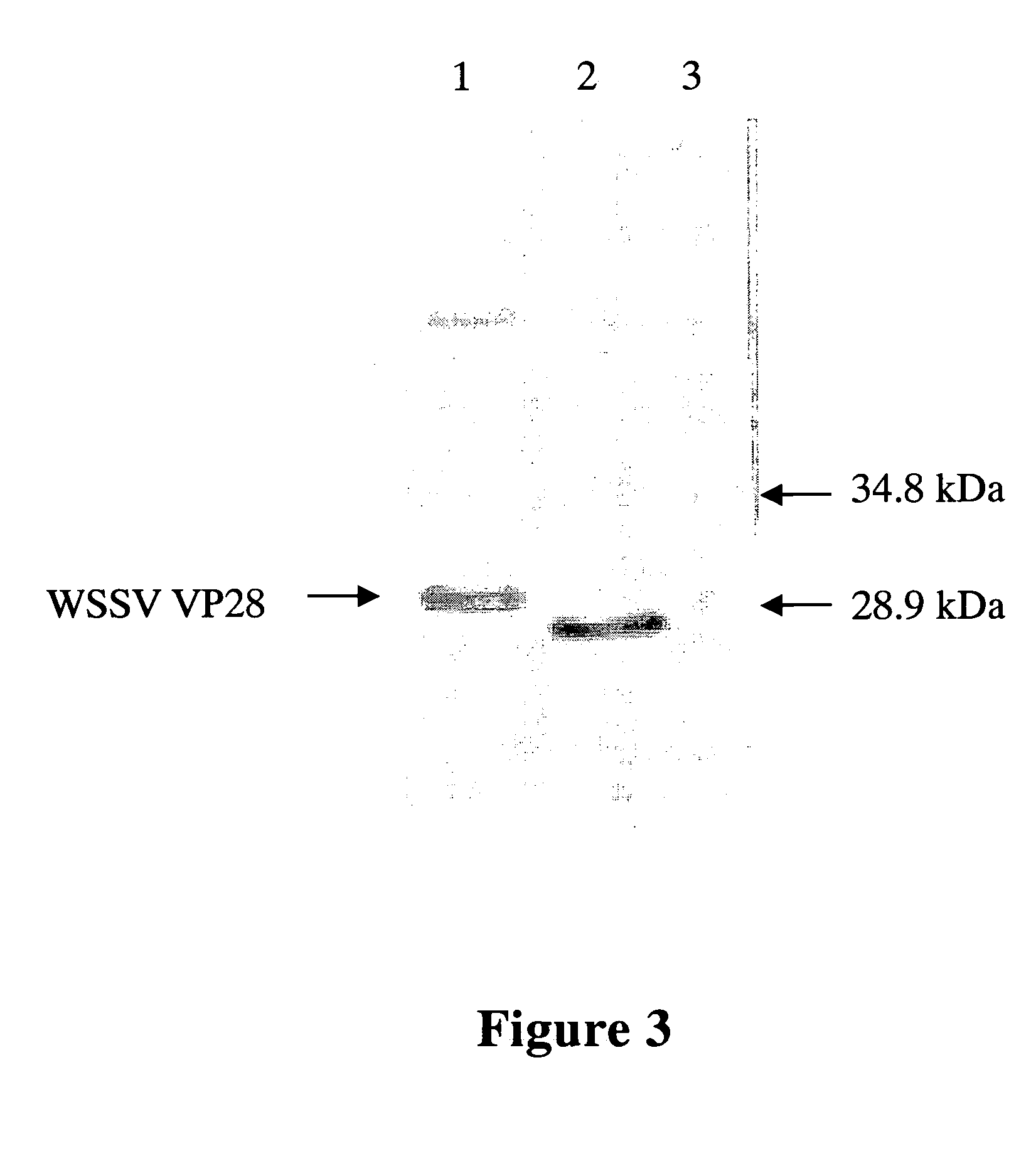
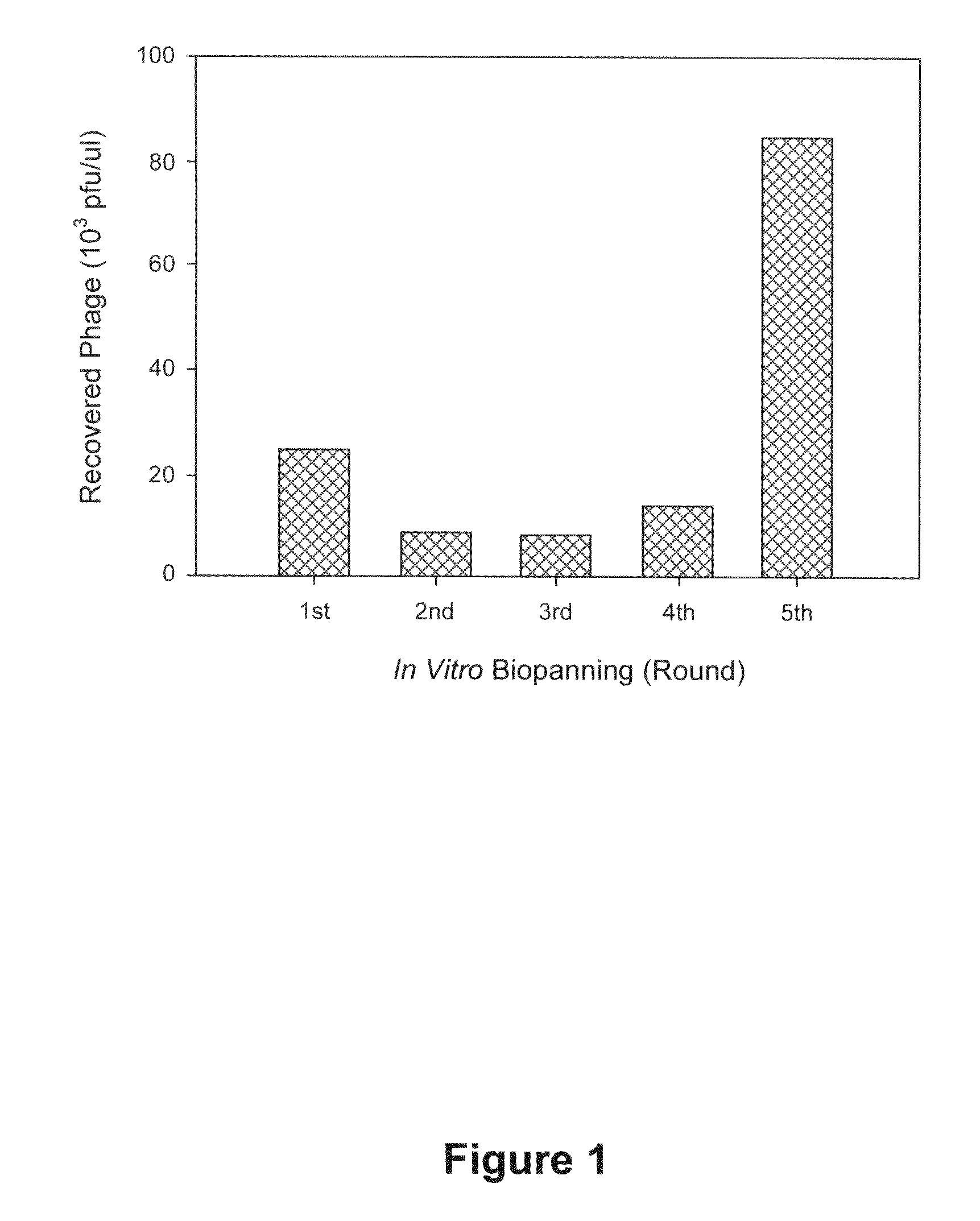
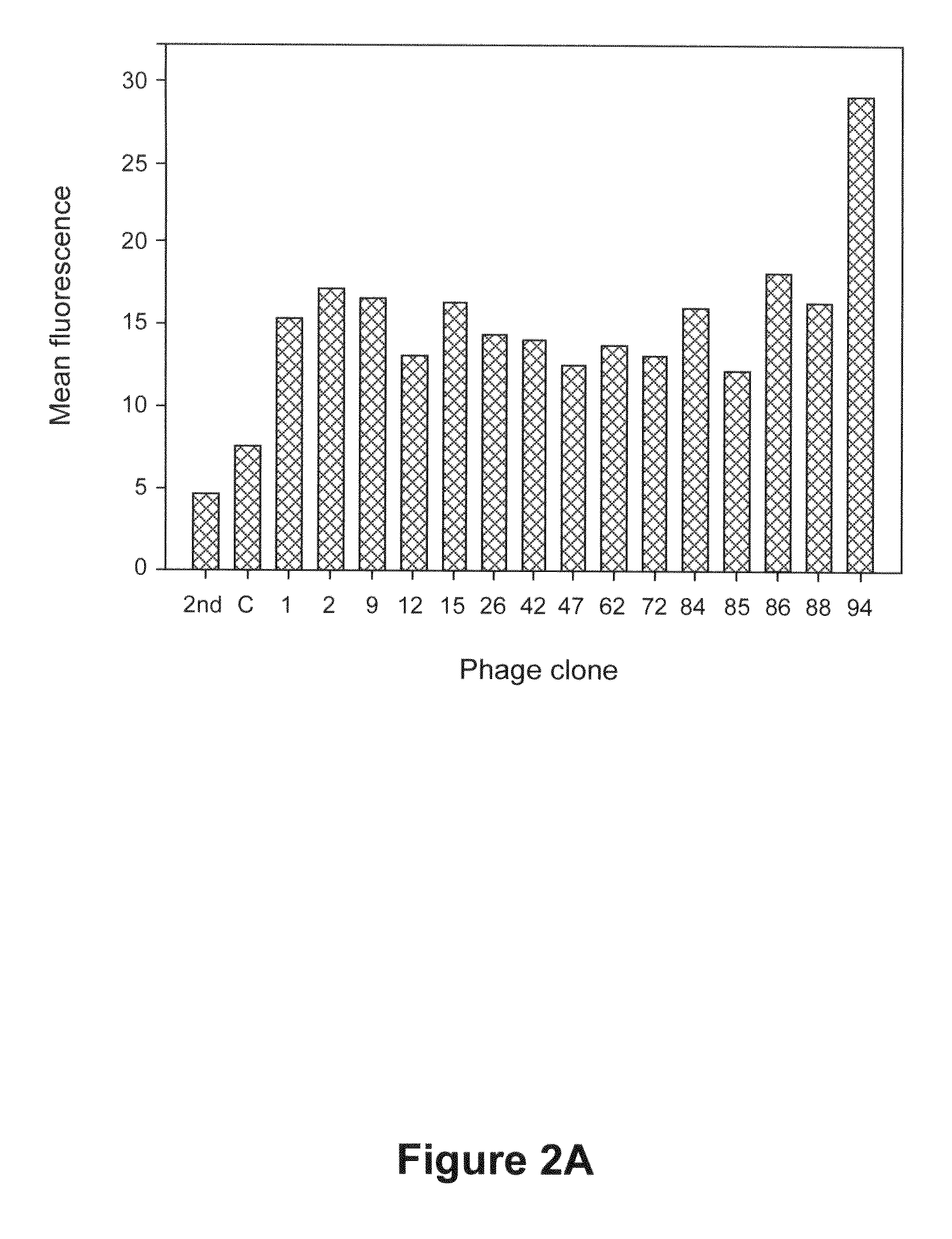
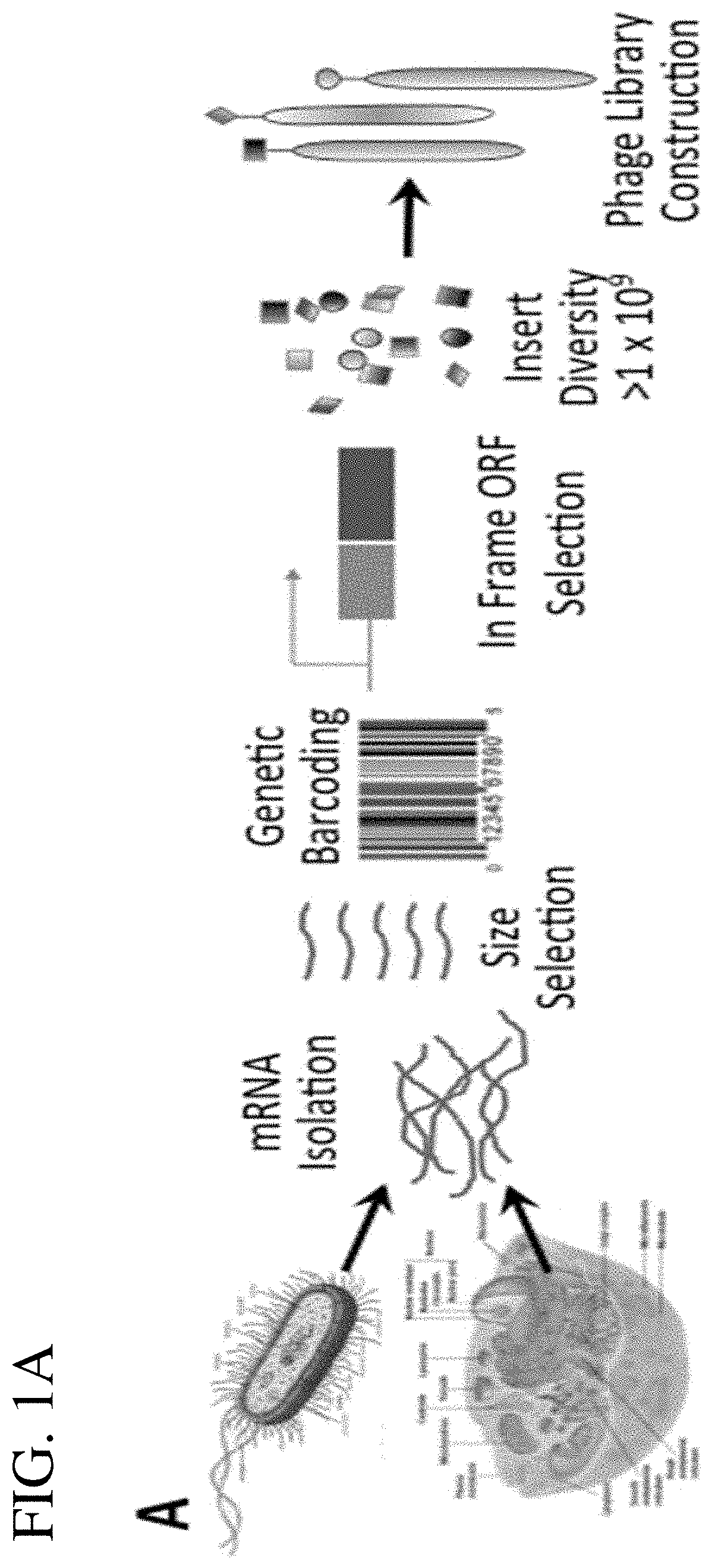
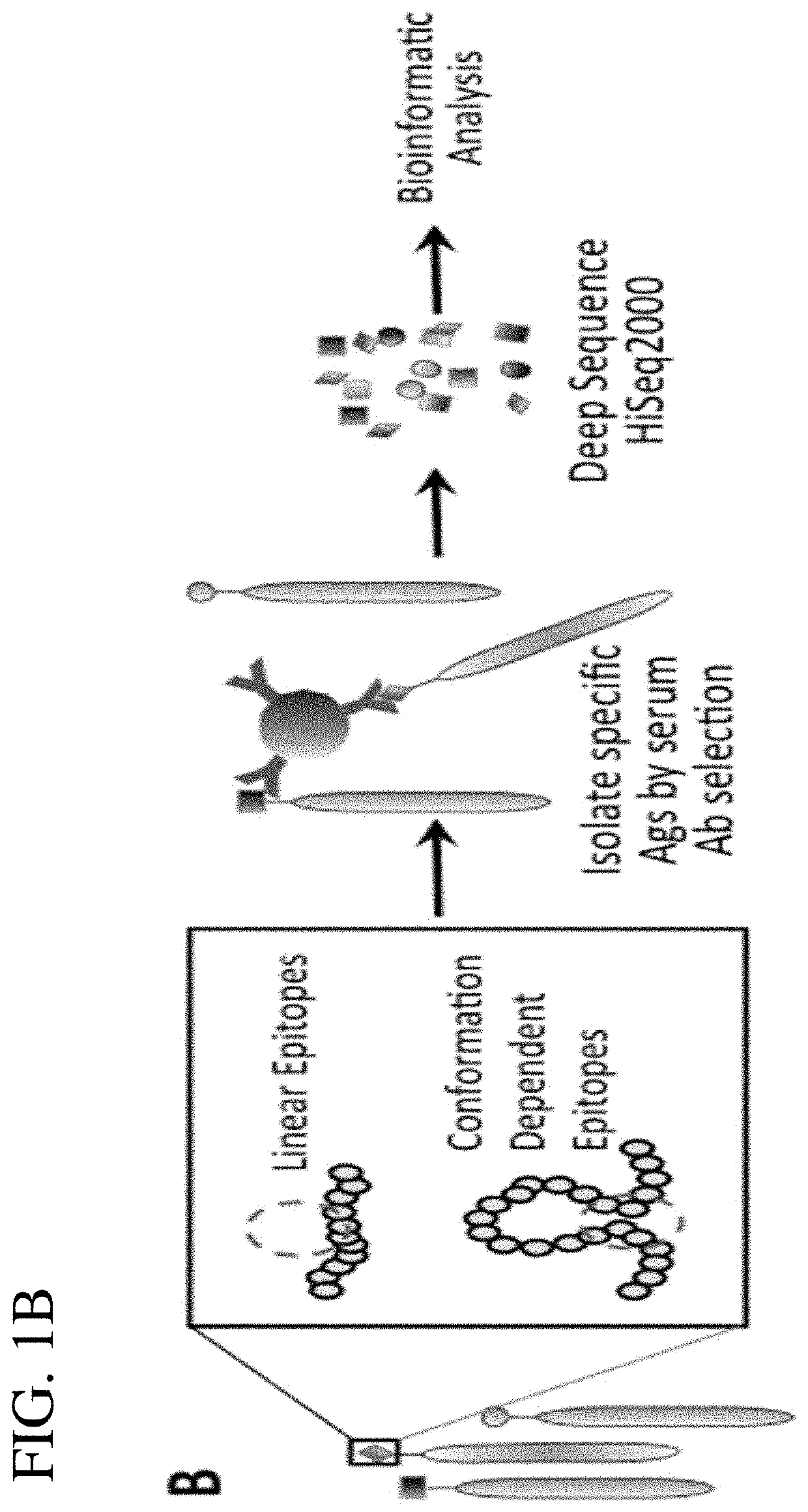
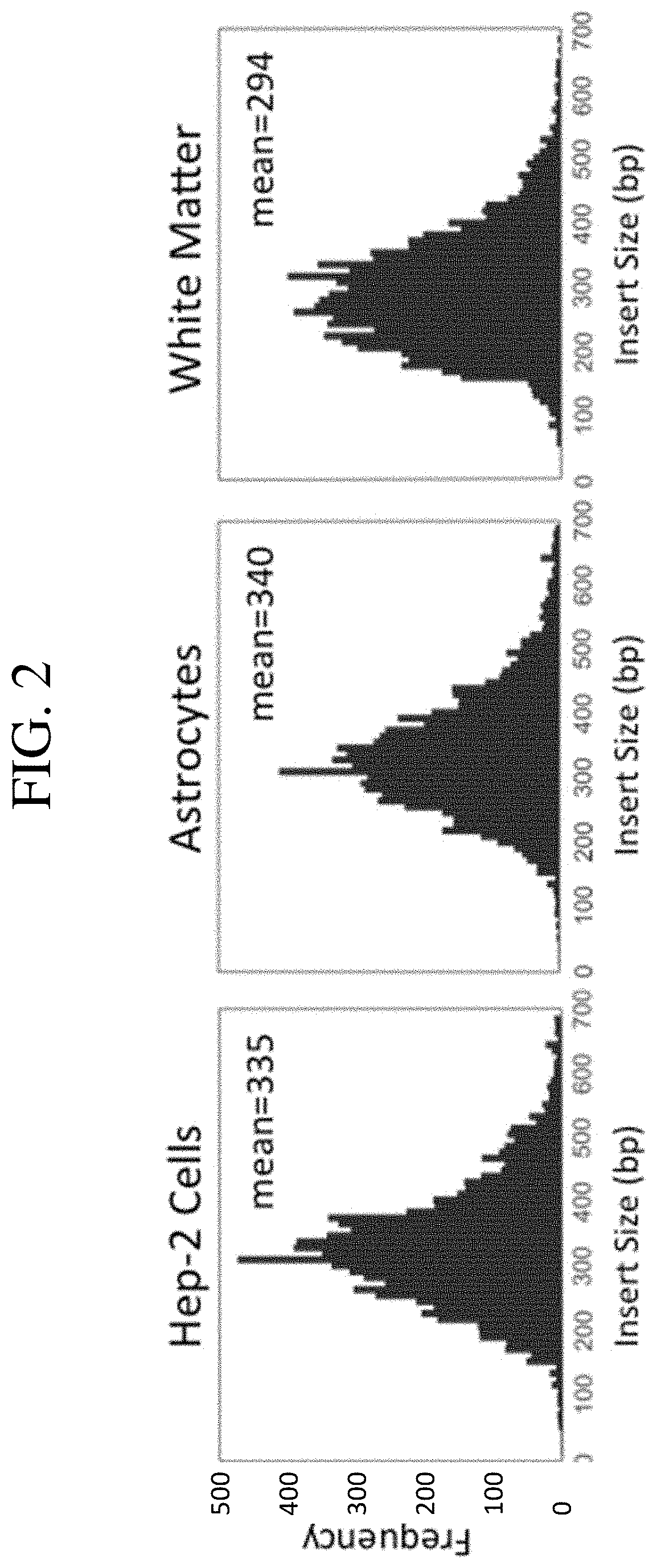
Patents
Literature
53 results about "Phage clone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polypeptide specifically combined with HepG2 cell surface
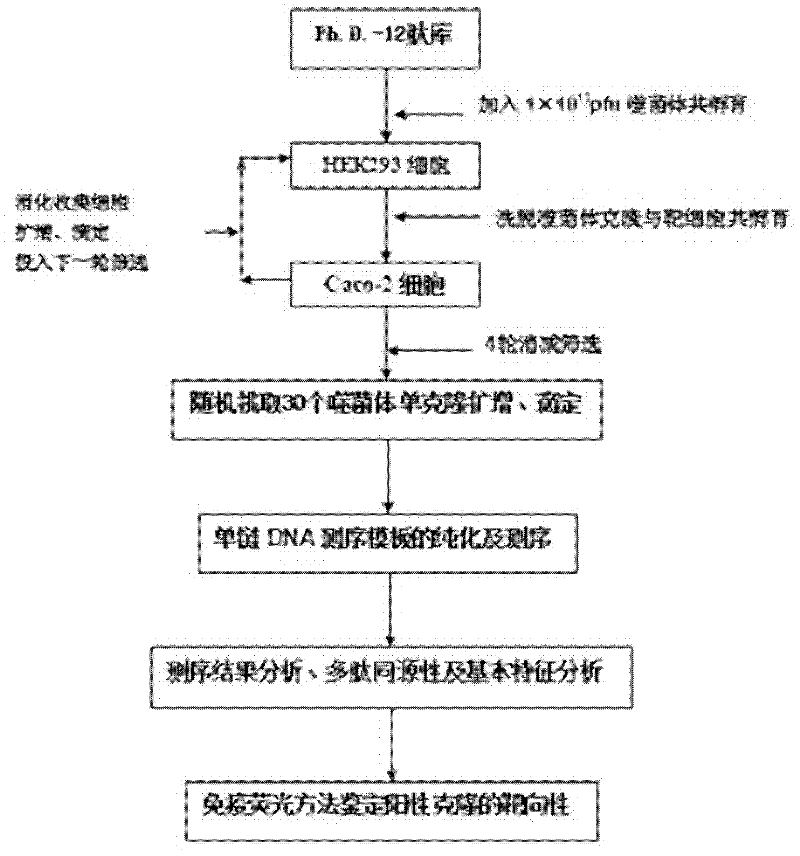
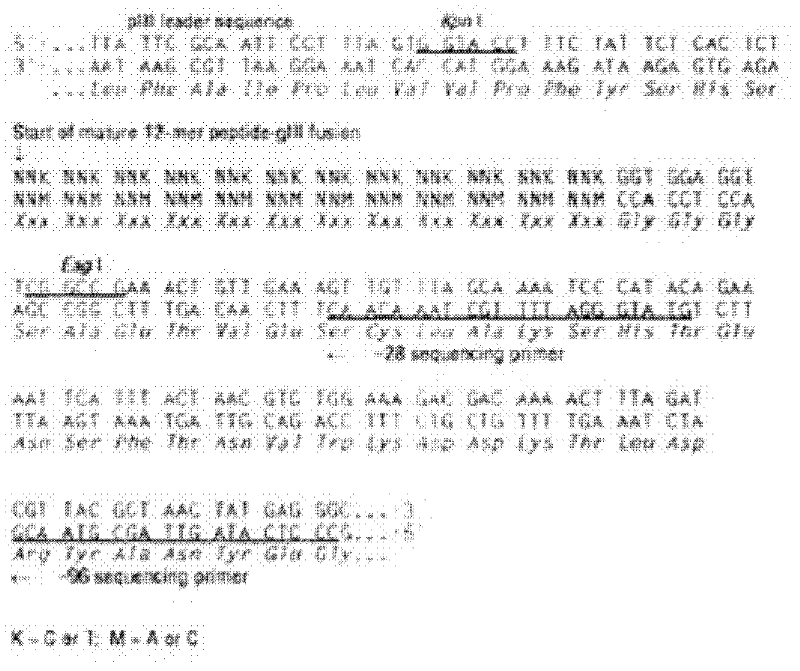
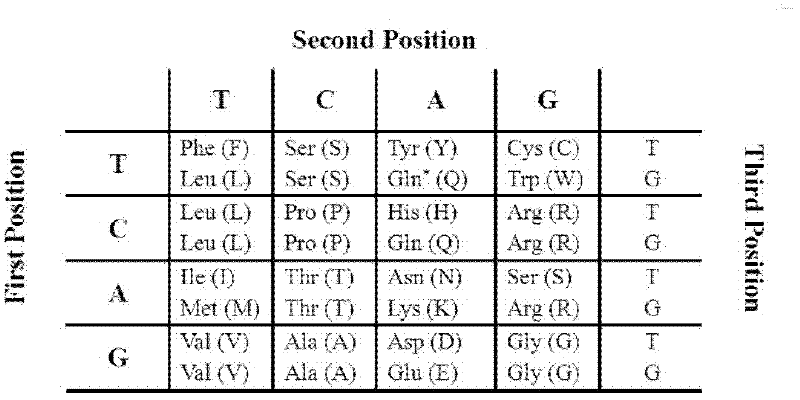
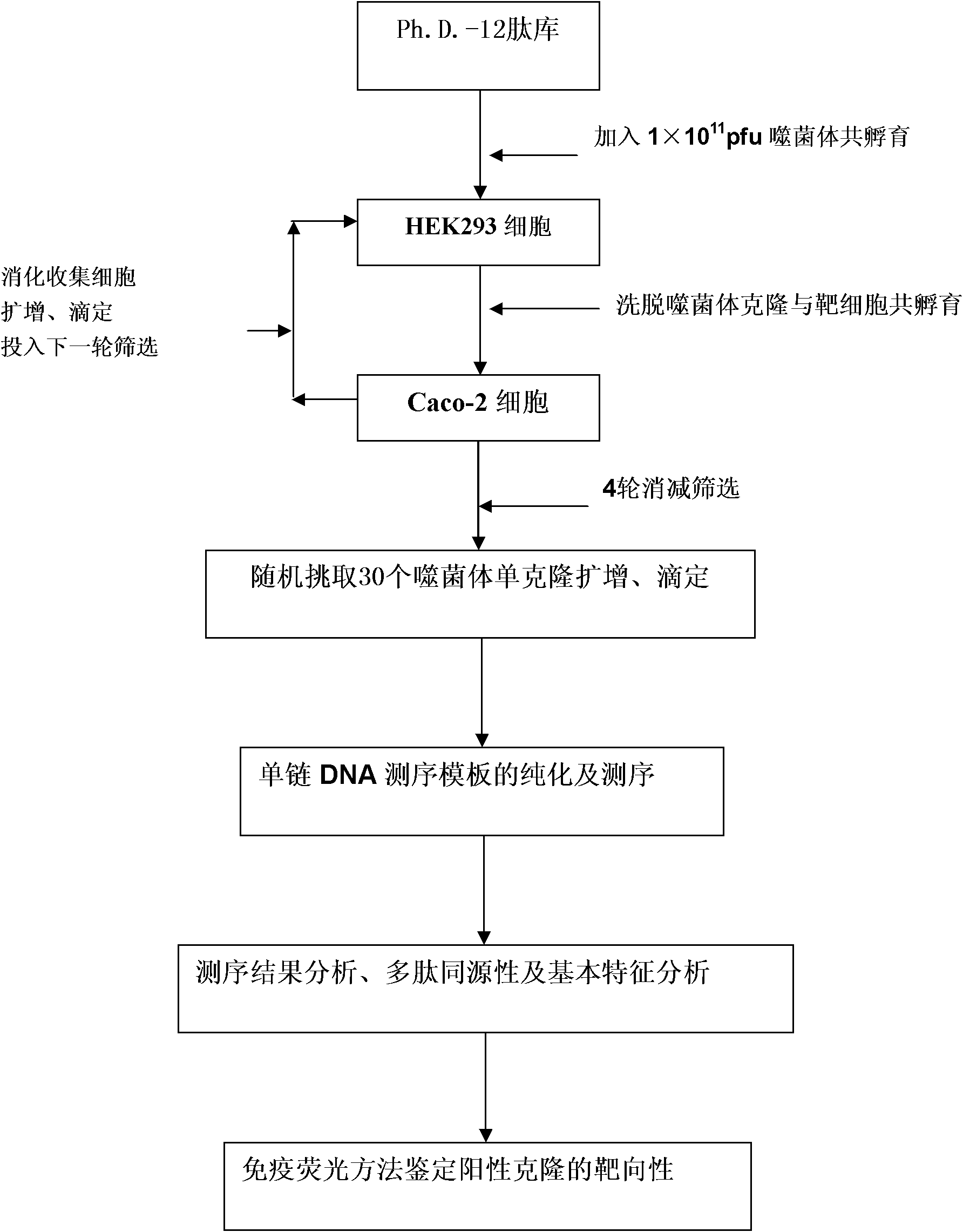
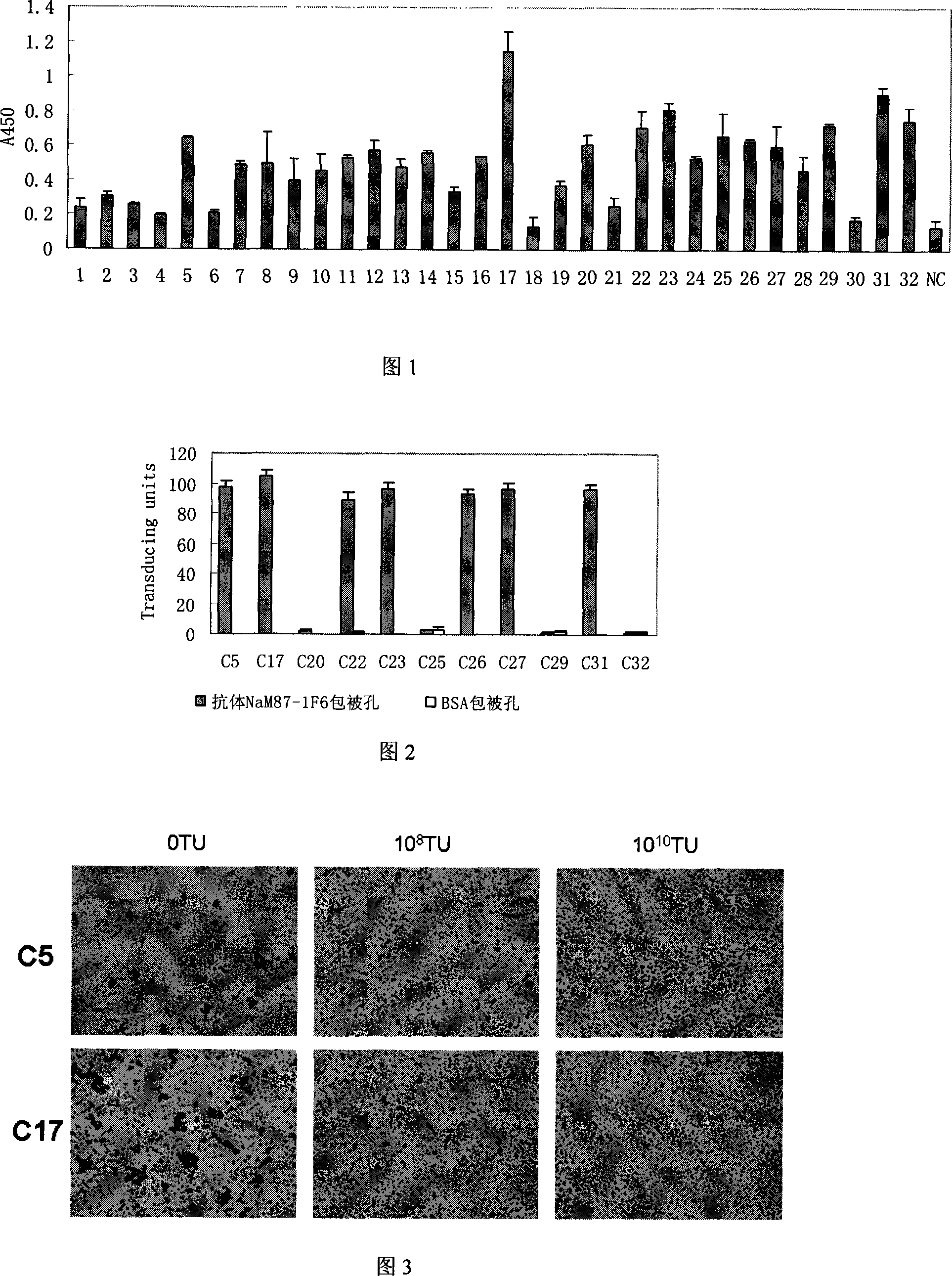
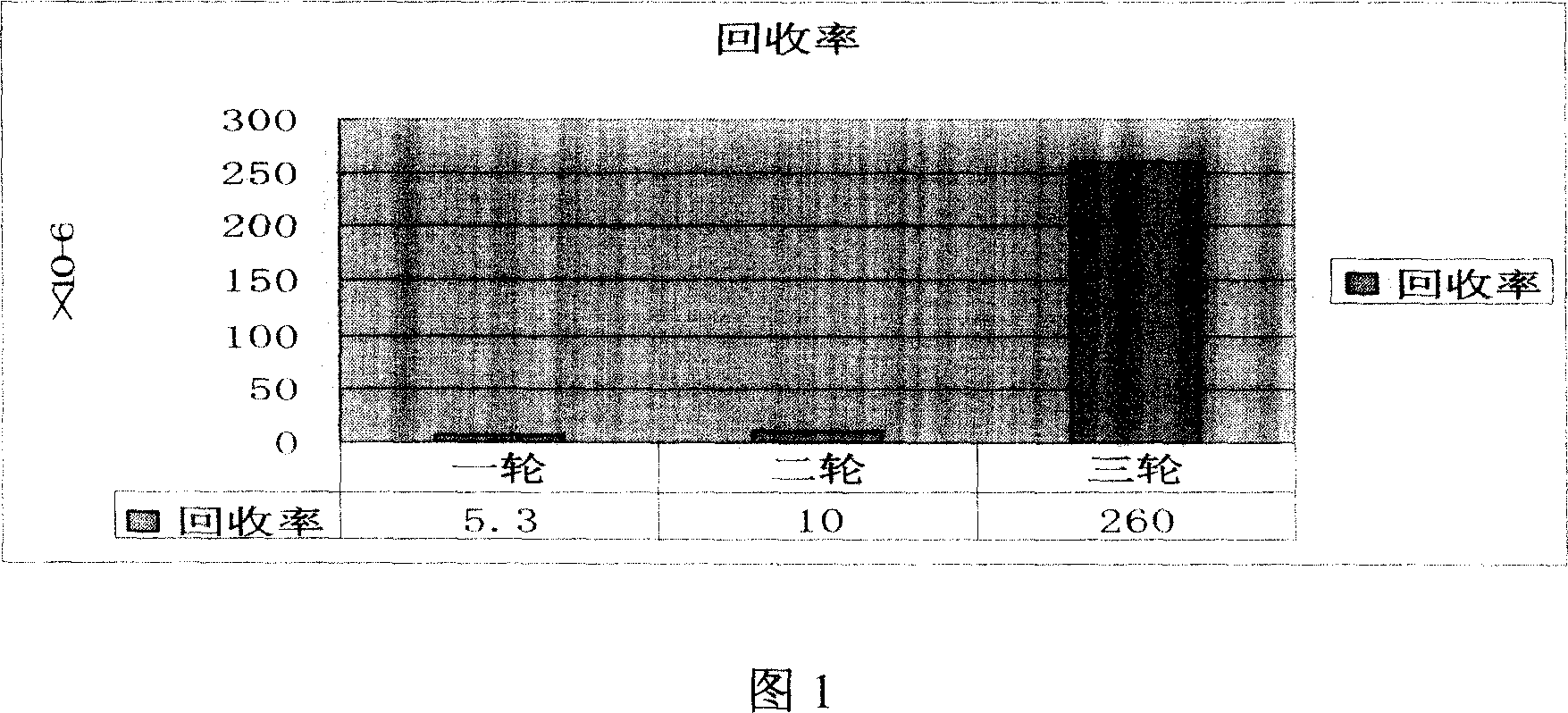
The invention discloses a polypeptide specifically combined with a HepG2 cell surface. According to the invention, four polypeptide segments are selected by utilizing a phage display random dodecapeptide library, the amino acid sequences of the four polypeptide segments are respectively LLADTTHHRPWT, LLADTPHHRPWT, FGWVTPHHELRS and SLSDLTHMGPWP. According to the invention, a polypeptide sequence combined with a liver cancer HepG2 cell is selected by utilizing a phage polypeptide display technology, and ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) identifies the affinity of phage clone and the liver caner cell, thus eight phage clones are obtained; four polypeptide sequences are obtained by sequencing, wherein the common amino acid sequence (basic sequence) is ***D(V)TT(P)HH*P(L)W(R)*; homology analysis indicates that the basic sequence of the polypeptide is possibly amino acid determinant on a ligand protein combined with a tumor cell surface receptor; cell immunofluorescence further identities that the target result of the positive clone of the phage prompts that the positive clone of the phage can be specifically combined with the HepG2 cell; and the selected specific polypeptide of the liver cancer HepG2 cell provides an experiment basis for early diagnosis of liver cancer, targeting delivery of an antitumor medicine and research and development of a targeting short peptide medicine.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Caco-2 cell surface specific binding polypeptide and screening method thereof
