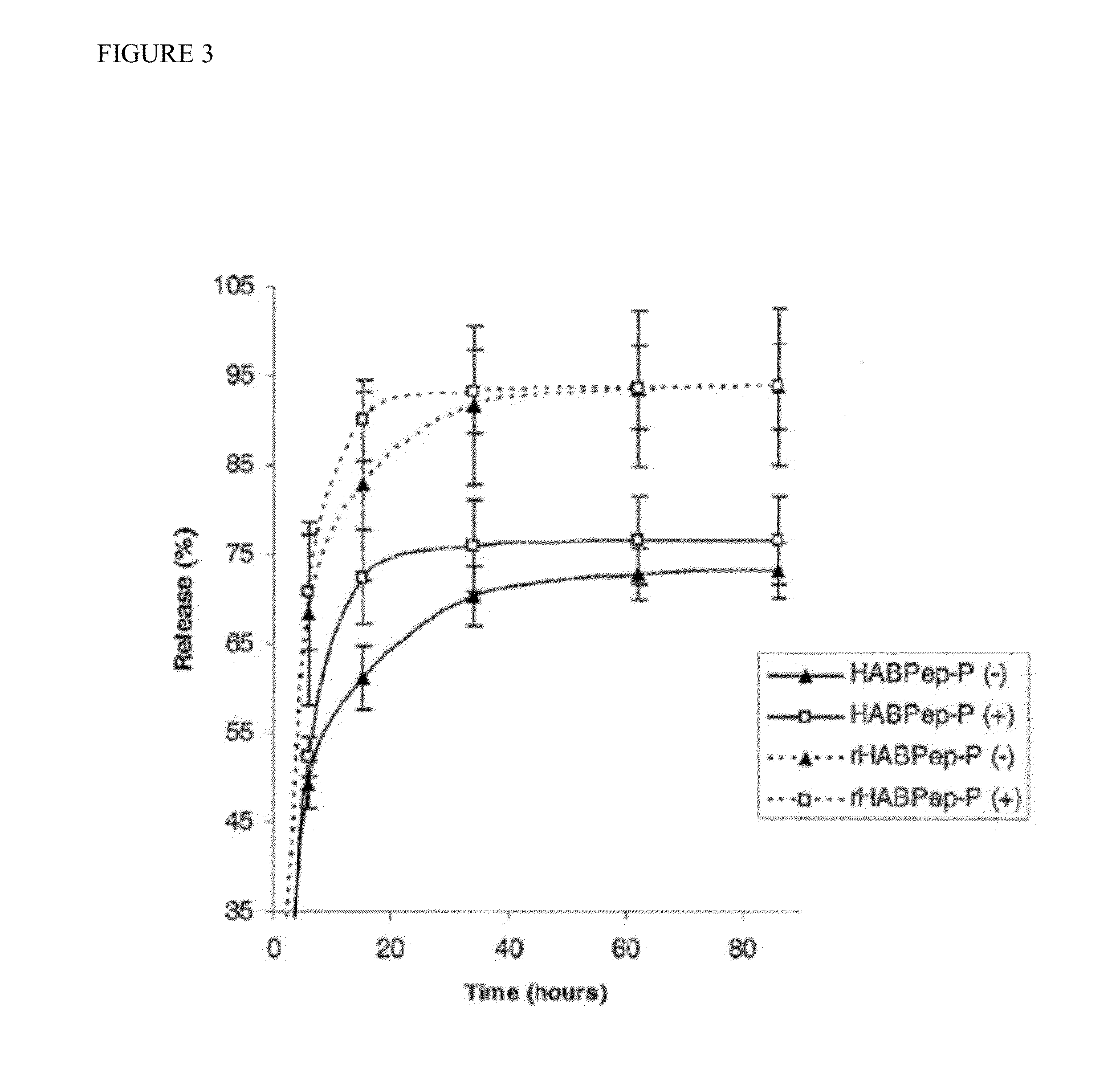
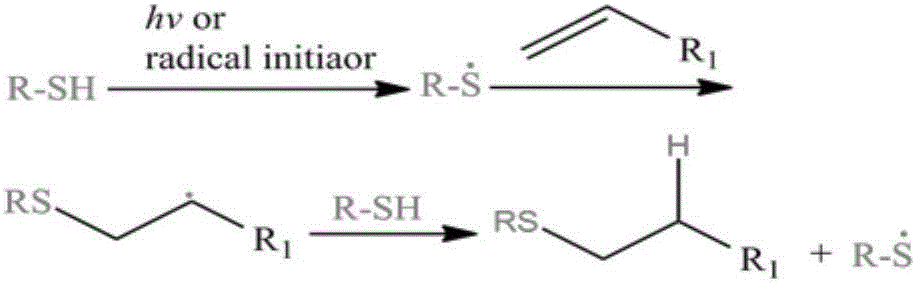
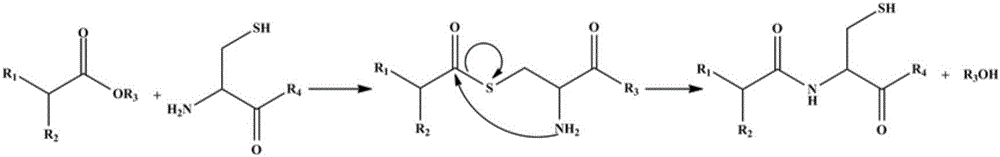
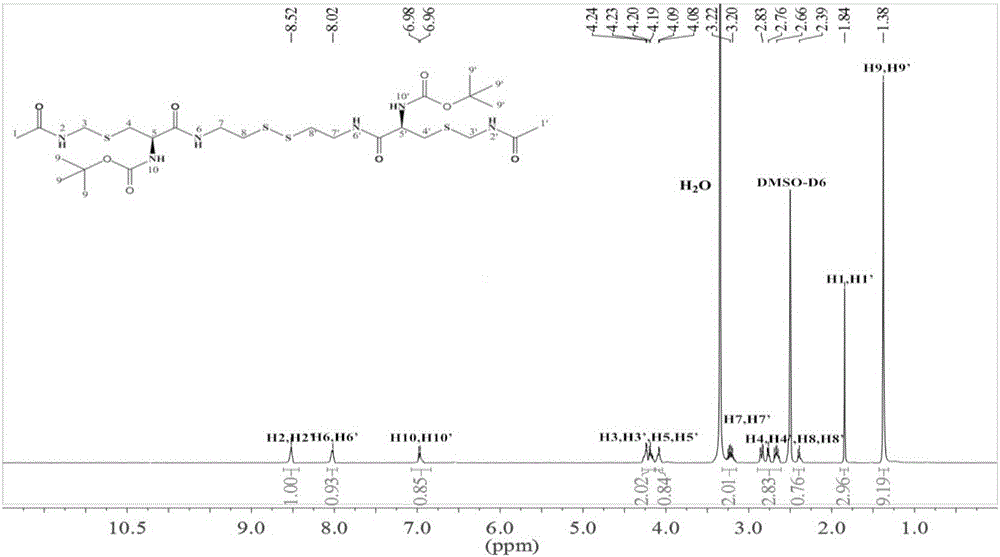
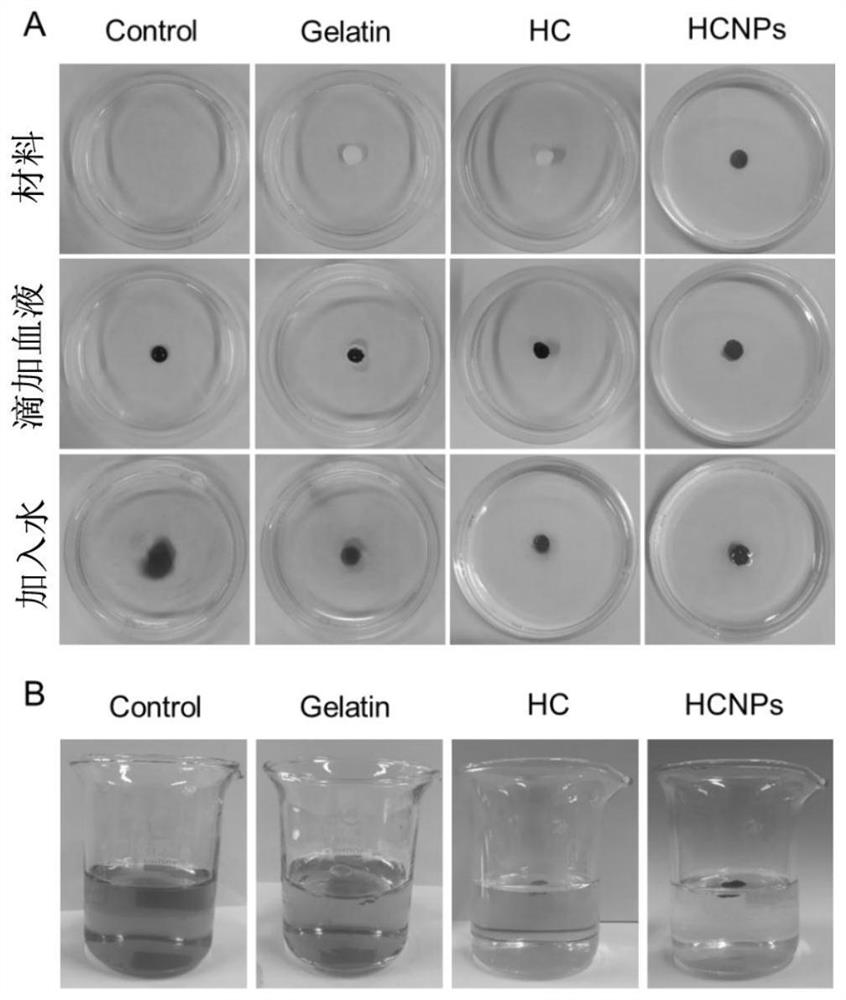
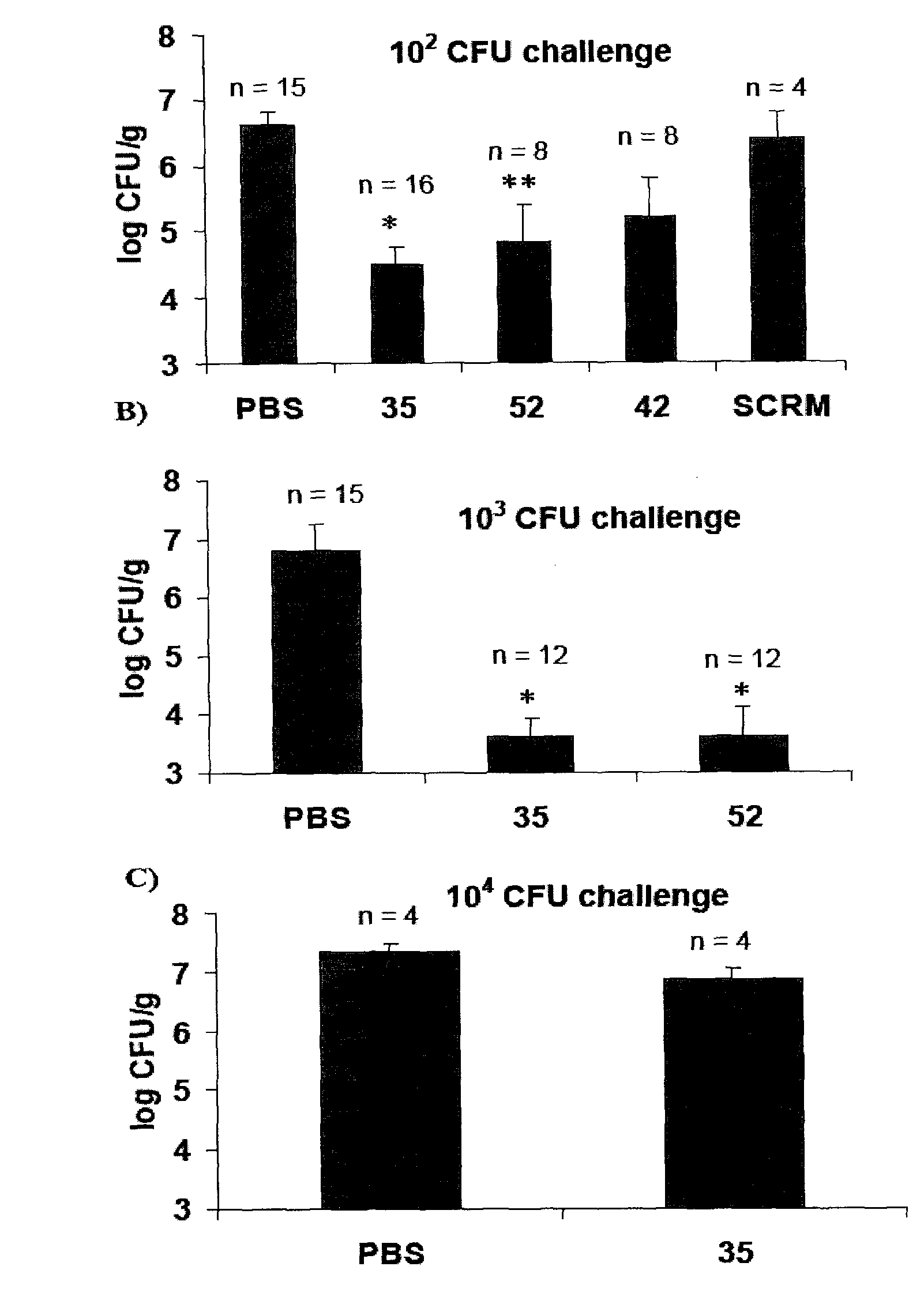
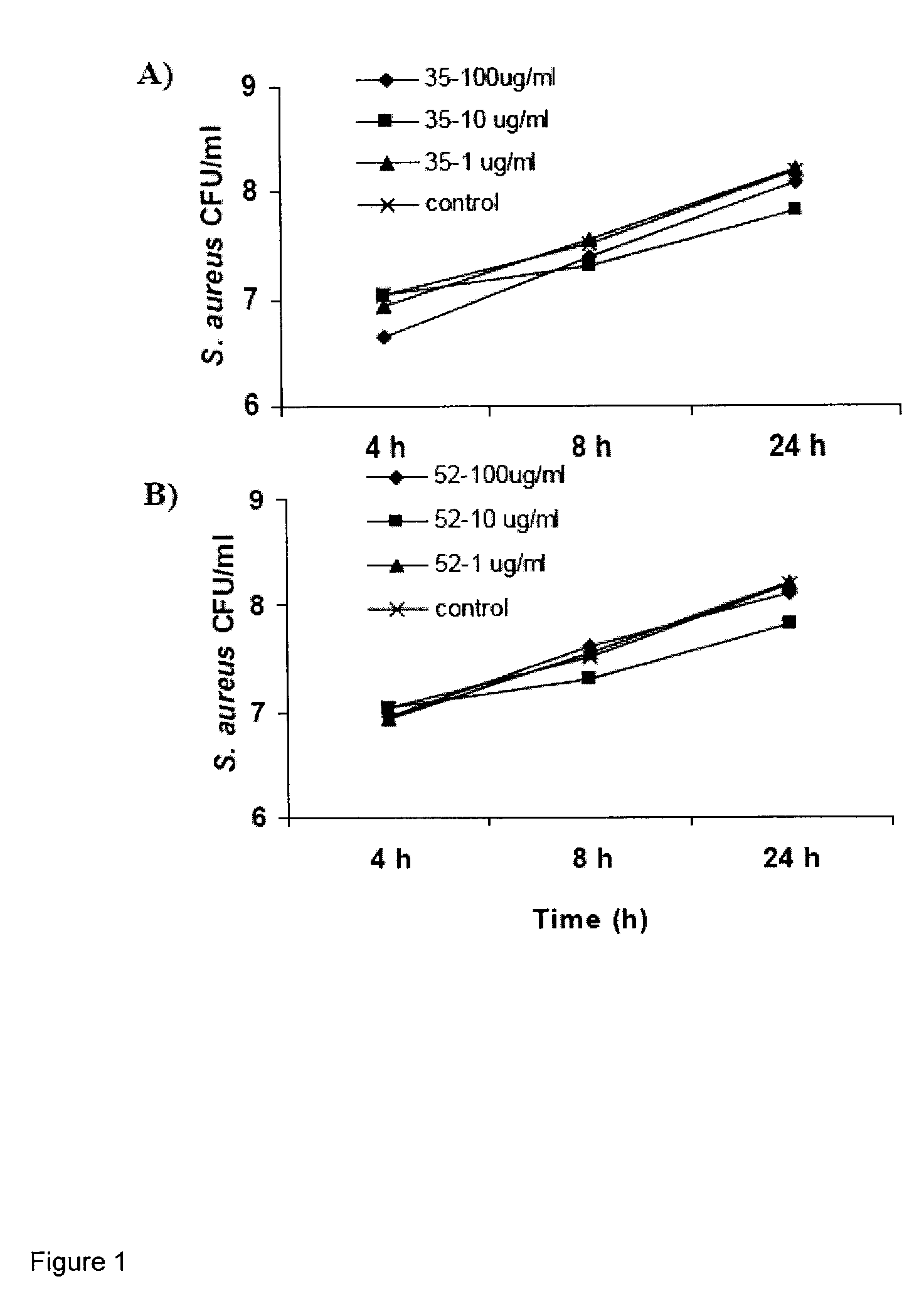
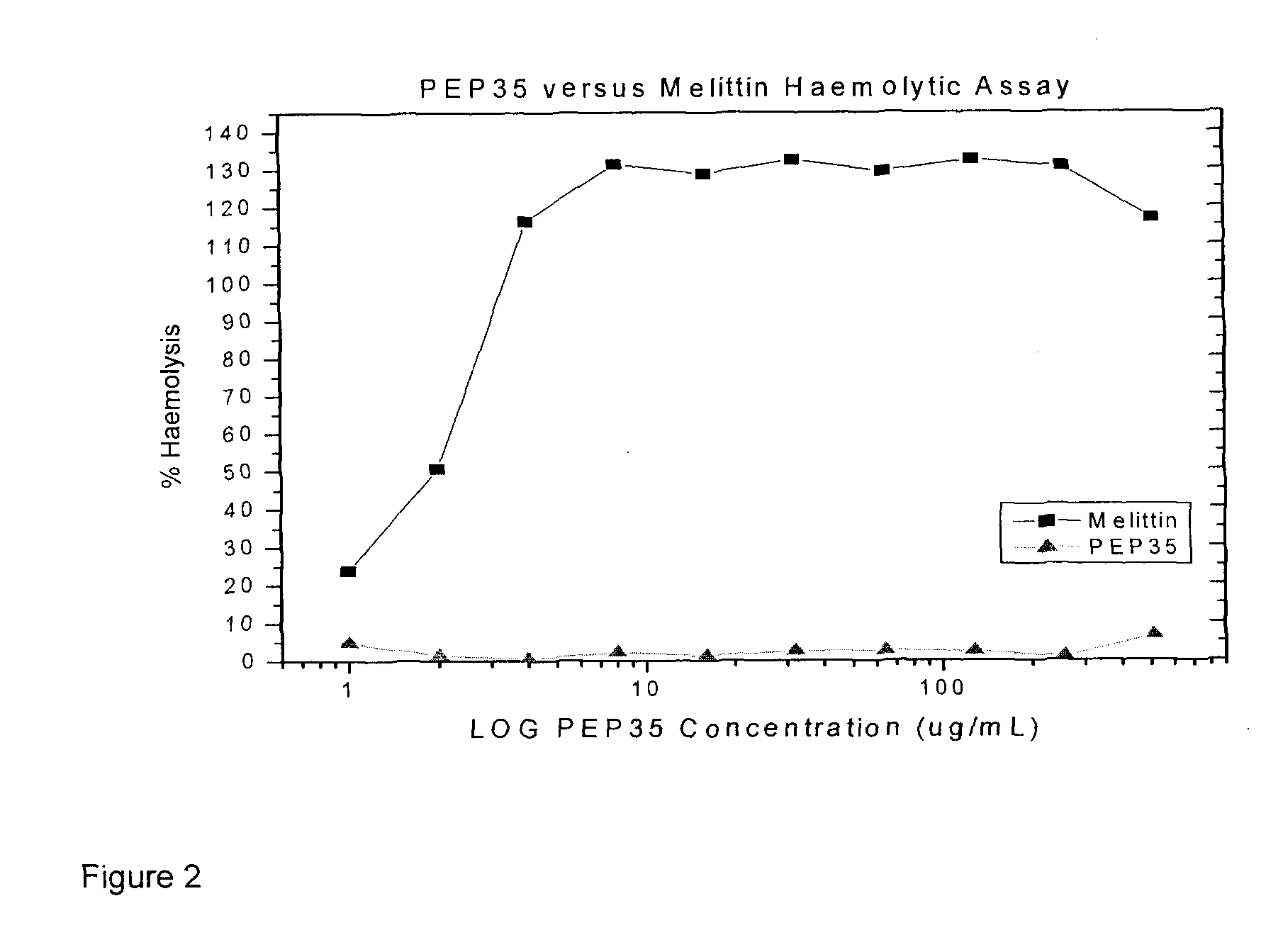
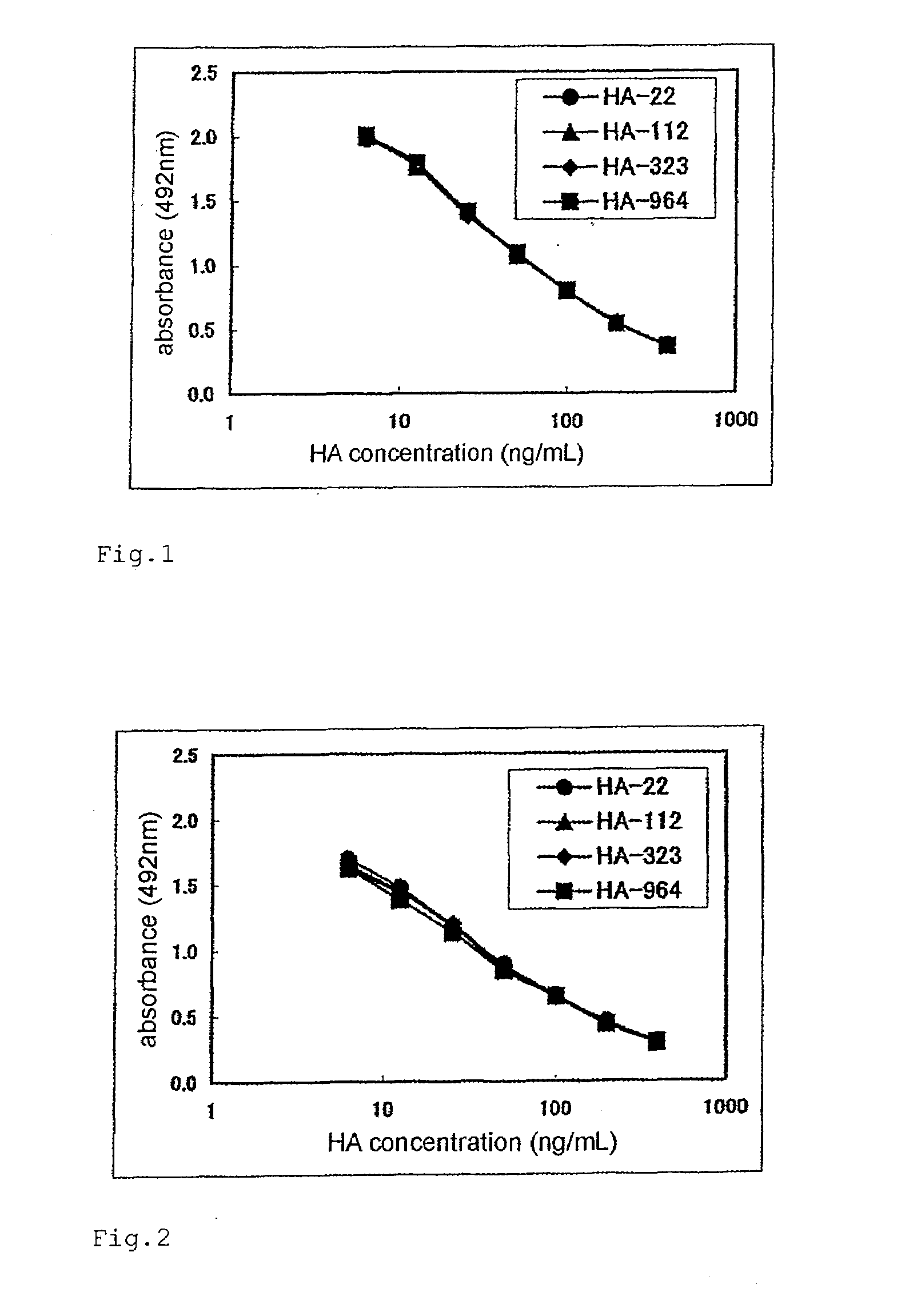
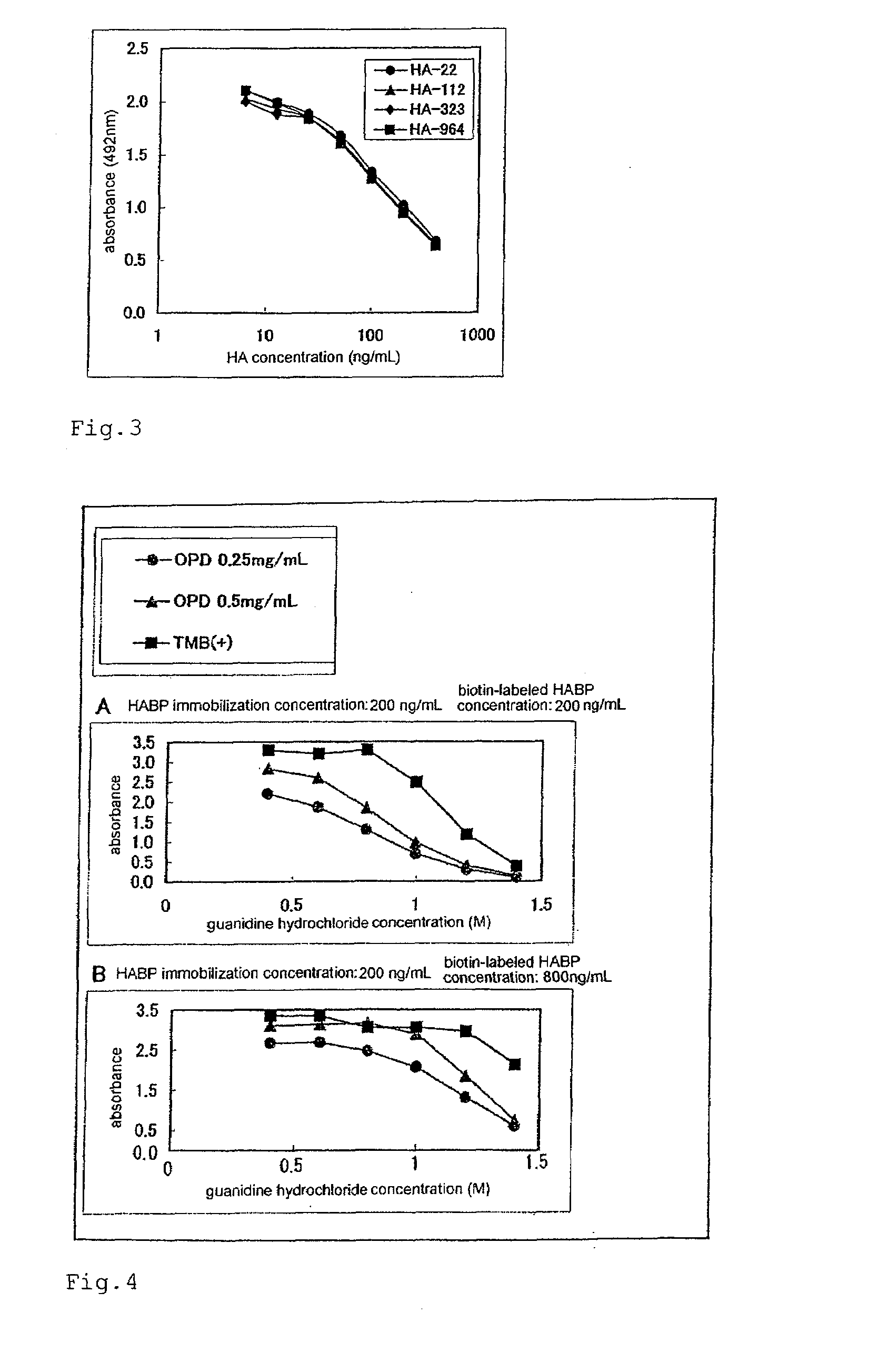
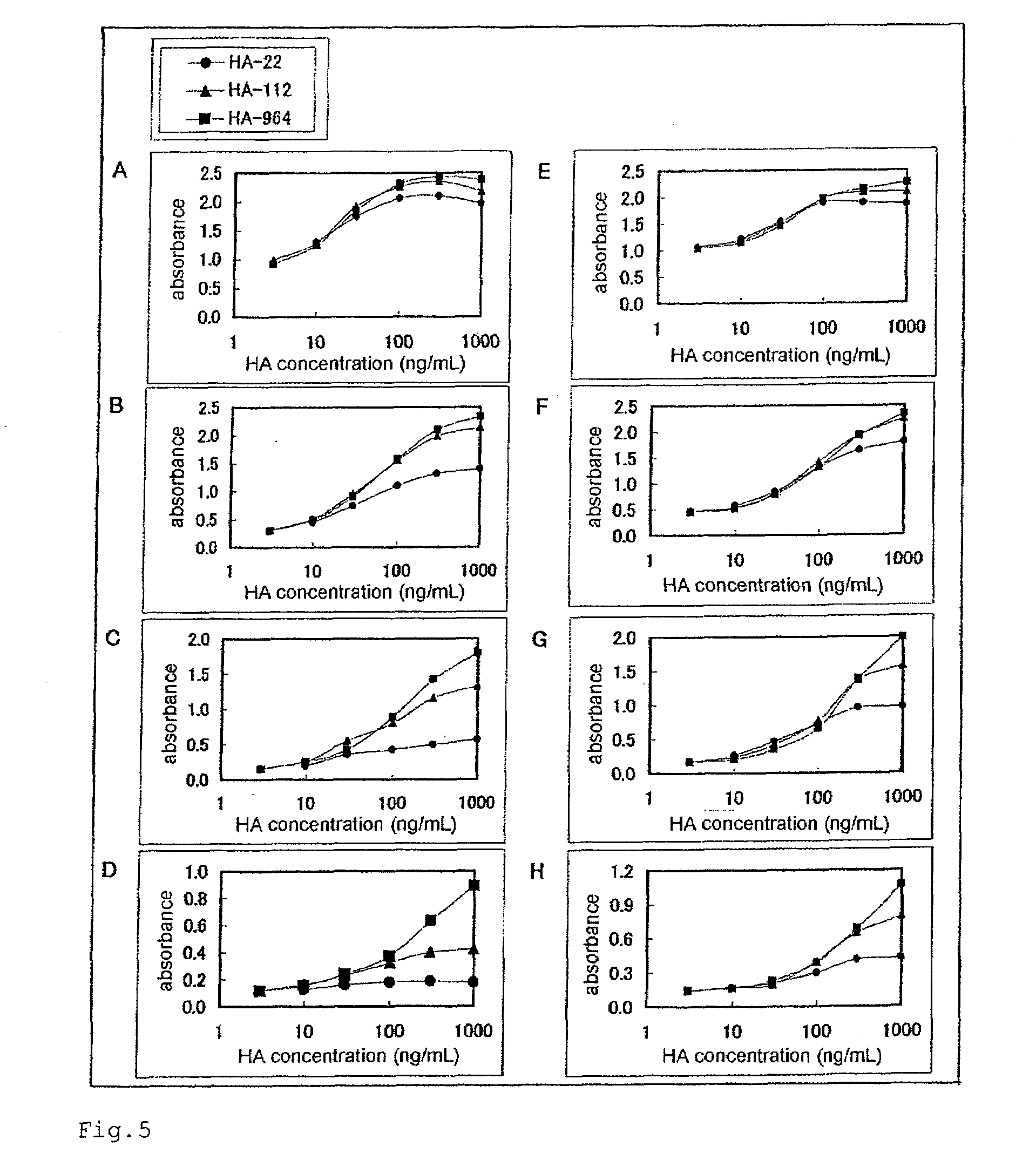
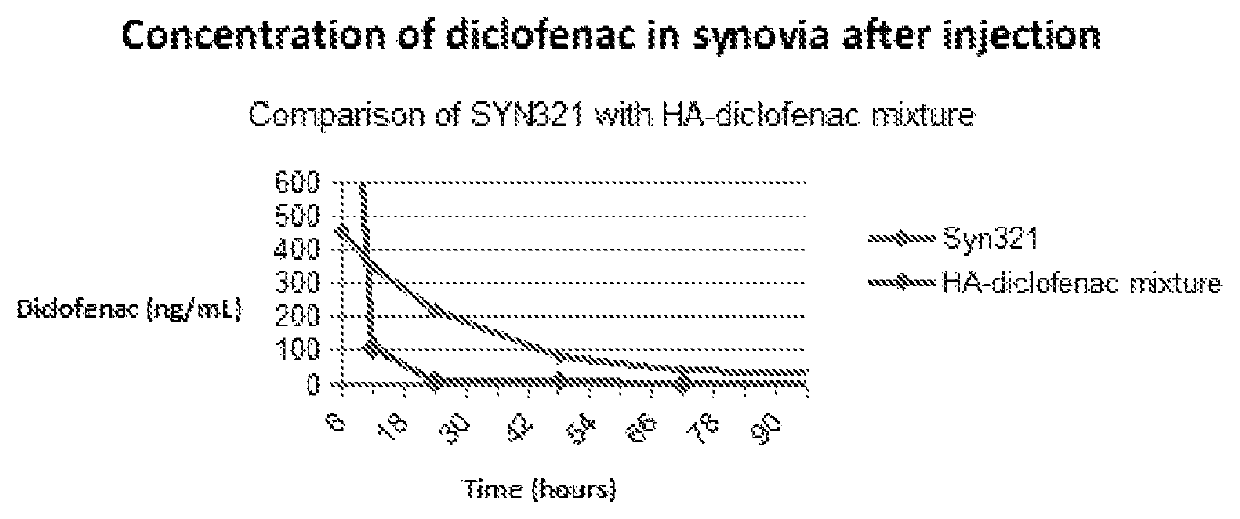
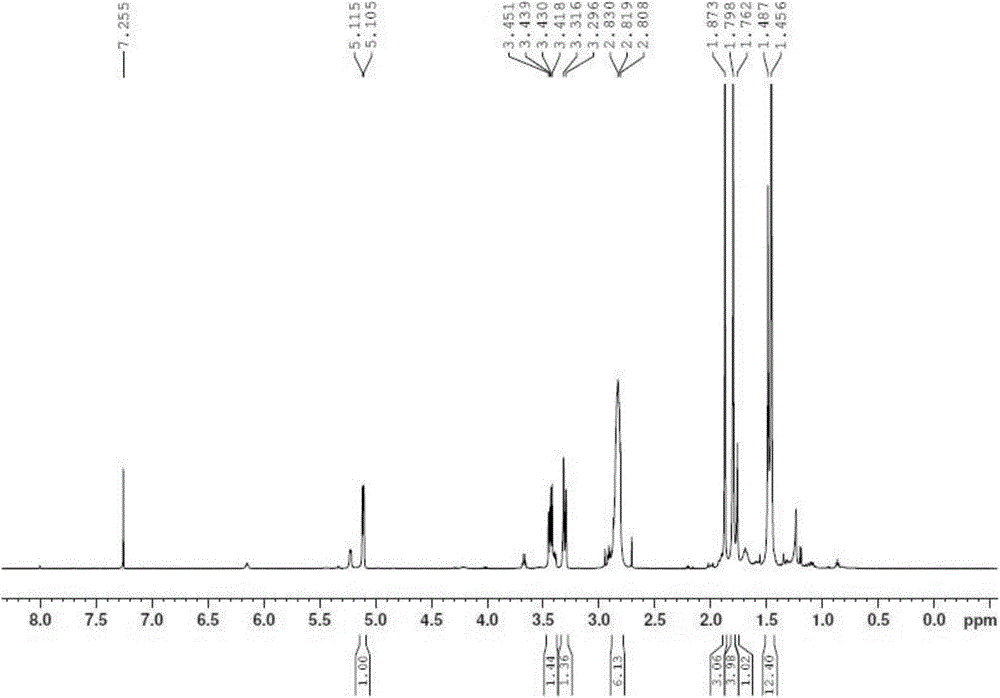
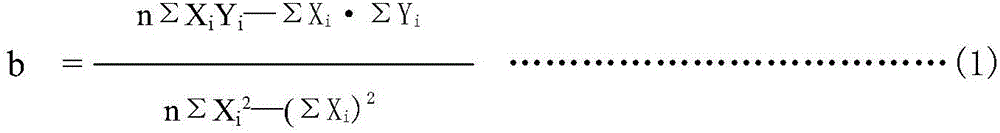
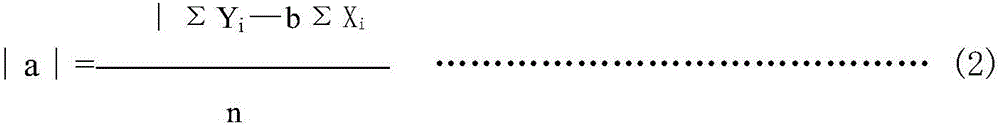
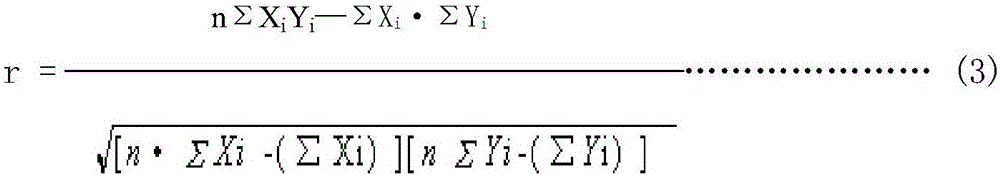Patents
Literature
46 results about "Hyaluronan binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
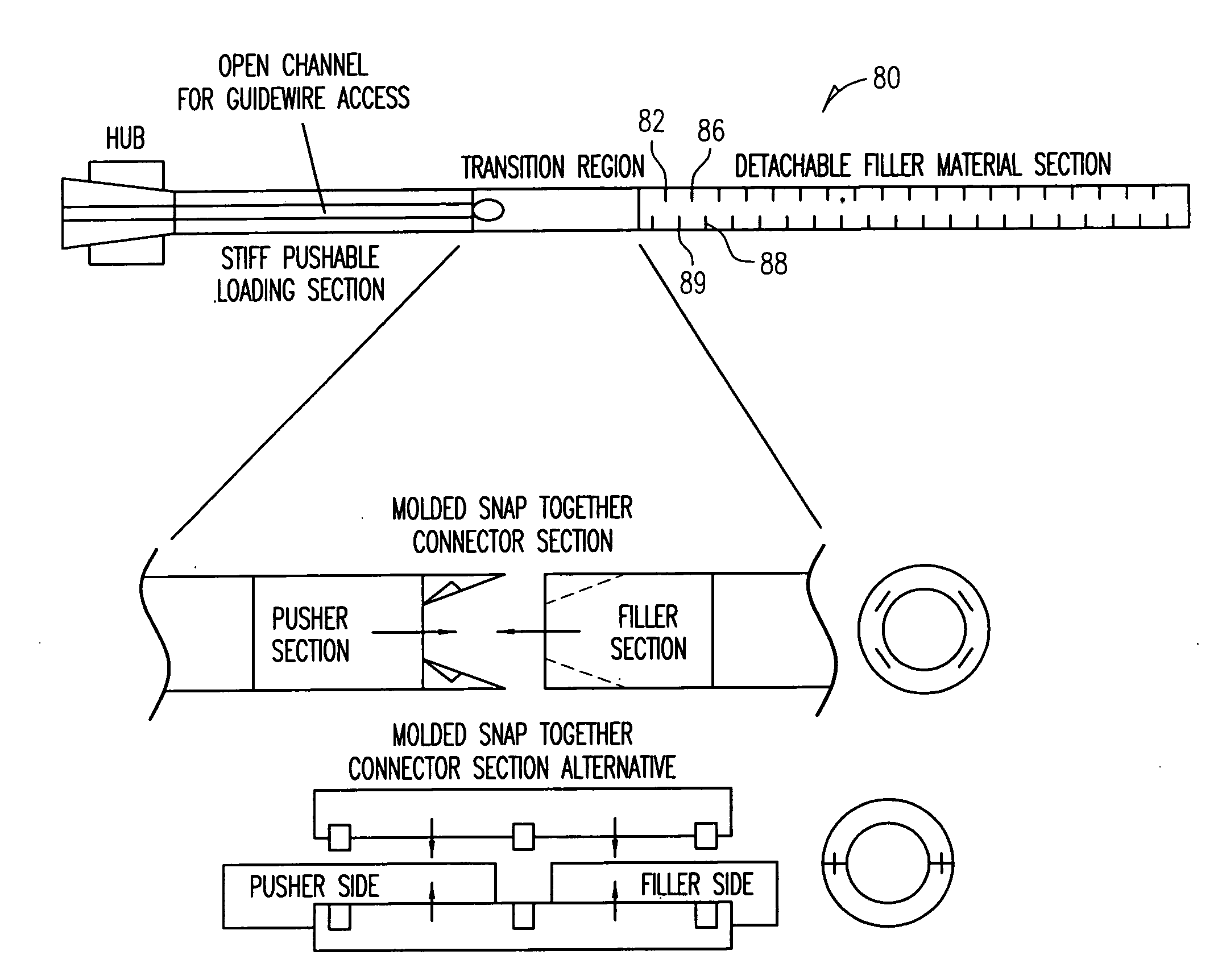
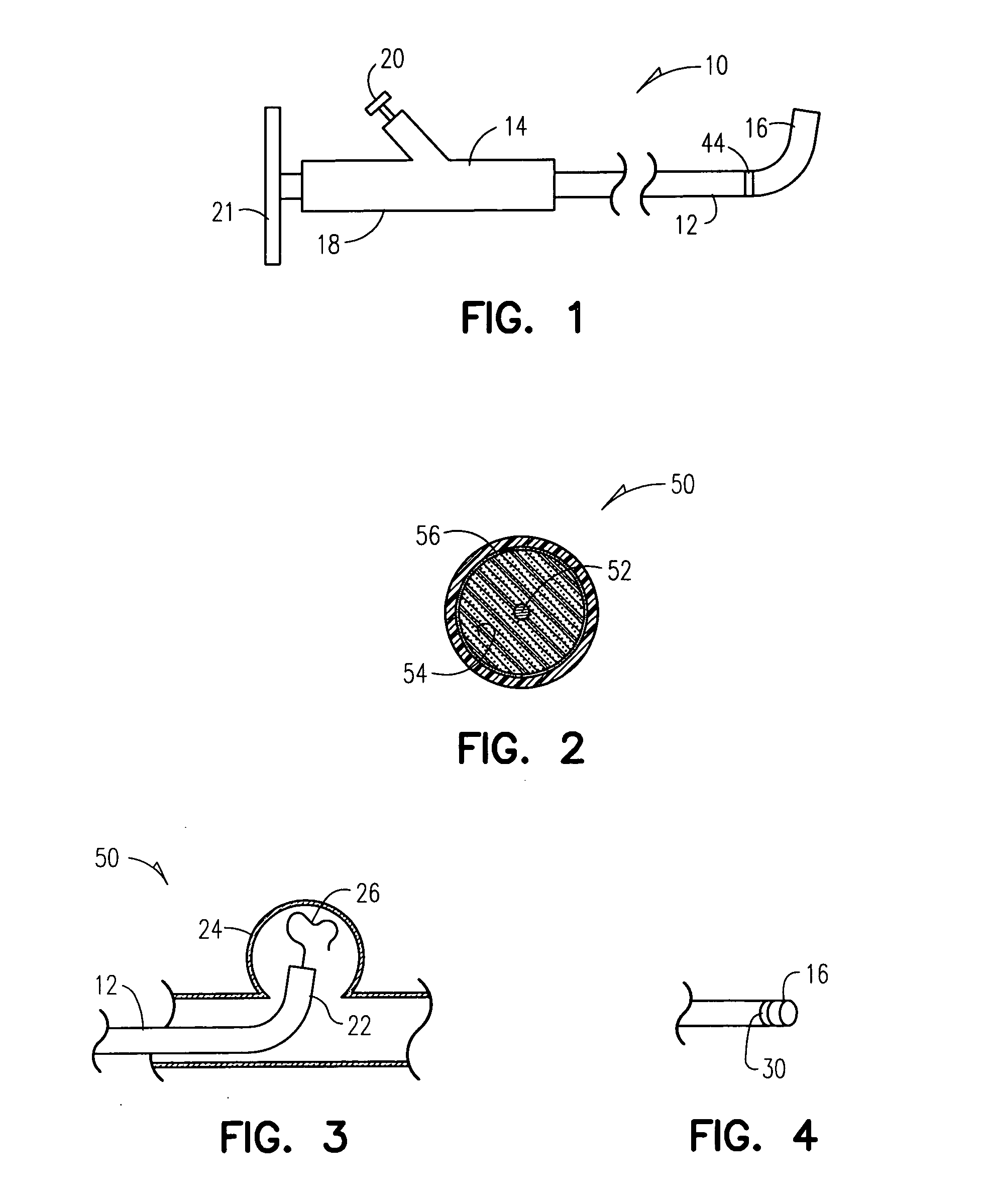
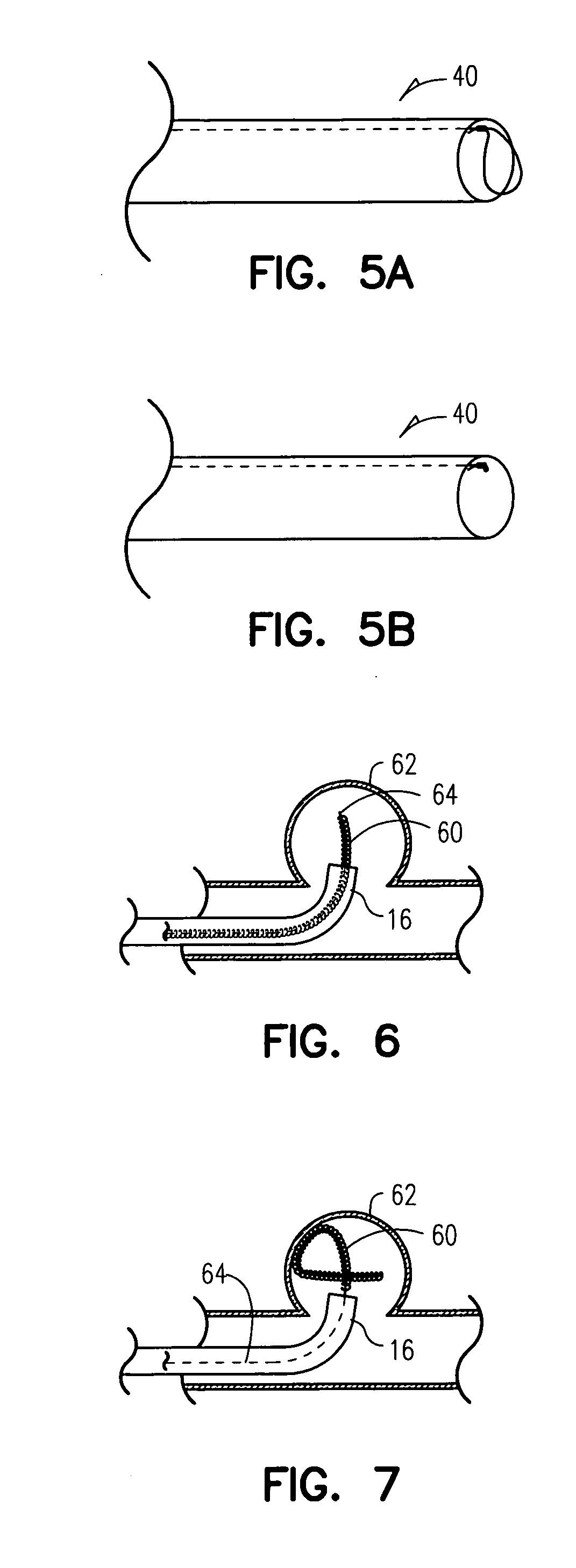
Multiple point detacher system
Embodiments of the invention include a method for treating an aneurysm, comprising: providing a biocompatible polymeric sleeve, string or coil or combination of sleeve, string or coil, made from a material selected from one or more of a group consisting of an acrylamide, a methacrylate, cyclodextran, synthetic elastin polymer, poly chelating amphiphilic polymers, hydrogels, hyaluronic acid conjugates, polyanhydrides, glycolipids, polysaccharides, and halamines, natural hydrogel, a synthetic hydrogel, silicone, polyurethane, polysulfone, cellulose, polyethylene, polypropylene, polyamide, polyimide, polyester, polytetrafluoroethylene, polyvinyl chloride, epoxy, phenolic, neoprene, polyisoprene, and a combination thereof; transporting the sleeve, string or coil to an aneurysm; filling the aneurysm with the sleeve, coil, or string; and detaching the sleeve, string or coil
Owner:NEUROVASX
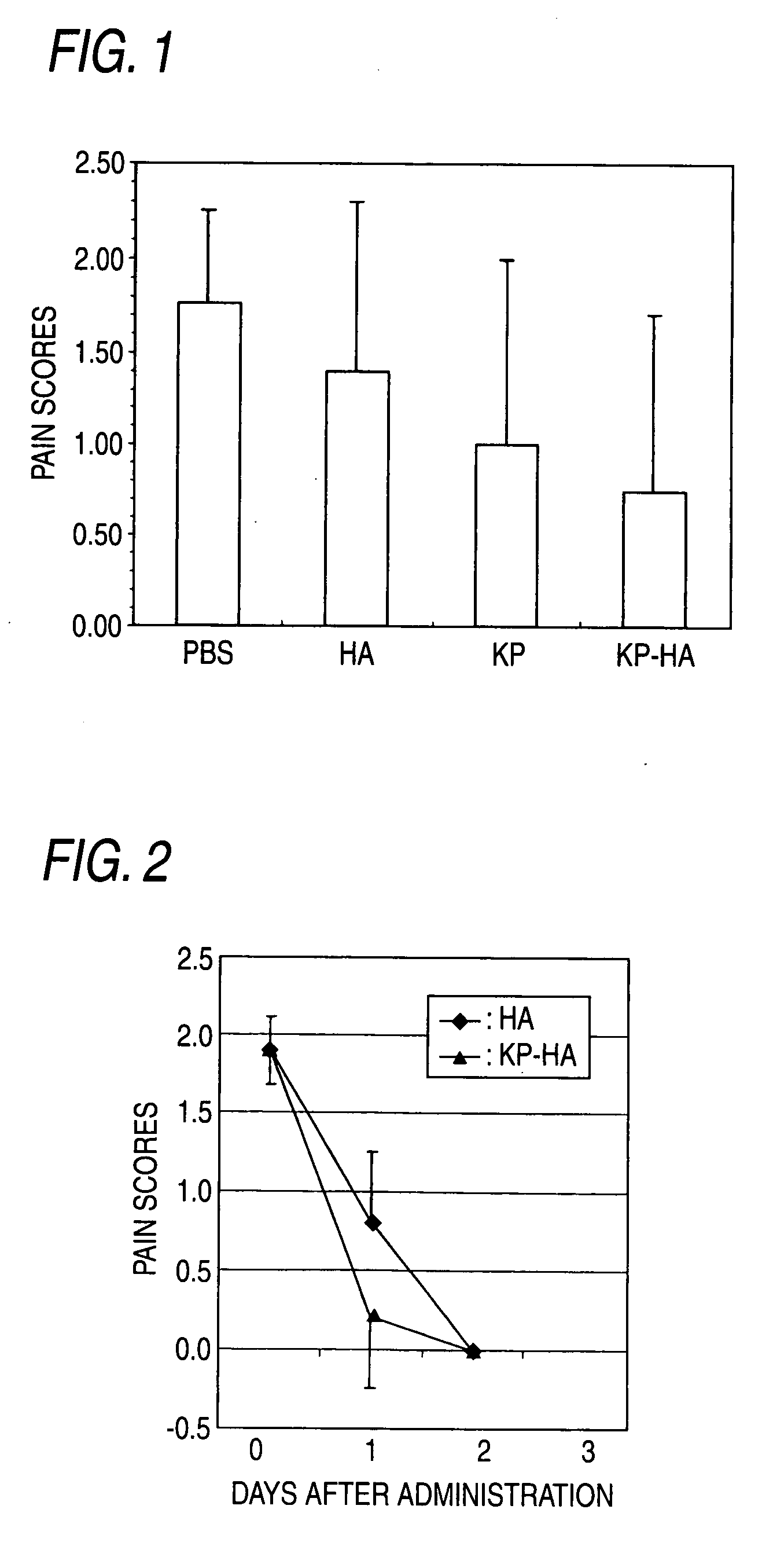
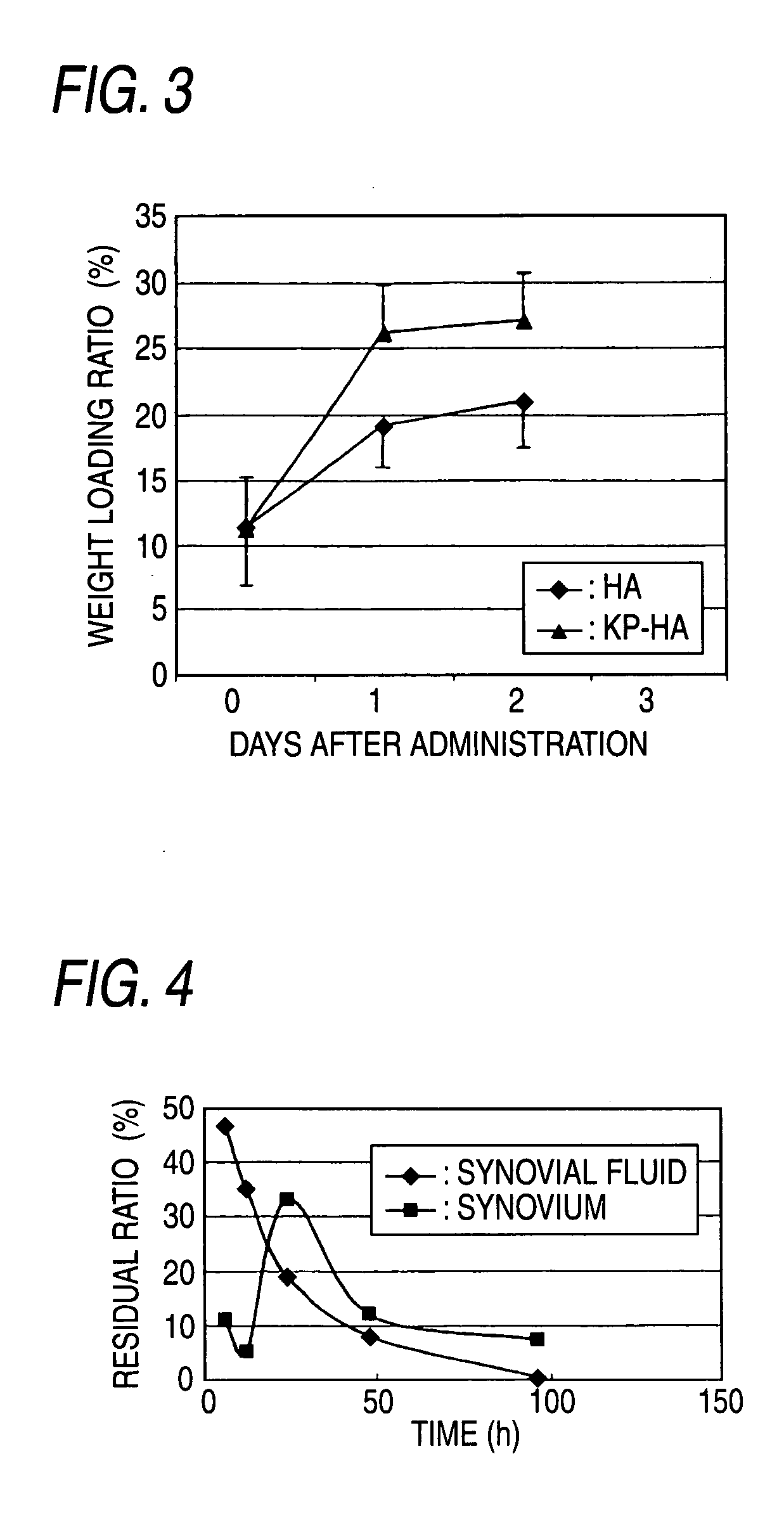
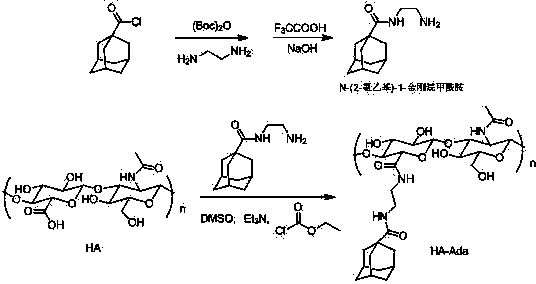
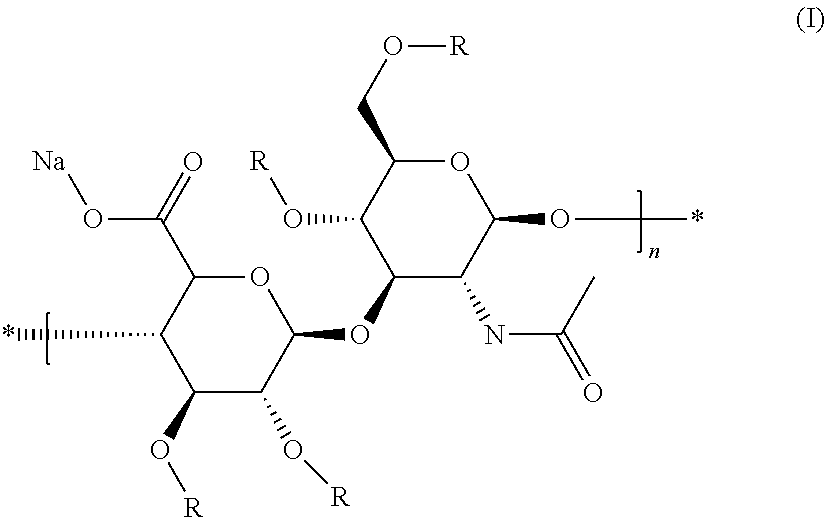
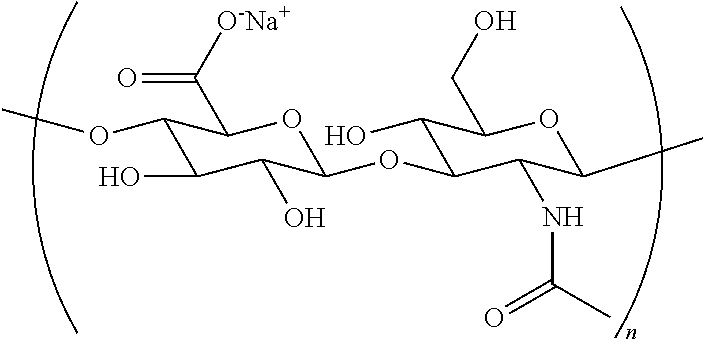
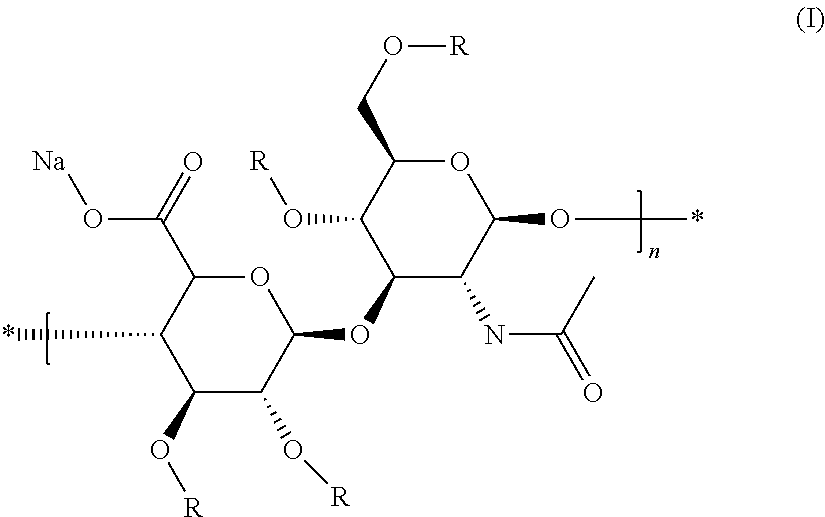
Hyaluronic Acid Derivative and Drug Containing the Same
ActiveUS20080221062A1Salicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideHyaluronic acidAnti-inflammatory analgesics
A hyaluronic acid derivative in which an anti-inflammatory drug is bound to hyaluronic acid through a covalent bond via a spacer having a biodegradable region, and a production process thereof.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
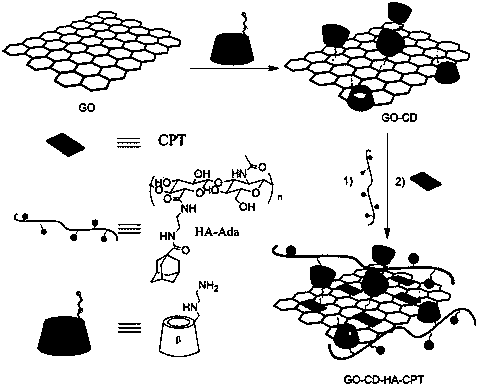
Graphene/hyaluronic acid assembly taking cyclodextrin as medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103920160AImprove stabilityGood biocompatibilityOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsCancer cellBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a graphene / hyaluronic acid assembly taking cyclodextrin as a medium. The graphene / hyaluronic acid assembly is a nano supermolecule assembly synthesized based on beta-cyclodextrin-modified graphene and adamantine-modified hyaluronic acid, wherein graphene is modified by beta-cyclodextrin; by virtue of strong host-guest interaction between beta-cyclodextrin and adamantine, graphene and hyaluronic acid are combined together to form the supermolecule assembly. The graphene / hyaluronic acid assembly has the advantages that the supermolecule assembly greatly improves stability and biocompatibility of the cyclodextrin-modified graphene under physiological conditions; by utilizing targeted recognition action of hyaluronic acid on tumor cells, the supermolecule assembly can selectively kill the cancer cells, and has anti-cancer activity higher than that of pure drug camptothecin; the targeted drug transmission system is simple in preparation process, easy to implement and low in material cost, and has potential application prospect in clinic treatment of cancers.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate, synthetic method and application in injectable in-situ hydrogel thereof
