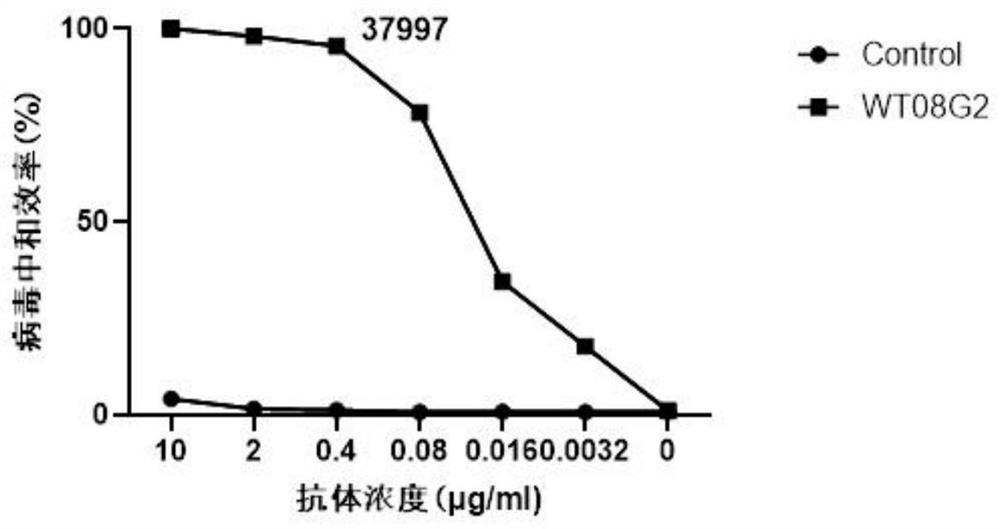
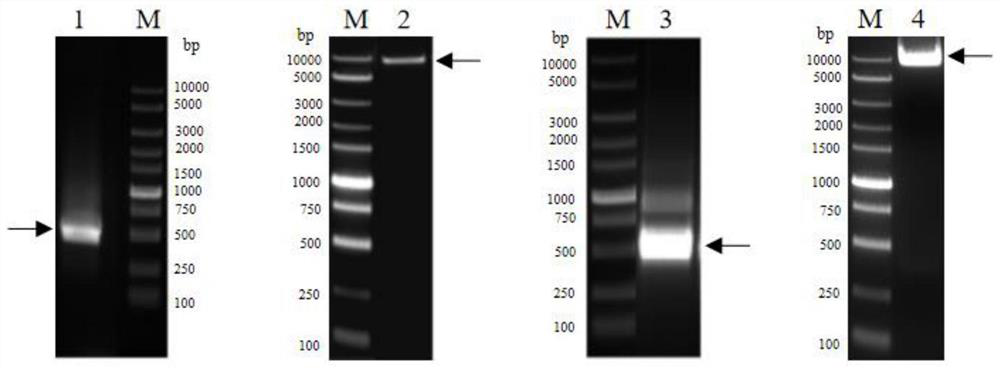
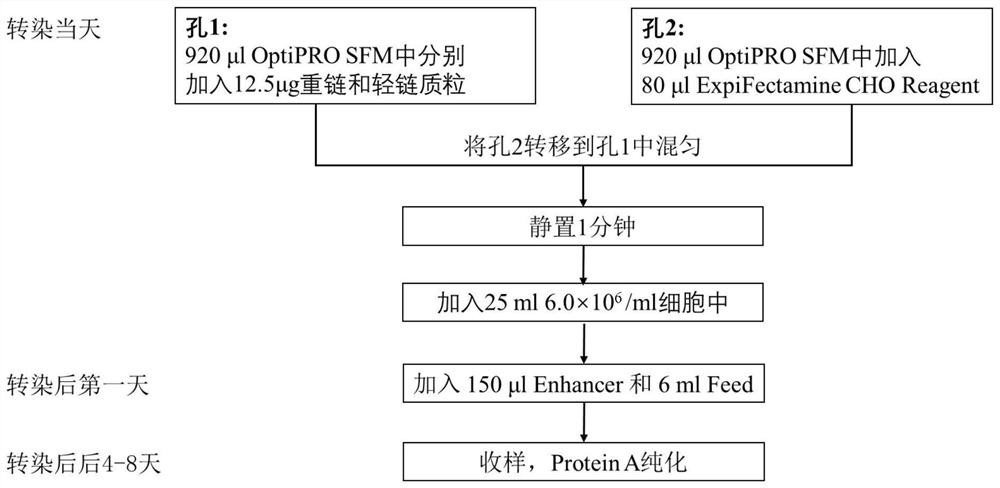
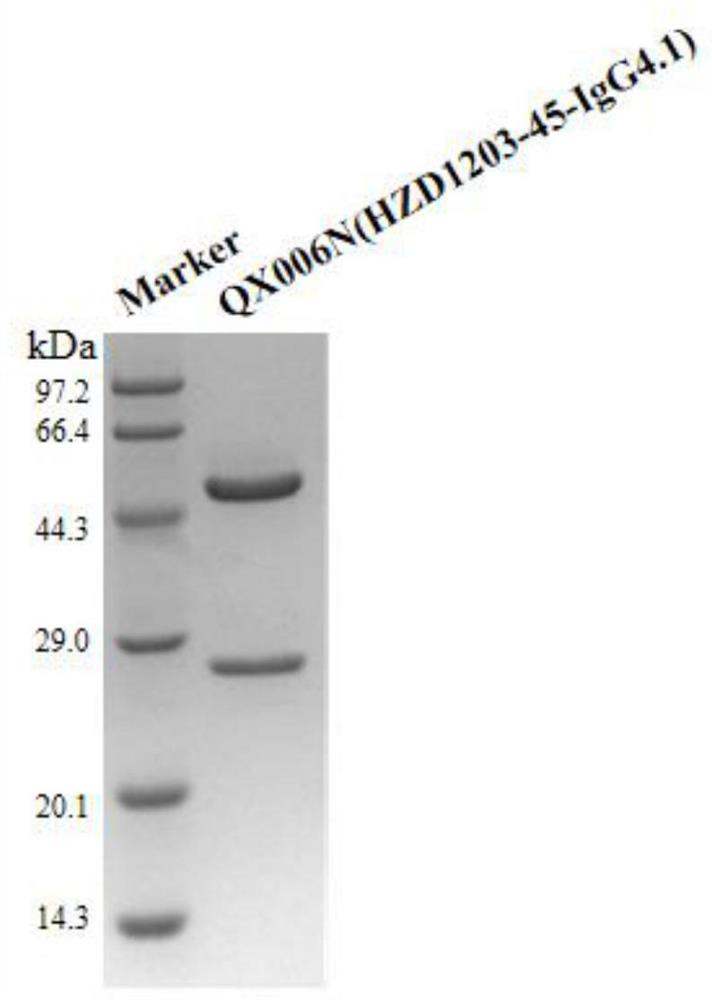
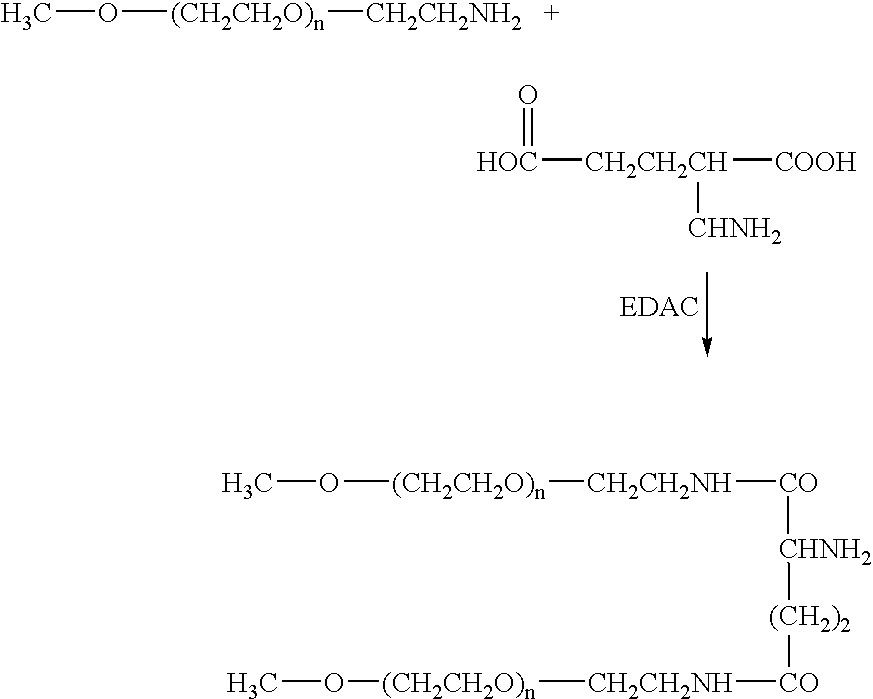Patents
Literature
63 results about "Interferon receptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The interferon receptor is a molecule displayed on the surface of cells which allows them to interact with the anti-viral substance interferon. The receptor is genetically coded for by number of different genes, as there are a few distinct types of interferon.
Double Specific Antibodies Substituting For Functional Proteins
InactiveUS20080075712A1Reduced activityOutstanding sustainabilityImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsNervous disorderBlood coagulation factor VIIIBlood Coagulation Factor X
The present inventors succeeded in separating bispecific antibodies that functionally substitute for ligands of type I interferon receptors comprising two types of molecules: AR1 chain and AR2 chain. Furthermore, the present inventors succeeded in