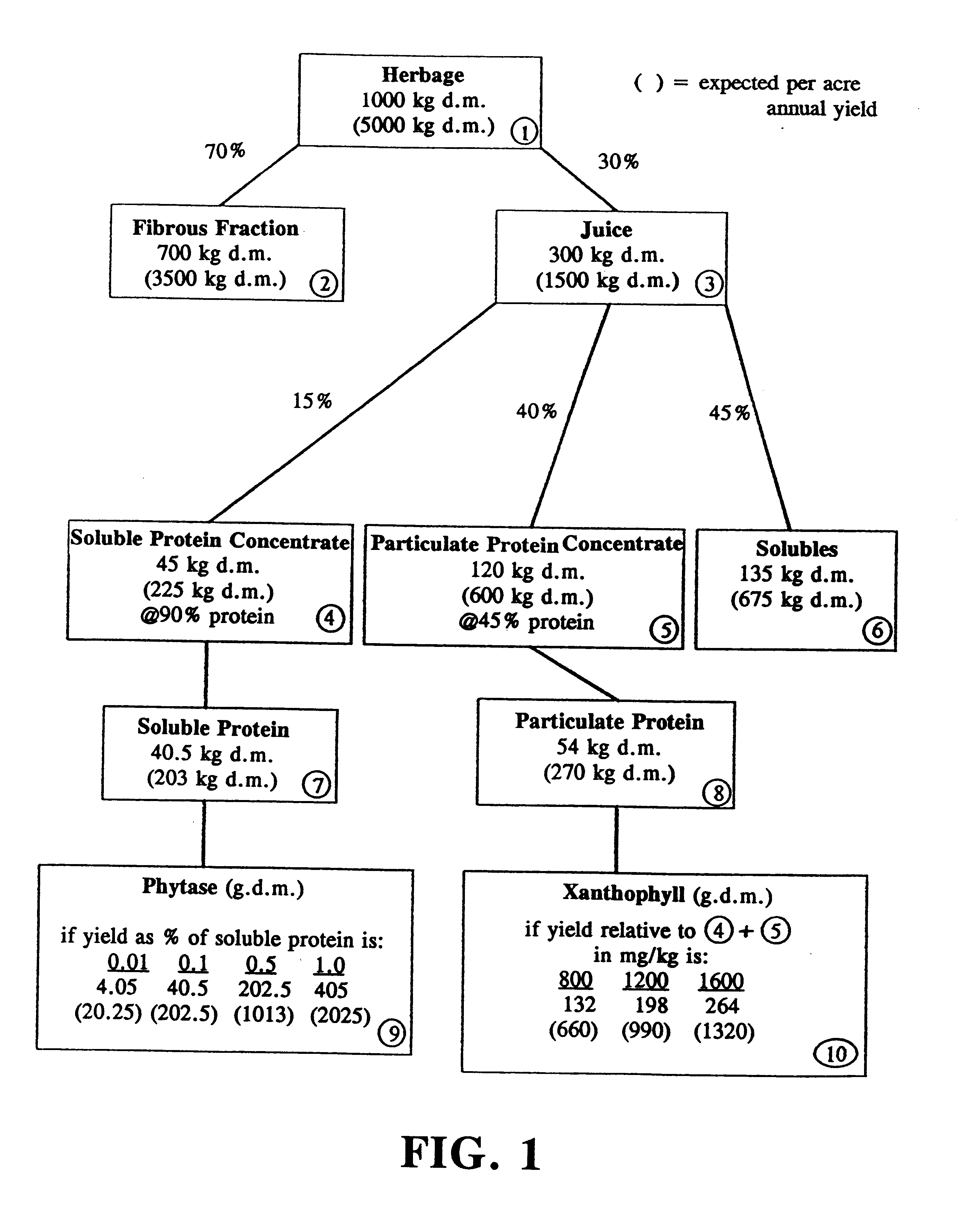
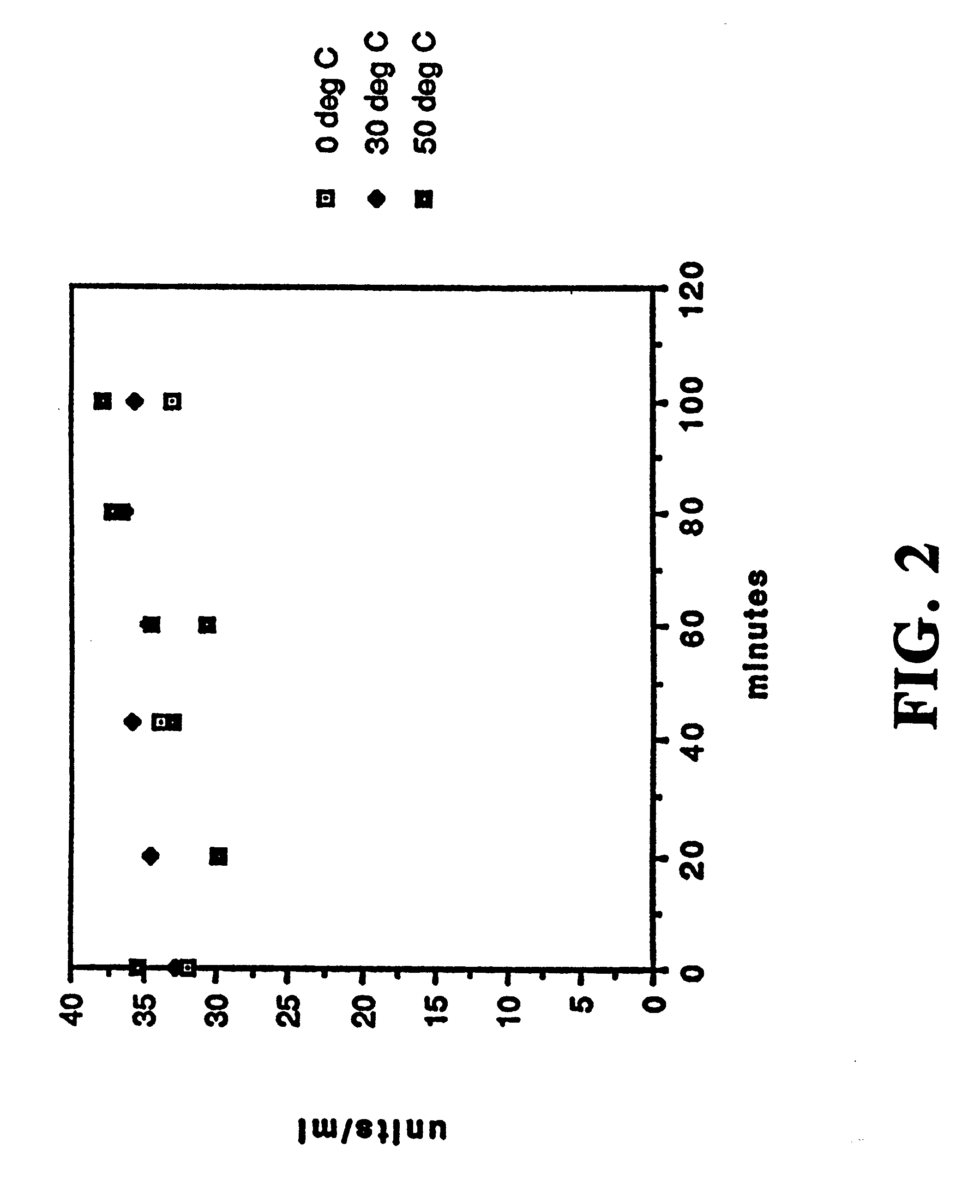
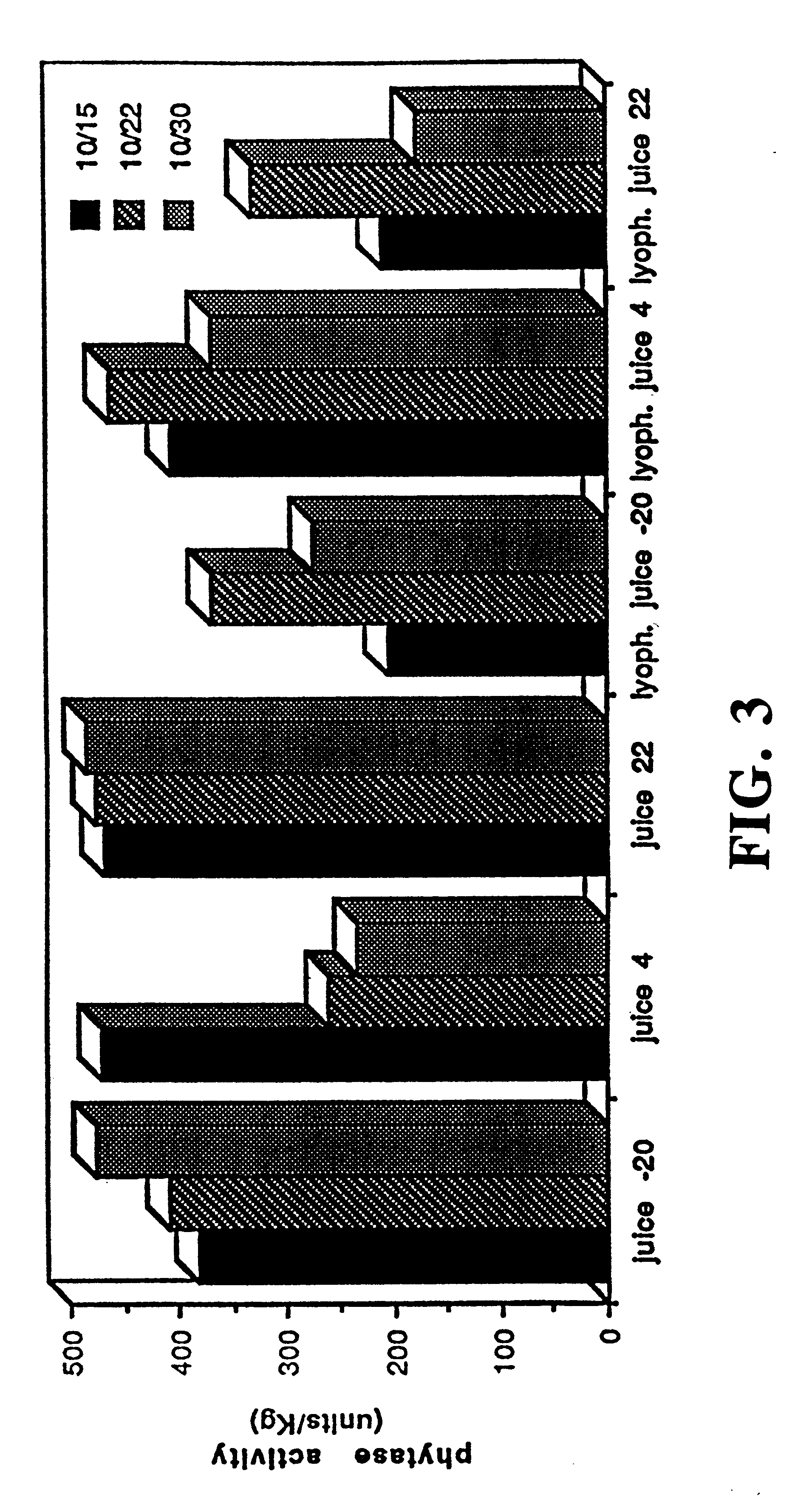
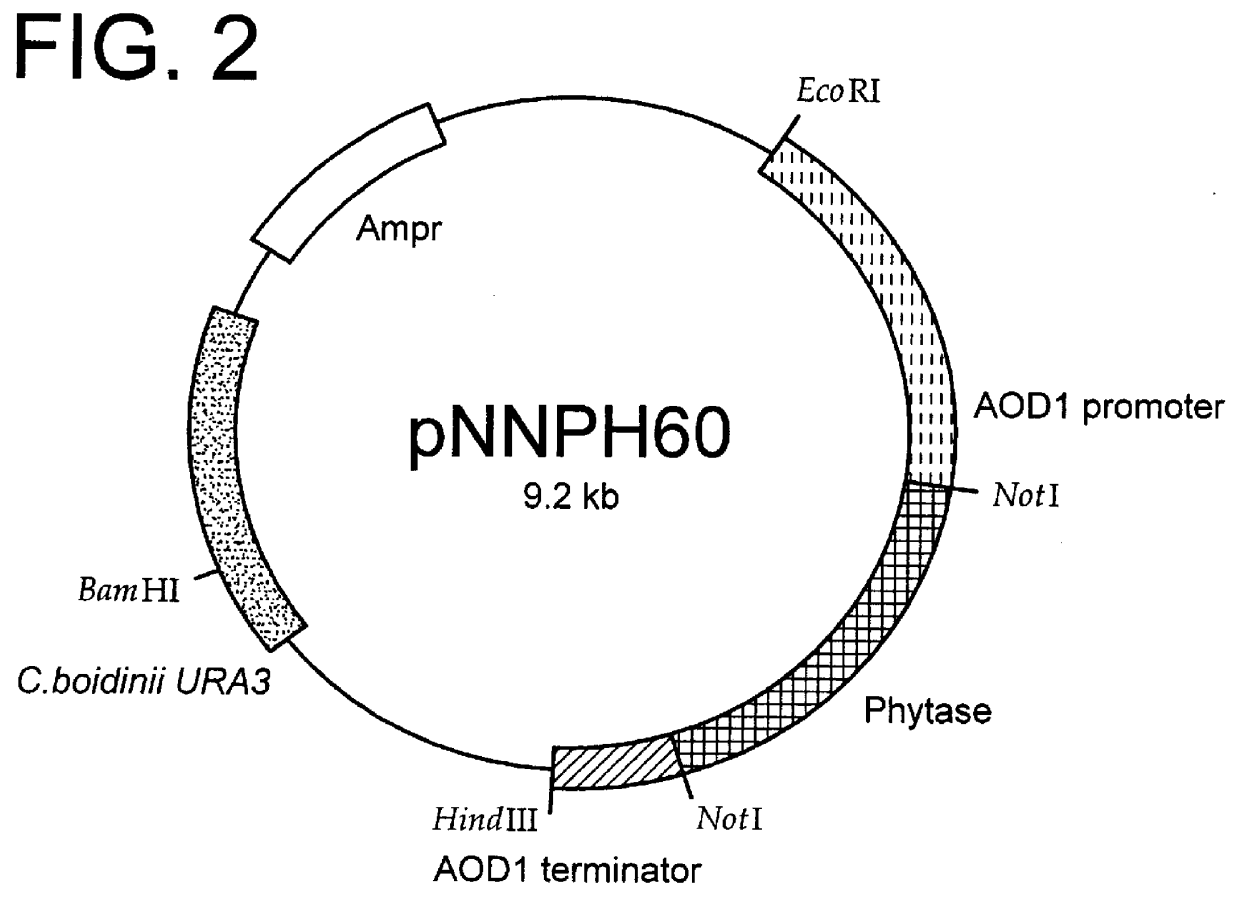
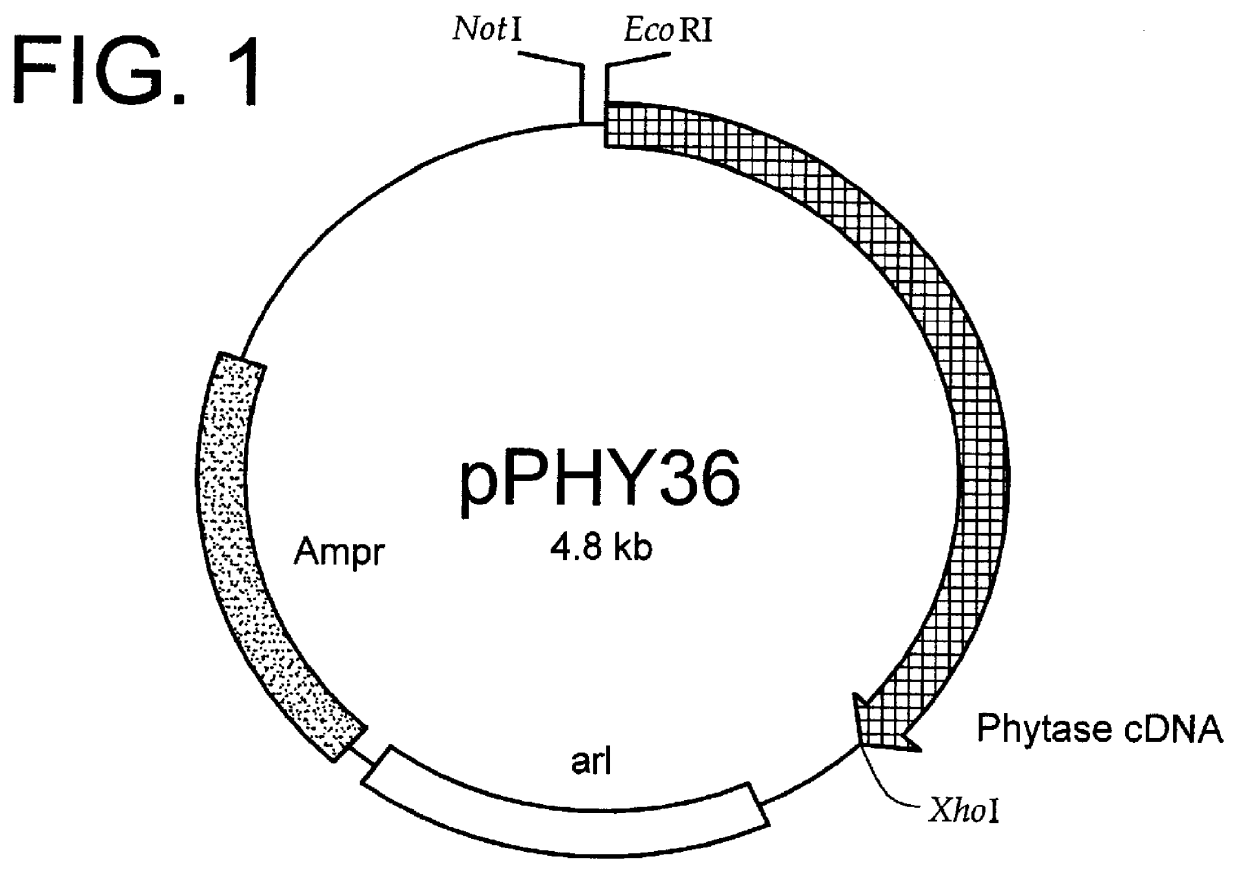
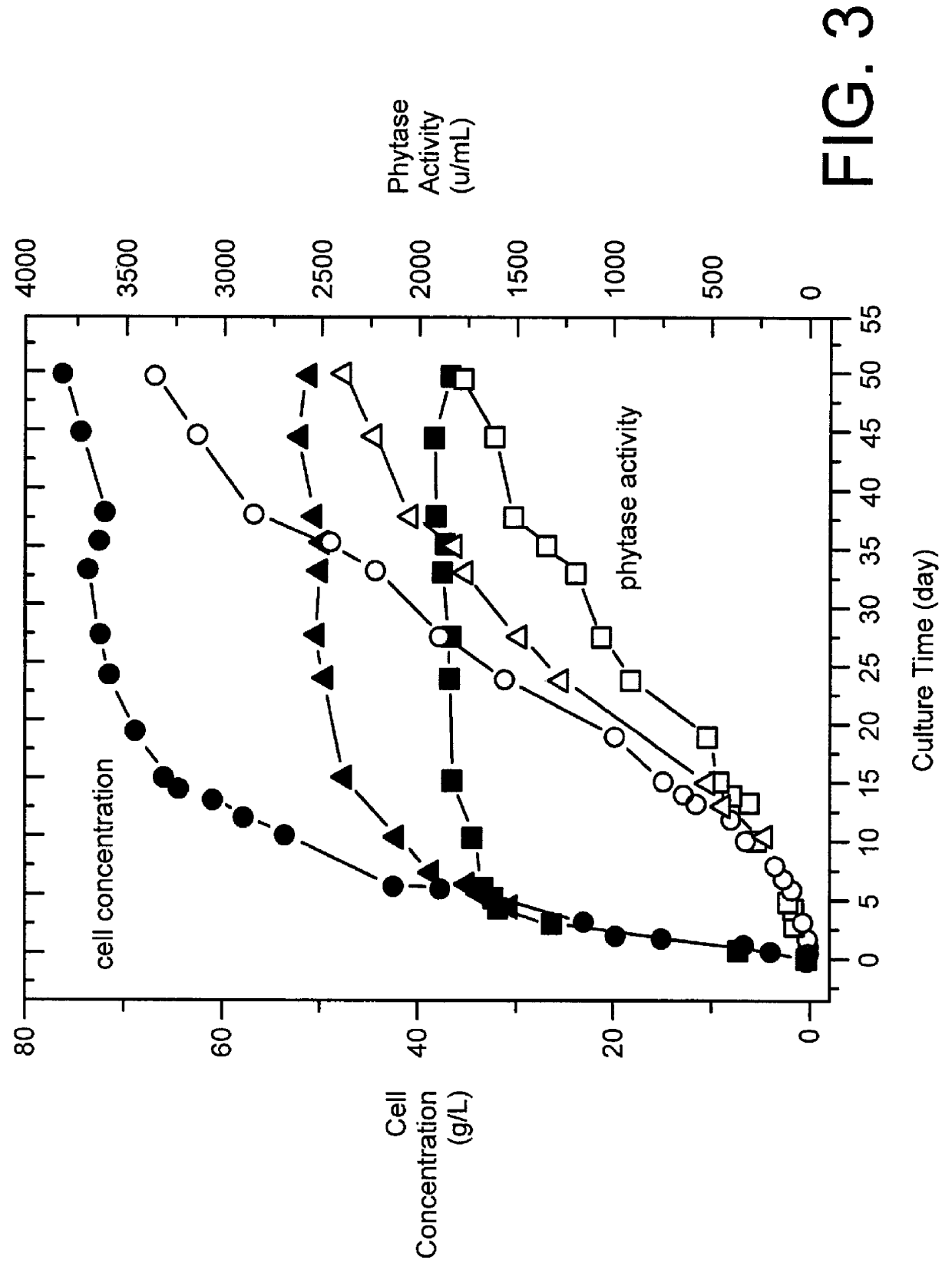
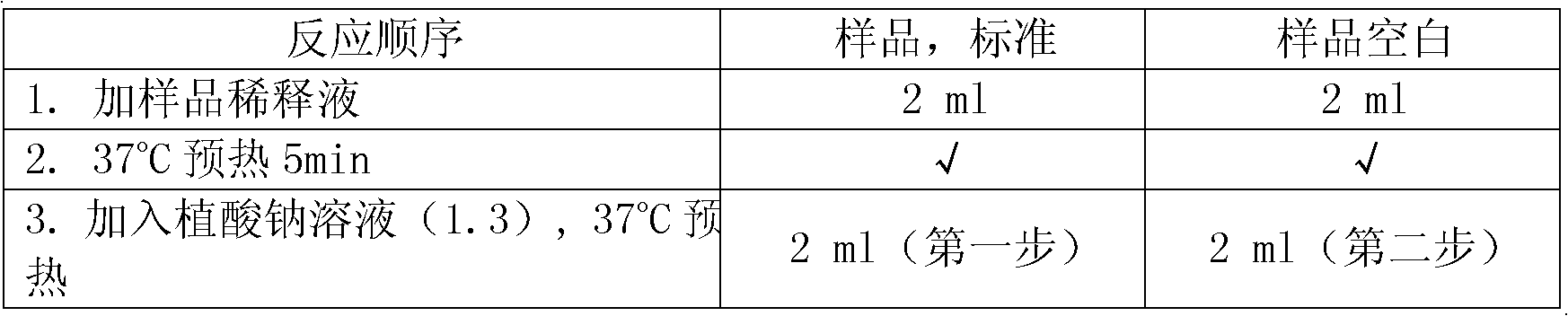
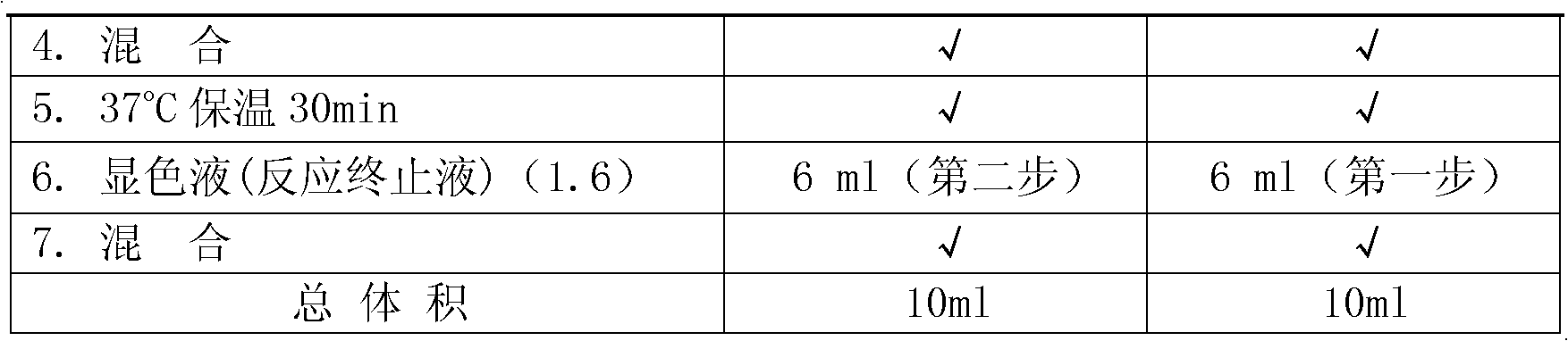
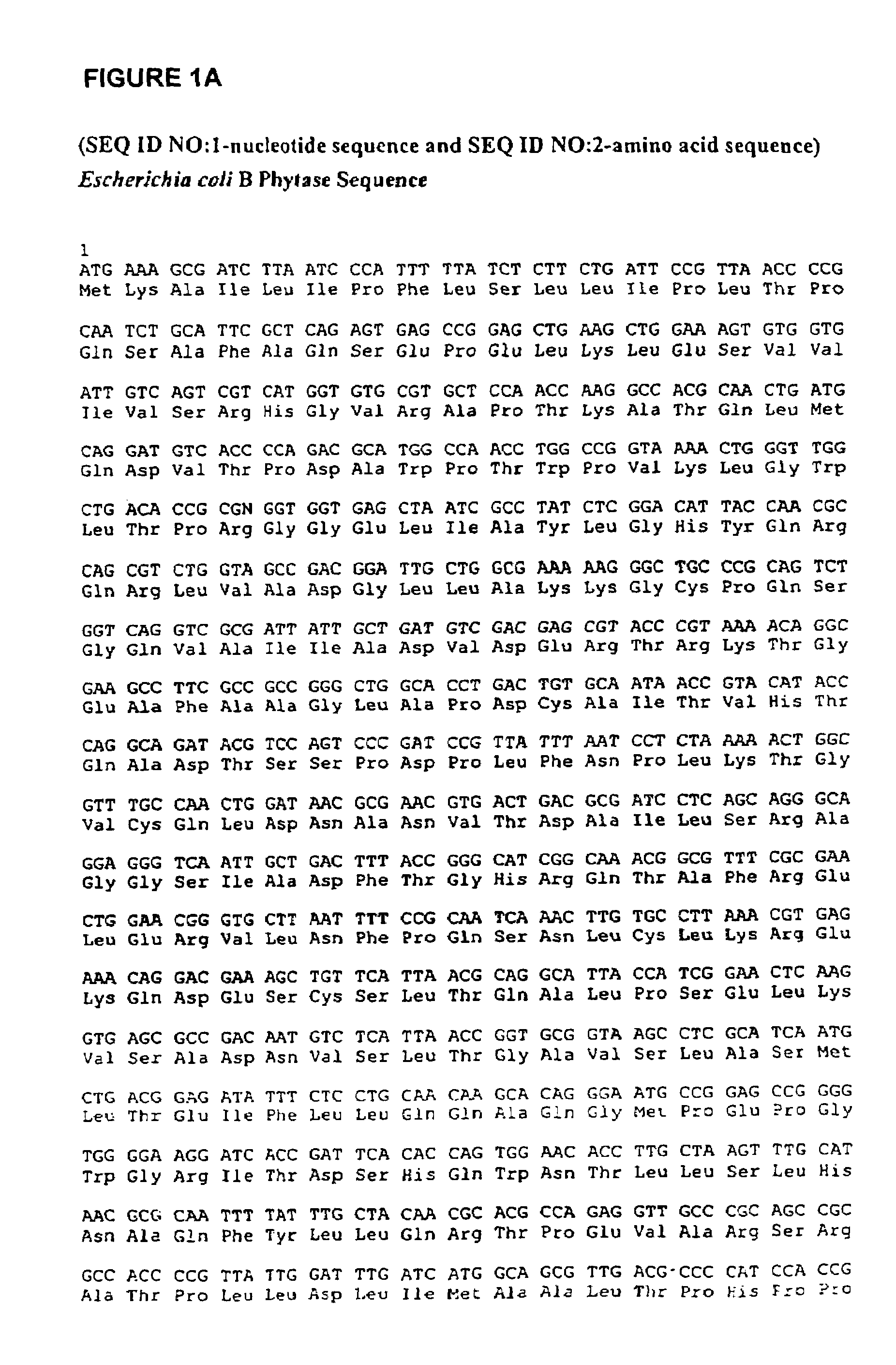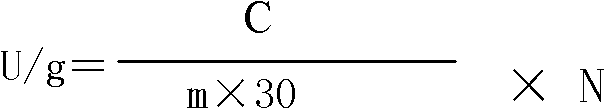Patents
Literature
92 results about "Phytase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phytases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods of making and using them
InactiveUS20050281792A1Improve publishing efficiencyHigh nutritional valueImmobilised enzymesBacteriaEscherichia coliAdditive ingredient
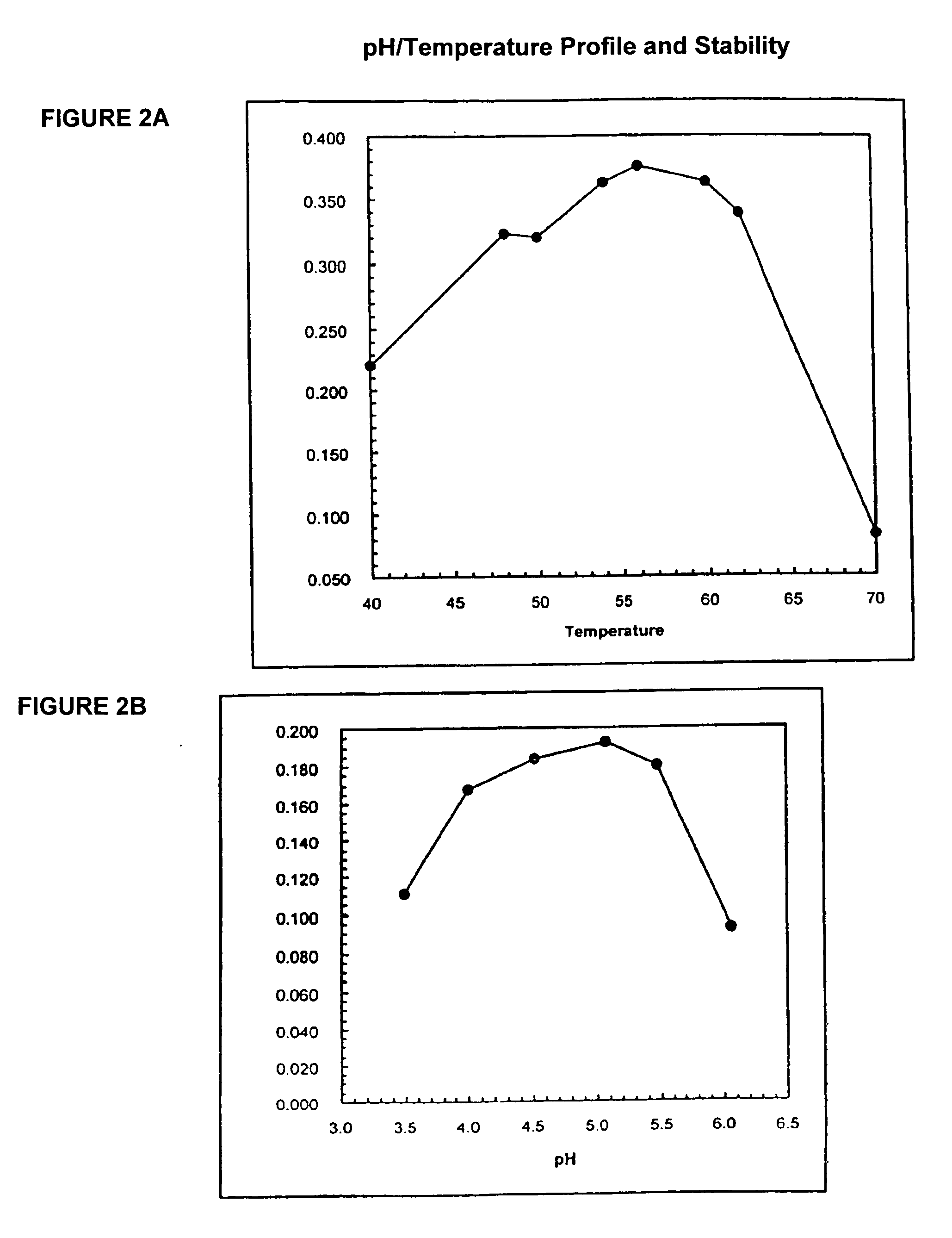
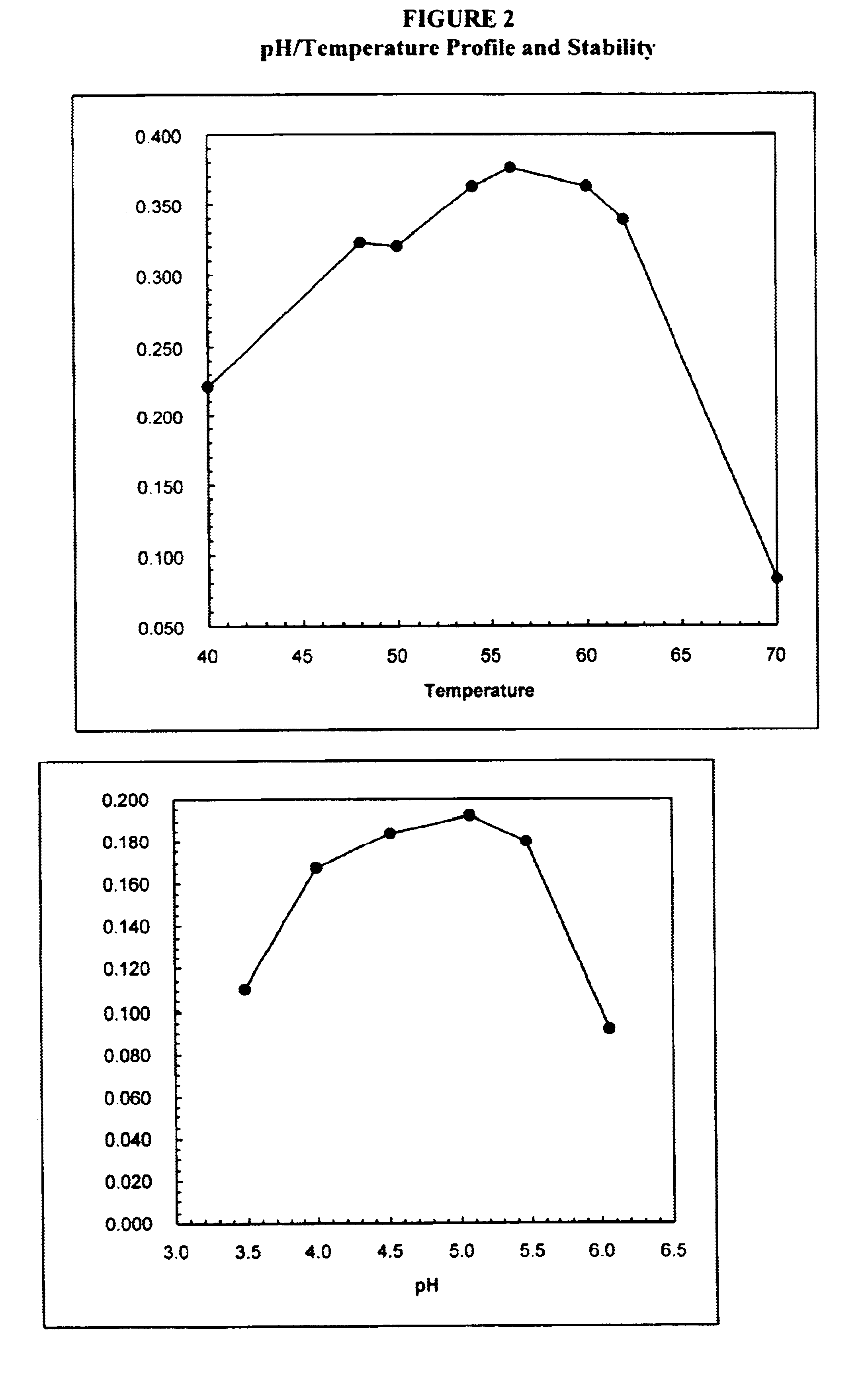
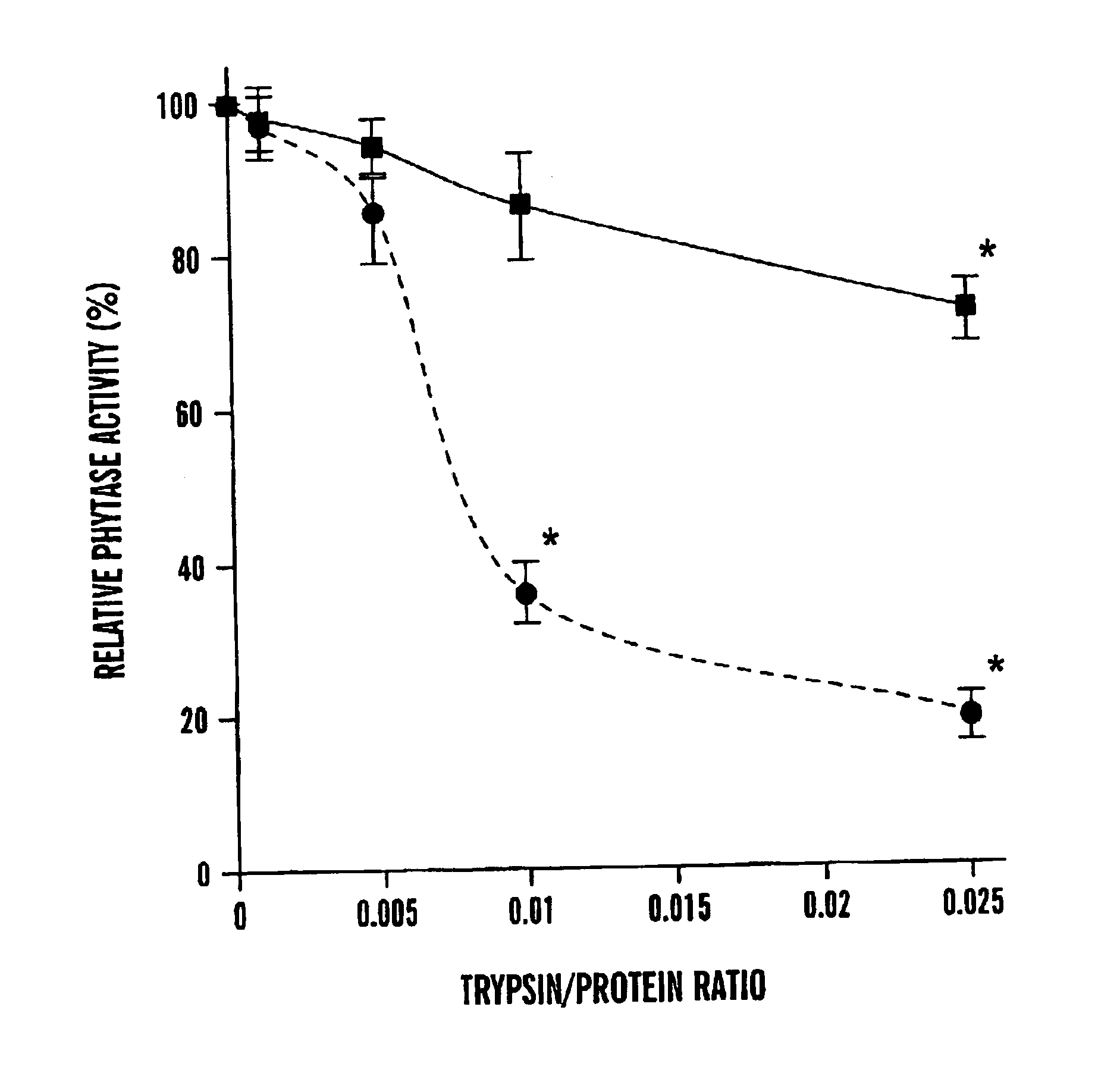
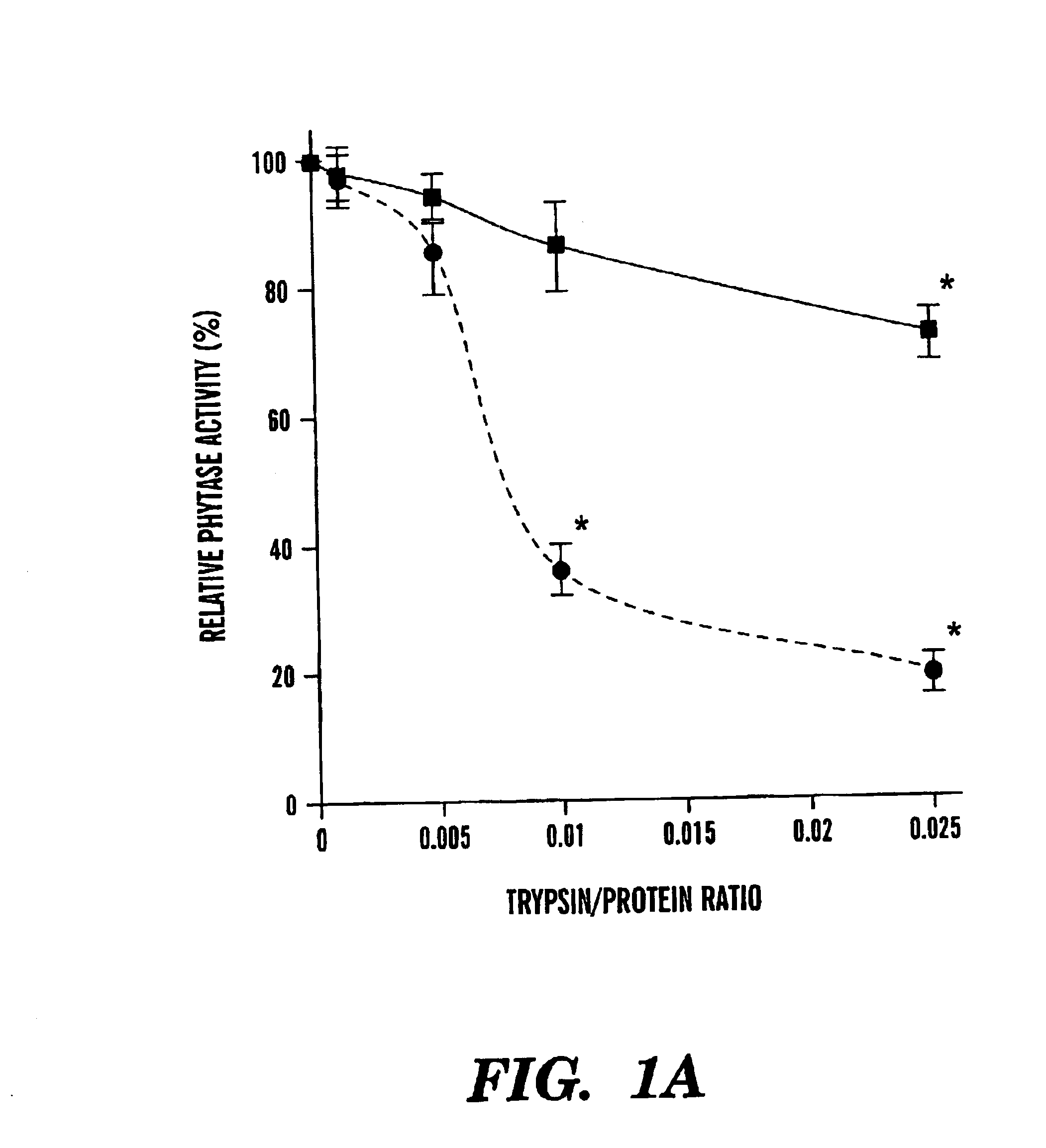
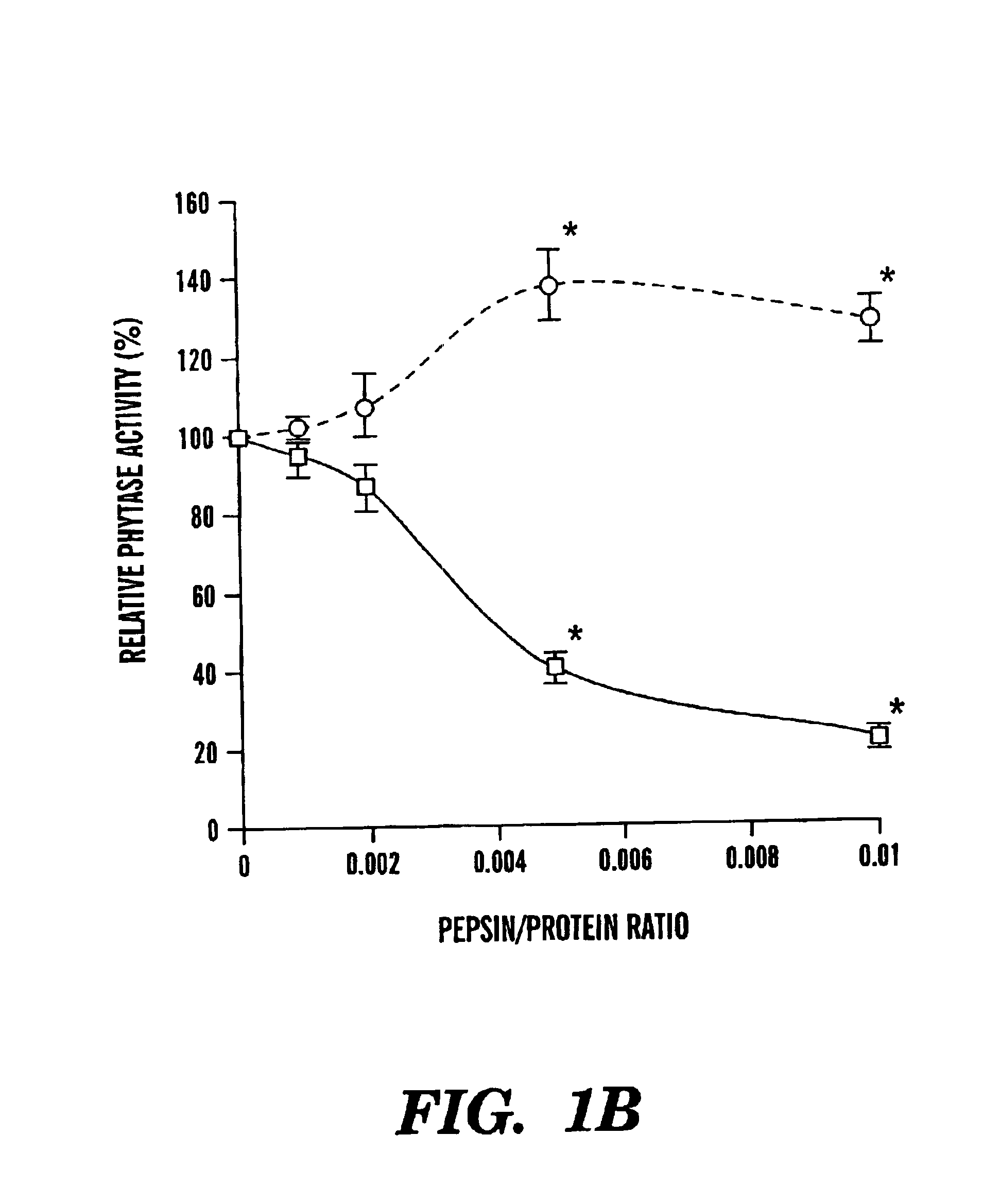
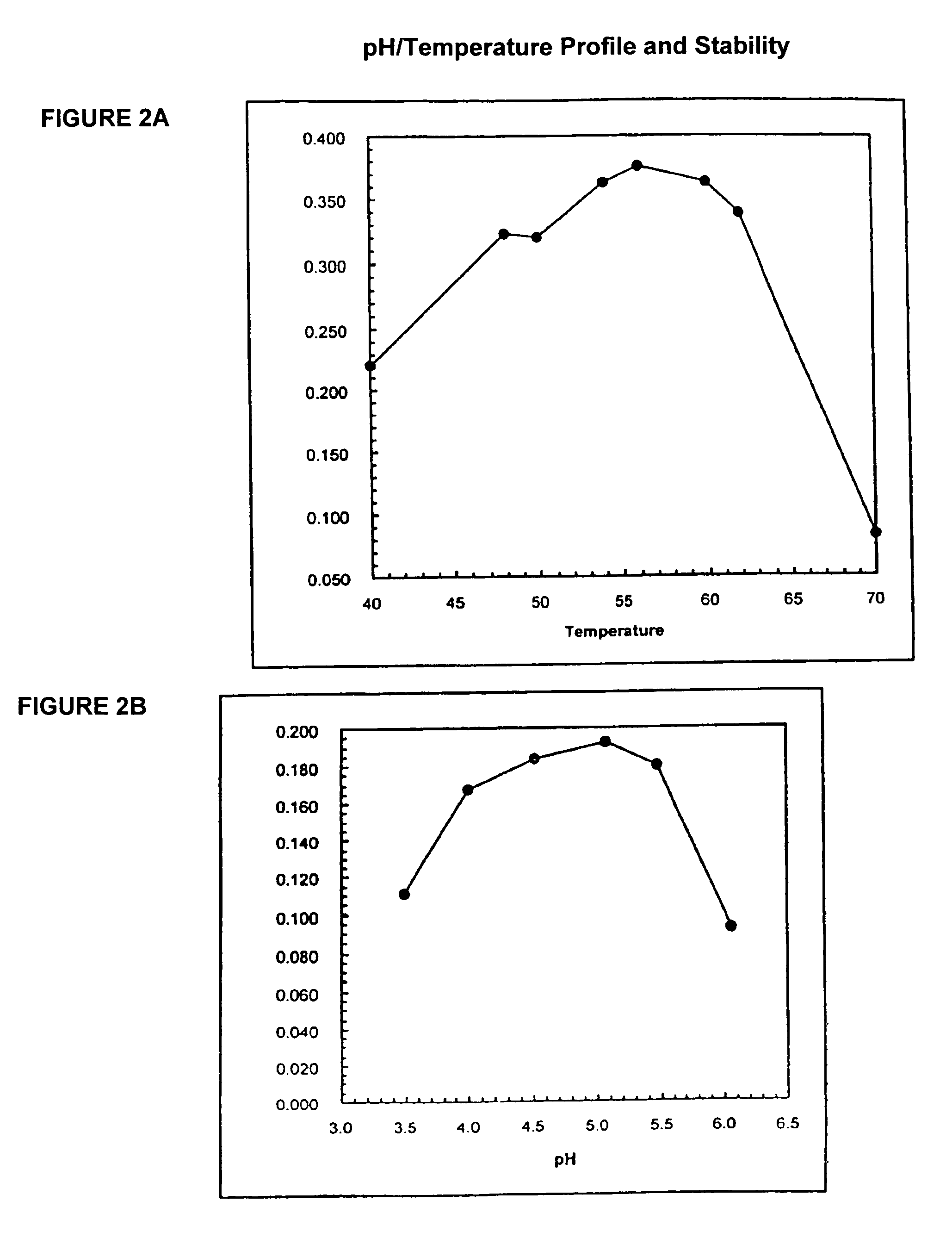
In one aspect, the invention provides a purified and modified phytase enzyme from Escherichia coli K12 appA phytase. The enzyme has phytase activity and improved thermal tolerance as compared with the wild-type enzyme. In addition, the enzyme has improved protease stability at low pH. Glycosylation of the modified phytase provided a further improved enzyme having improved thermal tolerance and protease stability. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells and can be used to aid in the digestion of phytate where desired. In one aspect, the phytase of the present invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Phytase-containing foodstuffs and methods of making and using them
InactiveUS6720014B1High nutritional valueImprove release efficiencyFungiBacteriaEscherichia coliPhytase activity
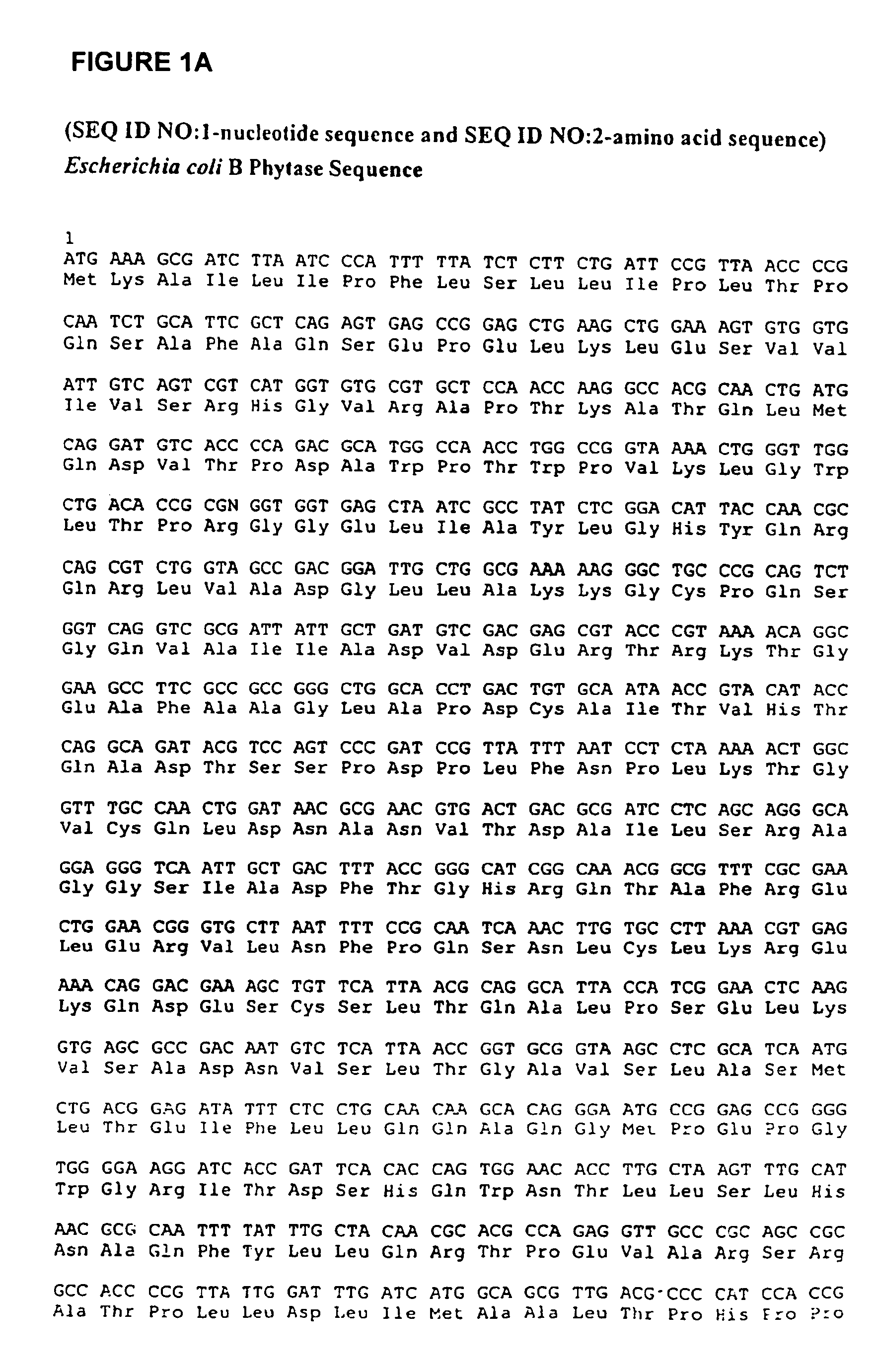
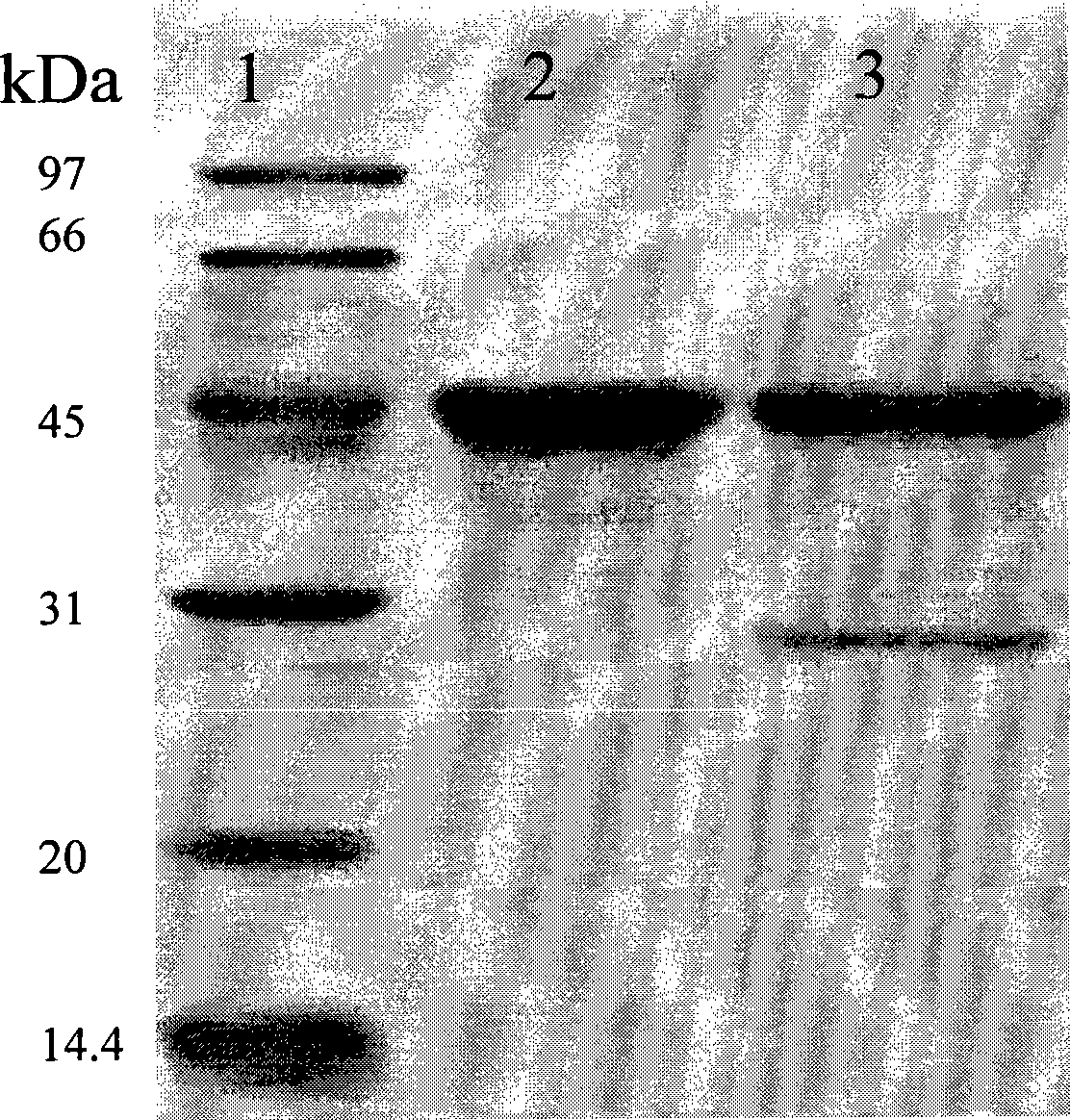
