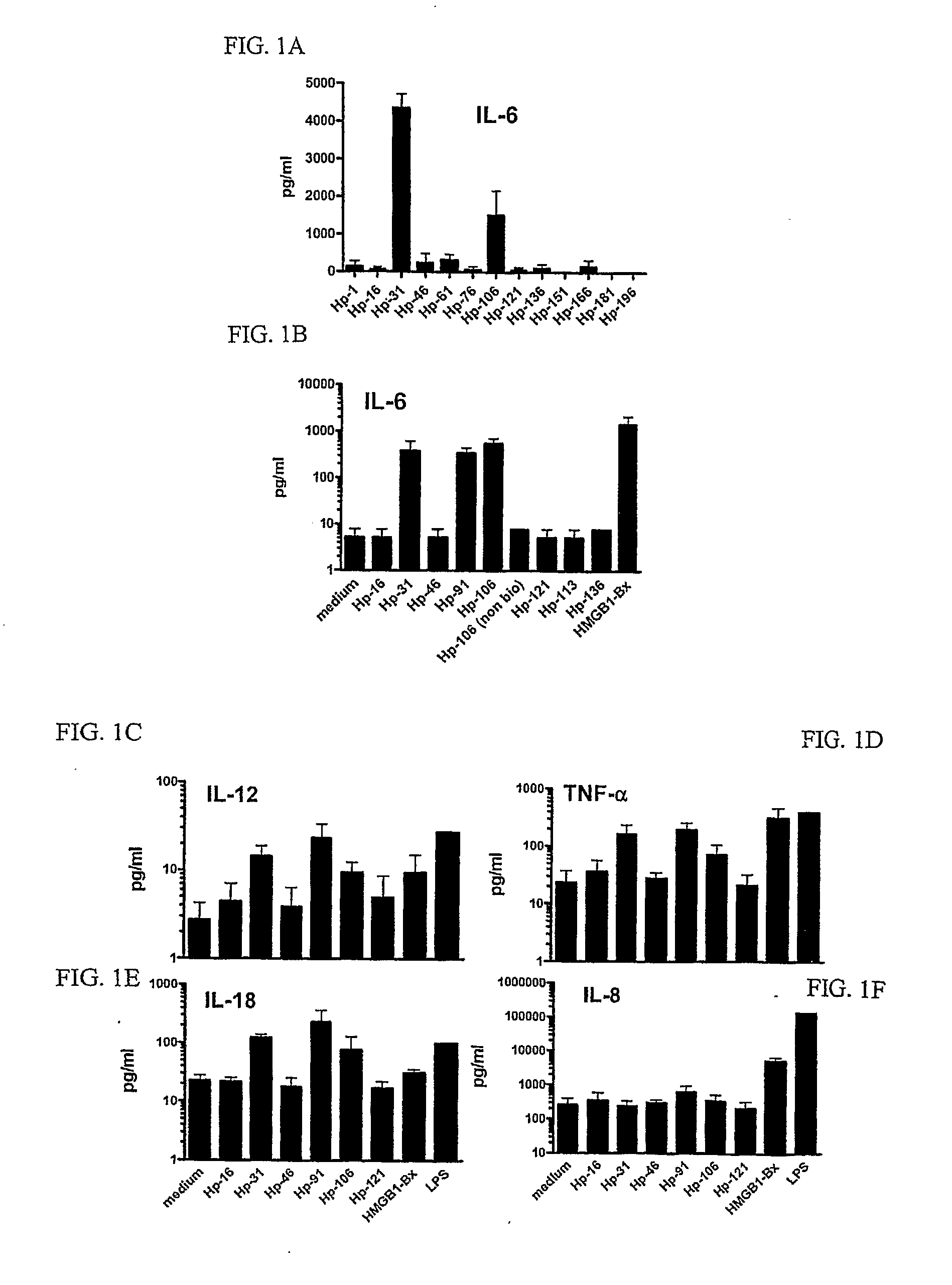
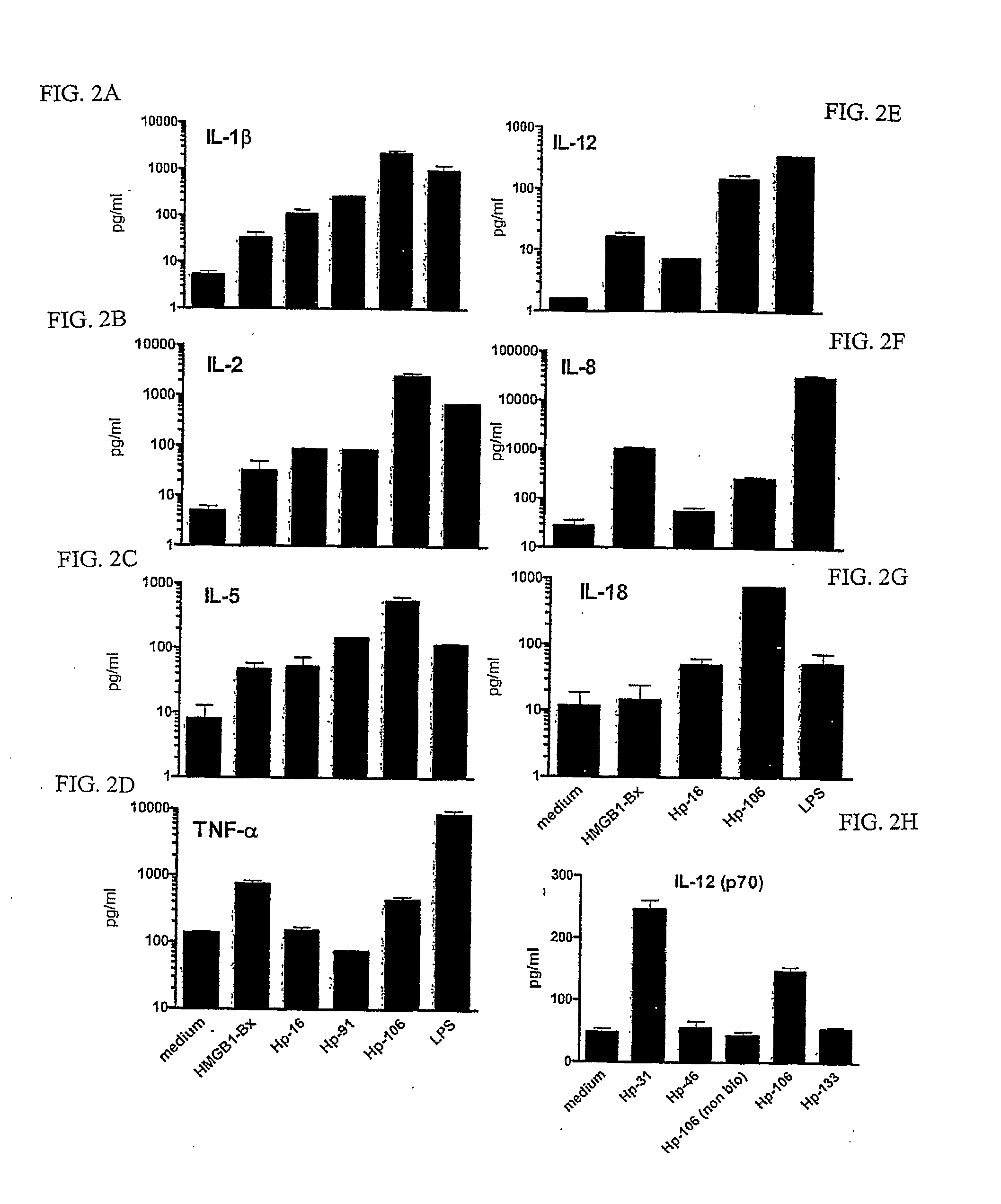
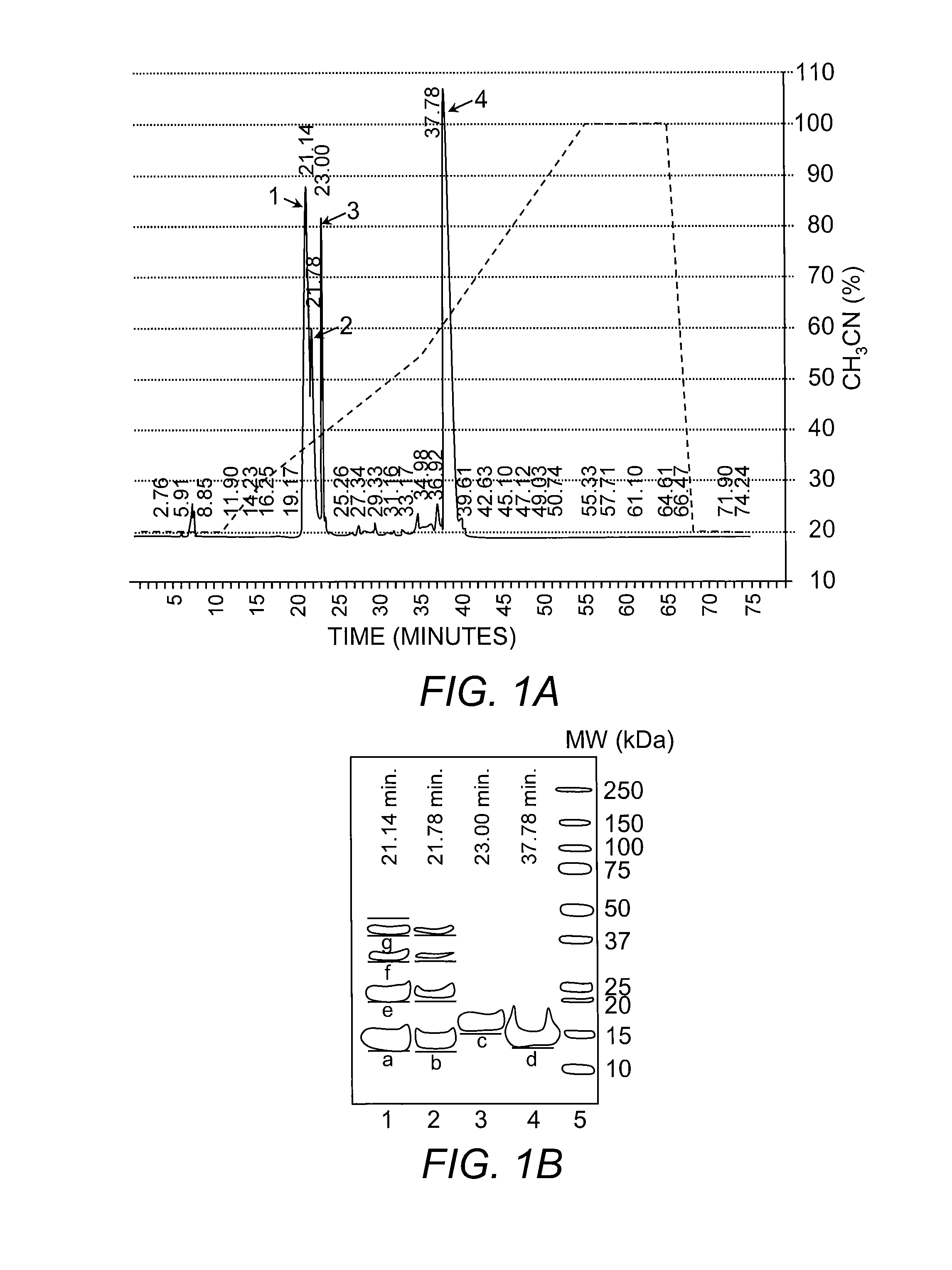
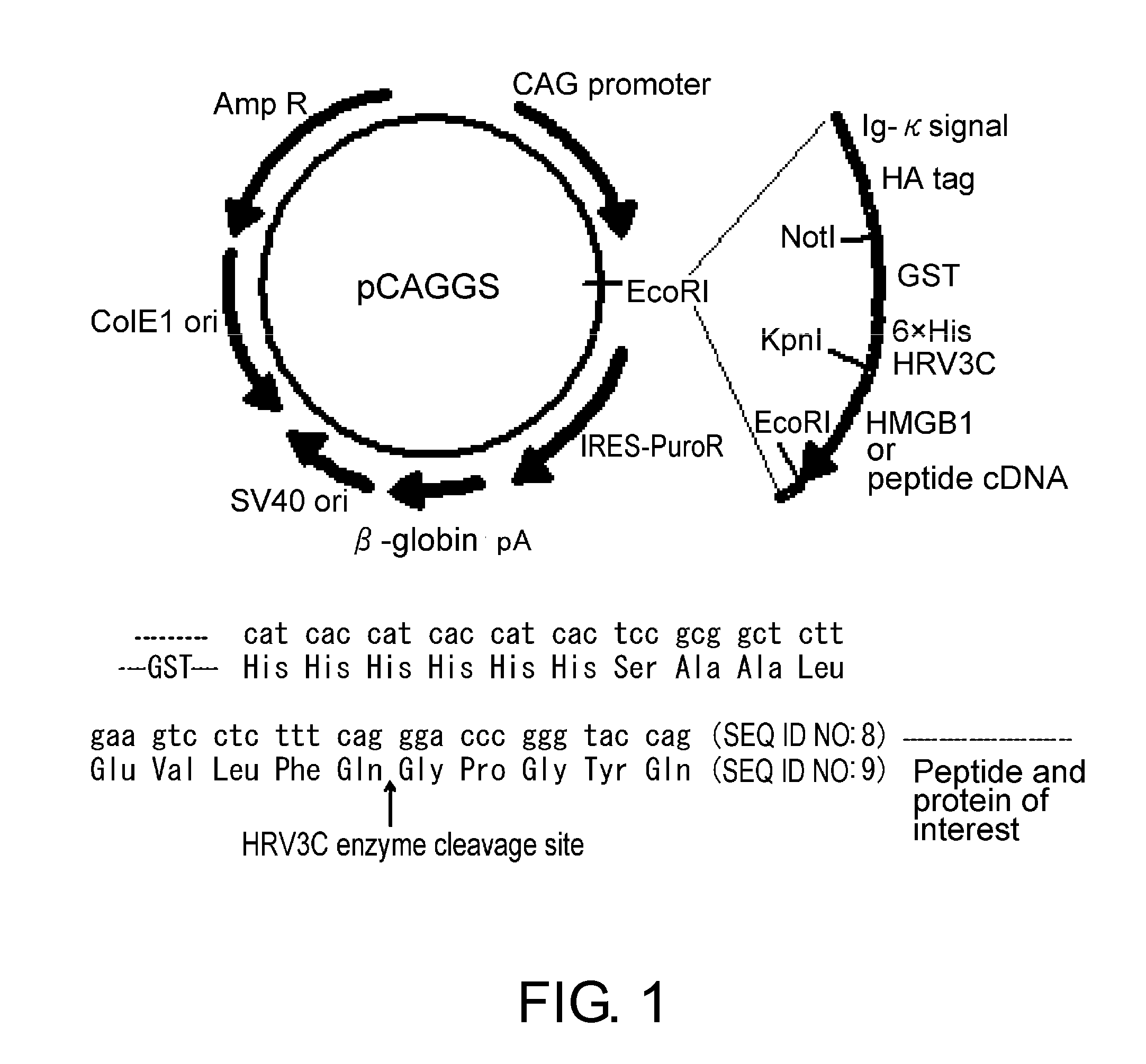
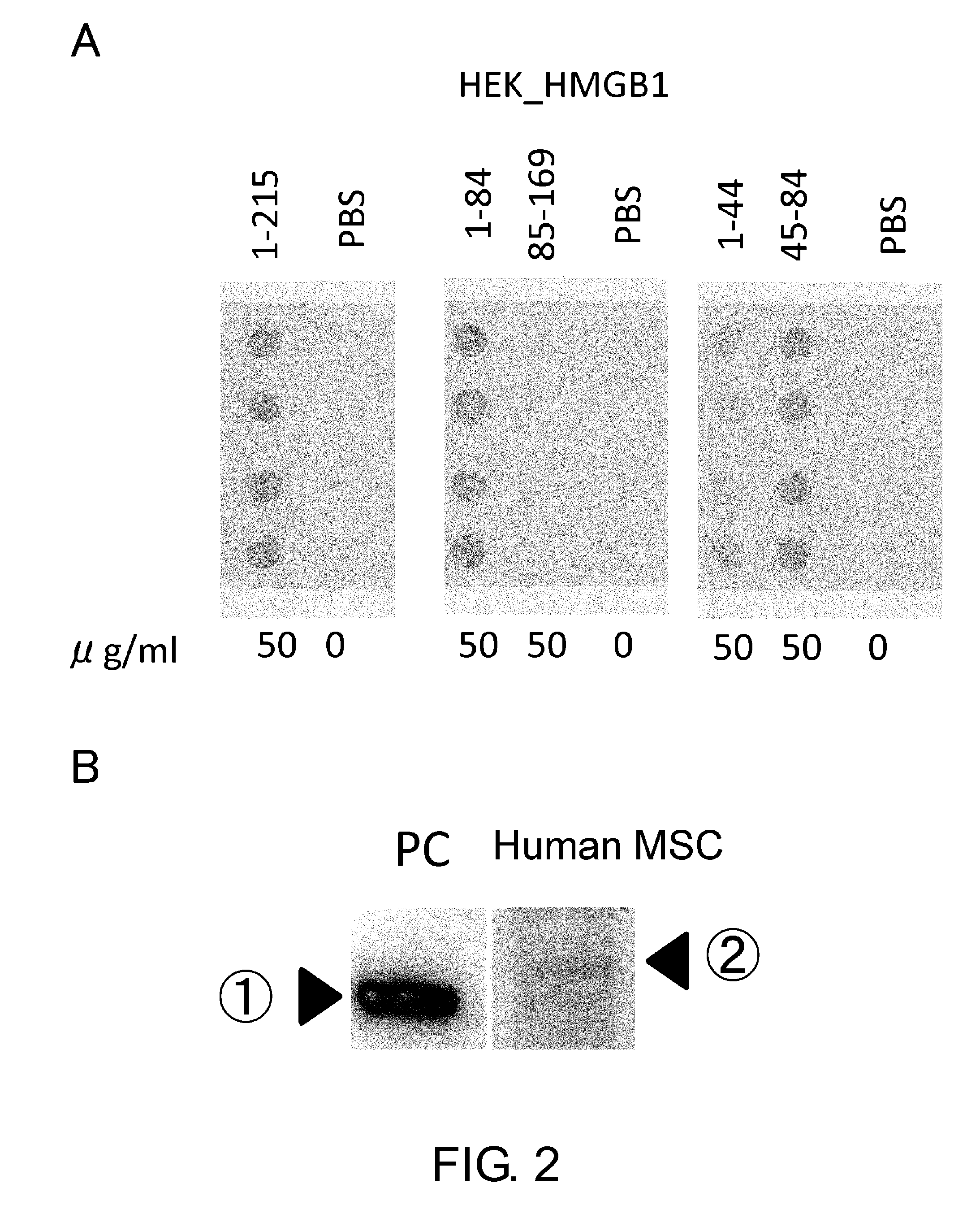
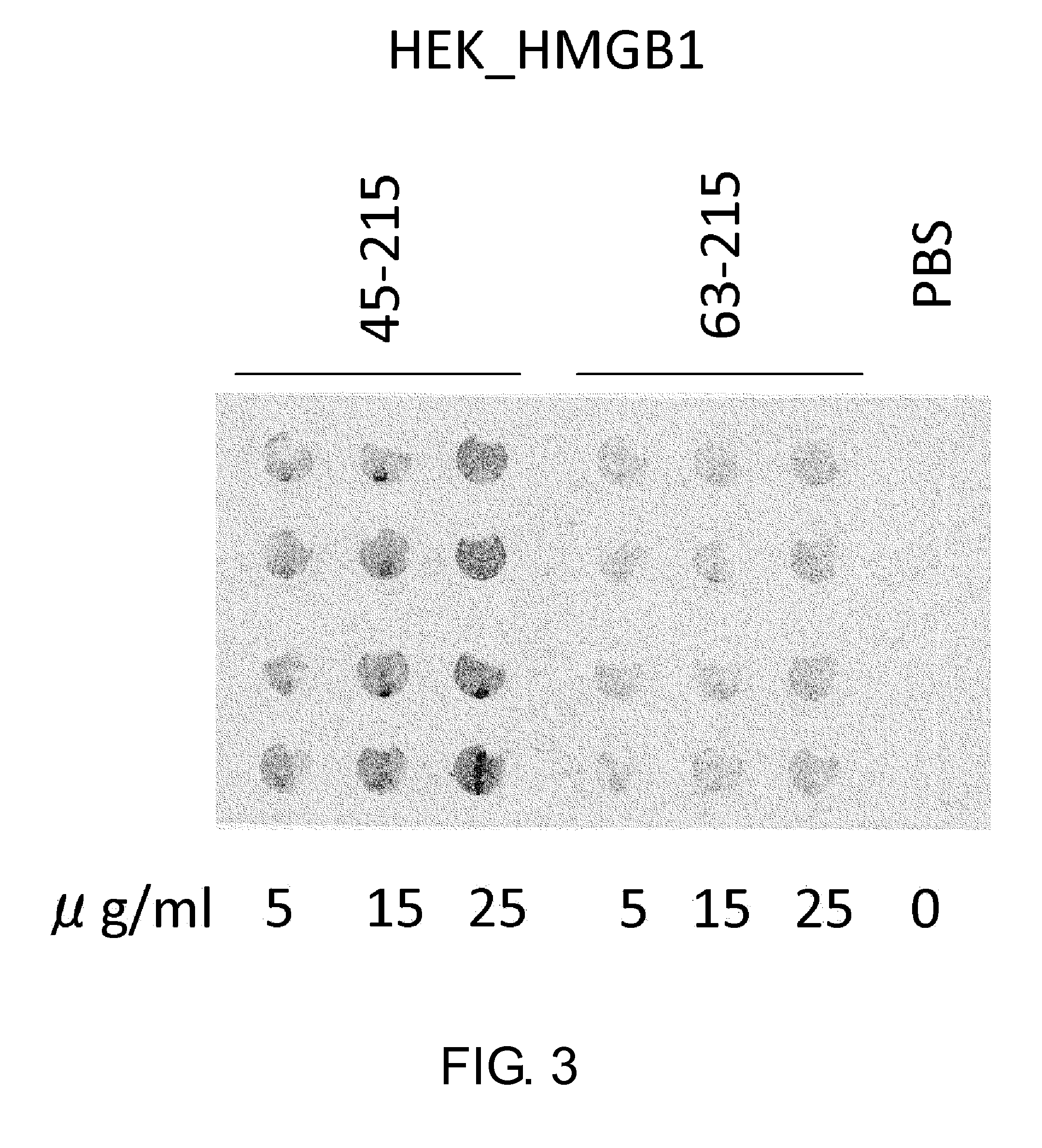
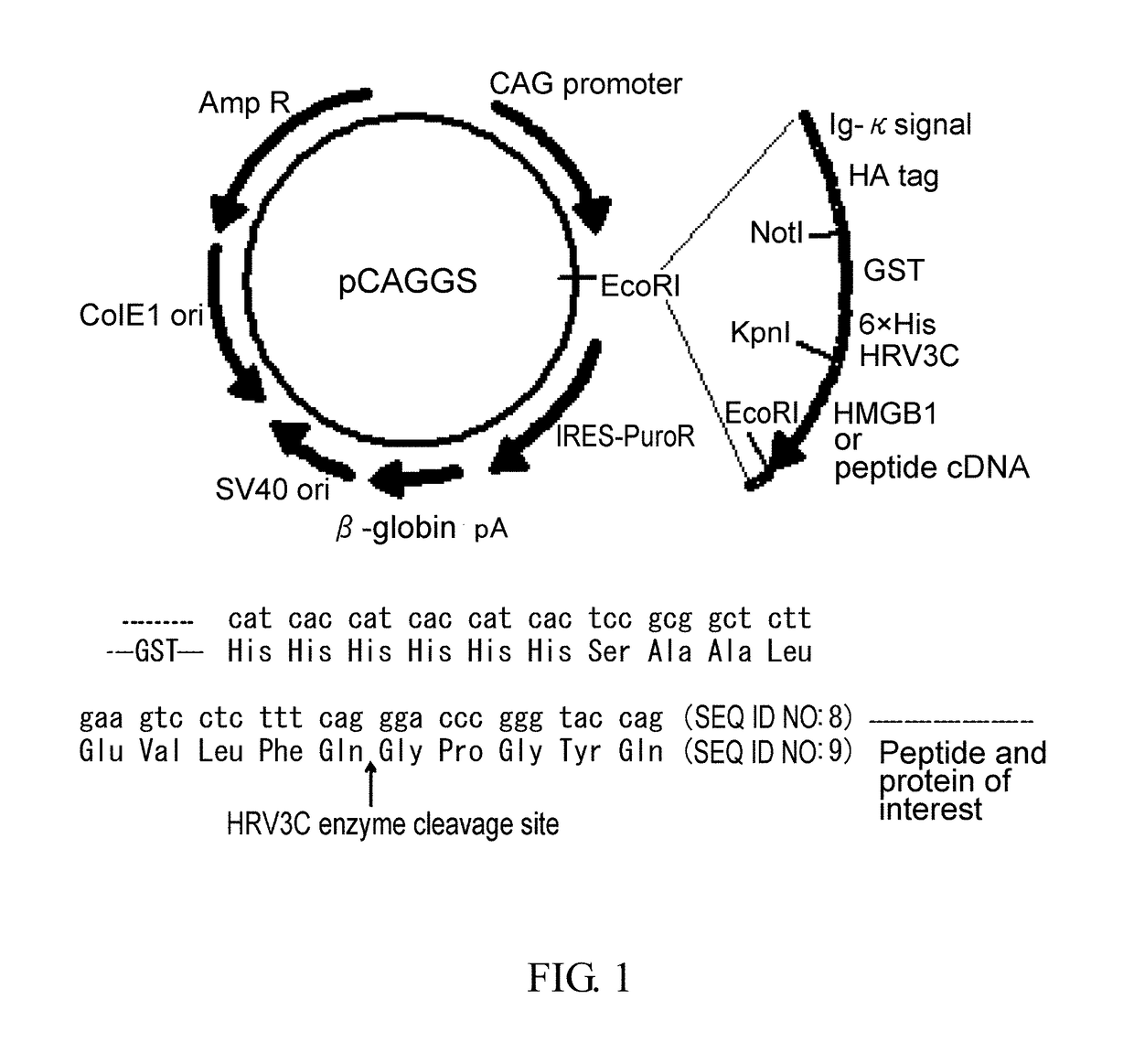
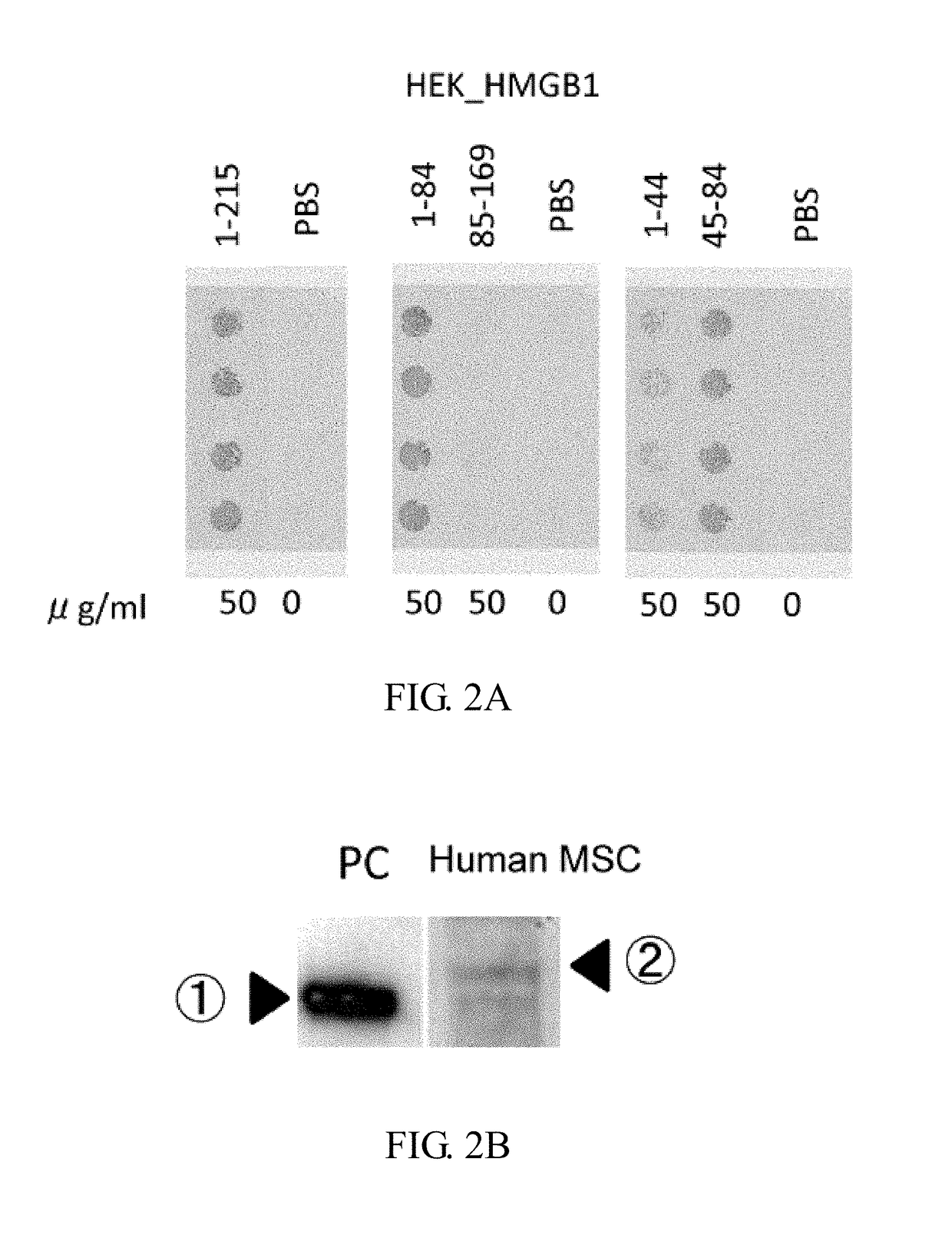
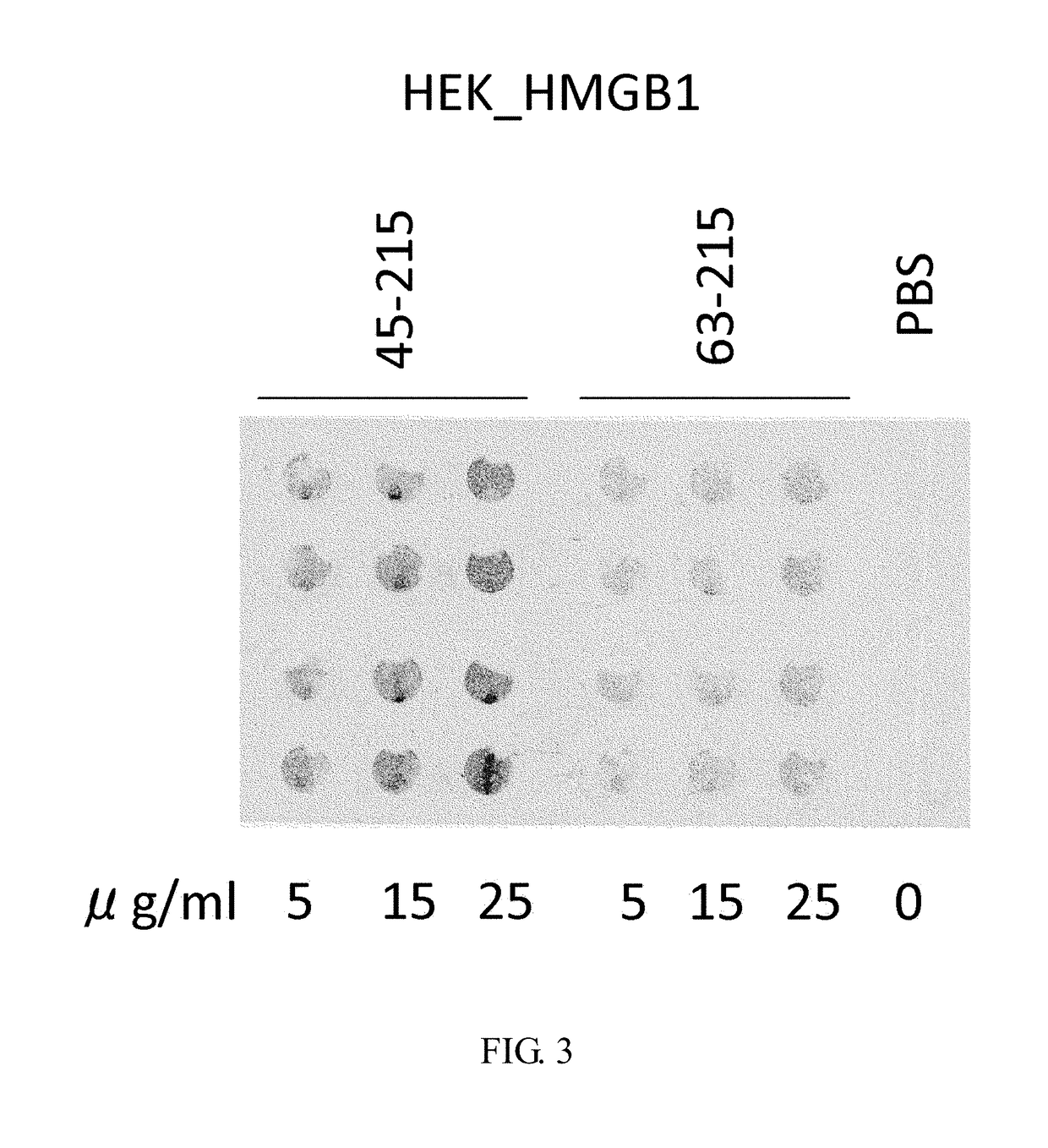
Novel Method for Treating Cardiac Infarction Using HMGB1 Fragment
ActiveUS20150273017A1Therapeutic effectAccelerate the accumulation processCytokine-induced proteinsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic effectUnexpected therapeutic effect
A fragment peptide having a proper length composed of a part of an HMGB1 protein was synthesized and the peptide was confirmed to exhibit therapeutic effects on myocardial infarction.
Owner:STEMRIM INC +1
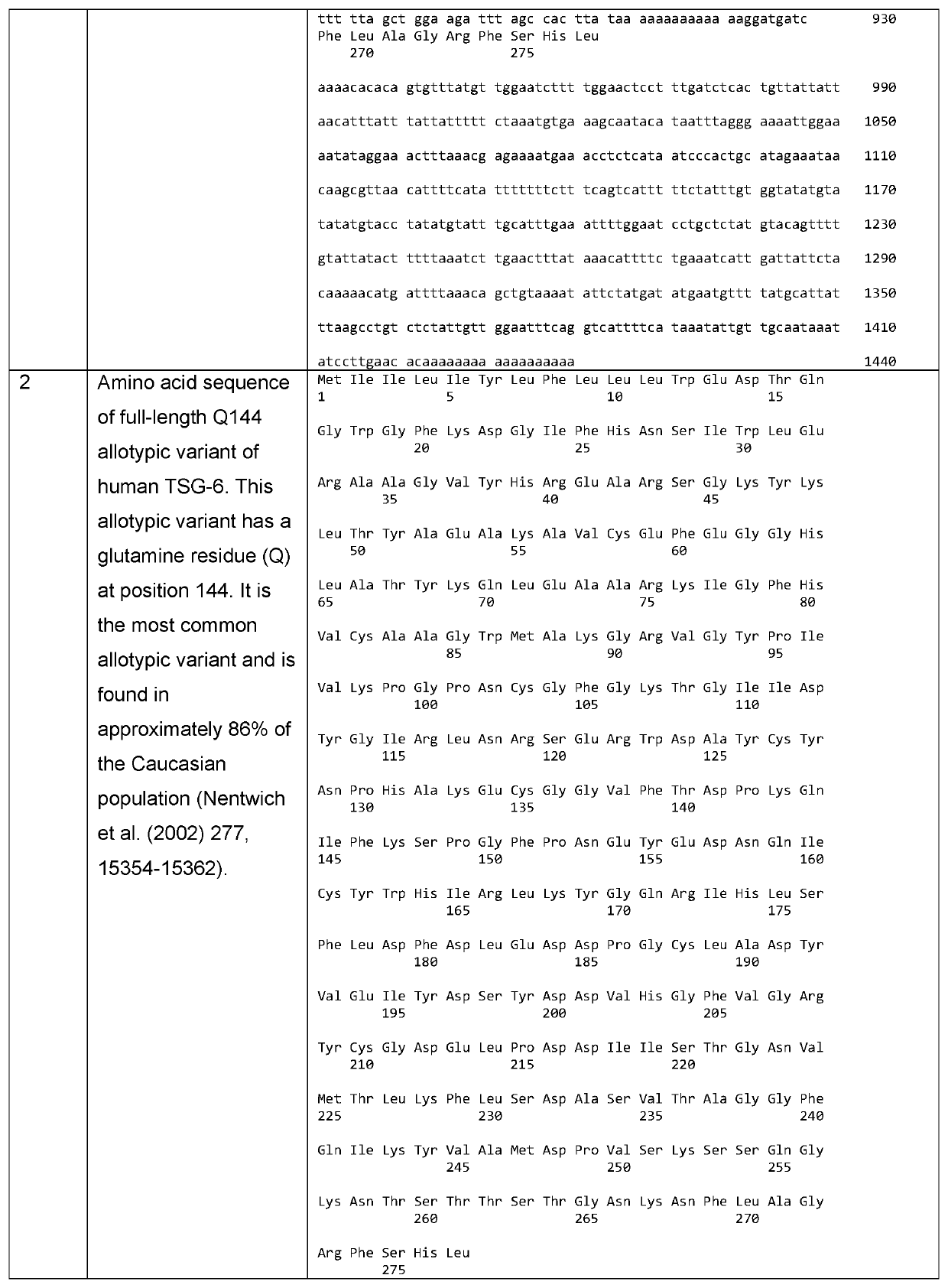
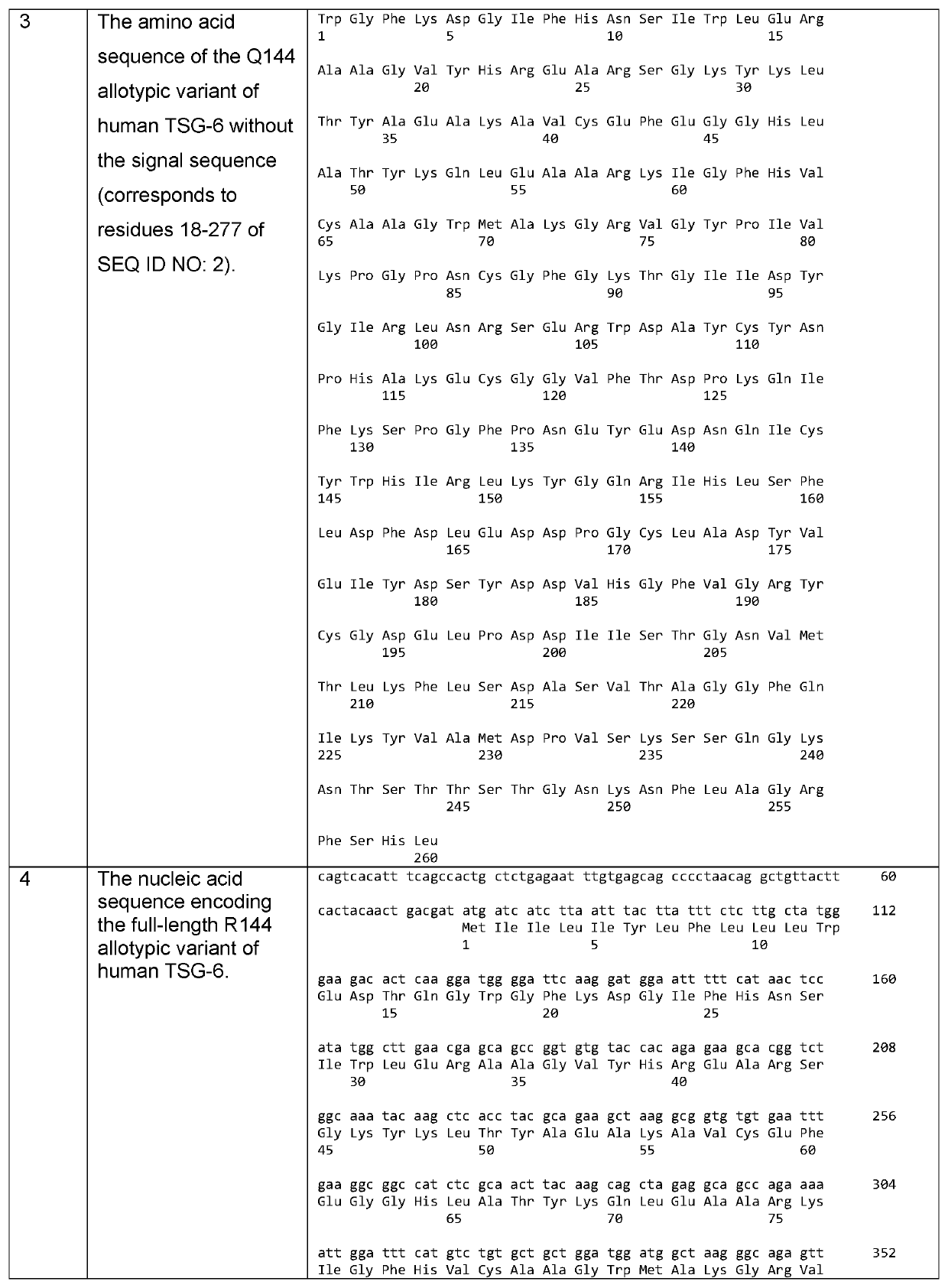
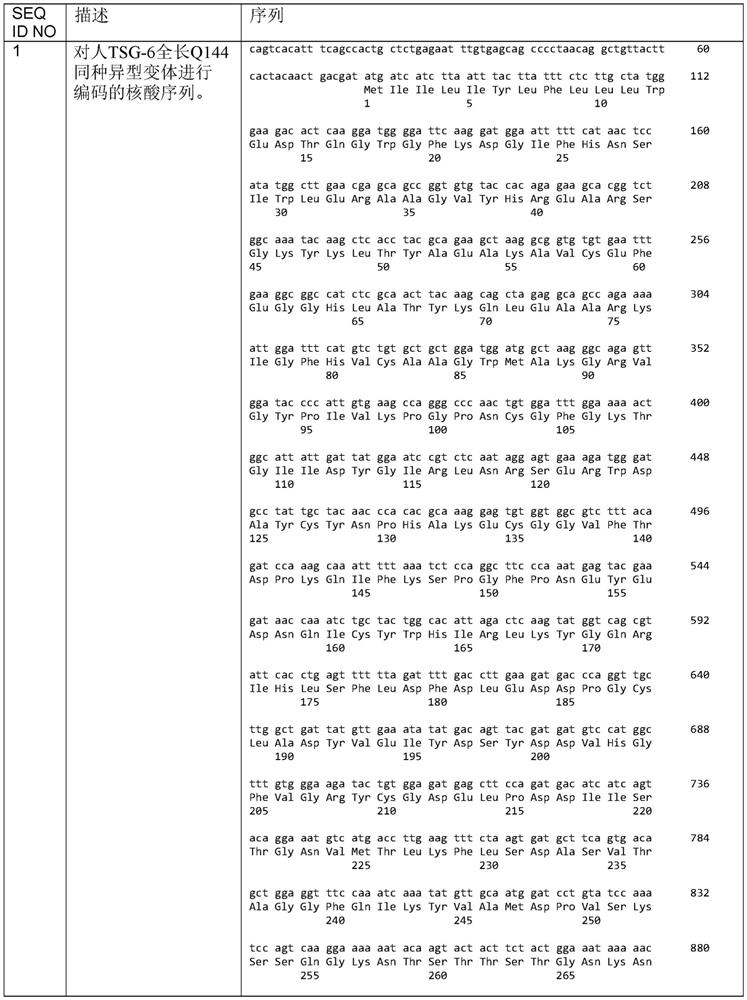
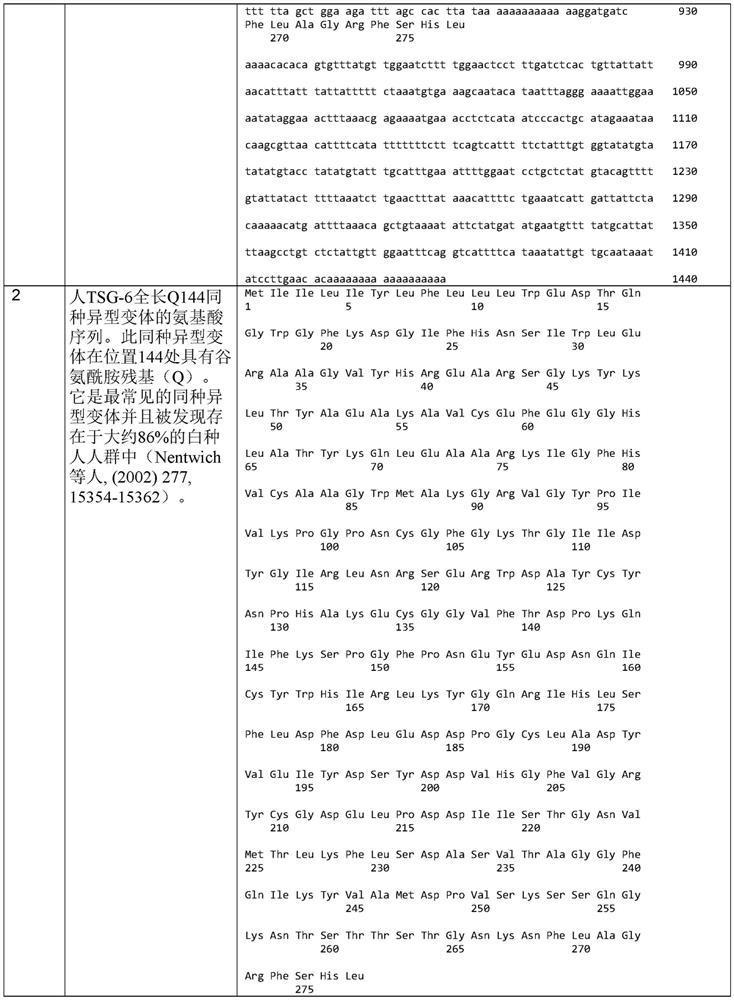
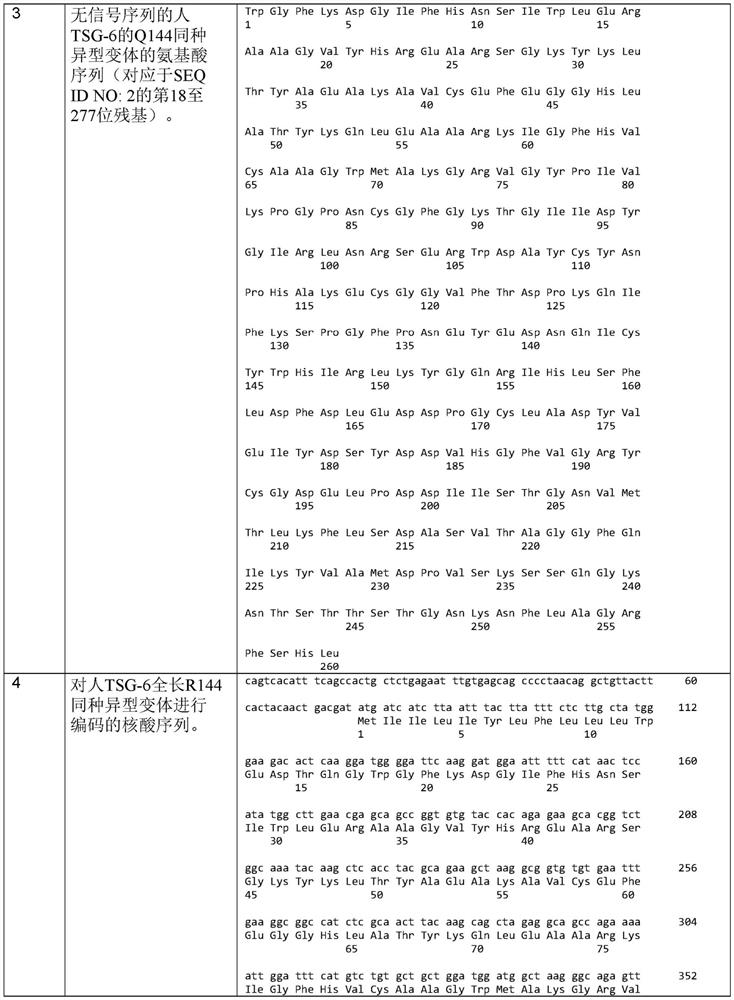
Recombinant human TSG-6 protein, preparation method thereof and application of recombinant human TSG-6 protein in treatment of acute inflammatory diseases
InactiveCN108530528AGood treatment effectCytokine-induced proteinsPeptide/protein ingredientsTSG-6Inclusion bodies
