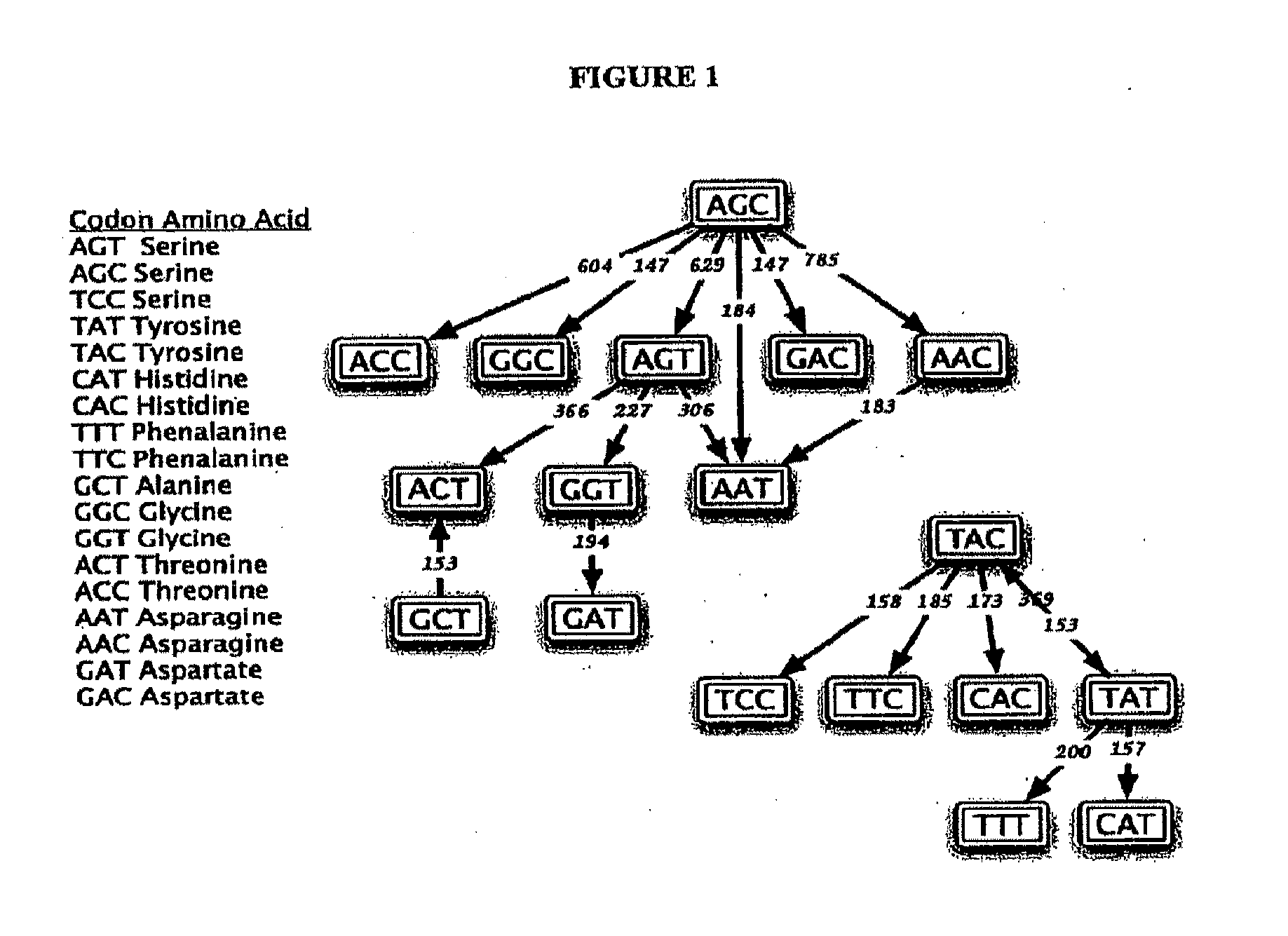
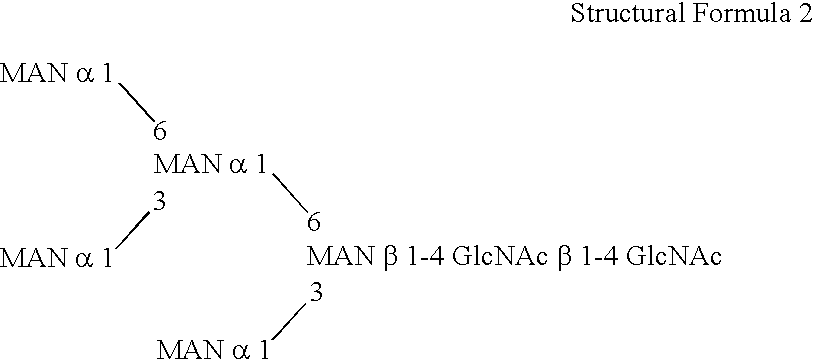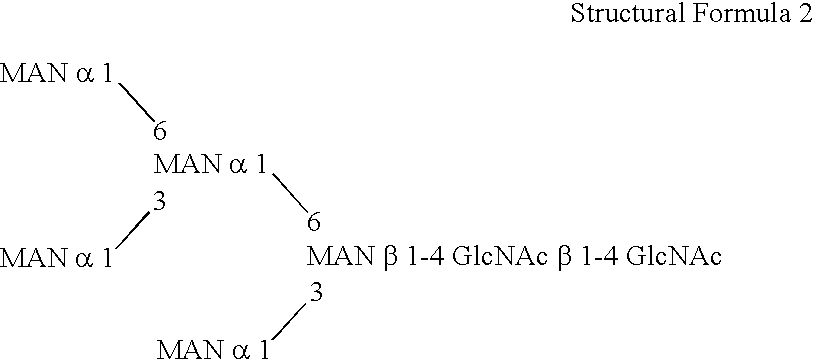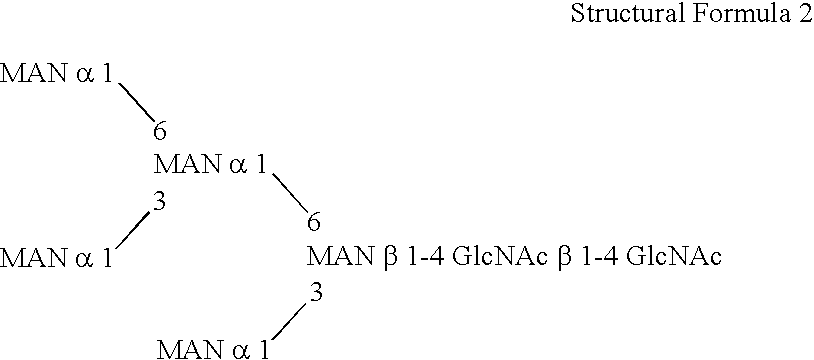Patents
Literature
292 results about "Synthetic gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Synthetic genes encoding cry1ac
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions containing a synthetic nucleotide sequence encoding a Cry1Ac protein are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also include transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated pesticidal nucleic acid molecules are provided, wherein the nucleotide sequences are set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:ATHENIX
Control of gene expression
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Novel elongase gene and method for producing multiple-unsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20040111763A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsElongaseTriacylglycerol VLDL
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequences stated in sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or their homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or transgenic organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. The invention furthermore relates to the use of the elongase gene sequences alone or in combination with further elongases and / or further fatty acid biosynthesis genes. The present invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacylglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF AG
Computational methods for synthetic gene design
The present invention is drawn to methods for designing synthetic nucleotide sequences encoding polypeptides of interest. The methods involve organizing a database of sequences as a set of N-length oligomer sequences and compiling a list of probability scores for each N-length sequence. The probability scores are used to substitute one or more higher-scoring sequences into the parent nucleotide sequence to generate an optimized sequence. The nucleotide sequence of interest may be further optimized by removing either or both of unintended open reading frames or undesired short DNA elements, and / or substituting oligomer sequences to achieve a specific G:C content. These methods may be used for optimizing expression of heterologous genes in any organism, particularly in plants. The method generates synthetic sequences with a composition similar to that of a target database. These synthetic sequences may be used, for example, for regulating pesticidal activity or herbicide resistance in organisms, particularly plants or plant cells.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Recombinant vaccine against botulinum neurotoxin