A purified recombinant phytase enzyme derived from Escherichia coli B. The enzyme has a molecular light of about 47.1 kilodaltons and has phytase activity. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells and can be used to aid in the digestion of phytate where desired. In particular, the phytase of the present invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Phosphatases with improved phytase activity
InactiveUS6974690B2Improved phytase activityHigh activityDough treatmentBacteriaProteinase activityPhytase activity
The present invention provides phosphatases with improved phytase activity. The invention provides proteolytic fragments of phosphatase having improved phytase activity. A recombinant gene encoding a phosphatase fragment having improved phytase activity is also provided. The invention also includes a method of increasing the phytase activity of phosphatase by treating the phosphatase with a protease. In addition, the invention provides a new phosphatase, AppA2, having improved properties.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Phytases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods of making and using them
InactiveUS7432097B2High nutritional valueImprove publishing efficiencyImmobilised enzymesBacteriaEscherichia coliAdditive ingredient
In one aspect, the invention provides a purified and modified phytase enzyme from Escherichia coli K12 appA phytase. The enzyme has phytase activity and improved thermal tolerance as compared with the wild-type enzyme. In addition, the enzyme has improved protease stability at low pH. Glycosylation of the modified phytase provided a further improved enzyme having improved thermal tolerance and protease stability. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells and can be used to aid in the digestion of phytate where desired. In one aspect, the phytase of the present invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Animal feed compositions containing phytase derived from transgenic alfalfa and methods of use thereof