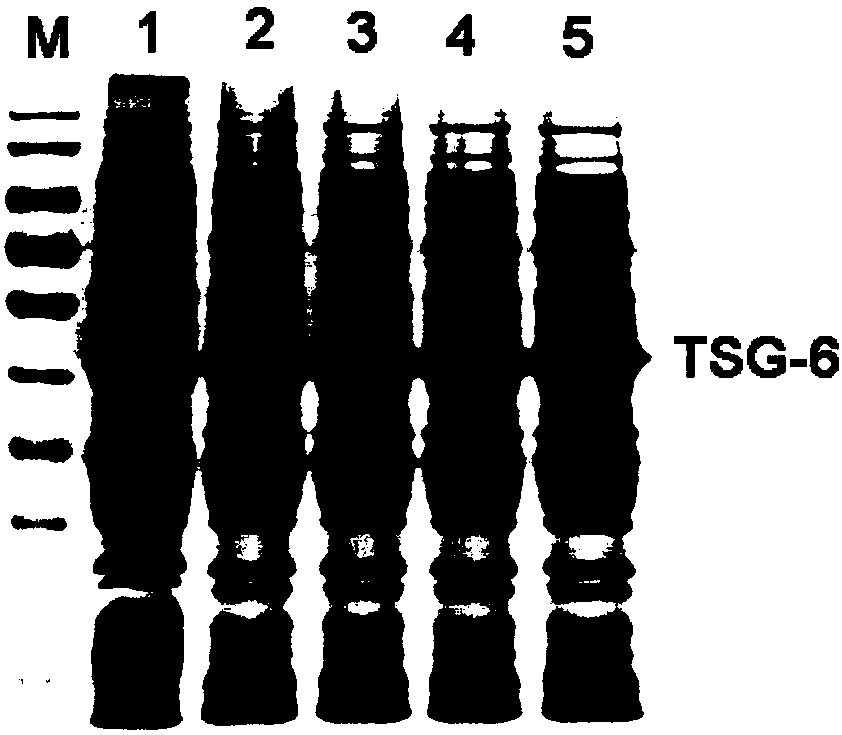
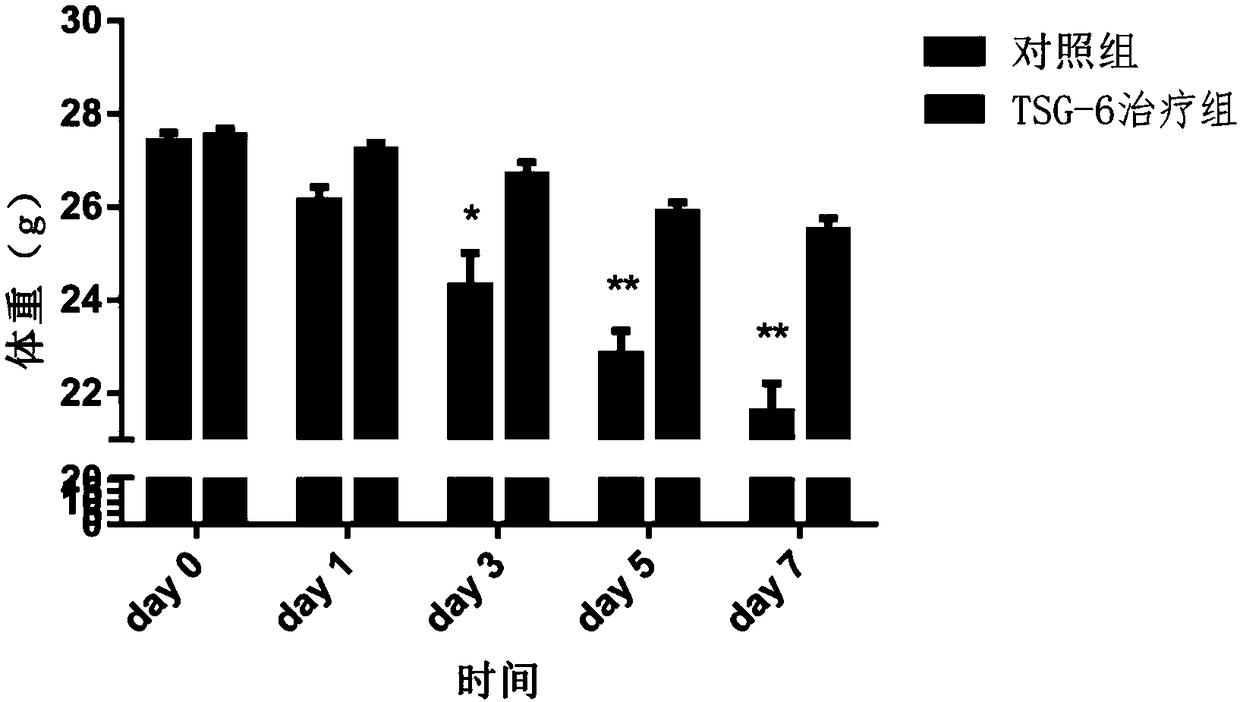
The invention discloses recombinant human TSG-6 protein, a preparation method thereof and application of the recombinant human TSG-6 protein in the treatment of acute inflammatory diseases. The aminoacid sequence of the recombinant human TSG-6 protein is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and the encoding gene nucleotide sequence of the recombinant human TSG-6 protein is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2. The recombinant human TSG-6 protein and the preparation method and application thereof have the advantages that a prokaryotic expression vector pET30a is utilized to build an Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) host strain capable of expressing the recombinant human TSG-6 protein, the strain is subjected to multiplication culture, isopropyl-beta-D-isopropylthiogalactoside induced expression and centrifuging are performed to obtain a thallus, the thallus is split and then inclusion body precipitate is collected centrifugally, and denaturation, renaturation and molecular-sieve purification are performed to obtain the recombinant human TSG-6 protein; the recombinant human TSG-6 protein