The invention discloses a cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate, a synthetic method and an application in preparation of injectable in-situ hydrogel thereof. According to the method, a hydroxy of hyaluronic acid is modified to obtain the cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate with a stable ether bond, and tetrabutyl ammonium hydroxide is introduced in the reaction process. The new method improves the solubility of hyaluronic acid and increases the reaction efficiency. The obtained cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate has a sulfhydryl active group which not only improves the adhesion of hyaluronic acid, but also can be further functionalized. According to the invention, injectable in-situ hydrogel is generated by a native chemical ligation reaction or a Michael addition reaction of the prepared cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate with a polyethylene glycol conjugate; rheological research shows that the generated hydrogel has good rheological properties, the gel performance is controllable, and the hydrogel has wide application prospects in the biological medicine field.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Hyaluronic acid modification products and drug carriers using them
InactiveUS7767806B2Good dispersionNot problematical in safetySugar derivativesPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsGlycolic acidBiocompatibility Testing
A hyaluronic acid modification product includes a polymer bonded to hyaluronic acid, the polymer being polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid or lactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer, providing a drug carrier which efficiently encapsulates low molecular weight drugs and provides sustained-release over a long term, control of blood residence, is well dispersible in an aqueous solution, and has excellent biocompatibility.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
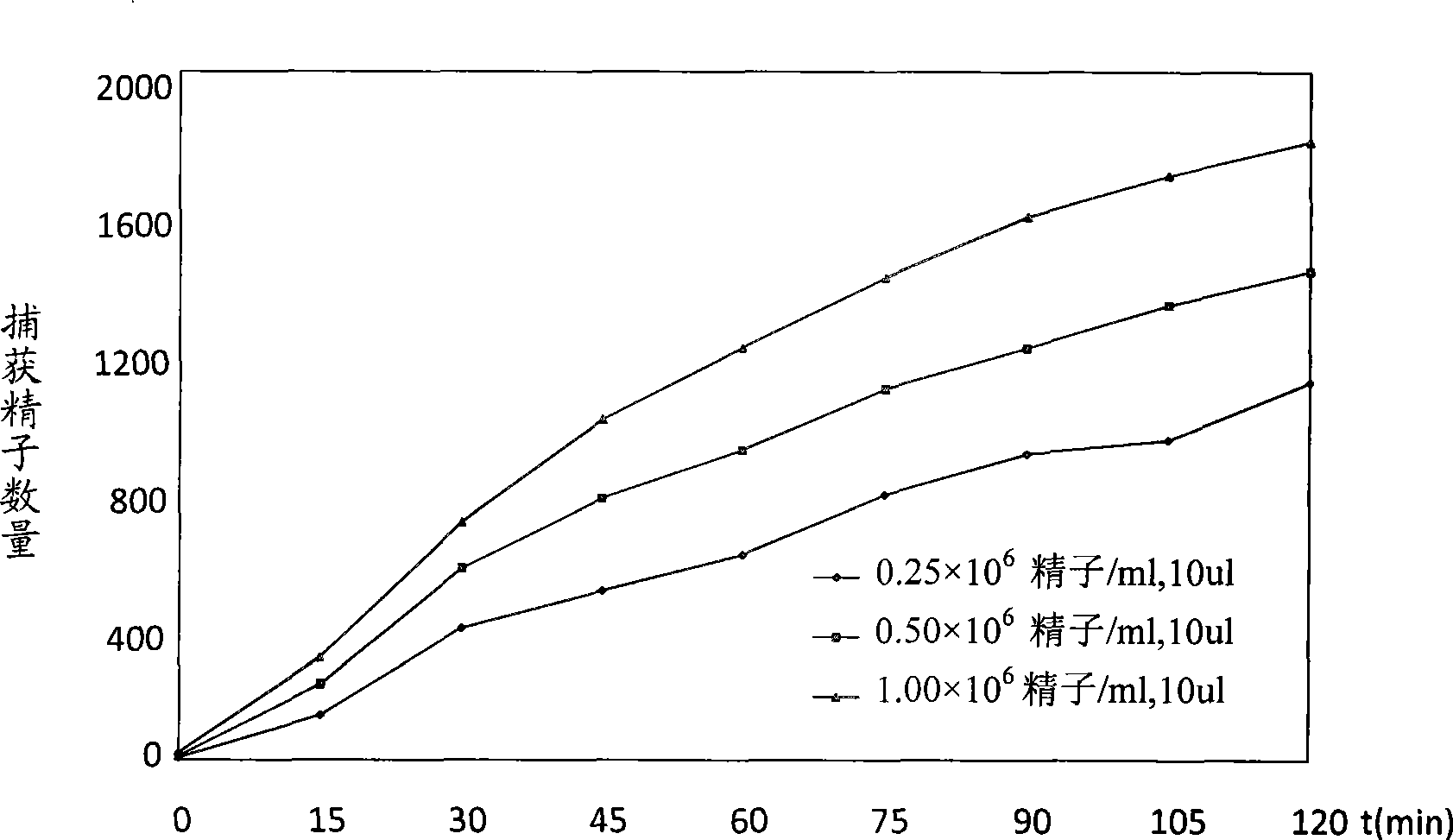
Coating carrier and its use in method for sperm maturity detection and non-invasive mature sperm separation
InactiveCN101487841ADeterminable maturity statusPromote maturityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMale infertilityEmbryo
The invention discloses a coated carrier and the application thereof in the method for detecting maturity of sperms and separating mature sperms noninvasively; the coated carrier is a carrier coated by hyaluronic acid, or hyalurate or hyaluronic acid derivatives; the detecting method is as follows: preparing specimens; loading the specimens to the coated carrier and covering with microscopic glass; reacting for 5-60 minutes at room temperature; observing by a microscope and counting; and calculating the combination ratio of hyaluronic acid of active sperms. The separating method is as follows: preparing specimens; loading the specimens to the coated carrier, reacting for 5-120 minutes at the temperature of 18-37 DEG C; and collecting the combined sperms. The coated carrier has the advantages of precise and reliable results, simple and fast operation, low cost and good