Method for detecting activity of trace of phytase in feed
A technology of phytase activity and detection method, applied in the field of detection of trace phytase activity in feed, can solve the problems of interfering with colorimetric reaction, low detection limit, affecting enzyme activity determination, etc., achieving significant technical effect and improving detection sensitivity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] 1. Reagents and solutions
[0063] All reagents in this method refer to analytical grade reagents and third-grade water in accordance with GB / T6682 unless otherwise specified. Do not use phosphorus-containing cleaning agents to clean experimental containers.
[0064] (1.1) 0.25mol / L acetic acid buffer solution (I): take by weighing 34.02g sodium acetate trihydrate (CH 3 COONa·3H 2 O) In a 1000ml volumetric flask, add 900ml of water and adjust the pH to 5.0±0.01 with hydrochloric acid, and distill the volume to 1000ml with distilled water, and store it at room temperature for two months.
[0065] (1.2) 0.25mol / L acetic acid buffer (Ⅱ): Weigh 34.02g sodium acetate trihydrate (CH 3 COONa·3H 2 O), 0.5g Trion X-100, 0.5g bovine serum albumin (BSA) in a 1000ml volumetric flask, add 900ml water and adjust the pH to 5.0±0.01 with hydrochloric acid, and distilled water to 1000ml, store at room temperature for two months efficient.
[0066] (1.3) 7.5mmol / L sodium phytate so...
Embodiment 2
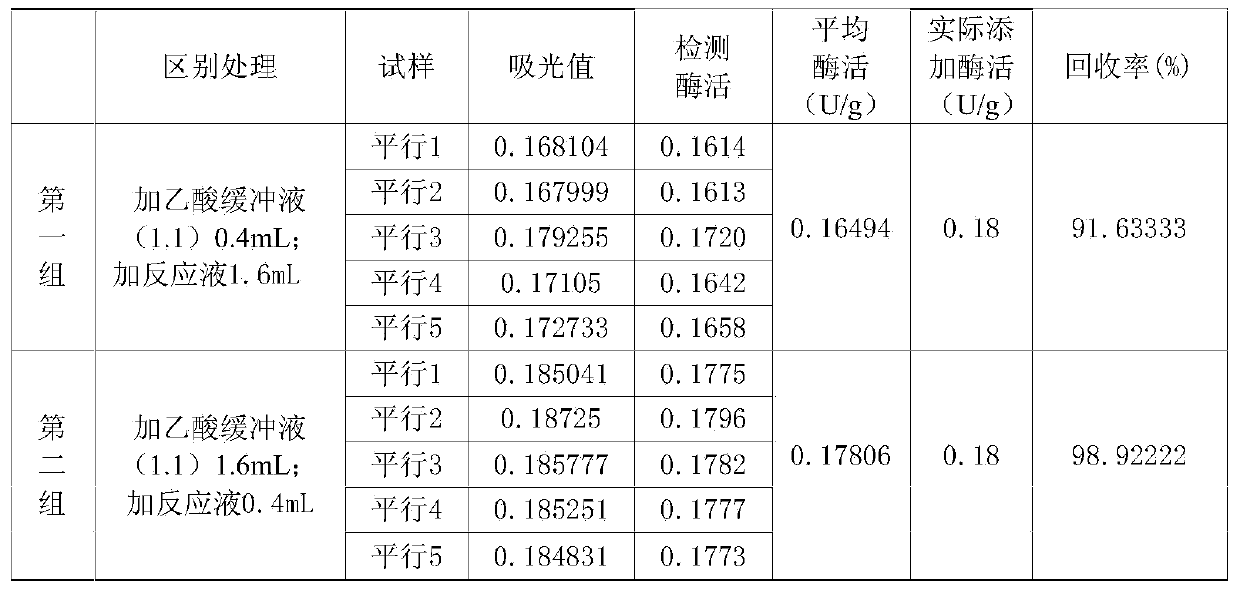
[0099] The detection method of embodiment 2 trace phytase (less than 0.2U / g)
[0100] Weigh 120 grams of a blank feed sample without phytase, add phytase to 0.18 U / g, mix thoroughly until uniform, then pulverize until all pass through a 20-mesh standard sieve, store in an airtight container at 4°C.
[0101] Take by weighing 10 parts of samples, every part of 10 grams; Sample is divided into two groups, and 5 parts of samples of the first group are detected according to operating steps described in 2.1 in Example 1 and reagent, solution consumption (table 1), and according to The regression equation obtained in 2.1 calculates the enzymatic activity of phytase in the sample; 5 samples of the second group are detected according to the operating steps and reagent and solution consumption described in Table 4, and simultaneously according to the description in 2.1 in Example 1 Recipe, with reference to the reaction steps, reagents, and solution dosages described in Table 4, redo th...
Embodiment 3
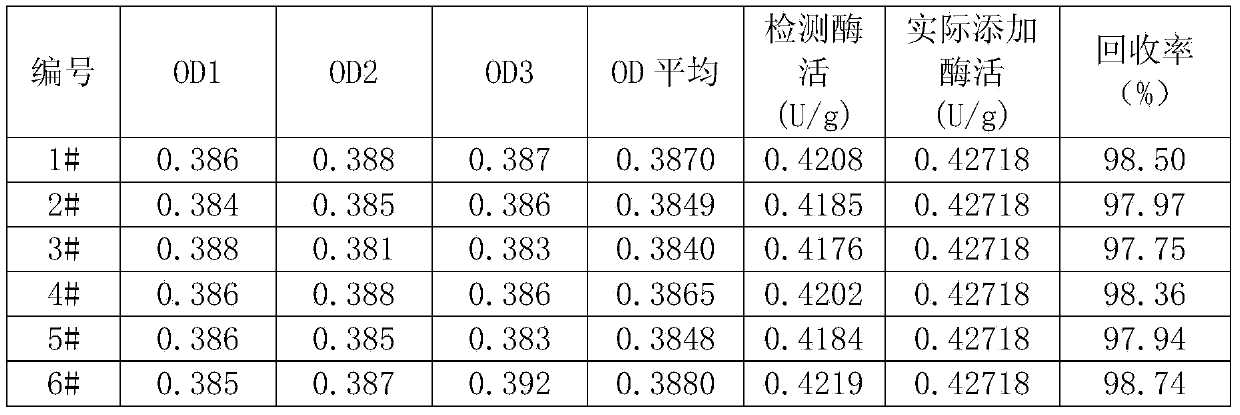
[0108] Enzyme activity detection of phytase in embodiment 3 commercially available feed samples
[0109] Take 80 grams of commercially available broiler feed samples from Shandong Liuhe Group, grind them until they all pass through a 20-mesh standard sieve, put them into airtight containers, and store them at 4°C.
[0110] Weigh 6 samples (1#, 2#, 3#, 4#, 5#, 6#), 10 grams each, accurate to 0.0002g, place them in 150ml Erlenmeyer flasks, add 50mL acetic acid buffer ( 1.1), a magnetic bar, after sealing with parafilm, put it on a magnetic stirrer, stir and extract at room temperature for 30 minutes. Shake well, take 20ml and centrifuge at 7000×g for 10min in a centrifuge. Take the supernatant and pass it through a 0.45 μm filter membrane, take 4ml of the filtrate and add it to a weighed (accurate to 0.0001g) ultrafiltration tube, and centrifuge at 7000×g until the residual liquid volume is about 0.4ml. Put the centrifuge tube on an analytical balance, add acetic acid buffer (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com