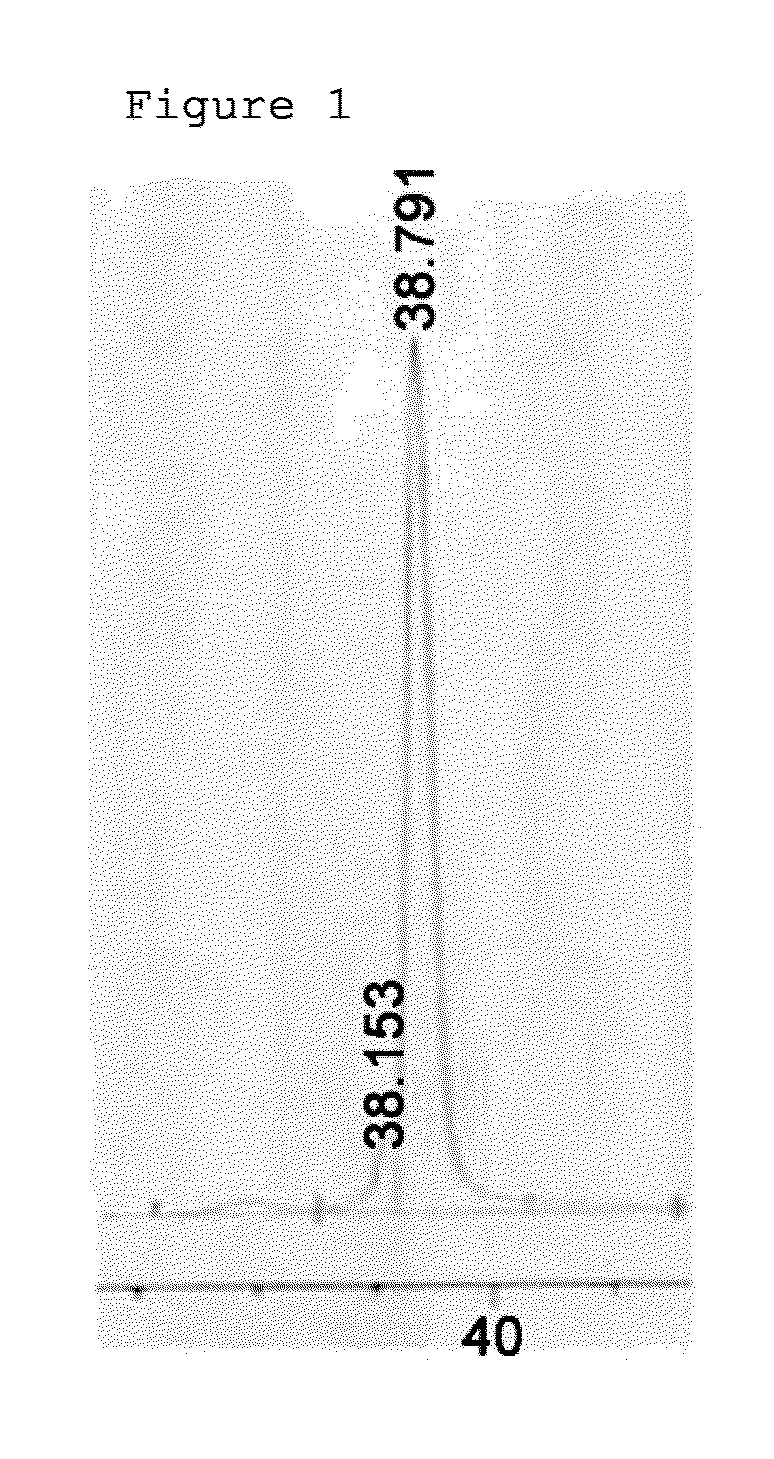
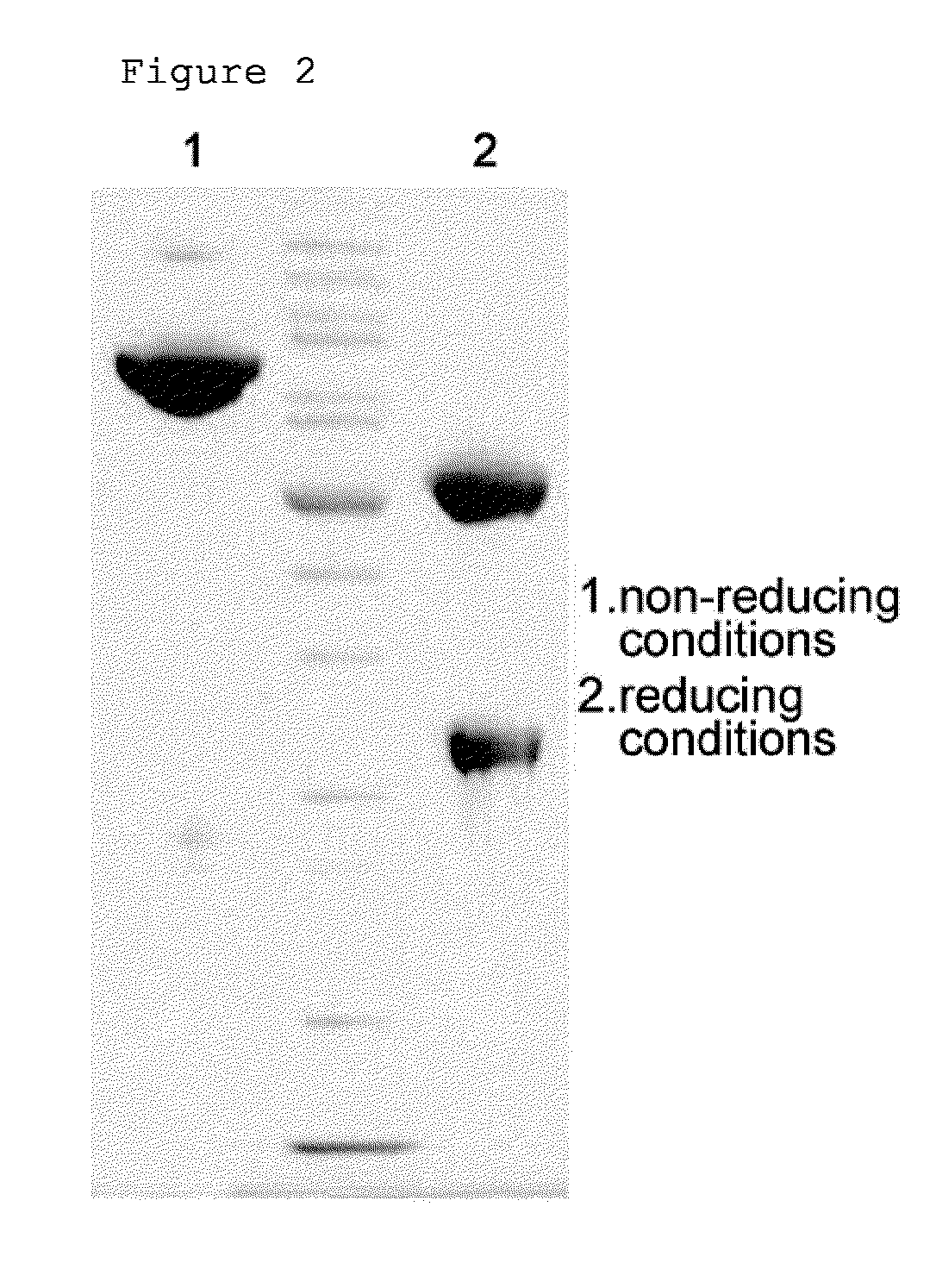
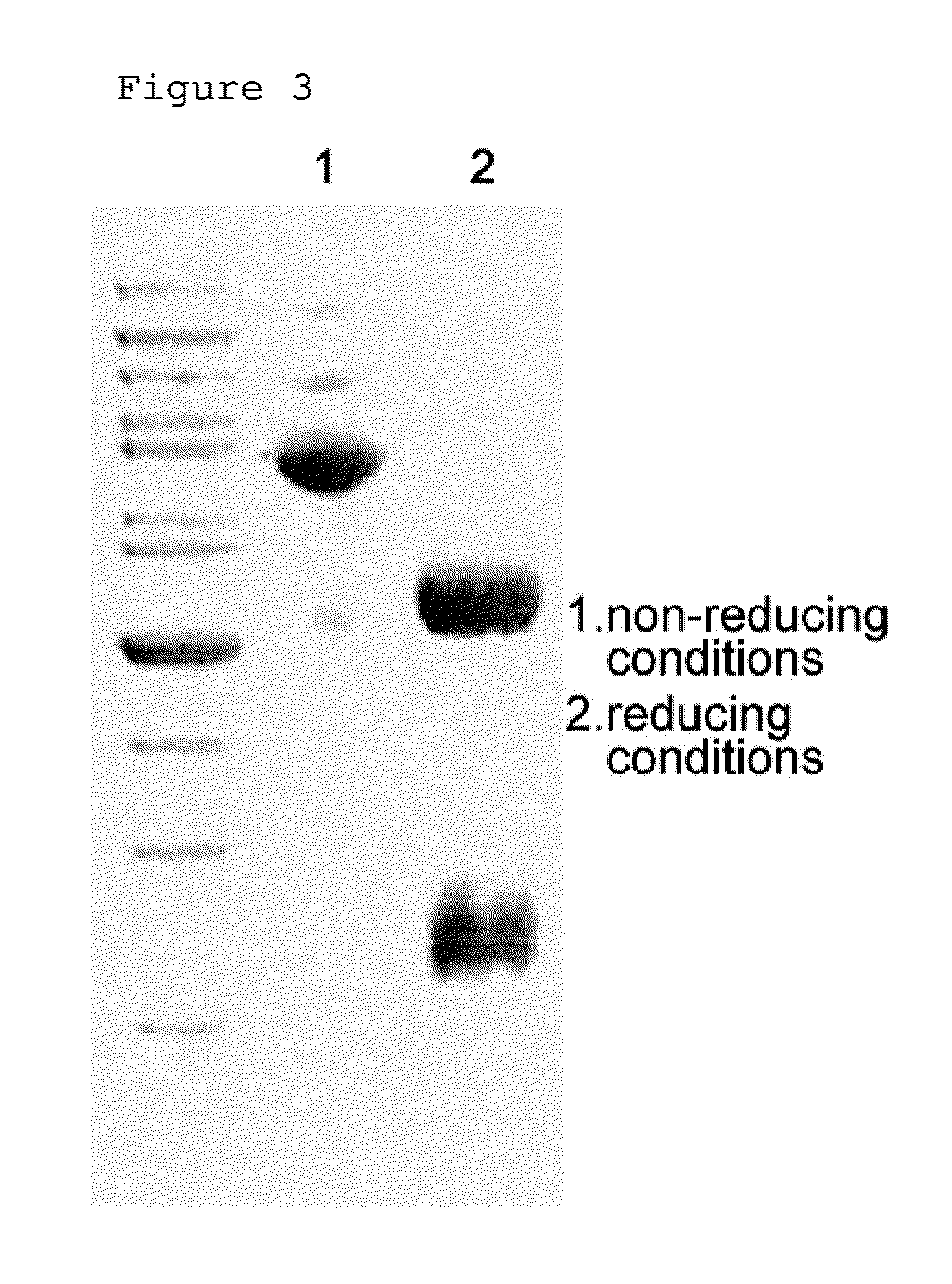
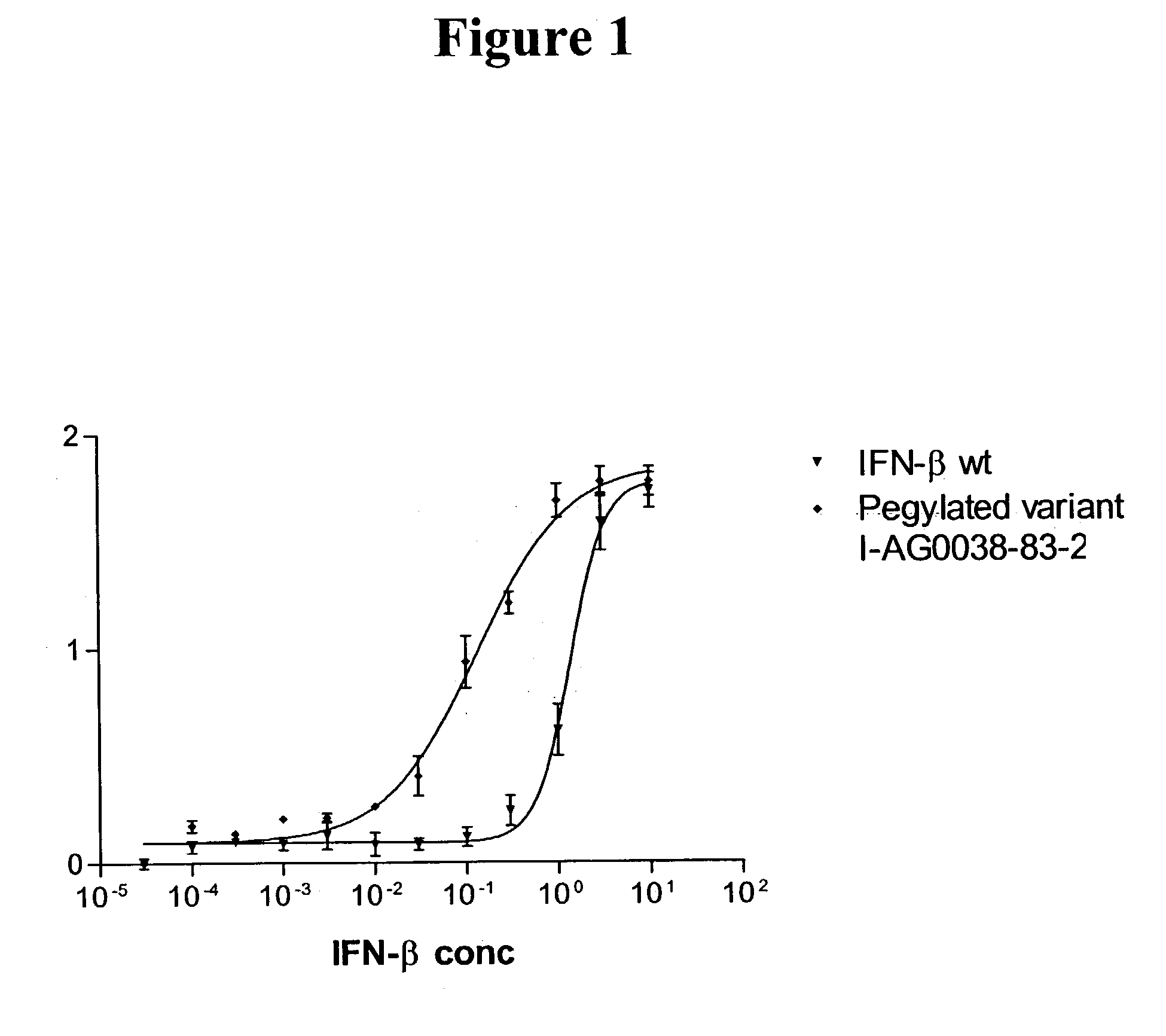
Patents
Literature
106 results about "Interferon beta" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interferon beta-1a (also interferon beta 1-alpha) is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified E. coli.
Targeted interferons demonstrate potent apoptotic and Anti-tumor activities
ActiveUS20100172868A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismInterferon alphaAntitumor activity
Novel chimeric moieties that show significant efficacy against cancers are provided. In certain embodiments the chimeric moieties comprise a targeting moiety attached to an interferon. In certain embodiments, the chimeric moieties comprise fusion proteins where an antibody that specifically binds to a cancer marker is fused to interferon alpha (IFN-α) or interferon beta (IFN-β).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Expression vector for animal cell containing nuclear matrix attachment region of interferon beta
InactiveUS7259010B2Increased foreign protein expression efficiencyReduce the amount of solutionVectorsSugar derivativesMammalNuclear matrix
The present invention relates to mammalian expression vectors including nuclear matrix attachment region of human interferon β, and more particularly to pPGM-1, pPGM-2 and pPGM-3 including nuclear matrix attachment region of interferon β gene. Those expression vectors confer position independent expression of the introduced foreign gene, thus increasing the frequency of colonies which efficiently express the recombinant protein.
Owner:PANGEN BIOTECH
Process For the Preparation of Glycosylated Interferon Beta
The present invention relates to a process for the production of interferon beta, and to an interferon beta composition having a unique glycosylation pattern.
