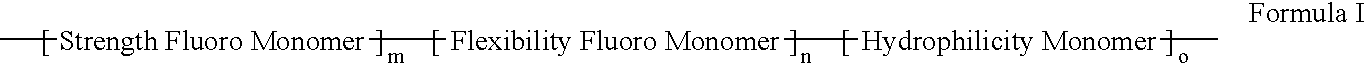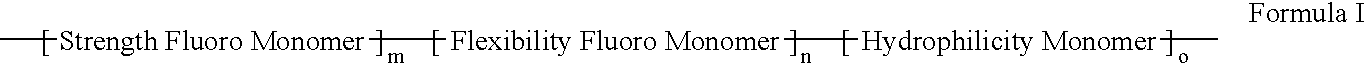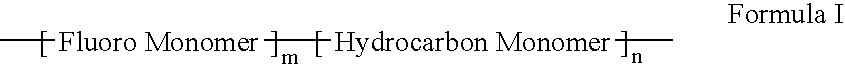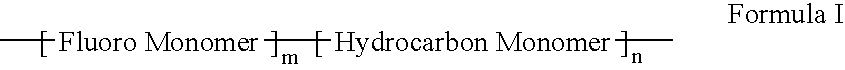Patents
Literature
970 results about "Biocompatible polymers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
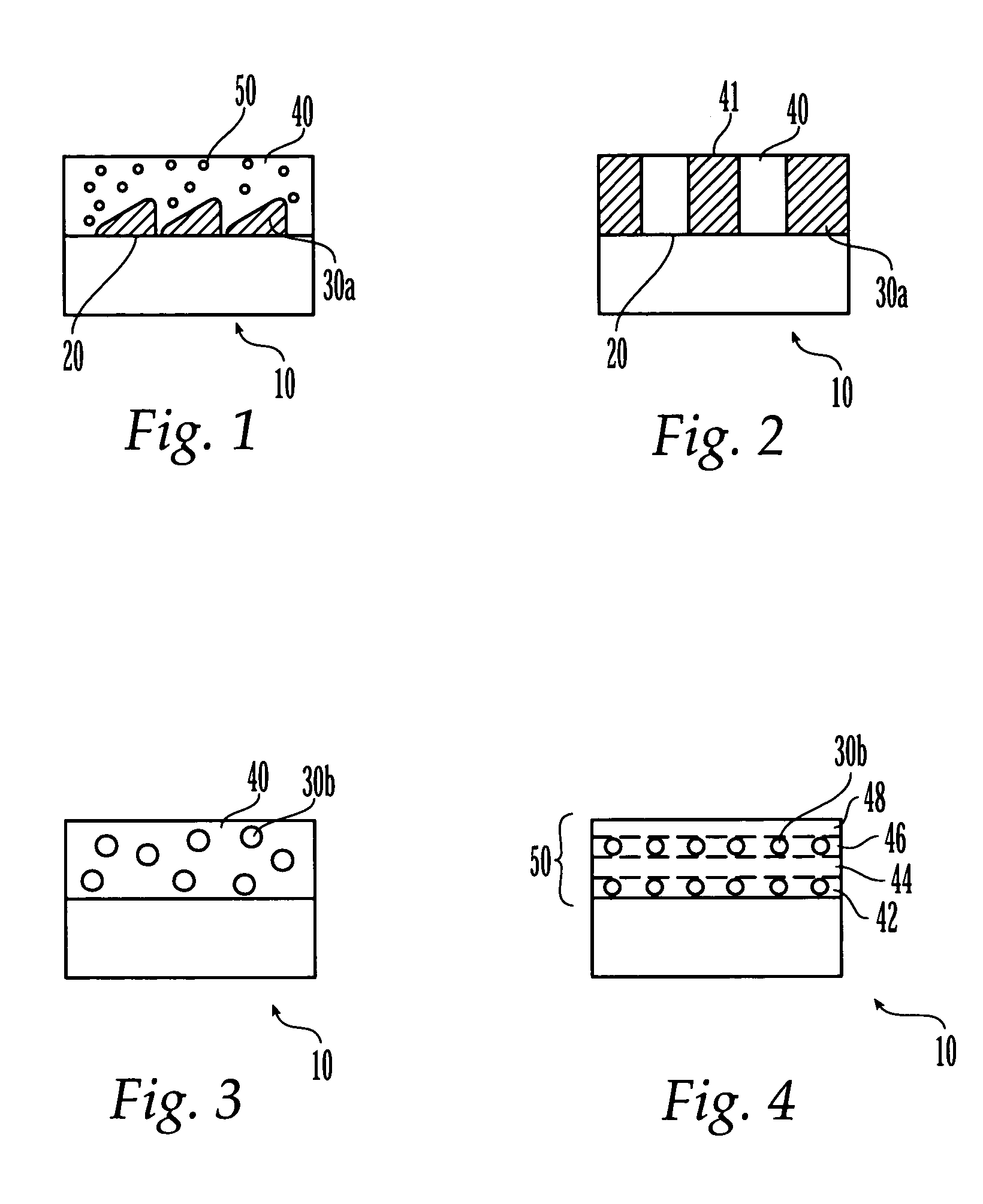
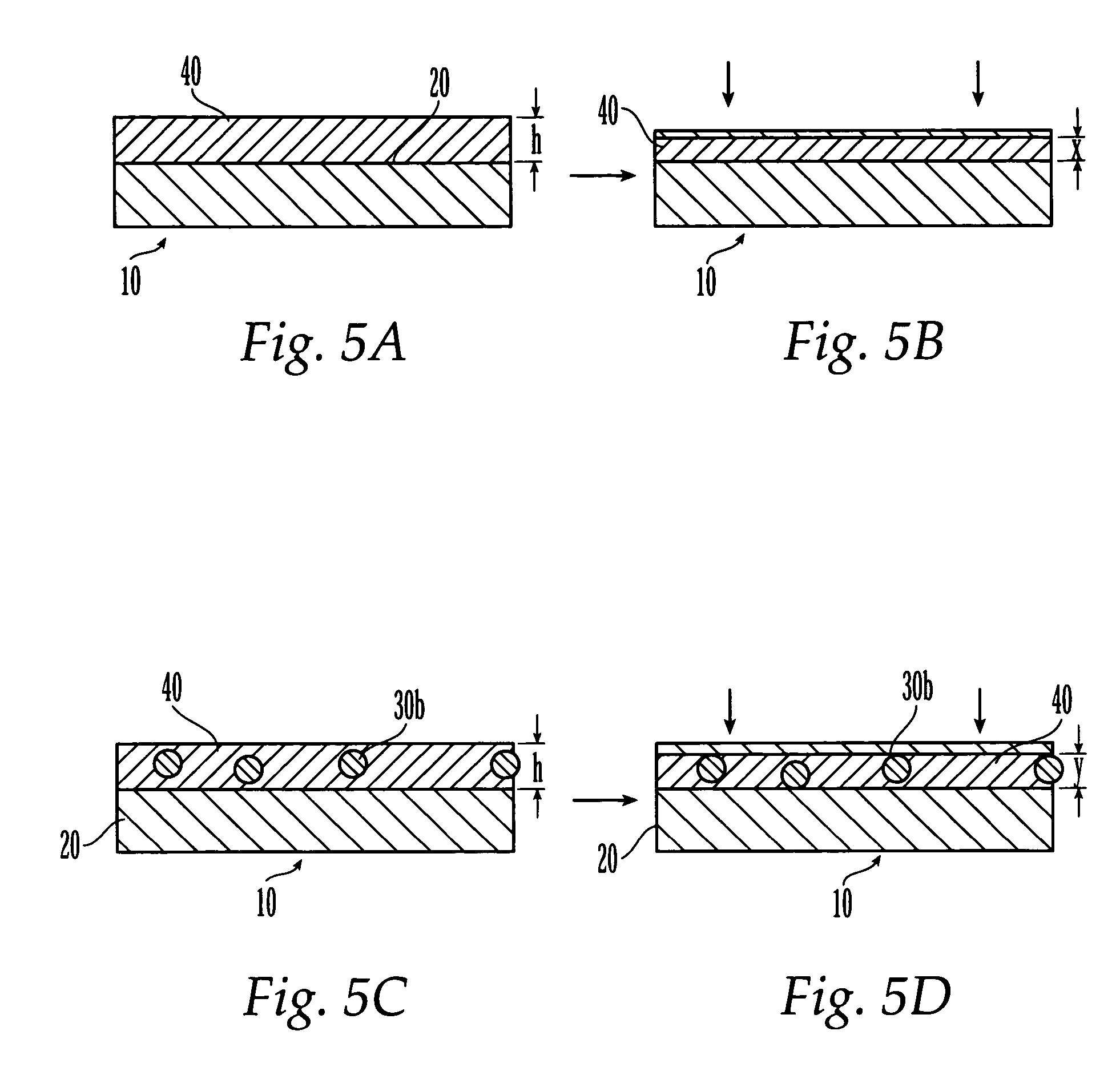
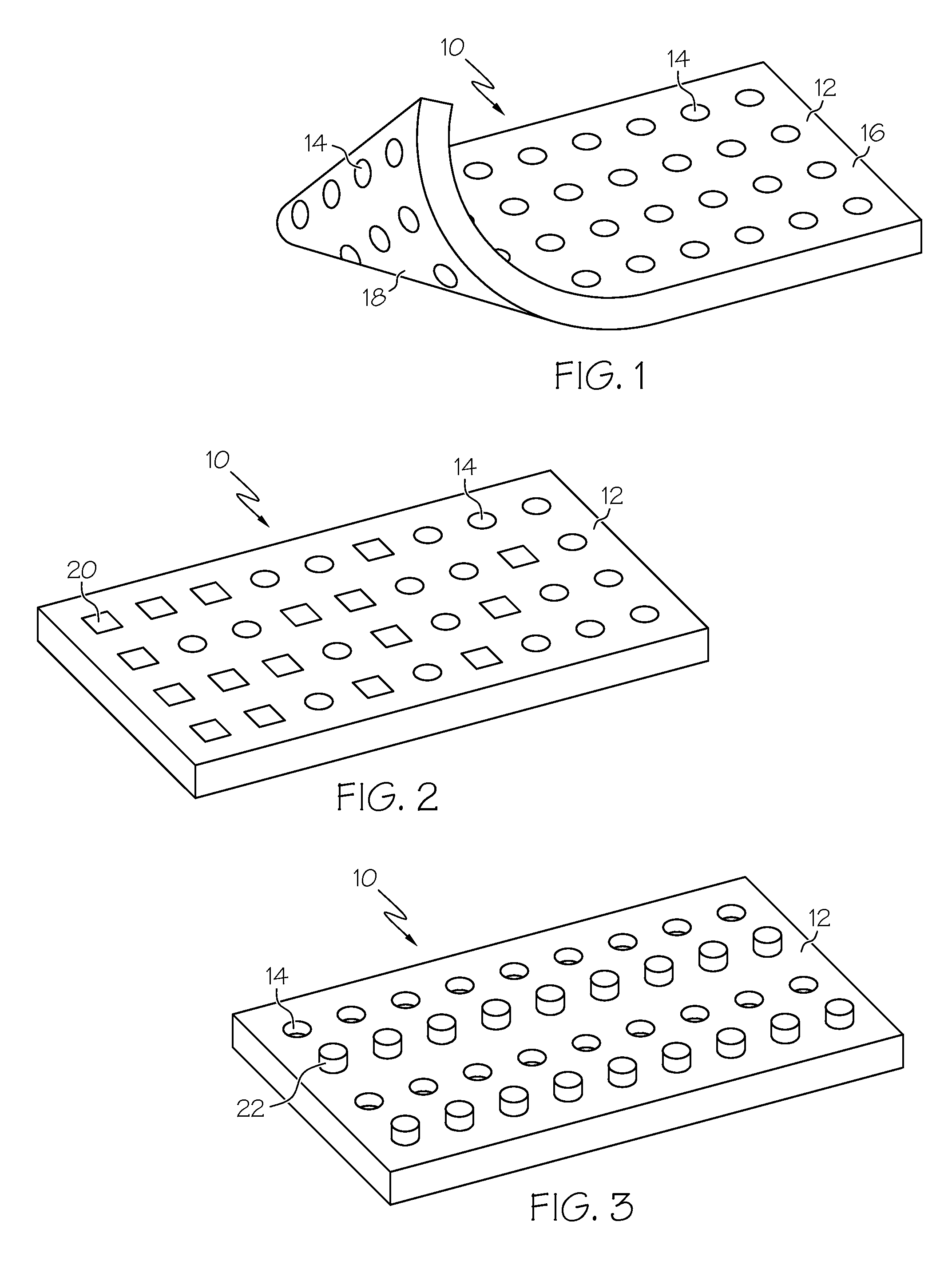
Porous tissue scaffoldings for the repair of regeneration of tissue
InactiveUS6333029B1Promote growthPromote regenerationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticRepair tissueOpen cell
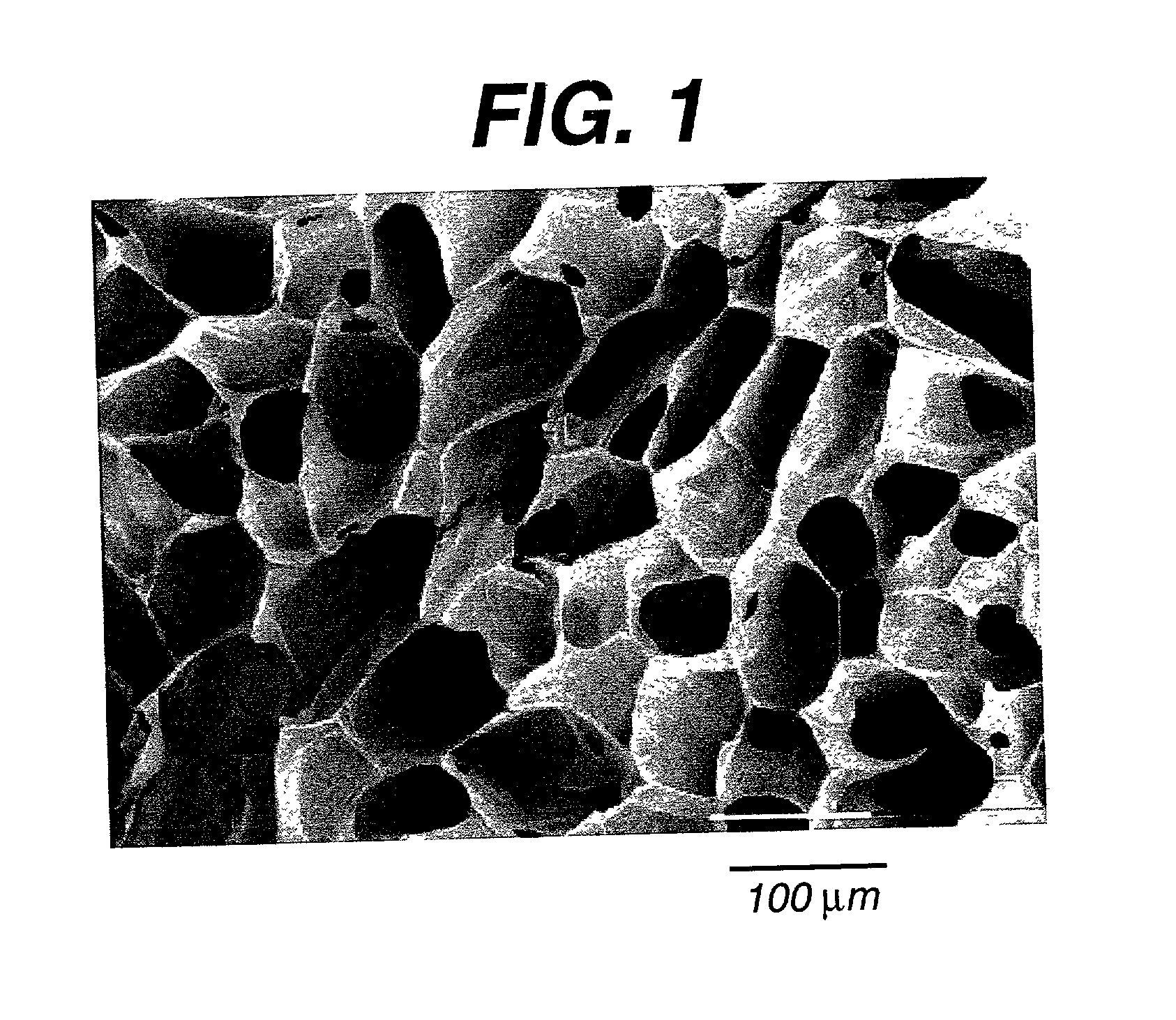
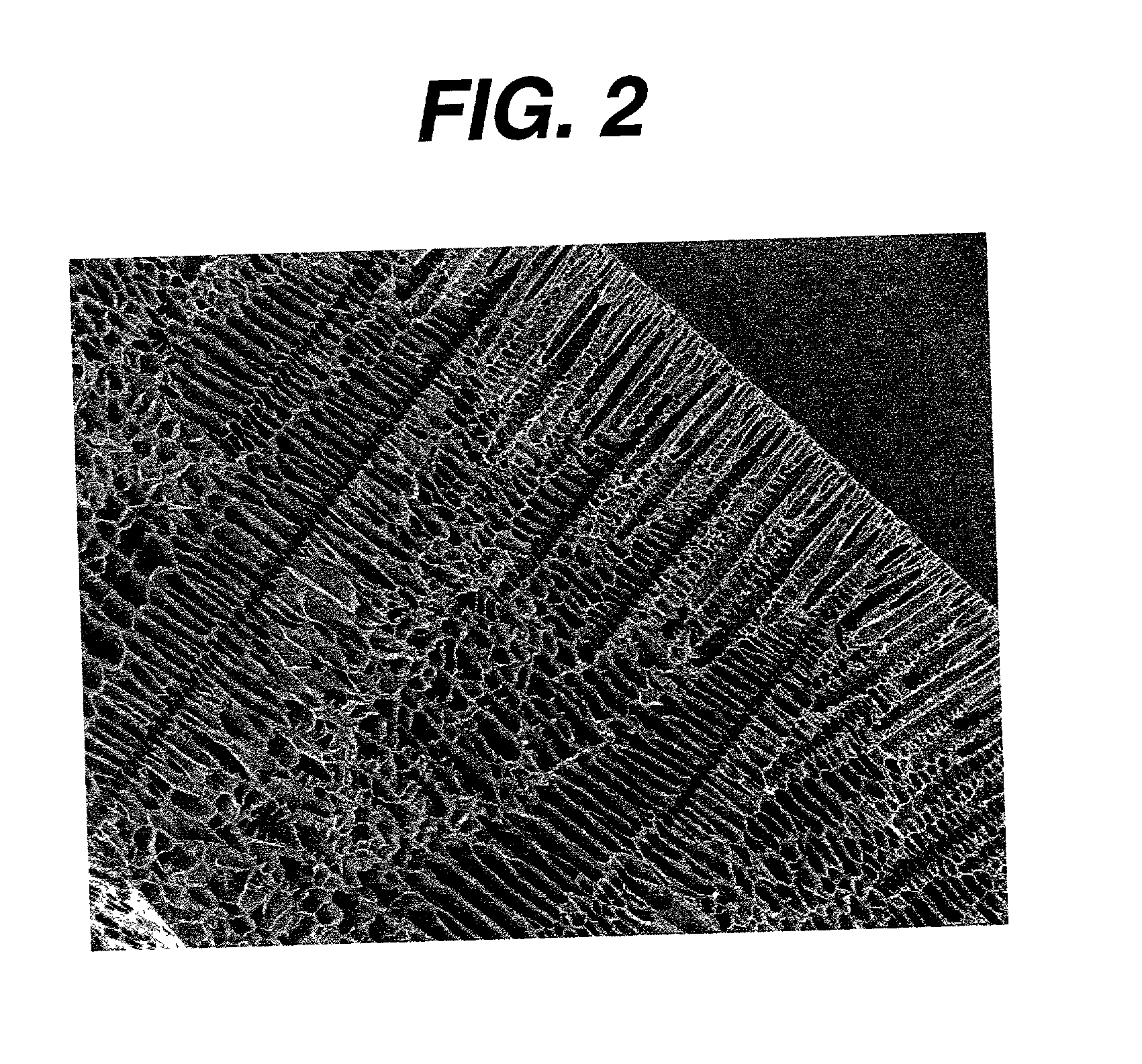
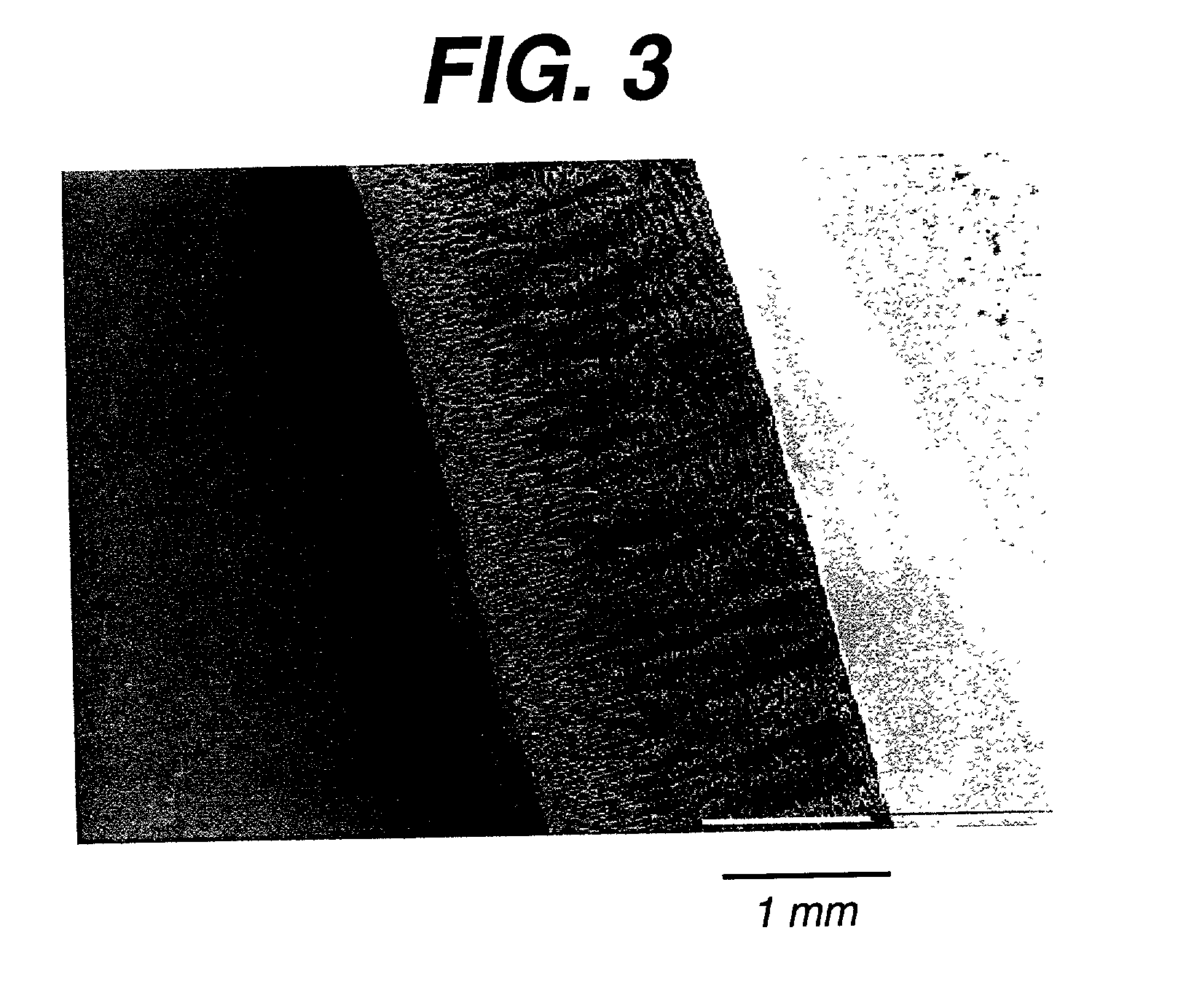
The present patent describes a three-dimensional inter-connected open cell porous foams that have a gradient in composition and / or microstructure through one or more directions. These foams can be made from a blend of absorbable and biocompatible polymers that are formed into foams having a compositional gradient transitioning from predominately one polymeric material to predominately a second polymeric material. These gradient foams are particularly well suited to tissue engineering applications and can be designed to mimic tissue transition or interface zones.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
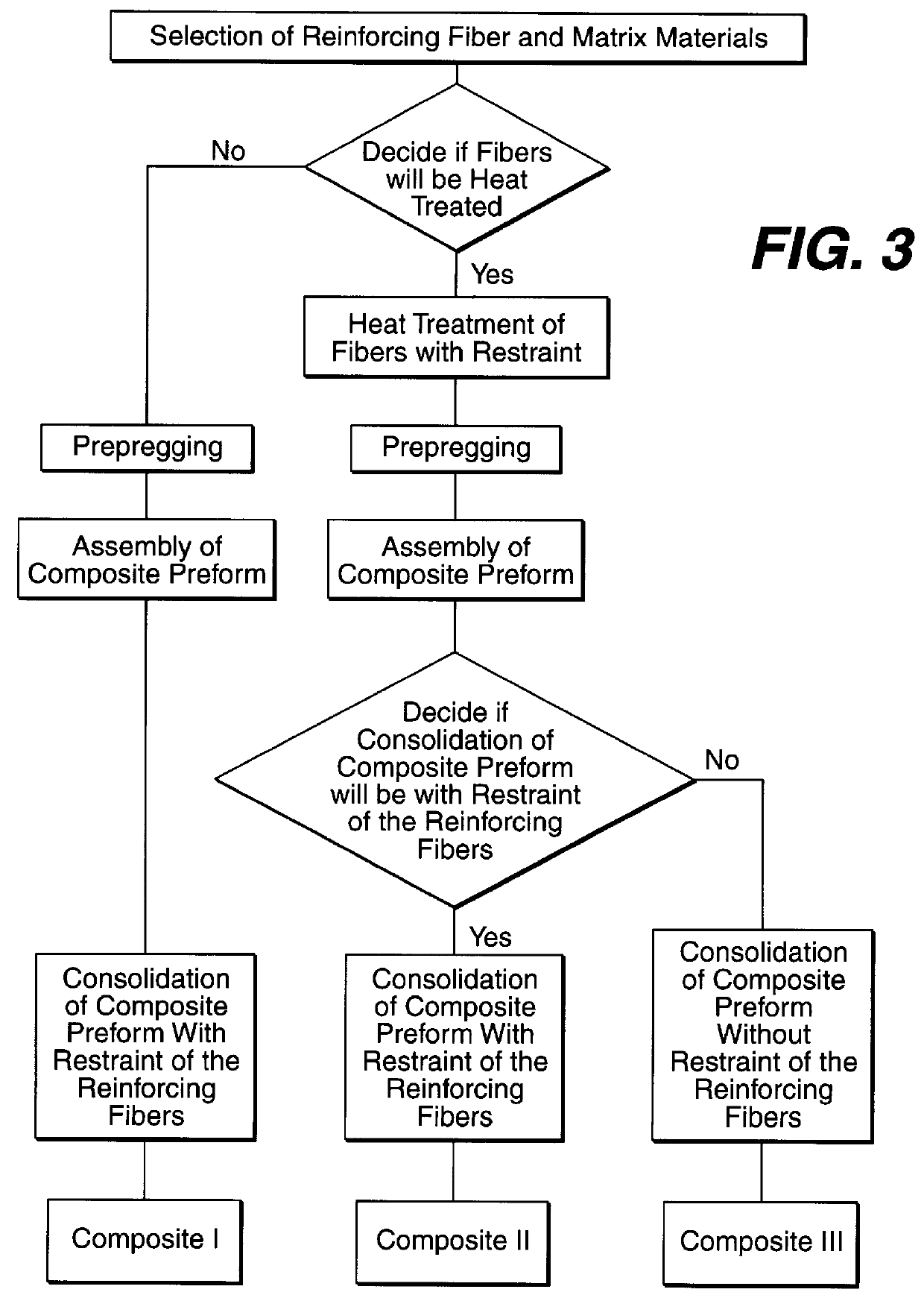
Fabrication of biocompatible polymeric composites
InactiveUS6147135ASure easyImprove performanceSuture equipmentsCosmetic preparationsFiberPolymer science
