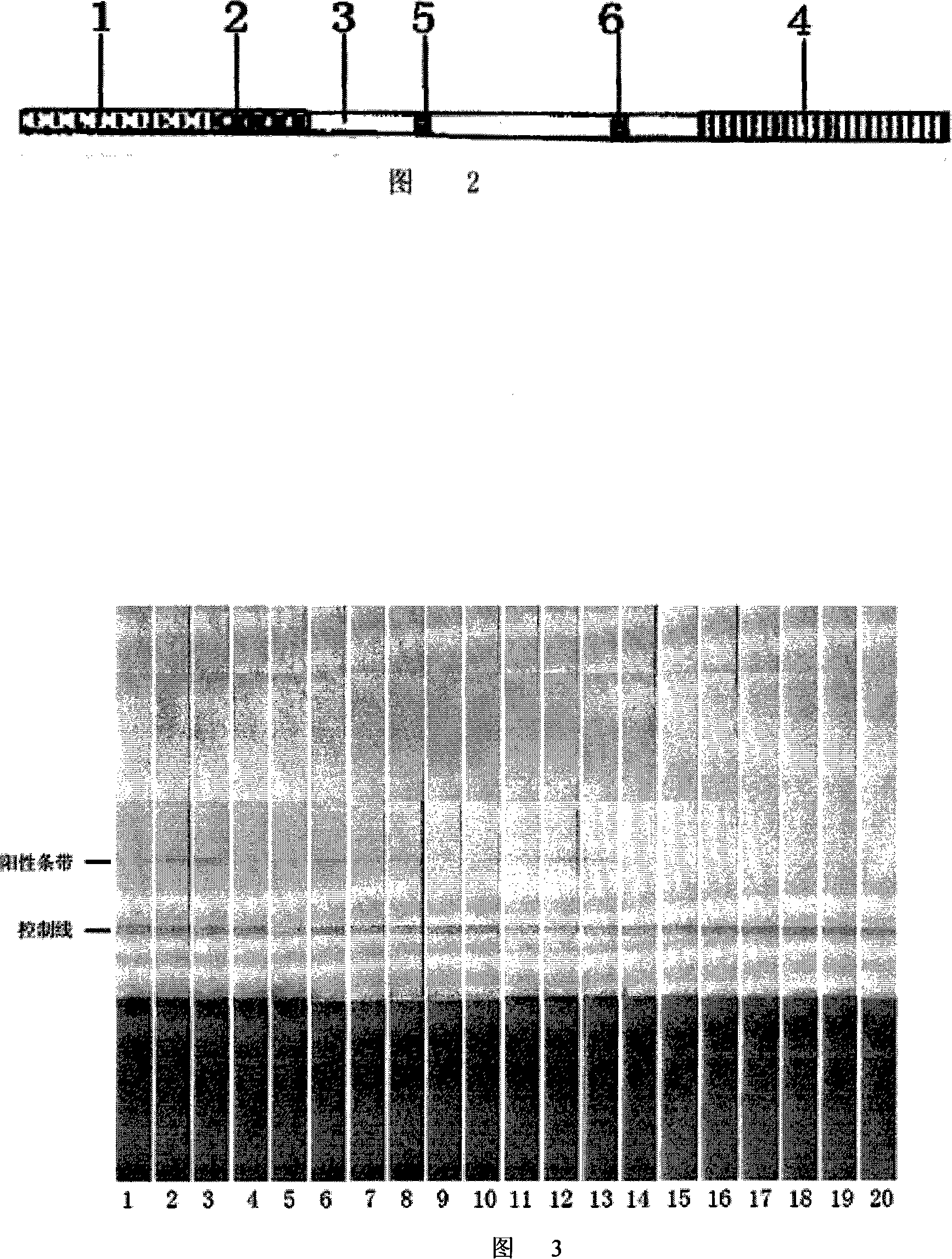
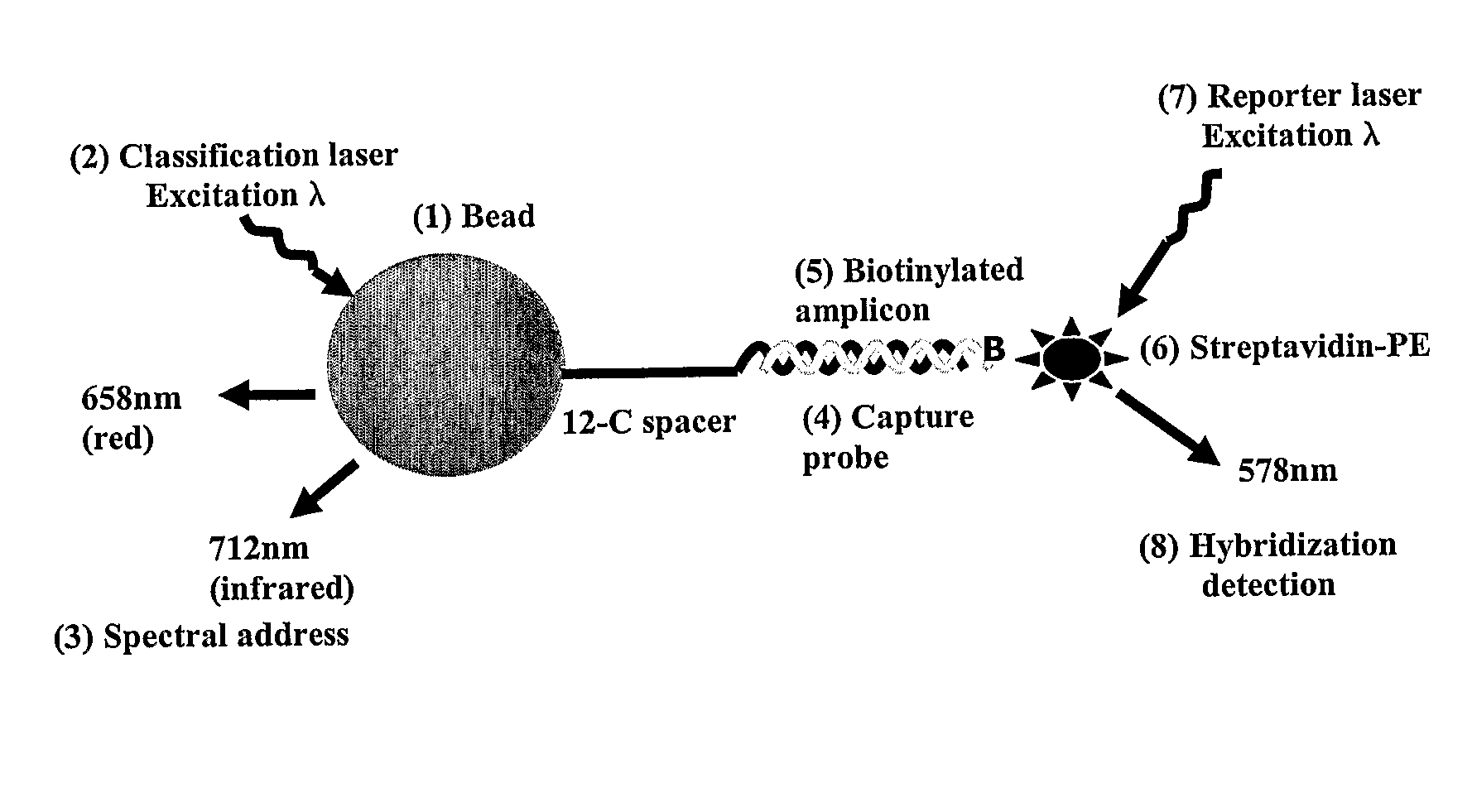
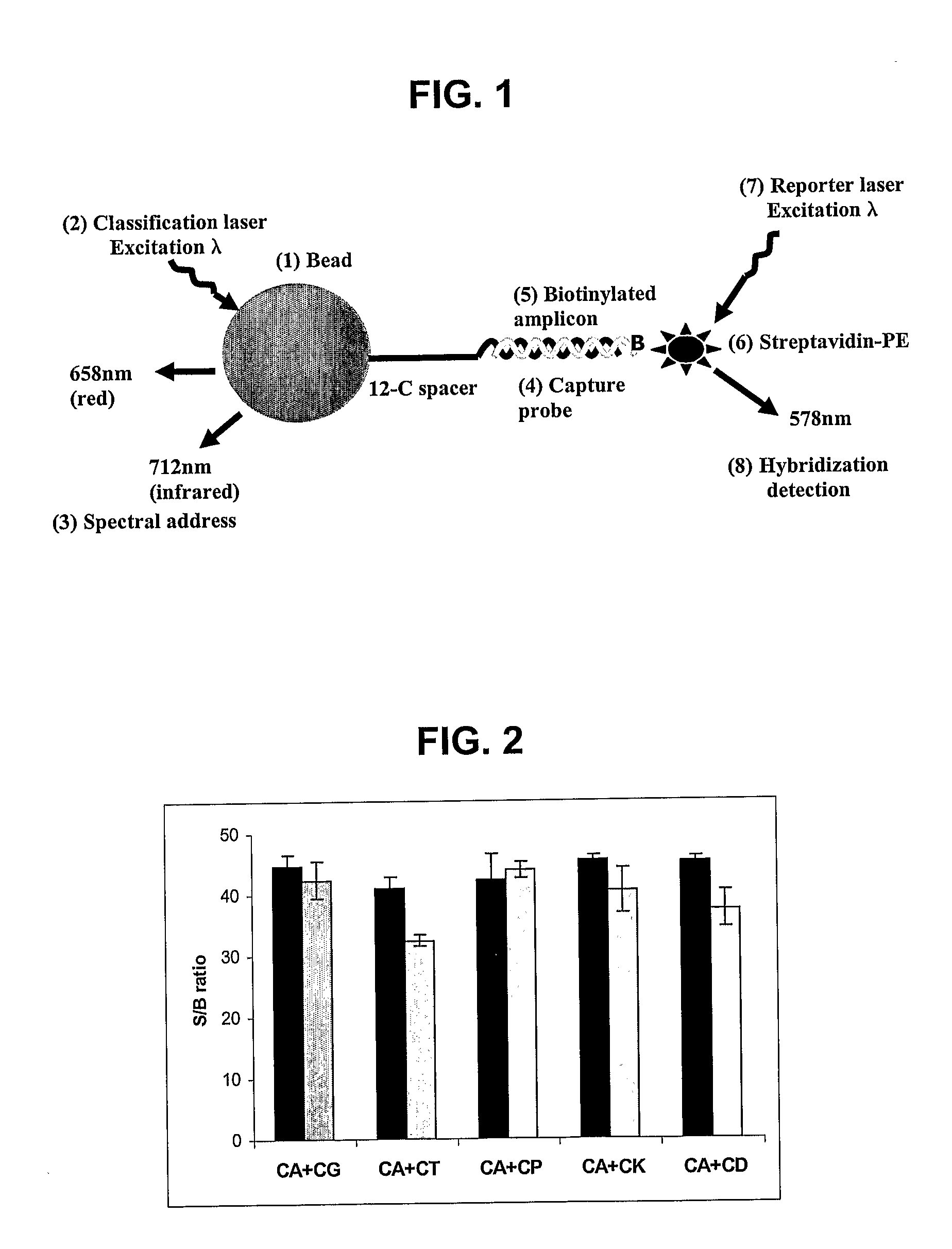
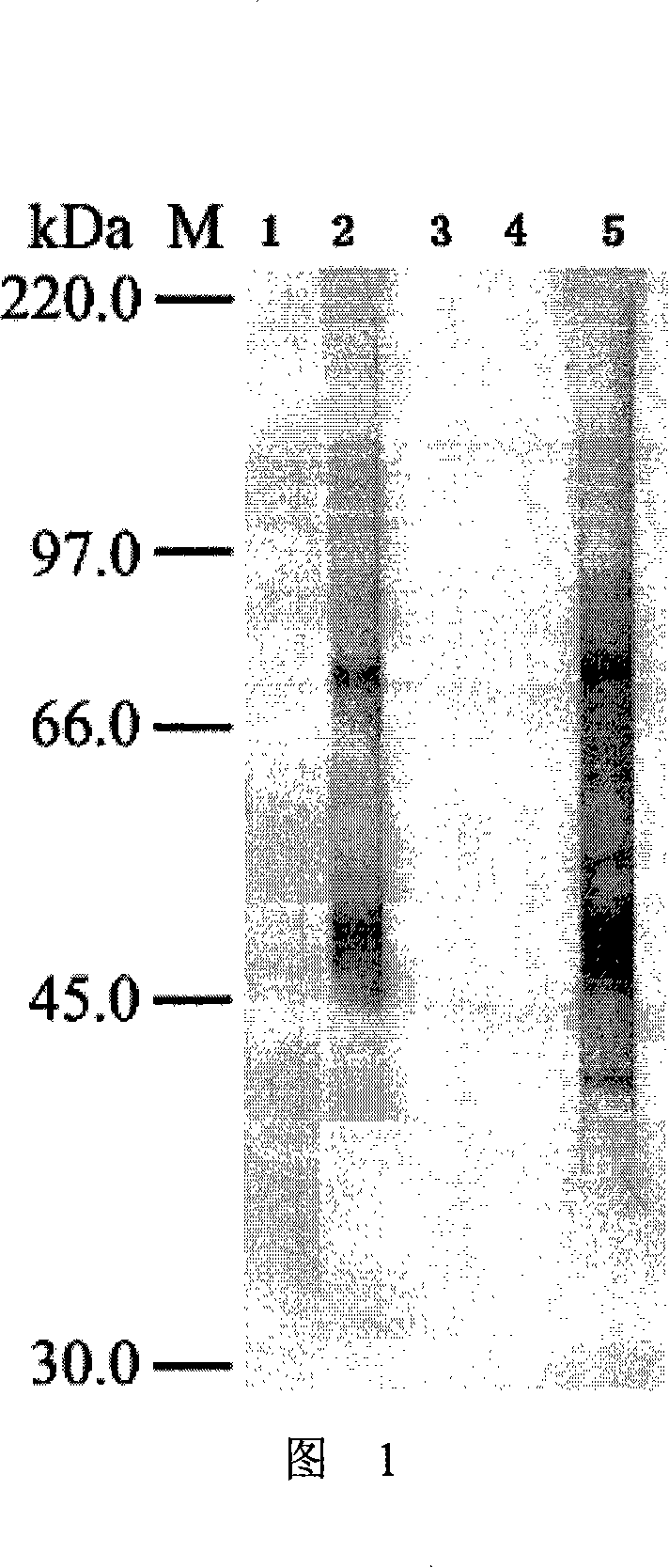Patents
Literature
441 results about "Candida famata" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Candida (fungus) Candida is a genus of yeasts and is the most common cause of fungal infections worldwide. Many species are harmless commensals or endosymbionts of hosts including humans; however, when mucosal barriers are disrupted or the immune system is compromised they can invade and cause disease.
