Cloning and expression of a novel phytase
一种植酸酶、植酸酶活性的技术,应用在新的植酸酶的克隆和表达领域,能够解决分离植酸酶手段有限、耗费时间和劳力、昂贵等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
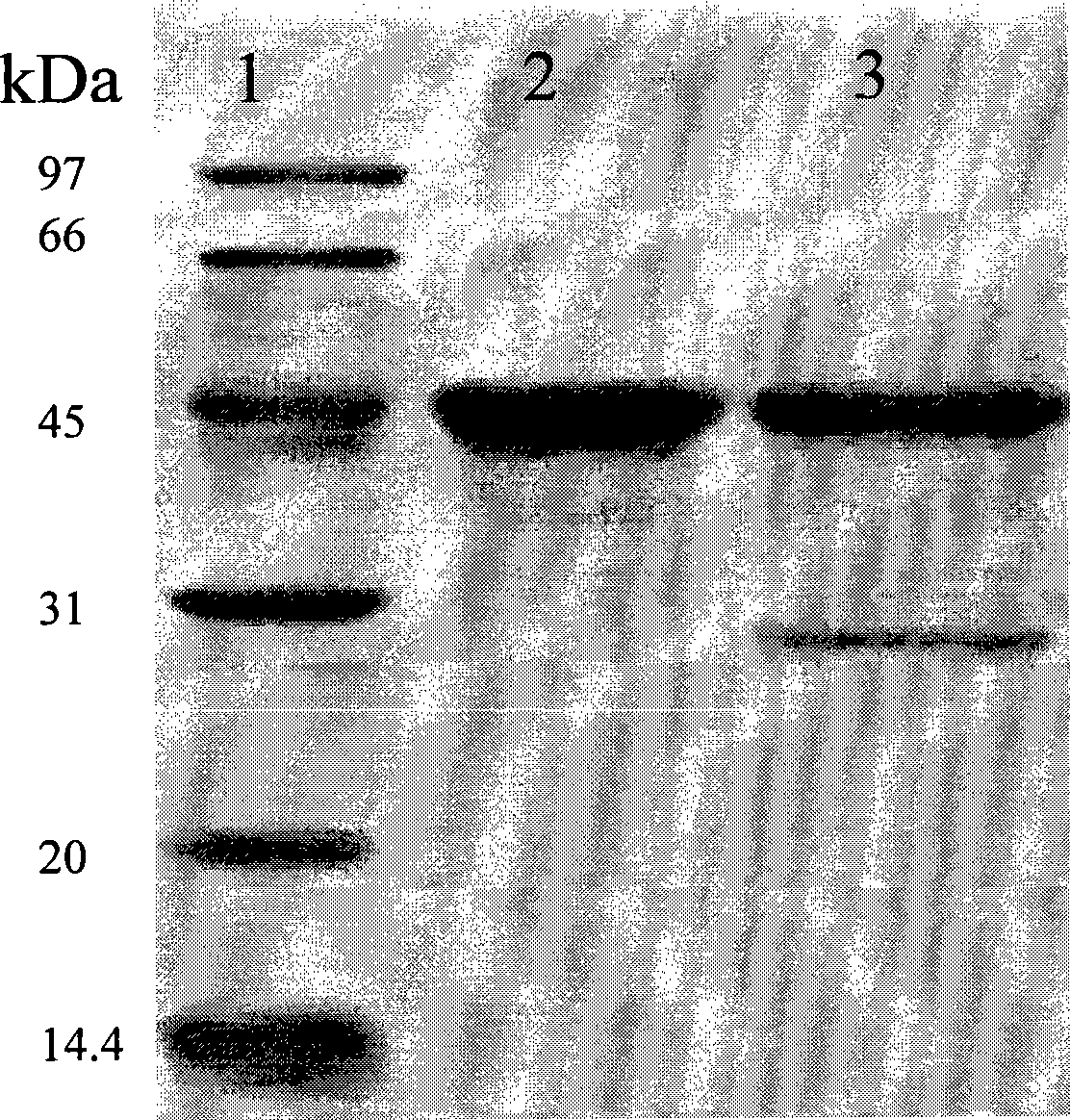
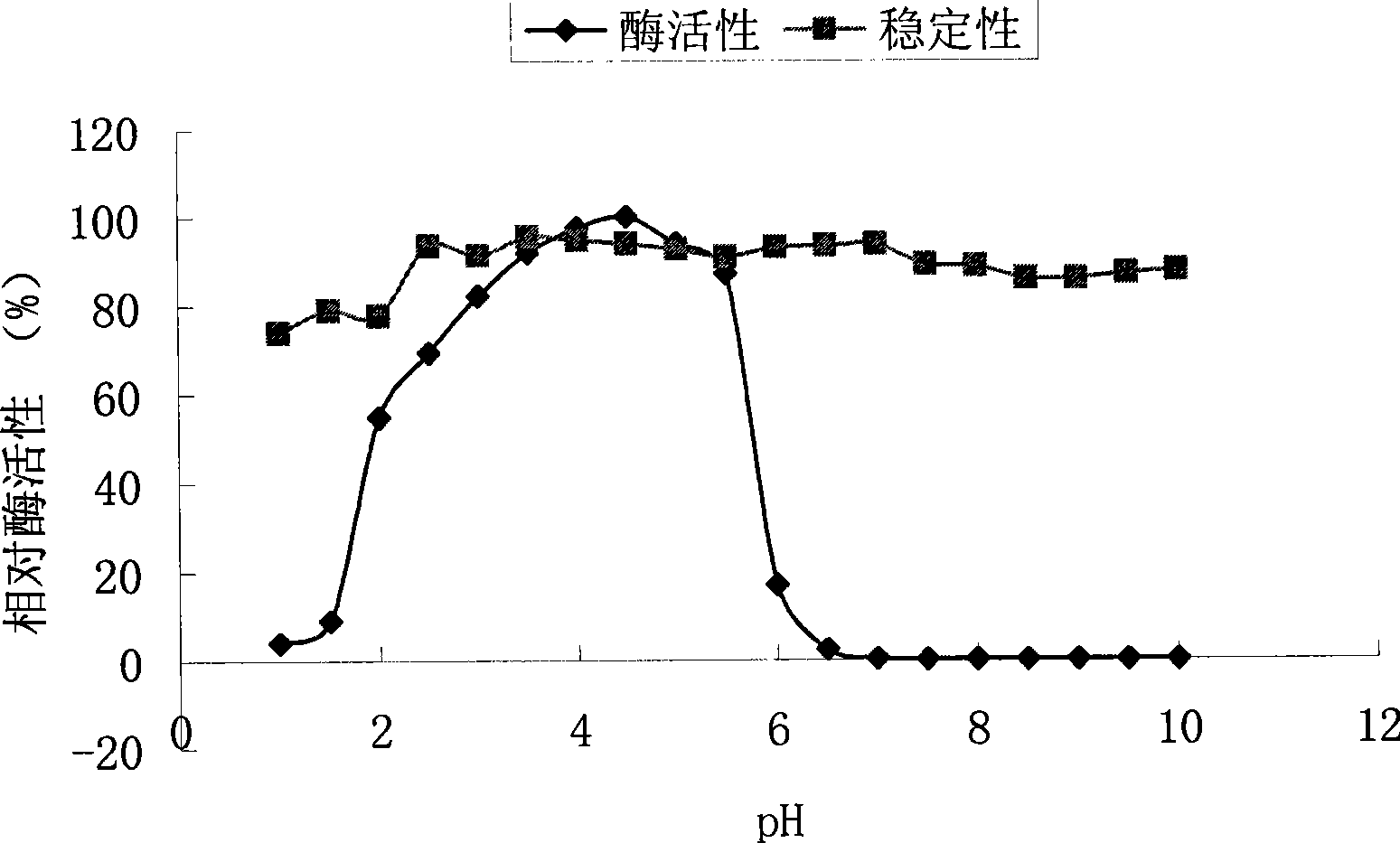
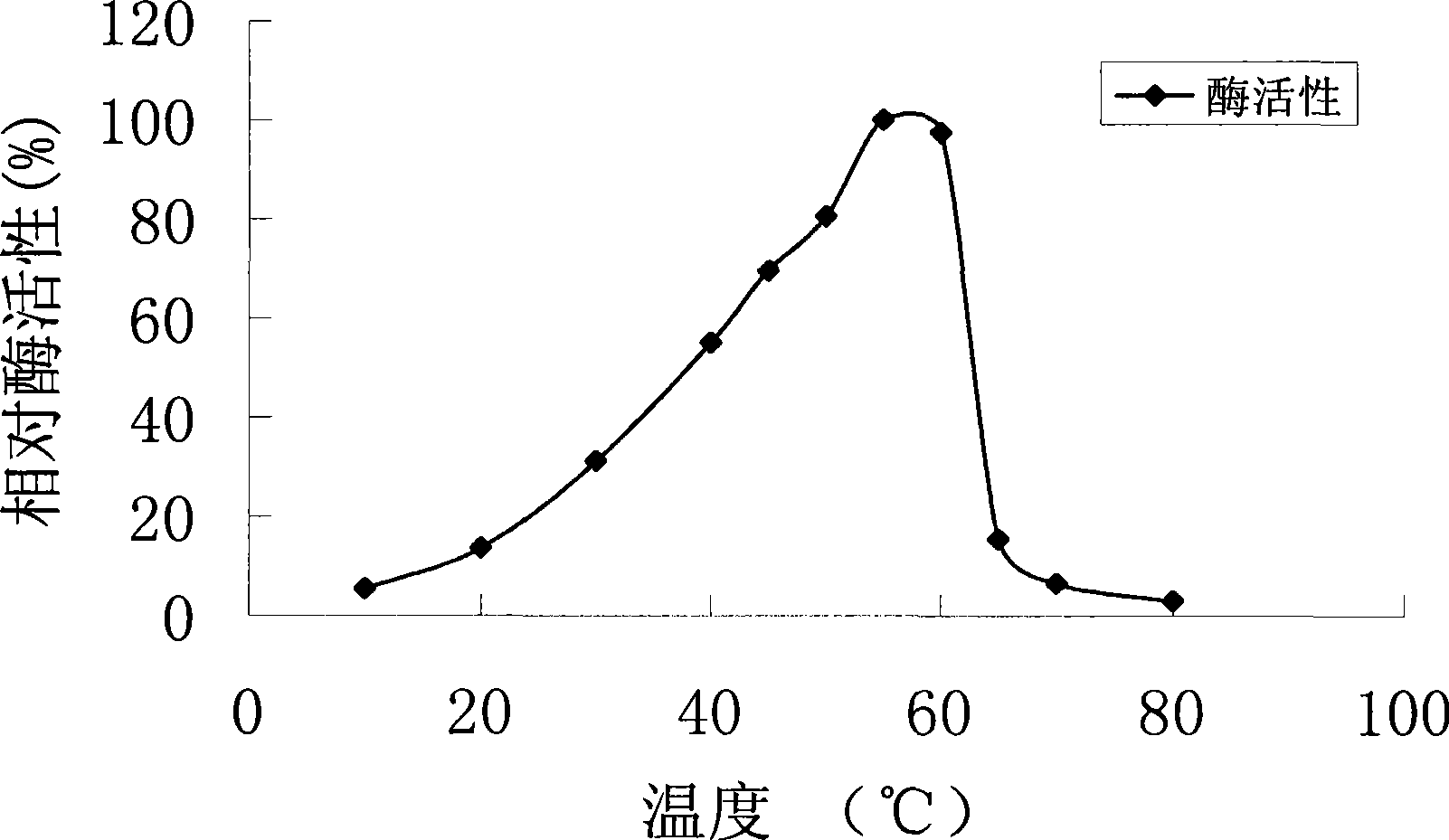
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] Example 1: Isolation of Phytase-producing Bacteria
[0066] Phytase-producing strains were isolated from permafrost samples from China No. 1 Glacier (Xinjiang). Specifically, in order to isolate phytase-producing strains, permafrost samples from China's No. 1 Glacier (Xinjiang) were collected in April 2005 and stored in a freezer for several days until they could be processed in the laboratory. Frozen soil was suspended in sterile water and diluted, then, the suspensions of different samples were inoculated into agar-free LB medium, followed by incubation at 4°C, 10°C, 15°C, and 30°C for 1–2 days, respectively. Then, the ferrous sulfate molybdenum blue method (see the following example 4 for details) was used to measure the phytase activity at different temperatures, in the culture fluid and cell