producing bispecific antibodies that substitute for the enzyme reaction-accelerating function of blood coagulation factor VIII / activated blood coagulation factor VIII, which bind to both blood coagulation factor IX / activated blood coagulation factor IX and blood coagulation factor X.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Mature dendritic cell compositions and methods for culturing same
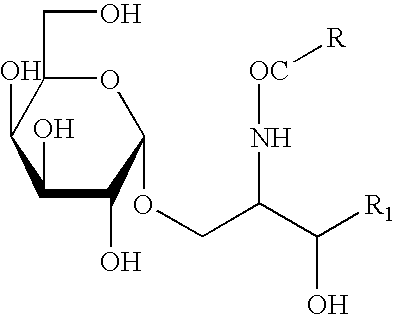
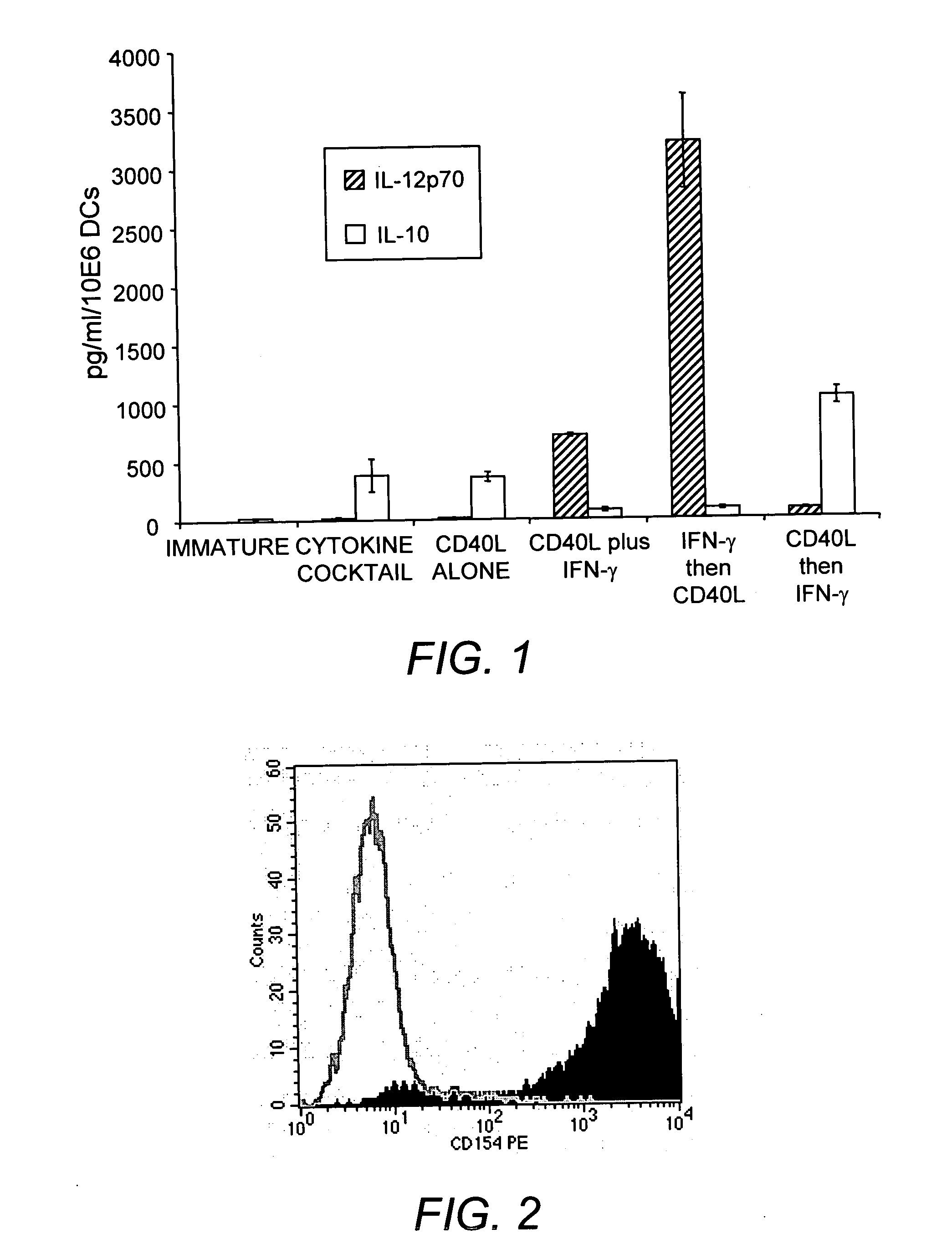
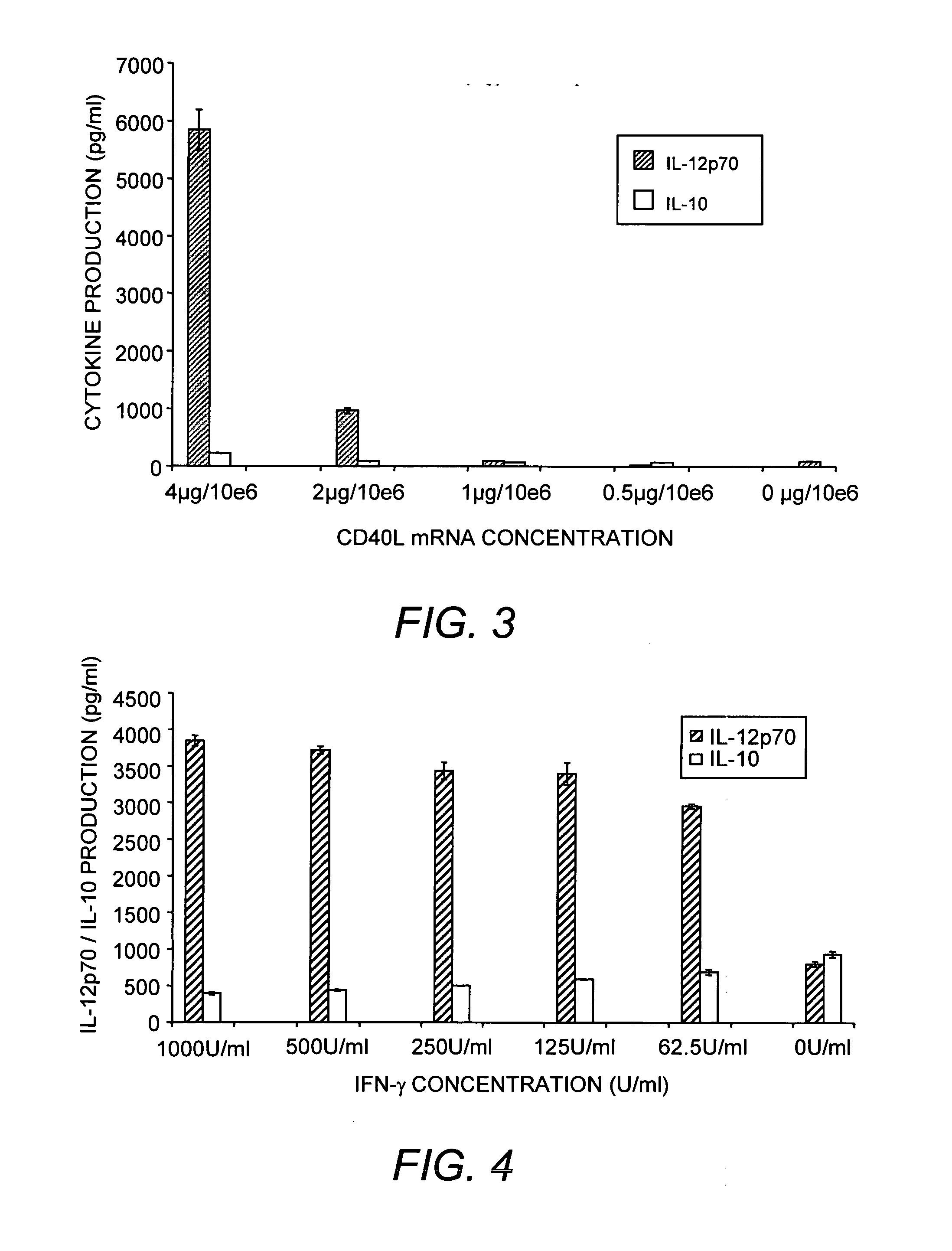
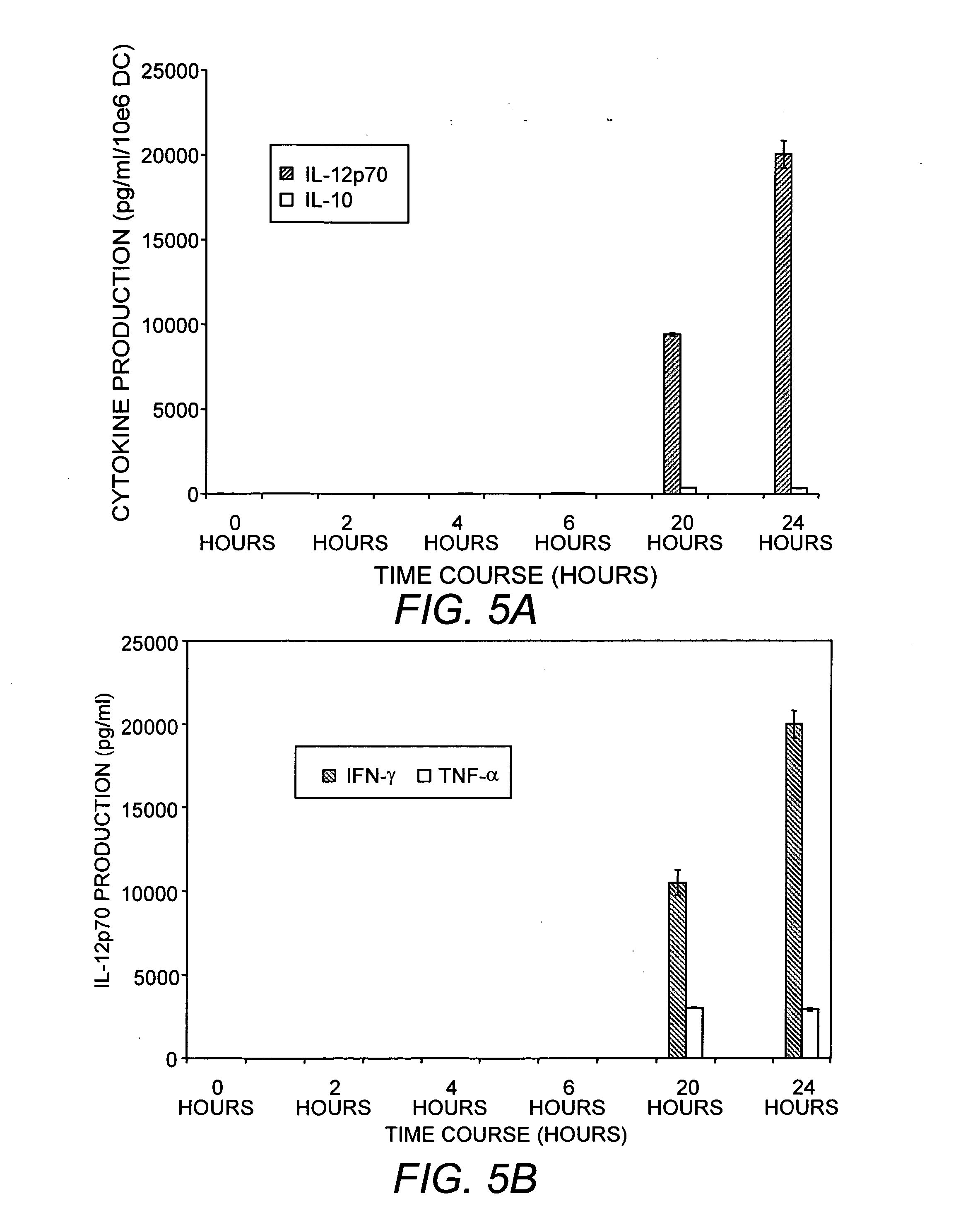
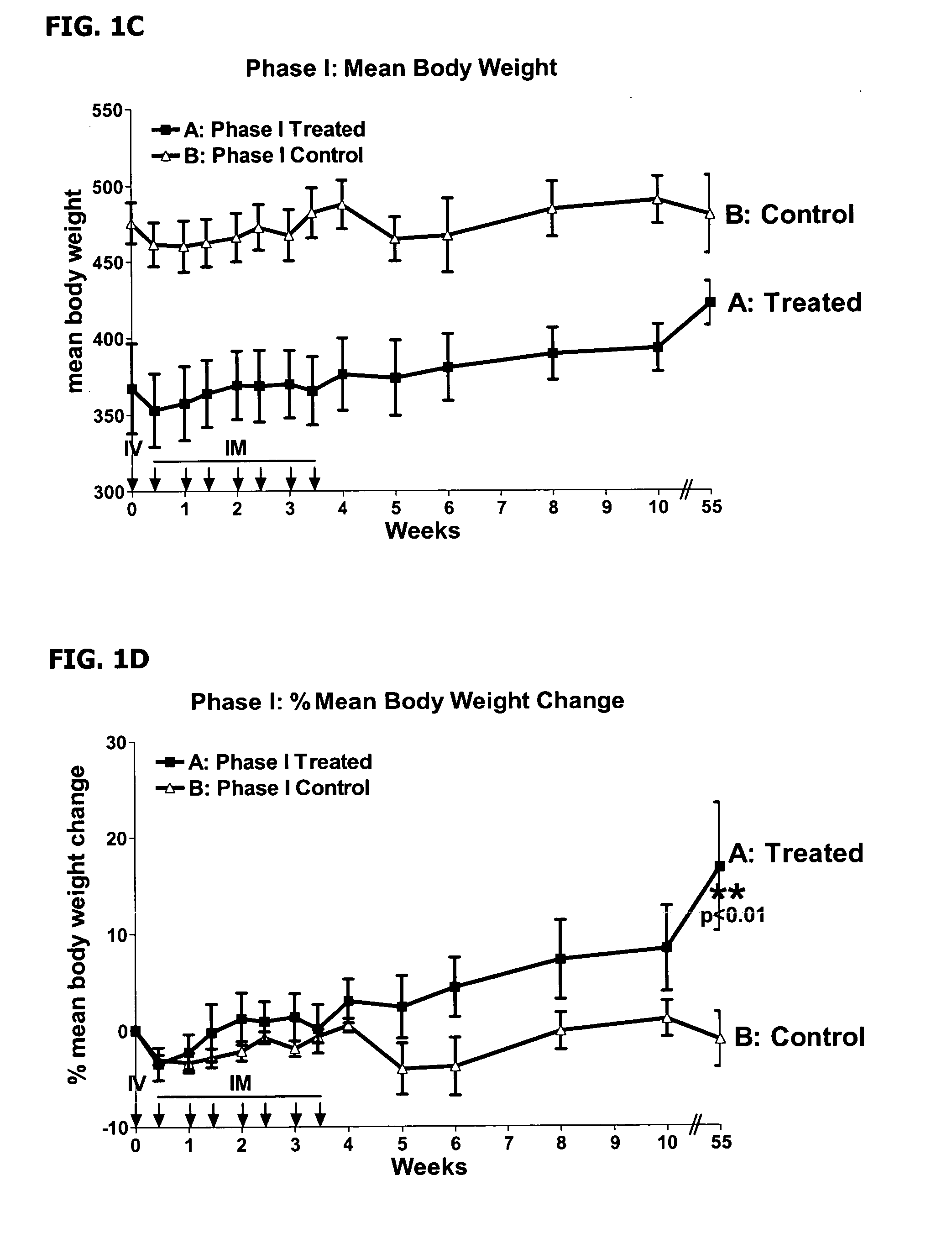
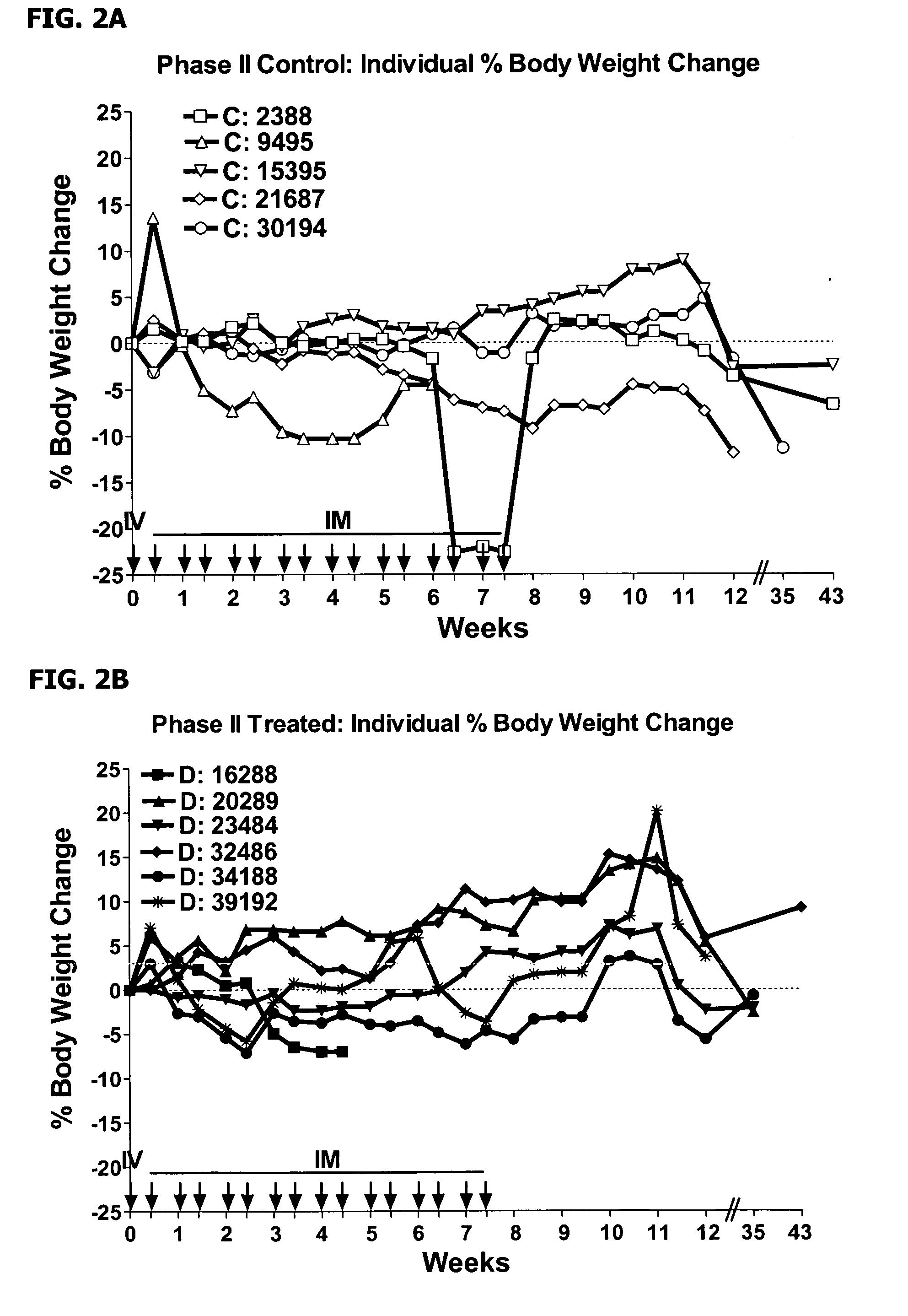
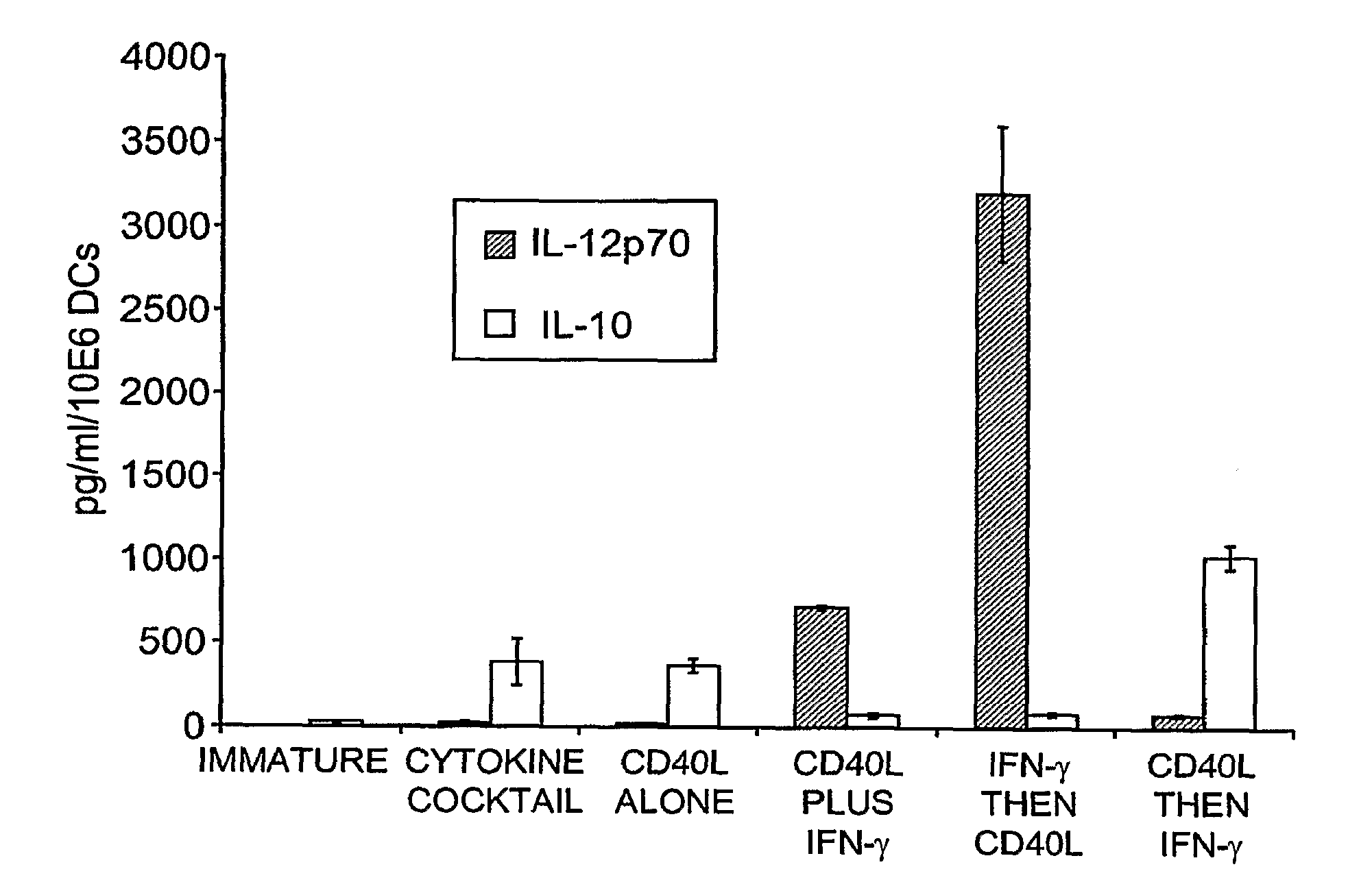
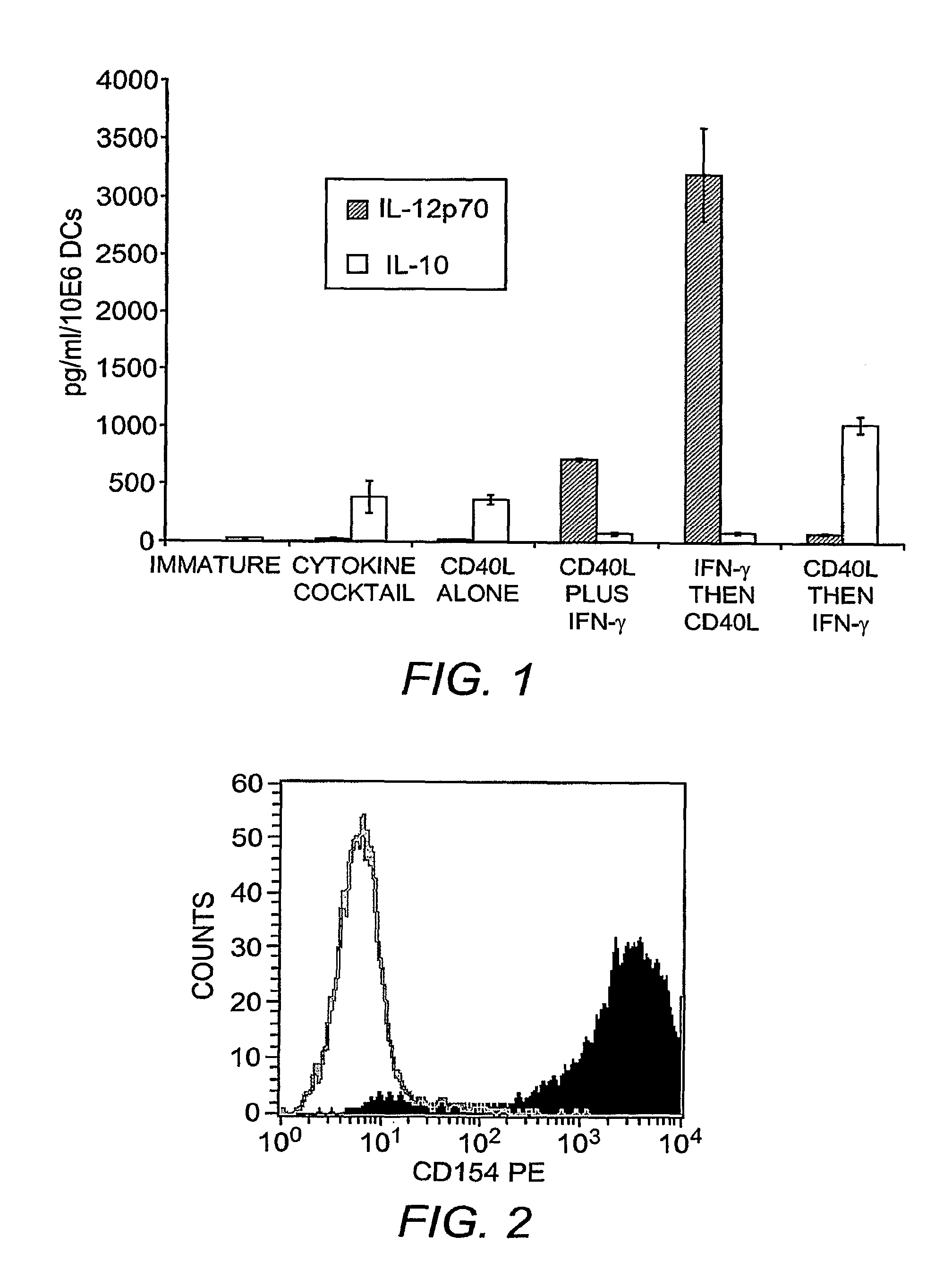
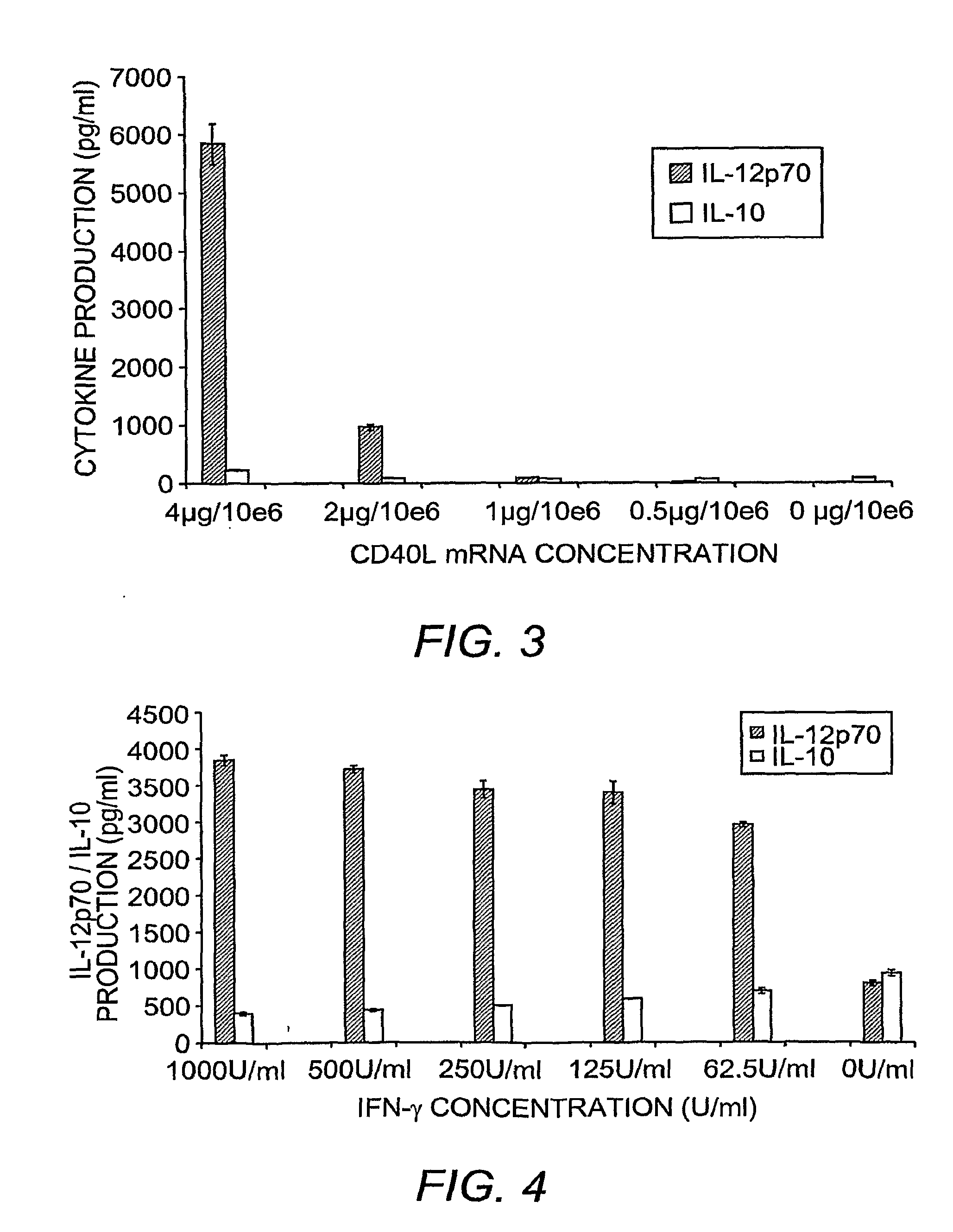
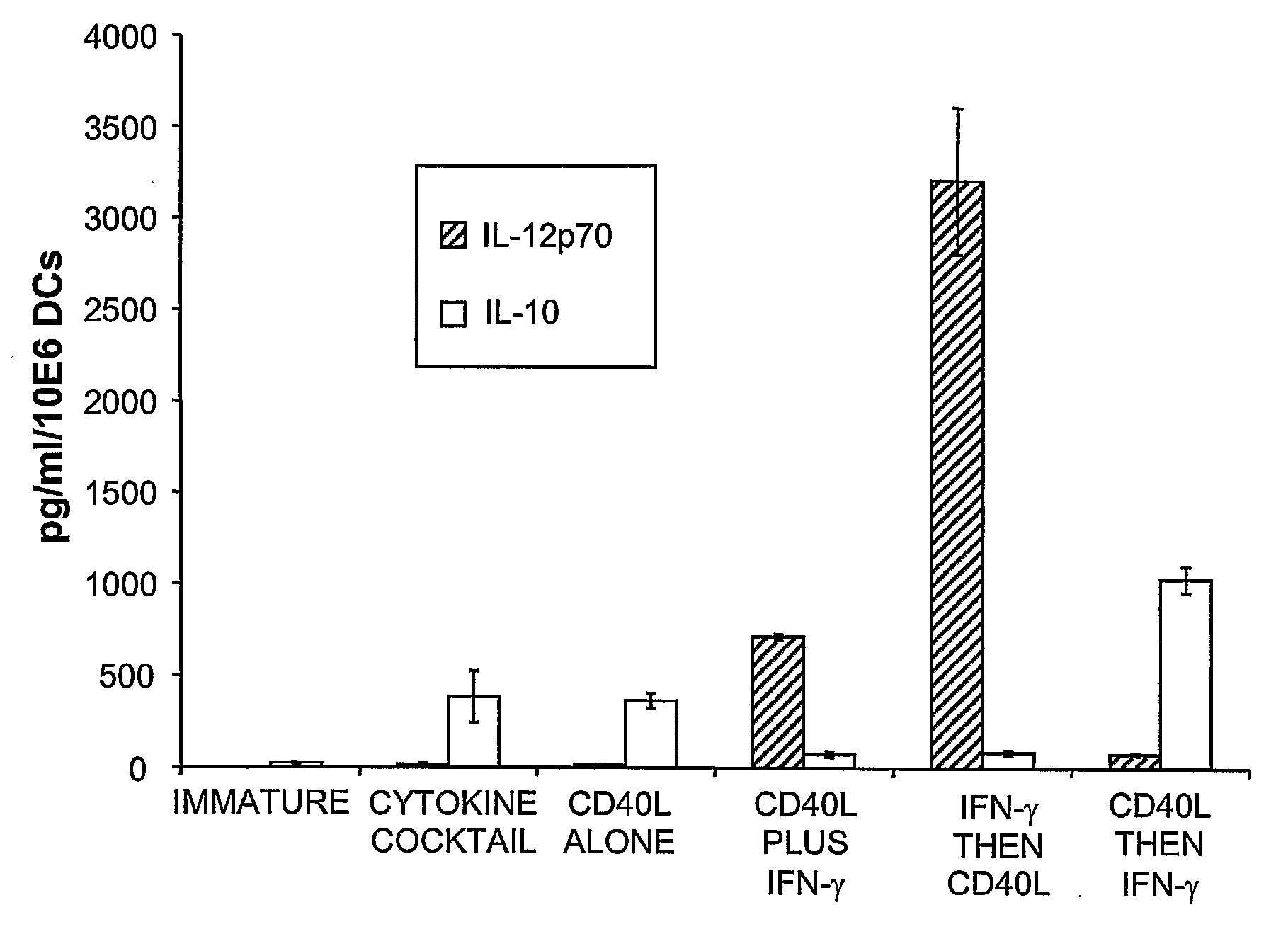
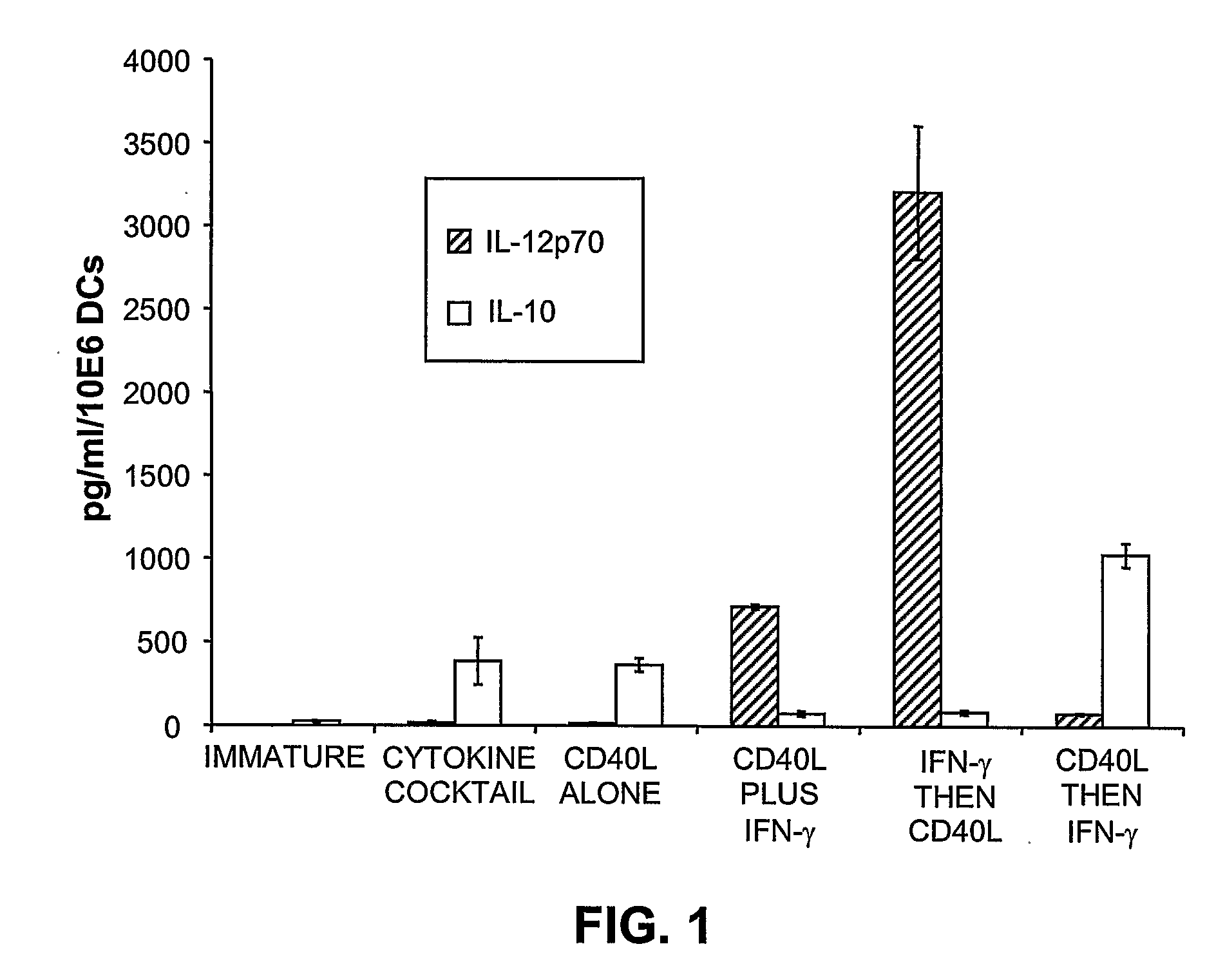
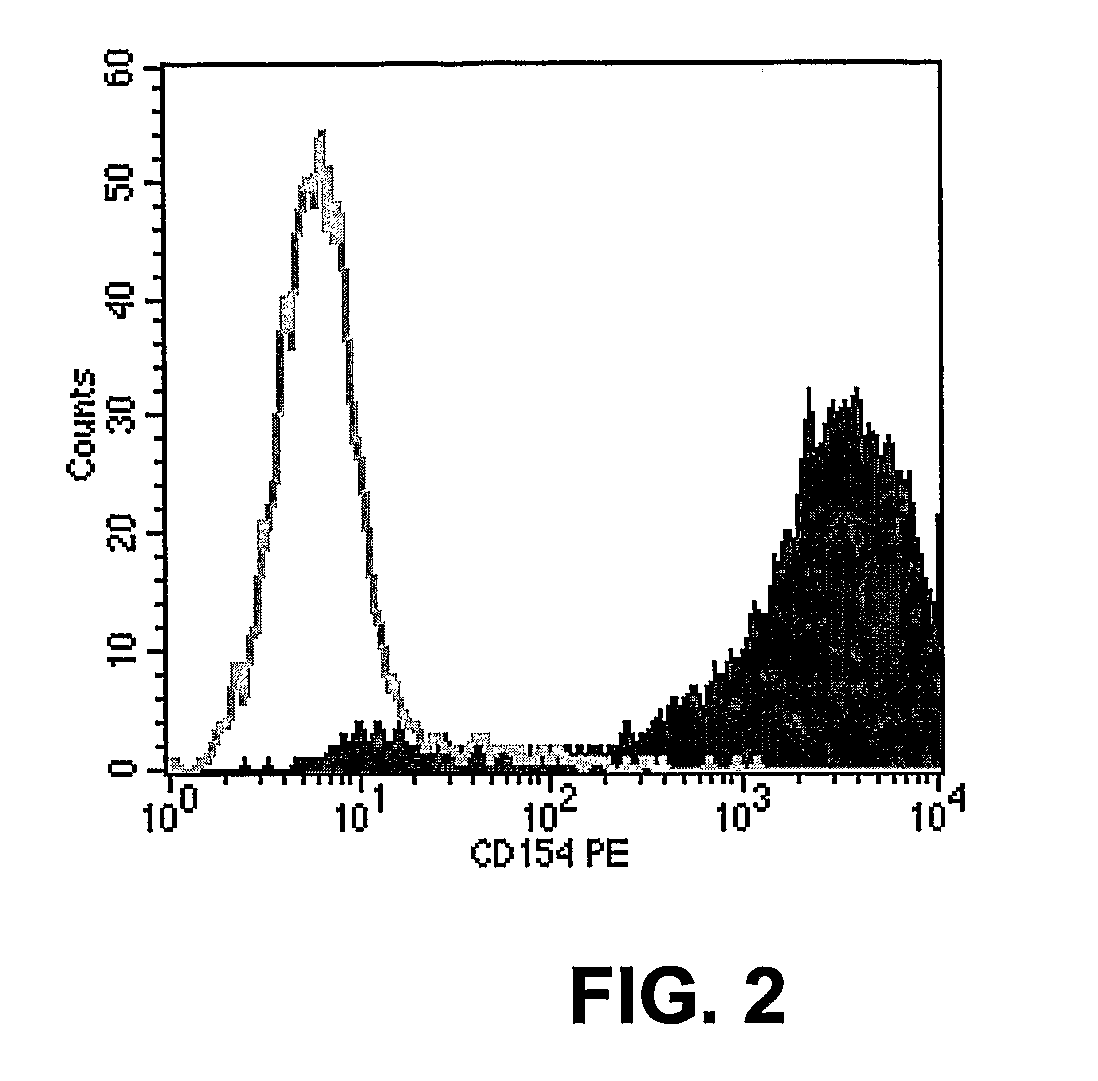
This invention provides methods to prepare and use immunostimulatory cells for enhancing an immune response. The invention provides a method for preparing mature dendritic cells (DCs), comprising the sequential steps of: (a) signaling isolated immature dendritic cells (iDCs) with a first signal comprising an interferon gamma receptor (IFN-γR) agonist and / or a tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor (TNF-αR) agonist to produce signaled dendritic cells; and (b) signaling said signaled dendritic cells with a second transient signal comprising an effective amount of a CD40 agonist to produce CCR7+ mature dendritic cells. Also provided by this invention are enriched populations of dendritic cells prepared by the methods of the invention. Such dendritic cells have enhanced immunostimulatory properties and increased IL-12 secretion and / or decreased IL-10 secretion. CD40 signaling can be initiated by one or more of polypeptide translated from an exogenous polynucleotide encoding CD40L (e.g., mRNA or DNA), an agonistic antibody to CD40 receptor or by CD40 ligand polypeptide. The enriched populations can be further modified by the administration of an immunogen to the DC. The DC will take up and process the immunogen on its cell surface.
