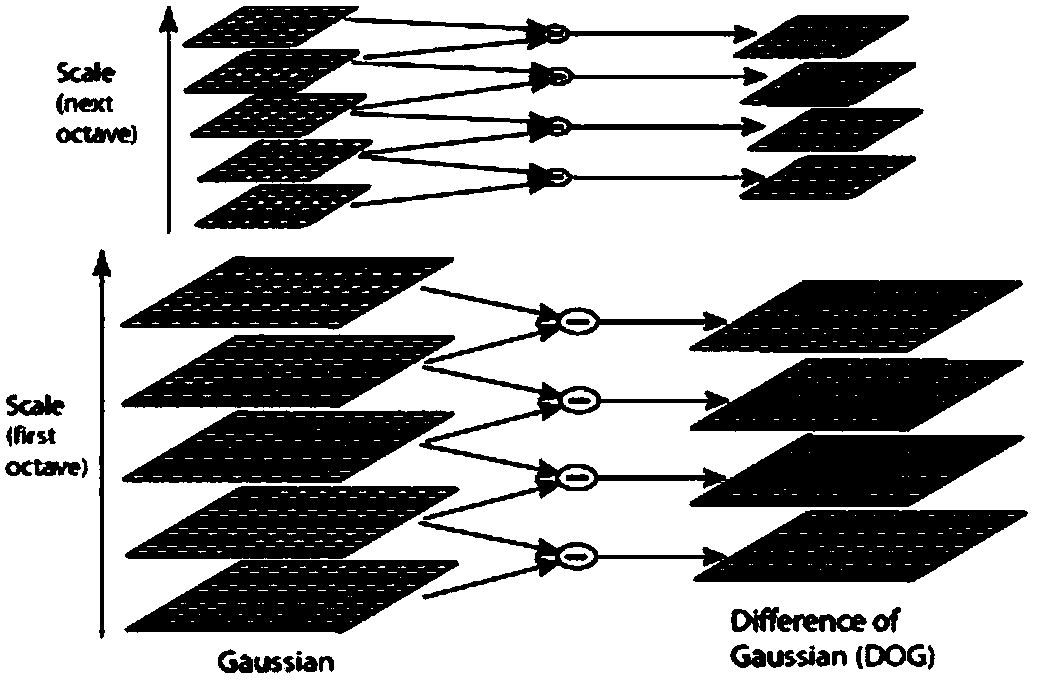
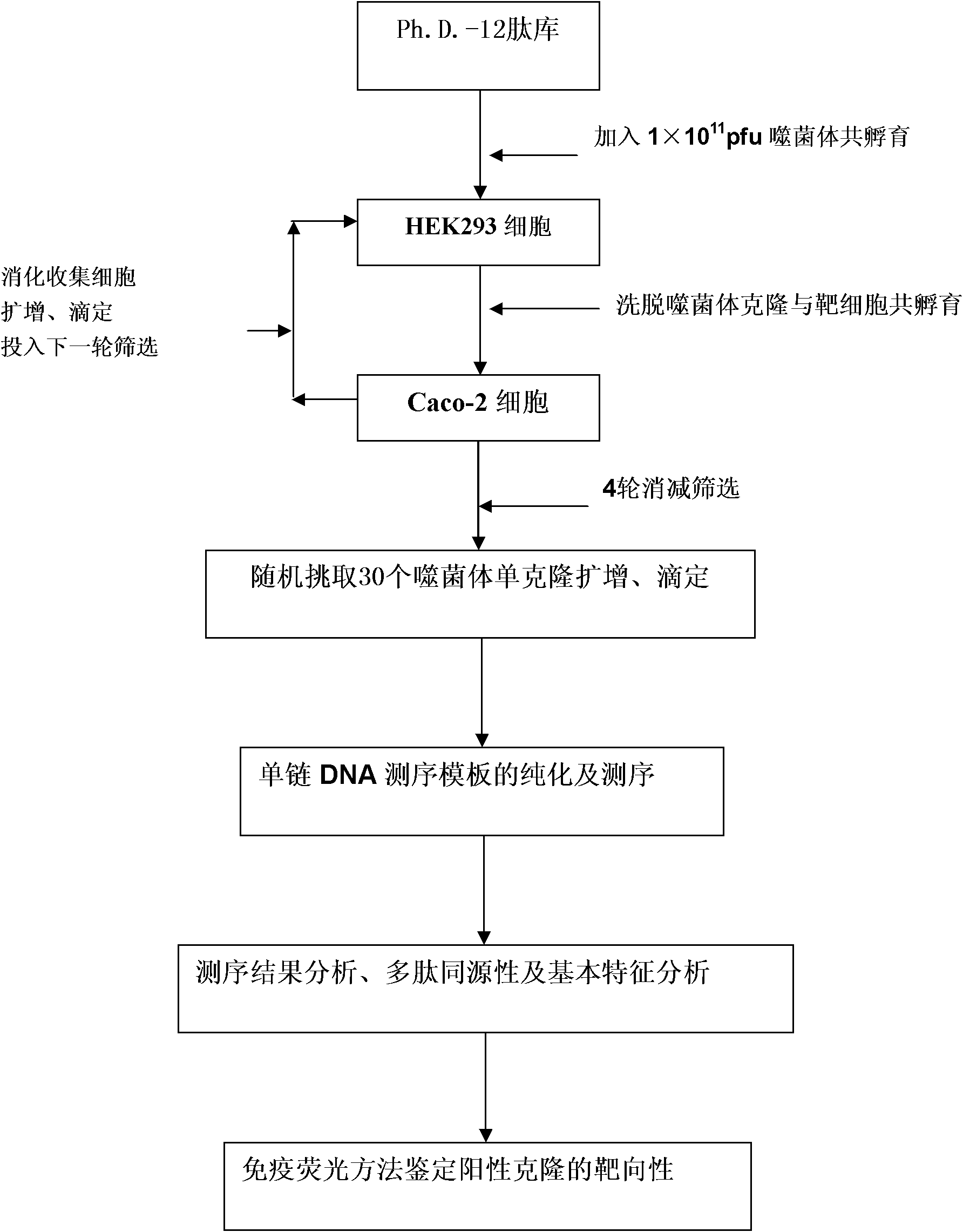
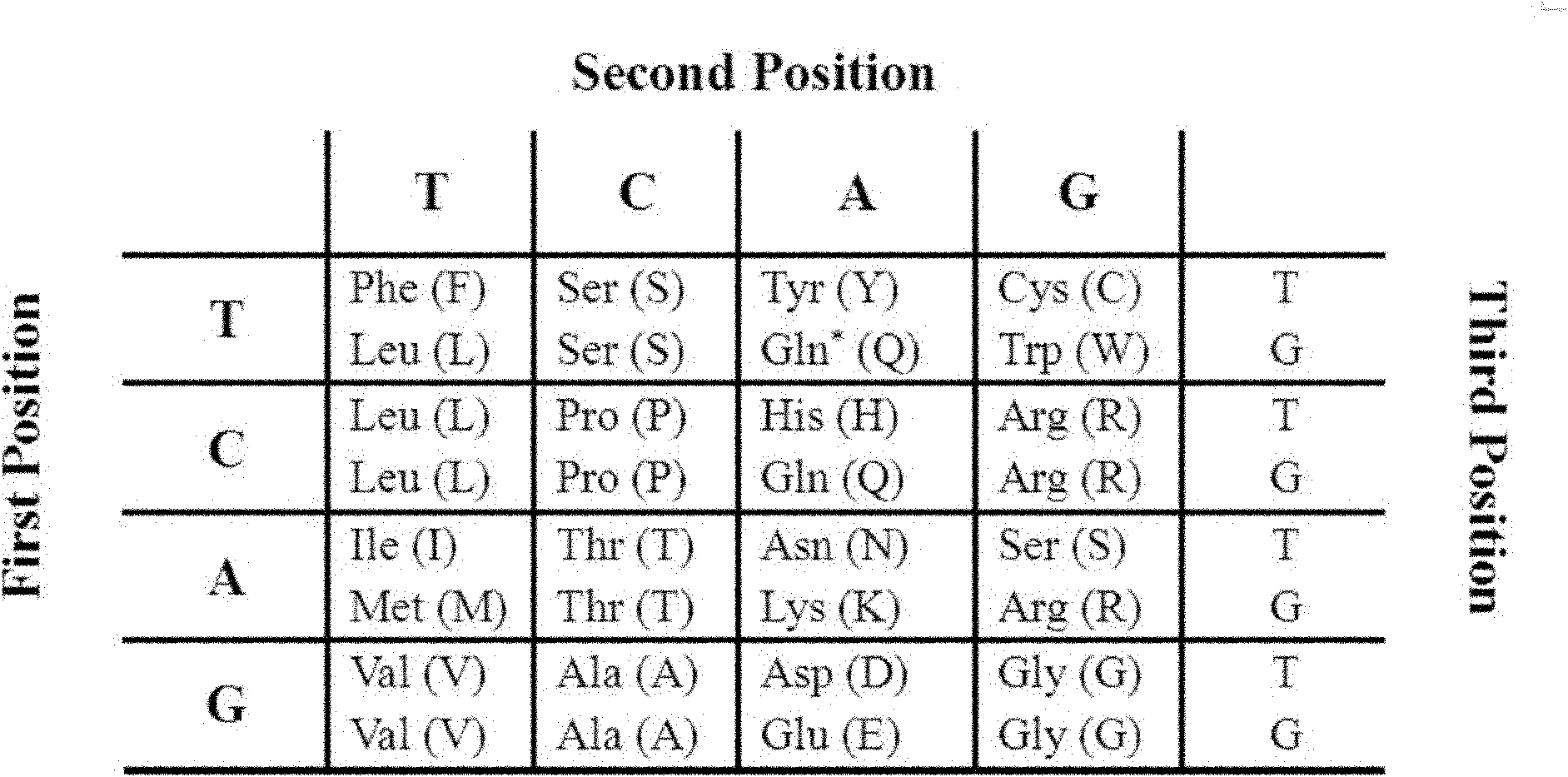
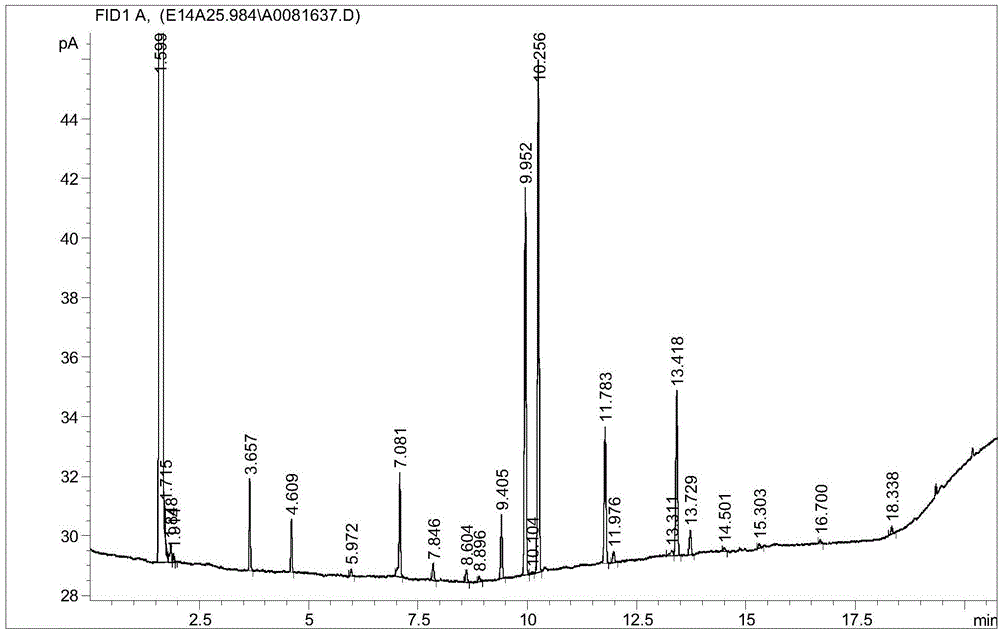
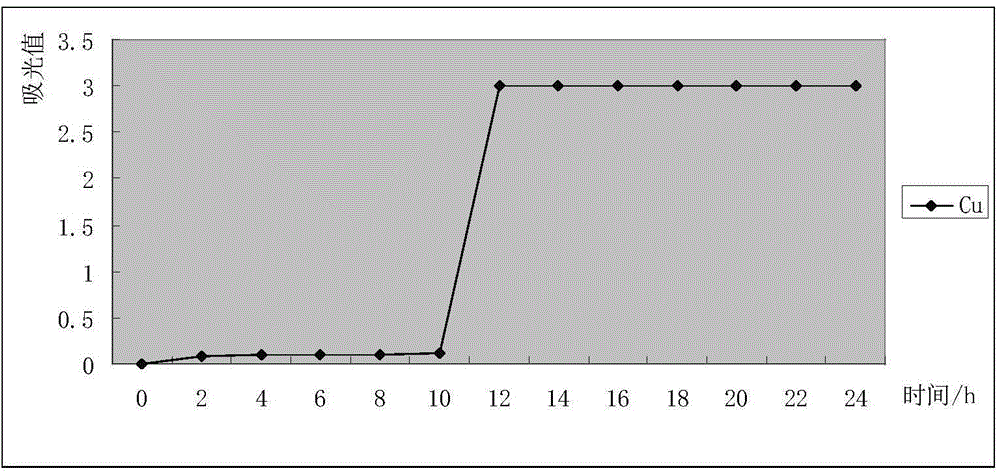
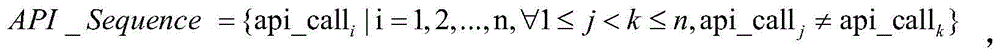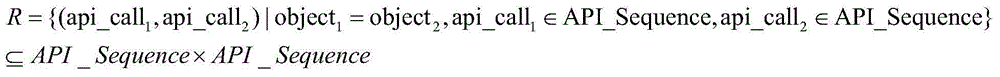Patents
Literature
125 results about "Homology analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
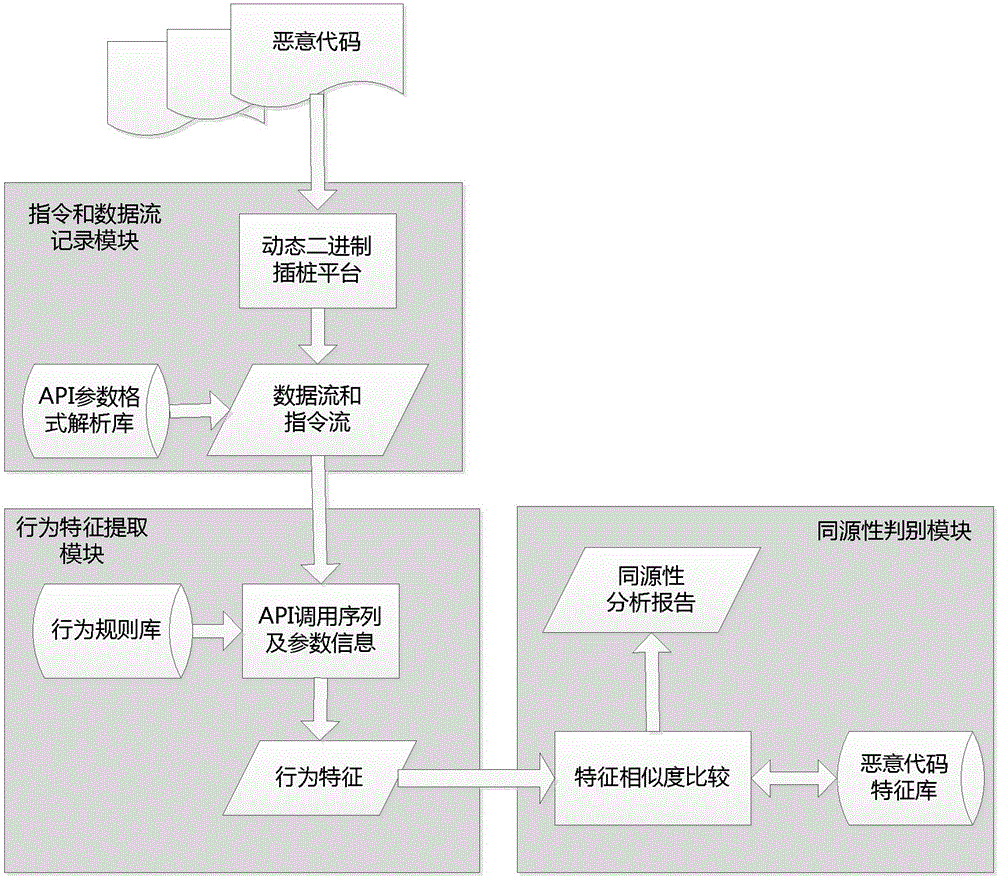
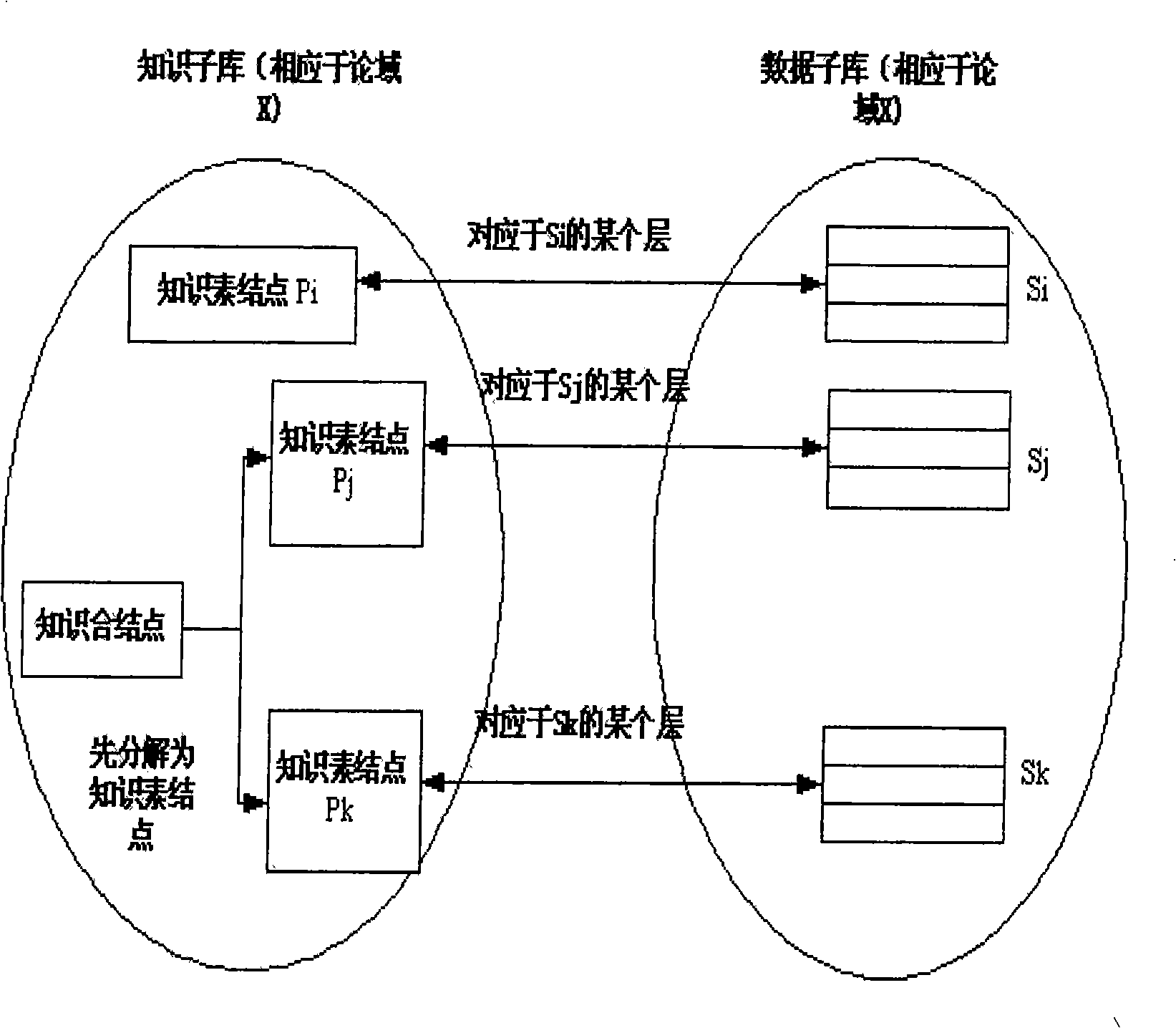
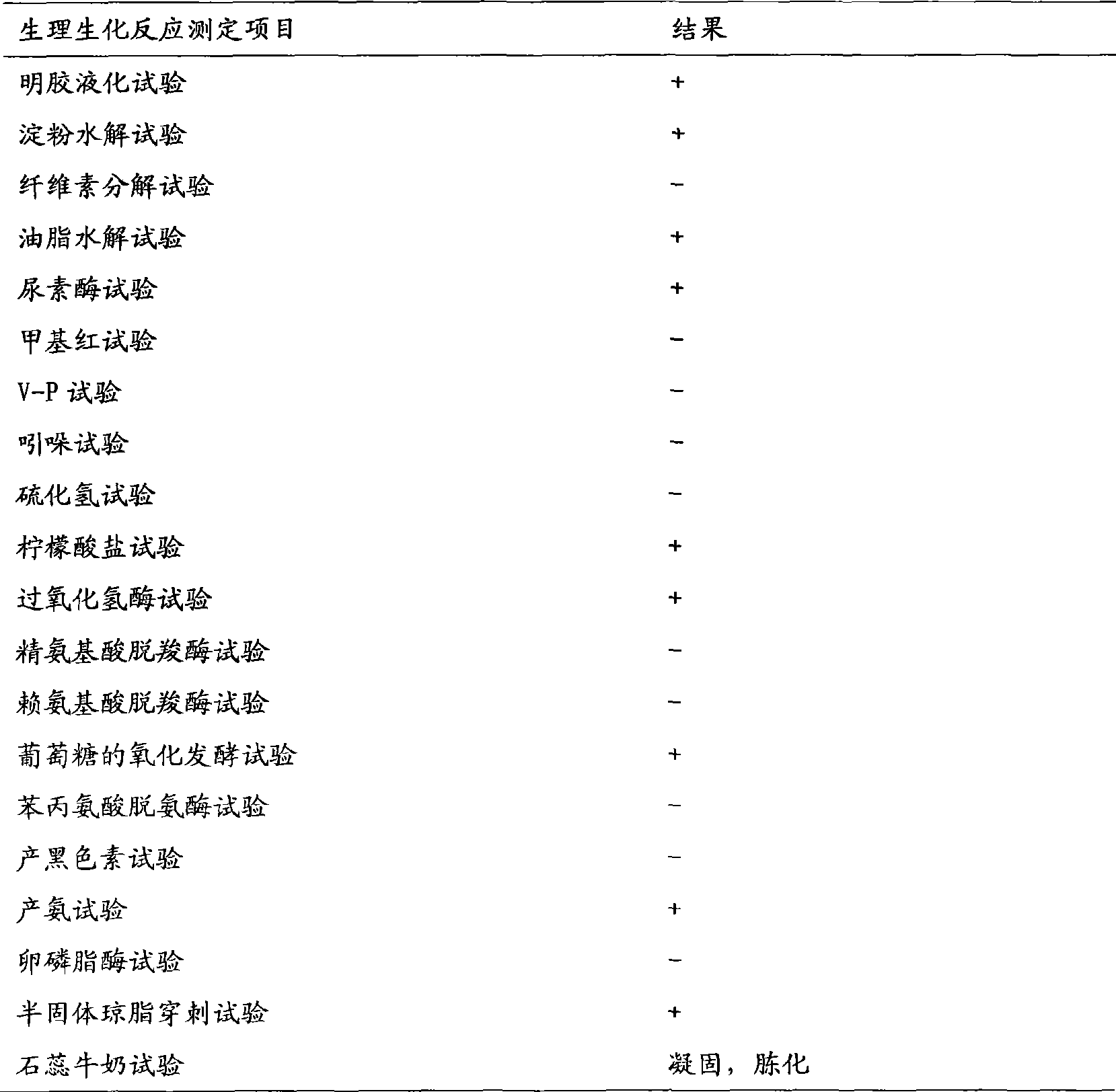
Behavior characteristic similarity-based malicious code homology analysis method
ActiveCN104866765AEasy to analyzeExact homologyPlatform integrity maintainanceProgramming languageAnalysis working
The invention provides a behavior characteristic similarity-based malicious code homology analysis method, which comprises the steps of: firstly extracting and quantifying behavior characteristics representing malicious codes based on a dynamic binary pile platform, on this base, measuring the similarity of the behavior characteristics among different malicious codes, and reflecting a homology judgment result of the malicious codes with the similarity of the behavior characteristics. By using the invention, the malicious codes collected in a network can be subject to homology analysis, and a powerful support is provided for tracing of a subsequent attack source. The method can correctly reflects the homology among samples of the malicious codes, correctly differentiates the samples of the malicious codes without homology, and has important guidance and reference significances in analysis work of the homology of the malicious codes.
Owner:PLA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE INFORMATION ENG UNIV PLA SSF IEU
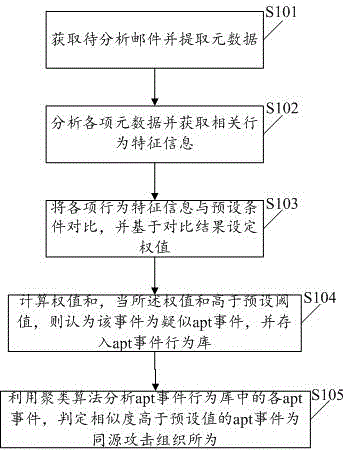
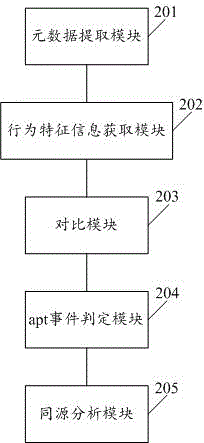
Apt event attack organization homology analysis method and apparatus
ActiveCN105721416AEfficient detectionEfficient identificationPlatform integrity maintainanceTransmissionCluster algorithmHomology analysis