The invention discloses a Caco-2 cell surface specific binding polypeptide. Four polypeptide fragments are screened by phage display of a random dodecapeptide library, and the amino acid sequences of the four polypeptide fragments are respectively as follows: SPSIDTRYSRLG, CVSVGMKPSPRP, SVSVGMKPSPRP and MVSMDSSPRDRL. According to the screening method disclosed by the invention, colorectal carcinoma Caco-2 cell binding polypeptide sequences are screened by a phage polypeptide display technology, the affinity of phage clones with colorectal carcinoma cells is judged by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), ten phage clones are obtained, and four polypeptide sequences are obtained by sequencing. The consensus amino acid sequence is XXSXXXXXXXRXX; homology analysis indicates that the polypeptide motif is likely to be the amino acid determinant on the tumor cell surface receptor binding ligand protein; by further judgment of cell immunofluorescence, the targeting result of the phage positive clones implicates that the phage positive clones can be specifically bound with Caco-2 cells; and the colorectal carcinoma Caco-2 cell specific polypeptide acquired by screening provides a preliminary experiment basis for early diagnosis of colorectal carcinoma, targeted delivery of antitumor drugs and development of targeted small peptide drugs.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
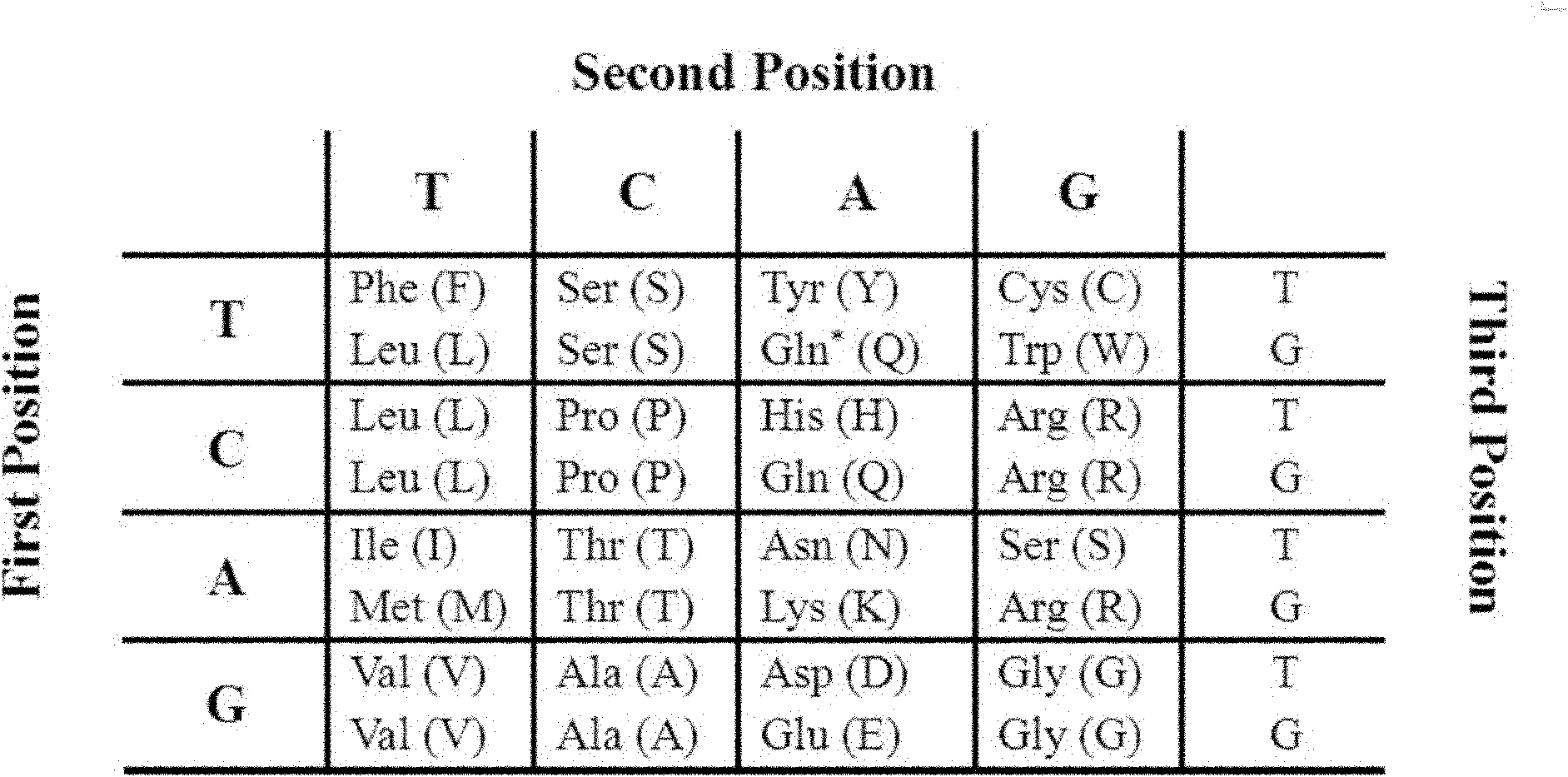
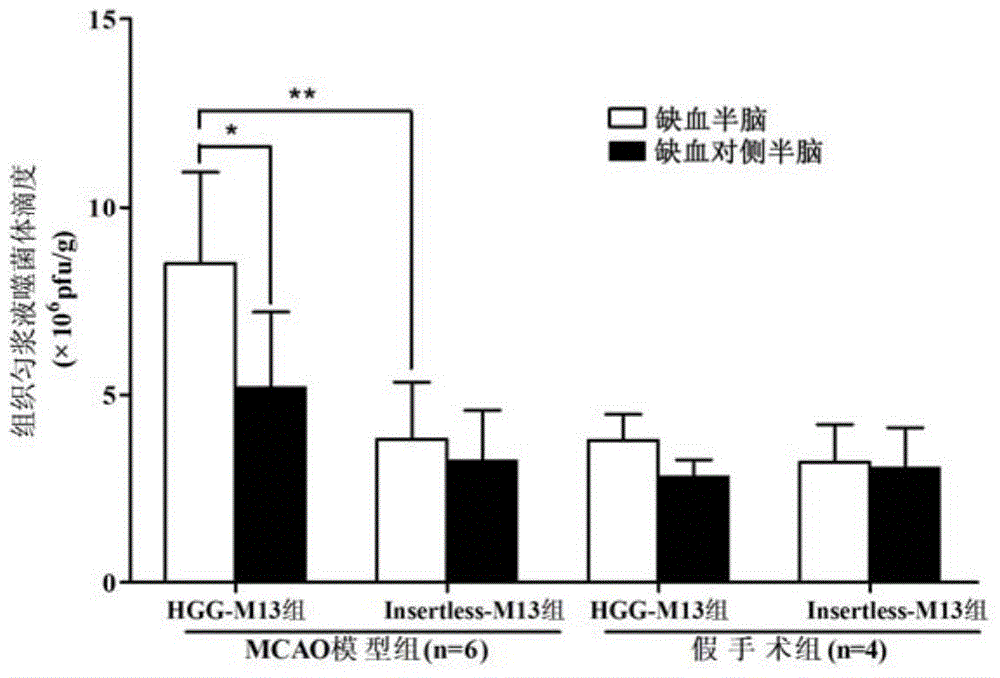
HGG (Human Gammaglobulin) polypeptide in combination with tissue specificity of cerebral arterial thrombosis and application thereof
ActiveCN104592352ASmall molecular weightHigh activityPeptidesMacromolecular non-active ingredientsTissue targetingNeuroprotective Drugs