Owner:COIMMUNE INC +1
Mature dendritic cell compositions and methods for culturing same
This invention provides methods to prepare and use immunostimulatory cells for enhancing an immune response. The invention provides a method for preparing mature dendritic cells (DCs), comprising the sequential steps of: (a) signaling isolated immature dendritic cells (iDCs) with a first signal comprising an interferon gamma receptor (IFN-γR) agonist and / or a tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor (TNF-αR) agonist to produce signaled dendritic cells; and (b) signaling said signaled dendritic cells with a second transient signal comprising an effective amount of a CD40 agonist to produce CCR7+ mature dendritic cells. Also provided by this invention are enriched populations of dendritic cells prepared by the methods of the invention. Such dendritic cells have enhanced immunostimulatory properties and increased IL-12 secretion and / or decreased IL-10 secretion. CD40 signaling can be initiated by one or more of polypeptide translated from an exogenous polynucleotide encoding CD40L (e.g., mRNA or DNA), an agonistic antibody to CD40 receptor or by CD40 ligand polypeptide. The enriched populations can be further modified by the administration of an immunogen to the DC. The DC will take up and process the immunogen on its cell surface.
Owner:COIMMUNE INC +1
Interferon alpha receptor 1 antibodies and their uses
ActiveUS20060029601A1Inhibit biological activityNervous disorderAntipyreticTransplant rejectionGraft versus host disease induction
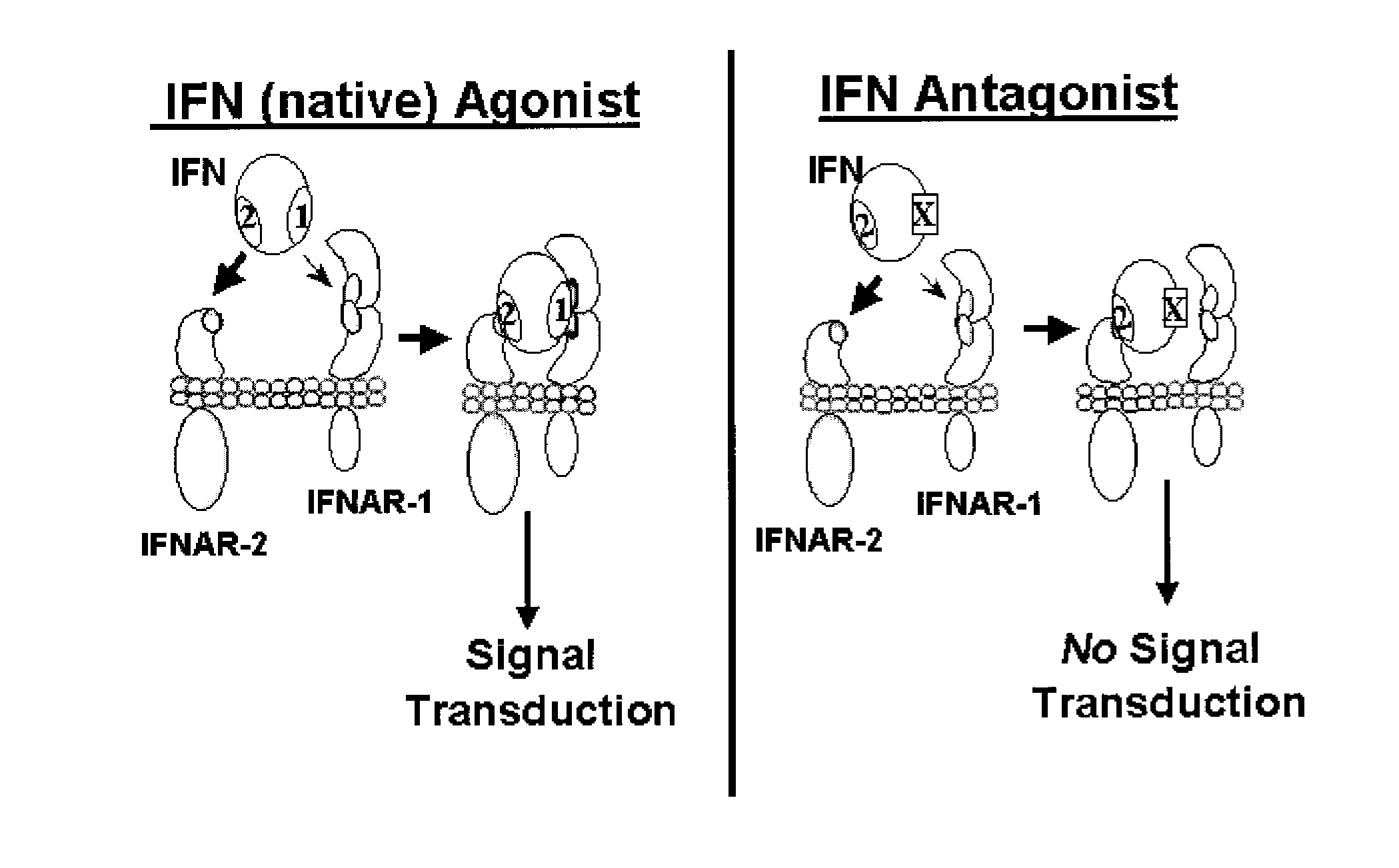
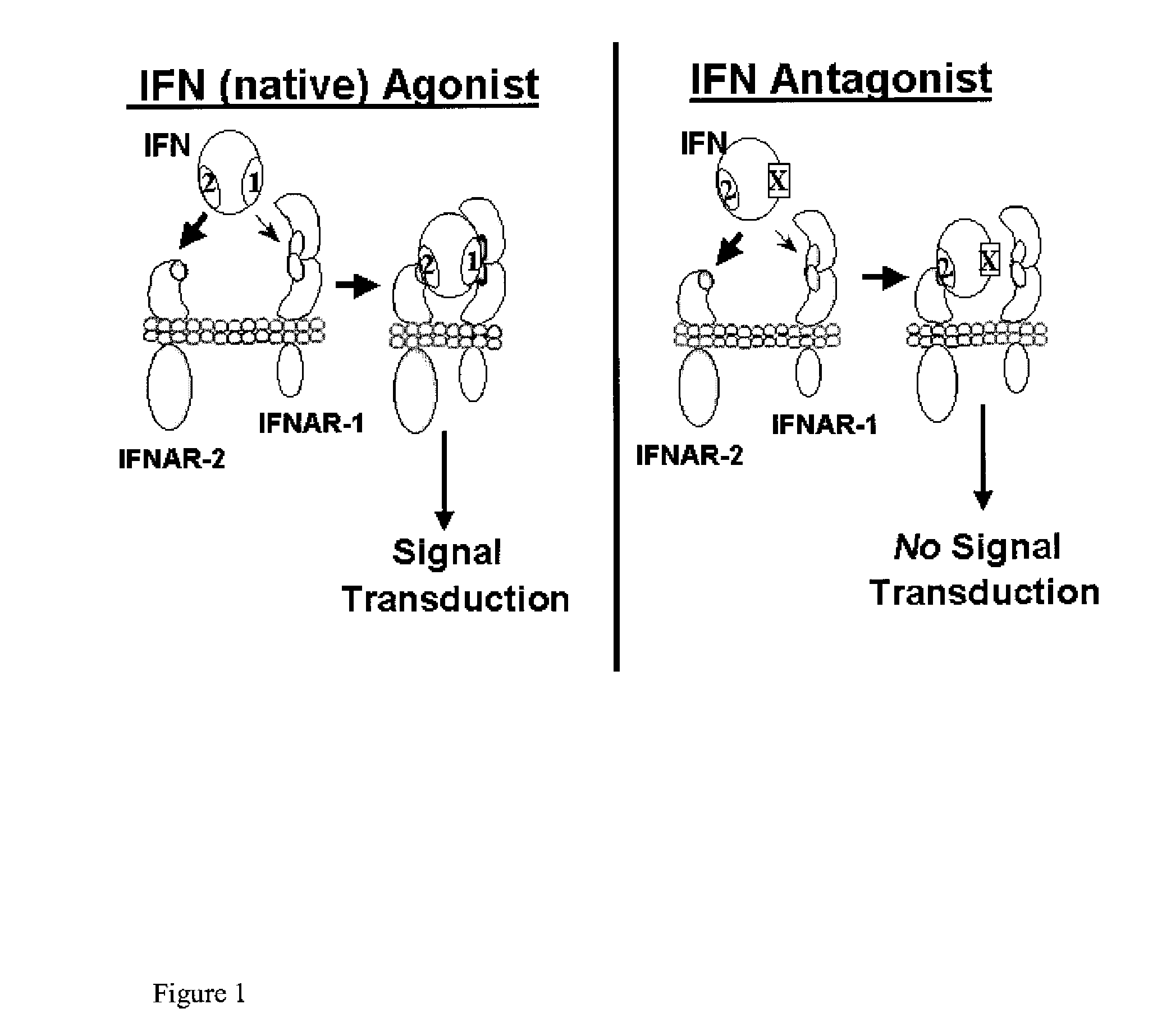
The present invention provides isolated human monoclonal antibodies that bind to IFNAR-1 and that are capable of inhibiting the biological activity of Type I interferons. Immunoconjugates, bispecific molecules and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies of the invention are also provided. The invention also provides methods for inhibiting Type I interferon-mediated disorders using the antibodies of the invention, including methods for treating autoimmune disorders, transplant rejection or Graft Versus Host Disease using the antibodies of the invention.
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Synthetic hyperglycosylated, and hyperglycosylated protease-resistant polypeptide variants, oral formulations and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20060204473A1Increased protease resistanceNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid typeInterferon receptor
The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites. The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites, as well as erythropoietin and darbepoetin alfa, each of which are linked to a penetrating peptide that facilitates translocation of a substance across a biological barrier as well as pharmaceutical compositions, including oral formulations, of the same. The present invention further provides oral formulations of hyperglycosylated or protease-resistant, hyperglycosylated polypeptide variants, which polypeptide variants lack at least one protease cleavage site found in a parent polypeptide, and thus exhibit increased protease resistance compared to the parent polypeptide, which polypeptide variants further include (1) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one non-native glycosylation site not found in the parent protein therapeutic or (2) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one native glycosylation site found but not glycosylated in the parent protein therapeutic. The present invention further provides compositions, including oral pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides containers, devices, and kits comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides therapeutic methods involving administering an effective amount of an oral pharmaceutical composition comprising a synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, a hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or a hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:ALIOS BIOPHARMA INC +1
Type I Interferon Antagonists
InactiveUS20110224407A1Binding affinityLow affinityDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsInterferon receptorCancer research
Disclosed in certain embodiments is a method of preparing a Type 1 interferon antagonist comprising modifying a Type 1 interferon at the site of interaction with the interferon receptor subunit IFNAR-1 such that the binding affinity of the interferon to the IFNAR-1 subunit is reduced as compared to the native interferon, and corresponding compositions and methods of treatment thereof.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD +1
Combination therapy for treating alphavirus infection and liver fibrosis
InactiveUS20070072181A1Improve liver functionReduce morbidityOrganic active ingredientsImpression capsMortality rateInterferon receptor
The present invention provides methods for treating alphavirus infections; methods of treating hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections; methods of treating West Nile virus infection; methods of reducing liver fibrosis; methods of increasing liver function in an individual suffering from liver fibrosis; methods of reducing the incidence of complications associated with HCV and cirrhosis of the liver; and methods of reducing viral load, or reducing the time to viral clearance, or reducing morbidity or mortality in the clinical outcomes, in patients suffering from viral infection. The methods generally involve administering effective amounts of an interferon receptor agonist and pirfenidone in combination therapy.