has a good curative effect on the acute pneumonia, caused by HCMV virus infection, of mice and provides a new thought for thetreatment of the acute inflammatory diseases caused by virus infection.
Owner:ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
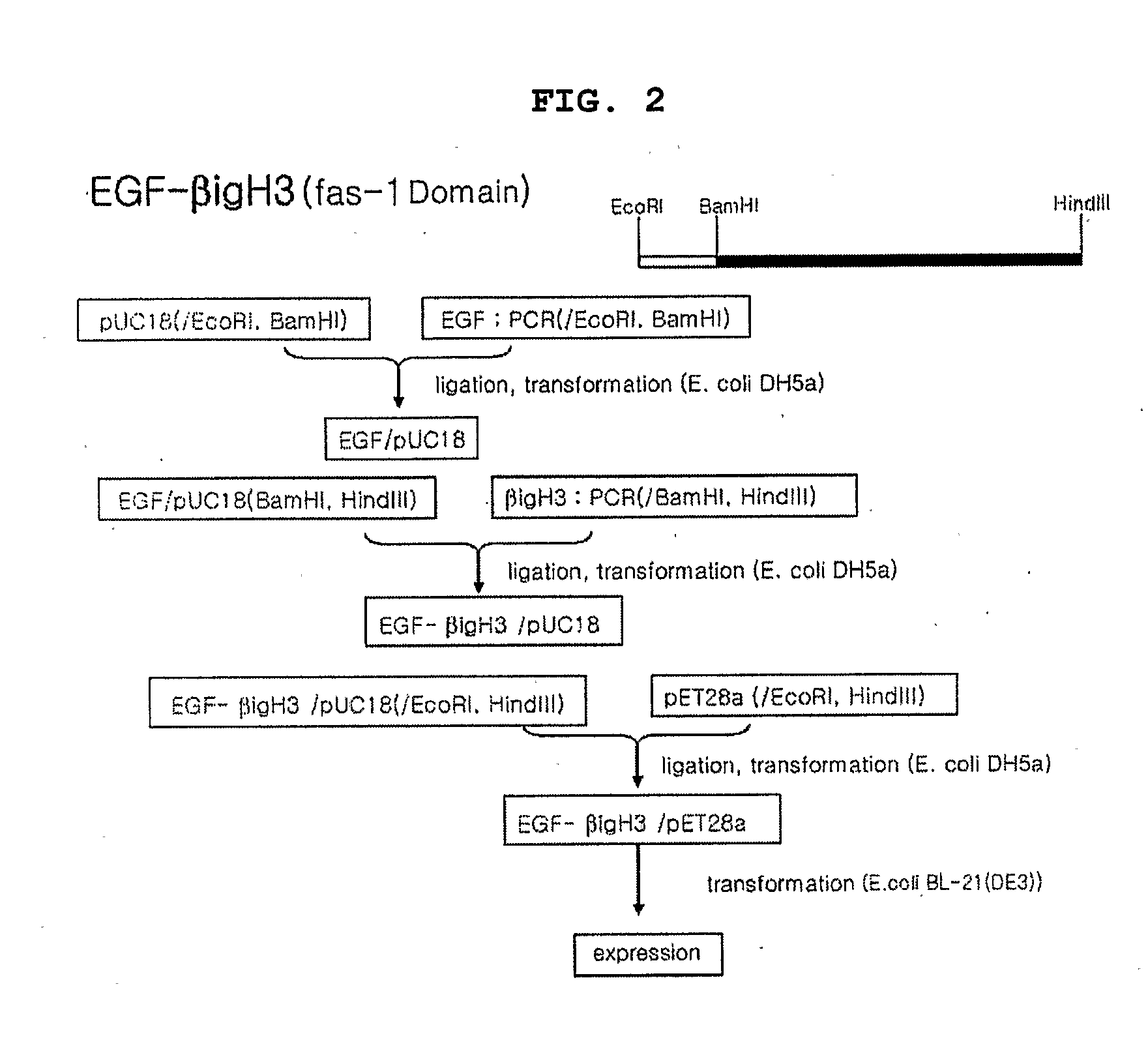
Method for Producing Epidermal Growth Factor Using Fusion Proteins Comprising Fas-1 Domain
InactiveUS20080280323A1Increase productionImprove stabilityCytokine-induced proteinsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCell adhesionCuticle
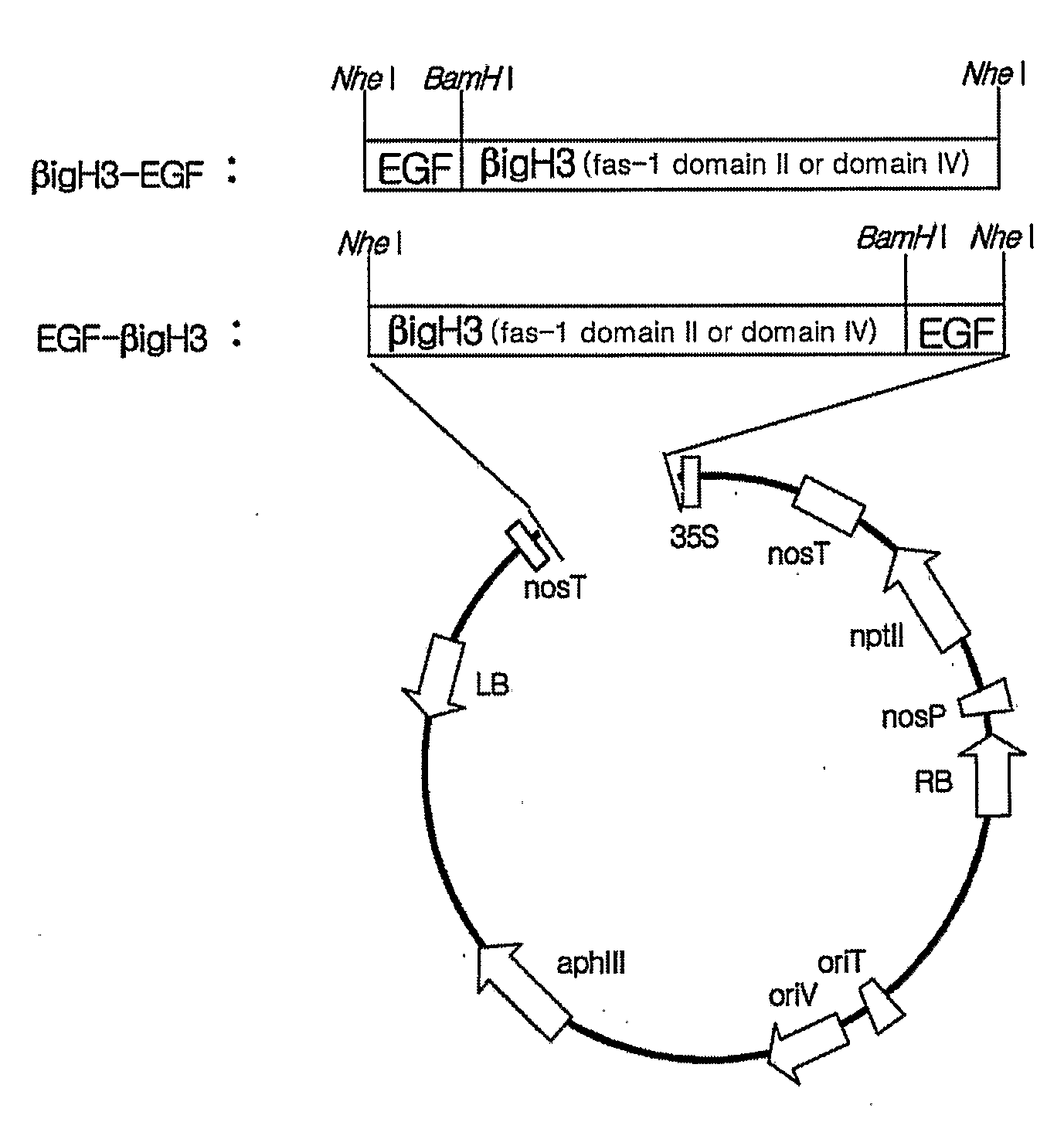
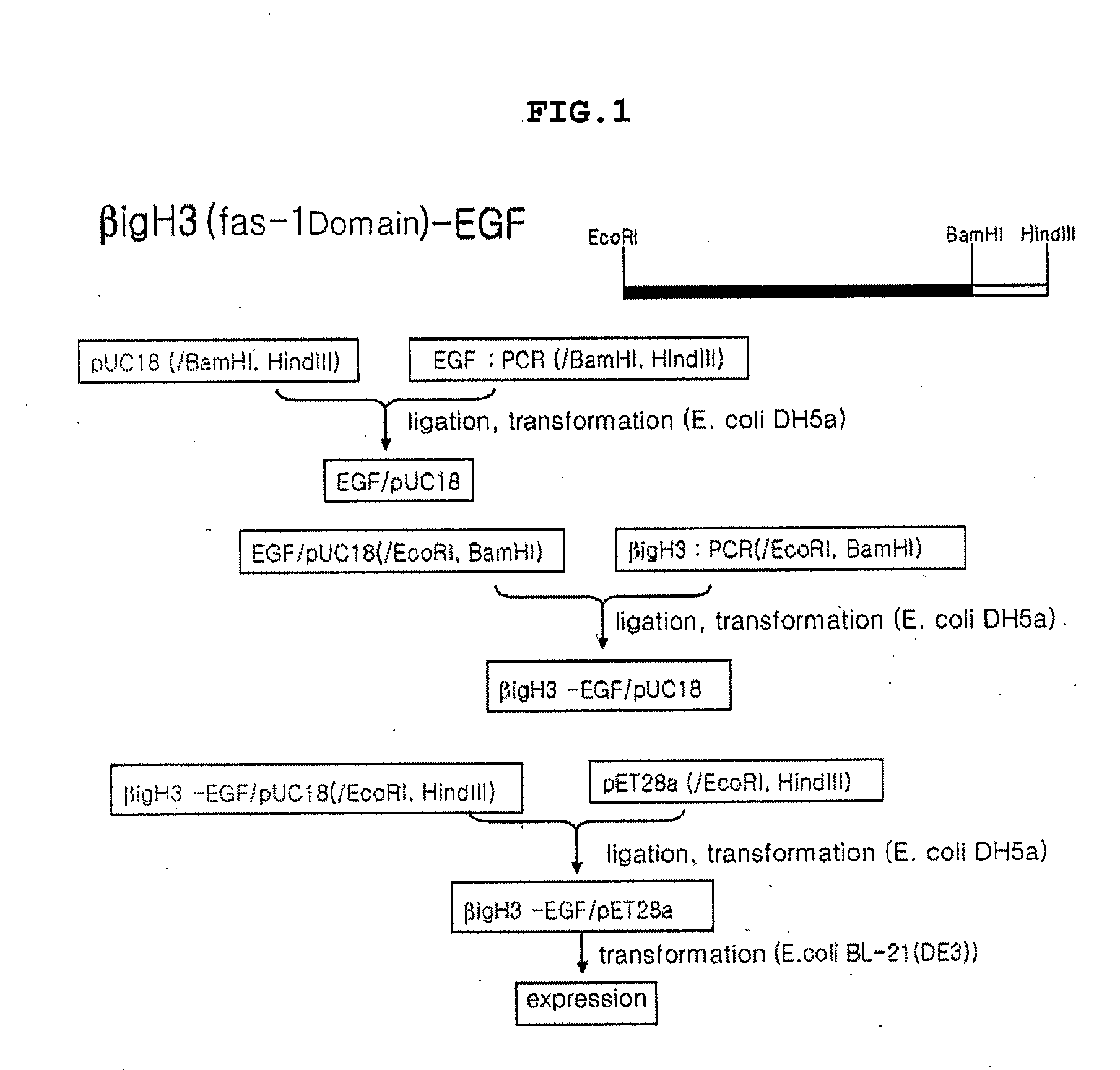
The present invention provides a fusion protein in which a polypeptide comprising Fas-1 domain is fused in frame to N-terminal or C-terminal of human EGF, a nucleotide sequence encoding the fusion protein, an expression vector containing the nucleotide sequence, a transformant transformed by the nucleotide sequence and a method for producing human EGF, improving stability of the protein and enhancing the functions of the same. The present invention provides human EGF with improved stability and enhanced functions by fusing a polypeptide comprising Fas-1 domain having the activities of cell adhesion and wound healing to human EGF.
