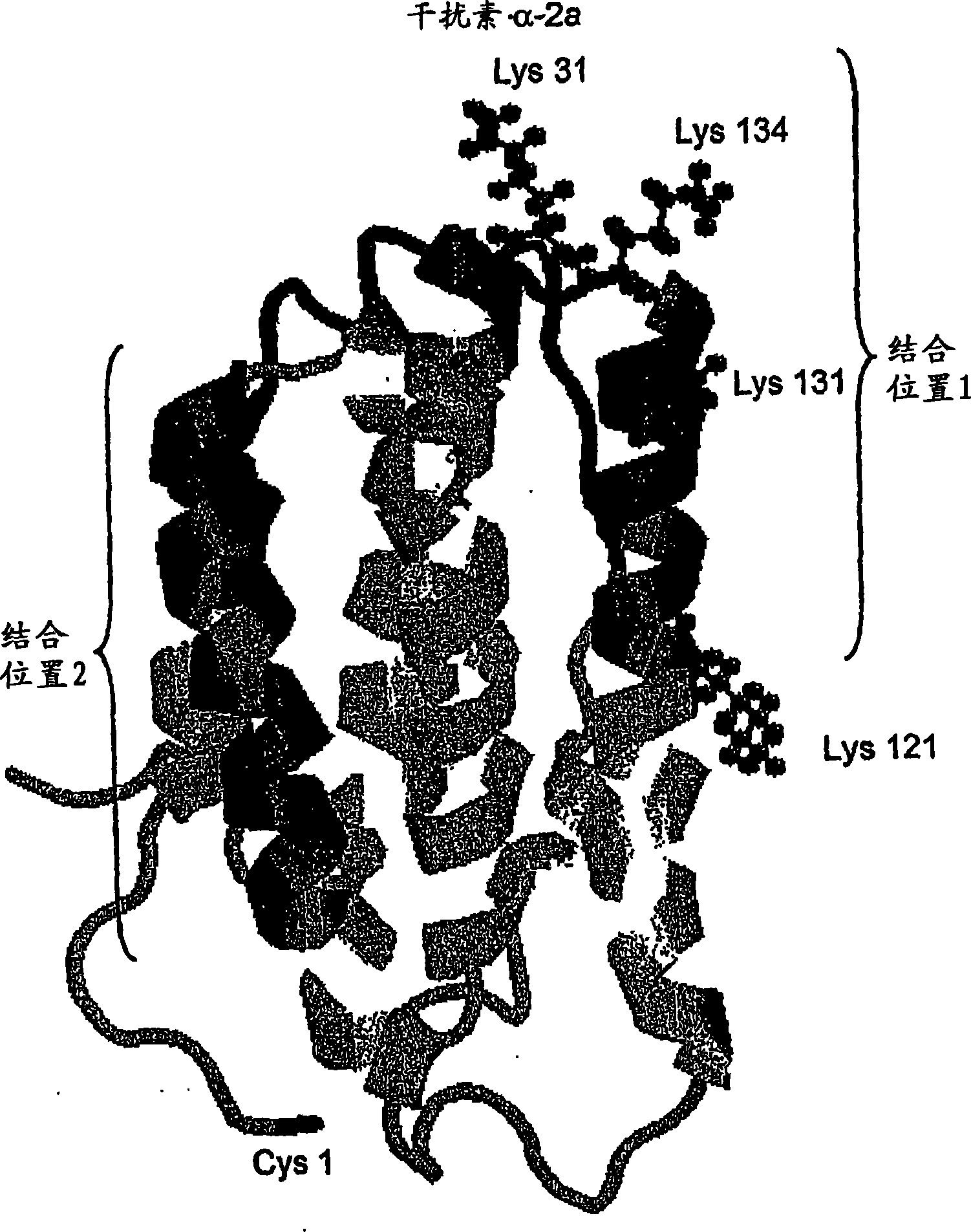
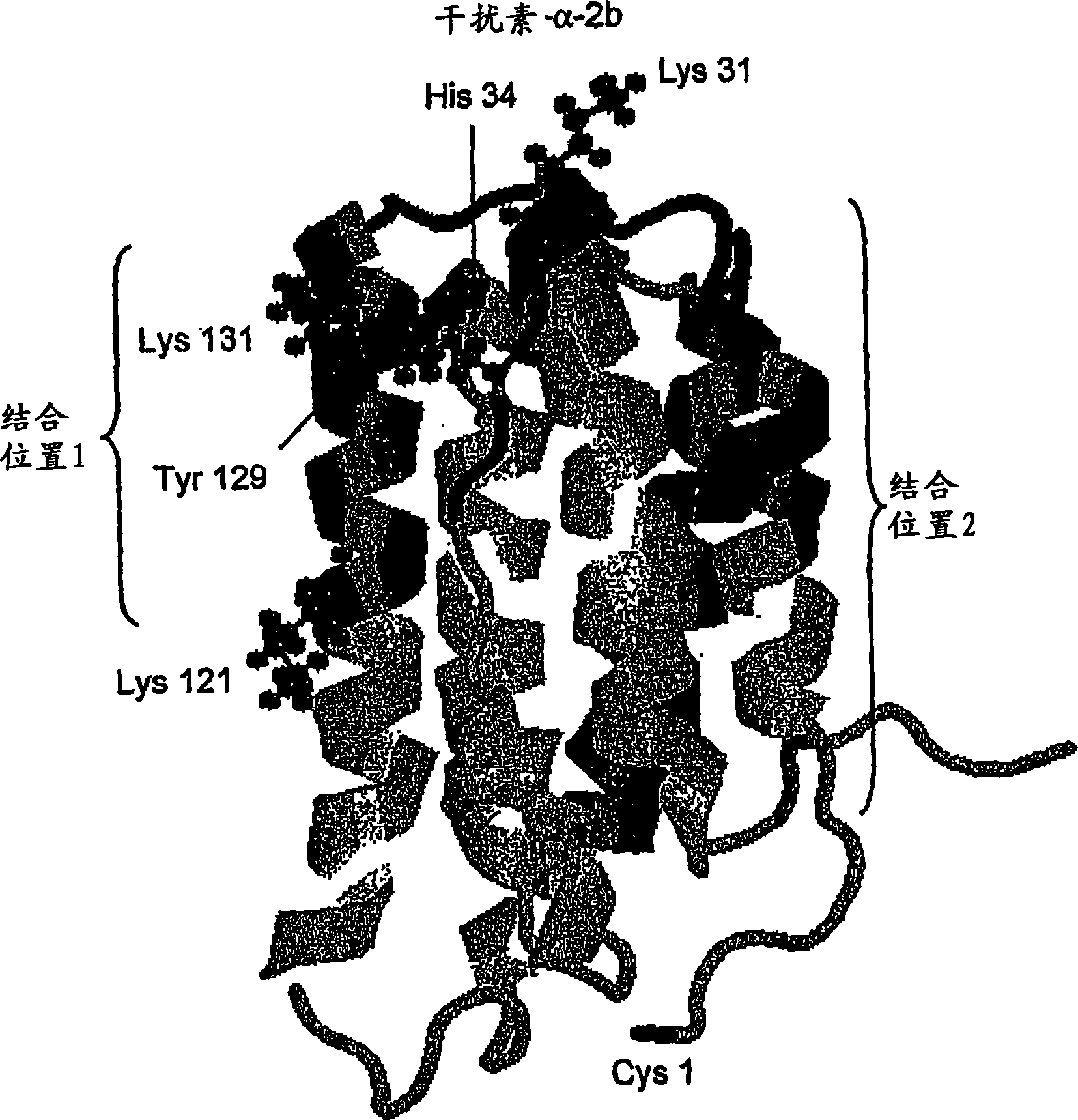
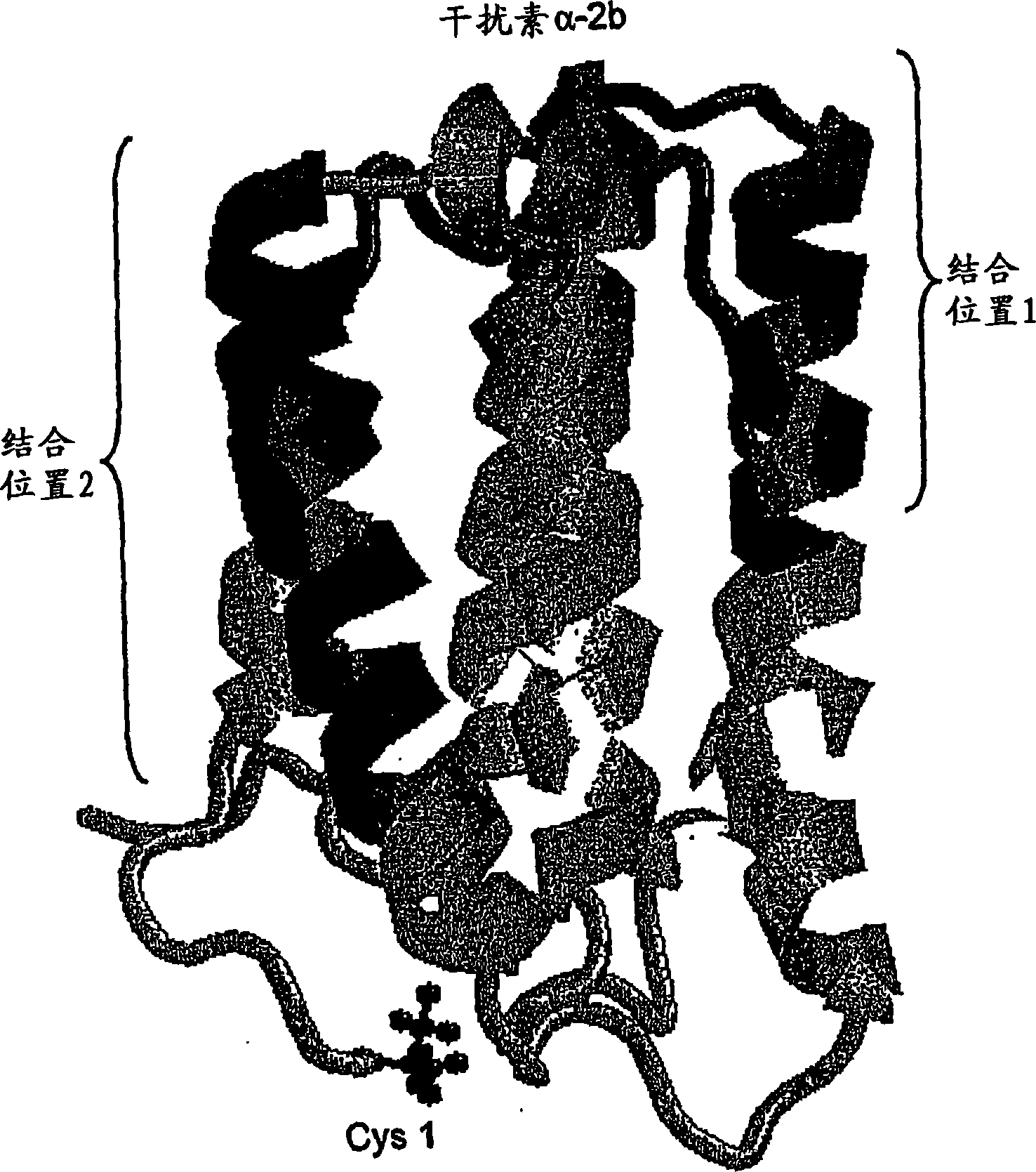
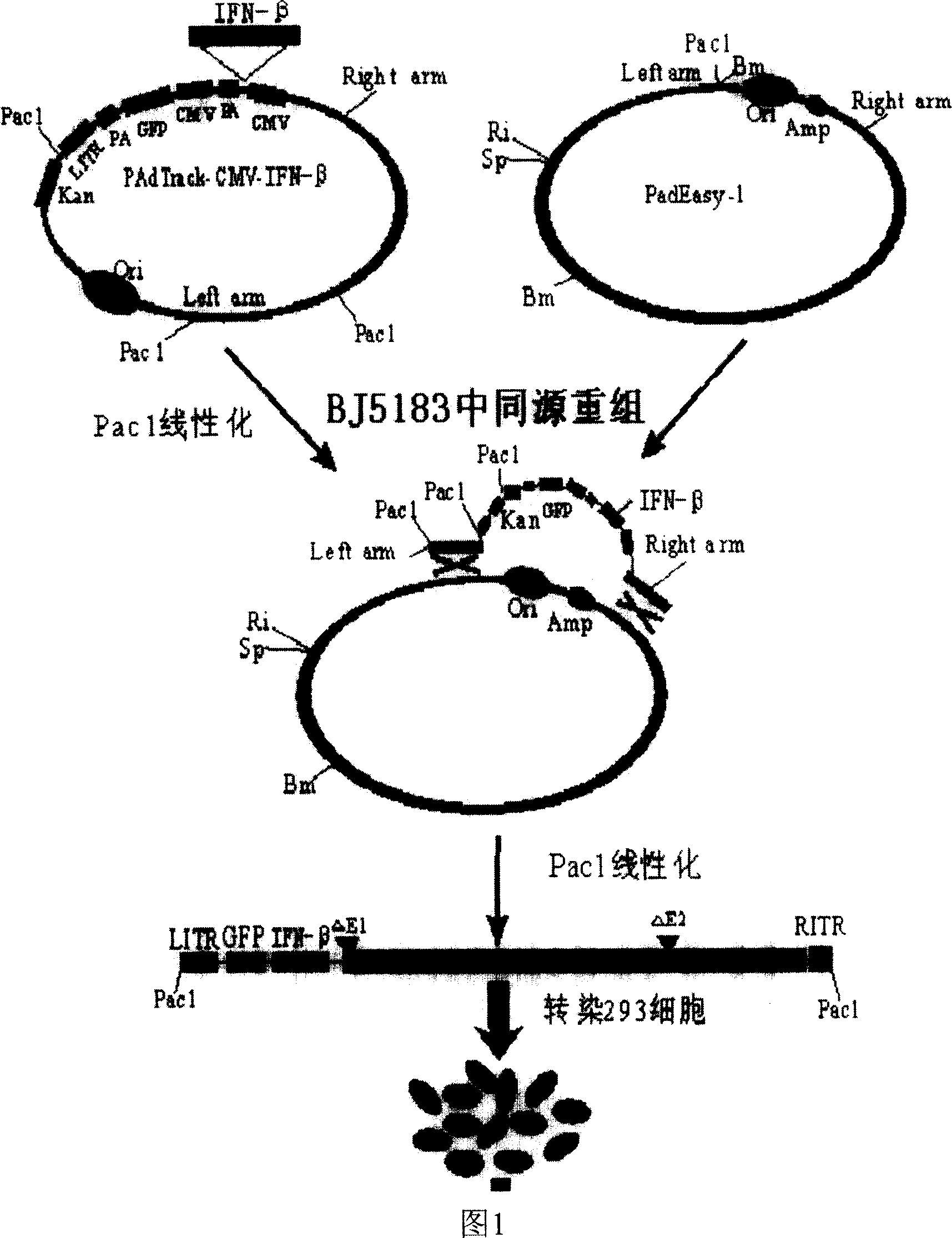
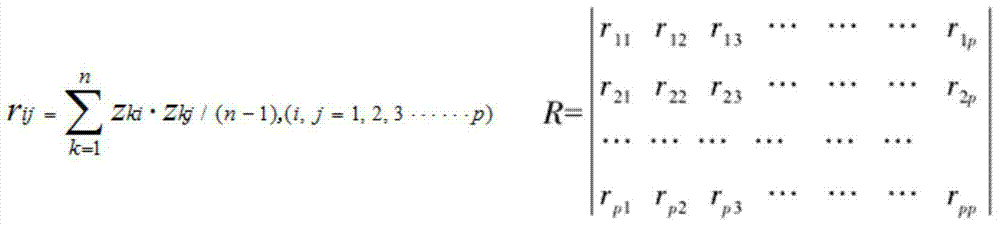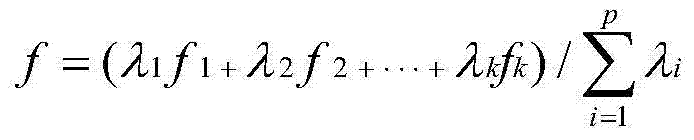Patents
Literature
53 results about "Beta interferons" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interferon beta-1a (also interferon beta 1-alpha) is a cytokine in the interferon family used to treat multiple sclerosis (MS). It is produced by mammalian cells, while interferon beta-1b is produced in modified E. coli.
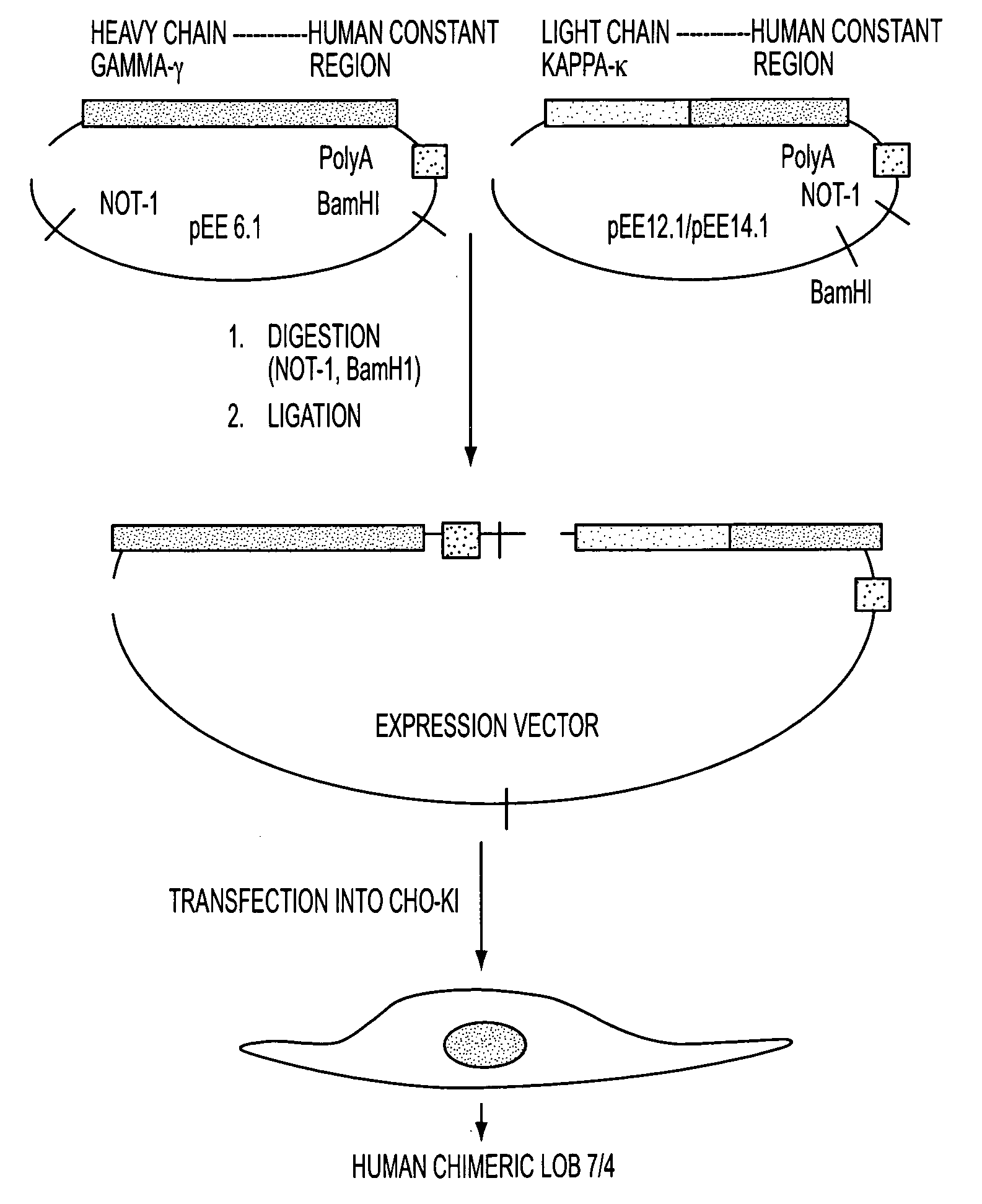
Human therapies using chimeric agonistic Anti-human cd40 antibody
Methods of human therapy using a chimeric anti-CD40 antibody, LOB 7 / 4 or humanized variants thereof, are provided. This CD40 antibody elicits agonistic effects on immunity when used as a monotherapy especially when used in the treatment of human lymphomas and leukemias and other solid tumors In addition, this agonistic CD40 antibody when administered in combination with certain molecules such as TLR agonists or interferons, e.g., alpha and beta interferon, elicits a synergistic effect on immunity.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Cladribine regimen for treating multiple sclerosis
ActiveUS20100021429A1Reduce adverse effectsOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderRegimenBeta interferons
The present invention relates to the use of multiple doses of Cladribine combined with beta interferon for the treatment of multiple sclerosis in patients who are refractory to at least one conventional therapy.