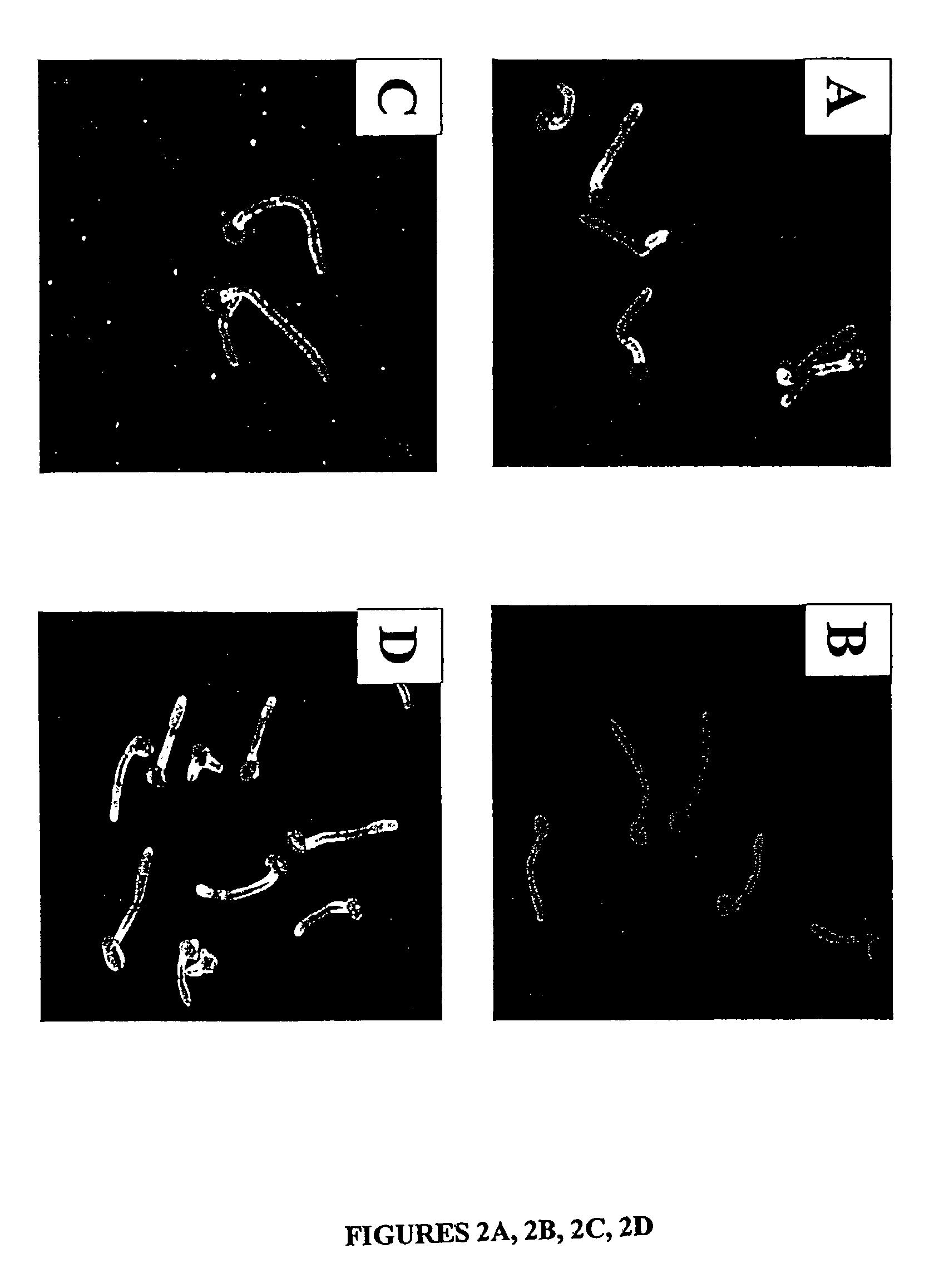
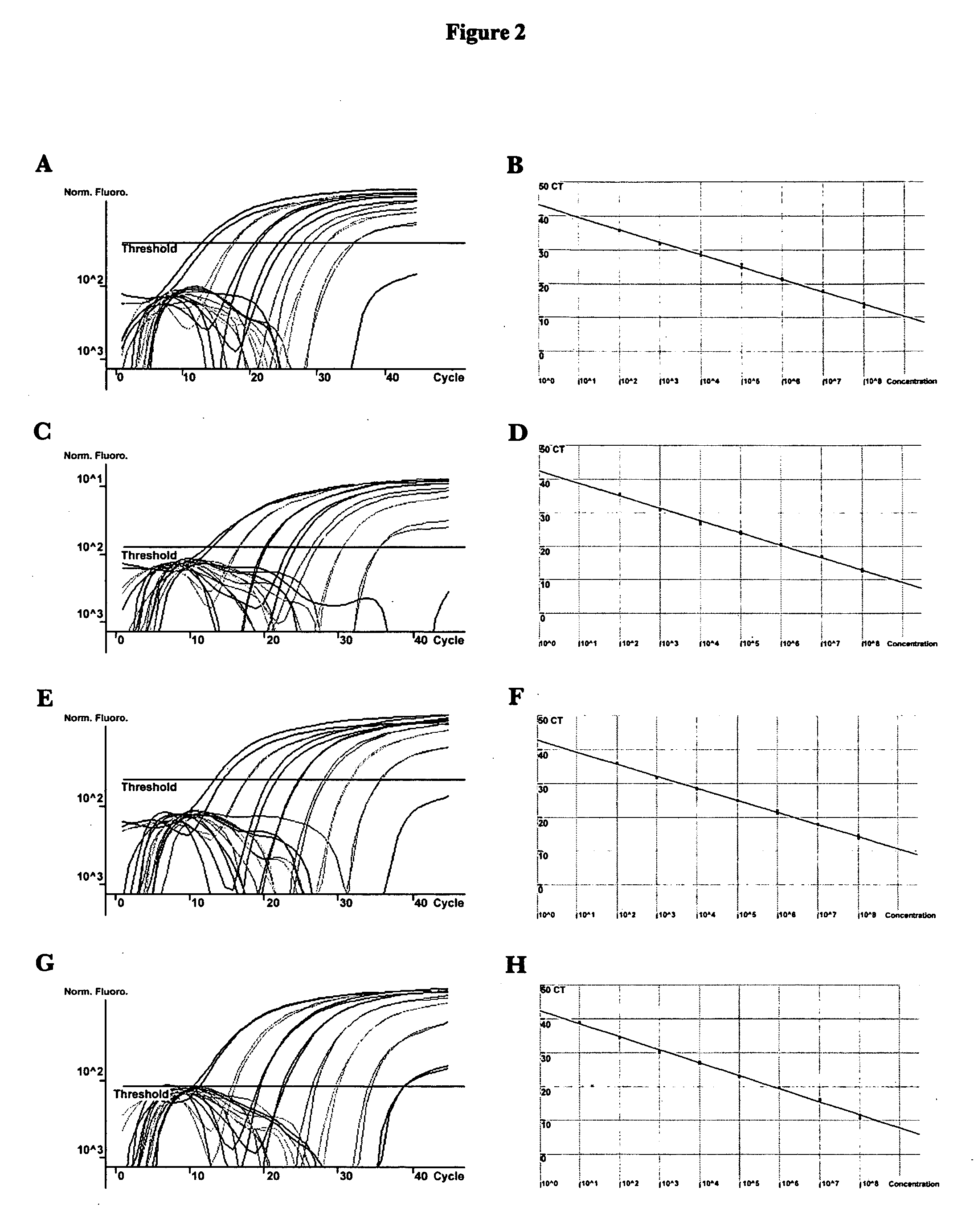
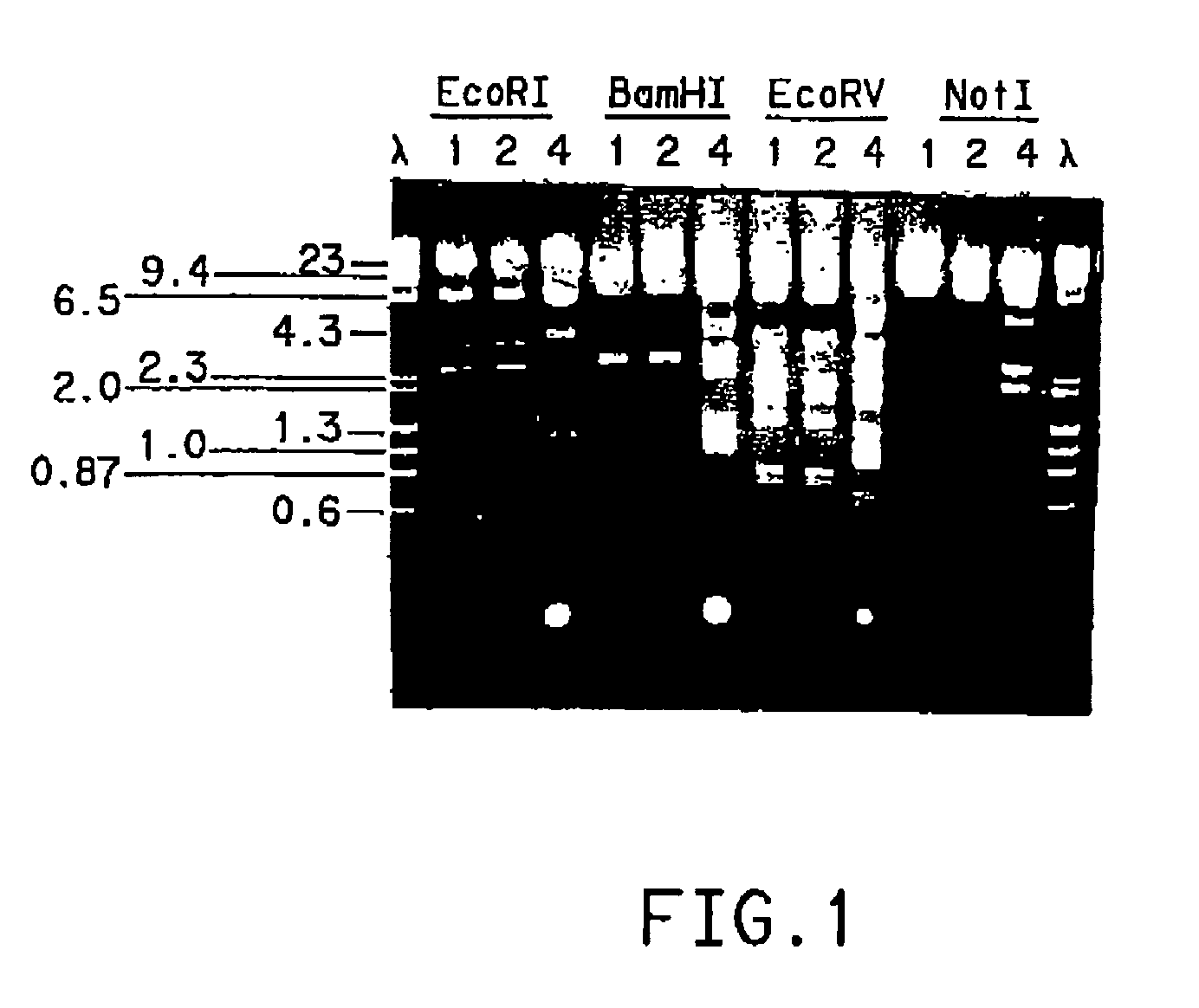
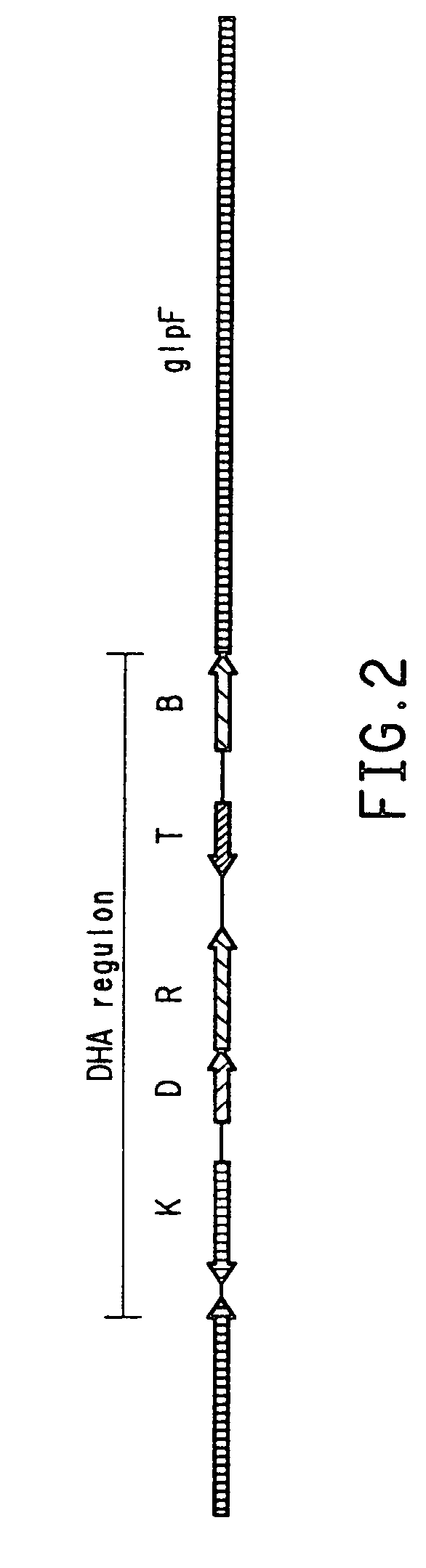
PCR identification and quantification of important Candida species
InactiveUS6017699AConvenient amountHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative determinationCombined use
The subject invention relates to a set of DNA primers which, when utilized in conjunction with the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay, can amplify and speciate DNA from five medically important Candida species. Furthermore, the PCR amplified products, generated by the primers, can also be used to create species specific probes which can also detect and confirm the five species of Candida. Thus, the present invention allows for early diagnosis and treatment of an infection. The assay is useful in the context of monitoring antifungal treatment regimens, screening potential antifungal agents, and similar applications requiring quantitative determinations.
Owner:UNIV OF PITTSBURGH THE
Pharmaceutical compositions and methods to vaccinate against candidiasis
InactiveUS20030124134A1Treat prevent alleviateToxic reductionPeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsHospitalized patientsVirulent characteristics
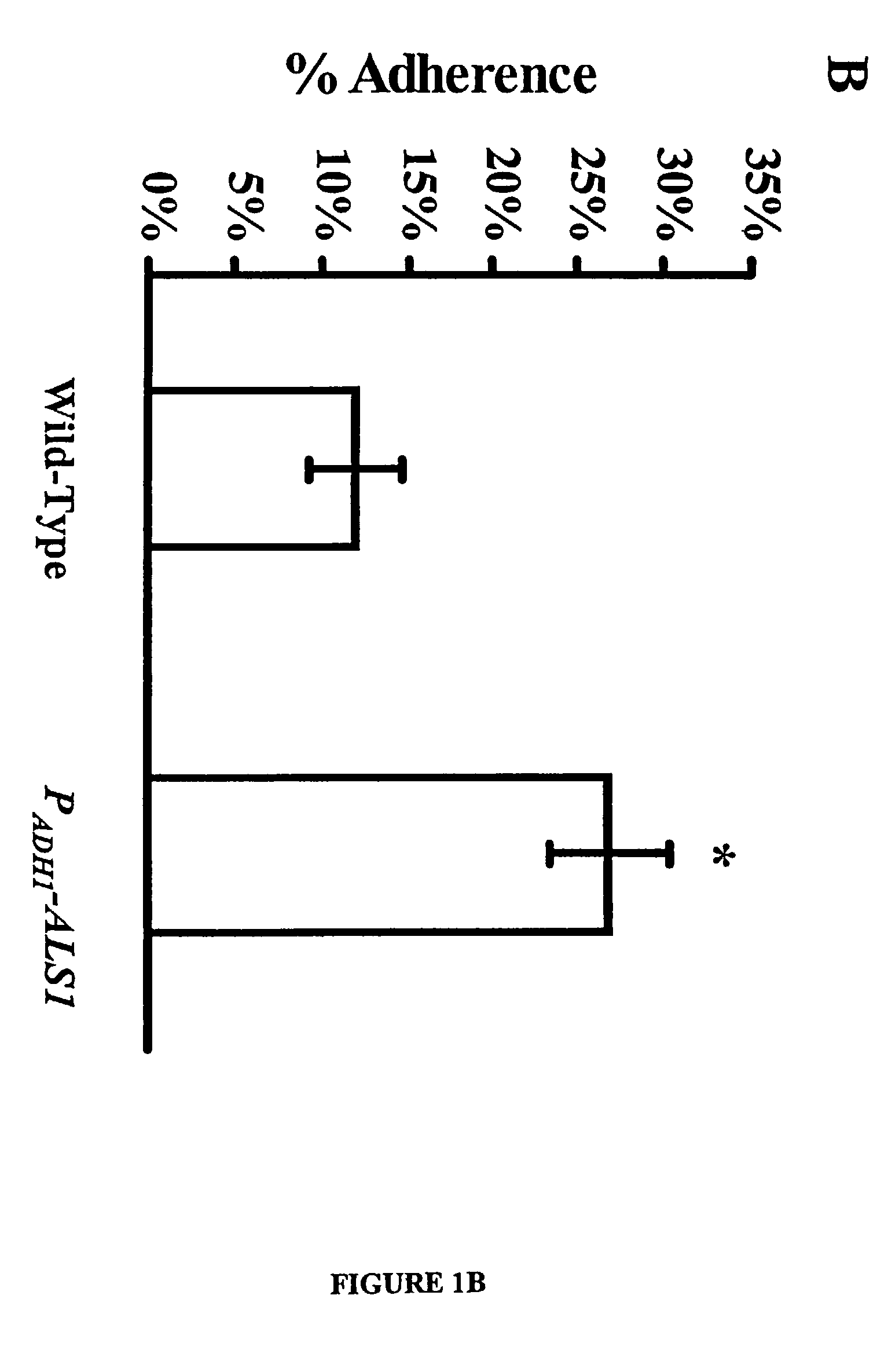
A Candida albicans bloodstream infections cause significant morbidity and mortality in hospitalized patients. Filament formation and adherence to host cells are critical virulence factors of C. albicans. Multiple filamentation regulatory pathways have been discovered, however the downstream effectors of these regulatory pathways remain unknown. The cell surface proteins in the ALS group are downstream effectors of the filamentation regulatory pathway. Particularly, Als1p mediates adherence to endothelial cells in vitro and is required for virulence. The blocking of adherence by the organism is described resulting from the use of a composition and method disclosed herein. Specifically, a pharmaceutical composition comprised of a gene, gene product, or specific antibody to the ALS gene family is administered as a vaccine to generate an immune response capable of blocking adherence of the organism.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT UCLA HARBOR MEDICAL CENT +1
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20040185478A1Reduce usageDetermine rapidly the bacterial resistance to antibioticsMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBacteroidesNeisseria meningitidis
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6'-lla, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6')-aph(2''), aad(6'), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Composition comprising a Lactobacillus pentosus strain and uses thereof
A novel probiotic strain termed Lactobacillus pentosus NCIMB 41114 is capable of preventing growth of pathogenic microorganisms in the GI tract. In particular, this bacterium inhibits Candida overgrowth, and can be employed to prevent and treat associated diseases, including IBS and thrush.
Owner:READING SCHOOL OF FOOD BIOSCI FOOD MICROBIAL SCI UNIT UNIV OF
Method and formulation for treating candidiasis using morinda citrifolia
InactiveUS7014873B2Good curative effectPrevent CandidiasisBiocideAnimal repellantsFruit juiceMonilinia laxa
The present invention features a novel use of processed ingredients from the Indian mulberry plant, and particularly a novel use of one or more processed Morinda citrifolia-based naturaceutical formulations comprising one or more of a processed Morinda citrifolia fruit juice, puree juice, oil or oil extract, dietary fiber, alcohol extract, etc., for inhibiting and preventing the overgrowth of Candida fungus and for treating Candidiasis and its associated symptoms.
Owner:TAHITIAN NONI INT INC
Species-specific, genus-specific and universal DNA probes and amplification primers to rapidly detect and identify common bacterial and fungal pathogens and associated antibiotic resistance genes from clinical specimens for diagnosis in microbiology laboratories
InactiveUS20030049636A1Low costRapid positioningMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBacteroidesNeisseria meningitidis
DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample DNA from (i) any bacterium, (ii) the species Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, Enterococcus faecium, Neisseria meningitidis, Listeria monocytogenes and Candida albicans, and (iii) any species of the genera Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, Enterococcus, Neisseria and Candida are disclosed. DNA-based methods employing amplification primers or probes for detecting, identifying, and quantifying in a test sample antibiotic resistance genes selected from the group consisting of blatem, blarob, blashv, blaoxa, blaZ, aadB, aacC1, aacC2, aacC3, aacA4, aac6'-lla, ermA, ermB, ermC, mecA, vanA, vanB, vanC, satA, aac(6')-aph(2''), aad(6'), vat, vga, msrA, sul and int are also disclosed. The above microbial species, genera and resistance genes are all clinically relevant and commonly encountered in a variety of clinical specimens. These DNA-based assays are rapid, accurate and can be used in clinical microbiology laboratories for routine diagnosis. These novel diagnostic tools should be useful to improve the speed and accuracy of diagnosis of microbial infections, thereby allowing more effective treatments. Diagnostic kits for (i) the universal detection and quantification of bacteria, and / or (ii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned bacterial and fungal species and / or genera, and / or (iii) the detection, identification and quantification of the above-mentioned antibiotic resistance genes are also claimed.
Owner:BERGERON MICHEL G +3
Methods and materials for the production of organic products in cells of Candida species
InactiveUS7141410B2Good conditionUse in synthesisSugar derivativesMicroorganismsHeterologousBiotechnology
The present invention relates to biocatalysts that are cells, optimally of the Crabtree-negative phenotype, comprising expression vectors encoding genes heterologous to the cell that enable increased production of organic products. More specifically, the invention relates to genetically modified Candida cells, methods for making the Candida cells, and their use in production of organic products, particularly lactic acid.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Method for preventing and/or treating infections, colonisations, or illnesses related to staphylococcus aureus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, streptococcus pyogenes, enterococcus faecium, enterobacter cloacae, proteus mirabilis, bacteroides fragilis, staphylococcus epidermidis, propionibacterium acnes, candida albicans and/or malassezia furfur
The subject matter of the present invention is a bacteria or mix of bacteria having an antagonistic activity with respect to stains of S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, Streptococcus pyogenes, Enterococcus faecium, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Bacteroides fragilis Staphylococcus epidermidis, Propionibacterium acnes, Candida albicans and / or Malassezia furfur as well as the use thereof in the treatment and / or prevention of infections or colonisations related to those pathogens. The invention pertains to care products containing one or more non-pathogenic antagonistic strains intended to prevent and / or treat infections or colonisations on skin, wounds, mucous membranes and appendages.
