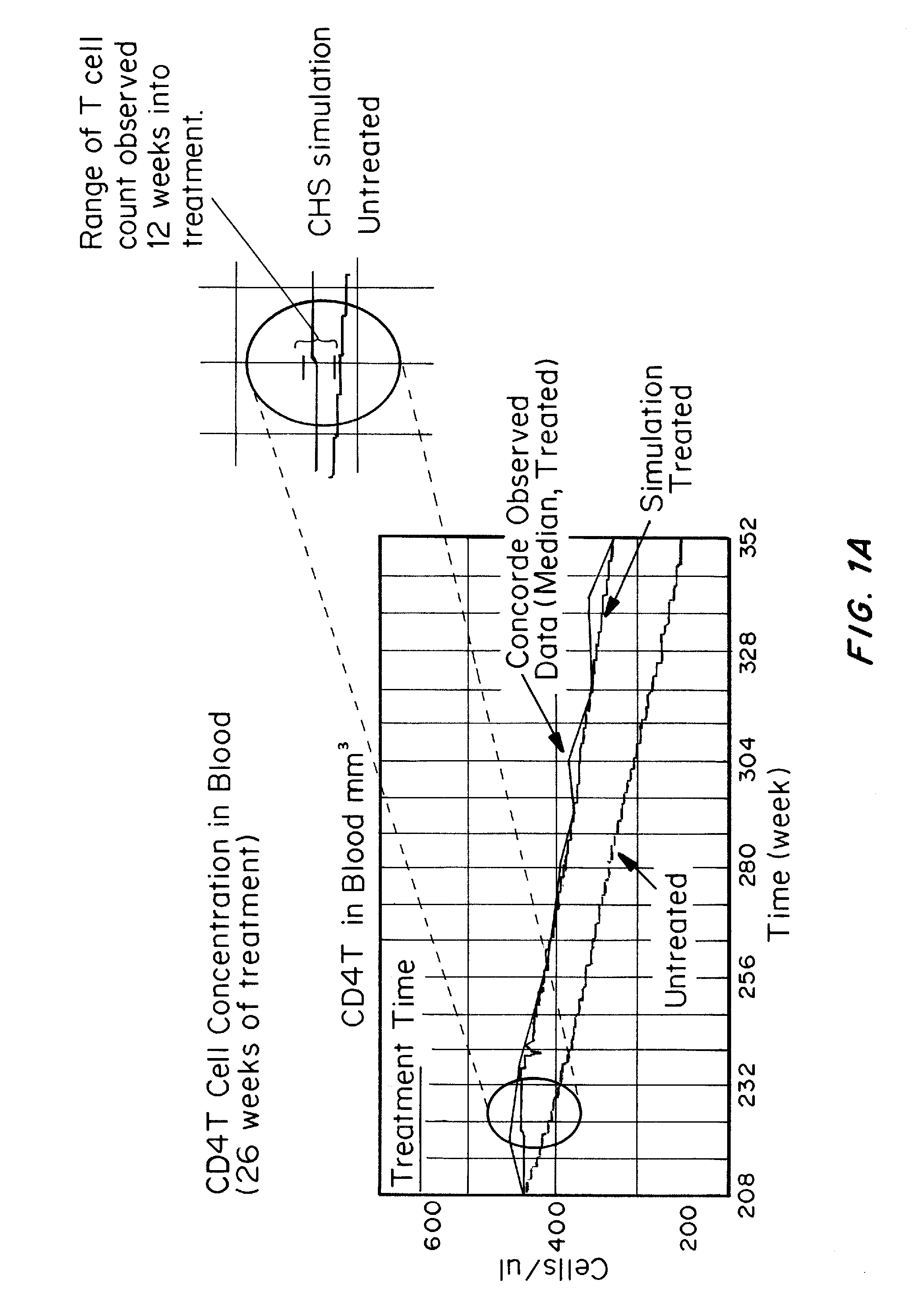
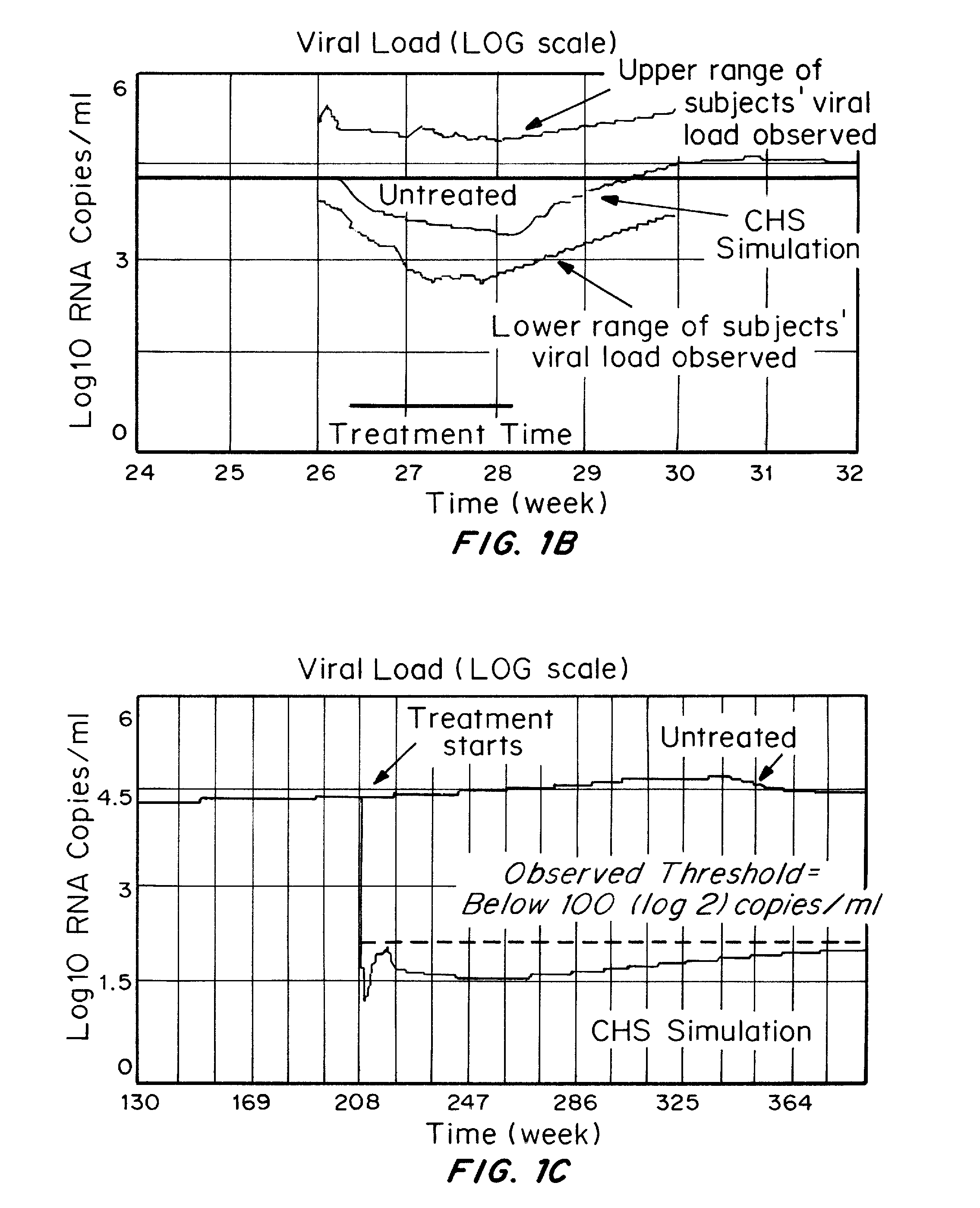
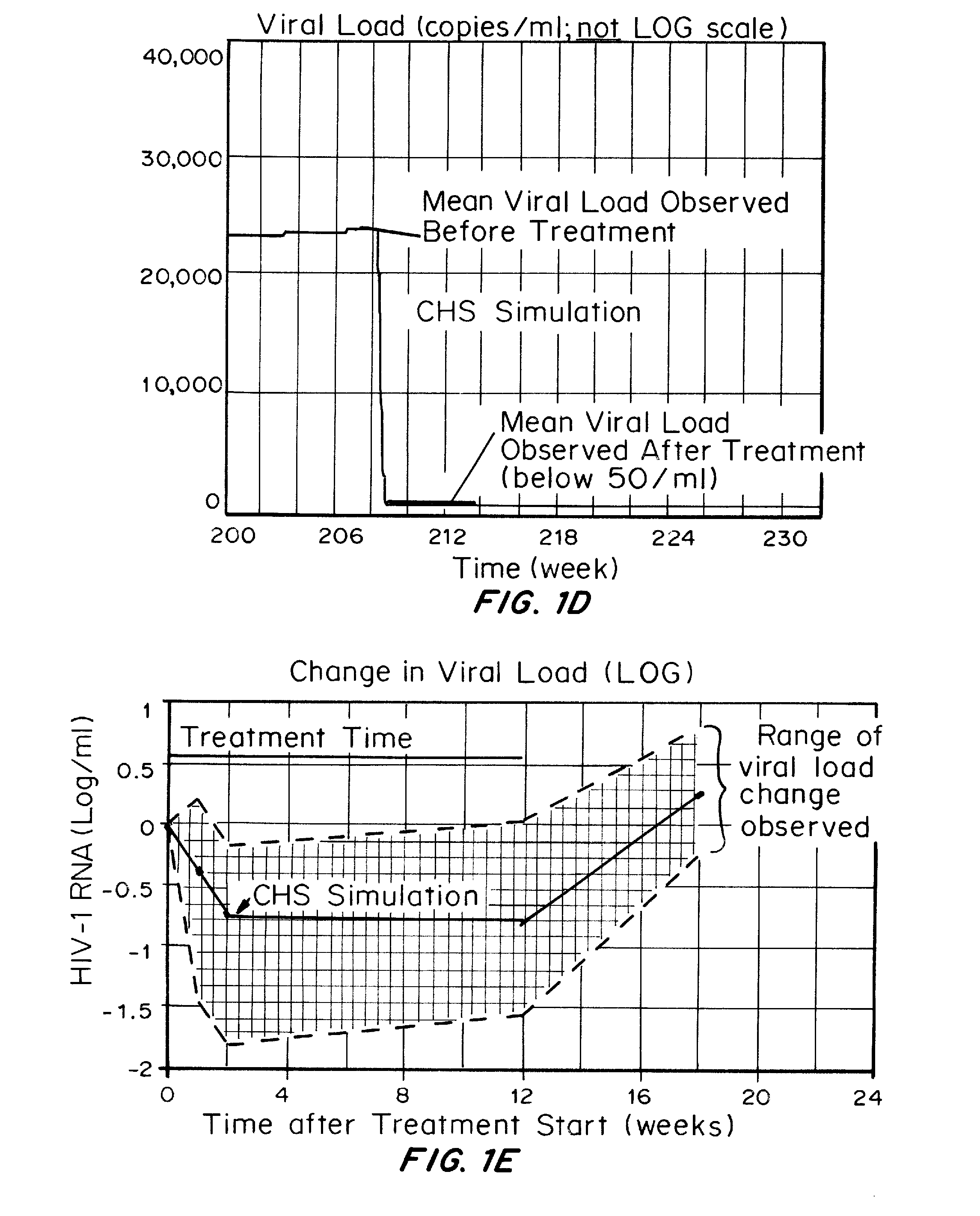
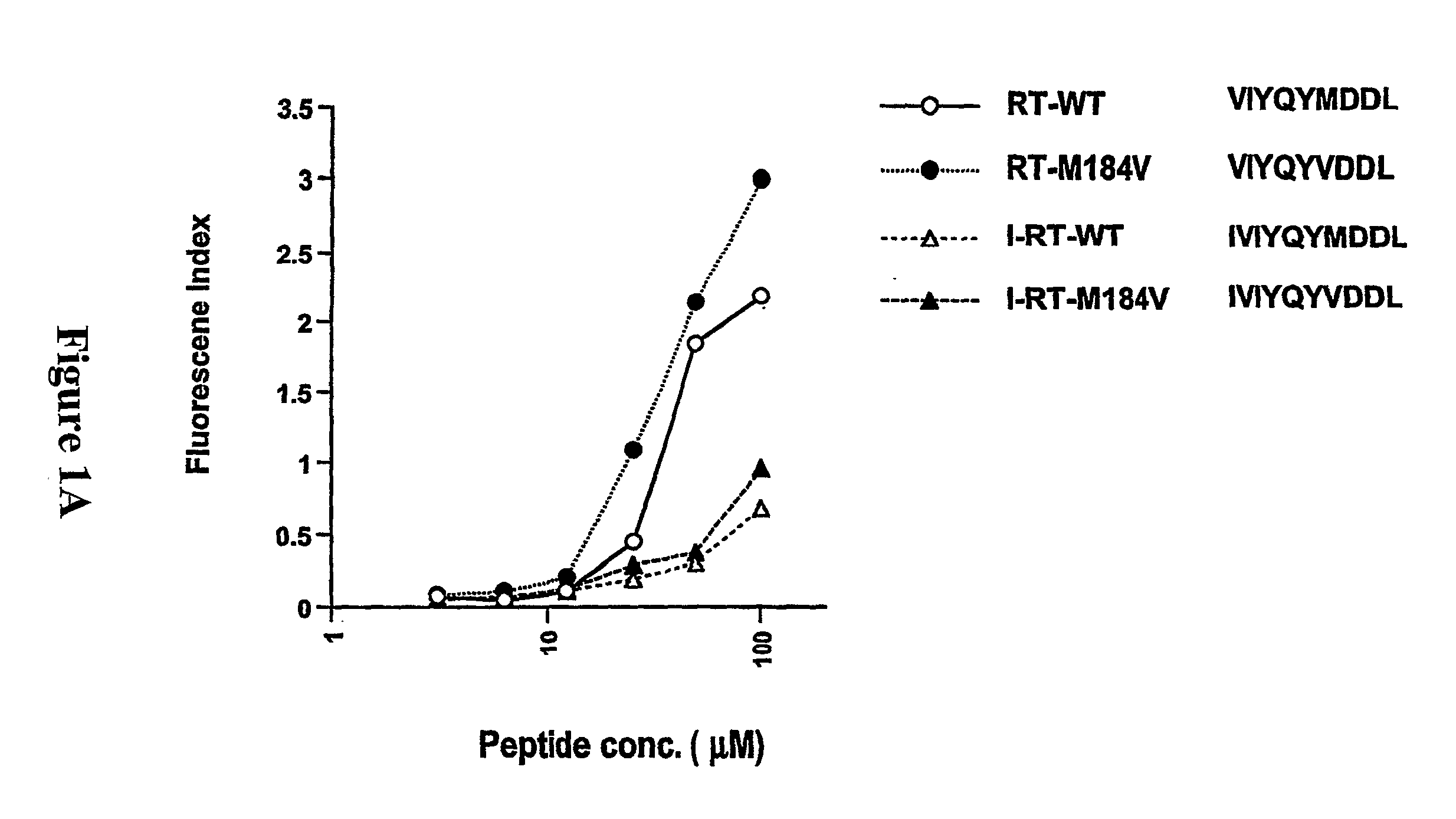
Patents
Literature
55 results about "Virus load" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Viral load, also known as viral burden, viral titre or viral titer, is a numerical expression of the quantity of virus in a given volume. It is often expressed as viral particles, or infectious particles per mL depending on the type of assay. A higher viral burden, titre, or viral load often correlates with the severity of an active viral infection.
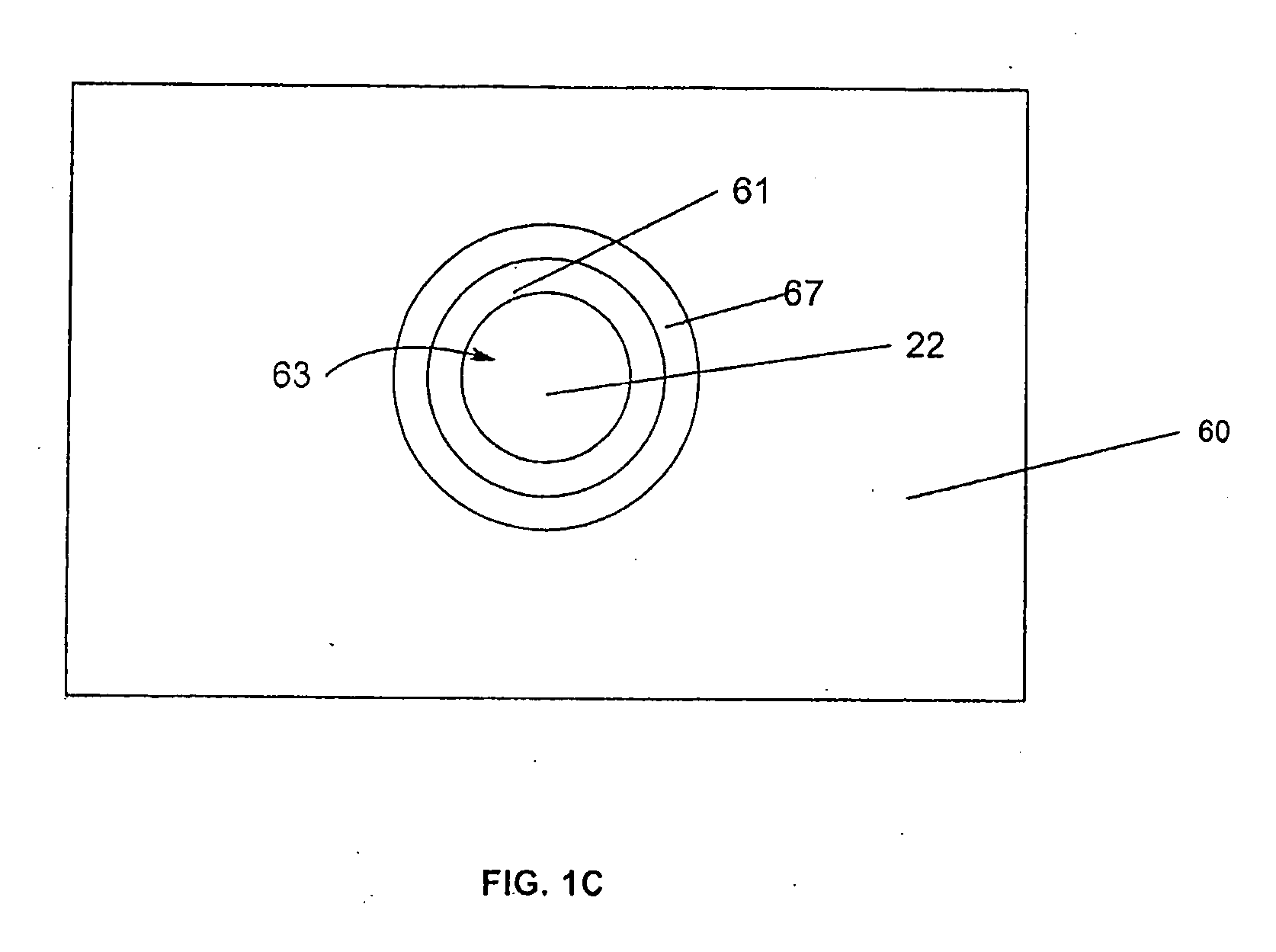
Assay for porcine circovirus production
ActiveUS7358075B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAssayCell culture media
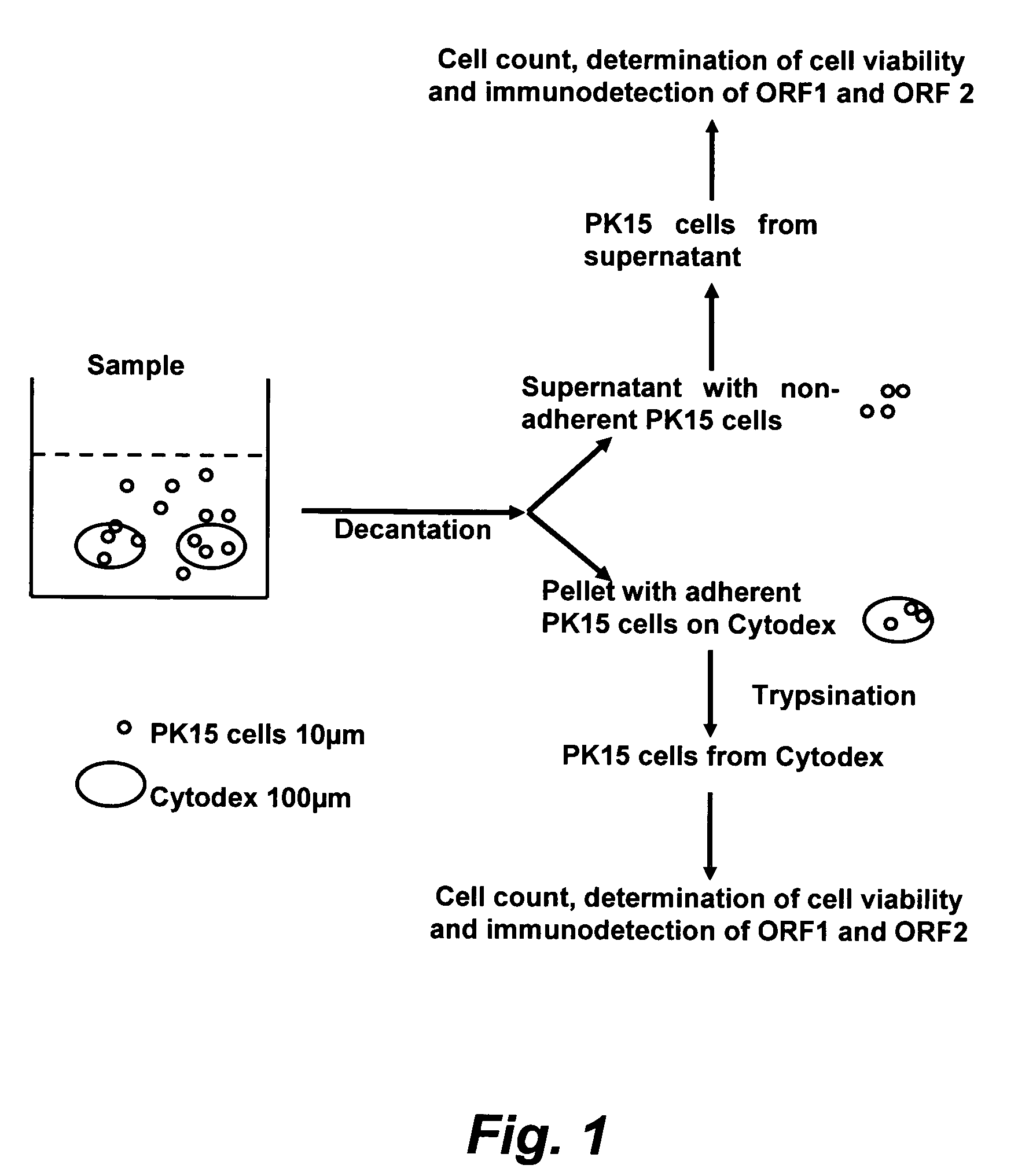
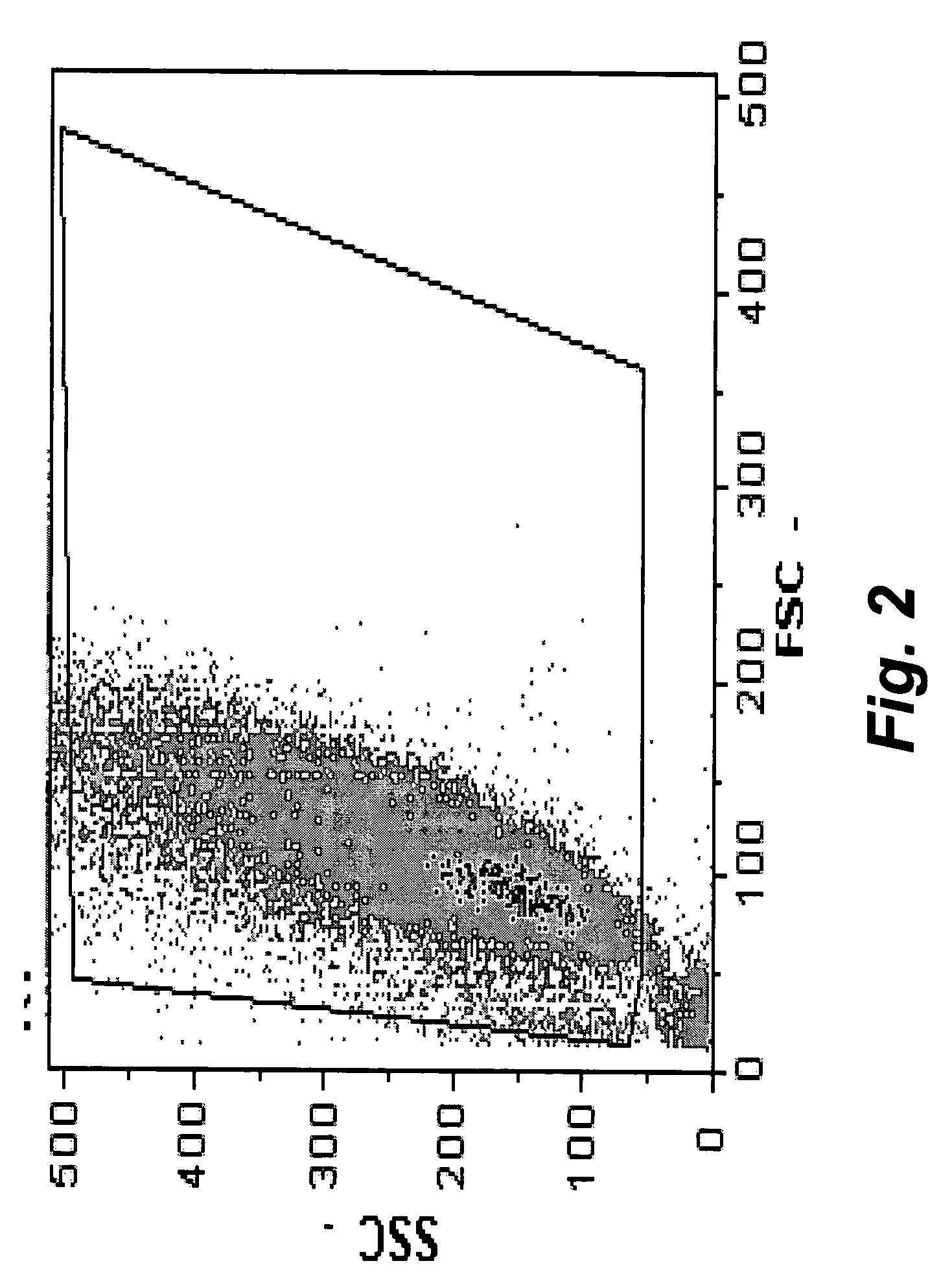
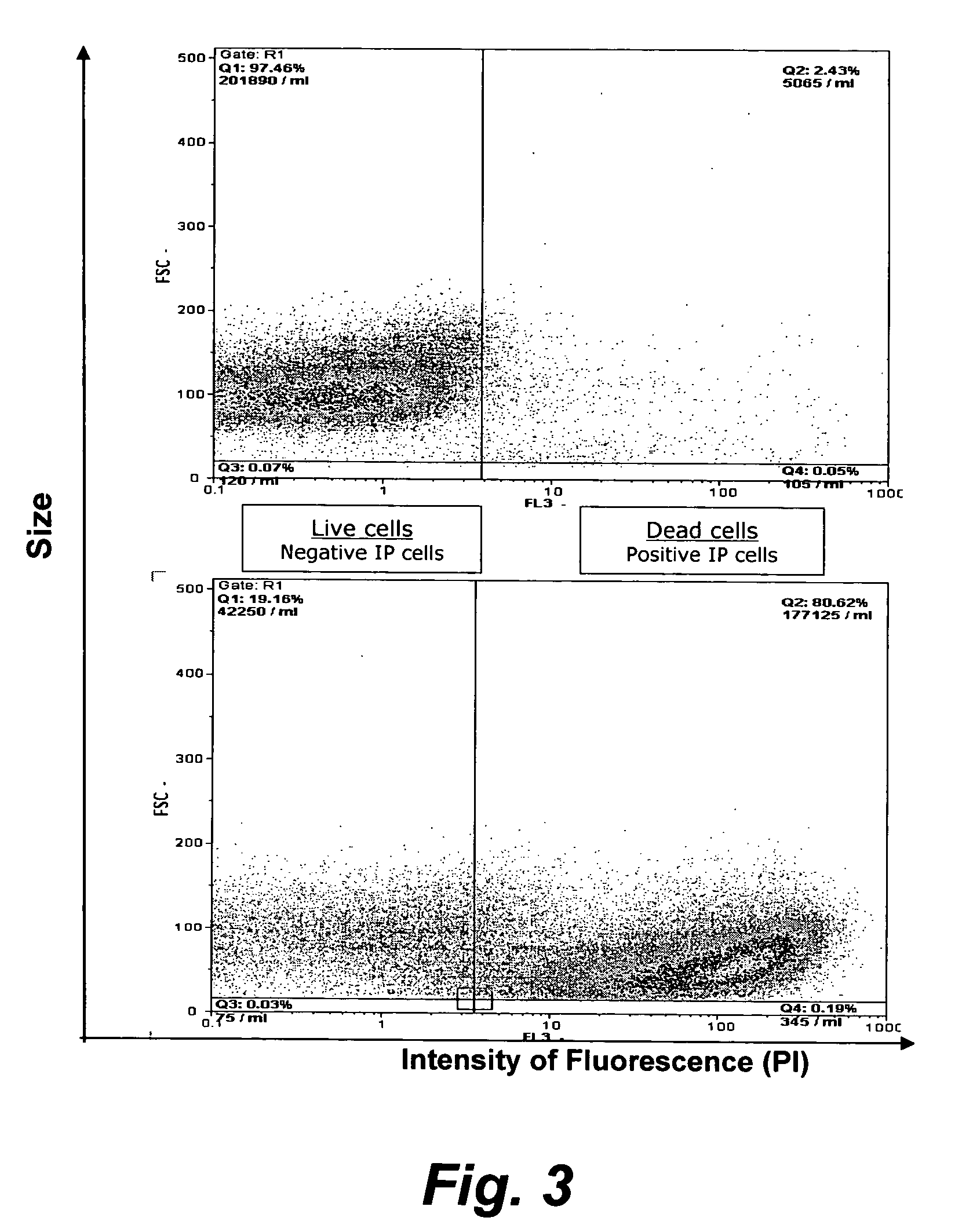
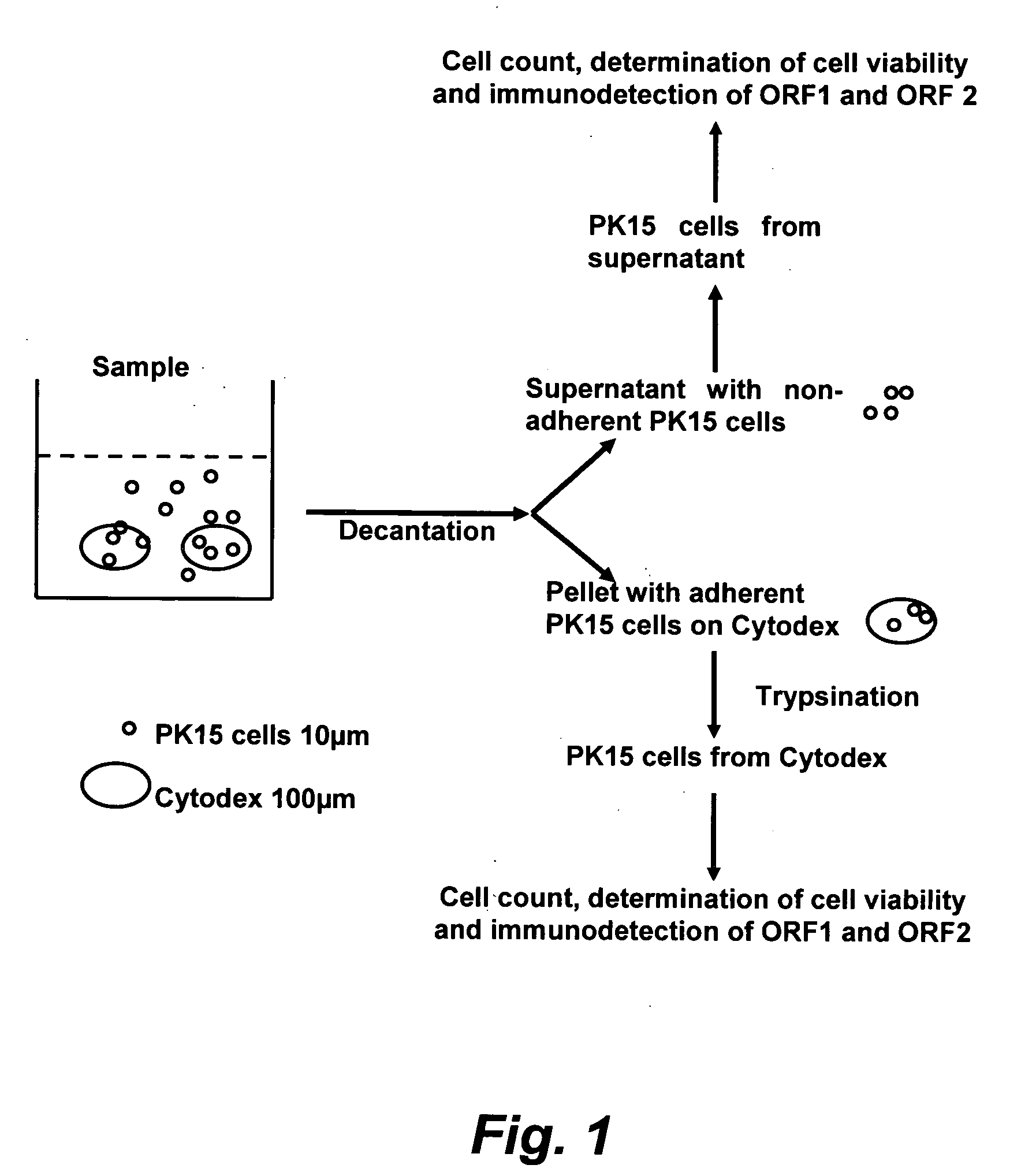
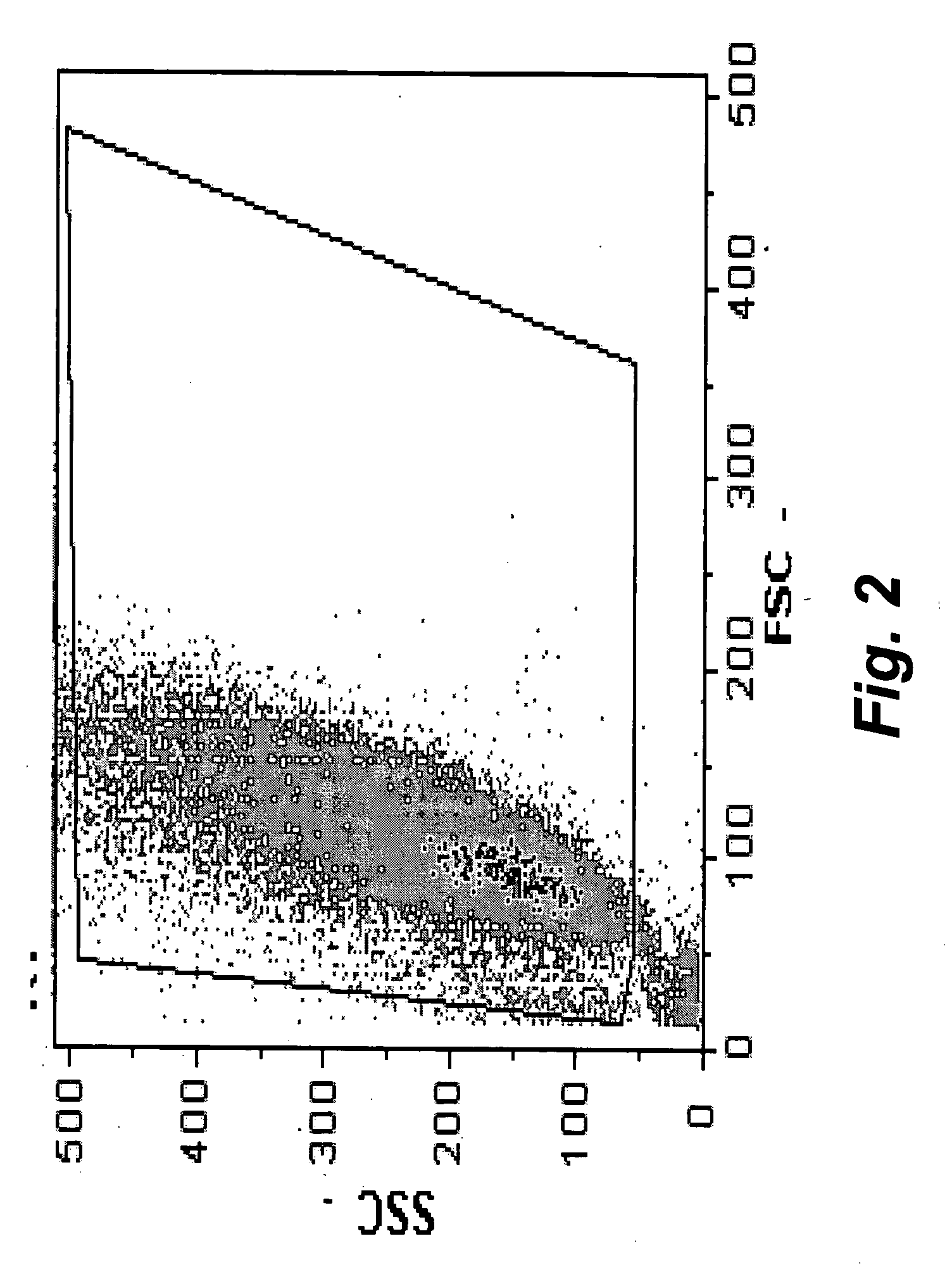
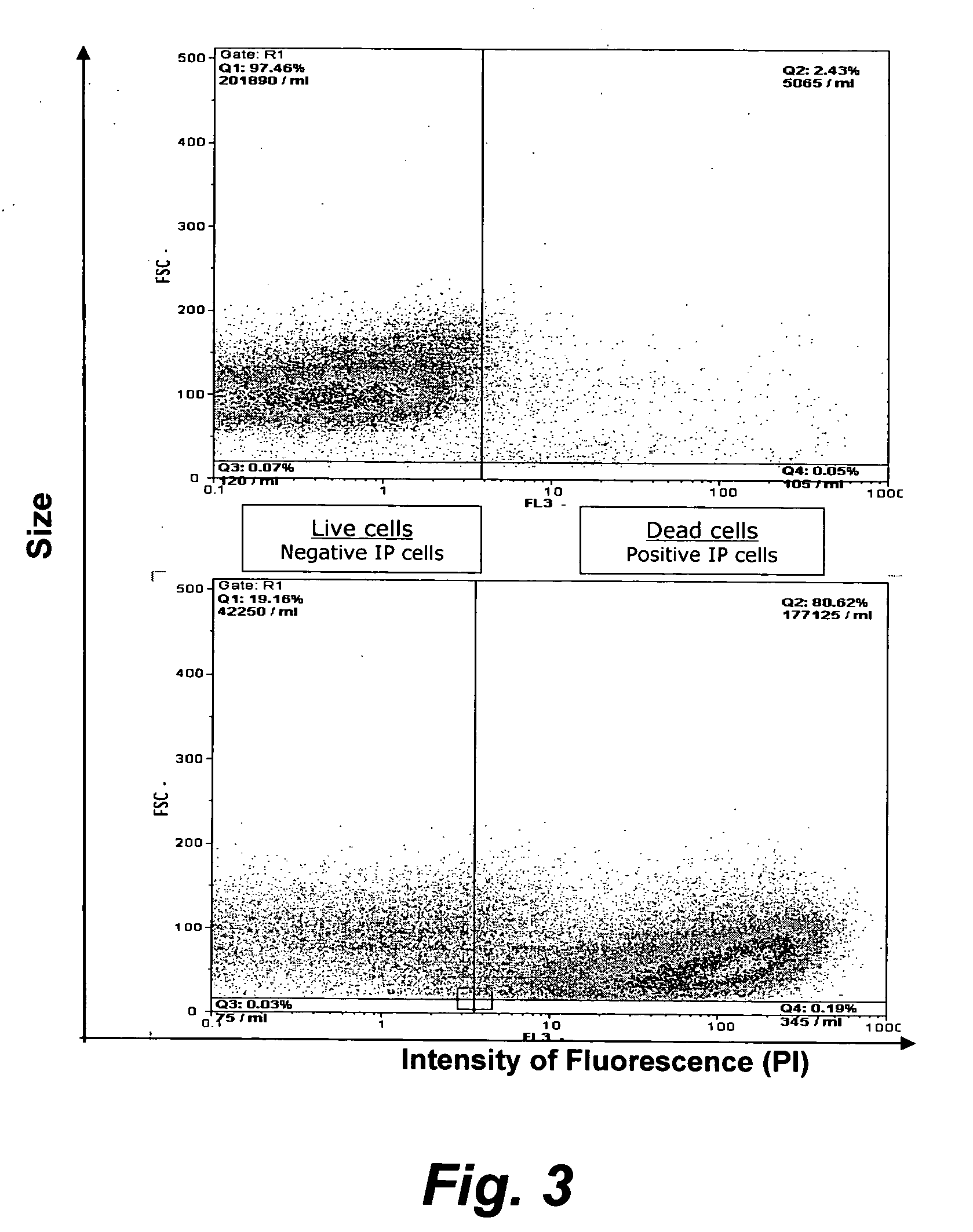