The invention discloses HGG (Human Gammaglobulin) polypeptide in combination with the tissue specificity of cerebral arterial thrombosis. The invention relates to a method for obtaining the polypeptide. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out in-vivo selection of a mouse MCAO (Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion) cerebral arterial thrombosis model by adopting an in-vivo phage display peptide library screening technology so as to obtain phage clones in combination with cerebral arterial thrombosis tissue; and randomly selecting the plurality of phage clones to sequence, and authenticating the in-vivo combination specificity of HGG peptide and coded phage clones HGG-M13 thereof. The invention further relates to application of the polypeptide in preparation of a high-sensitivity imaging molecular probe and a targeting delivery neuroprotective drug for cerebral stroke. The polypeptide can be synthesized through an artificial method; the polypeptide is low in molecular weight, high in activity and penetrating power, good in specificity and low in toxicity, and has good tissue targeting of cerebral arterial thrombosis in vivo; and therefore, the polypeptide is applicable to serving as a carrier of the high-sensitivity imaging molecular probe and the targeting delivery neuroprotective drug.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Blood group A antigen epitope mimic peptide and its filtration method
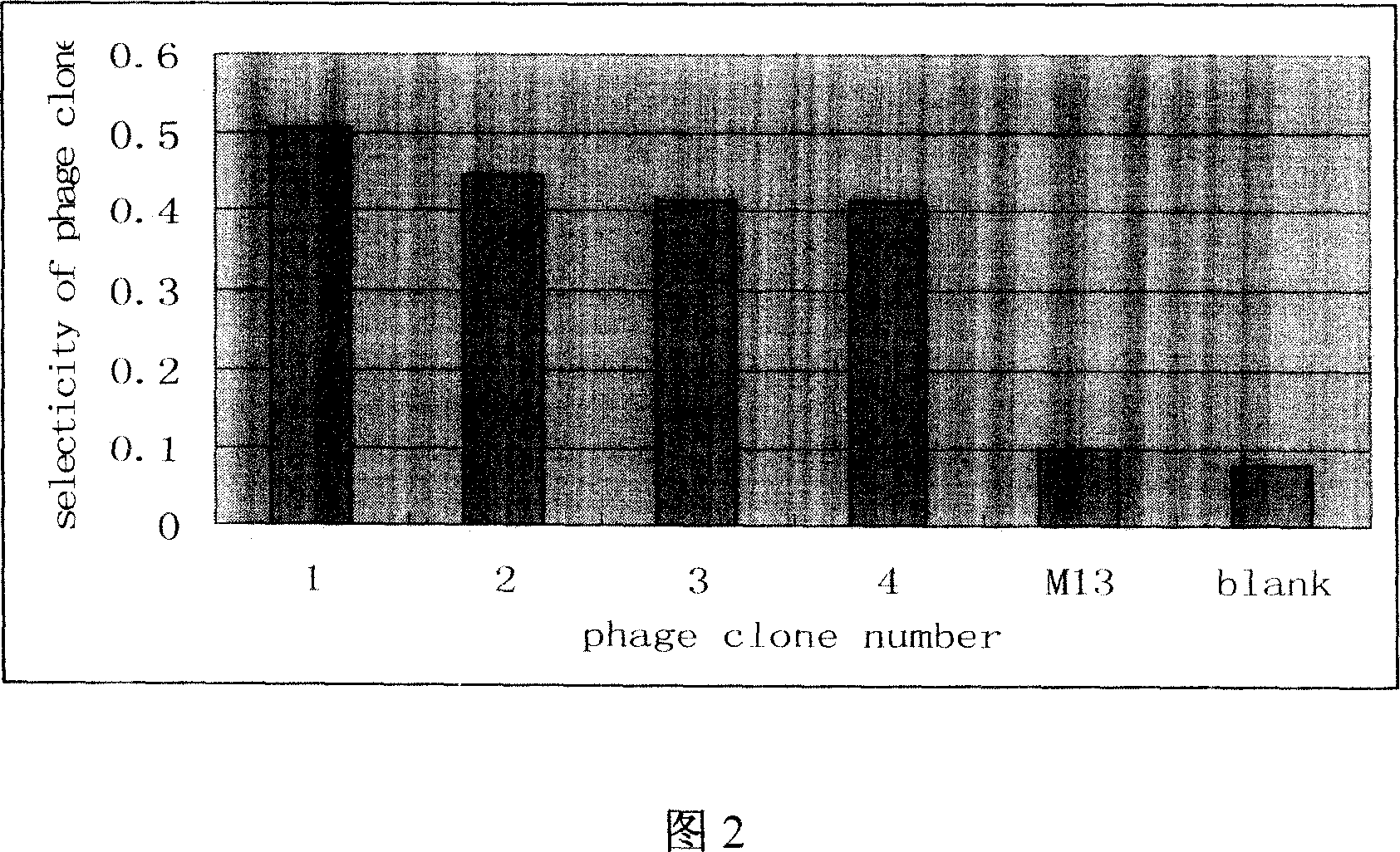
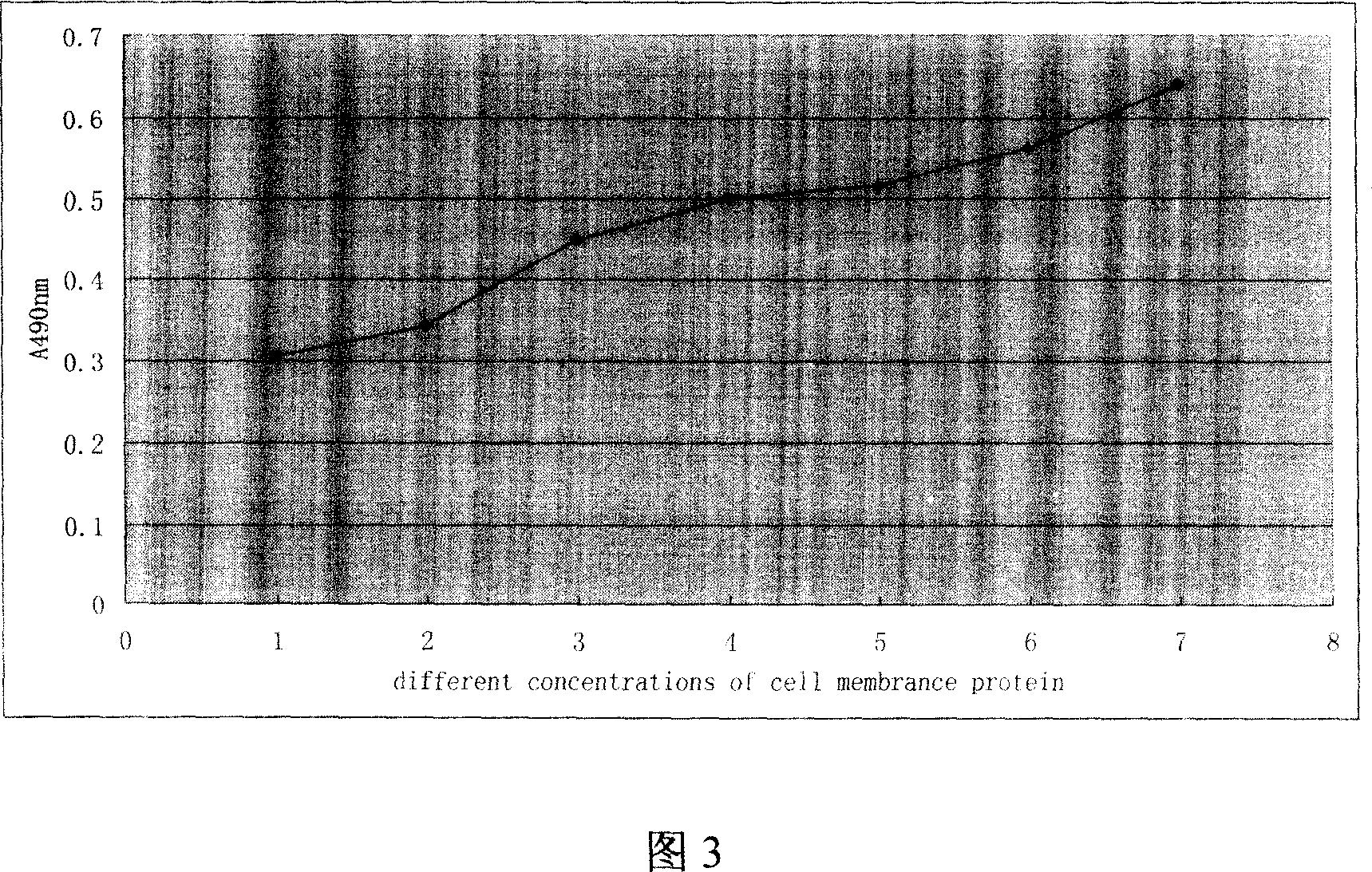
The invention discloses an epitope polypeptide of blood type A antigen and sieving method with amino acid sequence at Glu-Tyr-Trp-Tyr-Cys-Gly-Met-Asn-Arg-Thr-Gly-Cys or Gln-Ile-Trp-Tyr-Glu-Arg-Thr-Leu-Pro-Phe-Thr-Phe, which comprises the following steps: using NaHCO3 buffer to dilute blood type A antigen specific monoclonal antibody and cover ELISA board; adding bacteriophage into pore with monoclonal antibody; using glycine-alcaine buffer to elute the connected bacteriophage under indoor temperature; augumenting the bacteriophage in the host bacteria ER2738 after neutralizing as input in the next step; sieving for three times; cloning the 32nd bacteriophage after the third sieving; identifying to obtain the product; fitting for detecting blood type A antibody and affinity filtering.