Owner:ARES TRADING SA
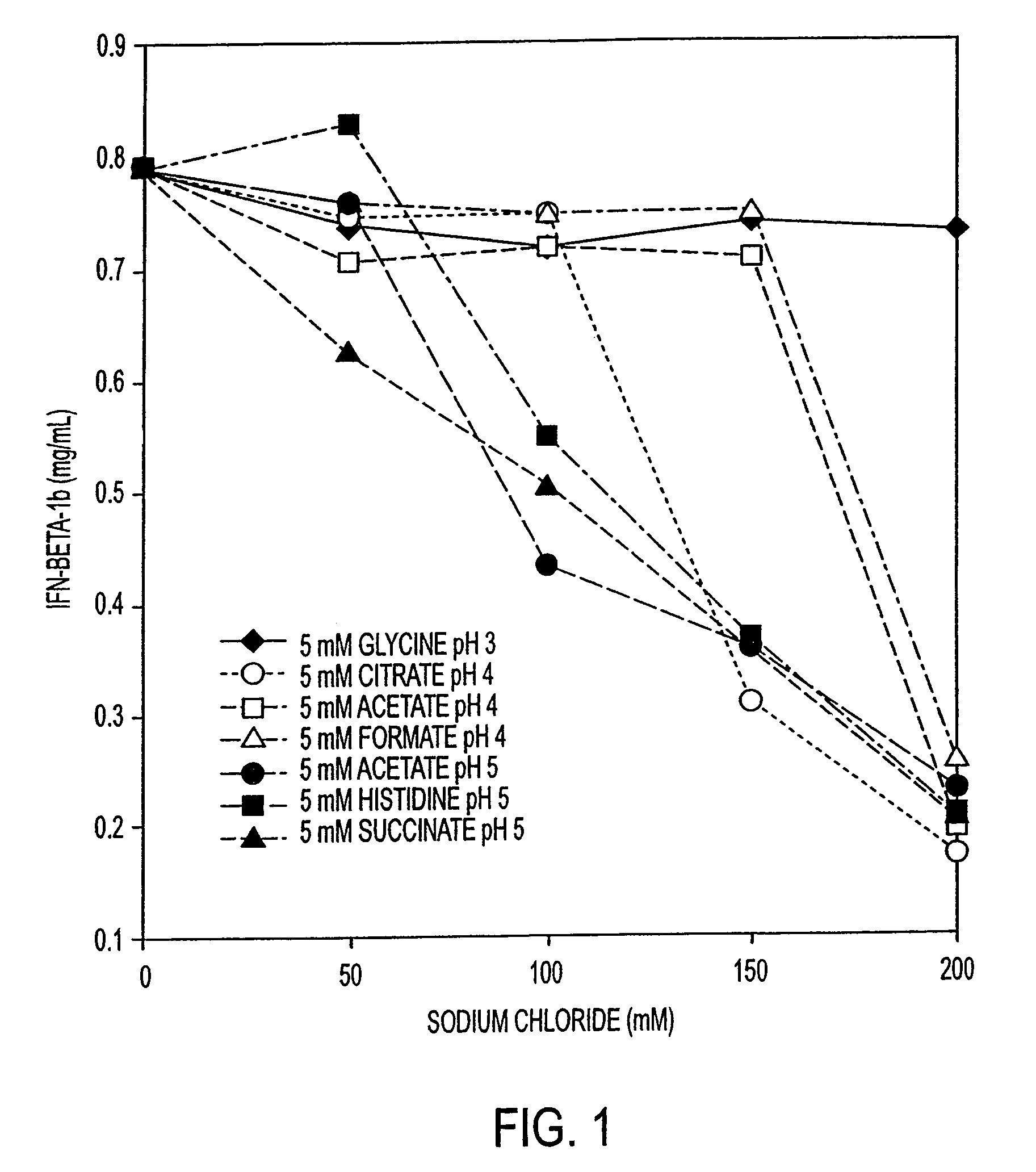
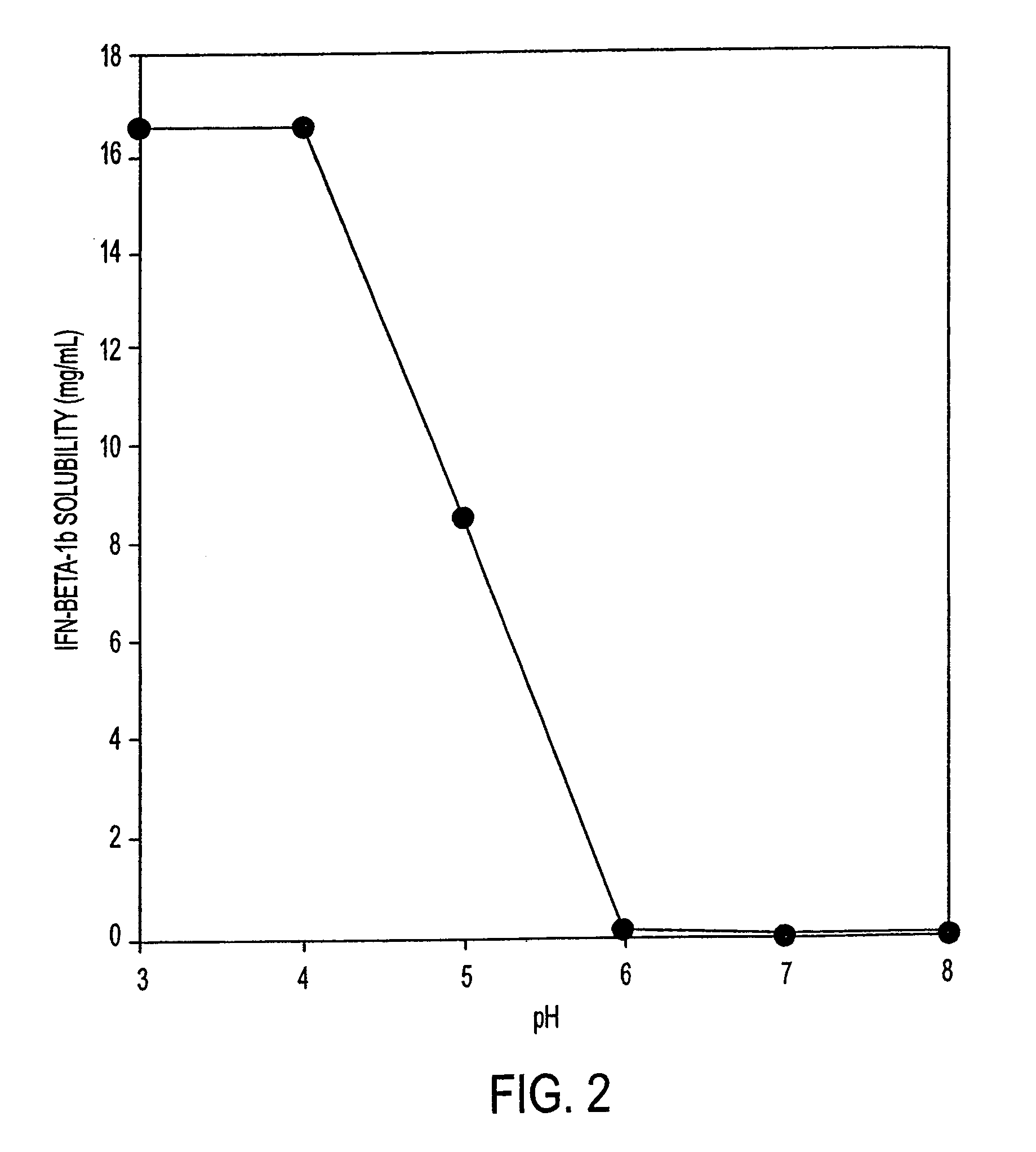
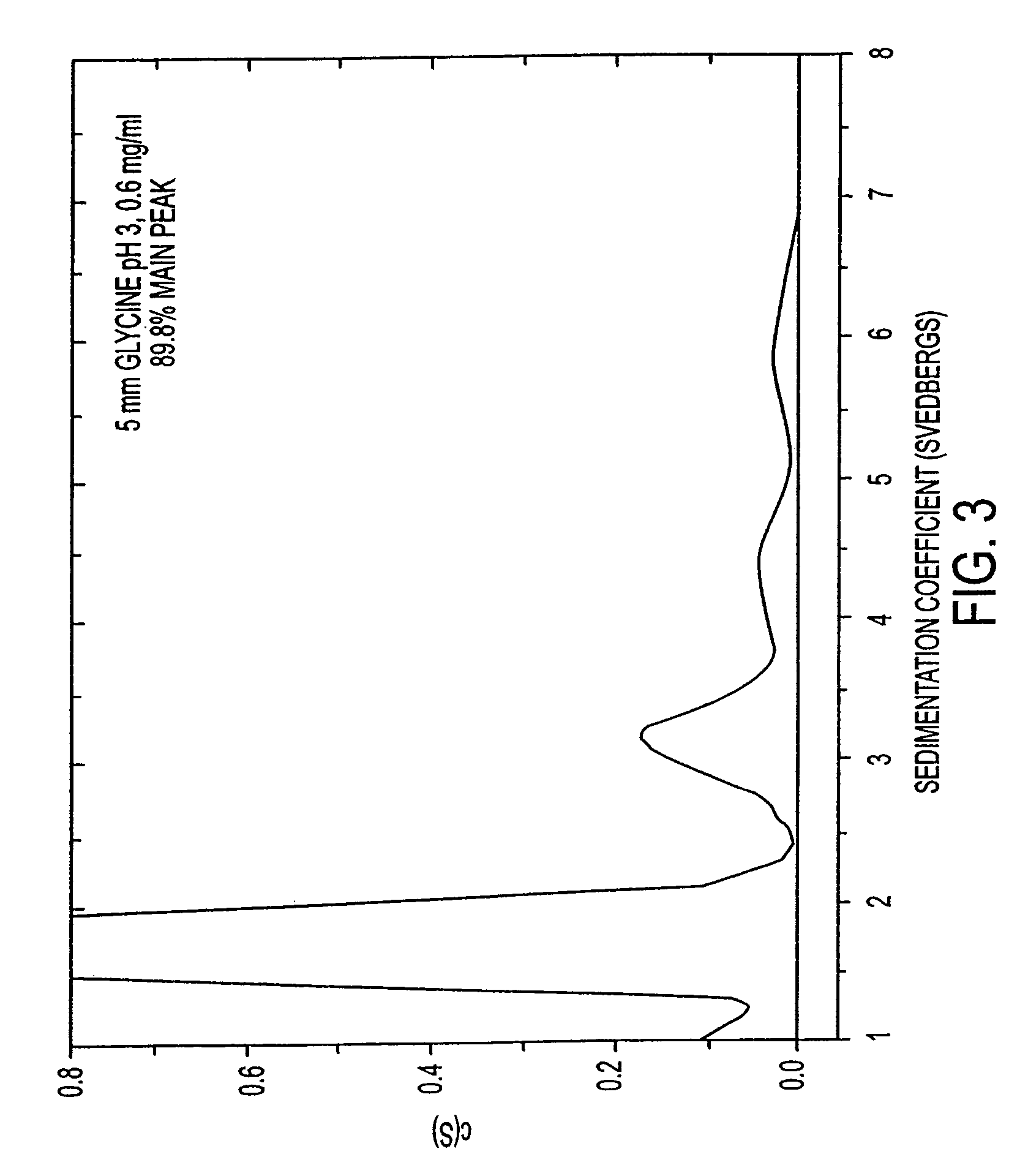
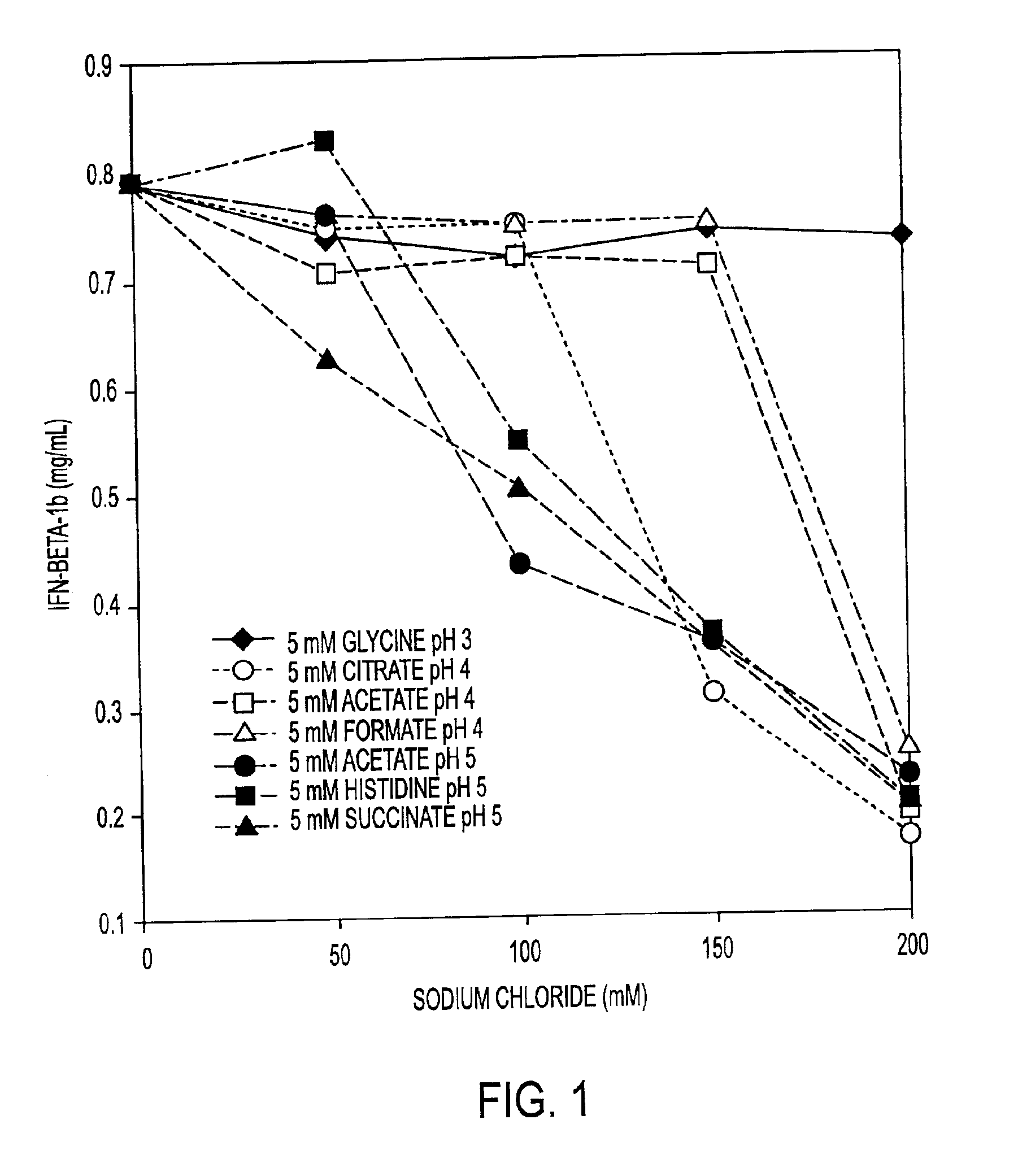
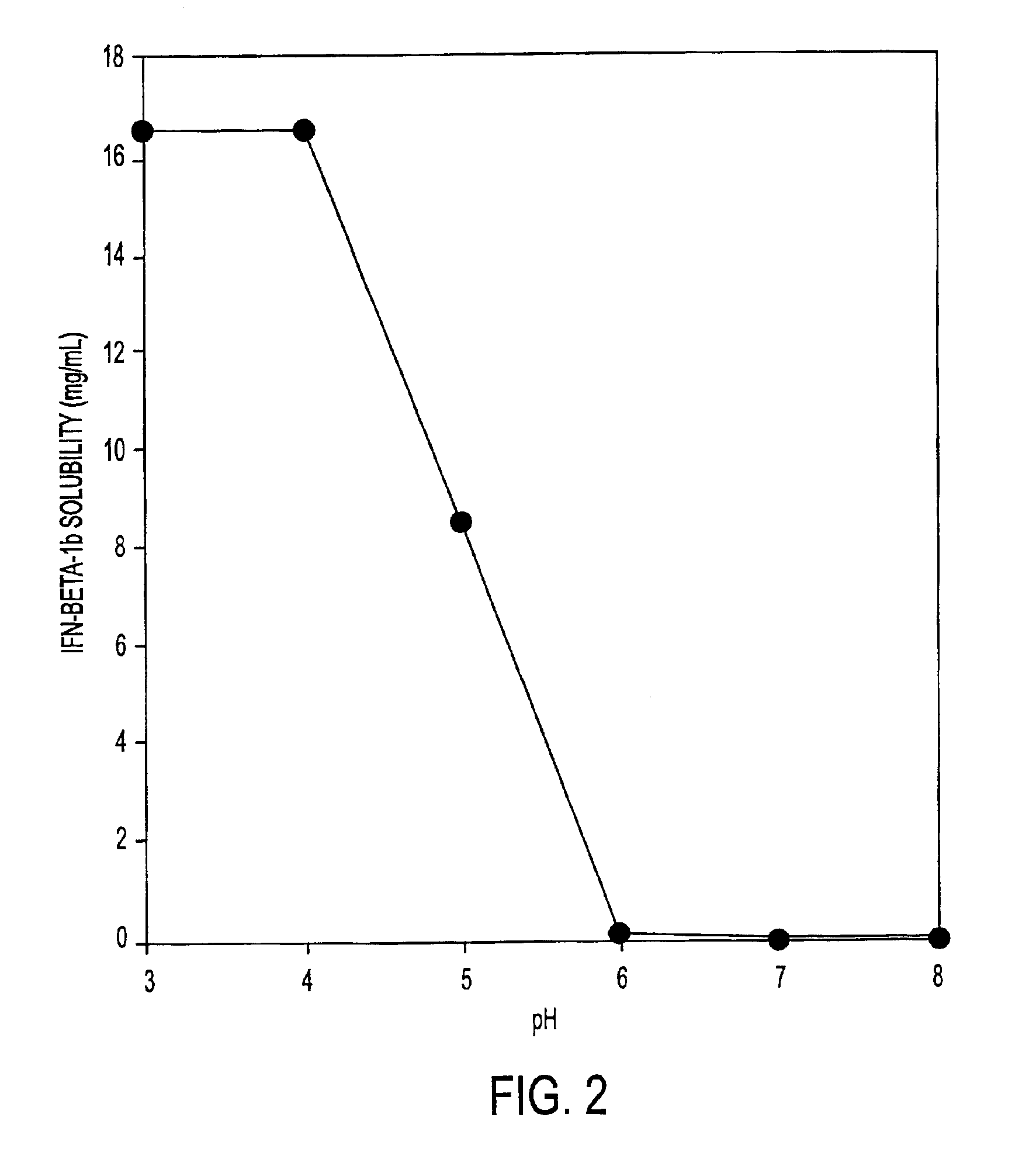
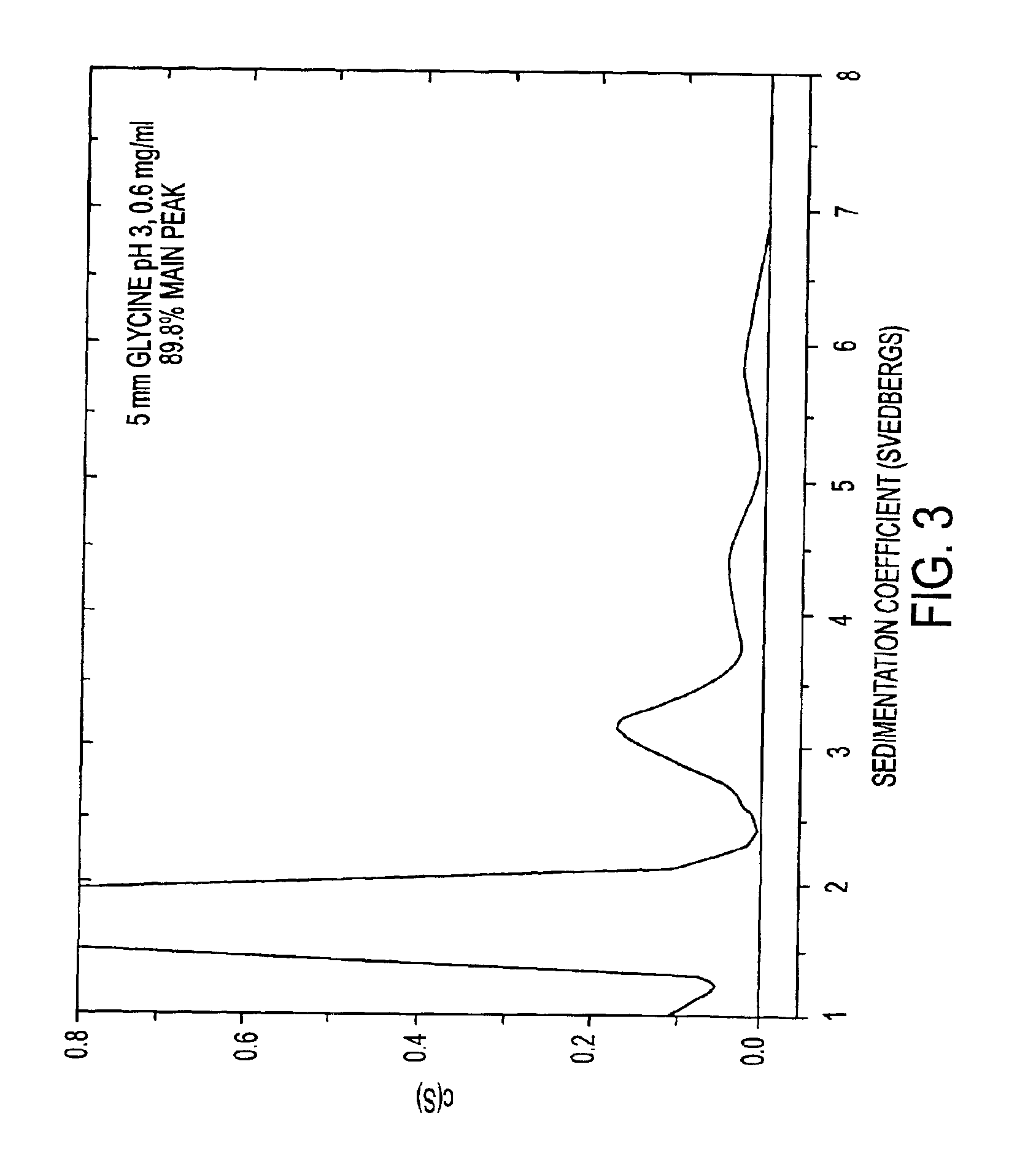
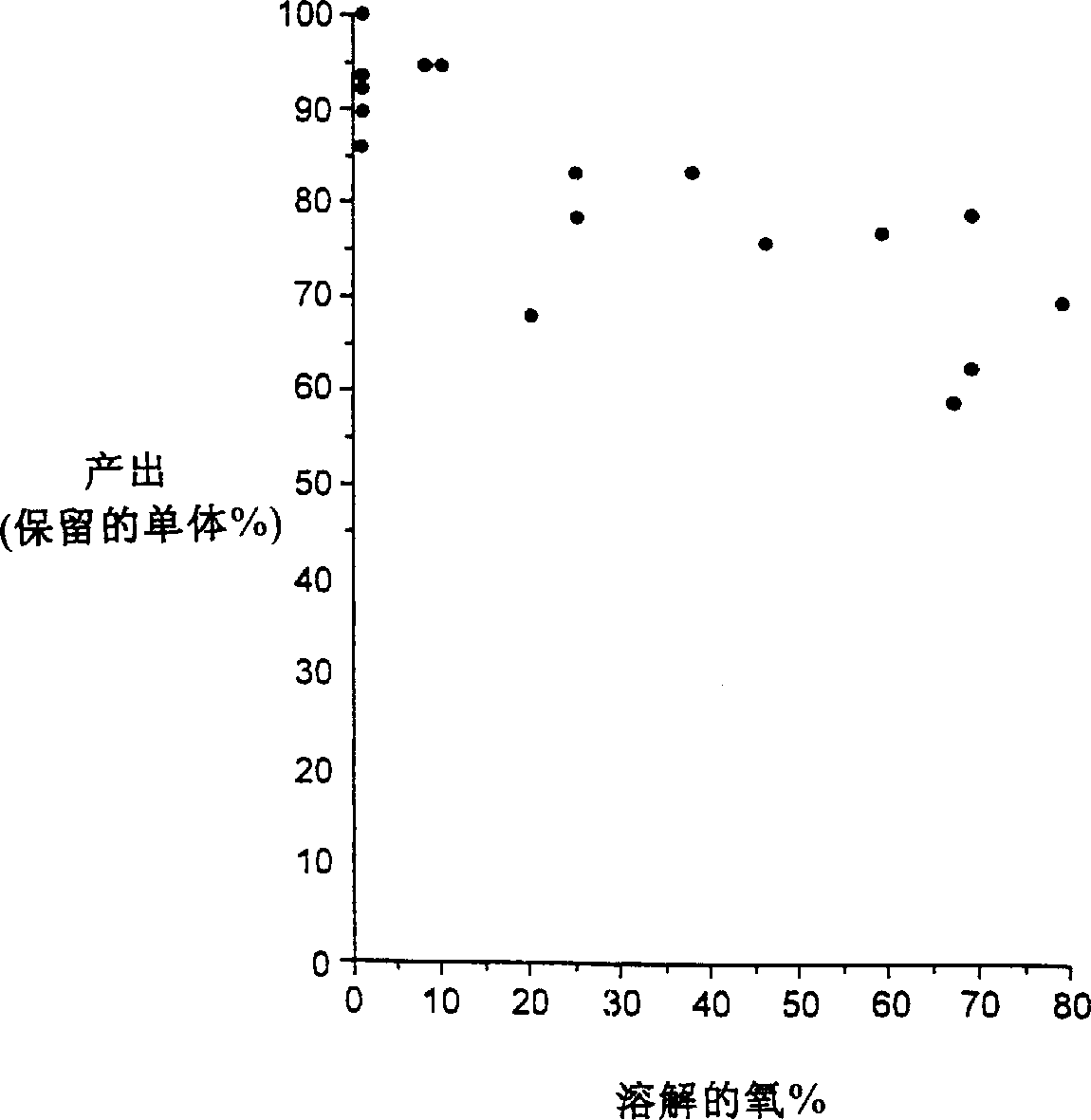
HSA-free formulations of interferon-beta
InactiveUS7371373B2Improve solubilityIncreasing the amount of monomeric IFN-βPowder deliveryNervous disorderSolubilityLow ionic strength
Stabilized pharmaceutical compositions comprising substantially monomeric interferon-beta (IFN-β) and methods useful in their preparation are provided. The compositions comprise the IFN-β solubilized in a low-ionic-strength formulation that maintains the composition at a pH of about 3.0 to about 5.0. Methods for preparing these compositions, and for increasing solubility of IFN-β in pharmaceutical compositions, are provided.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Assembly and folding of Fc-interferon-beta fusion proteins
InactiveUS20060228332A1Good biological propertiesImprove solubilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseSolubility
Disclosed are Fc-interferon-beta (Fc-IFN-β) fusion proteins and nucleic acid molecules encoding them. The Fc-IFN-β fusion proteins include variants of the interferon-beta (IFN-β) protein that are altered to achieve enhanced biological activity, prolonged circulating half-life and greater solubility. Also disclosed are methods of producing the fusion proteins and methods of using the fusion proteins and / or nucleic acid molecules for treating diseases and conditions alleviated by the administration of interferon-beta.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
HSA-free formulations of interferon-beta
InactiveUS6887462B2Improve solubilityIncreasing the amount of monomeric IFN-βPowder deliveryNervous disorderSolubilityLow ionic strength
Stabilized pharmaceutical compositions comprising substantially monomeric interferon-beta (IFN-β) and methods useful in their preparation are provided. The compositions comprise the IFN-β solubilized in a low-ionic-strength formulation that maintains the composition at a pH of about 3.0 to about 5.0. Methods for preparing these compositions, and for increasing solubility of IFN-β in pharmaceutical compositions, are provided.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Method of treating pulmonary disease with interferons