Owner:THREE RIVERS PHARMA LLC
Synthetic hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variants, oral formulations and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20060182716A1Skeletal disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsInterferon receptorCarbohydrate moiety
The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites. The present invention further provides oral formulations of protease-resistant or protease-resistant, hyperglycosylated polypeptide variants, which polypeptide variants lack at least one protease cleavage site found in a parent polypeptide, and thus exhibit increased protease resistance compared to the parent polypeptide, which polypeptide variants further include (1) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one non-native glycosylation site not found in the parent protein therapeutic or (2) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one native glycosylation site found but not glycosylated in the parent protein therapeutic. The present invention further provides compositions, including oral pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, the protease-resistant polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides containers, devices, and kits comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, the protease-resistant polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides therapeutic methods involving administering an effective amount of an oral pharmaceutical composition comprising a synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, a hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, a protease-resistant polypeptide variant, or a hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:LAWRENCE M BLATT +1
Hyperglycosylated polypeptide variants and methods of use
The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites. The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites, as well as erythropoietin and darbepoetin alfa, each of which are linked to a penetrating peptide that facilitates translocation of a substance across a biological barrier as well as pharmaceutical compositions, including oral formulations, of the same. The present invention further provides oral formulations of hyperglycosylated or protease-resistant, hyperglycosylated polypeptide variants, which polypeptide variants lack at least one protease cleavage site found in a parent polypeptide, and thus exhibit increased protease resistance compared to the parent polypeptide, which polypeptide variants further include (1) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one non-native glycosylation site not found in the parent protein therapeutic or (2) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one native glycosylation site found but not glycosylated in the parent protein therapeutic. The present invention further provides compositions, including oral pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides containers, devices, and kits comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides therapeutic methods involving administering an effective amount of an oral pharmaceutical composition comprising a synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, a hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or a hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:ALIOS BIOPHARMA INC +1
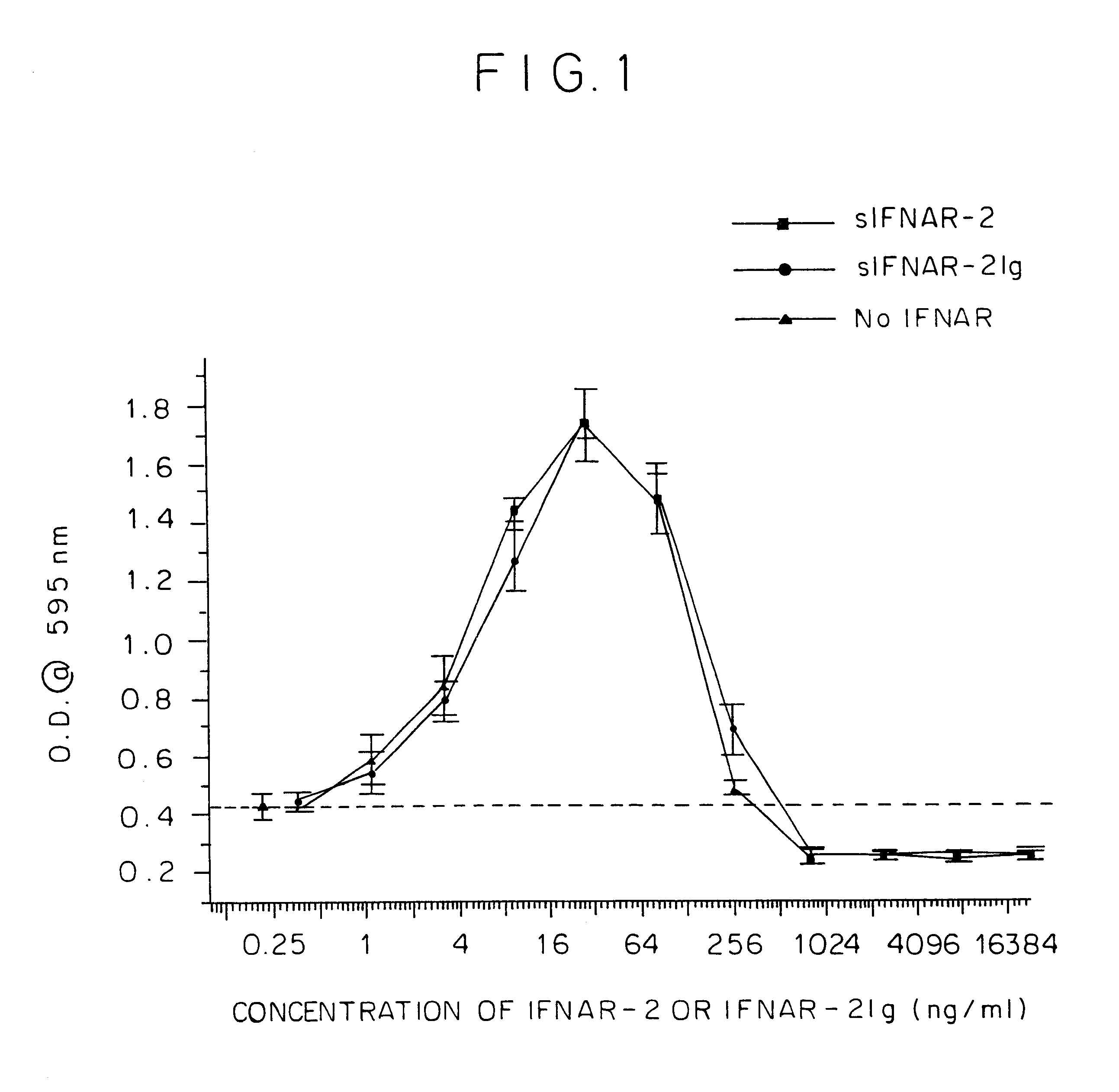
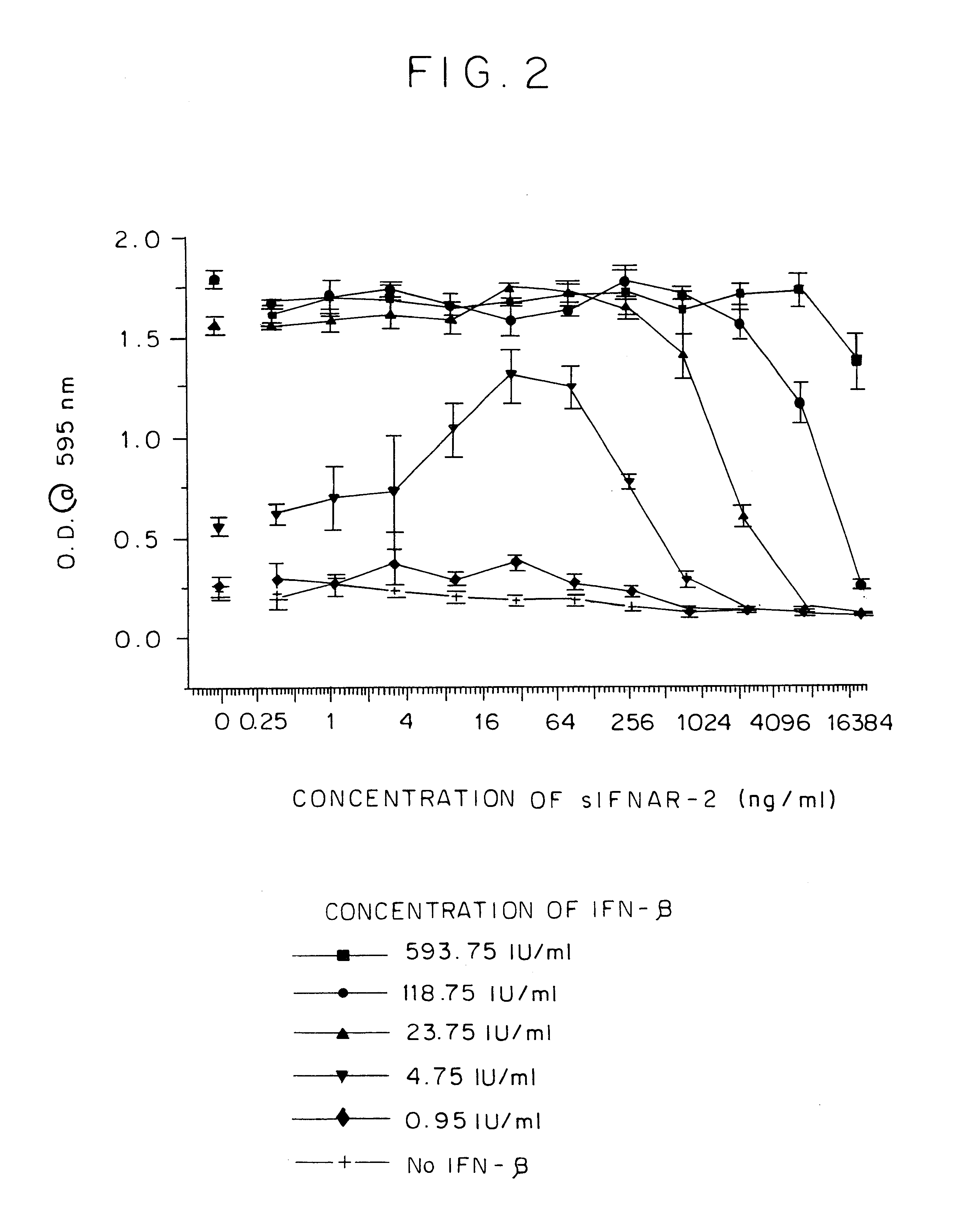
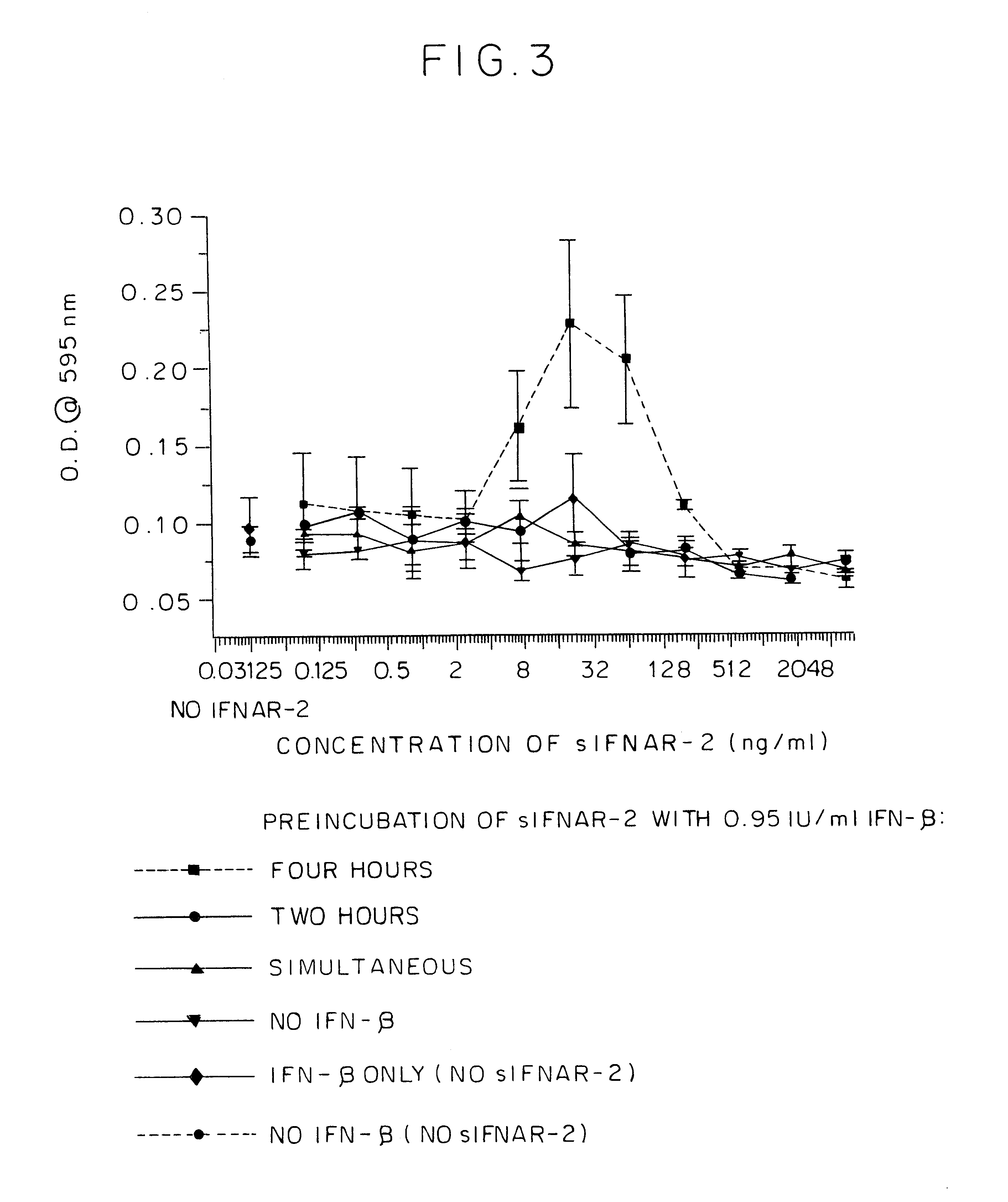
IFNAR2/IFN complex
The in vivo effect of Type I interferon (IFN) can be prolonged by administering the interferon in the form of a complex with an IFN binding chain of the human interferon alpha / beta receptor (IFNAR). Such a complex also improves the stability of the IFN and enhances the potency of the IFN. The complex may be a non-covalent complex or one in which the IFN and the IFNAR are bound by a covalent bond or a peptide. When bound by a peptide bond in the form of a fusion protein, the IFN may be separated from the IFNAR by means of a peptide linker. Such a fusion protein may be produced by recombinant DNA technology. Storing IFN in the form of such a complex improves the storage life of the IFN and permits storage under milder conditions than would otherwise be possible.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
Compositions and methods for the therapy of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
InactiveUS20050152901A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsUlcerative colitisInterferon receptor
Compositions and methods for the therapy of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), including Celiac Disease, Crohn's Disease, and Ulcerative Colitis, are disclosed. Illustrative compositions comprise one or more anti-type 1 interferon antagonists, such as anti-type 1 interferon receptor antibody antagonists and fragments thereof, as well as polypeptides and small molecules that inhibit the interaction of type 1 interferon with its receptor (IFNAR).
Owner:ER SQUIBB & SONS INC
Mature Dendritic Cell Compositions and Methods of Culturing Same
InactiveUS20120269832A1Mammal material medical ingredientsBlood/immune system cellsDendritic cellInterferon-gamma receptor
This invention provides novel CD40L polypeptides and nucleic acids, as well as antigen presenting cells and vaccines comprising such CD40L polypeptides and / or nucleic acids, and related methods for preparing the antigen presenting cells and vaccines. The antigen presenting cells and vaccines are useful for enhancing an immune response. The invention provides a method for preparing mature dendritic cells (DCs), comprising the sequential steps of: (a) signaling isolated immature dendritic cells (iDCs) with a first signal comprising an interferon gamma receptor (IFN-?R) agonist and / or a tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor (TNF-?R) agonist to produce signaled dendritic cells; and (b) signaling said signaled dendritic cells with a second transient signal comprising an effective amount of a CD40 agonist to produce CCR7+ mature dendritic cells. Also provided by this invention are enriched populations of dendritic cells prepared by the methods of the invention. Such dendritic cells have enhanced immunostimulatory properties and increased IL-12 secretion and / or decreased IL-10 secretion. CD40 signaling can be initiated by one or more of polypeptide translated from an exogenous polynucleotide encoding CD40L (e.g., mRNA or DNA), an agonistic antibody to CD40 receptor or by CD40 ligand polypeptide. The enriched populations can be further modified by the administration of an immunogen to the DC. The DC will take up and process the immunogen on its cell surface.