Owner:胡丽华 +1
Liver cancer cell specificity internalization short peptide and its in vitro screening and identification
InactiveCN101033251AStrong specificityGood effectLibrary screeningPeptidesSequence analysisWilms tumour
This invention relates to the special short peptide of hepatoma cell internalization and its screen and identification in vitro, belonging to the technology of tumor cell peptides screening and identification. It takes hepatoma cell BEL-7404 as the screening target cell, displays the random 12-peptide library for bacteria invader to conduct affinity panning. Through three times of screen, it randomly selects twenty negative colonies for amplification and sequence, to deduct the amino acid sequence of random peptide. Through cell ELISA, immunofluorescence, flow cytometry and other method, it further identifies the combination and internalization of bacteria invader clones and hepatoma cells. From sequencing and sequence analysis of the positive clones, four obtained different sequences have good combination with hepatoma cells, and the screened monoclone can internalize cells.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Chitosan affine heptapeptide and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN106518968AImprove stabilityHigh affinityLibrary screeningPeptidesSequence analysisScreening method
The invention discloses chitosan affine heptapeptide. The amino acid sequence of the chitosan affine heptapeptide is shown as any of SEQ ID NO.1-SEQ ID NO.6. Screening includes the steps that nanoparticles wrapped by chitosan are prepared through the ion gelation method, then the nanoparticles are mixed with a phage displayed peptide library, the peptide library is screened through centrifugal separation, and finally a phage clone obtained through screening is subjected to ELISA identification and sequence analysis. The provided short peptide has high affinity and can be bound to the surface of a chitosan material, surface properties of the mesoporous silicon nanoparticles wrapped by chitosan can be changed, and accordingly the application range is widened. More materials, methods and means are provided for developing nano materials, especially nanoparticle medicine carriers, with chitosan as the basis.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Specific combined polypeptide for lung cancer, preparation and uses thereof
InactiveCN101492505AEasy to detectReliable detectionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntibody ingredientsTumor targetBacterial virus
The invention discloses a polypeptide that can be specifically combined with lung cancer cells and a preparation method and application thereof. The polypeptide specifically combined with lung cancer cells shows peptide library reducing screening by a bacterial virus so as to obtain bacterial virus clone specifically with lung cancer; the bacterial virus clone having stronger affinity with lung cancer is identified by Elisa and an immunohistochemical method; and sequencing is sent so as to obtain a 12 polypeptide, and the amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The 12 polypeptide screened by the invention not only has the advantages of traditional antibody molecule but also has small molecular weight, strong penetrating power and easy arriving to tumor tissue; the 12 polypeptide has good tumor targeting effect and more sensibility of tumor diagnosis, and can be used for preparing a kit for tumor diagnosis and drug for curing tumors.
Owner:GUANGDONG PHARMA UNIV
Method for screening single chain antibodies of Microcystin-LR and verification thereof
InactiveCN101857866AEasy to filterEasy to identifyImmunoglobulins against fungi/algae/lichensBiological testingEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a method for screening single chain antibodies of Microcystin-LR and verification thereof. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out two rounds of affinity screening on the biotinylated Microcystin-LR in a human source synthetic antibody library by using an avidin labeled magnetic bead and a negative screening method; extracting total plasmid DNA from phage colonies produced in the second round, carrying out enzyme digestion with enzyme Sfi I, recycling gel to obtain single chain antibody genes, connecting the single chain antibody genes with soluble expression carrier pAK100CL which is processed by enzyme digestion in the same way, and electrically transforming the connected carrier into colibacillus XL1-Blue to obtain soluble expression single chain antibodies; and verifying the soluble expression single chain antibodies by using a competitive time-resolved fluorescence immune analytical method. The invention has the advantage of quick, simple and convenient screening, and can well expose the Microcystin-LR three-dimensional structure into the incubation system. The verification on the screening result has the advantages of high detection signal and strong anti-interference capacity against stroma.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Polypeptide in specific binding with breast cancer brain metastases cells
ActiveCN103145803AImprove anti-tumor effectSmall molecular weightPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsTumor targetSorbent
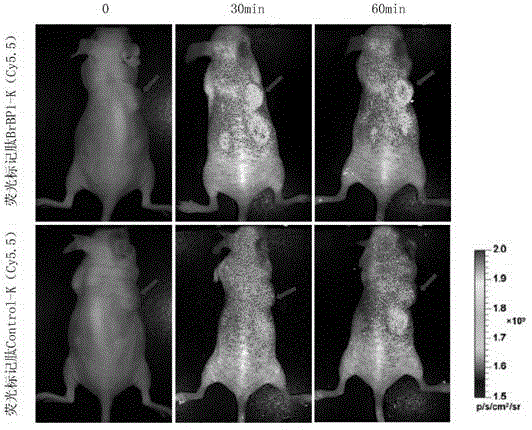
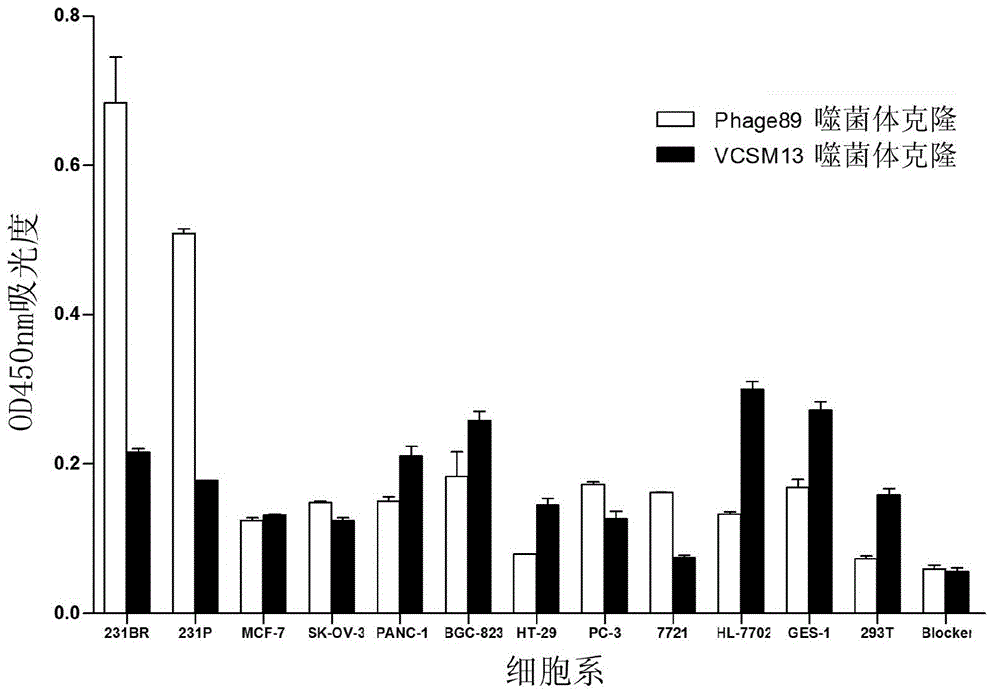
The invention discloses BrBP1 polypeptide in specific binding with breast cancer brain metastases cells, and further relates to a preparation method of the polypeptide. The method includes: by utilization of phage display technology, carrying out a plurality of rounds of whole-cell depletion screening, and screening out phage clones bound with a breast cancer brain metastases cell line; randomly picking out a plurality of the phage clones, and selecting strongly positive phage clones with a cell enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA) method; and after increasing the strongly positive phage clones, carrying out sequencing, and synthesizing the tested BrBP1 polypeptide in a manual mode. The polypeptide can be applied to preparation of medicine used for curing breast cancer brain metastases and kits used for early-stage diagnosis of the breast cancer brain metastases. The polypeptide can be synthesized with a manual method, is small in molecular weight, high in activity, strong in penetrating power, high in affinity and specificity and low in toxicity, has good tumor-targeting performance inside and outside a body, can also be internalized to enter cells, and is suitable for being used as vectors for targeted therapy.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Compositions for reducing virus infection rate in aquatic crustaceans and applications thereof
InactiveUS20050158326A1Improve abilitiesImprove survival rateMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against virusesInfection rateOrganism
Disclosed is a composition for reducing virus infection rates in crustaceans, which can be applied in prevention and / or treatment of viral infection in crustaceans, and therefore improves the survival rate. The composition comprises at least one of the antibodies that can bind specifically to virus, and the antibodies are selected from the group consisting of monoclonal antibody, phage display antibody and antibody produced by a recombinant organism. The monoclonal antibodies can be produced in a large scale from hybridoma cells with a bioreactor or by injecting into the abdominal cavities of mice. Alternatively, two other highly specific antibodies can be produced from phage clones and recombinant organisms. The composition can be used in the forms of therapeutic medicines, nutritious or feeding supplements in addition to feeds. Also, the composition can be used in an aqueous solution to expose the crustaceans to fulfill the needs of treatment and / or prevention of viral infection in crustaceans.
Owner:HAN TE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Specific affinity polypeptide for polyurethane interface and screening method of specific affinity polypeptide
The invention discloses a specific affinity polypeptide for a polyurethane interface and a screening method of the specific affinity polypeptide, and relates to the technical field of biological materials. The specific affinity polypeptide contains affinity peptide of a VHWDFRQWWQPS specific amino acid sequence. The screening method comprises the following steps: respectively adopting water-based polyurethane and solvent-based polyurethane coating materials as target interfaces; screening the peptide which is in specific affinity to the target interfaces by using a phage display technology, including affinity selection of a phage 12 peptide library and phage-cloned ELISA identification; and finally preparing positive phage clone DNA and carrying out sequence determination. Short peptide molecules can be rapidly, stably and efficiently combined on the surface of a polyurethane coating material through direct infiltration contact and can be stably combined on the surface of the solvent-based polyurethane material; a foundation is laid for further integration of active enzyme protein molecules and development of a rapid immobilization process of zymoprotein on the polyurethane surface; and a good method is also provided for development of the polyurethane material with biological activity.
Owner:陕西卓阳瑞信息科技有限公司
Polypeptide specifically bound on surface of hepatoma carcinoma cell
The invention discloses a polypeptide specifically bound on the surface of a hepatoma carcinoma cell. A polypeptide fragment is screened out from a phage display random dodecapeptide library, and the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide fragment is LWDMSTPHRPLT. The polypeptide sequence bound with the hepatoma carcinoma cells is screened out by use of the phage polypeptide display technology; the affinity of phage clones and the hepatoma carcinoma cells is identified by virtue of ELISA, and 8 phage clones are obtained; 4 polypeptide sequences are obtained by sequencing, and the shared amino acid sequence of the4 polypeptide sequences is L(H)***S(T)*P(H)H(S)*P(L)LT(L); the targeting result of further identifying the positive phage clones by use of cell immunofluorescence indicates that the positive phage clone is capable of specific binding with the hepatoma carcinoma cell; the screened-out hepatoma carcinoma cell specific polypeptide provides experimental basis for early diagnosis of the liver cancer, the targeting transport of an anti-tumor drug and the development of a targeting oligopeptide drug.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
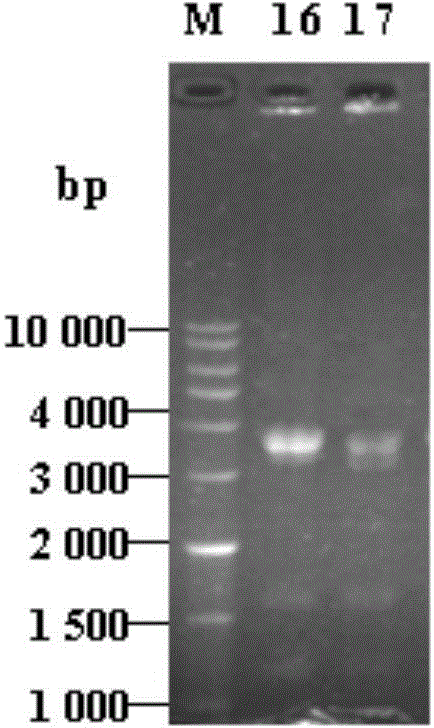
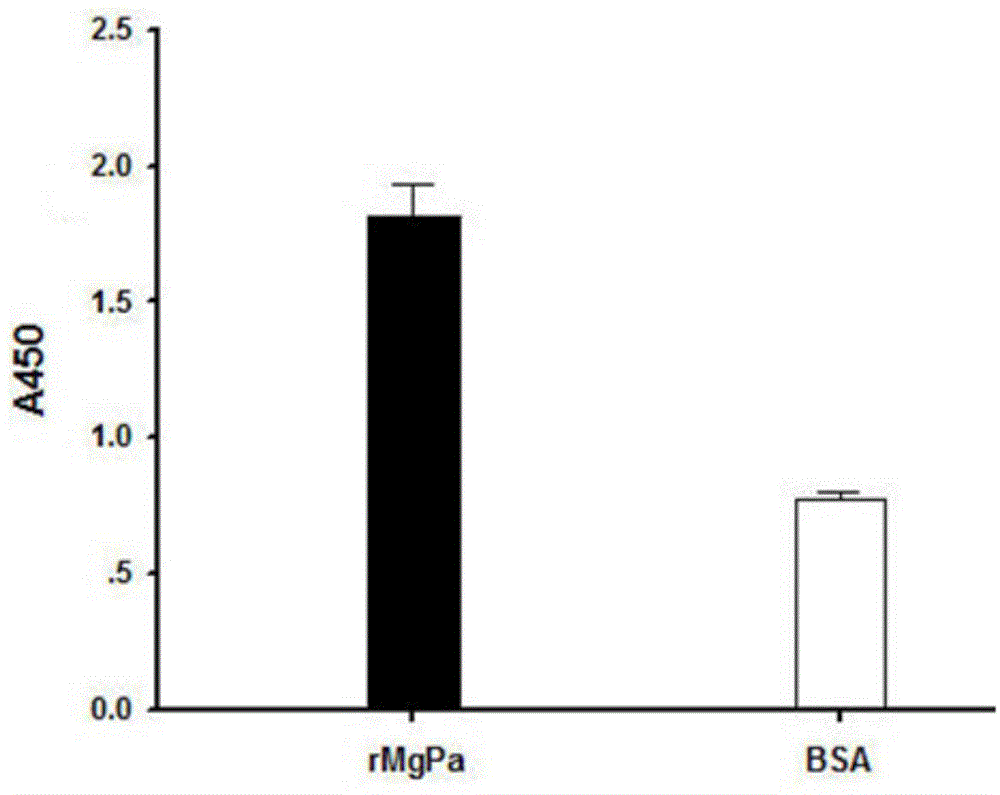
Polypeptide available for specific binding to mycoplasma genitalium adhesin protein MgPa and application thereof
InactiveCN104829693AGood effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA IntercalationAmino acid
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Use of phage chip as protein chip or gene chip
InactiveCN101059515AParticle stabilizationAvoid degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisEpitopeBacteriophage
The invention discloses an application for using bacteriophage chip as protein chip or gene chip, which selects bacteriophage peptide base or builds a bacteriophage display base, to obtain the bacteriophage clone of special external peptide (or antigen epitope), uses automatic or non-automatic method, to directly couple the bacteriophage with different external peptides according to preset array mode to one chip, to obtain the bacteriophage chip. The inventive chip can be a protein chip for showing external peptide, used to check, select and identify the special combine material in the antigen, ligand or natural or artificial compound in the samples, or the gene chip for cloning relative genes, to check the gene. The inventive bacteriophage chip has low cost, simple preparation, high stability, high specificity and long service life.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
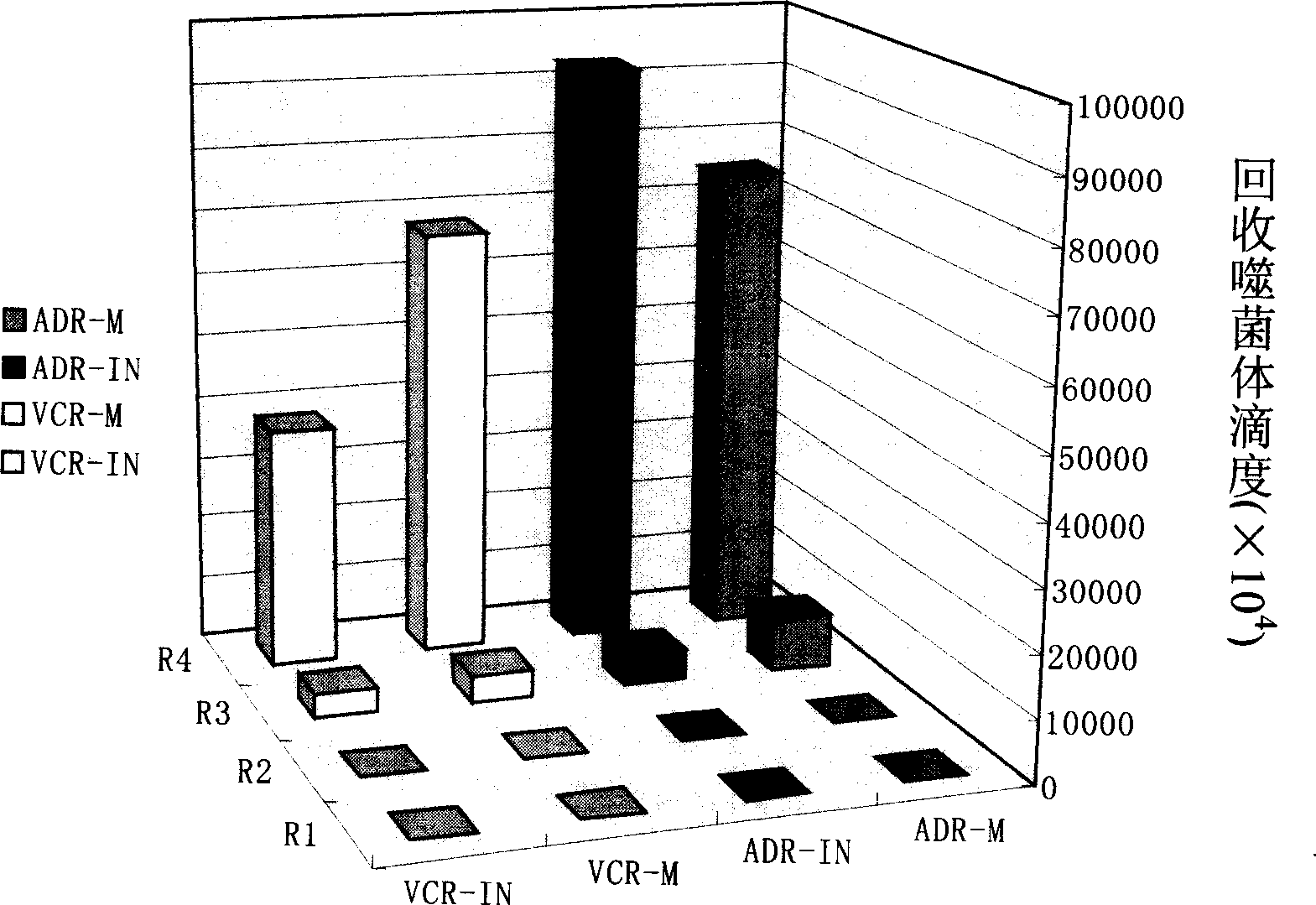
Screening method for human gastric cancer drug-resistant cell specific combination and drug-resistant reverse short peptide and sequence
InactiveCN1858253AReversal of resistance propertiesConfirmed drug resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingScreening methodCell membrane
The present invention belongs to the field of biomedicine technology, and is screening method and sequence for human gastric cancer drug resistant cell specific combination and drug resistant reverse short peptide. The present invention features that through the combined random bacteriophage peptide library and MTT extracorporeal drug sensitive test screening, bacteriophage cloning polypeptide capable of reversing the drug resisting characteristic of the drug resistant gastric cancer cell is obtained to lower the survival rate and IC50 value of drug resistant gastric cancer cell under chemotherapy medicine and result in statistic difference cloning (p<0.05). Bacteriophage polypeptide is utilized in screening whole cell and the ligand of specific expression molecule on drug resisting tumor cell membrane, so as to the bioactive polypeptide and corresponding bioactive short peptide and its sequence (GMBPs).