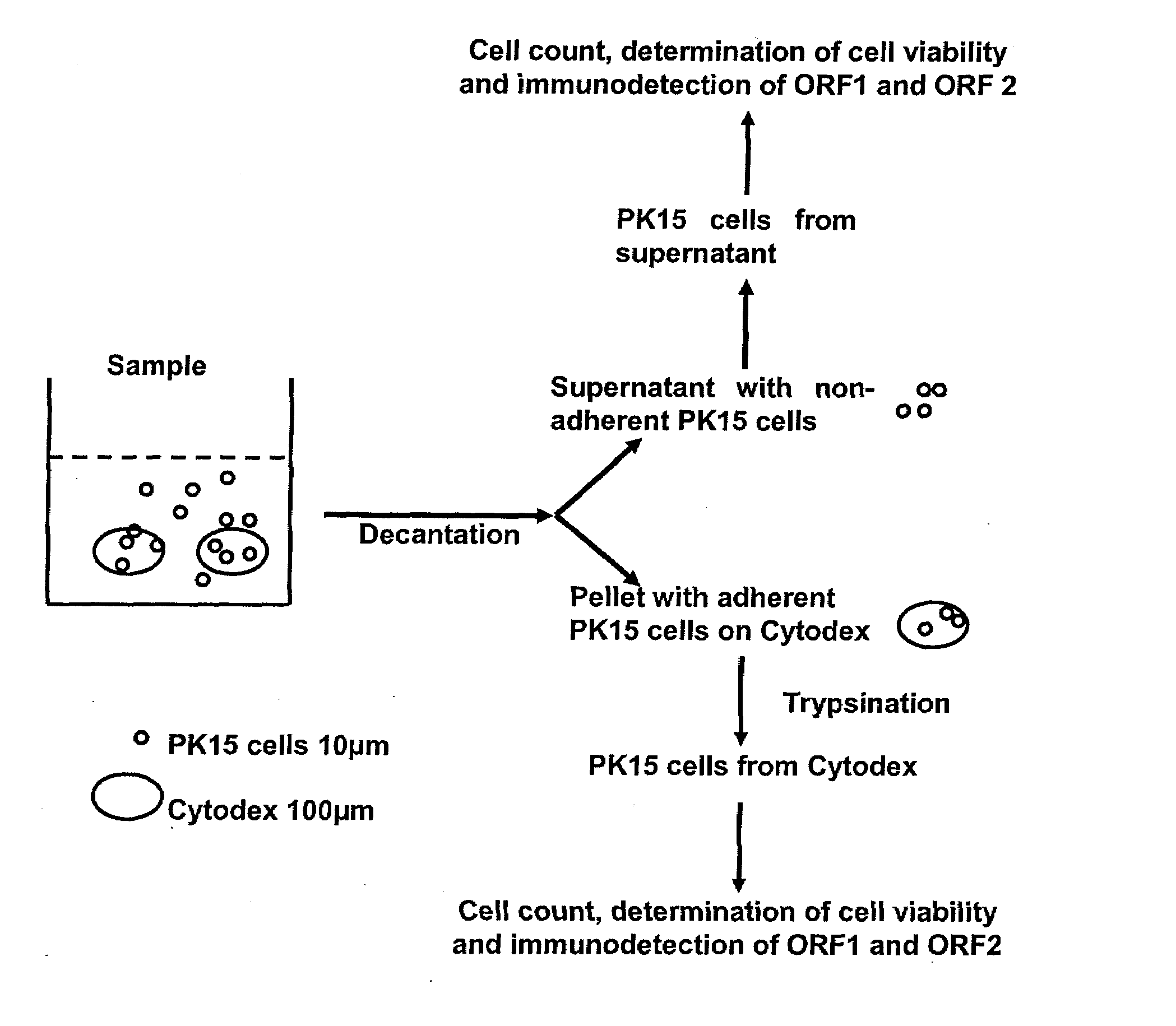
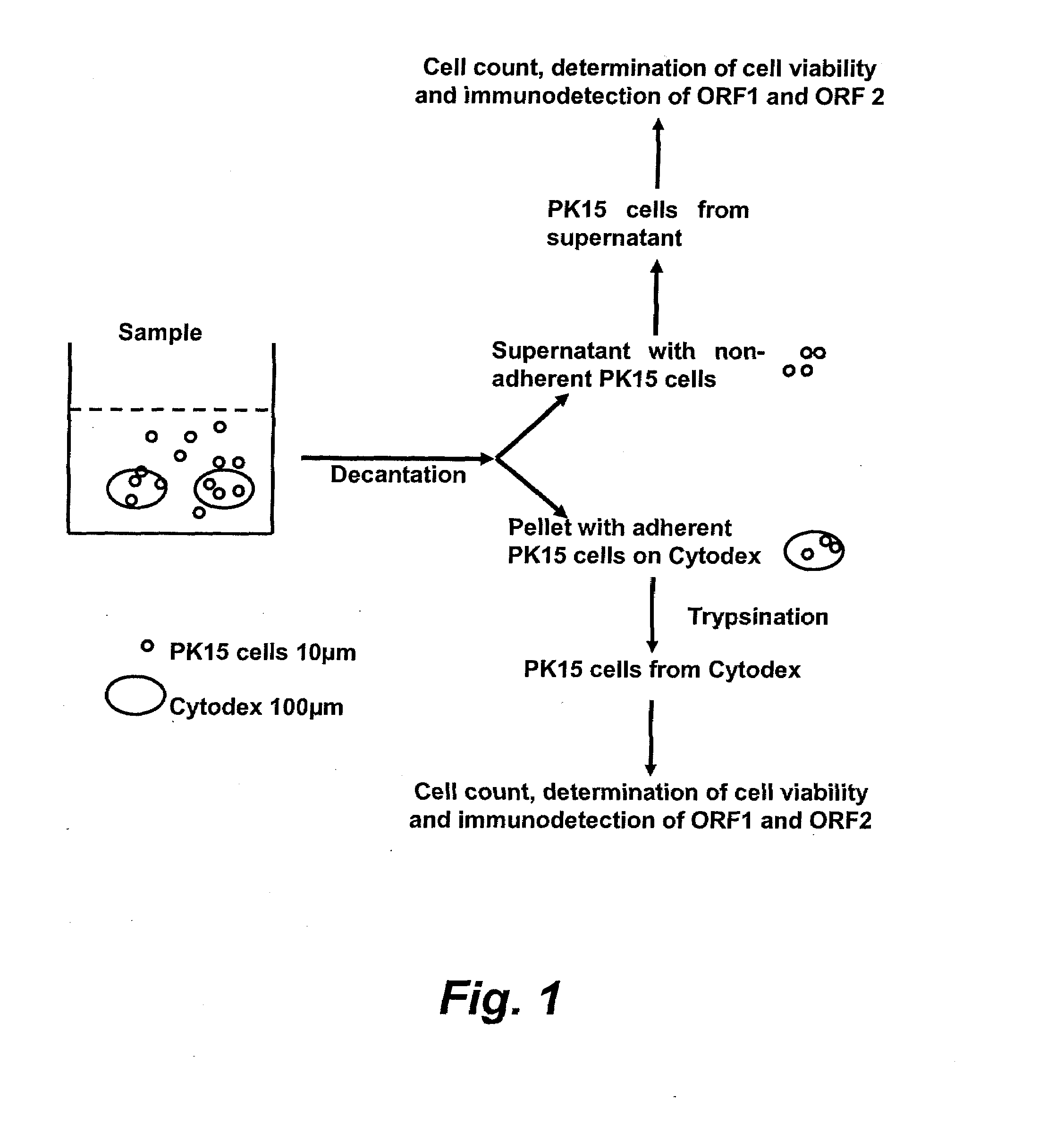
The present invention provides methods for the determination of the viral titer of a culture of host animal host cells infected with a circovirus. The FACS-based methods of the invention may include determining the viability of the host cells in a cell culture medium supernatant and of those cells that remain adherent to a solid support. Detecting and measuring the percentage of cells that expressed the viral antigens ORF1 and ORF2 may determine the viral load of the cultured host cells. The yield of the virus may be established by the detection and measurement of both antigens in supernatant cells, for example 5 to 7 days from when the host cells are transferred to a serum free medium. The methods of the invention may yield rapid quantitative data. This allows the repeated in-process monitoring of the viral production throughout the incubation period, and ready selection of the most appropriate harvesting point.