Owner:URGO RECH INNOVATION & DEVEMENT
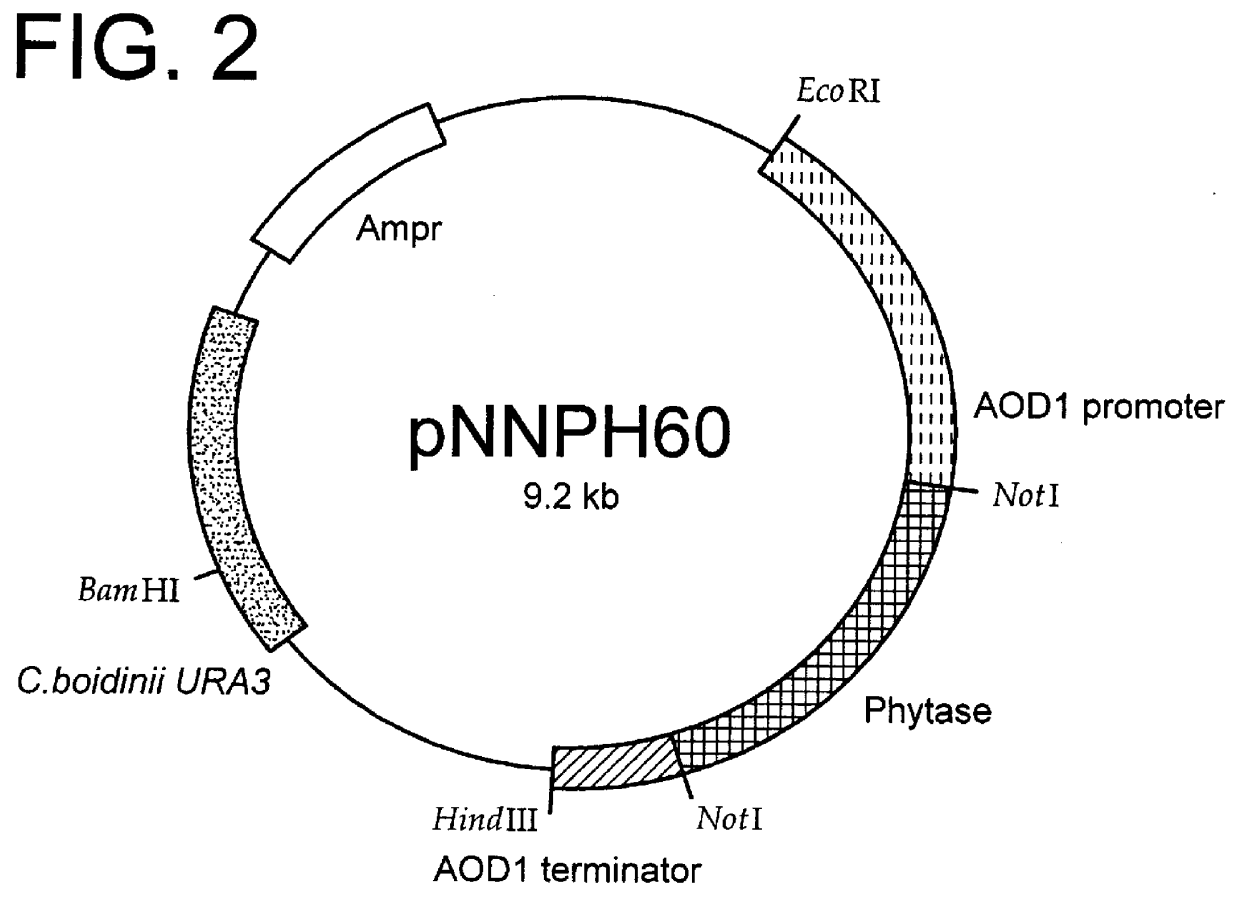
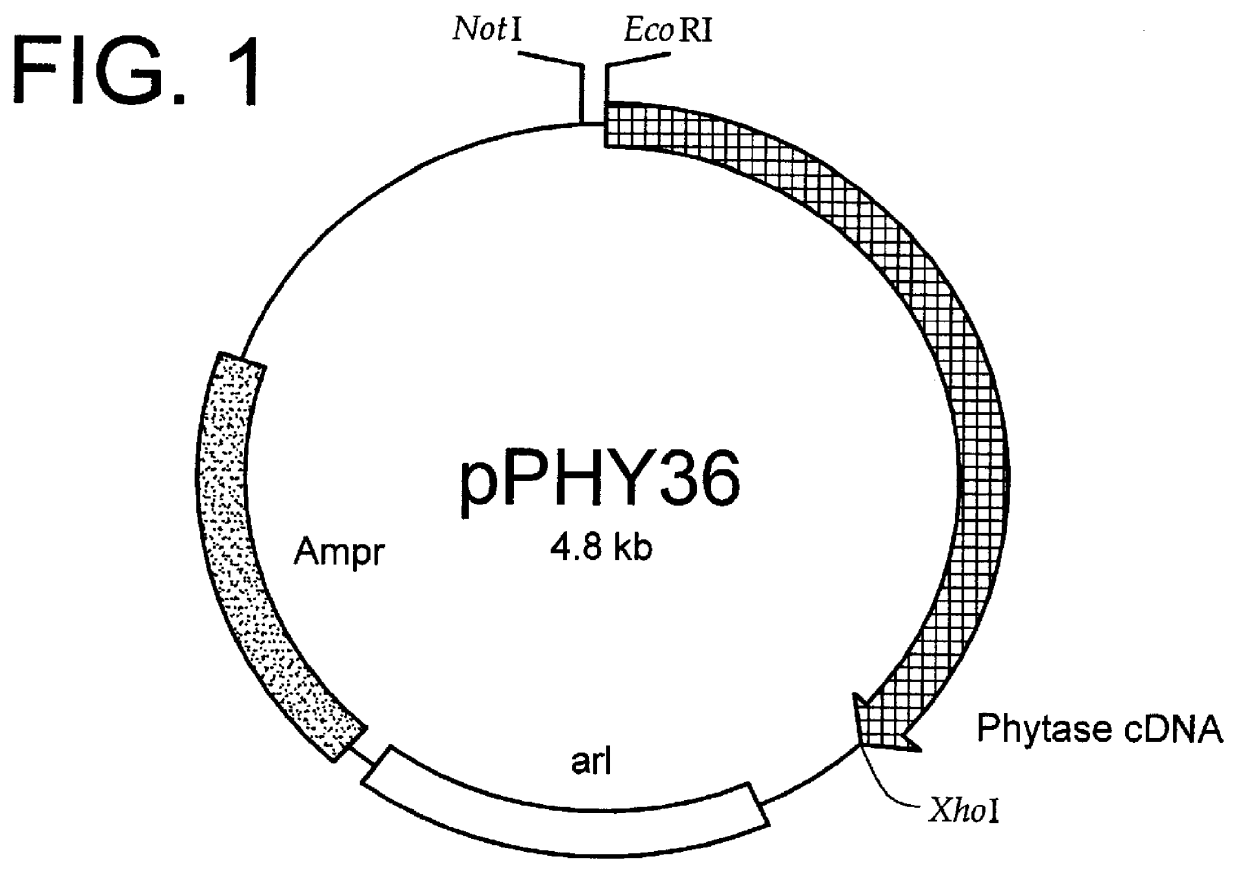
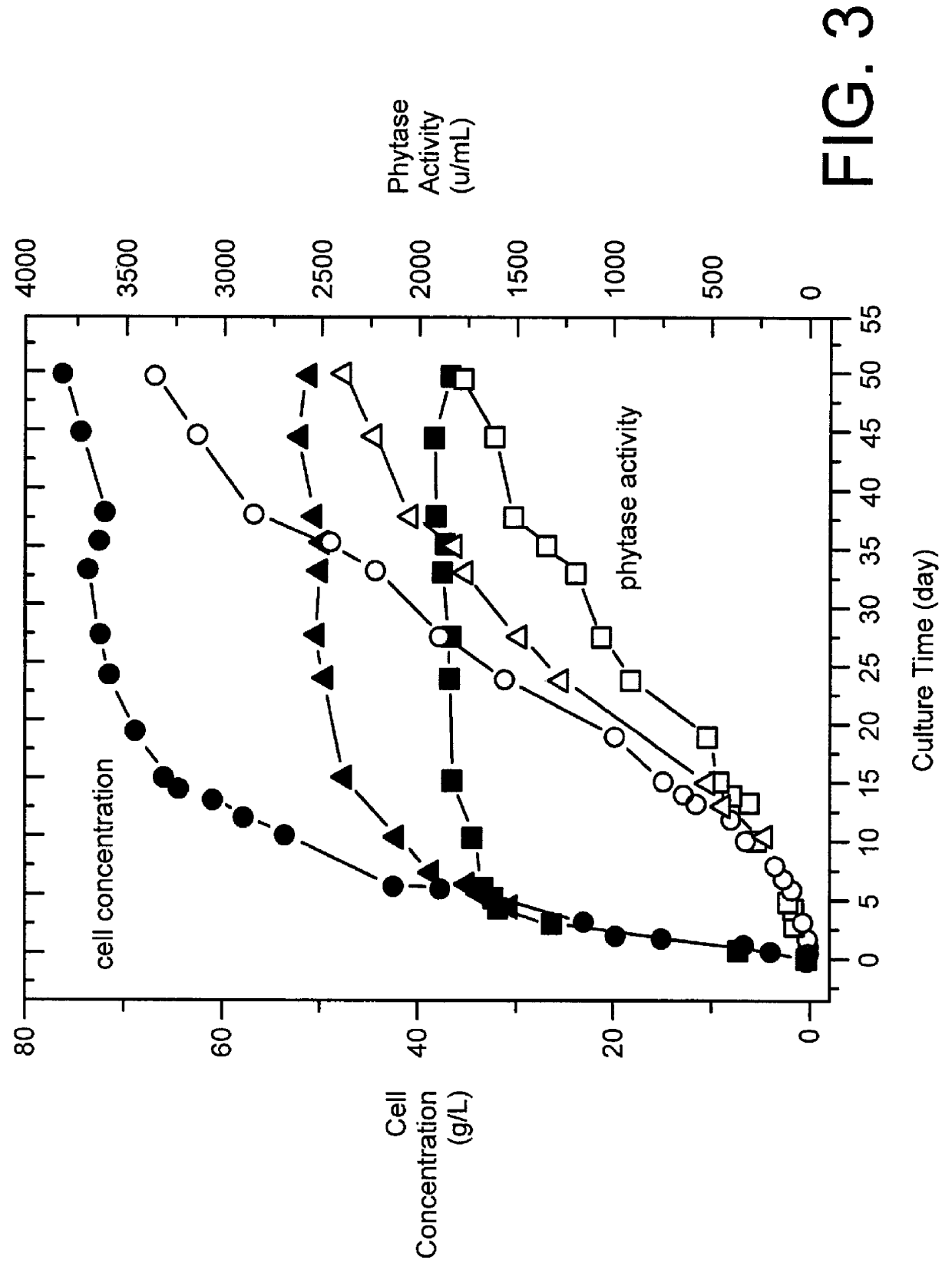
Method for producing phytase
InactiveUS6140077AIncreasing number of cellPrevent proliferationFungiHydrolasesLiquid mediumPhytase activity
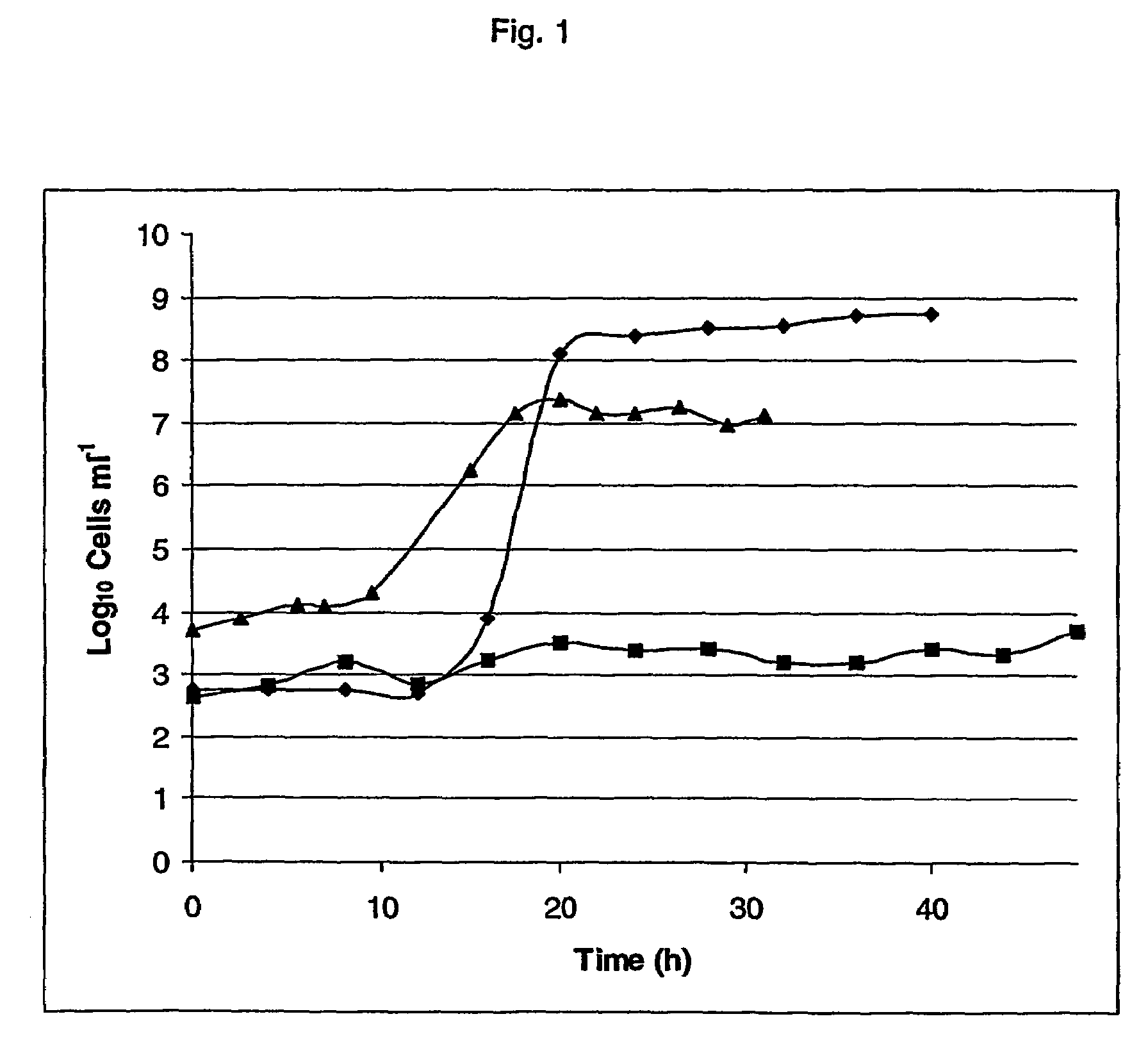
A method for producing phytase using a Candida boidinii transformant, by which phytase is secreted to liquid medium without substantially increasing the number of the transformant cells is disclosed. In this method, cells of a Candida boidinii transformant which is transformed with a recombinant vector comprising a promoter inducible with methanol and a gene located downstream of said promoter and operably linked to said promoter, which gene encodes a polypeptide having phytase activity, are cultured in a liquid culture medium containing phosphoric acid or a phosphate compound in an amount effective of restricting proliferation of said cells of Candida boidinii transformant such that the amount of said cells of Candida boidinii transformant is not substantially increased, while adding methanol to the culture medium, so as to make said cells secrete said phytase.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
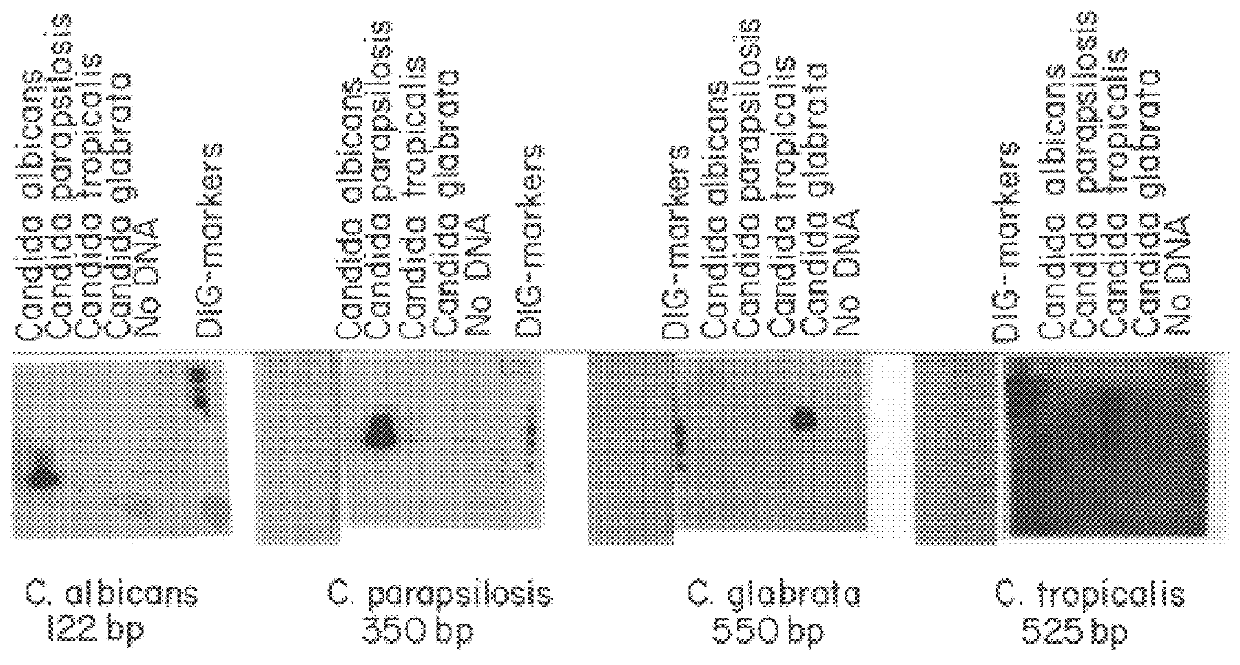
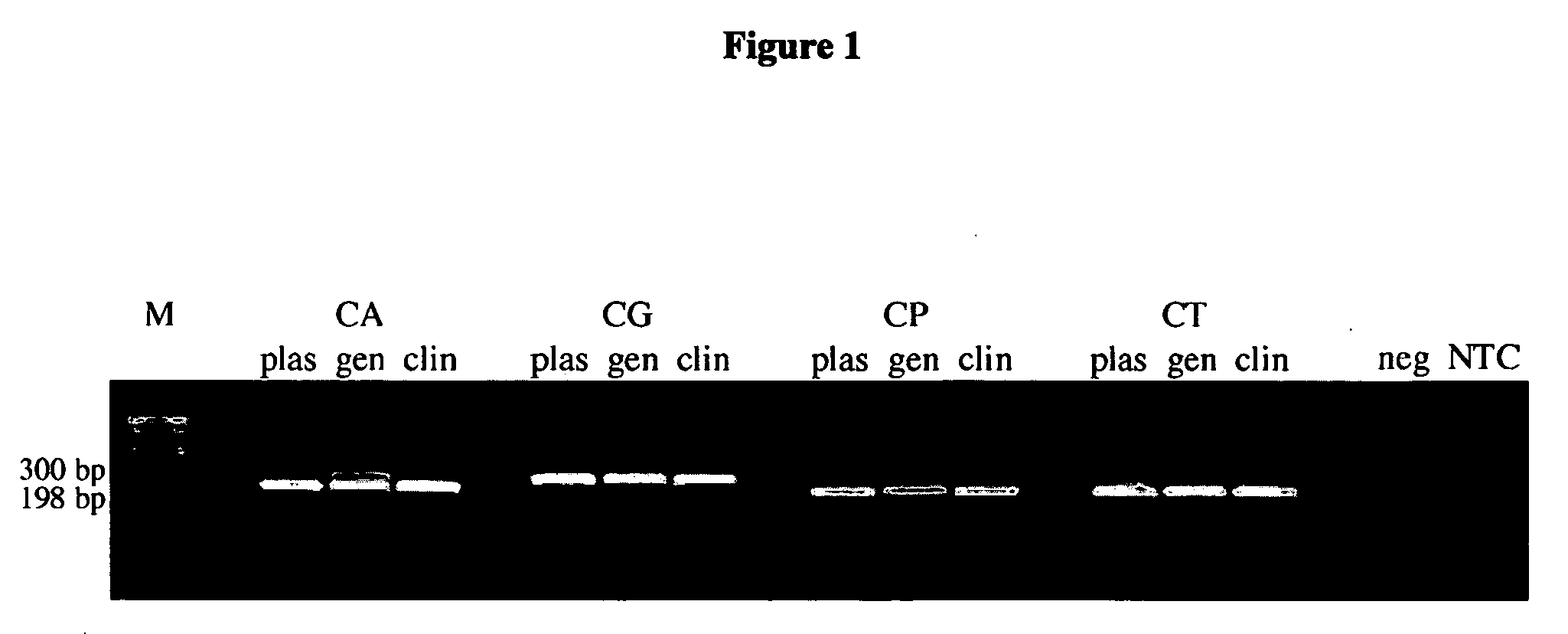
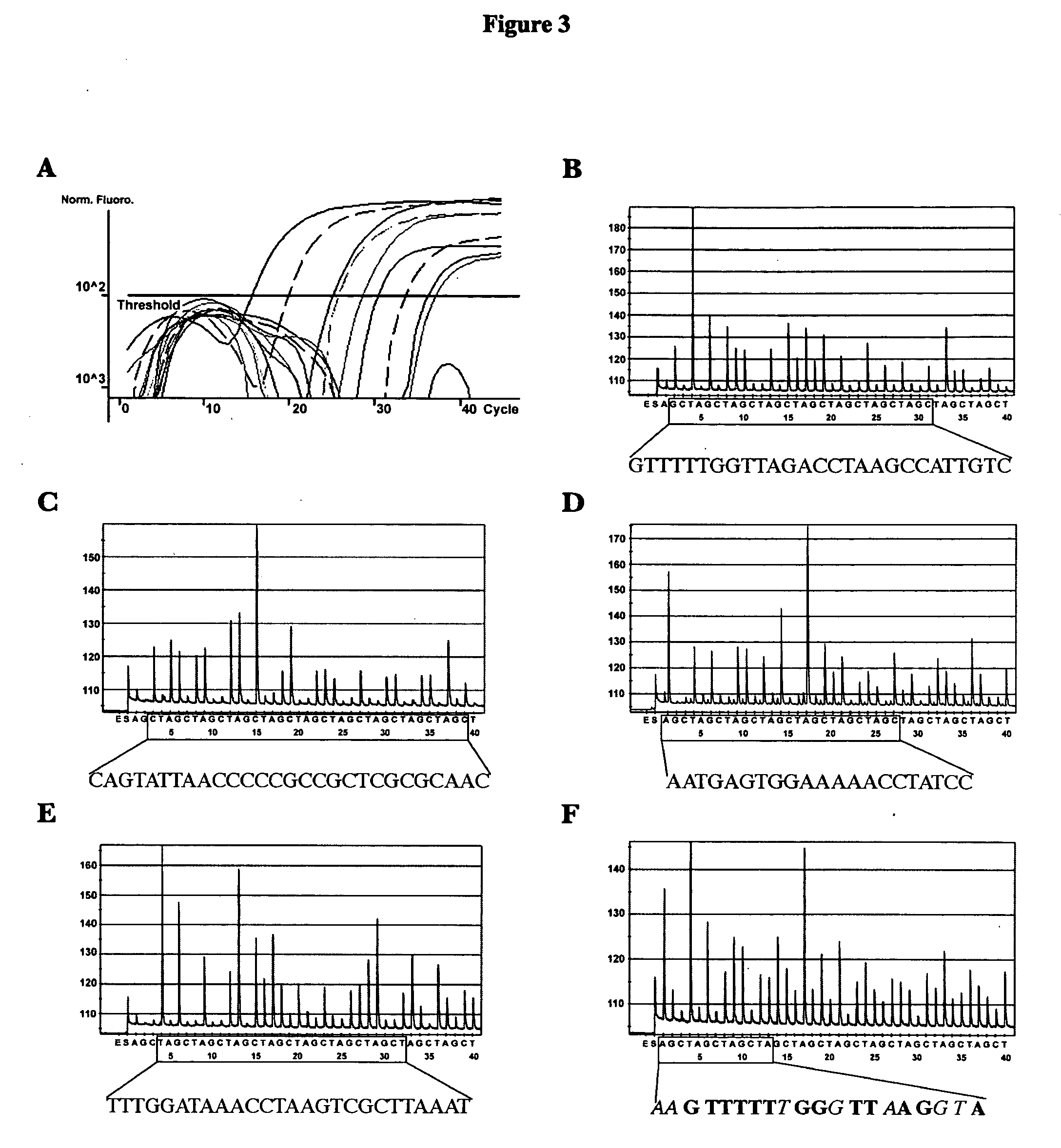
Methods and compositions for detecting and identifying species of Candida
ActiveUS20080102449A1Avoid disadvantagesMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationForward primerNucleotide
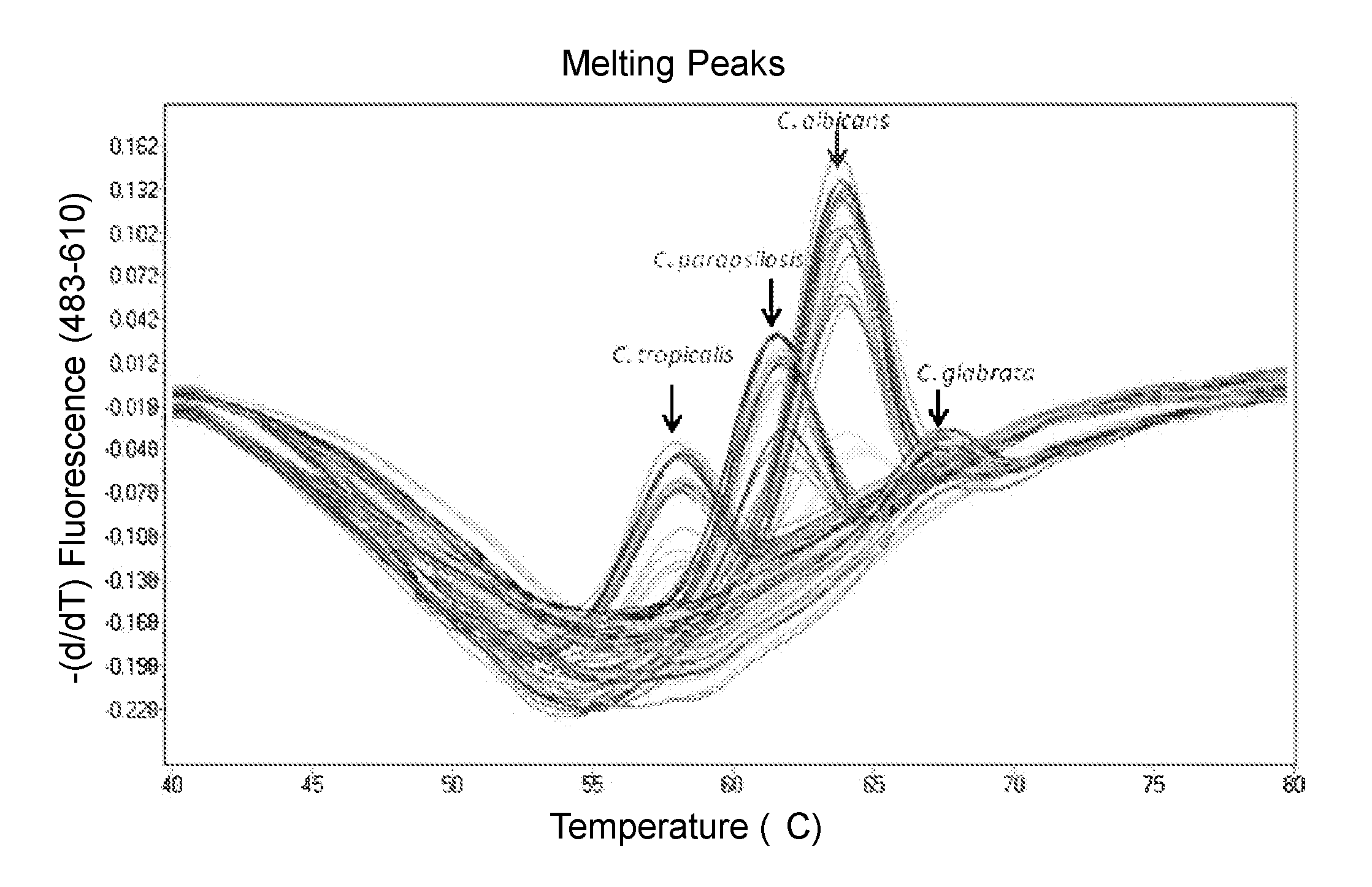
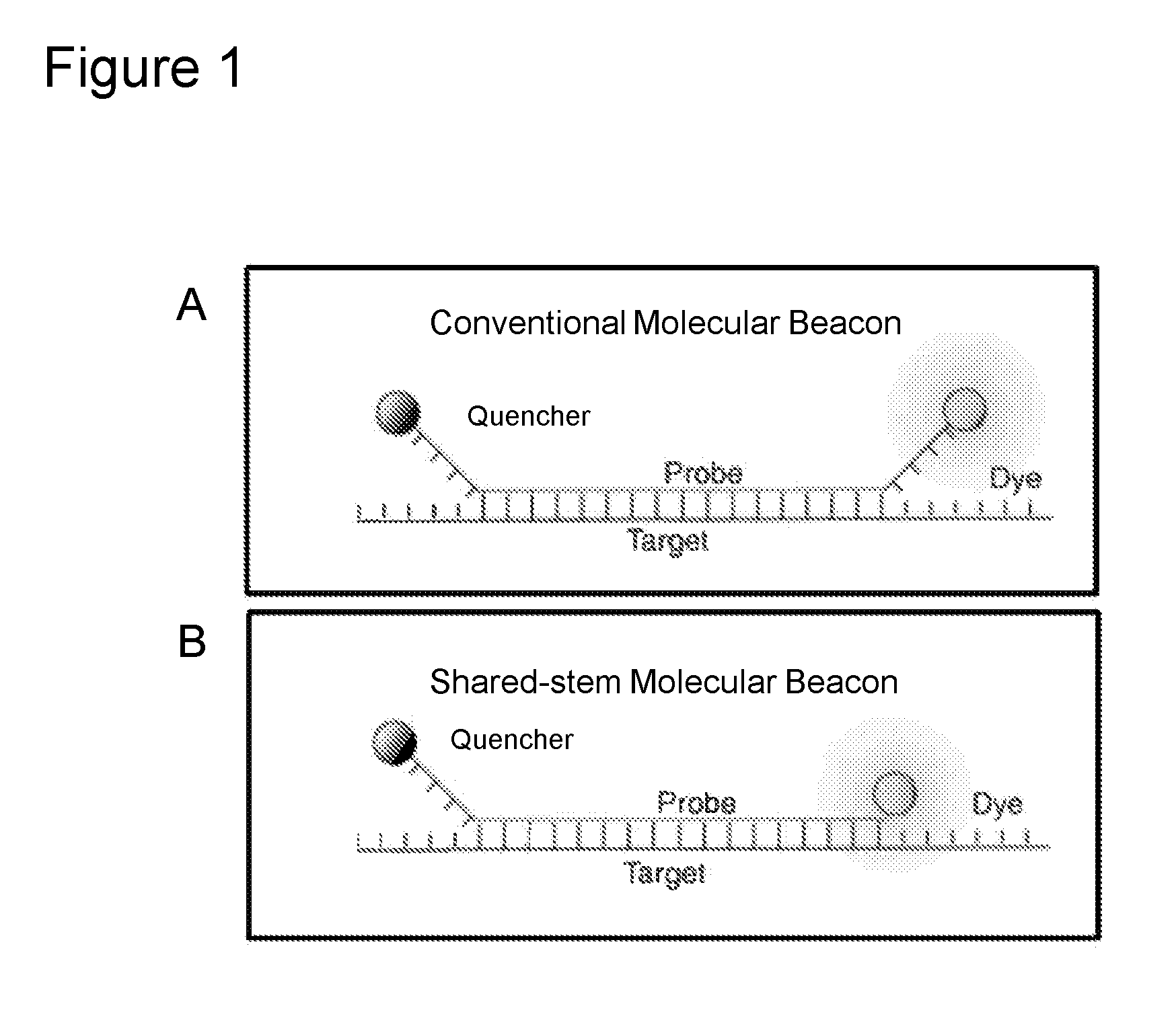
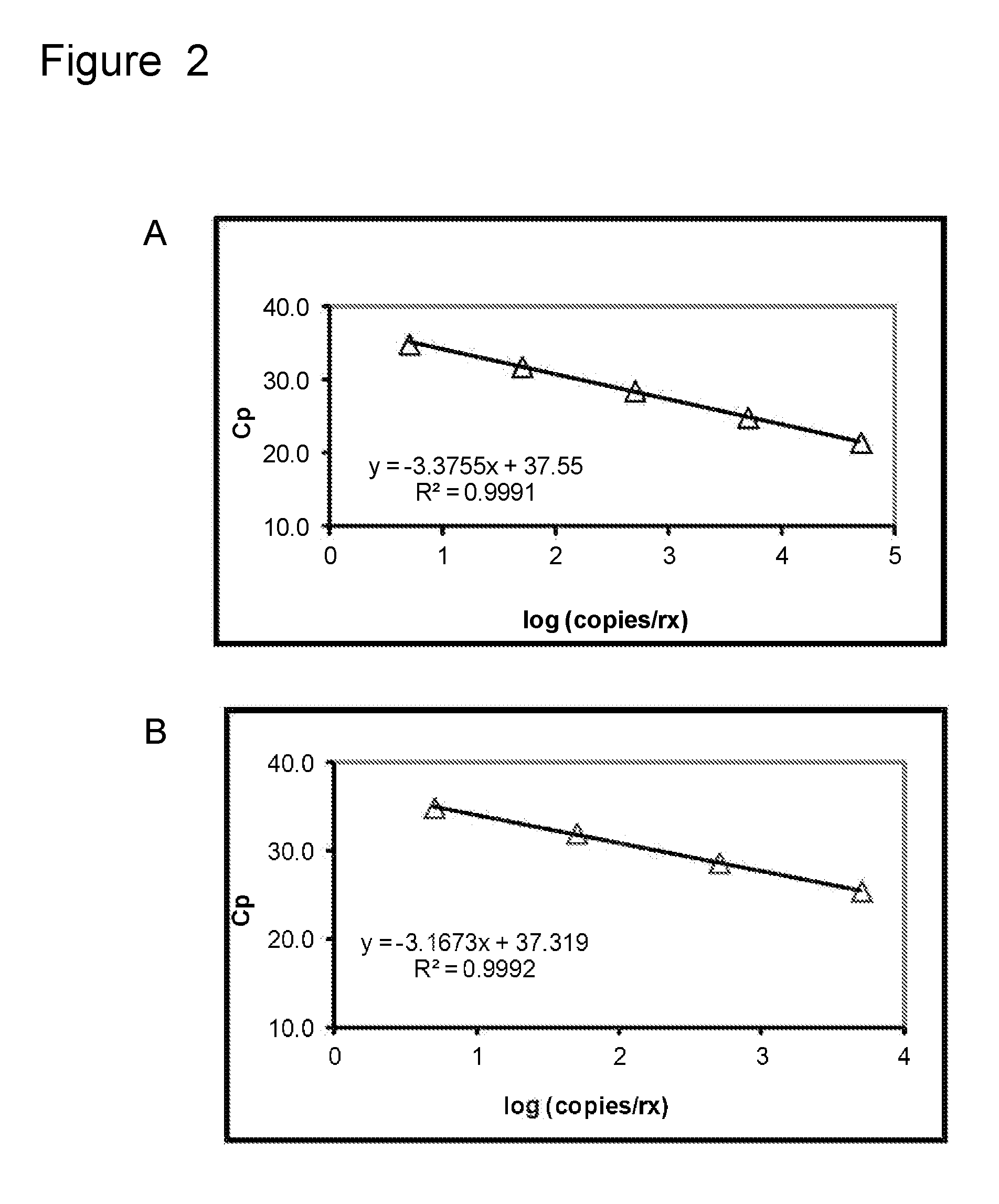