Owner:MERCK SERONO SA
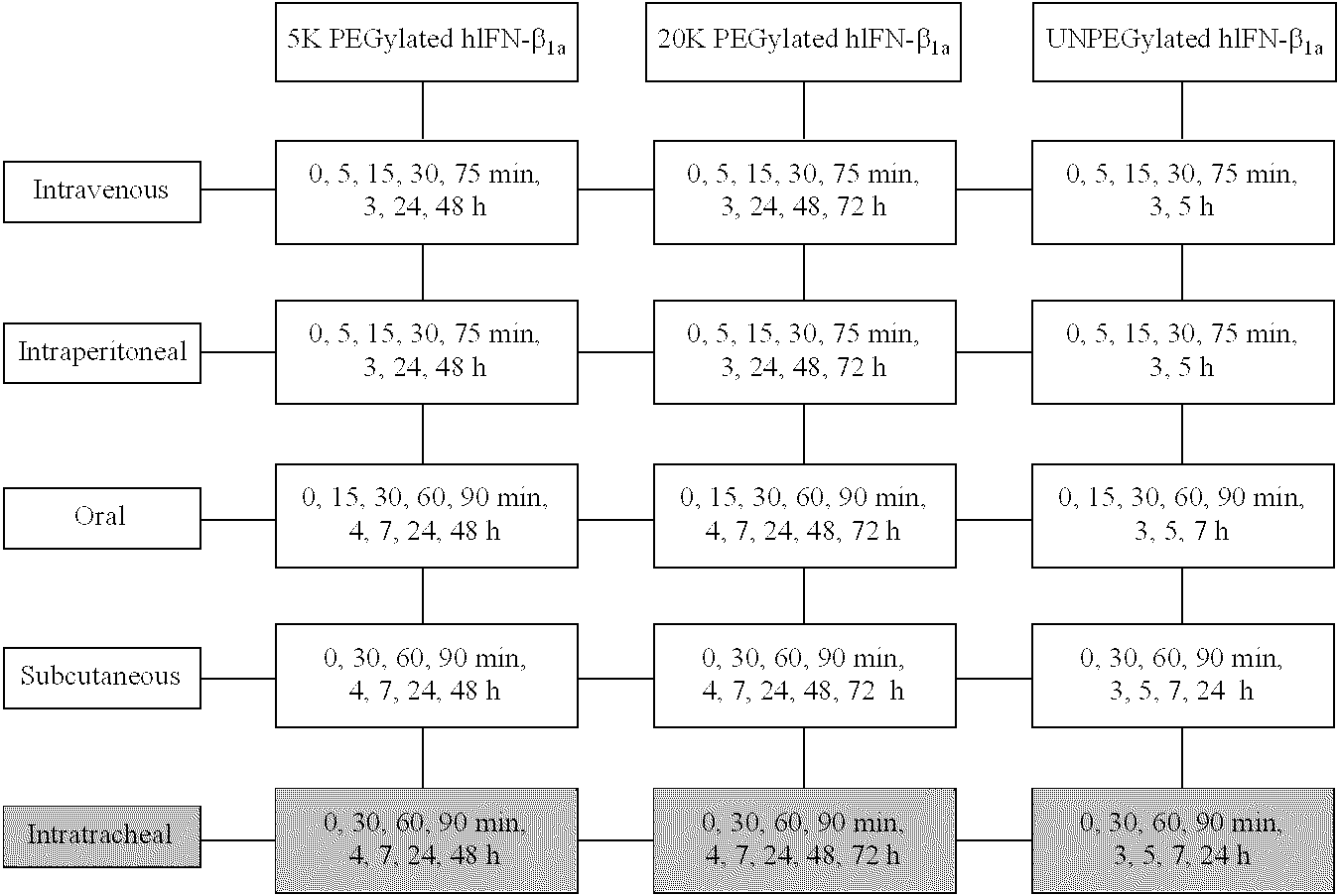
Polymer conjugates of interferon beta-1a and uses
InactiveUS6962978B2High activityNo effective loss in activitySenses disorderNervous disorderBeta interferonsBiochemistry
An interferon beta polypeptide comprising interferon-beta 1a coupled to a polymer containing a polyalkylene glycol moiety wherein the interferon-beta-1a and the polyalkylene glycol moiety are arranged such that the interferon-beta-1a has an enhanced activity relative to another therapeutic form of interferon beta (interferon-beta-1b) and exhibits no decrease in activity as compared to non-conjugated interferon-beta-1a. The conjugates of the invention are usefully employed in therapeutic as well as non-therapeutic, e.g., diagnostic, applications.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Gene expression profiling technology for treatment evaluation of multiple sclerosis
InactiveUS20050064483A1Microbiological testing/measurementNeutralizing antibodyGene expression profiling
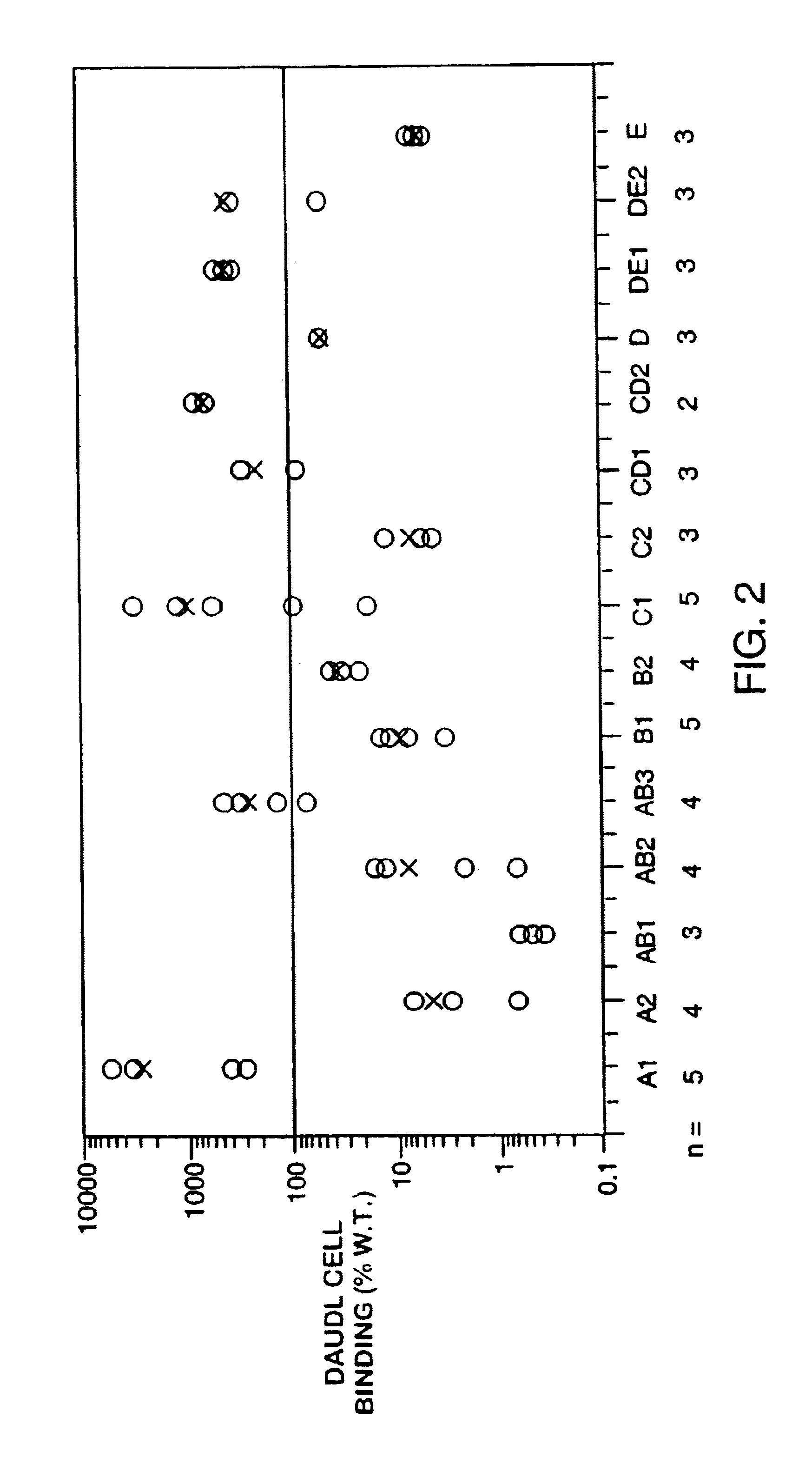
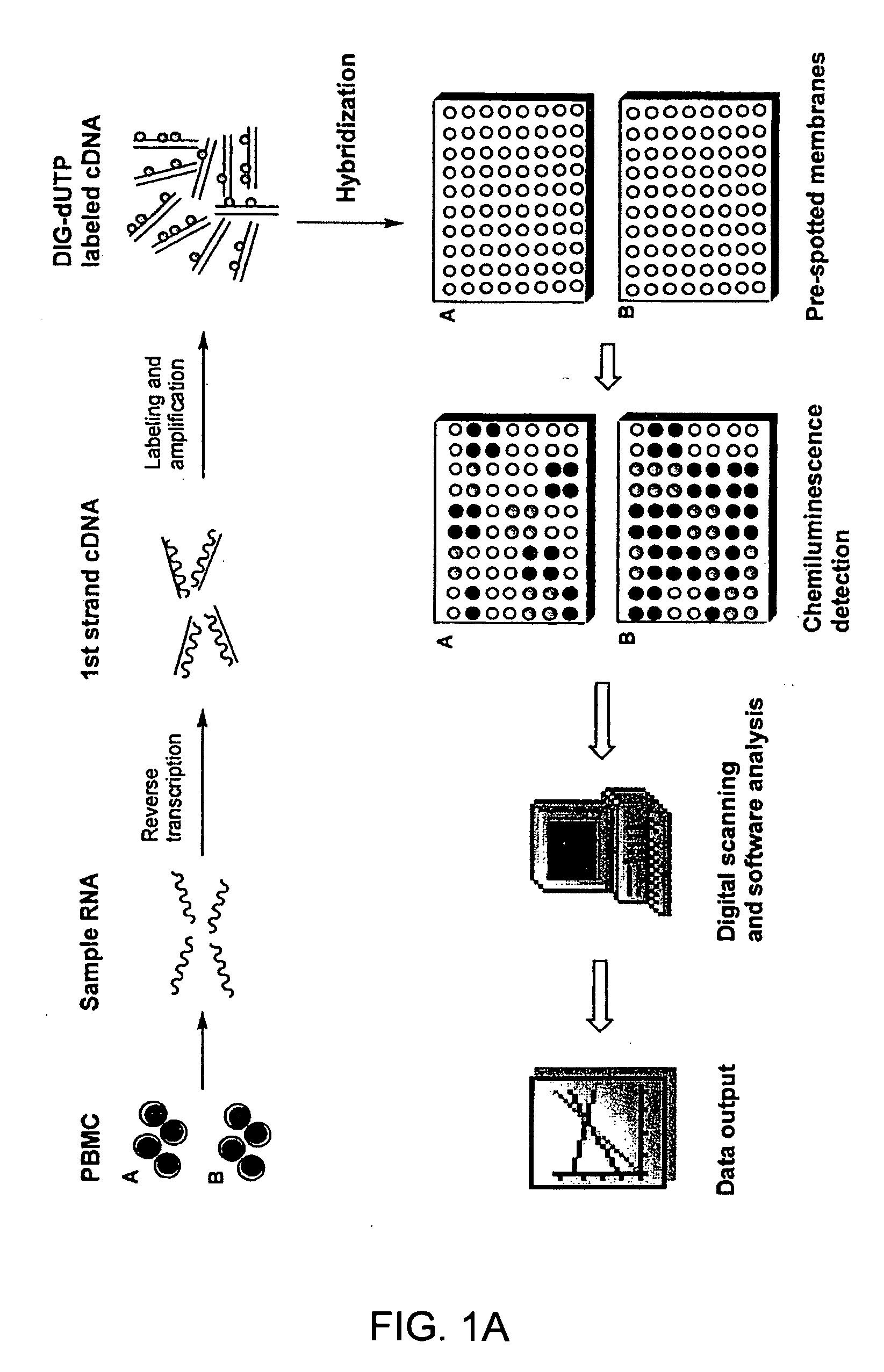
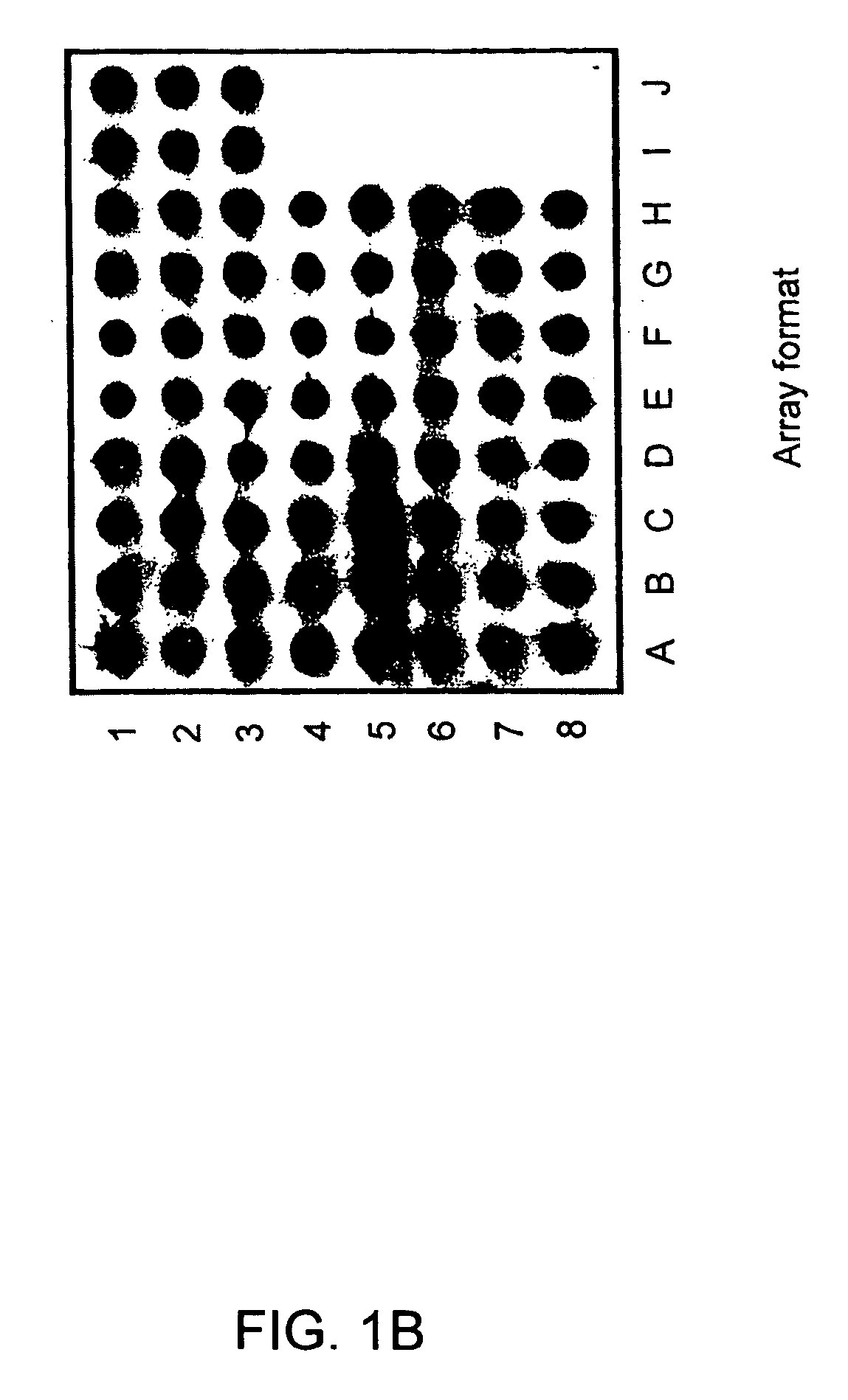
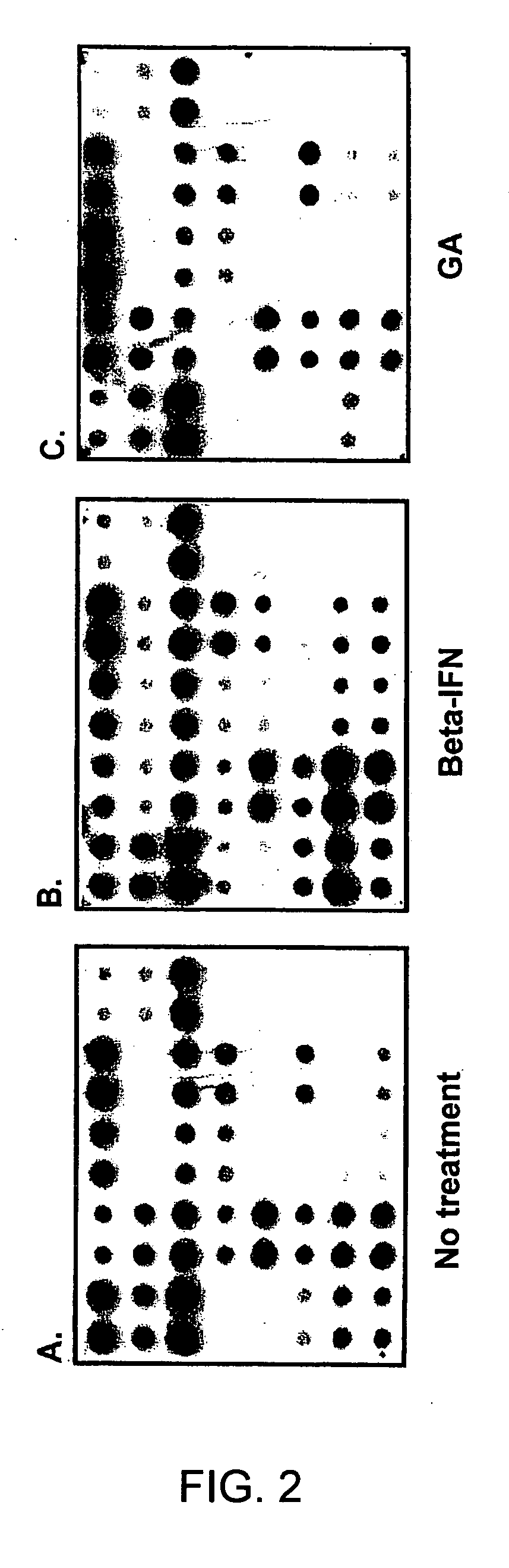
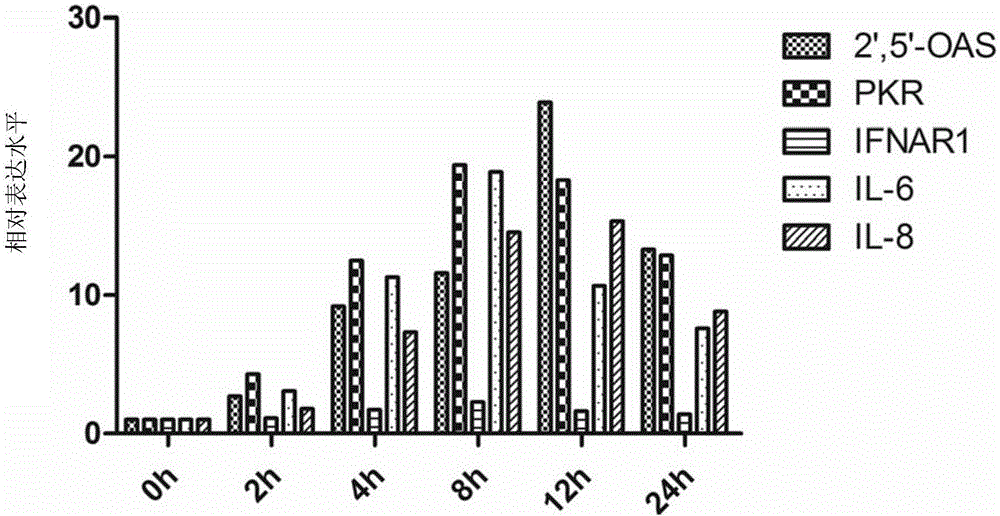
The invention relates to gene expression profiling technology to quantitatively measure the expression profiles of genes selected based on their role in inflammation and their susceptibility to regulation by current multiple sclerosis (MS) treatment agents, beta-interferon (IFN) and glatiramer acetate (GA). The invention also provides an assay for detection of beta-IFN neutralizing antibody based on the blocking effect of serum antibodies on the known regulatory properties of beta-IFN on PBMC and evaluation of treatment responses in MS patients.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Self-deleting free carrier and application thereof
ActiveCN103725710AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionCore functionBeta interferons
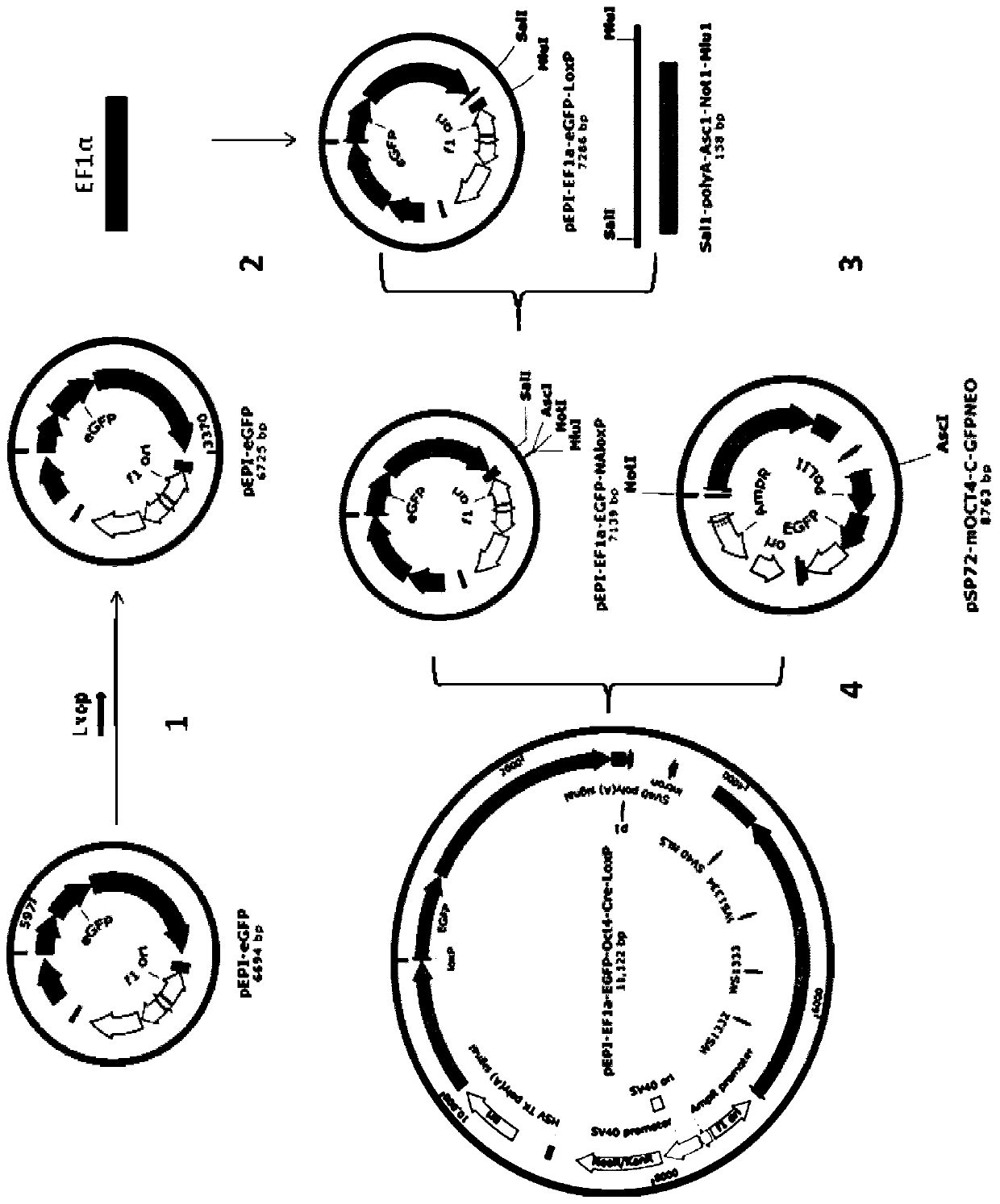
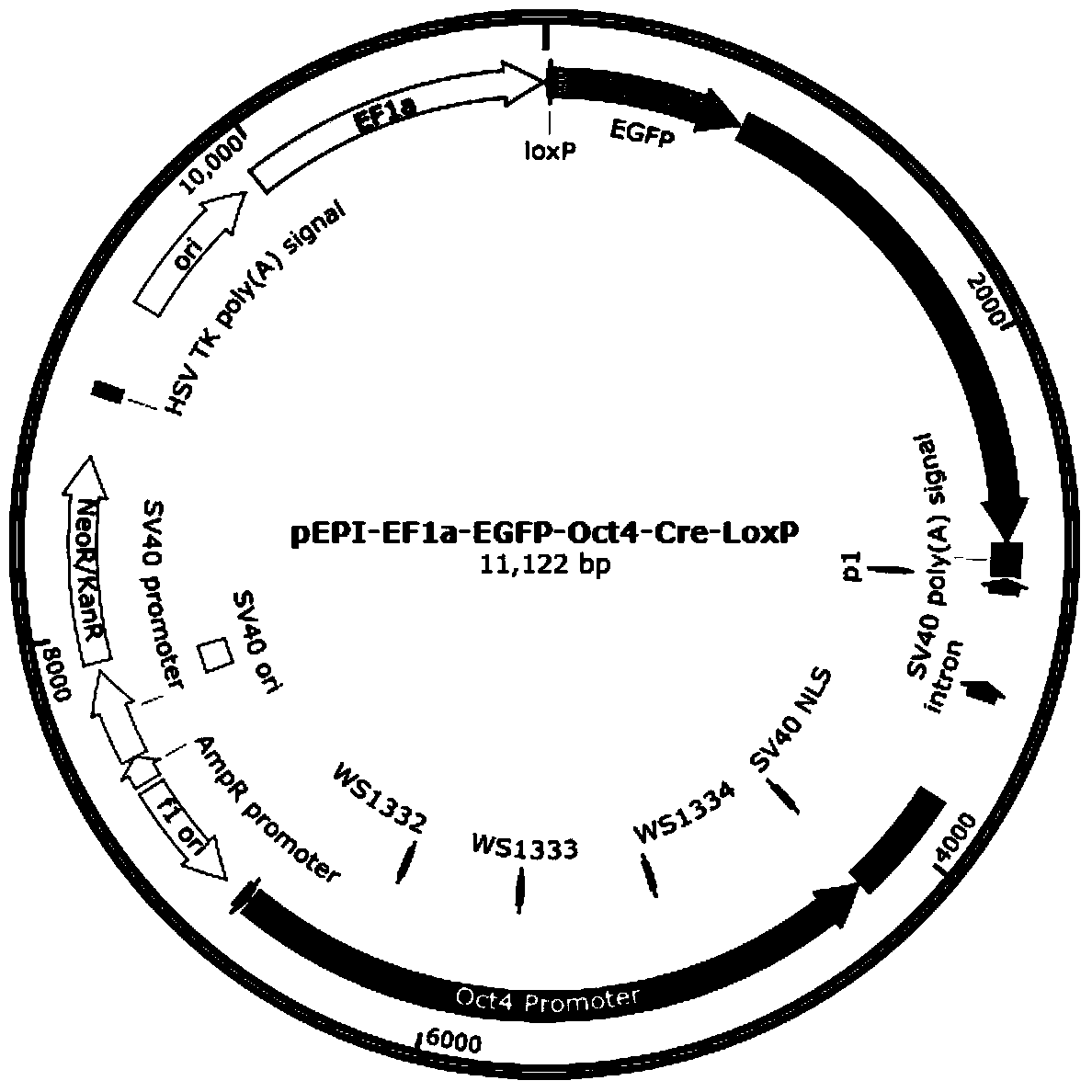
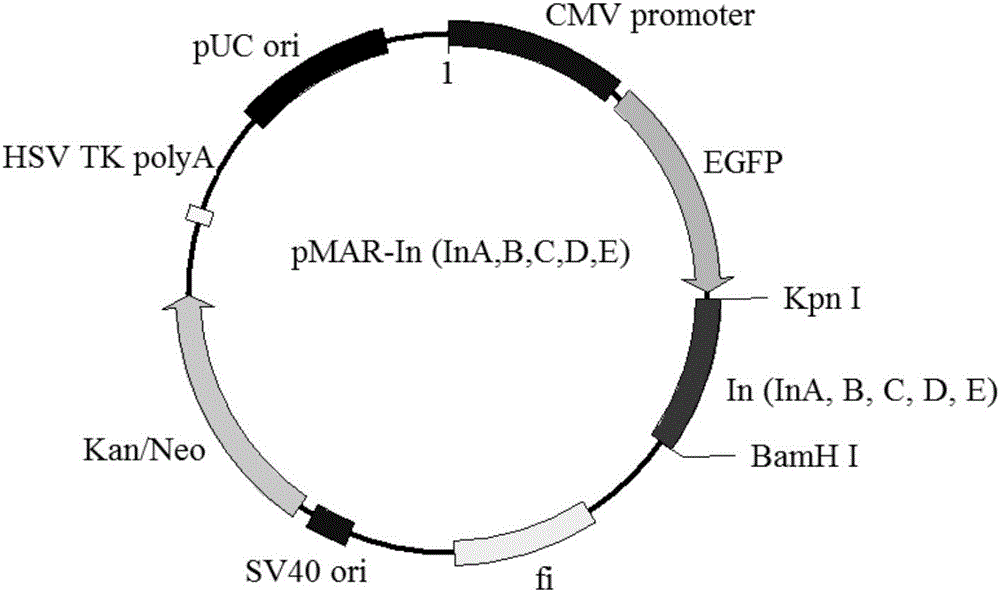