Owner:MERIAL INC
Assay for porcine circovirus production
ActiveUS20060246425A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisIncubation periodViral load
The present invention provides methods for the determination of the viral titer of a culture of host animal host cells infected with a circovirus. The FACS-based methods of the invention may include determining the viability of the host cells in a cell culture medium supernatant and of those cells that remain adherent to a solid support. Detecting and measuring the percentage of cells that expressed the viral antigens ORF1 and ORF2 may determine the viral load of the cultured host cells. The yield of the virus may be established by the detection and measurement of both antigens in supernatant cells, for example 5 to 7 days from when the host cells are transferred to a serum free medium. The methods of the invention may yield rapid quantitative data. This allows the repeated in-process monitoring of the viral production throughout the incubation period, and ready selection of the most appropriate harvesting point.
Owner:MERIAL INC
Combination therapy for treating alphavirus infection and liver fibrosis
InactiveUS20070072181A1Improve liver functionReduce morbidityOrganic active ingredientsImpression capsMortality rateInterferon receptor
The present invention provides methods for treating alphavirus infections; methods of treating hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections; methods of treating West Nile virus infection; methods of reducing liver fibrosis; methods of increasing liver function in an individual suffering from liver fibrosis; methods of reducing the incidence of complications associated with HCV and cirrhosis of the liver; and methods of reducing viral load, or reducing the time to viral clearance, or reducing morbidity or mortality in the clinical outcomes, in patients suffering from viral infection. The methods generally involve administering effective amounts of an interferon receptor agonist and pirfenidone in combination therapy.
Owner:THREE RIVERS PHARMA LLC
Modified nucleosides for the treatment of viral infections and abnormal cellular proliferation
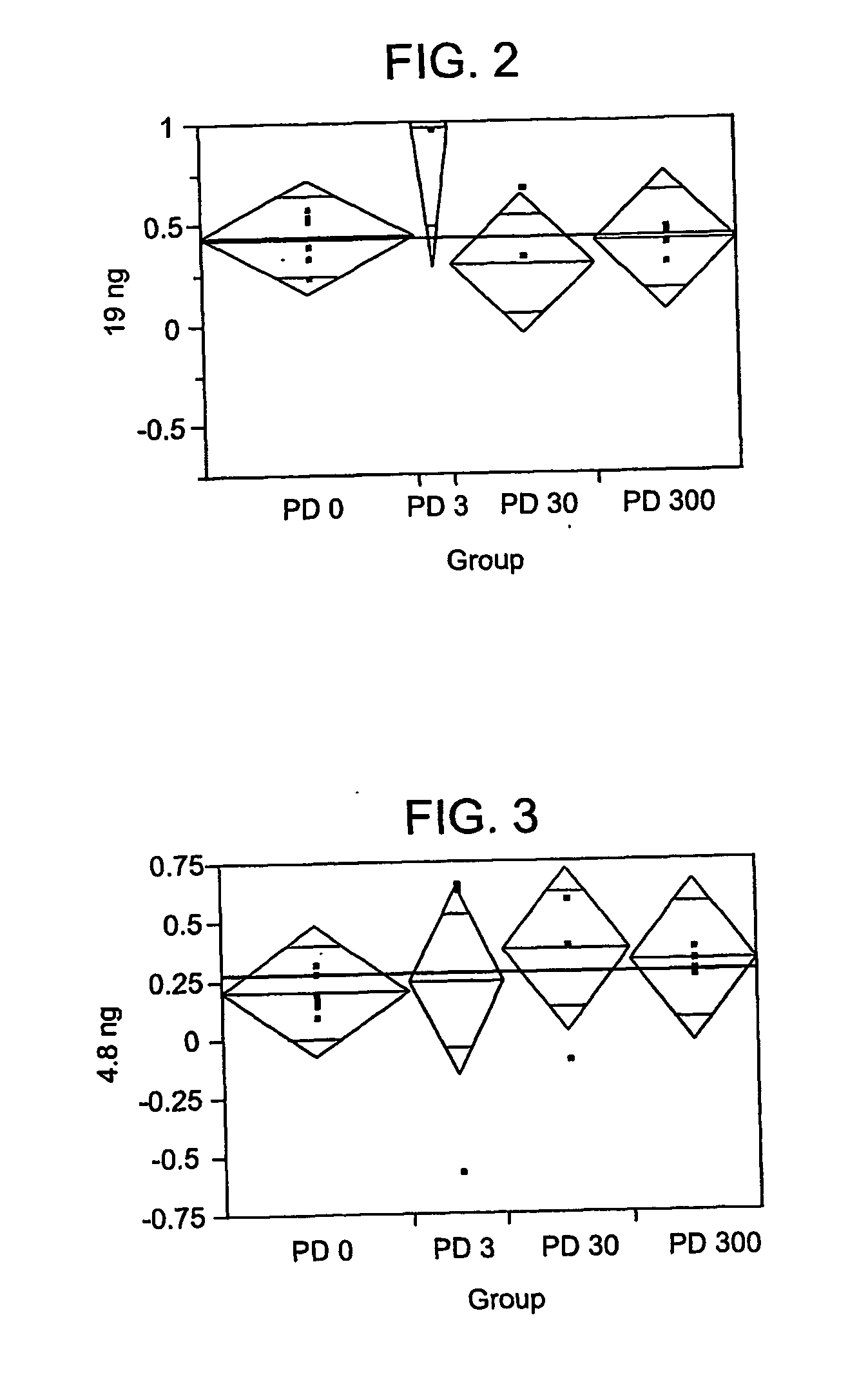
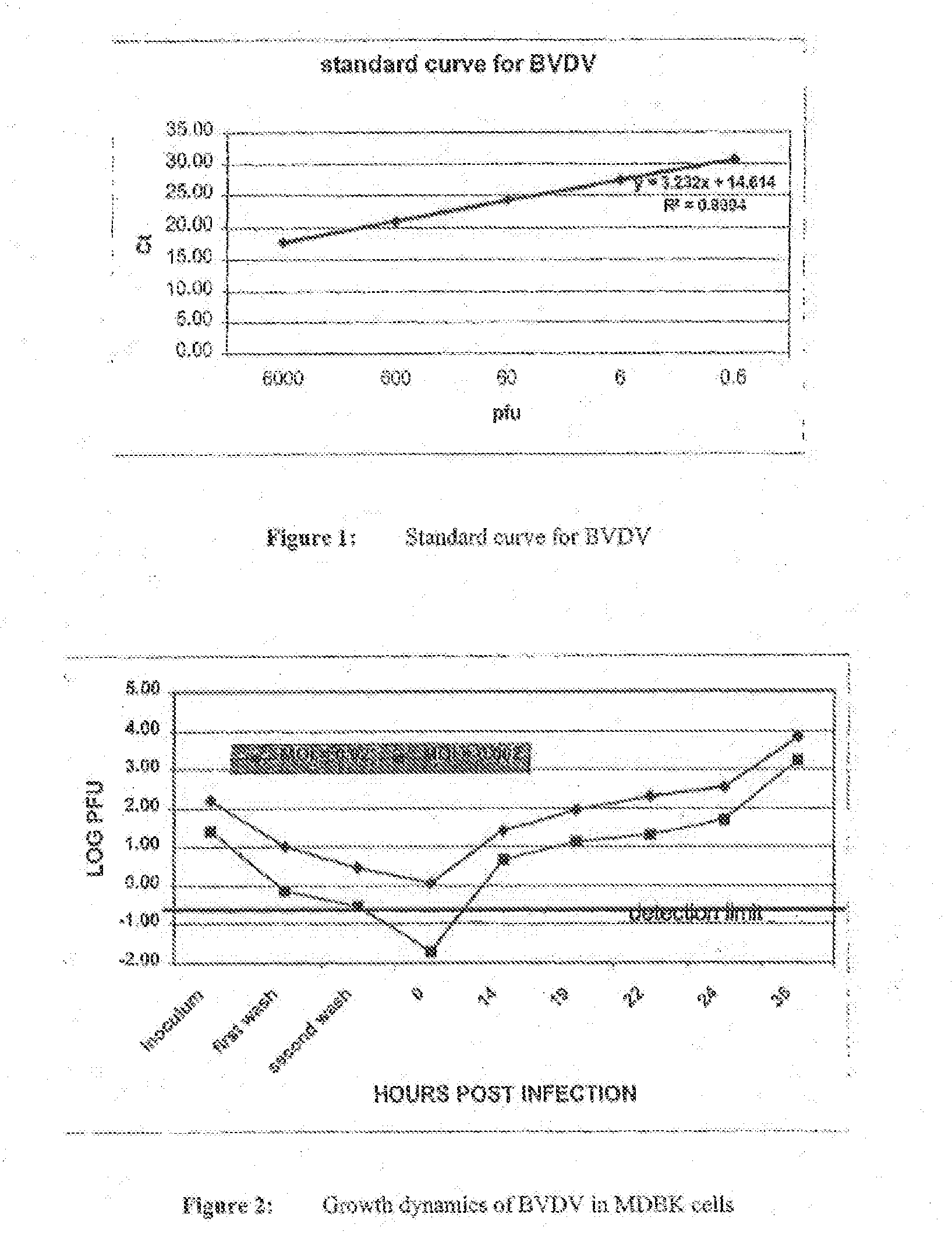
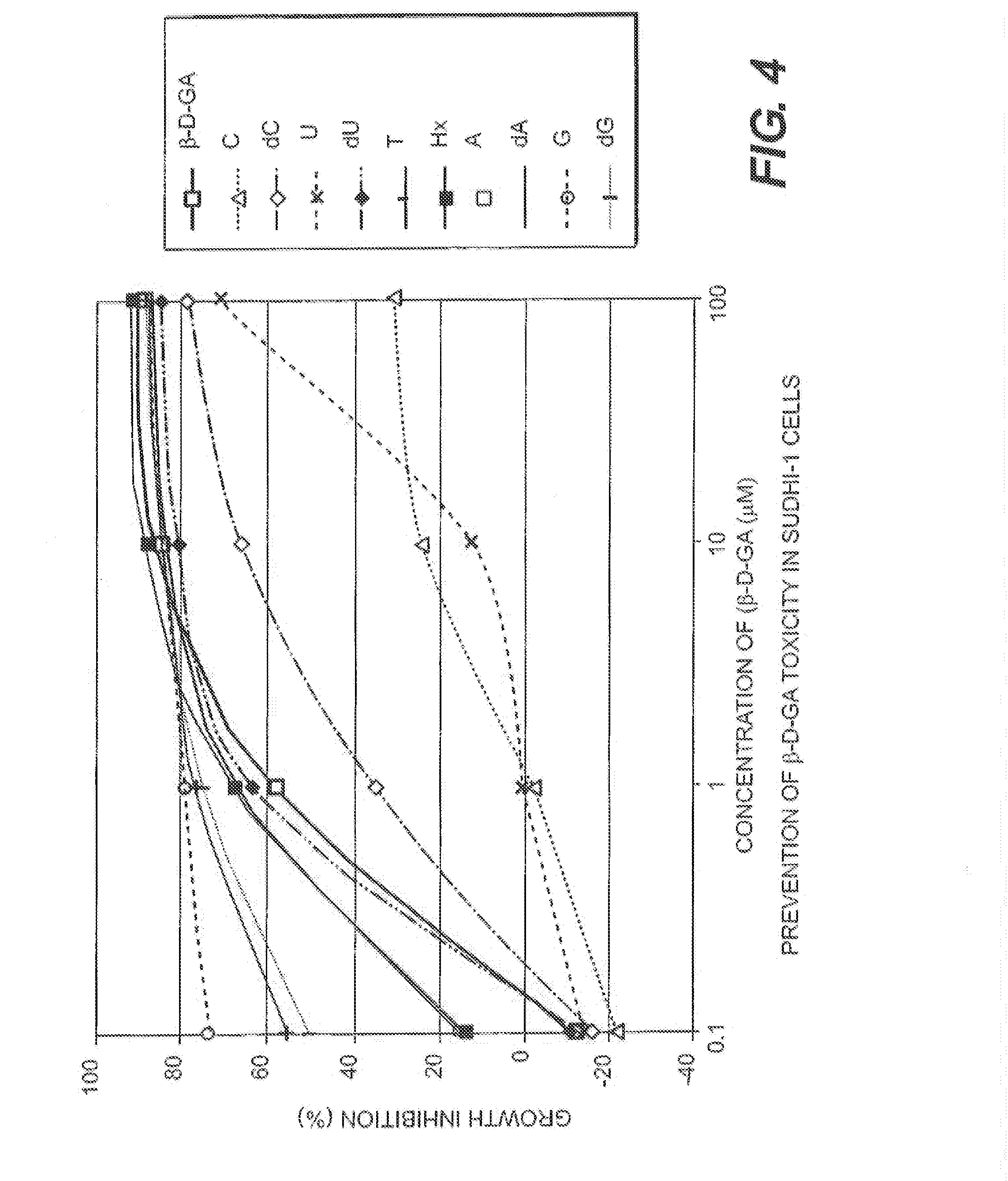
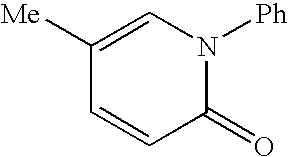
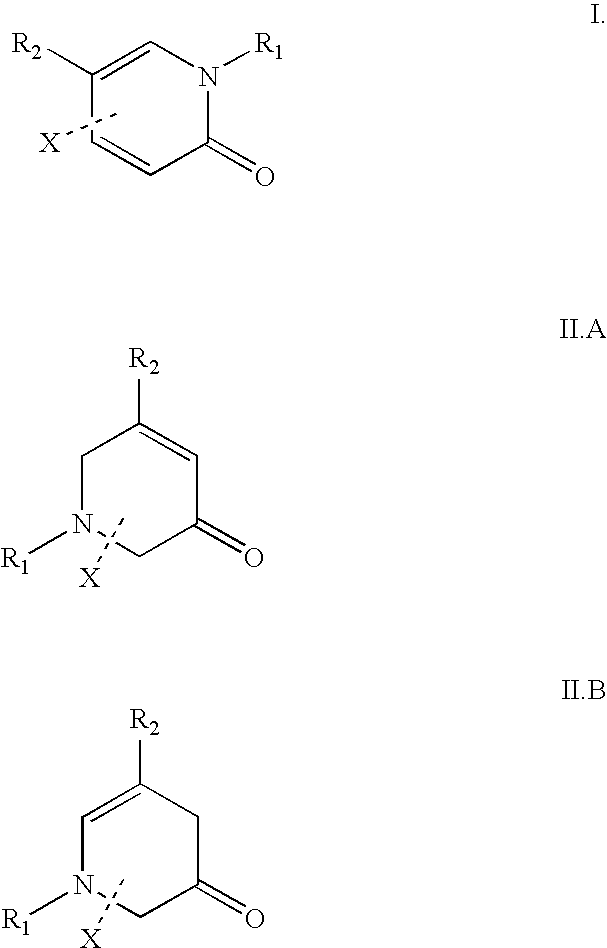
The disclosed invention is a composition for and a method of treating a Flaviviridae (including BVDV and HCV), Orthomyxoviridae (including Influenza A and B) or Paramyxoviridae (including RSV) infection, or conditions related to abnormal cellular proliferation, in a host, including animals, and especially humans, using a nucleoside of general formula (I)-(XXIII) or its pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug.This invention also provides an effective process to quantify the viral load, and in particular BVDV, HCV or West Nile Virus load, in a host, using real-time polymerase chain reaction (“RT-PCR”). Additionally, the invention discloses probe molecules that can fluoresce proportionally to the amount of virus present in a sample.
Owner:GILEAD SCI INC
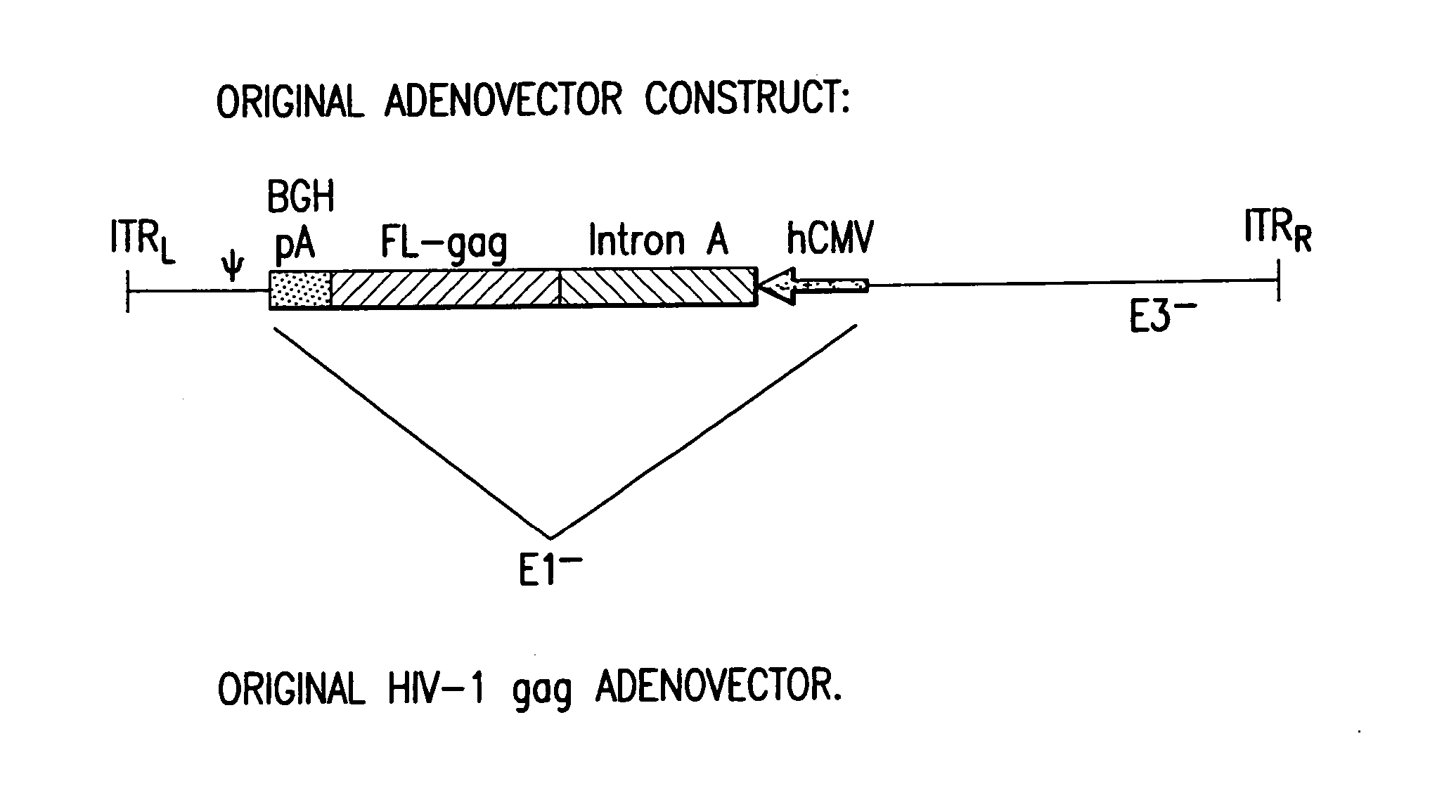
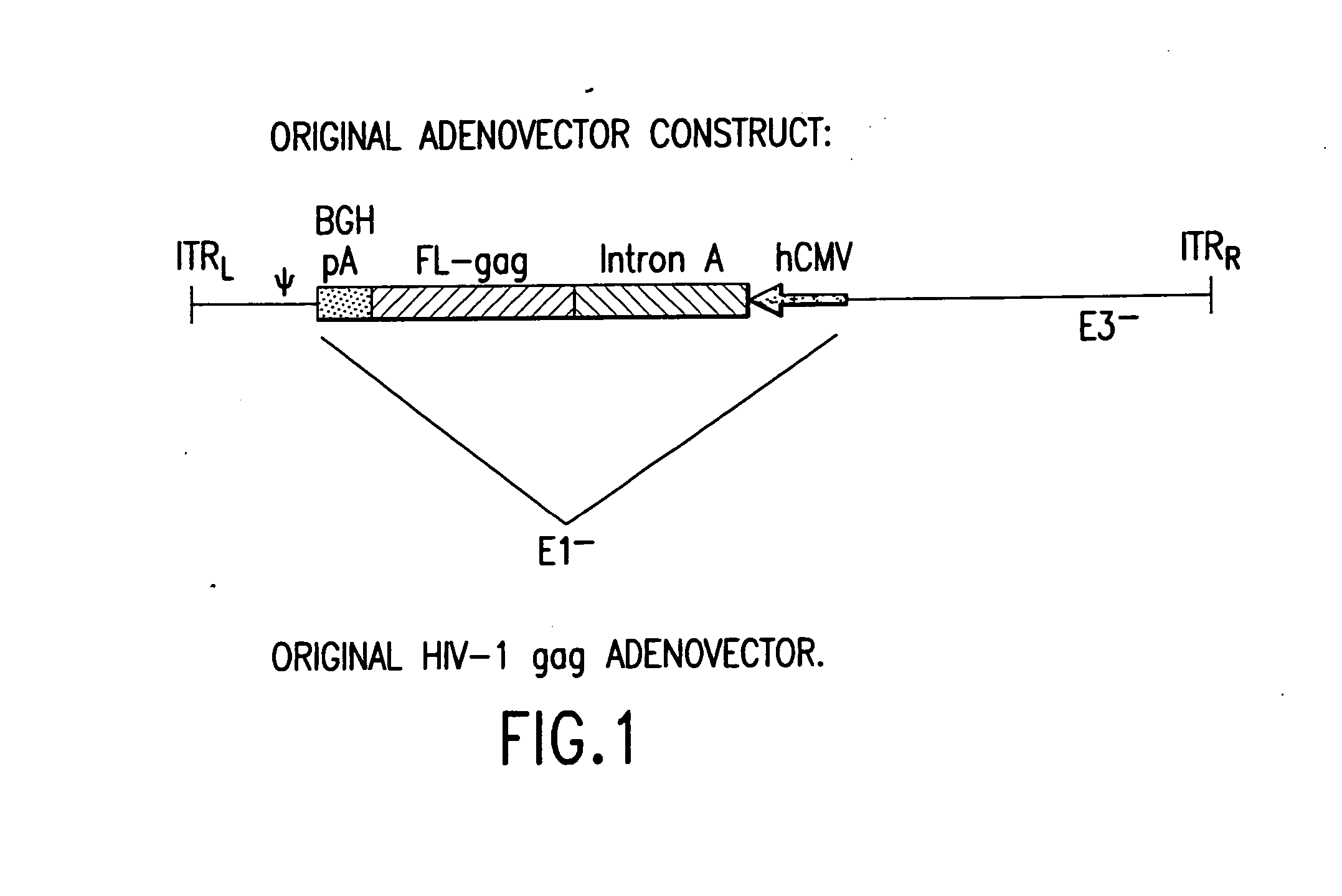
Enhanced first generation adenovirus vaccines expressing codon optimized HIV1-Gag, Pol, Nef and modifications
InactiveUS20070054395A1Genetically stableImprove featuresVectorsViral antigen ingredientsMammalReverse transcriptase
First generation adenoviral vectors and associated recombinant adenovirus-based HIV vaccines which show enhanced stability and growth properties and greater cellular-mediated immunity are described within this specification. These adenoviral vectors are utilized to generate and produce through cell culture various adenoviral-based HIV-1 vaccines which contain HIV-1 gag, HIV-1 pol and / or HIV-1 nef polynucleotide pharmaceutical products, and biologically relevant modifications thereof. These adenovirus vaccines, when directly introduced into living vertebrate tissue, preferably a mammalian host such as a human or a non-human mammal of commercial or domestic veterinary importance, express the HIV1-Gag, Pol and / or Nef protein or biologically modification thereof, inducing a cellular immune response which specifically recognizes HIV-1. The exemplified polynucleotides of the present invention are synthetic DNA molecules encoding HIV-1 Gag, encoding codon optimized HIV-1 Pol, derivatives of optimized HIV-1 Pol (including constructs wherein protease, reverse transcriptase, RNAse H and integrase activity of HIV-1 Pol is inactivated), HIV-1 Nef and derivatives of optimized HIV-1 Nef, including nef mutants which effect wild type characteristics of Nef, such as myristylation and down regulation of host CD4. The adenoviral vaccines of the present invention, when administered alone or in a combined modality regime, will offer a prophylactic advantage to previously uninfected individuals and / or provide a therapeutic effect by reducing viral load levels within an infected individual, thus prolonging the asymptomatic phase of HIV-1 infection.