The invention discloses an apt event attack organization homology analysis method and apparatus. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a mail to be analyzed and extracting metadata comprising sender information, receiver addressor information, addressee information, a theme, a text or an appendix; analyzing the metadata and obtaining correlation behavior feature information; comparing the behavior feature information with preset conditions, and based on comparison results, setting weights; calculating a weight sum, and when the weight sum is higher than a preset threshold, consuming that an event is a suspected apt event, and storing the event into an apt event behavior database; and analyzing each apt event in the apt event behavior database by use of a cluster algorithm, and determining an apt event whose similarity is higher than a preset value is initiated by a homologous attack organization. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the apt event can be effectively identified, and classified division of attack organizations of the apt event can be realized.
Owner:HARBIN ANTIY TECH
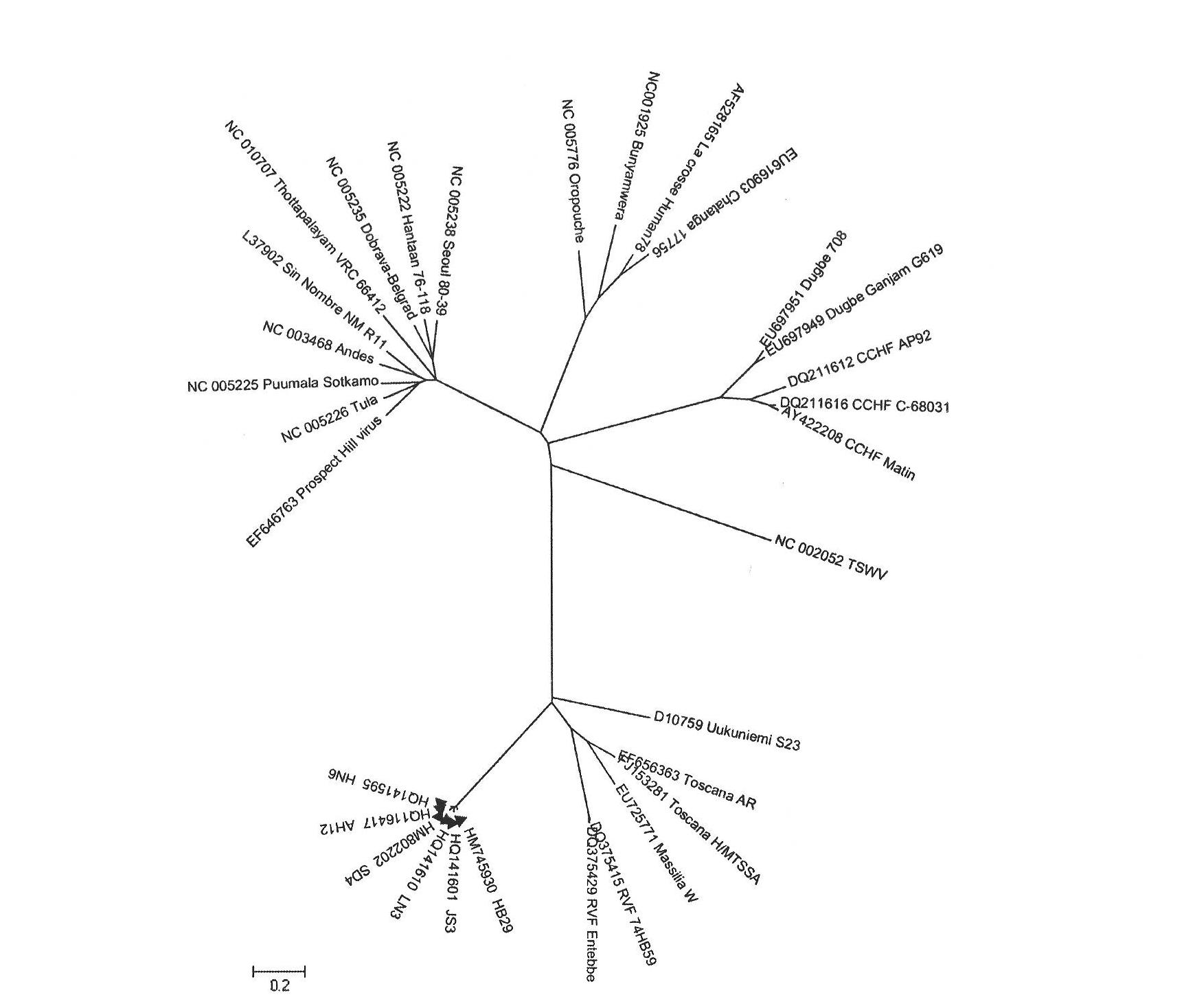
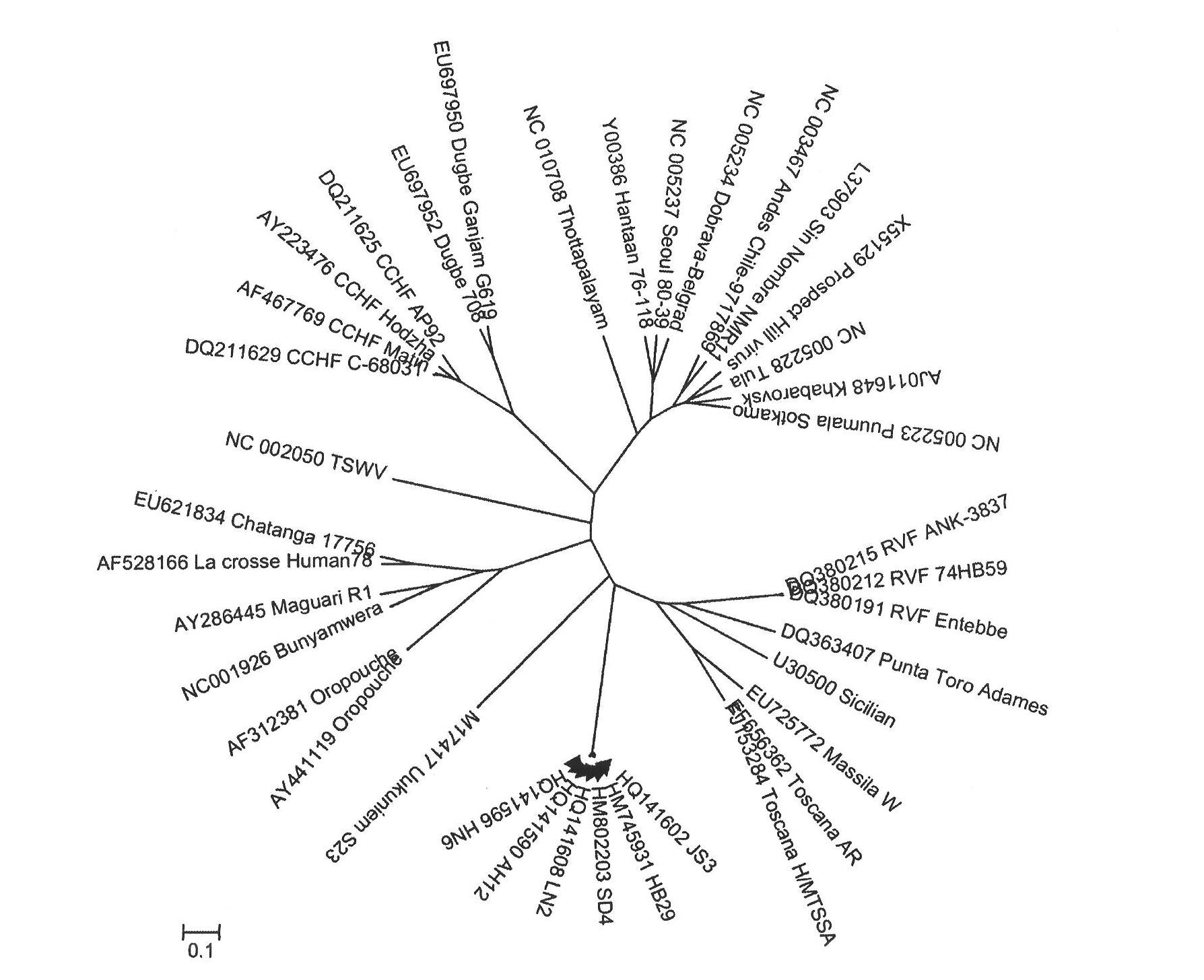
Entire gene sequence of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) and application
ActiveCN102070704AStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPolymerase LStructural protein
The invention relates to a severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV), an entire gene sequence represented by Hubei isolate HB29, amino acid sequences of coding proteins and application. The entire gene sequence of the virus is subjected to homology analysis. The virus belongs to bunyaviridae and comprises three gene segments, namely, L, M and S which represent polymerase and glycoprotein (Gn and Gc), nucleoprotein (NP) and non-structural proteins (NSs) of the virus respectively, and the three segments are all positioned on the branch of phlebovirus but farther from other viruses of phlebovirus. The entire gene sequence and the coding proteins of the virus can be used for developing drugs, vaccines or diagnostic reagents for preventing and treating the epidemic diseases caused by the SFTSV.