safety performance, and can be used for estimating sperms quality, sperms maturity and analysis of the causes of sterility disease of mails, and is applicable to assisting reproduction or reproduction research center to safely collect mature and active sperms, so that the goal of improving embryo quality greatly is achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Reduction trigger type polypeptide modified hyaluronic acid conjugate carrier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104586816AImprove utilization efficiencyGood carrier stabilityOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsSolubilityTumor target
The invention discloses a reduction trigger type polypeptide modified hyaluronic acid conjugate carrier and a preparation method thereof. The carrier is a nanoparticle mainly consisting of hyaluronic acid, hydrophobic groups, tumor targeted hydrophilic groups and a medicament, wherein the hydrophobic groups are bonded with hyaluronic acid through reduction sensitive bonds. The conjugate carrier can be self-assembled into the nanoparticle in an aqueous medium and is capable of supporting anti-tumor active medicine molecules. The reduction trigger type polypeptide modified hyaluronic acid conjugate carrier has the main advantages that (1) the carrier has a dual targeting capacity, so that the transfer efficiency of drugs in tumors is improved, and the untoward effect is reduced; (2) a disulfide bond linking arm is intruded into the conjugate and can be specifically degraded by high-concentration reduced glutathione in the tumor cells, so that the drugs are rapidly released, and the bioavailability of the drugs is improved; and (3) the anti-tumor drugs are loaded by virtue of a physical embedding action, so that the water solubility of the anti-tumor drugs is improved. The preparation method is simple, a process is mature, and the carrier has a good application prospect.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
New drug
InactiveUS20050054593A1Growth inhibitionKeep for a long timePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLymphatic SpreadMurine fibrosarcoma
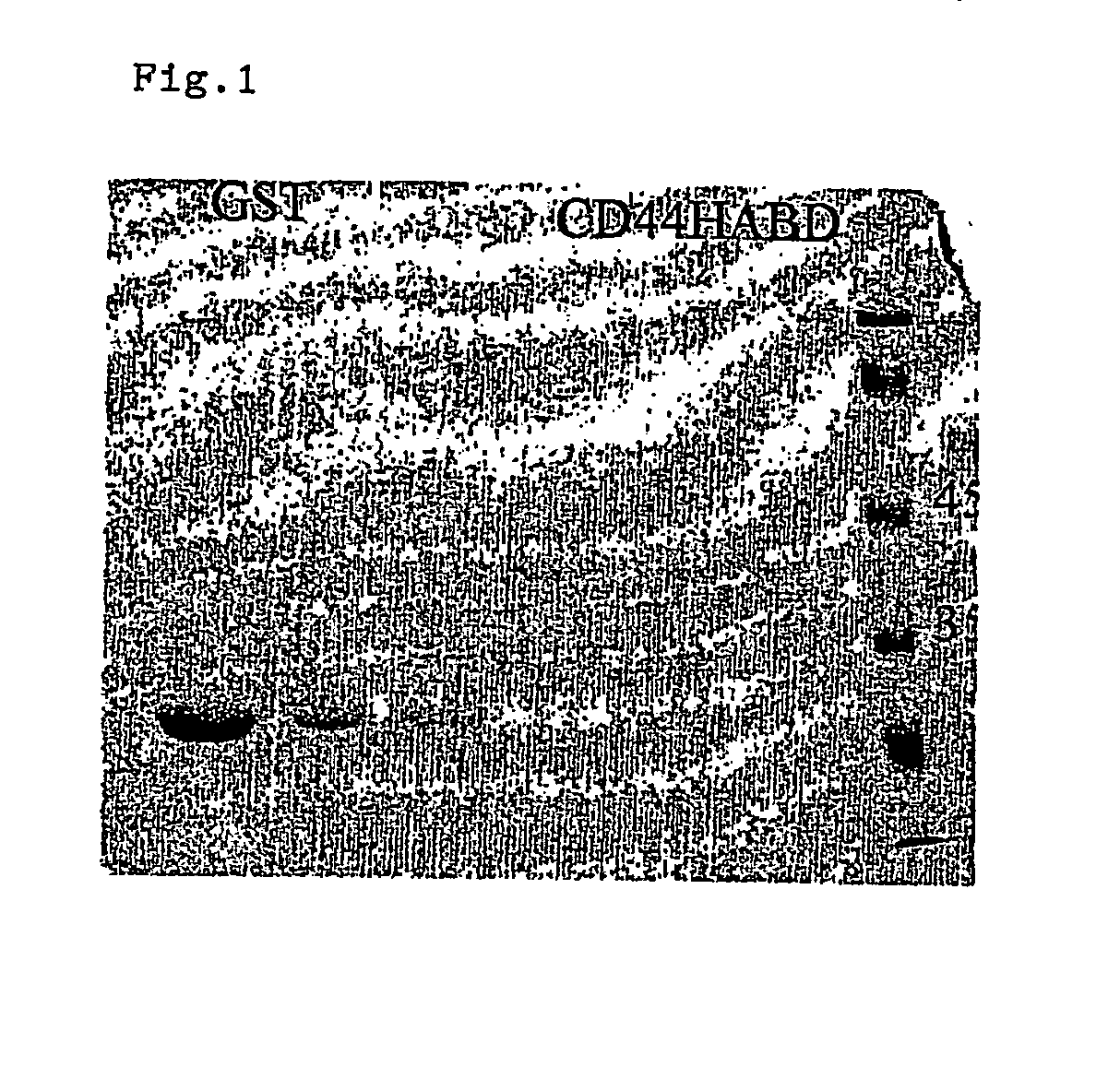
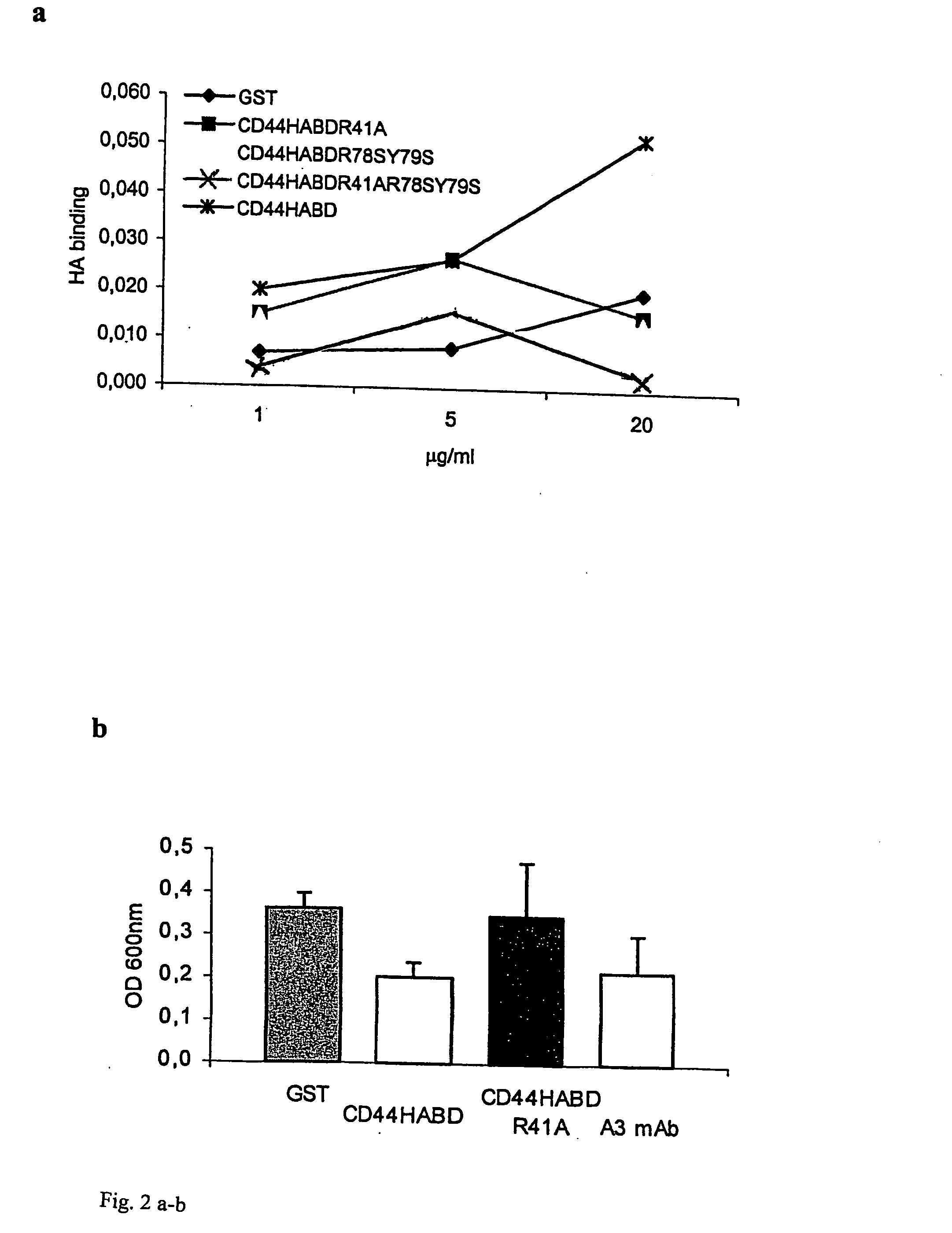
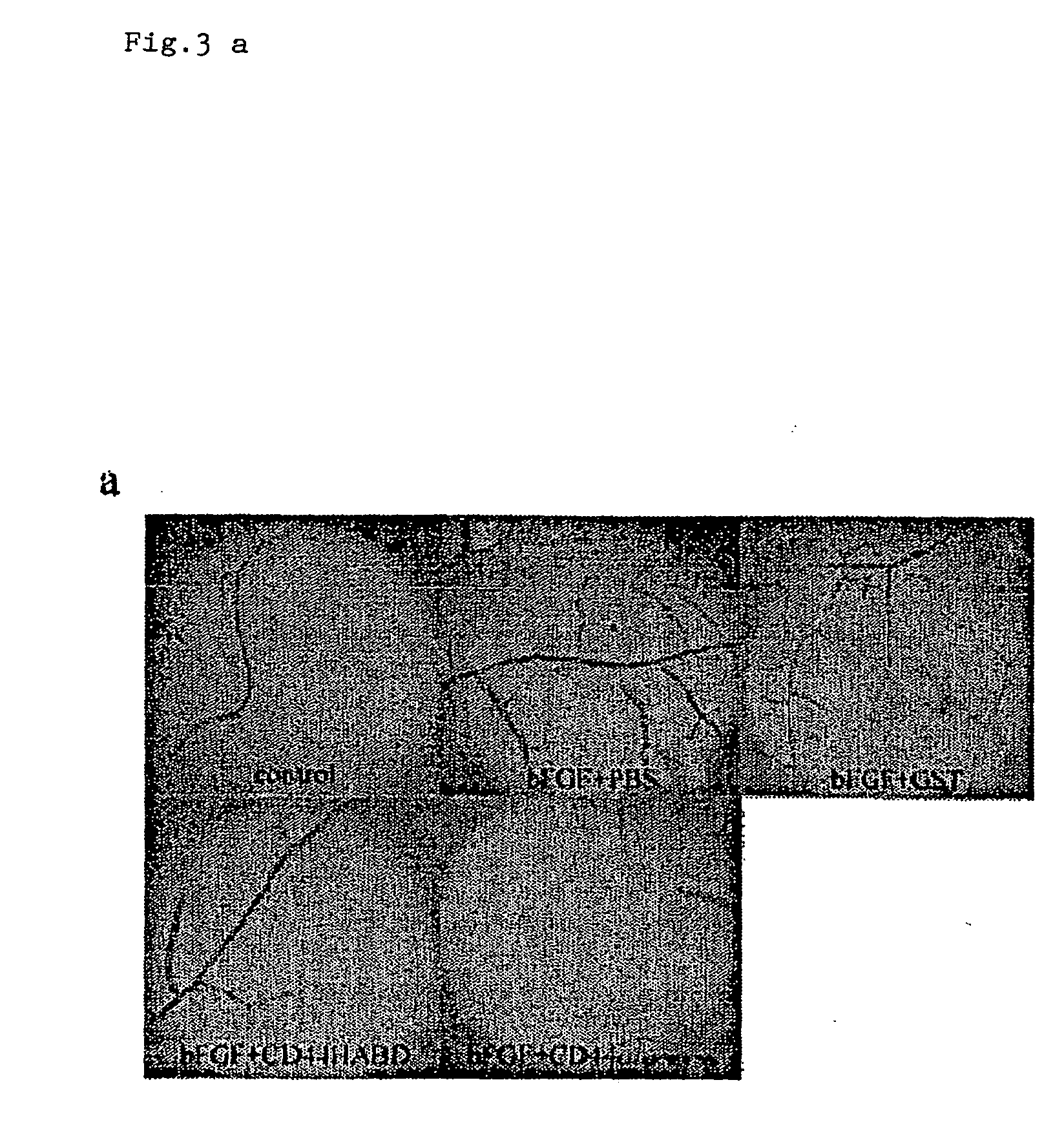
CD44, the receptor for hyaluronic acid, has complex functions in cellular physiology, cell migration and tumour metastasis. The inventors have previously found that human CD44 receptor overexpression in mouse fibrosarcoma cells inhibits subcutaneous tumour growth in mice [Kogerman et al., Oncogene 1997; 15:1407-16; Kogerman et al., Clin Exp Metastasis 1998; 16:83-93]. Here it is demonstrated that a tumour growth inhibitory effect of CD44 is caused by block of angiogenesis. Furthermore, the inventors have found that soluble recombinant CD44 hyaluronic acid binding domain (CD44HABD) inhibits angiogenesis in vivo in cLick and mouse and thereby inhibits human tumour growth of various origins. The anti-angiogenic effect of CD44-HABD is independent of hyaluronic acid (HA) binding, since non-HA-binding mutants of CD44HABD still maintain anti-angiogenic properties. The invention discloses soluble CD44 recombinant proteins as a novel class of angiogenesis inhibitors based on targeting of vascular cell surface receptor. A method of block of angiogenesis and treatment of human tumours using recombinant CD44 proteins as well as their analogues is disclosed. As a further embodiment of the invention, methods for screening for new drug targets using CD44 recombinant proteins and their analogues is presented.