Owner:EMINI EMILIO A +7
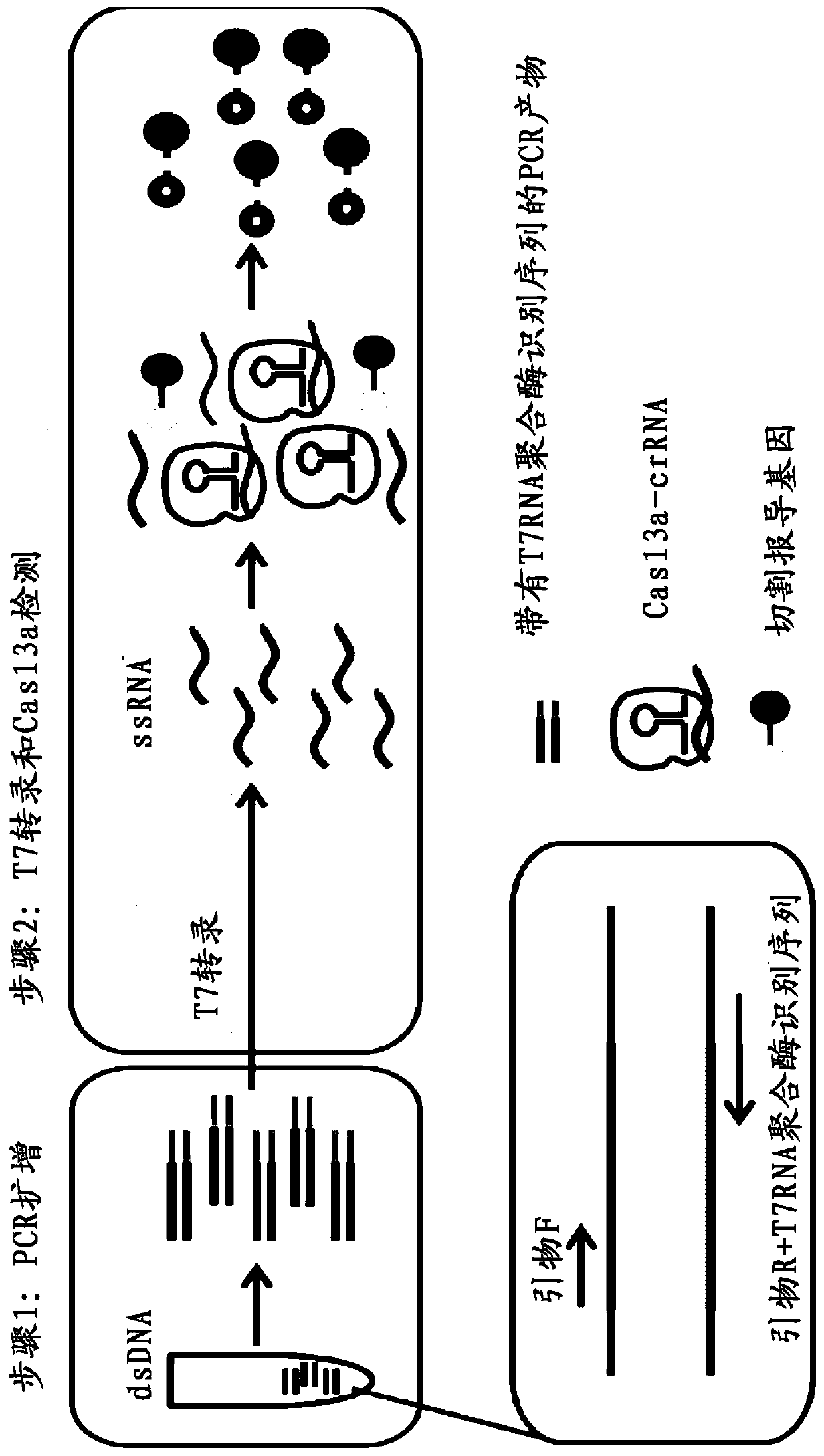
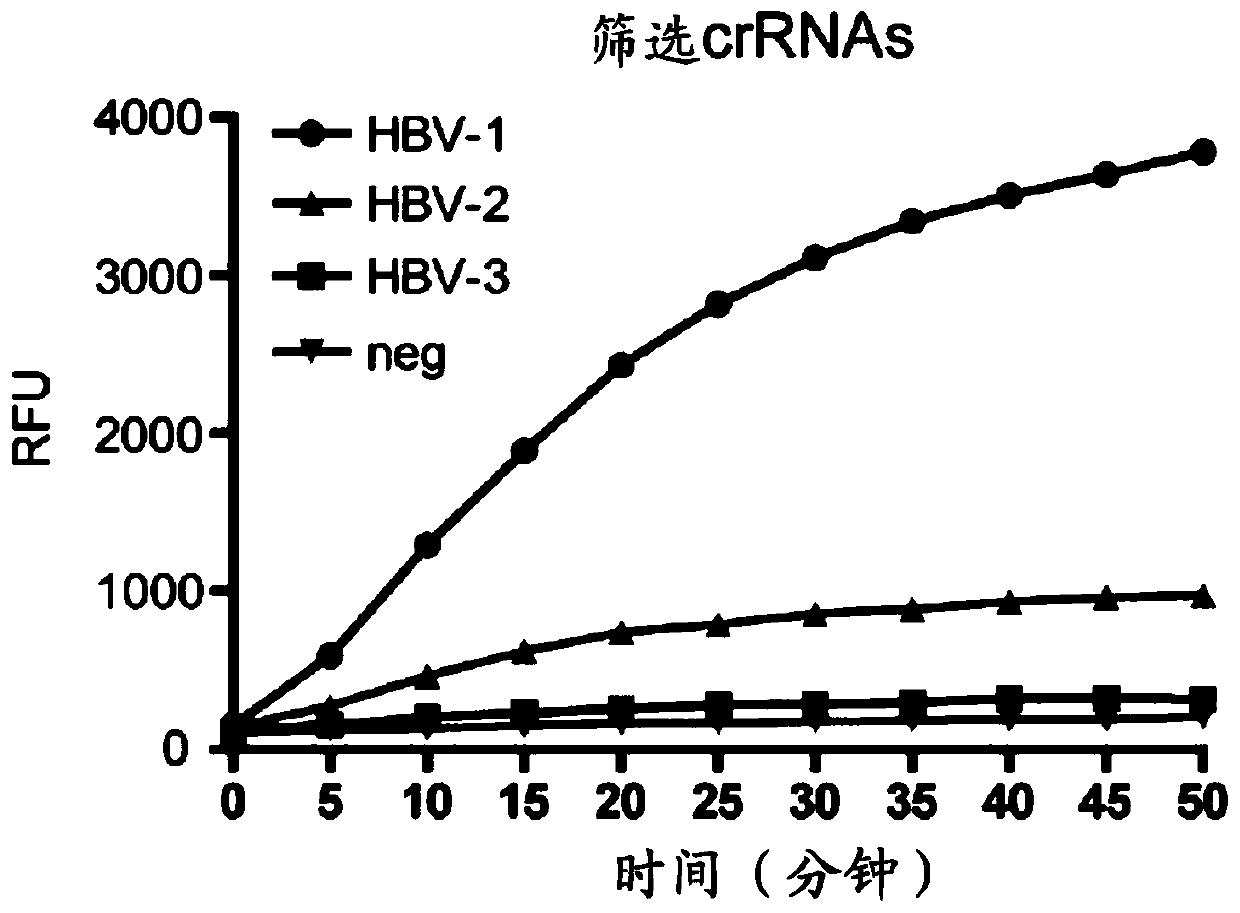
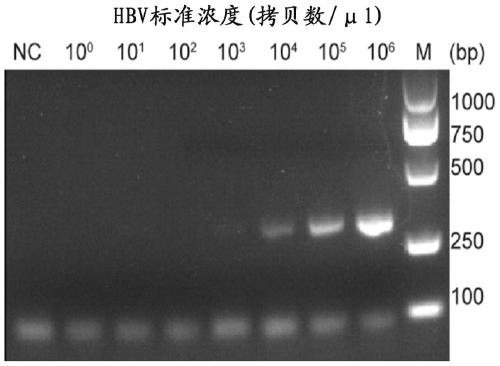
Application of crRNA targeted PCR-CRISPR system to detection of HBVDNA
ActiveCN110184389AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSerum samplesPolymerase L
The invention discloses a method for detecting HBVDNA through combination of PCR and CRISPR. The method comprises the steps of (1) amplifying nucleic acid of samples to be detected through a pair of upstream and downstream specific primers, wherein a sequence which can be recognized and transcribed by T7RNA polymerase is arranged at a 5' end of the downstream primer; and (2) detecting whether a targeting sequence exists or not in amplification products of the nucleic acid of the samples to be detected in a detection system containing crRNA, T7RNA polymerase, Cas13a protein and report RNA for recognizing an HBVDNA target sequence, wherein the section of the HBVDNA target sequence is 803<rd>-829nt. The invention further discloses crRNA capable of targeting HBVDNA specific sites and a reagent kit containing the crRNA. The method provided by the invention is simple, convenient and quick during detection of the content of the HBVDNA, and has extreme high sensitivity and specificity, single-copy HBV DNA is differentiated within 15 minutes after PCR amplification, and higher positive detection rate can be shown for serum samples low in virus load.
Owner:中国人民解放军疾病预防控制中心 +1
Methods and compositions for treatment of HIV infection
InactiveUS20160095850A1Reduce viral loadBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunodeficiency virusCD4 antigen
Methods and compositions for treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections have been developed which dampen immune activation with a bias more on the CD4 T cells relative to the CD8 T cell response, inhibit HIV replication, reactivate latent HIV, and inhibit infection of cells by HIV. Pushing latent HIV into active infections with hindrance of cell infection by the reactivated HIV can substantially reduce the number of cells infected with HIV and the viral load of HIV, which is not achieved using just the combination of ART and compounds which activate latent HIV. The methods involve administering to an HIV-infected subject three or more compounds which collectively dampen immune activation with a bias more on the CD4 T cells relative to the CD8 T cell response, inhibit HIV replication, reactivate latent HIV, and inhibiting infection of CD4 T cells by HIV.
Owner:COOPER HUMAN SYST
Vaccines and methods for prevention and treatment of drug-resistant hiv-1 and hepatitis b virus
ActiveUS20090317418A1Reduce viral loadLower viral loadSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviral drugResistant virus
The present invention provides methods for lowering a viral load of a virus resistant to an antiviral drug by inducing cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) to recognize a predetermined mutated epitope within a viral protein of the drug-resistant virus. CTLs are induced by immunizing a host with a peptide comprising the predetermined mutation. The immunostimulating peptide may be further improved by epitope-enhancement for inducing specific CTLs. The antiviral protection against drug-resistant virus shown by compositions of the present invention and mediated by human HLA-restricted CTL has not been previously achieved.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE DEPT OF
Rapid test including genetic sequence probe
InactiveUS20100105024A1Fast resultsSimple resultMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisCelluloseSpecific test
A rapid test kit may have a genetic probe, and antibody detecting probe or a combination of a genetic probe and an antibody detecting probe disposed within one or more test windows of the test kit. A cellulose filter paper membrane with a flow rate selected in a range of about 0.04 to about 0.4 ml / min / cm2 is used in one example. The test kit provides for rapid screening for DNA, RNA or fragments of DNA or RNA in a bodily fluid or antibodies indicating exposure to such DNA / RNA. The genetic probe may include single stranded DNA or a fragment of single stranded DNA, such as primer, immobilized on the filter paper, and a single stranded DNA, such as the same or a different primer, conjugated with a marker, such as a nanotube or nanoparticle. For example, a gold nanoparticle or a carbon nanotube may be used as a staining agent by conjugating the gold nanoparticle or the carbon nanotube to a genetic probe, such as a DNA primer capable of binding with a complementary DNA or viral RNA or a fragment of one of these. By comparing contrast or intensity of a test spot to a standard, a viral load may be reported. By comparing a test region using the genetic marker and a test region using an antigen to detect antibodies, a sensitive and specific test may be conducted during use of a vaccine to determine the effectiveness of the vaccine, for example.
Owner:ULTRAPID NANODIAGNOSTICS
Single standard product-based four-color fluorogenic quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method and kit
InactiveCN103146846AEasy to operateQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescencePcr methodDiagnosis laboratory
The invention discloses a single standard product-based quardruple four-color fluorogenic quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology. The technology is capable of detecting group A rotavirus (HRVA), norovirus group I (NVGI), norovirus group II (NVG II) and human astrovirus (HAstV) RNA in various treated specimen through one-step quardruple PCR amplification and quantifying virus load. The technology is characterized in that single standard product is adopted as positive control and quantitative standard in the quardruple four-color fluorogenic quantitative PCR detection for four viruses, thereby breaking through the deficiency that the traditional multiple fluorogenic quantitative PCR needs a plurality of standard products, improving the experiment detection efficiency, reducing the pollution probability and improving the preparation and production efficiency of the kit. The method and kit can be used for fast high-throughput test and epidemic monitoring in laboratories of HRVA, NVG I, NVG II and HAstV which can cause diarrhea syndromes. The single standard product-based four-color florogenic quantitative PCR method and the kit belong to the biotechnology field.
Owner:GUANGZHOU VIPOTION BIOTECH
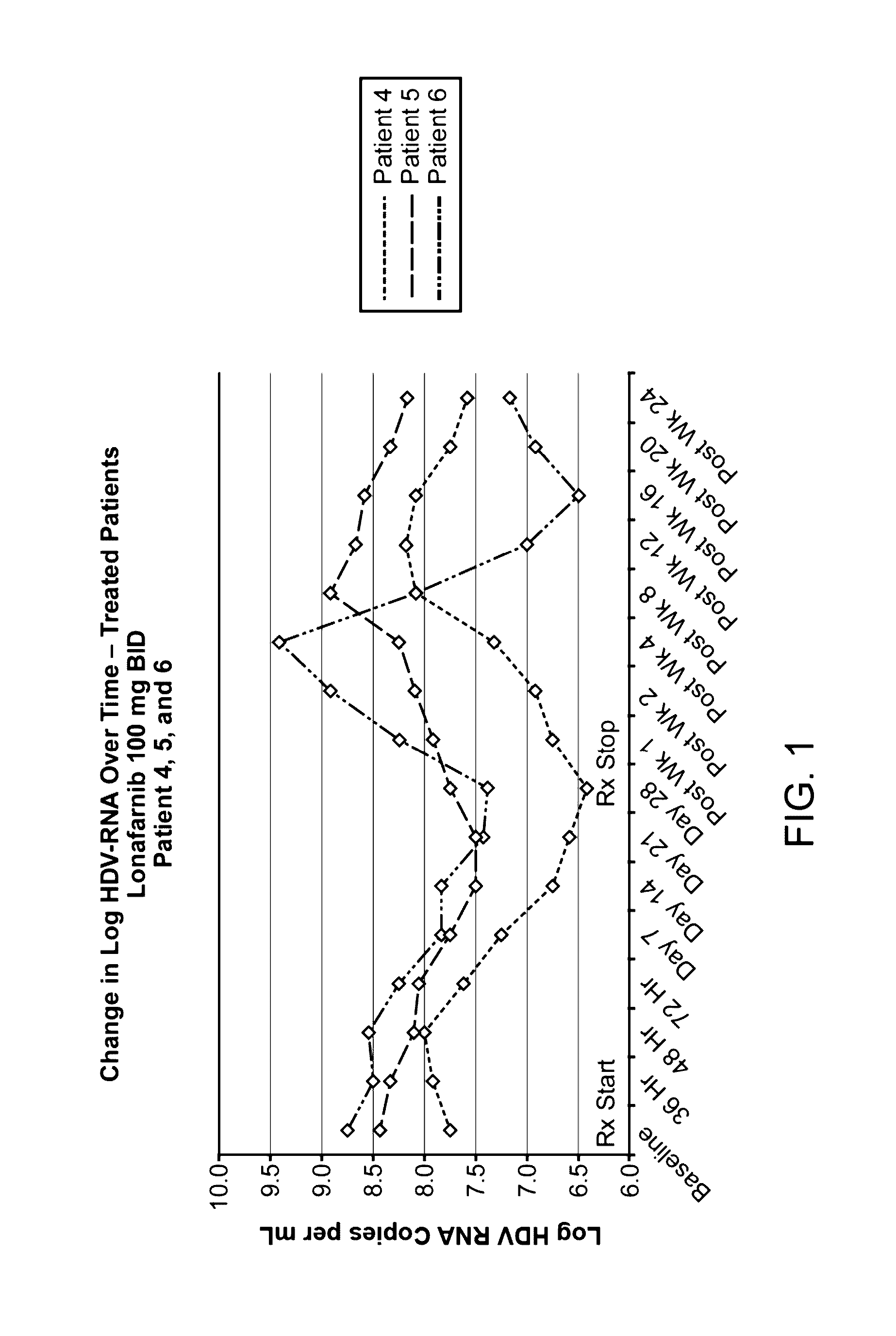
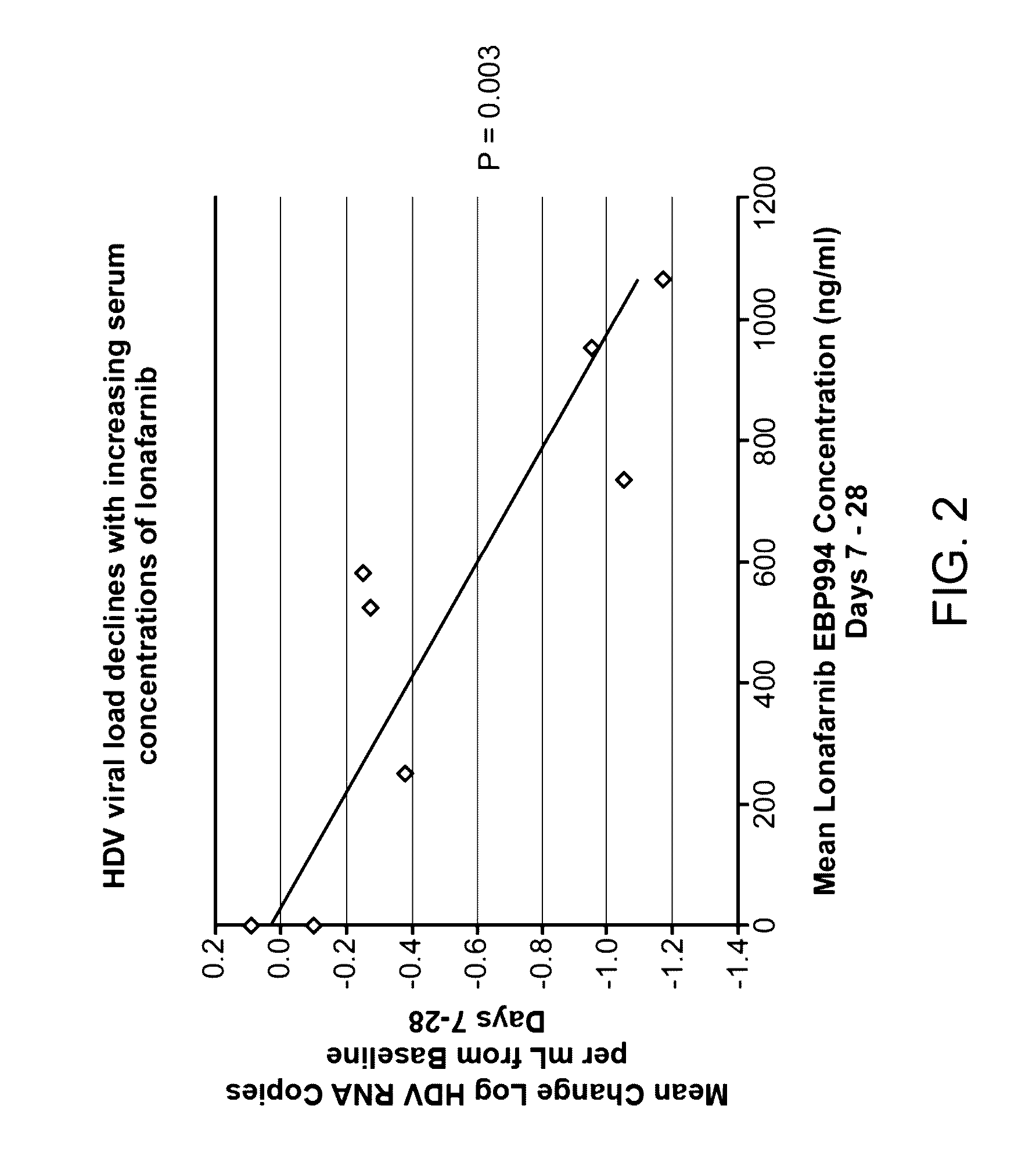
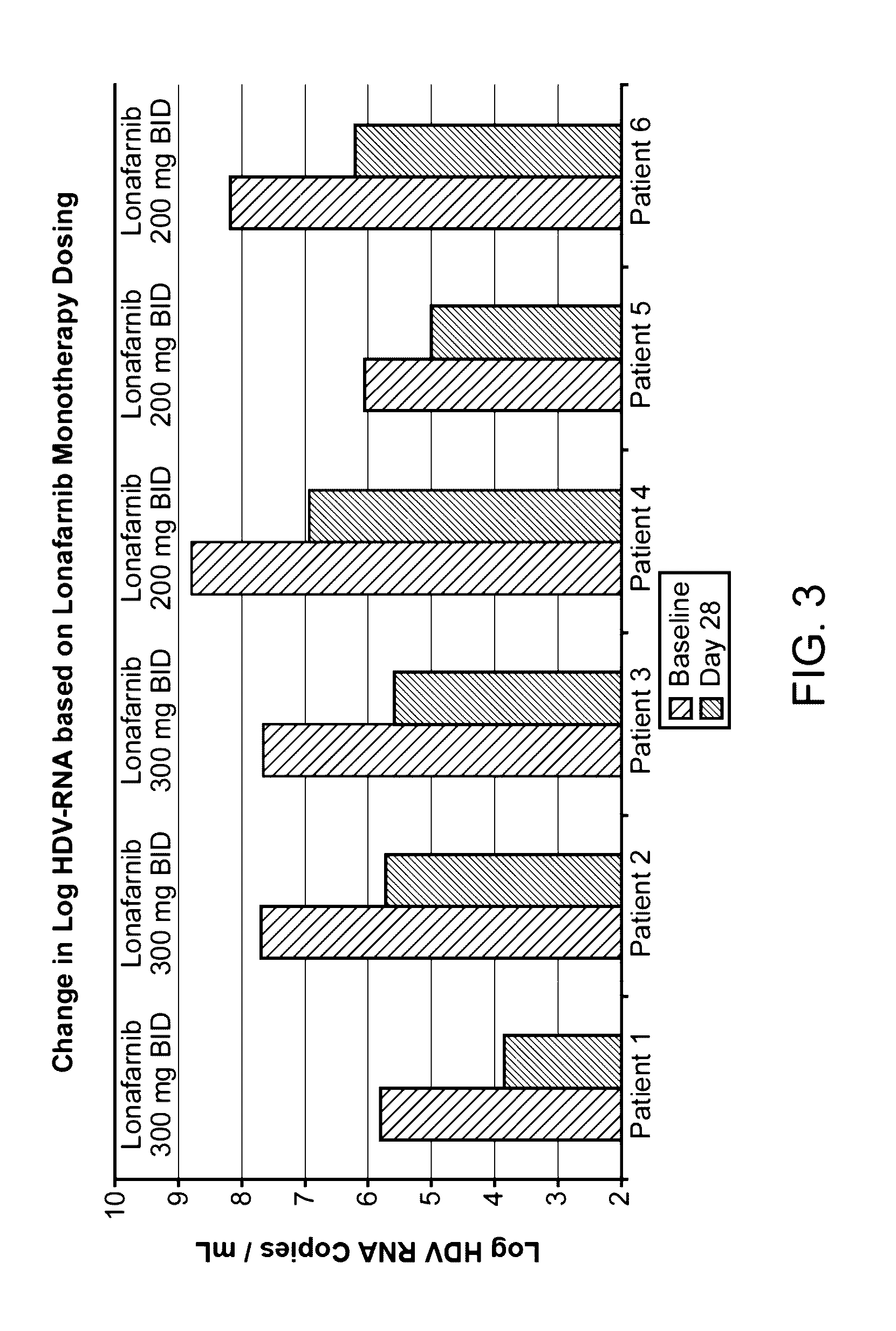
Treatment of hepatitis delta virus infection
ActiveUS20170042862A1Organic active ingredientsPowder deliveryInterferon therapyDeltaretrovirus Infections
Methods of reducing hepatitis delta virus (HDV) viral loads in a patient are provided. In some embodiments, the method comprises treating the patient with lonafarnib-ritonavir co-therapy. In some embodiments, the method further comprises treating the patient with an interferon.