Owner:NEXGEN BIOTECH +1
Methods of detecting inflammatory markers and treating inflammatory conditions in humans
The present invention provides methods and systems to accurately detect and measure in a biological sample from a patient, endogenous antibodies, e.g., IgA, to inflammatory proteins, which antibodies are useful as diagnostic markers for inflammatory conditions, including bowel disease (IBD), in patients. Such methods and systems identify whether a sample from the patient is associated with an inflammatory condition, by using non-invasive means, thus conveniently providing information useful for guiding treatment decisions.
Owner:VETICA LABS INC
Method for treating cardiac infarction using HMGB1 fragment
ActiveUS9623078B2Cytokine-induced proteinsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic effectMyocardial infarction
A fragment peptide having a proper length composed of a part of an HMGB1 protein was synthesized and the peptide was confirmed to exhibit therapeutic effects on myocardial infarction.
Owner:STEMRIM INC +1
Antibodies Against Hmgb1 and Fragments Thereof
In various embodiments, the present invention is drawn to antibodies or antigen-binding fragments thereof that bind to particular fragments of HMGB1, methods of treating a condition in a subject characterized by activation of an inflammatory cytokine cascade, methods of detecting and / or identifying an agent that binds to an HMGB1 polypeptide or fragment thereof, and methods of detecting HMGB1 in a sample.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
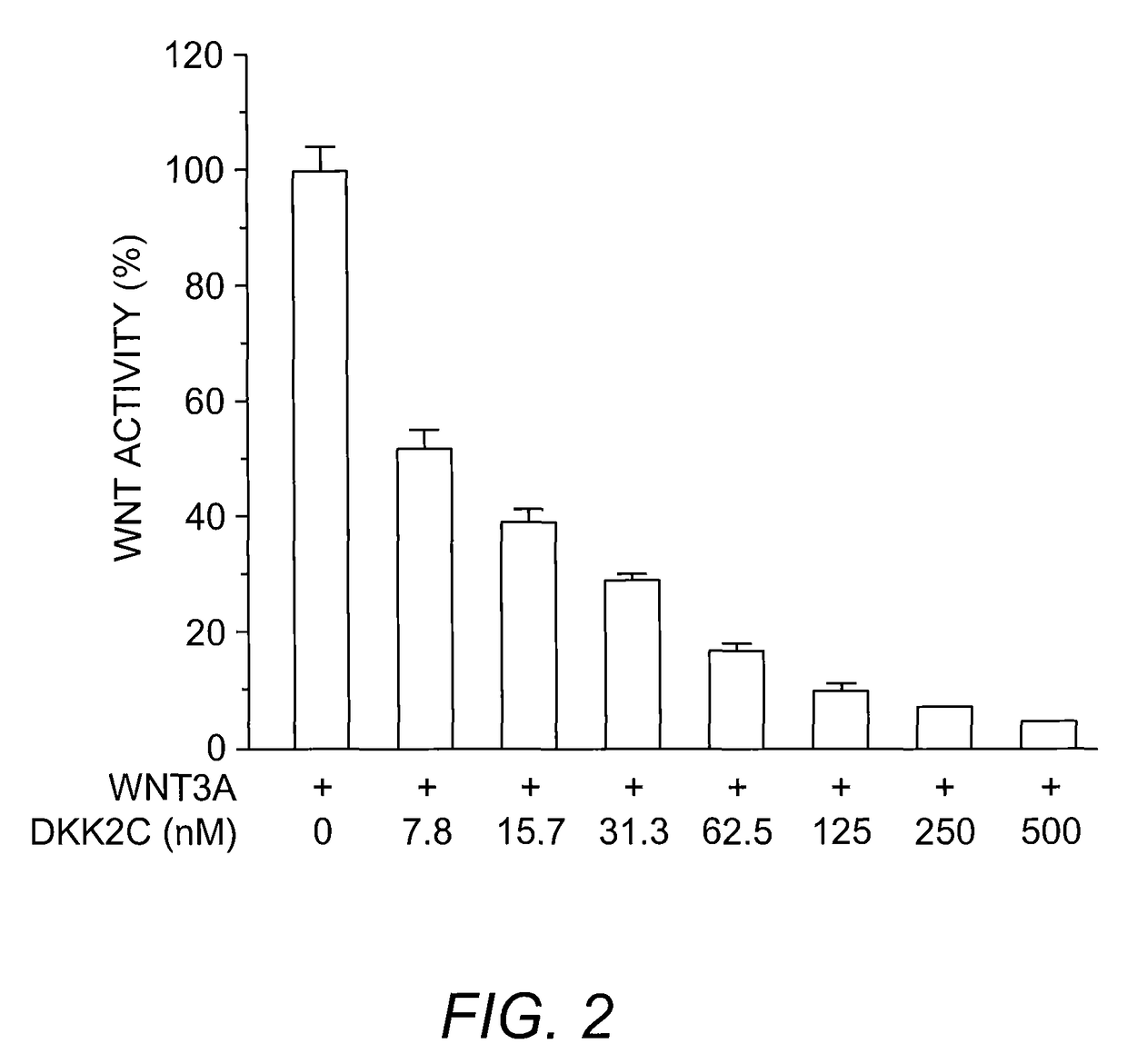
Prokaryotic Expression of Soluble, Active Dkk
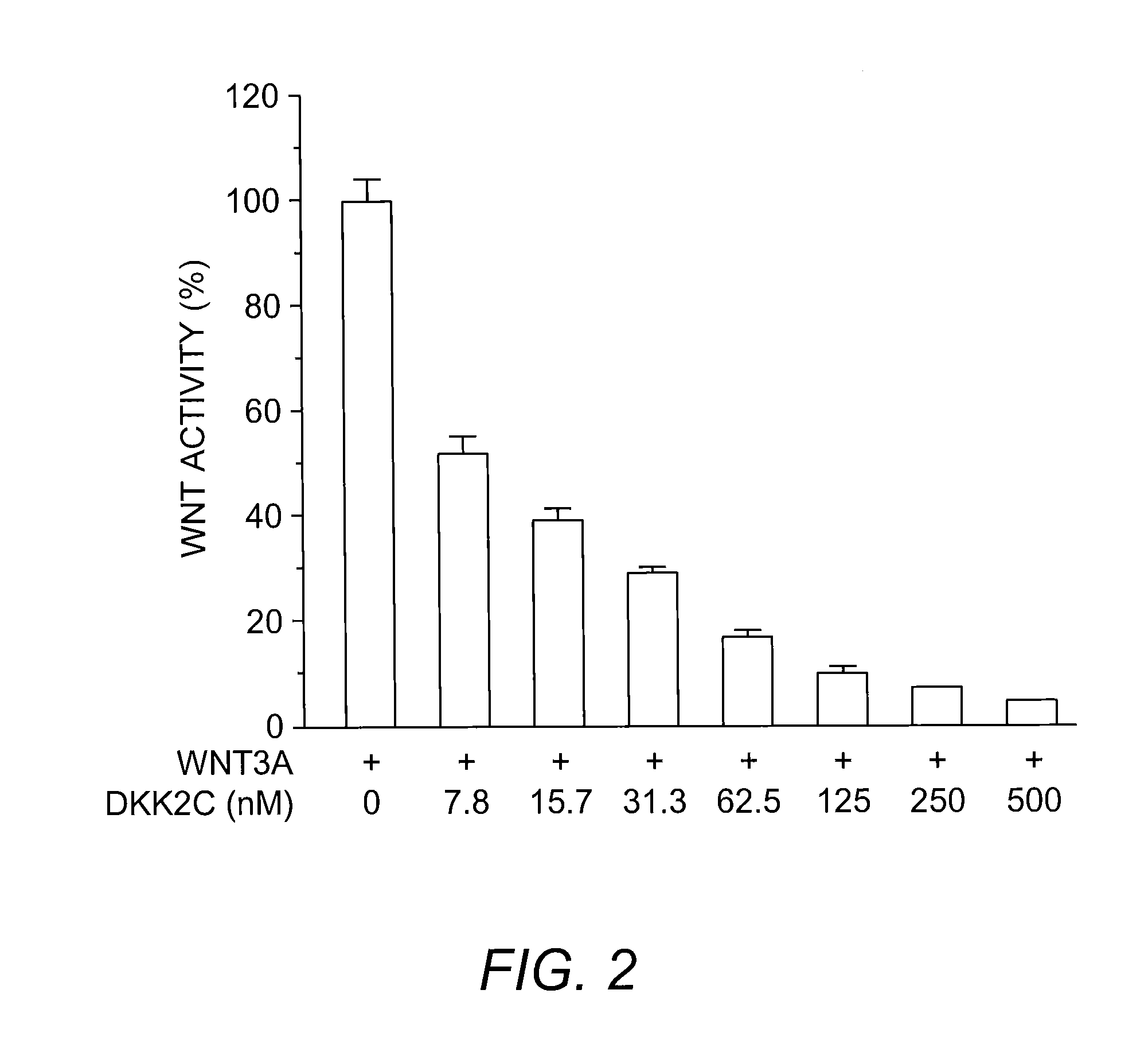
Dickkopf (Dkk) proteins inhibit the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Each of the members of the Dkk family has been previously cloned and expressed as a soluble protein in eukaryotic cells, while expression in bacterial cells has resulted in the formation of insoluble inclusion bodies that require further processing. The present invention provides compositions and methods for producing soluble, active dkk protein in prokaryotic host cells, by expressing the dkk protein as a fusion protein with a solubilization molecule, thereby providing an inexpensive and convenient source of pure active Dkk.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Interferon-induced human protein in pure form, monoclonal antibodies thereto and test kits containing these antibodies