Owner:CELECURE
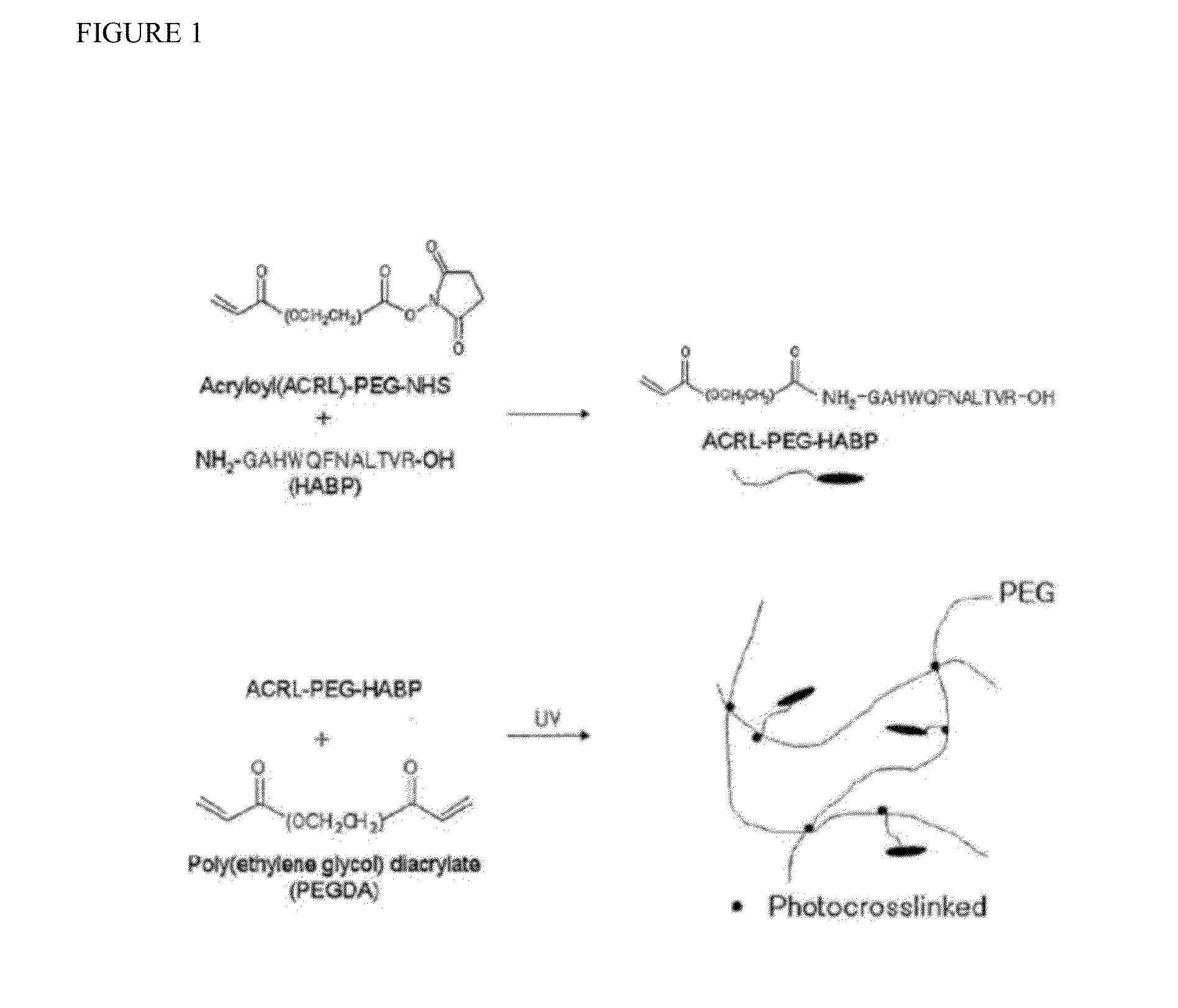
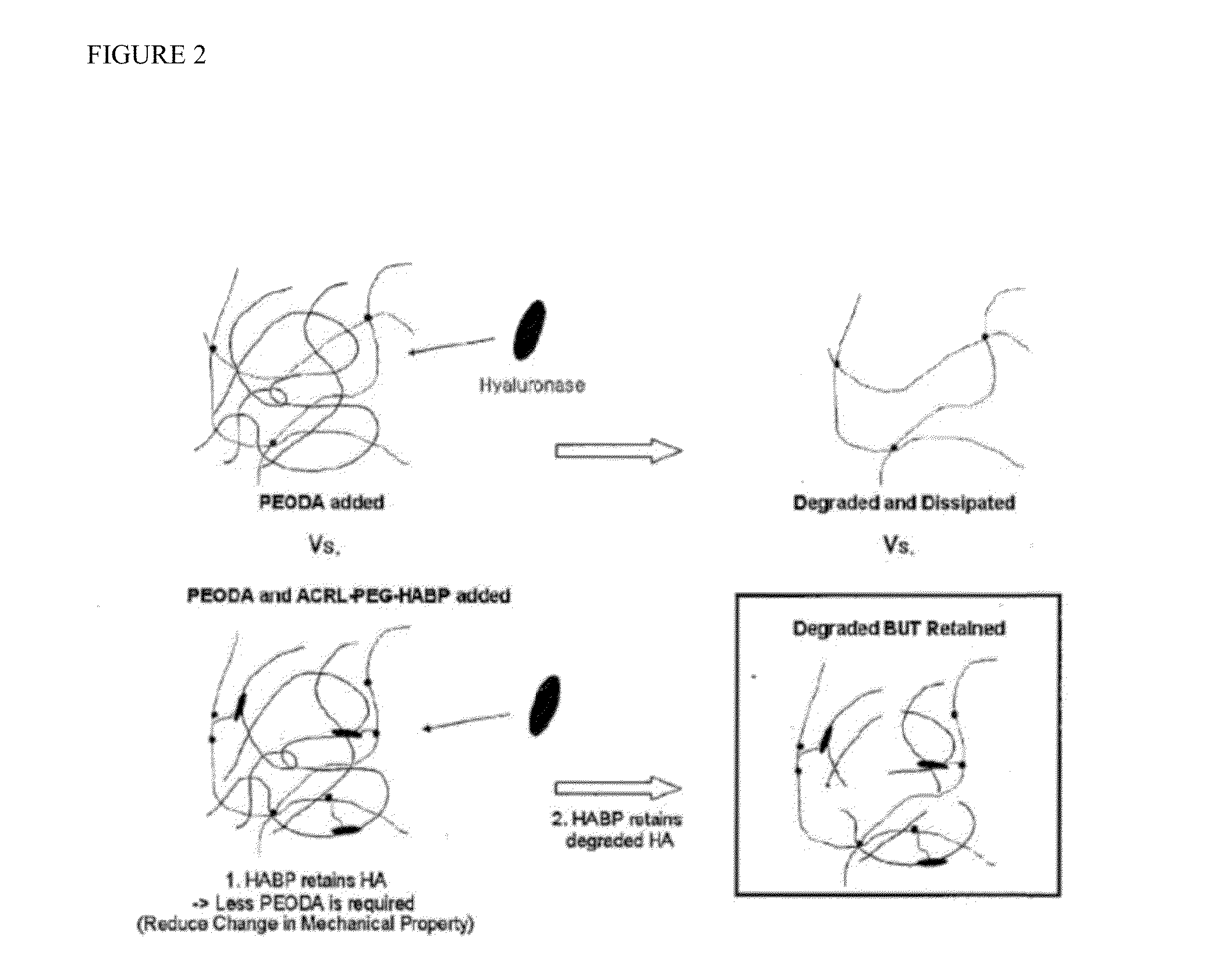
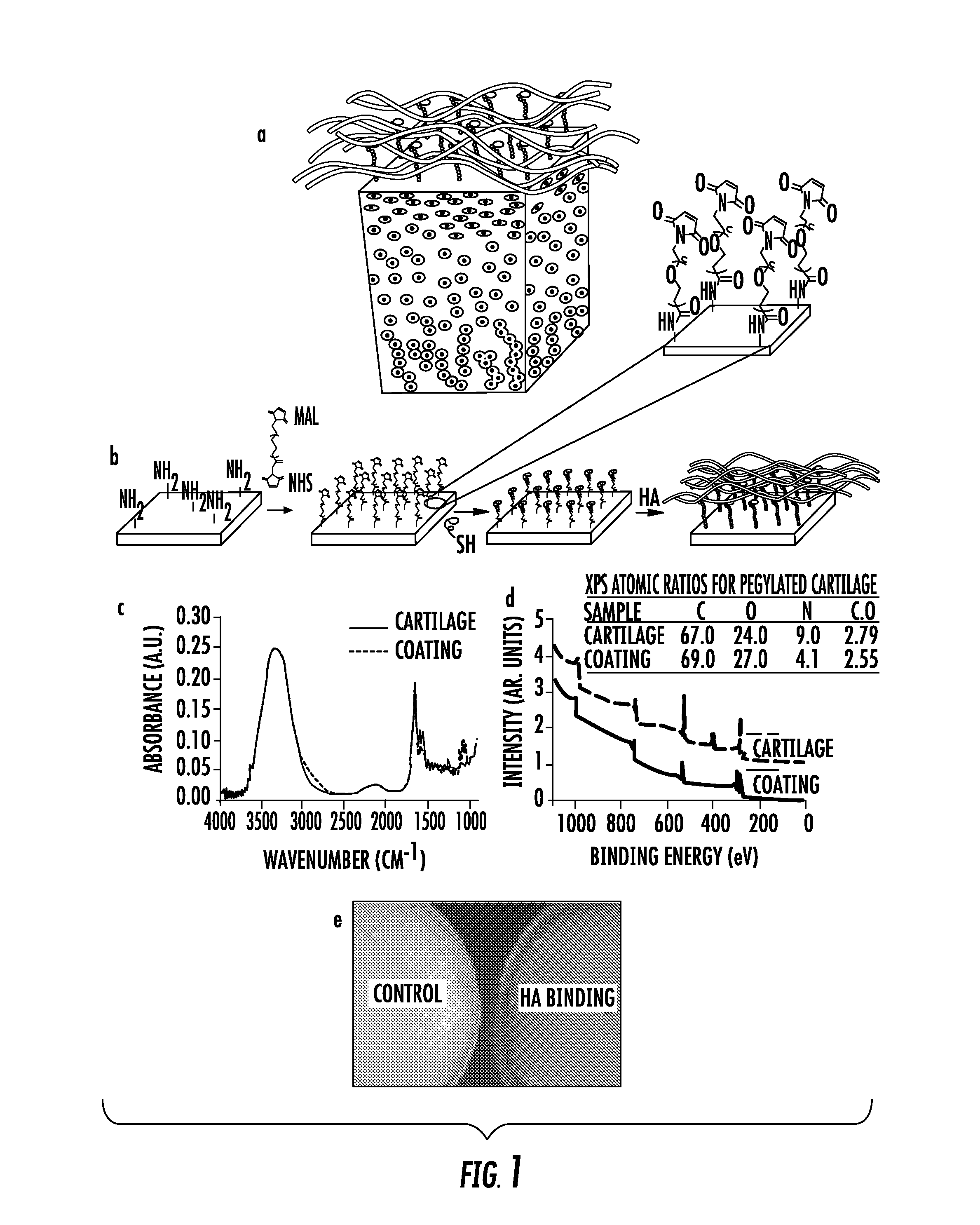
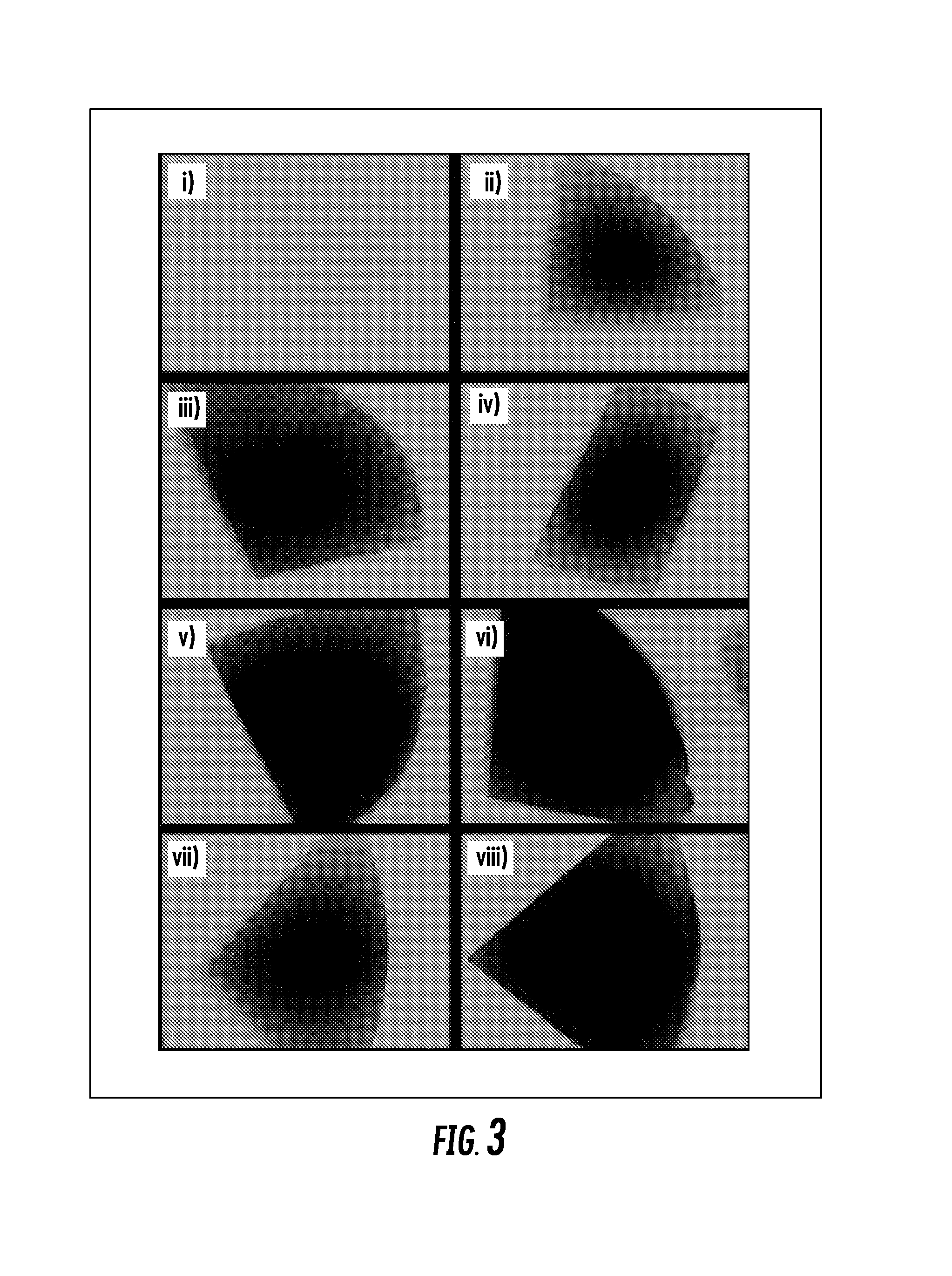
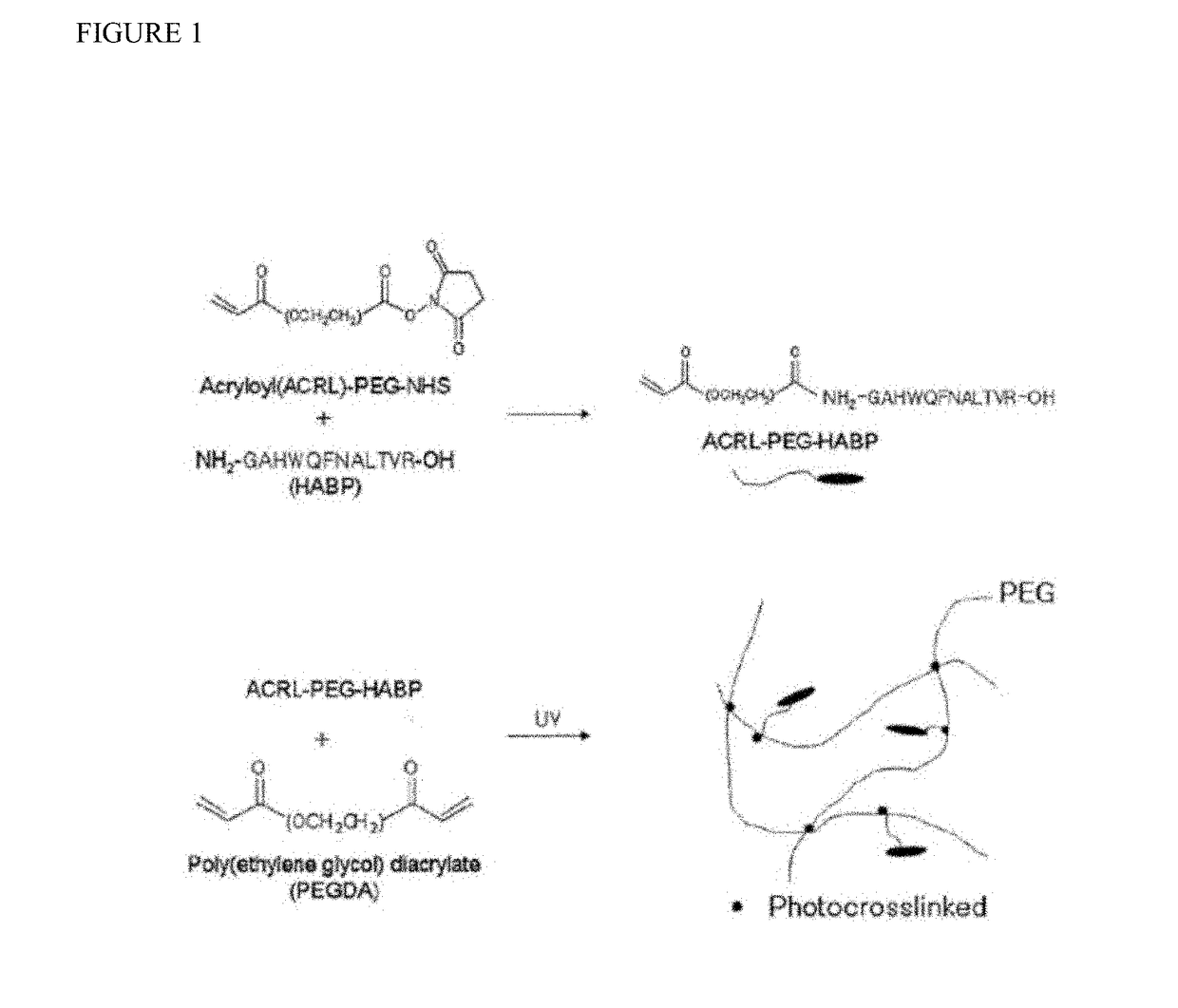
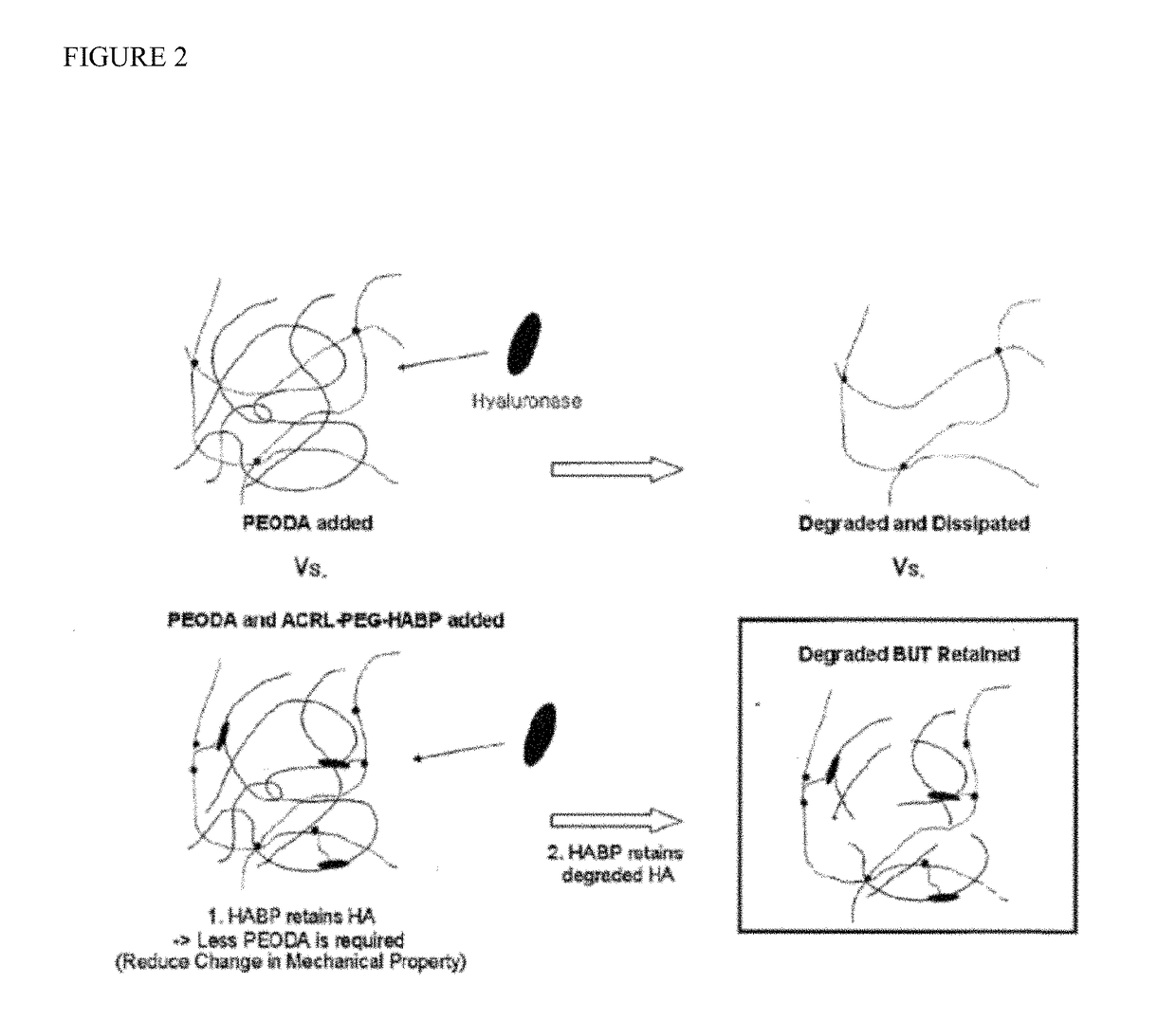
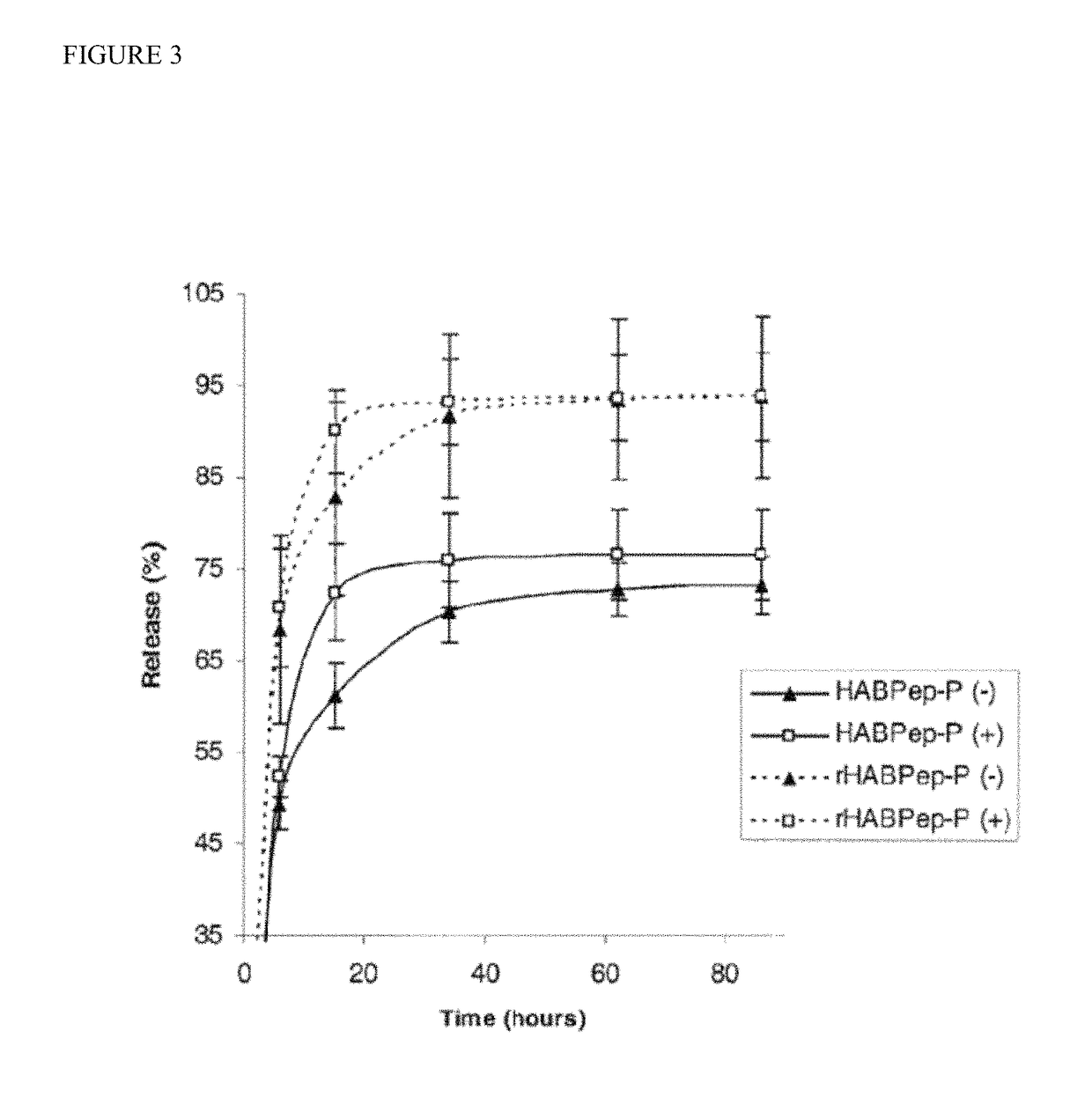
Biomaterials comprising hyaluronic acid binding peptides and bifunctional biopolymer molecules for hyaluronic acid retention and tissue engineering applications
ActiveUS20140369975A1Enhances boundary lubrication effectImprove joint lubricationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsBiopolymerBinding peptide
The present invention provides novel biomaterial compositions and methods having a technology to improve retention of hyaluronic acid (HA). The biomaterial compositions utilize small HA binding peptides that is tethered to synthetic biocompatible polymers. When tethered to the polymers, the peptide region allows the polymers to bind to HA. The biocompatible polymers are modified to contain a crosslinking group so that the HA can be incorporated into a scaffold and retained in place. The novel biomaterial 1 compositions can be made into hydrogel compositions and used in a variety of tissue applications, using mild crosslinking conditions and they also have the ability to be degraded with hyaluronidase if needed. Furthermore, the novel biomaterial compositions will enable enhanced interaction between the scaffold and encapsulated cells for a wide variety of tissue engineering applications. Methods of making hydrogel compositions and their use are also provided. The present invention also provides bifunctional biopolymer compositions comprising a biologically compatible polymer having at least one amine reactive moiety and at least one thiol reactive moiety and provides thiolated HA binding peptides which can be used together to coat or chemically modify cartilage or tissues having amine reactive residues with a biologically compatible polymer having HA binding peptides, which allow HA to bind to the surface of the cartilage or tissues. Methods of using same are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Cysteine-hyaluronic acid conjugate prepared through freeze drying and thiol-ene click chemistry, synthesis method and applications thereof
ActiveCN106478841AImproved rheological propertiesIncrease cell adhesionPharmaceutical delivery mechanismProsthesisCell adhesionFreeze-drying
The present invention discloses a cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate prepared through freeze drying and thiol-ene click chemistry, and a synthesis method thereof, and discloses applications of the hyaluronic acid conjugate in preparation of an injectable in-situ hydrogel, and applications of the formed injectable in-situ hydrogel in islet cell culture and insulin secretion. According to the present invention, a series of cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugates having different modification rates and stable ether bonds are obtained through freeze drying and thiol-ene click chemistry, wherein the cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate has the thiol active group, such that the further functionalized modification can be performed; and the hyaluronic acid conjugates having different modification rates and the polyethylene glycol conjugate can be subjected to the oxo ester-mediated natural chemical link reaction to obtain the an injectable in-situ formed hydrogel, wherein the obtained hydrogel has the good rheological property, the free thiol group can increase the cell adhesion of the hyaluronic acid and can be adopted as the cell scaffold material so as to be used in the islet cell culture and the insulin secretion stimulation, and the broad biomedical prospects are provided.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
Hyaluronic acid derivative and drug containing the same
A hyaluronic acid derivative in which an anti-inflammatory drug is bound to hyaluronic acid through a covalent bond via a spacer having a biodegradable region, and a production process thereof.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
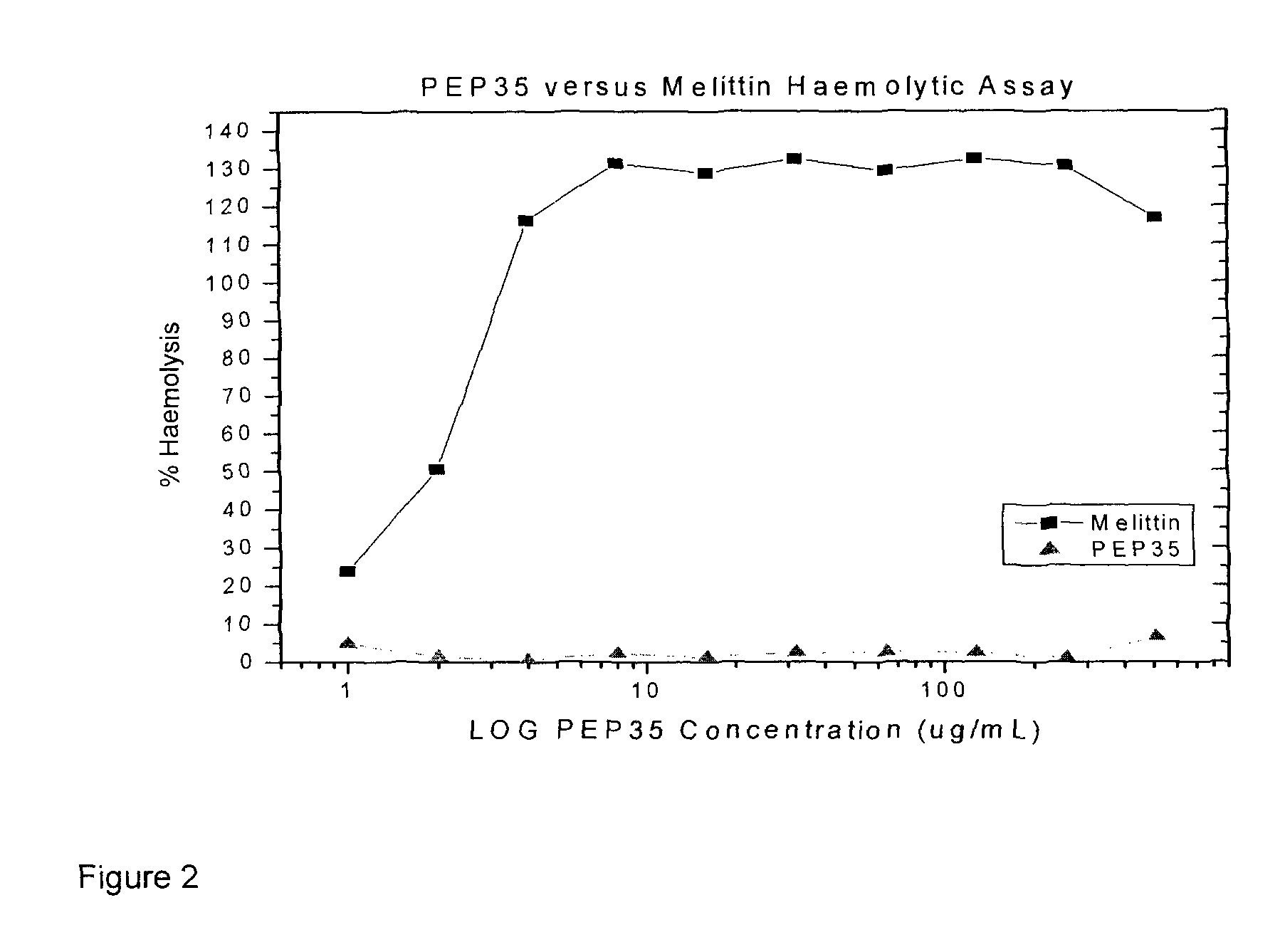
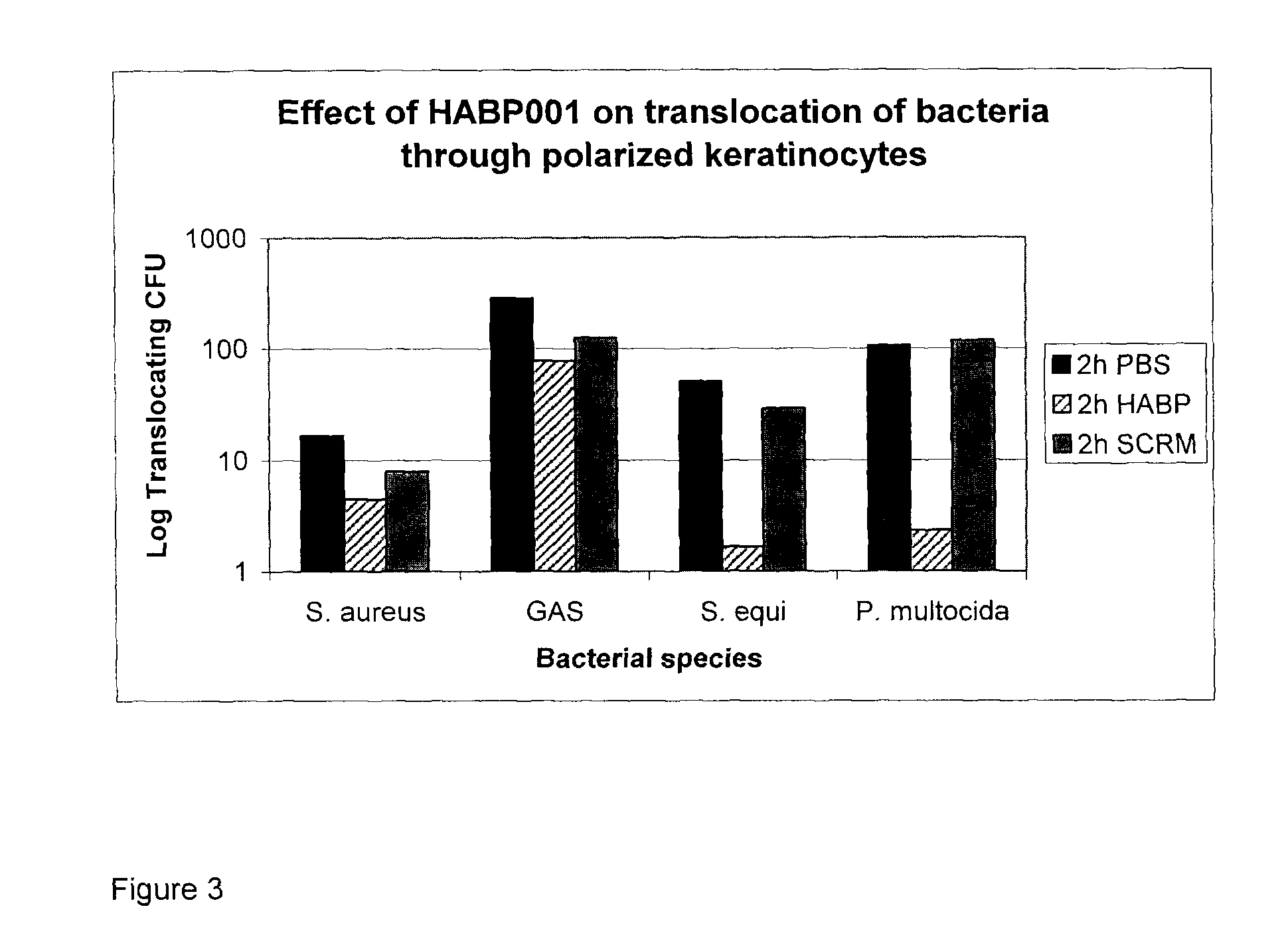
Hyaluronic acid binding peptides enhance host defense against pathogenic bacteria