disruption fluid of different samples. Phytase activity was detectable in the cell lysate, showing that these strains had intracellular phytase activity. Firstly, the samples...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2: analyze the characteristic of phytase producing bacterium H-27
[0068] The H-27 bacteria isolated in Example 1 were determined to be Gram-negative bacteria by the Gram staining method. This bacterium is a typical bacillus with a similar size to E. coli under the microscope. Some of its physiological and biochemical properties were further studied. The results showed that the bacteria were Gram-negative, facultative, anaerobic microorganisms, which could grow in anaerobic or aerobic environments. The optimal growth temperature of this bacterium is 30°C, and we also analyzed the 16s rRNA sequence of this bacterium. Using the Promega Taq kit, the 16SrDNA sequence (SEQ ID NO.1) of the bacterium was amplified by PCR, and the 16SrDNA sequence of the bacterium was compared with the reference sequence in GenBank by using BLAST and the multiple sequence alignment program CLUSTAL W . Results The base sequence of 16s rDNA showed 99.5% identity with Yersinia inte...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Embodiment 3: Cloning of phytase gene
[0071] Homologous cloning is very efficient and simple when the protein's gene is a known member of a multigene family.
[0072] Apparently, according to the classification of phytases, most phytases of bacterial origin belong to the histidine acid phosphatase (HAP) family. Through multiple sequence alignment programs CLUSTAL W and BLOCKS (http: / / blocks.fhcrc.org / blocks / make_blocks.html) to analyze the various sequences of the HAP family, we found that there are two conserved regions in the HAP enzyme, namely RHGXRXP and HD area. Based on these two conserved regions, a pair of degenerate primers can be designed to amplify part of the phytase sequence from Yersinia intermedia genomic DNA by PCR.
[0073] Acquisition of Partial Phytase Gene Sequence
[0074] Degenerate primers were designed based on the two conserved regions and synthesized using a DNA synthesizer. PCR amplification was performed using Yersinia intermedia genomi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com