Owner:COIMMUNE INC
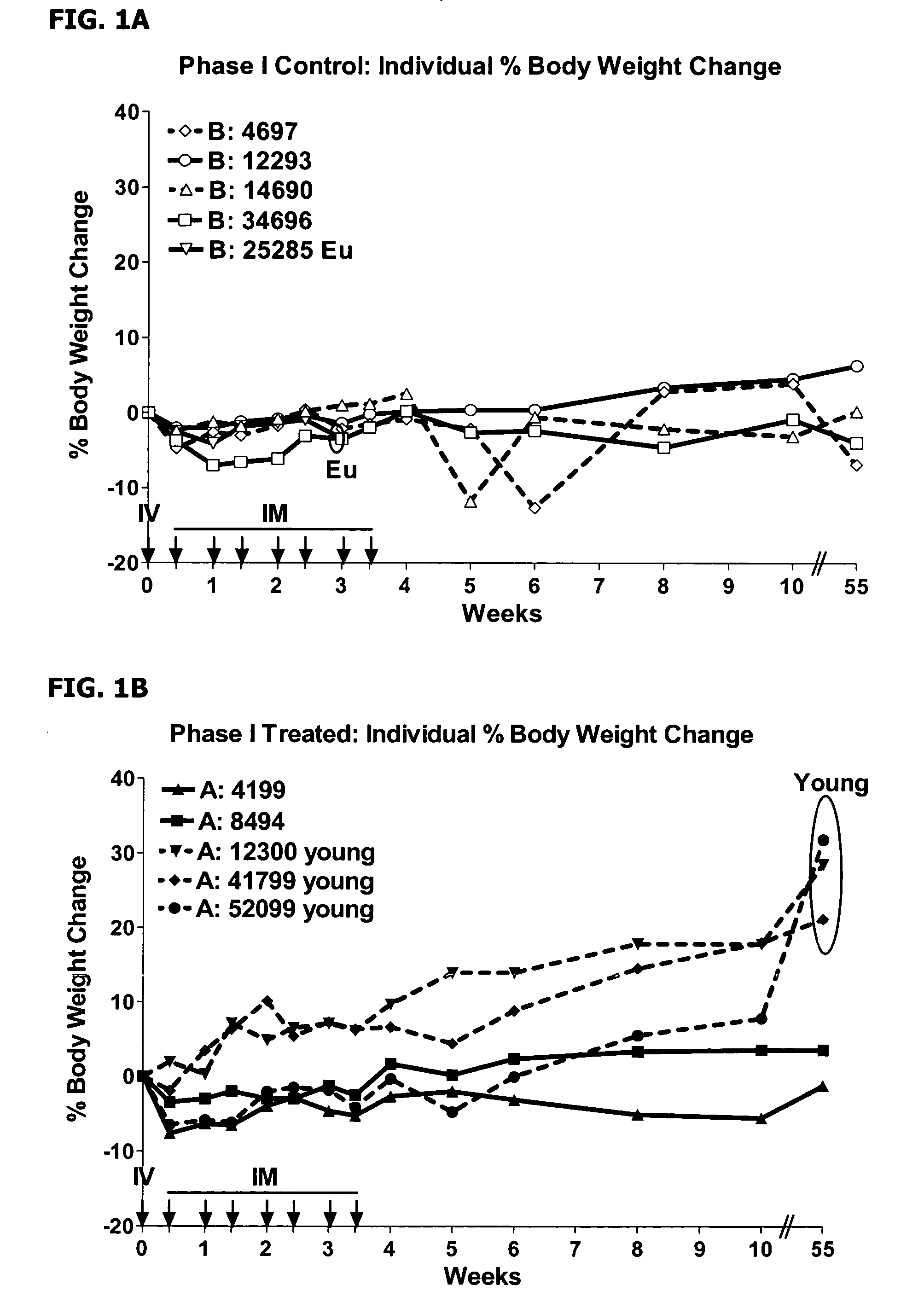
Targeted human-interferon fusion proteins
ActiveUS9492562B2Low affinityDecrease of bioactivityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsLow affinityDisease
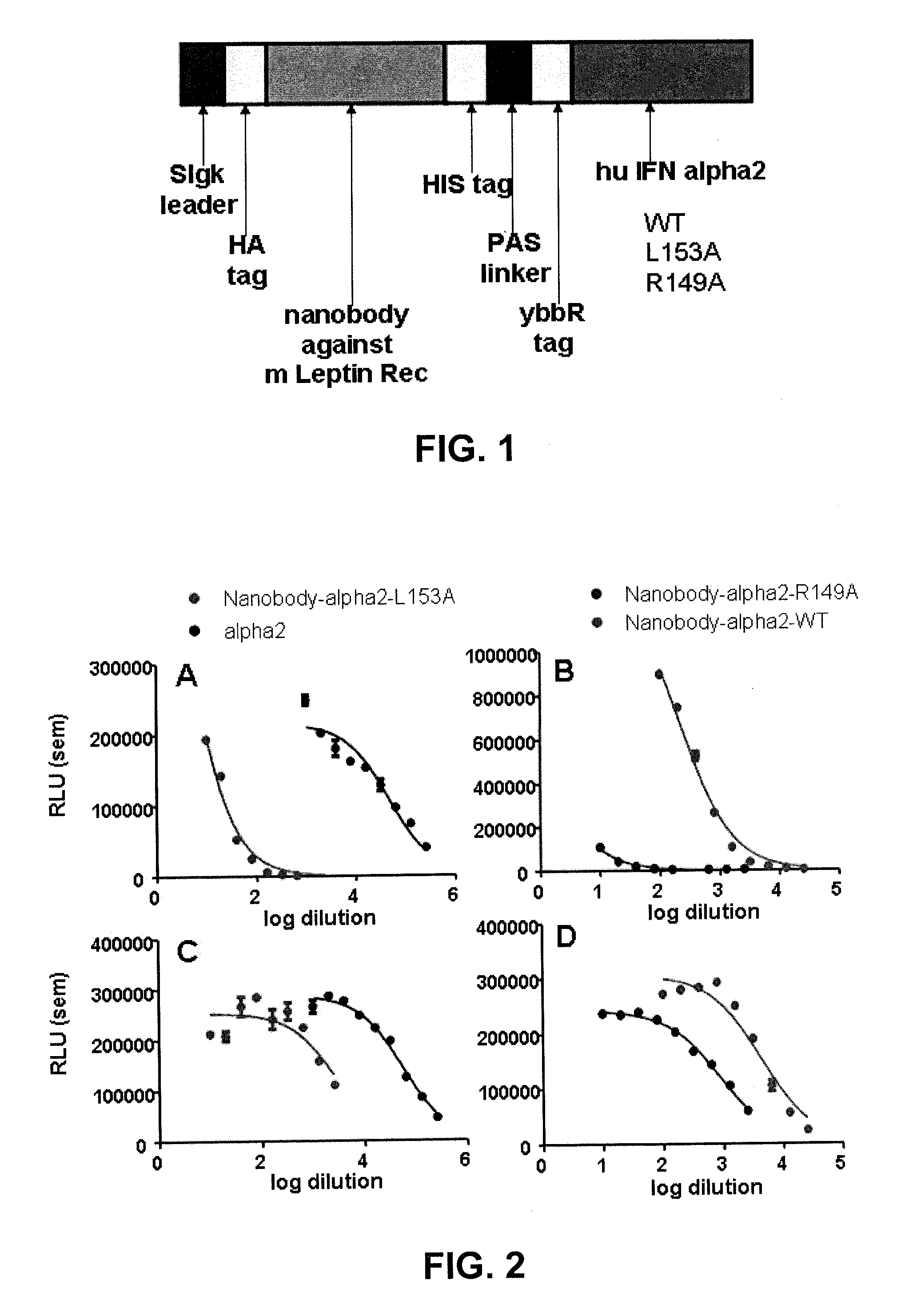
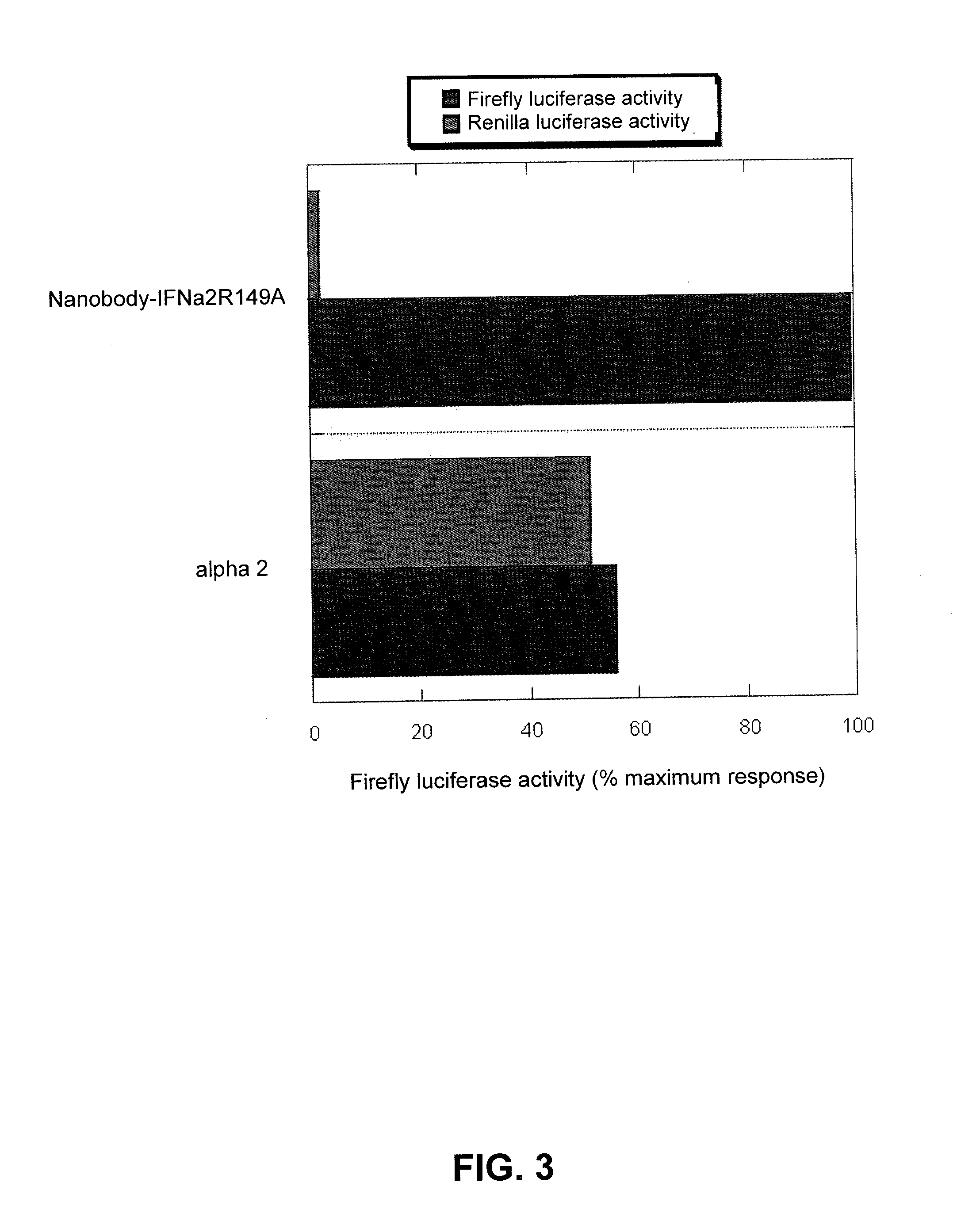
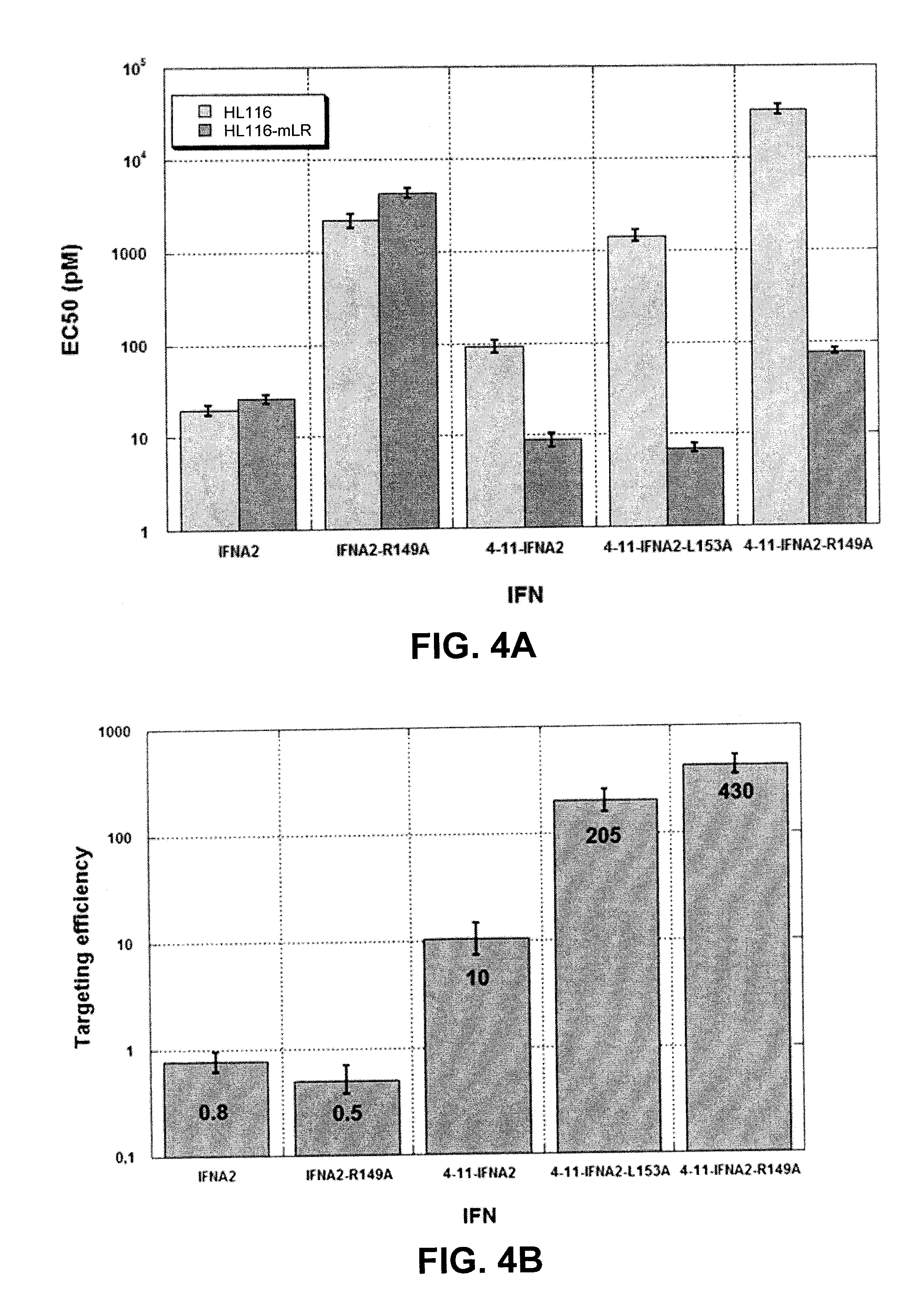
This disclosure relates to a modified α-helical bundle cytokine, with reduced activity via an α-helical bundle cytokine receptor, wherein the α-helical bundle cytokine is specifically delivered to target cells. Preferably, the α-helical bundle cytokine is a mutant, more preferably it is a mutant interferon, with low affinity to the interferon receptor, wherein the mutant interferon is specifically delivered to target cells. The targeting is realized by fusion of the modified α-helical bundle cytokine to a targeting moiety, preferably an antibody. This disclosure relates further to the use of such targeted modified α-helical bundle cytokine to treat diseases. A preferred embodiment is the use of a targeted mutant interferon, to treat diseases, preferably viral diseases and tumors.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +4
Mature Dendritic Cell Compositions and Methods of Culturing Same
InactiveUS20080145931A1Genetically modified cellsCulture processDendritic cellInterferon-gamma receptor
This invention provides methods to prepare and use immunostimulatory cells for enhancing an immune response. The invention provides a method for preparing mature dendritic cells (DCs), comprising the sequential steps of: (a) signaling isolated immature dendritic cells (iDCs) with a first signal comprising an interferon gamma receptor (IFN-γR) agonist and / or a tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor (TNF-αR) agonist to produce signaled dendritic cells; and (b) signaling said signaled dendritic cells with a second transient signal comprising an effective amount of a CD40 agonist to produce CCR7+ mature dendritic cells. Also provided by this invention are enriched populations of dendritic cells prepared by the methods of the invention. Such dendritic cells have enhanced immunostimulatory properties and increased IL-12 secretion and / or decreased IL-10 secretion. CD40 signaling can be initiated by one or more of polypeptide translated from an exogenous polynucleotide encoding CD40L (e.g., mRNA or DNA), an agonistic antibody to CD40 receptor or by CD40 ligand polypeptide. The enriched populations can be further modified by the administration of an immunogen to the DC. The DC will take up and process the immunogen on its cell surface.