InactiveUS20070065367A1Improve toleranceDecrease in TNF-aPowder deliveryDispersion deliveryInterferon therapyDisease
A method of treating a pulmonary disease such as, for instance idiophathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and asthma, comprising administering an aerosolized interferon such as interferon α, interferon β or interferon γ in a therapeutically effective amount is provided herein. Also, pharmaceutical compositions of one or more aerosolized interferon(s) are provided.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Stabilizing alkylglycoside compositions and methods thereof
ActiveUS8084022B2Convenient treatmentReduce aggregationPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderInterferon alphaImmunogenicity
The present invention relates to alkylglycoside-containing compositions and methods for increasing the stability, reducing the aggregation and immunogenicity, increasing the biological activity, and reducing or preventing fibrillar formation of a peptide, polypeptide, or variant thereof, for example interferons, such as interferon-alpha, interferon-beta, interferon-gamma, and variants thereof.
Owner:AEGIS THERAPEUTICS LLC
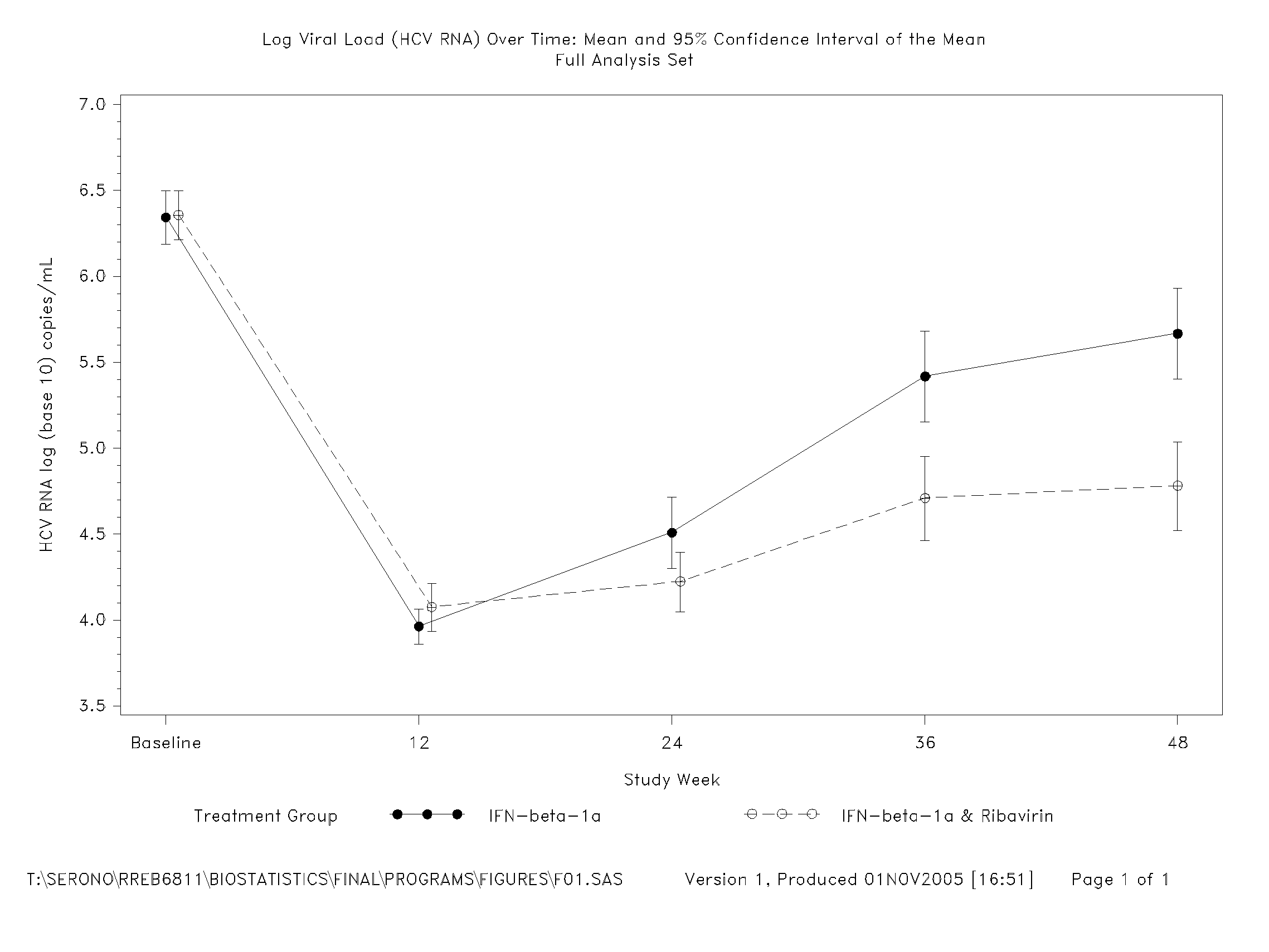
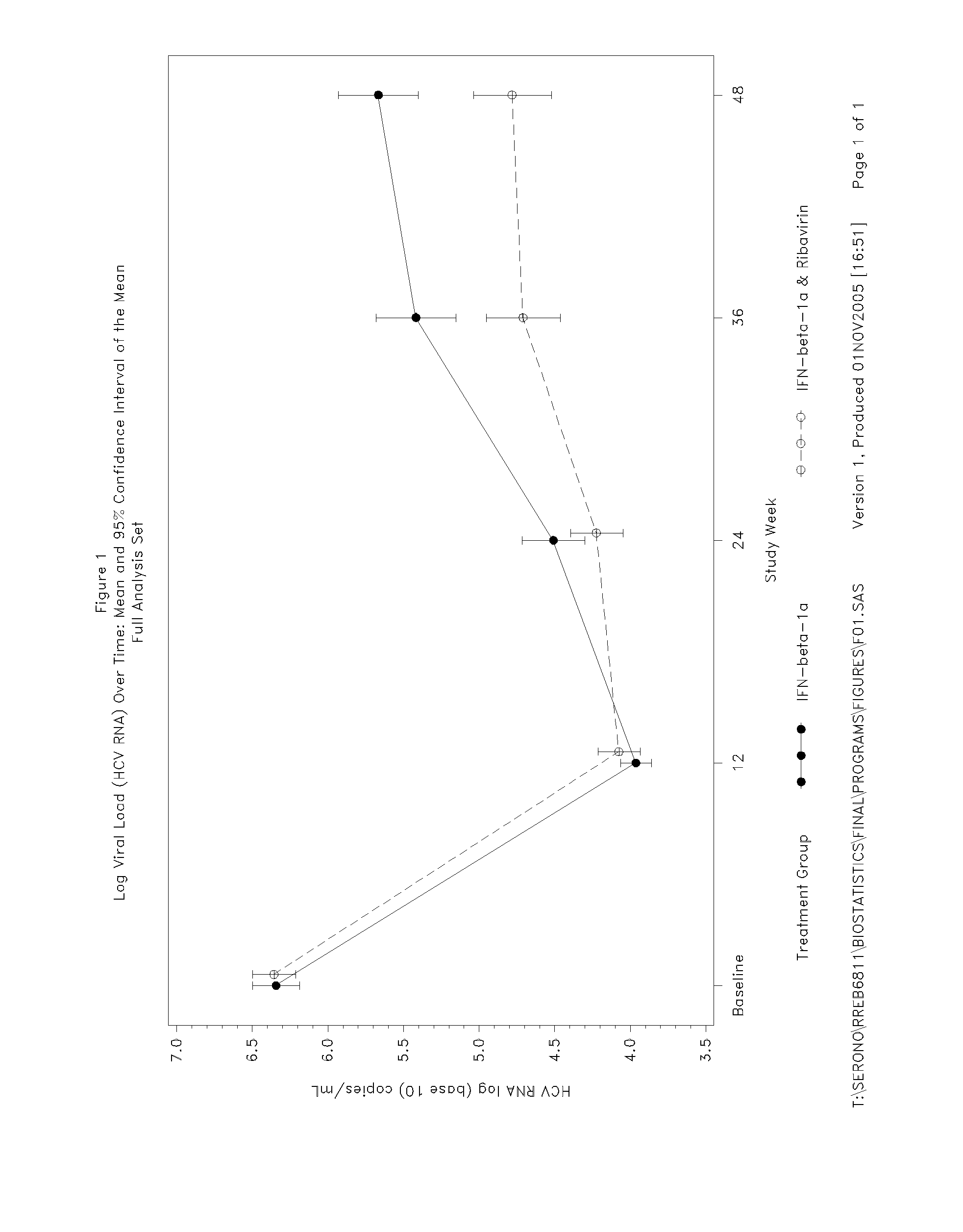
Treatment Of Hepatitis C In The Asian Population With Interferon-Beta
InactiveUS20080075696A1Good effectBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsGreek letter betaInterferon therapy
The invention relates to the use of IFN-beta in the manufacture of a medicament for the treatment of an HCV infection in a treatment-naïve patient belonging to the Asian population.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
Interferon-beta variants and conjugates
InactiveUS20030175241A1Renal clearance is reducedHigh molecular weightSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsInterferon alphaInterferon beta
The present invention provides new interferon beta conjugates, methods of preparing such conjugates and the use of such conjugates in therapy, in particular for the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Owner:PERSEID THERAPEUTICS +1
Neuroprotection in Demyelinating Diseases
InactiveUS20130287732A1Reduce demyelinationReduce axonal deathOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNervous systemDemyelinating disease