The invention relates to purified proteins induced in human cells by interferon alpha or beta, RNAs, DNAs and hybrid vectors coding for said proteins, hosts transformed with such a hybrid vector, processes for the preparation and purification of these proteins, DNAs, vectors and hosts, monoclonal antibodies specific to these proteins, monoclonal antibody derivatives, hybridoma cell lines secreting these monoclonal antibodies, the use of the monoclonal antibodies and their derivatives in the qualitative and quantitative determination of these proteins, test kits containing the monoclonal antibodies, and pharmaceutical preparations containing said proteins. A protein of the invention shows antiviral properties ascribed to interferons and may be a valuable indicator of the cell response to an interferon therapy.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Peptide for inducing regeneration of tissue and use thereof
ActiveUS20140206619A1Therapeutic effectCytokine-induced proteinsNervous disorderDamages tissueLiving body
Owner:STEMRIM INC +1
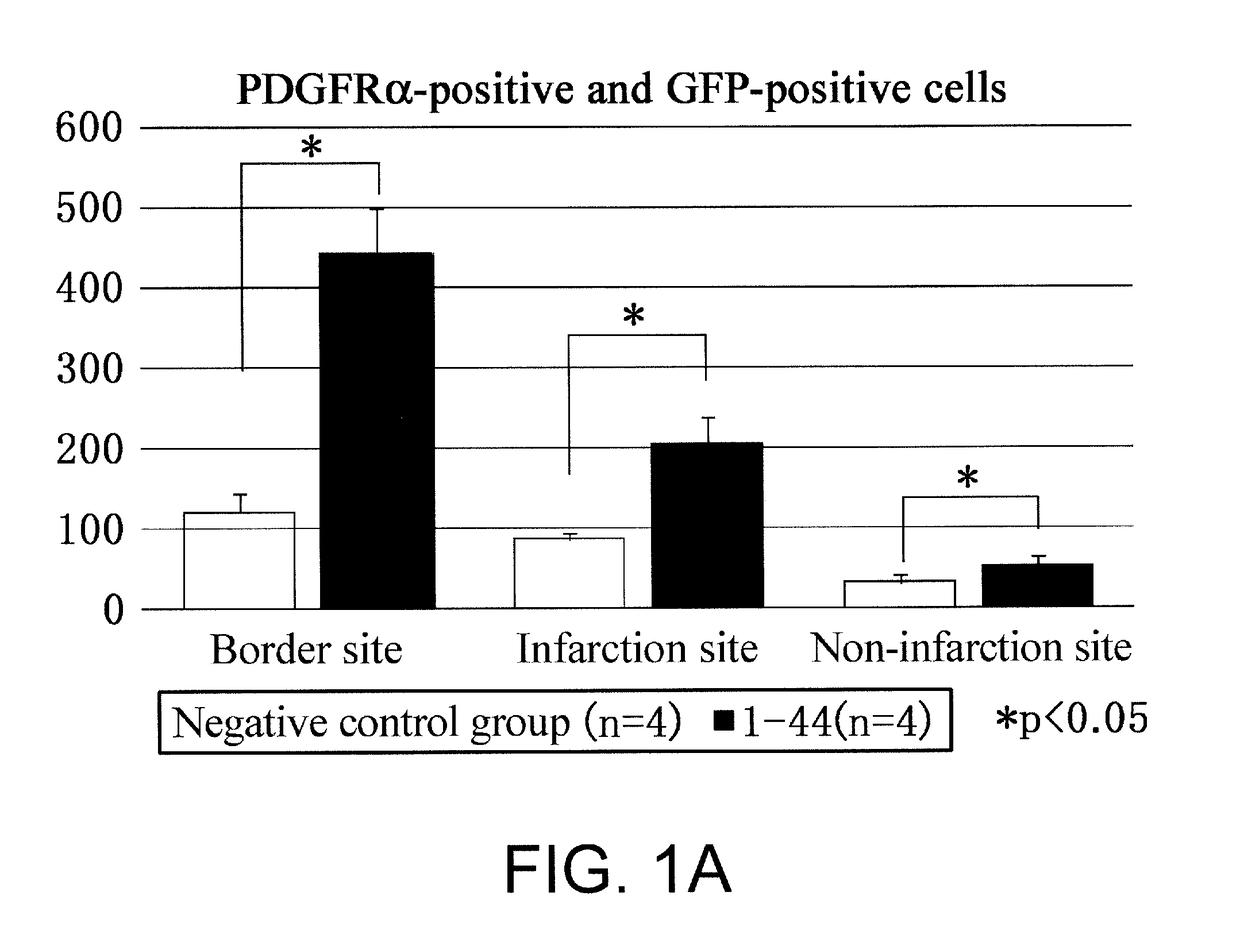
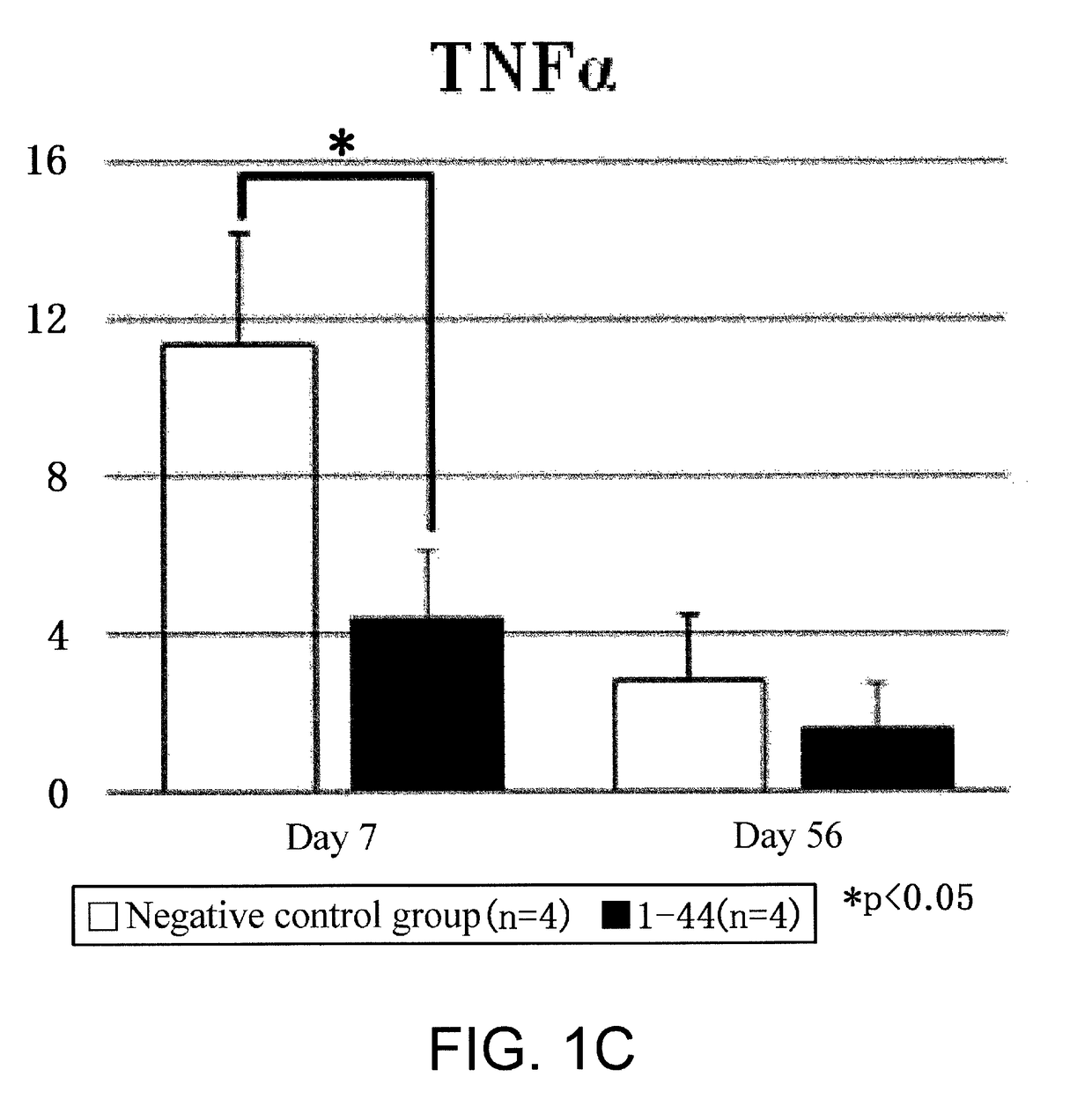
Peptide for inducing regeneration of tissue and use thereof
ActiveUS20180072785A1Small sizeEnhanced migration-promoting activityCytokine-induced proteinsNervous disorderDamages tissueLiving body
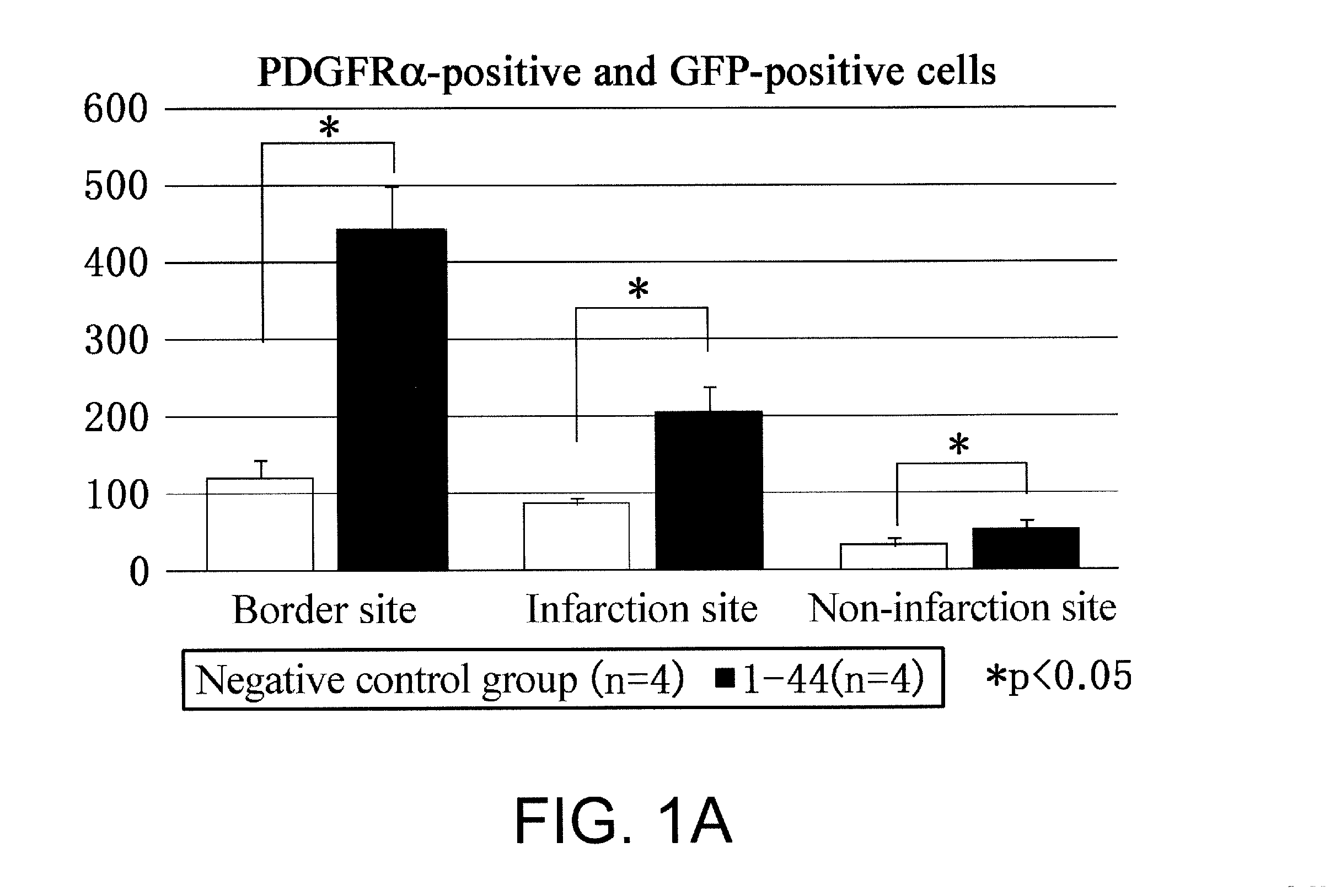
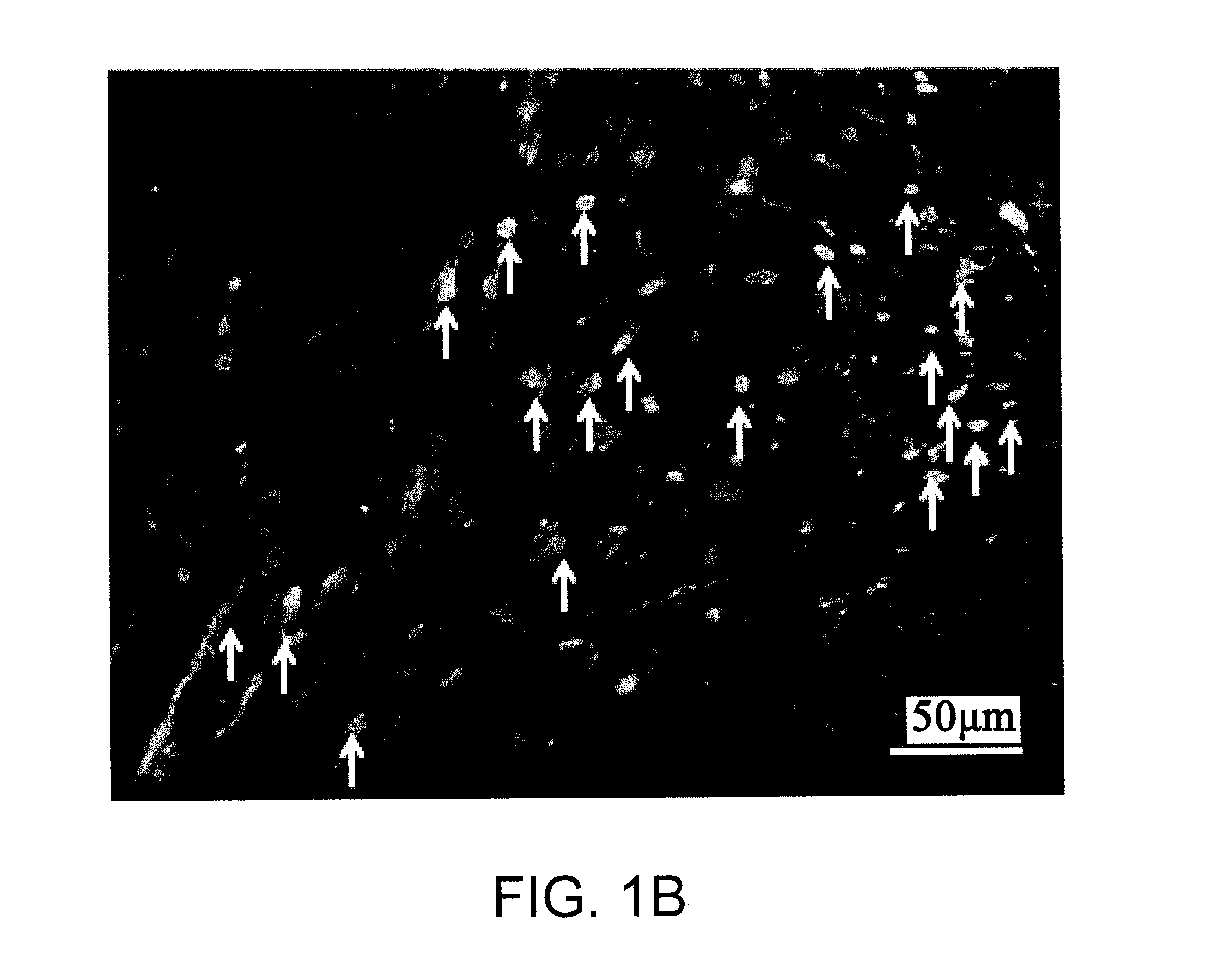
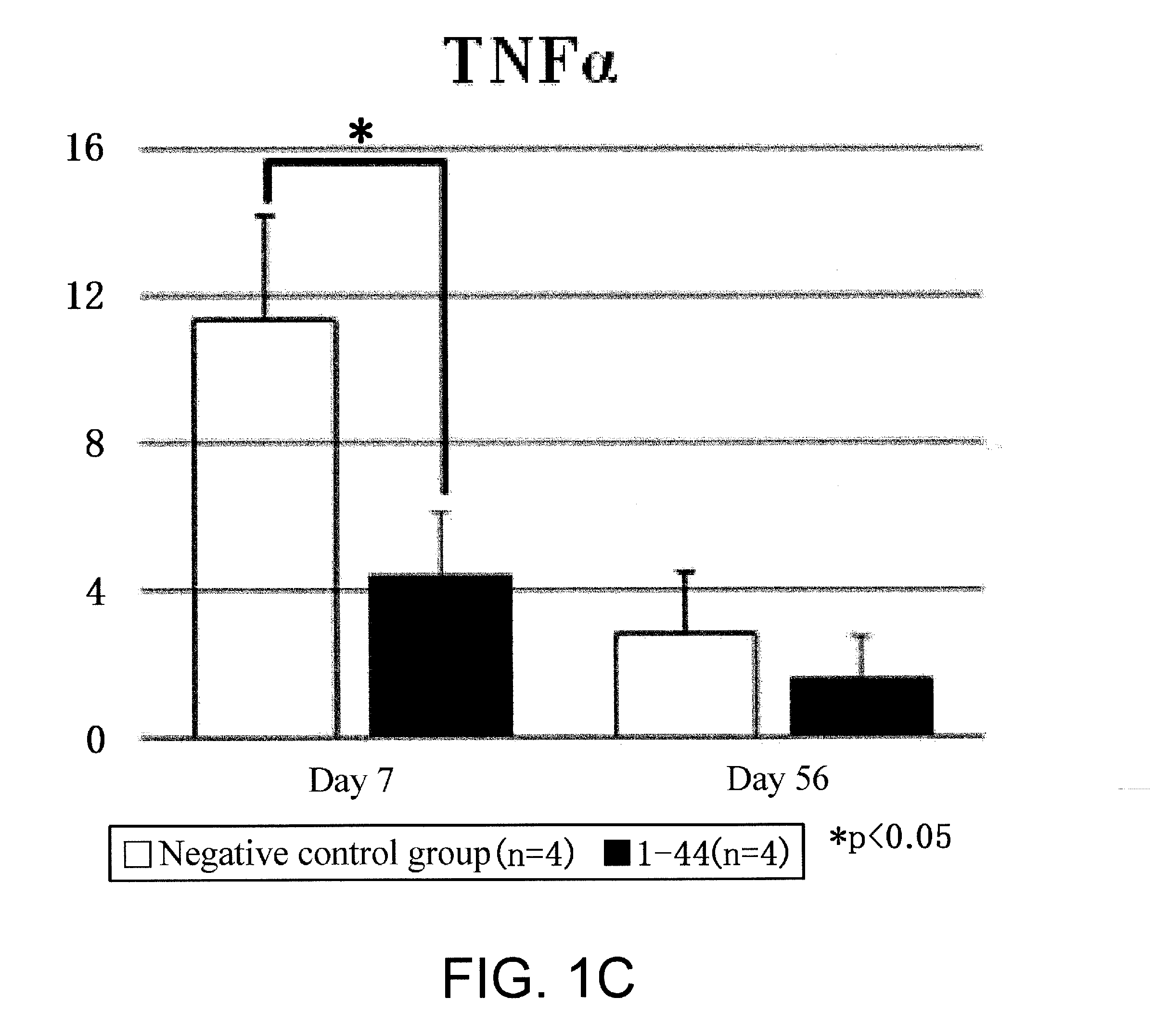
(Objective) An objective of the present invention is to provide therapeutic agents that, in association with stimulation of PDGFRα-positive cells such as bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, promote their mobilization into blood and accumulation in a damaged tissue, and induce tissue regeneration in a living body.(Means for solution) Multiple peptides were synthesized, and the migration-promoting activity of each peptide was evaluated. As a result, the present inventors successfully identified multiple peptides that have migration-promoting activity on a PDGFRα-positive bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell line (MSC-1). Further, the present inventors confirmed that the identified peptides also have migration-promoting activity on skin fibroblasts, which are PDGFRα-positive cells.
Owner:STEMRIM INC +1
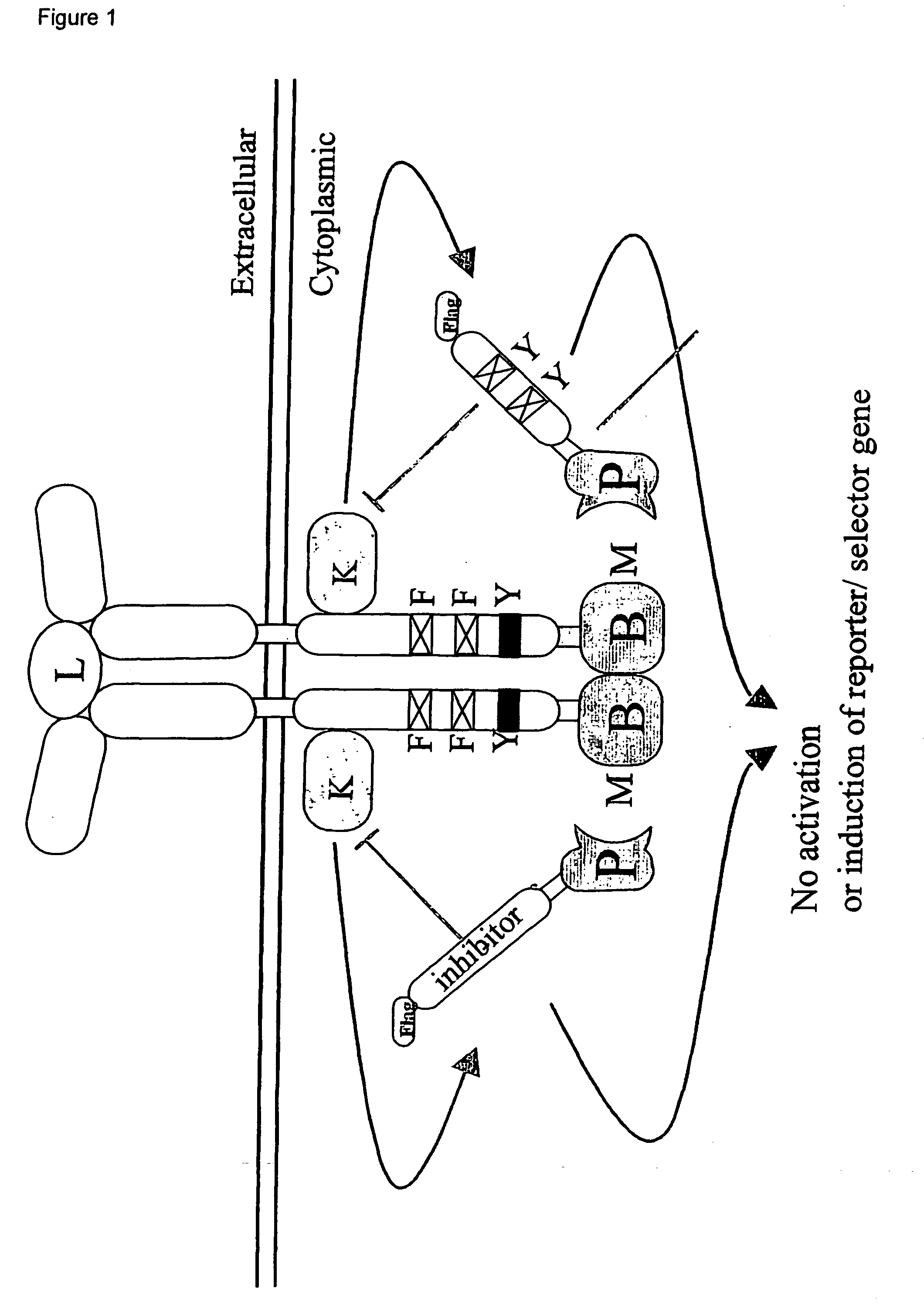
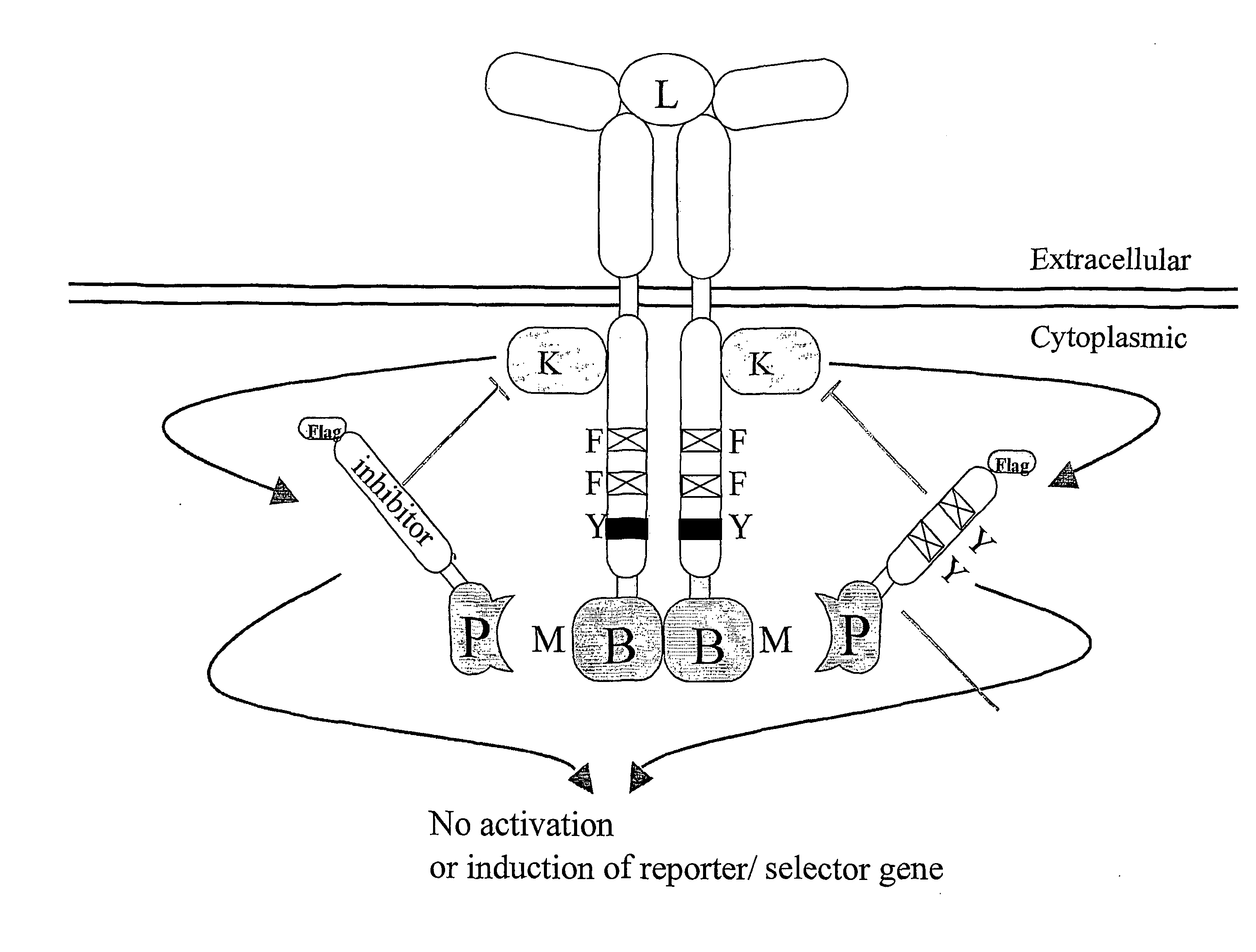
Reversed mammalian protein-protein interaction trap
InactiveUS20040166538A1Increase flexibilityEasy to identifyCytokine-induced proteinsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHeterologousLigand binding domain
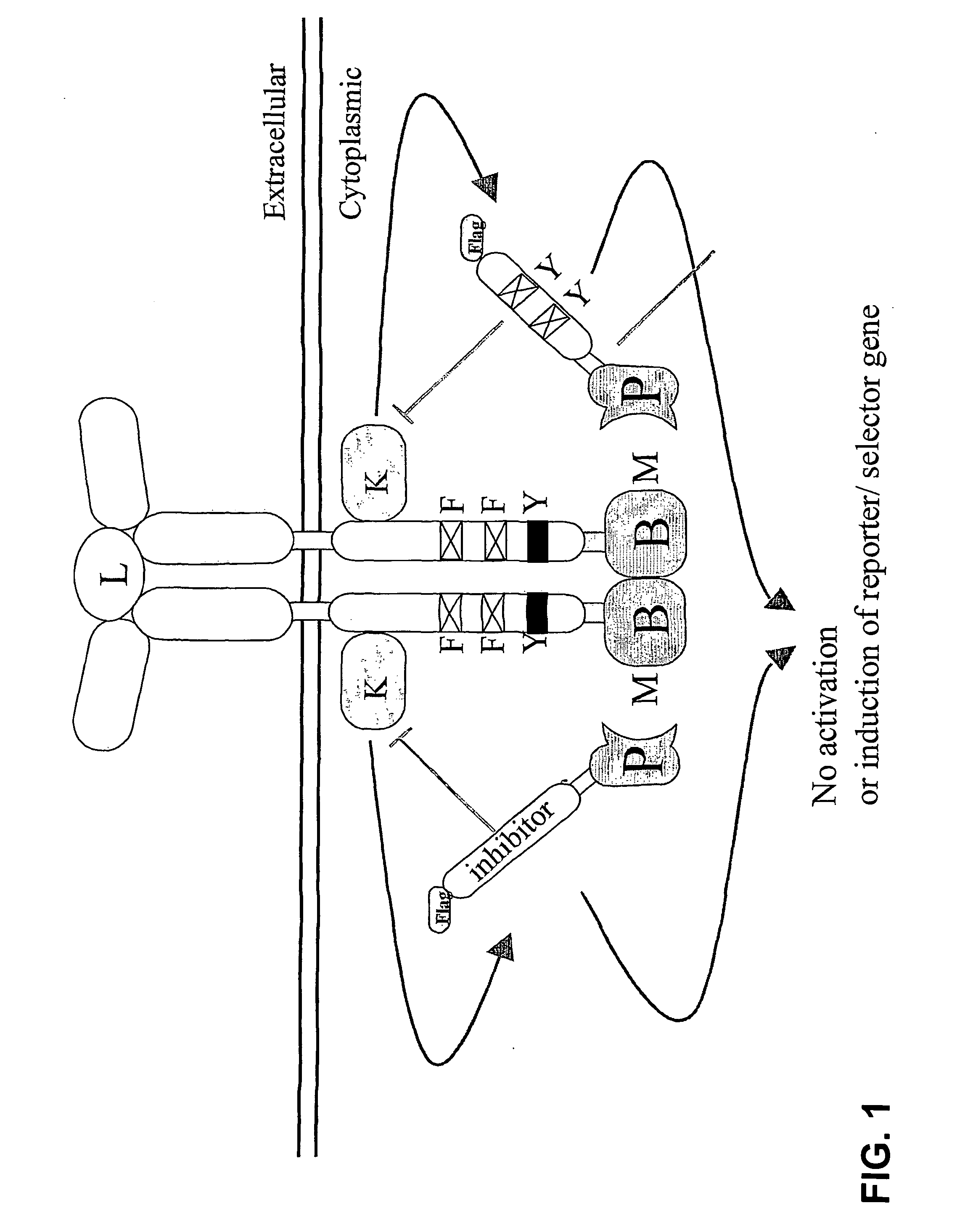
The present invention relates to a recombinant receptor, comprising a ligand-binding domain and a signaling domain that comprises a heterologous bait polypeptide, which receptor is inactivated by binding of a prey polypeptide to the heterologous bait peptide, either in presence or absence of a ligand binding to the ligand-binding domain. The receptor is activated by addition of a compound that disrupts the bait-prey interaction. The present invention also relates to a method of screening compounds that disrupt compound-compound-binding using the recombinant receptor.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW
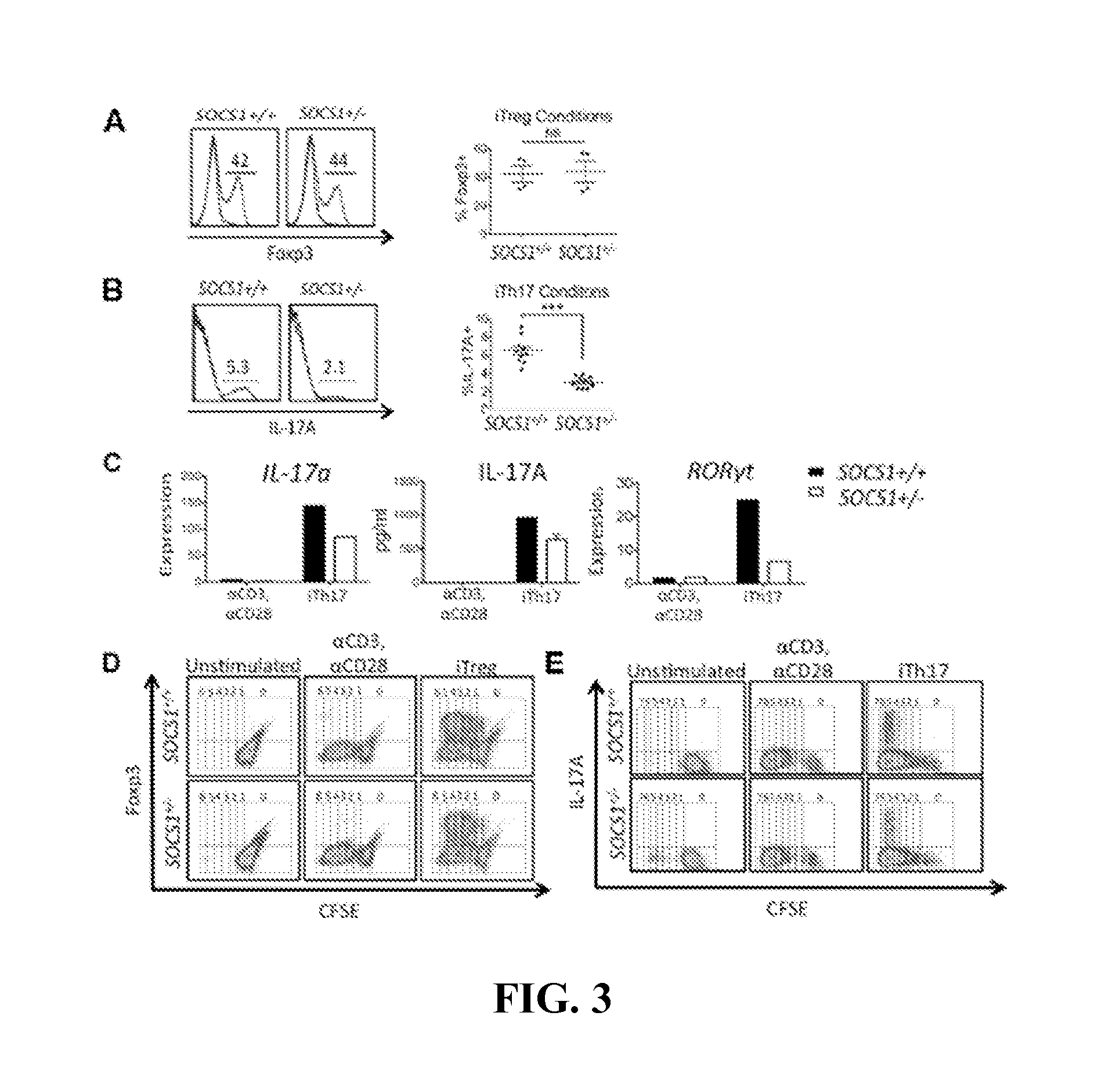
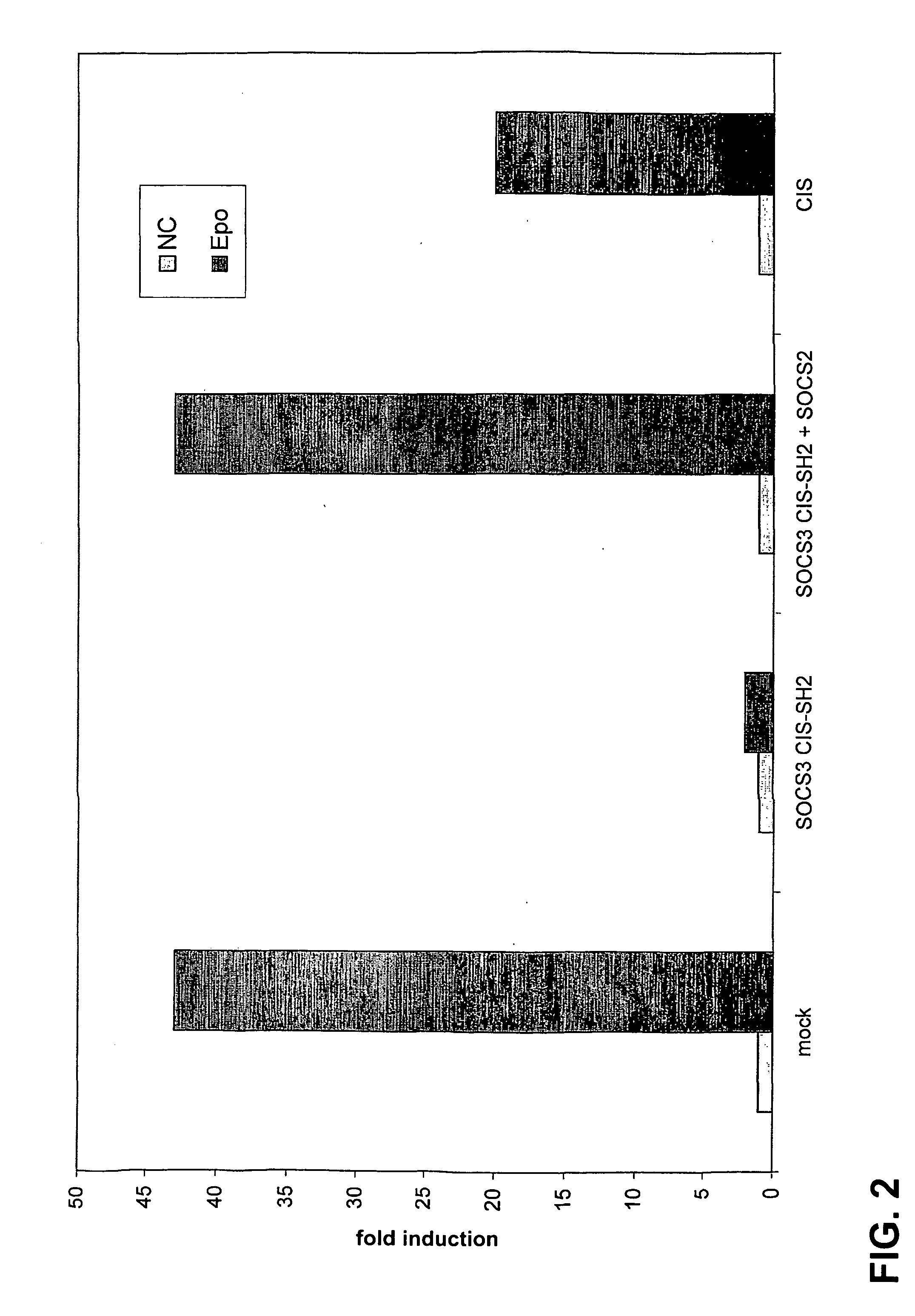
Socs mimetics for the treatment of diseases
ActiveUS20170008929A1Activation thresholdReduced SOCS expressionOrganic active ingredientsCytokine-induced proteinsMultiple copyProtein target
The subject invention concerns peptide mimetics of SOCS proteins and methods of use. In one embodiment, a peptide mimetic of the invention binds to a SOCS1 and a SOCS3 target protein. In a specific embodiment, a peptide mimetic of the invention comprises the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:1 and / or SEQ ID NO:2 and / or SEQ ID NO:51, or a functional fragment or variant thereof. In a further embodiment, a peptide of the invention can comprise multiple copies of the mimetic sequence. In one embodiment, a peptide of the invention comprises two or more copies of SEQ ID NO:1 and / or SEQ ID NO:2 and / or SEQ ID NO:51. In a specific embodiment, a peptide mimetic of the invention comprises the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:3 and / or SEQ ID NO:4 to and / or SEQ ID NO:52, or a functional fragment or variant thereof. The subject invention also pertains to methods of treating and / or preventing autoimmune conditions and / or disorders. In one embodiment, one or more peptide mimetics of the invention are used to treat an autoimmune condition or disorder in a person or animal. In a specific embodiment, a mimetic of the invention is used to treat SLE in a person or animal. The subject invention also concerns methods for diagnosing and / or monitoring progression of SLE in a person or animal.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
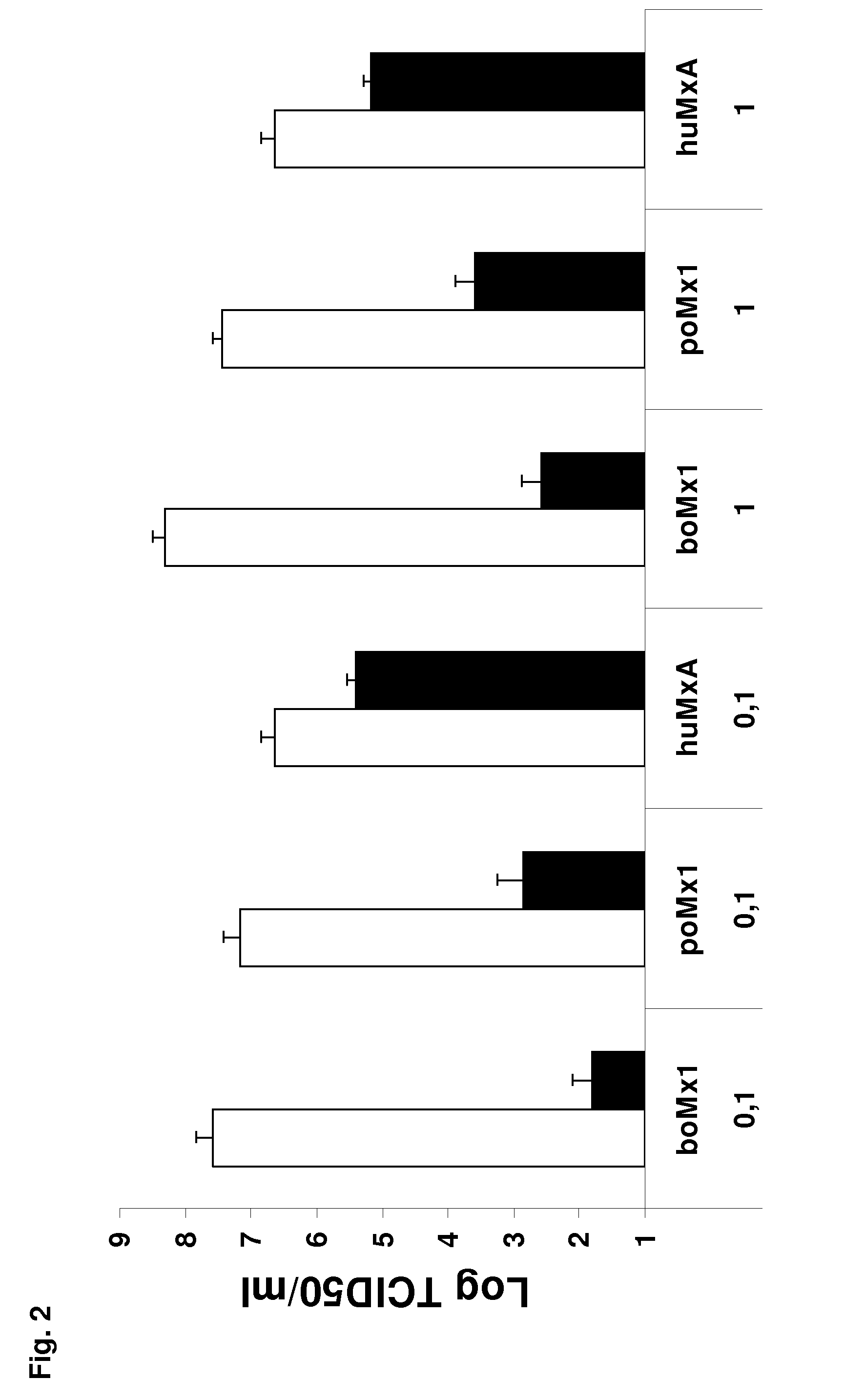
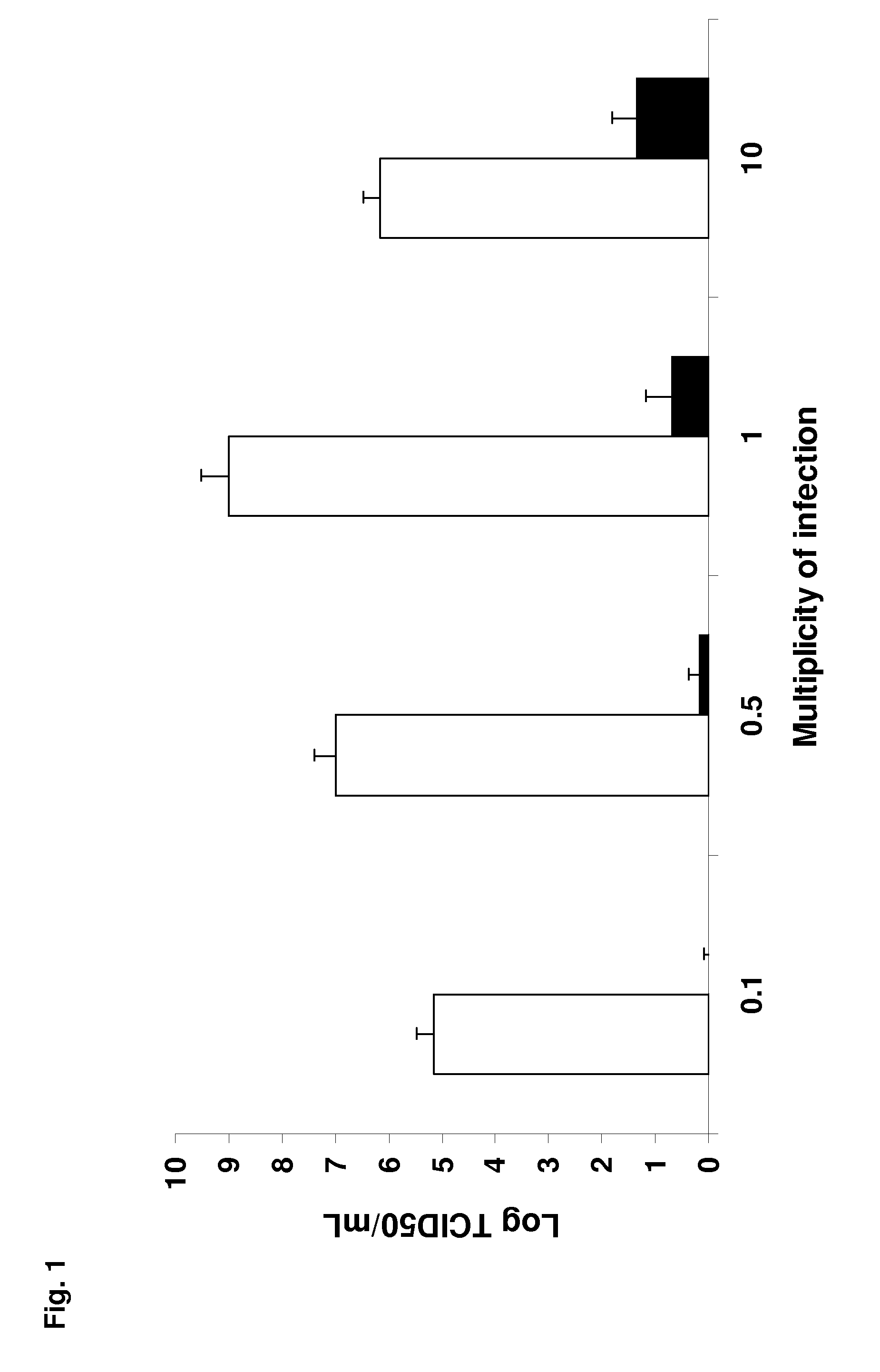
Polynucleotide for use in treatment of influenza a virus induced diseases, encoding modified mx protein, said modified mx protein, and a transgenic animal expressing gene encoding modified mx protein
InactiveUS20130245100A1High activityReduced activityCytokine-induced proteinsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseNucleotide
A method can be used for treating or reducing likelihood of an influenza A virus-induced disease in a mammal. The method includes administering a polynucleotide to the mammal. Theis polynucleotide includes a gene encoding Mx protein having a TRAF2 and / or a TRAF6 binding domain. The TRAF2 and / or TRAF6 binding domain can be represented by the sequences P-X-Q / E-E, P-X-Q / E-X-X-D, or P-X-E-E-X-E. The TRAF2 and / or TRAF6 binding domain can also be located in the Mx protein in a position which corresponds to the position of the hexapeptide PEEESE in the bovine Mx1 protein or in a position which is up to 20 amino acid residues upstream or downstream of that position.