Owner:KIRIN BREWERY CO LTD +1
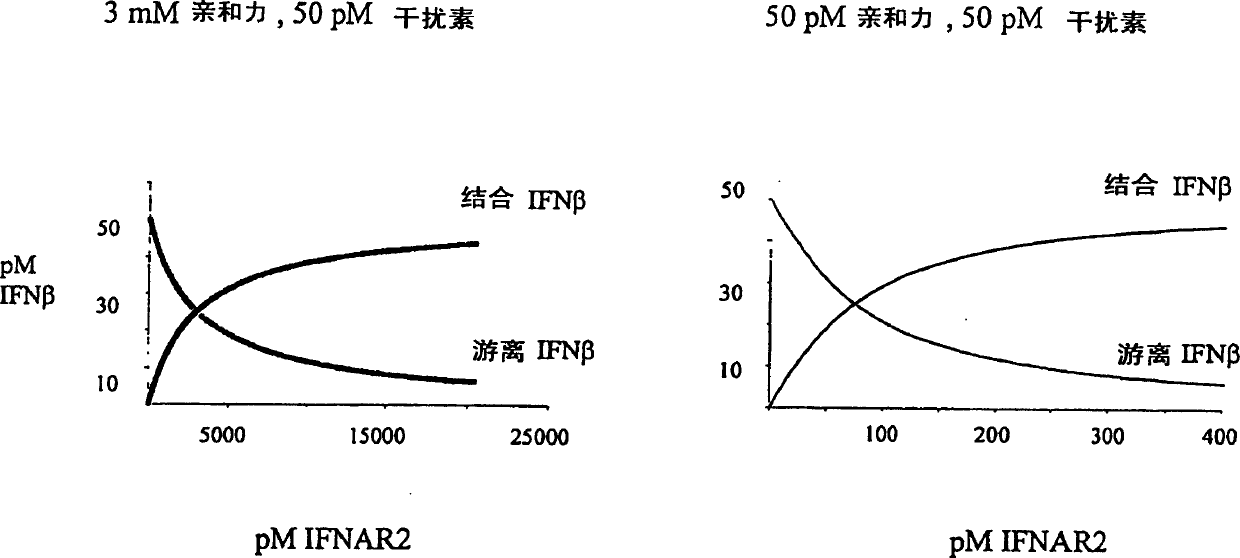
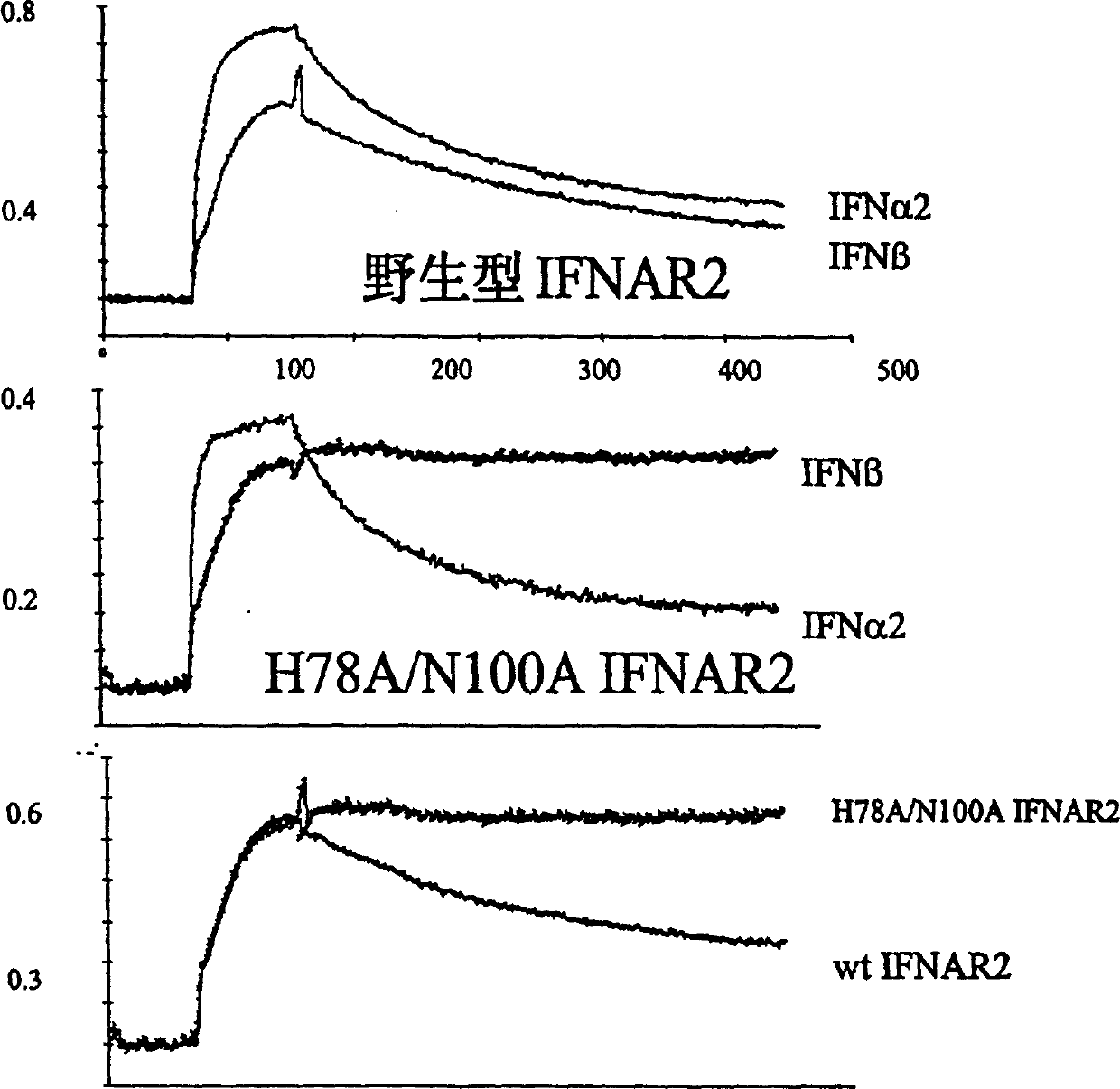
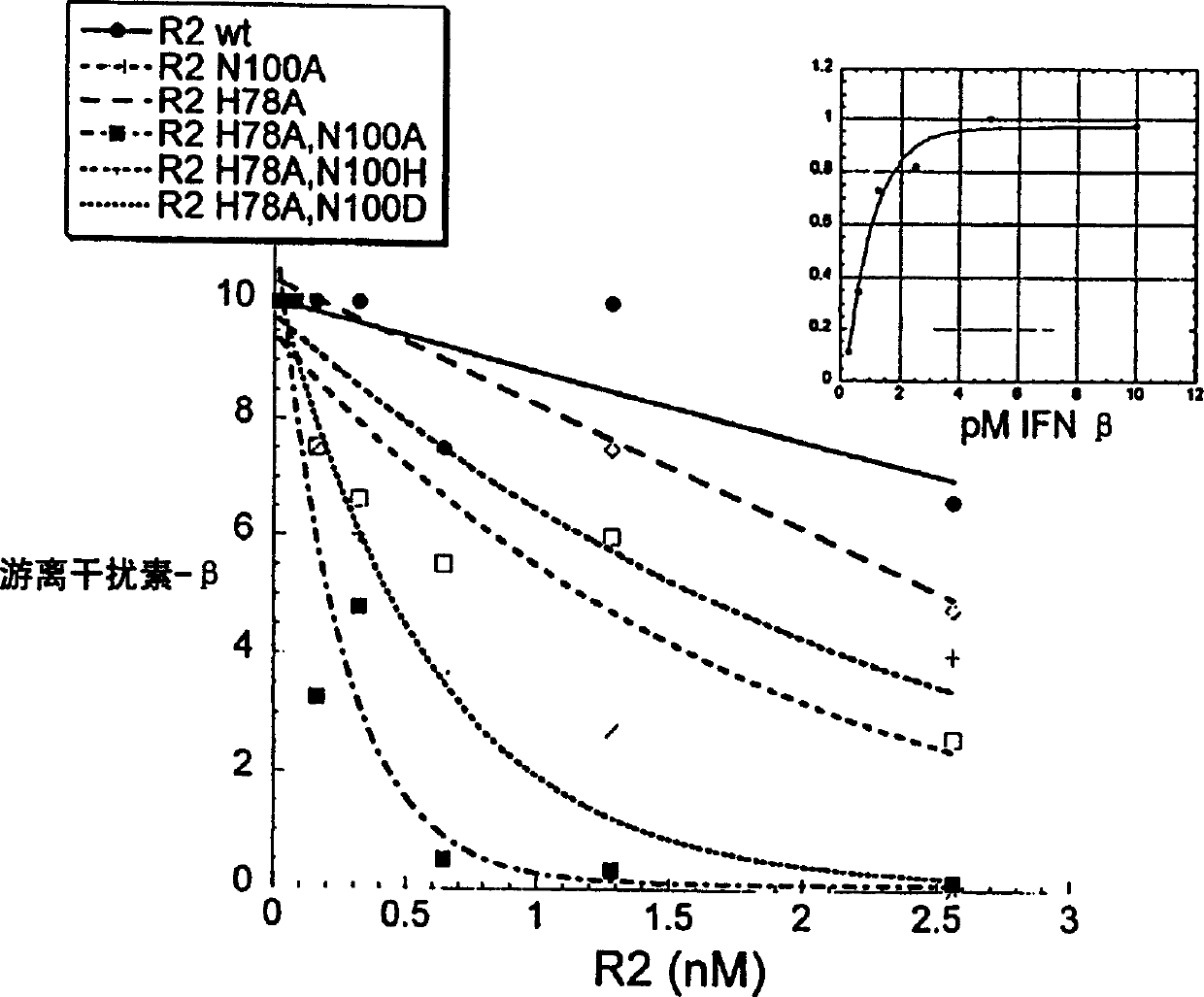
IFNAR2 mutants, their production and use
The present invention relates to mutant polypeptides of the beta chain of the type I interferon receptor (MIFNAR2) with enhanced affinity for interferon-beta, which prolong the in vivo action of IFN-beta compared to the wild-type protein.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Combination Therapy for Treating Hepatitis C Virus Infection
InactiveUS20070258946A1Reduce morbidityReduce viral loadPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsMortality rateInterferon receptor
The present invention provides methods of treating hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection; methods of reducing the incidence of complications associated with HCV and cirrhosis of the liver; and methods of reducing viral load, or reducing the time to viral clearance, or reducing morbidity or mortality in the clinical outcomes, in patients suffering from HCV infection. The methods generally involve administering to the individual i) a Type I interferon receptor agonist or a Type III interferon receptor agonist; ii) an immunomodulatory agent; and iii) an inhibitor of an HCV enzyme.
Owner:THREE RIVERS PHARMA LLC
Preparation method of anti-human IFNAR1 monoclonal antibody concentrated solution
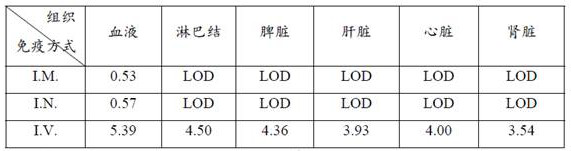
ActiveCN113527490ALow viscosityHigh recovery rateImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide preparation methodsHigh concentrationAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses a preparation method of an anti-human IFNAR1 monoclonal antibody concentrated solution, which comprises the following steps: first ultrafiltration concentration: concentrating a solution containing an anti-human interferon alpha receptor 1 (IFNAR1) monoclonal antibody until the protein concentration is 20-60mg / ml under the conditions that the flow rate is 120-300L / m<2>.h and the transmembrane differential pressure (TMP) is 0.6-1.5 bar, so as to obtain a concentrated sample; ultrafiltration replacement: replacing the concentrated sample with a replacement buffer solution, and obtaining an ultrafiltration replacement solution when the usage amount of the replacement buffer solution is 6-10 times of the weight of the concentrated sample; and second ultrafiltration concentration: uniformly mixing the ultrafiltration replacement solution and the alkaline amino acid mother liquor to enable the concentration of amino acid to be 100-150mM, and performing ultrafiltration concentration to obtain a concentrated solution with the protein concentration of 100-200mg / ml. According to the preparation method, the viscosity of the high-concentration antibody liquid medicine can be reduced, the stability can be improved, the method is simple and easy to implement, large-scale production can be carried out, the high purity of a sample can be guaranteed, and the high recovery rate can be obtained.
Owner:QYUNS THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Synthetic hyperglycosylated, and hyperglycosylated protease-resistant polypeptide variants, oral formulations and methods of using the same
The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites. The present invention further provides oral formulations of protease-resistant or protease-resistant, hyperglycosylated polypeptide variants, which polypeptide variants lack at least one protease cleavage site found in a parent polypeptide, and thus exhibit increased protease resistance compared to the parent polypeptide, which polypeptide variants further include (1) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one non-native glycosylation site not found in the parent protein therapeutic or (2) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one native glycosylation site found but not glycosylated in the parent protein therapeutic. The present invention further provides compositions, including oral pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, the protease-resistant polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides containers, devices, and kits comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, the protease-resistant polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides therapeutic methods involving administering an effective amount of an oral pharmaceutical composition comprising a synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, a hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, a protease-resistant polypeptide variant, or a hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:ALIOS BIOPHARMA INC
Human interferon alpha receptor binding related site mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111499718AStrong activation effectHigh induction effectPeptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemInterferon receptorHepatitis B virus
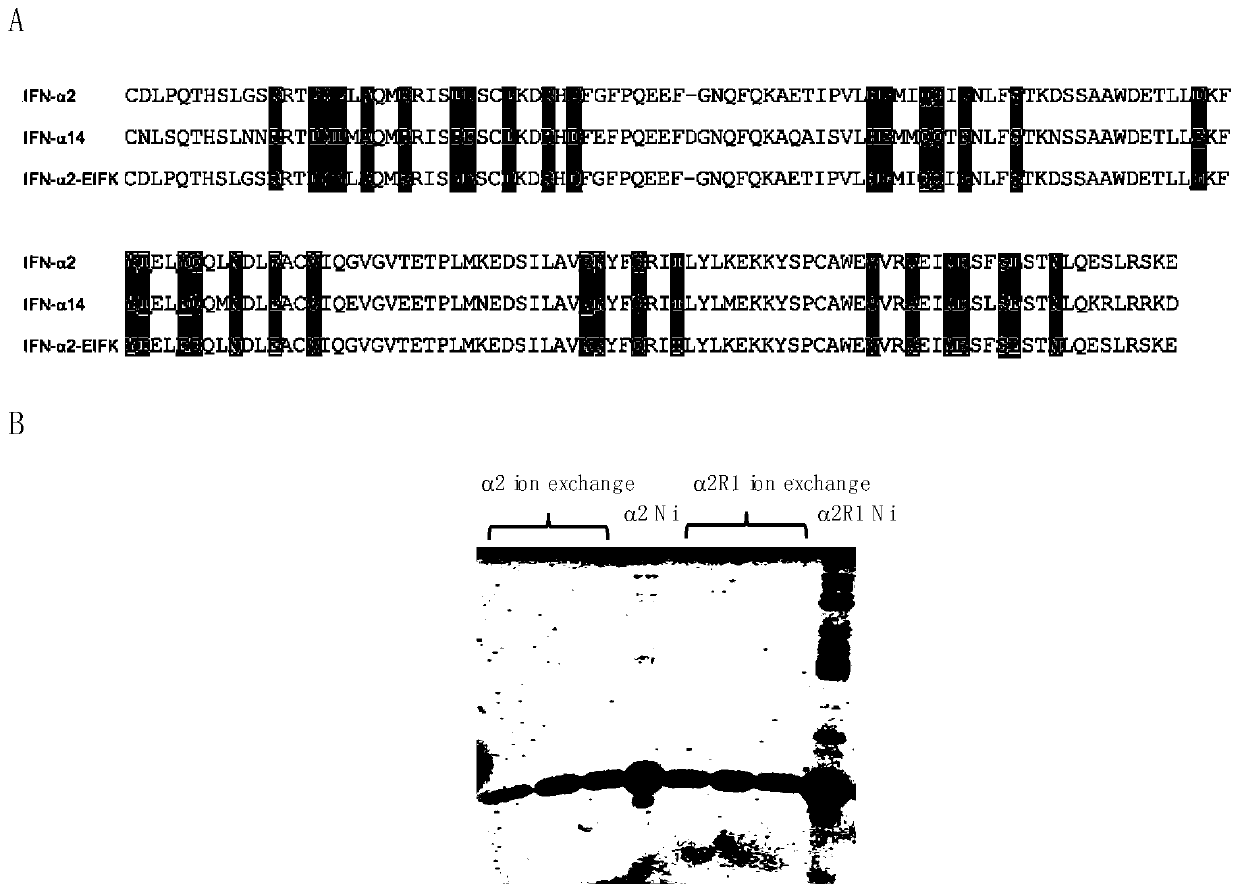
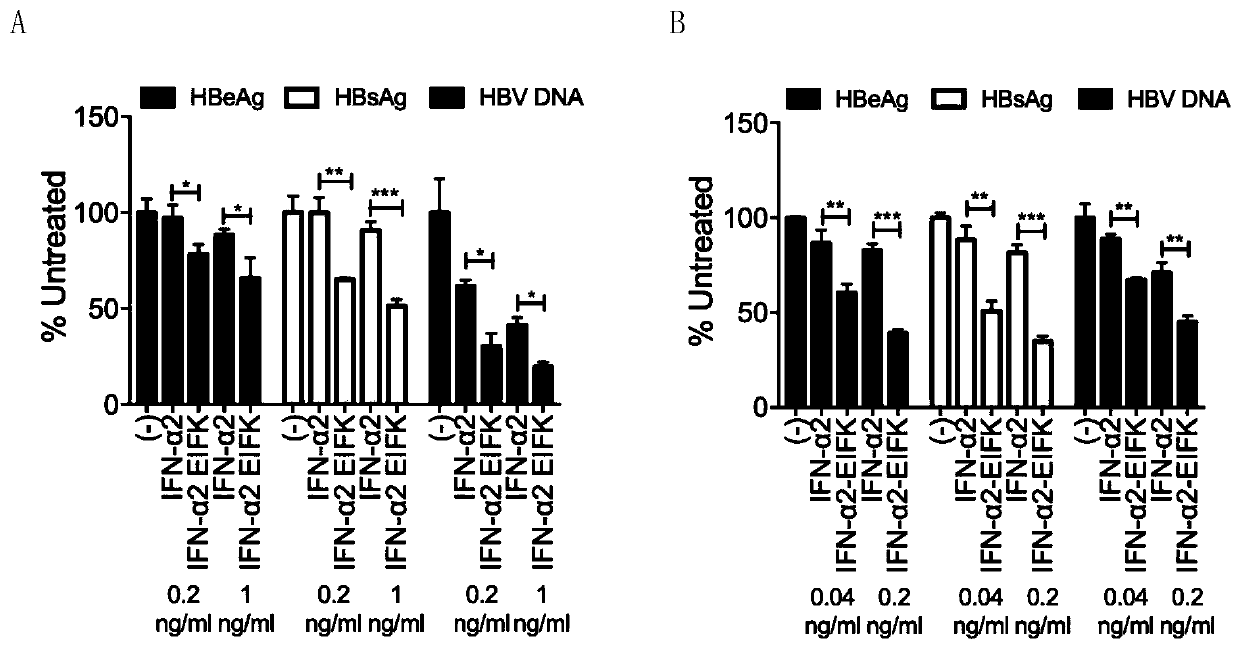
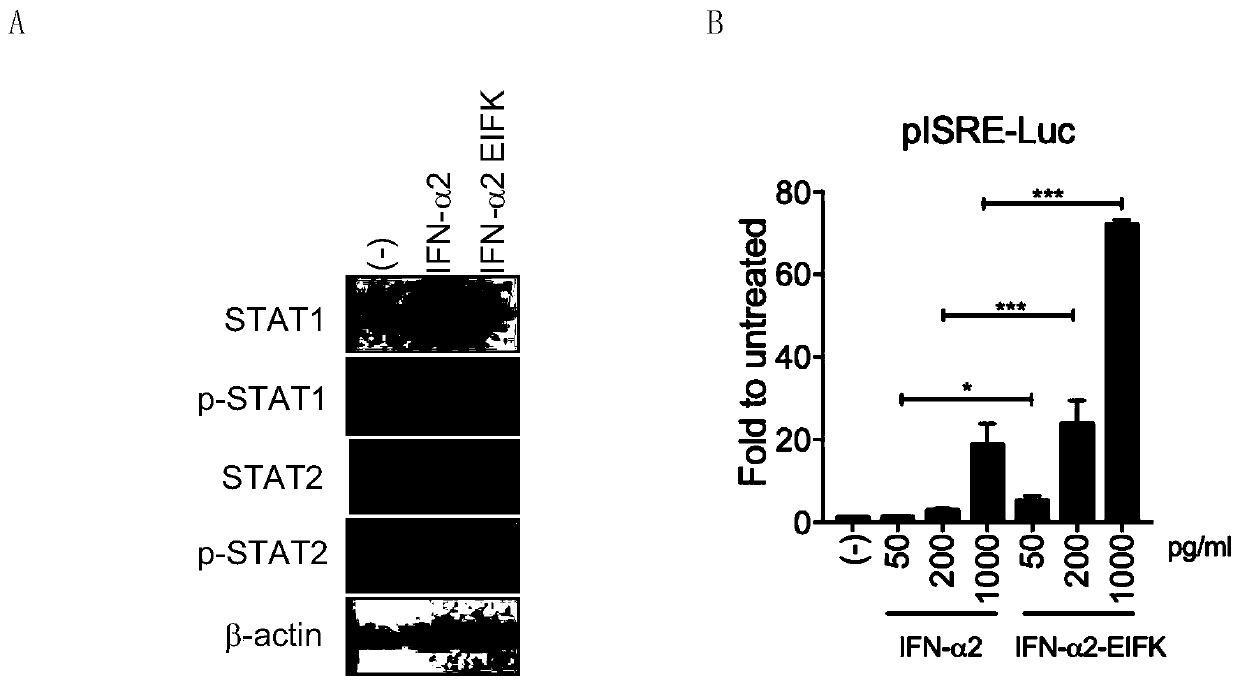
The invention belongs to the technical field of medicine and bioengineering, and relates to application of a human interferon alpha receptor binding related site mutant in preparation of an anti-hepatitis B virus preparation. The interferon alpha plays an antiviral role through a receptor compound combined by two subunits of I-type interferon receptors IFNAR1 and IFNAR2. According to the invention, mutation is carried out on a site where IFN-alpha2 is combined with IFNAR1, and prokaryotic purification expression is carried out in vitro; the recognition in an HBV infection model shows that thehuman interferon alpha receptor binding related site mutant IFN-alpha2-EIFK has stronger anti-hepatitis B virus activity than IFN-alpha2, and has no cytotoxic effect under the antiviral concentration.The IFN-alpha2 receptor disclosed by the invention is combined with a related site mutant, namely IFN-alpha2-EIFK, so that a novel anti-hepatitis B virus medicine can be further prepared.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Interferon-alpha induced genes
InactiveUS20070117145A1Microbiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisInterferon therapyInterferon receptor
The present disclosure relates to identification of previously known genes as being genes upregulated by interferon-α administration, in particular the human genes corresponding to the cDNA sequence in GenBank designated g4758303, g5453897, g4505186, g2366751, g33917, g4504962, g3978516, g5924396, g4505656, g1504007, g3702446, g4001802, g292289, g4557226, g4507646 and g4507170. Determination of expression products of these genes is proposed as having utility in predicting responsiveness to treatment with interferon-α and other interferons which act at the Type 1 interferon receptor.