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Peptides capable of binding to titanium, silver and silicone
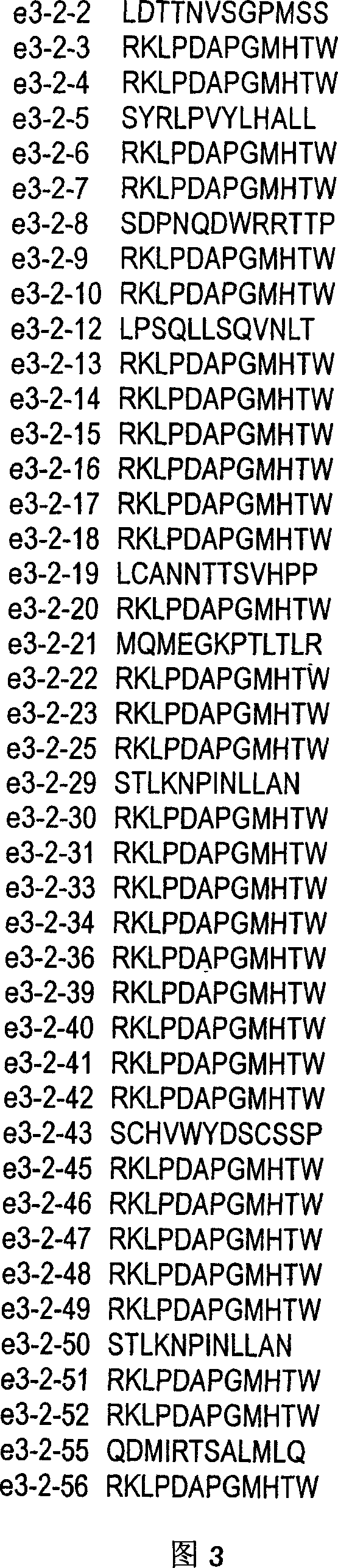
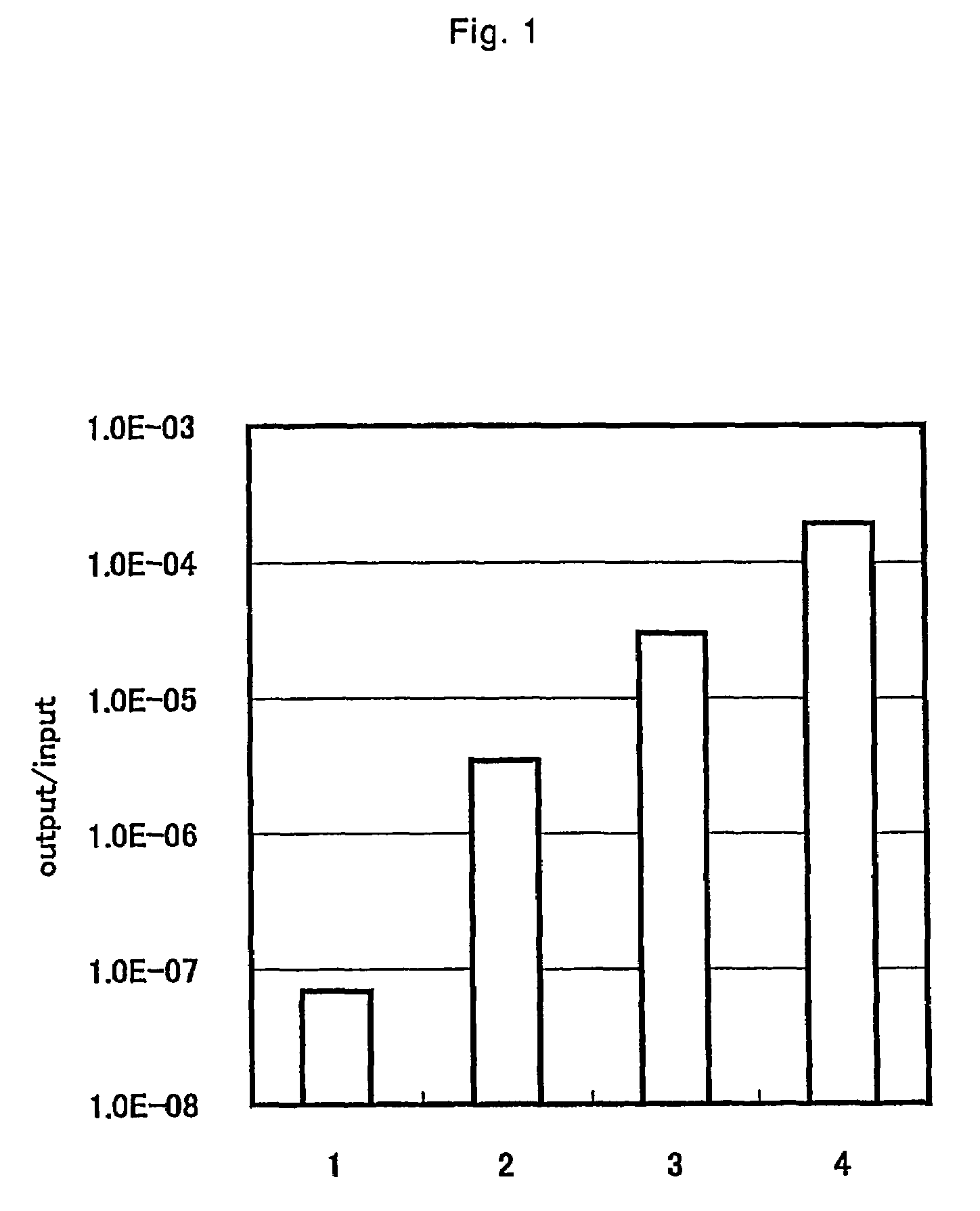
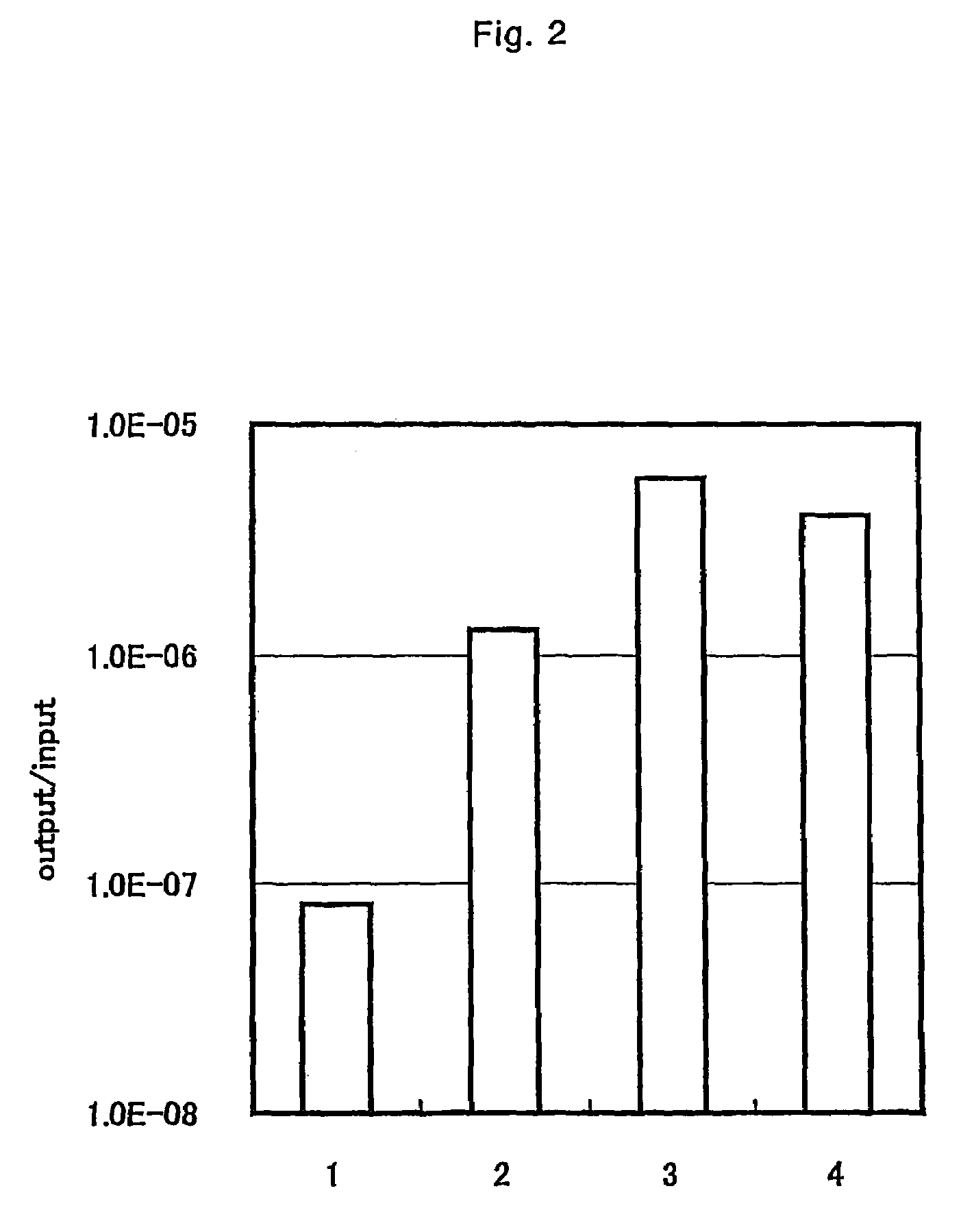
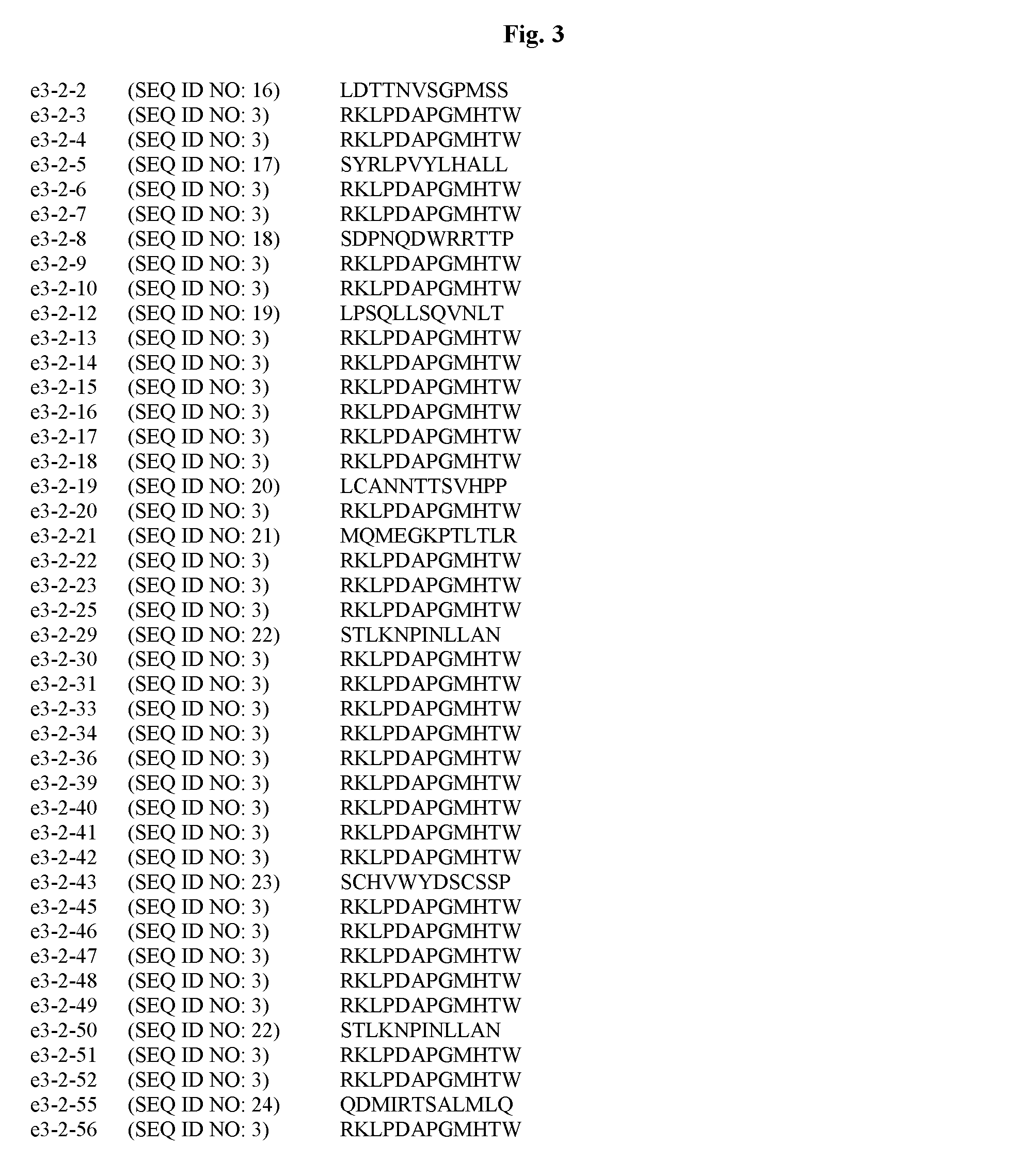
The present invention provides a peptide sequence, a phage, an artificial protein or a chimeric molecule having a binding ability to titanium, silver, silicon, necessary to confer higher capacity of titanium, silver, silicon material with the use of soft matters, or to provide a complex of a peptide, a phage, an artificial protein or a chimeric molecule, and titanium, having the peptide sequence and functional peptide sequence. By bringing into contact a population of phage wherein said phage of said population collectively express a library of different peptide sequence, recovering titanium bound to phage particles via peptide sequence by centrifugation, proliferating the obtained phage particles in bacteria, and repeating panning operation and concentrating titanium binding phage clones. Among the phage clones, peptide RKLPDAPGMHTW and the like is identified. As for a peptide having a binding ability to titanium, silver, silicon, RKLPDA or RALPDA can be exemplified.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
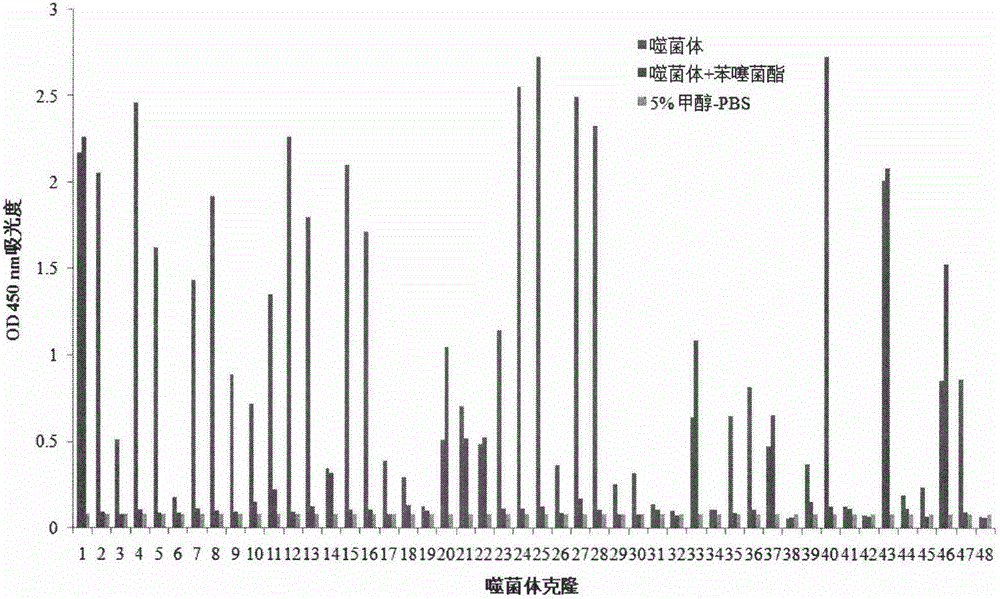
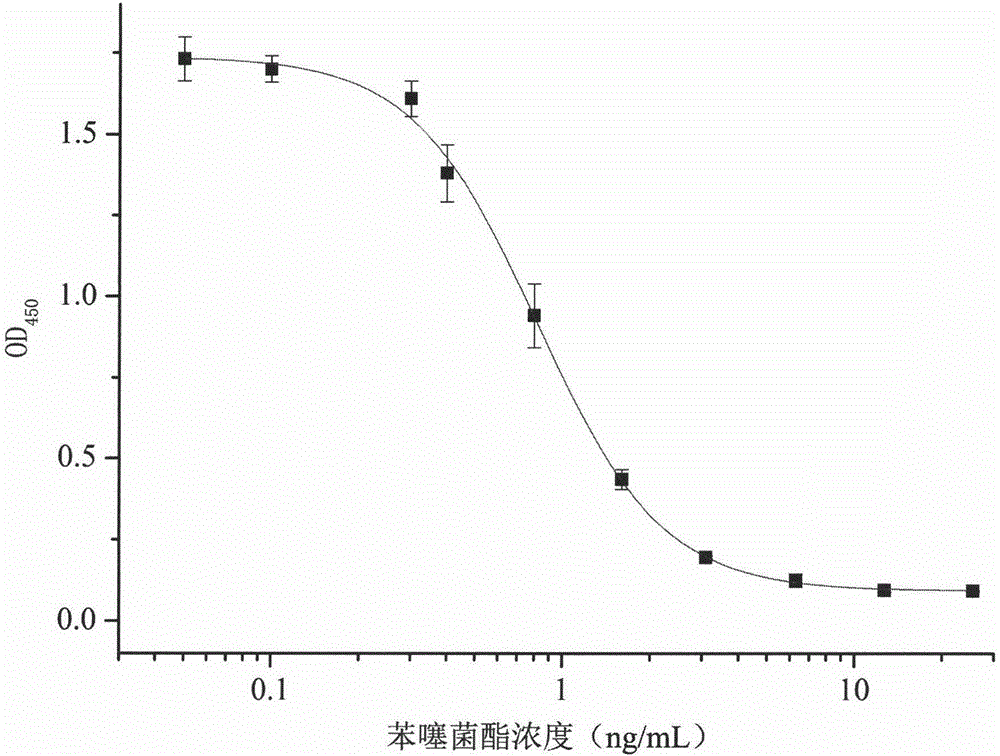
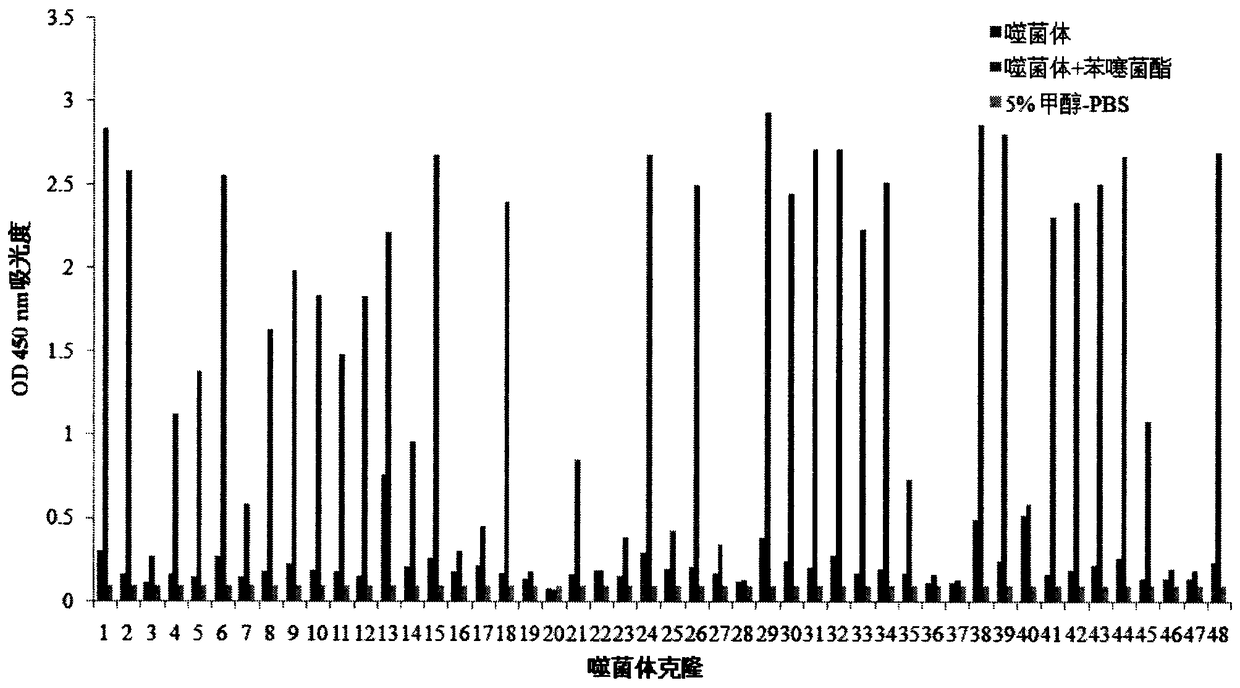
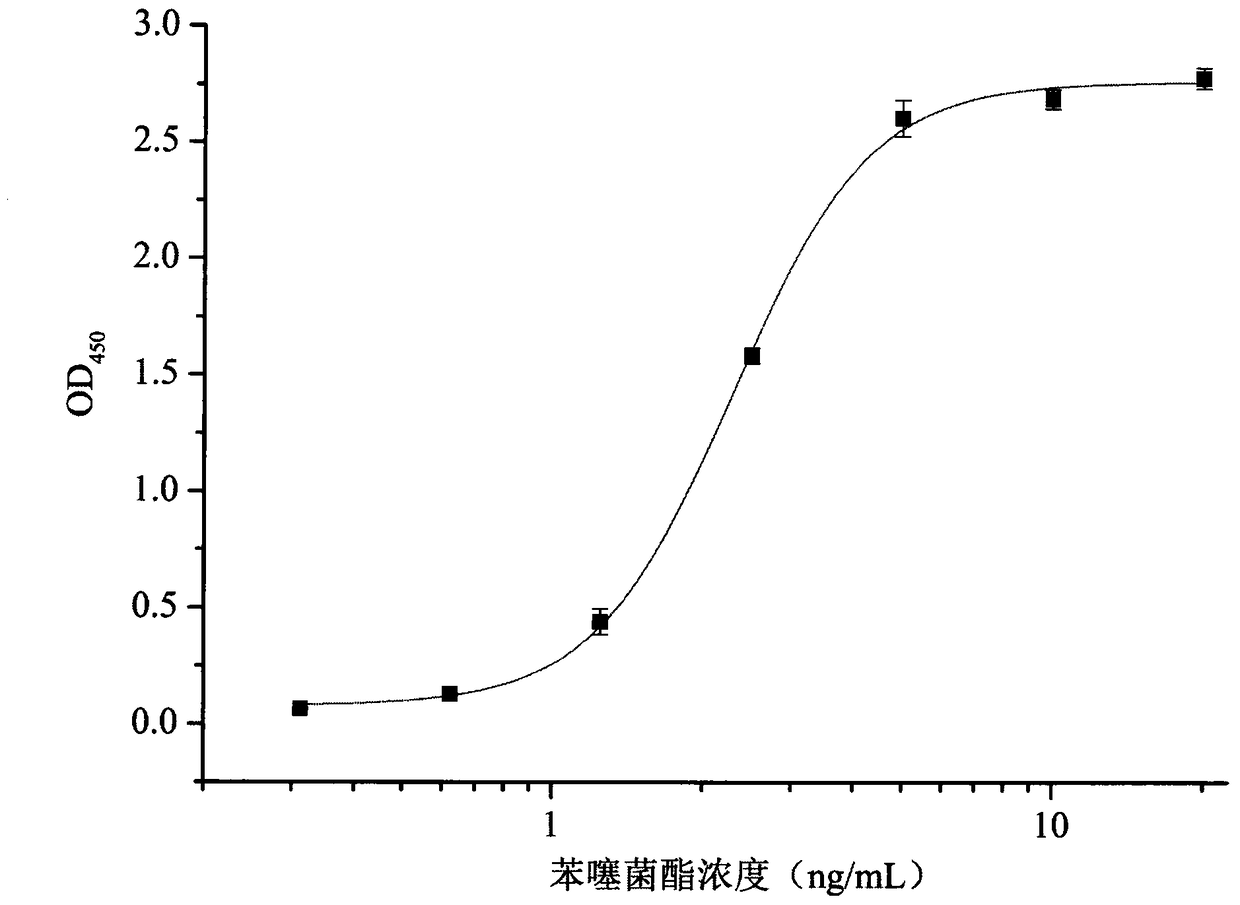
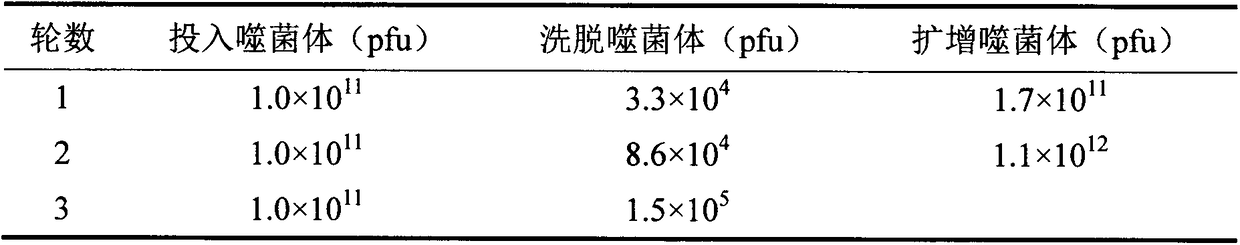
Polypeptide capable of specifically binding to benzothiostrobin immune complex and application thereof
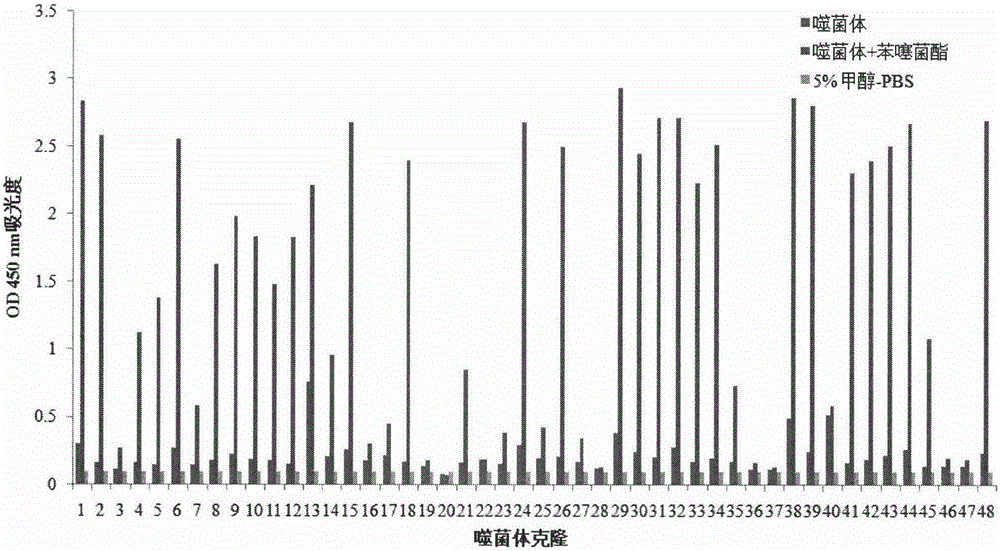
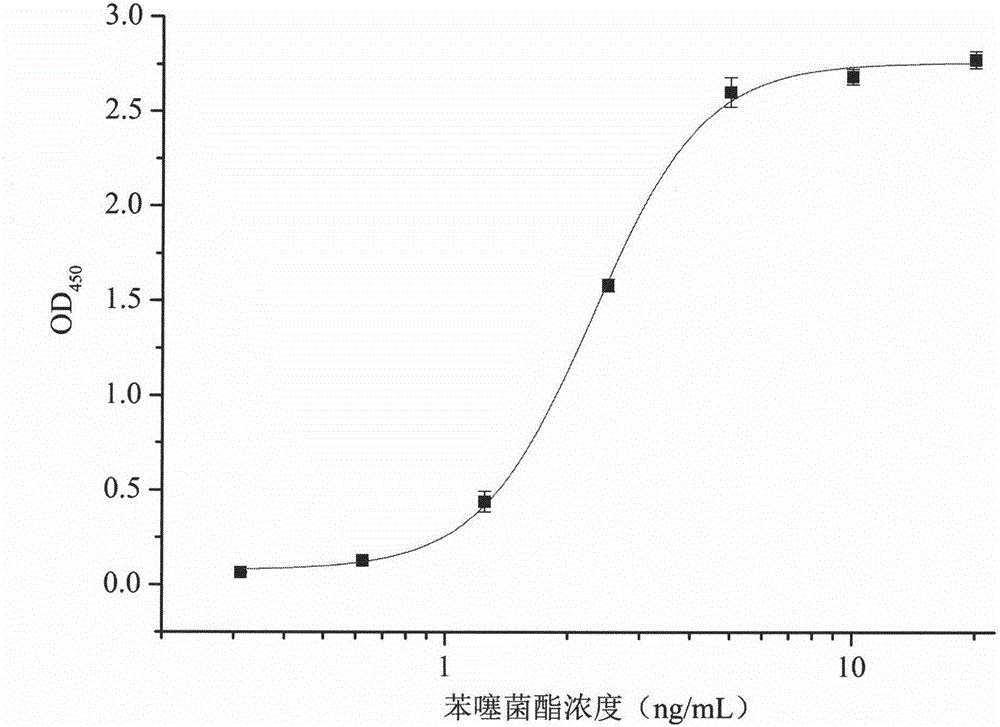
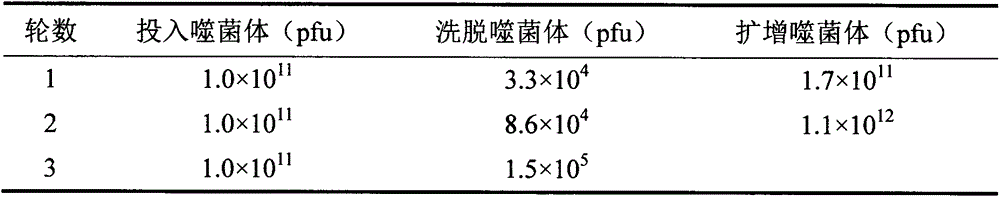
ActiveCN105153280AIncreased sensitivityImprove accuracyPeptidesBiological testingPhage elisaImmune complex deposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, relates to a polypeptide capable of specifically binding to a benzothiostrobin immune complex, and comprises application of the polypeptide in detection of benzothiostrobin. According to the invention, with a phage display technology, a phage display random cycle octapeptide library undergoes 3 rounds of panning by using the benzothiostrobin immune complex, and phage clones capable of binding to the benzothiostrobin immune complex are panned out; and a plurality of phage clones are randomly selected for amplification and plasmid extraction, and positive phage clones are selected through a non-competitive phage ELISA method and are sequenced so as to obtain polypeptide sequences. The invention also relates to the application of the phage display polypeptide in the detection of the benzothiostrobin. The non-competitive phage ELISA method established by using the phage display polypeptide can be applied in rapid, sensitive, simple, convenient and cheap detection of benzothiostrobin residues in the environment and agricultural products.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Peptides capable of binding to titanium silver silicone