Methods of treating neurological disorders, e.g., those characterized by demyelination and / or axonal loss (e.g., MS), are provided. The methods comprise administration of a therapeutically effective amount of at least one compound of Formula I:wherein R1 and R2 are independently selected from OH, O−, and (C1-6)alkoxy, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; and either glatiramer acetate or interferon-beta.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Modified interferon beta polypeptides and their uses
InactiveUS20120197006A1Improve stabilityImprove solubilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsInterferon alphaInterferon beta
Owner:AMBRX
Polymer conjugates of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, polypeptide hormones and antagonists thereof with preserved receptor-binding activity
Methods are provided for the synthesis of polymer conjugates of cytokines and receptor-binding antagonists thereof, especially a non glycosylated interferon-beta, which conjugates retain unusually high biological potency. Preparation of polymer conjugates according to the methods of the present invention diminishes or avoids steric inhibition of receptor-ligand interactions that commonly results from the attachment of polymers to receptor-binding regions of cytokines, as well as to agonistic and antagonistic analogs thereof. The invention also provides conjugates and compositions produced by such methods. The conjugates of the present invention retain a high level of biological potency compared to those produced by traditional polymer coupling methods that are not targeted to avoid receptor-binding domains of cytokines. In assays in vitro, the biological potency of the conjugates of non-glycosylated interferon-beta of the present invention is substantially higher than that of unconjugated interferon-beta and is similar to that of interferon-beta-1a that is glycosylated. The conjugates of the present invention also exhibit an extended half-life in vivo compared to the corresponding unconjugated cytokine. The present invention also provides kits comprising such conjugates and / or compositions, and methods of use of such conjugates and compositions in a variety of diagnostic, prophylactic, therapeutic and bioprocessing applications, including treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Owner:MOUNTAIN VIEW PHARMA
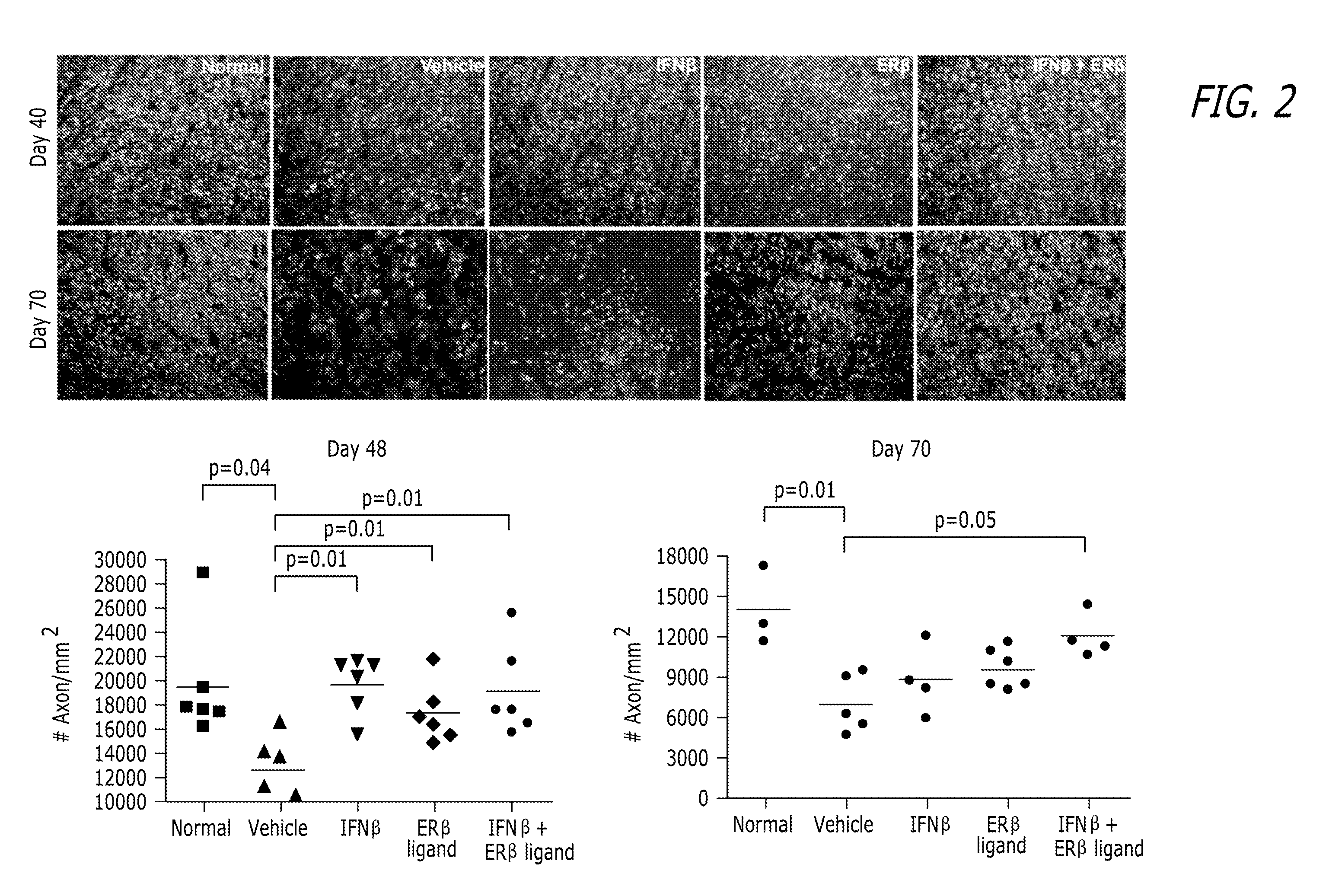
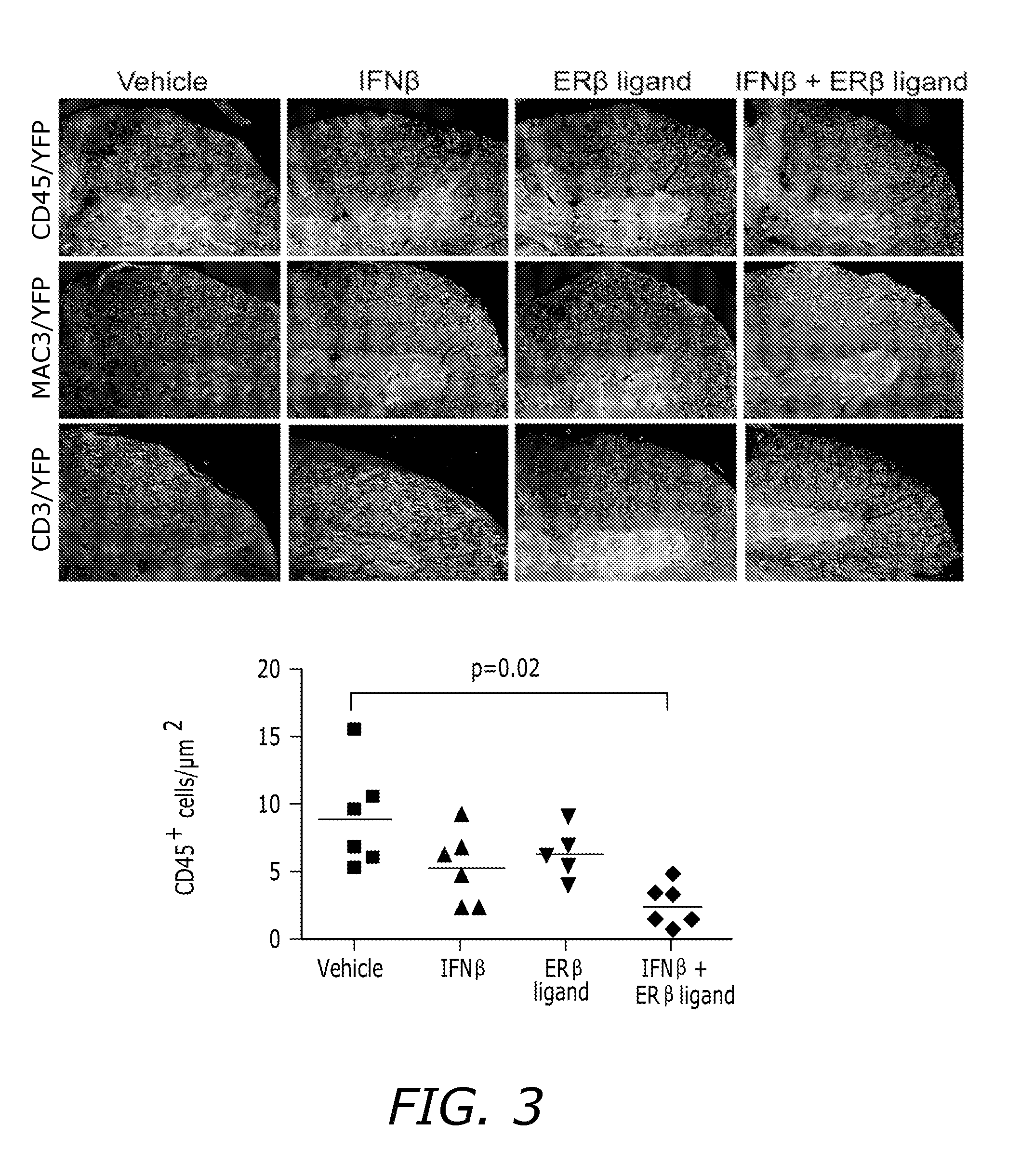
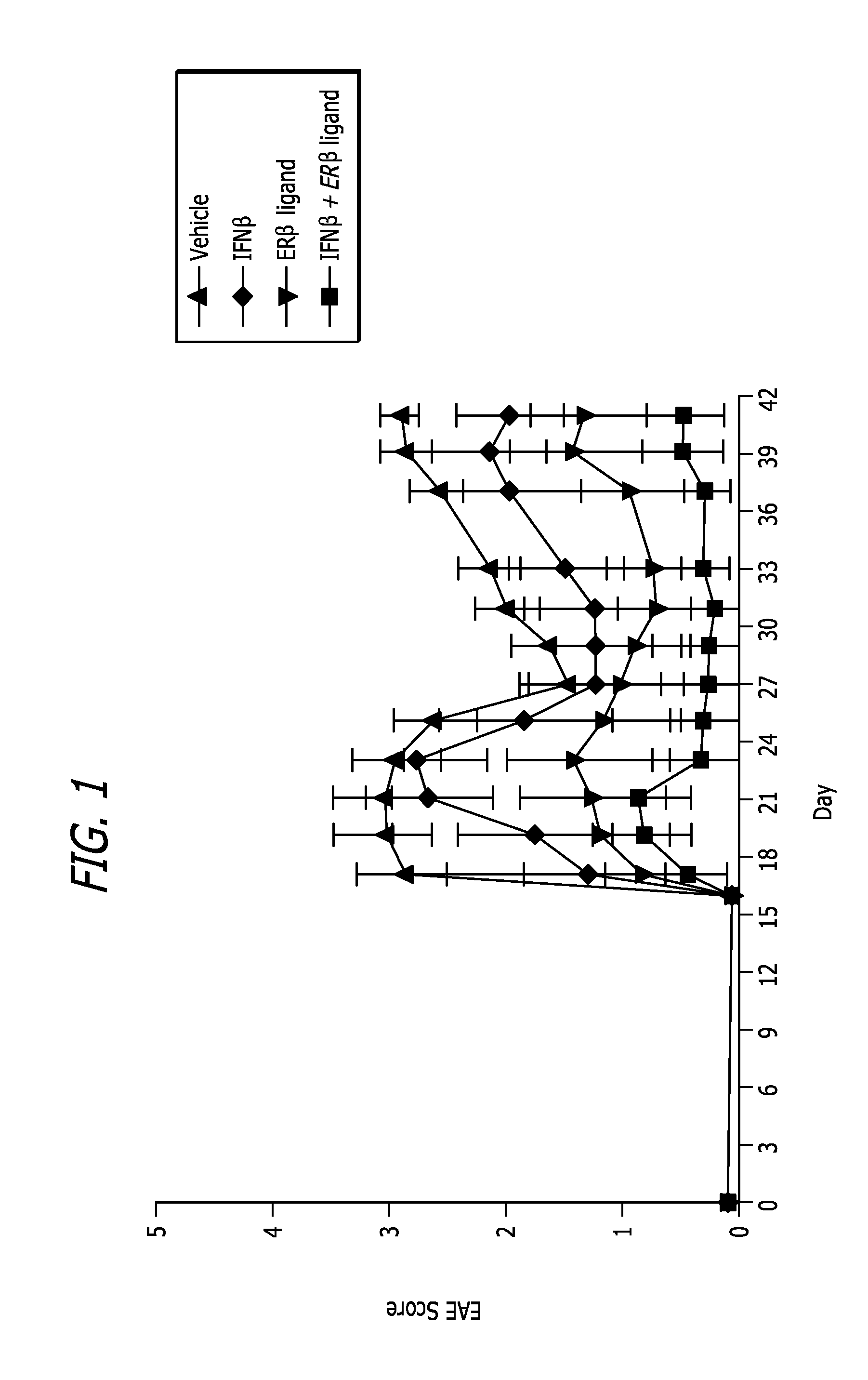
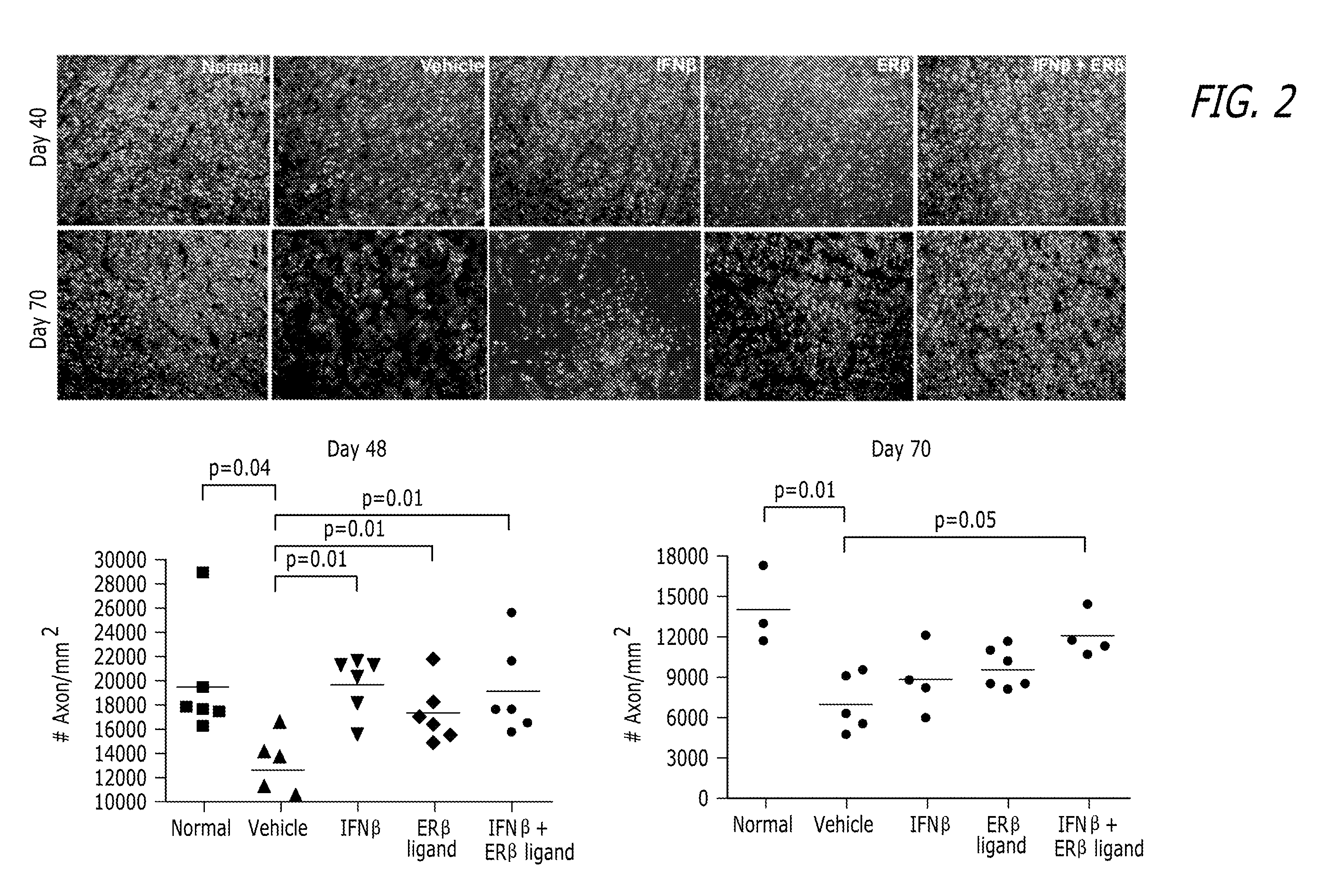
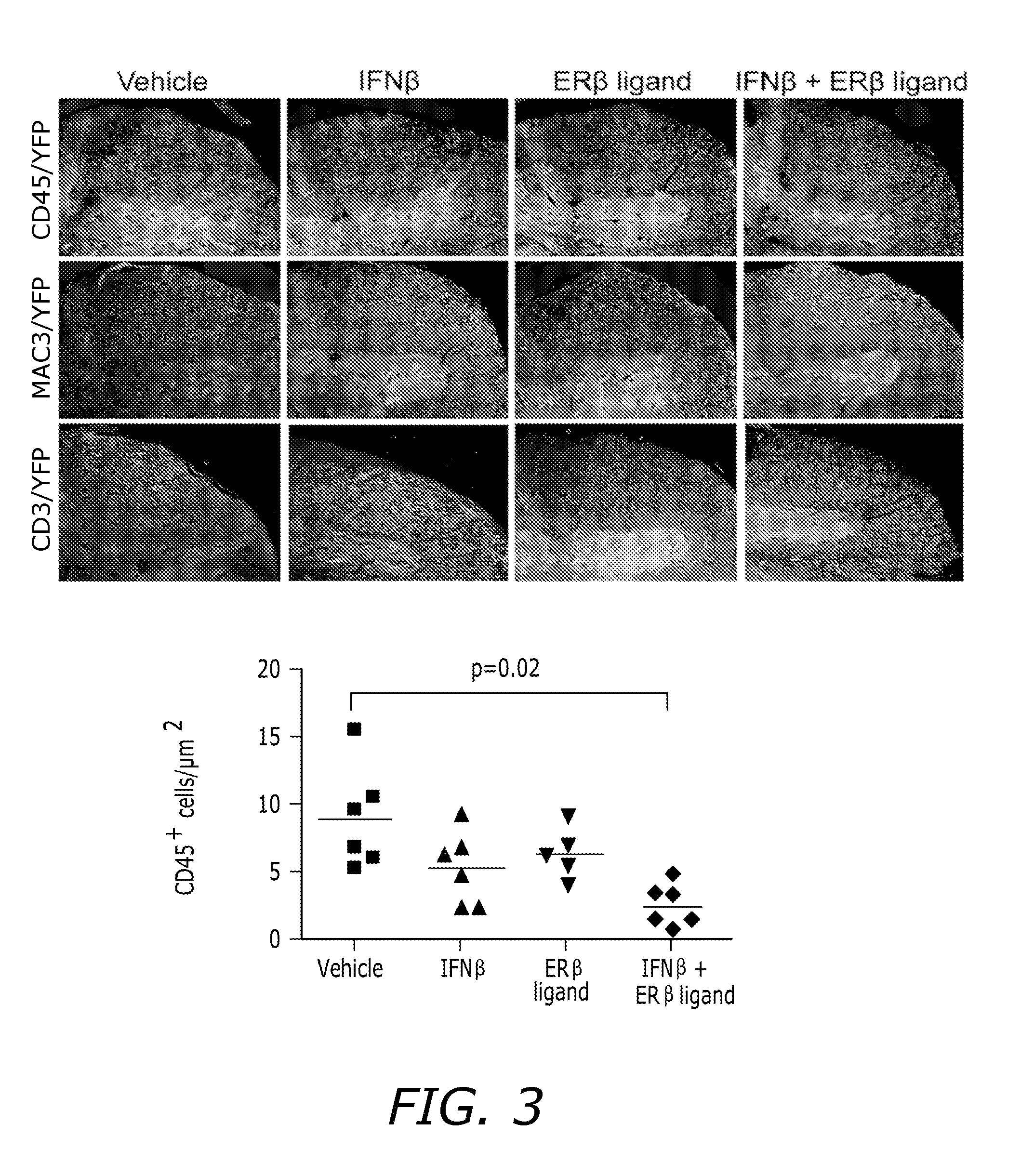
Estrogen receptor ligand and/or interferon beta treatment for neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20120282222A9Lower Level RequirementsDecreasing VLA-4 expressionBiocideNervous disorderBeta interferonsInterferon beta