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering, and particularly provides a self-deleting free carrier. A core function region of the free carrier comprises a human EF1alpha promoter sequence, a 1oxp sequence, an enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) encoding sequence, an S / MAR sequence from a human beta interferon gene, a PolyA sequence of SV40, an expression cassette sequence of a mice Oct4 promoter drive Cre gene, and a 1oxp sequence from 5'-terminal to 3'-terminal. Preparation of gene targeting cells and animals is carried out by using the carrier disclosed by the invention, genes can be deleted, screened and marked and no gene insertion mutation is generated, and the effect on adjacent gene expression caused by a marker gene and potential biological safety hazard on an organism are removed.
Owner:北京科芙兰德生物科学有限责任公司
Anti-beta-interferon monoclonal antibody and its application
InactiveCN102898521AImprove the efficiency of extracting IFN-βMonitor retention concentrationImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsMicroorganism based processesBeta interferonsHybridoma cell
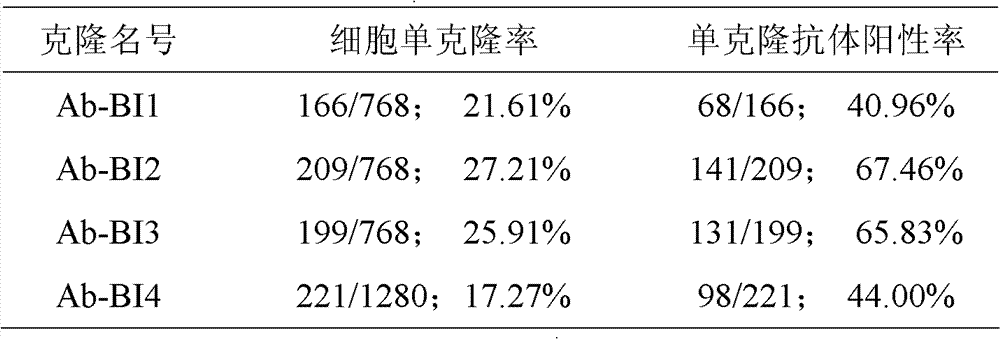
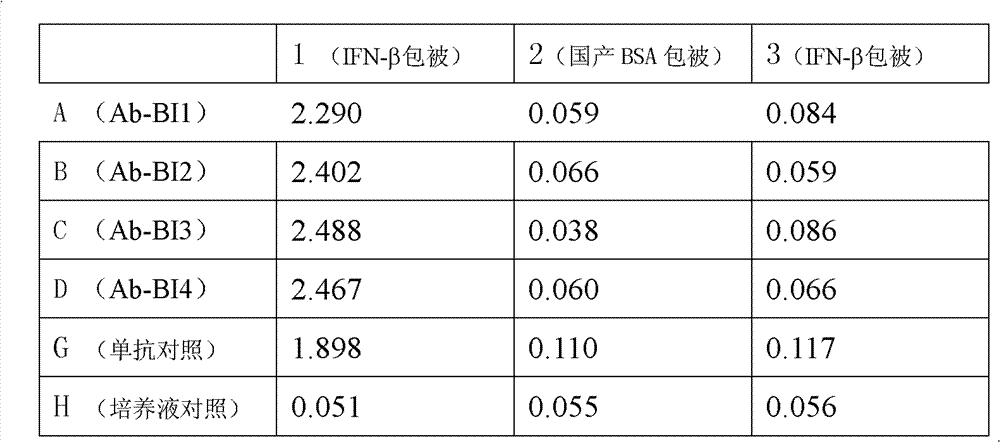
An anti-beta-interferon monoclonal antibody is generated by a hybridoma cell strain having a preservation number of CCTCC NO:C201121. A monoclonal antibody specifically combined with the beta-interferon having a sequence represented by SEQ ID No1 has a neutrality effect on the beta-interferon. The anti-beta-interferon monoclonal antibody can be used for the affinity chromatography purification and ELISA detection of the beta-interferon.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF IMMUNOLOGY
Polymer conjugates of cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, polypeptide hormones and antagonists thereof with preserved receptor-binding activity
Methods are provided for the synthesis of polymer conjugates of cytokines and receptor-binding antagonists thereof, especially a non glycosylated interferon-beta, which conjugates retain unusually high biological potency. Preparation of polymer conjugates according to the methods of the present invention diminishes or avoids steric inhibition of receptor-ligand interactions that commonly results from the attachment of polymers to receptor-binding regions of cytokines, as well as to agonistic and antagonistic analogs thereof. The invention also provides conjugates and compositions produced by such methods. The conjugates of the present invention retain a high level of biological potency compared to those produced by traditional polymer coupling methods that are not targeted to avoid receptor-binding domains of cytokines. In assays in vitro, the biological