Owner:STATION OF VIRUS PREVENTION & CONTROL CHINA DISEASES PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Lactobacillus plantarum and bacteriocins produced by lactobacillus plantarum and capable of inhibiting Gram negative bacteria
InactiveCN101812414AHigh activityBroad antibacterial spectrumBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAlcohol sugarsFermentation
The invention relates to a strain of lactobacillus plantarum and bacteriocins produced by the lactobacillus plantarum and capable of inhibiting Gram negative bacteria. The bacteriocins have the advantages of broad antibacterial spectrum, thermal stability and stable pH, degradability by protease, no residue in a human body and high safety. A lactobacillus plantarum strain is preserved on June 29, 2009 with a preservation number of CGMCC No.3151. A production strain is obtained by separating 'Jiaoke', a conventional dairy product in Inner Mongolia; on a MRS culture medium, colonies are ivory and round with a protruded center and orderly edges; the strain has two blunt round ends and a short and straight stem; and the size of the strain is 0.4 to 0.7 mu m *2 to 3 mu m. The strain is a non-spore Gram positive bacillus, and is identified as the lactobacillus plantarum through an API50CHL sugar alcohol fermentation test, a 16S rRNA sequence homology analysis test and a recA gene multiplex PCR method. The lactobacillus plantarum KLDS1.0391 is used as the production strain and is fermented and purified by using the improved MRS culture medium to obtain the bacteriocins of the lactobacillus plantarum. The bacteriocins are used in food preservatives.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting bird flue virus H5N1 subtype based on liquid phase chip
InactiveCN1858249AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBird fluFluorescence
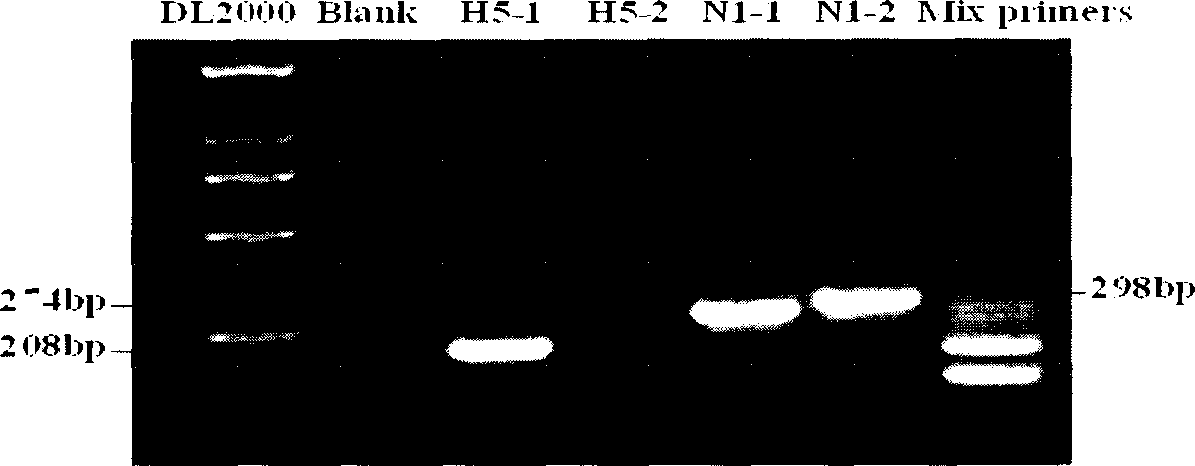
The present invention relates to liquid phase chip method of detecting bird flu virus H5N1 subtype. The liquid phase chip technology includes the homogeny analysis on all the H5 and N1 serum subtype nucleic acid sequence capable of being searched in the nucleic acid sequence bank by means of biological informatic means to find out conservative region, design degenerate primer and specific probe on the H5 and N1 gene fragment and couple the specific probe with fluorescent coding microsphere to make specific detecting microsphere as the liquid phase chip; and recognizing the H5 and N1 gene fragment specifically with the liquid phase chip through two rounds of PCR reaction and reading out the detection result in the chip detection instrument. The method can detect bird flu virus H5N1 subtype quickly for early diagnosis.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
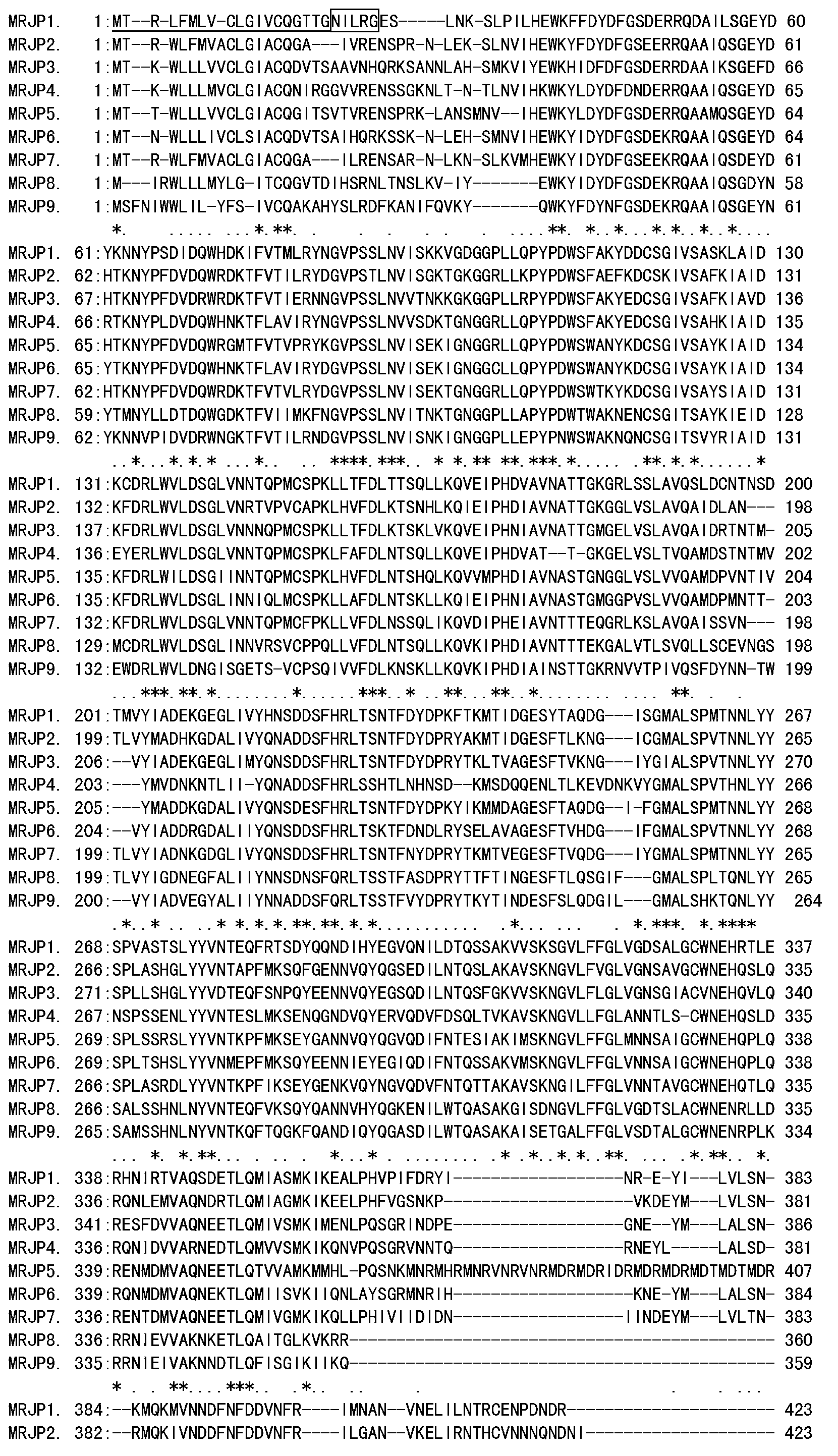
A specific antibody of major royal jelly protein MRJP1 and a preparation method thereof and Elisa quantitative detection thereof
ActiveCN103059135AStrong specificityIndividual bigSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansNew Zealand white rabbitSpecific antibody
The invention discloses a specific antibody of major royal jelly protein MRJP1 and a preparation method thereof and Elisa quantitative detection thereof. First, homology analysis is performed to amino acid sequences of proteins of all members of the Apismellifera major royal jelly protein MRJPs family (MRJP1-MRJP9) to select a specific polypeptide amino acid sequence unlike other MRJPs family members in MRJP1. The related specific polypeptide is synthesized by using a chemical method, and is used as an antigen to immunize New Zealand white rabbits; taking serum, and performing Elisa assay obtaining polyclonal antibody R2 with a relatively high titer, then purifying the antibody by using an affinity column prepared from the synthesized MRJP1 polypeptide. The titer of antibody R2 is detected via Elisa assay by using MRJP1 as the antigen, and the titer of the antibody is greater than 1:20000. The present invention provides a very reliable new rapid detection method for the qualitative and quantitative detection of MRJP1 in royal jelly, and also provides a very reliable technical means for quality control, freshness detection, and identification of genuine products of royal jelly and honey products for bee product quality supervision departments and processing and trading enterprises.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Polypeptide specifically combined with HepG2 cell surface
The invention discloses a polypeptide specifically combined with a HepG2 cell surface. According to the invention, four polypeptide segments are selected by utilizing a phage display random dodecapeptide library, the amino acid sequences of the four polypeptide segments are respectively LLADTTHHRPWT, LLADTPHHRPWT, FGWVTPHHELRS and SLSDLTHMGPWP. According to the invention, a polypeptide sequence combined with a liver cancer HepG2 cell is selected by utilizing a phage polypeptide display technology, and ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) identifies the affinity of phage clone and the liver caner cell, thus eight phage clones are obtained; four polypeptide sequences are obtained by sequencing, wherein the common amino acid sequence (basic sequence) is ***D(V)TT(P)HH*P(L)W(R)*; homology analysis indicates that the basic sequence of the polypeptide is possibly amino acid determinant on a ligand protein combined with a tumor cell surface receptor; cell immunofluorescence further identities that the target result of the positive clone of the phage prompts that the positive clone of the phage can be specifically combined with the HepG2 cell; and the selected specific polypeptide of the liver cancer HepG2 cell provides an experiment basis for early diagnosis of liver cancer, targeting delivery of an antitumor medicine and research and development of a targeting short peptide medicine.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
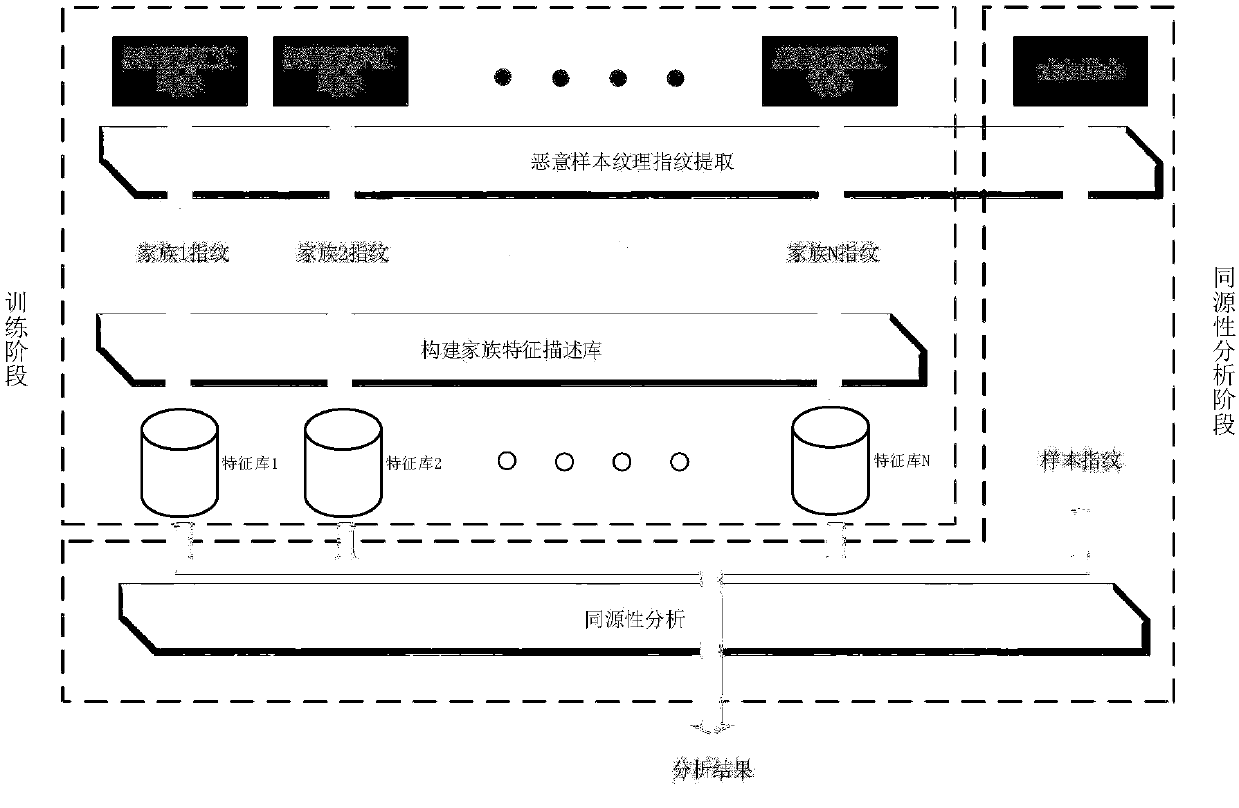
Malicious sample homology detection method based on image feature descriptor
InactiveCN107657175AImprove robustnessResolve interferenceCharacter and pattern recognitionPlatform integrity maintainanceInterference factorSample image
The invention discloses a malicious sample homology detection method based on an image feature descriptor. When the malicious sample homology detection method is used, malicious samples can be protected from confusion jamming, the homology of a malicious file can be quickly analyzed, and the method is high in efficiency, accuracy, robustness and expansibility. By use of the method, through a filevisualization algorithm, data preprocessing is carried out, the interference factors of a semantic level due to file decompiling or sand box operation are avoided, then, an image feature extraction technology is used in a homology analysis field to extract the feature descriptor of the malicious sample image, and a family feature description library is constructed by the image feature descriptor and is used for analyzing and comparing the homology of an unknown malicious program. The image feature descriptor obtained through the image feature extraction algorithm is high in robustness, and analysis efficiency and expansibility are high after the sample library is established.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
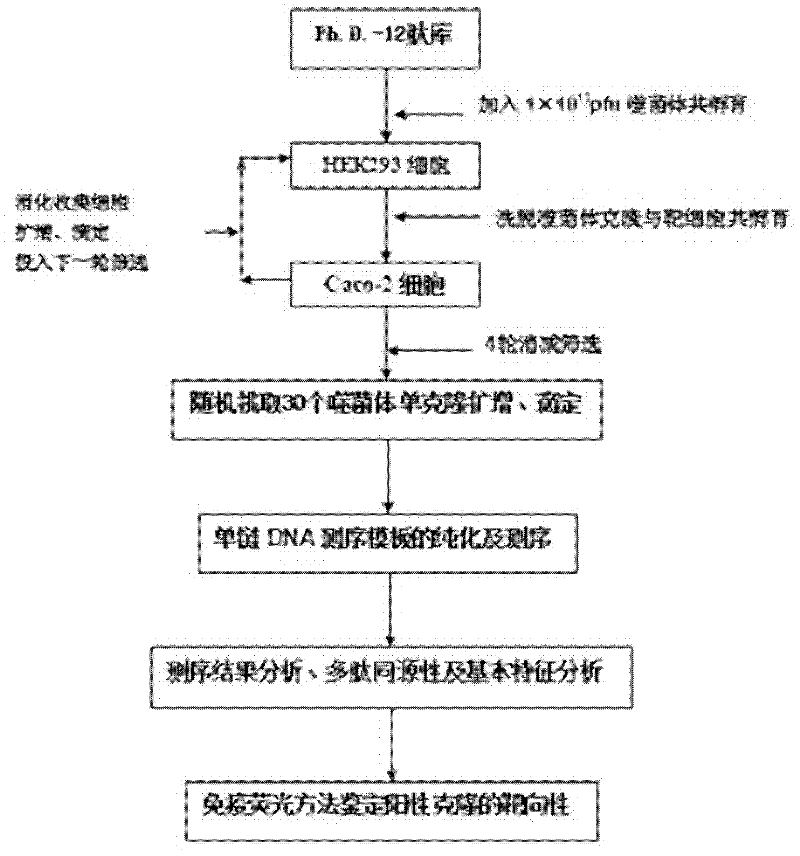
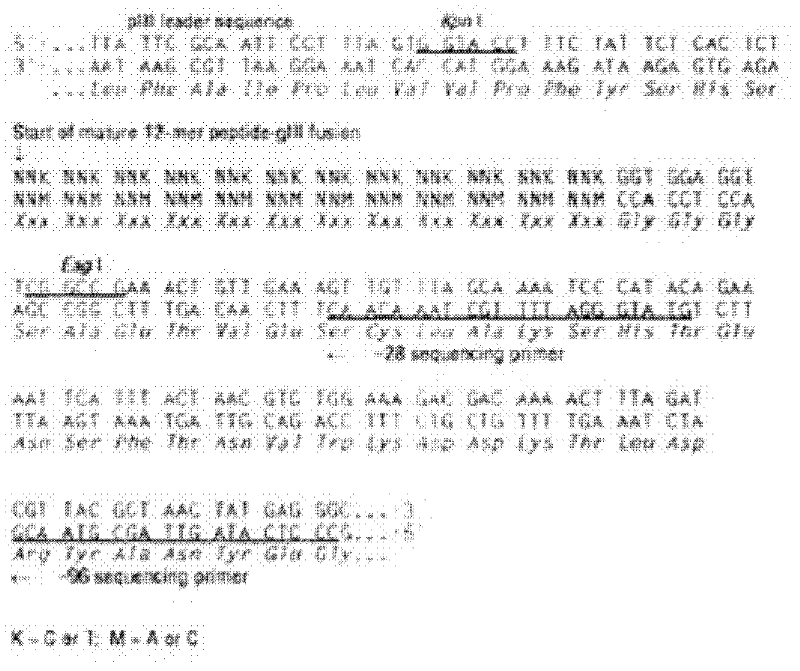
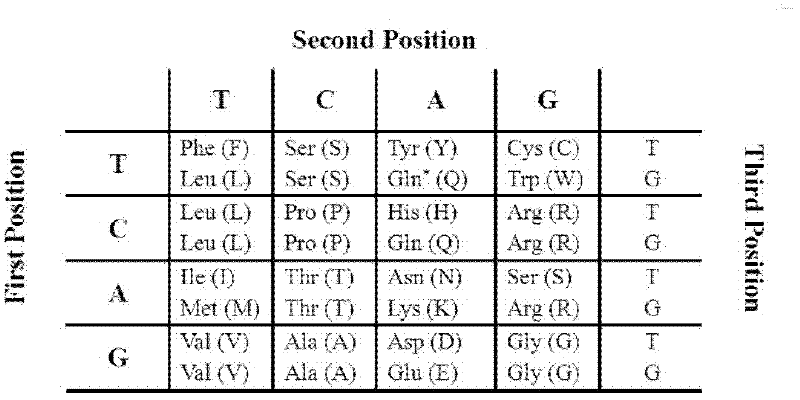
Caco-2 cell surface specific binding polypeptide and screening method thereof
The invention discloses a Caco-2 cell surface specific binding polypeptide. Four polypeptide fragments are screened by phage display of a random dodecapeptide library, and the amino acid sequences of the four polypeptide fragments are respectively as follows: SPSIDTRYSRLG, CVSVGMKPSPRP, SVSVGMKPSPRP and MVSMDSSPRDRL. According to the screening method disclosed by the invention, colorectal carcinoma Caco-2 cell binding polypeptide sequences are screened by a phage polypeptide display technology, the affinity of phage clones with colorectal carcinoma cells is judged by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), ten phage clones are obtained, and four polypeptide sequences are obtained by sequencing. The consensus amino acid sequence is XXSXXXXXXXRXX; homology analysis indicates that the polypeptide motif is likely to be the amino acid determinant on the tumor cell surface receptor binding ligand protein; by further judgment of cell immunofluorescence, the targeting result of the phage positive clones implicates that the phage positive clones can be specifically bound with Caco-2 cells; and the colorectal carcinoma Caco-2 cell specific polypeptide acquired by screening provides a preliminary experiment basis for early diagnosis of colorectal carcinoma, targeted delivery of antitumor drugs and development of targeted small peptide drugs.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Primer, probe and method for detecting entomophily or contact transmission pathogens by using liquid phase chip
