Construction of engineered strain capable of efficiently expressing phytase
A technology of engineering strains and phytase, applied in genetic engineering, bacteria, hydrolytic enzymes, etc., can solve the problems of excessive content, increased production costs, waste of phosphorus sources, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
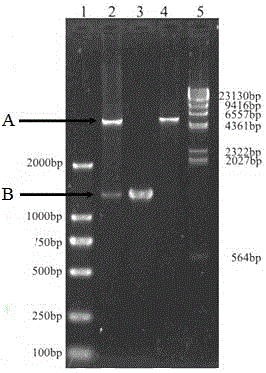
[0158] Escherichia coli Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) (hereinafter referred to as E. coli BL21 (DE3) appA Gene acquisition and recombinant vector construction
[0159] E. coli BL21 (DE3) was purchased from Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.
[0160] Prepare LB medium: peptone 10g / L, yeast extract powder 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L, 121°C, high temperature and high pressure sterilization, and store at 4°C.
[0161] Collect bacteria: the E. coli BL21 (DE3) was inoculated onto LB medium, cultured with shaking at 180-200 r / min at 37°C for 10-12 hours, and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5-10 minutes at 4°C to collect bacterial precipitates and use 1-2 mL of The bacteria were washed 1-3 times with distilled water, centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 5-10 min at 4°C, and the bacterial precipitate was collected.
[0162] Extract the target gene: use TGuide Bacterial Genomic DNA Extraction Kit (Tiangen Biochemical Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.) to extract and obtain E. coli...
Embodiment 2
[0177] Acquisition of Escherichia coli Phytase Recombinant Expression Engineering Strain
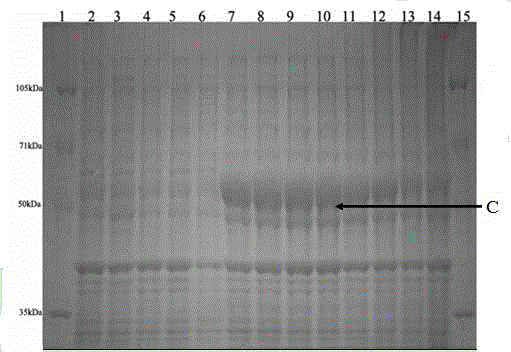
[0178] Obtaining of recombinant expression strains: the sequenced correct pET30a(+)- appA Transformation of recombinant expression plasmids into E. coli In the BL21(DE3) expressing host, detected by colony PCR method, it contains pET30a(+)- appA The positive recombinant expression engineering strain W of the recombinant plasmid.
[0179] Inoculate the W strain into 5 mL of fresh LB medium (containing 100 μg / mL kanamycin) at 1-3% inoculum amount, culture at 37°C, shake at 180-200 rpm for 4-6 hours, add lactose (final concentration is 0.45- 0.75mg / mL) for purpose induced expression. After continuous induction for 12 hours, samples were taken every hour, centrifuged at 10,000g for 5-10min at 4°C, and bacterial pellets were collected. The pellet was resuspended with 200-300μL 0.25mol / L sodium acetate buffer (pH5.5) (containing lysozyme at a final concentration of 0.05-0.15mg / mL), and in...
Embodiment 3
[0182] Mutagenesis screening was performed using lactose as inducer.
[0183] M6 mother liquor: 64g Na 2 HPO 4 , 15g KH 2 PO 4 , 2.5gNaCl, 5.0gNH 4 Cl plus 1L water for sterilization.
[0184] Improved M6 medium: under sterile conditions, take 200ml of M6 mother solution, add 2mL of 1mol / L sterilized MgSO 4 , add 100 μL of sterilized 1mol / L CaCl 2 , add 20mL of sterilized 10% lactose, add sterile water to make up to 1L.
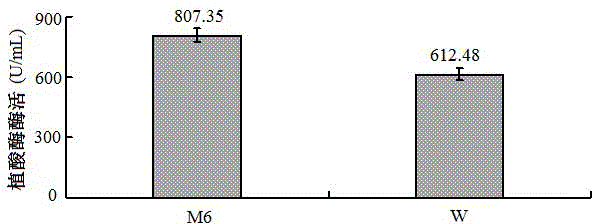
[0185] Screening of mutagenized strains: Dilute the W strain appropriately, spread it on the modified M6 medium (containing 100 μg / mL kanamycin), and cultivate overnight at 37°C. Spread a 1% agar plate containing 100 mmol / L sodium acetate buffer (pH5.5), 20 mmol / L sodium phytate and 50 mmol / L calcium chloride on the plate, and determine the enzyme activity according to the size of the plaque formed Finally, 100 positive recombinant mutagenized strains with phytase activity were obtained.
[0186] Induced expression of mutagenized strains: Induced exp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com