potency of the conjugates of non-glycosylated interferon-beta of the present invention is substantially higher than that of unconjugated interferon-beta and is similar to that of interferon-beta-1a that is glycosylated. The conjugates of the present invention also exhibit an extended half-life in vivo compared to the corresponding unconjugated cytokine. The present invention also provides kits comprising such conjugates and / or compositions, and methods of use of such conjugates and compositions in a variety of diagnostic, prophylactic, therapeutic and bioprocessing applications, including treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Owner:MOUNTAIN VIEW PHARMA
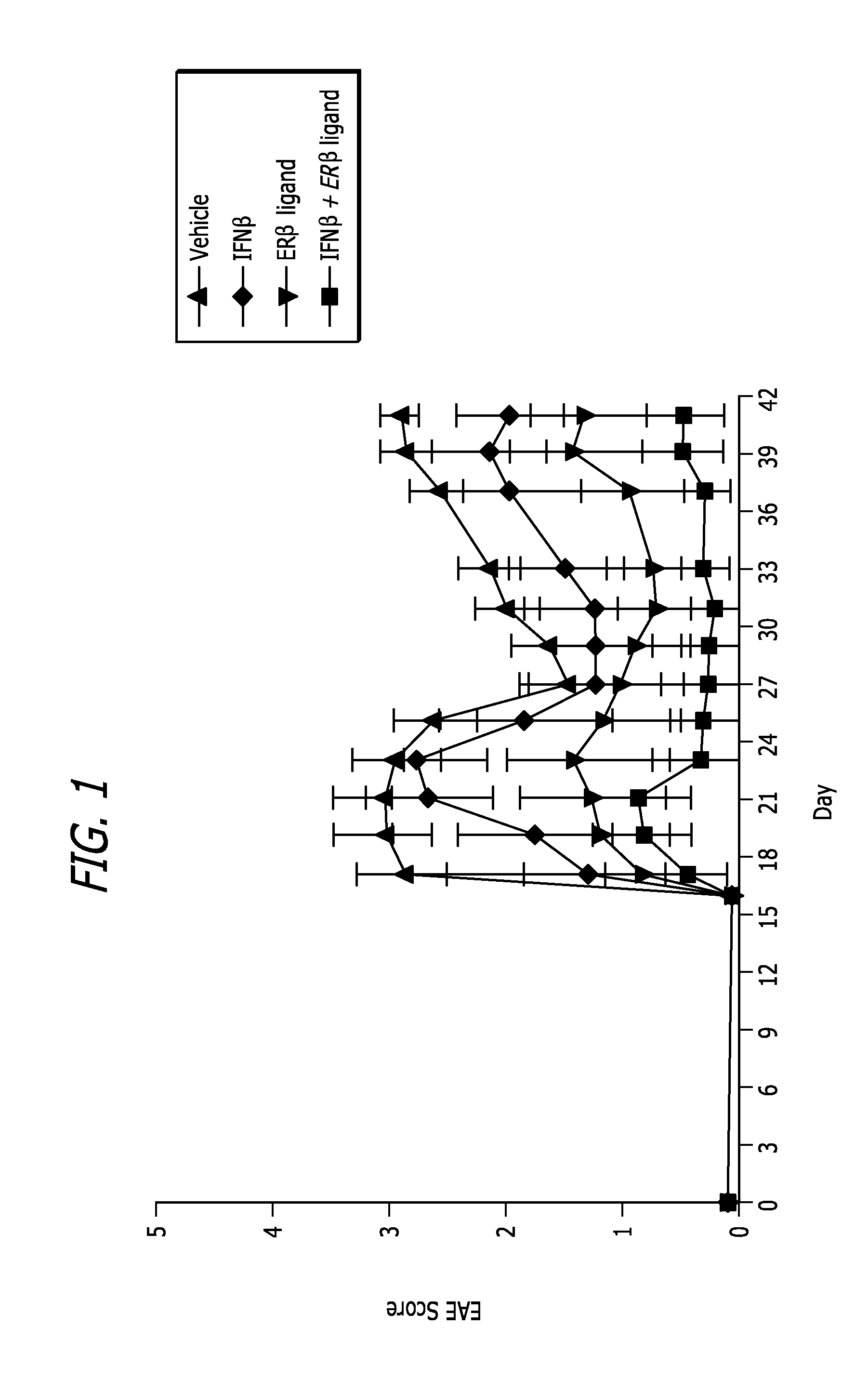
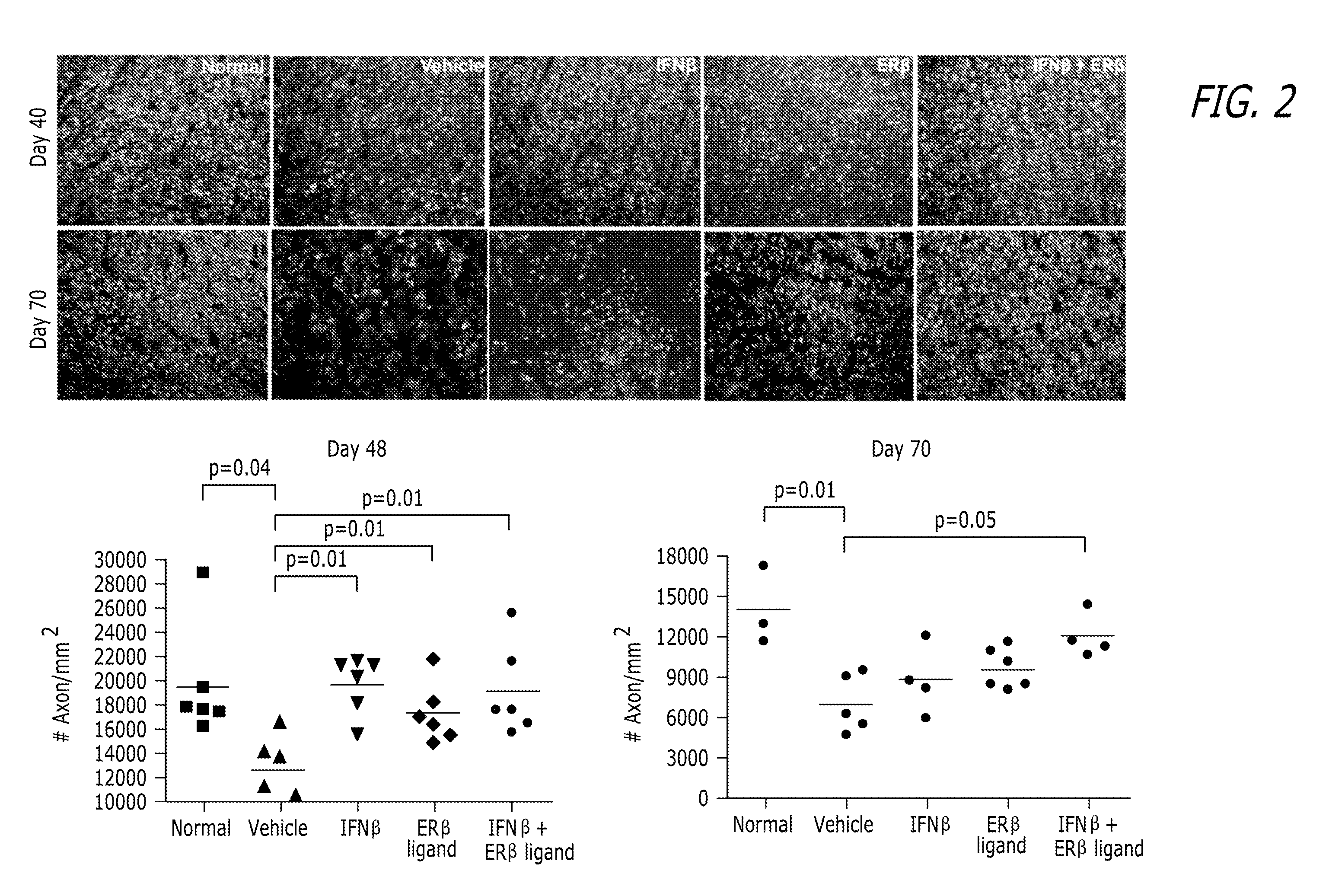
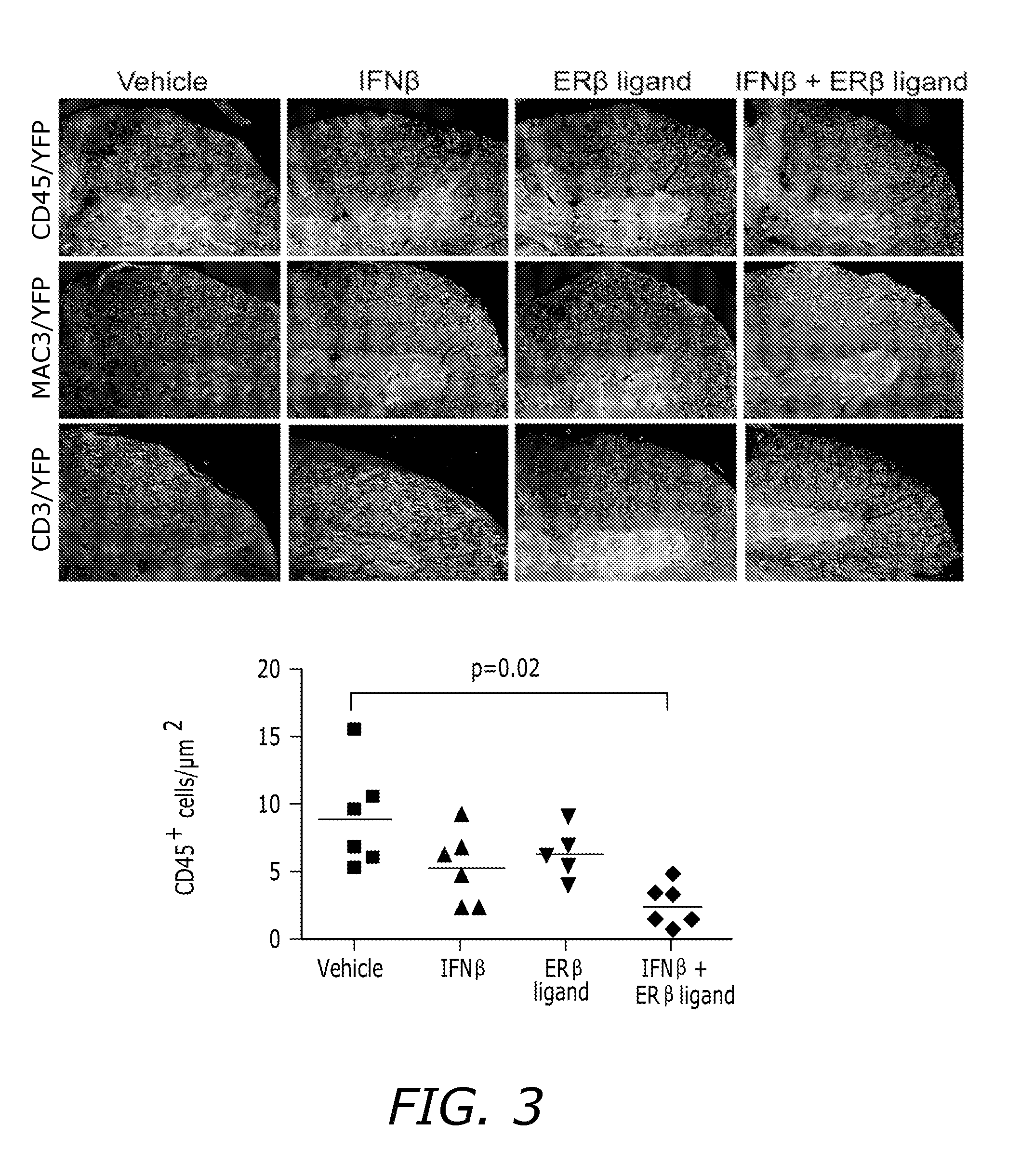
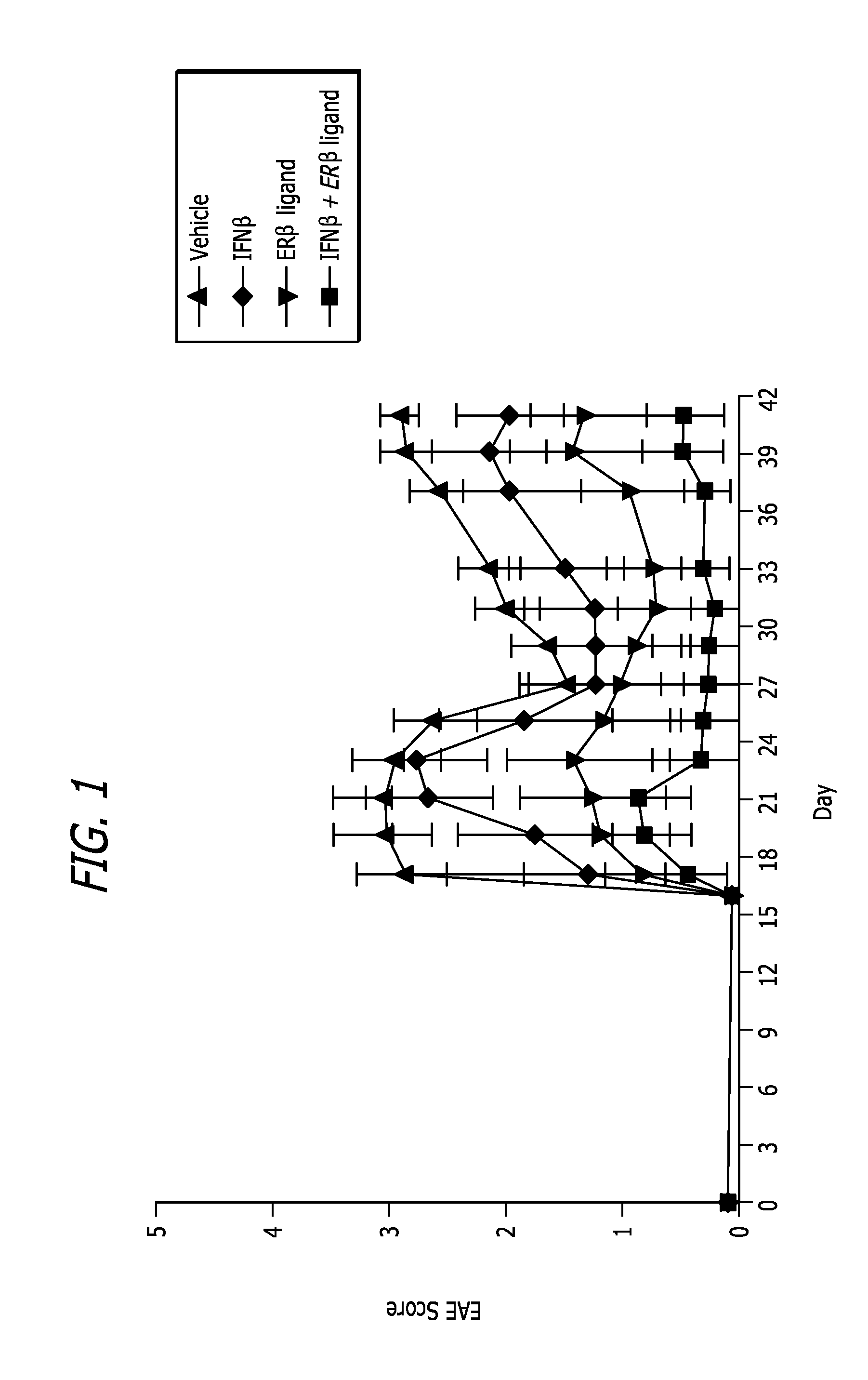
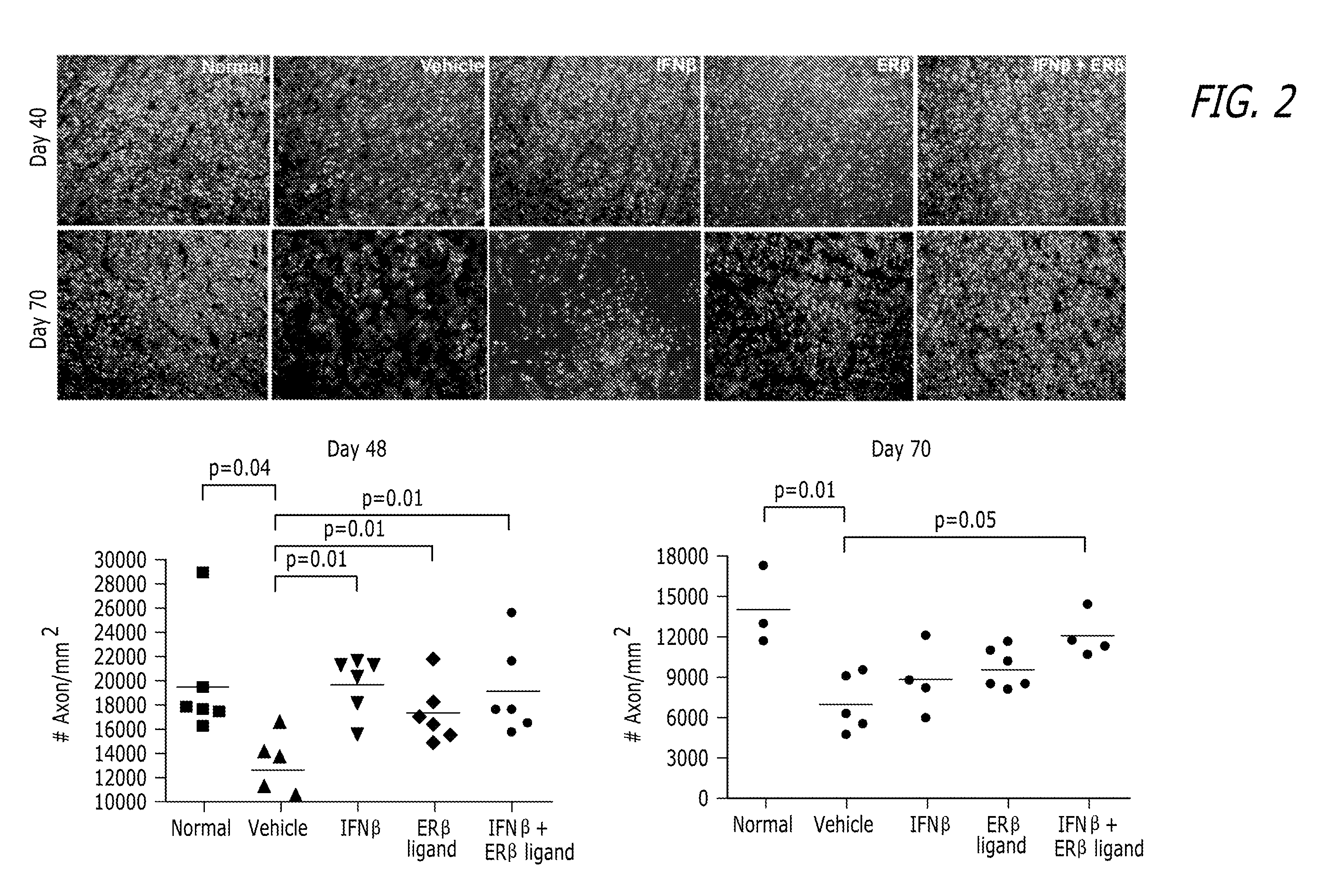
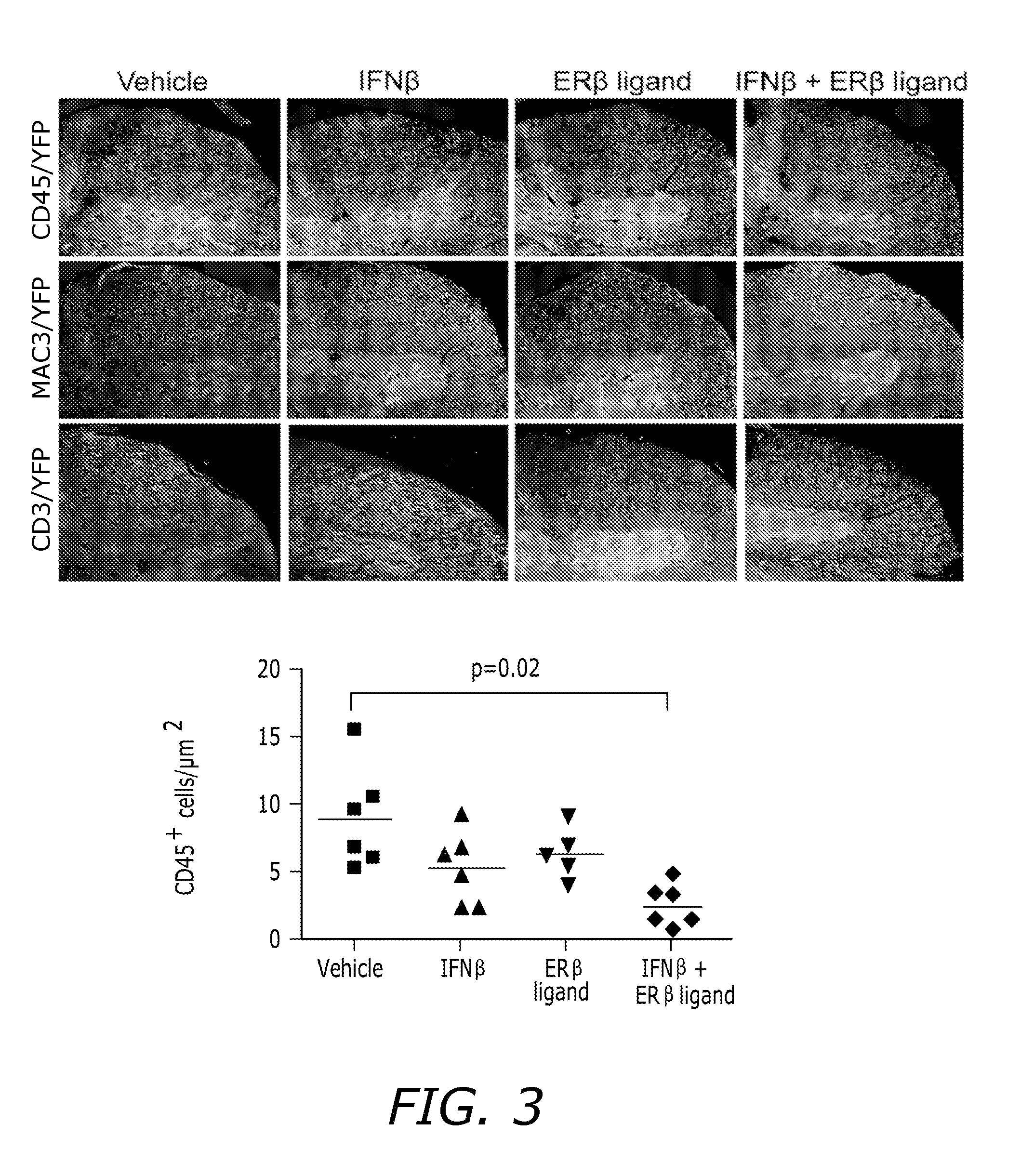
Estrogen receptor ligand and/or interferon beta treatment for neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20120282222A9Lower Level RequirementsDecreasing VLA-4 expressionBiocideNervous disorderBeta interferonsInterferon beta
This invention relates generally to novel treatments to prevent neurodegeneration in the central nervous system comprising a therapeutic dosage of an estrogen receptor ligand and / or an immunotherapeutic compound, such as beta-interferon, to ameliorate the effects of the neurodegenerative disease and to stimulate repair.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Prognostic method for the determination of the suitability of biopharmaceutical treatment
InactiveUS20100311052A1Microbiological testing/measurementSkeletal disorderPolymorphism analysisDisease cause
The invention refers to a method for the prognosis of a disease in a subject by the administration of a biopharmaceutical treatment in a subject suffering from, or likely to suffer from the disease, the method involving the analysis of SNP polymorphisms in the subjects pattern recognition receptor genes (PRRs), eg the analysis of polymorphisms' with the purpose of predicting the response of anti-TNFx antibody therapy in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Also the response to Beta-interferon in multiple sclerosis patients may be predicted. The genes whose polymorphisms are analysed may be TLRs, NOD-like receptors or retinoic acid-inducible gene I-like receptors (RLR).