Several species of bacteria capable of invasive infections, such as S. pyogenes, S. equi and P. multocida, contain hyaluronic acid (HA) in their capsules. Bacterial species such as Staphylococcus aureus and related Staphylococci have capsules that contain acidic polysaccharides. Bacterial capsule or bacterial surface binding peptides were synthesized and tested in a culture model of invasive bacterial infections, specifically translocation through polarized keratinocyte cultures. The peptides reduced the translocation of a variety of bacterial species, with a concomitant increase in bacterial internalization by the keratinocytes. In vivo, subcutaneous inoculation of encapsulated GAS treated with peptides delayed bacterial dissemination. In a mouse surgical wound model infected with S. aureus, treatment with peptides reduced the numbers of bacteria and inflammation at the wound site.
Owner:CANGENE CORP
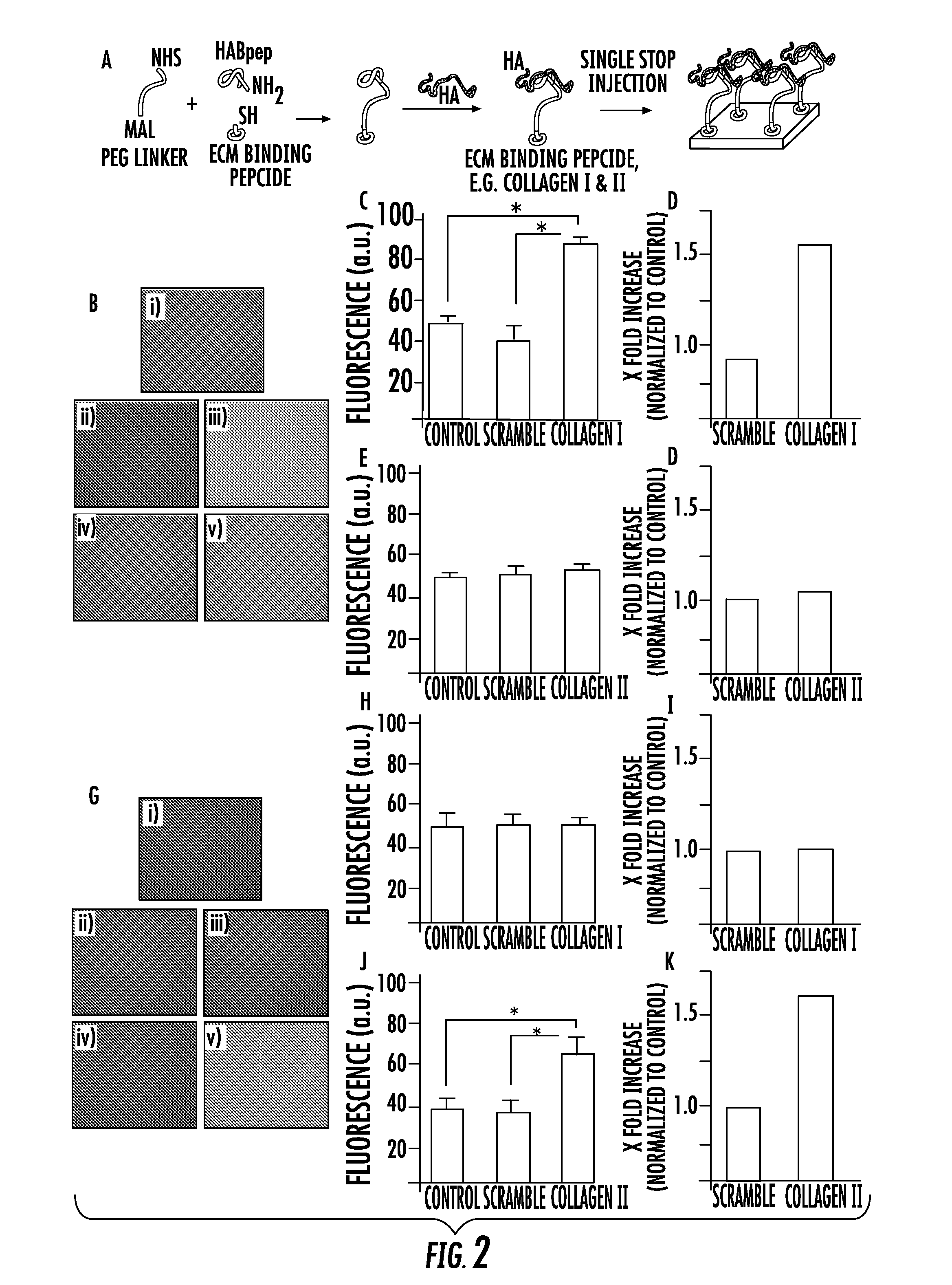
Biomaterials comprising hyaluronic acid binding peptides and extracellular matrix binding peptides for hyaluronic acid retention and tissue engineering applications
ActiveUS20160158270A1Improve the lubrication effectImprove joint lubricationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsExtracellular matrix bindingBinding peptide
The present invention provides novel biomaterial compositions and methods having a technology to improve retention of hyaluronic acid (HA). The biomaterial compositions utilize small HA binding peptides and extracellular matrix binding (ECM) peptides that are tethered to synthetic biocompatible polymers. When tethered to the polymers, the peptide region allows the polymers to bind to HA and to tissues such as cartilage. The novel biomaterial compositions can be used to coat or chemically modify cartilage or tissues with a biologically compatible polymer having HA binding peptides, which allow HA to bind to the surface of the cartilage or tissues. Methods of using same are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Biomaterials comprising hyaluronic acid binding peptides and bifunctional biopolymer molecules for hyaluronic acid retention and tissue engineering applications
ActiveUS9795686B2Improves chondrogenesis of bone marrow-derivedEnhances boundary lubrication effectAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryBiopolymerBinding peptide
The present invention provides novel biomaterial compositions and methods having a technology to improve retention of hyaluronic acid (HA). The biomaterial compositions utilize small HA binding peptides that is tethered to synthetic biocompatible polymers. When tethered to the polymers, the peptide region allows the polymers to bind to HA. The biocompatible polymers are modified to contain a crosslinking group so that the HA can be incorporated into a scaffold and retained in place. The novel biomaterial 1 compositions can be made into hydrogel compositions and used in a variety of tissue applications, using mild crosslinking conditions and they also have the ability to be degraded with hyaluronidase if needed. Furthermore, the novel biomaterial compositions will enable enhanced interaction between the scaffold and encapsulated cells for a wide variety of tissue engineering applications. Methods of making hydrogel compositions and their use are also provided. The present invention also provides bifunctional biopolymer compositions comprising a biologically compatible polymer having at least one amine reactive moiety and at least one thiol reactive moiety and provides thiolated HA binding peptides which can be used together to coat or chemically modify cartilage or tissues having amine reactive residues with a biologically compatible polymer having HA binding peptides, which allow HA to bind to the surface of the cartilage or tissues. Methods of using same are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
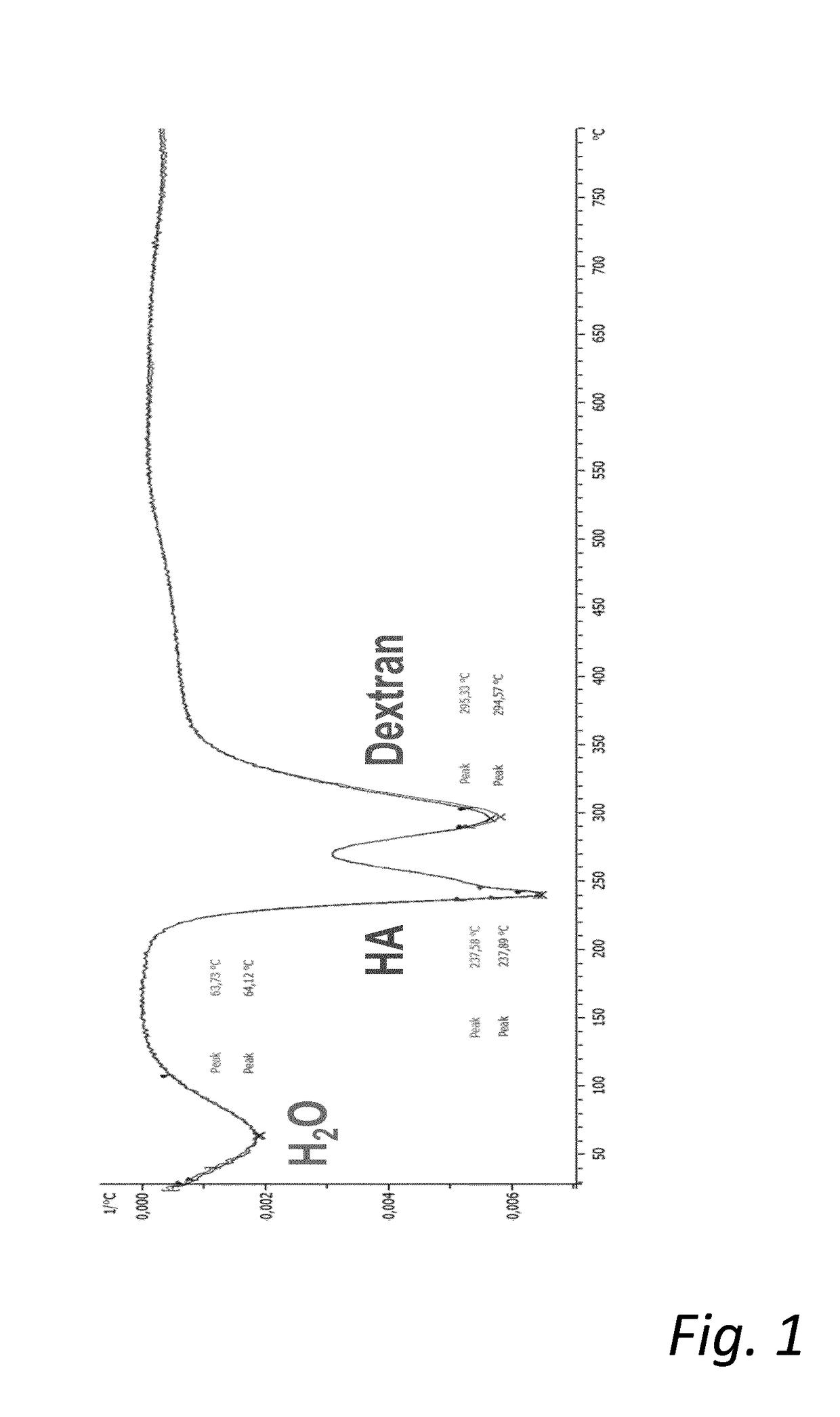
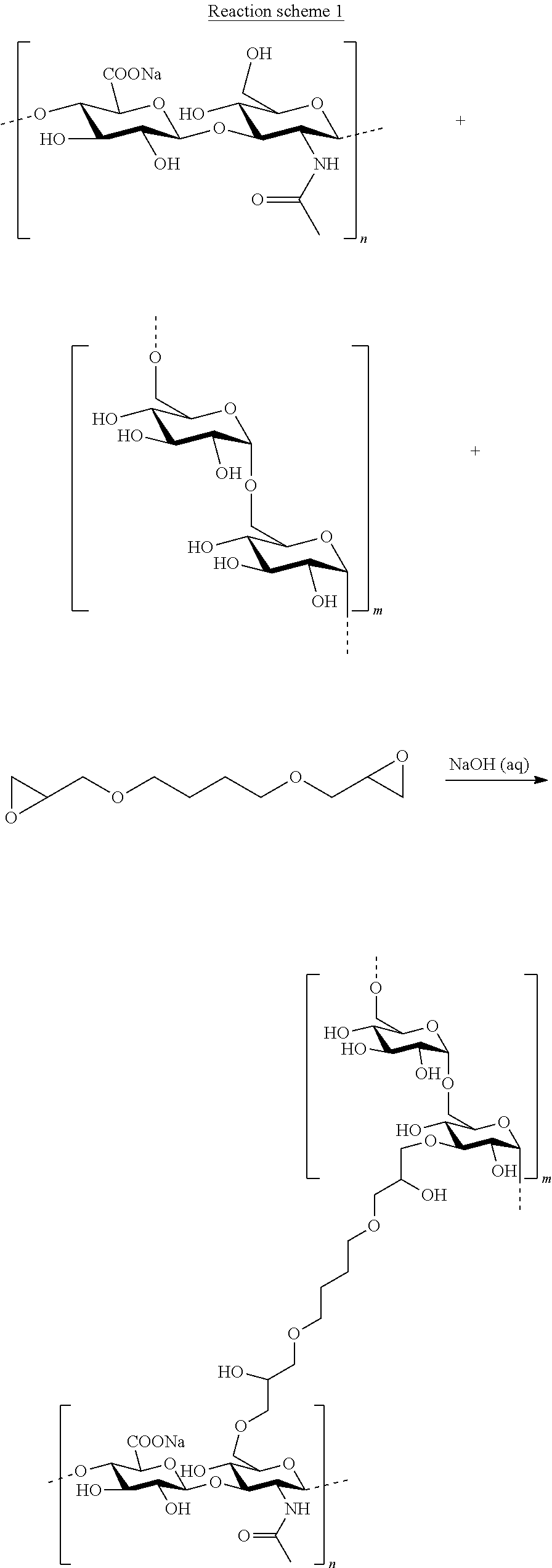
Mixed hydrogels of hyaluronic acid and dextran
InactiveUS20180155456A1Stability to heat degradationIncreased durabilityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue regenerationCross-linkEther
A process of preparing a cross-linked polysaccharide product including hyaluronic acid and dextran, the process including the steps of: (a) providing a hyaluronic acid and a dextran; (b) binding the dextran to the hyaluronic acid by ether bonds using a bi- or polyfunctional cross-linking agent, wherein the hyaluronic acid provided in step (a) is a cross-linked hyaluronic acid gel, and the dextran provided in step (a) is a non-cross-linked dextran; and wherein step (b) includes cross-linking the dextran to the hyaluronic acid by ether bonds using a bi- or polyfunctional cross-linking agent.