This invention relates generally to novel treatments to prevent neurodegeneration in the central nervous system comprising a therapeutic dosage of an estrogen receptor ligand and / or an immunotherapeutic compound, such as beta-interferon, to ameliorate the effects of the neurodegenerative disease and to stimulate repair.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Liquid interferon-beta formulations
InactiveUS20050186177A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOrganic chemistryInterferon beta
Owner:RENTSCHLER BIOTECH
Stable liquid interferon formulations
InactiveCN1245434AEasy to packImprove dose accuracyNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycineIonic strength
Liquid interferon compositions having a pH between 4.0 and 7.2 are described. The compositions comprise interferon-beta and a stabilizing agent at between about 0.3 % and 5 % by weight which is an amino acid selected from the group consisting of acidic amino acids, arginine and glycine. If needed, salt is added to provide sufficient ionic strength. The liquid composition has not been previously lyophilized or previously cavitated. The liquid is preferably contained within a vessel having at least one surface in contact with the liquid that is coated with a material inert to adsorption of interferon-beta. A kit for parenteral administration of a liquid interferon formulation and a method for stabilizing liquid interferon compositions are also described.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Method of treating tuberculosis with interferons
A method of treating tuberculosis comprising administering an aerosolized interferon such as interferon α, interferon β or interferon γ in a therapeutically effective amount is provided herein. Further, a method of reducing the infectivity of tuberculosis or reducing the number of infectious organisms present in the lungs of a patient suffering from tuberculosis comprising administering an aerosolized interferon such as interferon α, interferon β or interferon γ in a therapeutically effective amount is provided herein. Also, pharmaceutical compositions of one or more aerosolized interferon(s) are provided.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Long-acting interferon beta formulation using immunoglobulin fragment
ActiveUS20130028867A1Improve the level ofExtended half-lifeNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSerum ige