Methods and compositions useful in the detection and identification of species of Candida are disclosed. These species include Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis, each of which is a causative agent for vaginal candidiasis. The compositions of the invention are combinations of oligonucleotides. These oligonucleotides include pairs of forward and reverse primers for polymerase chain reactions, wherein each primer pair is capable of priming the synthesis of an amplicon specific to one of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis, but preferably is not capable of priming the synthesis of an amplicon specific to any of the other three species. In preferred embodiments, the forward primers of the primer pairs have identical sequences, while each reverse primer of the primer pairs has a unique sequence relative to all of the other reverse primers; or the reverse primers of the primer pairs have identical sequences, while each forward primer of the primer pairs has a unique sequence relative to all of the other forward primers. These unique primer sequences account for the species specificity of the resultant amplicons. The oligonucleotides also include probes capable of detecting these amplicons, and sequencing primers for determining, in primer extension reactions, the nucleotide sequences contained within the amplicons. In preferred methods of the invention, a biological sample is tested for the presence of at least one isolate of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida tropicalis by isolating nucleic acid from the sample, attempting a polymerase chain reaction in a mixture containing this nucleic acid and a plurality of these primer pairs, ascertaining whether any amplicon is produced in the mixture using an oligonucleotide probe, and determining the sequence of any resultant amplicon using the sequencing primers. The detection of an amplicon indicates that the sample contains at least one isolate of Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, or Candida tropicalis, and the nucleotide sequence data is used to determine which of these four Candida species is present.