Composite materials formed from biocompatible polymer fibers and biodegradable polymers are disclosed. The heat treatment conditions for the reinforcing fibers are described so that the mechanical properties of the fibers can be retained during composite consolidation process. The processing conditions and set-ups to consolidations are constrained to the temperatures lower than fiber heat treatment temperatures. The reinforcing fibers are restrained under tension so that the minimum relaxation occurs during consolidation process.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Therapeutic treatment and prevention of infections with a bioactive materials encapsulated within a biodegradable-biocompatible polymeric matrix
InactiveUS6309669B1Sustained release of active agent over timeEfficient and effective usePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAdjuvantEnd-group
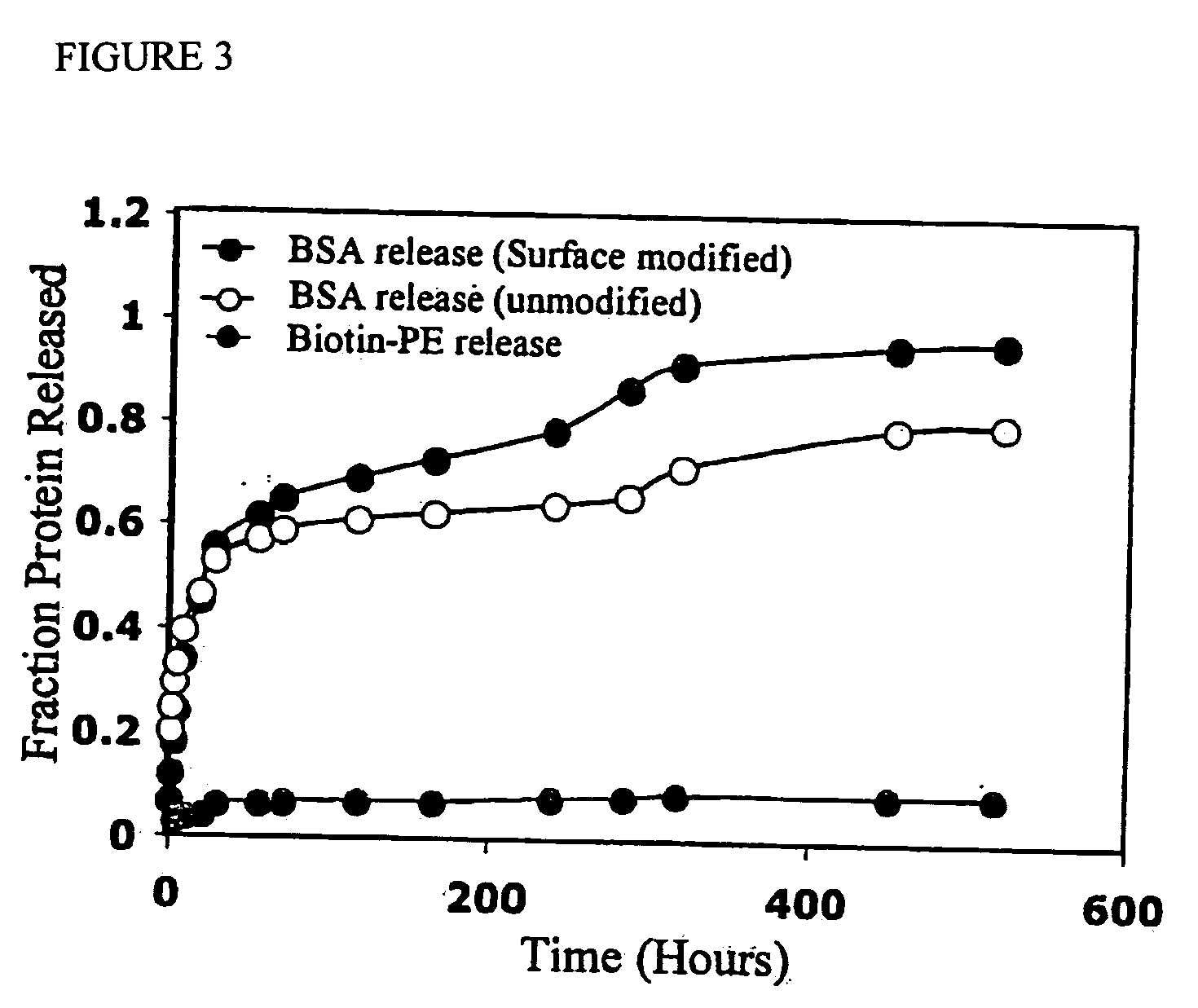
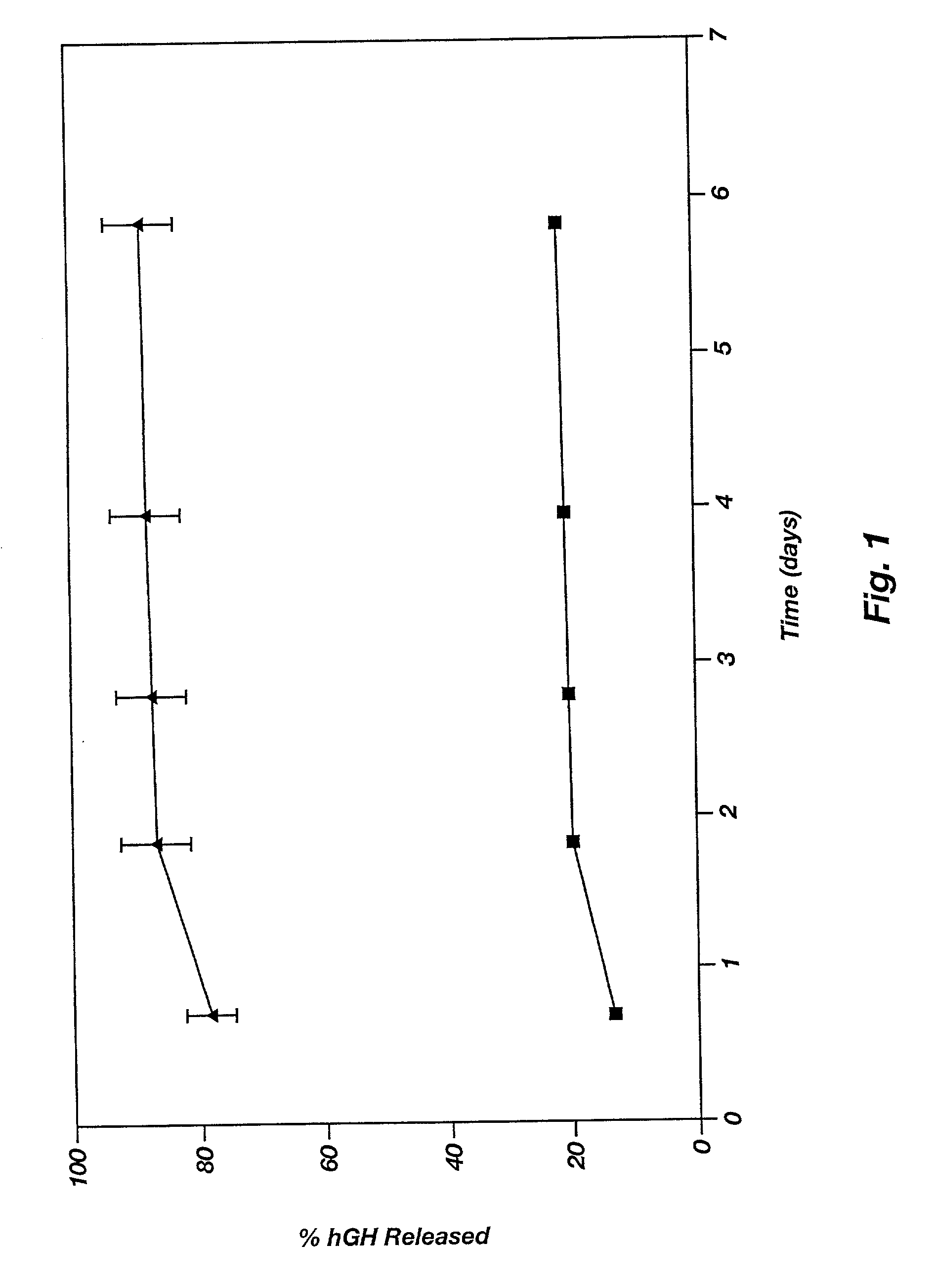
Novel burst-free, sustained release biocompatible and biodegrable microcapsules which can be programmed to release their active core for variable durations ranging from 1-100 days in an aqueous physiological environment. The microcapsules are comprised of a core of polypeptide or other biologically active agent encapsulated in a matrix of poly(lactide / glycolide) copolymer, which may contain a pharmaceutically-acceptable adjuvant, as a blend of upcapped free carboxyl end group and end-capped forms ranging in ratios from 100 / 0 to 1 / 99.