InactiveUS7081529B2Fast and efficient purificationBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteriaVaccinationRecombinant vaccines
This invention is directed to preparation and expression of synthetic genes encoding polypeptides containing protective epitopes of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT). The invention is also directed to production of immunogenic peptides encoded by the synthetic genes, as weel as recovery and purification of the immunogenic peptides from recombinant organisms. The invention is also directed to methods of vaccination against botulism using the expressed peptides.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Novel elongase gene, and process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids
InactiveUS20080160054A1Improve efficiencyIncrease productionOrganic active ingredientsFatty acid chemical modificationBiotechnologyFatty acid biosynthesis
The invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequences stated in sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or their homologs, derivatives or analogs, to a gene construct comprising this gene or its homologs, derivatives and analogs, and to its use. The invention also relates to vectors or transgenic organisms comprising an elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO: 3, SEQ ID NO: 5 and SEQ ID NO: 7 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs. The invention furthermore relates to the use of the elongase gene sequences alone or in combination with further elongases and / or further fatty acid biosynthesis genes. The present invention relates to a novel elongase gene with the sequence SEQ ID NO:1 or its homologs, derivatives and analogs.Furthermore, the invention relates to a process for the preparation of polyunsaturated fatty acids and to a process for introducing DNA into organisms which produce large amounts of oils and, in particular, oils with a high content of unsaturated fatty acids. Moreover, the invention relates to an oil and / or a fatty acid preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds and / or a triacylglycerol preparation with a higher content of polyunsaturated fatty acids with at least two double bonds.