Owner:MEDICAL DIAGNOSTIC LAB
Biochip for detecting pathogenesis fungus
InactiveCN1696311AReal-time detectionSensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMonilinia laxaCandida famata
A biochip for detecting the pathogenic funguses features that the DNA probes respectively for detecting one of 20 pathogenic funguses including Candida albicans, Aspergillus fumigatus, etc are immobilized on the glass plate, silicon chip, or high-molecular material.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
Plant lactobacillus strain and its application
InactiveCN1888051AImprove cleanlinessImprove adhesionBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsEscherichia coliStaphylococcus cohnii
The present invention discloses one plant lactobacillus strain and its application. The plant lactobacillus, Lactobacillus plantarum L323 CGMCC No. 1329, is separated from Chinese pregnant woman's vaginal secretion, and has relatively high bacteriotasis on common vaginal pathogens, such as staphylococcus aureus, candida albicans, colibacillus and vaginal Gardnar bacillus, and acid producing and H2O2 producing capacity higher than other lactobacillus. The plant lactobacillus, Lactobacillus plantarum L323 CGMCC No. 1329, may be used in preparing vaginal microbial preparation for preventing and / or treating vaginal infectious diseases.
Owner:TIANYOUDA BIO ENG SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Modified coconut oils with broad antimicrobial spectrum
InactiveUS20100016430A1Improve antibacterial propertiesAntibacterial agentsBiocideEscherichia coliCandida famata
Owner:MALAYSIAN AGRI RES & DEV INST MARDI
Antimicrobial hexapeptides
The invention encompasses hexapeptides consisting of alternating hydrophobic residues (B) at positions 2, 4, and 6, hydrophilic, charged residues (X) at positions 1 and 3, and a naphthylalanine (Nal), an aliphatic or aromatic residue (O) at position five, represented generally by the formula XBXBOB, which exhibit antimicrobial activity against infections caused by a variety of pathogens. These pathogens may include gram positive or negative bacteria, acid-fast bacteria such as mycobacteria, parasites, dermatophytes, or fungal pathogens. Typical fungal pathogens include Candida albicans and typical dermatophytes include Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. The hexapeptides of the present invention exhibit antifungal activity, antibacterial activity, desirable stability, and lack toxicity to the mammal receiving treatment.
Owner:HELIX BIOMEDIX INC
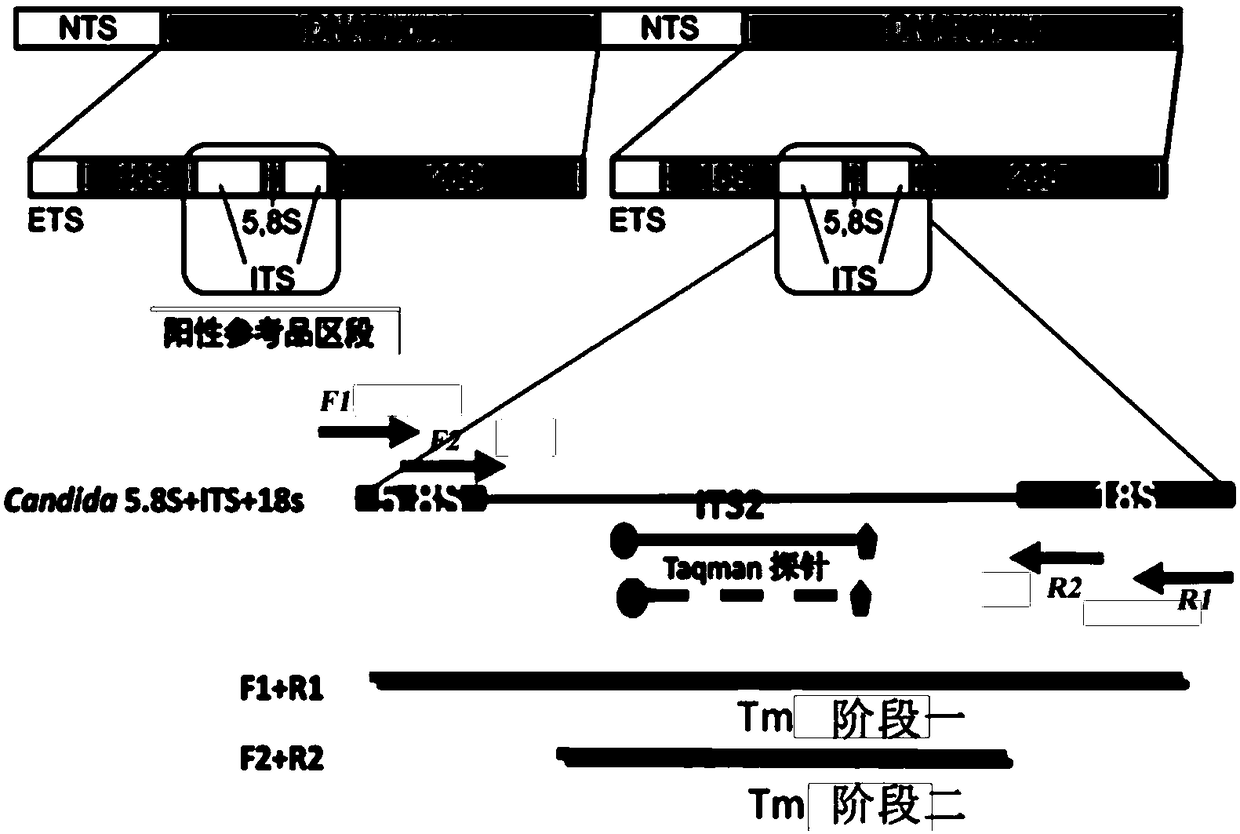
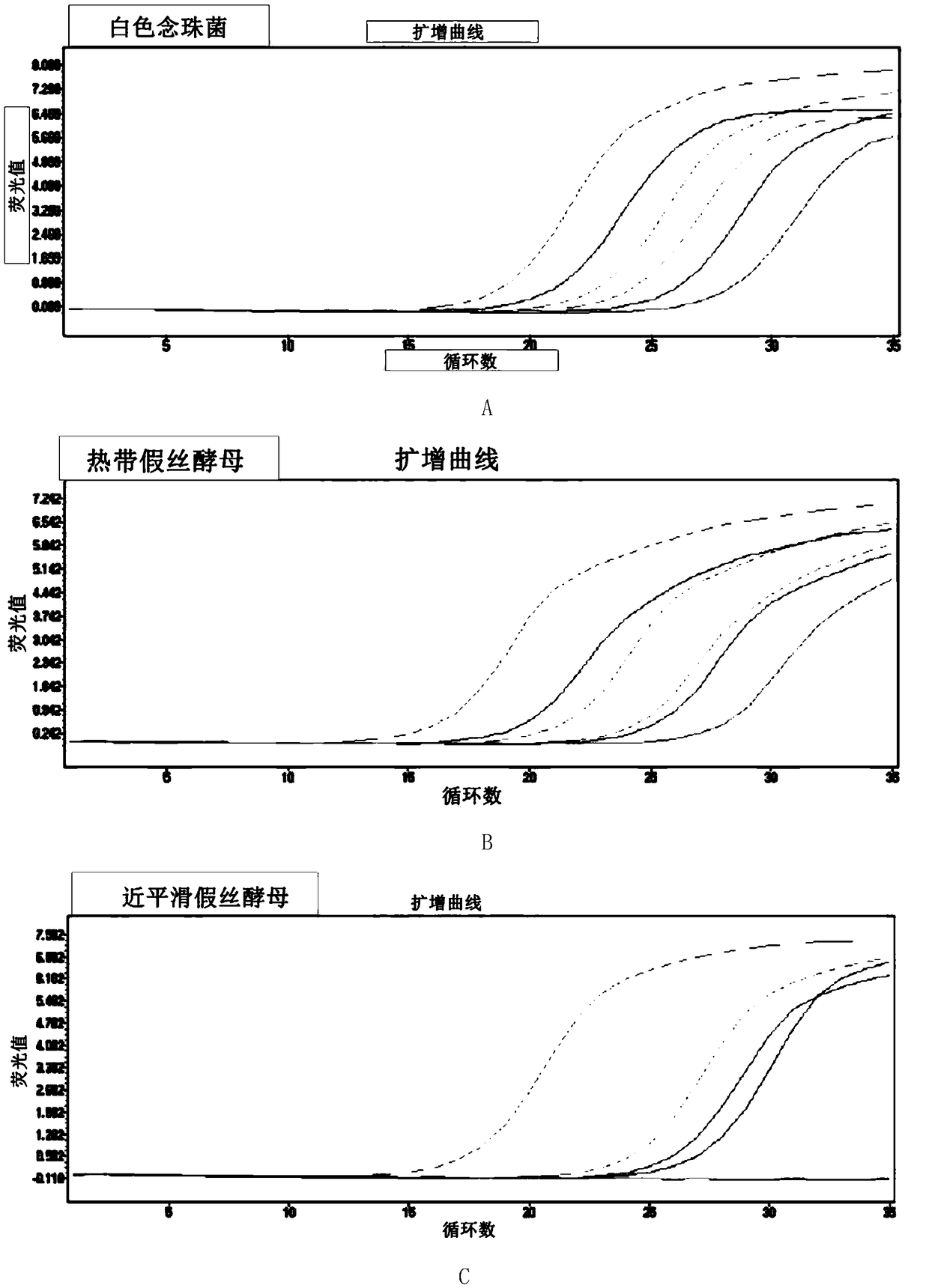
Fluorescence quantitative PCR primer, probe and kit for detecting ordinary pathogenic fungi
InactiveCN104450936AOvercome limitationsSolve the problem of fungal infectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceCandida tropicalis
The invention discloses a fluorescence quantitative PCR primer, a probe and a kit for detecting ordinary pathogenic fungi. A specific primer and a TaqMan probe are independently designed, and a fluorescence PCR detection method which can be used for simultaneously detecting 15 clinically ordinary pathogenic fungi, including 8 candida mycoderma bacteria (candida albicans, candida glabrata, candida parapsilosis, candida kefyr, candida sake, candida kruse, candida guilliermind and candida tropicalis), four aspergilli (aspergillus niger, aspergillus flavus, aspergillus terreus and aspergillus fumigates), cryptococcus, rhizopus oryzae and mucor circinelloides, is established. The method is relatively high in sensitivity and specificity, and has significant meanings for early diagnosis and treatment on invasive infections with fungi.
Owner:天津宝瑞生物技术有限公司
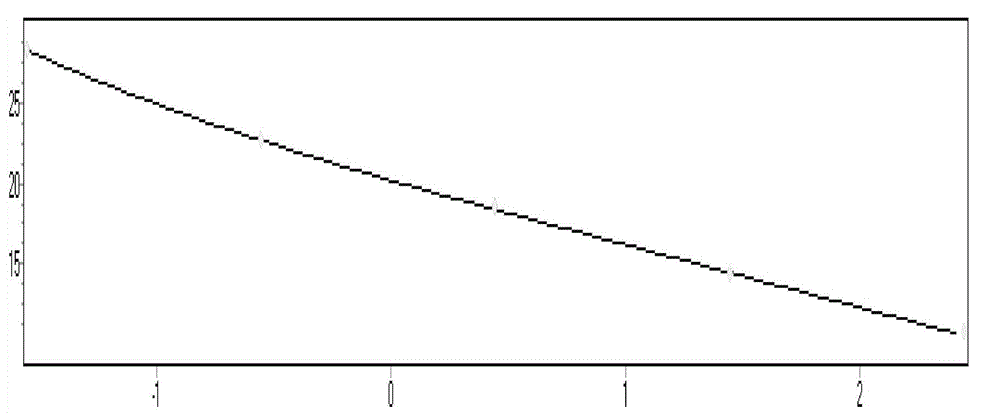
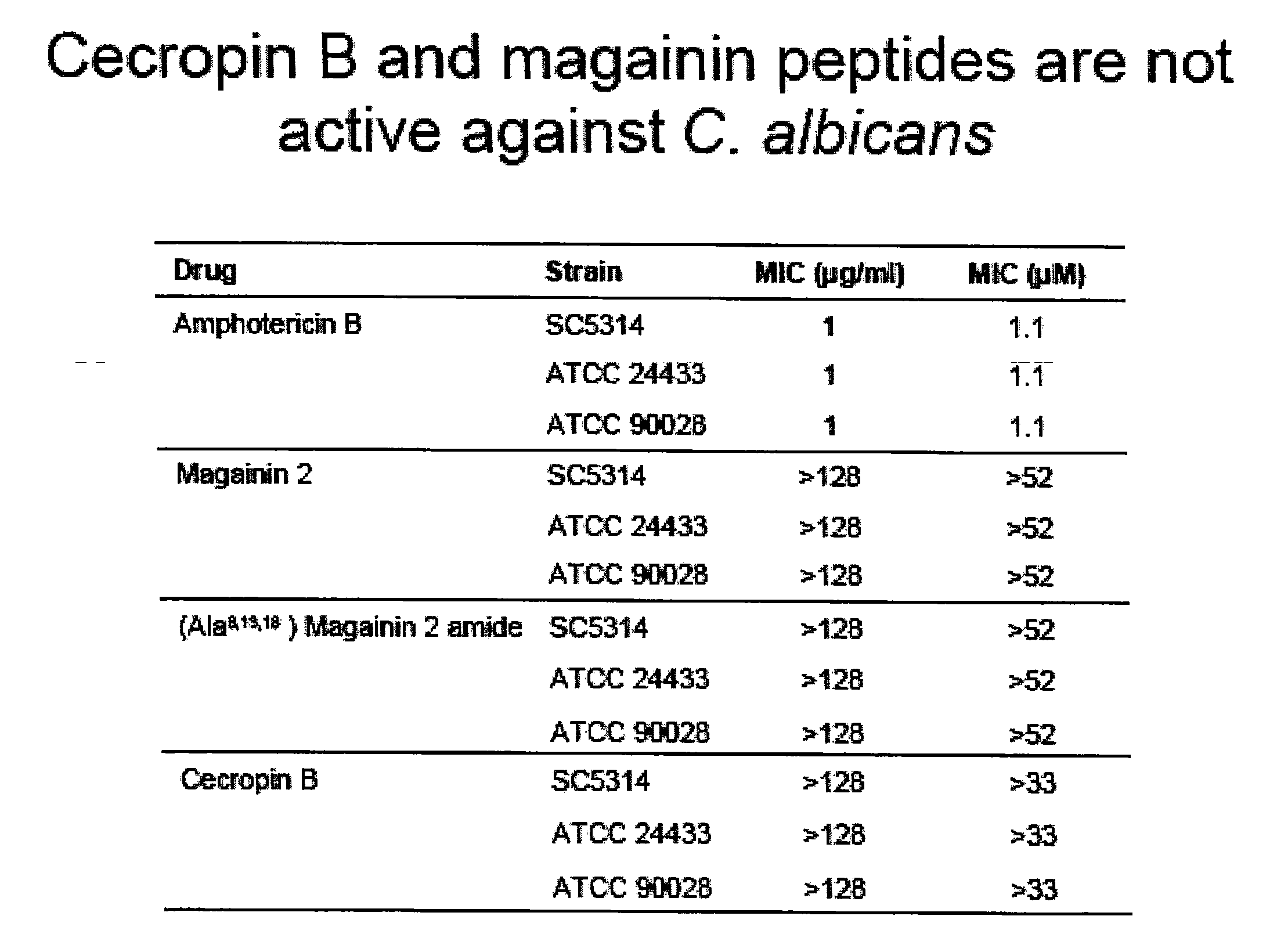
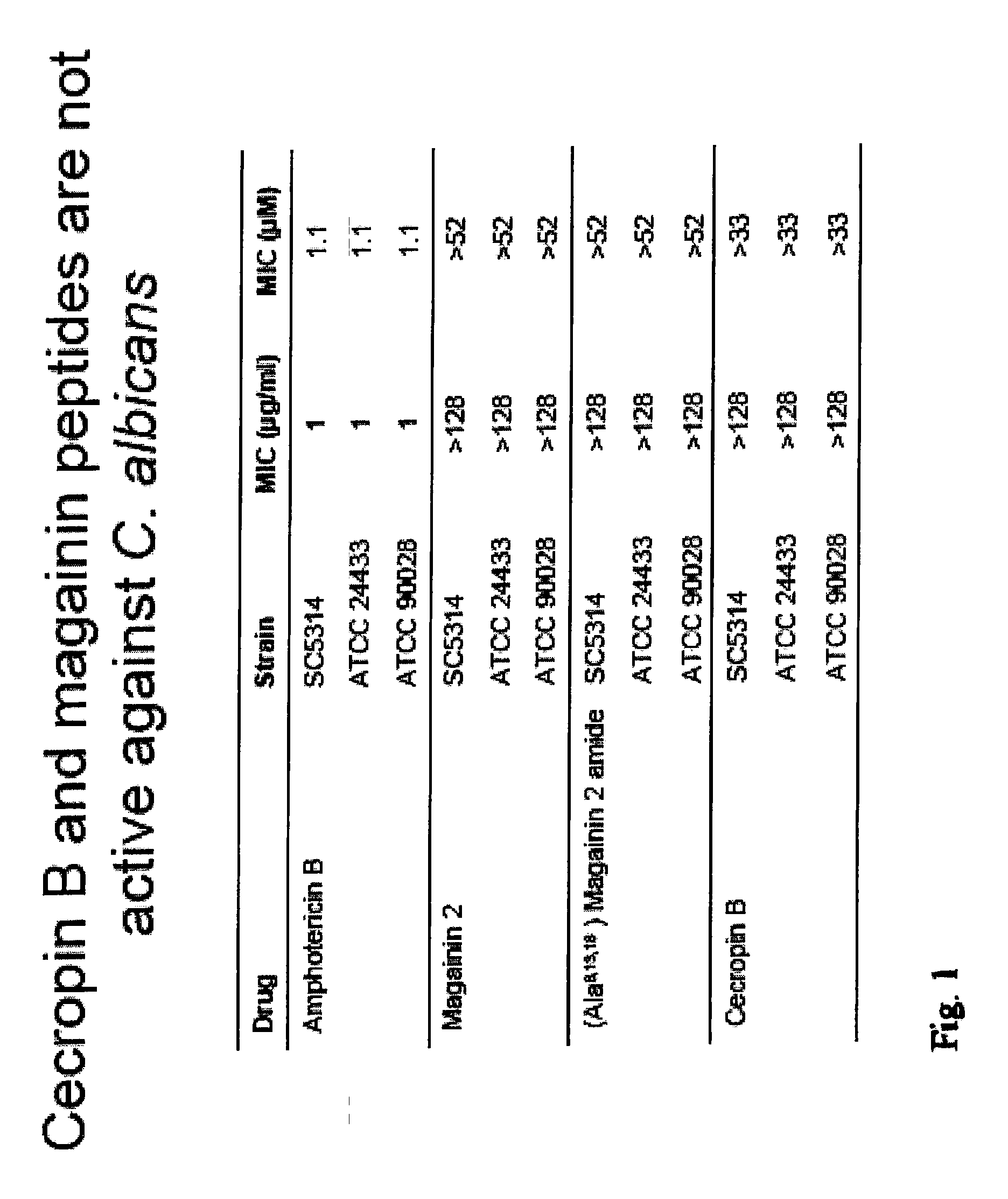
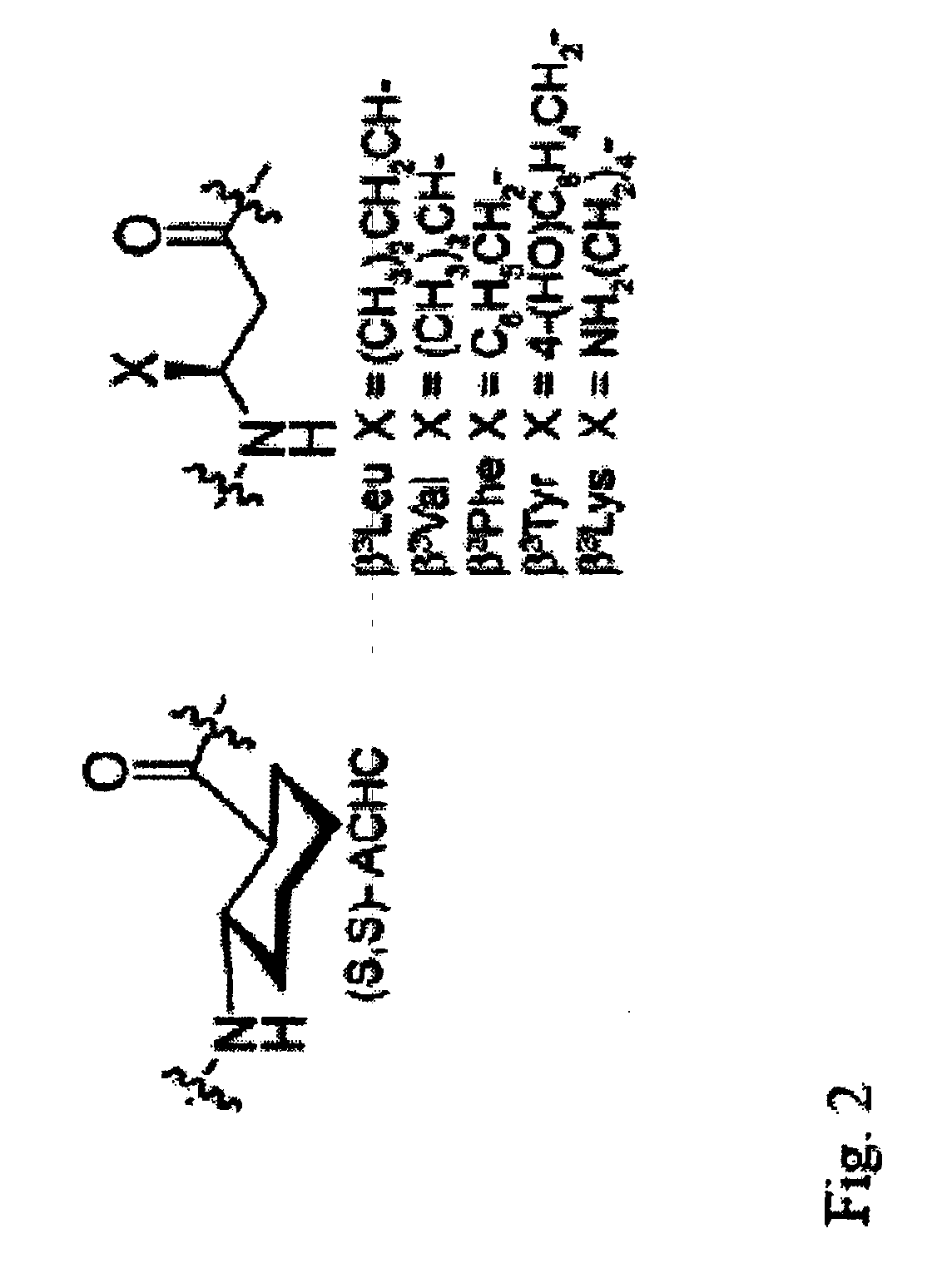
Beta-peptides with antifungal activity
The present invention is directed to the design, synthesis and use of various β-peptides exhibiting antifungal activity. The β-peptides are relatively short in length, adopt globally amphiphilic conformations, and cause little lysis of human red blood cells at concentrations that kill Candida albicans, a common human fungal pathogen.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Processes for the bioconversion of a fermentable carbon source to 1,3-propanediol by a single microorganism