Owner:ARMY GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE
Bioactive agent delivering system comprised of microparticles within a biodegradable to improve release profiles
InactiveUS6589549B2Improve stabilityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsActive agentEngineering
A composition and method for releasing a bio-active agent or a drug within a biological environment in a controlled manner is disclosed. The composition is a dual phase polymeric agent-delivery composition comprising a continuous biocompatible gel phase, a discontinuous particulate phase comprising defined microparticles and an agent to be delivered. A microparticle containing a bio-active agent is releasably entrained within a biocompatible polymeric gel matrix. The bioactive agent release may be contained in the microparticle phase alone or in both the microparticles and the gel matrix. The release of the agent is prolonged over a period of time, and the delivery may be modulated and / or controlled. In addition, a second agent may be loaded in some of the microparticles and / or the gel matrix.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Targeted and high density drug loaded polymeric materials
ActiveUS20060002852A1Increase molecular densityHigh densityPowder deliveryBiocideAntigenWound dressing
Polymeric delivery devices have been developed which combine high loading / high density of molecules to be delivered with the option of targeting. As used herein, “high density” refers to microparticles having a high density of ligands or coupling agents, which is in the range of 1000-10,000,000, more preferably between 10,000 and 1,000,000 ligands per square micron of microparticle surface area. A general method for incorporating molecules into the surface of biocompatible polymers using materials with an HLB of less than 10, more preferably less than 5, such as fatty acids, has been developed. Because of its ease, generality and flexibility, this method has widespread utility in modifying the surface of polymeric materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering, as well other other fields. Targeted polymeric microparticles have also been developed which encapsulate therapeutic compounds such as drugs, cellular materials or components, and antigens, and have targeting ligands directly bound to the microparticle surface. Preferred applications include use in tissue engineering matrices, wound dressings, bone repair or regeneration materials, and other applications where the microparticles are retained at the site of application or implantation. Another preferred application is in the use of microparticles to deliver anti-proliferative agents to the lining of blood vessels following angioplasty, transplantation or bypass surgery to prevent or decrease restenosis, and in cancer therapy. In still another application, the microparticles are used to treat or prevent macular degeneration when administered to the eye, where agents such as complement inhibitors are administered.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Biocompatible wires and methods of using same to fill bone void
