Method for detecting phytase
A detection method and technology for phytase, applied in the preparation of test samples, measurement of color/spectral characteristics, etc., can solve the problems affecting the accurate quantification of phytase activity, background value interference, etc., to avoid background value interference, fast measured effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
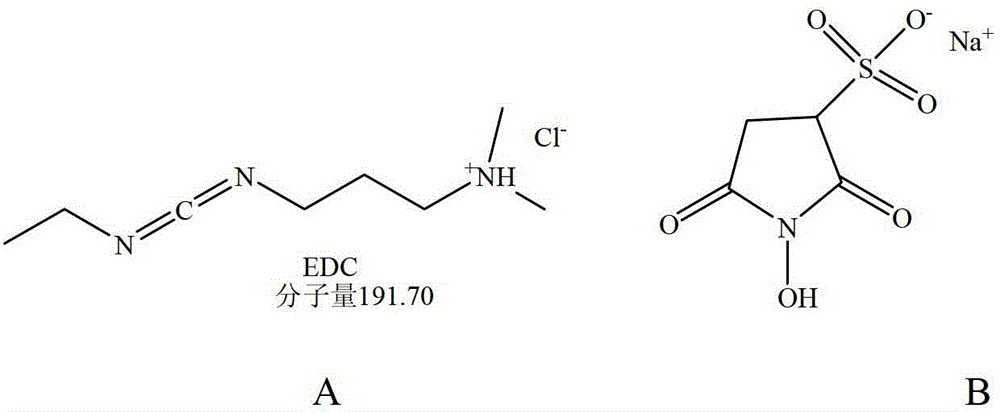
[0020] like figure 1 As shown, the nano-microspheres are monodisperse carboxylated polystyrene microspheres with a particle diameter of figure 2 A) Activation for 30min, then add 1ml 50mM protective agent Sulfo-NHS (N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide) ( figure 2 B) 15 minutes to make the microspheres form a stable active ester intermediate, then add 2ml of 5mM sodium phytate and incubate at 30°C for 1-2 hours, collect the nanospheres coupled with phytic acid molecules after washing.
Embodiment 2
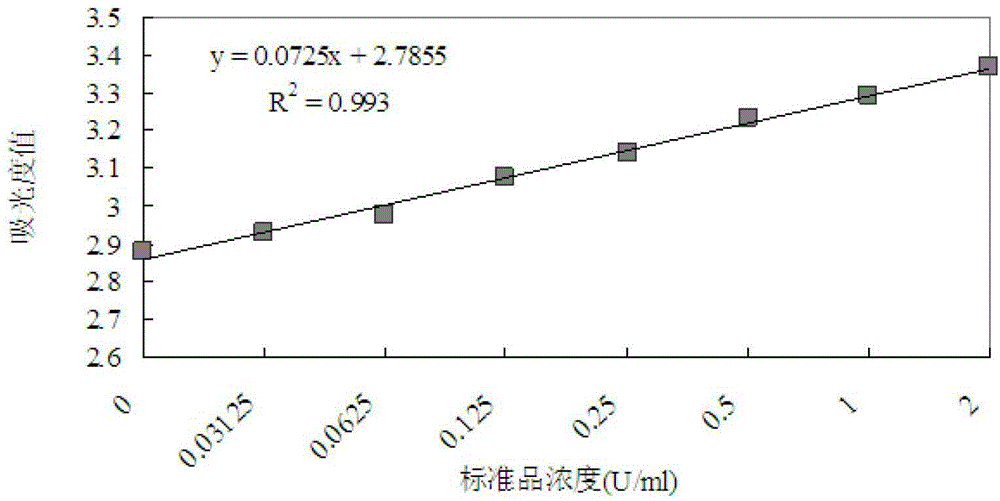
[0022] As shown in Table 1, the nano-microspheres coupled with phytic acid molecules were prepared into a 2.5% (w / v%, weight / volume percentage, specifically g / 100ml) suspension with 0.1M acetic acid buffer, and the pH was adjusted to 5. 0. Take 80 μl of microspheres and add 20 μl of sample or phytase standard. Using phytase pure protein as a standard, set up 8 concentration gradients (2U / ml, 1U / ml, 0.5U / ml, 0.25U / ml, 0.125U / ml, 0.0625U / ml, 0.03125U / ml and 0U / ml). After preheating at 37°C for 5 minutes, mix well for 5 minutes, and keep at 37°C for 30 minutes. Centrifuge at 4°C and 15,000×g for 20 min, and collect the supernatant. Next, add 100 μl of 5% (w / v%, specifically g / 100ml) trichloroacetic acid (stop solution) and 100 μl of chromogen (1.5% (w / v%, specifically g / 100ml) sodium molybdate and 2.7% (w / v%, specifically refers to g / 100ml) ferrous sulfate according to the ratio of 4:1, ready to use), immediately after mixing, colorimetric measurement at a wavelength of 700n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com