Owner:BIOMONITOR
Cysteine variants of beta interferon
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Methods of inducing cytotoxic immune response and recombinant simian ademovirus compositions useful therein
InactiveCN1518457ASsRNA viruses negative-senseGenetic material ingredientsSimian AdenovirusesImmunodeficiency virus
The present invention provides a method of inducing a CD8+ T cell response against a selected molecule by delivering the molecule via a recombinant simian adenovirus. The present invention also provides a method for inducing alpha interferon and beta interferon by delivering a recombinant simian adenovirus to a subject. The methods and compositions of the invention are particularly suitable for use in the prevention and treatment of human immunodeficiency virus, human papillomavirus infections and cancer treatment.
Owner:THE WISTAR INST OF ANATOMY & BIOLOGY +1
Polymer conjugates of interferon beta-1a and uses
InactiveUS20070098688A1High activityNo effective loss in activitySenses disorderNervous disorderBeta interferonsBiochemistry
An interferon beta polypeptide comprising interferon-beta 1a coupled to a polymer containing a polyalkylene glycol moiety wherein the interferon-beta-1a and the polyalkylene glycol moiety are arranged such that the interferon-beta-1a has an enhanced activity relative to another therapeutic form of interferon beta (interferon-beta-1b) and exhibits no decrease in activity as compared to non-conjugated interferon-beta-1a. The conjugates of the invention are usefully employed in therapeutic as well as non-therapeutic, e.g., diagnostic, applications.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Enhanced Antiviral Activity Against Foot and Mouth Disease
InactiveUS20090269372A1Effectively ensureEarly protection against FMDVSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHigh dosesIn vivo
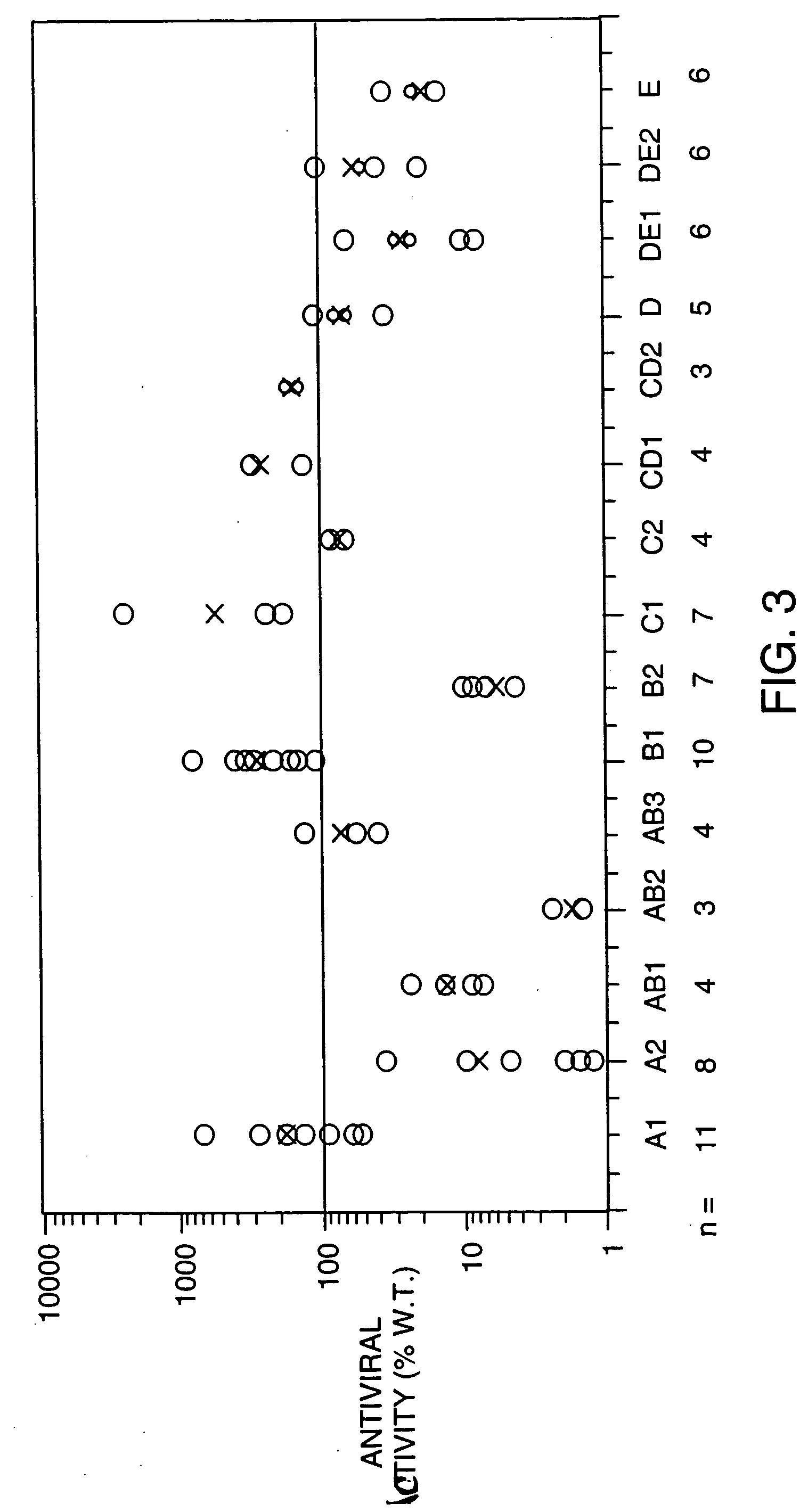
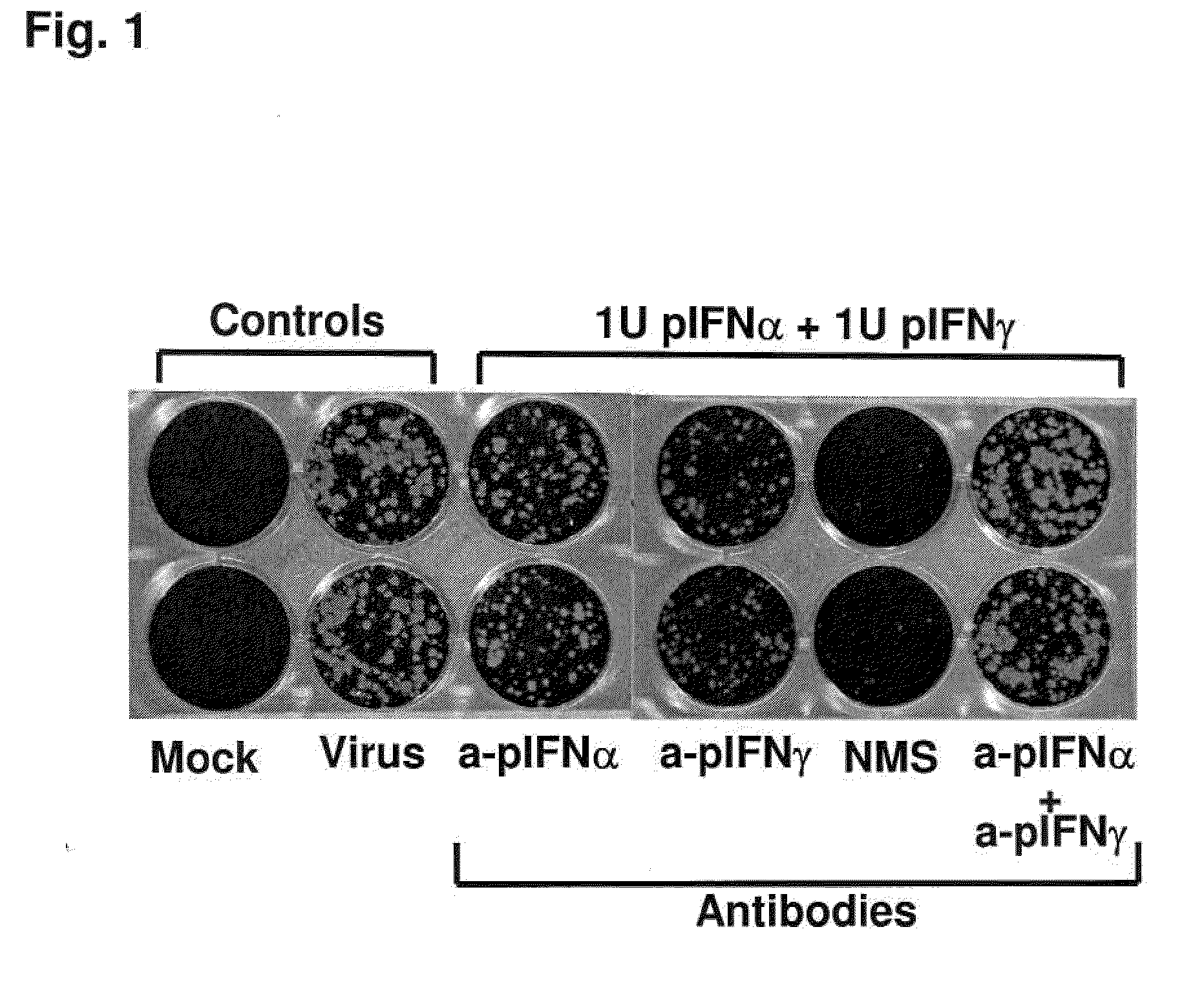
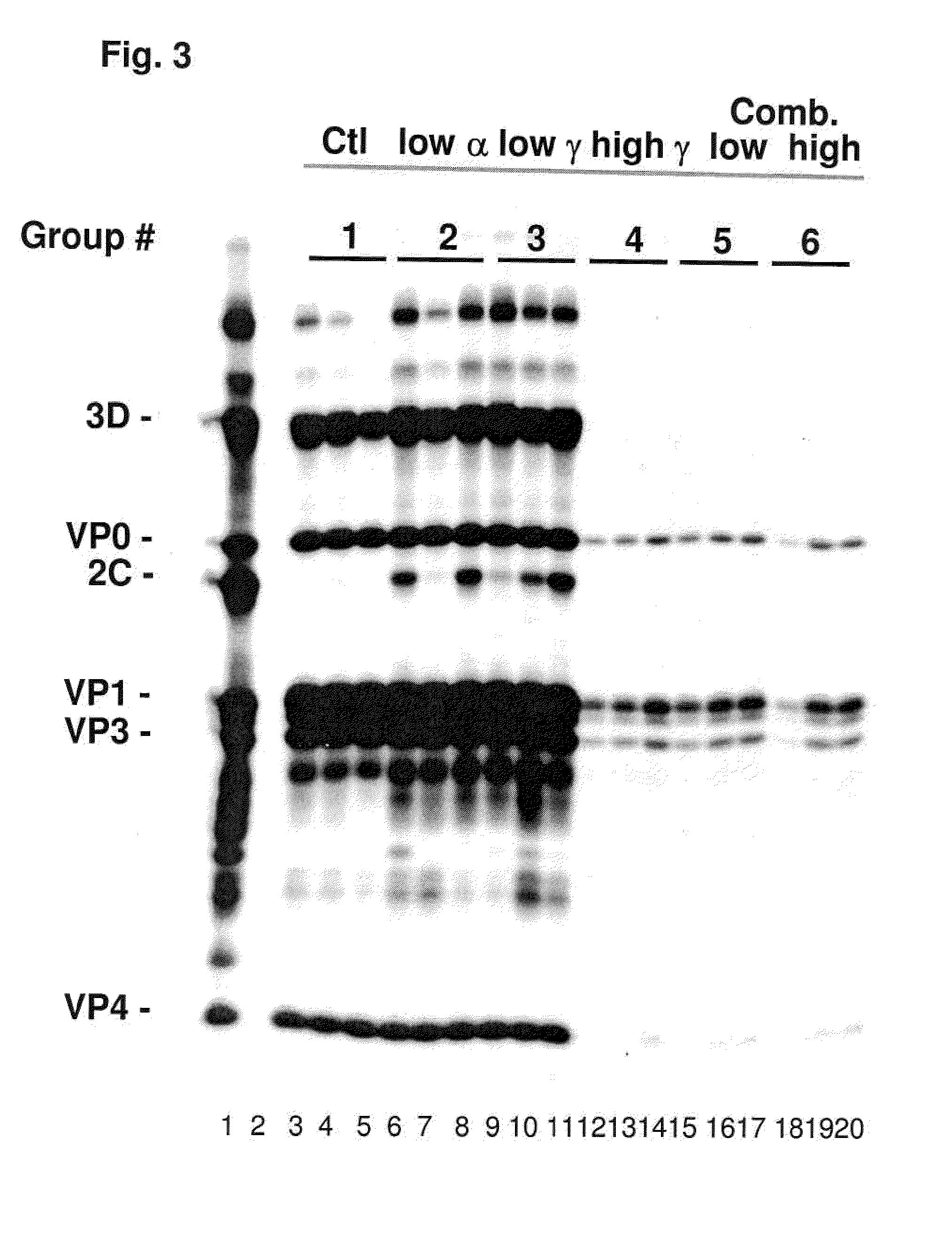
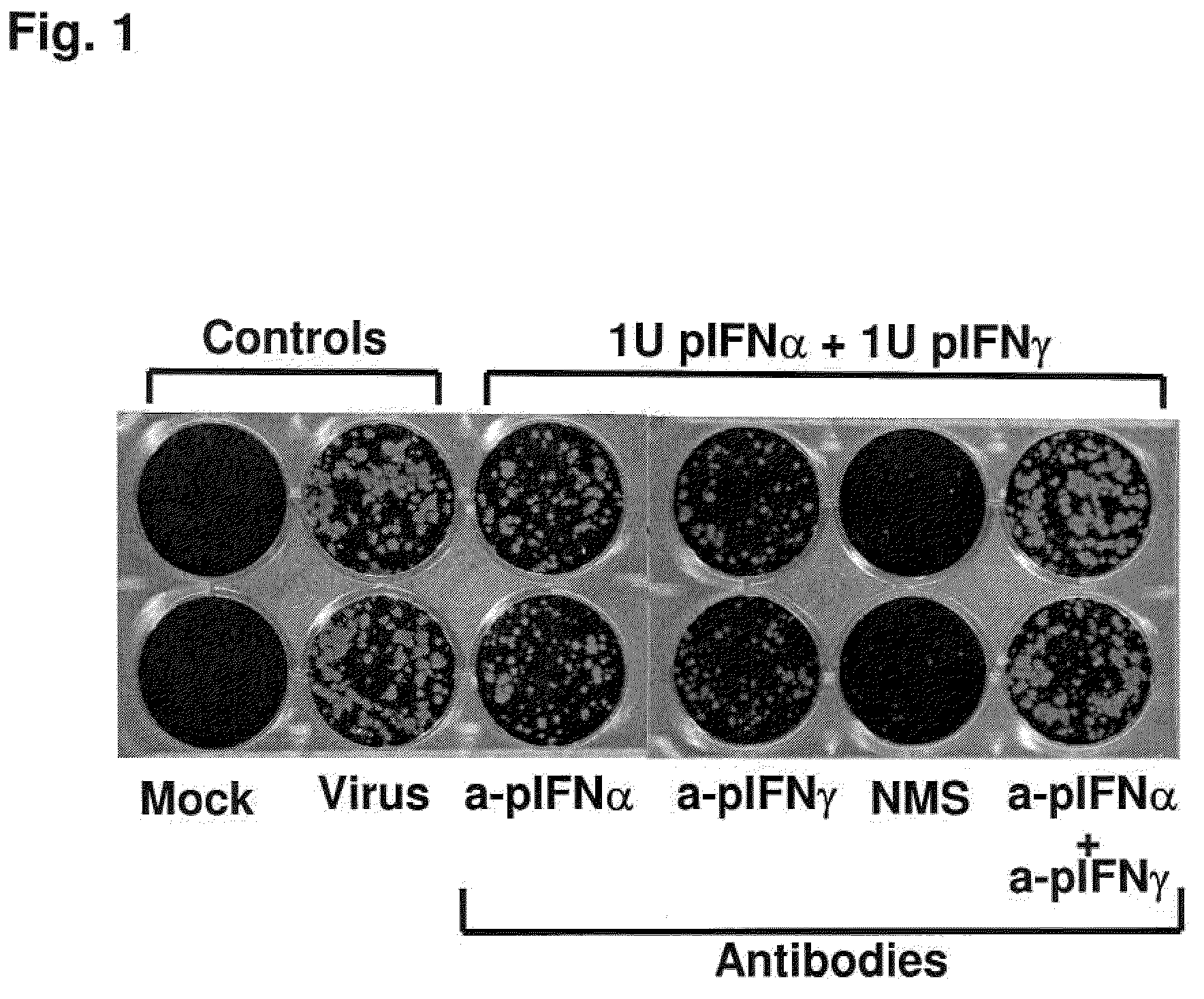
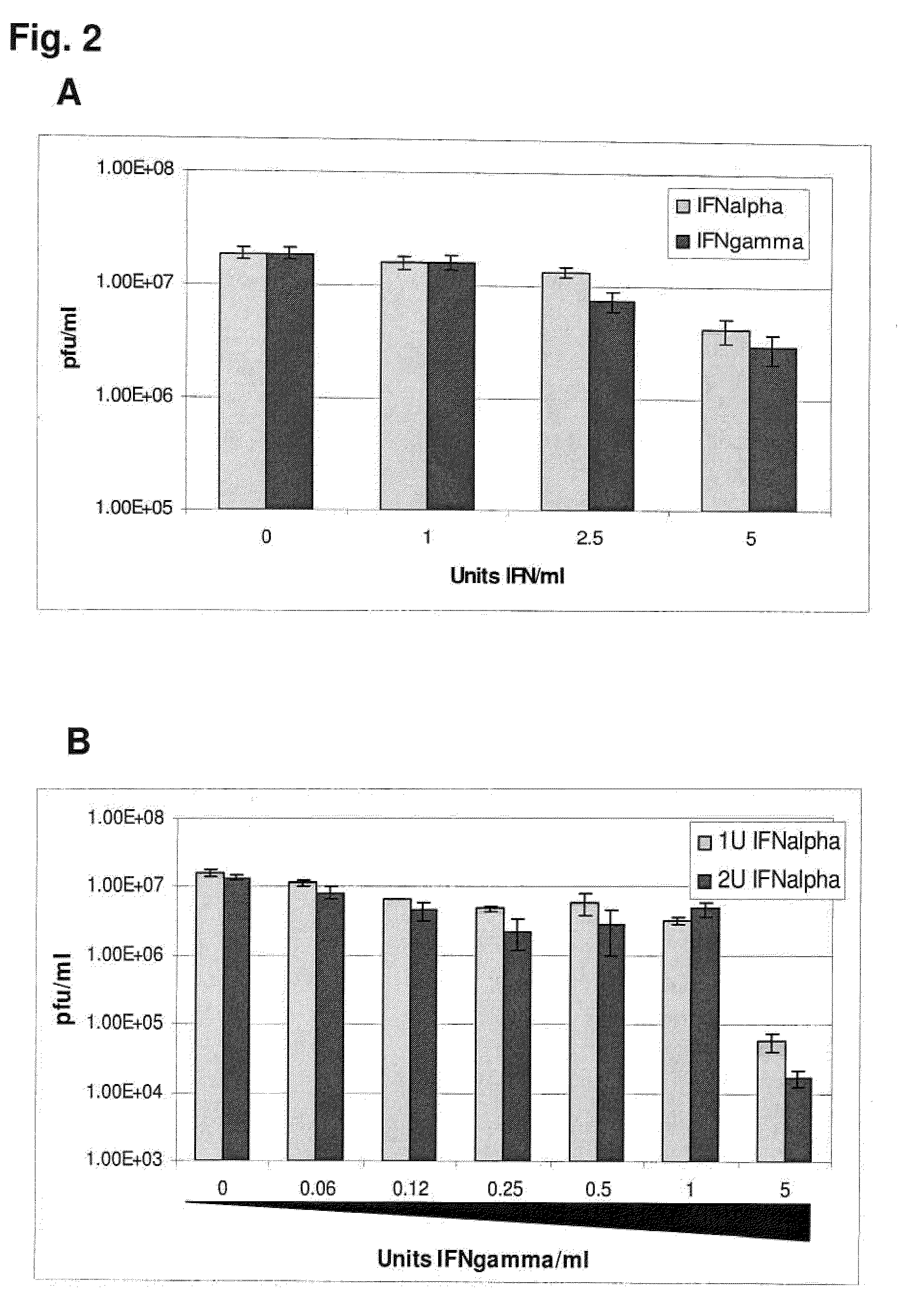
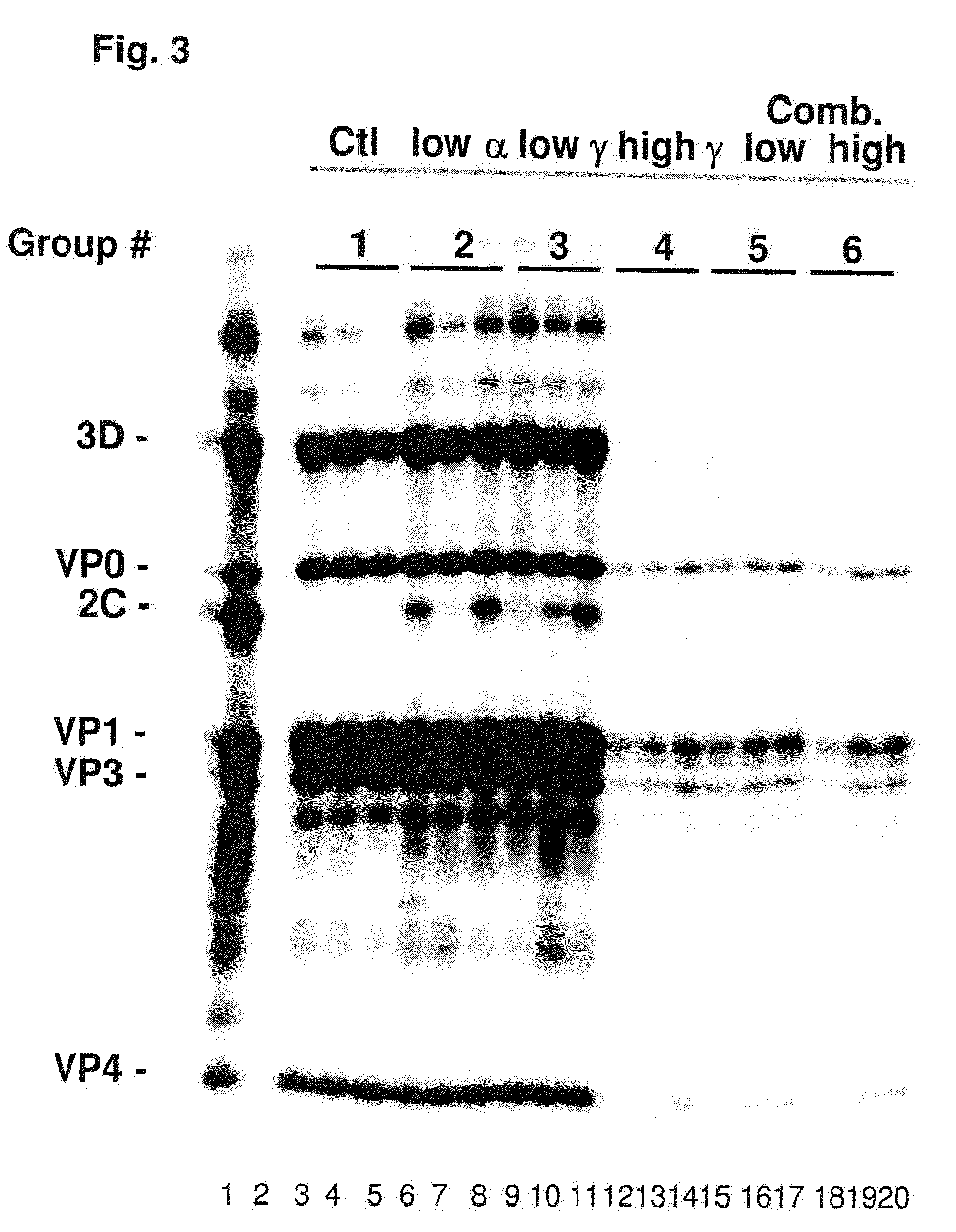
Previously, we showed that type I interferon (alpha / beta interferon [IFN-α / β]) can inhibit foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) replication in cell culture, and swine inoculated with 109 PFU of human adenovirus type 5 expressing porcine IFN-α (Ad5-pIFN-α) were protected when challenged 1 day later. In this study, we found that type II pIFN (pIFN-γ) also has antiviral activity against FMDV in cell culture and that, in combination with pIFN-α, it has a synergistic antiviral effect. We also observed that while each IFN alone induced a number of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs), the combination resulted in a synergistic induction of some ISGs. To extend these studies to susceptible animals, we inoculated groups of swine with a control Ad5, 108 PFU of Ad5-pIFN-α, low- or high-dose Ad5-pIFN-γ, or a combination of Ad5-pIFN-α and low- or high-dose Ad5-pIFN-γ and challenged all groups with FMDV 1 day later. The control group and the groups inoculated with either Ad5-pIFN-α or a low dose of Ad5-pIFN-γ developed clinical disease and viremia. However, the group that received the combination of both Ad5-IFNs with the low dose of Ad5-pIFN-γ was completely protected from challenge and had no viremia. Similarly the groups inoculated with the combination of Ad5s with the higher dose of Ad5-pIFN-γ or with only high-dose Ad5-pIFN-γ were protected. The protected animals did not develop antibodies against viral nonstructural (NS) proteins, while all infected animals were NS protein seropositive. No antiviral activity or significant levels of IFNs were detected in the protected groups, but there was an induction of some ISGs. The results indicate that the combination of type I and II IFNs act synergistically to inhibit FMDV replication in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Interferon-beta-1a-immunoglobulin fusion proteins and uses
InactiveUS7527946B2High activityNo effective loss in activitySenses disorderNervous disorderBeta interferonsMutant
A fusion polypeptide is described having the amino acid sequence X-Y-Z, or portion thereof, comprising the amino acid sequence of a glycosylated interferon-beta (X); Y is an optional linker moiety; and Z is a polypeptide comprising at least a portion of a polypeptide other than glycosylated interferon-beta. It is preferred that X is human interferon-beta-1a. Mutants of interferon-beta-1a are also described.
Owner:BIOGEN MA INC
Method for preparing fusion protein contg. human interferon-alpha 2 and human seralbumin and its products
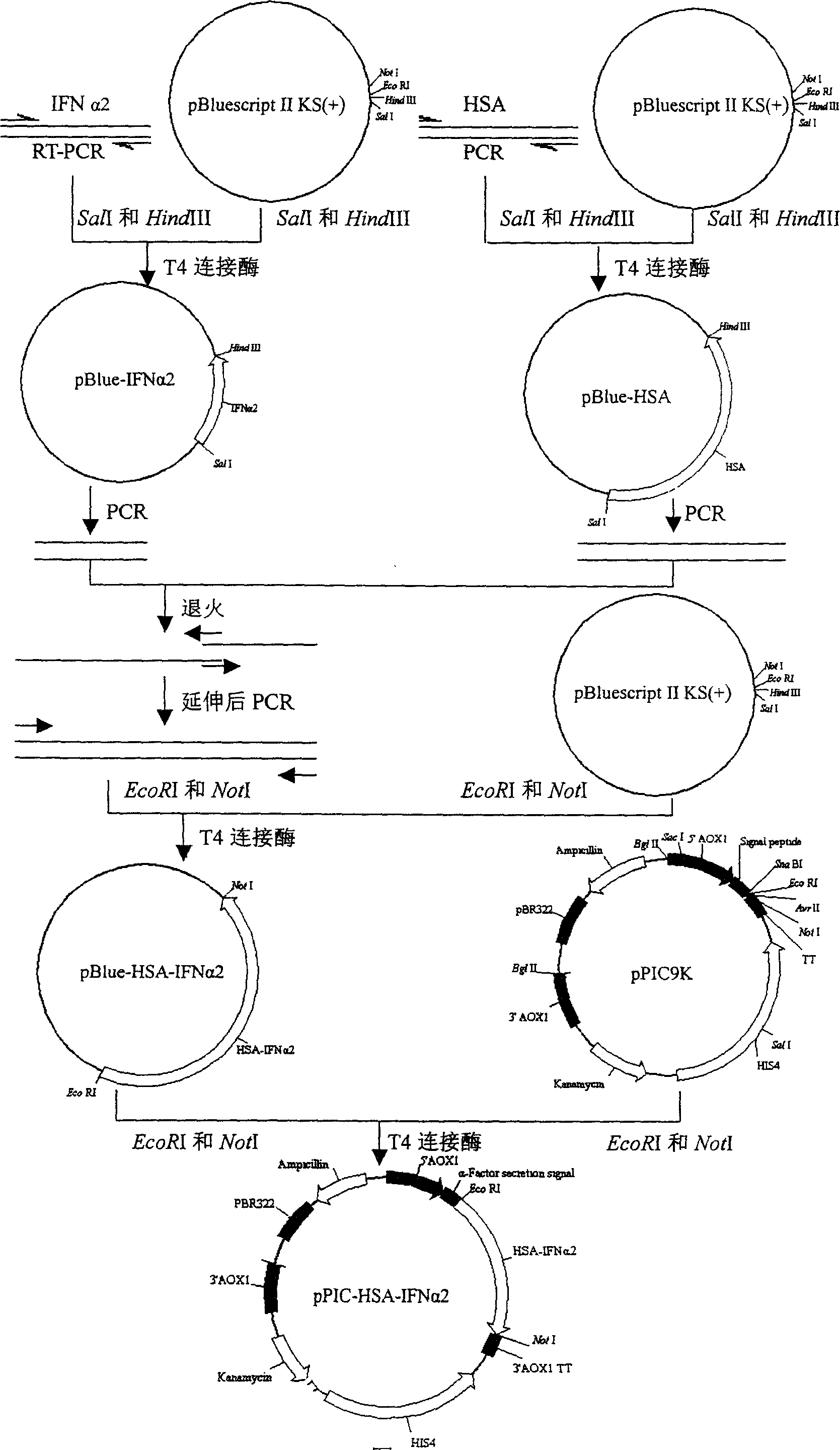
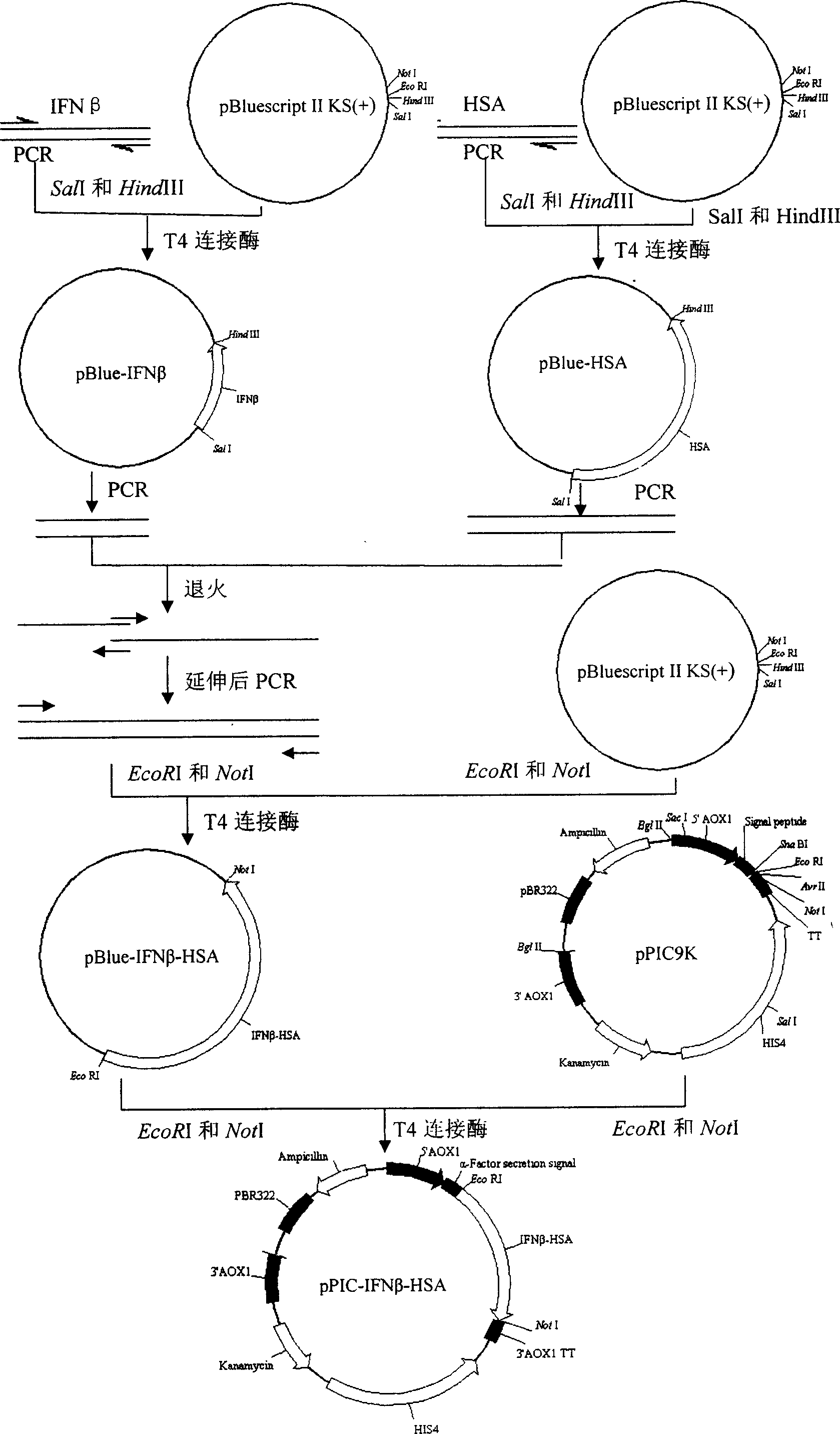
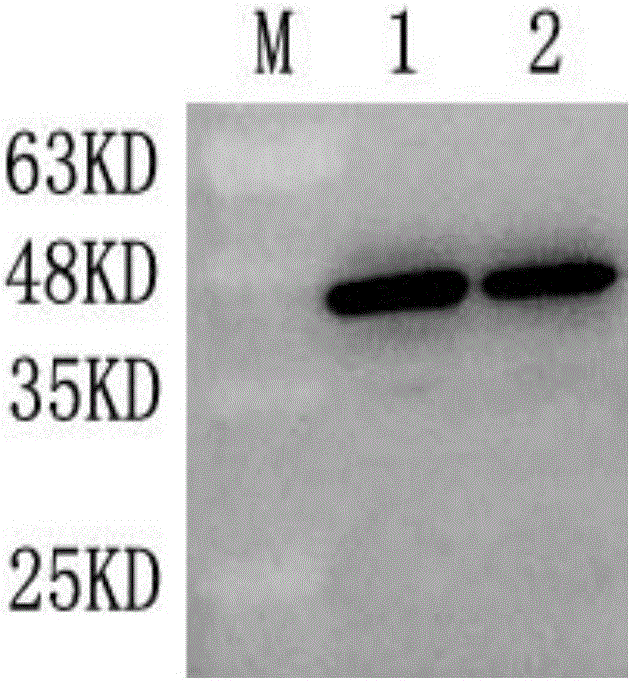
The invention relates to a manufacture method and product for confluence albumen of human alpha-2 interferon and human serum albumin that uses superposing PCR technology, connecting IFN alpha-2 cDNA and HAS cDNA, with out any connecting peptide to gain IFN alpha-2 HSA cDNA melting gene to be integrated into host chromosome to take expression. The confluence albumen includes the first area of at least 85% sequence same source as human beta-interferon and the second area of at least 85% sequence of same source of human serum albumin. The invention has good application prospect in medicine field.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for treating inflammatory bowel disease