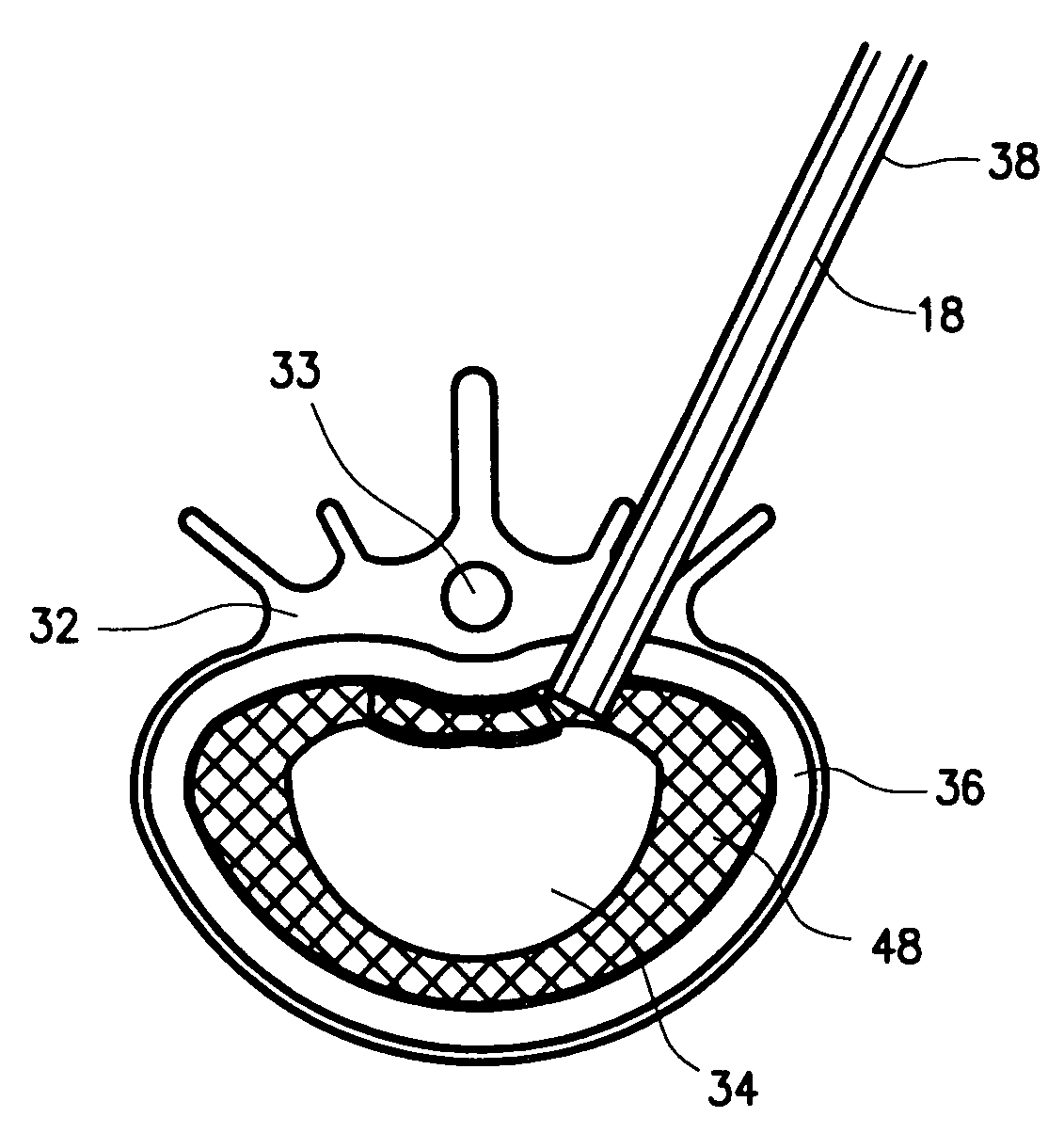
InactiveUS20050015148A1Reduce compression fractureInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsWire rodBone structure
Devices, kits, and methods are provided for reducing a bone fracture, e.g., a vertebral compression fracture, is provided. The device comprises a plurality of resilient wires composed of a biocompatible material, such as a biocompatible polymer (e.g., polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA)). The wires can be introduced into the cavity of the bone structure to form a web-like arrangement therein. The web-like arrangement can be stabilized by applying uncured bone cement onto the arrangement to connect the wires at their contacts point. The bone cavity can then be filled with a bone growth enhancing medium.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Isoelastic prosthetic filet stitch fabric
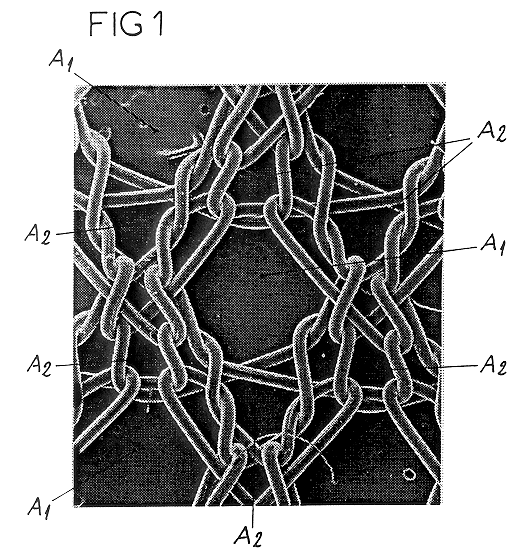
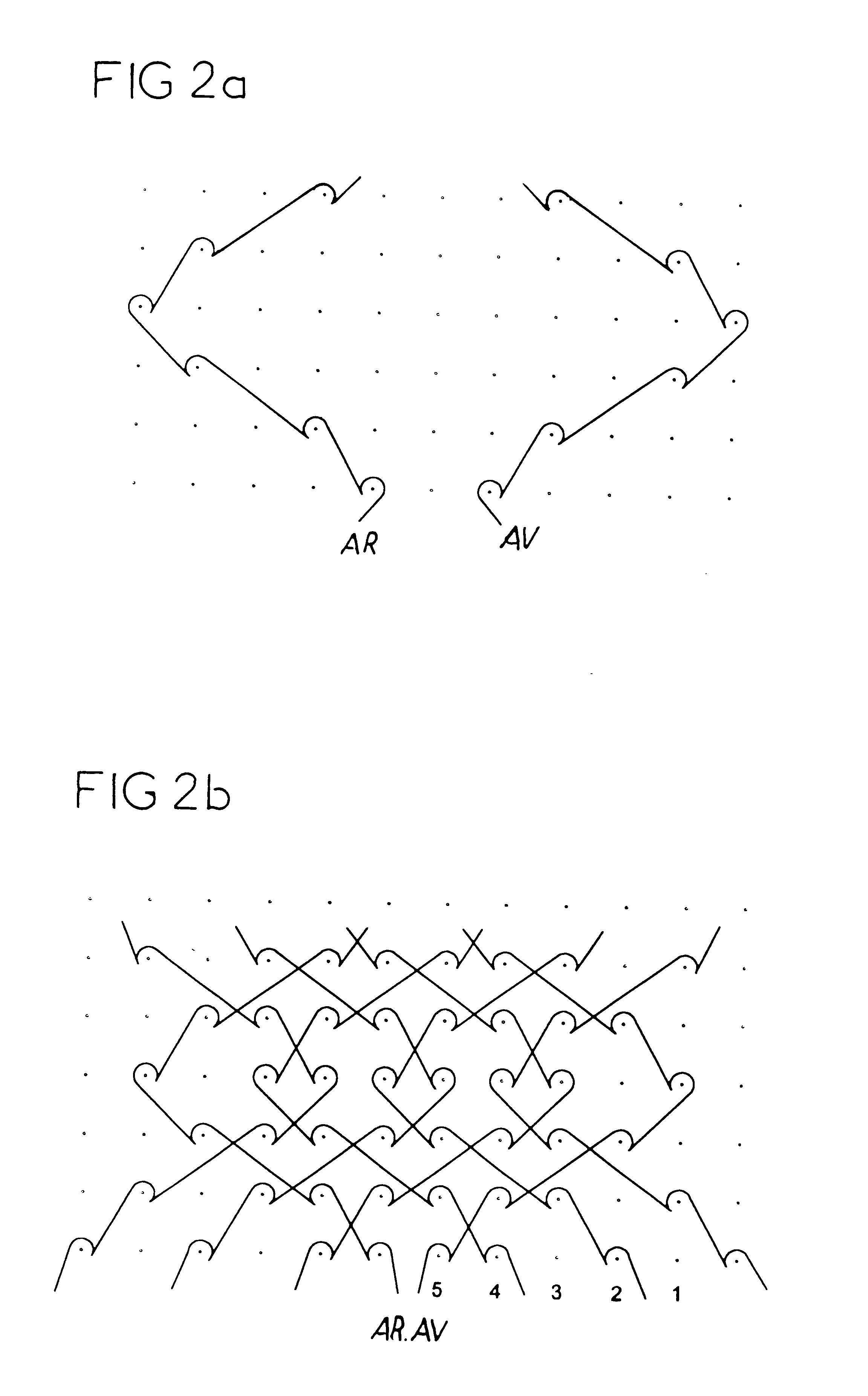
This knit is produced on the basis of a biocompatible polymer material monofilament, whose pattern is defined by a front lap and a rear lap of yarns knitted together and determines a plurality of cells each having a substantially polygonal shape. The pattern gives the knit a multidirectional tensile behavior such as obtained by a front lap capable of being obtained by knitting according to a scheme 5-4 / 4-3 / 2-1 / 0-1 / 1-2 / 3-4 and by a rear lap capable of being obtained by knitting according to a scheme 0-1 / 1-2 / 3-4 / 5-4 / 4-3 / 2-1.
Owner:SOFRADIM PROD SAS
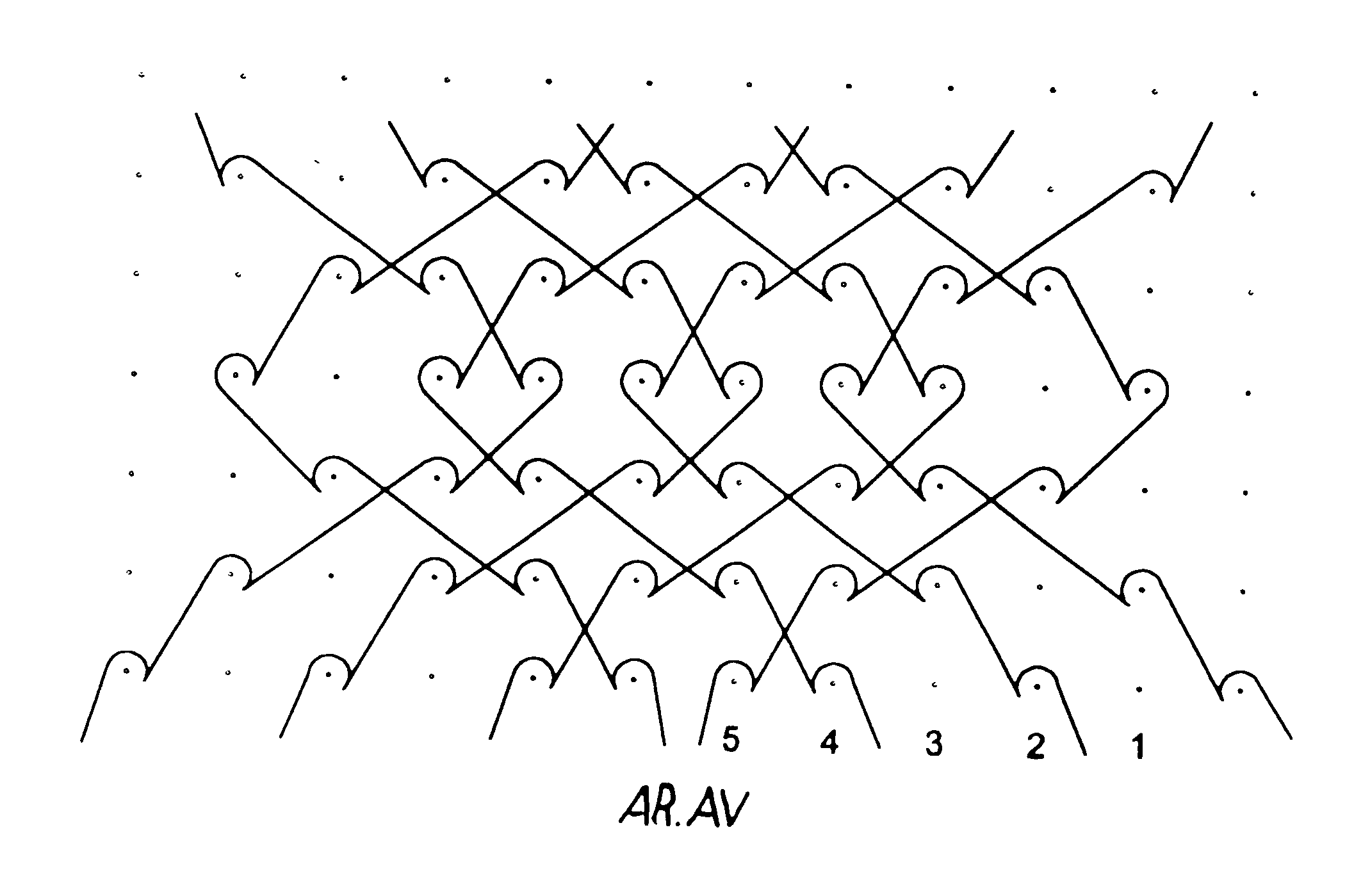
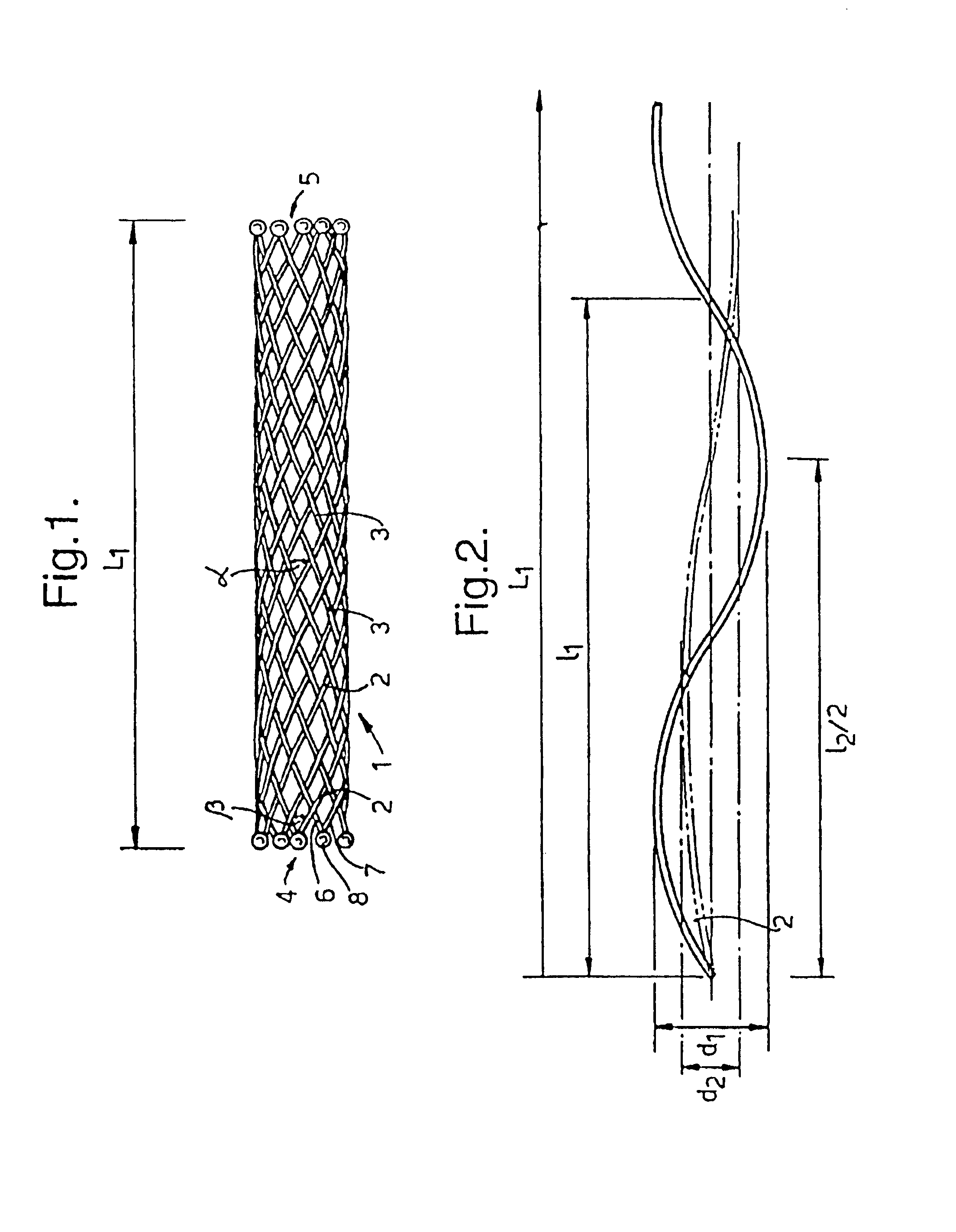
Biocompatible crosslinked coating and crosslinkable coating polymer composition for forming such a coating
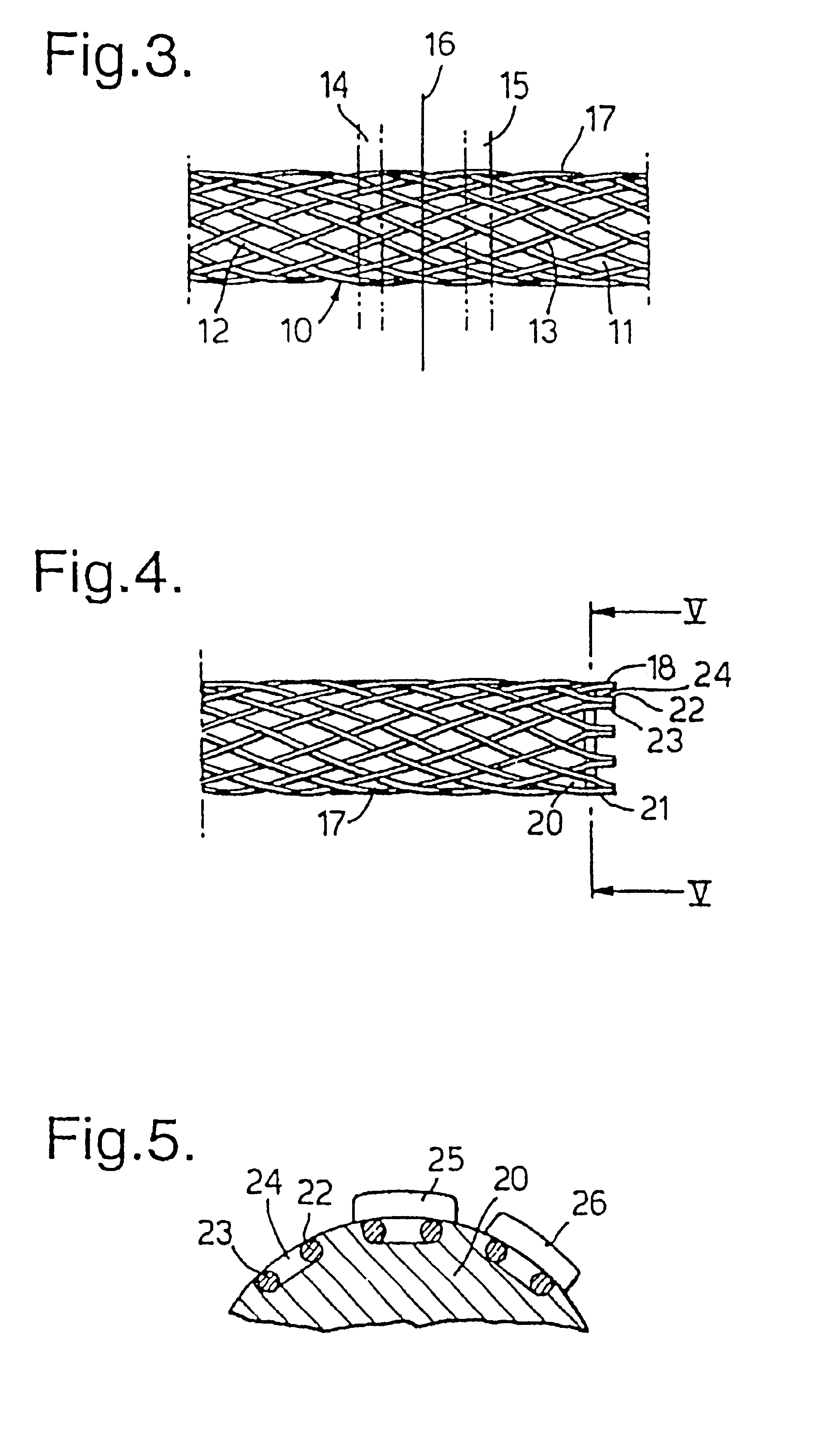
A braided stent (1) for transluminal implantation in body lumens is self-expanding and has a radial expanded configuration in which the angle α between filaments is acute. Some or all of filaments (6,7) are welded together in pairs at each end (4,5) of the stent to provide beads (8), thereby strengthening the stent and assisting its deployment from a delivery device. The stent is preferably completely coated using a biocompatible polymeric coating, said polymer preferably having pendant phosphoryl choline groups. A method of making the stent by braiding and welding is described as well as a delivery device for deploying the device.The present invention provides a biocompatible crosslinked coating and a crosslinkable coating polymer composition for forming such a coating. The biocompatible crosslinked coating may be formed by curing a polymer of 23 