Owner:UNIV LIEGE
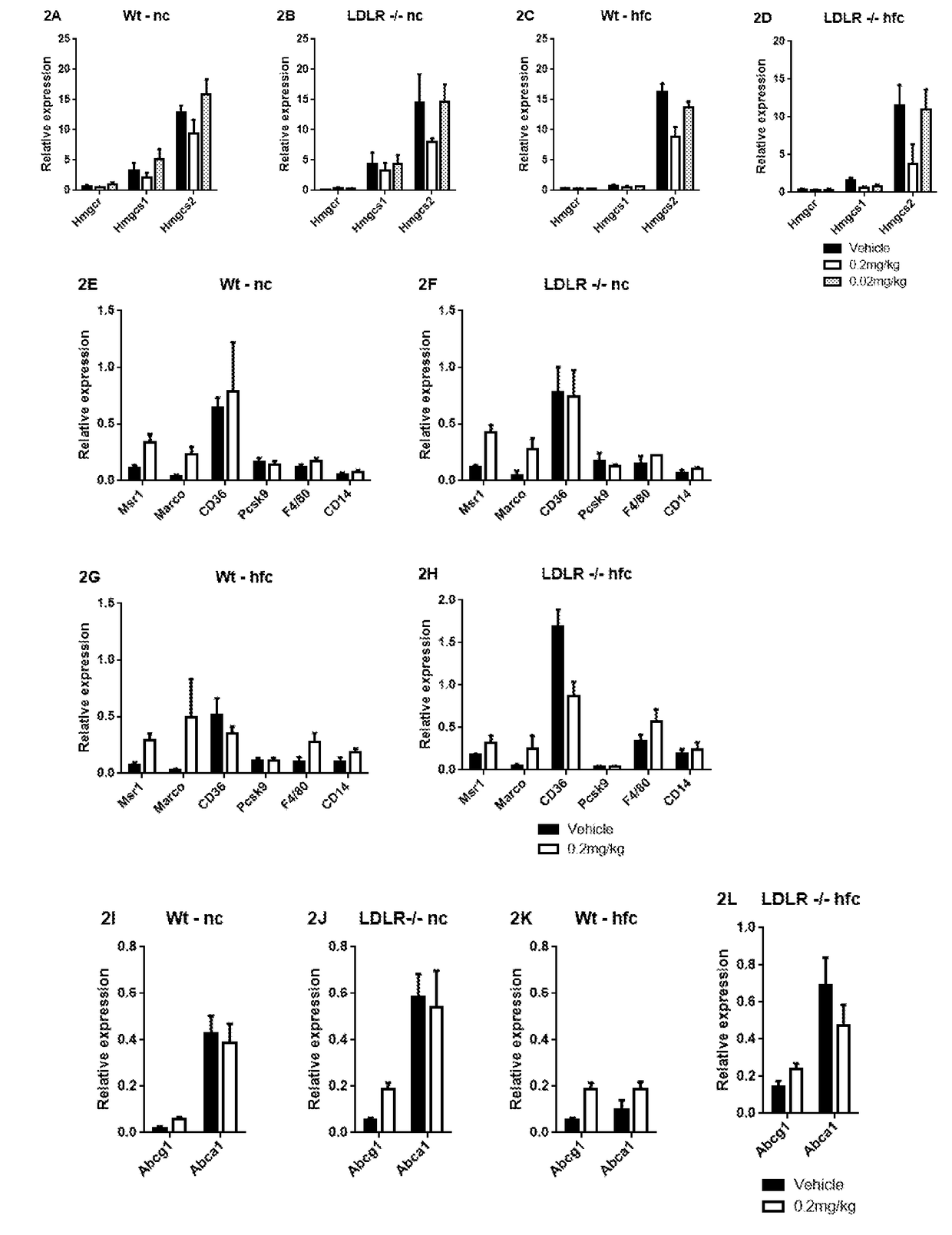
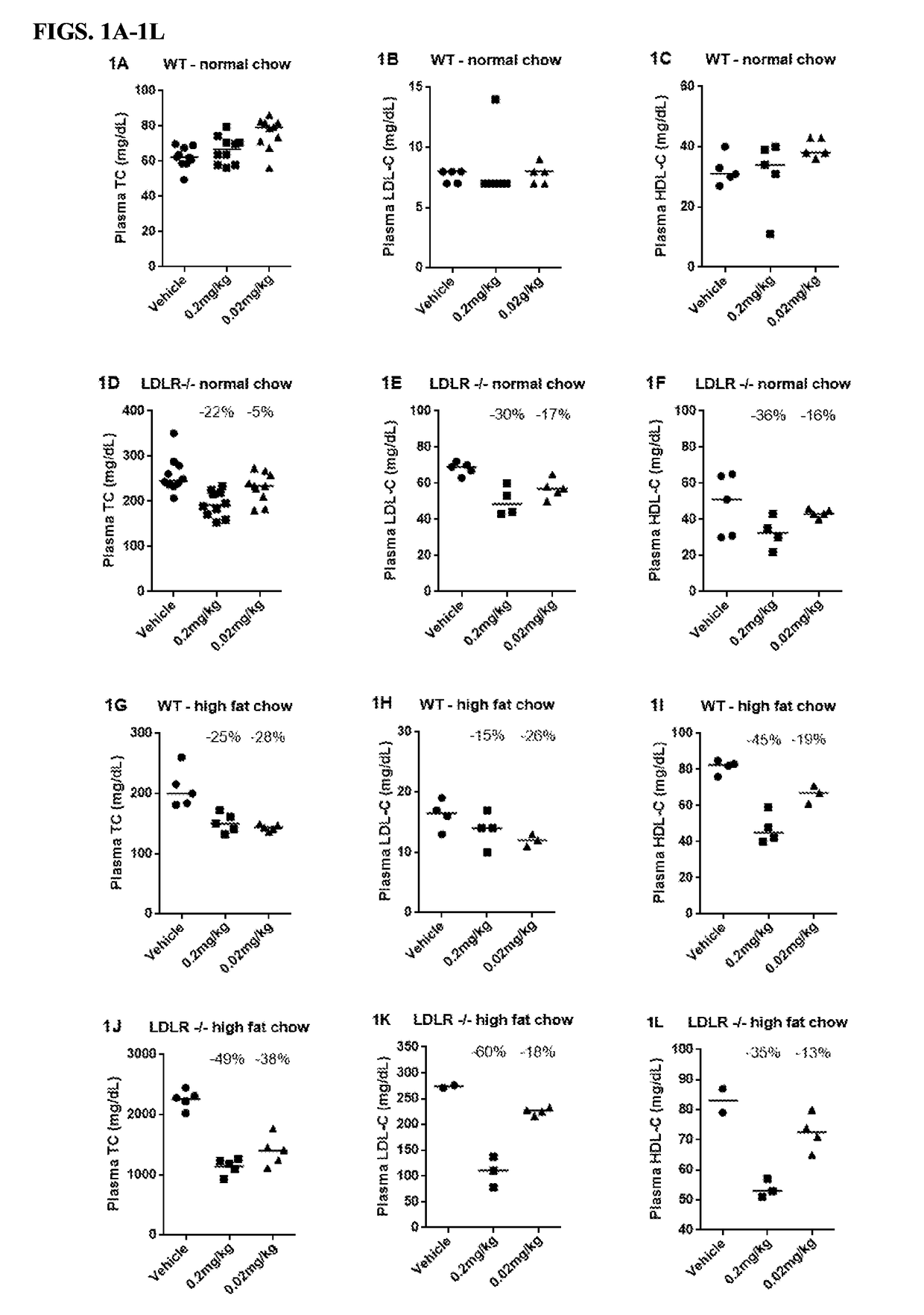
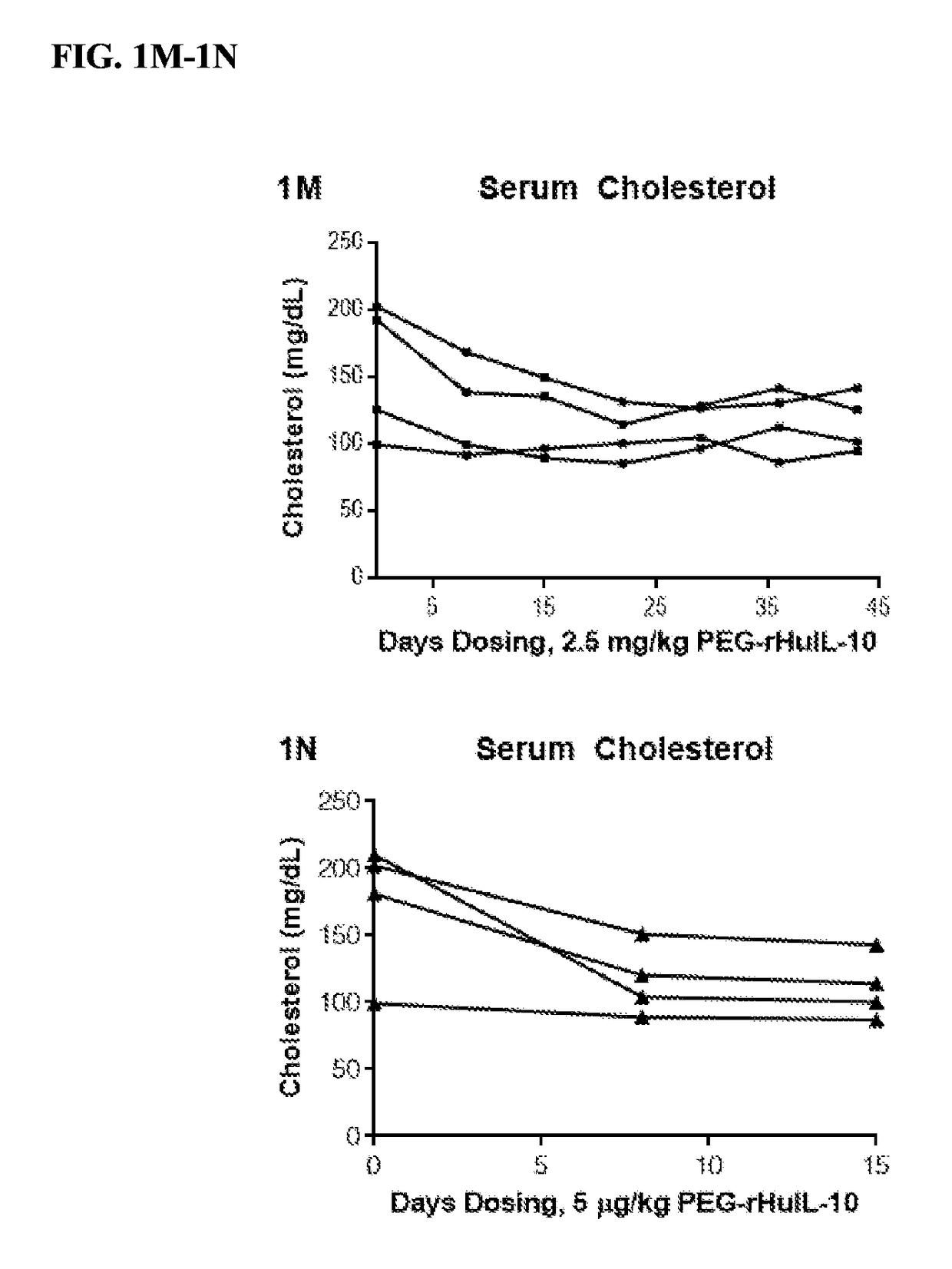
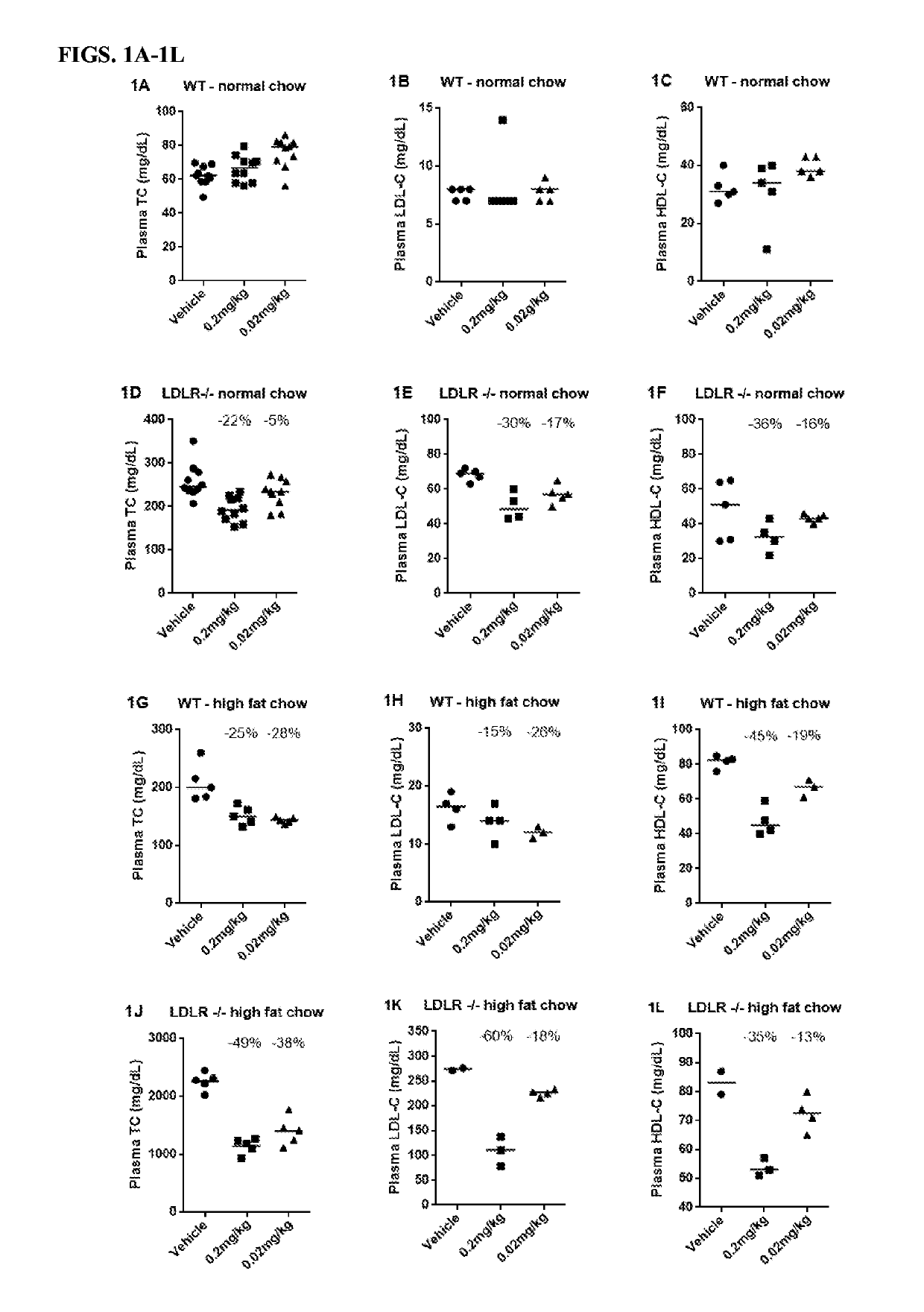
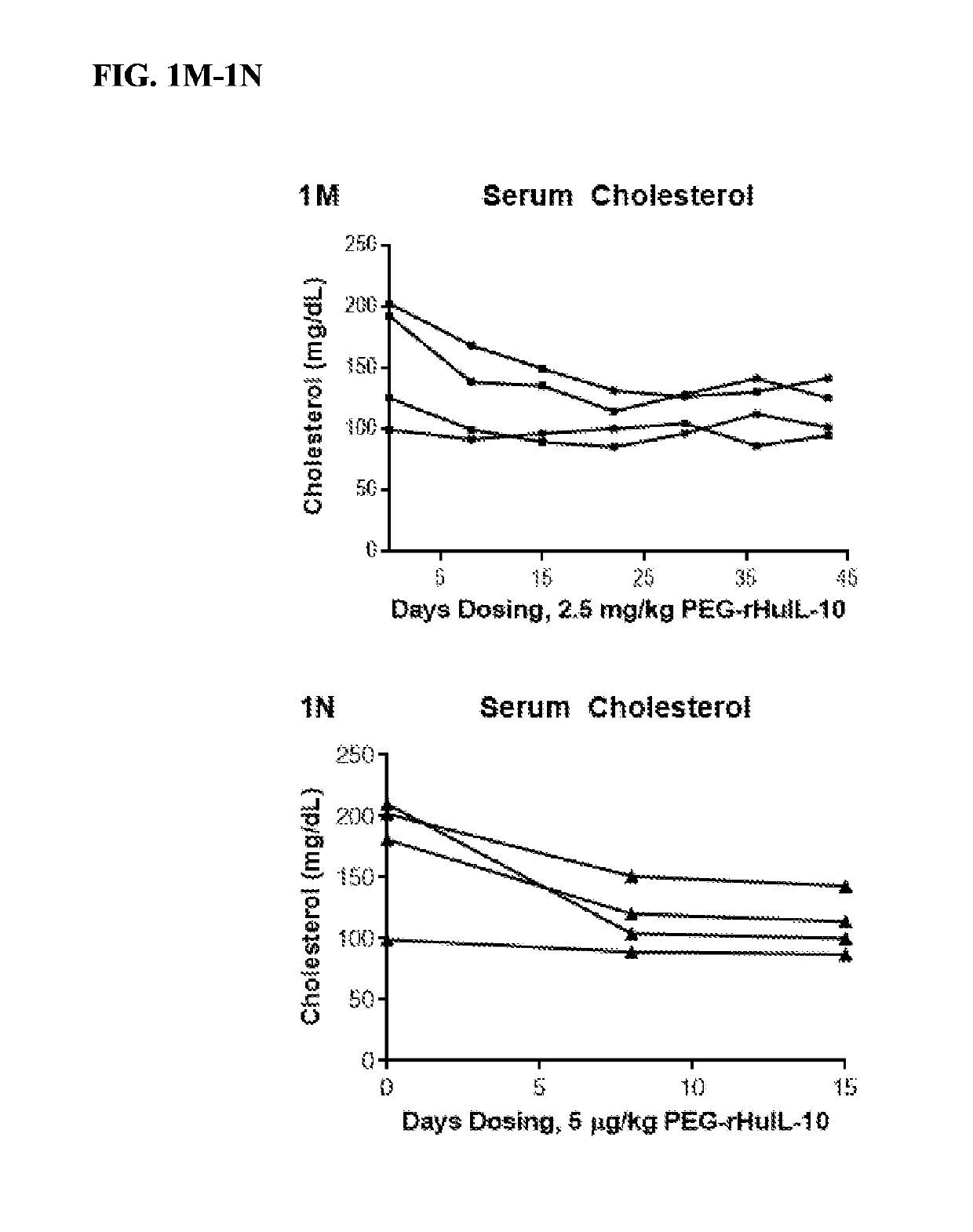
Methods of Lowering Serum Cholesterol
ActiveUS20170296653A1Lower cholesterol levelsHigh activityCompounds screening/testingCytokine-induced proteinsDiseaseSerum ige
Methods of treating subjects having diseases, disorders, or conditions, including disorders associated with cholesterol homeostasis, responsive to agents modulating Kupffer cell function, including methods of administration and dosing regimens associated therewith, are provided. Methods of treating subjects having liver diseases, disorders, or conditions, including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, with an IL-10 agent are also provided.
Owner:ARMO BIOSCI
Prokaryotic expression of soluble, active Dkk
Dickkopf (Dkk) proteins inhibit the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Each of the members of the Dkk family has been previously cloned and expressed as a soluble protein in eukaryotic cells, while expression in bacterial cells has resulted in the formation of insoluble inclusion bodies that require further processing. The present invention provides compositions and methods for producing soluble, active dkk protein in prokaryotic host cells, by expressing the dkk protein as a fusion protein with a solubilization molecule, thereby providing an inexpensive and convenient source of pure active Dkk.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Reversed mammalian protein-protein interaction trap
InactiveUS20100174049A1Enhanced interactionEasy to useCytokine-induced proteinsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHeterologousLigand binding domain
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW
Methods of lowering serum cholesterol
ActiveUS10293043B2Easy to recycleIncrease ratingsCompounds screening/testingCytokine-induced proteinsDecreased serum cholesterolLiver disease
Methods of treating subjects having diseases, disorders, or conditions, including disorders associated with cholesterol homeostasis, responsive to agents modulating Kupffer cell function, including methods of administration and dosing regimens associated therewith, are provided. Methods of treating subjects having liver diseases, disorders, or conditions, including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, with an IL-10 agent are also provided.
Owner:ARMO BIOSCI
Peptides and derivatives thereof showing cell attachment, spreading and detachment activity
InactiveUS7070956B2Cytokine-induced proteinsPeptide/protein ingredientsWound healingLymphatic Spread
The present invention relates to peptides and derivatives thereof showing cell attachment, spreading and detachment activity. Particularly, the present invention relates to the peptide NKDIL and EPDIM and derivatives thereof which promote the cell attachment activity through interaction with a α 3β 1 integrin as a functional cell receptor and include aspartic acid and isoleucine essential for cell attachment and detachment activity. The peptides and derivatives thereof in the present invention can be used for developing a study of cell attachment activity mediated through various extracellular matrix protein containing β ig-h3, wound healing, tissue regeneration and metastasis inhibition.