Owner:EIGER BIOPHARMLS
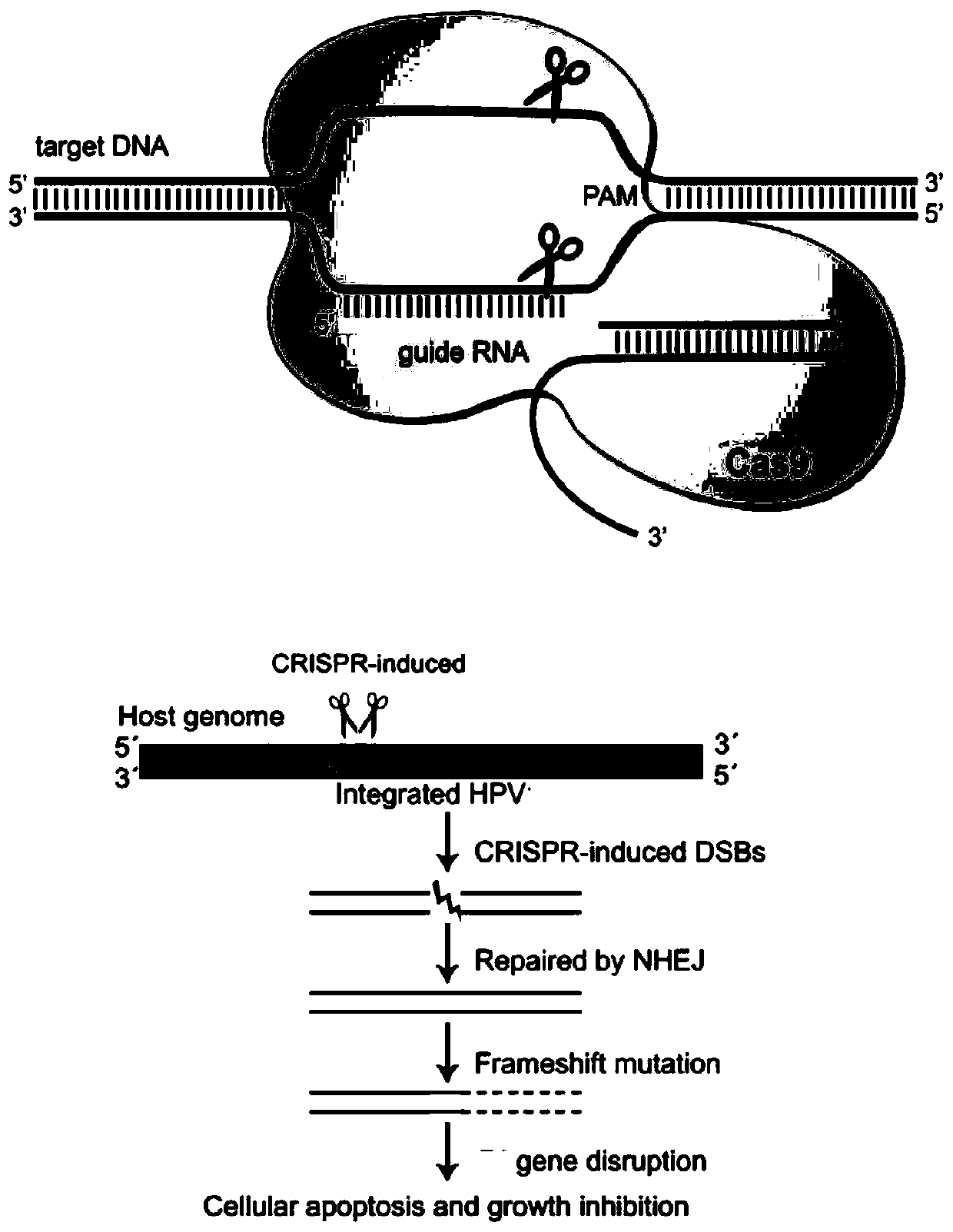
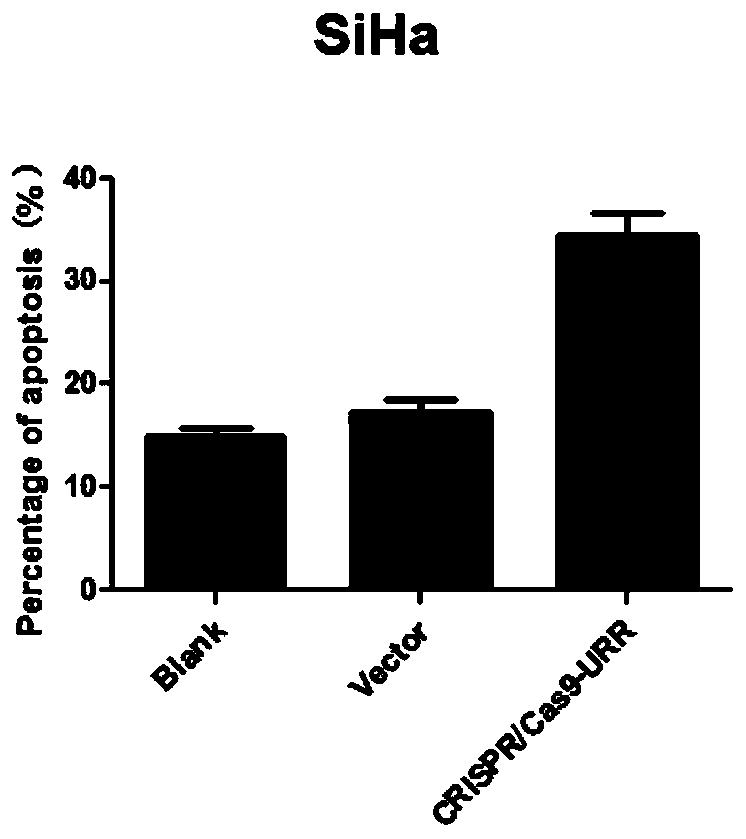
Plasmid, system and preparation for targeted knockout of human papilloma virus (HPV) URR (upstream regulatory region) genes and preparation method of plasmid, system and preparation
The invention relates to a plasmid, system and preparation for targeted knockout of human papilloma virus (HPV) URR (upstream regulatory region) genes and a preparation method of the plasmid, system and preparation. The plasmid comprises sgRNA, Cas9 and an expression vector PX330 which can bind to the HPV URR genes. When transfected into cells, the plasmid specifically induces coding shift mutations of HPV oncogenic elements in corresponding HPV subtype positive cells to loss carcinogenic properties, even too much DSB can lead to cell apoptosis to reduce virus load, remove virus and pathological cells and reverse cancerous transformation, and important clinical application value is achieved. The preparation can effectively kill HPV positive tumor cells and effectively treat HPV positive tumor cells and is simple in preparation and low in cost.
Owner:ZHUHAI SHU TONG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Assay for porcine circovirus production
ActiveUS20080241821A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisAssayCell culture media
The present invention provides methods for the determination of the viral titer of a culture of host animal host cells infected with a circovirus. The FACS-based methods of the invention may include determining the viability of the host cells in a cell culture medium supernatant and of those cells that remain adherent to a solid support. Detecting and measuring the percentage of cells that expressed the viral antigens ORF1 and ORF2 may determine the viral load of the cultured host cells. The yield of the virus may be established by the detection and measurement of both antigens in supernatant cells, for example 5 to 7 days from when the host cells are transferred to a serum free medium. The methods of the invention may yield rapid quantitative data. This allows the repeated in-process monitoring of the viral production throughout the incubation period, and ready selection of the most appropriate harvesting point.
Owner:MERIAL INC
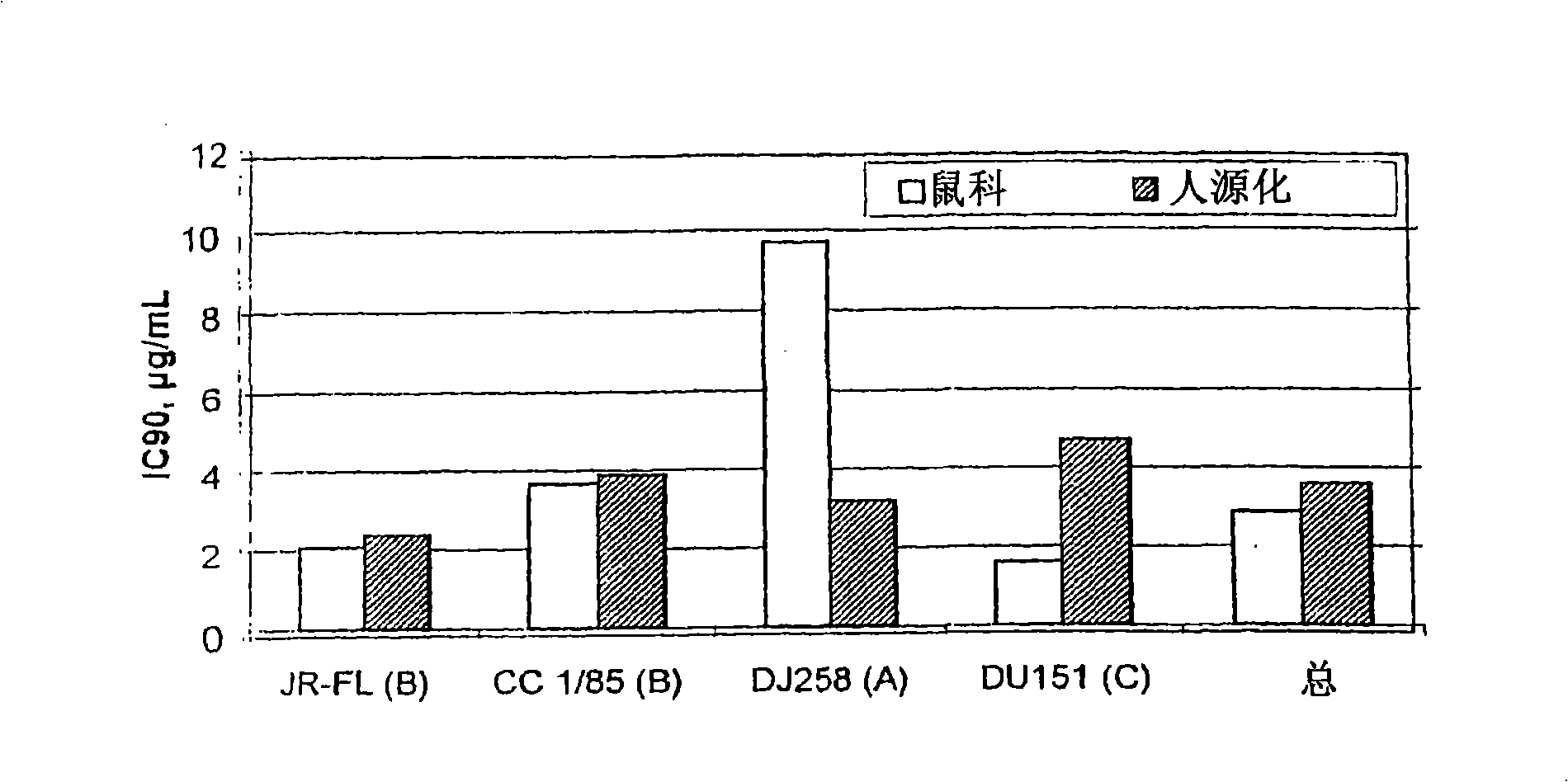
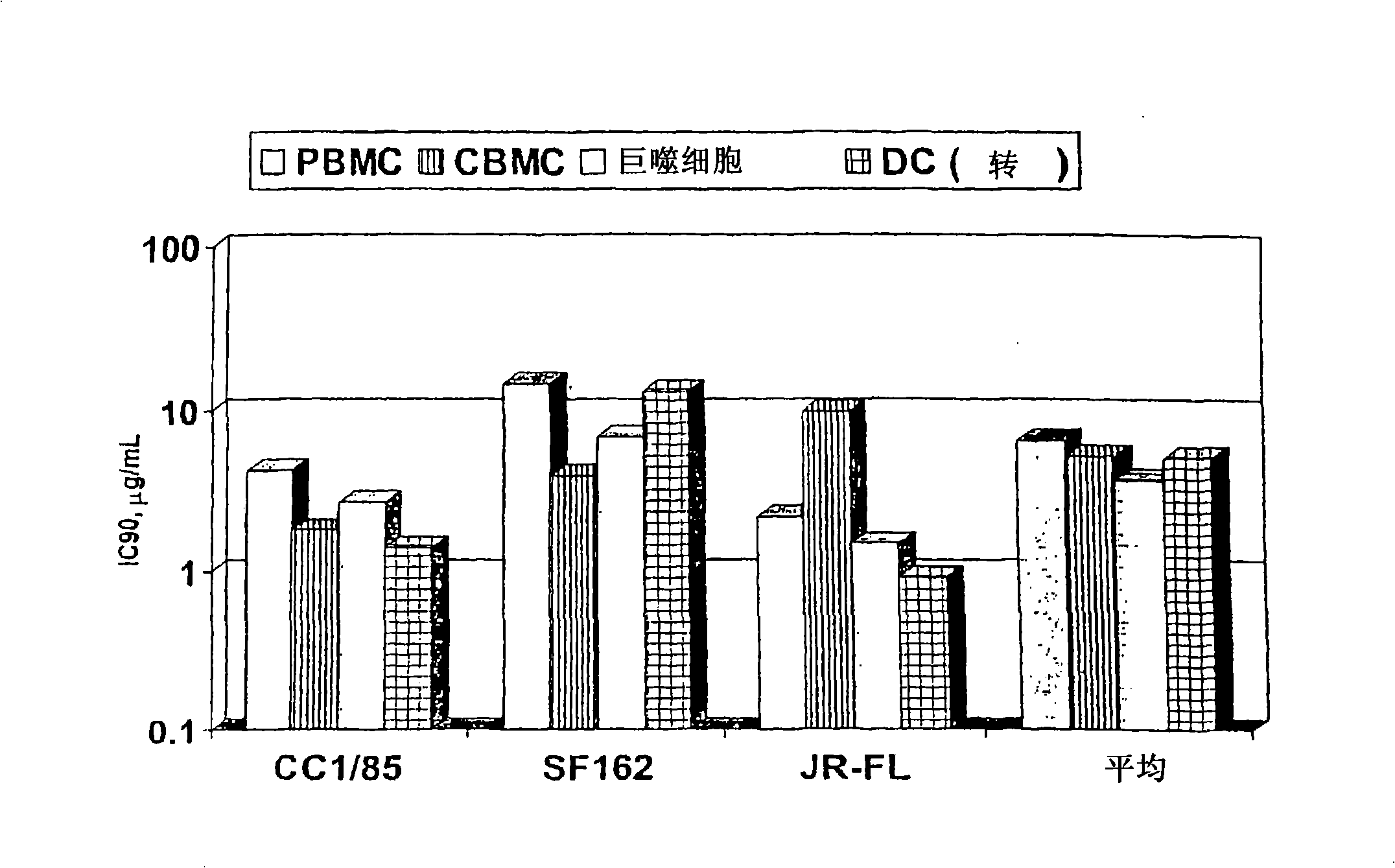
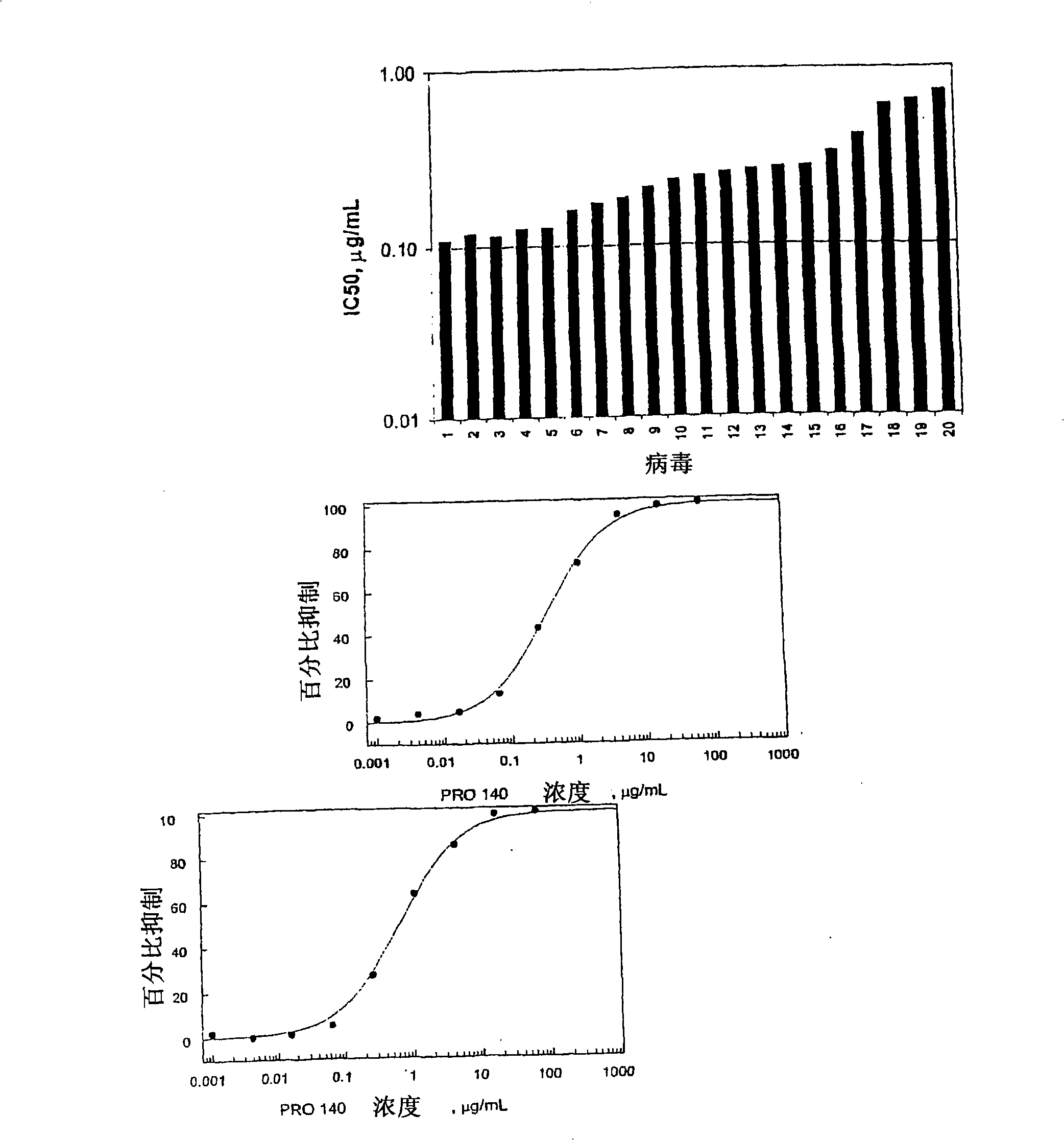
Methods for reducing viral load in HIV-1-infected patients
InactiveUS20080241135A1Reduce loadAvoid fusesPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementReduced doseHIV receptor
This method provides a method for reducing HIV-1 viral load in an HIV-1-infected human subject which comprises administering to the subject at a predefined interval effective HIV-1 viral load-reducing doses of (a) a humanized antibody designated PRO 140, or of (b) an anti-CCR5 receptor monoclonal antibody. This invention also provides a method for inhibiting in a human subject the onset or progression of an HIV-1-associated disorder, the inhibition of which is effected by inhibiting fusion of HIV-1 to CCR5+CD4+ target cells in the subject. This invention also provides a method for treating a subject infected with HIV-1 comprising administering to the subject (a) a monoclonal antibody which (i) binds to a CCR5 receptor on the surface of the subject's CD4+ cells and (ii) inhibits fusion of HIV-1 to the subject's CCR5+CD4+ cells, and (b) a non-antibody CCR5 receptor antagonist, in amounts effective to treat the subject.