A value-added composition of matter containing plant matter from transgenic alfalfa which expresses exogenous phytase activity is disclosed. The phytase activity is a gene product of an exogenous gene encoding for phytase which has been stably incorporated into the genome of alfalfa plants. The transgenic alfalfa expresses phytase activity in nutritionally-significant amounts, thereby enabling its use in animal feeds to eliminate the need for phosphorous supplementation of livestock, poultry, and fish feed rations.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for producing phytase
InactiveUS6140077AIncreasing number of cellPrevent proliferationFungiHydrolasesLiquid mediumPhytase activity
A method for producing phytase using a Candida boidinii transformant, by which phytase is secreted to liquid medium without substantially increasing the number of the transformant cells is disclosed. In this method, cells of a Candida boidinii transformant which is transformed with a recombinant vector comprising a promoter inducible with methanol and a gene located downstream of said promoter and operably linked to said promoter, which gene encodes a polypeptide having phytase activity, are cultured in a liquid culture medium containing phosphoric acid or a phosphate compound in an amount effective of restricting proliferation of said cells of Candida boidinii transformant such that the amount of said cells of Candida boidinii transformant is not substantially increased, while adding methanol to the culture medium, so as to make said cells secrete said phytase.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
Phytase enzymes, nucleic acids encoding phytase enzymes and vectors and host cells incorporating same
A novel DNA is provided which encodes an enzyme having phytase activity isolated from Penicillium. Also provided for is a method of isolating DNA encoding an enzyme having phytase activity from organisms which possess such DNA, transformation of the DNA into a suitable host organism, expression of the transformed DNA and the use of the expressed phytase protein in feed as a supplement.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC +1