Owner:GALDERMA SA
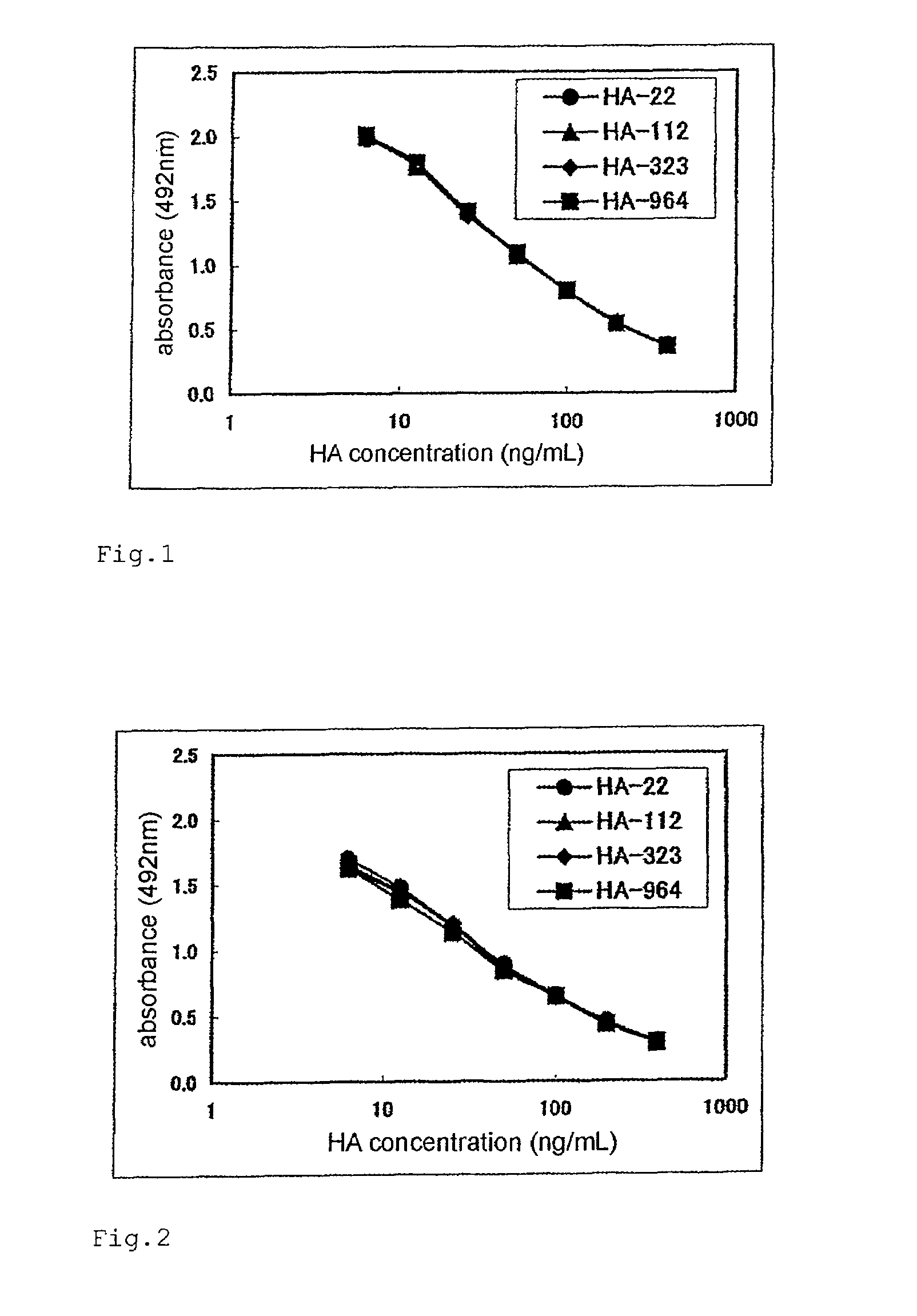
Method for determination of molecular weight of hyaluronic acid
InactiveUS8163498B2Short timeBiological material analysisPeptide preparation methodsProtein CChemistry
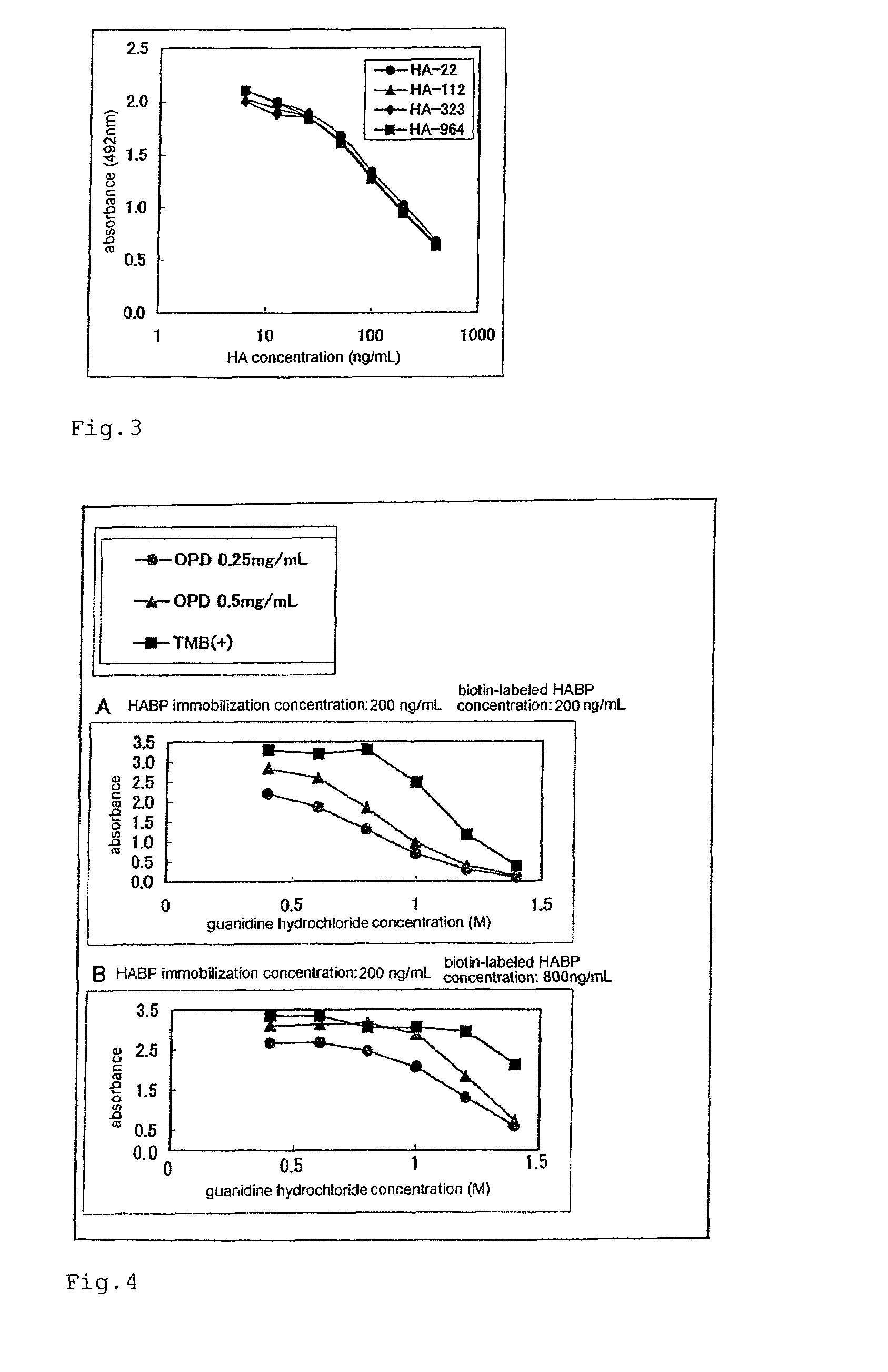
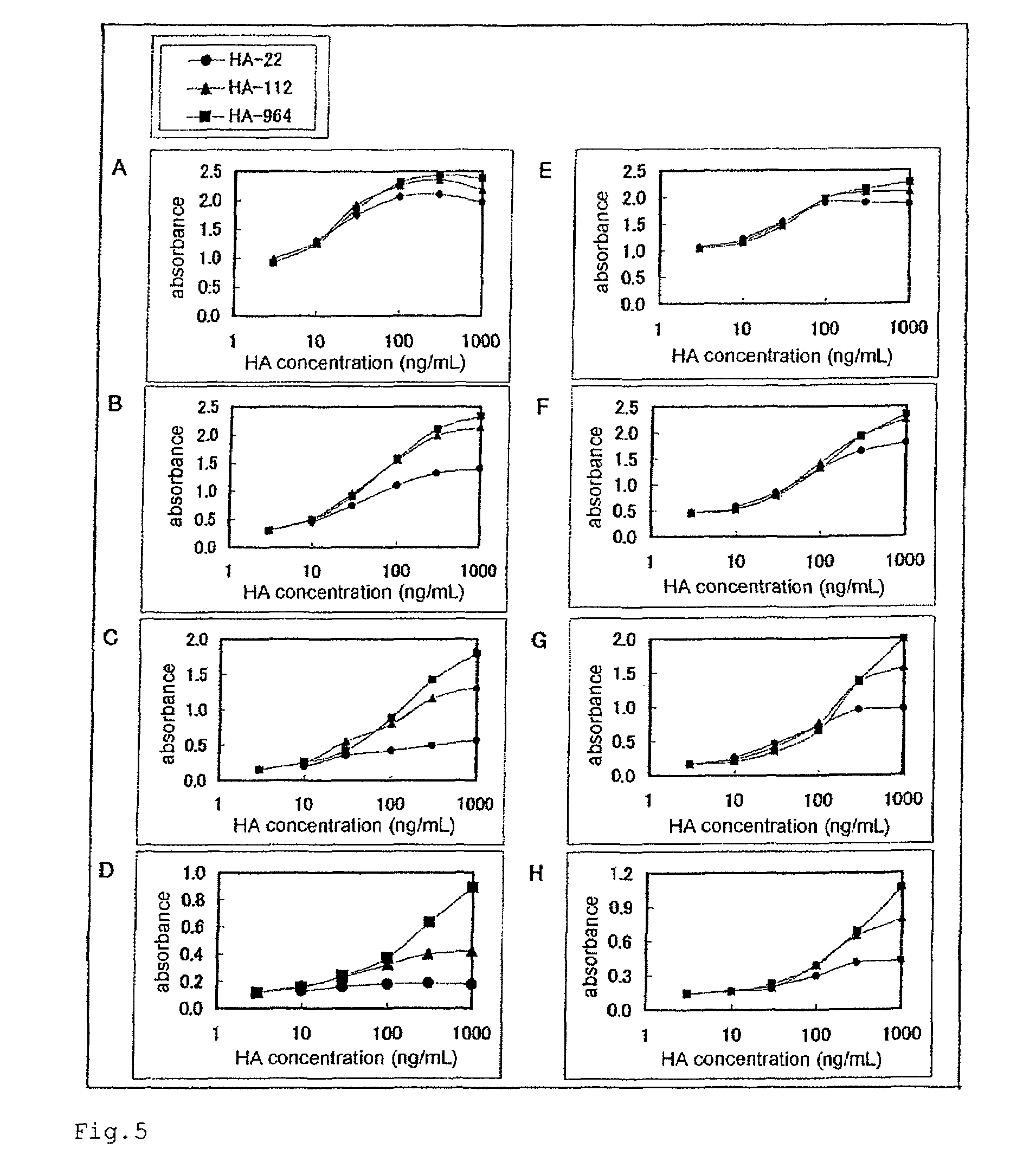
A method of measuring a molecular weight of hyaluronic acid, comprising at least reacting hyaluronic acid in a sample containing the hyaluronic acid with a hyaluronic acid-binding protein to measure an amount of the hyaluronic acid-binding protein that is bound to the hyaluronic acid in the sample or a value that reflects the amount.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
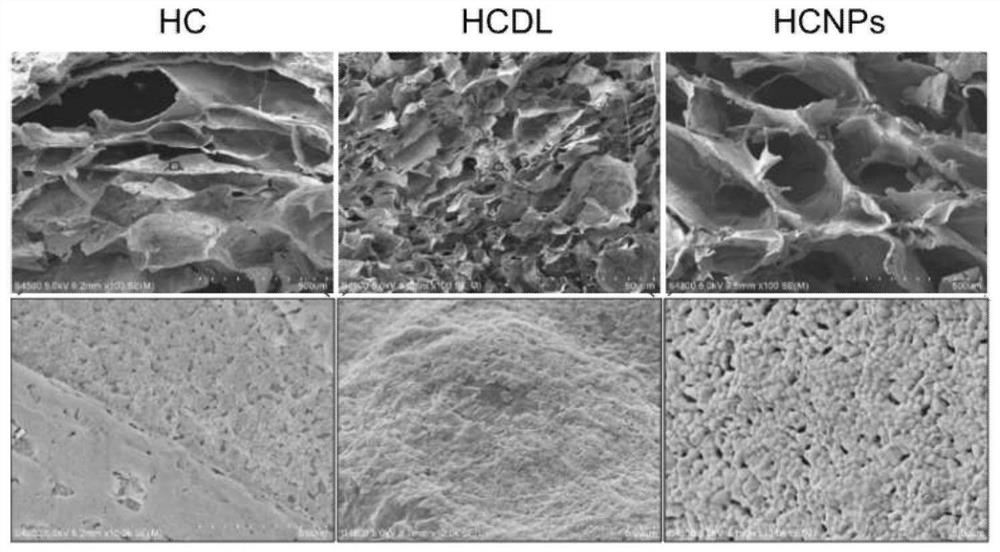
Crosslinked hemostatic sponge with hemostatic and postoperative anti-tumor functions and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112933288AGood hemostatic effectGood biocompatibilitySurgical adhesivesLiposomal deliveryResidual TumorsTumor cells
The invention provides a crosslinked hemostatic sponge with hemostatic and postoperative anti-tumor functions. The cross-linked hemostatic sponge is composed of a composite three-dimensional network structure formed by cross-linked modified hyaluronic acid and collagen substances and controlled-release drug-loaded nanoparticles distributed in the composite three-dimensional network structure, and the cross-linked hemostatic sponge has a porous structure. The cross-linked modified hyaluronic acid is formed by self-crosslinking of modified hyaluronic acid, the controlled-release drug-loaded nanoparticles are combined with the cross-linked modified hyaluronic acid through chemical bonds, and the drug loaded by the controlled-release drug-loaded nanoparticles is an anti-tumor drug. The cross-linked hemostatic sponge provided by the invention not only can reduce bleeding and reduce the number of circulating tumor cells, but also can slowly release and release anti-tumor drugs into residual tumor cells and scattered tumor cells through the cross-linked and loaded drug co-delivery nanoparticles, continuously kills cancer cells, and effectively inhibits recurrence and metastasis of postoperative tumors.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Hyaluronic Acid Binding Peptides Enhance Host Defense Against Pathogenic Bacteria
ActiveUS20090030180A1Avoid infectionAvoid bacterial infectionAntibacterial agentsPeptide-nucleic acidsBacteroidesCulture model
Several species of bacteria capable of invasive infections, such as S. pyogenes, S. equi and P. multocida, contain hyaluronic acid (HA) in their capsules. Bacterial species such as Staphylococcus aureus and related Staphylococci have capsules that contain acidic polysaccharides. Bacterial capsule or bacterial surface binding peptides were synthesized and tested in a culture model of invasive bacterial infections, specifically translocation through polarized keratinocyte cultures. The peptides reduced the translo-cation of a variety of bacterial species, with a concomitant increase in bacterial internalization by the keratinocytes. In vivo, subcutaneous inoculation of encapsulated GAS treated with peptides delayed bacterial dissemination. In a mouse surgical wound control model infected with S. aureus, treatment with peptides reduced the numbers of bacteria and inflammation at the wound site.
Owner:CANGENE CORP
Novel hyaluronic acid binding peptide (HaBP) and transdermal absorption and subcutaneous targeted release preparation
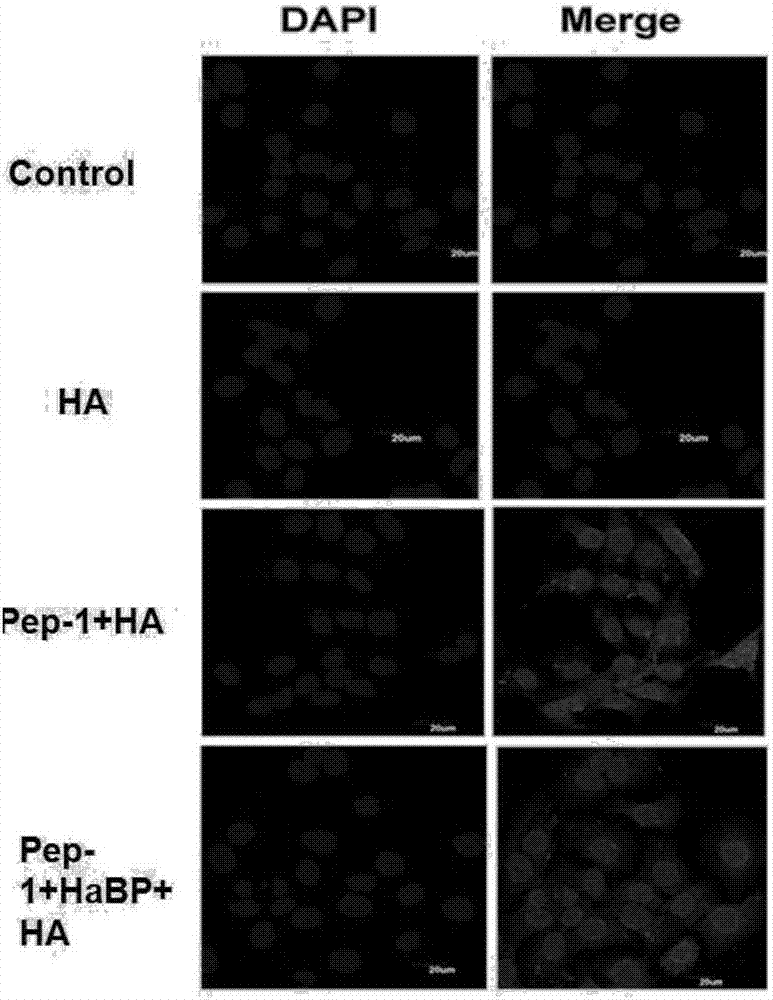
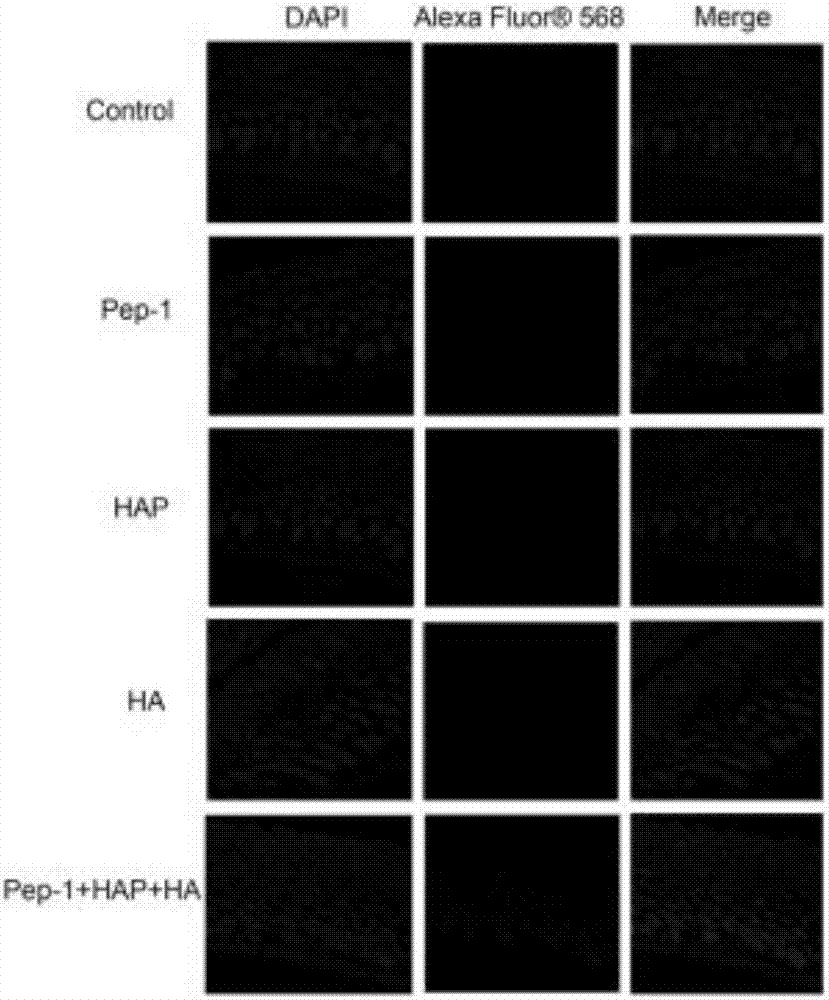
ActiveCN107226846AOvercome the defects of lower transdermal absorption rateOvercome the defect of low skin penetrationPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifCosmetic preparationsCuticleBiological macromolecule
The invention provides a novel hyaluronic acid binding peptide (HaBP) and a transdermal absorption and subcutaneous targeted release preparation. The HaBP can be specifically bound with hyaluronic acid (HA). When the HaBP, cell-penetrating peptides and HA are subjected to incubation and mixing under certain conditions or when the HaBP, cell-penetrating peptides and a subcutaneous endogenous proteinase restriction enzyme cutting site are connected together to construct a fusion protein and the fusion protein and HA are subjected to incubation, the transmembrane transport and transdermal absorption of the HA can be obviously promoted, and the subcutaneous targeted release of the HA can be implemented. The method provided by the invention overcomes the defect of low transdermal absorptivity when the HA is used as a biomacromolecular substance, so that the HA can efficiently go through the skin cuticle and perform subcutaneous targeted release to promote cell proliferation so as to perform the actual functions in the aspects of skin care, moisturizing, wrinkle reduction, whitening and the like, thereby providing a new idea and new method for development and production of related cosmetic products and biological drugs.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Novel protein capable of binding to hyaluronic acid, and method for measurement of hyaluronic acid using the same
ActiveUS20110053220A1Having no fluctuation among productsLow costSugar derivativesDepsipeptidesBiochemistryHyaluronic acid
The present invention relates to a polynucleotide encoding a protein comprising an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, wherein the protein encoded by the polynucleotide has a hyaluronic acid binding ability, the protein, a method for measuring hyaluronic acid using the protein, and a reagent kit for measuring hyaluronic acid comprising the protein as a constituent.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Hyaluronan conjugates with pharmaceutically active substances, methods and compositions
ActiveUS20160367684A1Increase productionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderChain lengthReagent
A method for manufacturing a hyaluronan conjugate comprises providing hyaluronan in solution or gel form, reacting the hyaluronan in solution or gel form with anhydride reagent to provide a hyaluronan hemi-ester with a chain of length L between the hyaluronan and the ester group, and subsequently binding the hyaluronan hemi-ester to a pharmaceutically active compound. A hyaluronan conjugate comprises hyaluronan having free hemi-ester-groups and a pharmaceutically active compound bound to the hyaluronan via hemi-ester groups, wherein the hemi-ester groups have a chain length of 2-9 atoms. The hyaluronan conjugate is suitable for use in various methods of treatment in human or veterinary medicine and for preparation of a medicament for use in human or veterinary medicine.