mole % (methacryloyloxy ethyl)-2-(trimethylammonium ethyl) phosphate inner salt, 47 mole % lauryl methacrylate, 5 mole % γtrimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate and 25 mole % of hydroxy propyl methacrylate. The crosslinkable coating polymer may include 23 mole % (methacryloyloxy ethyl)-2-(trimethylammonium ethyl) phosphate inner salt, 47 mole % lauryl methacrylate, 5 mole % γtrimethoxysilyl propyl methacrylate and 25 mole % of hydroxy propyl methacrylate.<?insert-end id="INS-S-00001" ?>
Owner:BIOCOMPATIBLES UK LTD
Poly(amino acid) targeting moieties
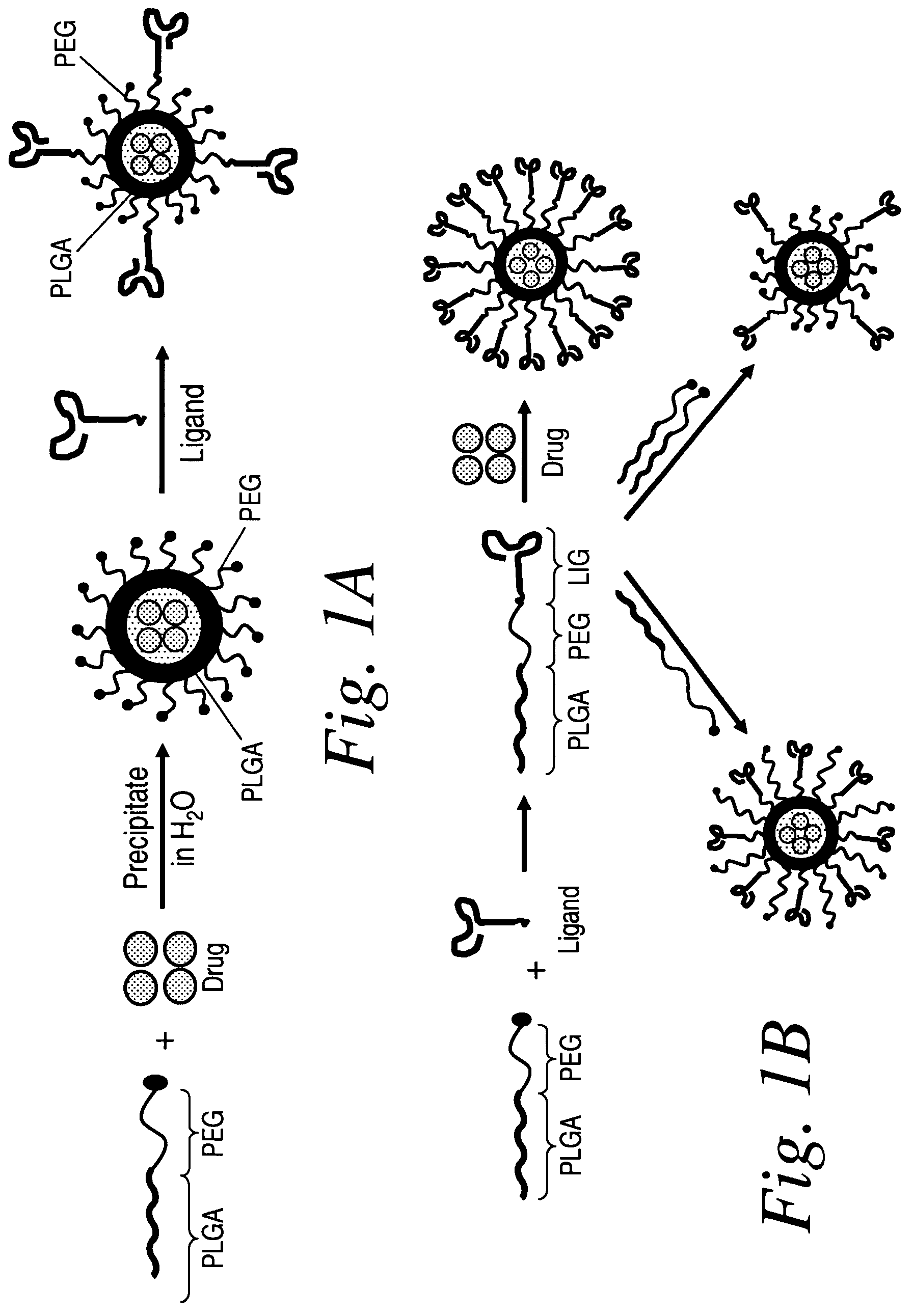
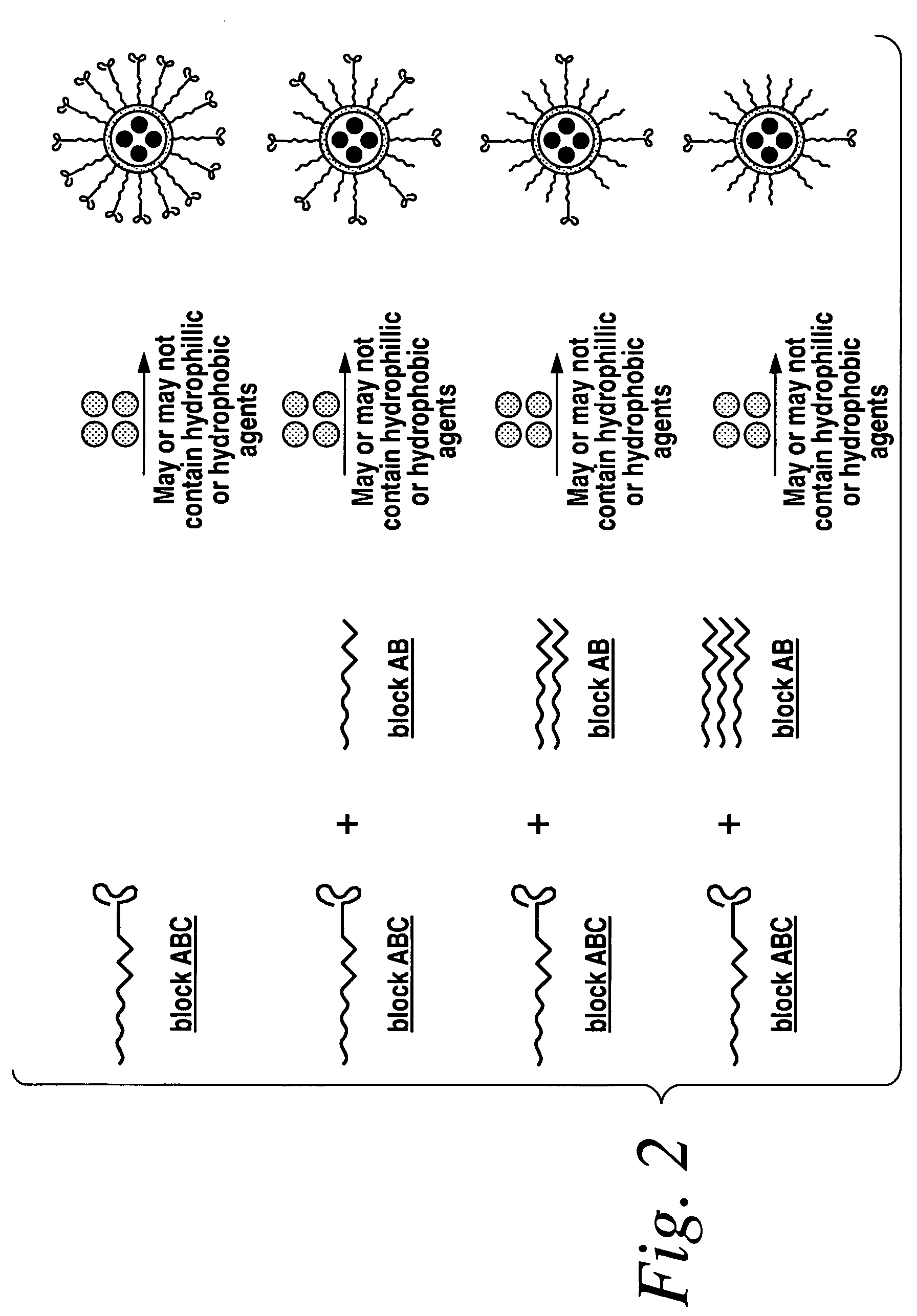
The present invention generally relates to polymers and macromolecules, in particular, to polymers useful in particles such as nanoparticles. One aspect of the invention is directed to a method of developing nanoparticles with desired properties. In one set of embodiments, the method includes producing libraries of nanoparticles having highly controlled properties, which can be formed by mixing together two or more macromolecules in different ratios. One or more of the macromolecules may be a polymeric conjugate of a moiety to a biocompatible polymer. In some cases, the nanoparticle may contain a drug. Other aspects of the invention are directed to methods using nanoparticle libraries.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMENS HOSPITAL INC +1
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS7442210B2Easy to integrateFree from painSuture equipmentsBone implantPolyesterPolypropylene
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
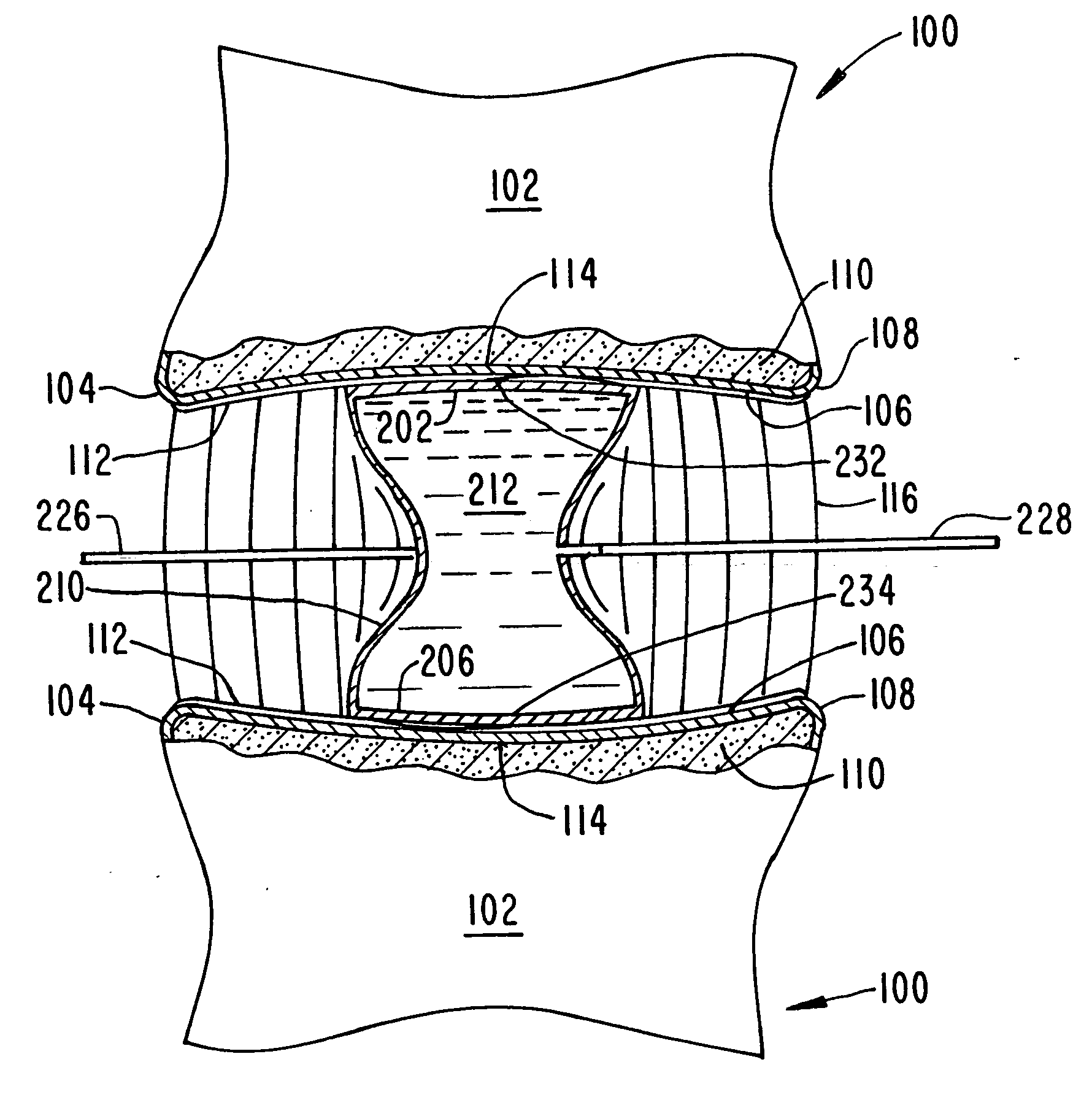
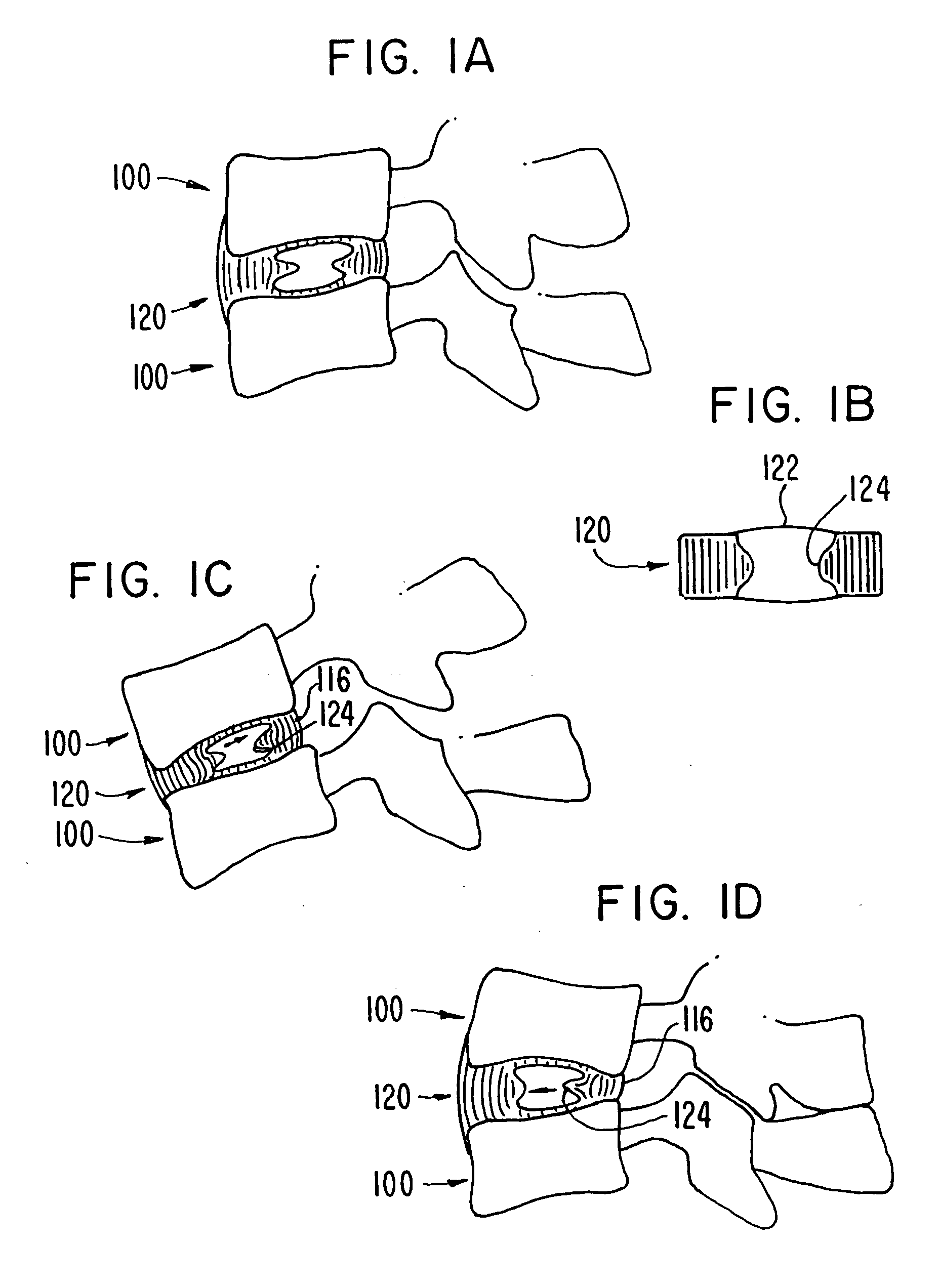
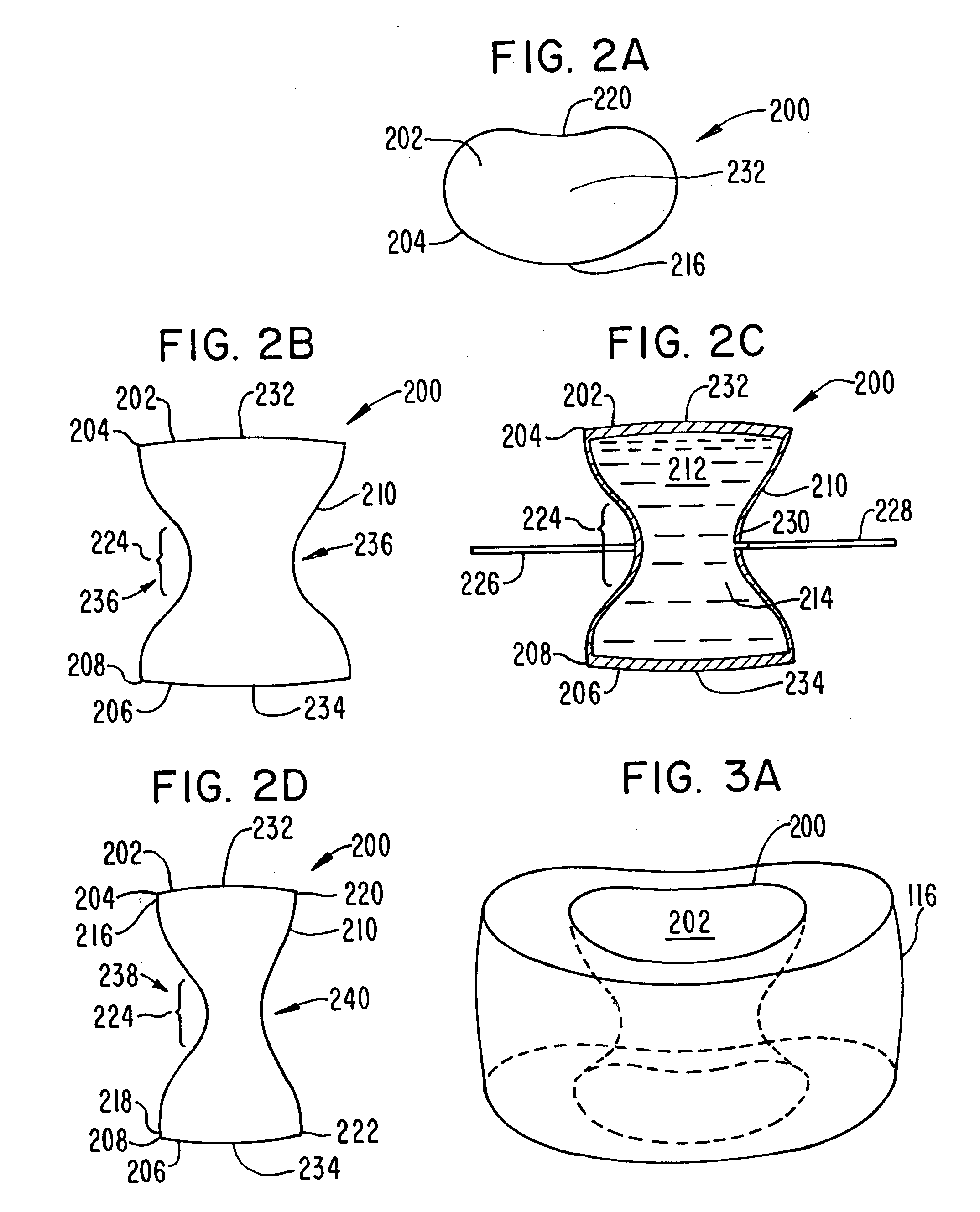
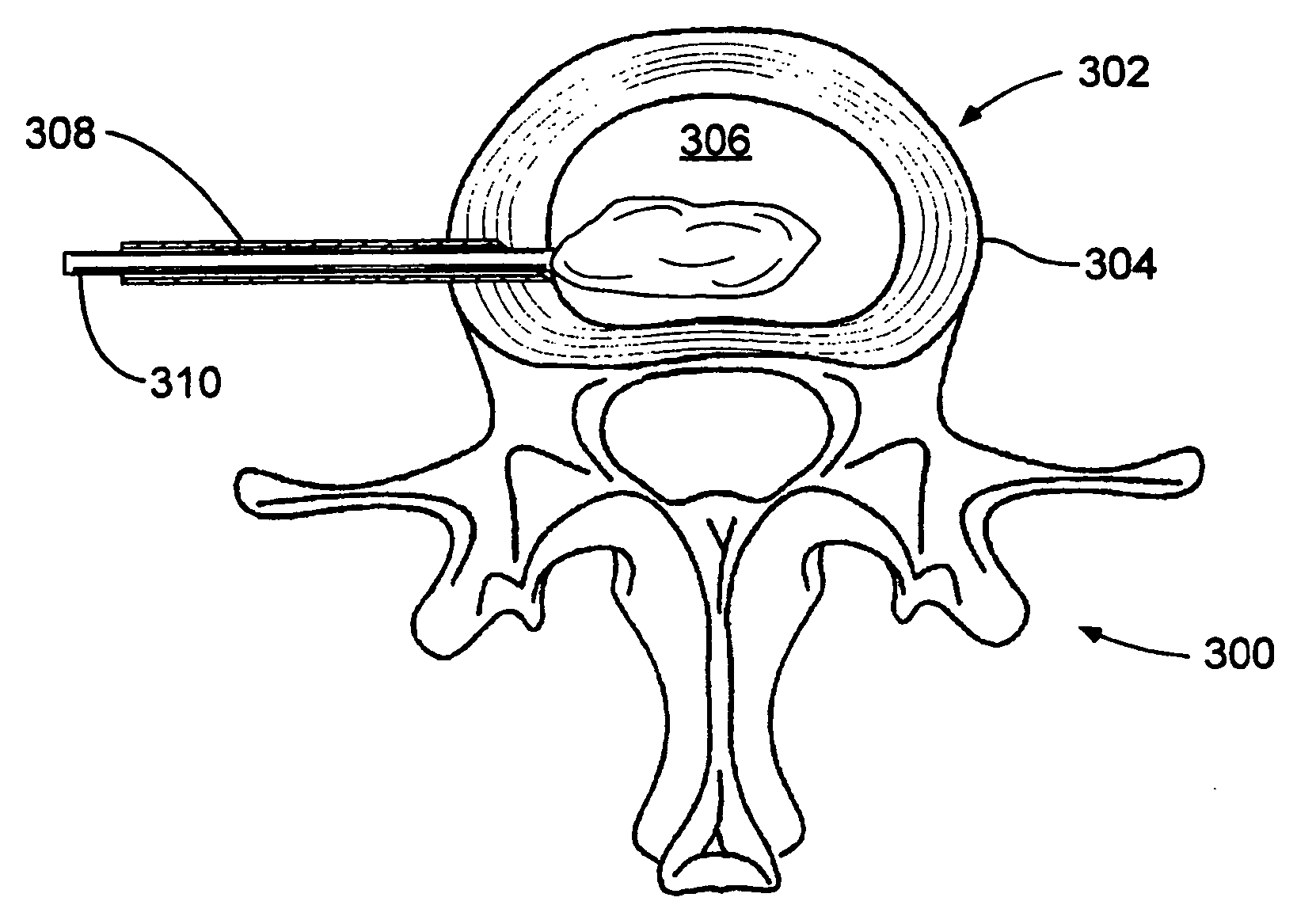
Intervertebral disk and nucleus prosthesis
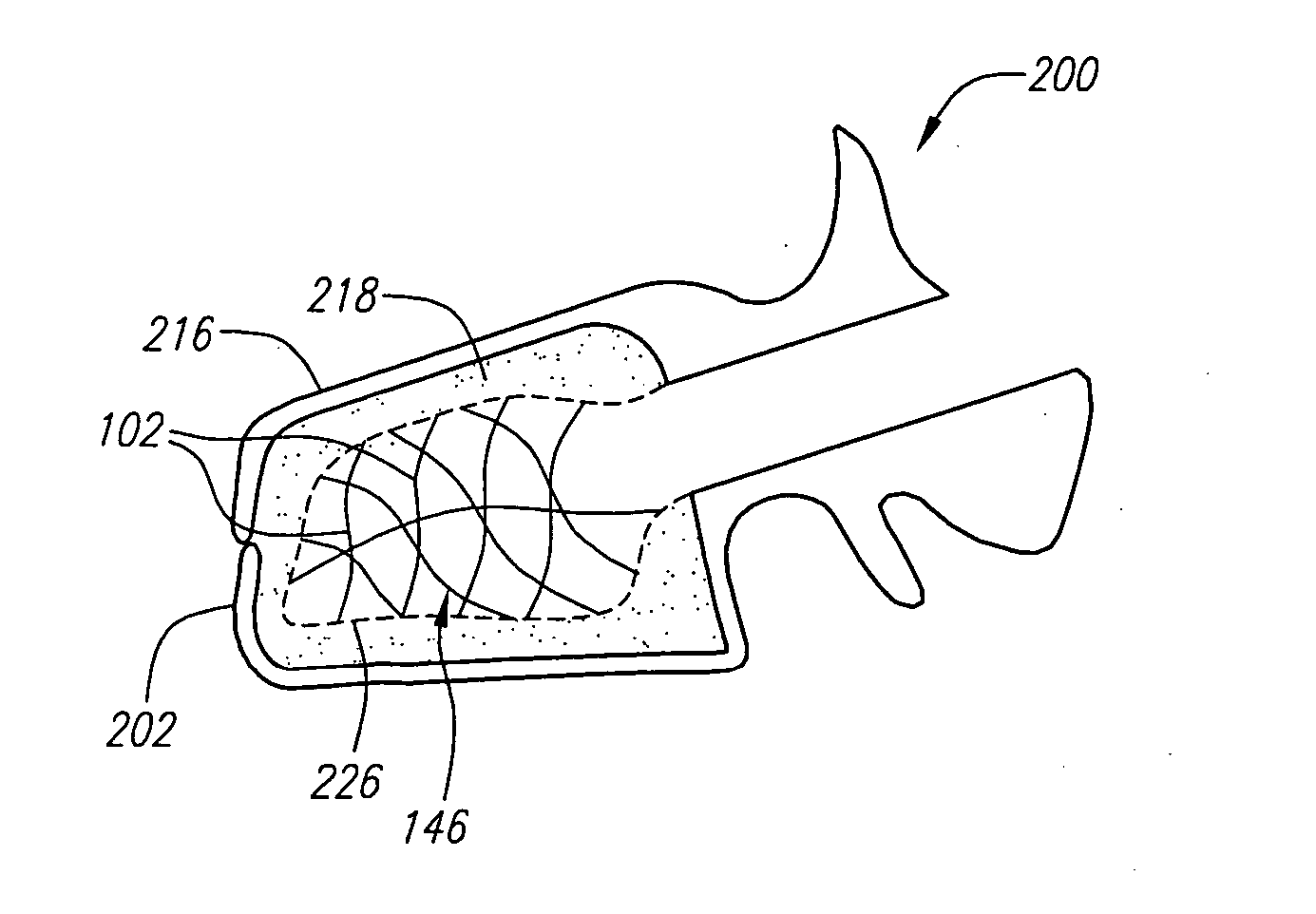
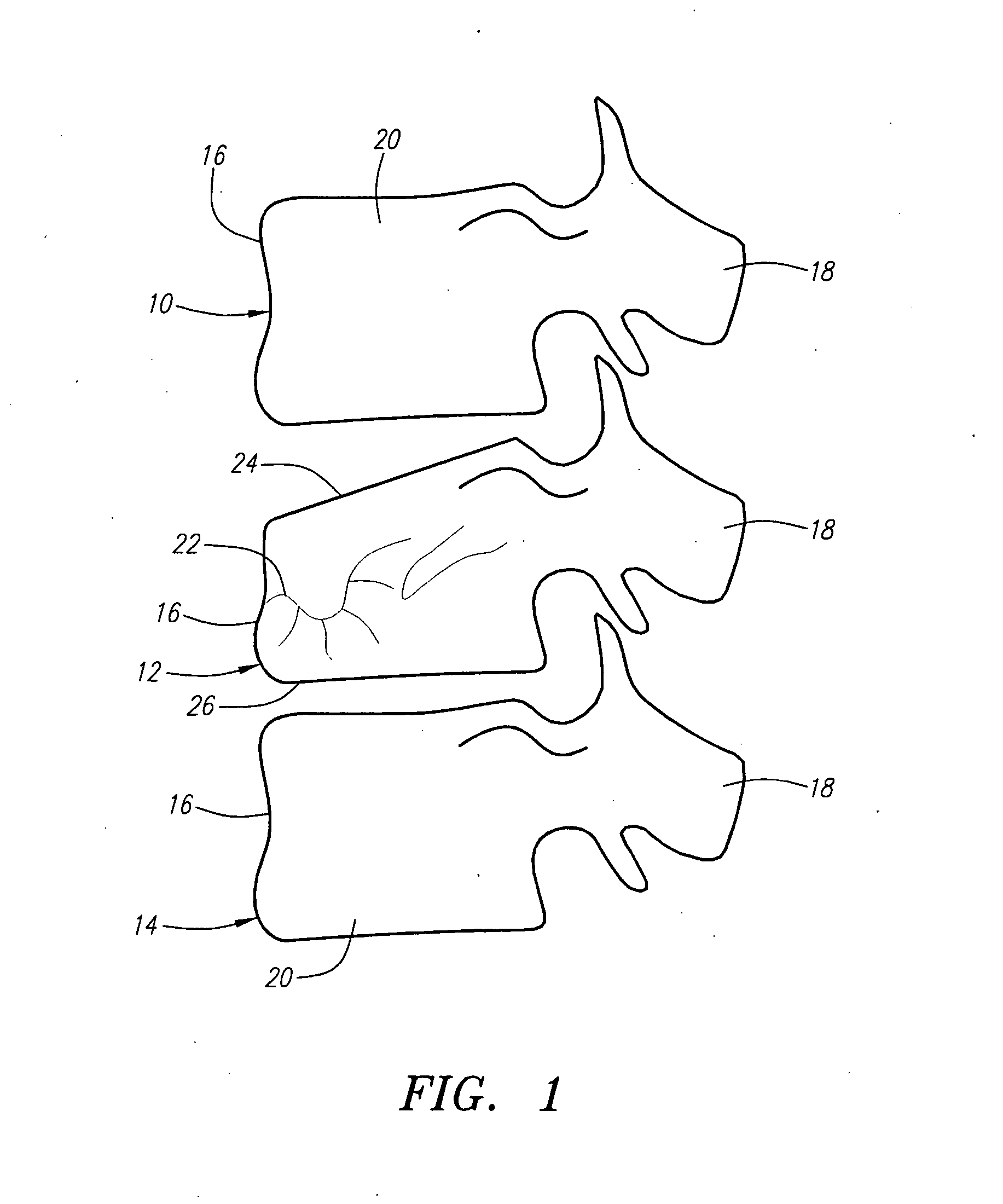
A prosthetic implant for replacing a nucleus pulposus of an intervertebral disk includes upper and lower endwalls of discoid cross-section, each having an antero-posterior diameter less than its transverse diameter, and an hourglass-shaped sidewall connecting the peripheries of the upper endwall and lower endwall to enclose an interior volume filled with a substantially incompressible liquid or soft plastic material. A total prosthesis for replacing the entire human intervertebral disk has an annular core made of a first biocompatible polymer surrounding a central cavity, transitional plates affixed respectively to the upper and lower surfaces of the annular core, the upper and lower transitional plates being made of a second biocompatible material having an elastic modulus greater than that of the first biocompatible polymer, and upper and lower endplates adapted to contact adjacent vertebrae and affixed respectively to the upper and lower transitional plates.