The present invention relates to a long-acting interferon beta formulation having improved in vivo duration and stability, comprising an interferon beta conjugate that is prepared by covalently linking interferon beta with an immunoglobulin Fc region via a non-peptidyl polymer, and a preparation method thereof. The long-acting interferon beta formulation of the present invention maintains in vivo activity of interferon beta at a relatively high level and remarkably increases the serum half-life thereof, thereby being used for various diseases, for which interferon is efficacious.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Modified interferon beta with reduced immunogenicity
InactiveUS7381795B2Modify characteristicExtended circulation timeSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsInterferon alphaIn vivo
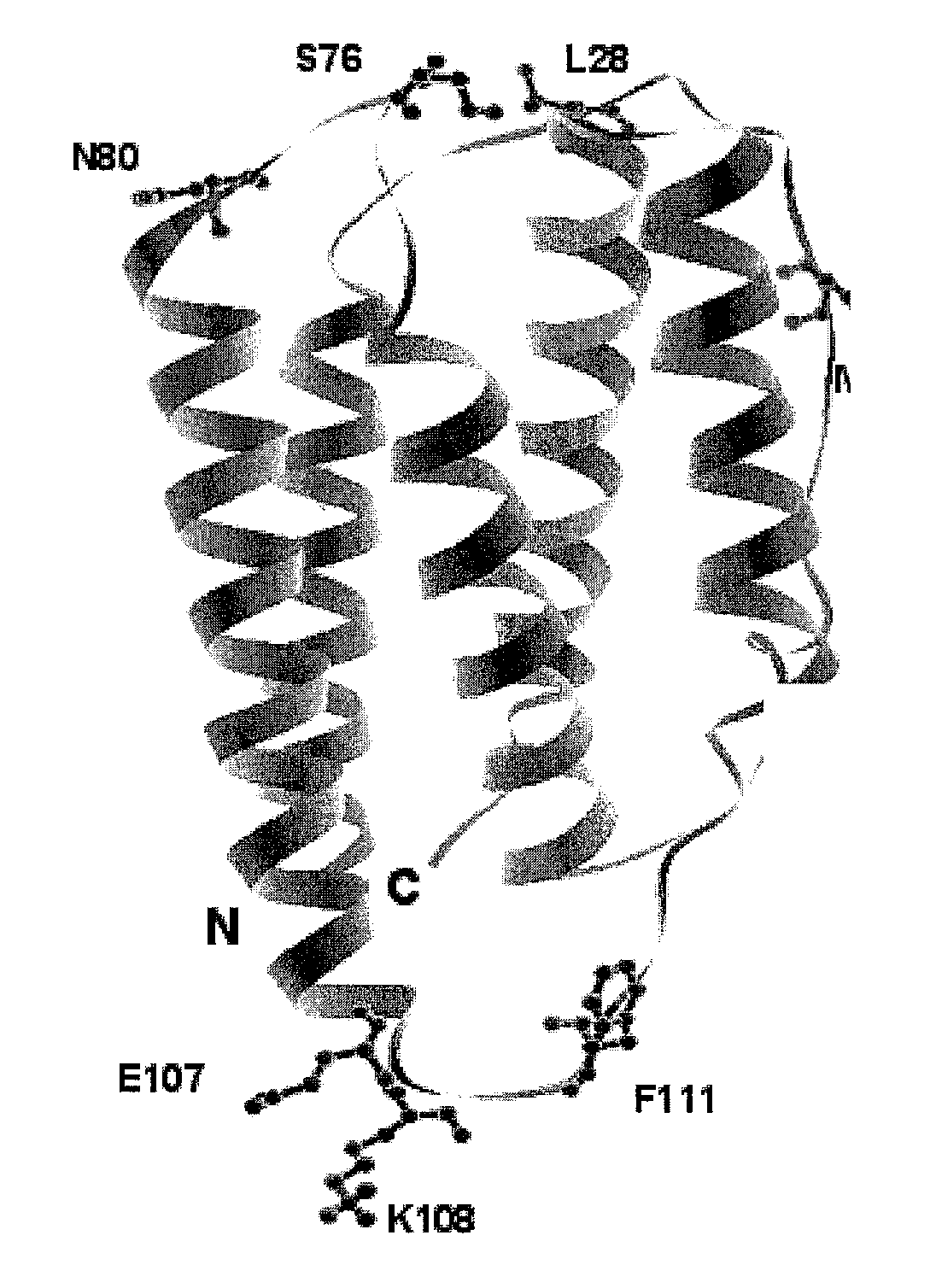
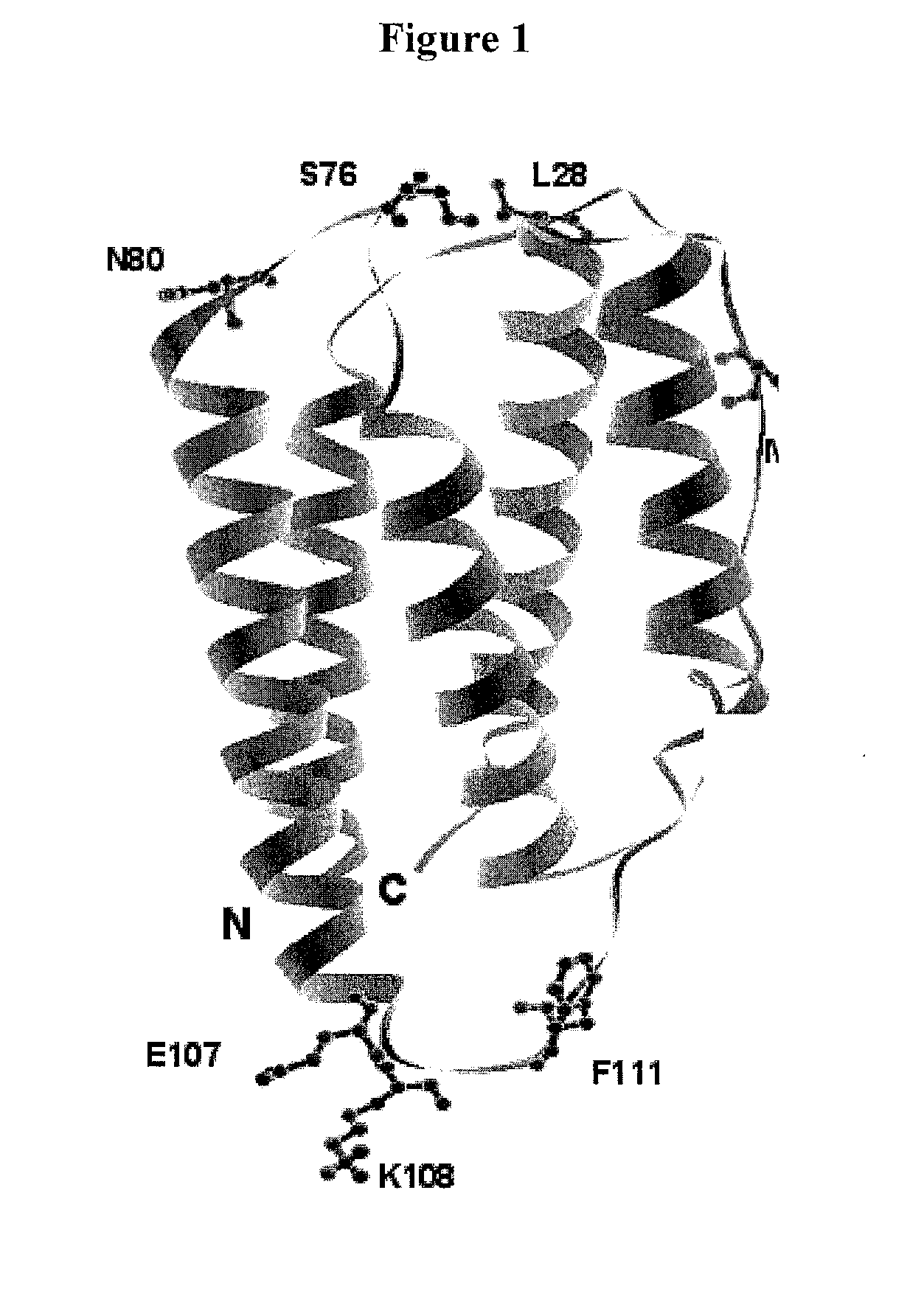
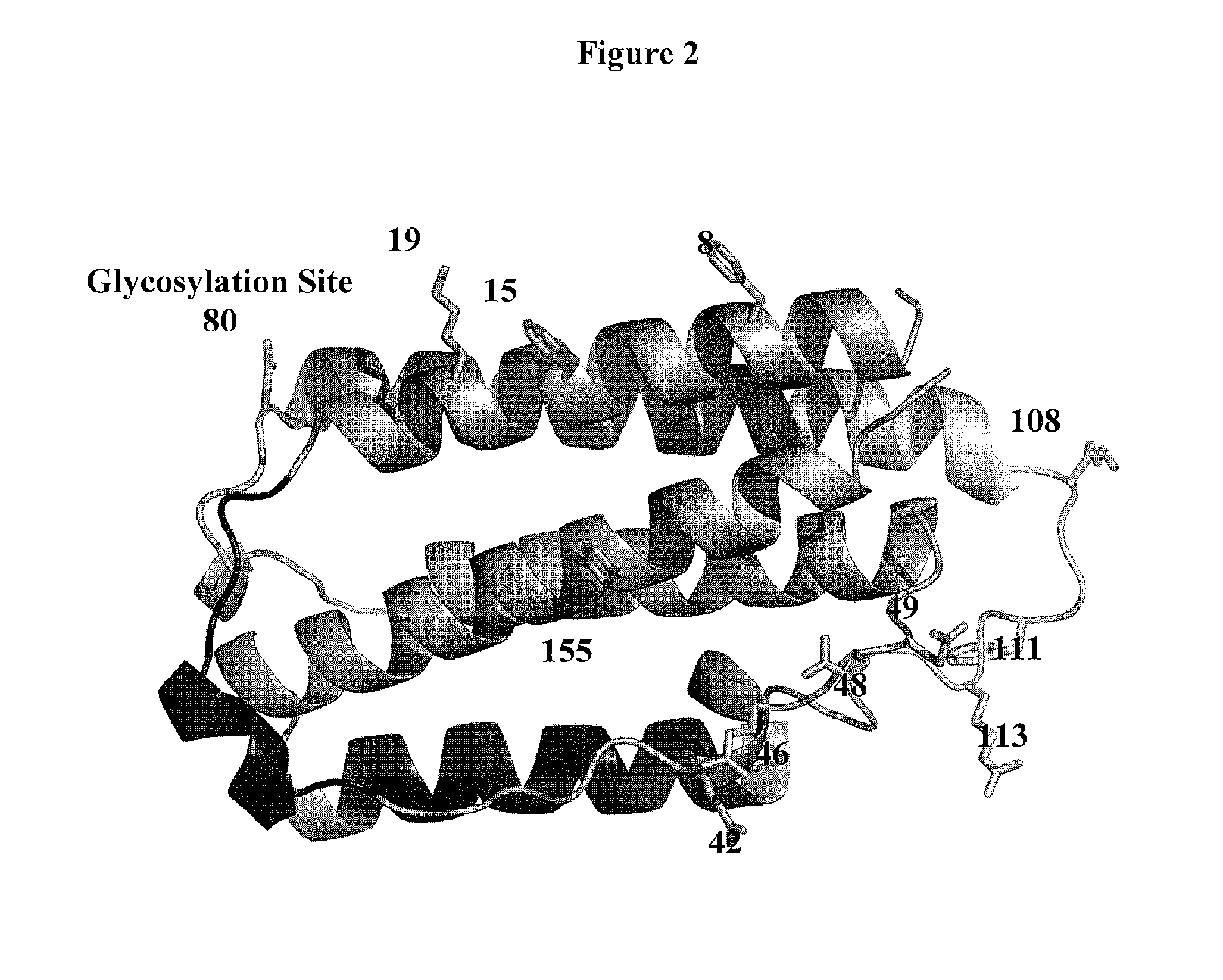
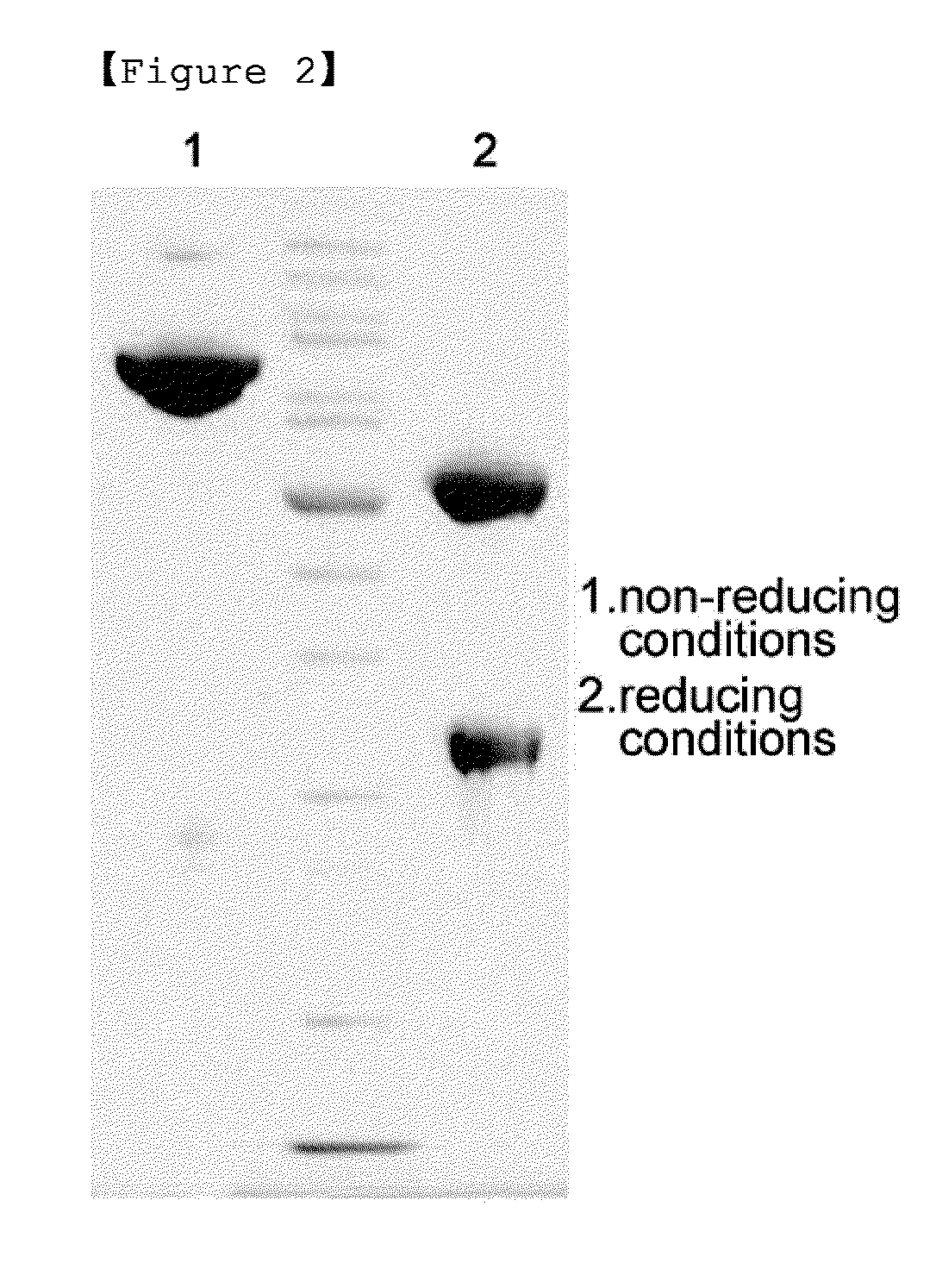
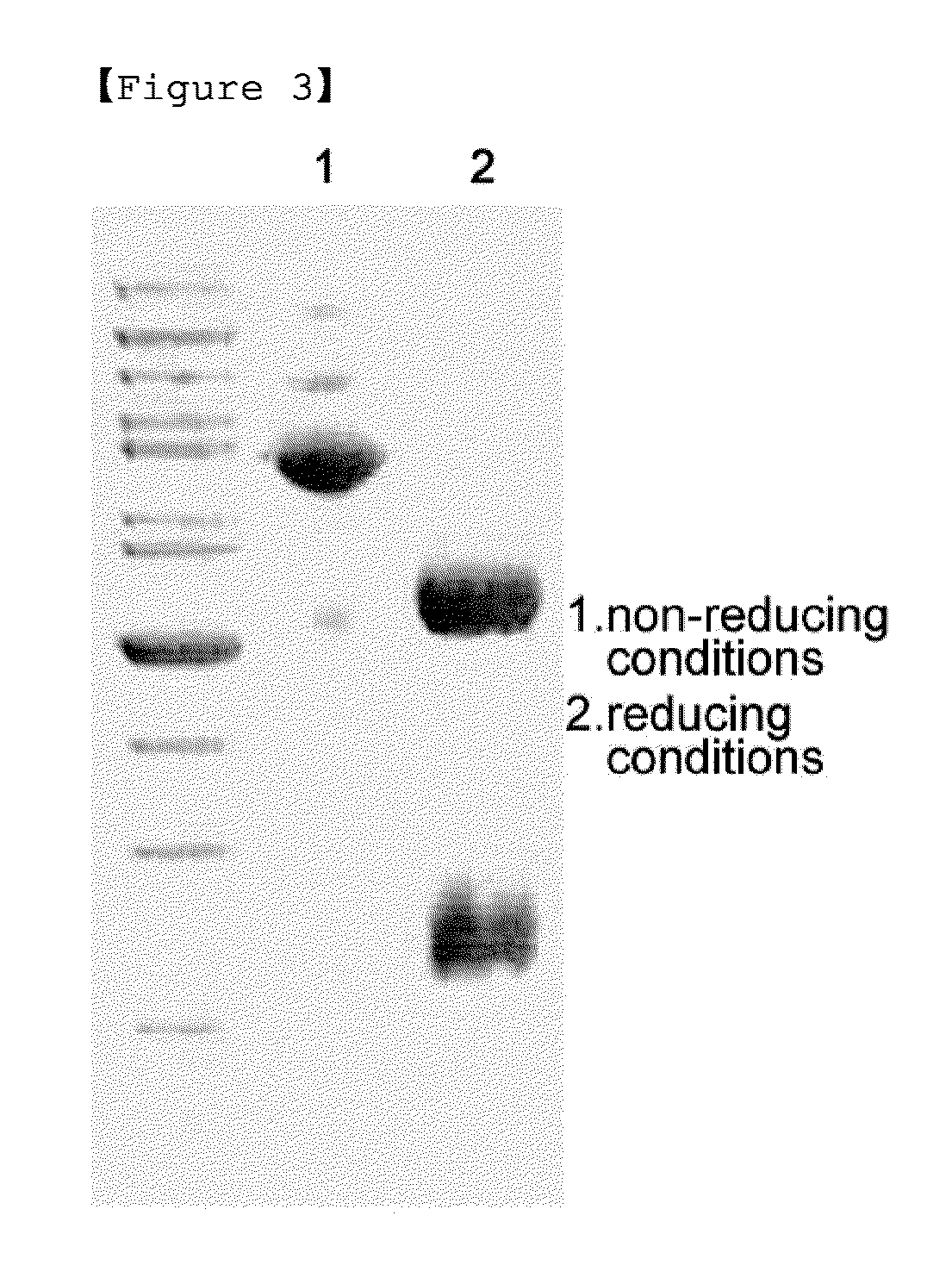
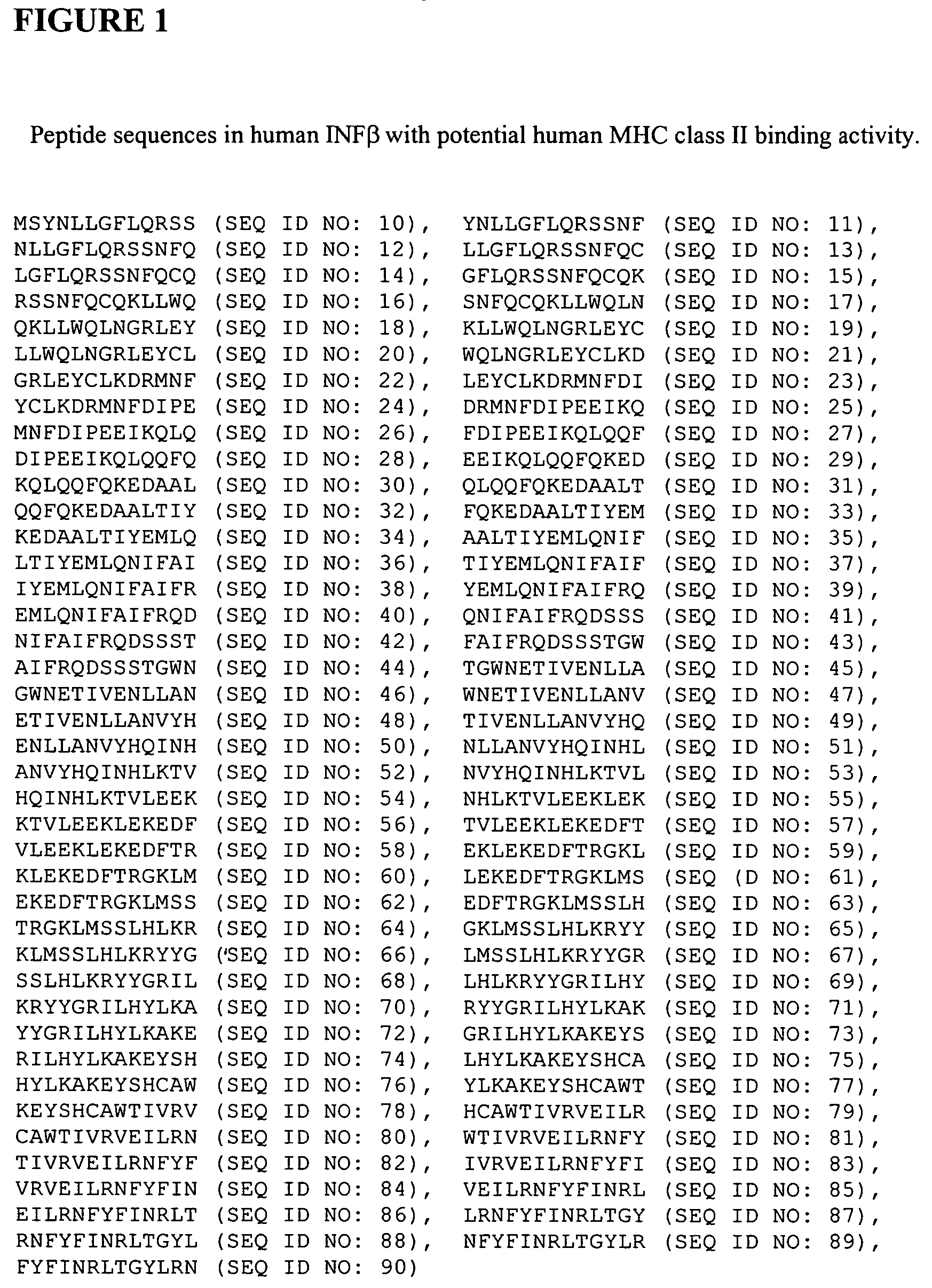
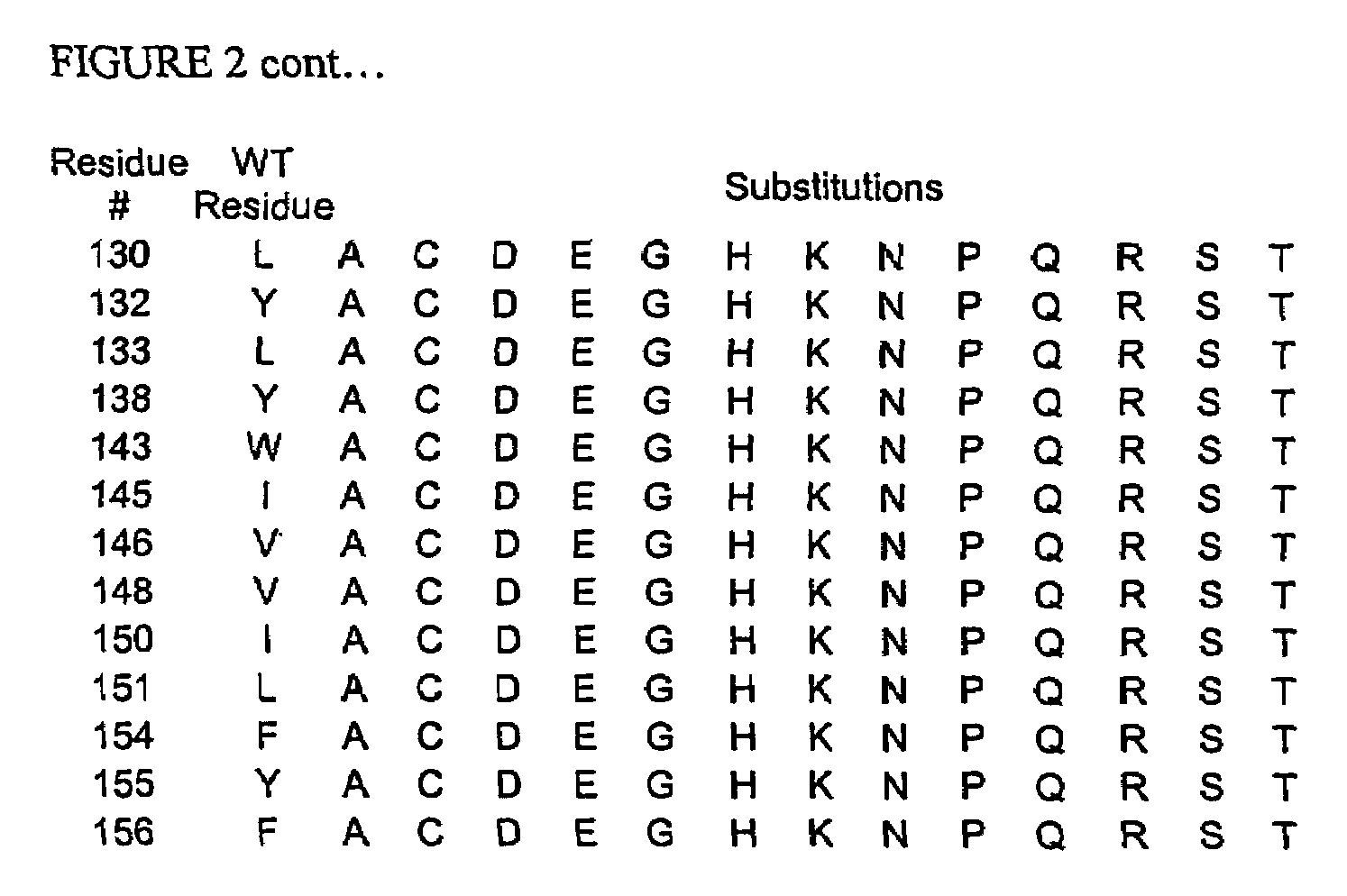
A modified interferon beta (INFβ) is provided, which is less immunogenic than human INFβ (SEQ ID NO: 1) when administered to a human in vivo. The modified INFβ comprises an amino acid residue sequence that differs from SEQ ID NO: 1 by a substitution at one or more residues of SEQ ID NO: 1. Preferred substitutions are at residues selected from the group consisting of residue 50, 59, 60, 62, 63, 66, 67, 69, 70, 125, 126, 129, 130, 132, 133, and 138. Examples of suitable substitutions include F50A, L57A, I59A, Y60N, M62A, L63A, I66T, F67H, I69A, F70A, Y125A, Y126A, I129A, L130A, Y132S, L133A, Y138H, and Y138A.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
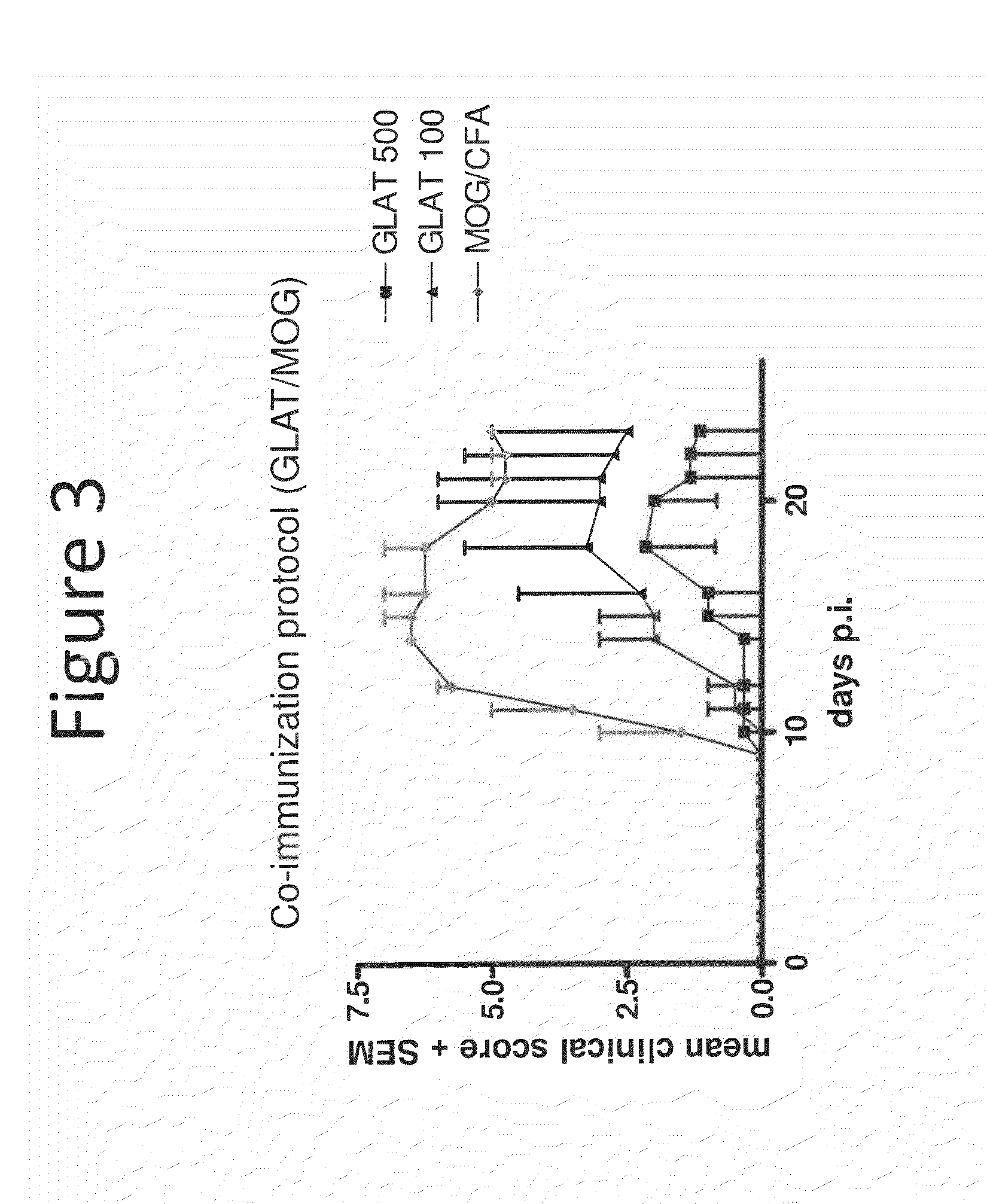
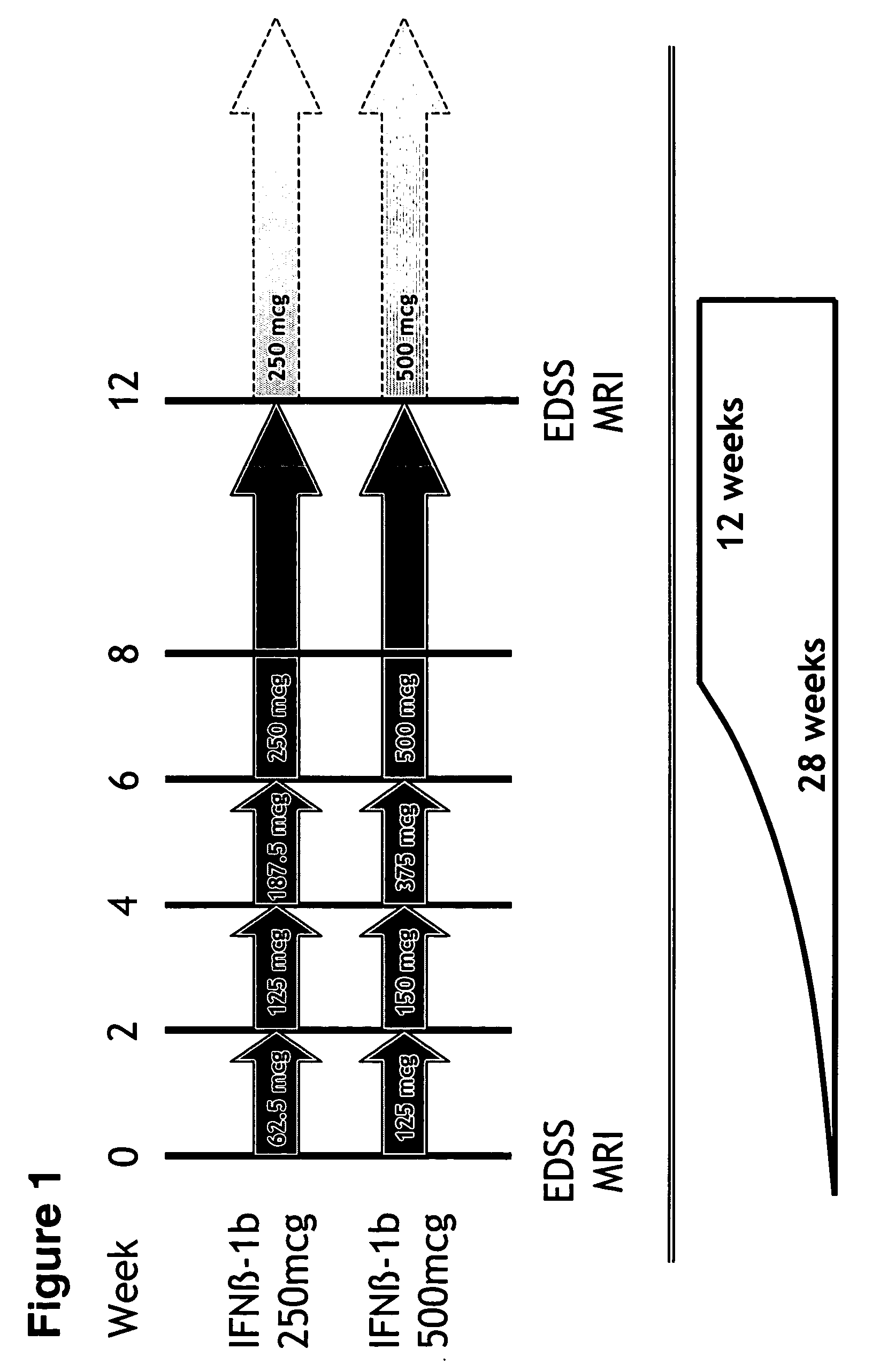
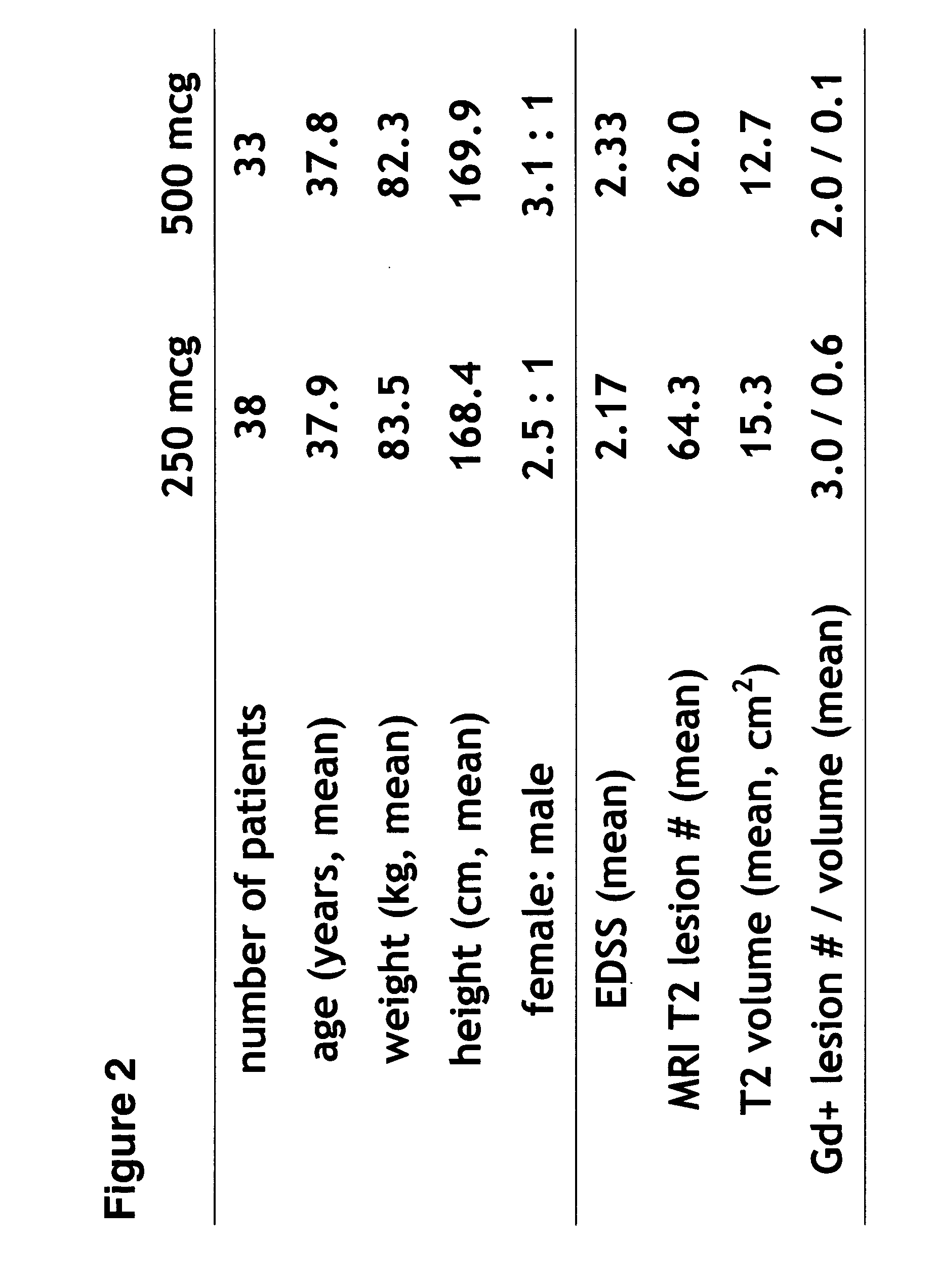
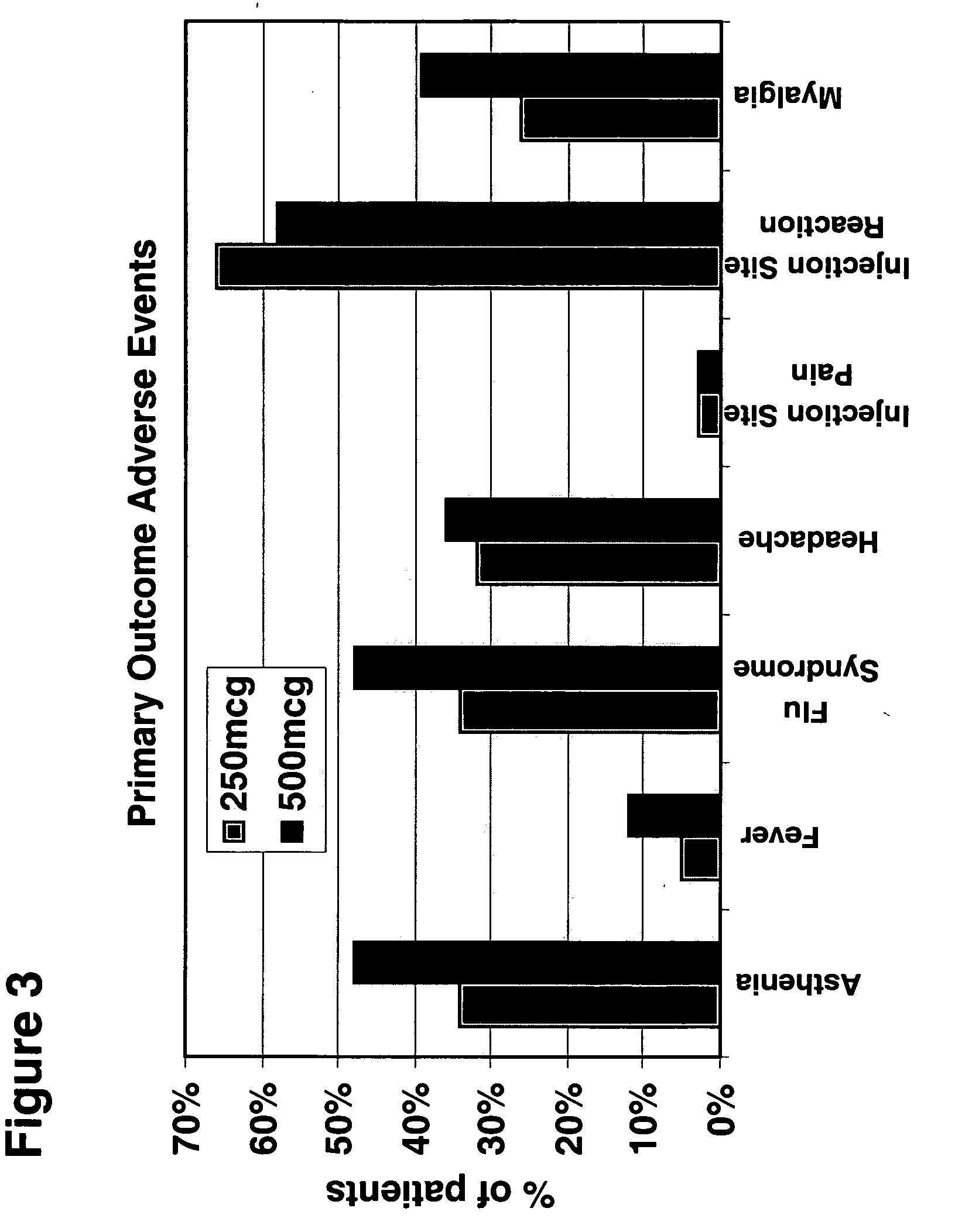
Higher-doses of interferon-beta for treatment of multiple sclerosis
The present invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising a new, therapeutically effective dose of an isolated interferon-beta (IFN-β) mutein for treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS) and methods of treating MS using such pharmaceutical compositions. More particularly, the pharmaceutical compositions of the present invention comprise a new, therapeutically effective dose of an isolated IFN-β mutein.