Owner:PHARM PACIFIC PTY LTD
Chikungunya virus E2 protein rabbit monoclonal antibody and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of biological medicines, and provides an amino acid sequence of a chikungunya virus (CHIKV) E2 protein rabbit monoclonal antibody and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the CHIKV E2 protein rabbit monoclonal antibody comprises an amino acid sequence of a heavy chain and an amino acid sequence of a light chain of the antibody. The antibody expressed by mammalian cells can neutralize infection of CHIKV genotypes which are mainly popular in the world on the cells in vitro, and can protect type I interferon receptor genes from knocking out mice to resist fatal CHIKV infection in vivo. The antibody is modified, such as humanized modification or preparation of a single-chain antibody, and is expected to be used for treating severe CHIKV infection.
Owner:THE NAVAL MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Liquid formulation comprising anti-human interferon alpha receptor 1 (ifnar1) monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN113521276BLow viscositySignificant clinical effectPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsComplementarity determining regionAntiendomysial antibodies
The invention discloses a liquid preparation comprising anti-human interferon alpha receptor 1 (IFNAR1) monoclonal antibody, said liquid preparation comprising anti-human interferon alpha receptor 1 (IFNAR1) with a protein concentration of 100-200 mg / ml ) monoclonal antibody and basic amino acids at an amino acid concentration of 5‑300 mM; the anti-IFNAR1 monoclonal antibody comprises three heavy chain complementarity determining regions (CDR‑H1, CDR‑H2 and CDR‑H3) and three light chain complementary Determining regions (CDR‑L1, CDR‑L2 and CDR‑L3), wherein: (a) the amino acid sequence of CDR‑H1 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; (b) the amino acid sequence of CDR‑H2 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; (c) the amino acid sequence of CDR-H3 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3; (d) the amino acid sequence of CDR-L1 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 4; (e) the amino acid sequence of CDR-L2 is shown in shown in SEQ ID NO: 5; and (f) the amino acid sequence of CDR‑L3 is shown in SEQ ID NO: 6. The liquid preparation has a low viscosity and can be easily injected by a syringe, so it can be used as an injection, especially a hypodermic injection.
Owner:QYUNS THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Antisense modulation of interferon gamma receptor 2
InactiveUS20050153924A1Modulate expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsInterferon receptorInterferon-gamma receptor
Antisense compounds, compositions and methods are provided for modulating the expression of Interferon gamma receptor 2. The compositions comprise antisense compounds, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding Interferon gamma receptor 2. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of Interferon gamma receptor 2 expression and for treatment of diseases associated with expression of Interferon gamma receptor 2 are provided.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Method for detecting gene specifying allergic predisposition
A method of detecting genes which comprises detecting gene polymorphisms in allergy-predisposition-related genes; i.e., interleukin 12 receptor IL-1 β2 chain and β1 chain genes, interleukin 18 receptor α chain gene, interferon γ receptor 1 chain gene and interleukin 12.p40 subunit gene, to thereby detect allergic predisposition. Use of the present method enables contribution to the prevention of onset of allergic diseases and to the treatment of allergic diseases.
Owner:BML INC +1
Polymorphic marker that can be used to assess the efficacy of interferon therapy
InactiveCN101182587AMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsInterferon therapyMedicine
The invention provides a polymorphism sign found in an area of interferon receptor gene, which can be used for evaluating the curative effect of the interferon. Therefore, the invention also relates to the method for evaluating the personal curative effect of interferon and the device for finishing the method.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Compositions and methods for treating coronavirus infection and sars
InactiveUS20090068142A1Reduce riskReduce loadOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsInterferon type IIIType II interferon
The present invention provides methods of treating a coronavirus infection, and methods of reducing viral load, or reducing the time to viral clearance, or reducing morbidity or mortality in the clinical outcomes, in patients suffering from a coronavirus infection. The present invention further provides methods of reducing the risk that an individual will develop a pathological coronavirus infection, that has clinical sequelae. The present invention further provides methods of reducing the risk that an individual will develop SARS. The present invention further provides methods of treating SARS. The methods generally involve administering a therapeutically effective amount of a Type I or Type III interferon receptor agonist and / or a Type II interferon receptor agonist for the treatment of a coronavirus infection.
Owner:THREE RIVERS PHARMA LLC
Mumps virus attacking animal model and establishment method thereof
ActiveCN114794018AIncrease capacityEffective infectionCompounds screening/testingAnimal husbandryIntramuscular injectionIntravenous IG
The invention relates to a mumps virus attacking animal model and an establishment method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention provides a mumps virus counteracting animal model. The mumps virus counteracting animal model is an interferon receptor deletion animal which is intravenously injected with mumps virus. Research finds that compared with common mice, the mumps virus load in blood of the interferon receptor-deleted mice is remarkably improved after the mumps virus is attacked by the interferon receptor-deleted mice, and compared with intramuscular injection and intranasal injection, the mumps virus load in blood of the interferon receptor-deleted mice is remarkably improved after the mumps virus is injected into the interferon receptor-deleted mice through caudal veins, so that the mumps virus load in blood of the interferon receptor-deleted mice is remarkably improved. Intravenous injection of the mumps virus to the interferon receptor-deficient animal can break through species limitation, effective infection of the mumps virus in the animal body is realized, and symptoms similar to human infection (for example, remarkable replication in various visceral organs) are formed, so that the mumps virus challenge animal model can be used as the mumps virus challenge animal model.
Owner:BEIJING CELL FUSION BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD +1
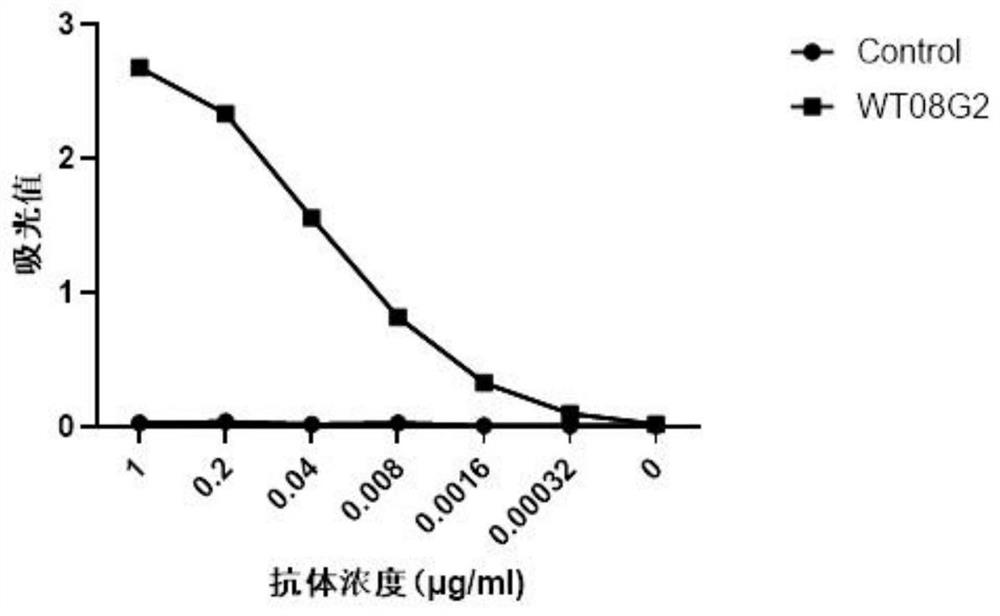
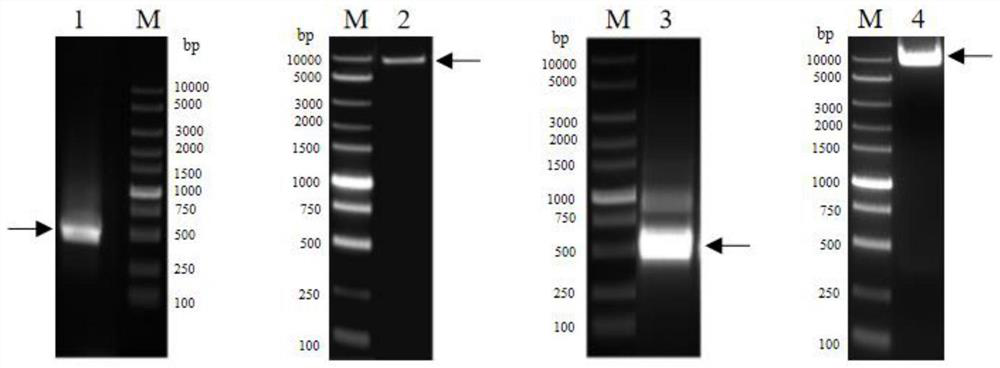
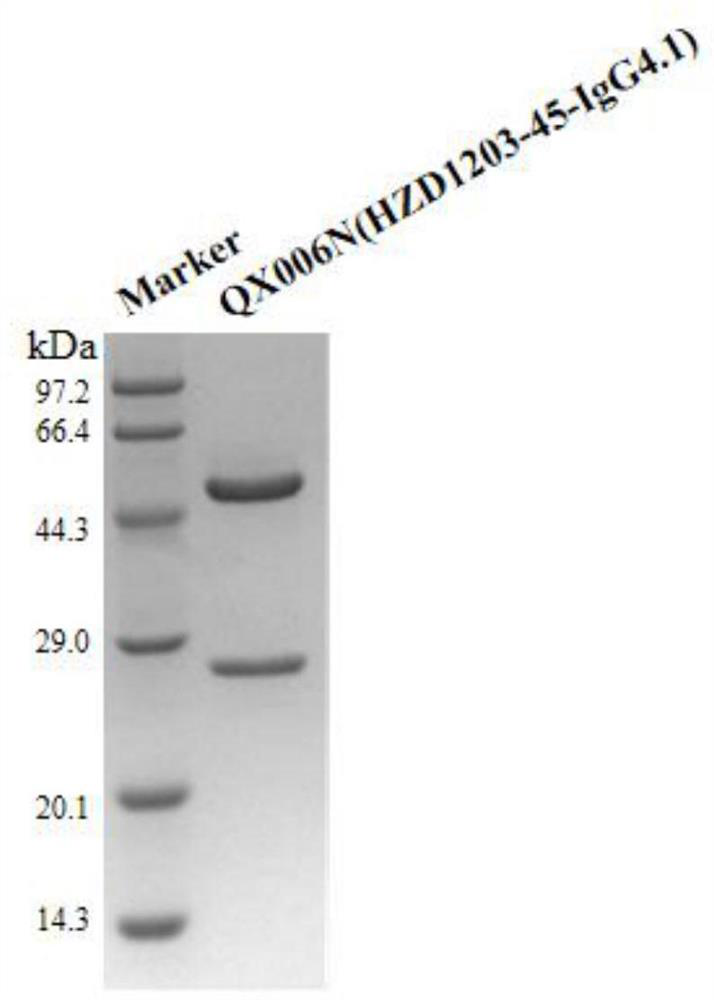
Anti-human interferon alpha receptor 1 monoclonal antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN113278071ASignificant clinical effectNervous disorderAntipyreticDiseaseComplementarity determining region
The invention relates to an anti-human interferon alpha receptor 1 (IFNAR1) monoclonal antibody and application thereof. The anti-human interferon alpha receptor 1 (IFNAR1) monoclonal antibody comprises three heavy chain complementary determining regions (CDR-H1, CDR-H2 and CDR-H3) and three light chain complementary determining regions (CDR-L1, CDR-L2 and CDR-L3). Wherein (a) the amino acid sequence of the CDR-H1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, (b) the amino acid sequence of CDR-H2 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; (c) the amino acid sequence of the CDR-H3 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3; (d) the amino acid sequence of the CDR-L1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4; (e) the amino acid sequence of the CDR-L2 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 5; and (f) the amino acid sequence of the CDR-L3 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 6. The affinity of the anti human interferon alpha receptor 1 (IFNAR1) monoclonal antibody for binding human IFNAR1 is equivalent to that of the anti human IFNAR1 monoclonal antibody Anifrolumab, the neutralizing activity of the anti-human IFNAR1 monoclonal antibody for binding with the human IFNAR1 monoclonal antibody at the cellular level is equivalent to that of the Anifrolumab, and the anti-human IFNAR1 monoclonal antibody is expected to show a good clinical effect in the aspect of preventing and treating related diseases.
Owner:QYUNS THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Human interferon-kappa mutant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN112521480AIncrease productivityImprove renaturation efficiencyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycineWild type
The invention relates to a human interferon kappa (hIFNkappa) mutant and a preparation method thereof. The hIFN-kappa variant is obtained by mutating free cysteine (C) at the 166th site of an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 of hIFN-kappa into serine (S) or mutating into glycine (G) or alanine (A) with a structure similar to that of serine. Compared with a strain containing a wild type hIFN-kappa sequence, the hIFN-kappa produced by expression of the plasmid strain containing the mutant sequence is relatively high in yield, higher in affinity of binding with an interferon-kappa receptor and better in in-vitro activity.
Owner:山东晶辉生物技术有限公司
Affinity purification method for lowering protein content of host cell in monoclonal antibody production
InactiveCN113621063AAffinity craft is simple and easyHigh yieldImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide preparation methodsComplementarity determining regionHeavy chain
The invention discloses an affinity purification method for lowering protein content of a host cell in monoclonal antibody production. The method comprises the following steps: balancing an affinity chromatography medium by using a first balance buffer solution to obtain a balanced affinity chromatography medium, and combining monoclonal antibody fermentation liquor with the balanced affinity chromatography medium; and then, carrying out intermediate pre-elution leaching, and then, carrying out final elution to remove host-cell proteins so as to obtain a monoclonal antibody. The monoclonal antibody is a separated monoclonal antibody against a human interferon alpha receptor 1 (IFNAR1), and comprises three heavy-chain complementary determining regions (CDR-H1, CDR-H2 and CDR-H3) and three light-chain complementary determining regions (CDR-L1, CDR-L2 and CDR-L3). The method is simple and easy to implement, amplified purification production can be carried out, cell fermentation supernatant does not need pretreatment, the elution sample yield is relatively high, meanwhile, a HCP residual quantity is also kept at a relatively low level (the residual control quantity is not higher than 0.1%), and therefore, the pressure for removing HCP in a subsequent purification step is relieved.
Owner:QYUNS THERAPEUTICS CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com