Owner:SYNARTRO AB
Novel protein capable of binding to hyaluronic acid, and method for measurement of hyaluronic acid using the same
InactiveUS20110195512A1Having no fluctuation among productsLow costSugar derivativesBiological testingNucleotidePolynucleotide
The present invention relates to a polynucleotide encoding a protein comprising an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, wherein the protein encoded by the polynucleotide has a hyaluronic acid binding ability, the protein, a method for measuring hyaluronic acid using the protein, and a reagent kit for measuring hyaluronic acid comprising the protein as a constituent.
Owner:WAKO PURE CHEMICAL INDUSTRIES
Method for determination of molecular weight of hyaluronic acid
A method of measuring a molecular weight of hyaluronic acid, comprising at least reacting hyaluronic acid in a sample containing the hyaluronic acid with a hyaluronic acid-binding protein to measure an amount of the hyaluronic acid-binding protein that is bound to the hyaluronic acid in the sample or a value that reflects the amount.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Hyaluronan conjugates with pharmaceutically active substances, methods and compositions
A method for manufacturing a hyaluronan conjugate comprises providing hyaluronan in solution or gel form, reacting the hyaluronan in solution or gel form with anhydride reagent to provide a hyaluronan hemi-ester with a chain of length L between the hyaluronan and the ester group, and subsequently binding the hyaluronan hemi-ester to a pharmaceutically active compound. A hyaluronan conjugate comprises hyaluronan having free hemi-ester-groups and a pharmaceutically active compound bound to the hyaluronan via hemi-ester groups, wherein the hemi-ester groups have a chain length of 2-9 atoms. The hyaluronan conjugate is suitable for use in various methods of treatment in human or veterinary medicine and for preparation of a medicament for use in human or veterinary medicine.
Owner:SYNARTRO AB
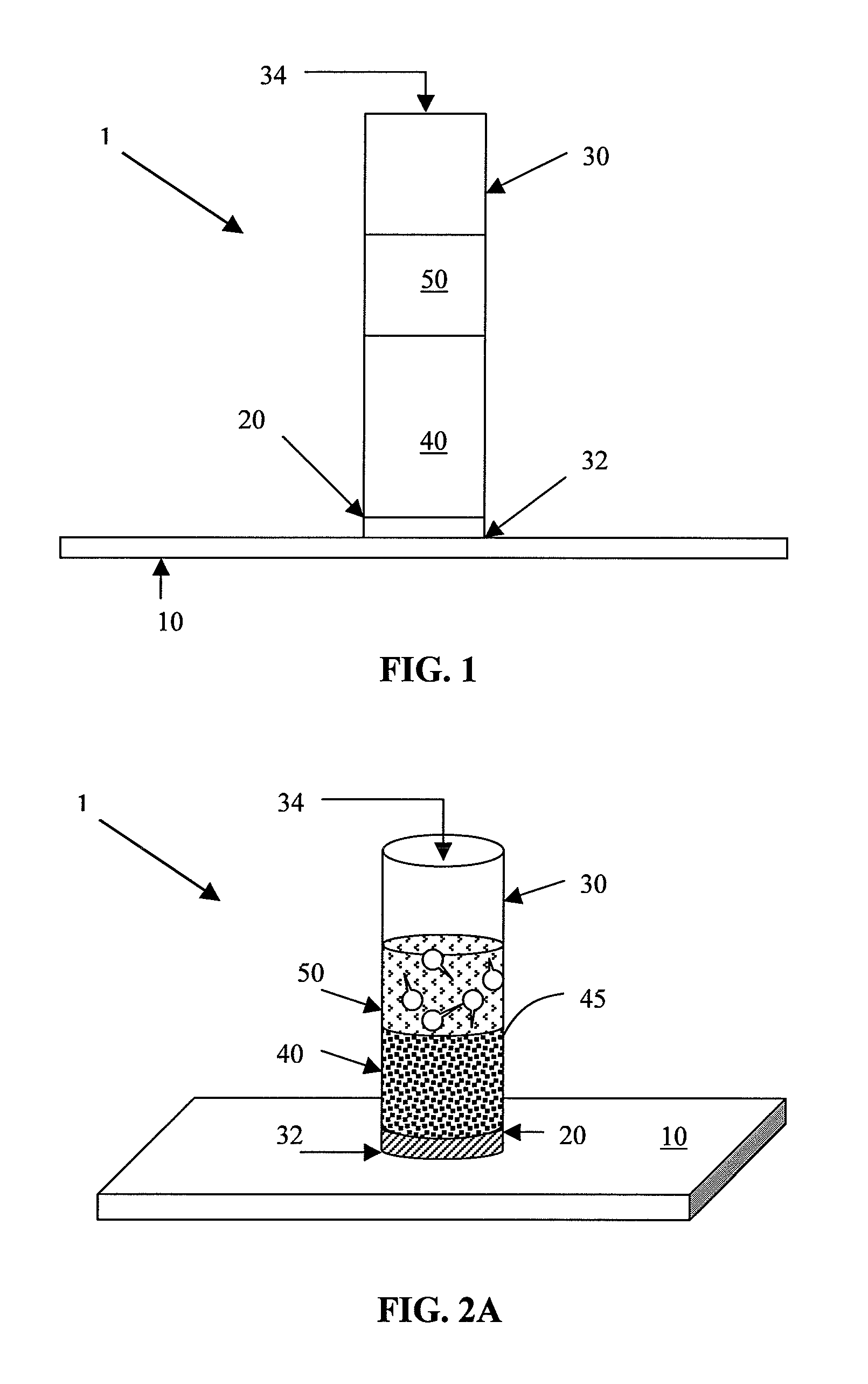
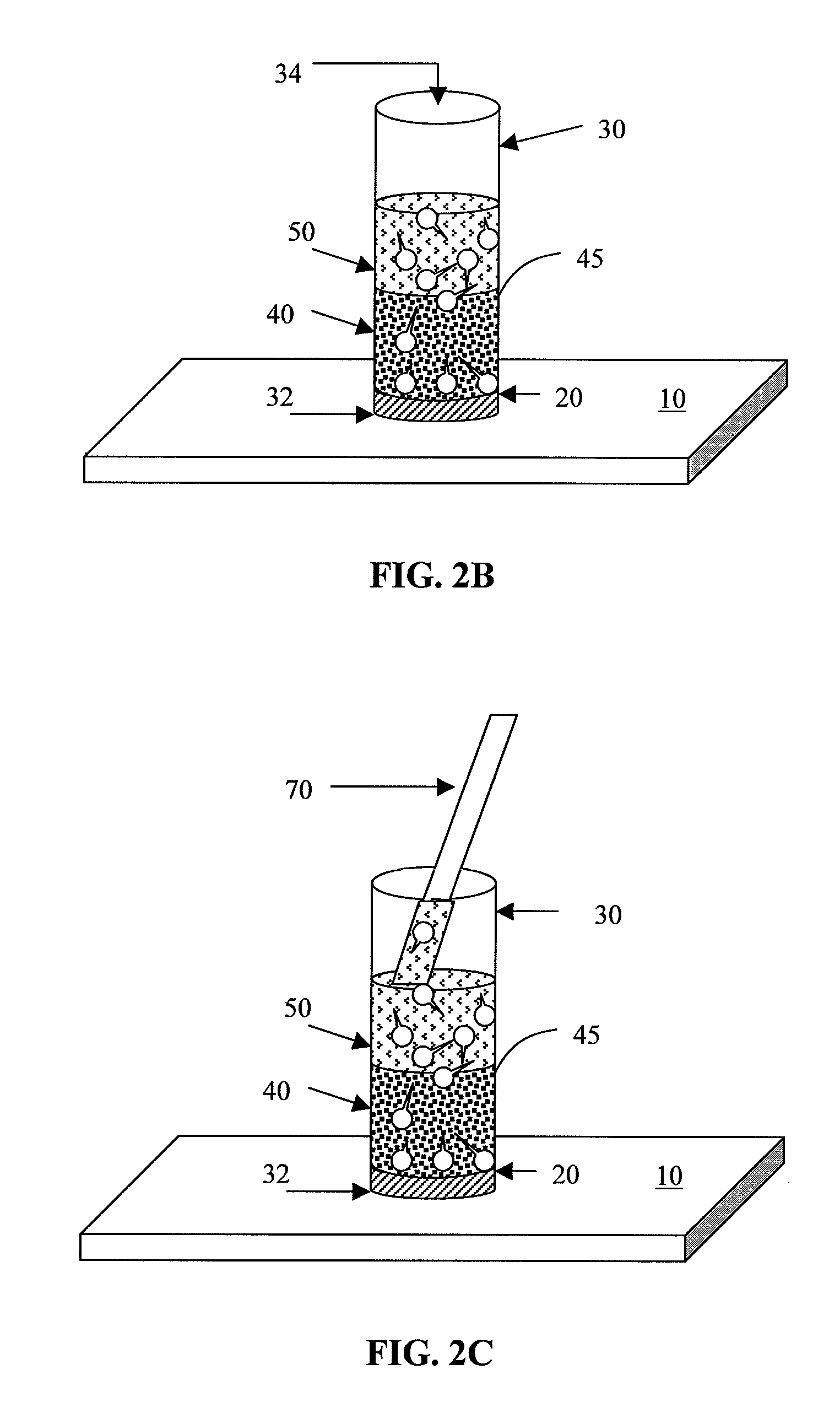
Integral sperm preparation for intracytoplasmic sperm injection
InactiveUS20130029312A1Avoid layeringImprove sperm qualityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRapid processingMature sperm
Methods, systems and apparatus for preparing sperm for ICSI by combining selective enrichment benefits of sperm gradient preparation, sperm swim-up preparation and hyaluronan-binding for selection of mature sperm into a single processing unit. The single processing unit of the invention reduces operator labor steps and time, is efficient, easy to use, offers quick processing time and provides highly motile, mature and specific individual sperm that retain desired sperm characteristics selected by each individual selection principal that are ready for capture and use in ICSI.
Owner:BIOCOAT
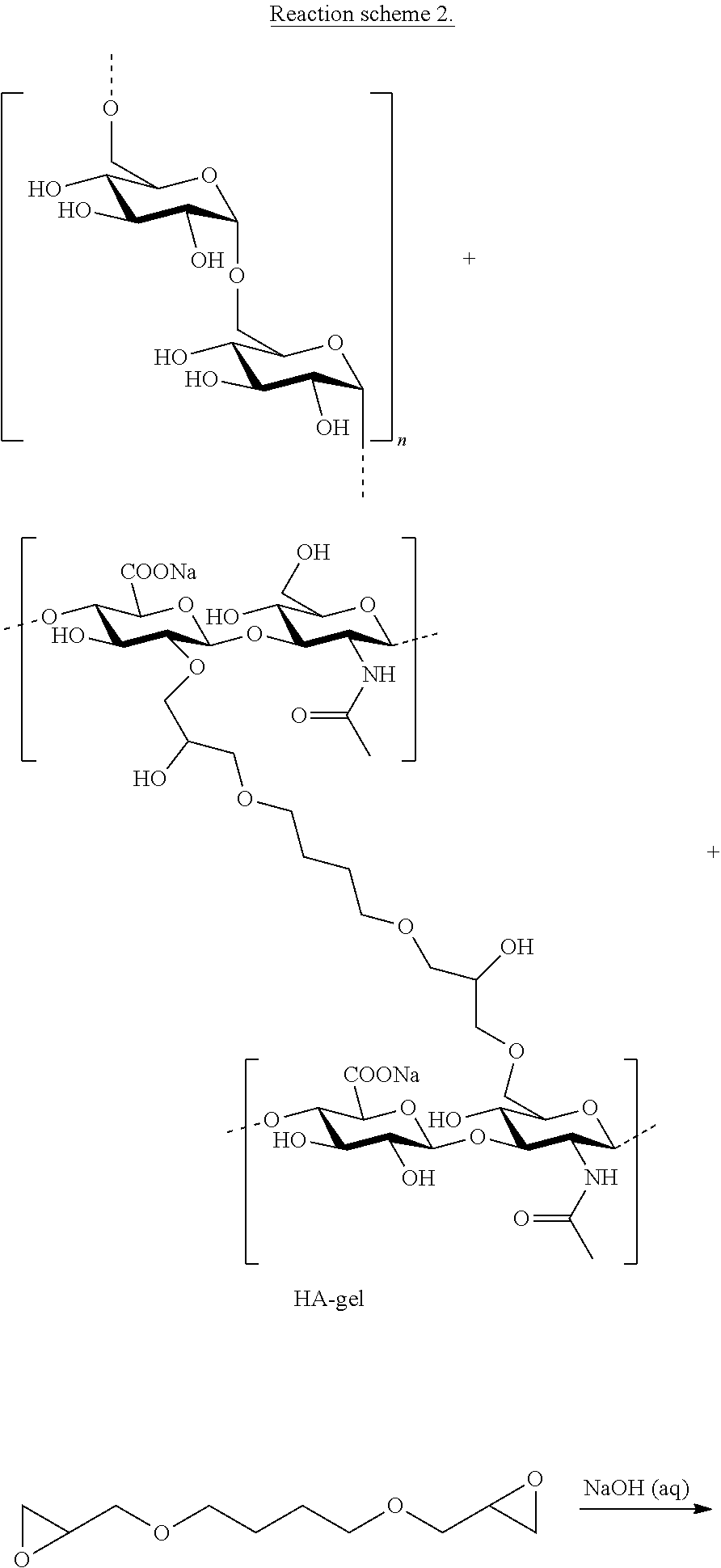
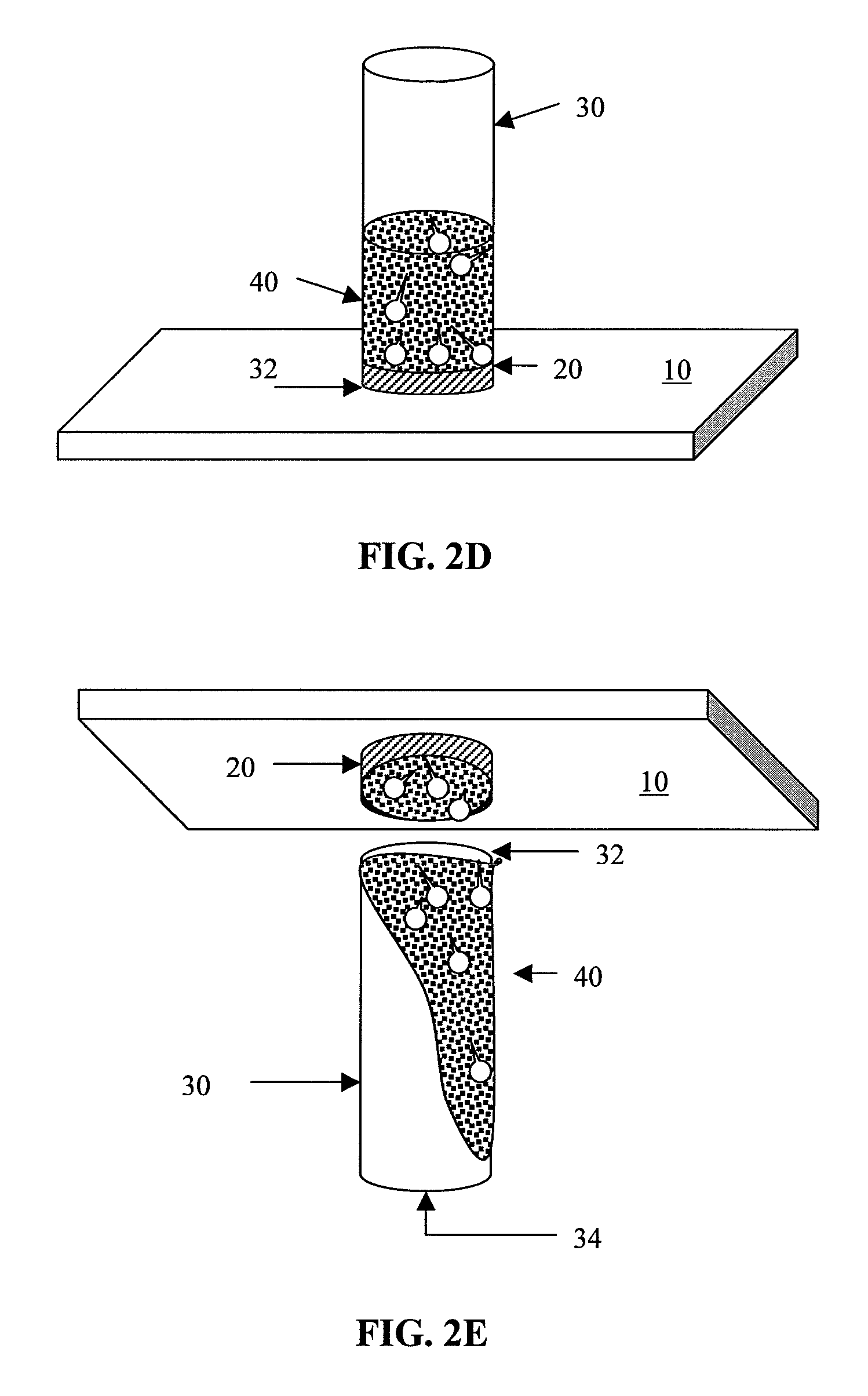
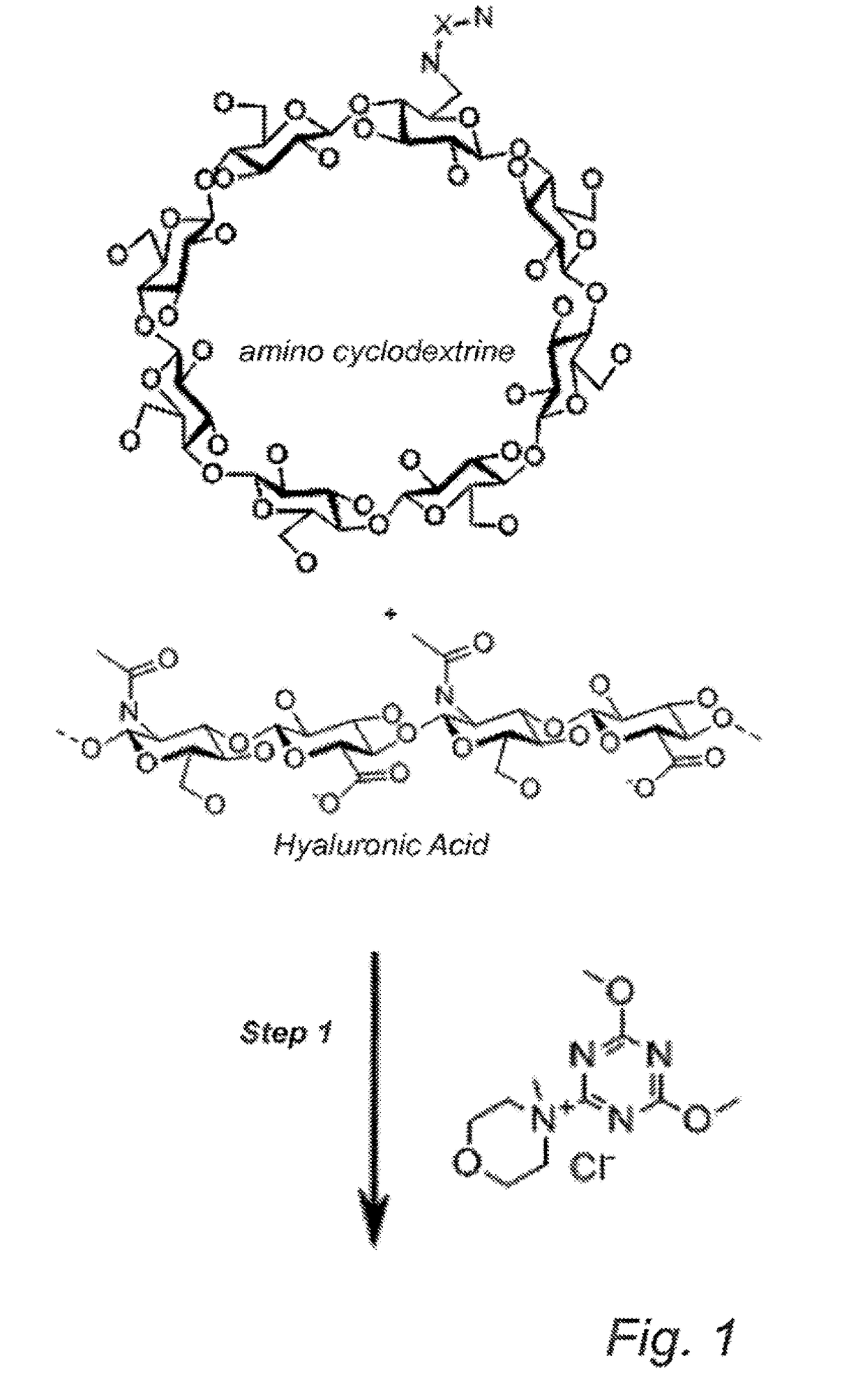
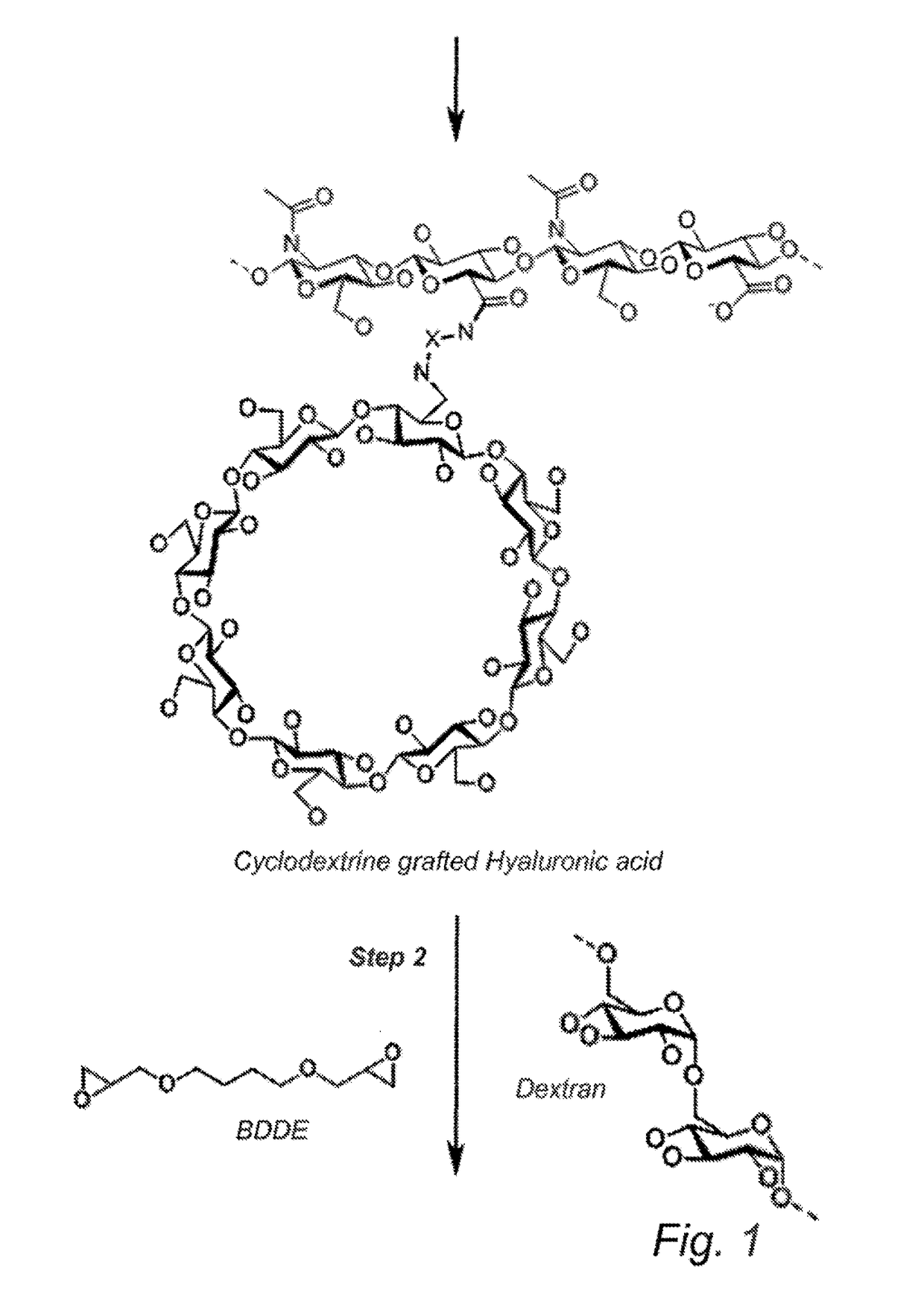
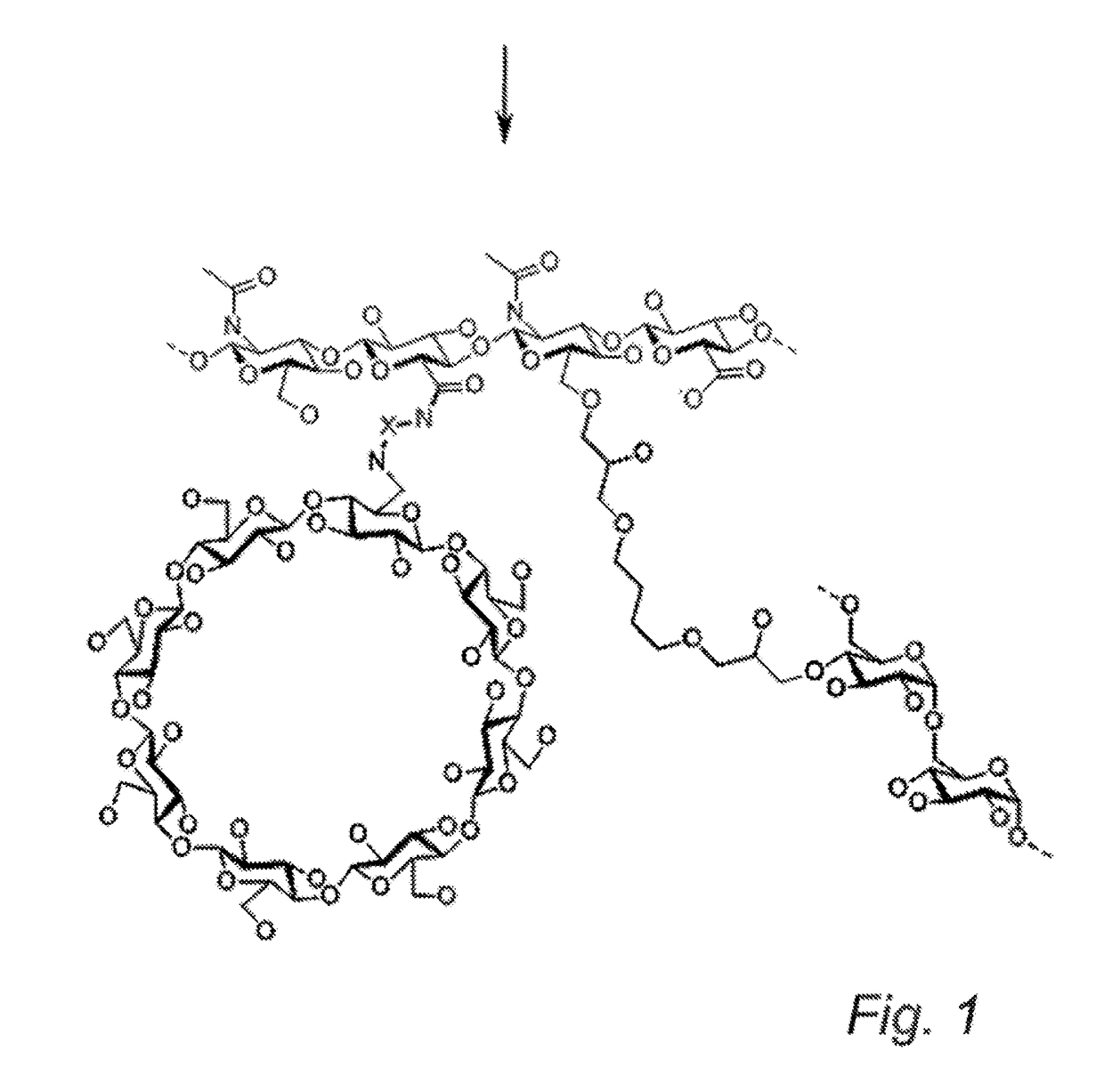
Cyclodextrin-grafted hyaluronic acid crosslinked with dextran and uses thereof
InactiveUS20170196991A1Optimized formulaEqually distributedCosmetic preparationsHydroxy compound active ingredientsCross-linkEther
A hydrogel product including one or more cyclodextrin molecules grafted to hyaluronic acid and dextran, wherein the cyclodextrin-grafted hyaluronic acid is cross-linked to the dextran. The one or more cyclodextrin molecules are grafted, e.g. by amide bonds, to the hyaluronic acid prior to the cross-linking with dextran. The cyclodextrin-grafted hyaluronic acid may be cross-linked to the dextran by ether bonds.