InactiveUS20070122384A1Salicyclic acid active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsUlcerative colitisEnteropathy
A method for treating inflammatory bowel disease by administering interferon beta in conjunction with factor XIII to a mammal afflicted with the disease. The IBD may either be ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease. The factor XIII used may be recombinant or nonrecombinant. The interferon beta used can be naturally occurring interferon beta, interferon beta-1a or interferon beta-1b.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Estrogen receptor ligand and/or interferon beta treatment for neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20110256096A1Lower Level RequirementsDecreasing VLA-4 expressionBiocideNervous disorderBeta interferonsInterferon beta
This invention relates generally to novel treatments to prevent neurodegeneration in the central nervous system comprising a therapeutic dosage of an estrogen receptor ligand and / or an immunotherapeutic compound, such as beta-interferon, to ameliorate the effects of the neurodegenerative disease and to stimulate repair.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
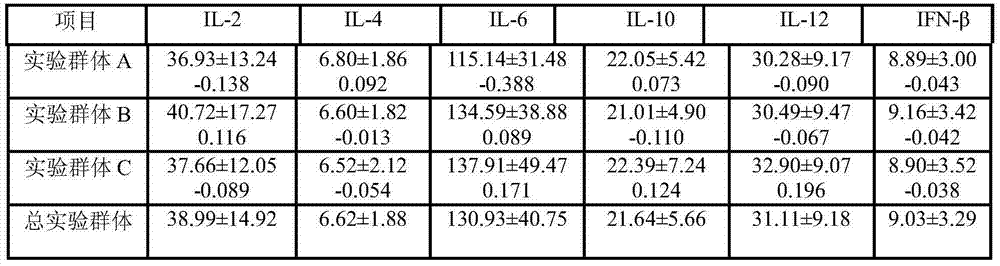
Sutai pig common disease-resistance combined selection index selecting breeding method
InactiveCN103931560ASolving the Dilemma of Choosing the Optimal Quantitative MetricAccelerating progress in breeding for disease resistanceAnimal husbandryInterleukin 6Animal science
The invention relates to a sutai pig common disease-resistance combined selection index selecting breeding method. The method comprises the steps that front-cavity venous blood of 35-day-old piglets is collected, concentration of interleukin 2(IL-2), concentration of interleukin 4(IL-4), concentration of interleukin 6(IL-6), concentration of interleukin 10(IL-10), concentration of interleukin 12(IL-12) and concentration of beta interferon (IF-N-beta) are measured after serum samples are obtained, test pig groups are grouped at the same time, then data of the six indexes are converted into standardization Z values, the standardization Z values are substituted into a built combined selection index formulation to calculate a combined selection index value of each pig group, and individuals having higher disease resistance generally are determined according to the values. The detection method is easy to operate, high in accuracy, and capable of achieving automatic direct detection, and will give great play to disease-resistance breeding practice of the pigs.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Enhanced antiviral activity against foot and mouth disease
InactiveUS7833533B2Early protection against FMDVEffectively ensureSsRNA viruses positive-sensePeptide/protein ingredientsHigh dosesIn vivo
Previously, we showed that type I interferon (alpha / beta interferon [IFN-α / β]) can inhibit foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV) replication in cell culture, and swine inoculated with 109 PFU of human adenovirus type 5 expressing porcine IFN-α (Ad5-pIFN-α) were protected when challenged 1 day later. In this study, we found that type II pIFN (pIFN-γ) also has antiviral activity against FMDV in cell culture and that, in combination with pIFN-α, it has a synergistic antiviral effect. We also observed that while each IFN alone induced a number of IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs), the combination resulted in a synergistic induction of some ISGs. To extend these studies to susceptible animals, we inoculated groups of swine with a control Ad5, 108 PFU of Ad5-pIFN-α, low- or high-dose Ad5-pIFN-γ, or a combination of Ad5-pIFN-α and low- or high-dose Ad5-pIFN-γ and challenged all groups with FMDV 1 day later. The control group and the groups inoculated with either Ad5-pIFN-α or a low dose of Ad5-pIFN-γ developed clinical disease and viremia. However, the group that received the combination of both Ad5-IFNs with the low dose of Ad5-pIFN-γ was completely protected from challenge and had no viremia. Similarly the groups inoculated with the combination of Ad5s with the higher dose of Ad5-pIFN-γ or with only high-dose Ad5-pIFN-γ were protected. The protected animals did not develop antibodies against viral nonstructural (NS) proteins, while all infected animals were NS protein seropositive. No antiviral activity or significant levels of IFNs were detected in the protected groups, but there was an induction of some ISGs. The results indicate that the combination of type I and II IFNs act synergistically to inhibit FMDV replication in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Attachment expression vector of cells of human and other mammals, expression system, preparation method and application
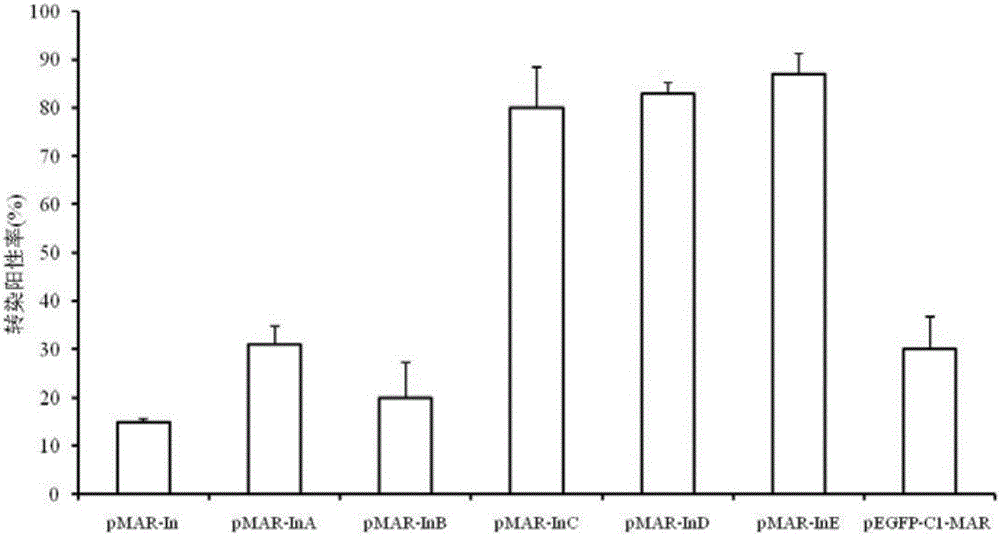
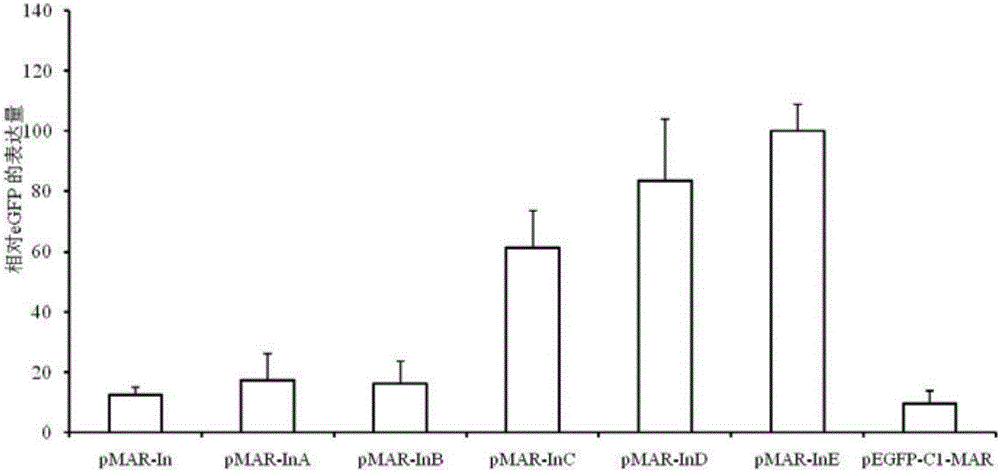
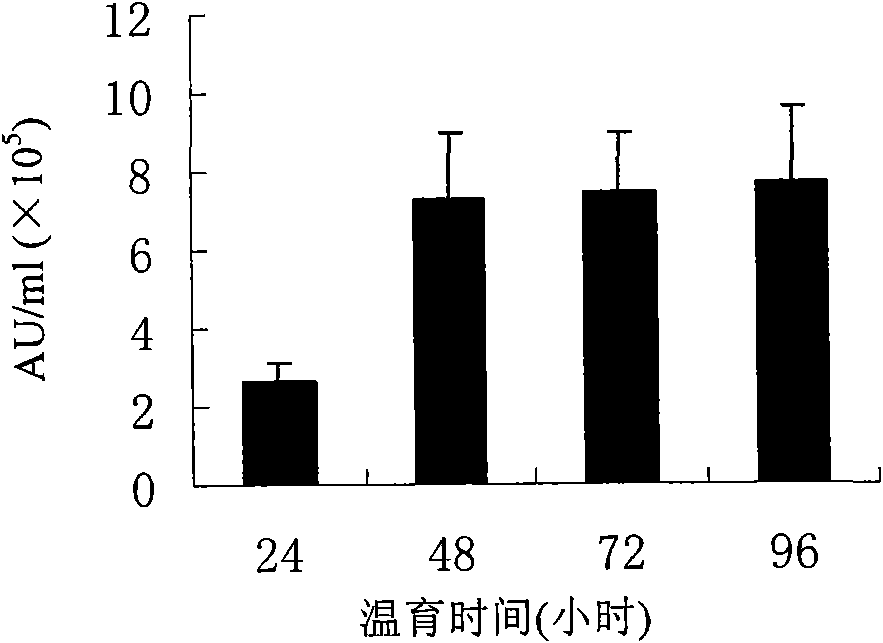
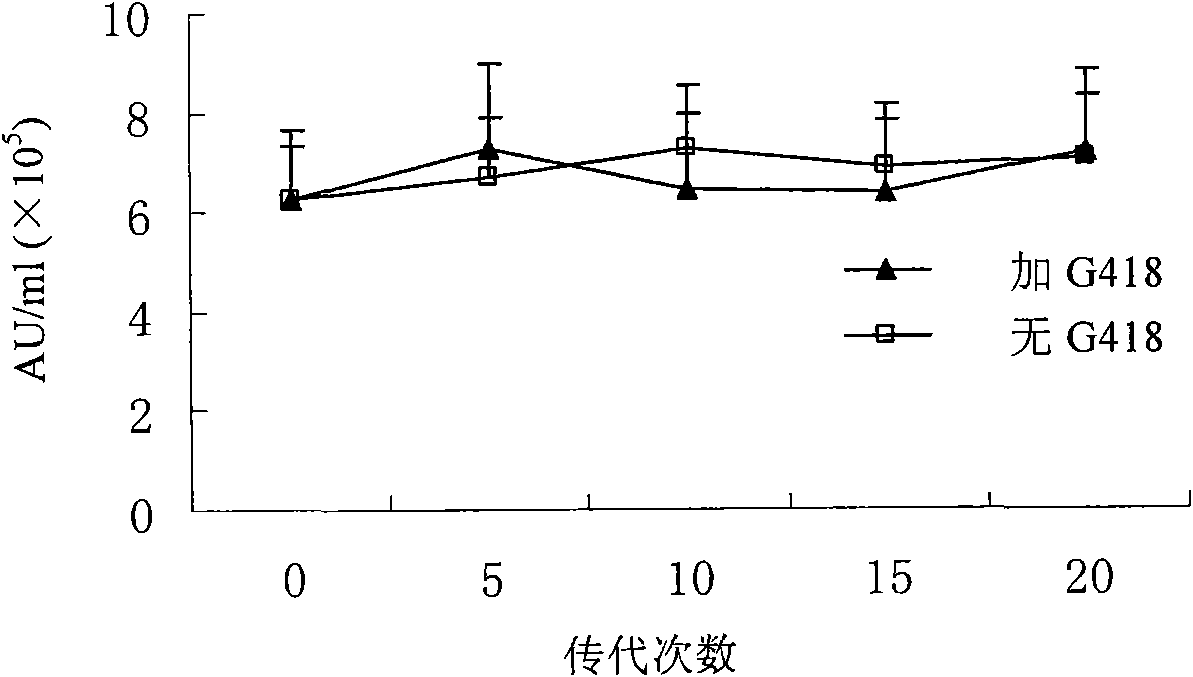
ActiveCN106497973AEfficient expressionExpression continuedNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetAgricultural science