Overexpression of phytase genes in yeast systems
The present invention relates to a method of producing a heterologous protein or polypeptide having phytase activity in a yeast system. The invention also provides proteins having phytase activity which have increased thermostability. Yeast strains which produce a heterologous phytase and the vectors used to produce the phytase are also provided.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Phytases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
ActiveUS20100136113A1Increase feeding valuePromote digestionImmobilised enzymesPowder deliveryThermal denaturationNucleotide
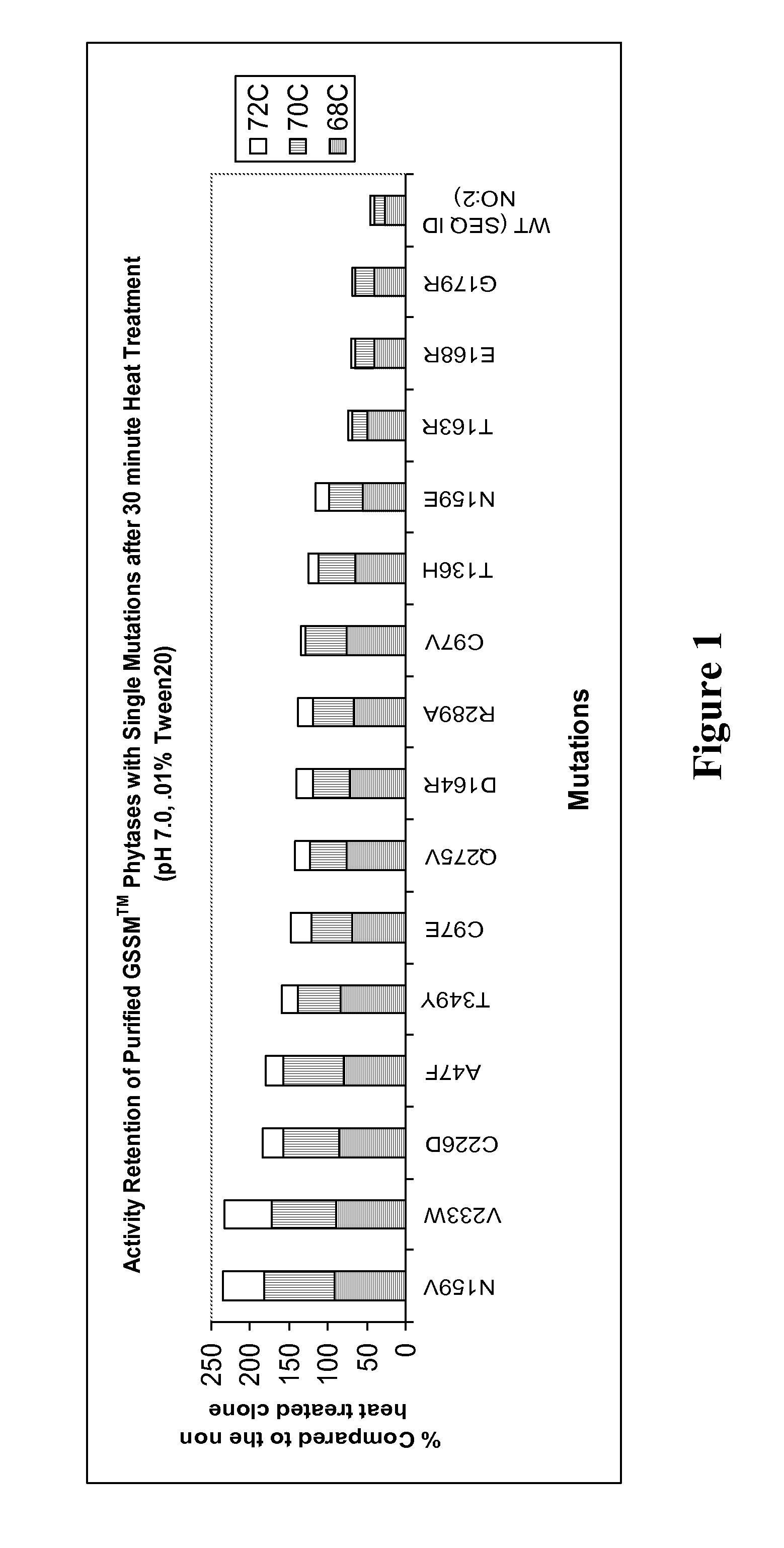
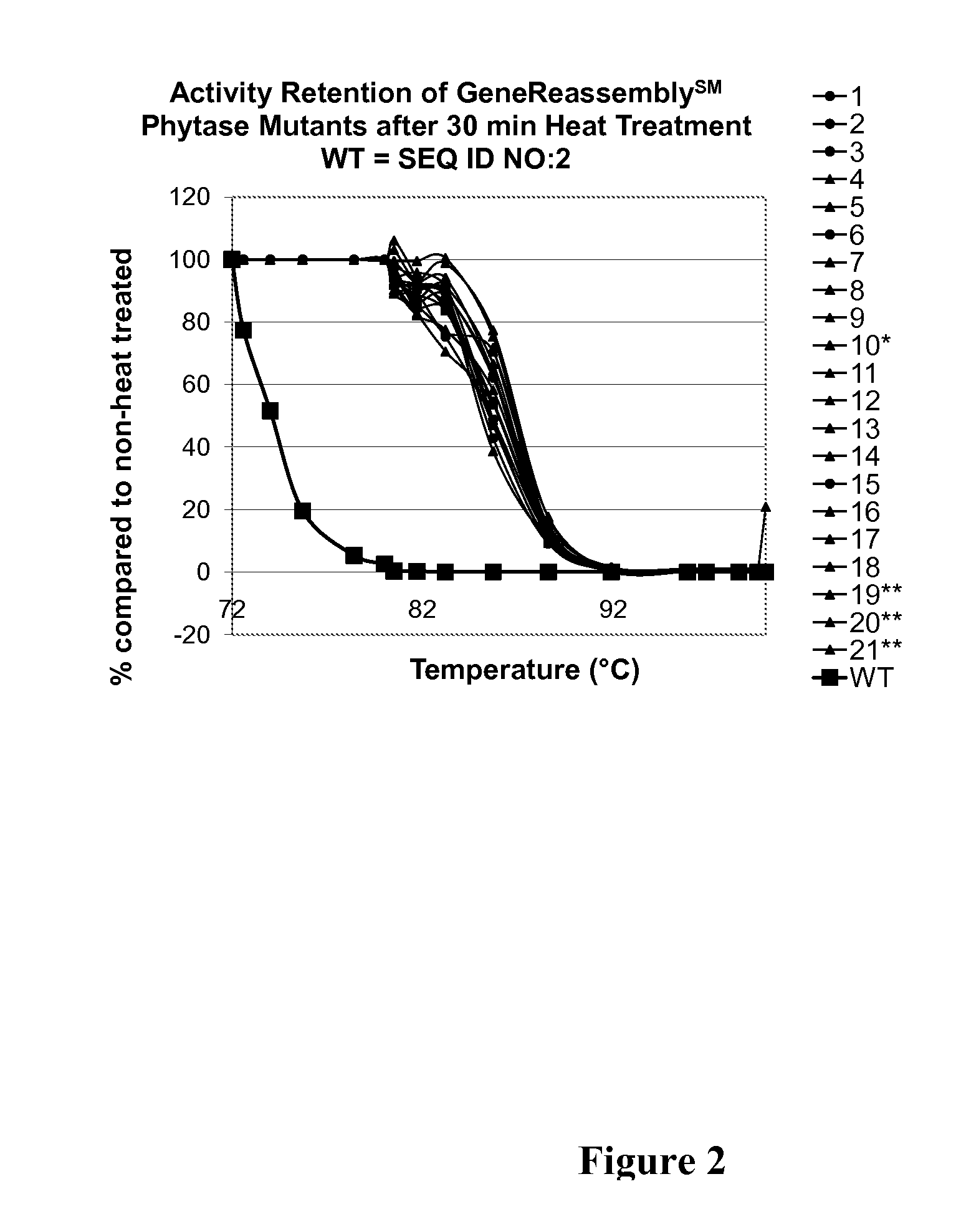
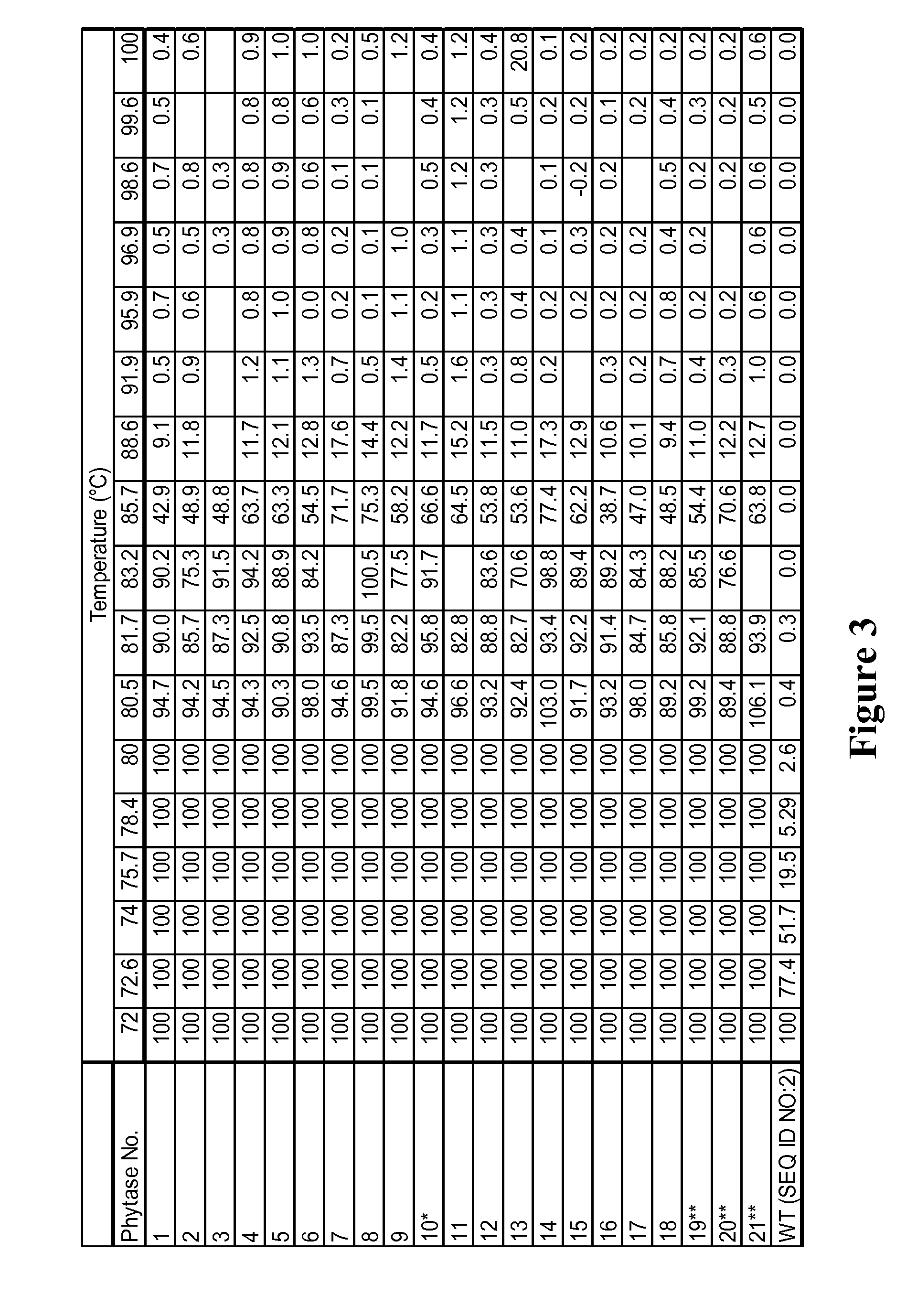
This invention relates to phytases, polynucleotides encoding them, uses of the polynucleotides and polypeptides of the invention, as well as the production and isolation of such polynucleotides and polypeptides. In particular, the invention provides polypeptides having phytase activity under high temperature conditions, and phytases that retain activity after exposure to high temperatures. The phytases of the invention can be thermotolerant and / or thermostable at low temperatures, in addition to higher temperatures. The phytases of the invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients. The phytases of the invention can be formulated as foods or feeds or supplements for either to, e.g., aid in the digestion of phytate. The foods or feeds of the invention can be in the form of pellets, liquids, powders and the like. In one aspect, phytases of the invention are stabile against thermal denaturation during pelleting; and this decreases the cost of the phytase product while maintaining in vivo efficacy and detection of activity in feed.