Owner:SCHERING AG
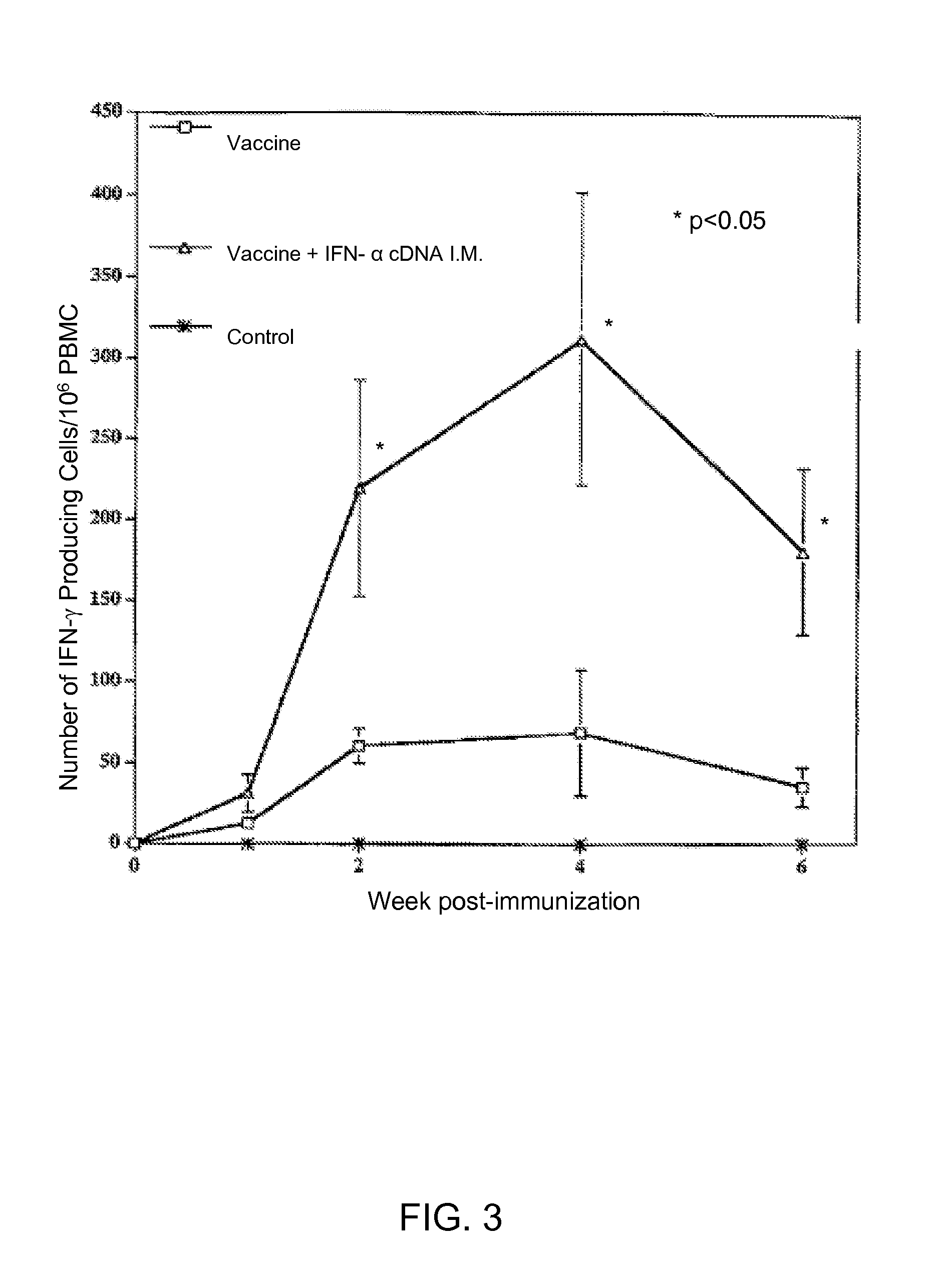
Enhancement of immune response to vaccine by interferon alpha
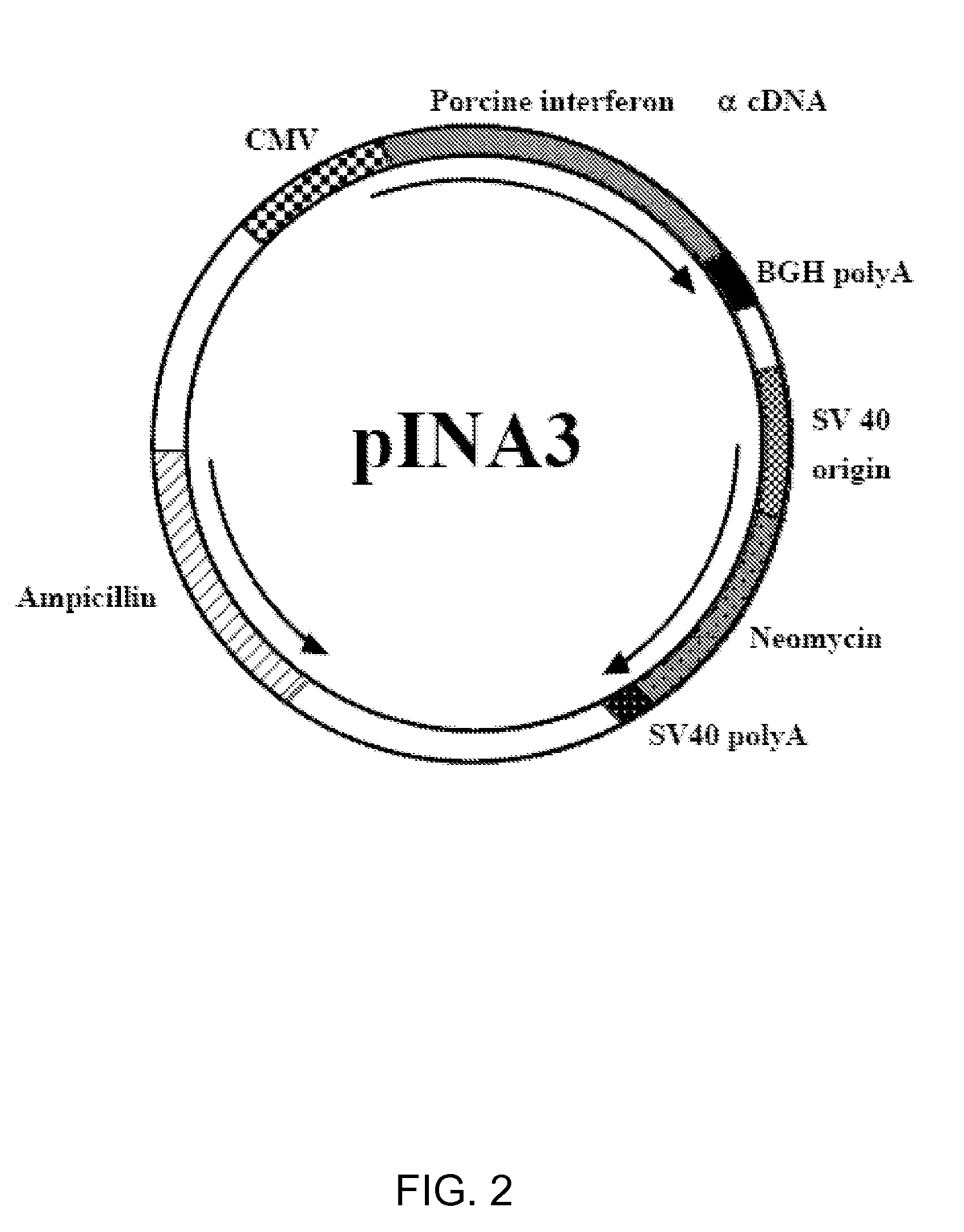
Exogenous cDNA capable of expressing interferon α activity, exogenous interferon α protein, inducers of endogenous interferon α protein activity, inducers of endogenous interferon β protein activity, inducers of endogenous interfereon Γ activity, or inducers of other immune-enhancing activity can be combined with a vaccine to enhance an immune response. Specifically disclosed are adjuvant and vaccine combinations where the adjuvant comprises a cDNA capable of expressing interferon α activity, a complex comprising polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidilic acid, or a complex comprising polyriboinosinic-polyribocytidilic acid, poly-L-lysine, and carboxymethylcellulose and where the vaccine is a live vaccine virus derived from a virus causing porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome disease.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
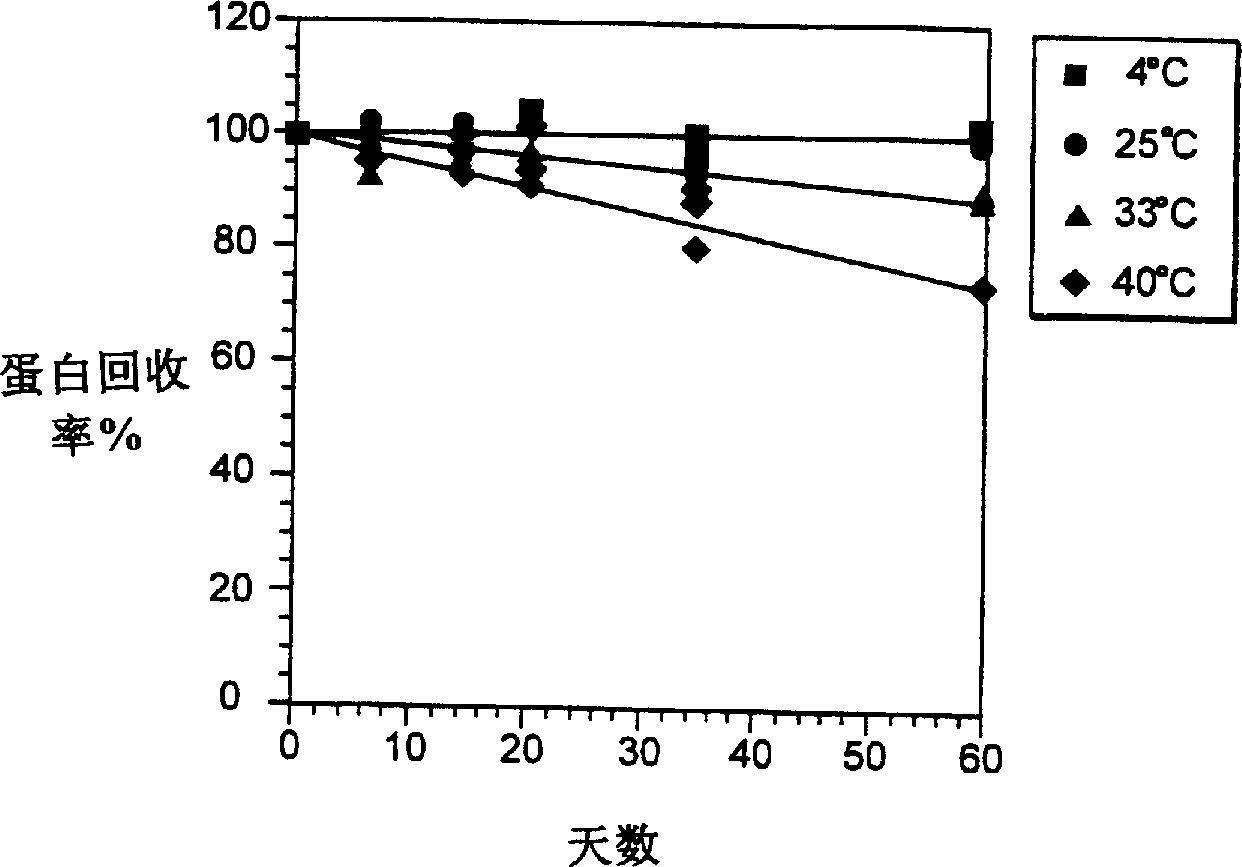
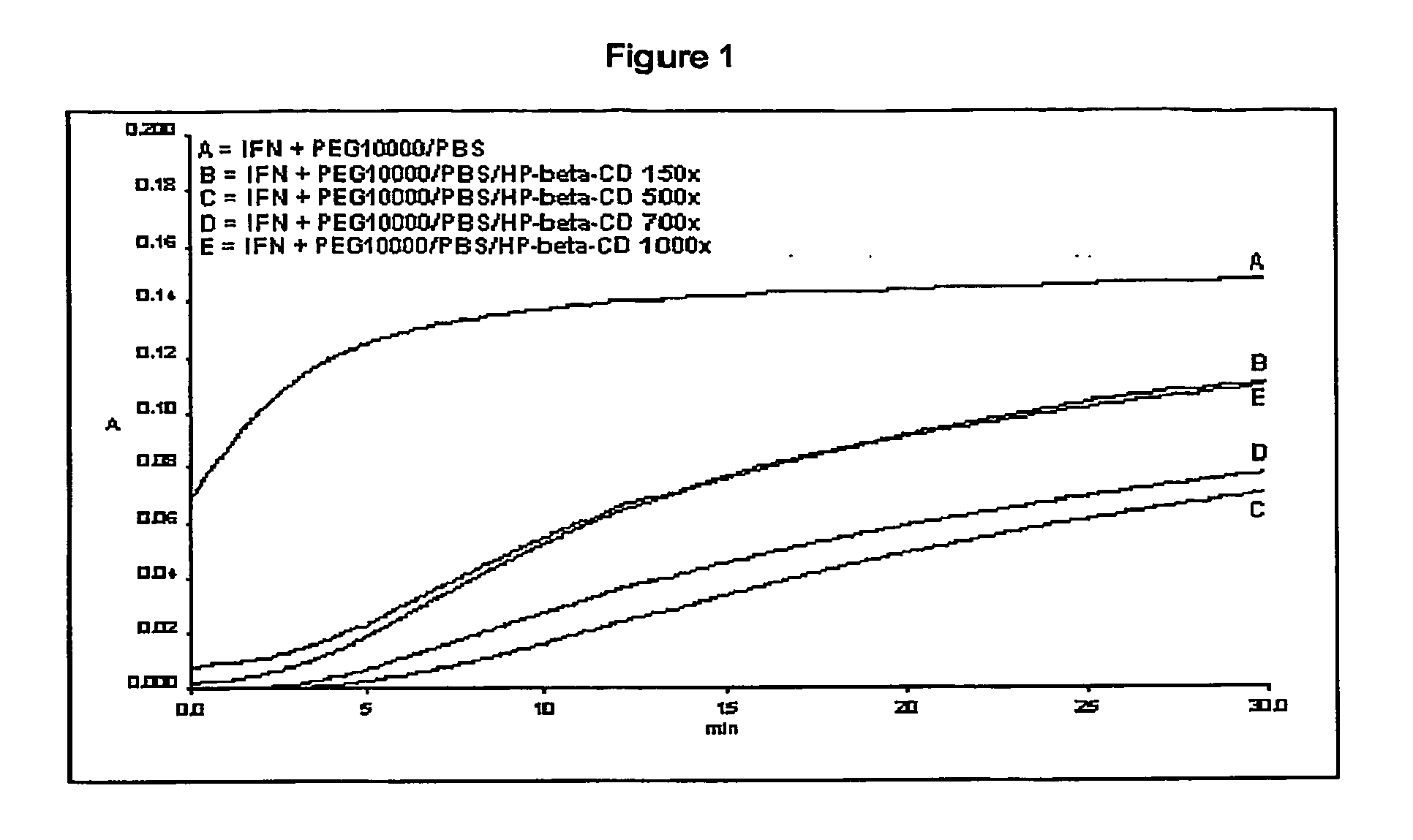
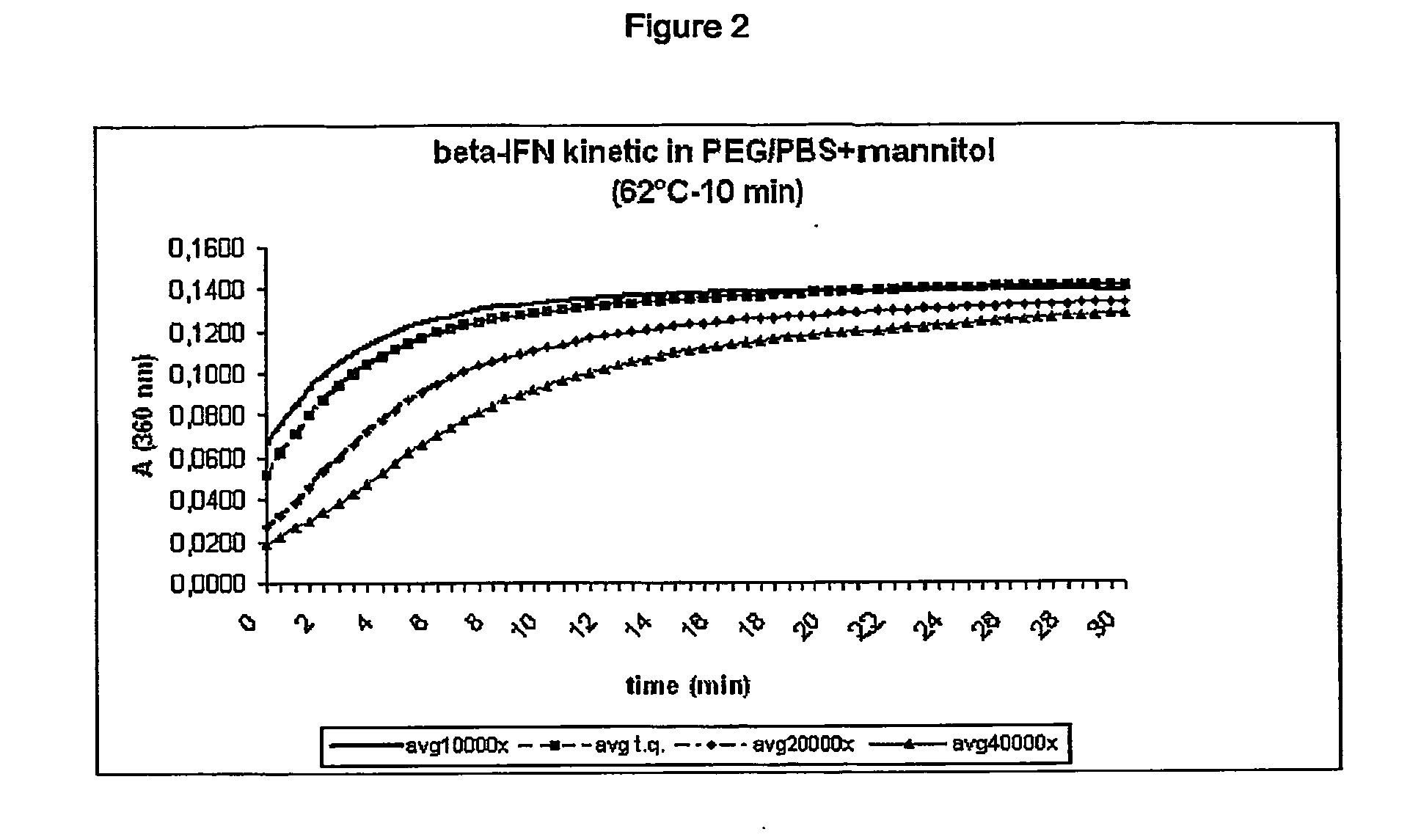
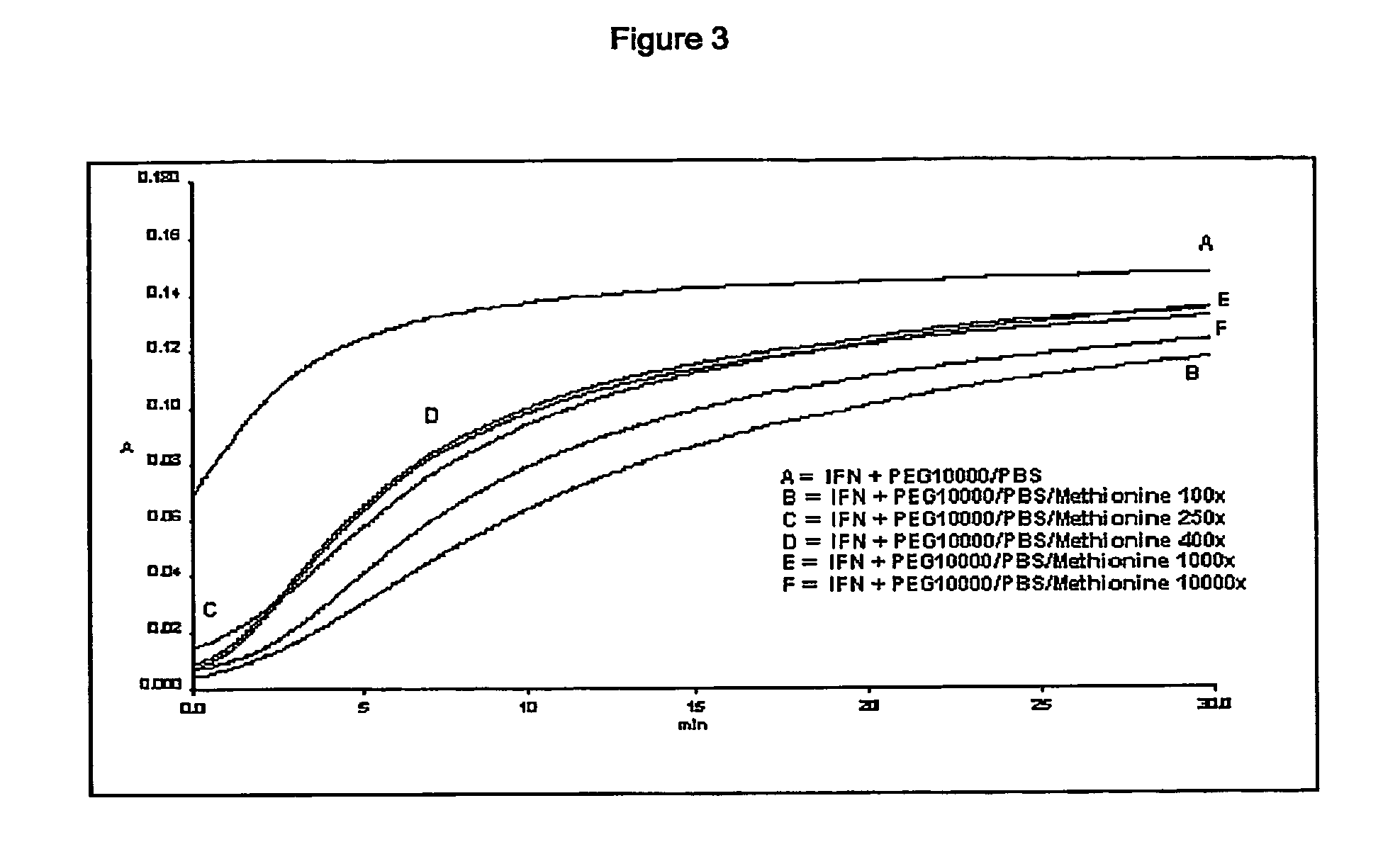
Stabilized interferon liquid formulations
ActiveUS20070104682A1Prolong residenceOptimize treatment planBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMedicineCyclodextrin
Stabilized liquid pharmaceutical composition comprising an interferon (IFN) or an isoform, mutein, fused protein, functional derivative, active fraction or salt thereof, wherein said formulation is a solution that comprises a buffer, a cyclodextrin, an isotonicity agent and an anti-oxidant are described here. Preferably the interferon is interferon beta-1a and the cyclodextrin is HPBCD. These formulations are stable at room temperature, thus bringing the advantage of lower costs for formulation storage and increased safety for the patient with respect to possible “errors” during handling. As a matter of fact, having such formulations stable at room temperature reduces the risk of formation of degradation products potentially responsible for adverse events (e.g. immunogenicity).