The invention discloses an attachment expression vector of cells of human and other mammals, an expression system, a preparation method and application and belongs to the technical fields of genetic engineering and gene therapy. A segment beta-interferon MAR (matrix attachment region) sequence (or an nucleotide sequence which is 95 percent homologous with the sequence or more), which is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, SEQ ID NO: 2 or SEQ ID NO: 3, is inserted into the attachment expression vector; compared with an expression vector containing a whole-length MAR sequence or a 387bp MAR sequence, the vector can efficiently, lastingly and stably express exogenous target genes; especially, the expression of the vector containing an E-segment MAR sequence is optimum and the expression vector can be used for the gene therapy. In the vector, a multiple cloning site where the segment MAR sequence is inserted into the vector is located at the downstream of eGFP (enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein); on one hand, transgene silencing can be overcome; on the other hand, an expression level of a target protein can be improved and the effectiveness of subsequent monoclonal cell strain screening are improved.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
CHO cell line expressing porcine beta interferon and application thereof
InactiveCN101603032AImprove stabilityExcellent specific activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsDiseaseDrug biological activity
The invention discloses a CHO cell line expressing vertebrate beta interferon, which contains genes coding beta interferon of the animal. The invention particularly discloses a CHO cell line expressing porcine beta interferon. The invention also relates to a method utilizing the CHO cell line to produce standard plasmids of vertebrate beta interferon and porcine beta interferon obtained by the method, and the porcine beta interferon has higher specific activity and stability, can be used as standard plasmids for porcine beta interferon biological activity detection, can be used for preventing and treating porcine infectious diseases and has significant application prospect and market prospect.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for preparing fusion protein contg. human interferon-beta and human seralbumin and its products
The invention relates to a manufacture method and product for confluence albumen of human beta interferon and human serum albumin that uses superposing PCR technology, connecting IFN beta cDNA and HAS cDNA, with out any connecting peptide to gain IFN beta-HSA cDNA melting gene to be integrated into host chromosome to take expression. The confluence albumen includes the first area of at least 85% sequence same source as human beta-interferon and the second area of at least 85% sequence of same source of human serum albumin. The invention has good application prospect in medicine field.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Oral avian interferon fusion protein and applications of oral avian interferon fusion protein as immunopotentiators
ActiveCN106832004AImprove early immunityEasy to operateBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAnti virusOral medication
The present invention discloses an oral avian interferon fusion protein and applications of the oral avian interferon fusion protein as an immunopotentiator, wherein the fusion protein comprises chicken alpha interferon and chicken beta interferon. The invention further provides applications of the fusion protein, wherein the applications comprise the application of the fusion protein as an immunopotentiator, the application of the fusion protein as an oral immunopotentiator, the preparation of an immunopotentiator, the preparation of an oral immunopotentiator, the application of the fusion protein as a vaccine immunopotentiator, the application of the fusion protein as an oral vaccine immunopotentiator, the application of the fusion protein as an avian influenza virus vaccine immunopotentiator, the application of the fusion protein as an oral avian influenza virus vaccine immunopotentiator, the preparation of a vaccine, the preparation of an avian influenza virus vaccine, the application of the fusion protein as an anti-virus preparation, the preparation of an anti-virus preparation, the application of the fusion protein as an anti-vesicular stomatitis virus preparation, and the preparation of an anti-vesicular stomatitis virus preparation. According to the present invention, the fusion protein as the immunopotentiator or anti-virus preparation can be subjected to oral administration, and provides good clinical effects for the improvement of the early immunity of chickens.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
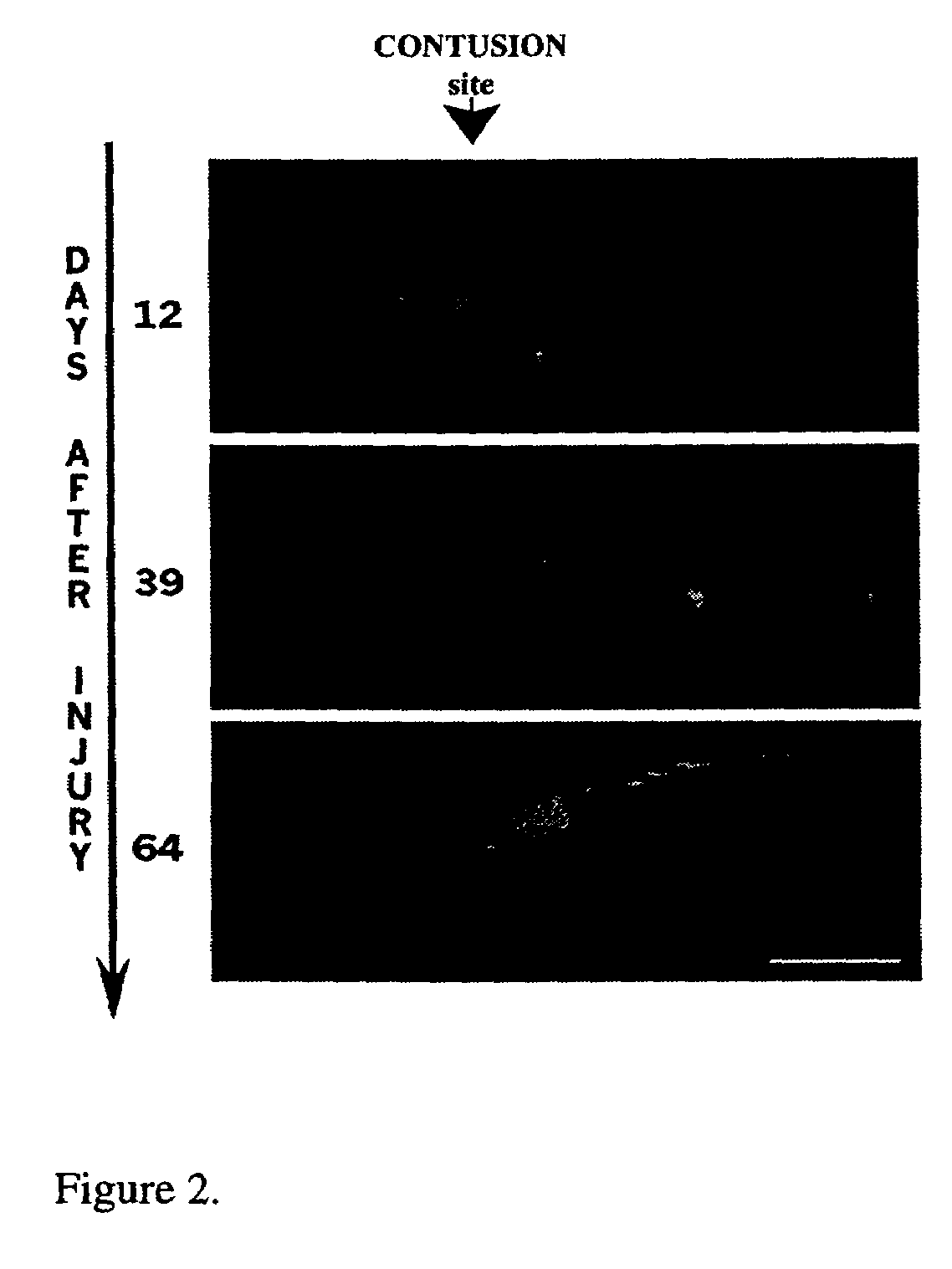
Beta interferon for the treatment of chronic spinal cord injury
InactiveUS7462349B2Novel and effective treatmentReducing progressive secondary damagePeptide/protein ingredientsBeta interferonsClinical method
The invention is intended to adapt an already established clinical procedure for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS)—the use of beta interferon—to treat chronic human spinal cord injury. The present invention relates to the prevention of chronic inflammation and demyelination following spinal cord injury.