Owner:BASF ENZYMES
Overexpression of phytase genes in yeast systems
The present invention relates to a method of producing a heterologous protein or polypeptide having phytase activity in a yeast system. The invention also provides proteins having phytase activity which have increased thermostability. Yeast strains which produce a heterologous phytase and the vectors used to produce the phytase are also provided.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Preparation method of microbial fermentative feedstuff
ActiveCN101305769AImprove digestibilityIncrease the number ofFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFeed conversion ratioCulture mediums
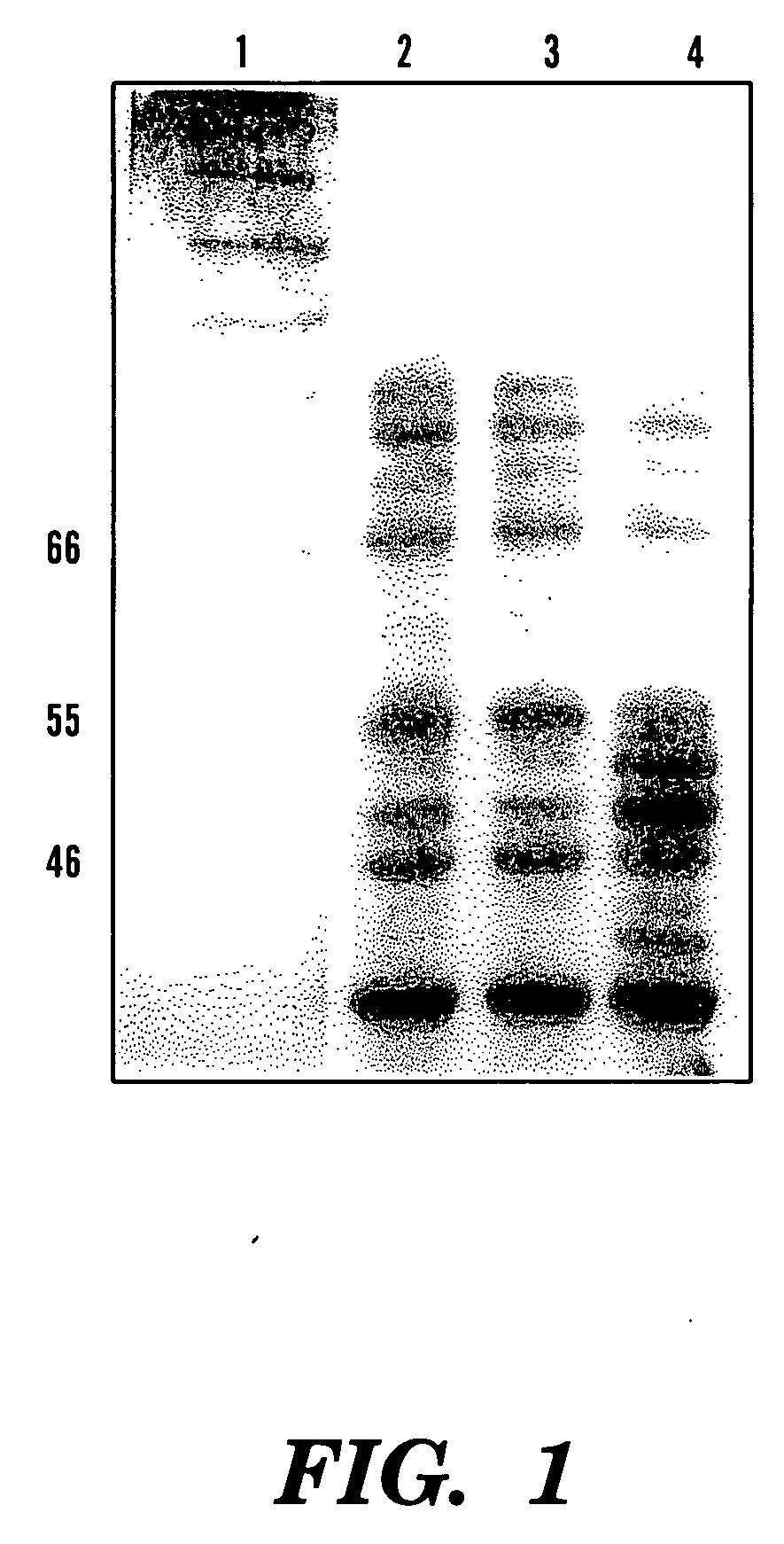
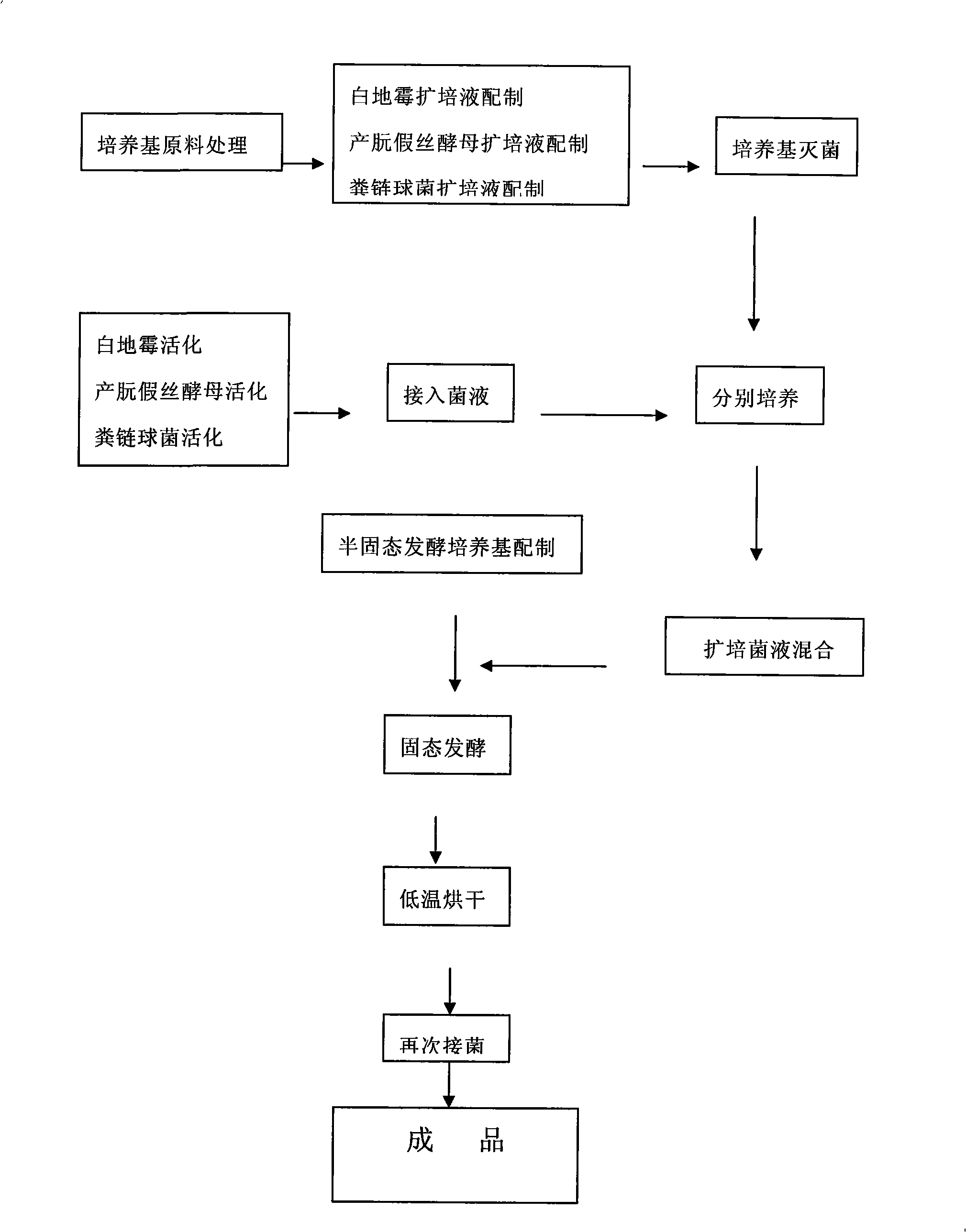
The invention discloses a method for preparing a microorganism fermentation feed. The method comprises the main technological processes as follows: respectively culturing Candida utilis, Geotrichum candidum and Streptococcus faecalis with molasses in combination with a liquid microorganism culture medium as the main raw materials; mixing the Candida utilis culture solution, the Geotrichum candidum culture solution and the Streptococcus faecalis culture solution at a certain ratio to obtain a mixed bacteria solution; subjecting to solid fermentation in a semi-solid fermentation culture medium including molasses liquefied liquid, corn coat, vegetable meal, cotton seed meal, wheat bran, soybean meal and apple pomace; baking at a low temperature when the fermentation is finished; and pulverizing to obtain the microorganism fermentation feed. In the microorganism fermentation feed, the viable count of beneficial microorganism is larger than 1*10<9>cfu / g, and the phytase activity is higher than 1,400IU / kg. The feed has the functions of supplementing the number of milk cow (sheep) rumen microorganism, regulating rumen fermentation function, and improving feed conversion and utilization ratio.
Owner:内蒙古柯宏生物科技有限公司
Phytases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
ActiveUS20120066781A1Increase feeding valuePromote digestionImmobilised enzymesFungiPhytase activityDigestion
This invention relates to phytases, polynucleotides encoding them, uses of the polynucleotides and polypeptides of the invention, as well as the production and isolation of such polynucleotides and polypeptides. In particular, the invention provides polypeptides having phytase activity under high temperature conditions, and phytases that retain activity after exposure to high temperatures. The invention further provides phytases which have increased gastric lability. The phytases of the invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients. The phytases of the invention can be formulated as foods or feeds or supplements for either to, e.g., aid in the digestion of phytate.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Cloning and expression of a novel phytase
ActiveCN101426907AEfficient fermentation productionEasy to produce by fermentationHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisMonogastric
The present invention relates to a novel phytase enzyme, a novel isolated nucleic acid molecule coding the enzyme, and a novel Yersinia intermedia having phytase activity. Particularly, the present invention relates to the phytase having (a) Theoretical molecular weight 45.5 kDa, (b) high specific activity 3960+-248 U / mg, (c) high stability at high temperature and wide pH, (d) optimal pH of 4.0-5.0, (e) optimal temperature of 50-60 DEG C, (f) high resistance to pepsin and trypsin. The phytase is very suitable to be used in feed of monogastrics as feed additive. The present invention also relates to a recombinant vector comprising said nucleic acid molecule, a recombinant host cell (e.g., Pichia pastoris ) harboring said recombinant vector, and a method for producing phytase using the recombinant host cell. The present invention further provides a feed additive comprising said phytase and / or host cells expressing a phytase as effective ingredient. In addition, the present invention provides a novel method for isolating phytase from a target organism.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
High-efficiency phytate degradation bacterium Rahnella aquatils and application thereof in prompting plant growth
ActiveCN103122329APromote germinationPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSolubilityBacteroides
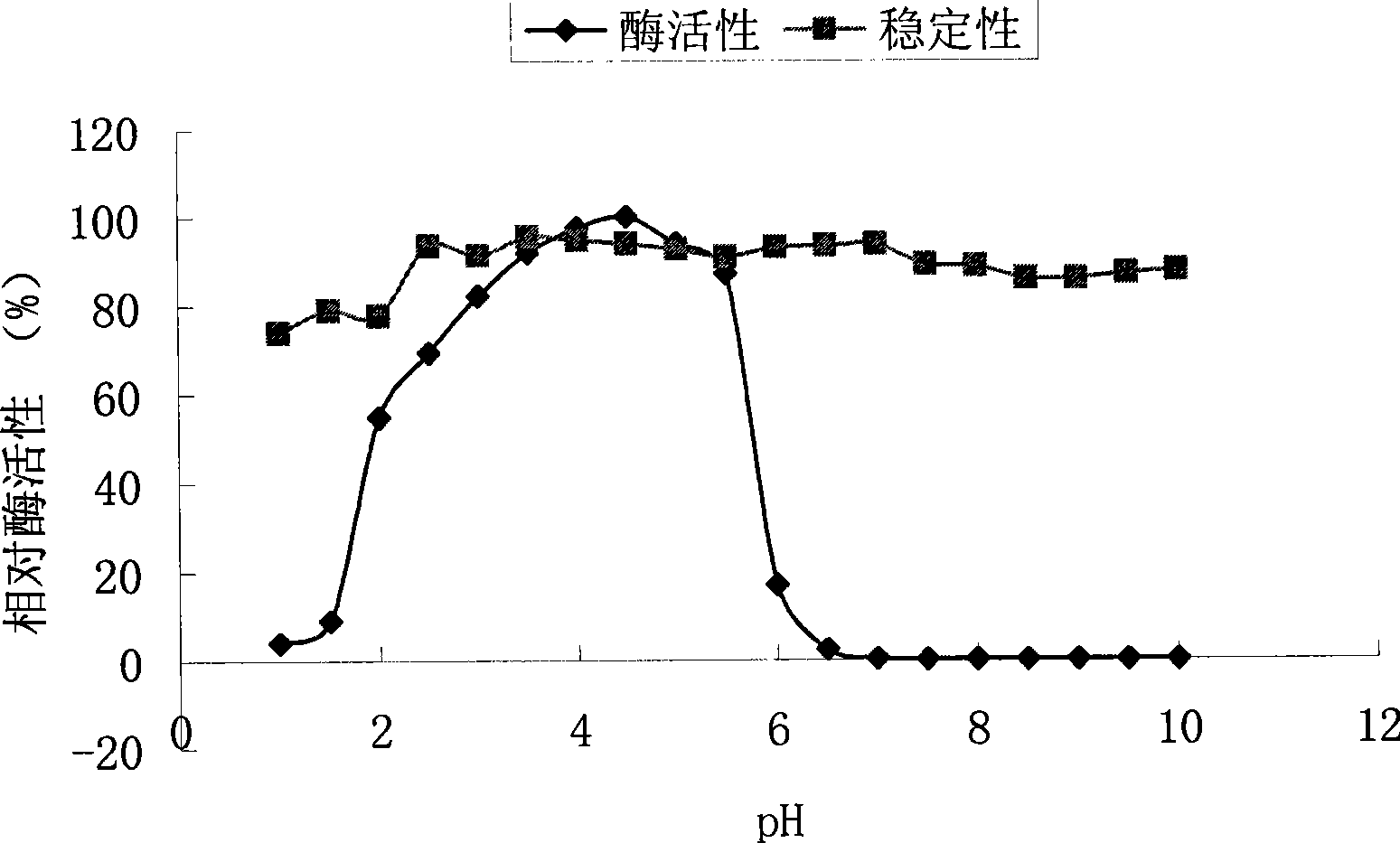
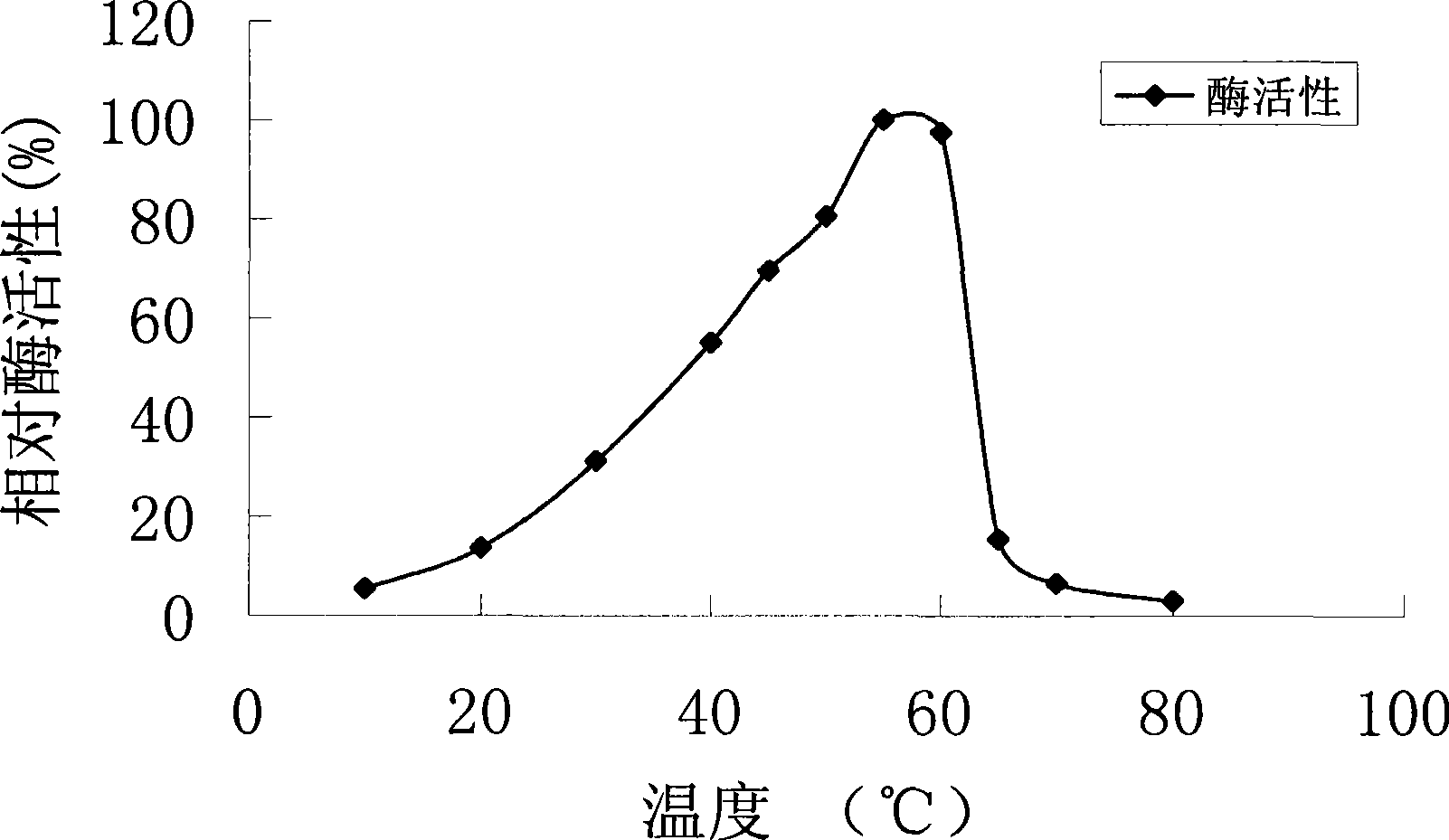
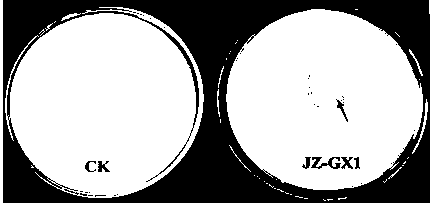
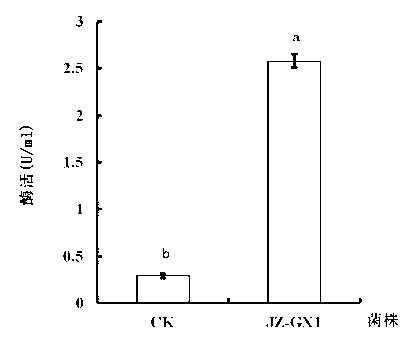
The invention discloses a high-efficiency phytate degradation bacterium Rahnella aquatils and an application thereof in prompting plant growth. The classification naming of the high-efficiency phytate degradation bacterium is Rahnella aquatils JZ-GX1 which is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, the preservation number is CCTCCNO: M2012439, the preservation date is, November 6th, 2012, and the preservation address is Wuhan, China. The Rahnella aquatils JZ-GX1 disclosed by the invention has higher phytase activity, can effectively degrade slightly solubility phytate such as calcium phytic acid and the like; and the bacterium also can produce phytohormone IAA. A series of growth prompting tests show that compared with a reference phase, the bacterium has a significant prompting function to the sprouting and growth of corn and the growth of poplar trees and piney. Excellent bacterium resources are provided for biological bacterial fertilizers for plants such as corn, poplar trees and piney.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Microdetermination method for phytase in feedstuff
ActiveCN101493418AEliminates the effects of hydrolysis reactionsLow detection limitPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionAcetic acidPhytase activity
The invention discloses a micro-determination method of phytase activity added in feedstuff. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing dialysis treatment on a sample by taking acetic buffer solution I as an outer dialysate, reducing inorganic phosphorus content in the feedstuff to eliminate influence of the inorganic phosphorus on the phytase hydrolytic reaction in the feedstuff; secondly, fetching 1ml of liquid to react to replace 0.2 ml of the liquid in the existing method, adding 1 ml of the acetic buffer solution I to replace 1.8 ml of the acetic buffer solution I in the existing method so that blank extinction of the sample is in a reasonable determination range to avoid determination error which is caused by high content of the inorganic phosphorus in the sample blank; and thirdly, adding the known enzyme to the feedstuff, checking whether the known enzyme is lost during the processes of sampling, dialysis and determination by determining the known enzyme. The method can accurately determine the content of the phytase added to the feedstuff.