InactiveCN102181532AThe detection process is fastEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesMulti analyteNucleotide
The invention relates to a primer, a probe and a method for detecting entomophily or contact transmission pathogens by using a liquid phase chip, which are used for detecting nine clinical common entomophily or contact transmission infectious disease pathogens. The invention can detect the nine clinical common entomophily or contact transmission infectious disease pathogens based on an MASA (multi-analyte suspension array) liquid phase chip technology, homology analysis is performed respectively according to all nucleotide sequences of 9 target viruses which can be retrieved in a gene bank mainly, the degenerate primer and the specific probe are designed, two turns of PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and molecular hybridization are further performed, and a Luminex100 system is further usedfor detection, thereby determining types of the pathogens contained in the sample. The invention is most important for adopting a correct treatment scheme and timely taking measures for preventing disease transmission by detection and early diagnosis of the 9 clinical common entomophily or contact transmission infectious disease pathogens. The invention has the advantages of fast detection speed,simpleness in operation, high sensitivity, good specificity and the like, and is conductive to popularization.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
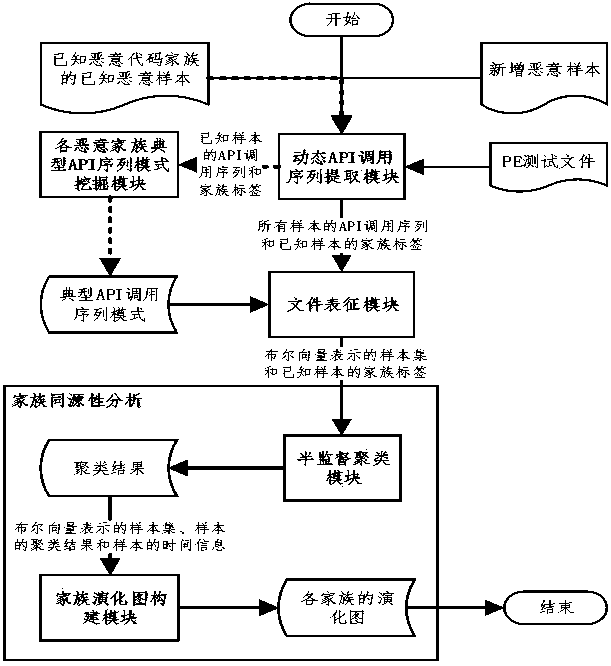
Malicious code family homology analysis based on semi-supervised density clustering
ActiveCN109190653AAccurate Homology Analysis ResultsAccurate family divisionCharacter and pattern recognitionPlatform integrity maintainanceTheoretical computer scienceVolumetric Mass Density
As most of the new malicious code belong to the known malicious code family, the information of existing samples in the virus library is utilized to assist malicious code to analyze the family homology to achieve more accurate family clustering, on the basis of accurate family clustering, the family diagram of malicious code is constructed to visualize the evolutionary relationship between the varieties of malicious code in the same family and predict the development direction of the varieties, and technical support is provided for the in-depth analysis of malicious code. Combined with the evolution characteristics of malicious code, the invention provides a malicious code homology analysis model which supports family graph construction, and the experimental results show that the model iseffective. A semi-supervised density clustering algorithm is provided, and experiments show that the algorithm can achieve accurate family clustering and provide clues for the discovery of unknown families. An algorithm based on asymmetric similarity measure is provided to construct family evolution diagrams for each malicious family and visualize the evolutionary relationships among malicious samples within the same family.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
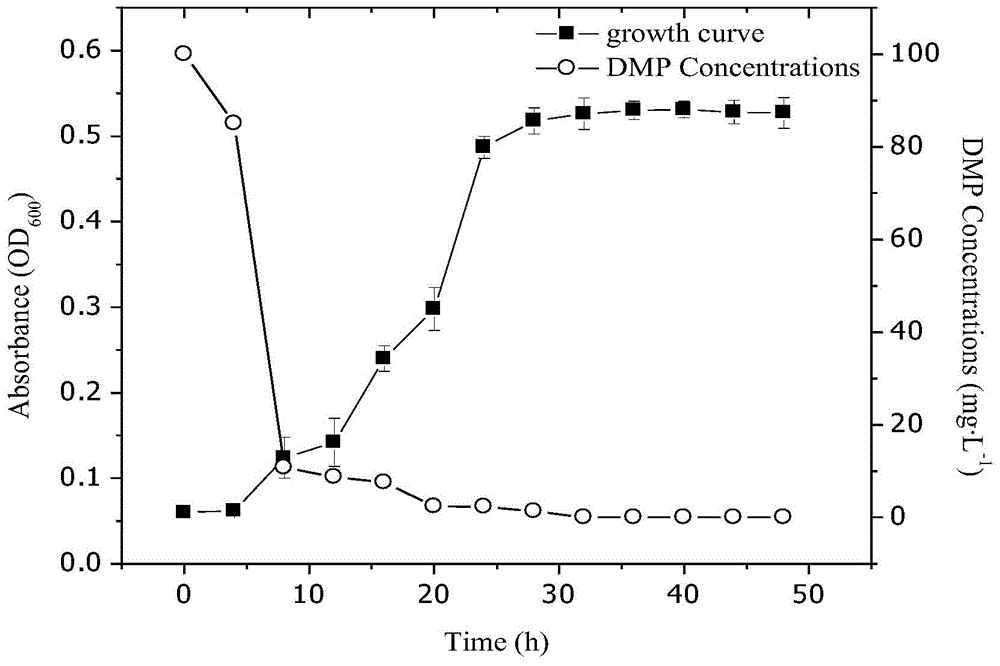
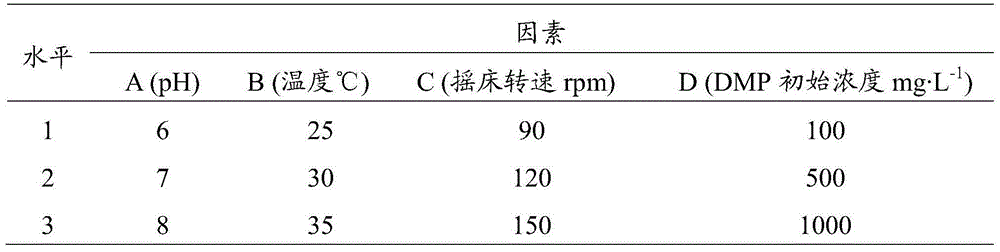
Bacillus strain capable of efficiently degrading DMP (dimethyl phthalate), culture method and application thereof to remediation of soil PAEs (phthalic acid esters) pollution
The invention discloses a bacillus strain capable of efficiently degrading DMP (dimethyl phthalate), a culture method and application thereof to remediation of soil PAEs (phthalic acid esters) pollution. A strain QD-9-10 which grows by mainly taking DMP as a carbon source is separated and identified from black soil covered with mulching films for a long term by adopting inorganic salt culture medium. According to morphological characteristic observation of a colony and 16SrDNA base sequence determination and homological analysis, the identification result of the bacterium is that QD-9-10 belongs to Bacillus subtilis. According to results of orthogonal experiments, the optimum culture method of the strain QD-9-10 is to perform culture by adopt inorganic salt culture medium under culture conditions that pH is 8.0, temperature is 35DEG C and shaking speed is 150rpm and DMP initial concentration is 100mg L<-1>, and biomass reaches the maximum at 32h. In addition, according to substrate utilization tests, the strain QD-9-10 can also utilize other common PAEs. Accordingly, the Bacillus subtilis QD-9-10 strain has a capability of degrading DMP and other common PAEs, and has a certain application prospect in aspects of degrading PAEs pollutants and remedying soil PAEs pollution.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY +1
Method for detecting influenza virus by liquid phase chip
ActiveCN101717830AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceMicrosphere
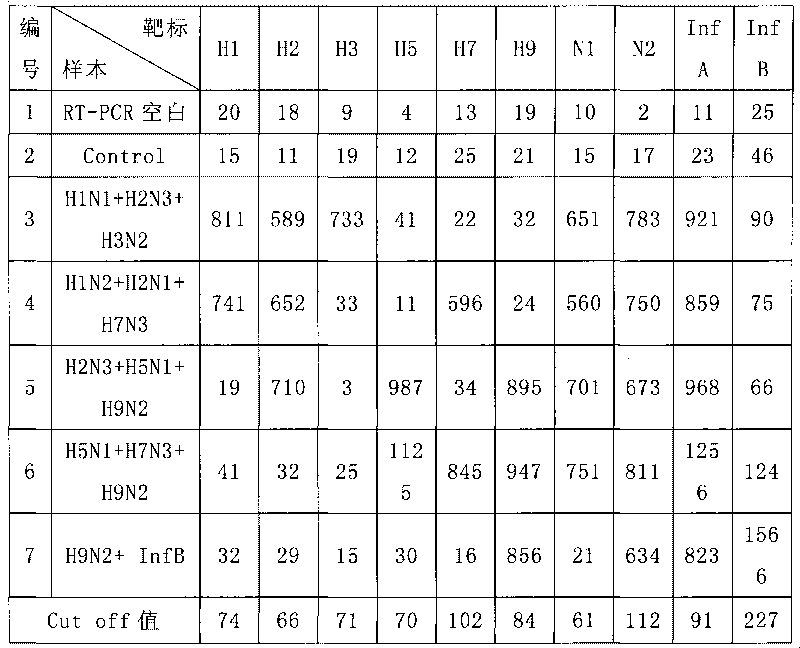
The invention discloses a method for detecting influenza virus by a liquid phase chip. The method is used for carrying out homology analysis on all Non Structural nucleotide sequences of A type influenza virus and B type influenza virus as well as H1, H2, H3, H5, H7 and H9 of the A type influenza virus and hypotypes of N1 and N2, and primers and specific probes are designed aiming at the corresponding gene segments; an improved nest-PCR method is adopted for PCR amplification by using nested primers with different lengths; amination treatment is carried out the 5' end of the specific probe, and the specific probe is coupled with a fluorescent coded microballoon; incubation hybridization is carried out on the PCR amplification product and the mixed microballoon coupled with the specific probe; and finally Luminex 100 is used for detecting. The detection method has higher specificity and sensitivity as well as rapid detection speed, and can be used for indentifying and monitoring the influenza viruses.
Owner:SHANDONG ACV BIOTECH CO LTD
Sample homology analysis method based on dynamic behavior chain and dynamic characteristics
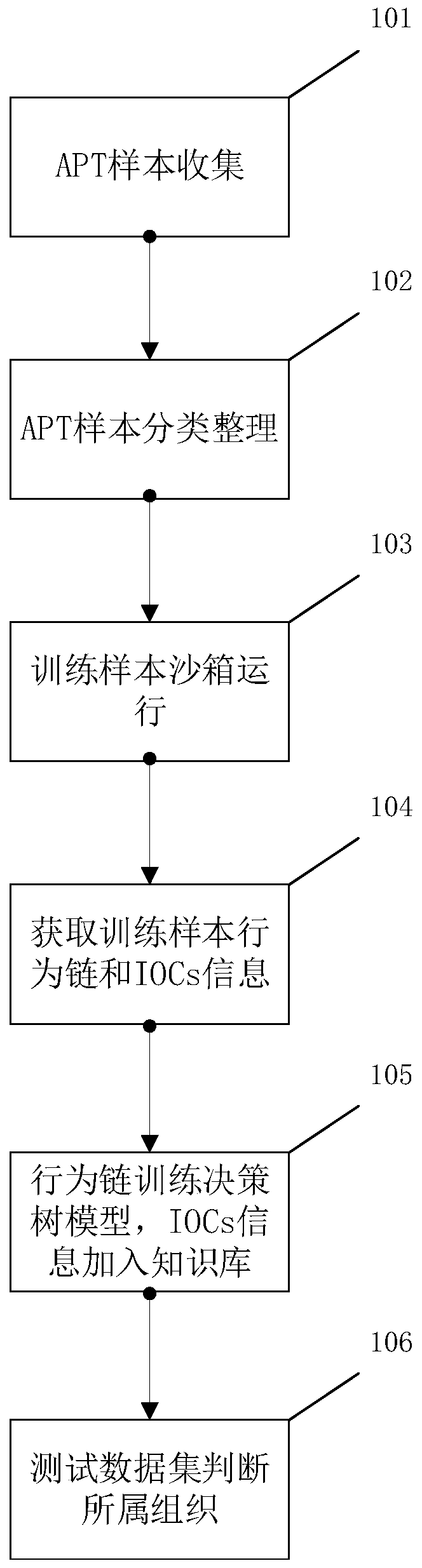
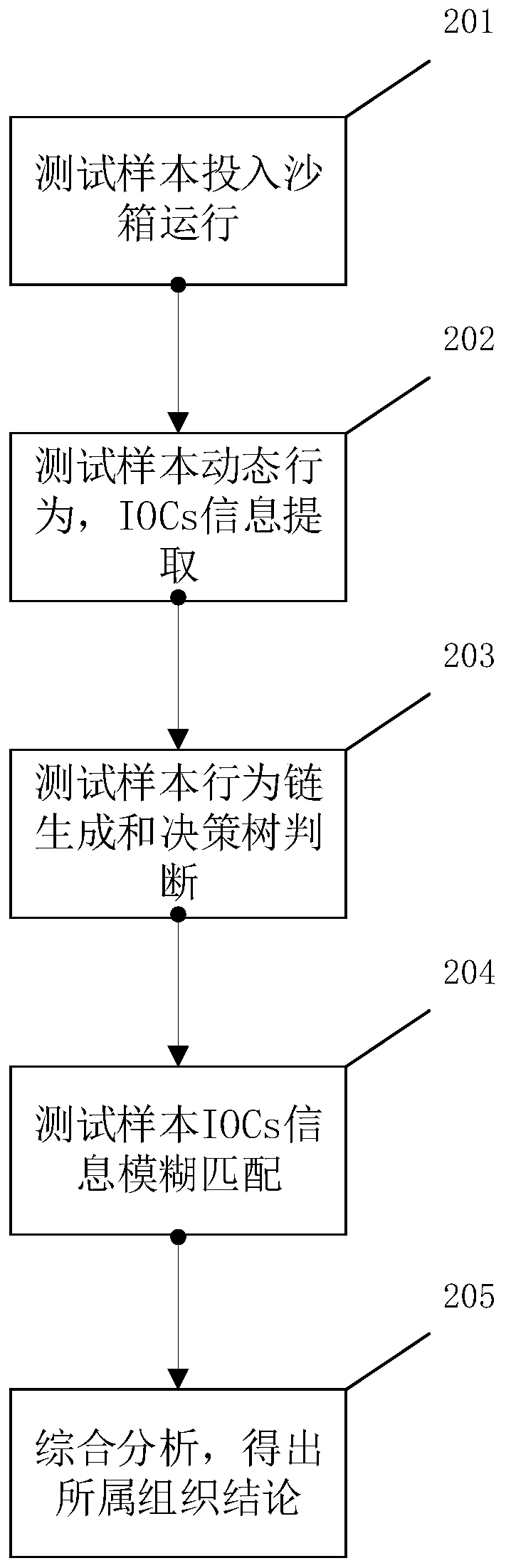
ActiveCN110222715AEfficient and accurate homology analysisSolve one-on-one situationsCharacter and pattern recognitionTransmissionSingle sampleData set
The invention provides a sample homology analysis method based on a dynamic behavior chain and dynamic characteristics. The method comprises the following steps: 1, collecting and sorting attack samples; 2, classifying the training sample set; 3, putting the training sample set into a sandbox for operation; 4, sorting the samples to generate a dynamic behavior chain; 5, training a homologous analysis decision tree model by using a behavior chain extracted from the training data set; 6, extracting a behavior chain and sample IOCs information; 7, enabling the test data set to judge the APT organization to which the test data set belongs or the malicious family and type to which the test data set belongs through the decision tree model; 8, subjecting the test data set to fuzzy matching with IOCs information through a knowledge base, and obtaining homologous information; 9, obtaining a final homologous analysis conclusion. According to the method, the effect of carrying out sample homologous analysis based on the dynamic behavior chain and the dynamic characteristics on the malicious samples starting from the dynamic behavior is achieved, and the practical problems of single sample characteristic, low manual analysis efficiency, high investment and the like caused by a traditional homologous analysis means are solved.