Owner:ARES TRADING SA
Method for treating multiple sclerosis
InactiveUS20100172869A1Maximize efficacyReduce adverse side effectsNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDosing FrequencyInterferon alpha
Methods for treating multiple sclerosis (MS) and clinically isolated syndromes suggestive of MS are provided. The methods comprise administering a therapeutically effective dose of interferon-beta (IFN-beta) to a subject in need thereof, where the dose is administered intramuscularly with a dosing frequency of two- to three-times per week.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Long-acting interferon beta formulation comprising an immunoglobulin fragment
ActiveUS9421244B2Improve the level ofExtended half-lifeNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseSerum ige
The present invention relates to a long-acting interferon beta formulation having improved in vivo duration and stability, comprising an interferon beta conjugate that is prepared by covalently linking interferon beta with an immunoglobulin Fc region via a non-peptidyl polymer, and a preparation method thereof. The long-acting interferon beta formulation of the present invention maintains in vivo activity of interferon beta at a relatively high level and remarkably increases the serum half-life thereof, thereby being used for various diseases, for which interferon is efficacious.
Owner:HANMI SCI CO LTD
Interferon-beta variants and conjugates
InactiveUS20030175240A1Avoid heterogeneous conjugationOptimize conjugationPeptide/protein ingredientsNanomedicineInterferon alphaInterferon beta
The present invention provides new interferon beta conjugates, methods of preparing such conjugates and the use of such conjugates in therapy, in particular for the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Owner:PERSEID THERAPEUTICS +1
Method for treating or preventing ischemia reperfusion injury or multi-organ failure
This invention relates to a method for prevention or treatment of ischemia reperfusion injury or multi-organ failure in an individual by administering to said individual an effective amount of an interferon beta.
Owner:FARON PHARMA OY
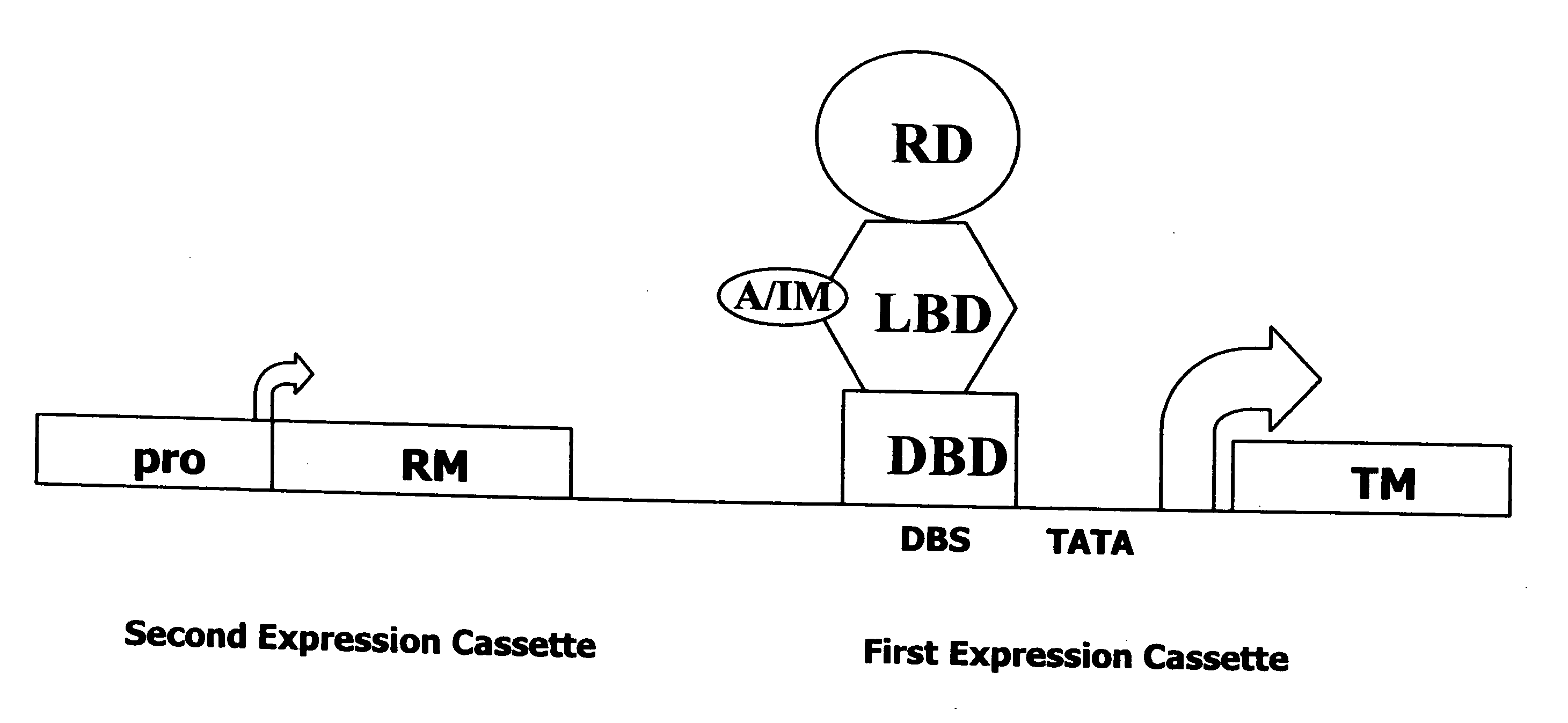
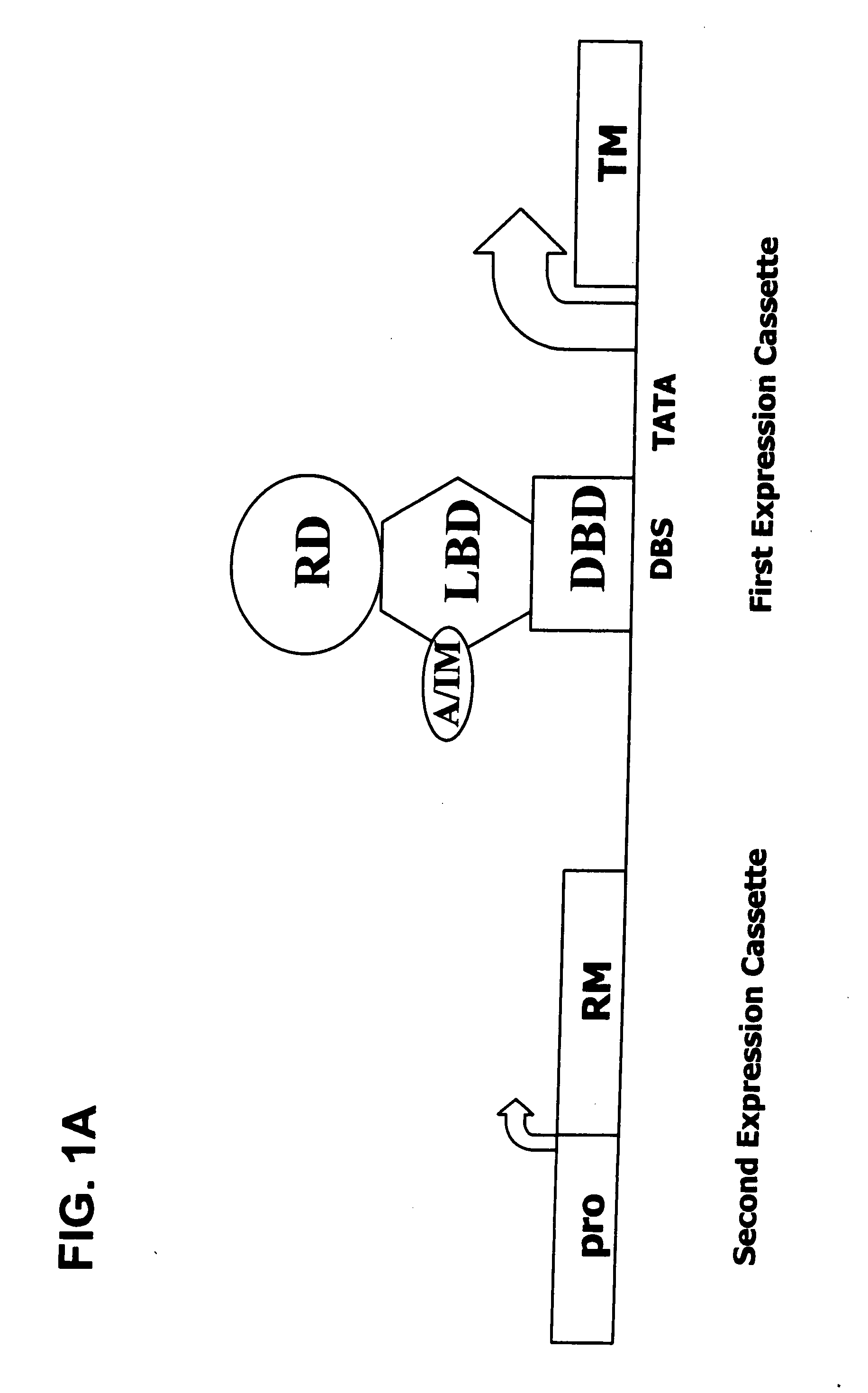
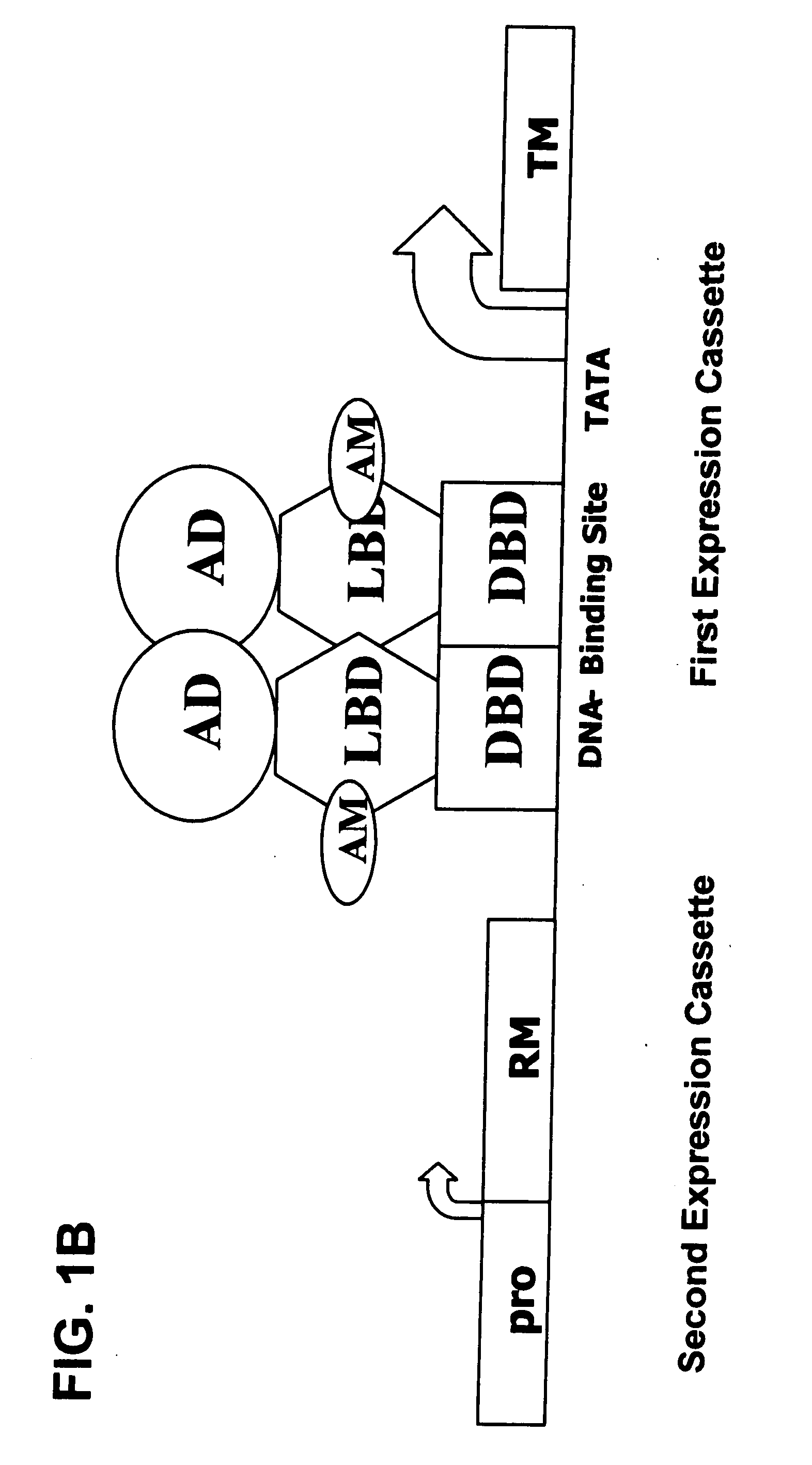
Interferon-beta gene therapy using an improved, regulated expression system
InactiveUS20080076729A1Minimize side effectsMaximizing therapeutic efficacyGenetic material ingredientsPeptidesDiseaseInterferon alpha
The present invention provides an improved, expression system for the regulated expression of an encoded protein or nucleic acid therapeutic molecule in the cells of a subject, for use in the treatment of disease. In particular, the present invention provides an improved, regulated gene expression system, and pharmaceutical compositions and uses thereof for treatment of disease.
Owner:SCHERING AG
Estrogen receptor ligand and/or interferon beta treatment for neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20110256096A1Lower Level RequirementsDecreasing VLA-4 expressionBiocideNervous disorderBeta interferonsInterferon beta
This invention relates generally to novel treatments to prevent neurodegeneration in the central nervous system comprising a therapeutic dosage of an estrogen receptor ligand and / or an immunotherapeutic compound, such as beta-interferon, to ameliorate the effects of the neurodegenerative disease and to stimulate repair.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Assembly and folding of fc-interferon-beta fusion proteins
InactiveUS20090191154A1Good biological propertiesImprove solubilityHybrid immunoglobulinsPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityDisease
Disclosed are Fc-interferon-beta (Fc-IFN-β) fusion proteins and nucleic acid molecules encoding them. The Fc-IFN-β fusion proteins include variants of the interferon-beta (IFN-β) protein that are altered to achieve enhanced biological activity, prolonged circulating half-life and greater solubility. Also disclosed are methods of producing the fusion proteins and methods of using the fusion proteins and / or nucleic acid molecules for treating diseases and conditions alleviated by the administration of interferon-beta.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Combination treatment method with interferon-tau
InactiveUS20090035273A1Simple methodReduce adverse eventsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsInterferon alphaEffective treatment
A method of treating conditions responsive to therapy with interferon-alpha or interferon-beta is provided, where the dose of interferon-alpha or interferon-beta is reduced and a dose of interferon-tau is additionally administered. The method results in efficacious therapy with a reduction in unwanted adverse events.
Owner:PEPGEN CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com