Owner:GUANGDONG VTR BIO TECH
Modified Aspergillus niger phytase
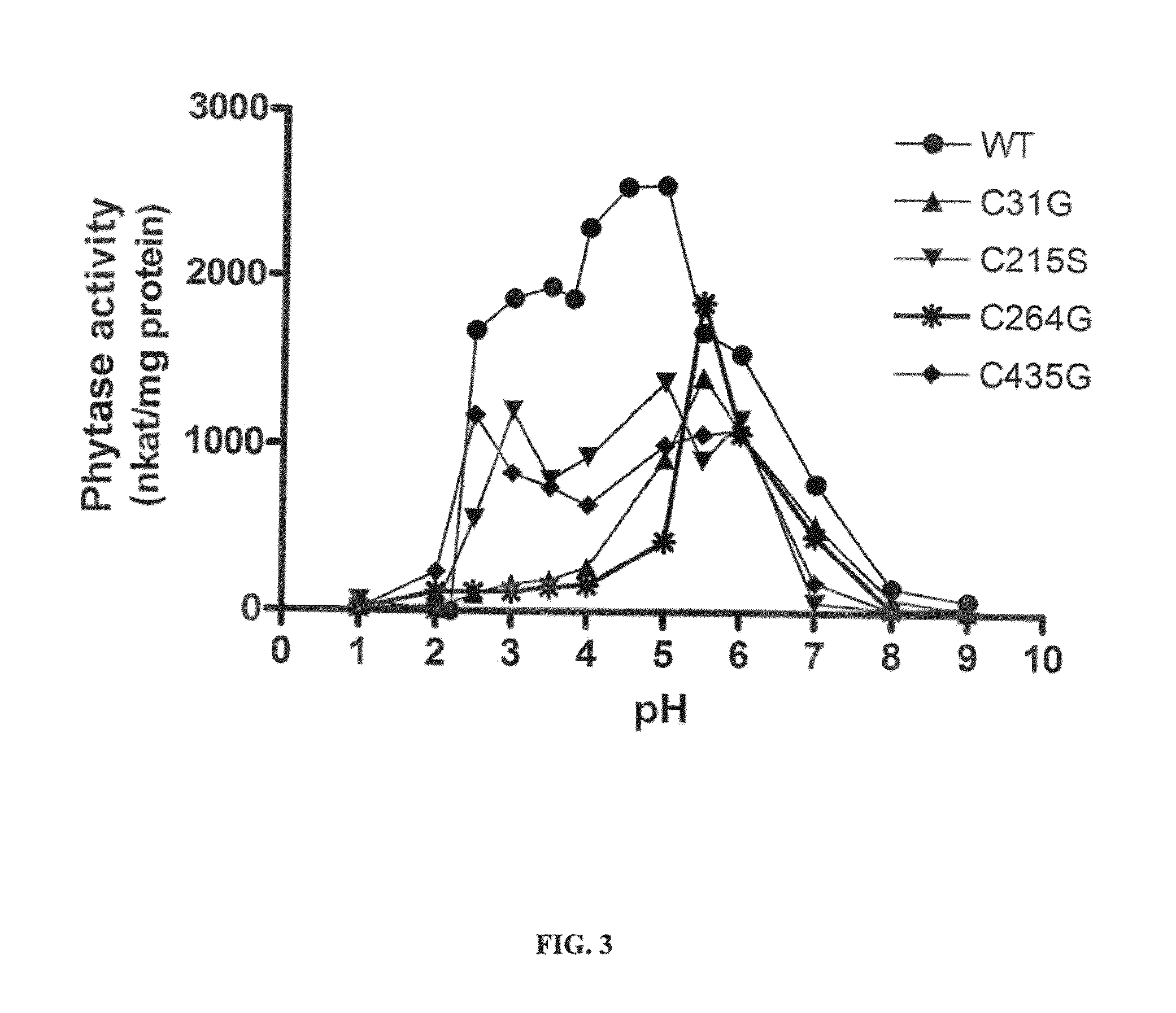
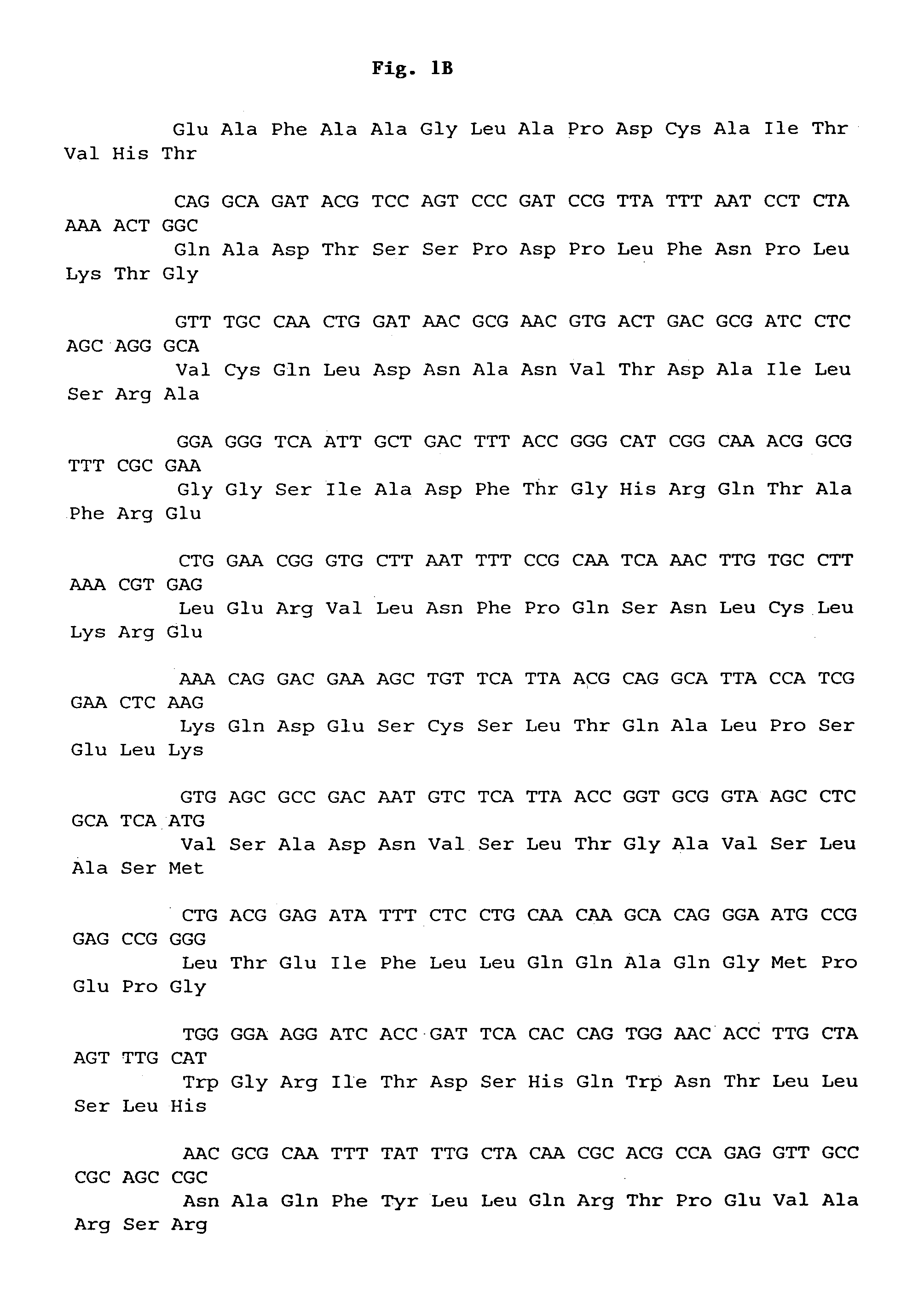
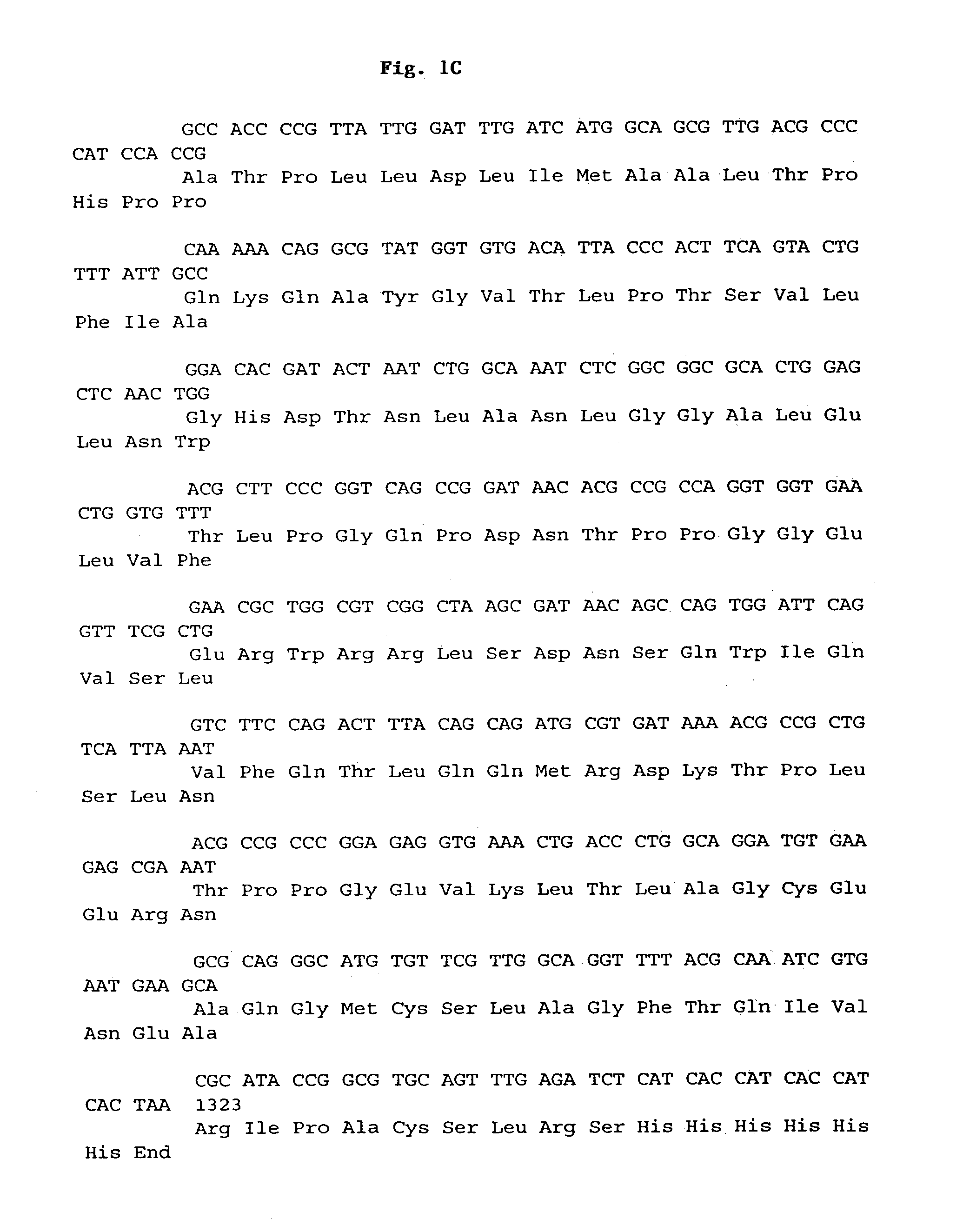
InactiveUS8334124B1HydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhytase activityAmino acid substitution
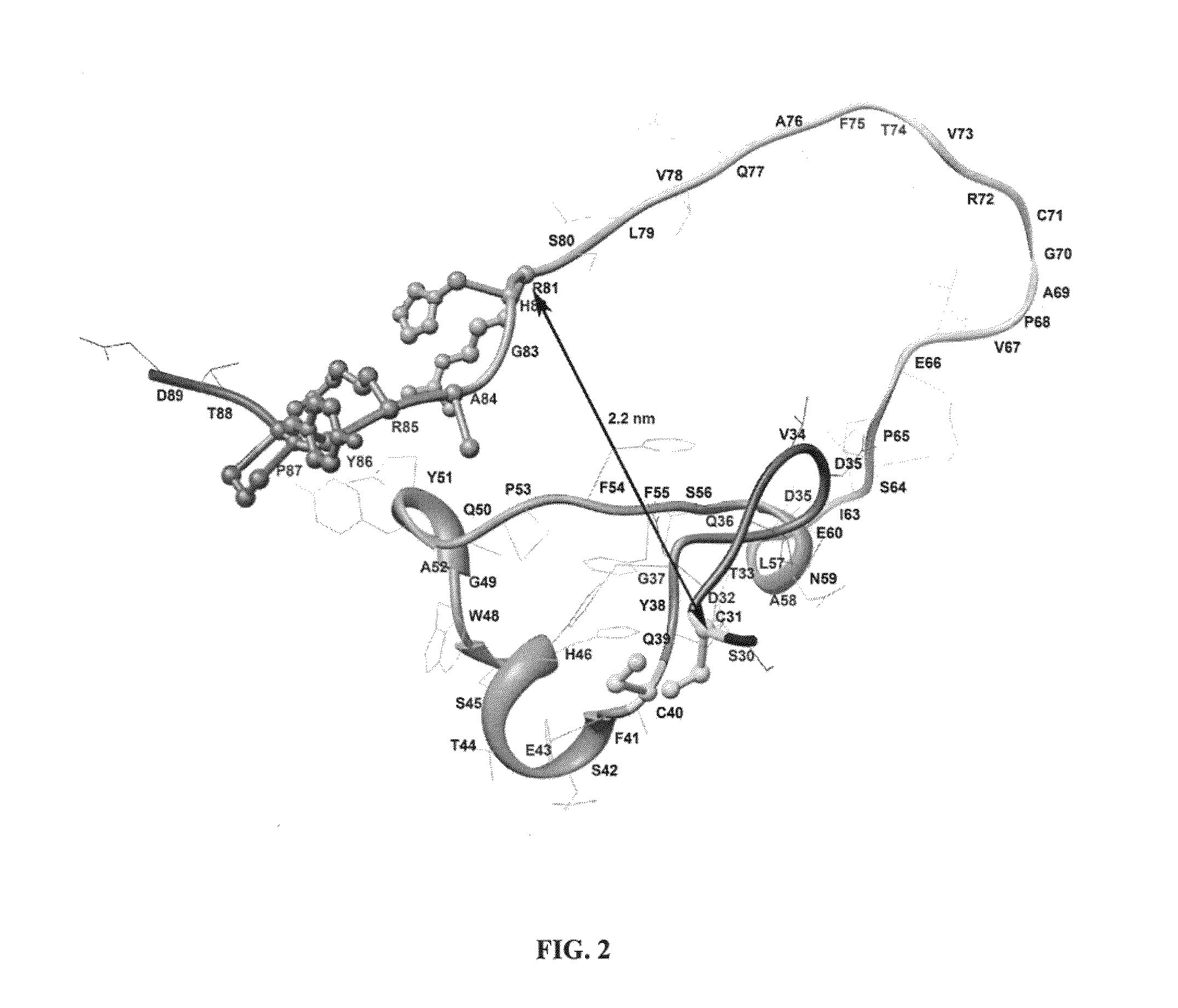
Disclosed herein is site-directed mutagenesis of a cloned phyA gene employed to replaced cysteine residues involved in disulfide bridge formation with another amino acid. Also disclosed herein is an isolated mutant phytase comprising an amino acid sequence having at least 96 percent sequence identity to SEQ. ID. NO: 6 and containing a double-substitution amino acid residue substitution of residue 31 and residue 40 of SEQ. ID. NO: 6, wherein said isolated mutant phytase has phytase activity.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Phytase expression systems and methods of making and using them
InactiveUS7232677B2High nutritional valueImprove publishing efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiEscherichia coliPhytase activity
The invention provides a purified or recombinant phytase enzyme (SEQ ID NO:2) initially derived from Escherichia coli B. The enzyme has a molecular weight of about 47.1 kilodaltons and has phytase activity (SEQ ID NO:2). The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells and can be used to aid in the digestion of phytate where desired. In particular, the phytase of the present invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Compound microbial fertilizer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses compound microbial fertilizer and a preparation method thereof. The compound microbial fertilizer is prepared from Bacillus atrophaeus and trichoderma which are taken as main active components, and can be used for controlling fungal diseases such as vegetable gray mold and the like in the field. The Bacillus atrophaeus in the compound microbial fertilizer has an inhibiting action on various plant pathogenic fungi, and meanwhile, the trichoderma LTR-2 has phytase activity, so that the compound microbial fertilizer can be used for controlling various plant diseases caused by the plant pathogenic fungi, has the functions of increasing utilization of phosphorus in soil by plants, improving the soil structure, promoting the plant growth and the like, and is multifunctional.