Owner:PROGENICS PHARMA INC
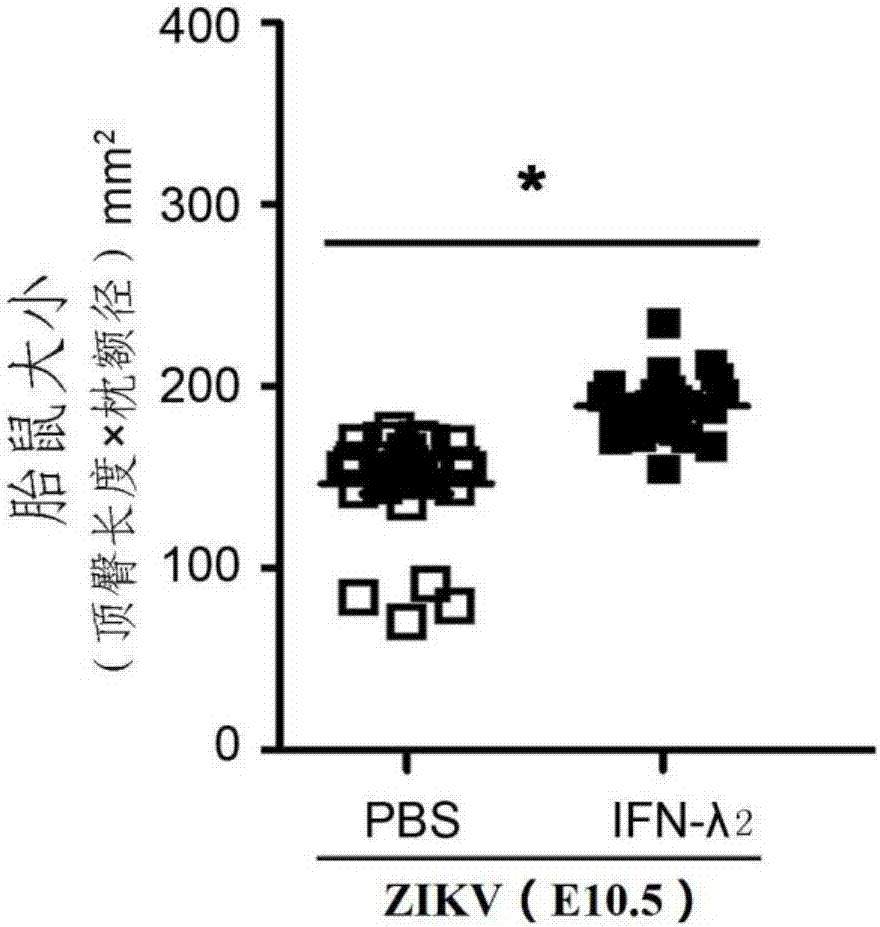
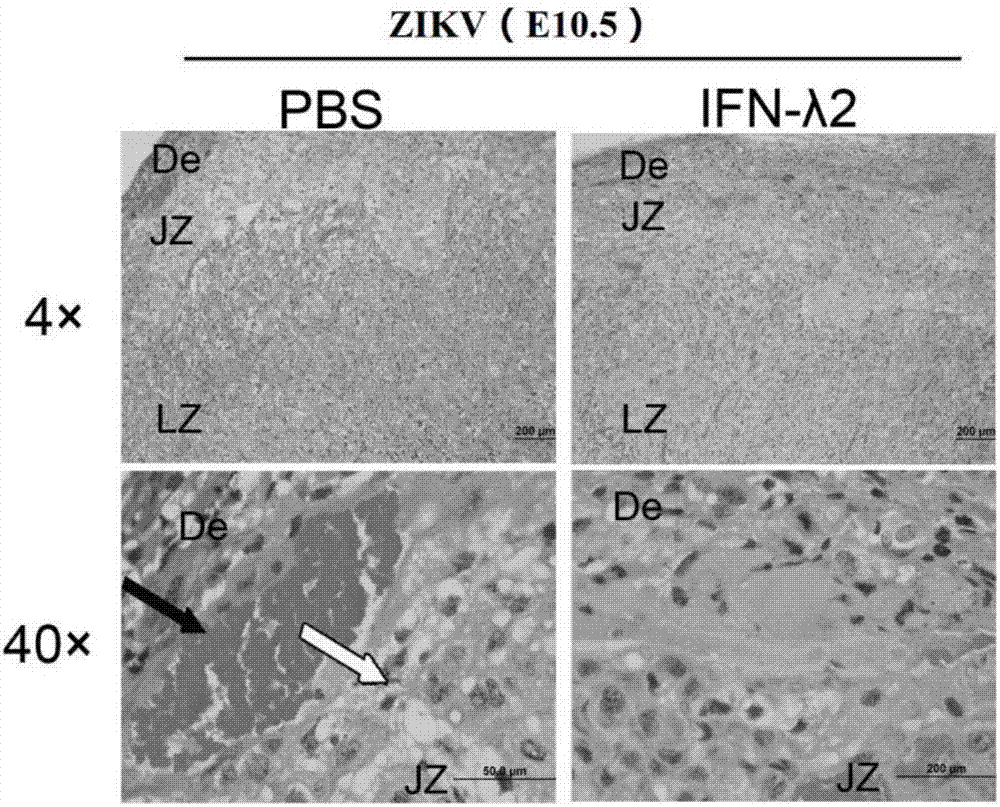
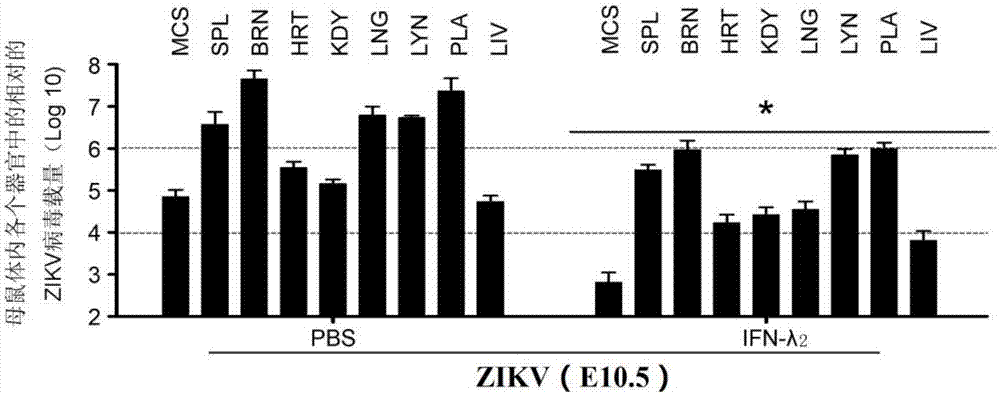
Novel application of IFN-lambda in Zika virus infection
ActiveCN107412739AEfficient preventionHighly effective therapeuticPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsZika virusPlacenta
The invention relates to a novel application of IFN-lambda in Zika virus infection and particularly provides an application of IFN-lambda 2 in preparation of a drug for preventing or treating Zika virus infection. Tests prove that delayed growth of fetal rats and placenta injury due to the Zika virus can be relieved by means of IFN-lambda 2, the relative Zika viral load in all organs of a mother rat and the fetal rats is detected through q-PCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction), and the fact that IFN-lambda 2 can inhibit reproduction of the Zika virus in the mother rat and the fetal rats is further verified. Besides, the invention further illustrates a mechanism of the IFN-lambda 2 in inhibiting Zika virus reproduction by the means of cytobiology. A new way and method are provided for preventing or treating microcephalus caused by Zika virus infection.
Owner:义乌国信白蚁防治有限公司
Hepatitis E virus fluorescent quantitative PCR detection method
InactiveCN101122563AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescenceTiter
The invention relates to a test method in the bioengineering field, in particular to a fluorescence quantitative PCR test method used for quantitatively test the titer of Hepatitis E virus (HEV) in a clinical specimen. The steps of invention include the design of virus specific quantitative PCR primers and probes, the construction of standard molecular, the extraction of a virus sample RNA, the cDNA synthesis of the sample RNA and the establishment and optimization of the fluorescence quantitative PCR test method. The testing sensitivity of the invention can reach to 10 degrees magnitude virus copy. The invention is equipped with good stability and specificity, which can be used for mass samples test and is capable of precisely measuring the virus load of the sample.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
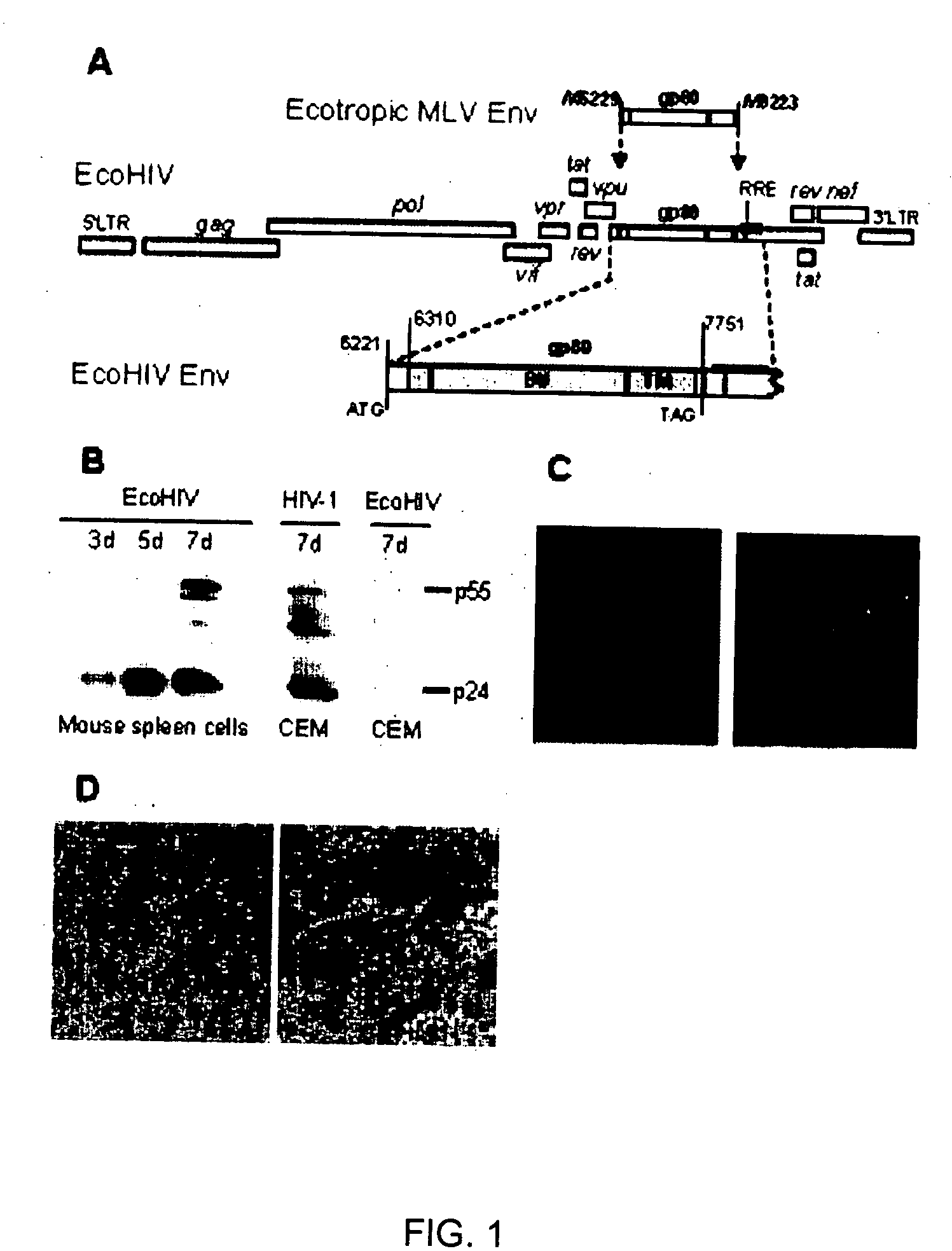
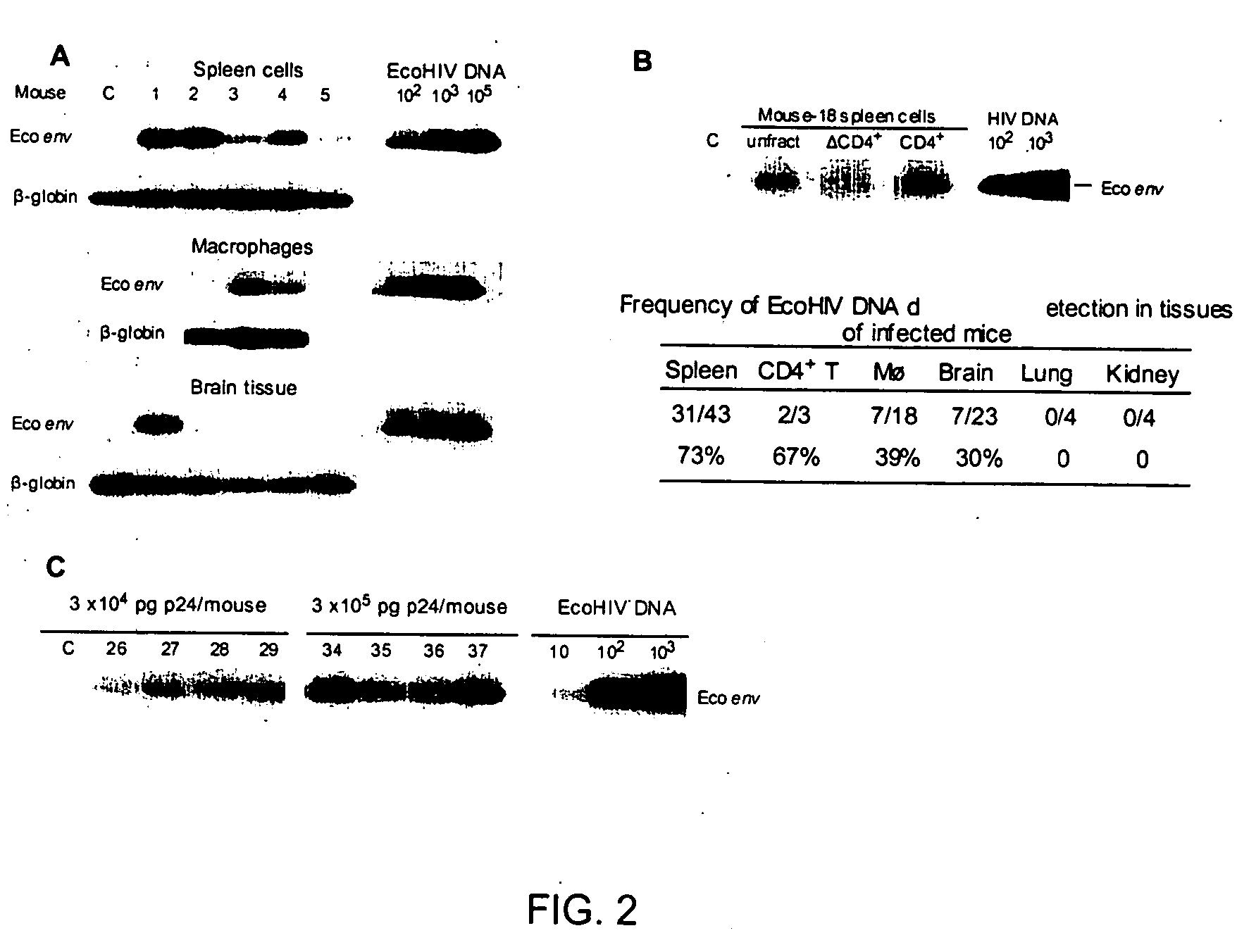
Development of a murine model of HIV-1 infection on the basis of construction of EcoHIV, a chimeric, molecular clone of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and ecotropic moloney murine leukemia virus competent to infect murine cells and mice
The present invention provides a chimeric HIV-1 construct, EcoHIV, capable of replication in a rodent cell. The invention also provides a convenient and safe rodent model of HIV-1 infection and AIDS. Methods for producing a rodent model of HIV-1 infection are also provided. Additionally, the invention provides the means to test immunogenic compositions or pharmaceutical interventions effective in preventing infection, reducing viral load, or reducing disease symptoms in a subject.
Owner:POTASH MARY +1
Combination Therapy for Treating Hepatitis C Virus Infection
InactiveUS20070258946A1Reduce morbidityReduce viral loadPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsMortality rateInterferon receptor
The present invention provides methods of treating hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection; methods of reducing the incidence of complications associated with HCV and cirrhosis of the liver; and methods of reducing viral load, or reducing the time to viral clearance, or reducing morbidity or mortality in the clinical outcomes, in patients suffering from HCV infection. The methods generally involve administering to the individual i) a Type I interferon receptor agonist or a Type III interferon receptor agonist; ii) an immunomodulatory agent; and iii) an inhibitor of an HCV enzyme.
Owner:THREE RIVERS PHARMA LLC
Human Antibodies Interacting with Hiv Gp41
ActiveUS20070248613A1Prolonging asymptomatic phaseAvoid infectionCompound screeningBiocideAntibody fragmentsHeptad repeat
Human scFvs are disclosed which interact with a conformational epitope along the pre-hairpin, N-helix coiled coil structure within the heptad repeat 1 (HR1) region of gp41 of HIV. These antibodies, as well as IgG conversions, are shown to neutralize diverse HIV isolates. Isolated nucleic acid molecules are also disclosed which encode relevant portions of these antibodies, as well as the purified forms of the expressed antibodies or relevant antibody fragments, such as VH and VL chains. The antibody compositions disclosed within this specification may provide for a therapeutic treatment against HIV infection by reducing viral load levels within an infected individual, thus prolonging the asymptomatic phase of HIV infection. These antibodies will also be useful in assays to identify HIV antiviral compounds as well as allowing for the identification of candidate HIV vaccines, such as HIV peptide vaccines.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC +3
Methods for reducing viral load in hiv-1-infected patients
InactiveCN101495145AStrong inhibitory activitySmall doseBiocideAntibody ingredientsReduced doseHIV receptor
This method provides a method for reducing HIV-I viral load in an HIV-1-infected human subject which comprises administering to the subject at a predefined interval effective HIV-I viral load- reducing doses of (a) a humanized antibody designated PRO 140, or of (b) an anti-CCR5 receptor monoclonal antibody. This invention also provides a method for inhibiting in a human subject the onset or progression of an HIV-I -associated disorder, the inhibition of which is effected by inhibiting fusion of HIV-I to CCR5CD4 target cells in the subject. This invention also provides a method for treating a subject infected with HIV-I comprising administering to the subject (a) a monoclonal antibody which (i) binds to a CCR5 receptor on the surface of the subject's CD4 cells and (ii) inhibits fusion of HIV-I to the subject's CCR5CD4 cells, and (b) a non-antibody CCR5 receptor antagonist, in amounts effective to treat the subject.
Owner:原基因药物有限公司
Methods of treating hepatitis c virus infection
InactiveUS20110243894A1Reduce morbidityReduce viral loadBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsSteatosisMortality rate
The present invention provides methods of treating hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection; methods of reducing the incidence of complications associated with HCV and cirrhosis of the liver; and methods of reducing viral load, or reducing the time to viral clearance, or reducing morbidity or mortality in the clinical outcomes, in patients suffering from HCV infection. Also provided are methods of treating liver steatosis and liver fibrosis.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
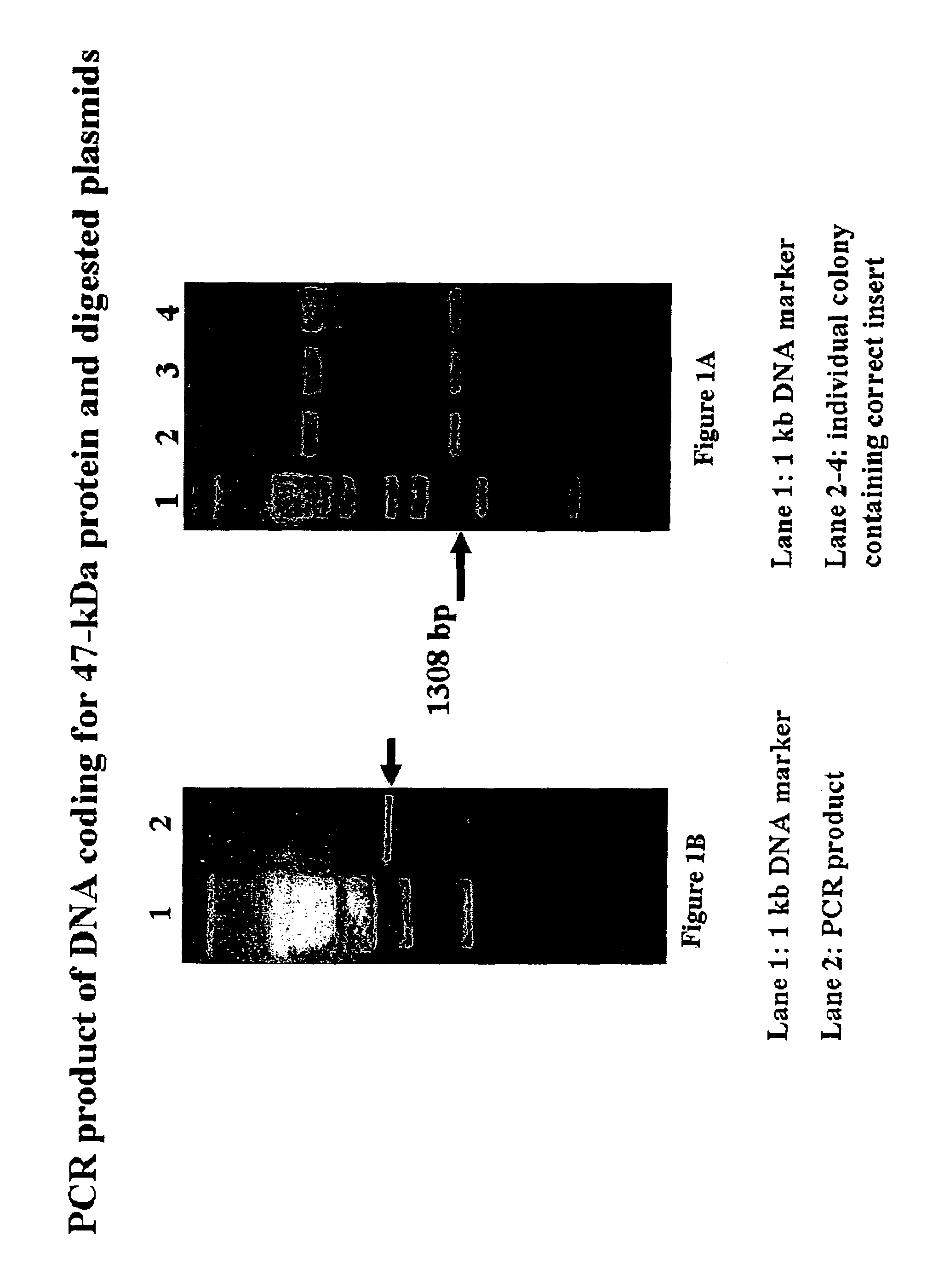
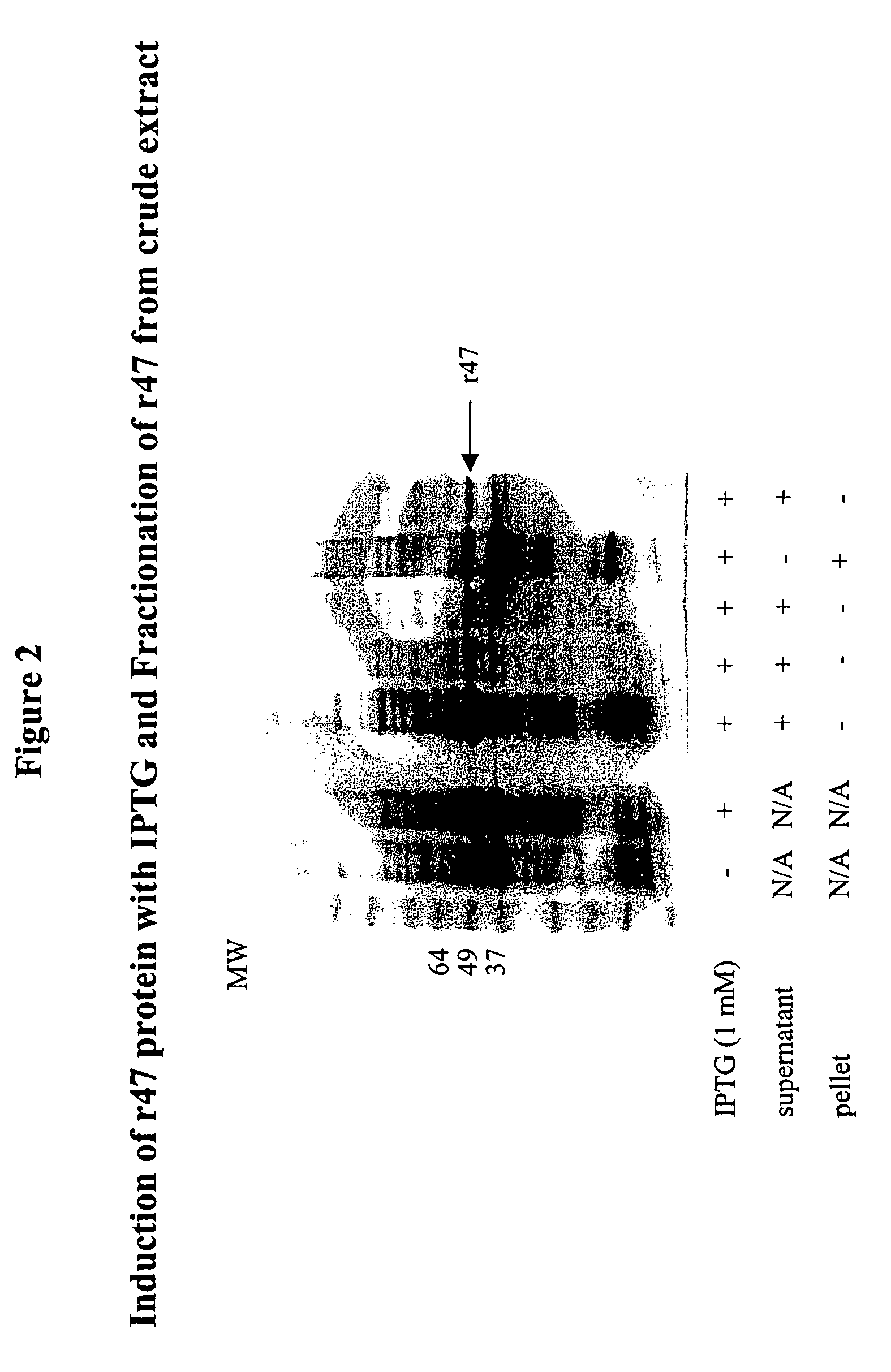
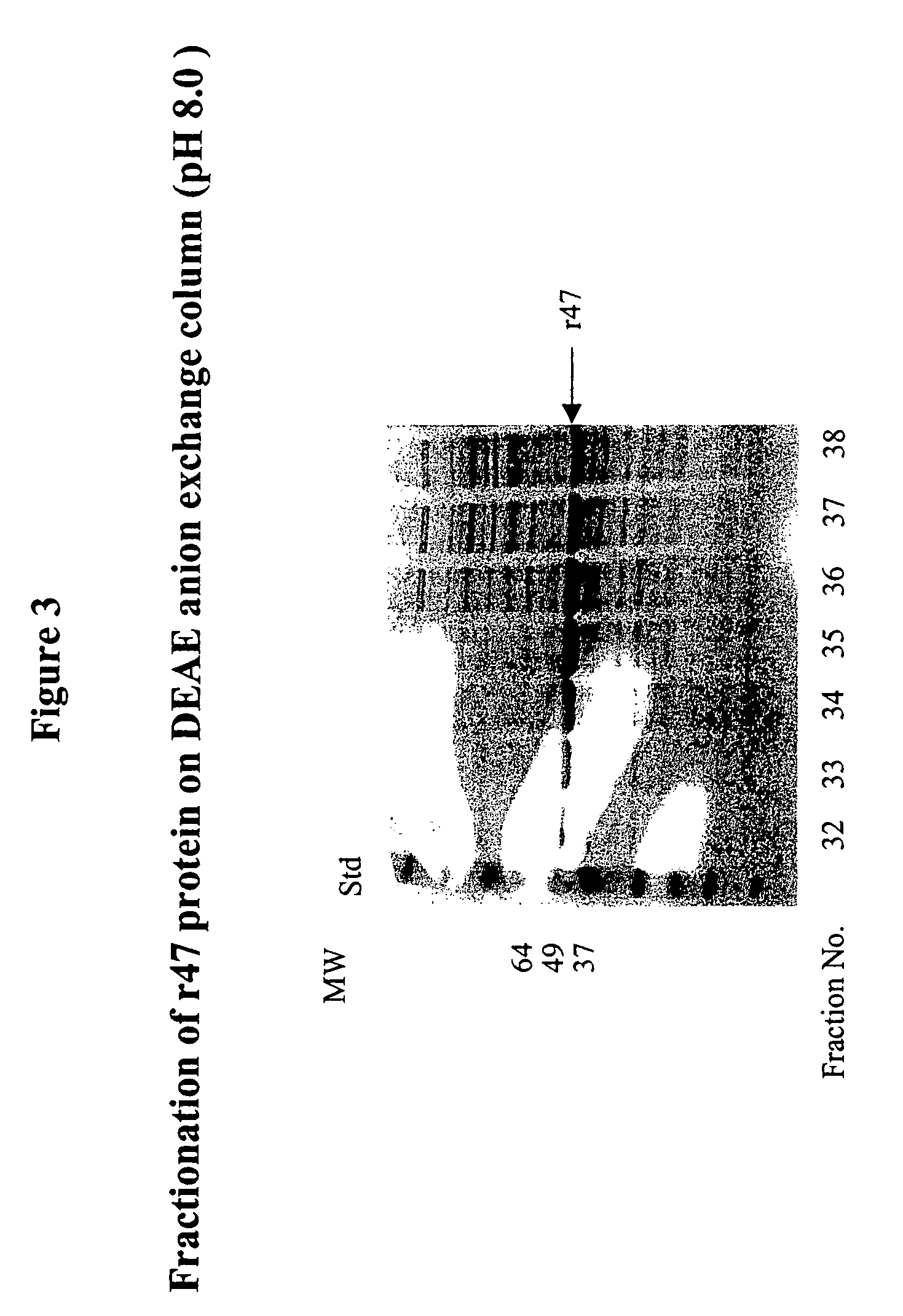
Orientia tsutsugamushi truncated recombinant outer membrane protein (r47) and (r57) vaccines diagnostics and therapeutics for scrub typhus
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Bivalent inactivated vaccine for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome and preparation method thereof
PendingCN113521271AEasy to prepareSimple and fast operationSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsPig farmsNeutralising antibody
The invention discloses a bivalent inactivated vaccine for porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome and a preparation method thereof. The bivalent inactivated vaccine for the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome comprises the following two inactivated viruses: a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus with the strain number of PRRSV-ZJ / H strain and the preservation number of CCTCC NO: V202130, and a porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus with the strain number of PRRSV-ZJ / NB strain and the preservation number of CCTCC NO: V202140. The bivalent inactivated vaccine prepared by the invention can effectively prevent and control two major prevalent PRRS virus types in the current field, and a needle of the PRRS inactivated vaccine is immunized in a commercial pig field which is naturally infected or is immunized by using a PRRS attenuated live vaccine, so that the virus specificity neutralizing antibody can be obviously improved, the virus load in the infected pig body can be reduced, the PRRS epidemic situation can be quickly and effectively controlled, the daily gain of pigs can be obviously improved, and the economic benefits of pig farms are increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU JIANLIANG VETERINARY BIOLOGICAL PREPARATIONS CO LTD
Application of macromolecular protein in anti-RNA virus disinfectant
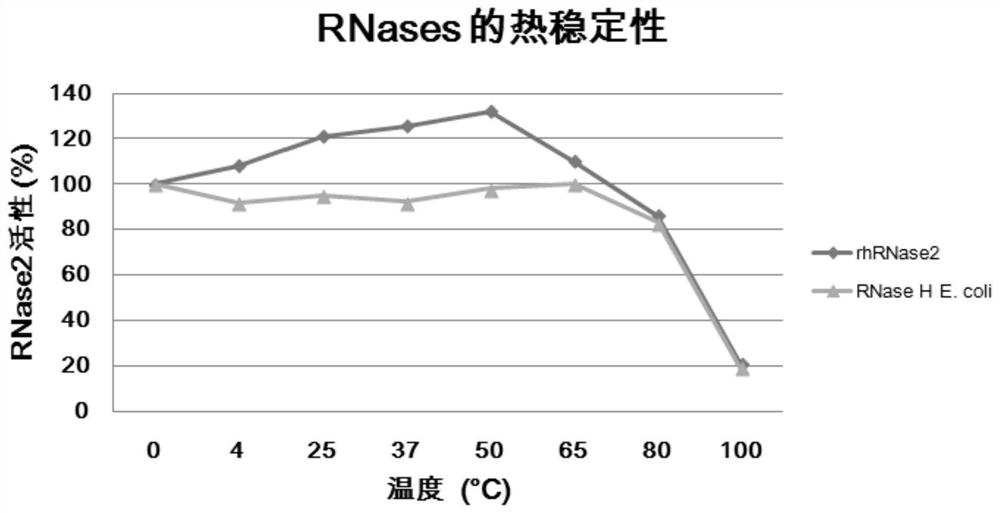
The invention provides an application of macromolecular protein in an anti-RNA virus disinfectant. The macromolecular protein is one or more of natural immune polypeptide and protein secreted by bacteria, fungi, animals or plants in the biological field, the disinfectant acts on the body surface environment, the in-vitro environment or the oral and nasal cavity environment, and the macromolecularprotein is human RNase 2 and / or RNase 3. The RNase 2 and RNase 3 in the disinfectant are very stable in structure and lasting in activity, can inhibit viruses in vitro and directly destroy virus outermembranes, and meanwhile can degrade virus genomes, and can reduce the infection virus load in the in-vitro environment; compared with the existing small molecule disinfectant, the disinfectant has the advantages of long action time, high efficiency, no irritation to human bodies, environmental protection, cyclic effect exertion and the like, and is expected to have great application prospects inthe aspect of prevention of respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract RNA virus infection of novel coronavirus, influenza virus and the like.