Owner:NAT COMP NETWORK & INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT CENT
Aspergillus niger inulin endopeptidase gene and recombinant Pichia strain for expressing same
The invention concerns aspergillus niger 9891 CGMCC NOú‘0991, which produces alantin endonuclease, and clones alantin endonuclease gene. The result of target gene fragment sequence analysis indicates that open reading frame of gene not containing signal peptide is 1485bp, and codes 509 amino acid, the said protein molecular weight is 55.9KD. The homolog of said gene with counterpart of aspergillus niger (Ohtak.et alú¼ 1998)and Aspergillus ficuum(Uhmú¼t.ú¼et alú¼1998) are respectively 92úÑ and 95úÑ. The alantin endonuclease gene is inserted into Pichia pastoris expression vector, thus recombinant of transformed Pichia pastoris is obtained. The said gene expresses in Pichia pastoris, and expressed product has its function. The expression amount of good recombinant I3-50 is 84 times higher than alantin endonuclease of initial strain. Recombinant yeast is induced and fermented. The analysis about recombinant enzyme shows that its optimum PH is 5.5ú¼ and optimum reaction temperature is 55íµ..
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES +1
Intelligent forecast model construction technology of fist class protein secondary structure
InactiveCN101408911AEnsure optimizationEnsuring Prediction AccuracySpecial data processing applicationsFistProtein secondary structure
The invention discloses a technology for constructing an intelligent prediction model of a protein secondary structure, and the model is integrated by a structural model with multi-layer recursive and stepwise refinement. The model CPM fuses an inventive KAAPRO method, a novel homologous analysis method, an improved SVM method and the like. The CPM breaks through the technical route of the traditional single physical and chemical attribute analysis or a single structural sequence analysis, and adopts a preferred route by combining the structural sequence analysis and the physical and chemical attribute analysis to ensure the optimization of the whole model good prediction precision and better universality. The CPM is mined by a high-starting-point alpha / beta base and goes through domain knowledge and background knowledge; and the CPM can better predict the secondary structure of a meta-alpha / beta protein and has the highest precision of 86% (the highest precision of the similar type is 81%).
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
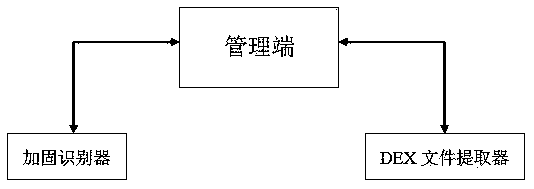
Universal automatic DEX shelling method and system
InactiveCN107742078ARealize unpackingEfficient identificationDecompilation/disassemblyReverse engineeringSoftware engineeringData reorganization
The invention relates to the technical field of Android application reinforcement protection and the technical field of DEX shelling, and aims at providing a universal automatic DEX shelling method and system. According to the method and system, shelling codes are inserted into a portable interpreter of an Android Dalvik virtual machine. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: comparing all the classes in an Android Manifest.xml configuration file and all the classes obtained through decompilation by utilizing contrastive analysis so as to judge whether an application is reinforced, and recognizing a reinforcement service used by the application through homology analysis; and taking Man Activity of the application as a DEX shelling starting mark, recovering real byte codes of the application, extracting recovered real data and finally recombining the data into a new DEX file, wherein the recombination process refers to modification of corresponding pointers. The system is good in universality, can bypass all the Anti-debugging protection technologies, and can extract original DEX files of reinforced applications without carrying out manual analysis and understanding reinforcement strategies of reinforcement services in the shelling process. The invention provides a new solution for automatic DEX shelling of reinforced applications.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
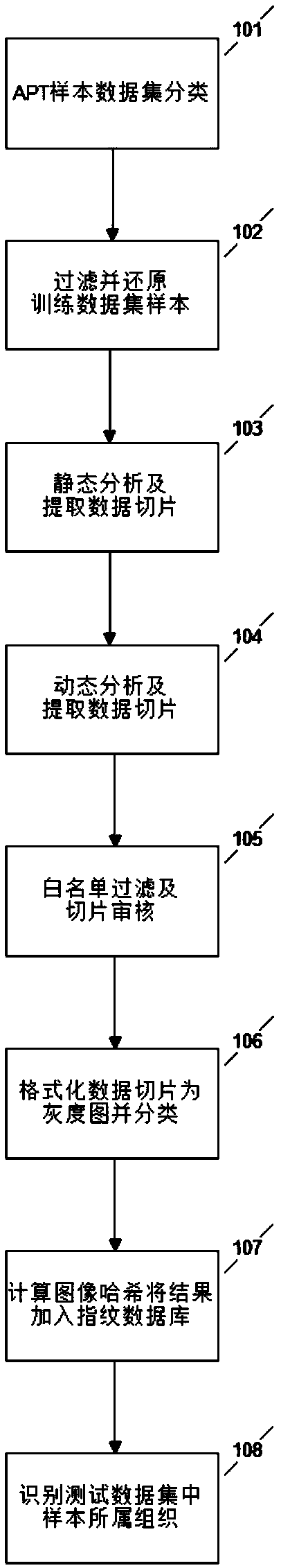
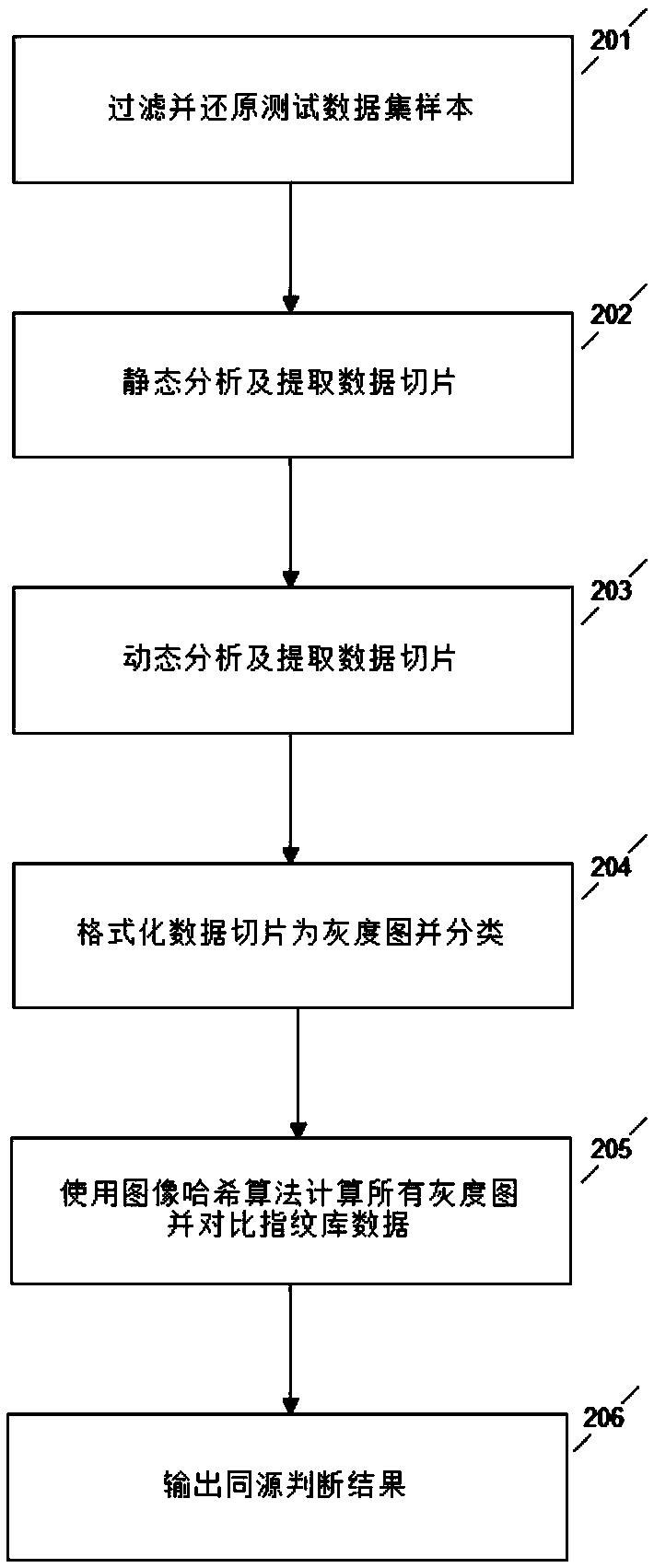
Sample homology analysis method based on data slice and image hash combination
ActiveCN109190657ATimely identificationReduce false alarm rateCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionData set
The invention provides a sample homology analysis method based on data slice and image hash combination, which comprises the following steps: 1, collecting a malicious sample of known APT organization; 2, filtering and restoring the sample of that training data set; 3, carrying out static analysis on that sample and extracting data slice; 4, dynamically analyzing samples and other training data sets, and extracting data slices; 5, filtering the white list data slices and manually reviewing and arranging the slice format for all the data slices; 6, formatting all data slices into grayscale image form and classify according to functions; 7, calculating all gray images and classify and storing that calculated results to a fingerprint database; 8, testing organization of the sample in the testdataset. Through the above steps, a sample homology analysis method based on data slice and image hash combination is realized, the labor and time cost are reduced, and the problem of lag and highlydependent on manual analysis in the existing APT homology sample analysis is solved.
Owner:NAT COMP NETWORK & INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT CENT
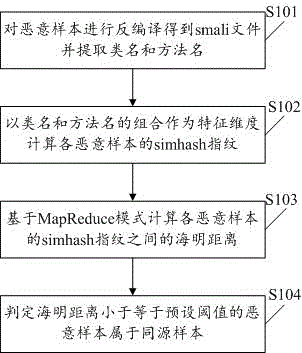
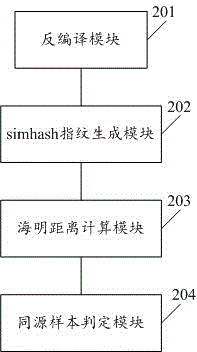
Method and system for judging homology of massive malicious samples
InactiveCN105989287AImprove accuracyShorten the timePlatform integrity maintainanceSoftware engineeringHomology analysis
The invention discloses a method and system for judging homology of massive malicious samples. The method comprises the following steps: decompiling the malicious samples to obtain smali files and extracting class names and method names; calculating simhash fingerprints of the malicious samples by taking a combination of the class names and the method names as a characteristic dimensionality; calculating Hamming distances between the simhash fingerprints of the malicious samples on the basis of a MapReduce mode; and determining the malicious samples, the Hamming distances of which are less than or equal to a preset threshold value, as homological samples, wherein the class names are names of abstract objects in program codes and the method names are function names contained in the abstract objects in the program codes. According to the method and system disclosed in the invention, homology analysis can be carried out on massive samples, so that the processing time is shortened, and the correctness of homology judgement is improved.