The present invention provides a peptide sequence, a phage, an artificial protein or a chimeric molecule having a binding ability to titanium, silver, silicon, necessary to confer higher capacity of titanium, silver, silicon material with the use of soft matters, or to provide a complex of a peptide, a phage, an artificial protein or a chimeric molecule, and titanium, having the peptide sequence and functional peptide sequence. By bringing into contact a population of phage wherein said phage of said population collectively express a library of different peptide sequence, recovering titanium bound to phage particles via peptide sequence by centrifugation, proliferating the obtained phage particles in bacteria, and repeating panning operation and concentrating titanium binding phage clones. Among the phage clones, peptide RKLPDAPGMHTW (SEQ ID NO: 3) and the like is identified. As for a peptide having a binding ability to titanium, silver, silicon, RKLPDA (SEQ ID NO: 1) or RALPDA (SEQ ID NO: 2) can be exemplified.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Method for screening polypeptide specifically bound with human colon cancer cells and application of polypeptide
ActiveCN106967154ASmall molecular weightOvercoming immune allergic reactionsPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesCancer cellScreening method
The invention relates to a polypeptide specifically bound with the surfaces of colon cancer cells and application of the polypeptide. A method for screening the polypeptide includes steps of (1), incubating clone strains with amplified bacteriophage dodecapeptide libraries and the colon cancer cells together, discarding the clone strains which are not bound with the colon cancer cells, screening the clone strains and then amplifying the screened clone strains which are bound with the colon cancer cells; (2), repeatedly carrying out the step (1) by four times, continuously enriching bacteriophage clone strains to obtain clone strains with high colon cancer cell affinity and repeatedly verifying the binding capacity of the bacteriophage clone strains in liquid phases; (3), incubating the bacteriophage clone strain obtained at the step (2) and normal colonic epithelial cells and removing non-specifically bound clone strains; (4), carrying out sequencing on positive clone strains; (5), verifying the specificity of the polypeptide on the clone cancer cells and tissues by the aid of immunofluorescence. The polypeptide and the application have the advantages that short peptides which are specifically bound with the colon cancer cells are screened by the aid of technologies for displaying peptide libraries by the aid of bacteriophage, and the polypeptide can be used as a molecular marker or targeted carrier or the like for targeted therapeutic medicines.