Owner:KALDERON NURIT
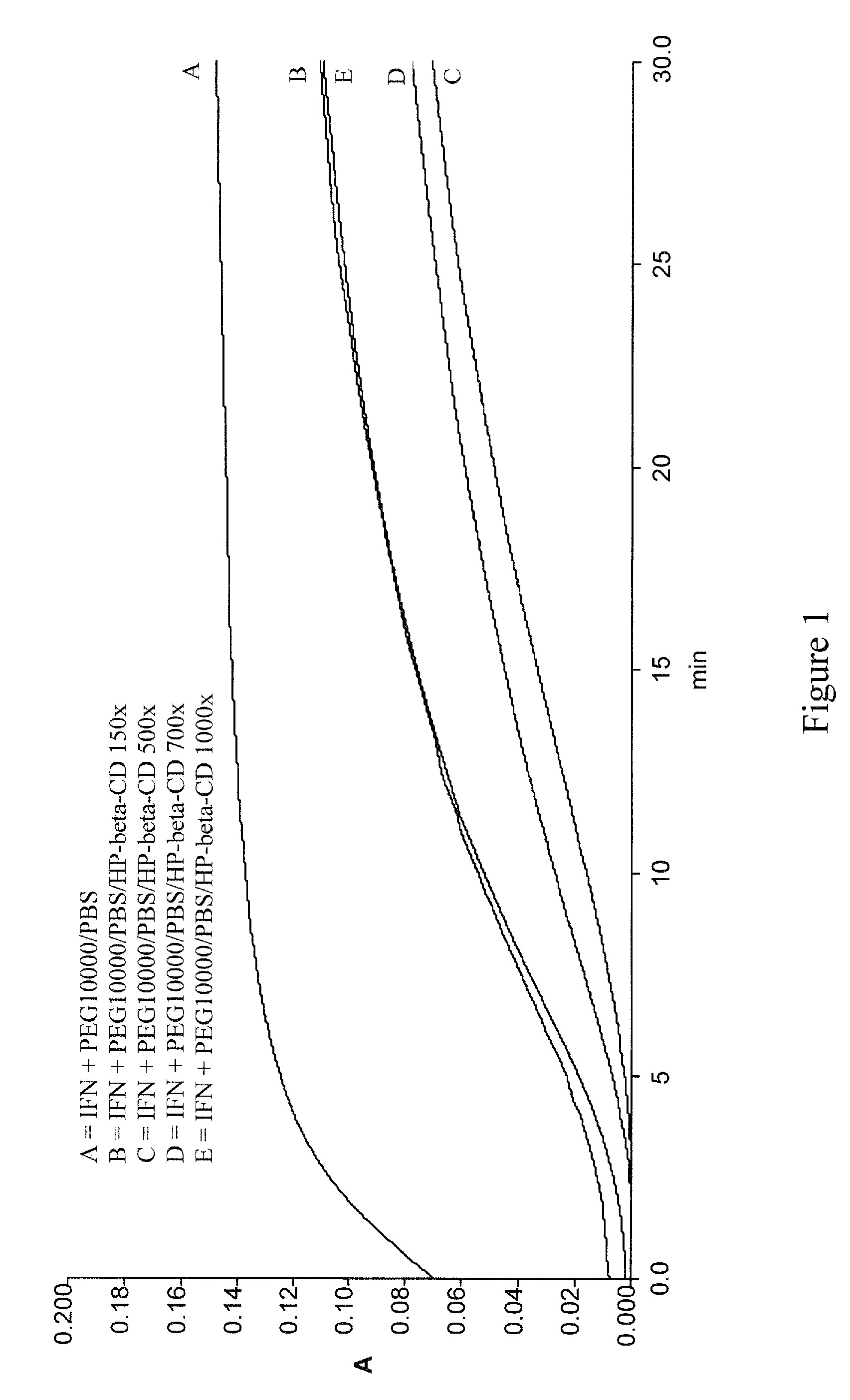
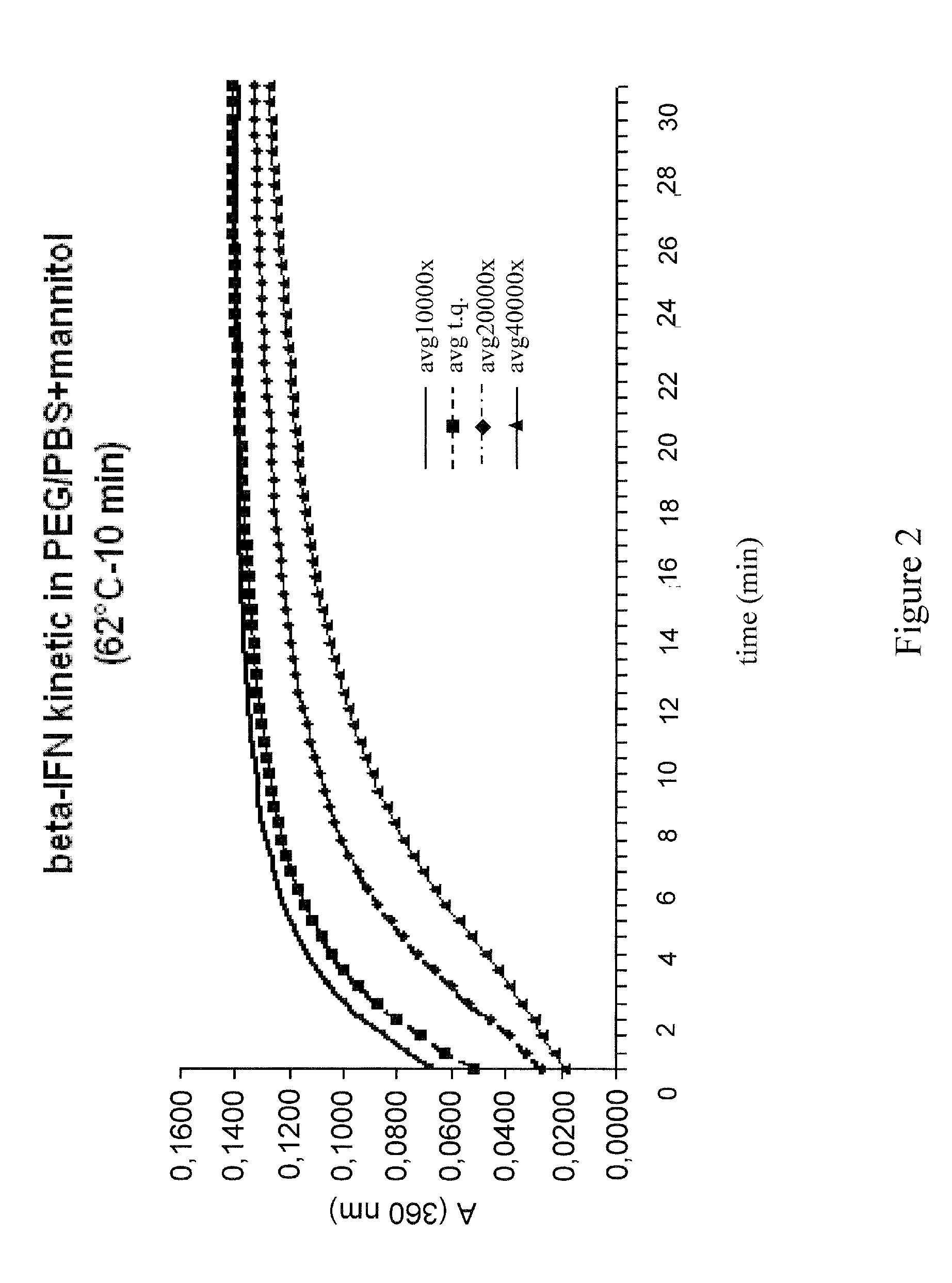
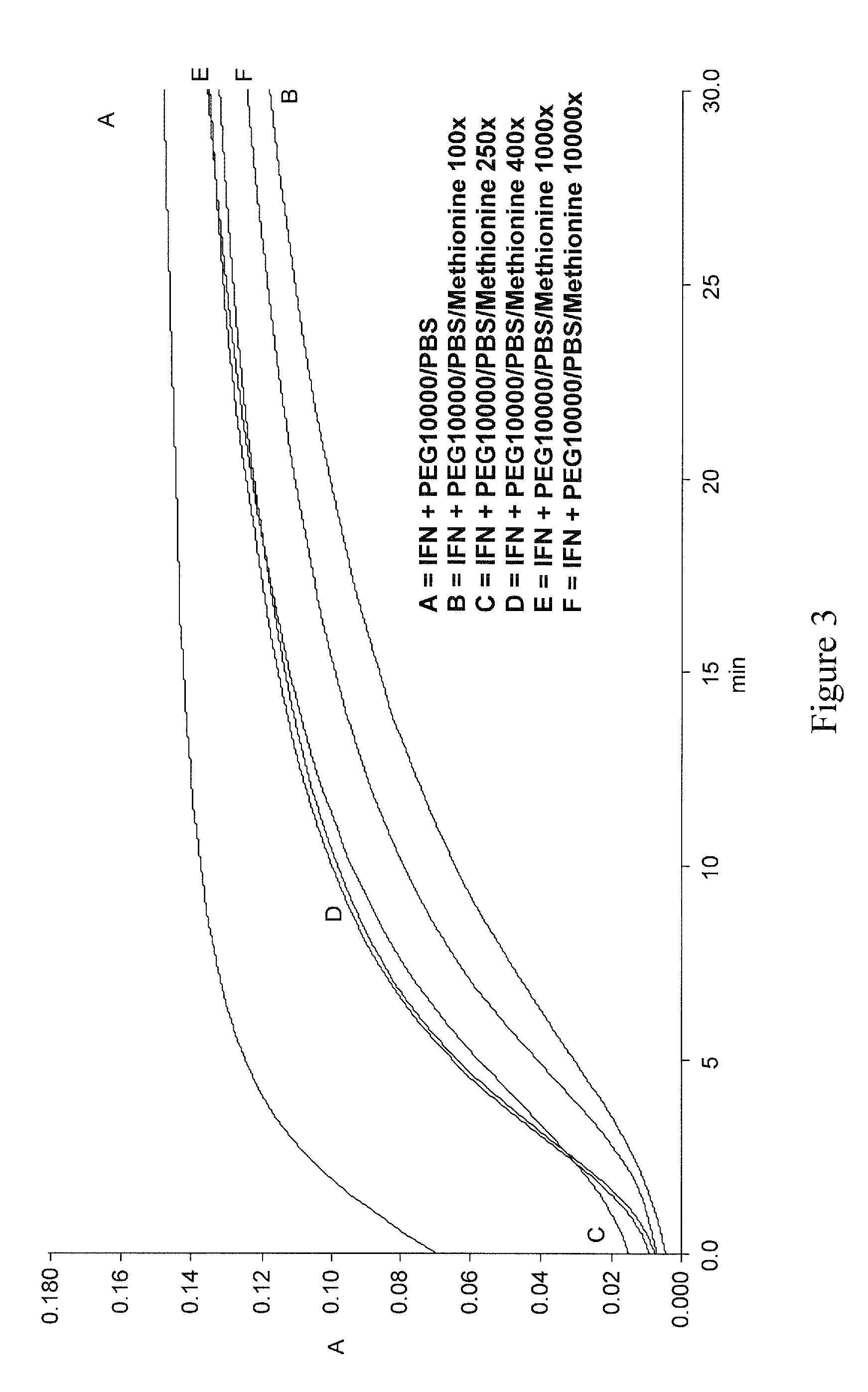
Stabilized interferon liquid formulations
ActiveUS7846427B2Prolong residenceOptimize treatment planOrganic active ingredientsBiocideCyclodextrinCvd risk
Stabilized liquid pharmaceutical composition comprising an interferon (IFN) or an isoform, mutein, fused protein, functional derivative, active fraction or salt thereof, wherein said formulation is a solution that comprises a buffer, a cyclodextrin, an isotonicity agent and an anti-oxidant are described here. Preferably the interferon is interferon beta-1a and the cyclodextrin is HPBCD. These formulations are stable at room temperature, thus bringing the advantage of lower costs for formulation storage and increased safety for the patient with respect to possible “errors” during handling. As a matter of fact, having such formulations stable at room temperature reduces the risk of formation of degradation products potentially responsible for adverse events (e.g. immunogenicity).
Owner:ARES TRADING SA
Process and culture medium for the production of cells infected by a multiple sclerosis-associated virus
In a process for the in vitro production of a culture or cell line infected by a viral strain associated with multiple sclerosis (MS), a body sample is taken from an individual suffering from MS. The sample is cultivated in a culture medium that promotes the growth of infected cells to obtain a culture of primary infected cells. A sample of the culture of primary cells or a subculture of the latter is cultivated in series, by successive passages in the culture medium to obtain the culture or cell line infected by a virus associated with MS. The culture medium also contains a beta-interferon antibody or an antibody that is directed against an antigenically close molecule, the antibody playing an inhibiting role in viral expression and allowing long-lasting expression and propagation of the viral strain in the culture or cell line.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX SA
Biologic sensor for detecting human beta interferon and its special polypeptide
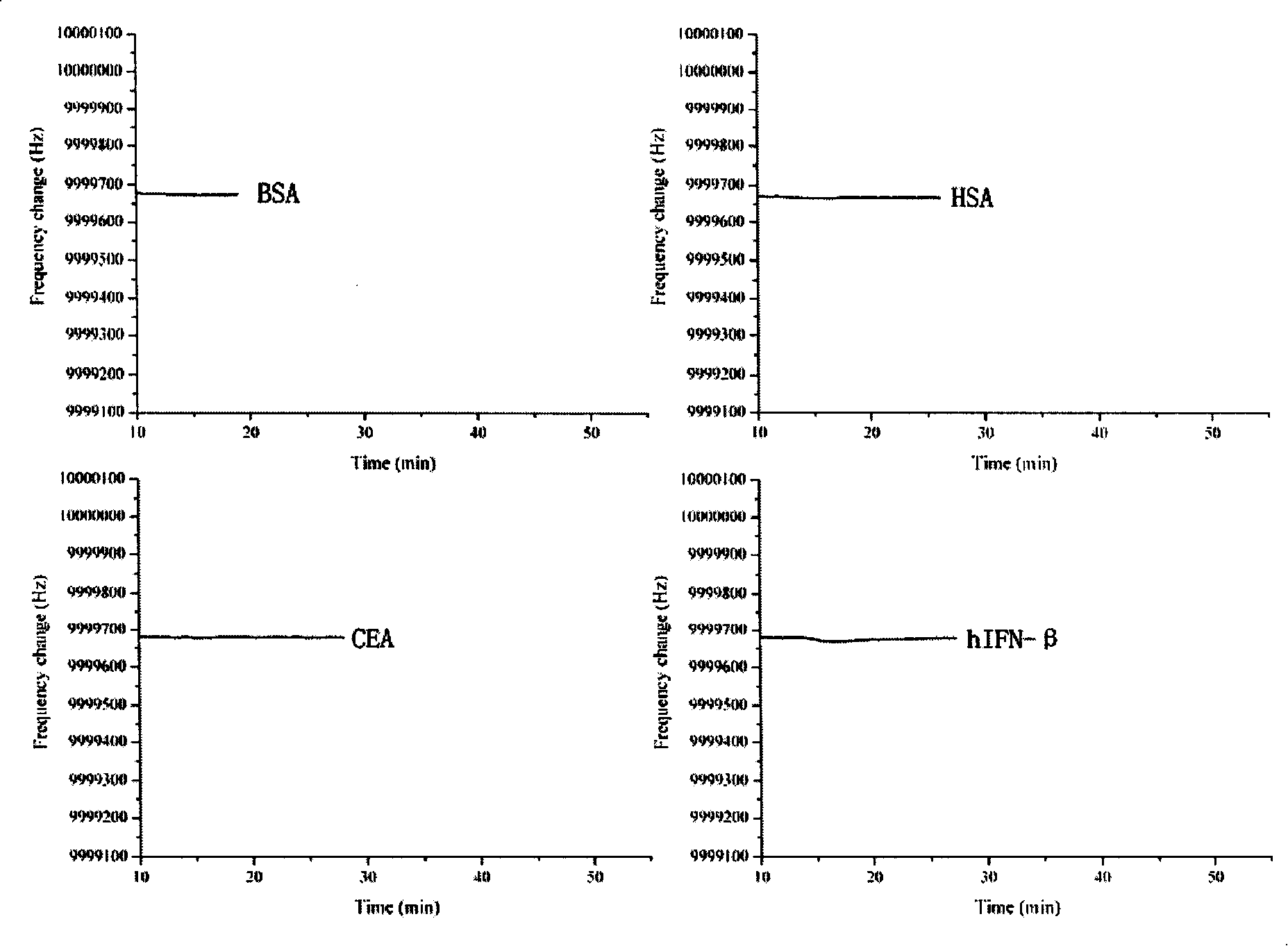
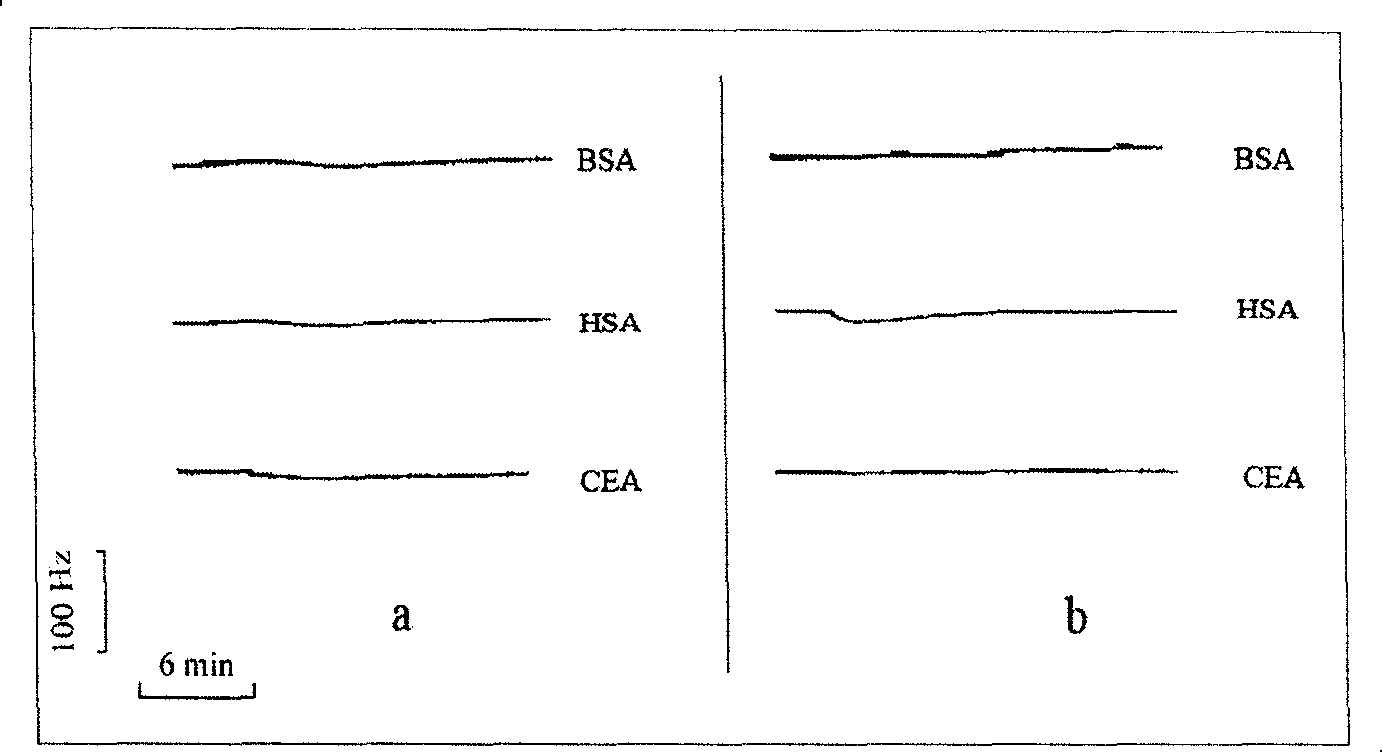
InactiveCN101221185AApparent specific bindingGood choiceBiological testingSignal responseBeta interferons
The invention discloses a biological sensor for detecting the human interferon Beta and the dedicated polypeptide thereof. The amino acid sequence of the polypeptide provided by the invention is SEQ No.1, for example. The biological sensor for detecting the human interferon Beta of the invention includes an identifying element and a transducer, wherein, the identifying element is the polypeptide which at least contains the SEQ No.1 amino acid sequence or the derivative thereof. The invention designs and synthesizes an antisense peptide which has the specific interaction with the human interferon Beta, and a biological sensor is prepared by using the antisense peptide, thus realizing the detection of the human interferon Beta. The biological sensor of the invention shows the obvious special combination of the human interferon Beta and has good selectivity; the signal response and the sample size of the human interferon Beta show a linear relation, the reproducibility is good, and the invention can be used for the quantitative detection of human interferon Beta.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing medicine using silkworm expressed human beta interferon
InactiveCN1405309AHigh clinical application valueRelieve the pain of injectionsPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedLarva currensHepatitis B virus
The invention refers to a method of using the bacilliform reformed virus with human beta-interferon gene to infect the silkworm grub and chrysalis in order to produce the human beta interferon and the prepared oral drugs. It includes the following: utilize the silkworm bacilliform virus-expressing system to reform the human beta-interferon gene for obtaining the reformed virus; inoculate the silkworm grub and chrysalis and the reformed virus for expression, and after separation, purification, refrigeration and desiccation, make them into oral drugs which has the remarkable action on the second-type hepatitis virus by the axamination on animals.
Owner:特菲(天津)生物医药科技有限公司
Porcine beta-interferon recombinant adenovirus and its construction method and application
InactiveCN1970764AStable potencyNot pathogenicPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsDiseaseShuttle vector
The invention discloses a pig alpha-interferon recombinant adenovirus and constructing method and application to prepare antiviral vaccine, which comprises the following steps: augmentating pig alpha-interferon IFN-alpha gene; cloning; constructing recombinant shuttle vector with IFN-alpha gene; establishing recombinant adenovirus plasmid carrier; obtaining recombinant adenovirus. The invention grows and expresses IFN-beta protein to make body stimulated by IFN-beta protein continuously, which generates neutralizing antibody of IFN-beta protein to protect pig permanently.
Owner:广东省农业科学院兽医研究所
Production process of chicken beta interferon optimized gene and recombinant chicken beta interferon
InactiveCN106399322AEfficient expressionEfficient purificationMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesEscherichia coliCytopathic effect
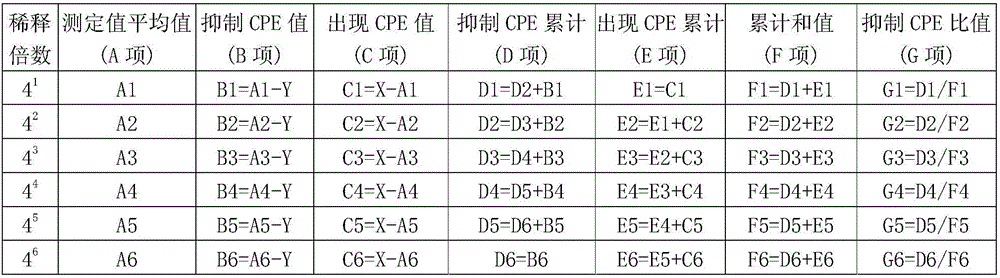
The invention discloses a production process of a chicken beta interferon optimized gene and a recombinant chicken beta interferon. The process includes the steps of: S1. conducting codon optimization on published chicken beta interferon genes in NCBI according to the preference of Escherichia coli codon and performing artificial synthesis of the optimized chicken beta interferon gene; S2. designing primers: according to the codon optimized interferon gene, designing a pair of primers; S3. constructing a recombinant expression plasmid; S4. transforming and identifying the recombinant expression plasmid; and S5. carrying out induced expression of the recombinant expression plasmid in Escherichia coli; and S6. extracting the expression product and conducting protein refolding and purification: S61. extraction and treatment of an inclusion body; S62. inclusion body denaturation; S63. denaturation fluid renaturation; and S64. nickel column affinity purification. The process provided by the invention expresses and purifies the recombinant chicken beta interferon protein by means of prokaryotic expression, and detects the interferon's activity of inhibiting vesicular stomatitis virus proliferation by means of cytopathic effect inhibition, and the activity unit reaches 2.73*10<6>UI / mg.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com