Owner:WUHAN ANTIY MOBILE SECURITY
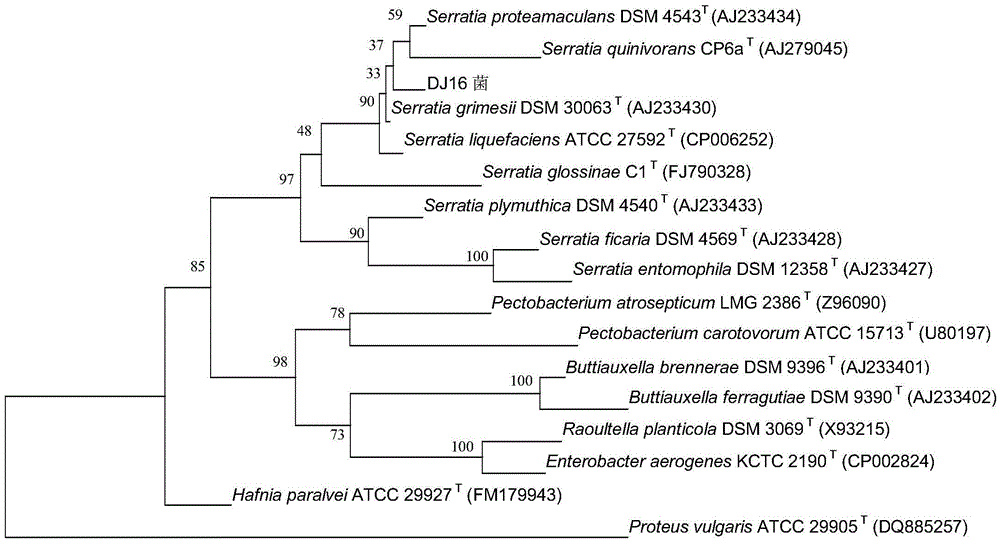
Tolerant serratia grimesii for enriching heavy metals and application of serratia grimesii
InactiveCN104560796ASignificant progressNon-pathogenicBacteriaWater contaminantsSerratiaSequence analysis
The invention discloses tolerant serratia grimesii for enriching heavy metals and an application of the serratia grimesii. Bacterium is subjected to 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis to obtain a gene nucleotide sequence of the 16S rRNA as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table. By homology analysis, the strain is proven to belong to the serratia grimesii, named as DJ16 and preserved in China Typical Culture Collection Center on 19th Nov, 2014, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO: M 2014578. The serratia grimesii DJ16 disclosed by the invention can be used for enriching the heavy metals in soil and water.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
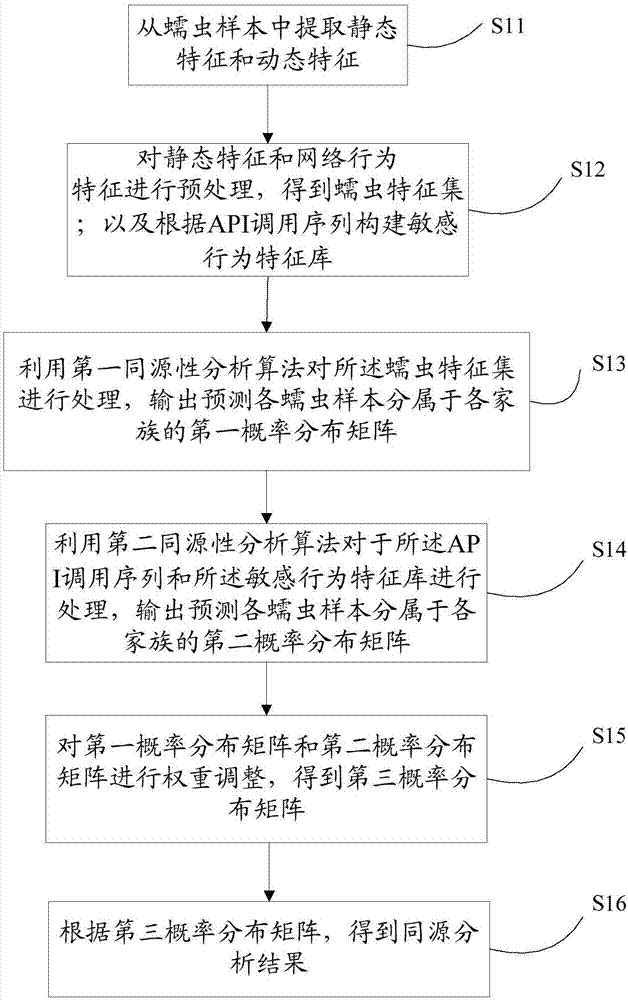
Worm homologous analysis method and device
ActiveCN107169355ASmall scaleImprove analysis efficiencyPlatform integrity maintainanceFeature setAlgorithm
The invention discloses a worm homologous analysis method and device. The method comprises the following steps of: extracting static features and dynamic features in a worm sample, wherein the dynamic features comprise network behavior features and an application programming interface API calling sequence; preprocessing the static features by utilizing the network behavior features to obtain a worm feature set; constructing a sensitive behavior feature library according to the API calling sequence; processing the worm feature set by utilizing a first homologous analysis algorithm so as to output a first probability distribution matrix; processing the API calling sequence and the sensitive behavior feature library by utilizing a second homologous analysis algorithm so as to output a second probability distribution matrix; carrying out weight adjustment on the first probability distribution matrix and the second probability distribution matrix to obtain a third probability distribution matrix; and obtaining a homologous analysis result according to the third probability distribution matrix. According to the method and device disclosed by the invention, the efficiency and correctness of the worm homologous analysis are improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
A malicious code homology analysis method based on system call control flow graph
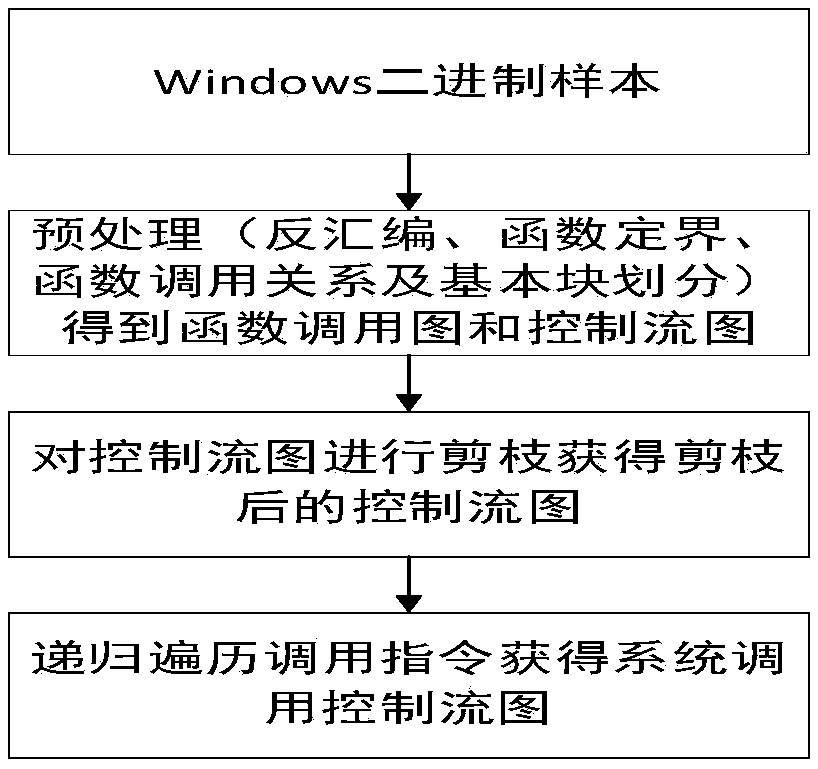
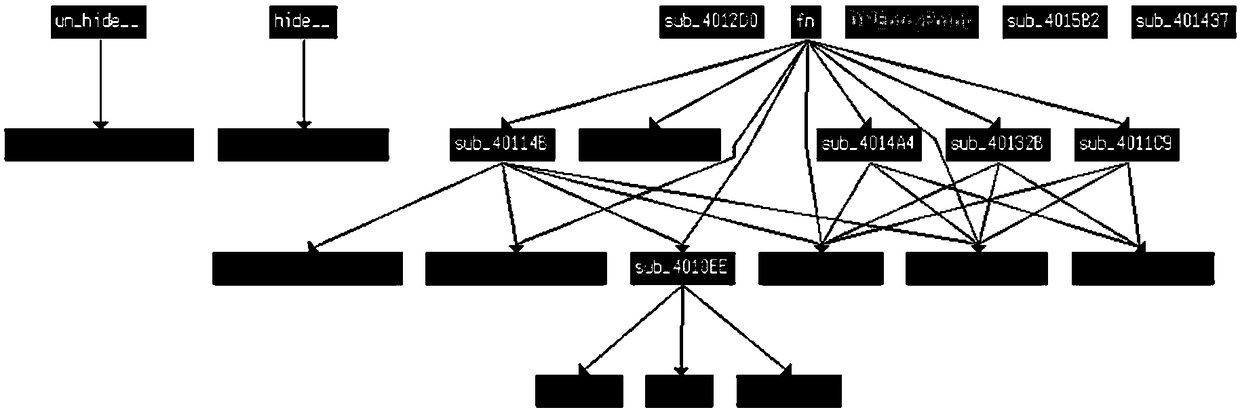
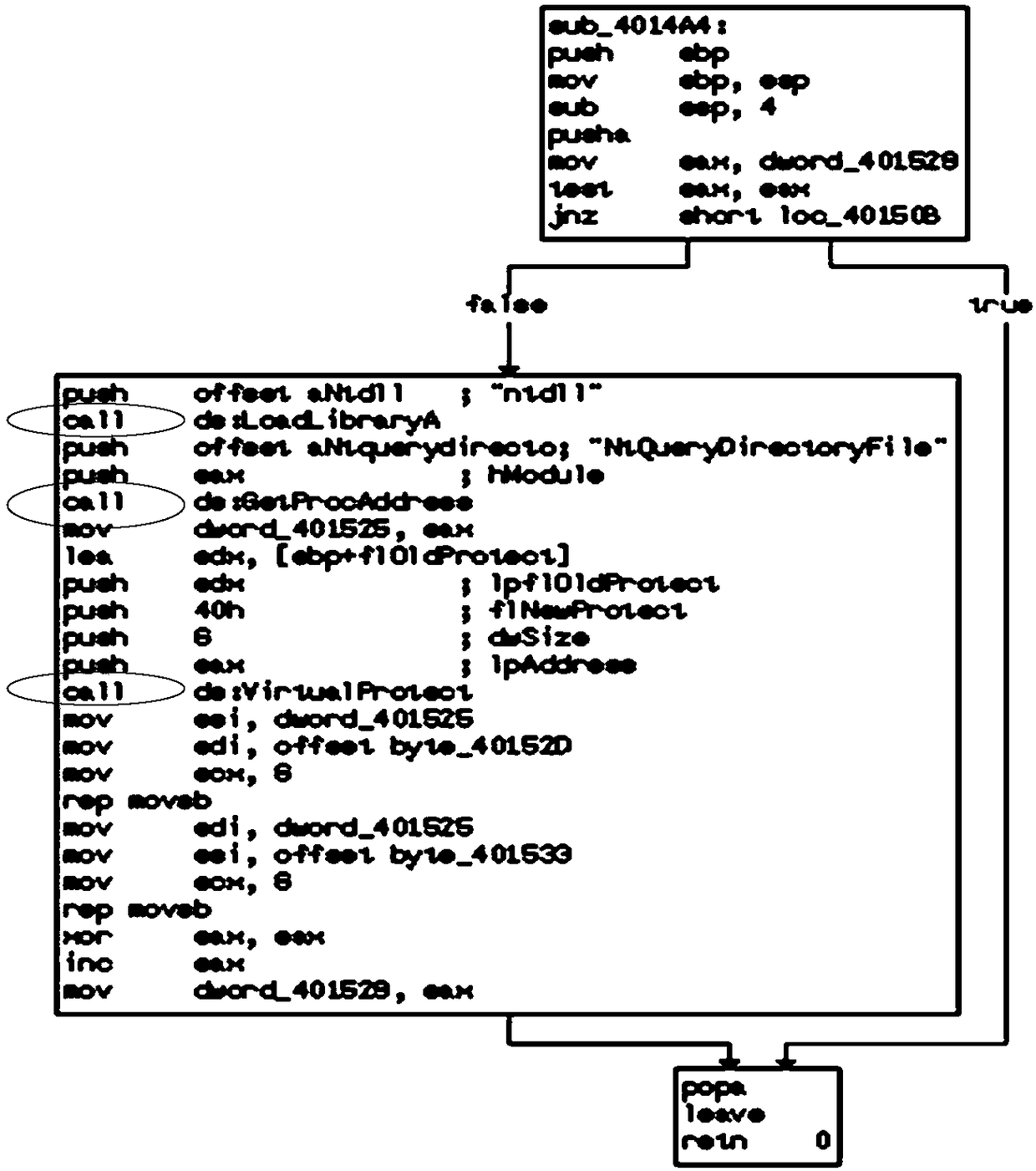
ActiveCN109101816AGood abstractionAvoid confusionPlatform integrity maintainanceControl flowSystem call
The invention discloses a malicious code homology analysis method based on a system call control flow diagram. Firstly, a system call control flow diagram of a program to be analyzed is constructed. The system call control flow graph is a directed unweighted graph composed of system call nodes, and the direction of edges indicates the order of system call execution. The system call control flow diagrams of different programs to be analyzed are compared to realize homology analysis according to the similarity of the diagrams as a similarity measure of homology analysis. The invention utilizes the system call control flow diagram to carry out homology analysis, and the system call control flow diagram completely ignores the details of the software code and only pays attention to the called system call function, thus simplifying the amount of data to be processed, and therefore, the control flow diagram based on the system call has the best abstraction degree to the program behavior. Moreover, because only system calls are considered, the confusion of instruction layer is avoided to a large extent, and the anti-confusion effect is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
Primer, probe and method for detecting respiratory infectious disease pathogen by using liquid chip
InactiveCN102181576AThe detection process is fastEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMulti analyteNucleotide
The invention discloses a primer, a probe and a method for detecting a respiratory infectious disease pathogen by using a liquid chip, which are used for detecting nine clinically common respiratory infectious disease pathogens. In the invention, the nine clinically common respiratory infectious disease pathogens are detected by a multi-analyte suspension array (MASA) liquid chip technology and are subjected to homology analysis mainly according to all nucleotide sequences of nine targeted viruses which can be searched in a gen bank; a degenerate primer and a specific probe are designed; and a polymerase chain reaction (PRC) and molecular hybridization are performed for two times, and then a Luminex 100 system is used for detection, so that the types of the pathogens in a sample are determined. The detection and early diagnosis of the nine clinically common respiratory infectious disease pathogens provided by the invention are extremely significant in the aspect of preventing diseasesfrom propagating by correct treatment schemes and timely responding measures. The primer, the probe and the method have the advantages of high detection speed, high sensitivity, high specificity and the like, are easy to operate and are suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Isolated culture method and use of Streptomycete from sea
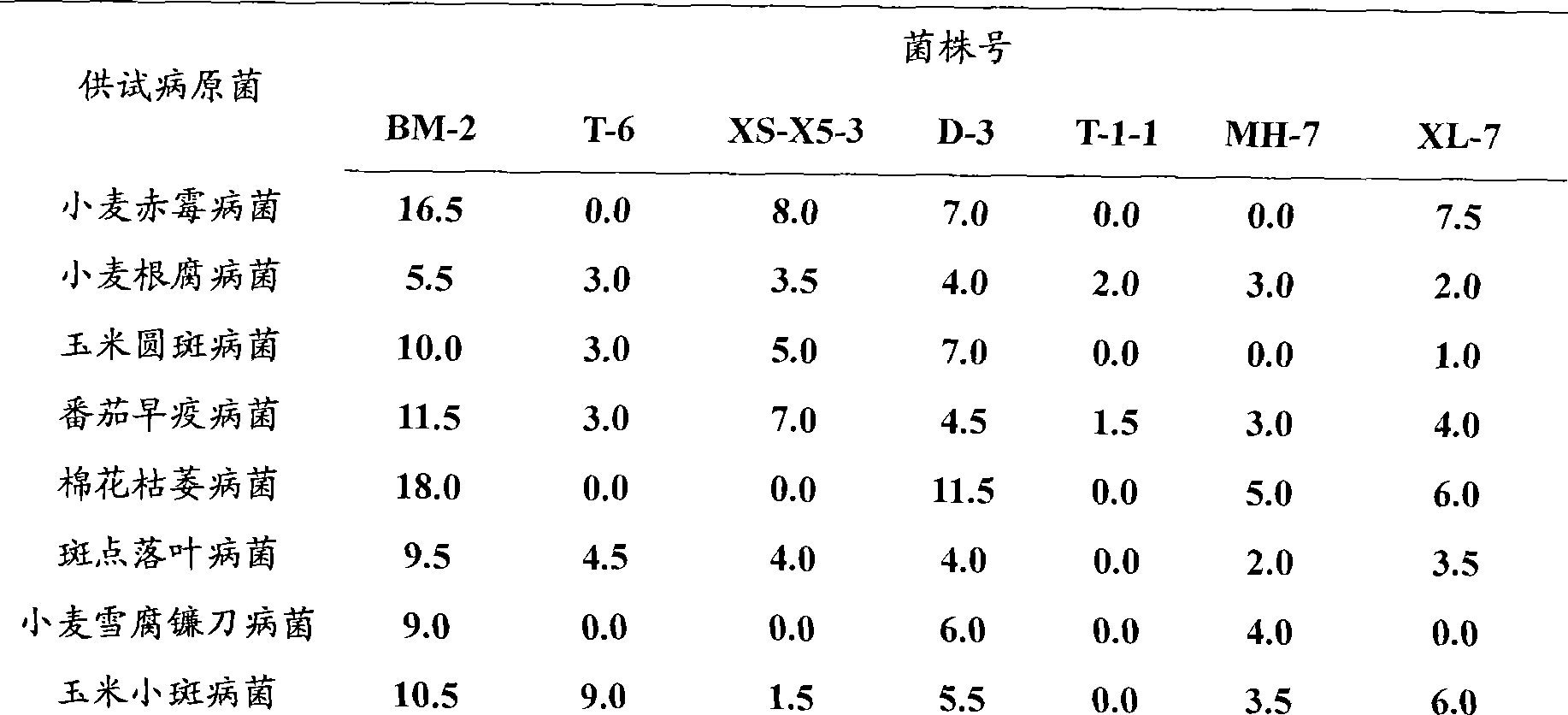
The invention relates to a separation culture method of BM-2 (Streptomyces sp.BM-2) from sea, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps of accumulation culture, thalli separation and purification, strain screening, strain identification, and the like. According to the test results of morphology, physiology and biochemistry, and the analysis of the homology of 16SrDNA, separated and cultured stains are BM-2(Streptomyces sp. BM-2). The BM-2(Streptomyces sp. BM-2) has the function of inhibiting various plant pathogenic fungi, colon bacillus, bacillus subtilis and aeromonas hydrophila.