Owner:K2M
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20060287726A1Easy to integrateFree from painSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPolyesterClosed loop
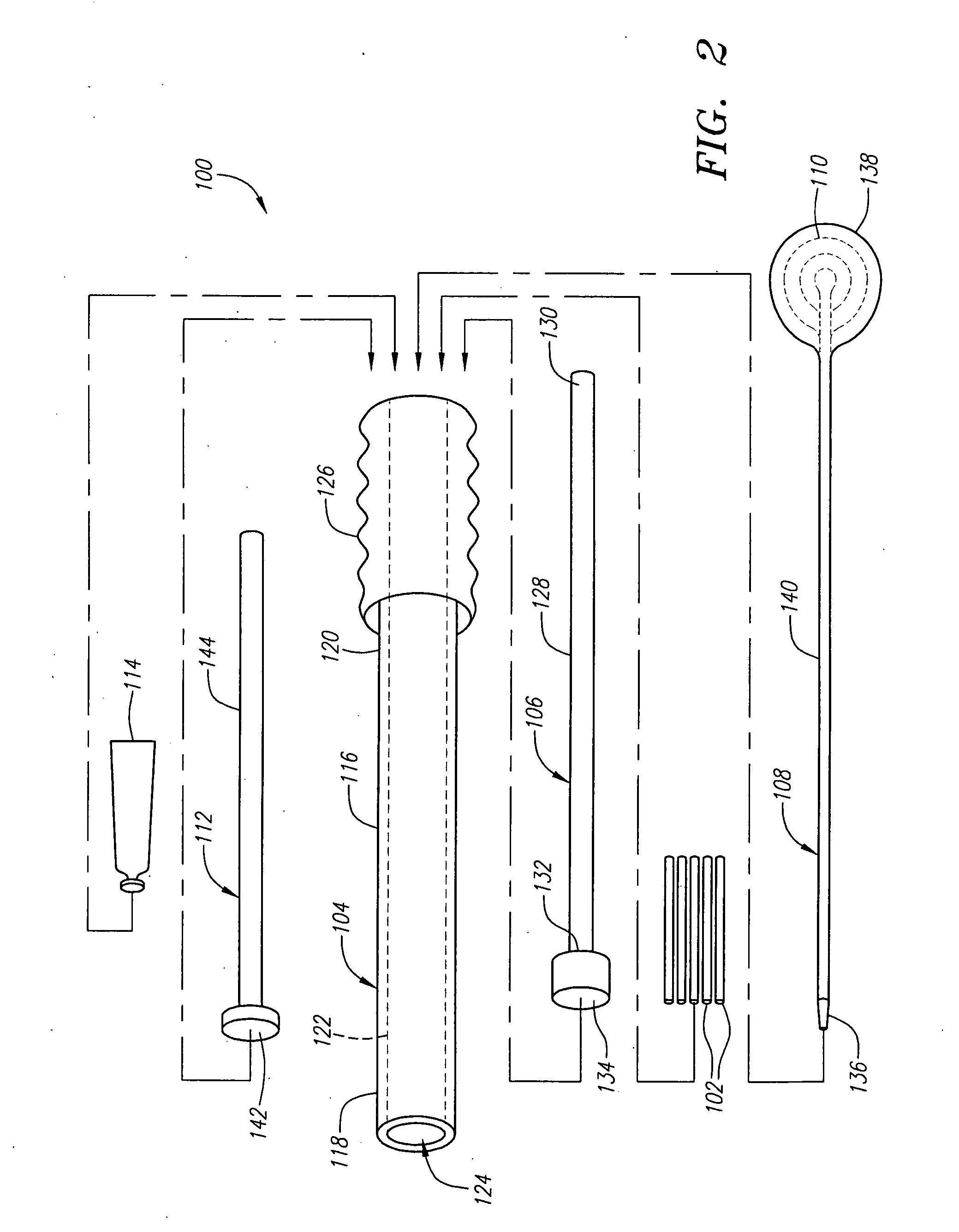
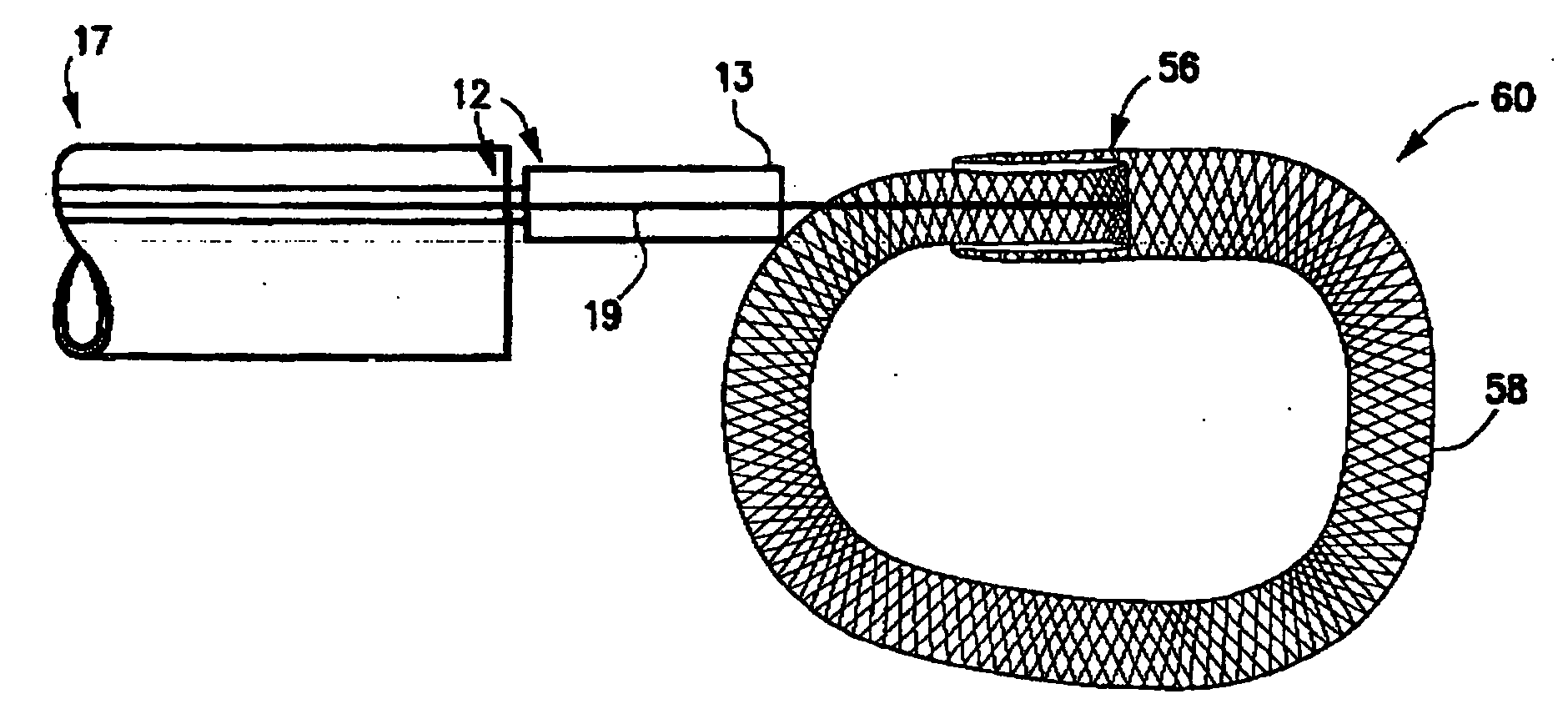
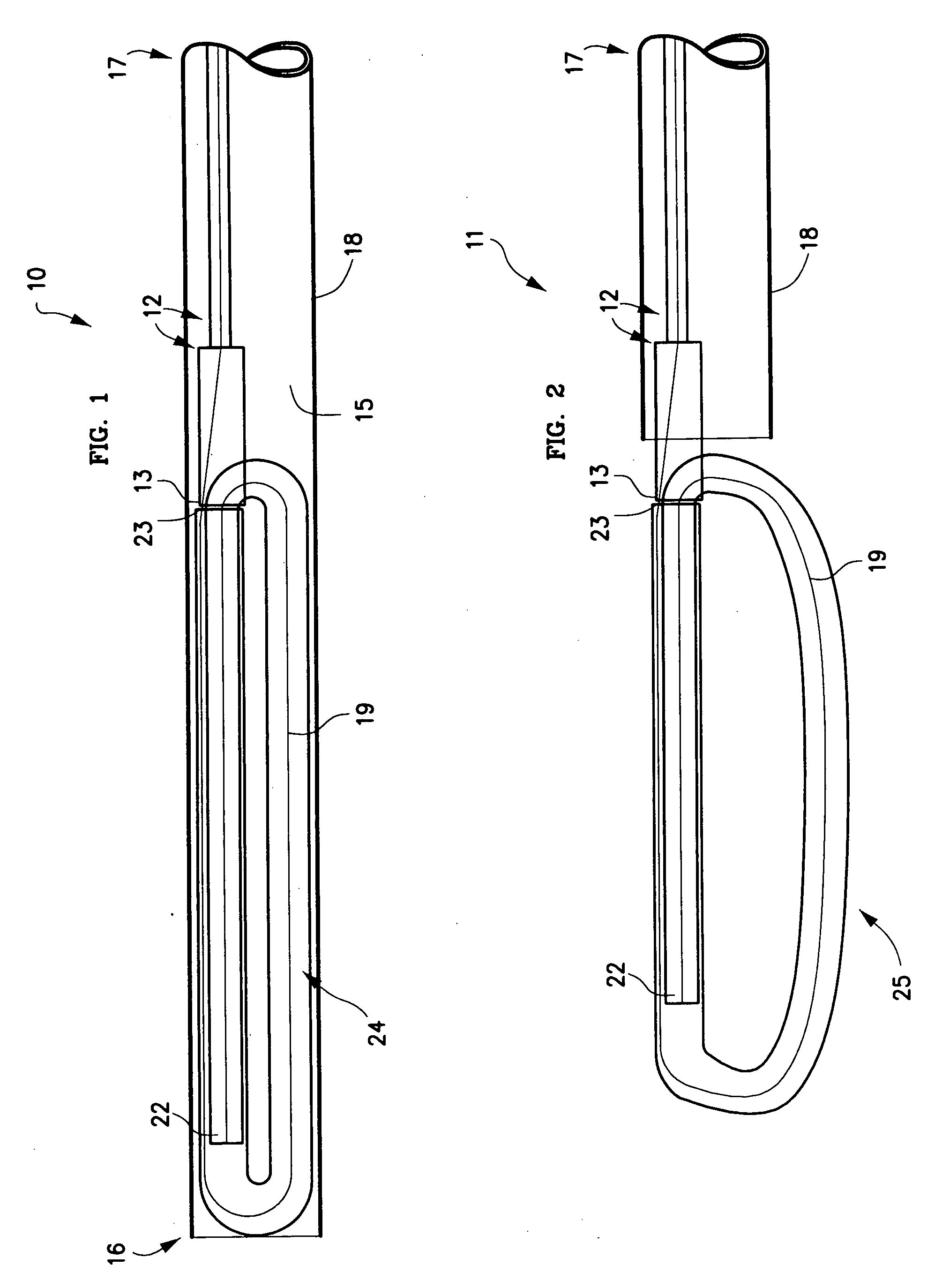
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed of a woven or braided material and may be made of a polymer such as nylon, polyurethane, polyester, polyethylene, polypropylene or any of the well known and biocompatible polymers. Alternatively the expansile portion of the catheter may be formed from a metallic braid of stainless steel, elgiloy, Nitinol, or other biocompatible metals. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
Methods for embolizing blood vessels
InactiveUS6335384B1Reduce molecular weightEasy to adjustHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsParticulatesMedicine
Disclosed are methods useful for treating vascular lesions wherein a non-particulate agent such as a metal coil is introduced into a vascular site (e.g., an aneurysm cavity) in conjunction with an embolizing composition comprising a biocompatible polymer and a biocompatible solvent.The biocompatible solvent is miscible or soluble in blood and also solubilizes the polymer during delivery. The biocompatible polymer is selected to be soluble in the biocompatible solvent but insoluble in blood. Upon contact with the blood, the biocompatible solvent dissipates from the embolic composition whereupon the biocompatible polymer precipitates. Precipitation of the polymer in the presence of the non-particular agent permits the agent to act as a structural lattice for the growing polymer precipitate.In another embodiment, the biocompatible polymer composition can be replaced with a biocompatible prepolymer composition containing a biocompatible prepolymer.
Owner:MICRO THEREPEUTICS INC
Methacrylate copolymers for medical devices
A polymer of hydrophobic monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains the polymer and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer or polymer blend and optionally a biobeneficial material and / or a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Implantable or insertable medical devices for controlled drug delivery
Implantable or insertable medical devices are provided, which comprises: (a) a biocompatible polymer; and (b) at least one therapeutic agent selected from an anti-inflammatory agent, an analgesic agent, an anesthetic agent, and an antispasmodic agent. The medical devices are adapted for implantation or insertion at a site associated with pain or discomfort upon implantation or insertion. In many embodiments, the therapeutic will be selected from at least one of (i) ketorolac and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof (e.g., ketorolac tromethamine) and (ii) 4-diethylamino-2-butynylphenylcyclohexyl glycolate and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof (e.g., oxybutynin chloride). Also provided are uses for the implantable or insertable medical devices, which uses comprise reducing pain or discomfort accompanying the implantation or insertion of such devices. Further uses may comprise reducing microbial buildup along the device. Methods for manufacturing implantable or insertable medical devices are also provided.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Porous osteoimplant
ActiveUS20080069852A1Accelerate the remodeling processImprove permeabilityBone implantSkeletal disorderBone growthBone defect
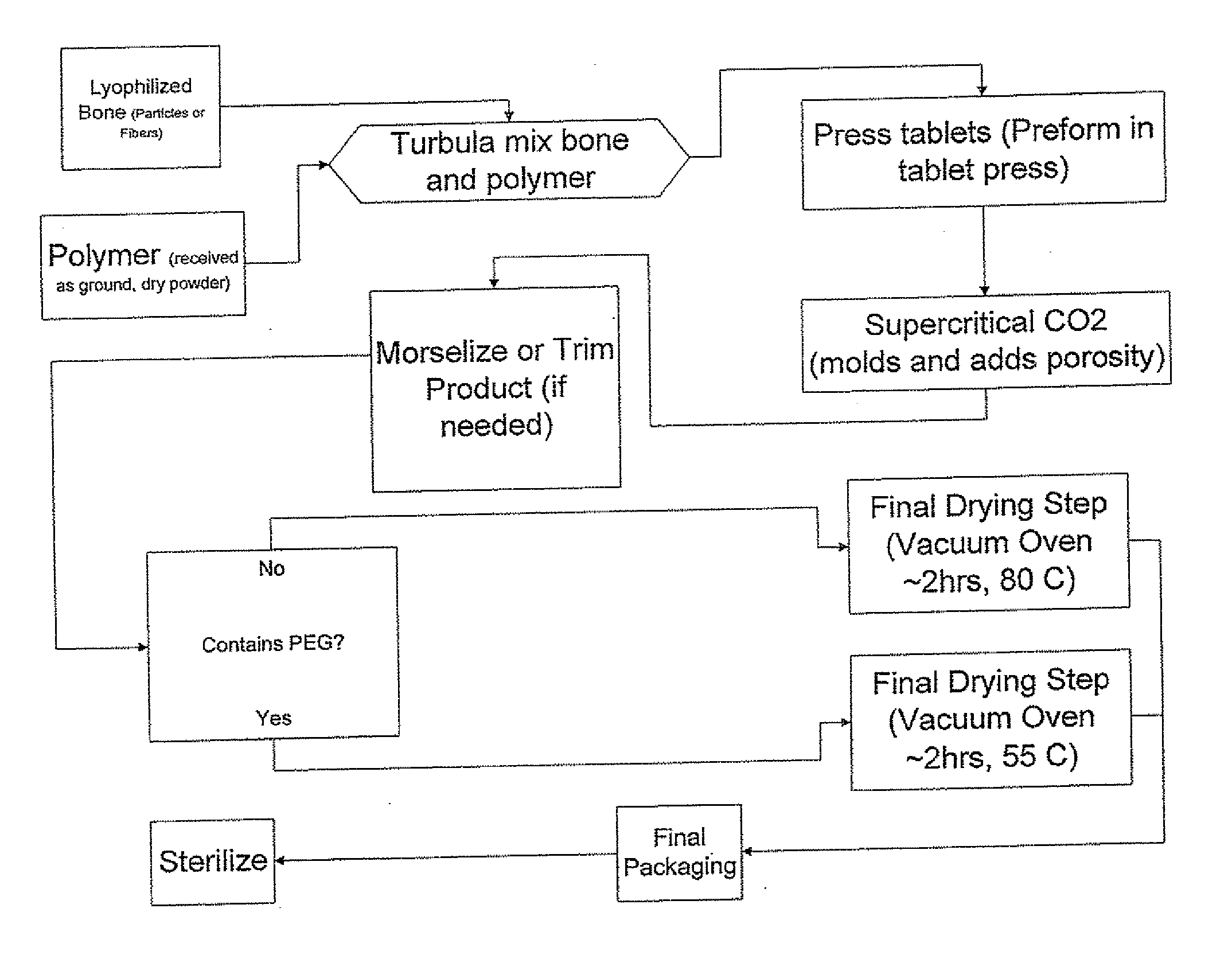
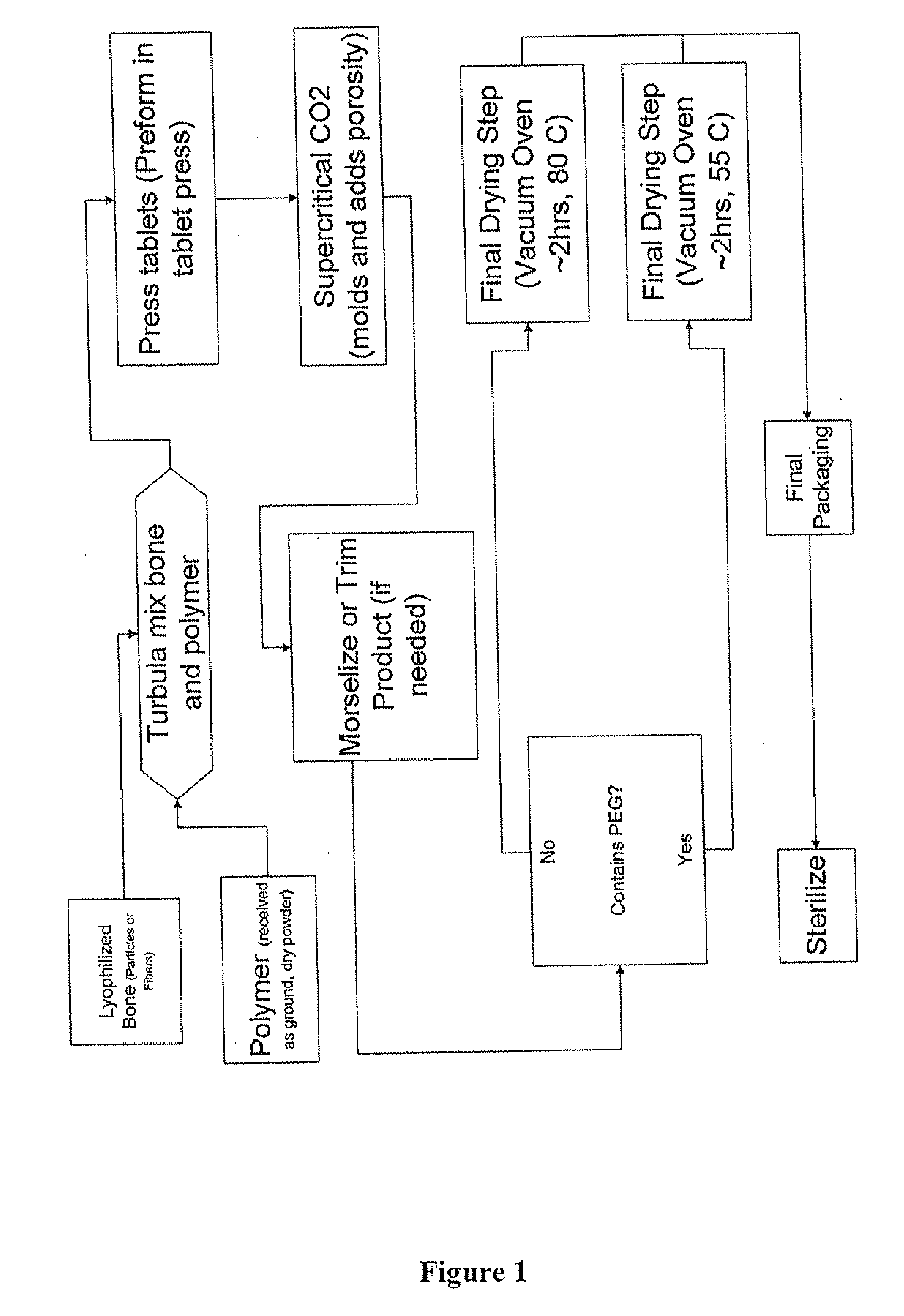
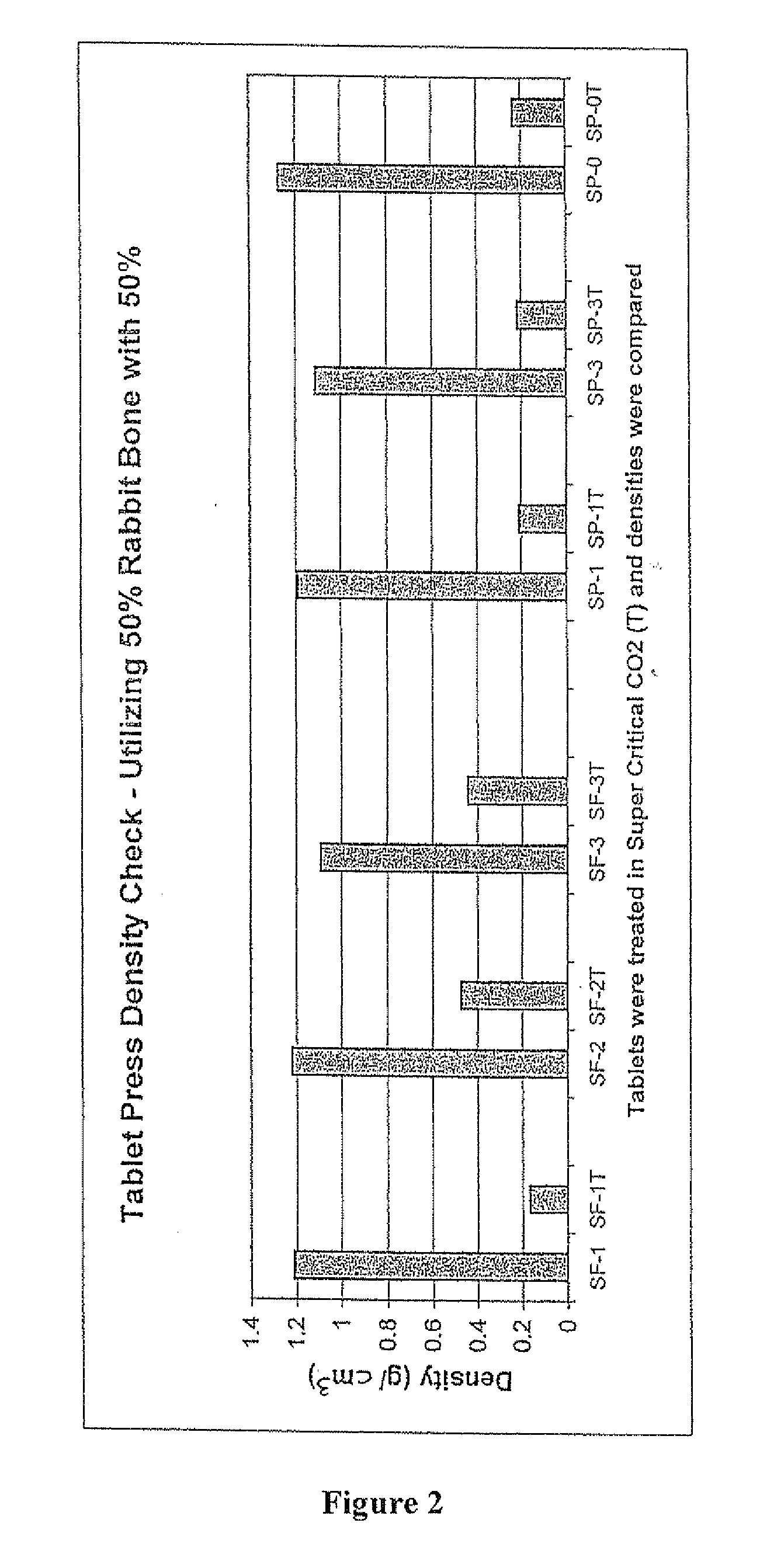
The invention is directed toward porous composites for application to a bone defect site to promote new bone growth. The inventive porous composites comprise a biocompatible polymer and a plurality of particles of bone-derived material, inorganic material, bone substitute material or composite material. In certain embodiments, the porous composites are prepared using a method that includes a supercritical fluid (e.g., supercritical carbon dioxide) treatment. The invention also discloses methods of using these composites as bone void fillers.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Bioactive agent delivering system comprised of microparticles within a biodegradable to improve release profiles
InactiveUS20020076441A1Improve stabilityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsActive agentPharmaceutical drug
A composition and method for releasing a bio-active agent or a drug within a biological environment in a controlled manner is disclosed. The composition is a dual phase polymeric agent-delivery composition comprising a continuous biocompatible gel phase, a discontinuous particulate phase comprising defined microparticles and an agent to be delivered. A microparticle containing a bio-active agent is releasably entrained within a biocompatible polymeric gel matrix. The bioactive agent release may be contained in the microparticle phase alone or in both the microparticles and the gel matrix. The release of the agent is prolonged over a period of time, and the delivery may be modulated and / or controlled. In addition, a second agent may be loaded in some of the microparticles and / or the gel matrix.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Hydrogel balloon prosthesis for nucleus pulposus
Owner:SYNTHES USA +1
Methods for preparing coated drug particles and pharmaceutical formulations thereof