Owner:GALDERMA SA
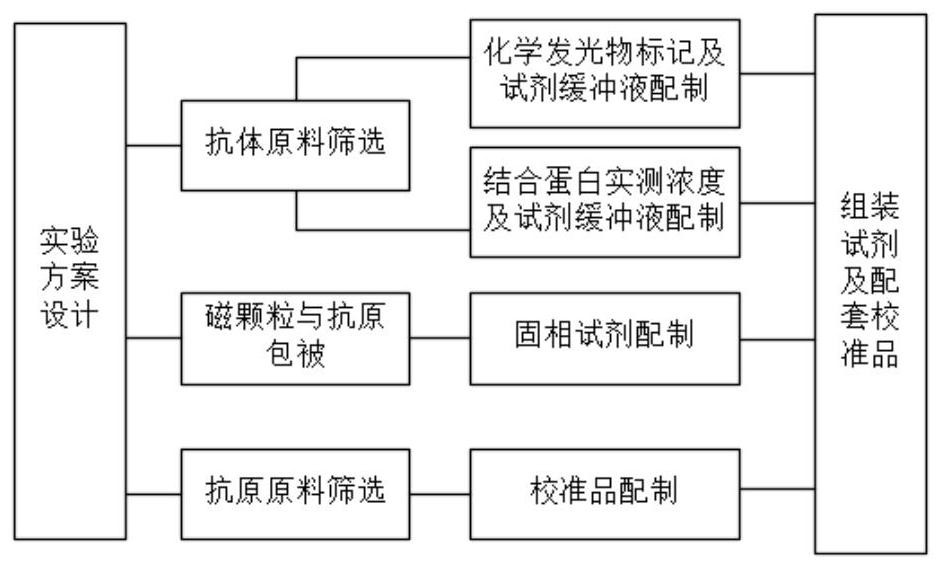
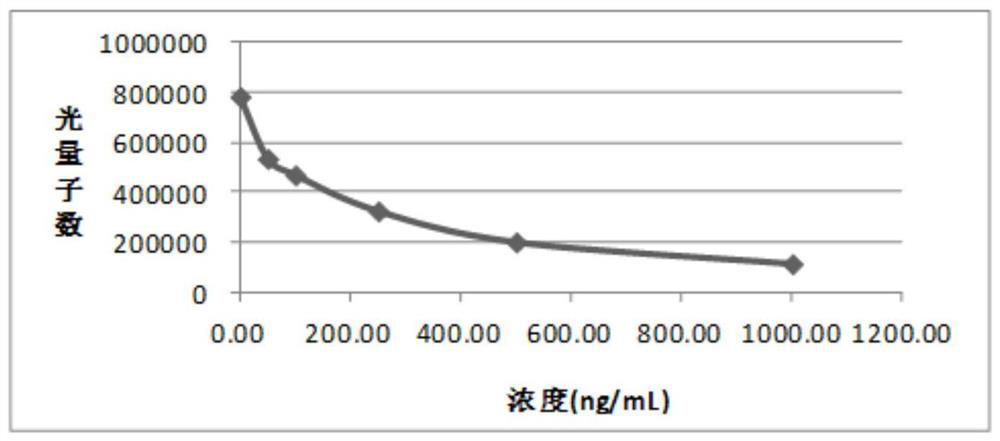
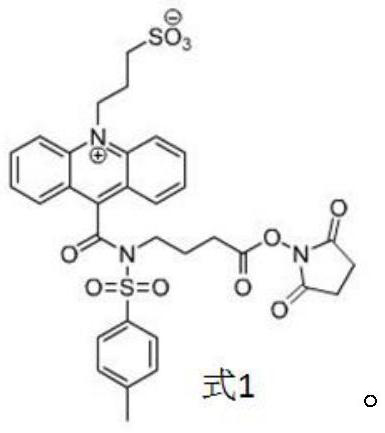
Hyaluronic acid chemiluminescence immunoassay kit and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a hyaluronic acid chemiluminescence immunoassay kit and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of in-vitro detection. The detection kit comprises: abuffer solution of a hyaluronic acid antigen coated with R1 reagent magnetic particles; R2 is a buffer solution of a hyaluronic acid binding protein monoclonal antibody marked by a chemiluminescent marker; and R3 is a buffer solution of hyaluronic acid binding protein. The R1, R2 and R3 reagents are assembled into a finished product reagent, namely the hyaluronic acid chemiluminescence immunoassaykit, and the chemiluminescence immunoassay kit can take a full-automatic chemiluminescence immunoassay instrument as a detection tool to finish detection of hyaluronic acid by using a competition method. The chemiluminiscence immunoassay kit is matched with an instrument, so that the time required by clinical detection is shortened, and the detection sensitivity is improved.
Owner:DIRUI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
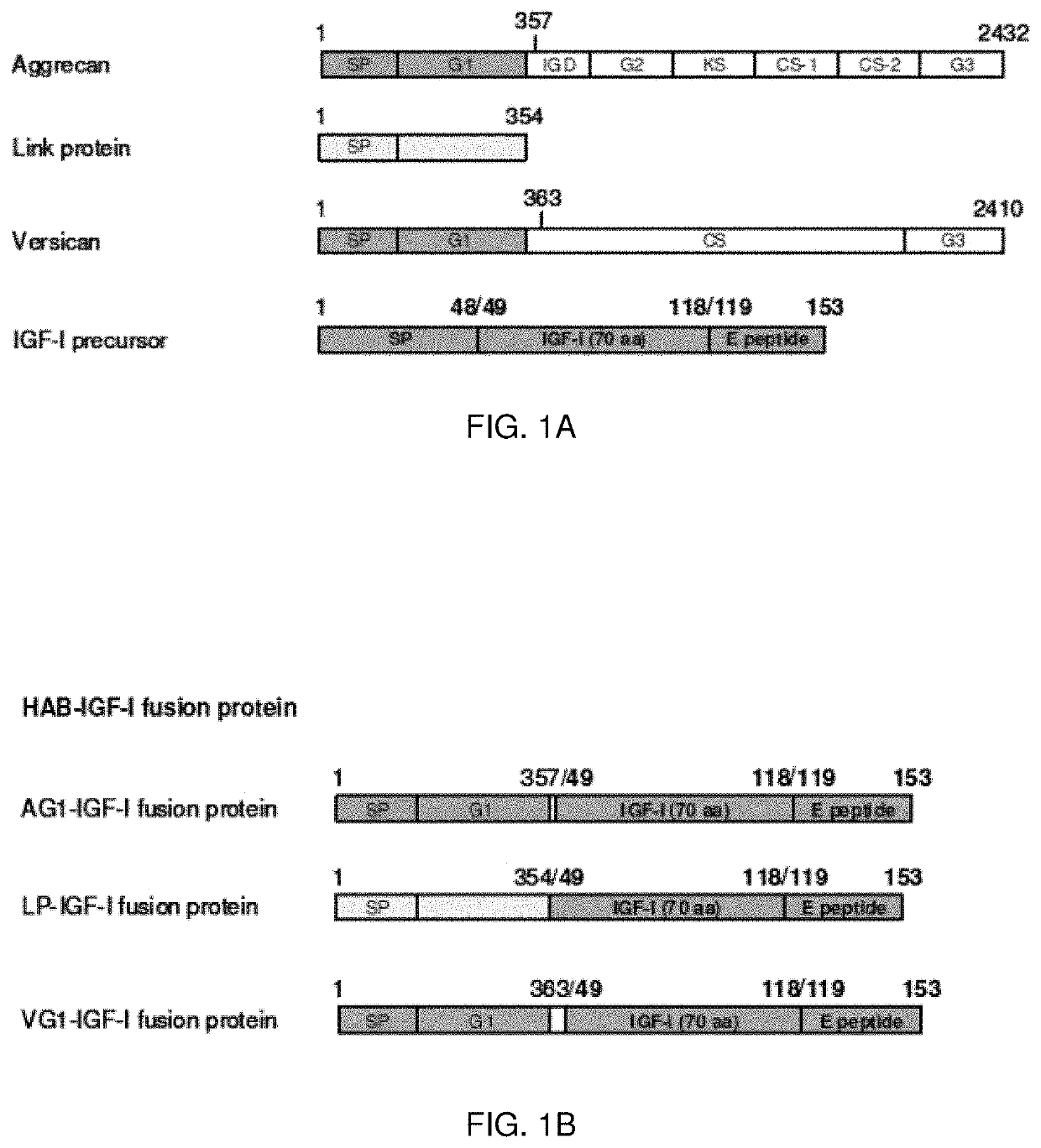
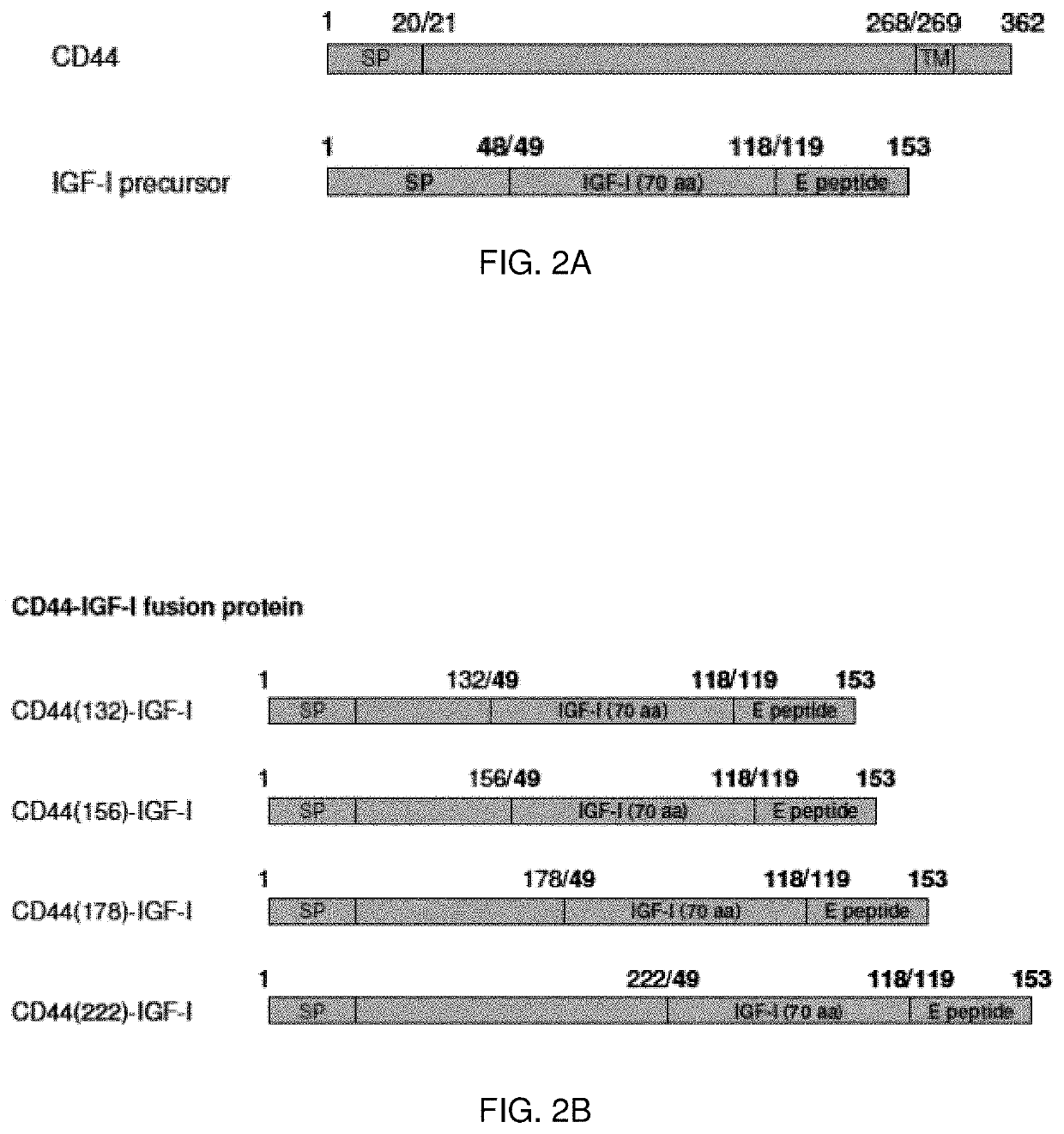
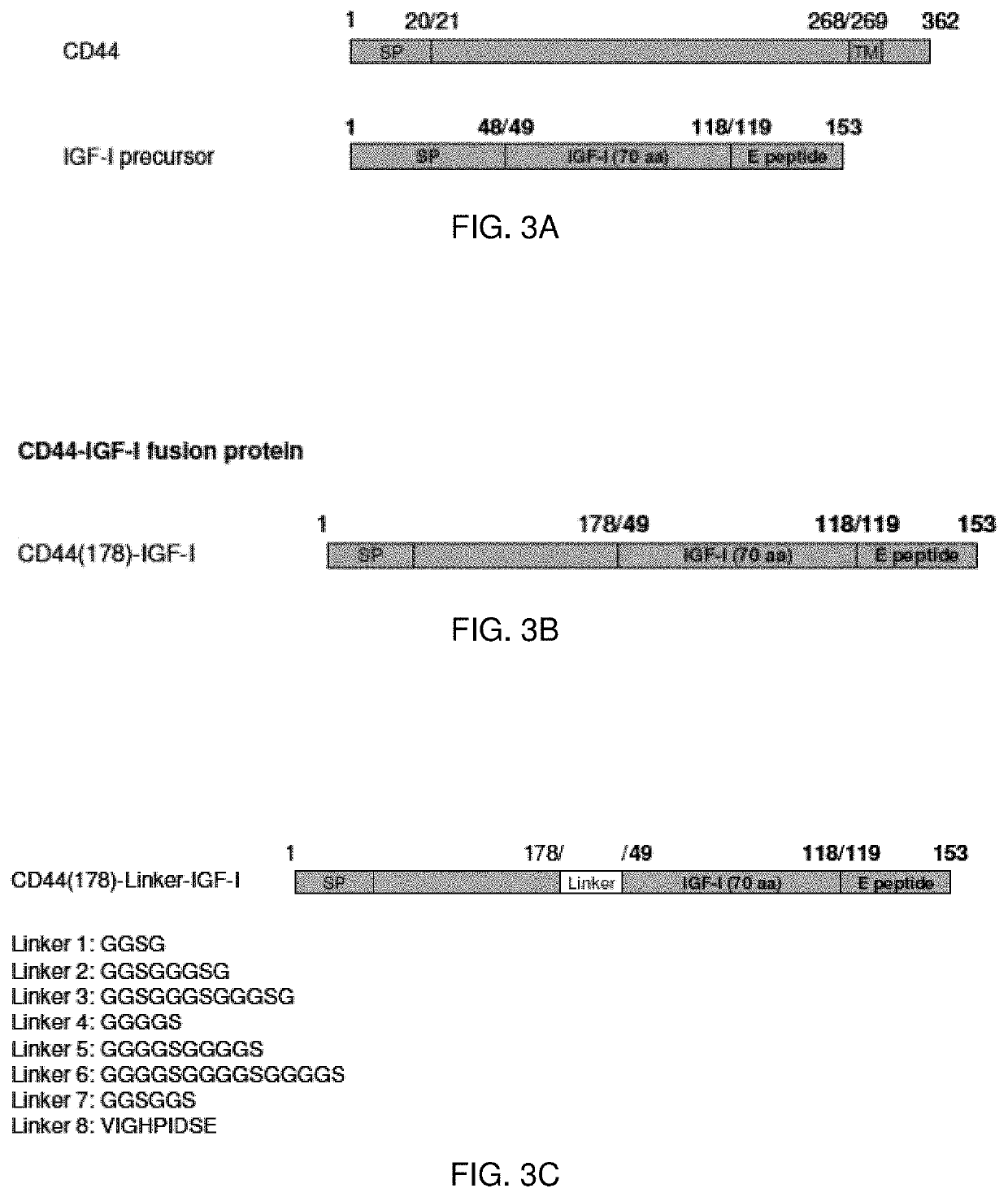
Hyaluronic Acid Binding Domain-Growth Factor Fusion Protein cDNAs and Fusion Proteins for Cartilage Matrix Preservation and Report
InactiveUS20200038521A1Improve responsivenessImprove athletic performanceConnective tissue peptidesPolypeptide with affinity tagOrganic chemistryAmino acid
The present invention provides isolated nucleic acid compounds, amino acids compounds and related materials, along with methods to make and use the compounds. In particular, there are provided gene therapy materials useful for inducing positive physiological responses in tissues, and fusion proteins encoded by the gene therapy materials.
Owner:INDIANA UNIVERISY RES & TECH CORP +1
Cysteine-functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugates and their synthesis and application in injectable in situ formed hydrogels
The invention discloses a cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate, a synthetic method and an application in preparation of injectable in-situ hydrogel thereof. According to the method, a hydroxy of hyaluronic acid is modified to obtain the cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate with a stable ether bond, and tetrabutyl ammonium hydroxide is introduced in the reaction process. The new method improves the solubility of hyaluronic acid and increases the reaction efficiency. The obtained cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate has a sulfhydryl active group which not only improves the adhesion of hyaluronic acid, but also can be further functionalized. According to the invention, injectable in-situ hydrogel is generated by a native chemical ligation reaction or a Michael addition reaction of the prepared cysteine functionalized hyaluronic acid conjugate with a polyethylene glycol conjugate; rheological research shows that the generated hydrogel has good rheological properties, the gel performance is controllable, and the hydrogel has wide application prospects in the biological medicine field.
Owner:HAINAN UNIV
Measuring reagent for hyaluronic acid and preparation method of measuring reagent
InactiveCN106198994AAvoid punctureReduce human errorDisease diagnosisBiological testingSodium azideBovine serum albumin
The invention relates to a measuring reagent for hyaluronic acid and a preparation method of the measuring reagent, and belongs to the technical field of testing of biochemical methods. The measuring reagent comprises a reagent R1, a reagent R2 and a hyaluronic acid calibration product, wherein the reagent R1 is prepared from the following components: 50 mmol / L of a Tris buffer solution, 0.1 mg / L of a hyaluronic acid binding protein, 0.1 percent of bovine serum albumin and 0.1 percent of sodium azide; the reagent R2 is prepared from the following components: 0.2 percent of hyaluronic acid binding protein specific antibody-wrapped latex, 0.5 percent of bovine serum albumin and 0.09 percent of sodium azide; the hyaluronic acid calibration product is prepared from the following components: hyaluronic acid, 50 mmol / L of a phosphate buffer solution and 0.1 percent of sodium azide. The measuring reagent is applied to measurement of hyaluronic acid, and has the advantages of fastness, sensitivity, high accuracy, high stability, simplicity and convenience for operation, and the like.
Owner:浙江达美生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com