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH
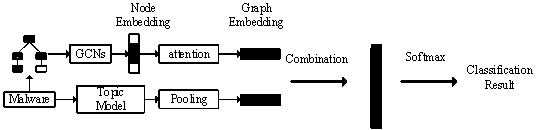
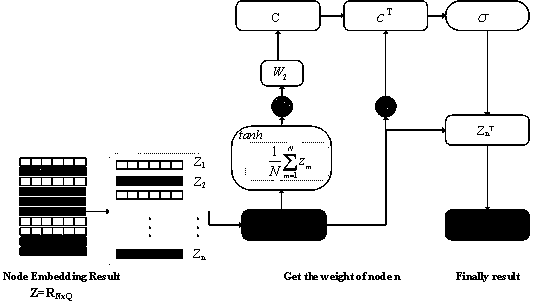
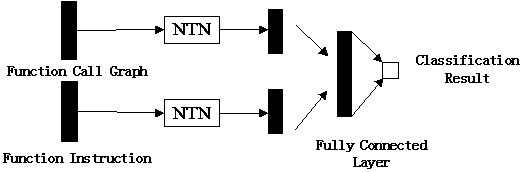
Malicious code homology analysis method based on graph convolution network and topic model
The invention provides a malicious code homology analysis method based on a graph convolution network and a topic model. According to the method, two static features are extracted from malicious codesto form mixed features, an attention mechanism and a topic model are used for carrying out weighting processing on key features, and then a normalized classification model is used for classifying thekey features. The method mainly comprises the following steps: (1) extracting a function call graph and function instruction distribution characteristics of malicious codes by utilizing IDA; (2) performing node embedding on the function call graph by using an improved graph convolution network; (3) performing graph embedding operation on node embedding by using an attention mechanism; (4) performing dimensionality reduction and transformation on function instruction distribution by using a semi-supervised topic model; (4) combining the mixed features by using a neural tensor network; and (5)carrying out family classification on the malicious software by utilizing the normalized classification model.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
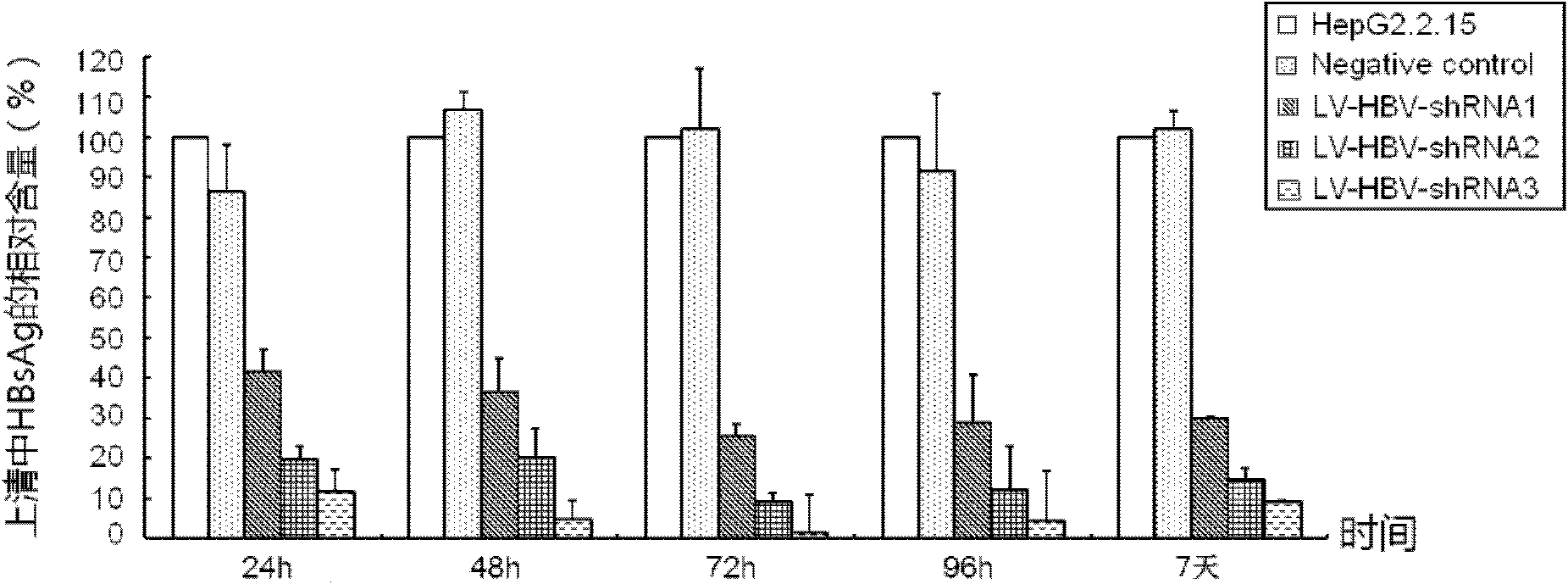
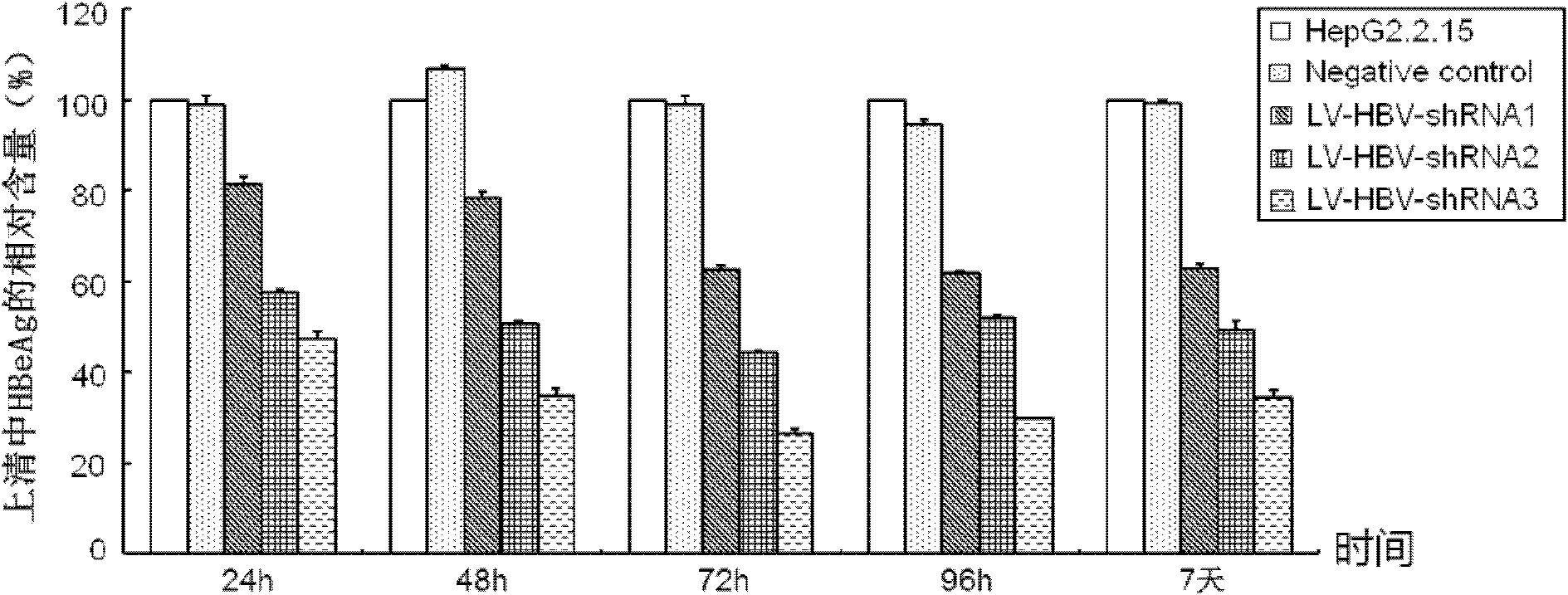
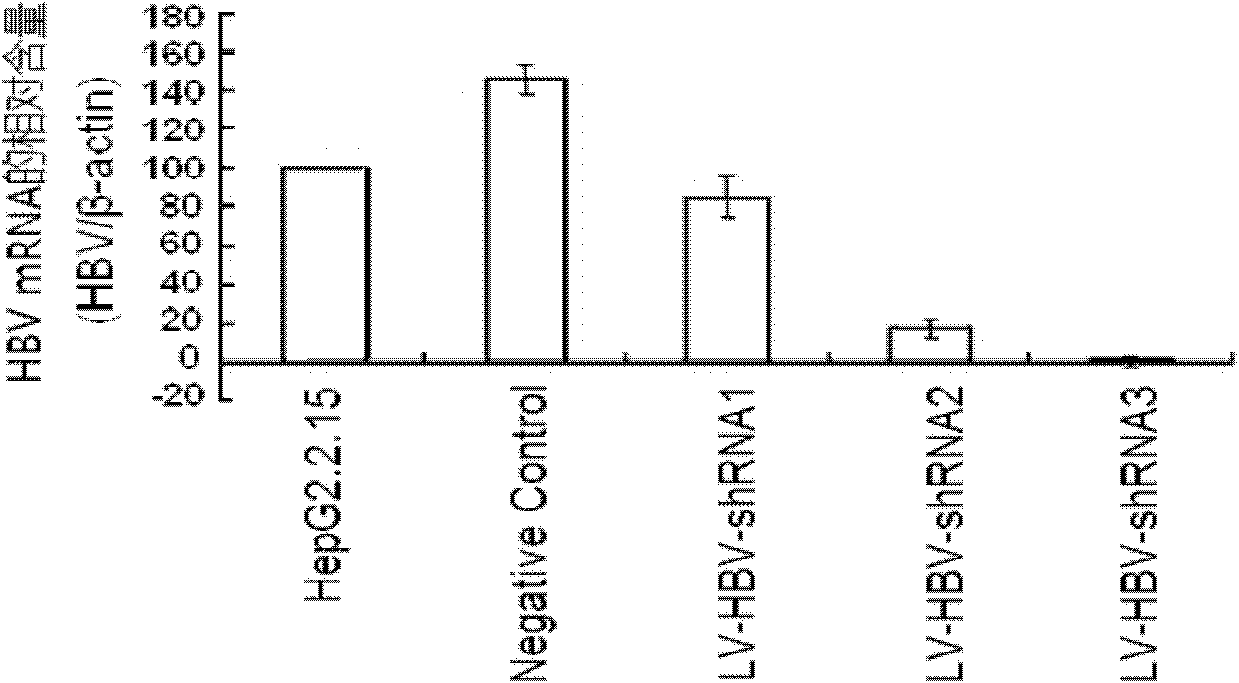
Mediating method of RNAi (ribonucleic acid interference) utilizing lentiviral vector
InactiveCN102206645AStrong inhibition of replicationStrong inhibition of expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationControl systemNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to a mediating method of RNAi (ribonucleic acid interference) utilizing a lentiviral vector. The method comprises the following specific steps of: firstly carrying out homology analysis on the nucleic acid sequence of relevant viruses to find out conserved regions and designing siRNA (small interfering ribonucleic acid) corresponding to the conserved regions of the related viruses; and cloning the siRNA to an expression plasmid pLVTH, then co-transfecting 293T cells together with pCMV-dR8.91 and pMD2.G, collecting the supernatant of the transfected cells, carrying out ultracentrifugation, purification and concentration to obtain a high-titer lentiviral vector expressing the siRNA, then carrying out cotransduction into target cells together with LV-tTR-KRAB, and strictly controlling the acting time and dose of siRNA drugs utilizing tetracycline analogue DOX. Because of high transduction rate and a stringent control system, the mediating method can actually evaluate the in-vivo antiviral action of the siRNA and can track the whole process of drug interference action, thus having clinical application prospects.
Owner:成都康珞生物科技有限公司
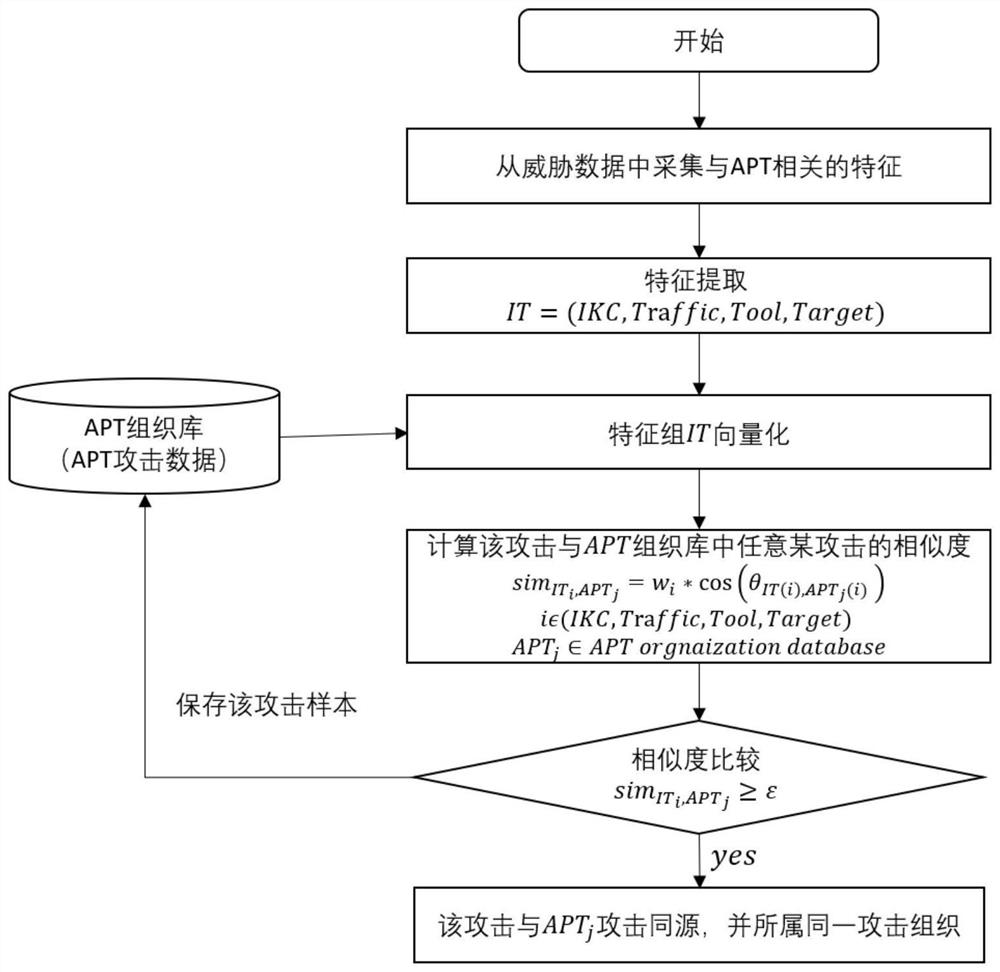
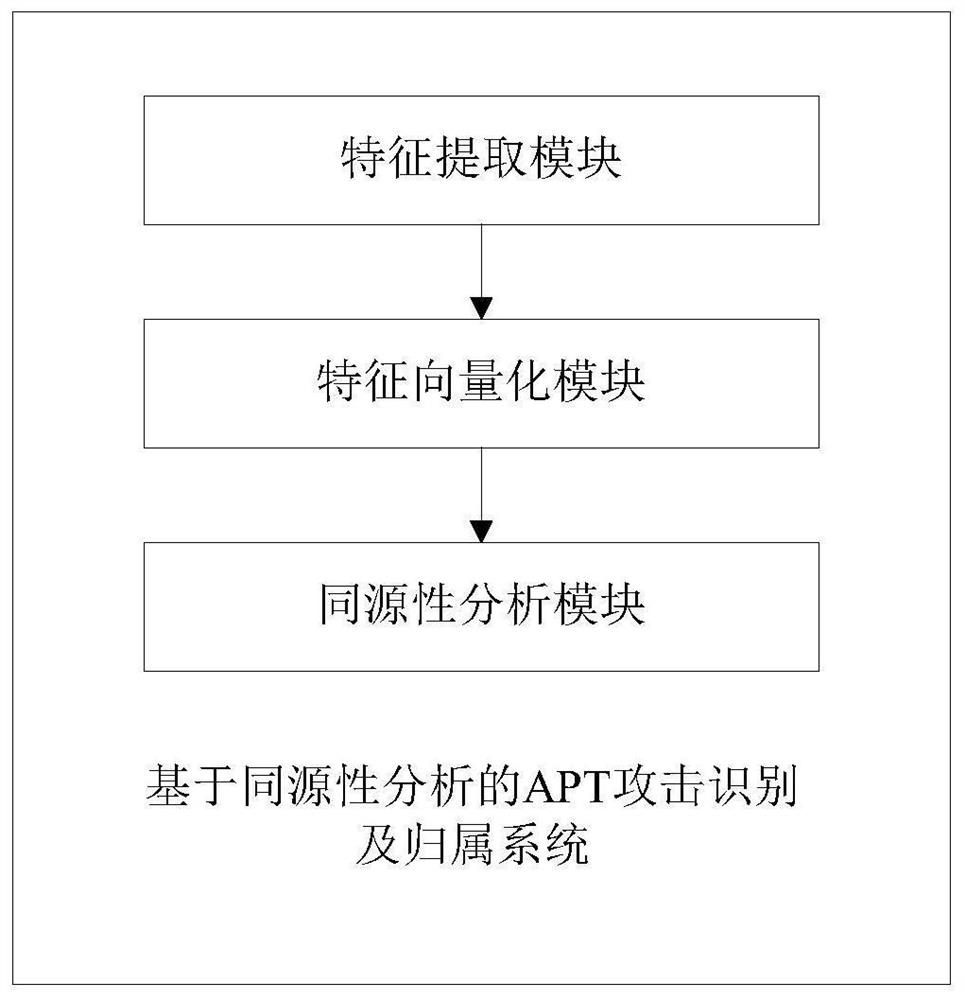
APT attack identification and affiliation method and system based on homology analysis, and storage medium
The invention discloses an APT attack identification and affiliation method and system based on homology analysis, and a storage medium, and the method comprises the following steps: collecting attackdata related to APT from monitored threat data, and extracting feature element values in each set in a defined APT quaternion feature group; carrying out feature vectorization on any existing APT attack feature tuples in a certain APT organization library; and calculating similarity of the feature vectors of the two groups of attacks, discovering a relationship between the attack and the selectedAPT attack and an organization to which the attack belongs, and storing an attack sample into an APT organization library. According to the method, the IKC attack chain and other features capable ofdistinguishing APT organizations are fused to form the multi-dimensional feature set, similarity calculation is carried out in combination with the weights, APT attack events can be effectively detected, similar APT attacks can be found based on a known APT organization library, and attack scene construction and attacker tracking are facilitated. The APT attack organization of subsequent events iseffectively identified.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY
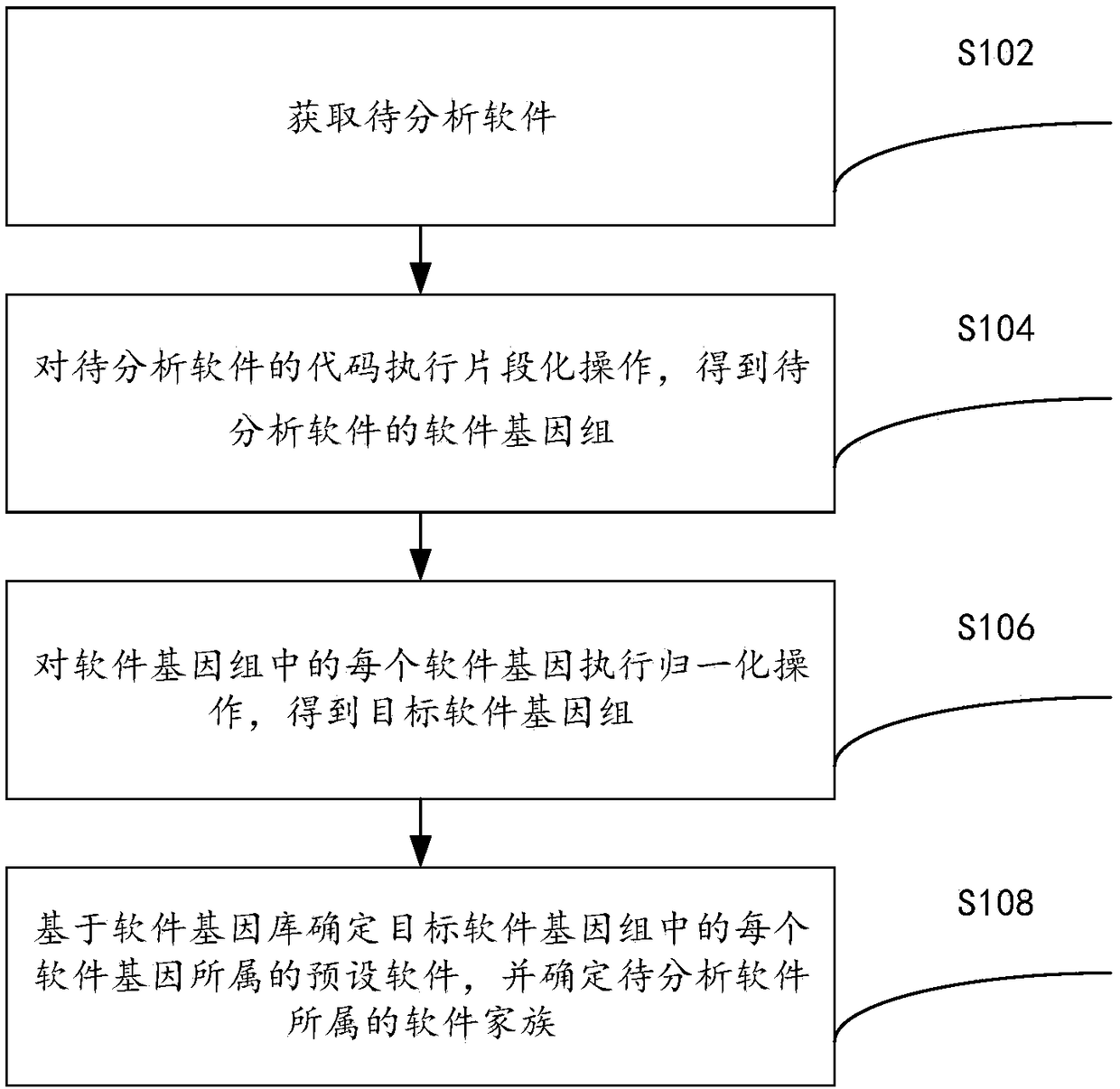
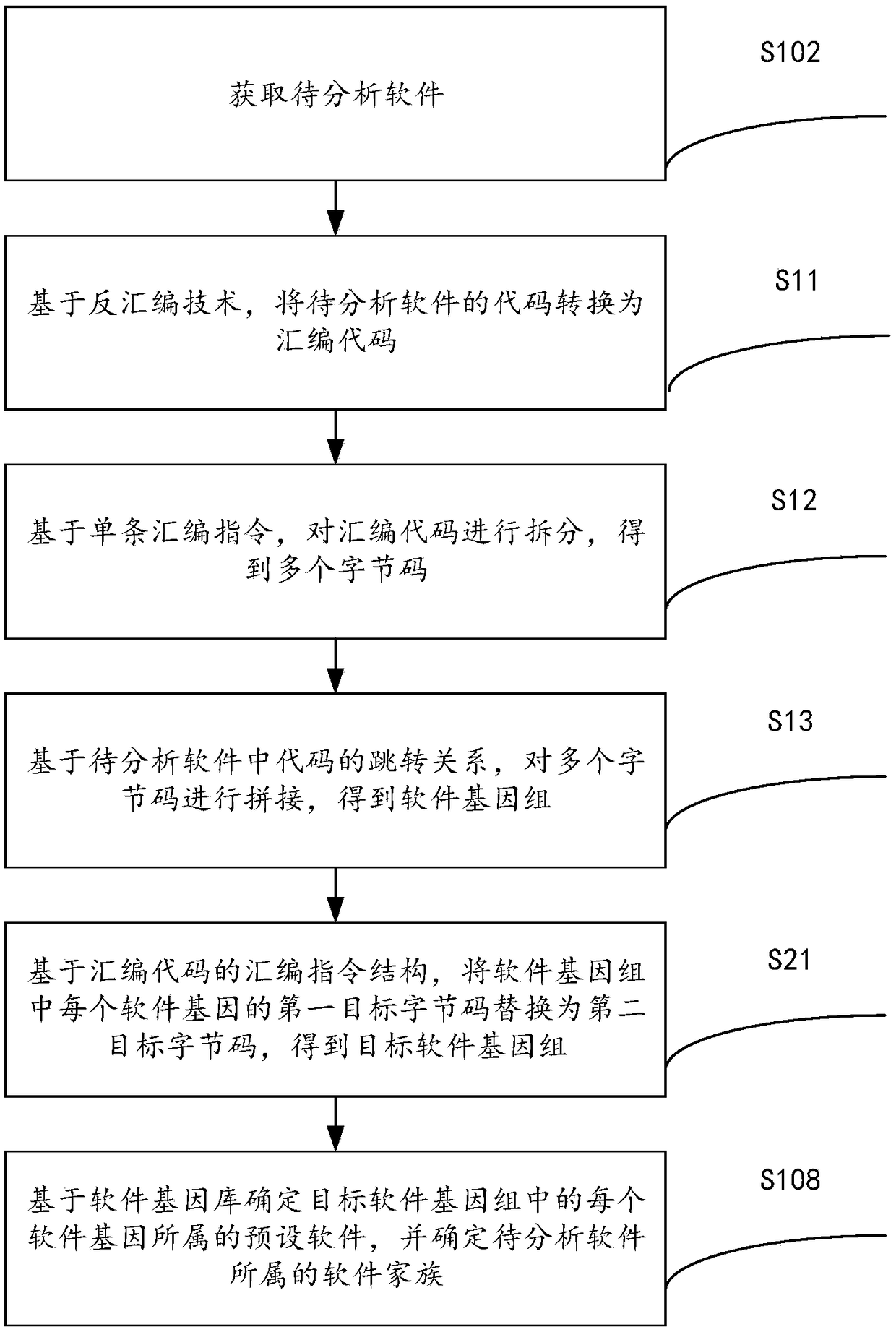
Software homology analysis method and a software homology analysis device based on software genes
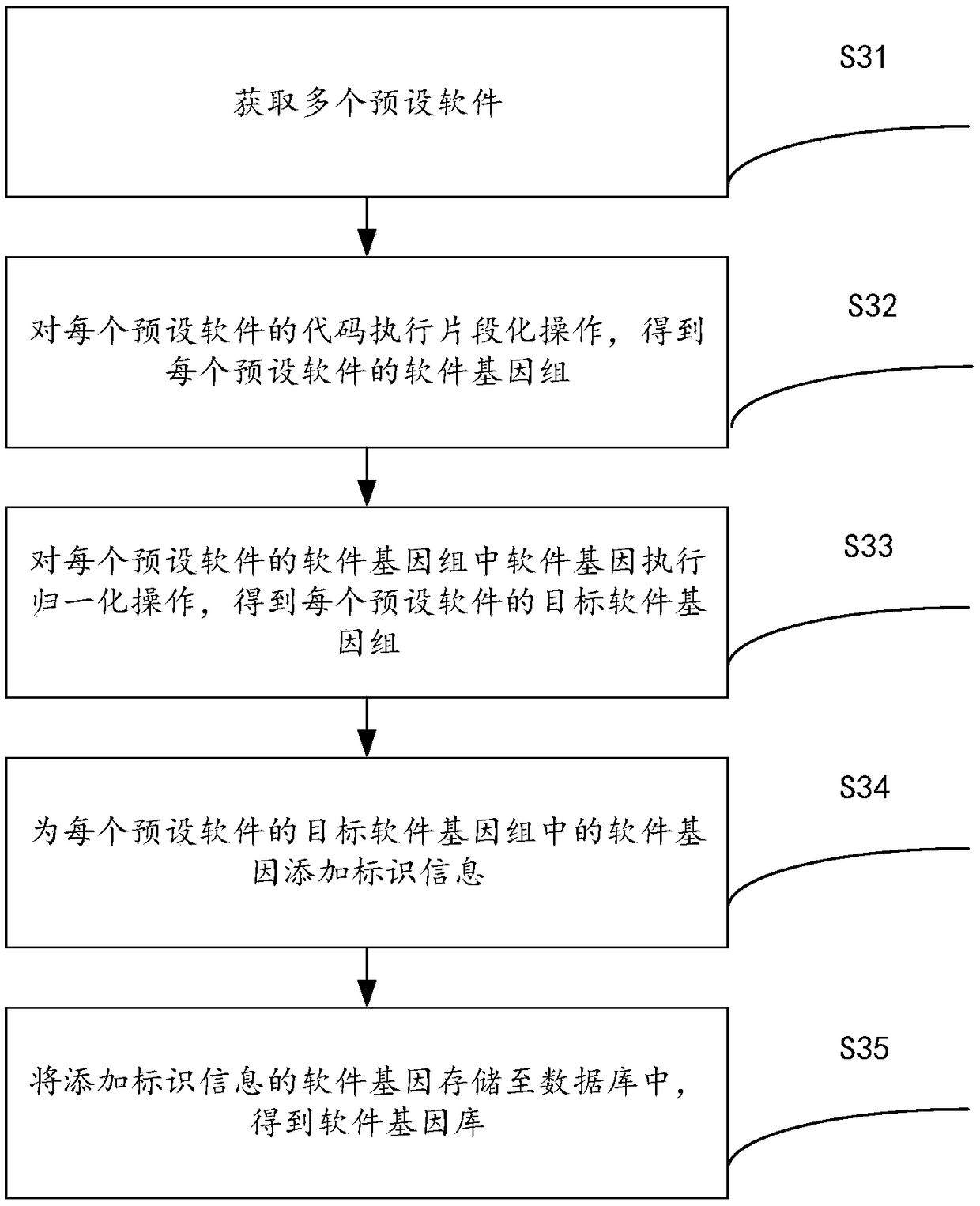
