LAMP detection method for clostridium difficile AB toxins and special primer and kit thereof
A technology for Clostridium difficile and detection methods, which is applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and determination/inspection of microorganisms, etc., which can solve the problem of cumbersome interpretation methods, unfavorable toxin typing of Clostridium difficile, and inability to achieve rapid visual inspection. Problems such as interpretation of results, to achieve the effect of simple operation, simple result identification, and efficient amplification
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0059] Embodiment 1 Implement the present invention through the following steps:
[0060] 1. Primer design for LAMP detection of Clostridium difficile
[0061] (1) Primer design for LAMP detection of Clostridium difficile tcdA: The repetitive sequence of Clostridium difficile tcdA was retrieved from the American Gene Database (GenBank: X92982.1), and it was found to be Clostridium difficile through homology analysis by BLAST software Specific conserved sequence (SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence list), and then according to the conserved target DNA sequence, use the software Primer design V4 to design primers for LAMP detection of Clostridium difficile. As a result, three sets of primer pairs were optimized, F3 and B3 is the first group, FIP and BIP are the second group, LF and LB are the third group, and the specific primer sequences are shown in Table 1.
[0062] Table 1 tcdA primers used for LAMP detection of Clostridium difficile
[0063]
[0064] (2) Primer design for LAM...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Example 2 Optimum temperature screening experiment of the Clostridium difficile LAMP detection method of the present invention: Using the primers and amplification reaction system of Example 1, under the same reaction system, the genomic DNA of Clostridium difficile under different reaction conditions (temperature) was carried out. LAMP detection to obtain the optimal reaction temperature for the amplification reaction.
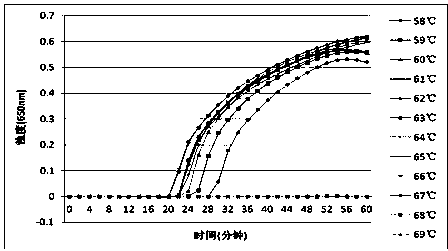
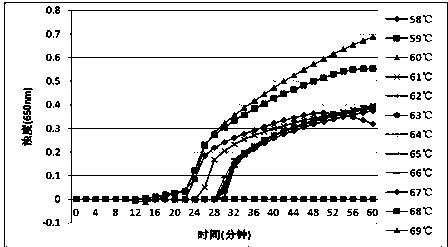
[0071] After testing, the turbidimeter detection result of the optimal temperature screening of the LAMP detection method of Clostridium difficile tcdA of the present invention (such as figure 1 shown): the optimal temperature under the reaction condition of 58-69°C for 60 minutes is 61°C. The turbidimeter detection result of the LAMP detection method optimal temperature screening of Clostridium difficile tcdB of the present invention (as figure 2 Shown): The optimal temperature is 60°C under the reaction condition of 58-69°C constant temperature fo...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Example 3 Specific detection of the LAMP detection method for Clostridium difficile of the present invention.
[0073] 1. The specificity detection of the LAMP detection method of Clostridium difficile tcdA of the present invention: Bacillus megaterium, Vibrio sharkus, Pseudomonas maltophilia, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Vibrio cholerae O139 group, Bacillus anthracis, enterohemorrhagic large intestine Bacillus, Yersinia enterocolitica, Vibrio parahaemolyticus, Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli, Enteroadhesive Escherichia coli, Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli, Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, Yersinia pestis, Pneumonia Streptococcus, Neisseria meningitidis, Burkholderia pseudomallei, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Acinetobacter baumannii, Escherichia coli, Bordetella pertussis, Haemophilus influenzae, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Genomic DNA of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae type B, and Acinetobacter brucei (all the above strains are from t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com