Owner:武汉愔紫生物科技有限公司
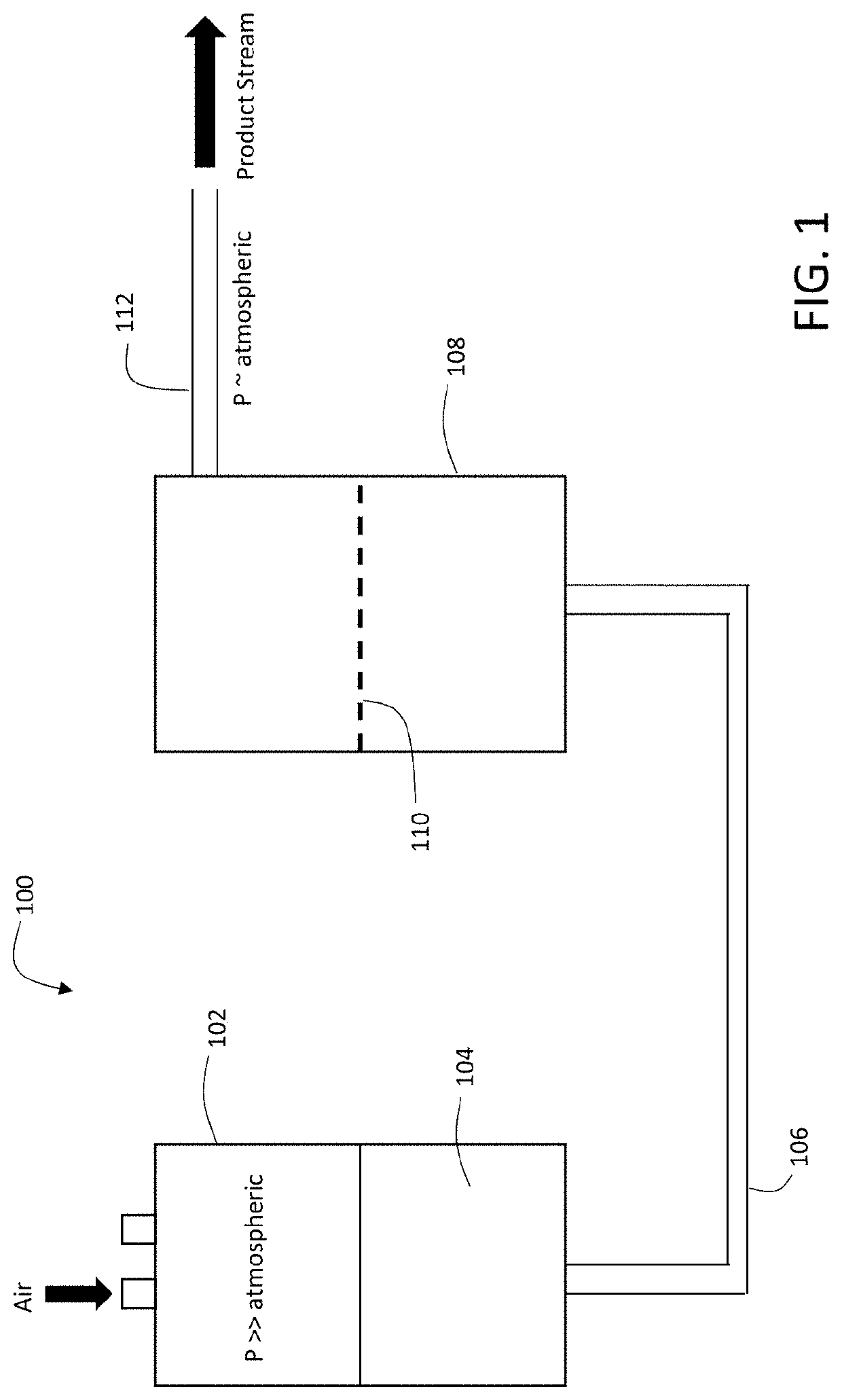
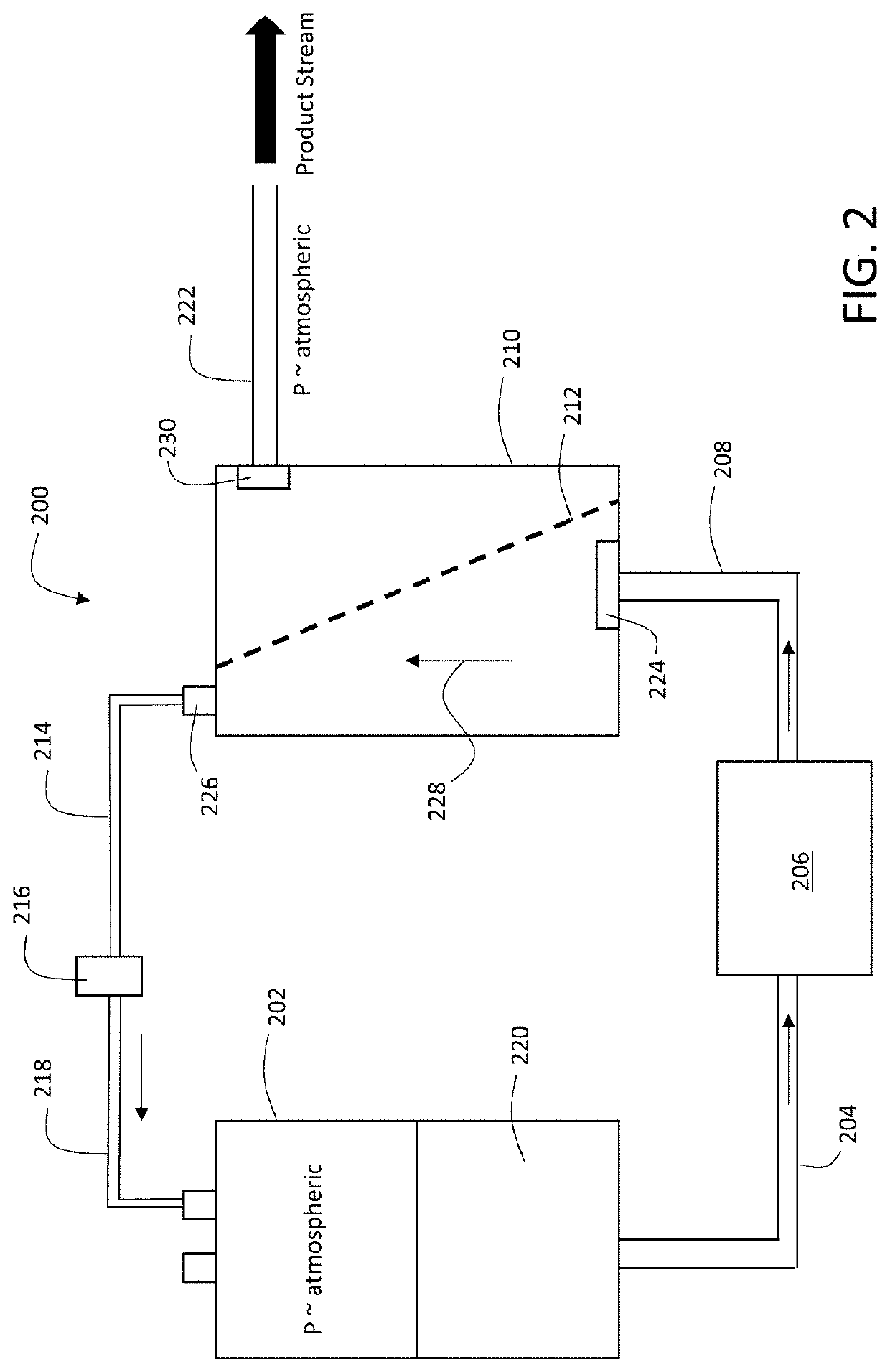
Tangential Viral Filtration
ActiveUS20200290044A1Low amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSemi-permeable membranesEngineeringViral filter
Viral filters include a filter member featuring a first surface and a second surface and having a thickness extending between the first and second surfaces in a first direction, and a plurality of channels formed in the filter member, each of the channels having a channel axis, where during use, a solution carrying a viral load flows in a direction parallel to the first surface, and at least a portion of the viral load enters the membrane through the first surface and propagates in the first direction, and where for at least 50% of the channels in the filter member, the channel axis is oriented at an angle of between 5 degrees and 85 degrees relative to the first direction.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Method of reducing viral load
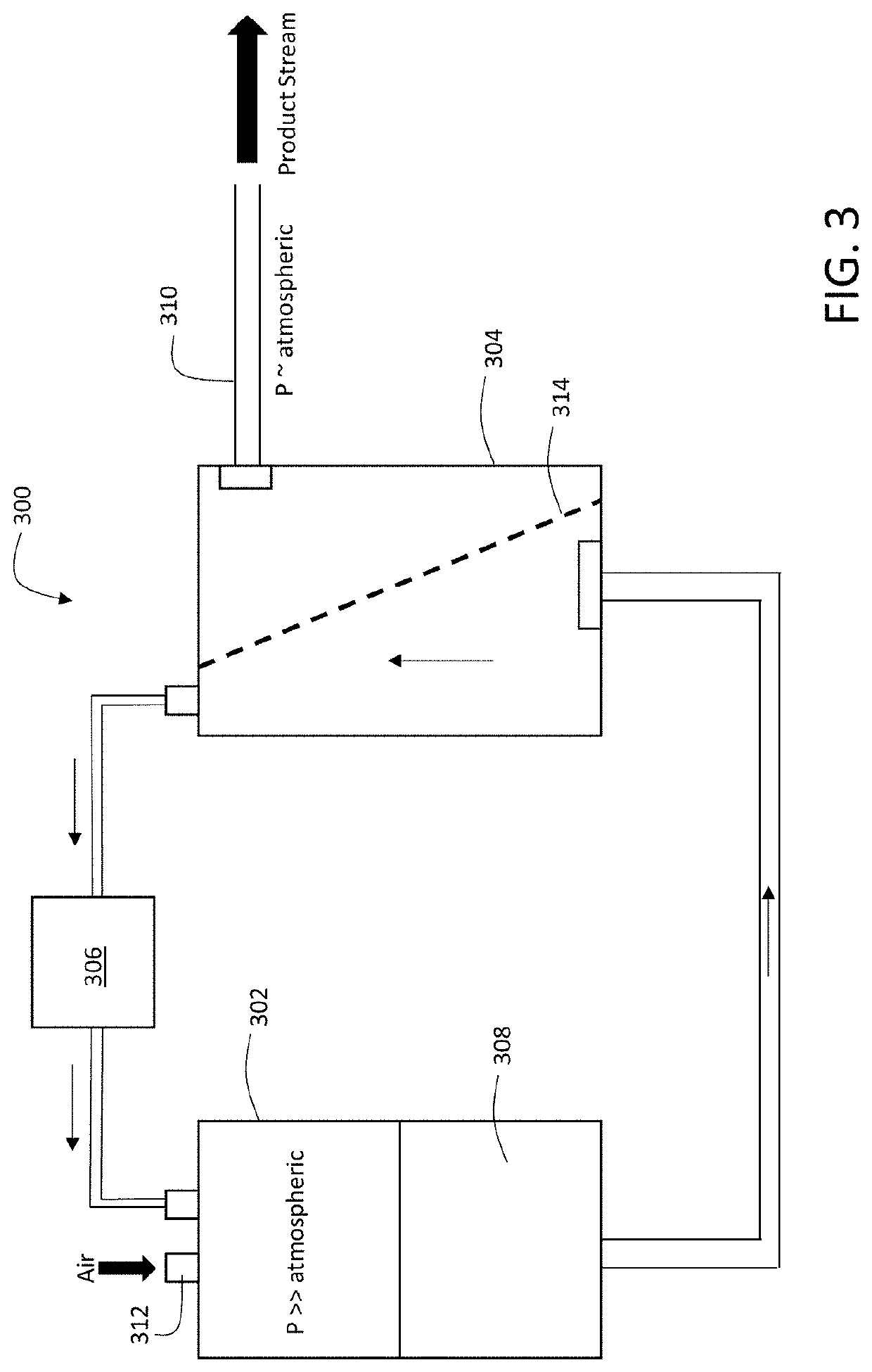
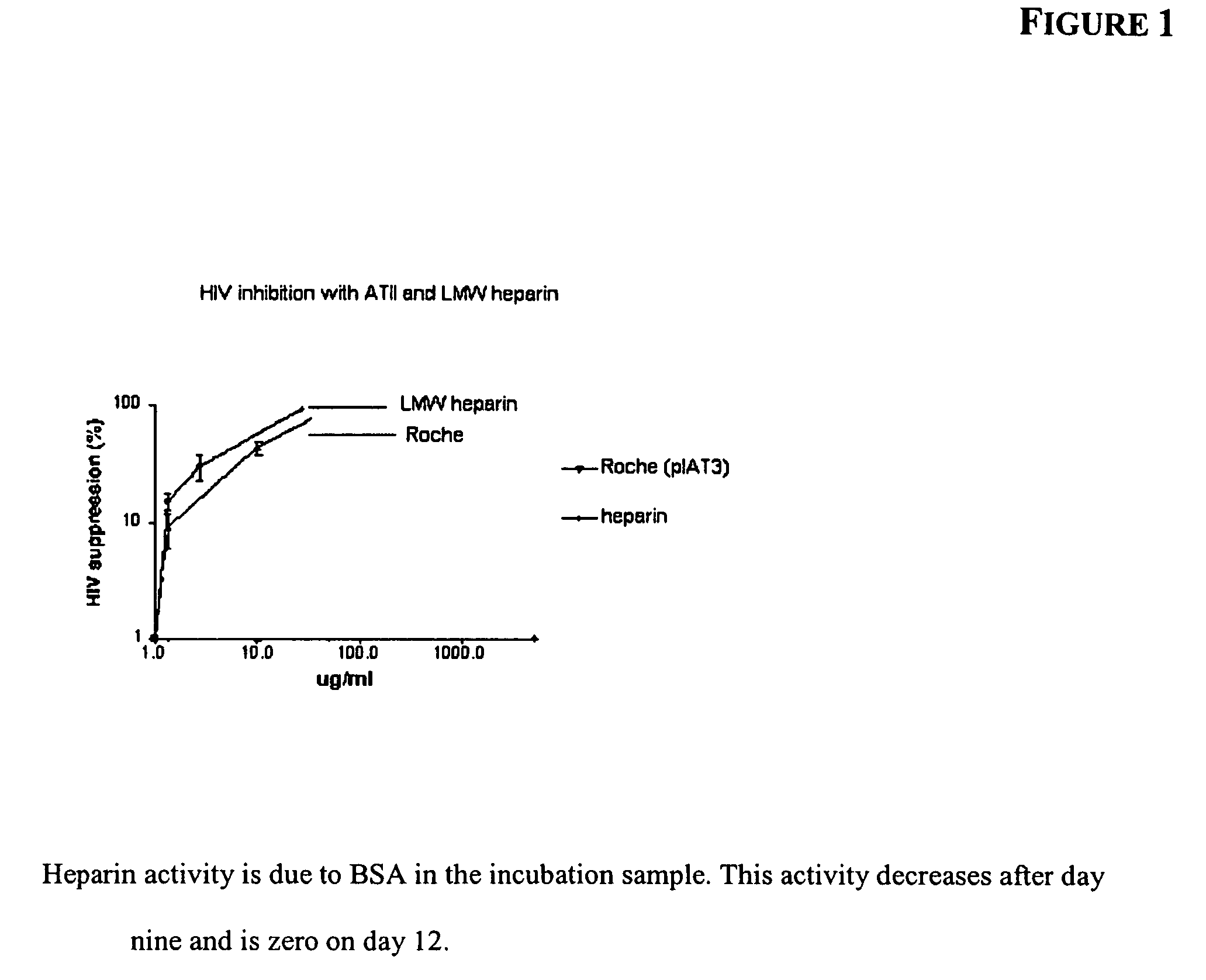
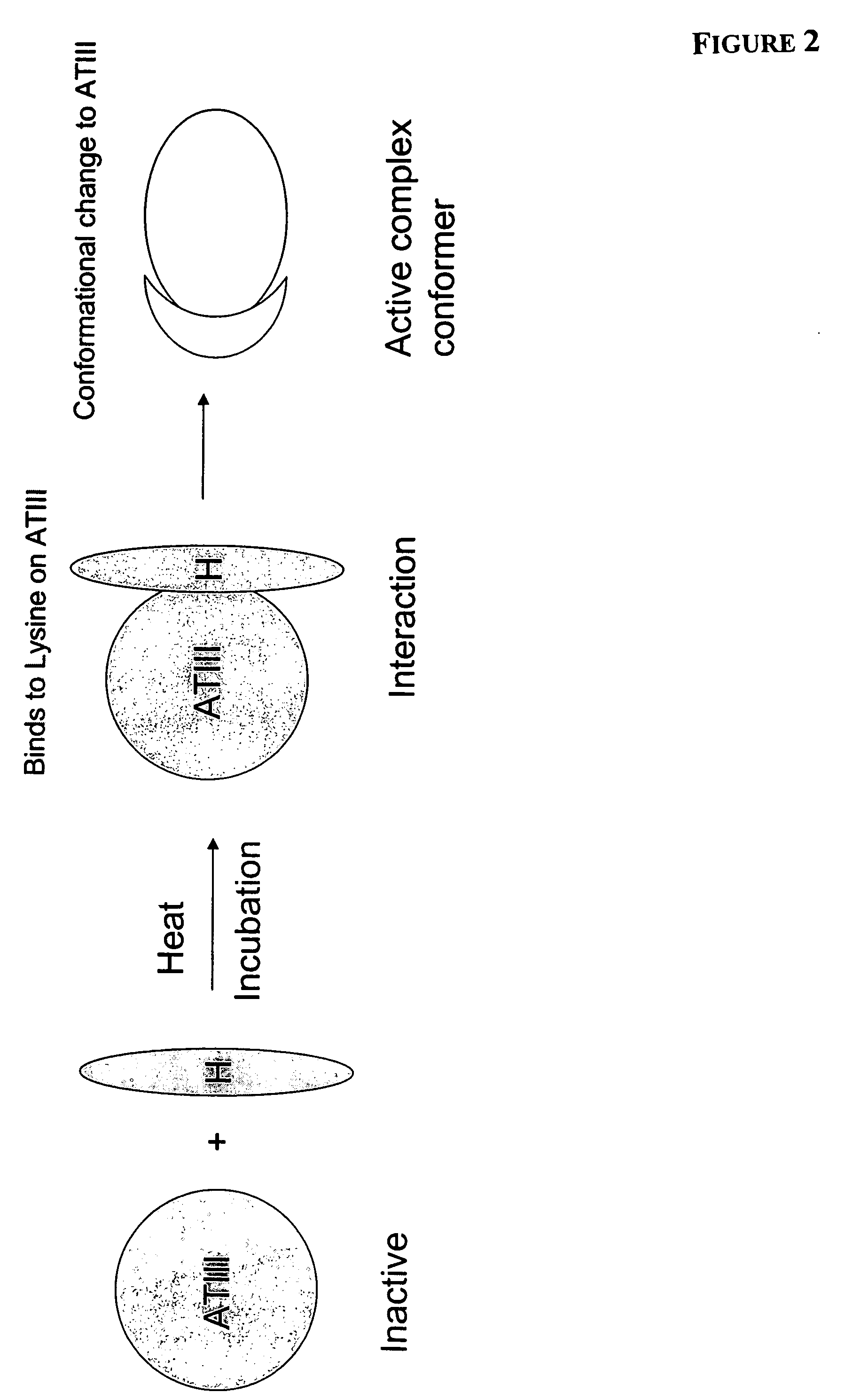
InactiveUS7498130B2Short test timeEliminate needBiocideOrganic active ingredientsWhole blood productThrombin activity
Methods of activating ATIII in situ in a blood product are disclosed, as is the use of such methods and blood products in treating infectious diseases, inflammatory disorders and diseases or conditions that are mediated by thrombin activation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
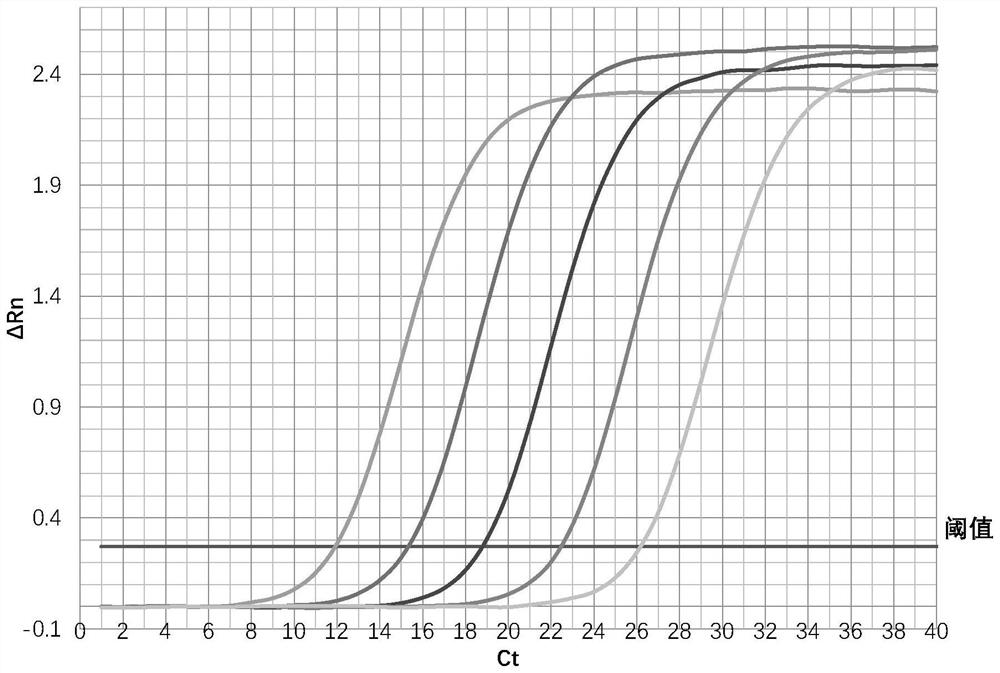
HIV-1 viral load real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection specific primer pair and kit
InactiveCN111705164AEasy to operateShorten detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAIDS diagnosisHuman immunodeficiency virus type I
The invention relates to the field of biomolecular detection, in particular to a HIV-1 viral load real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection specific primer pair and kit. The specific primer pair is used for precisely, simply and conveniently quantitative detection of human immunodeficiency virus type I (HIV-1) RNA. A one-step fluorescence quantitative RT-PCR technology is used to detect HIV-1 viral load. The operation ensures the accuracy and sensitivity of amplification results, the time is shortened, the pollution is reduced, the simplicity and convenience of a fluorescence quantitative PCR detection method are improved, and the HIV-1 viral load real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection specific primer pair and kit can be used for the quantitative detection of HIV-1 and as a clinical auxiliary diagnosis method on HIV-1 infection and a monitoring method of clinical treatment effect.