InactiveCN109508546ASolve technical problems with low accuracyImprove accuracyReverse engineeringPlatform integrity maintainanceSoftware engineeringHomology analysis
The invention provides a software homology analysis method and a software homology analysis device based on software genes, which relate to the technical field of network security. The method comprises the following steps: Executing fragmentation operation on the code of the software to be analyzed to obtain the software genome of the software to be analyzed; Performing normalization operation oneach software gene in the software genome to obtain a target software genome; determining The preset software to which each software gene belongs in the target software genome based on the software gene library, and determine the software family to which the software to be analyzed belongs, wherein the software gene database comprises software genes of each preset software and identification information of each software gene, adopting The identification information to characterize the preset software to which the software gene belongs and the software family to which the preset software to which the software gene belongs, which solves the technical problem that the existing software homology analysis method has low accuracy in determining the software family to which the software to be analyzed belongs.
Owner:HANGZHOU ANHENG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Primers, probes and method for detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosis drug-resistant gene mutation sites
ActiveCN105603084AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPectobacteriumGene mutation
The invention relates to primers, probes and a method for liquid-phase chip detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis drug-resistant gene mutation sites. The primers, probes and method are used for detecting drug-resistant gene mutation sites in Mycobacterium tuberculosis for drugs isoniazide, rifampicin and fonoquantel. The isoniazide drug-resistant mutation sites are positioned in katG gene and inhA gene; the rifampicin drug-resistant mutation sites are positioned in rpoB gene; and the fonoquantel drug-resistant mutation sites are positioned in gyrA gene. The method comprises the following steps: respectively carrying out homology analysis according to the nucleotide sequences of the four drug-resistance related genes in the gene bank, designing the primers and probes, carrying out PCR (polymerase chain reaction) twice, carrying out molecular hybridization, and carrying out detection by using a Luminex200 system, thereby determining whether the sample contains the drug-resistant mutation sites. The detection of drug-resistant gene mutation sites is of crucial importance for treating Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by adopting correct therapeutic schedules. The primers, probes and method have the advantages of high detection speed, high sensitivity, high specificity and the like, are simple to operate, and are beneficial to popularization and application.
Owner:HAINAN MEDICAL COLLEGE +1
Agapanthus praecox gibberellin receptor APGID1b protein, and encoding gene and probe thereof
InactiveCN103342741AImprove viewing valueMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiologyAmino acid
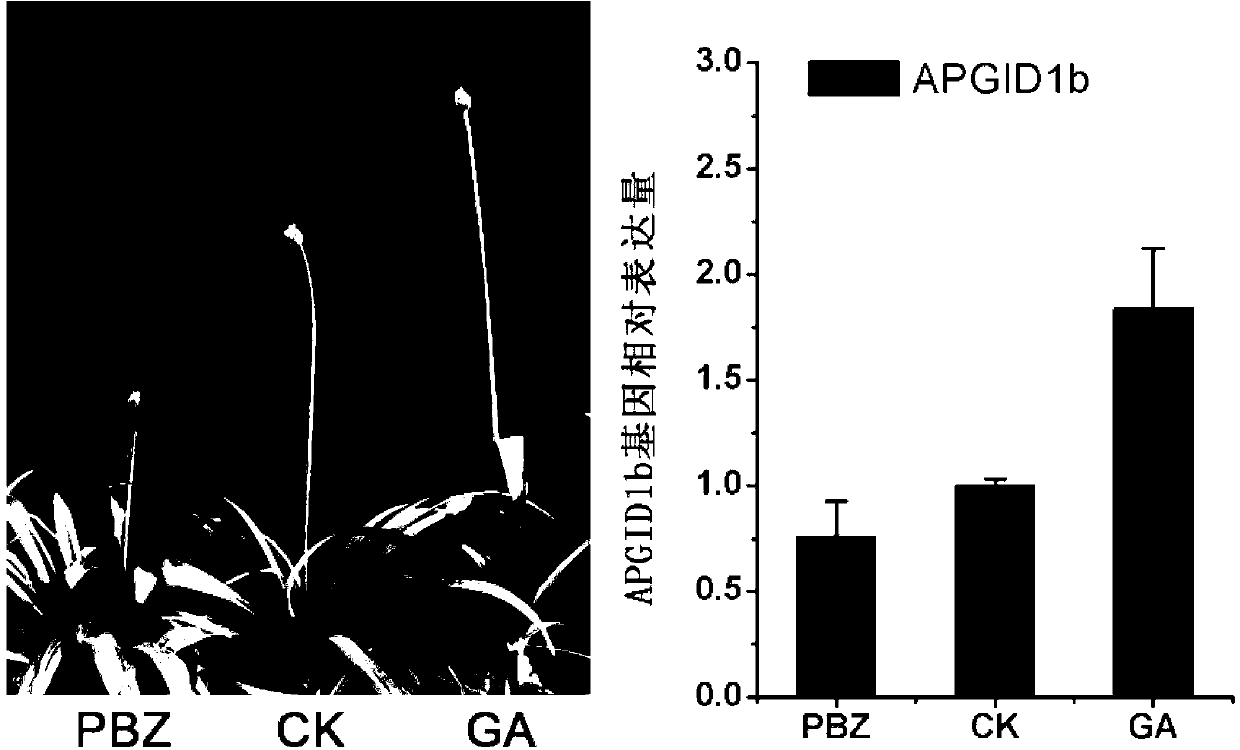
The invention relates to an agapanthus praecox gibberellin receptor APGID1b protein, and an encoding gene and a probe thereof. The protein is the following protein of (a) or (b): (a) a protein composed by an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2; and (b) a protein derived from the protein of (a), having agapanthus praecox gibberellin receptor activity, and composed by a sequence obtained by substituting, deleting or adding one or a plurality of amino acids of the amino acid sequence as shown in the SEQ ID NO.2. Furthermore, the invention provides a nucleic acid sequence encoding the protein, and the detection probe. Applications comprise the following steps: amplifying to obtain a 3' end and a 5' end of an APGID1b gene by an RACE technique, carrying out gene full-length sequence splicing and homology analysis, through spatial and temporal expression mode analysis and external source regulation substance processing, analyzing different conditions of APGID1b gene expression, so as to verify gene functions. Spatial and temporal expression characteristics of the agapanthus praecox gibberellin receptor APGID1b gene are regulated by utilizing a gene engineering technology, and thus the plant height of a plant can be changed.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com