Owner:REGEN BIOTECH INC
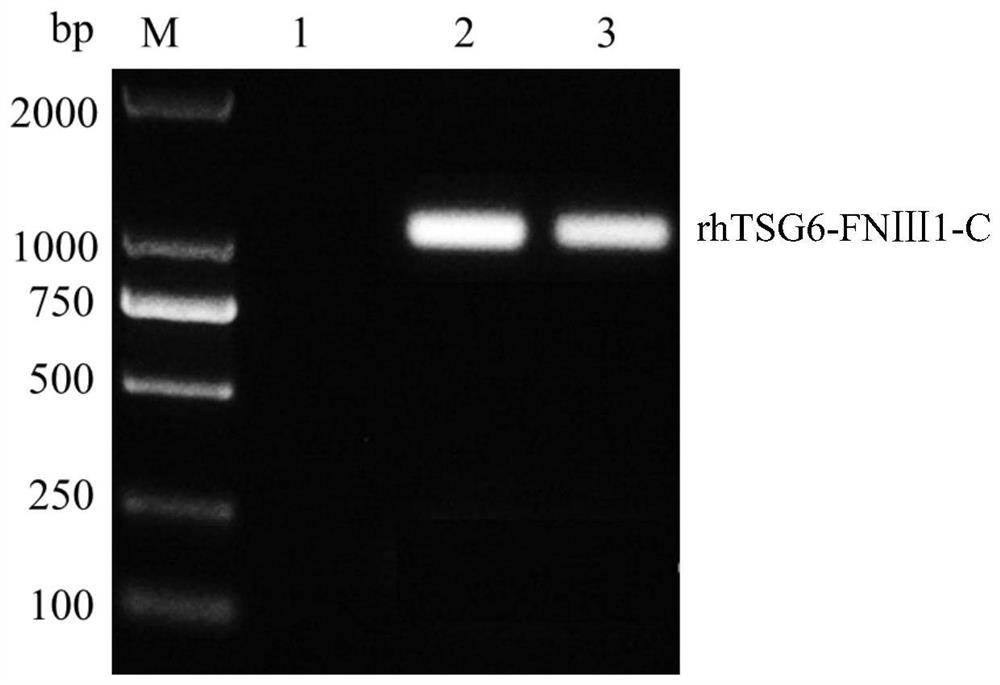
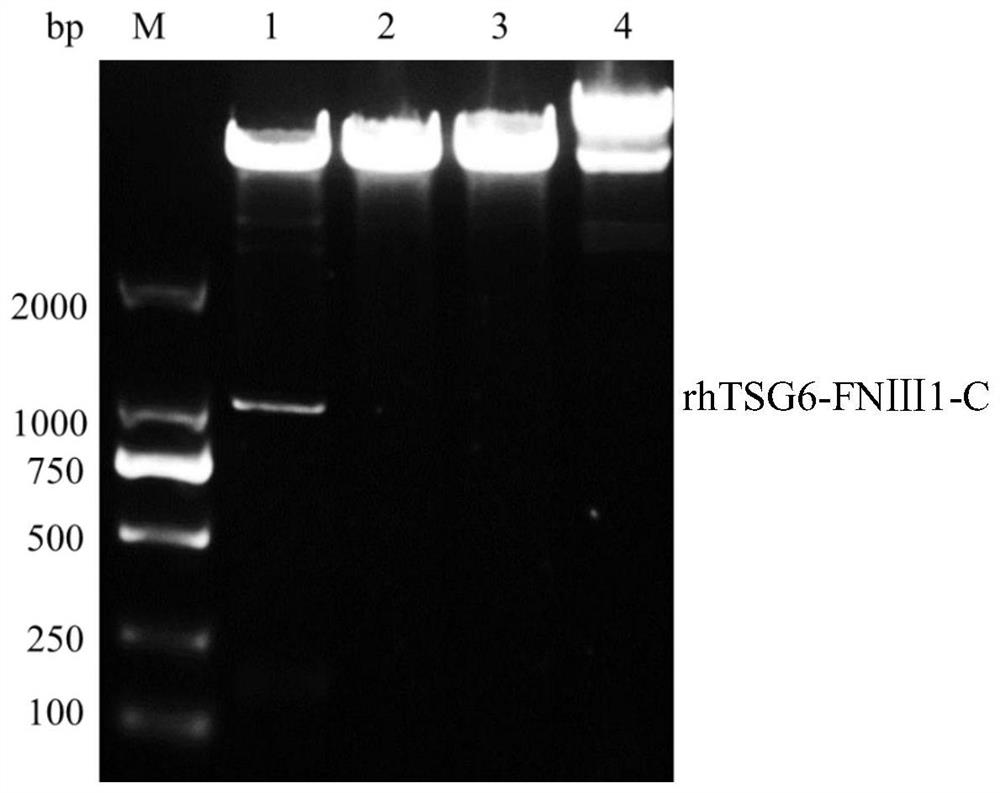
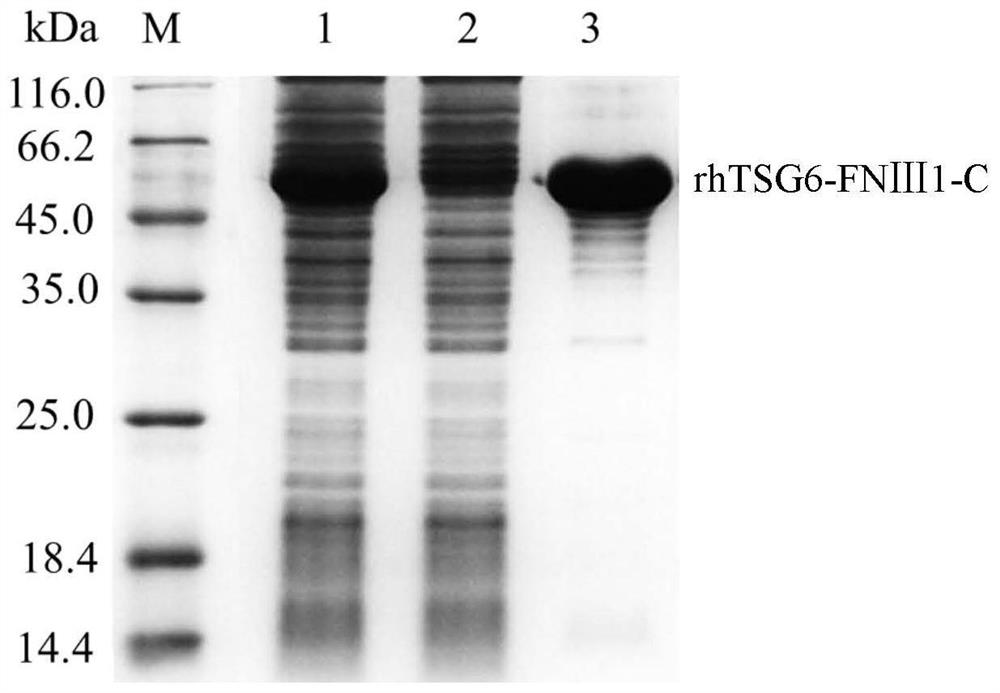
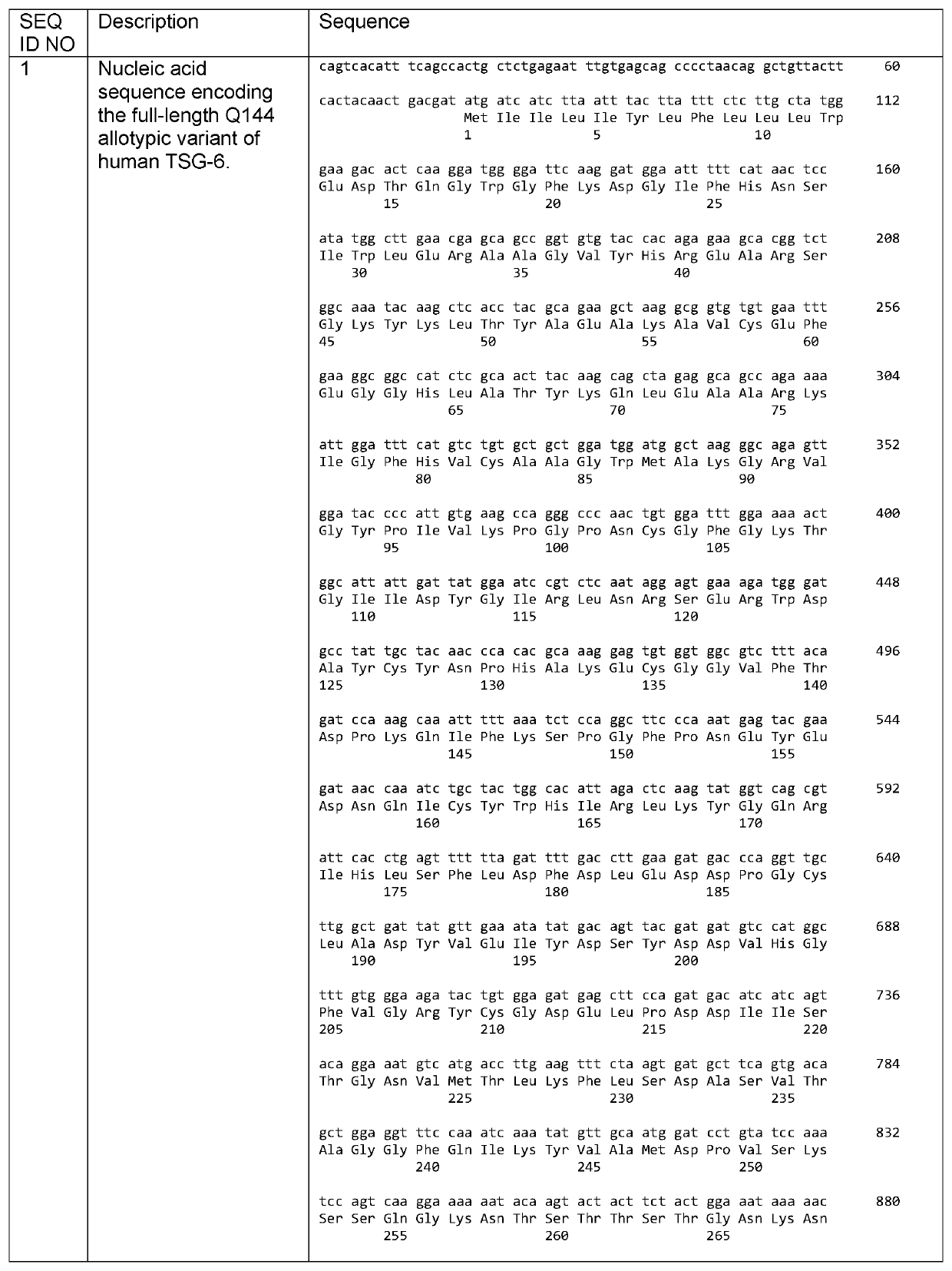
rhTSG6-FNIII-C fusion protein and application thereof in skin care composition and preparation method of the rhTSG6-FNIII-C fusion protein
ActiveCN112876569ALess likely to cause allergiesSimple ingredientsCosmetic preparationsCytokine-induced proteinsAllergyGenetic engineering
The invention relates to the technical field of cosmetics, and discloses an rhTSG6-FNIII-C fusion protein, an application of the rhTSG6-FNIII-C fusion protein in a skin care composition and a preparation method of the rhTSG6-FNIII-C fusion protein. The rhTSG6-FNIII-C fusion protein is prepared through a genetic engineering prokaryotic expression technology. The specific method comprises the following steps: carrying out codon optimization on a gene sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1; constructing a recombinant expression vector and transforming; inducing and expressing the recombinant Escherichia coli; and separating and purifying an expression product, so that the rhTSG6-FNIII-C fusion protein is prepared. The skin care composition has various dosage forms, such as an aqueous solution, an ointment, a suppository, a cream and a mask, and has good skin care effects of improving skin wrinkles, keeping skin elasticity, reducing skin inflammation and allergy risks and the like, so that the skin care composition can be applied to the field of functional cosmetics or medical cosmetology.
Owner:WUHU TIANMING BIOTECH CO LTD
Interferon-alpha induced gene
InactiveUS20050265967A1Prediction of responsivenessCytokine-induced proteinsPeptide/protein ingredientsInterferon therapyInterferon receptor
The present invention relates to identification of a gene upregulated by interferon-administration corresponding to the cDNA sequence set forth in SEQ. ID. No. 1. Determination of expression products of this gene is proposed as having utility in predicting responsiveness to treatment with interferon- and other interferons which act at the Type 1 interferon receptor. Therapeutic use of the protein encoded by the same gene is also envisaged.
Owner:PHARM PACIFIC PTY LTD
Tsg6 polypeptide fragment for dry eye disease
The present invention relates to the treatment of dry eye disease and particularly, although not exclusively, to the treatment of dry eye disease with a LINK_TSG6 polypeptide.
Owner:UNIV OF MANCHESTER
TSG6 polypeptide fragments for dry eye disease
The present invention relates to the treatment of dry eye disease, and in particular, to (but not limited to) the treatment of dry eye disease with a LINKTSG6 polypeptide.
Owner:UNIV OF MANCHESTER
Binding compounds specific for cysteine-rich soluble protein C23
InactiveUS7560533B2Cytokine-induced proteinsPeptide preparation methodsCompound specificSpecific antibody
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Animal model and method for studying gene-gene interactions
InactiveUS9974290B2High sensitivityWide genetic backgroundCytokine-induced proteinsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsGene interactionIndividual animal
The invention concerns a non-human animal model useful for sensitively studying gene-gene interactions over a wide genetic background; methods for producing the animal model; and methods for studying gene-gene interactions using an animal model of the invention.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Compositions and methods for visualization of the vitreous
ActiveUS20170202981A1Simple structureReduce confusionPowder deliveryCytokine-induced proteinsMetaboliteOcular structure
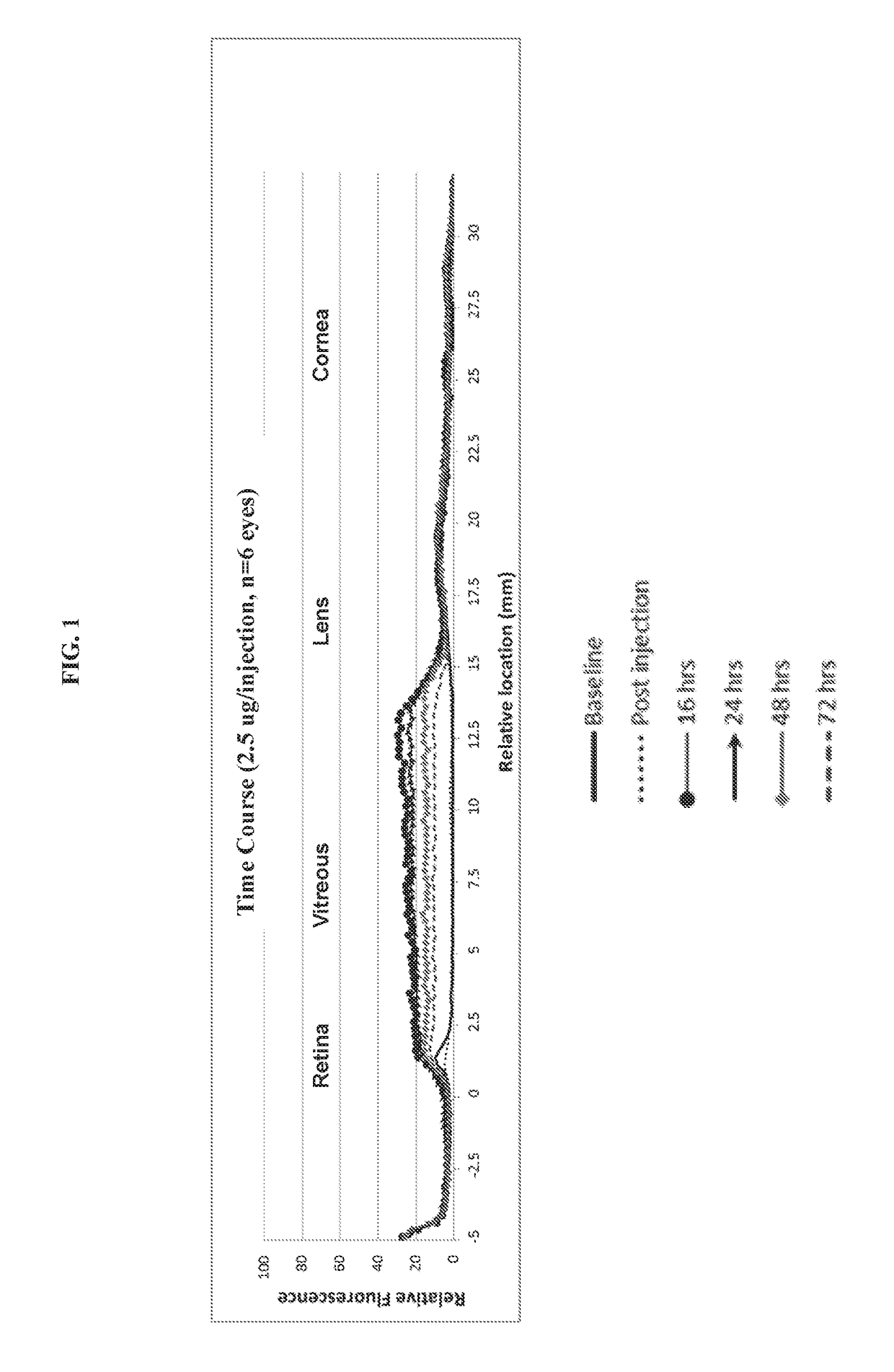
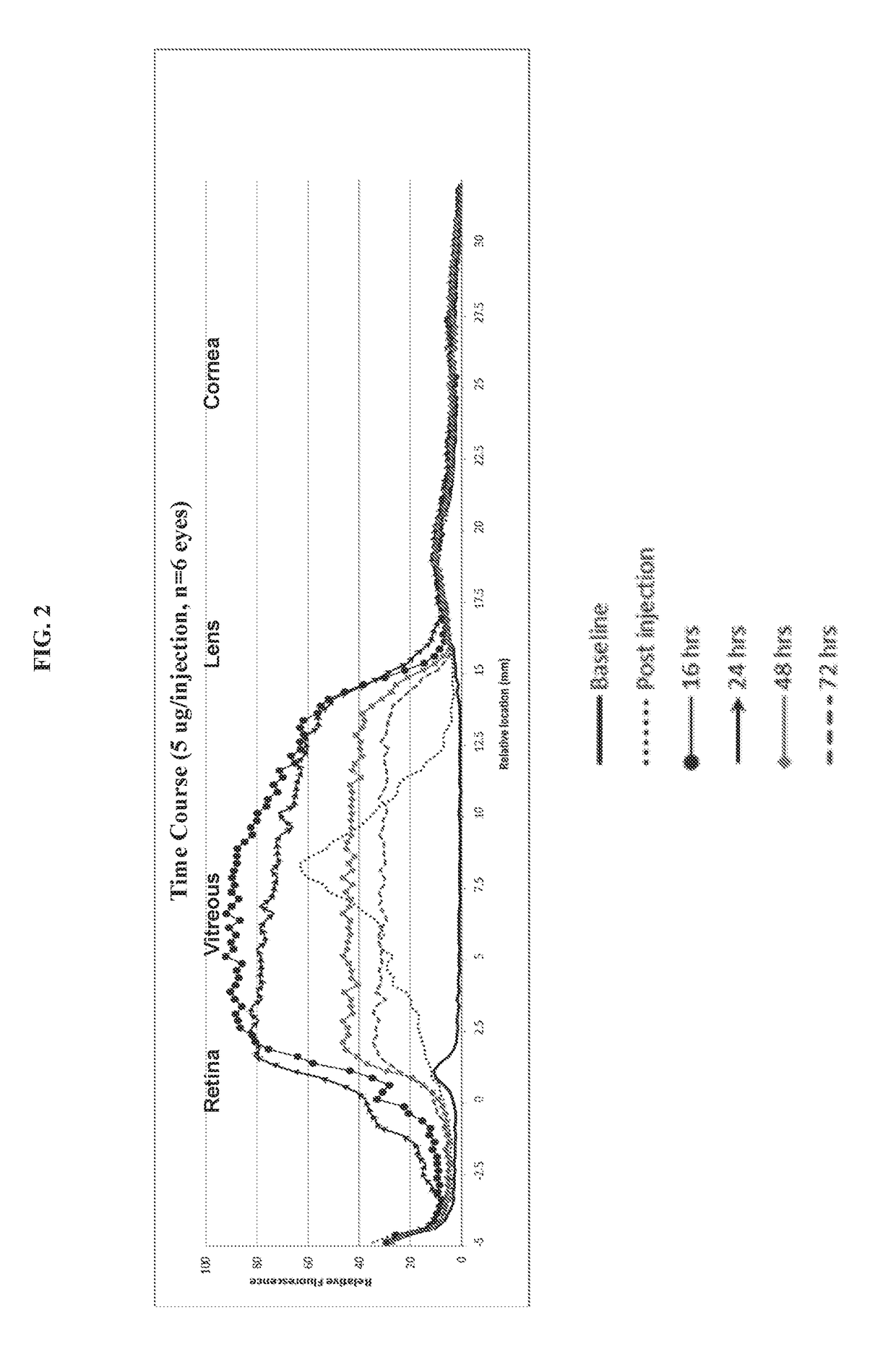
The invention provides compositions for rendering a vitreous cavity visible during a surgical procedure to alleviate a structural disorder caused by the vitreous in an eye, and methods of using the compositions. The compositions are vitreous delineating agents that comprise a hyaluronan binding peptide linked to an optically detectable moiety. Such compositions can be in a formulation that may be a solution, a suspension, or an emulsion, and would be injected into the vitreous shortly prior to use. The composition may additionally contain a therapeutic agent, a diagnostic agent, or a chemosensing material, in use, the composition marks or delineates the vitreous by binding preferentially to the hyaluronan that permeates the vitreous humor and binding little or not at all to surrounding tissues such as the retina. The interface between the labelled vitreous humor and the non-labelled surrounding vital tissues produces a visible signal, thereby allowing a surgeon to clearly visualize the entire vitreous cavity and distinguish it from vital ocular structures. Use of the method improves the accuracy and safety of a vitrectomy and thus prevents suboptimal outcomes or the need for repeated procedures. The compositions comprising chemosensing material are useful as long-lasting biosensors, which when used in the vitreous enable repetitive, non-invasive, in vivo measurements of metabolites or pharmacologic agents in the vitreous of animals or humans.
Owner:ALCON INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com