IFNAR2 mutants, their production and use
A mutant and carrier technology, applied in the field of mutant polypeptides, can solve the problems of low bioavailability and no clear correlation of IFNβ bioavailability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0153] Example 1: Expression and purification of proteins
[0154] E. coli expressed IFNAR2-EC (extracellular domain) and IFNa were purified by ion exchange and size exclusion chromatography as described (Piehler & Schreiber, 1999A). The expression level of the IFNAR2-EC mutant was as high as the wild type. Wild-type glycosylated IFN-[beta] was produced in CHO (as described in EP220574). Determine protein concentration from absorbance at 280 nm (Piehler & Schreiber, 1999A), 1:280 = 18,070 M-1 for IFNα2; 1:280 = 30,050 M-1 for IFN-β; 1:280 = 1:280 for IFNAR2-EC 26,500M-1 (for IFNAR2-EC which is the tryptophan mutant of W102A and W74F, corrected to 1:280=21,100M-1). Protein purity was analyzed by SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions.
Embodiment 2
[0155] Example 2: Generation of IFNAR-EC mutants
[0156]High-fidelity polymerases pwo (Boehringer Mannheim) and pfu (Stratagene) were used as template pT72CR2 (Piehler & Schreiber, 1999A) and nucleotide primers containing mutated codons as detailed in (Albeck & Schreiber, 1999). PCR for site-directed mutagenesis. After phosphorylation and ligation, E. coli TG1 cells were transduced with the mutated plasmid. The full sequence of the expressed gene containing the mutation was verified by DNA sequencing (Ausubel et al., Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, Greene Publications and Wiley Interscience, New York, NY, 1987-1995; Sambrook et al., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory , Cold Spring Harbor, NY, 1989).
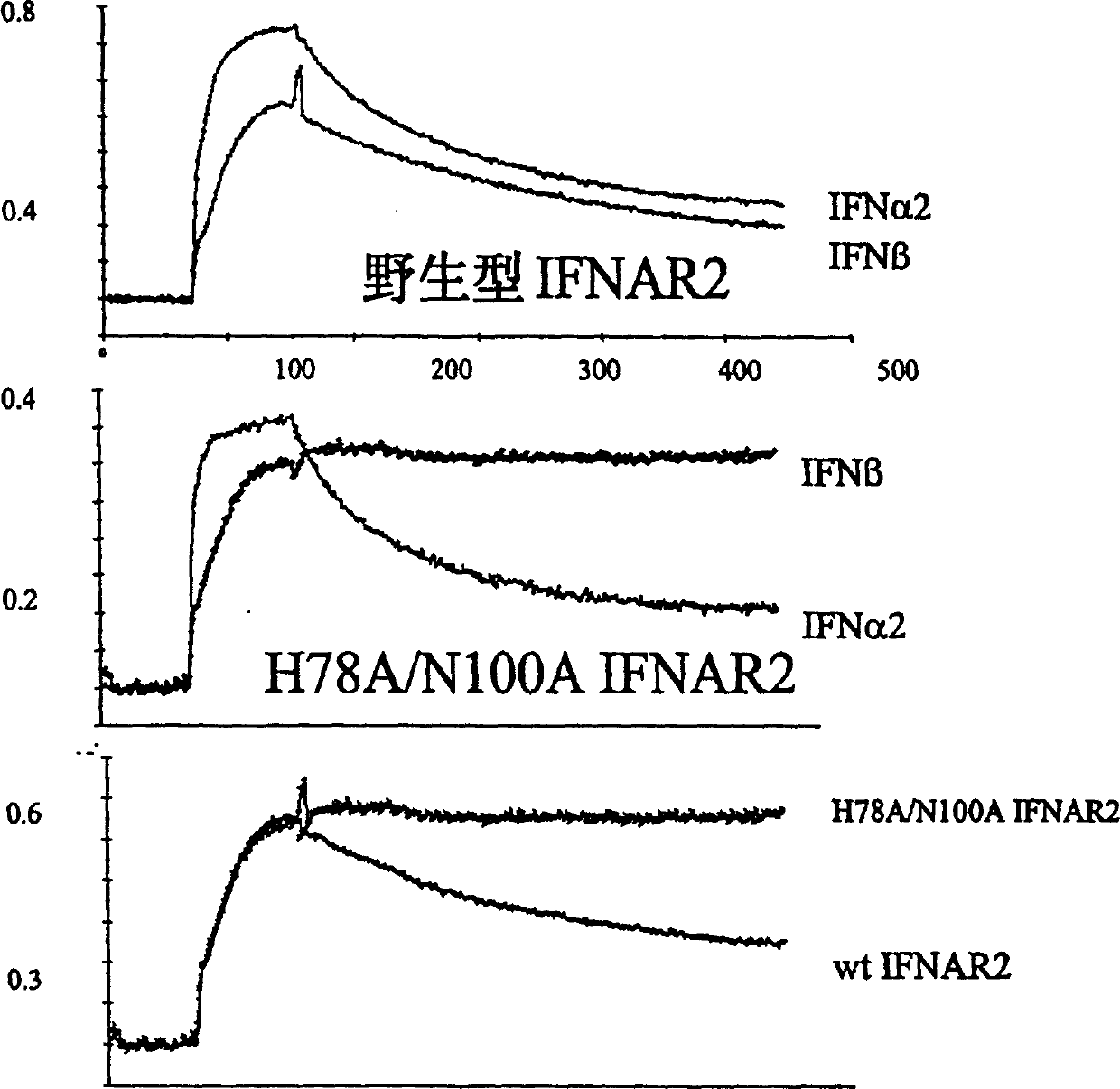
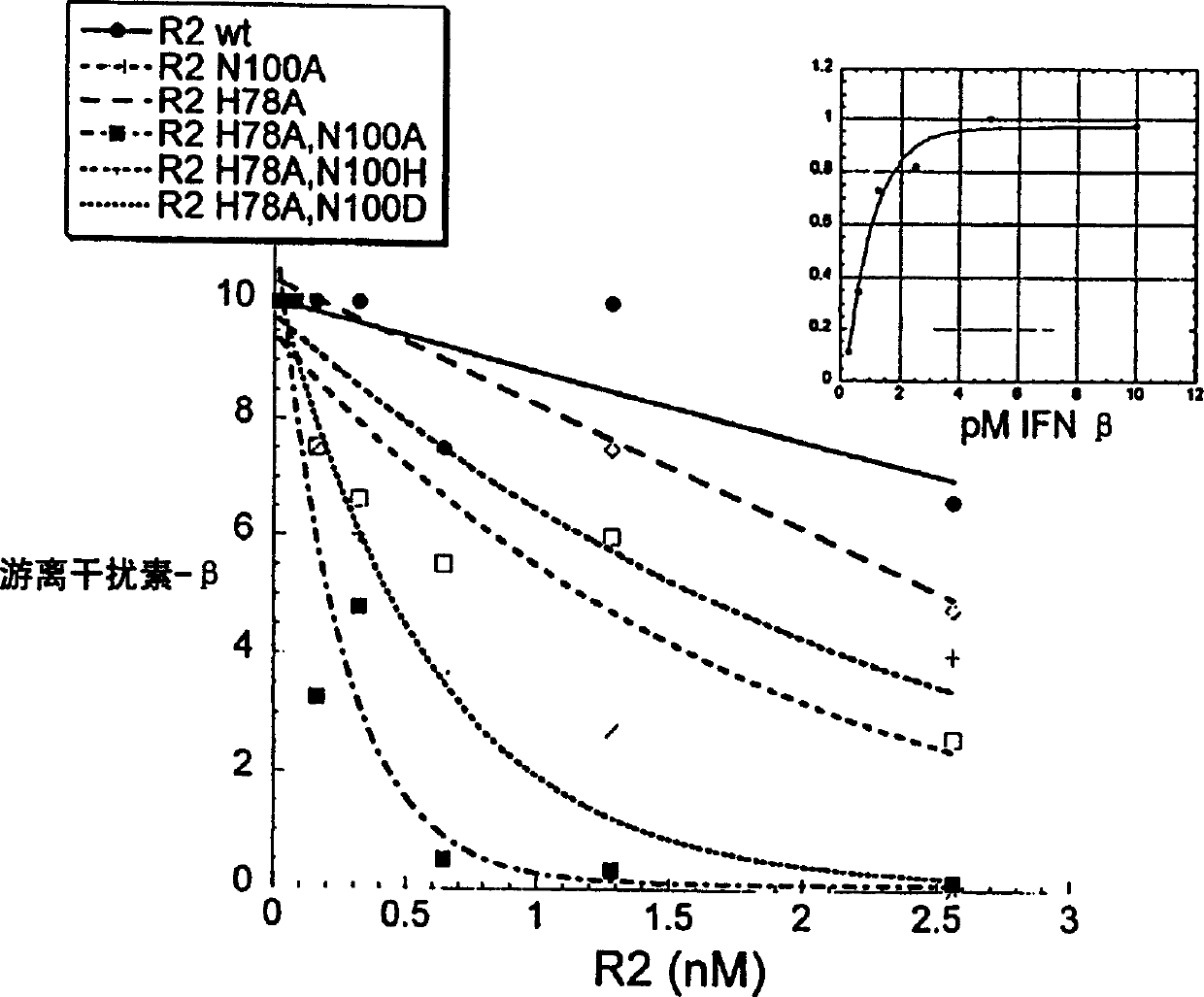
[0157] There are two amino acid residues in the generated mutant: 78-position histidine (H78) and 100-position asparagine (N100) are mutated: A-both become alanine (H78A / N100A), B- to alanine and aspartic acid (H78A / N100D), respect...