Owner:BEIJING LIANGXIN BIOLOGICAL TECH DEV CO LTD
Application of geraniin to preparation of medicine for restraining novel coronaviruses
ActiveCN112022867APrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsIntracellularPharmaceutical drug
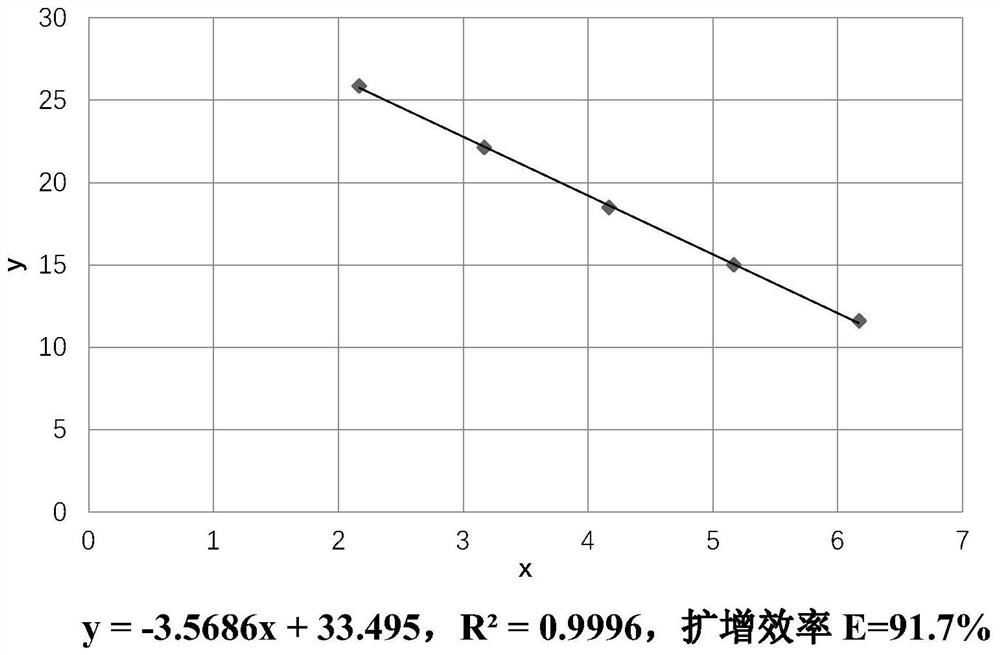
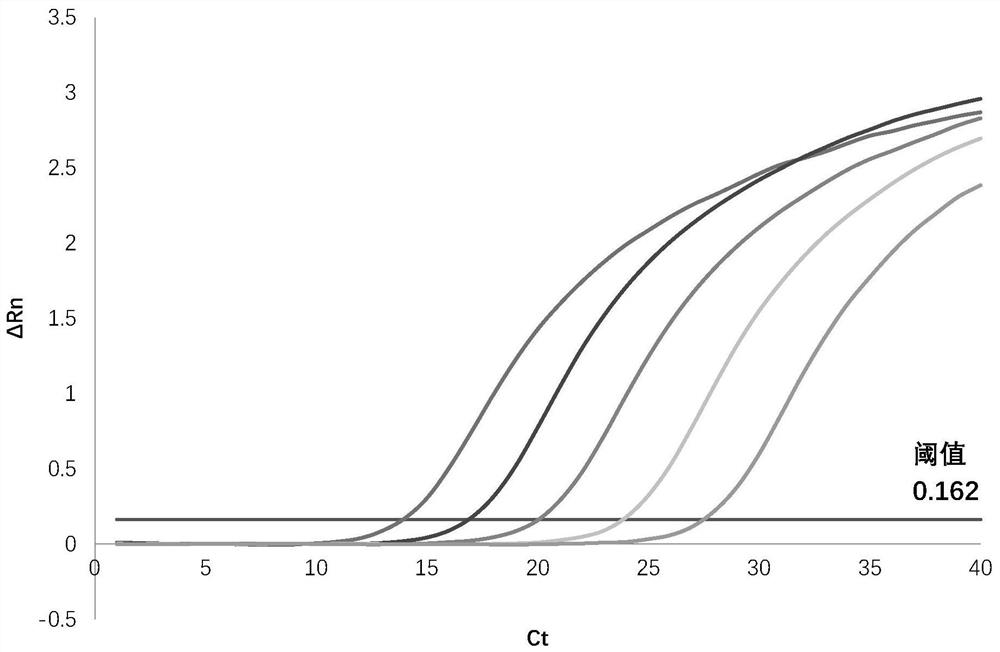
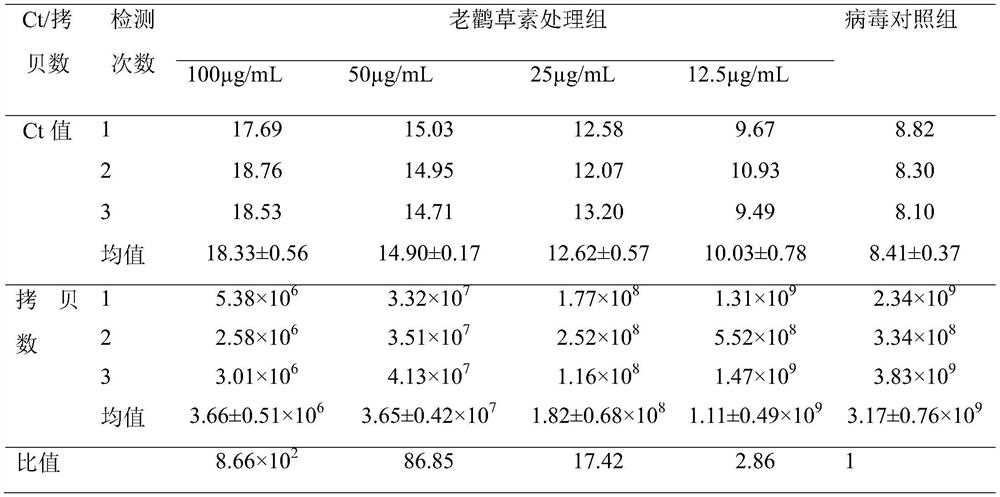
The invention discloses an application of geraniin to preparation of a medicine for restraining novel coronaviruses. The geraniin is applied to treatment of infection caused by the novel coronavirusesfor the first time, and through research, the inventor finds that the geraniin can effectively inhibit proliferation of the novel coronaviruses in cells, so that the geraniin can be used for treatingpneumonia diseases caused by infection of the novel coronaviruses. Therefore, the application range of the geraniin is expanded, and a new thought is provided for prevention and treatment of the novel coronaviruses. Through research, the inventor finds that 12.5-100 [mu] g / mL of the geraniin can effectively inhibit proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 in cells. Compared with virus infected cells (virus control group) which are not treated by any medicines, after the virus infected cells are treated by 100[mu]g / mL of the geraniin for 48 hours, the intracellular SARS-CoV-2 virus load is averagely reduced by 8.66 * 10<2> times.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Novel process for separating and determining the viral load in a pancreatin sample
ActiveCN101821389AMicrobiological testing/measurementPancreatinBiochemical engineeringQuantitative determination
Processes for separating a viral load from a pancreatin sample and for quantitatively determining the viral load in a pancreatin sample with high sensitivity are described herein.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
Treatments to eliminate HIV reservoirs and reduce viral load
ActiveUS10323289B2Decrease in levelPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory ReceptorsCD8
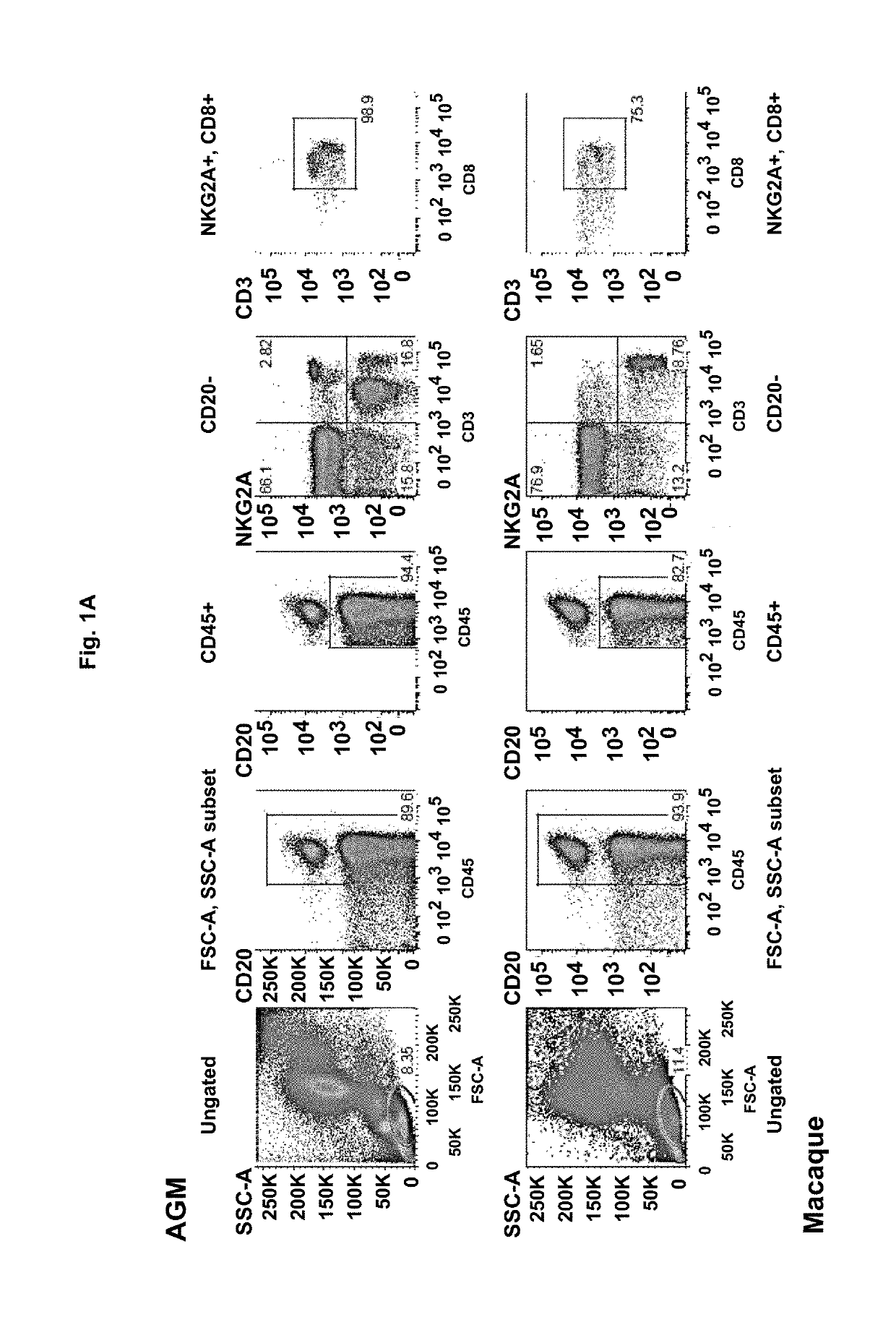
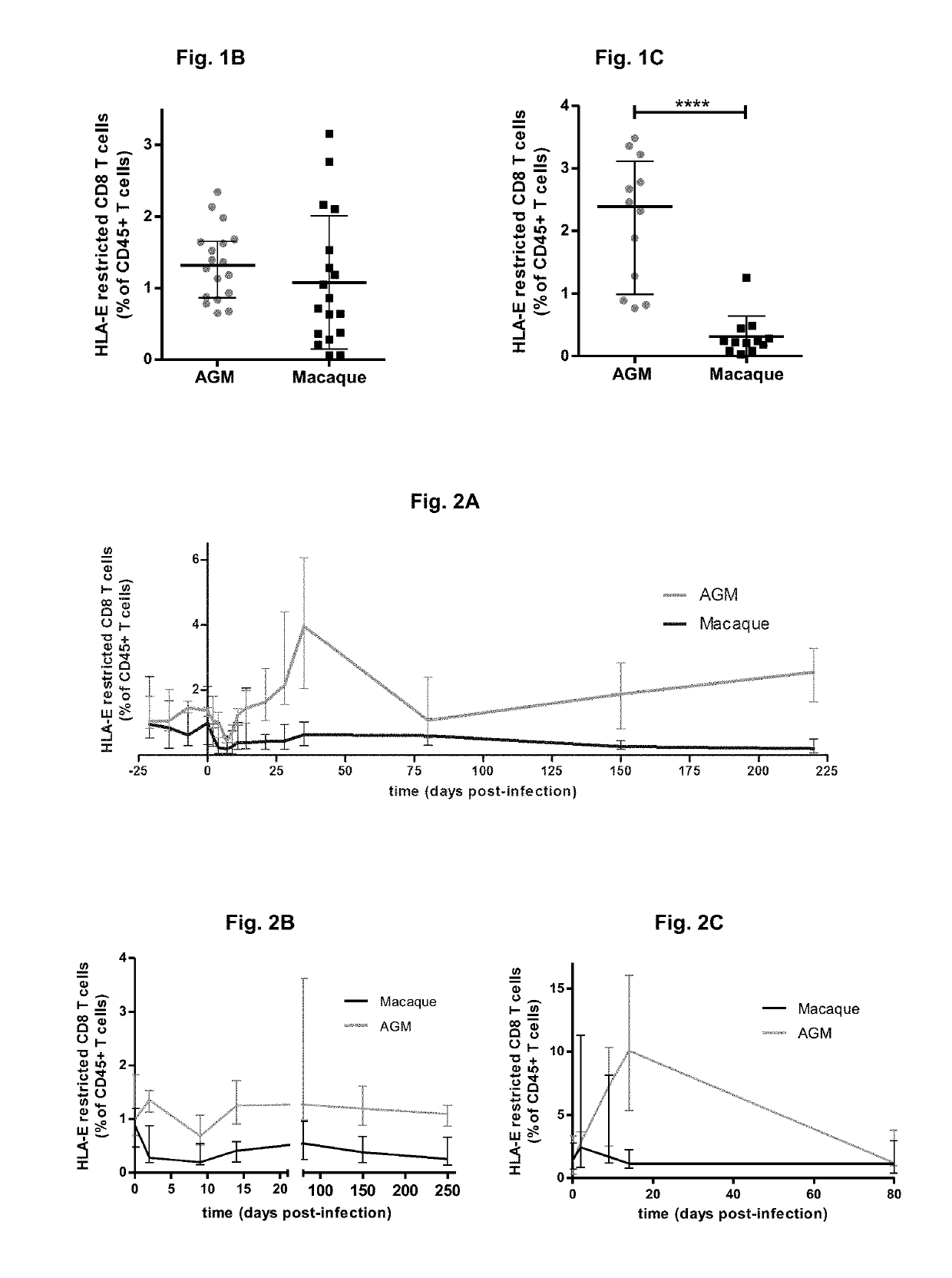
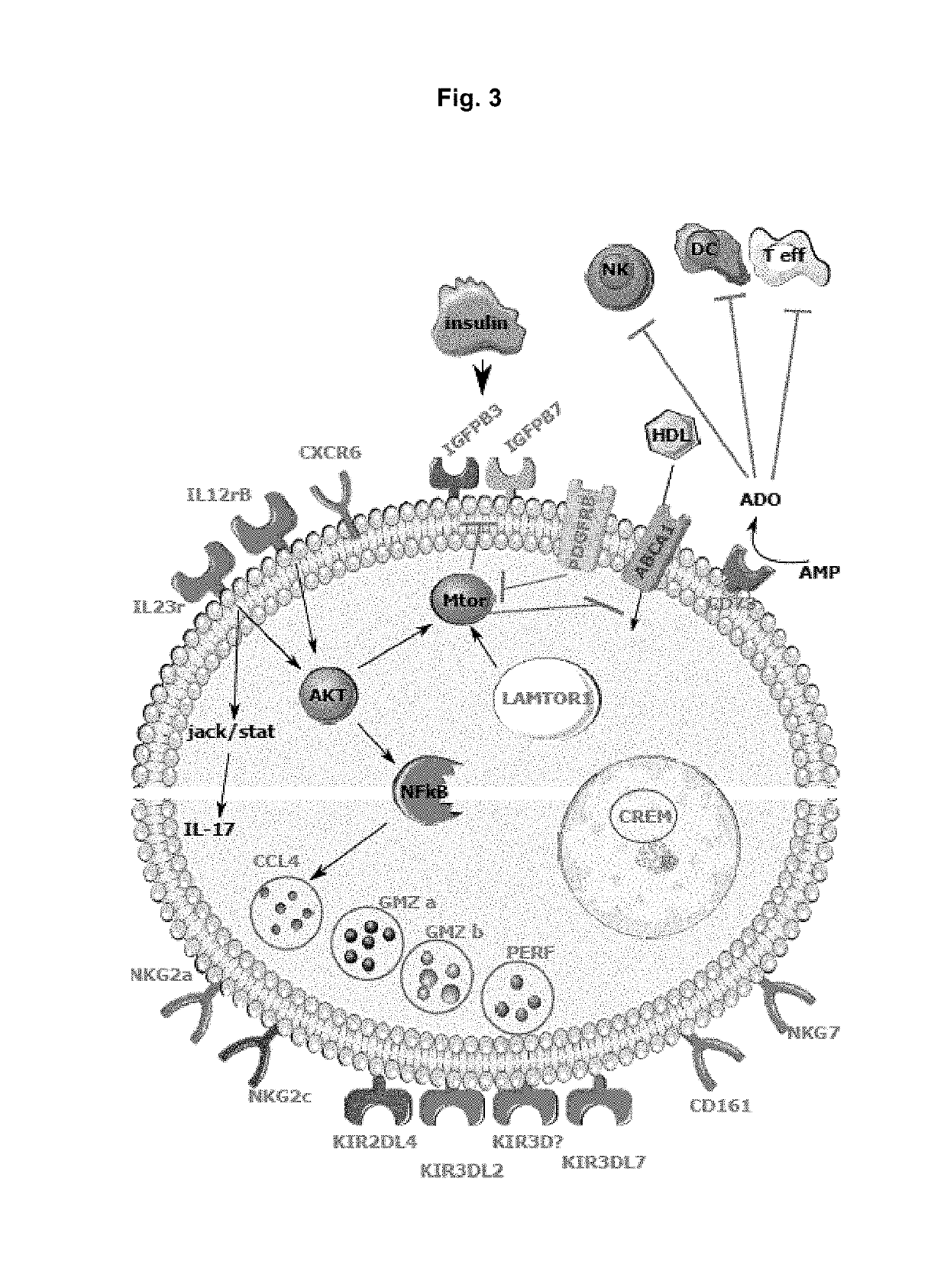
The present invention relates to a compound inducing activation of HLA-E-restricted CD8 T cells and / or NK cells in a human subject, and reducing HIV viral load, such as glatiramer acetate and glatiramer acetate related active substances and products, for use in the treatment of HIV infection. Macaques chronically infected by SIV have been treated with glatiramer acetate. One of the animals had already progressed to the stage of AIDS. We injected 18 mg of glatiramer acetate three times per week for only 2 weeks. Surprisingly, a strong impact on viral load was observed in response to the treatment. Viremia decreased by 1 log during glatiramer acetate treatment. Even more surprising was the fact that this decrease persisted after stopping the treatment reaching almost a 2 logs decrease in one animal. This is a major result as compared to cART as stopping cART leads to a rebound of the viral load within days. This decrease was correlated with activation of HLA-E restricted CD8 T cells, but not to other classical CD8+ T cells.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com