Owner:孟祥军
Polypeptide specifically combined with benzothiostrobin antibodies and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and relates to polypeptide specifically combined with benzothiostrobin antibodies, including an application of the polypeptide to the detection of benzothiostrobin. According to the polypeptide, a phage display technique is adopted, and the benzothiostrobin antibodies which are purified by a protein A column are used for screening a phage display random octapeptide library for three rounds, so as to screen phage clones combined with the benzothiostrobin antibodies; a plurality of phage clones are selected at random for amplification and plasmid extraction, positive phage clones are selected by adopting a phage ELISA (enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay) method, and the positive clones are sequenced, so as to obtain a polypeptide sequence. The invention further relates to the application of the phage display polypeptide to the detection of the benzothiostrobin. A phage enzyme-linked immunoassay method established by using the phage display polypeptide can be used for quickly, sensitively and conveniently detecting benzothiostrobin residues in the environment and agricultural products with low cost.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
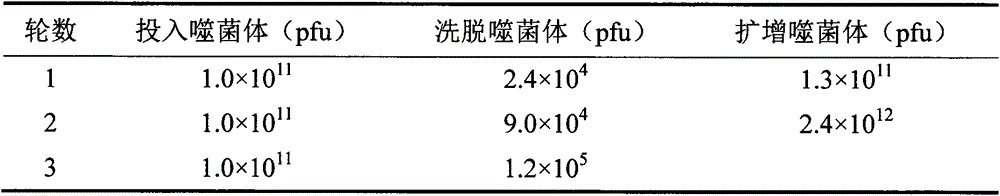
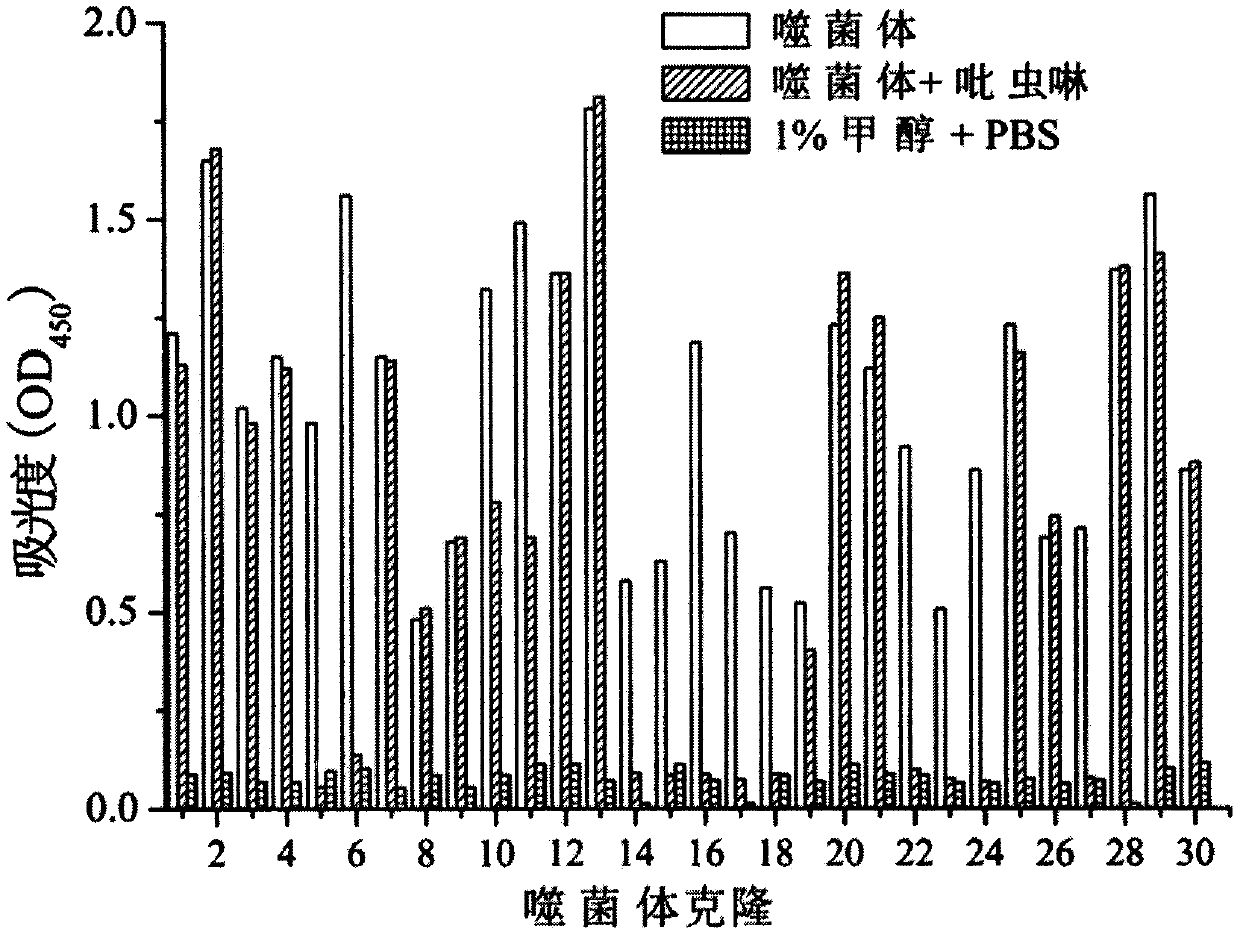
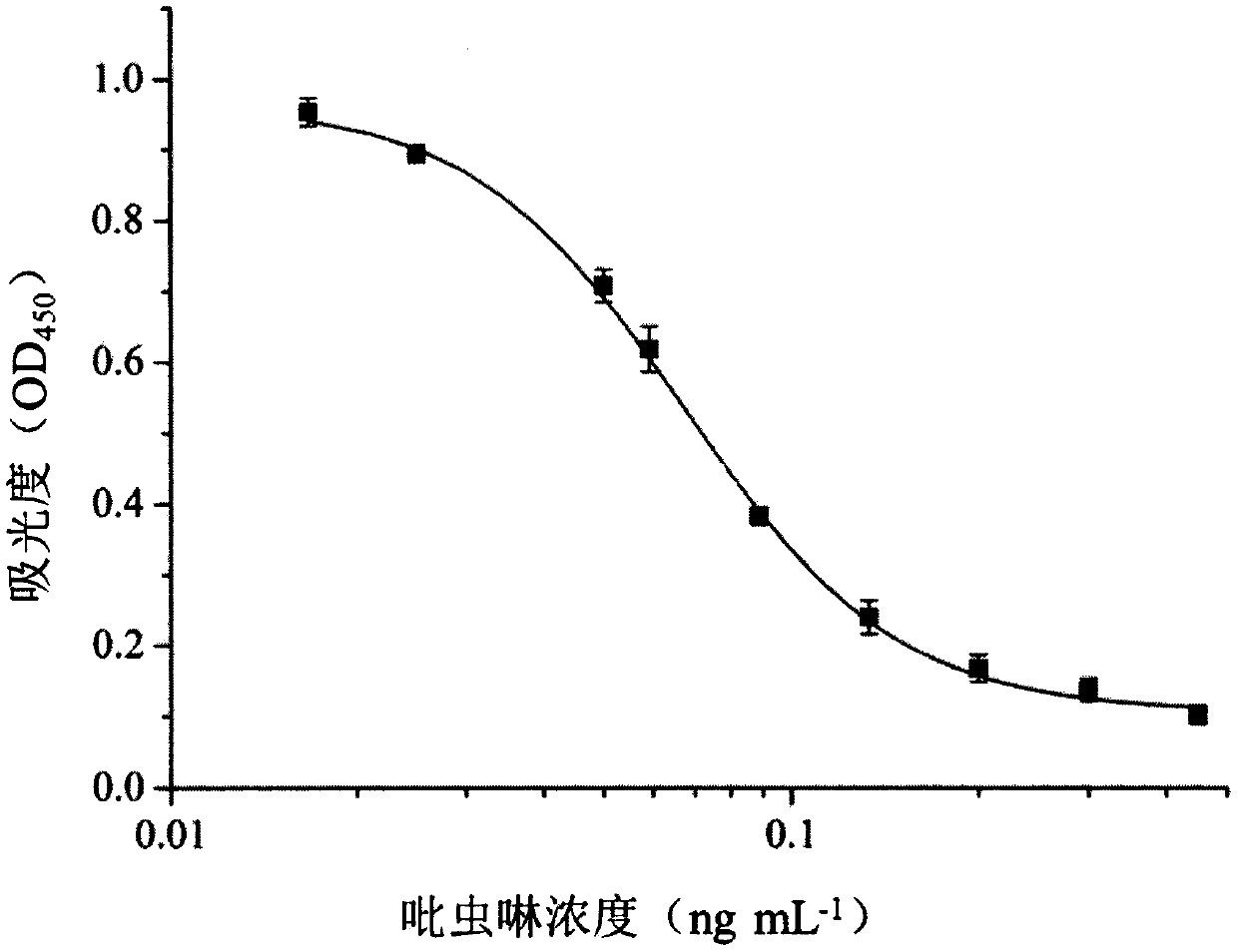
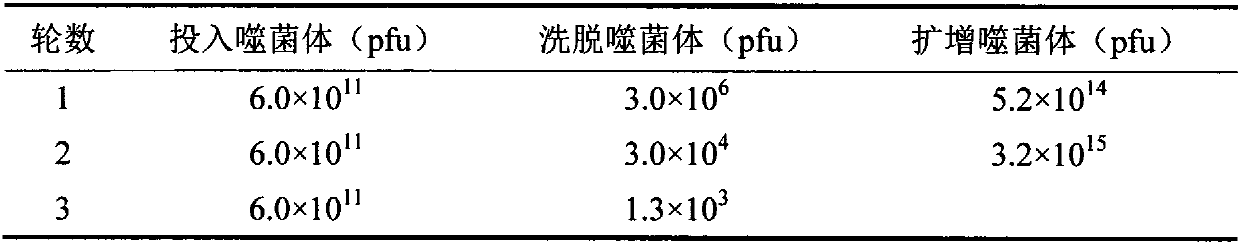
Phage display polypeptide specifically binding to imidacloprid antibody and application thereof
InactiveCN110256531AIncreased sensitivityImprove accuracyPeptidesBiological testingPhage elisaBacteriophage
The invention belongs to the biotechnology field, and relates to a polypeptide specifically binding to an imidacloprid antibody and an application of the polypeptide in detection of imidacloprid. A phage display technology is adopted, a phage display random linear dodecapeptide library is screened three times by the imidacloprid antibody purified by a protein A column, and phage clones that bind to the imidaclone antibody are screened out; a number of phage clones are randomly picked up for amplification and plasmid extraction, positive phage clones are selected by a phage ELISA method, and the positive clones are sequenced to obtain a polypeptide sequence. The invention also relates to the application of the phage display polypeptide in detection of imidacloprid. The phage enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method established by the phage display polypeptide can be used for rapid, sensitive, simple and cheap detection of imidacloprid residues in environment and agricultural products.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
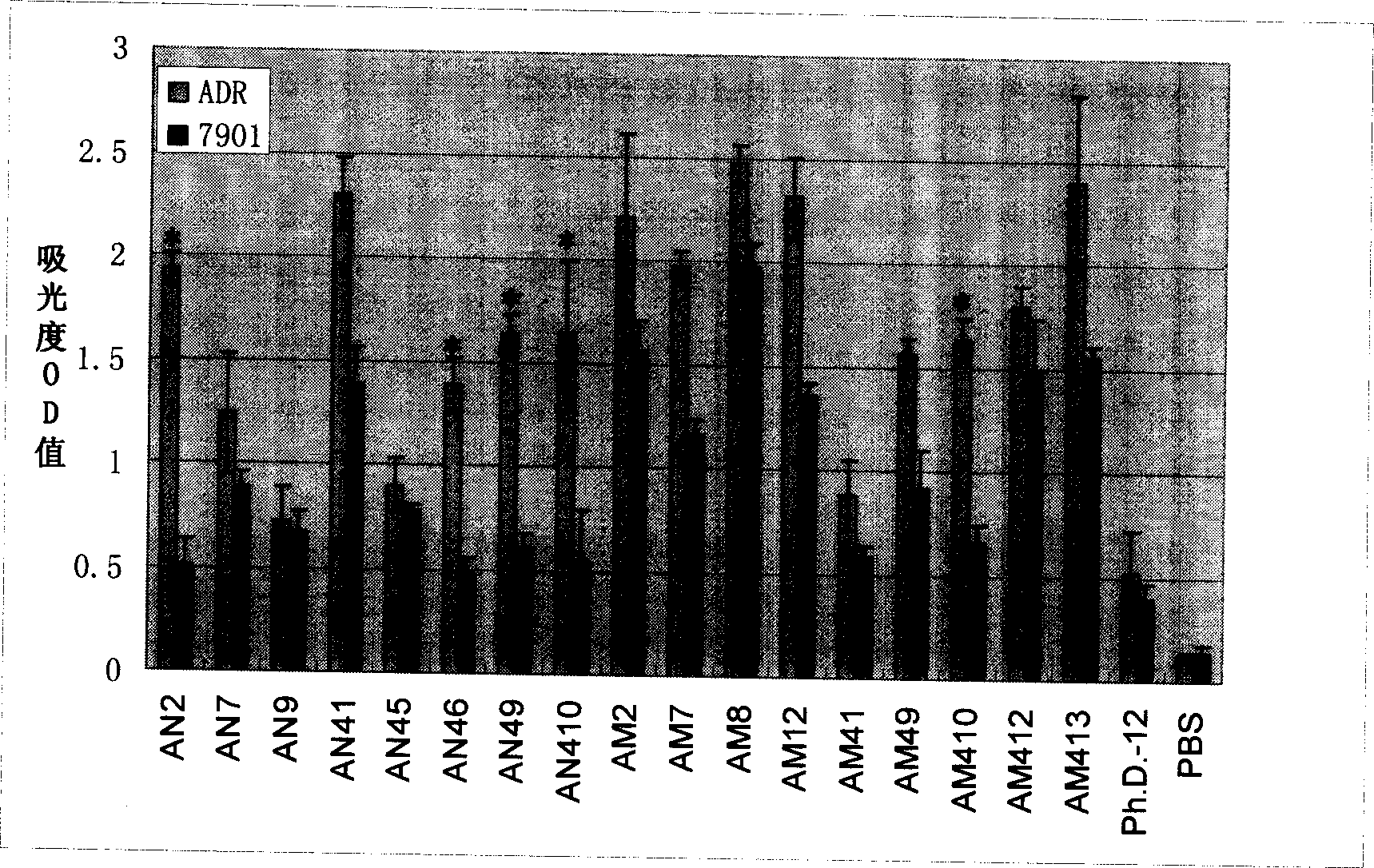
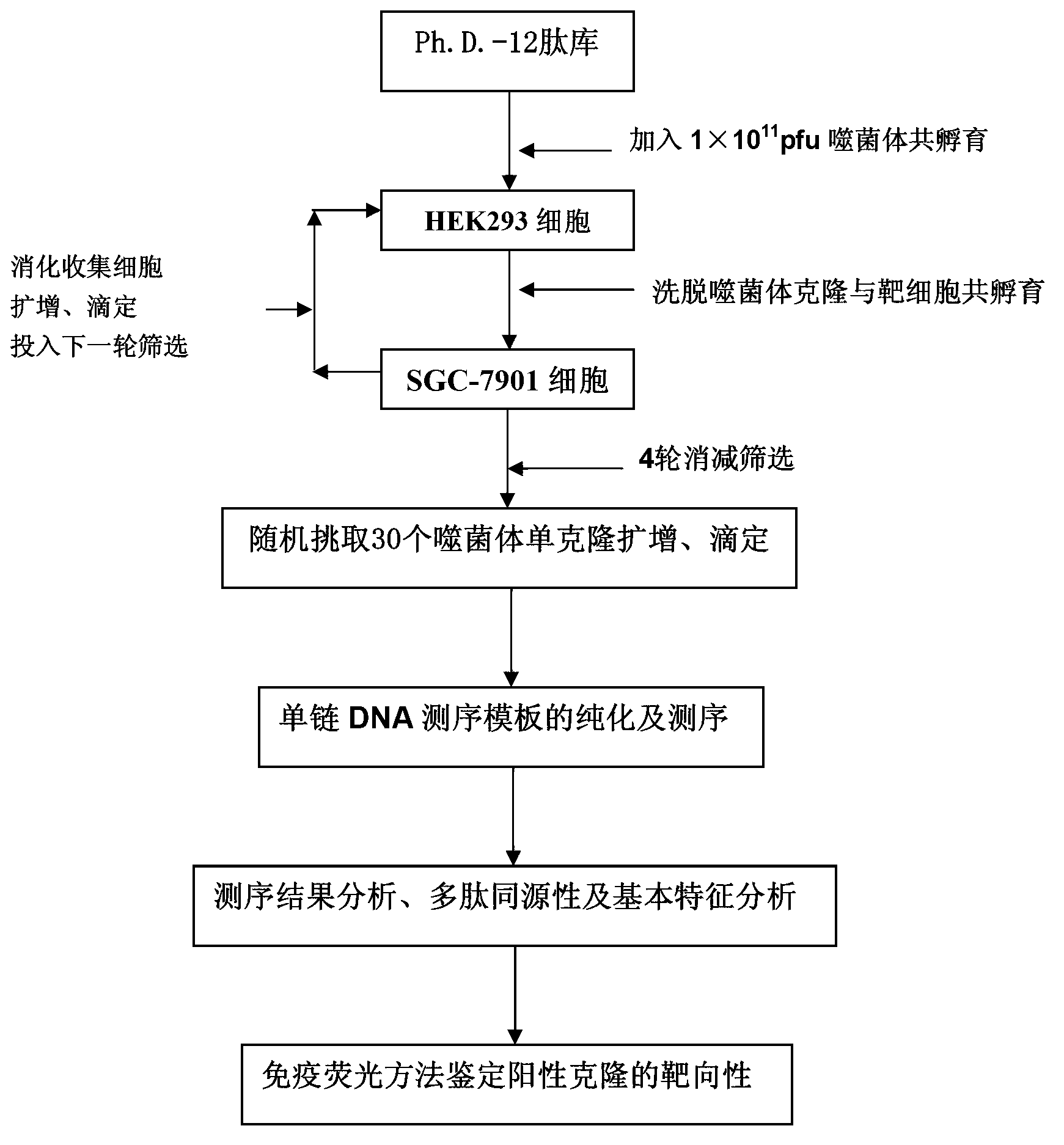
Polypeptide specifically bound to surface of SGC-7901 cell
The invention discloses polypeptide specifically bound to surface of an SGC-7901 cell. A random dodecapeptide library is displayed by bacteriophage to obtain five polypeptide segments in a screening manner; the amino acid sequences respectively are YTHNESSPKDTH, YTVPDYKHNSAH, THPWQITSVNFK, DVFPHSRPADEL and IHKDPANKSLVP. A polypeptide sequence bound to a gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell is screened by utilizing a phage peptide display technology; the affinity of phage clones and the gastric cancer is identified by enzyme-linked immuno sorbent assay (ELISA); 14 phage clones are obtained; five polypeptide sequences are obtained by sequencing. The homology analysis shows that the polypeptide sequence motif can be amino acid determinants bound to a tumor cell surface receptor on ligandin; the targeted results of positive phage clones are further identified by cell immunofluorescence to prompt the positive phage clones to be specifically bound to the SGC-7901 cell; an experimental evidence is provided for early diagnosis of the gastric cancer, targeted transportation of an antitumor medicament, and research and development of targeted short-peptide medicaments by the screened gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell specificity polypeptide.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
Application of Phage Chip as Protein Chip or Gene Chip
InactiveCN101059515BParticle stabilizationAvoid degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementAntigen epitopeAntigen
The invention discloses the application of a phage chip as a protein chip or a gene chip. The present invention obtains phage clones displaying specific exogenous peptides (or antigenic epitopes) by screening phage peptide libraries or constructing phage display libraries, and displays different exogenous peptides in an automatic or non-automatic manner according to a pre-designed array pattern. The phages were directly coupled to the same chip substrate to obtain a phage chip. The chip can be used not only as a protein chip displaying exogenous peptides, but also for the detection, screening and identification of antibodies, ligands and specific binders in natural or synthetic compounds in various samples of human and experimental animals, and as a clone The gene chip of related genes is used for the detection of related genes. The phage chip has the remarkable characteristics of low cost, simple preparation, high stability, high specificity, easy long-term storage and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Human agkistrodon acutus venom immune ScFv antibody library and construction method thereof
InactiveCN103361742APeptide librariesImmunoglobulins against animals/humansSpecific iggScFv Antibodies
The invention relates to the antibody engineering medicine and particularly relates to the phage antibody display technology, namely a construction method of a human agkistrodon acutus venom immune ScFv antibody library. The method comprises the following steps of: performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification by use of human specific IgG light chain and heavy chain primers to obtain PCR products; mixing all PCR products to obtain a light chain PCR mixed product and a heavy chain PCR mixed product respectively; introducing specific primers by taking the light chain PCR mixed product and heavy chain PCR mixed product as templates, and performing PCR amplification to obtain a Linker-VL fragment and a VH-Linker fragment; connecting the obtained Linker-VL fragment and the obtained VH-Linker fragment to obtain a VH-Linker-VL fragment; and importing the obtained VH-Linker-VL fragment into a phage cloning vector to obtain an original library of the human agkistrodon acutus venom immune ScFv antibody library.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Peptides specific for hepatocellular carcinoma cells and applications thereof
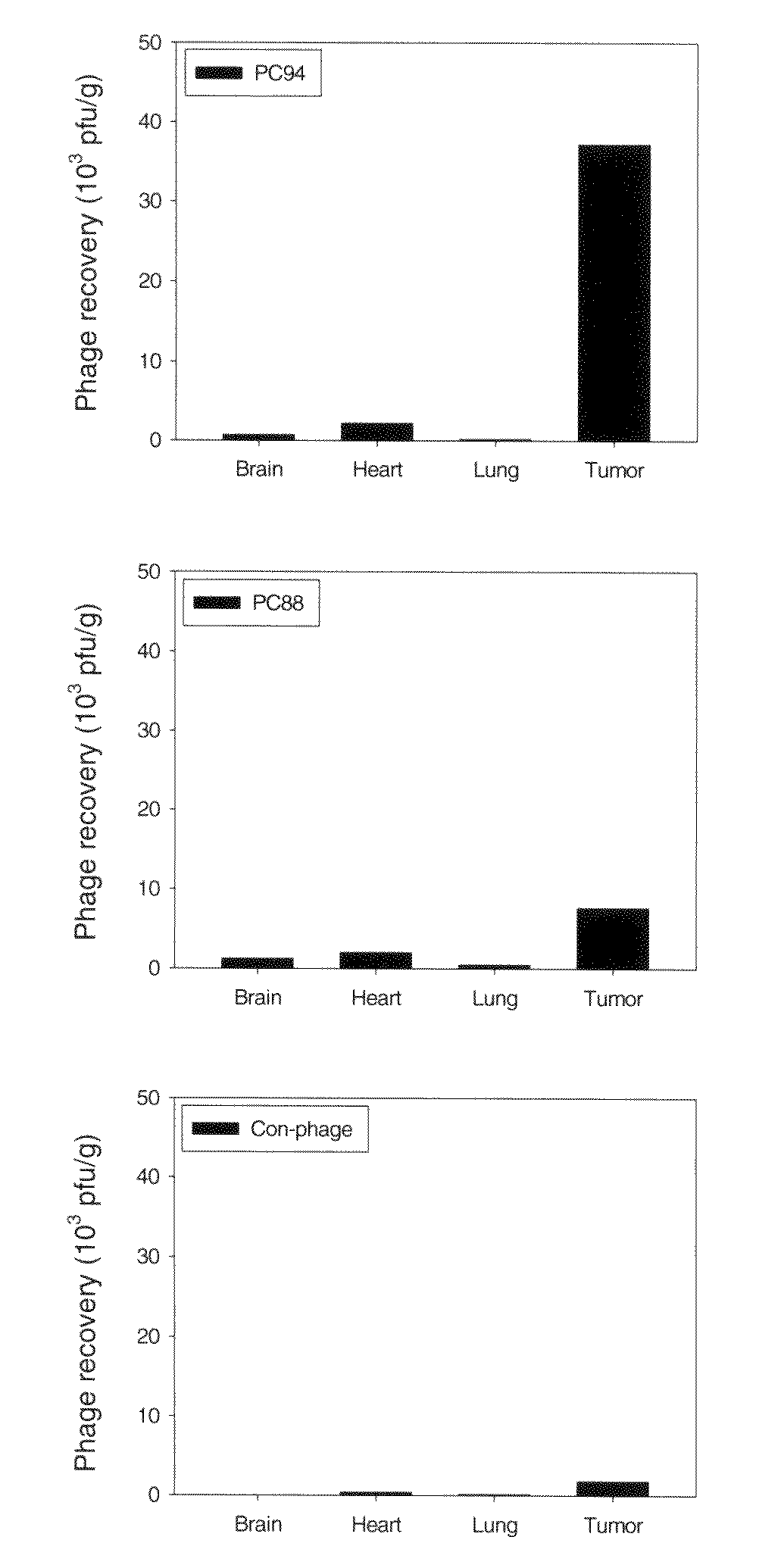