Embodiment 3
[0158] Example 3: Thermodynamic and Kinetic Analysis
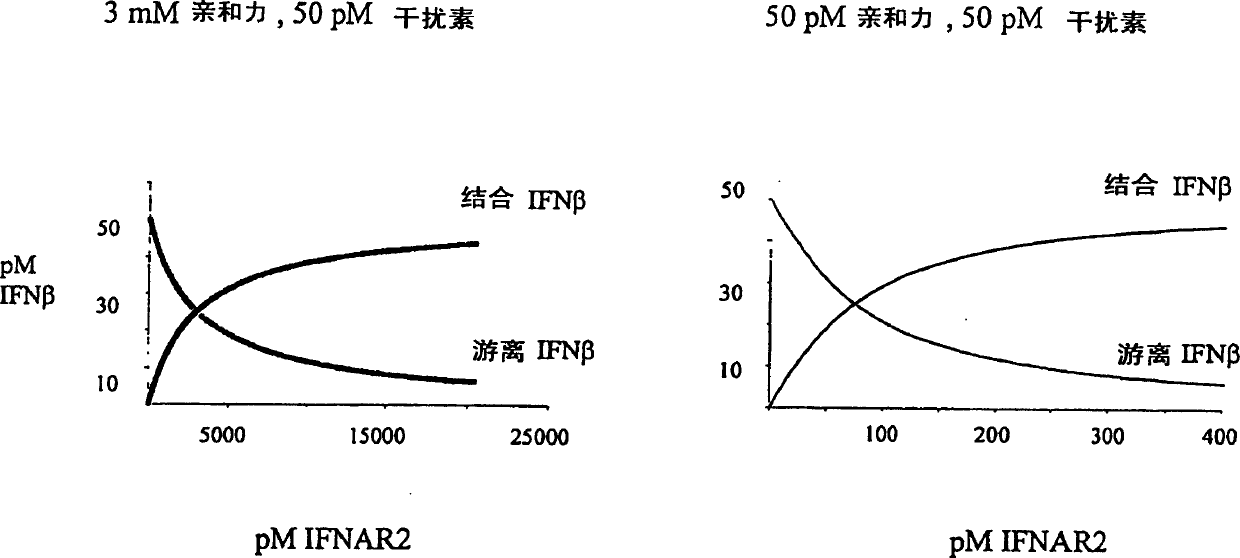
[0159] All thermodynamic and kinetic data were obtained from label free heterozygous phase assays. The interaction between IFN-β2 and IFNAR2-EC was monitored by reflectance interference spectrophotometry [RifS] under flow-through conditions as described in Piehler & Schreiber, 1999A. This method is similar to Biacore and is used to accurately determine the binding affinity between two proteins. IFNAR2-EC (wild type or mutant) was immobilized by means of immobilized specific antibodies (as described in Piehler & Schreiber, 2001). All assays for IFN-β, IFNα2 and IFNAR2-EC were performed in 50 nM Hepes and 500 mM NaCI, 0.01% TritonX100, pH 7.4. The interaction at 500 mM NaCI was determined to eliminate the non-specific reaction of IFN-[beta] with the surface seen at 150 mM NaCI.
[0160] Association and dissociation kinetics were determined with standard injection protocols and corrected for with blank runs. Dissociatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com