A process is provided for the bioconversion of a carbon substrate to 1,3-propanediol by a single organism utilizing microorganisms, such as, Citrobacter, Enterobacter, Clostridium, Klebsiella, Aerobacter, Lactobacillus, Aspergillus, Saccharomyces, Zygosaccharomyces, Pichia, Kluyveromyces, Candida, Hansenula, Debaryomyces, Mucor, Torulopsis, Methylobacter, Escherichia, Salmonella, Bacillus, Streptomyces and Pseudomonas, containing the genes encoding for an active glycerol or diol dehydratase enzyme by contacting these organisms with a carbon substrate under the appropriate fermentation conditions. Specifically, Citrobacter and, Klebsiella provide the source of exogenous genes for such active dehydratase enzyme.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO +1
Detection method of invasive fungus infection, detection kit and application
ActiveCN109055502ASimplify detectionSimplify operabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCell freeFluorescence
The invention provides a fast multiplex PCR identification diagnosis detection method of invasive fungus infection based on cfDNA (cell free DNA). The method can be used for identifying the invasive infection caused by clinic common and high-incidence Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, Candida krusei, Candida glabrata and Aspergillus fumigtus. An amplification primer is designed according to characteristic genome segments of each fungus category and species; a detection fluorescence probe of a strain can be distinguished according to the amplification segment design; the real time PCR can be performed on a sample to be tested; high sensitivity of nested PCR and high specificity and multi-target performance advantages of multiple fluorescent hybrid probe PCR are integrated for identifying the fungus strain. The invention also provides a PCR diagnosis kit for the invasive fungus infection and application thereof.
Owner:DIASYS DIAGNOSTIC SYST SHANGHAI
Biooxidation capabilities of Candida sp
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
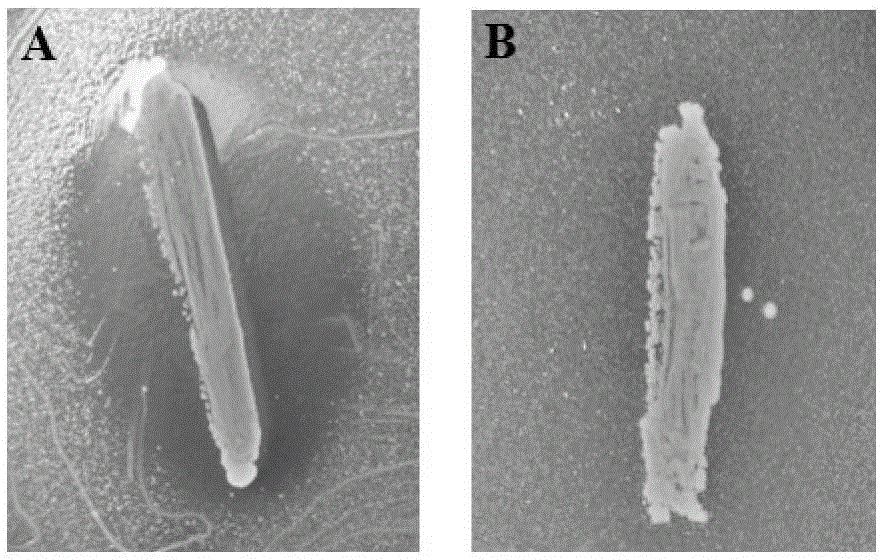
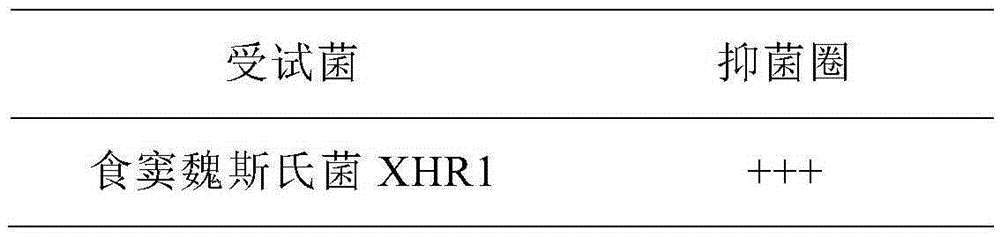
Weissella cibaria XHR1 and applications thereof and weissella cibaria XHR1 containing pickled vegetable
ActiveCN105255787AImprove micro-ecological levelExpansion of industrial productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWeissella cibariaCandida famata
The invention provides a weissella cibaria XHR1 and applications thereof and a weissella cibaria XHR1 containing pickled vegetable. The preparation of the pickled vegetable is implemented through the steps of adding a culture solution of weissella cibaria XHR1 and bacterial powder of lactobacillus plantarum CICC 20764 into a pickled vegetable fermentation starting solution for pickling vegetables, so that the final concentration of weissella cibaria XHR1 is 10<6>-10<7> cfu / mL eventually, and then the final concentration of lactobacillus plantarum CICC 2076 is 10<5>-10<6> CFU / mL; and then, adding vegetables into the pickled vegetable fermentation starting solution, and carrying out vegetable pickling according to a traditional vegetable fermentation process, so that the pickled vegetable disclosed by the invention is obtained finally. According to the invention, prebiotic lactobacillus for inhibiting the growth of Candida albicans is applied to the fermentation of Sichuan pickled vegetables, so that the consumer group is wider, and the micro ecological level of alimentary canals of wide consumers can be improved, thereby inhibiting Candida albicans diseases from the perspective of public health.
Owner:XIHUA UNIV
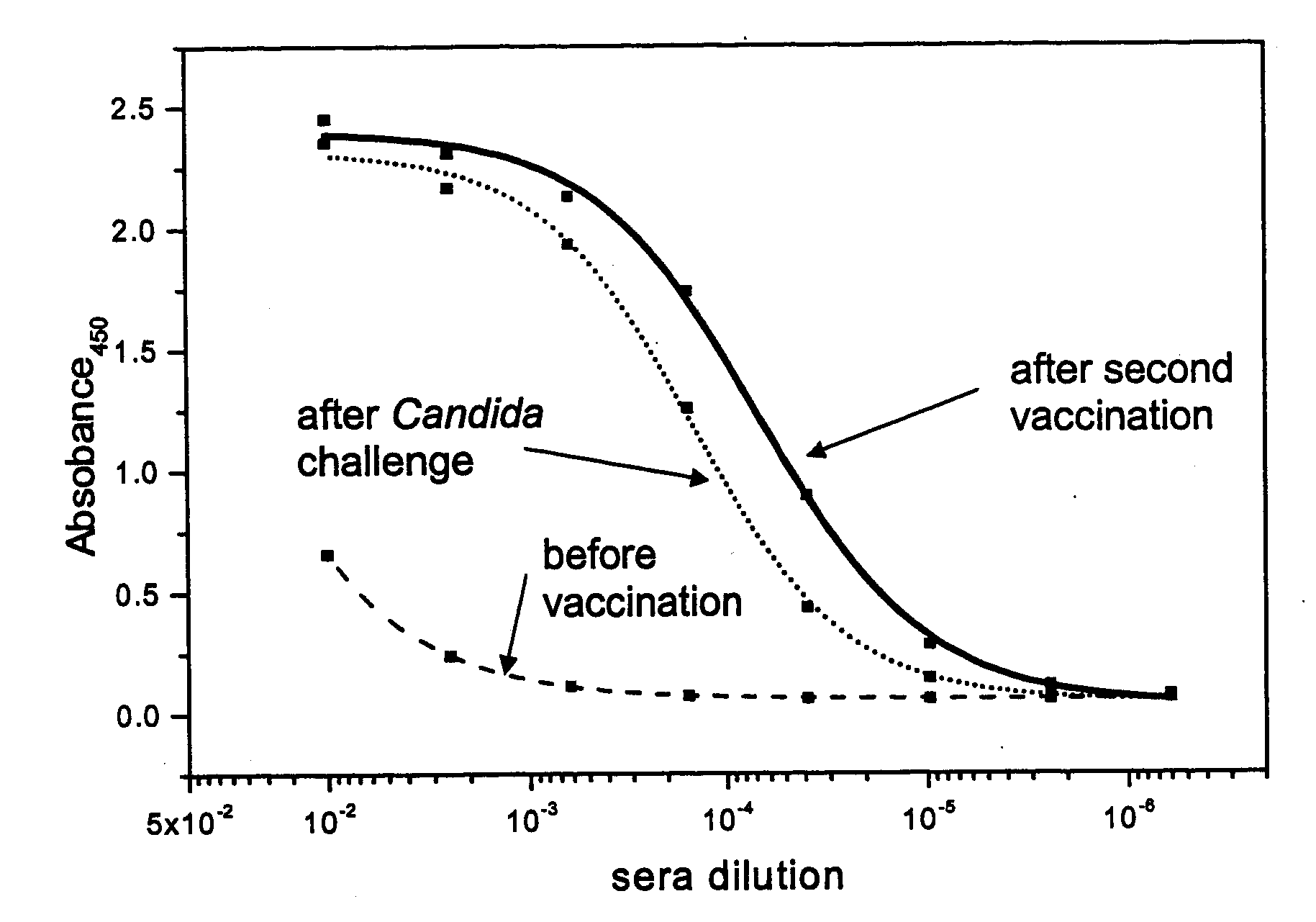
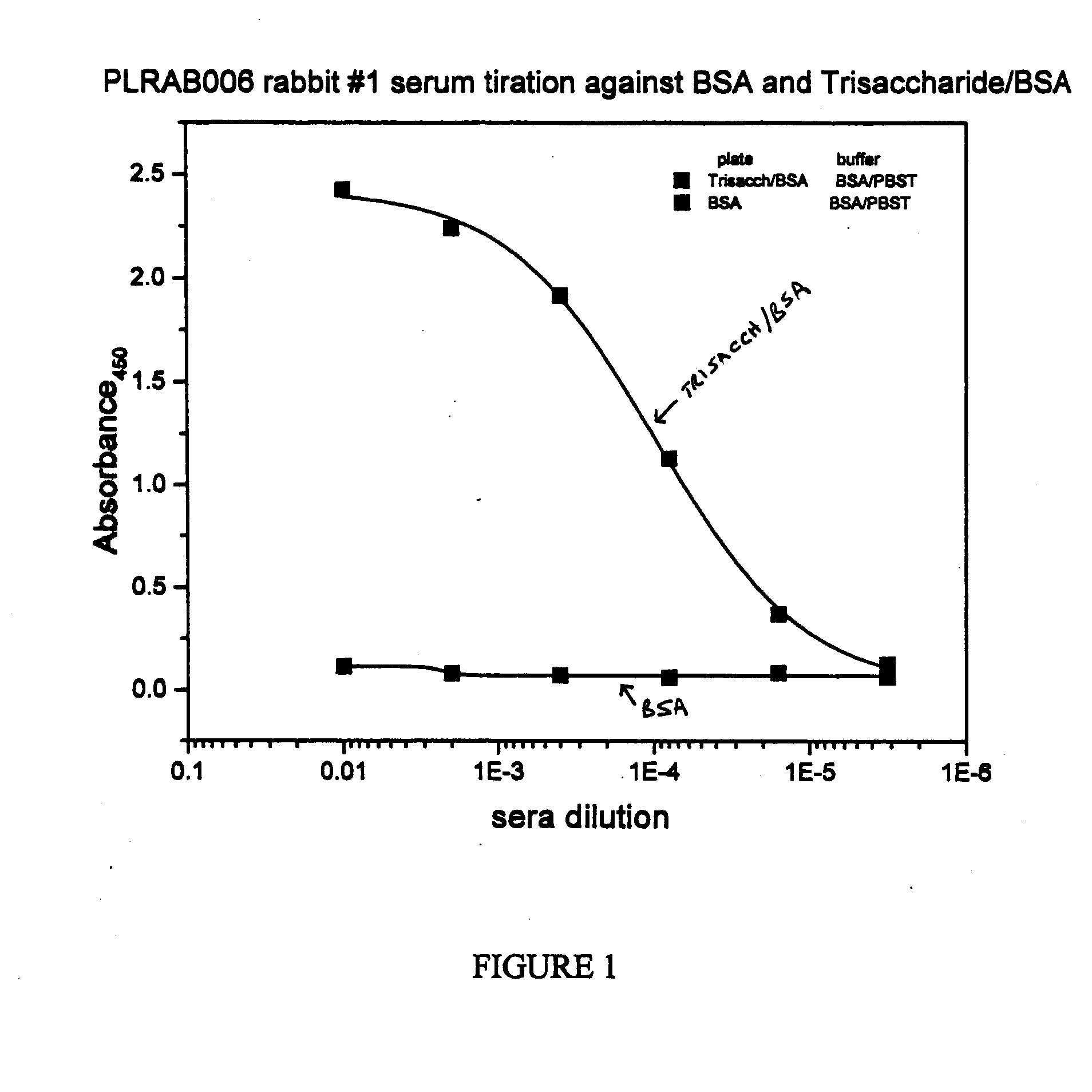
Synthetic Anti-Candida Albicans Oligosaccharide Based Vaccines
The present invention provides immunogenic oligosaccharide compositions and methods of making and using them. In particular, the compositions comprise native O-linked and S-linked oligosaccharides coupled to a protein carrier via a linker, wherein the resultant conjugate elicits a protectively immunogenic response, particularly in vaccines against pathogenic Candida species and more particularly against Candida albicans. Preferably the pathogenic Candida species are those that possess cell wall oligosaccharide compositions similar to the β-mannan component of Candida albicans cell walls.