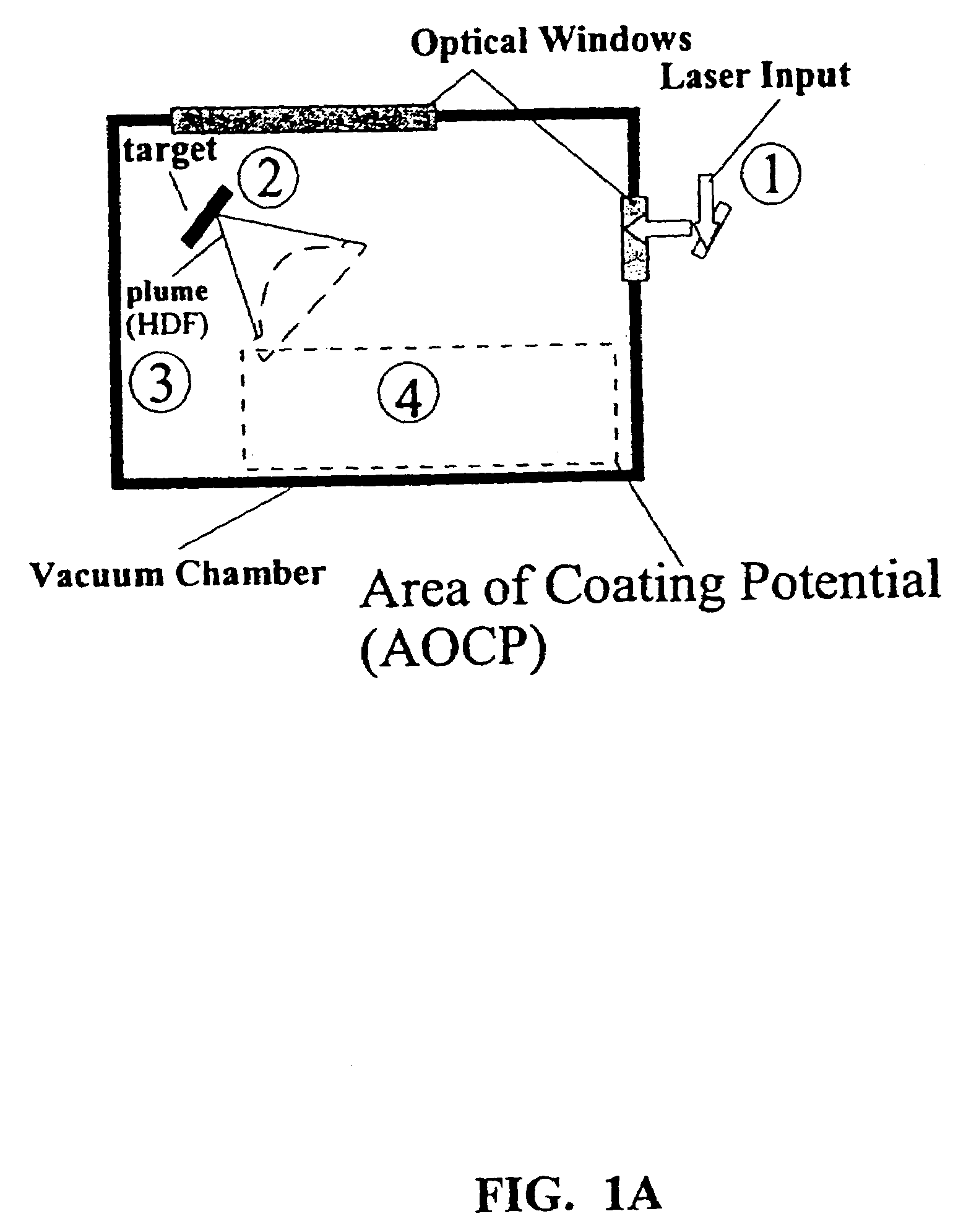
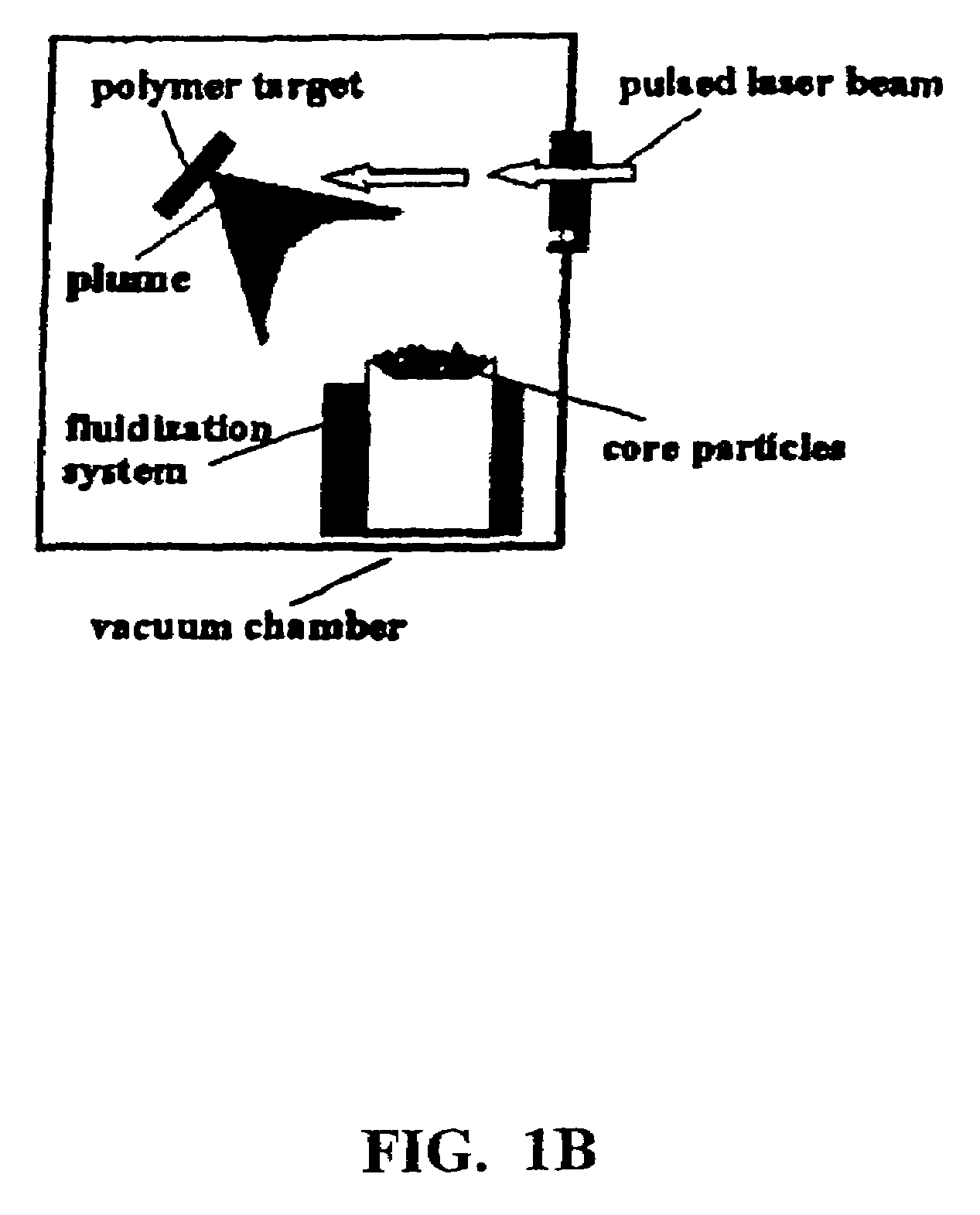
Disclosed are methods using pulsed laser ablation to prepare coated drug particles of uniform size and thickness. The coated drug particles ranged in size from several nanometers to several millimeters in diameter size, and were coated with organic polymer particle having average diameter sizes from about 1 to 50 nm. In illustrative embodiments, coated drug particles or drug delivery particles are disclosed comprising a biodegradable or biocompatible polymer coating having controlled thickness and controlled coating uniformity, that offer superior pharmaceutical properties for controlled delivery and increased bioavailability.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV PF +2
Silk biomaterials and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7674882B2Avoid problemsReduce usagePeptide/protein ingredientsFilament/thread formingFiberIn vivo
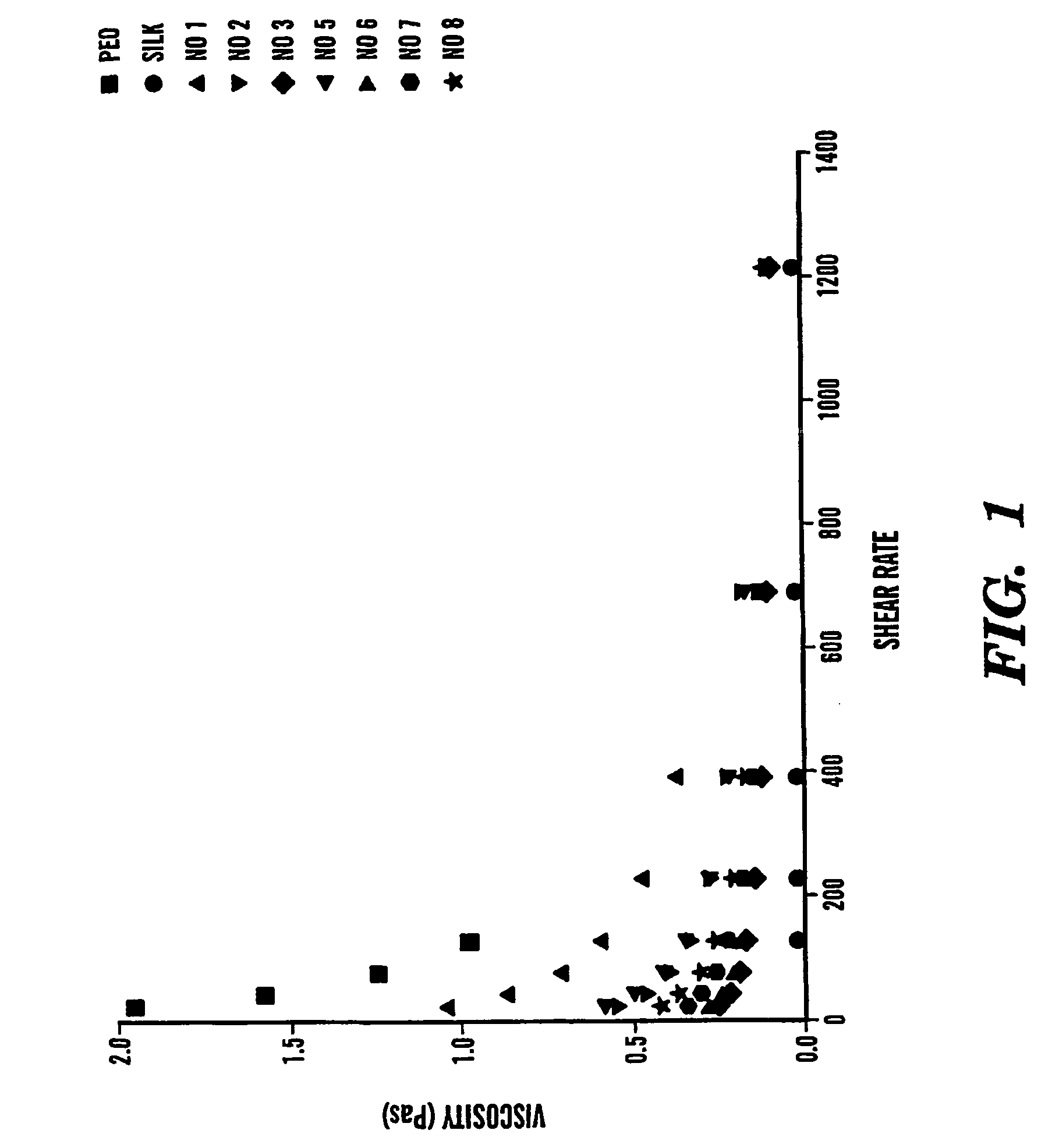
The present invention provides an all-aqueous process and composition for production of silk biomaterials, e.g., fibers, films, foams and mats. In the process, at least one biocompatible polymer, such as poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO) (a well-documented biocompatible material), was blended with the silk protein prior to processing e.g., electrospinning. We discovered that this step avoids problems associated with conformational transitions of fibroin during solubilization and reprocessing from aqueous solution which lead to embrittled materials. Moreover, the process avoids the use of organic solvents that can pose problems when the processed biomaterials are exposed to cells in vitro or in vivo.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
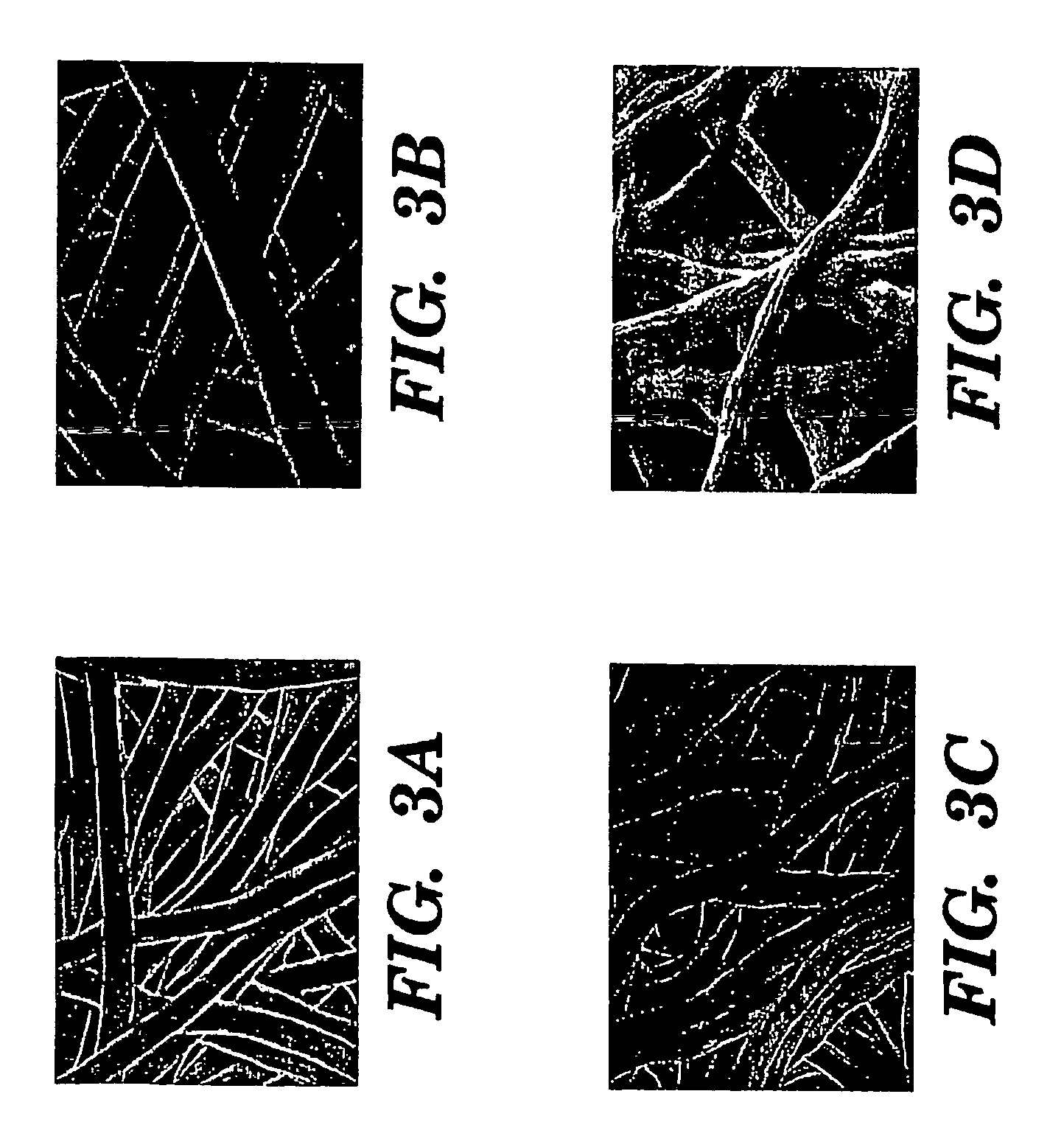
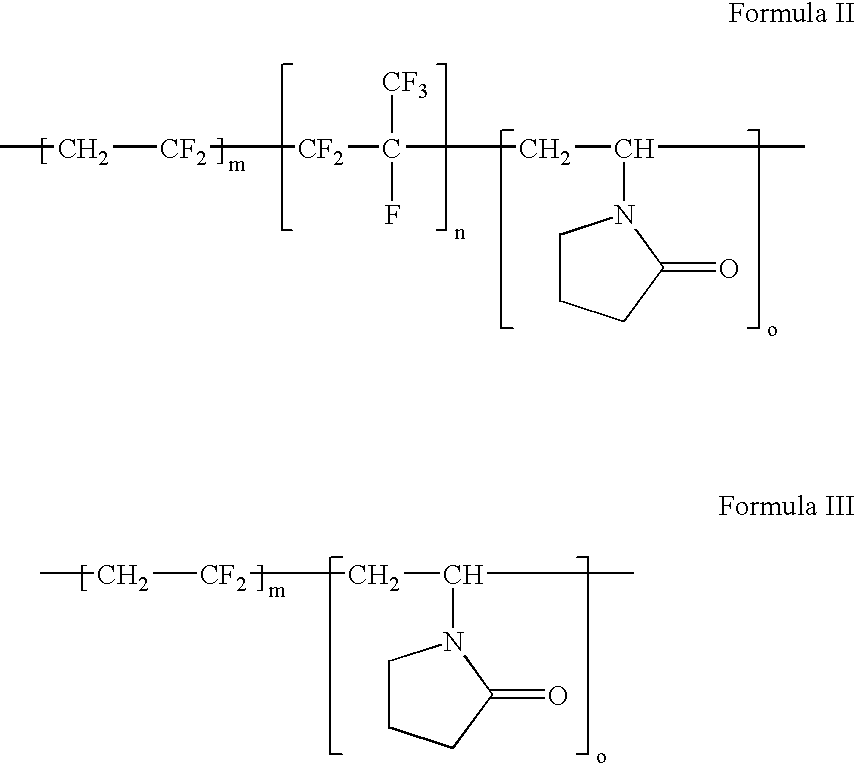
Polymers of fluorinated monomers and hydrophilic monomers
ActiveUS20060047095A1Improve propertiesProvide flexibilityFibre treatmentSurgeryDiseasePolymer science
A polymer of fluorinated monomers and hydrophilic monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains a polymer of fluorinated monomers and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer of fluorinated monomers or polymer blend described herein and optionally a bioactive agent can form a coating on an implantable device such as a drug-delivery stent. The implantable device can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, patent foramen ovale, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Medical device having a coating layer with structural elements therein and method of making the same
InactiveUS20060025848A1Efficient methodCounteracting forceStentsSurgeryInsertion stentCompressibility
The invention pertains to coated medical devices, such as stents and balloon catheters, for delivering a biologically active material to body tissue of a patient. The medical device has a coating layer comprising a biocompatible polymer, non-polymer material, or biologically active material disposed on its surface, and at least one structural element embedded within the coating layer. The structural elements reduce the compressibility of the coating layer. The structural element may be any shape or configuration. A biologically active material may be dispersed within the coating layer or structural elements. Methods for making such medical devices are also disclosed.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Medical devices with triggerable bioadhesive material
Described herein are implantable medical devices comprising a biocompatible polymer comprising a triggerable bioadhesive property that allows the device to adhere to body tissue. The triggerable bioadhesive property of the polymer can be triggered or activated by exposure to a stimulus. Also, the present invention pertains to methods of making an implantable medical device comprising a biocompatible polymer comprising a triggerable bioadhesive property that allows the device to adhere to body tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Knotless suture anchor having discrete polymer components and related methods
InactiveUS20080319478A1Robust monolithic designLow mechanical strengthSuture equipmentsWound clampsDrive shaftSuture anchors
A knotless bone anchor and method for securing soft tissue, such as tendons, to bone, includes a plurality of discrete components. In one variation of the invention, the bone anchor includes a proximal toggle component, an intermediate plug component, and a distal sleeve component. Suture is looped around the plug component and once the anchor is actuated, the suture is compressed between the plug and the sleeve components. Advantageously, one or more of the components may be made of a biocompatible polymer. The polymeric components may be detachably joined to a drive shaft using a plurality of sacrificial fills. The sacrificial fills are broken or severed during deployment of the anchor. Related instruments and methods are also described.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Foam composite for the repair or regeneration of tissue
InactiveUS20030077311A1Variable mechanical strengthFacilitate cell migration and nutrient flowBiocidePowder deliveryRegeneration tissueBiology
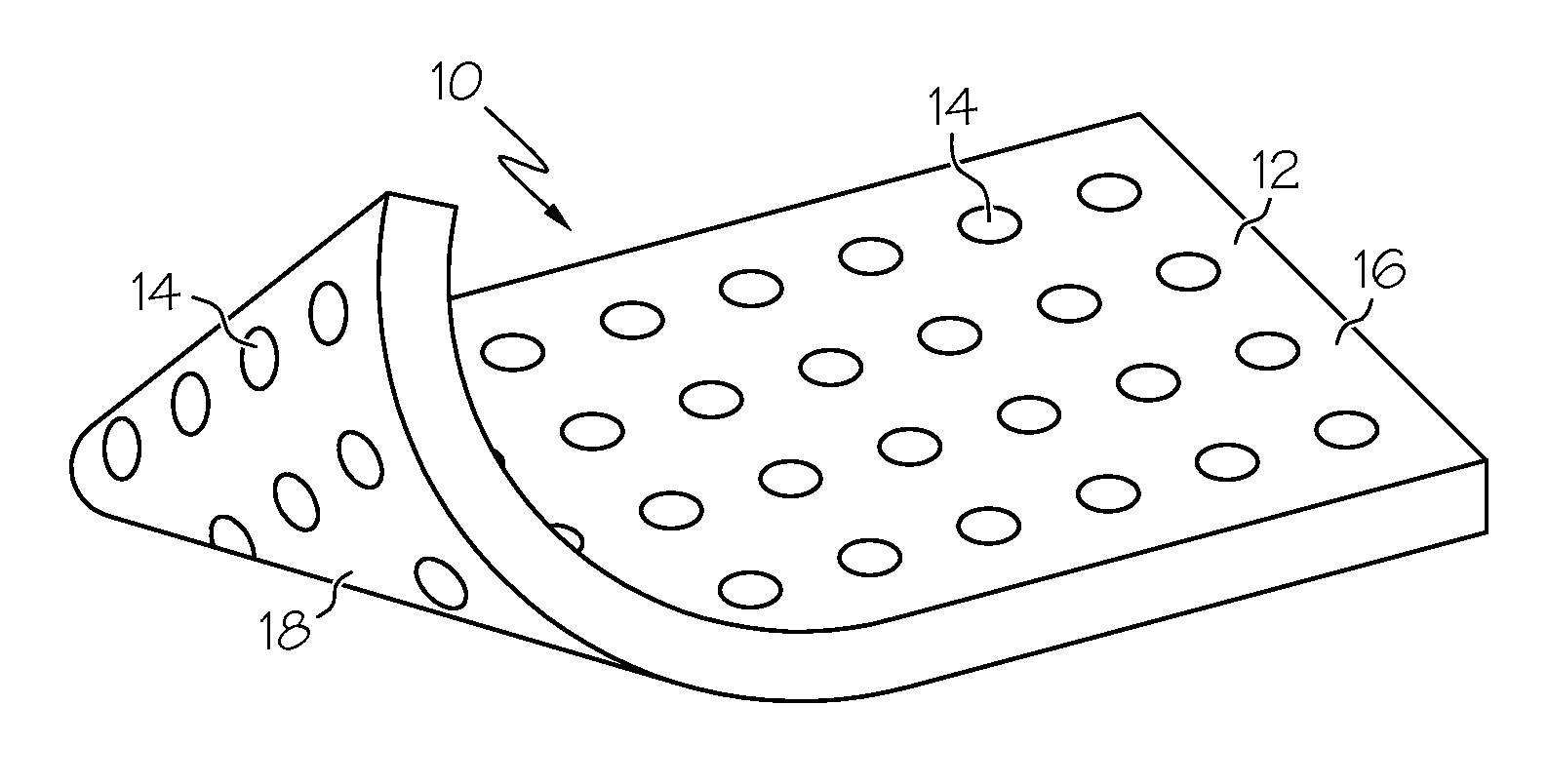