Owner:昆明保腾生化技术有限公司 +1
High-temperature-resistant phytase activity estimation method
InactiveCN106434850AReduce mistakesThe test data is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh humidityIce water
The invention is applicable to the technical field of feed stuff and processing technology, provides a high-temperature-resistant phytase activity estimation method and solves the problem that the influence of various links in practical production environments on high-temperature-resistant phytase is not taken into full consideration by a current phytase measuring method. The method includes the steps: firstly, sufficiently mixing feed samples with the high-temperature-resistant phytase, placing mixture into a high-pressure sterilization pot, performing reaction for 3 minutes at the temperature of 75-90 DEG C, rapidly taking out an aluminum-plastic bag after reaction, and rapidly cooling the aluminum-plastic bag in ice-water mixture; secondly, simulating digestion in an in-vitro microenvironment; finally, measuring phosphorus by a colorimetric method to obtain the content of water-soluble phosphorus released by the feed samples with phytase functions in simulated gastric environments, and activity of the high-temperature-resistant phytase is estimated. By simulating high-temperature and high-humidity granulation environments of granules and the quantity of water-soluble phosphorus multiply released by substrates in the gastric environments, in-vitro practical action effects of the high-temperature-resistant phytase after simulation of the granulation process are judged.
Owner:沈阳波音饲料有限公司
Phytases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
ActiveUS8877478B2Increase feeding valueLow costImmobilised enzymesPowder deliveryThermal denaturationPhytase activity
This invention relates to phytases, polynucleotides encoding them, uses of the polynucleotides and polypeptides of the invention, as well as the production and isolation of such polynucleotides and polypeptides. In particular, the invention provides polypeptides having phytase activity under high temperature conditions, and phytases that retain activity after exposure to high temperatures. The phytases of the invention can be thermotolerant and / or thermostable at low temperatures, in addition to higher temperatures. The phytases of the invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients. The phytases of the invention can be formulated as foods or feeds or supplements for either to, e.g., aid in the digestion of phytate. The foods or feeds of the invention can be in the form of pellets, liquids, powders and the like. In one aspect, phytases of the invention are stabile against thermal denaturation during pelleting; and this decreases the cost of the phytase product while maintaining in vivo efficacy and detection of activity in feed.
Owner:BASF ENZYMES
Method for detecting phytase activity in feed
ActiveCN102033064ALarge relative deviationEliminate distractionsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemical compositionPhytase activity
The invention relates to a method for detecting phytase activity in a feed and belongs to the technical field of chemical composition analysis of feeds. In the method, phytase in the feed is completely leached through novel extract and diluent and a detection flow, the interference of inorganic phosphorus present in the feed on the detection is eliminated, the coefficient of variation of the detected result is small, and the method has the advantages of short detection period, high sensitivity, high repeatability and high accuracy.
Owner:WUHAN SUNHY BIOLOGICAL
Animal Feed Compositions and Uses Thereof
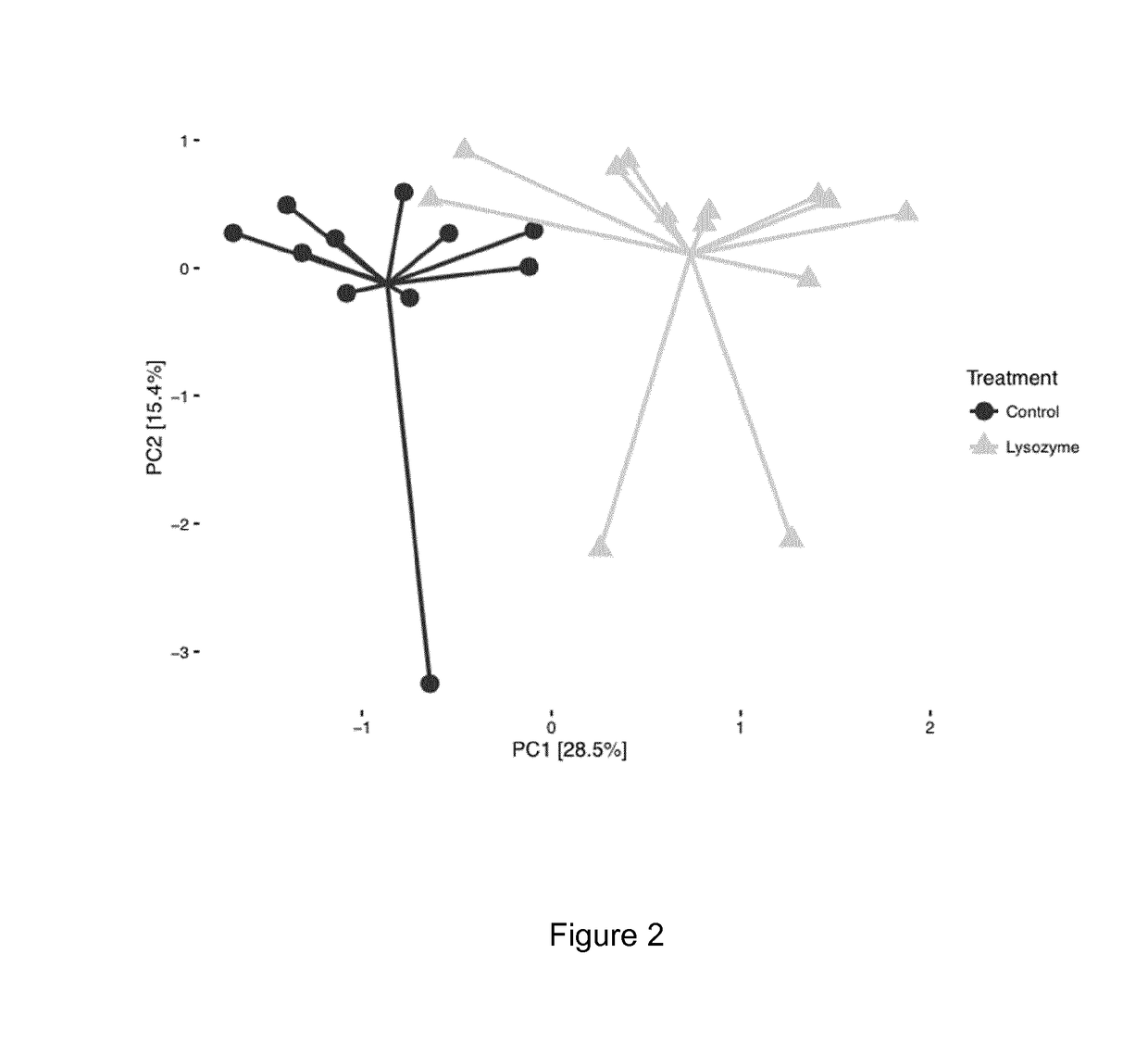
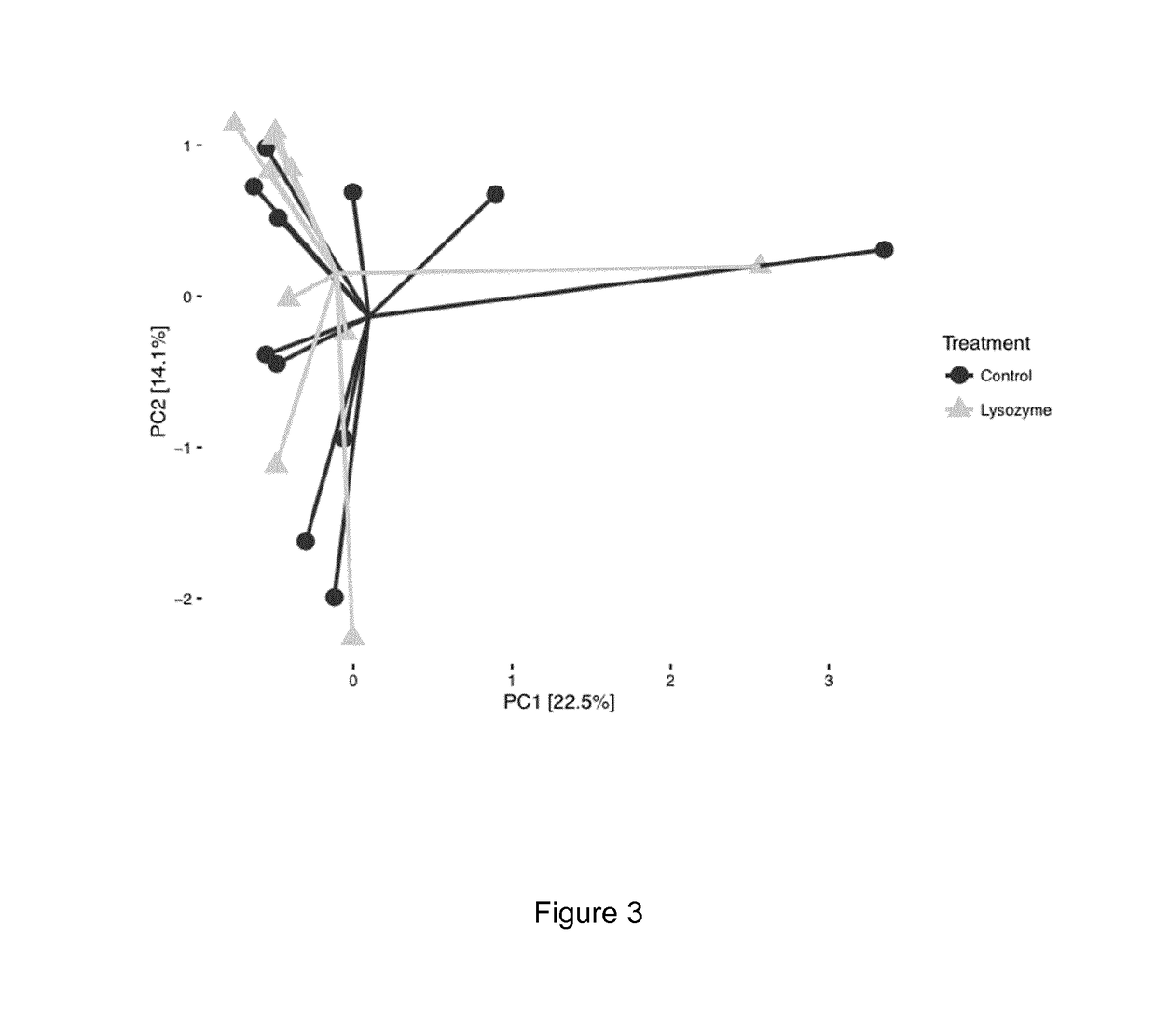
The present invention relates to animal feed compositions comprising polypeptides having lysozyme activity and polypeptides having phytase activity and uses thereof.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS +1
Scavenger for removing residual pesticide, and use of method
InactiveCN1760356AFacilitate strippingImprove cleanlinessAnionic surface-active compoundsDetergent compounding agentsScavengerPhytase activity
Owner:TIANJIN GUARD T & D
Construction of engineered strain capable of efficiently expressing phytase
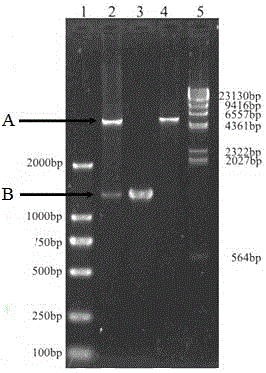
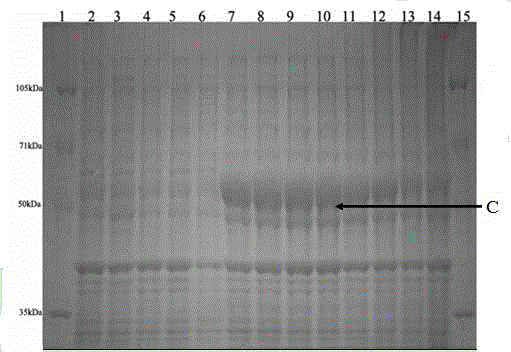
InactiveCN103555688AImprove conversion rateConducive to transcriptionBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
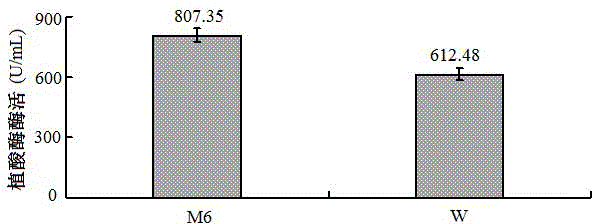
The invention provides construction of an engineered strain capable of efficiently expressing phytase, relates to the technical field of biology, and specifically relates to a mutagenesis engineered strain capable of efficiently expressing escherichia coli phytase with a relatively wide adaptation scope. A recombinant expression plasmid pET30a(+)-appA is converted and enters an escherichia coli expression host, so that a recombinant expression engineered strain W is obtained, and then a new escherichia coli phytase recombinant expression engineered strain M6 is obtained through lactose mutagenesis. Compared with the engineered strain W, the engineered strain M6 has no gene mutation, but is higher in phytase activity, and the enzyme activity reaches 807.35 U / mL by employing shaking culture. Compared with phytase expressed by the engineered strain W, phytase expressed by the engineered strain M6 is improved by 17.44% in pepsin tolerance and improved by 34.77% in trypsin tolerance. The engineered strain M6 is capable of efficiently expressing phytase with the relatively wide adaptation scope; and the mutagenic phytase can be used as a feed additive, is capable of digesting and utilizing phytate in animal alimentary canal in a relatively good manner, reducing discharge of organophosphorus and promoting ecological culture of livestock and poultry industry.