Owner:THE GOVERNORS OF THE UNIV OF ALBERTA
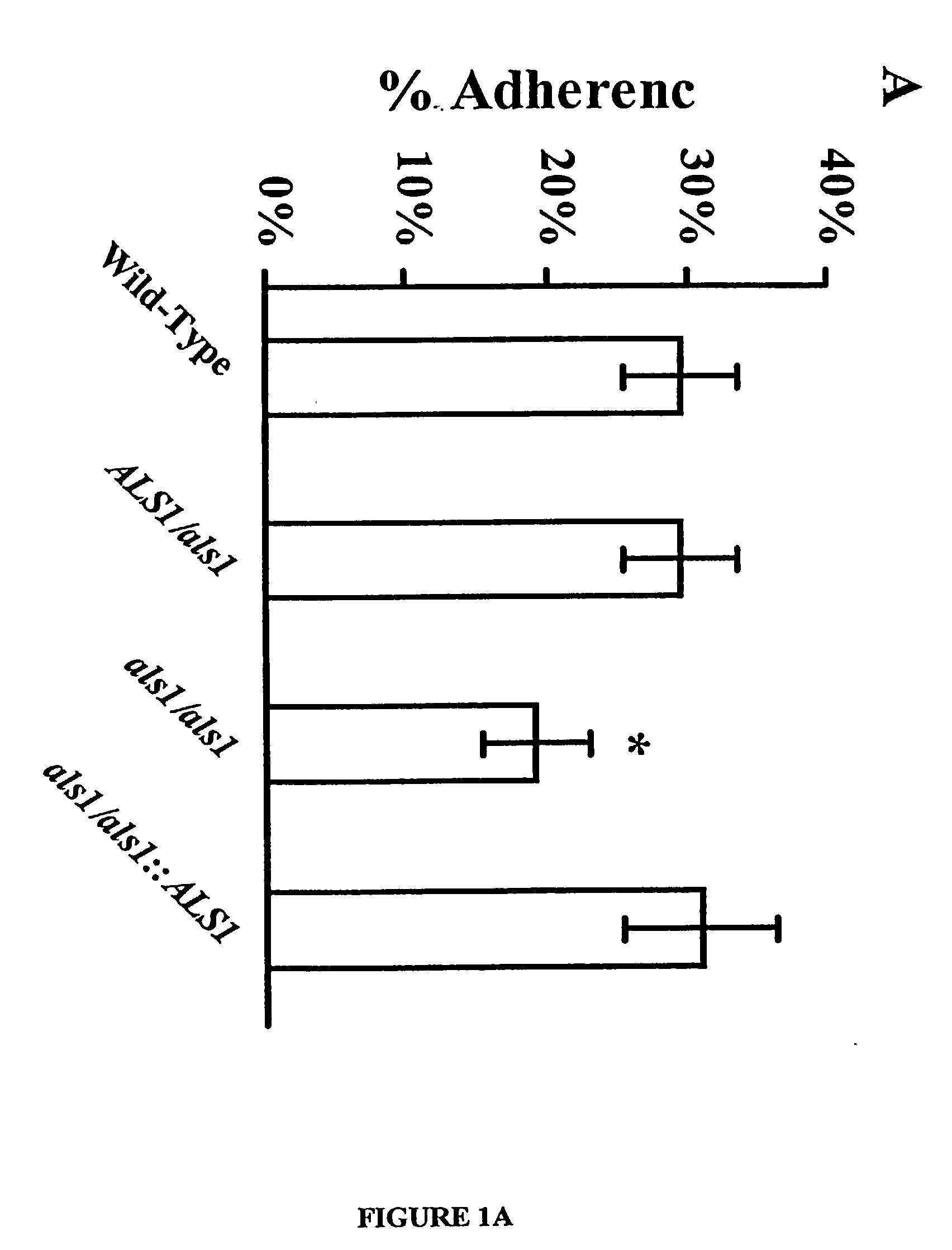
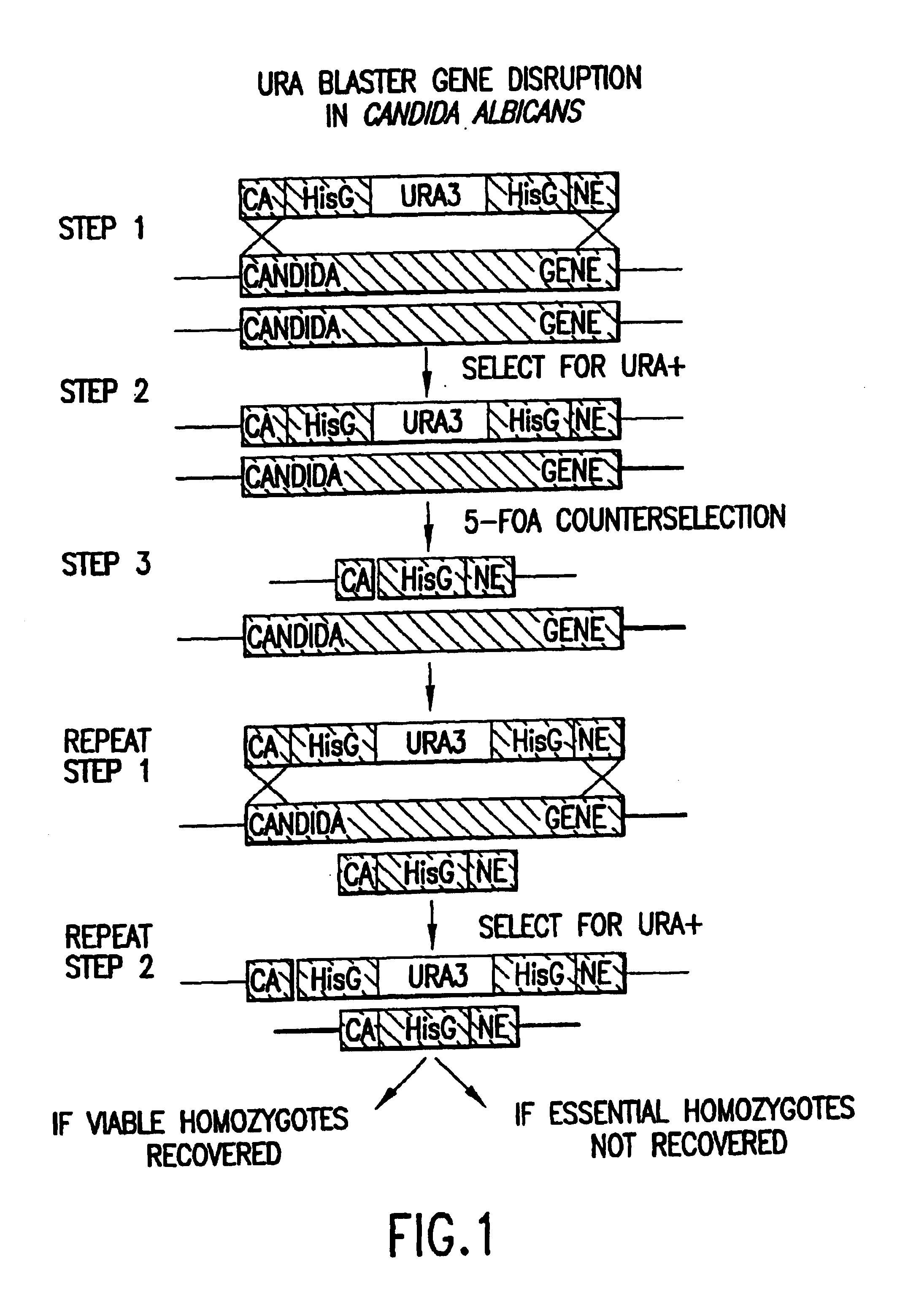
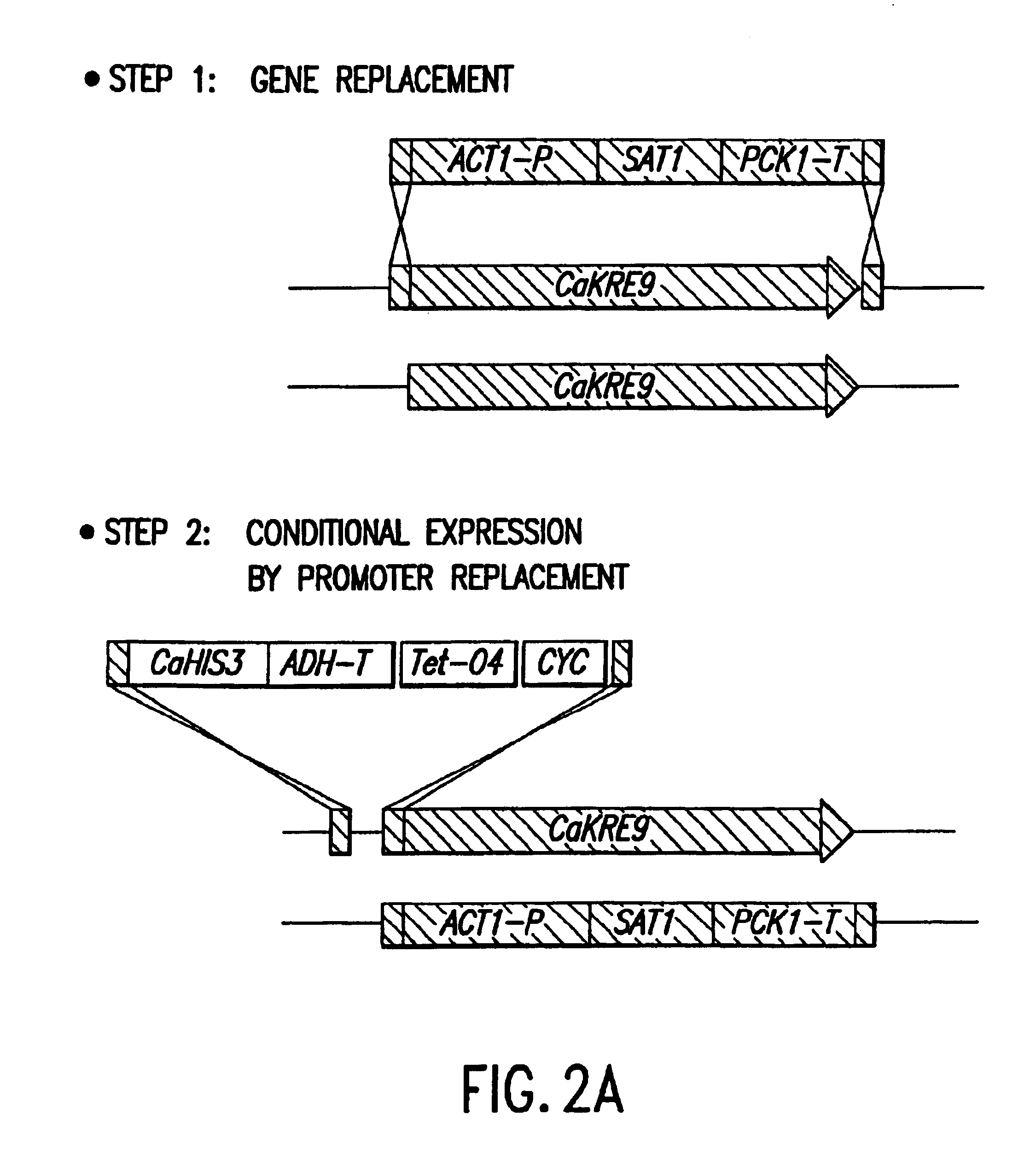
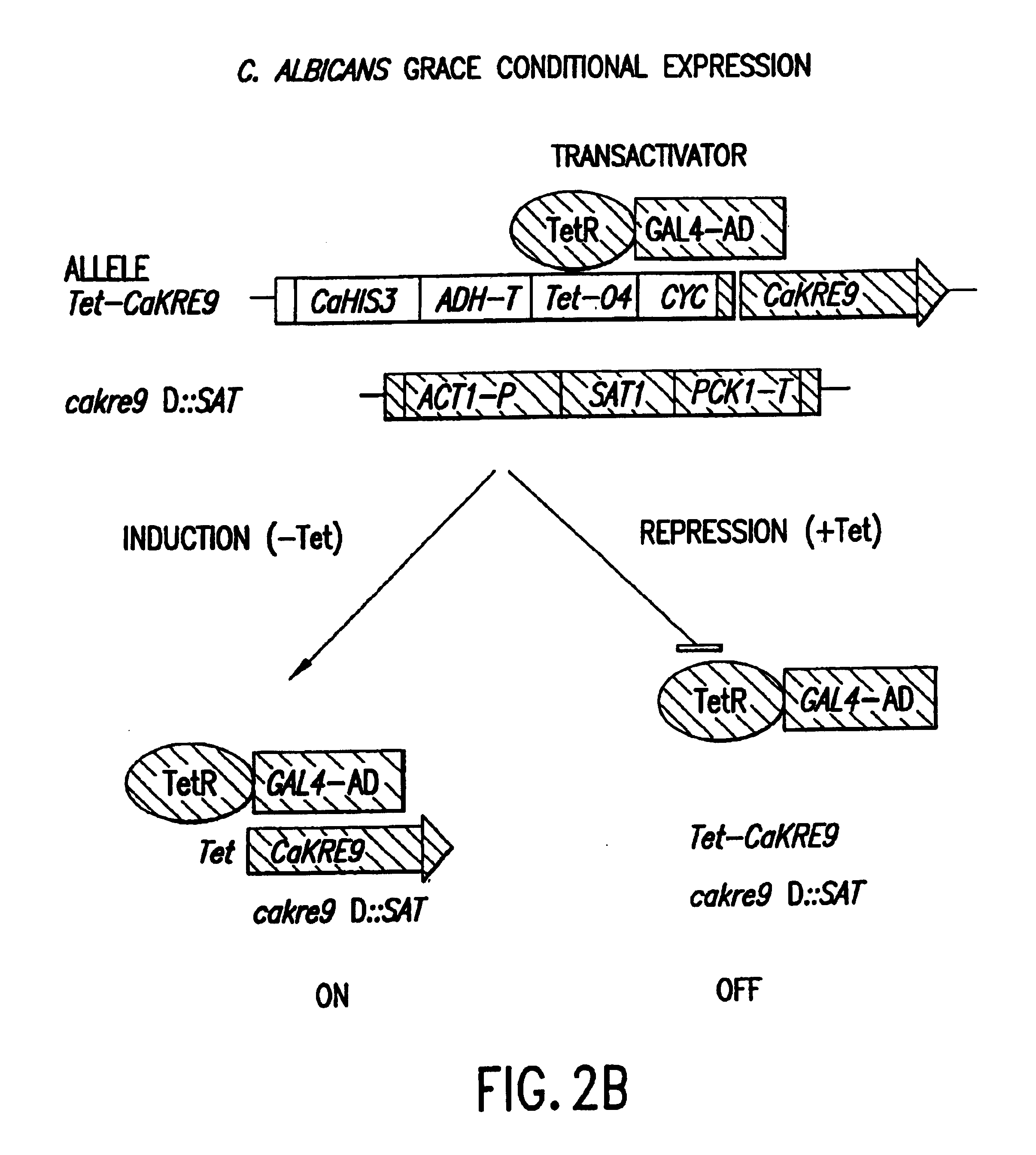
Gene disruption methodologies for drug target discovery
InactiveUS6783985B1Efficient and effectiveAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMicroorganismsVirulent characteristicsScreening method
The present invention provides methods and compositions that enable the experimental determination as to whether any gene in the genome of a diploid pathogenic organism is essential, and whether it is required for virulence or pathogenicity. The methods involve the construction of genetic mutants in which one allele of a specific gene is inactivated while the other allele of the gene is placed under conditional expression. The identification of essential genes and those genes critical to the development of virulent infections, provides a basis for the development of screens for new drugs against such pathogenic organisms. The present invention further provides Candida albicans genes that are demonstrated to be essential and are potential targets for drug screening. The nucleotide sequence of the target genes can be used for various drug discovery purposes, such as expression of the recombinant protein, hybridization assay and construction of nucleic acid arrays. The uses of proteins encoded by the essential genes, and genetically engineered cells comprising modified alleles of essential genes in various screening methods are also encompassed by the invention.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC
Bacillus subtilis strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101974465AGood antibacterial effectEnhanced inhibitory effectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliMonilinia laxa
The invention discloses a Bacillus subtilis strain and application thereof. The strain is named as Bacillus subtilis ZJU007 and preserved in the China general microbiological culture collection center (CGMCC) of Chinese Academy of Sciences on yard No.1 on Beichen West Road, in Chaoyang district in Beijing on September 3rd, 2010, and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.4140. A bactericidal substance generated by the strain of the invention has very strong inhibition effect on Candida albicans and has better bacteriostasis effect compared with common fungicidin. The bactericidal substance not only has very strong bacteriostasis effect on the Candida albicans and other yeast like fungi, and the like, but also has excellent effect on Aspergillus niger and other filamentous fungi, and meanwhile, has better bacteriostasis effect on escherichia coli and other bacteria.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
LOCAL ADMINISTRATION OF CHICKEN YOLK IMMUNE GLOBULINS (IgY) TO TREAT AND PREVENT FUNGAL INFECTIONS
InactiveUS20100233162A1Easy to produceTreatment and prophylaxisEgg immunoglobulinsSenses disorderAntigenYolk
The present invention relates to a composition comprising IgY antibodies against at least two different fungi, the use of the composition for the preparation of a pharmaceutical especially for prophylaxis and / or therapy of all kinds of fungal infections, such as conditions caused by organisms belonging to the Candida genus or Aspergillus genus, especially of fungi that are less sensitive to antimycotica and a diagnotstic method using the IgY antibodies. Further it relates to immunisation of birds with a combination of at least two different species of fungi to the Candida genus or Aspergillus genus and a diagnostic method for fungi. It also relates to relates to a novel method for treatment and / or prophylaxis of fungal infections, especially infections by fungi which have lowered sensitivity or resistance to antimycotics. The method is both safe and effective. This is achieved by using IgY directed against fungi, in particular against Candida species, which have a lowered sensitivity or resistance against antimycotics. The specific IgY has been obtained by hyper immunising birds with one or several fungi as antigen in order to stimulate the production of immune globulins (IgY) against such fungi. The present invention also relates to a pharmaceutical product from eggs of birds containing immune globulin or a fragment thereof, which can be combined with other preparations, nutritients or pharmaceuticals for simultaneous, separate or sequential use in the prophylaxis or therapy of gastrointestinal infections in newborn infants.