The present patent describes a biocompatible composite made of a first fibrous layer attached to a three-dimensional inter-connected open cell porous foams that have a gradient in composition and / or microstructure through one or more directions. These composites can be made from blends of absorbable and biocompatible polymers. These biocompatible composites are particularly well suited to tissue engineering applications and can be designed to mimic tissue transition or interface zones.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Biomaterial including micropores
A biomaterial including a designed pattern of micropores one at least one surface of the biomaterial is described. The micropores can be provided in a regular or irregular pattern, and can be either continuous or discontinuous. The biomaterial may be formed from a variety of materials, such as a biocompatible polymer or biocompatible tissue. The biomaterial including micropores on a surface may be used for a variety of medical applications such as tissue scaffolding, drug delivery, or tissue fixation.
Owner:APPLIED MEDICAL RES
Mechanical apparatus and method for artificial disc replacement
InactiveUS20060287727A1Increase the diameterEasy to integrateSuture equipmentsBone implantPolyesterClosed loop
The present invention relates to a device and method which may be used to reinforce the native annulus during spinal surgery. The device is a catheter based device which is placed into the inter-vertebral space following discectomy performed by either traditional surgical or endoscopic approaches. The distal end of the catheter is comprised of an expansile loop which may be increased in diameter by advancement of a portion of the catheter via its proximal end, such proximal end remaining external to the body. The expansile loop may be formed of a woven or braided material and may be made of a polymer such as nylon, polyurethane, polyester, polyethylene, polypropylene or any of the well known and biocompatible polymers. Alternatively the expansile portion of the catheter may be formed from a metallic braid of stainless steel, elgiloy, Nitinol, or other biocompatible metals. The expansile loop may be formed such that when the loop is diametrically contracted the loop feeds into its other end, similar to a snake eating its own tail. Stabilization of the outer portion of the loop and pulling out the inner portion will thereby increase the overall diameter of the loop while maintaining it as a closed loop or torus. The present invention comprises four embodiments and can be used to 1) facilitate disk fusing, 2) perform an artificial replacement of the nucleus, 3) perform an artificial replacement of the annulus, or 4, perform an artificial replacement of both the nucleus and annulus.
Owner:OUROBOROS MEDICAL INC
Collagen matrix for soft tissue augmentation
InactiveUS20050142161A1Minimize patient discomfortMinimize side effectsOrganic active ingredientsBiocideWrinkle skinTissue defect
The present invention includes methods and materials for soft tissue implant formed from biologically-compatible polymeric matrixes. The matrixes may have pores sized for in-growth of soft tissue. The material may be utilized with collagen or other matrix materials. This material may be used in a method of reforming soft tissues by implanting the material within soft body tissues to modify soft tissue defects such as wrinkles or biopsy tissue defects and to reshape soft tissue.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Biomedical device, method for manufacturing the same and use thereof
InactiveUS20120165954A1Reduce usageEasy to processBone implantCeramic shaping apparatusLead zirconate titanatePorosity
A three-dimensional biomedical device having an osteoinductive first area with a controlled porosity and a second area, which is produced by laser technology from a powder including one of ceramics, metals, metal alloys, bioactive glasses, lead zirconate titanate and biocompatible polymers, or mixtures thereof. The ratio of the porosities from the second area to the first area is equal or less than one, preferably from 0.001 to 0.9. A method for manufacturing the device for fitting in a bone defect, wherein a virtual object is designed with a computer-aid designed software, and the device is manufactured by laser technology including layering a powder onto a plate (7) so that a layer of a predetermined thickness is formed; the laser beam (8) selectively processes the powder to produce a processed layer, and, thus, layer after layer, the layers are joined together until the biomedical device is formed.
Owner:NIMAL DIDIER
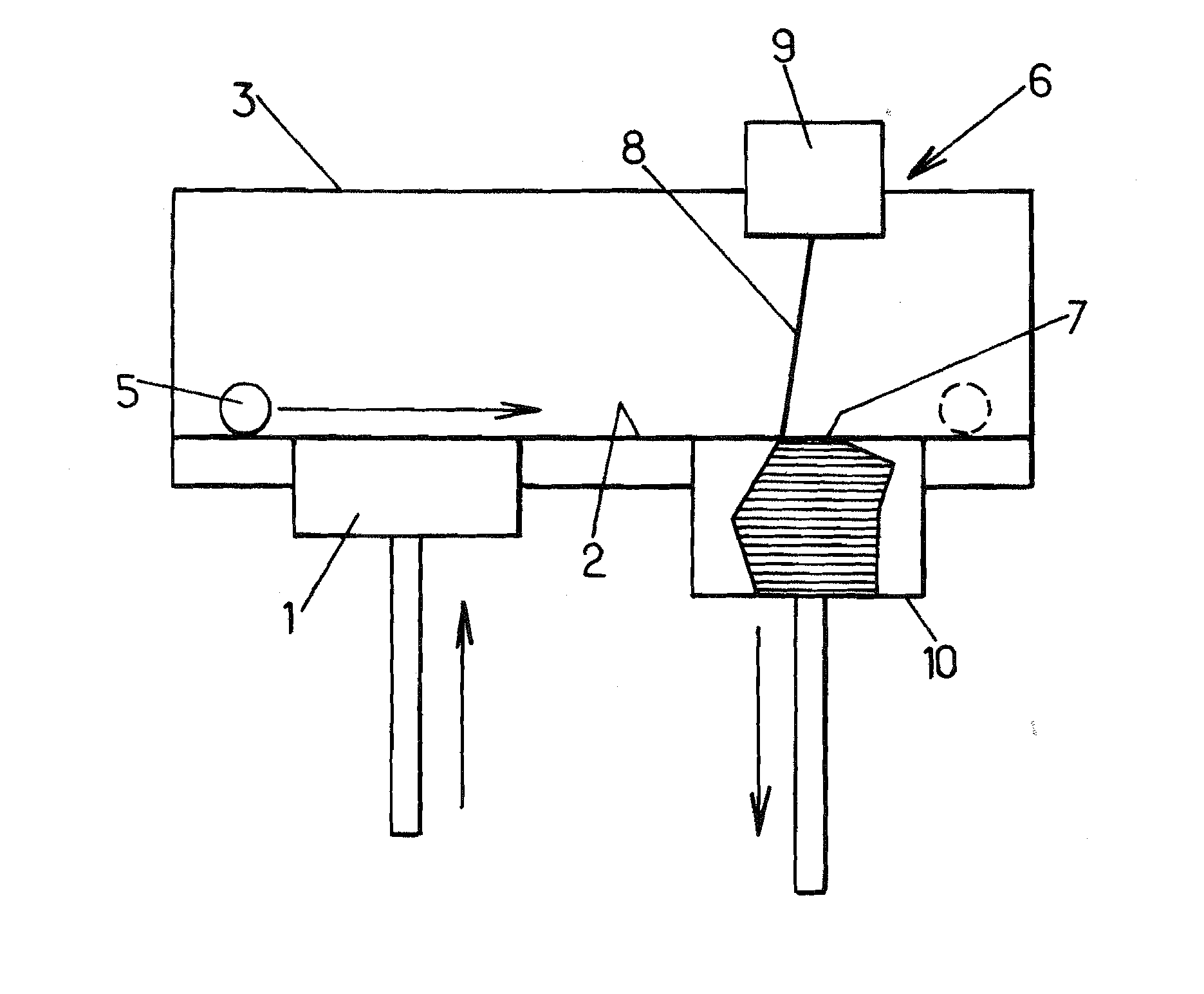
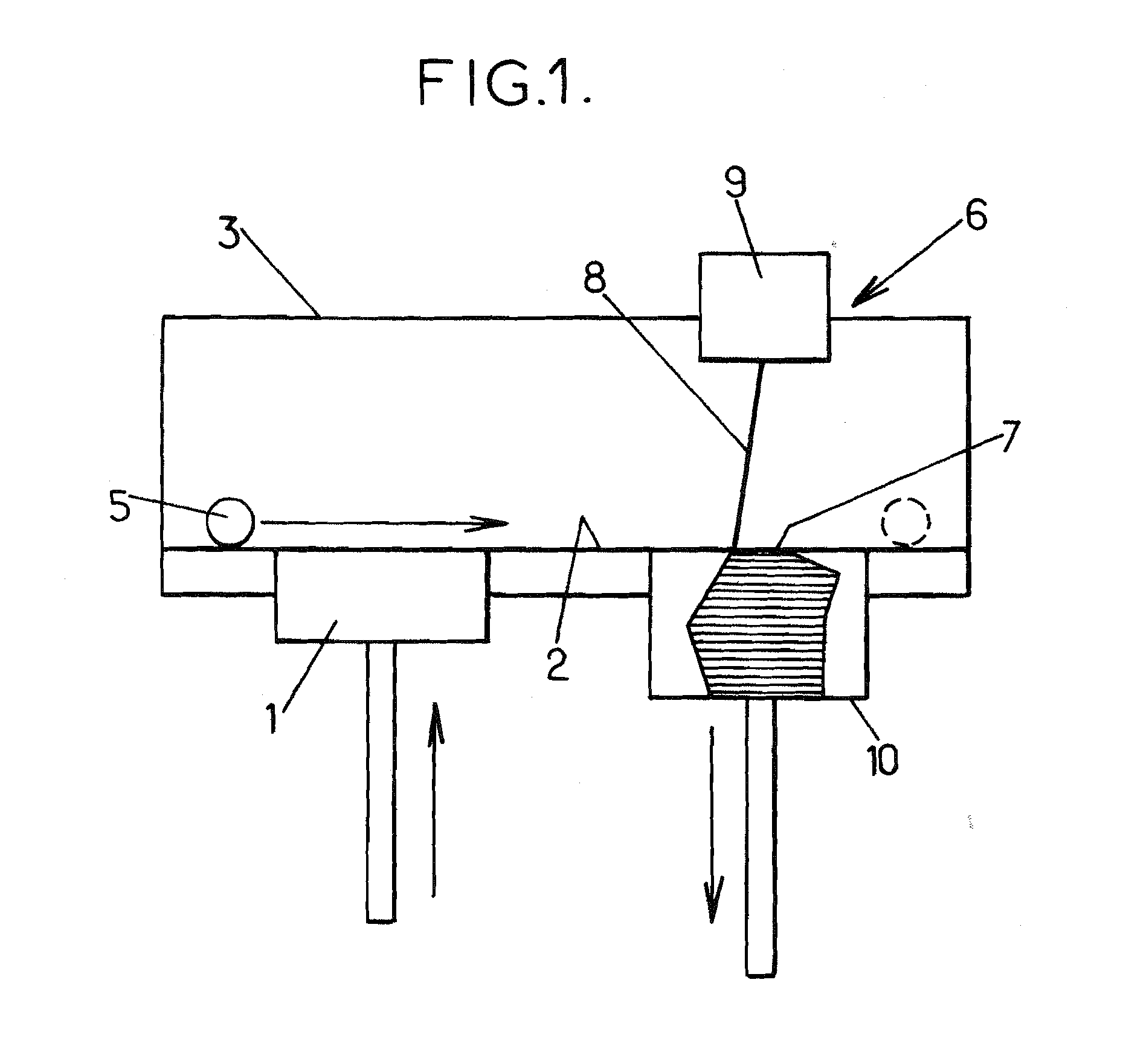
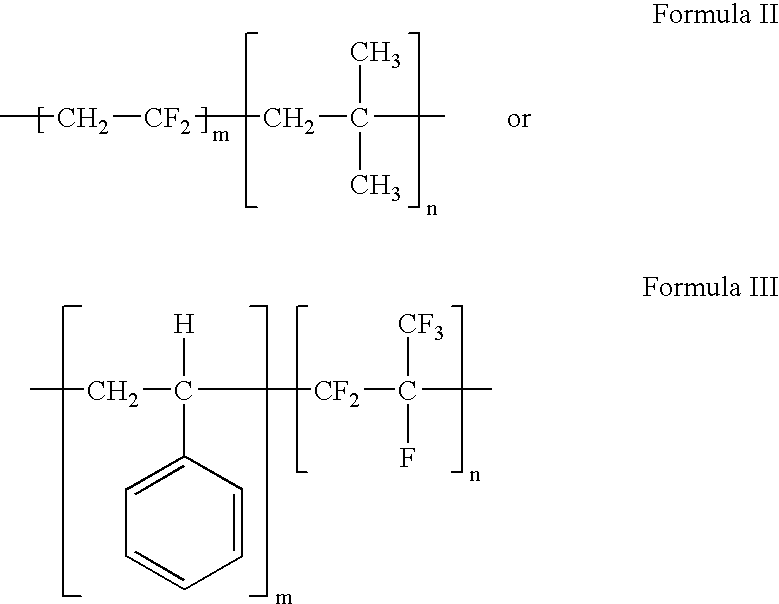
Polymers of fluorinated monomers and hydrocarbon monomers
InactiveUS20060134165A1Provide mechanical strengthGive flexibilityStentsSurgeryAbnormal tissue growthPolymer science
A polymer of fluorinated monomers and hydrocarbon monomers is provided. It is also provided a polymer blend that contains a polymer formed of fluorinated monomers and hydrocarbon monomers and another biocompatible polymer. The polymer or polymer blend described herein and optionally a bioactive agent can form an implantable device such as a stent or a coating on an implantable device such as a drug-delivery stent, which can be used for treating or preventing a disorder such as atherosclerosis, thrombosis, restenosis, hemorrhage, vascular dissection or perforation, vascular aneurysm, vulnerable plaque, chronic total occlusion, claudication, anastomotic proliferation for vein and artificial grafts, bile duct obstruction, ureter obstruction, tumor obstruction, or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com