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fourth leading cause of cancer death worldwide. Novel treatment strategies derived from increased knowledge of molecular oncology are constantly being developed to cure this disease. Here, we used phage display to identify novel peptides, including (SP94), which binds specifically to HCC cells. In vitro, the phage clone PC94 binds to HCC cell lines. In vivo, PC94 homed specifically to tumor tissues but not to normal visceral organs in SCID mice bearing human HCC xenografts. The homing ability could be competitively inhibited by synthetic peptide, SP94. PC94 localized to tumor tissues but could not be detected in SP94-competed tumor tissues or in normal organs. In addition, PC94 recognized the tumor tissue but not non-tumor tissue in surgical specimens from HCC patients, with a positive rate of 61.3% (19 / 31). With the conjugation of SP94 and liposomal doxorubicin, a targeted drug delivery system enhanced the therapeutic efficacy against HCC xenografts through enhanced tumor apoptosis and decreased tumor angiogenesis. Our results indicate that SP94 can improve the systemic treatment of patients with advanced HCC.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
An optimized and highly potent anti-inflammatory peptide targeting md-2
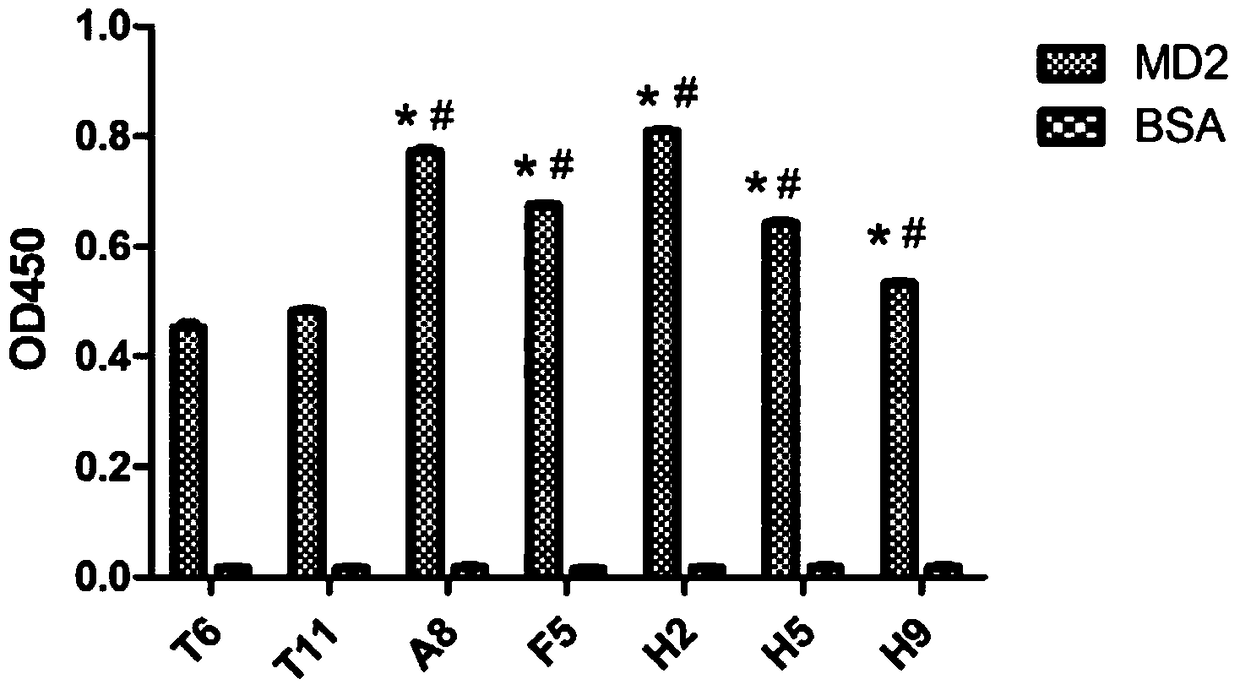
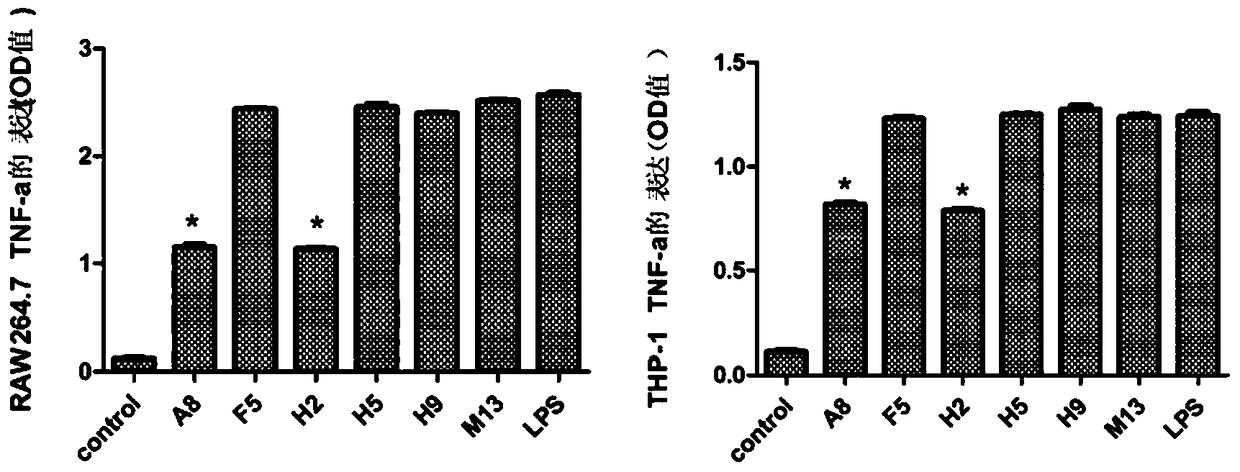
InactiveCN105061559BHigh affinityReduce synthesisAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein targetCytokine
T6 and T11 are based, a mutational peptide library is constructed by adopting an NNK strategy, MD-2 (myeloid differential protein 2) full-length protein is used as target protein, and the mutational peptide library is subjected to affinity selection, so as to realize high-affinity phage clone. Through cell factor generation inhibiting experiment and detection of expression of inflammatory medium in animal serum, the fact that fusion peptide shown in one phage clone can simulate anti-inflammatory polypeptide of MD-2 is discovered, and the amino acid sequence of the anti-inflammatory polypeptide is KRKMRMNTRRL. The combination of the anti-inflammatory polypeptide and MD-2 full-length protein is higher than original T6 and T11 clone, the possibility that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulates macrophage to synthesize and release inflammatory medium can be obviously reduced, and the anti-inflammatory effect is obviously higher than that of original polypeptide.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Polypeptide specifically bound to benzathystrobin immune complex and use thereof
ActiveCN105153280BIncreased sensitivityImprove accuracyPeptidesBiological testingPhage elisaImmune complex deposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, relates to a polypeptide capable of specifically binding to a benzothiostrobin immune complex, and comprises application of the polypeptide in detection of benzothiostrobin. According to the invention, with a phage display technology, a phage display random cycle octapeptide library undergoes 3 rounds of panning by using the benzothiostrobin immune complex, and phage clones capable of binding to the benzothiostrobin immune complex are panned out; and a plurality of phage clones are randomly selected for amplification and plasmid extraction, and positive phage clones are selected through a non-competitive phage ELISA method and are sequenced so as to obtain polypeptide sequences. The invention also relates to the application of the phage display polypeptide in the detection of the benzothiostrobin. The non-competitive phage ELISA method established by using the phage display polypeptide can be applied in rapid, sensitive, simple, convenient and cheap detection of benzothiostrobin residues in the environment and agricultural products.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Antigen display system and methods for characterizing antibody responses
Provided herein is an antigen display library for detecting antibodies produced by an individual; and methods of using the antigen display library to generate an antibody signature, the method comprising contacting a biological sample containing antibodies from an individual with the antigen display library, isolating phage clones displaying antigenic epitopes recognized by antibody in the sample, and identifying the antigenic epitopes that were recognized by antibody in the sample. Also provided are kits for generating an antibody signature comprising the antigen display library, a substrate for isolating phage clones bound by antibody, and may further comprise reagents useful for generating the antibody signature.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
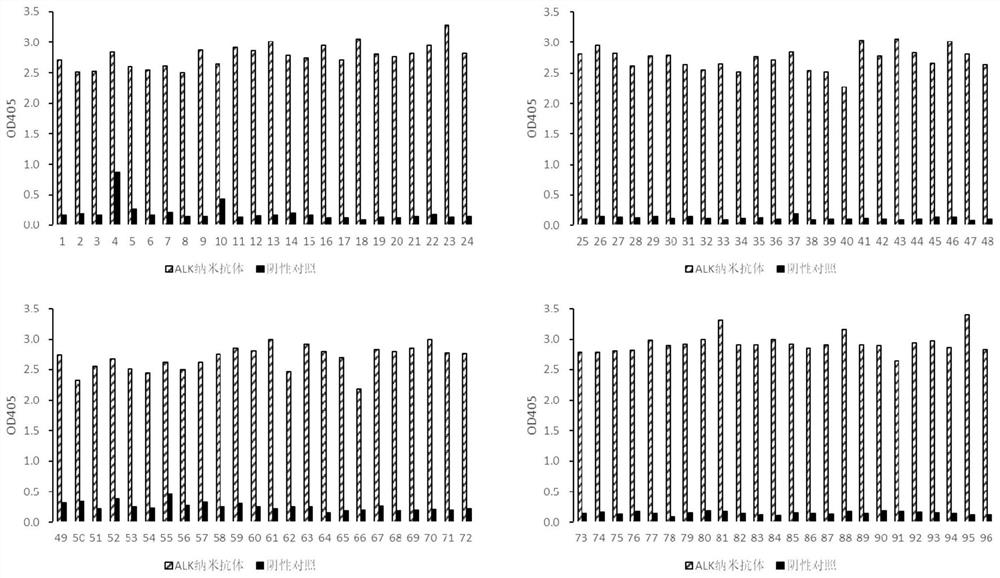
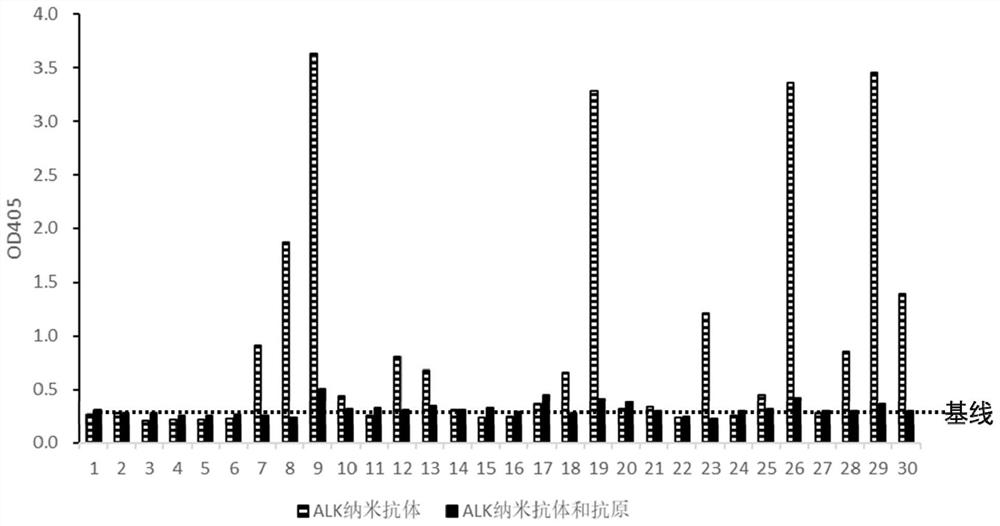
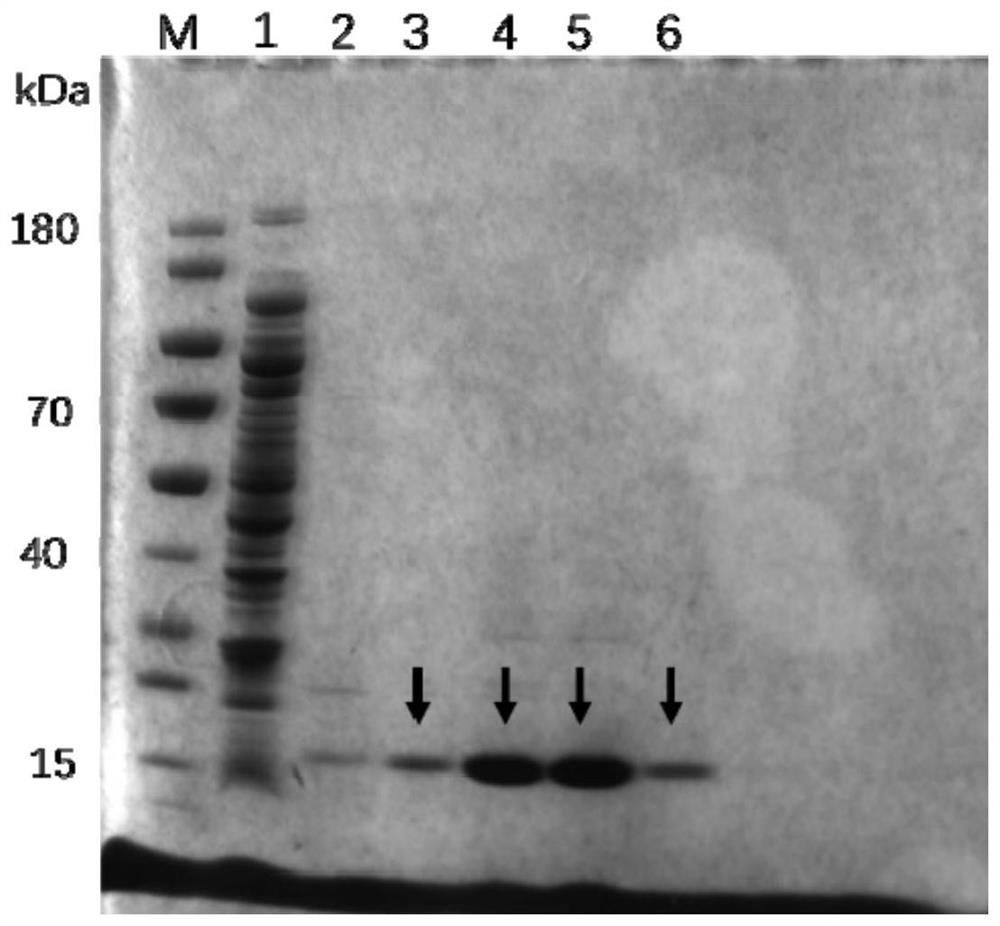
ALK nano antibody developed based on phage display technology and application thereof
ActiveCN112794914AHigh affinityStrong specificityFermentationGenetic engineeringEscherichia coliComplementarity determining region
The invention discloses an ALK nano antibody developed based on a phage display technology and an application of the ALK nano antibody. The nano antibody provided by the invention comprises a complementarity determining region consisting of a CDR1, a CDR2 and a CDR3, the amino acid sequence of the CDR1 is the 21st-28th site of SEQ ID No.1; the amino acid sequence of the CDR2 is from the 46th-52nd site of SEQ ID No.1; and the amino acid sequence of the CDR3 is the 91th-107th sites of SEQ ID No.1. A camel nano antibody natural library is constructed by utilizing camel PBMC cells, and high-affinity ALK nano antibody phage clones are screened from the library by utilizing a phage display technology and are converted into an escherichia coli expression system for mass expression, so that the development and production cost of the ALK antibody is effectively reduced, the immunohistochemical verification of a clinical sample shows that the ALK nano antibody disclosed by the invention has higher sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:SHENZHEN HUADA GENE INST +1
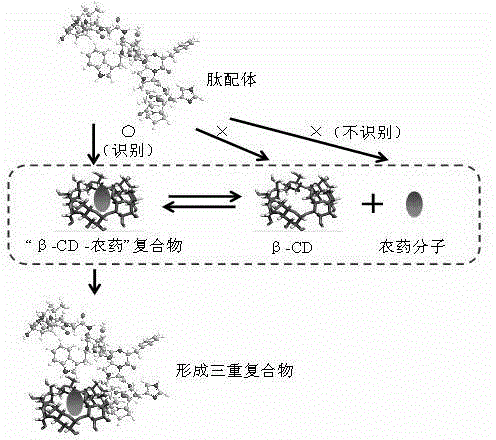
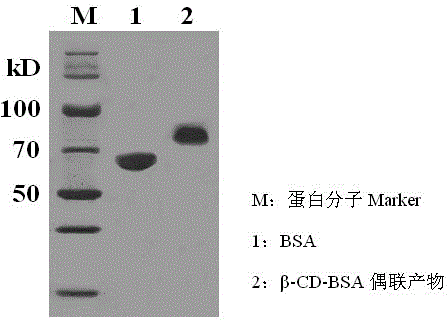
Preparation method of peptide ligand for non-competitive detection of water-soluble pesticide residues
The invention discloses a preparation method of a peptide ligand for non-competitive detection of water-soluble pesticide residues. The preparation method comprises the following steps: coupling beta-cyclodextrin (beta-CD) with bovine serum albumin (BSA), enveloping the coupling products with a solid phase carrier to complex with chlorpyrifos; performing four-round screening on commercialized phage display peptide libraries by using 'positive and negative alternative screening' strategy; separating and selecting mono phage clones from the fourth-round screening elution products, identifying the mono phage clone capable of specifically recognizing 'beta-CD-pesticide' complex; finally sequencing the identified phage clone to determine the insertion of polypeptide fragment and obtain the amino acid sequence information of the polypeptide. The preparation method has the advantages that the molecular modification of the detection object is not needed, and the obtained peptide ligand is used for constructing the non-competitive detection of water-soluble pesticide residues.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF ARTS & SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com