Owner:BENGT AGERUP
Antibody for detecting aspergillus
ActiveCN101149377AEasy to operateStrong specificityFused cellsBiological testingPenicillium marneffeiCandida famata
This invention provides the capture antibody and the detection antibody to detect the aspergillus, the two antibody is the single clone antibody of the cross oncocyte CCTCC NO.C200731 and CCTCC NO.C200730, they can unites the glucoprotein whose molecular weight is 25-100kDa in the cell wall of the aspergillus, the reaction with the Penicillium marneffei, white oidiomycosis, smoothness oidiomycosis, tropic oidiomycosis, close smoothness oidiomycosis, Candida krusei are all negative. The antibody in this invention can make into the immunity reagent to detect the aspergillus in common use.
Owner:ZHUJIANG HOSPITAL SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIV
Multivalent silver pharmaceuticals
Novel pharmaceuticals are described based on multivalent silver compounds containing Ag(II) or Ag(III) capable of killing pathogenic gram positive and negative bacteria, fungi and algae such as E. coli, Staphylococcus aureus and epidermidis, and Candida albicans. The efficacy of these compounds is enhanced by oxidizing agents such as persulfates. They can also be utilized to preserve pharmaceutical, cosmetic and chemical specialty products against these pathogens.
Owner:N JONAS & AKA N JONAS
Compositions and Methods for the Detection of Candida Species
InactiveUS20080248970A1Improve the signal-to-background ratioSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesSingle sampleMonilinia laxa
Compositions and methods for detecting and / or differentiating among Candida organisms, including C. albicans and C. dubliniensis, are disclosed. Exemplary methods involve screening a sample suspected of containing at least one or more Candida sp. for the presence or absence of a nucleic acid sequence specific for each such fungal pathogen. Some disclosed methods permit the rapid and simultaneous detection and identification of several fungal pathogens (e.g., up to 100 fungi) in a single sample.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
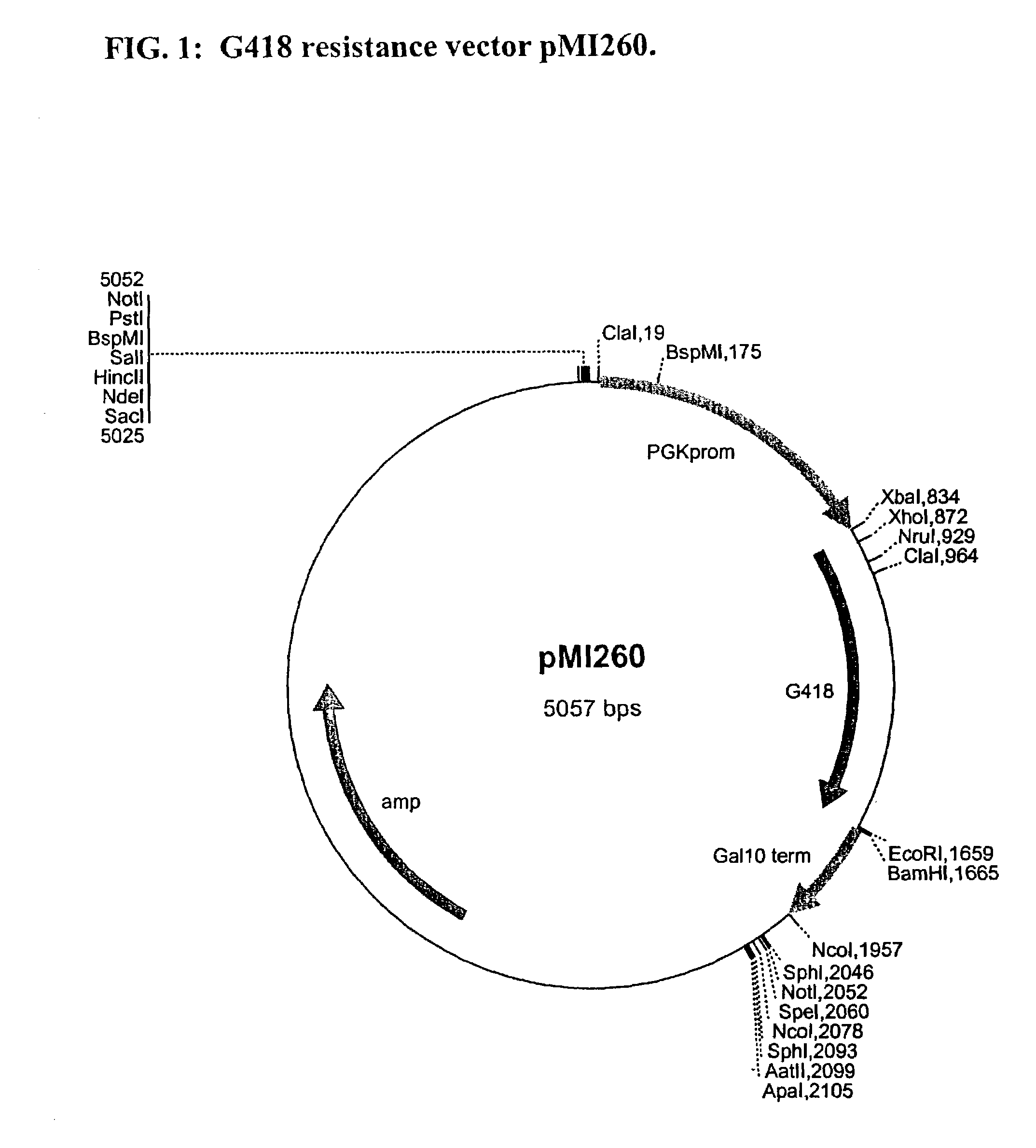
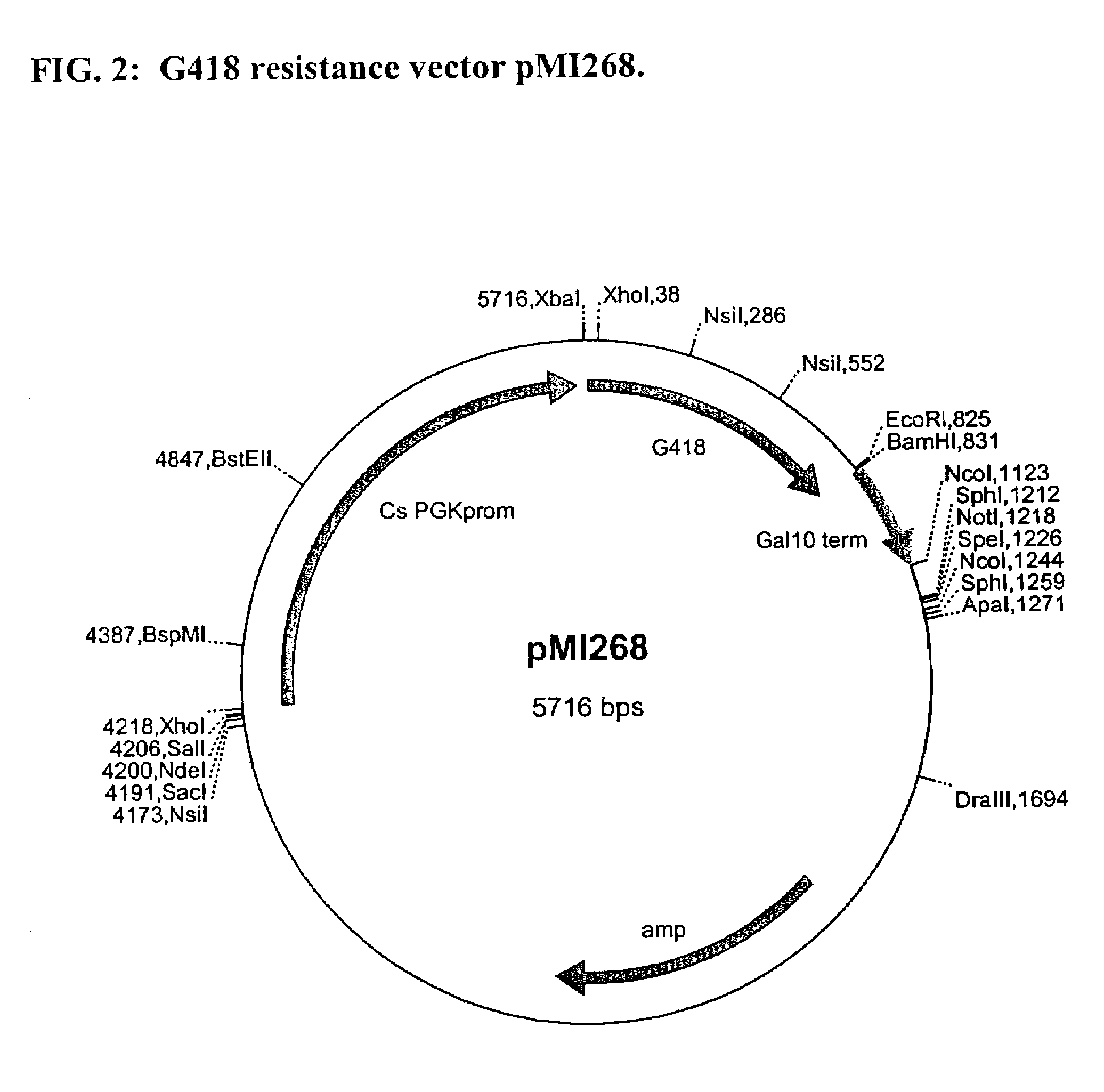
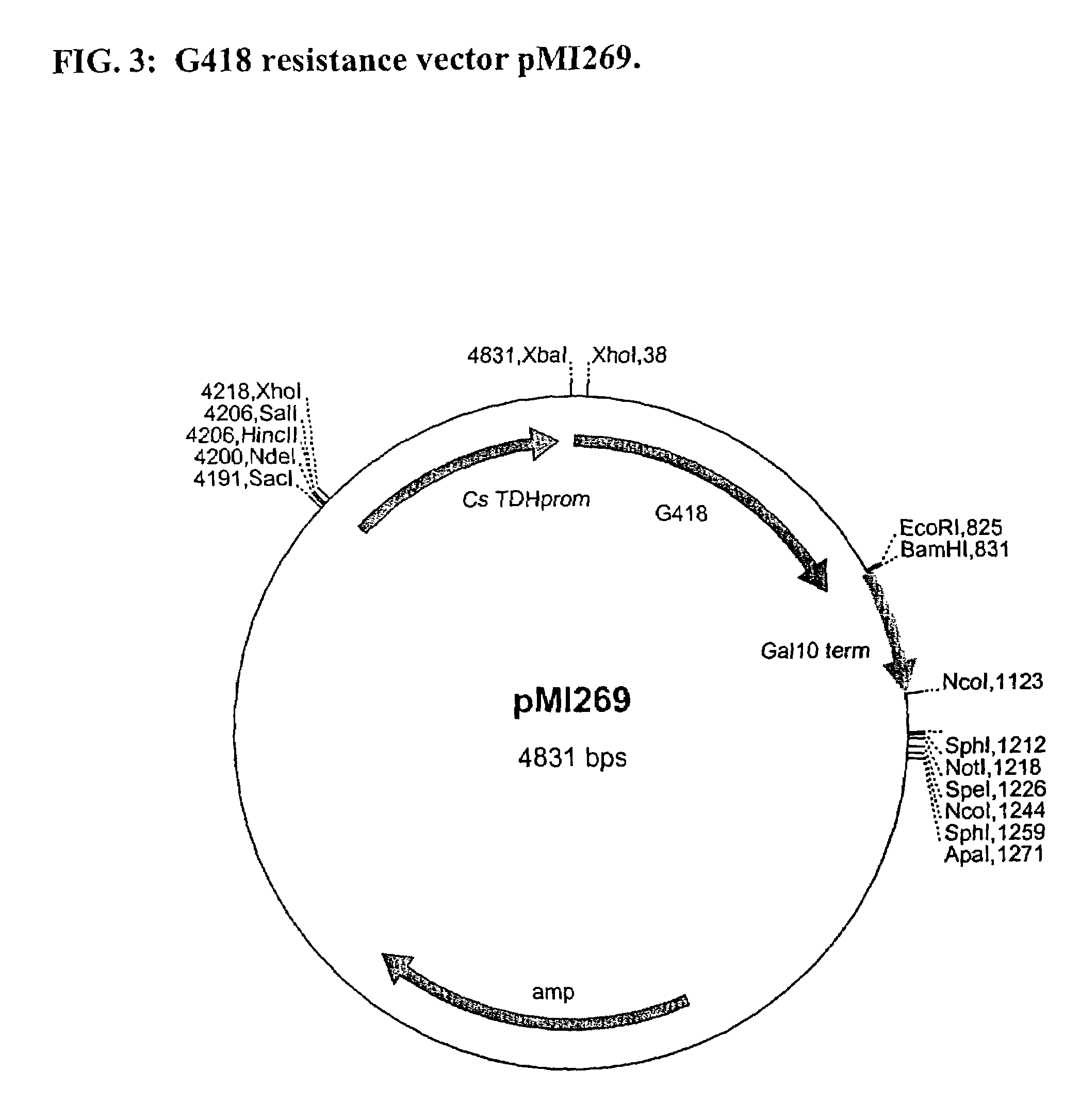
Dominant selectable marker for gene transformation and disruption in yeasts
InactiveUS20010031724A1Good antifungal activityGene manipulationFungiBacteriaAntifungal drugCandida famata
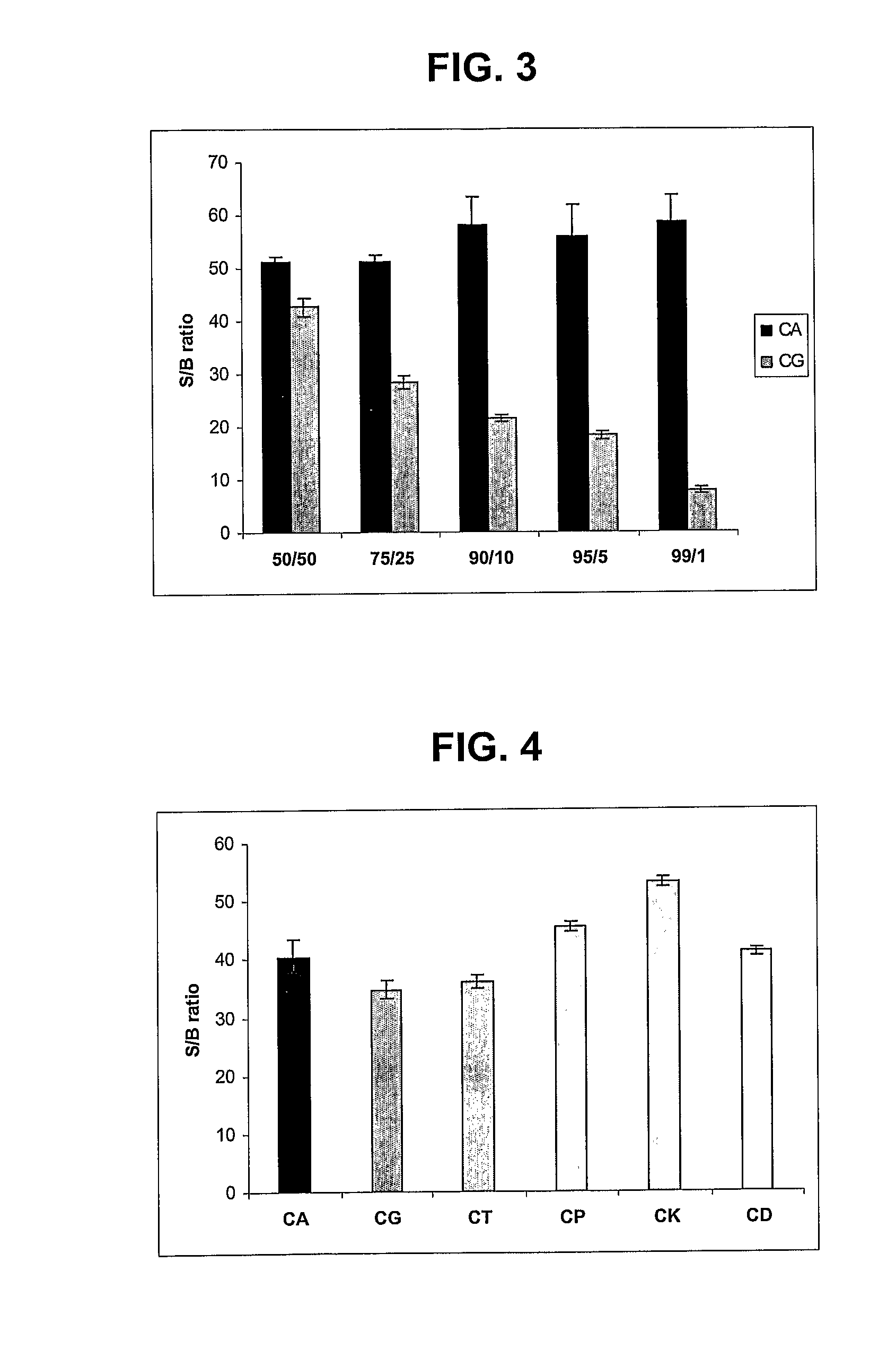
The present invention provides a novel dominant selectable marker system in yeast that is based on an aminoglycoside, nourseothricin (NST). This compound possesses a powerful antifungal activity against Candida albicans and S. cerevisiae. The invention provides a cognate drug resistance marker for use in gene transformation and disruption experimentation in Candida albicans and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In particular, the invention presents: 1) direct utility for gene manipulations in both clinically and experimentally relevant strains regardless of genotype and without affecting growth rate, or hyphal formation; and 2) applicability to antifungal drug discovery, including target validation and various forms of drug screening assays.
Owner:EVOLVA INC
Methods to prevent vertical transmission of infectious diseases
InactiveUS20080269205A1Prevent vertical transmissionPrevent the spread of diseaseAntiviralsRadiation therapyEscherichia coliMonilinia laxa
The present invention presents a method of preventing vertical transmission of an infectious disease comprising: (a) applying a photosensitizing composition to host tissues of birth canal of a mother during the intrapartum period; and (b) applying light to the host tissues after the step (a) at a wavelength absorbed by the photosensitizing composition so as to inhibit or eliminate infectious disease microorganisms that come into contact with the host tissues. The infectious disease may be caused by human immunodeficiency virus type 1, hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, Group B Streptococcus, cytomegalovirus, Listeria monocytogenes, Chiamydia trachomatis, Escherichia coli, herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus, Toxoplasma gondii, human papilloma virus, and Candida.
Owner:ONDINE INT
Compositions and methods for detection of Candida species
The invention features compositions and methods for the detection of Candida species in biological samples, such as human tissue samples. The invention features species specific nucleic acid probes that can hybridize to target nucleic acid molecules in Candida species and can be used in a variety of detection assays, such as fluorescence based assays or NMR based assays. The compositions and methods of the invention can be used to rapidly and accurately detect one or more Candida species in patients and can be used to assist in point-of care-decisions for treating Candida infections.
Owner:T2 BIOSYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com