Owner:蒋和生 +1
Culture medium and method for producing phytase by using vinegar residue as raw material through solid fermentation
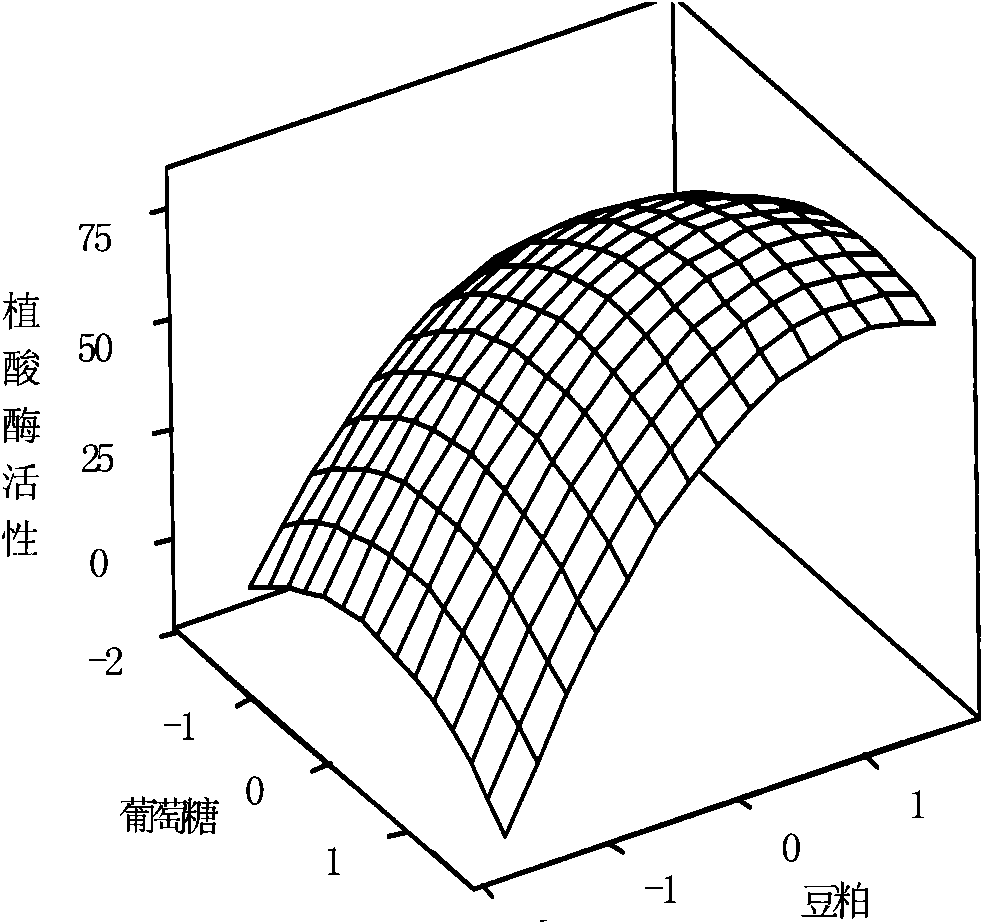
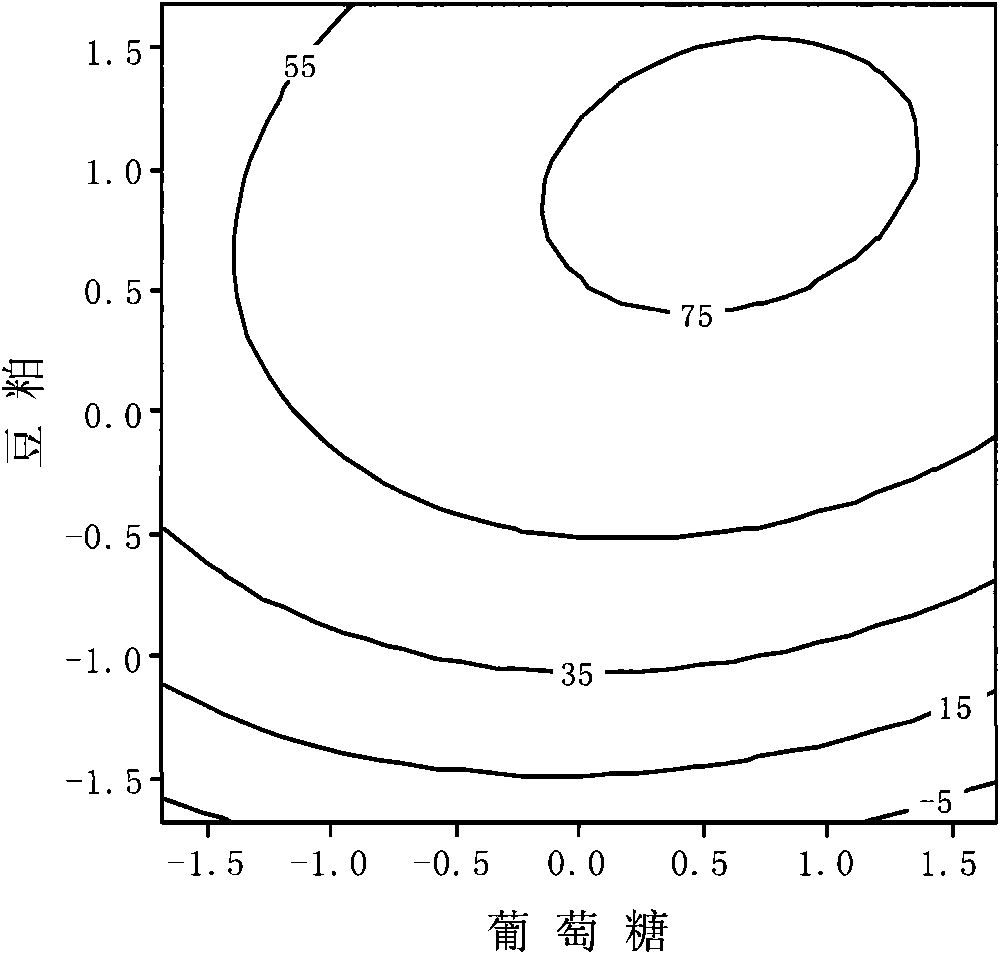
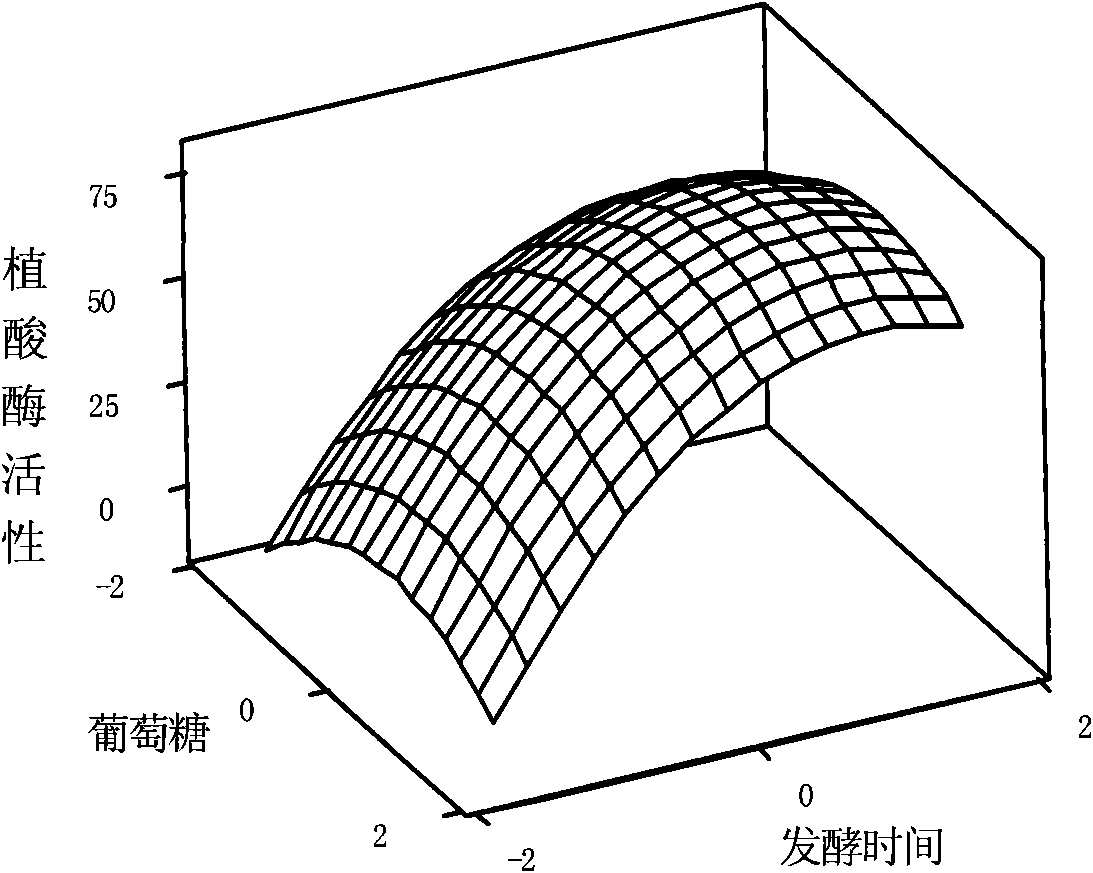
The invention provides a culture medium and a method for producing phytase by using vinegar residues as raw materials through solid fermentation. The adopted culture medium of the method comprises vinegar residues, glucose and bean slag, wherein according to the total weight of a solid culture medium, the content of the glucose is 7.2 percent by weight, and the content of the bean slag is 5.1 percent by weight. By a PB test, three factors of the glucose, the bean slag and fermentation time which have obvious influence for a fermentation result are obtained and a method of steepest ascent is adopted to select factor levels of a maximum response value for the selected important factors, then, a central composite test is adopted to be combined with response surface analysis (RSM) to obtain arelational expression between the response value and the important factors, and the important factor level of the maximum response value is calculated, thereby an optimal fermentation condition for producing the phytase through the solid fermentation is ensured, namely, the content of the glucose is 7.2 percent by weight, the content of the bean slag is 5.1 percent by weight, and the fermentationtime is 271 hours. By a verifying test, the activity even value of the phytase is 98.37U / g DMR under the condition.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Polypeptide having a phytase activity and nucleotide sequence coding therefor
The invention relates to a recombinant DNA molecule coding for a polypeptide having a phytase activity after expression in a procaryotic or eucaryotic host cell. Said recombinant DNA molecule comprises a DNA sequence selected from a) DNA sequences that have been obtained by variations of the mature wild type E.coli phytase sequence, at least one amino acid being mutated between positions 189 and 211 and / or between positions 137 and 152 in comparison to the wild type sequence; b) DNA sequences having a homology of between 70 % and 100 % in relation to the sequences according to a); and c) DNA sequences related to the sequences according to a) and b) as a result of the degeneracy of the genetic code. During the expression of the recombinant DNA molecule in an adapted host cell, said recombinant DNA molecule is associated with an increased activity of the thus coded protein in the culture supernatant. The invention also relates to thus coded proteins.
Owner:AB ENZYMES GMBH
Method for detecting phytase
InactiveCN102980854ARapid determinationAvoid background value interferencePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsMicrospherePhytic acid
The invention belongs to the field of biological detection, and relates to a method for detecting phytase in samples. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: forming a surface rapid reaction system by combining phytase with phytic acid in a solvent phase by coupling dispersing-type nano microspheres and phytic acid molecules by utilizing a carboxyl-amino chemical coupling method, wherein a product orthophosphate enters the solvent phase directly, and unreacted inositol derivatives are still remained in solid-phase microspheres; removing the microspheres through low-temperature and high-speed centrifuging, adding color developing agents into the solvent phase under the acidic condition so as to generate a blue compound, and carrying out colorimetric determination at the wavelength of 700nm. For the method, the phytase activity is determined rapidly, meanwhile, the unreacted inositol derivatives are still remained in solid-phase microspheres, and the background value interference caused by the reaction of the incompletely reacted phytic acid molecules and the color developing agents in the conventional method is prevented, so that the trace amount determination becomes possible; and the method for detecting phytase is suitable for trace amount phytase sample determination for specific environment samples, such as soil, water bodies and rhizosphere residues.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method of detecting phytase activity or protease activity
InactiveUS20120264153A1Microbiological testing/measurementFlow propertiesProteinase activityPhytase activity
A method of detecting a phytase activity or a protease activity is described. The method comprises the steps of: (a) providing a composition comprising a phytate / protein complex in a liquid or a gel; wherein the phytate / protein complex provides a detectable property to the composition; (b) providing a sample that comprises or is suspected of comprising phytase activity and / or protease activity, wherein the phytase and / or protease activity is capable of causing a change in the detectable property of the composition; (c) contacting the composition with the sample; and (d) determining if there is a detectable change in detectable property of the composition.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Phytases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
ActiveUS9695403B2Increase feeding valueLow costPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesPhytase activityDigestion
This invention relates to phytases, polynucleotides encoding them, uses of the polynucleotides and polypeptides of the invention, as well as the production and isolation of such polynucleotides and polypeptides. In particular, the invention provides polypeptides having phytase activity under high temperature conditions, and phytases that retain activity after exposure to high temperatures. The invention further provides phytases which have increased gastric lability. The phytases of the invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients. The phytases of the invention can be formulated as foods or feeds or supplements for either to, e.g., aid in the digestion of phytate.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Method for detecting activity of trace of phytase in feed
InactiveCN104007110ASmall coefficient of variationHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorColor/spectral properties measurementsPhytase activityNational standard
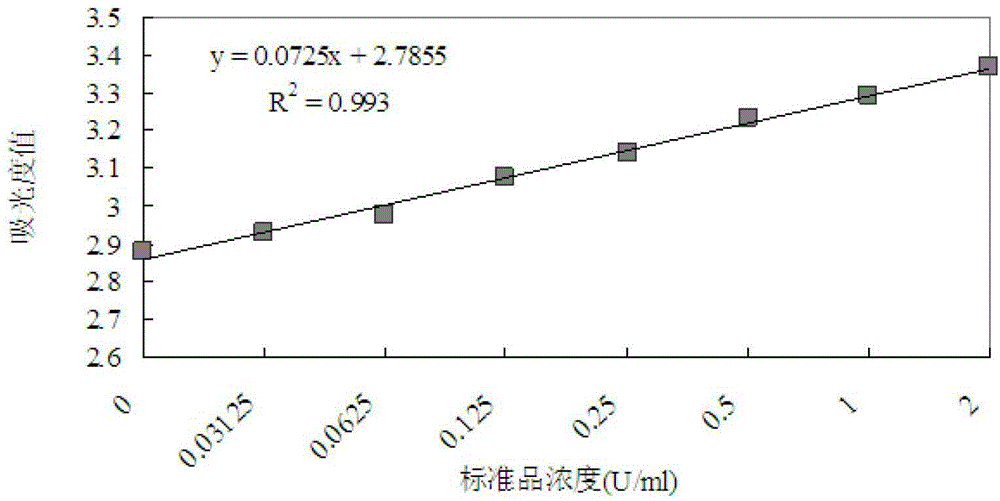
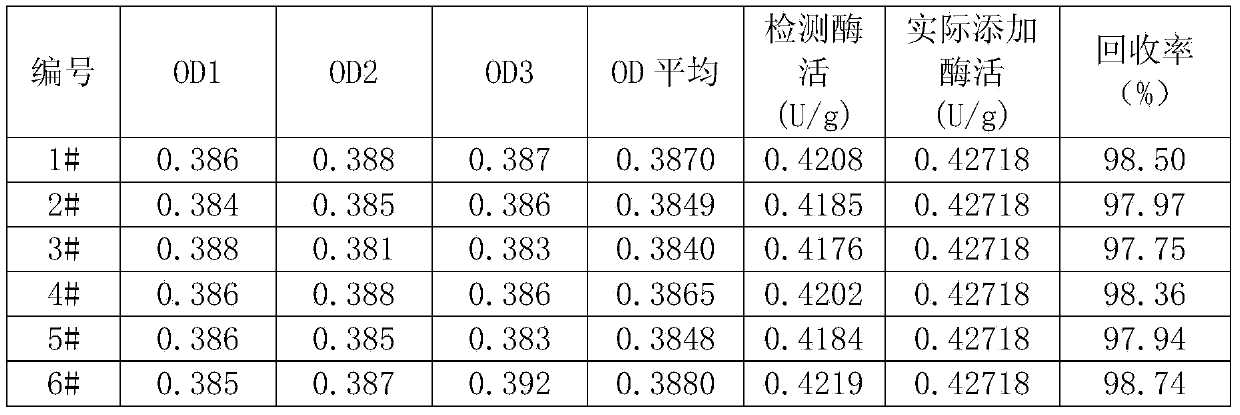
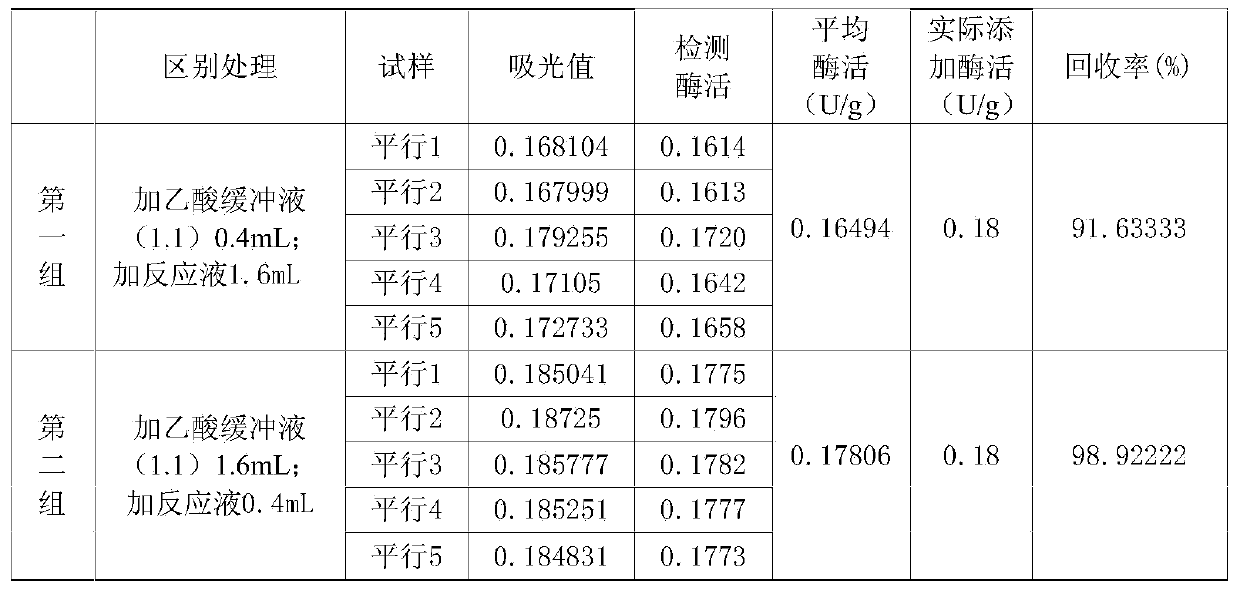
The invention discloses a method for detecting the activity of a trace of phytase in feed. Based on an existing method, sampling weight and phytase fluid volume in a reaction system are increased, so that the detection sensitivity of phytase in the feed can be obviously improved, and the linear detection limit is reduced to 0.1 U / g. when the enzyme activity of the phytase in the feed is 0.18 U / g, the enzyme activity recovery rate detected by utilizing the method is up to 98.92 percent, the variable coefficient is only 0.5 percent (n is equal to 6), and the errors in the twice experiment are small, so that the correctness and the accuracy of the method provided by the invention meet the requirement of national standard GB / T18634-2009 determination of feed phytase activity-spectrophotometry, and the unexpected technical effect is achieved.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com