Owner:BASF AG
Methods and compositions for multiplex RNA guided genome editing and other RNA technologies
ActiveUS20160264981A1Facilitate RNA-guided multiplex genome editingVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationGenome editingGene silencing
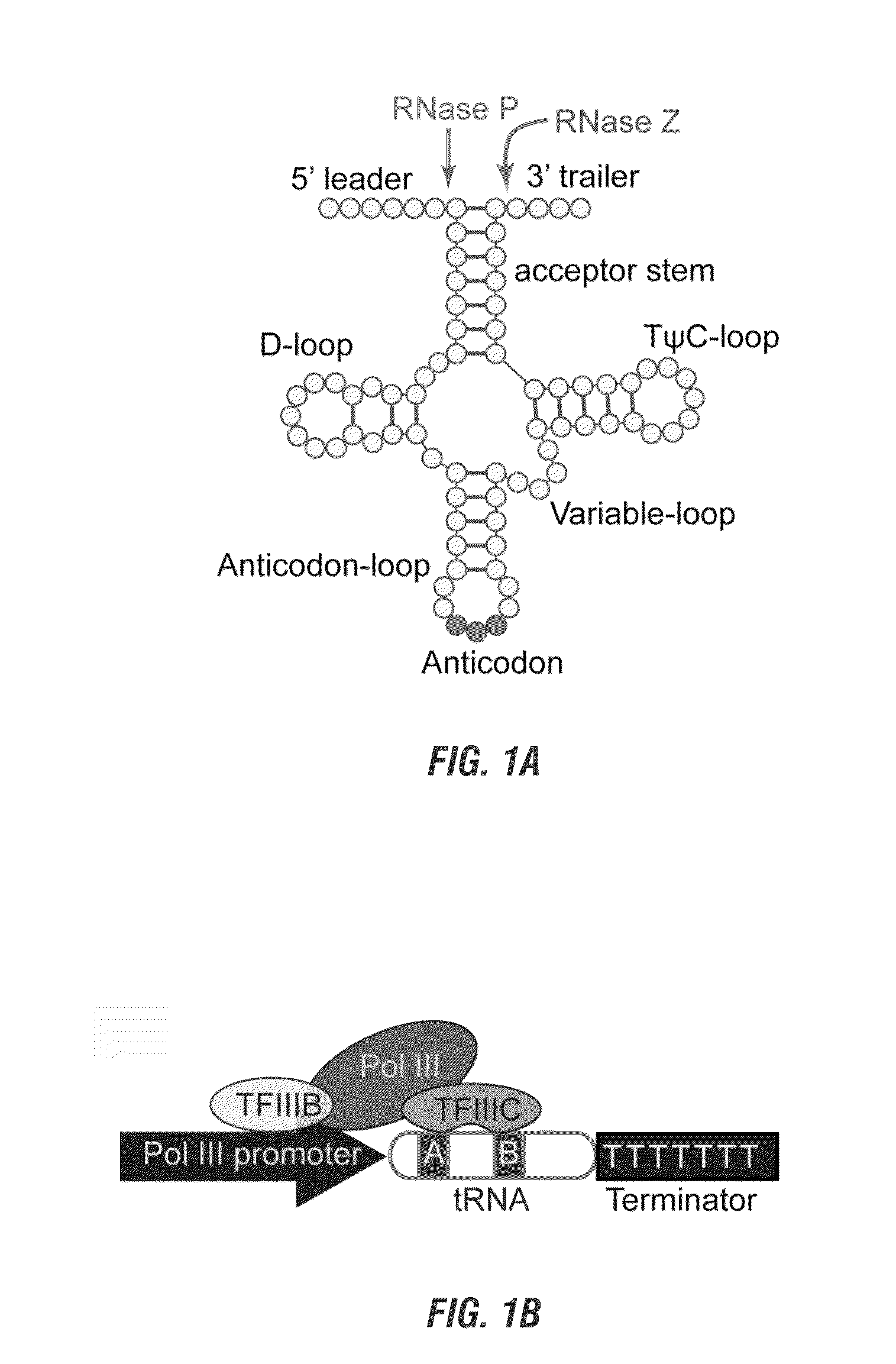
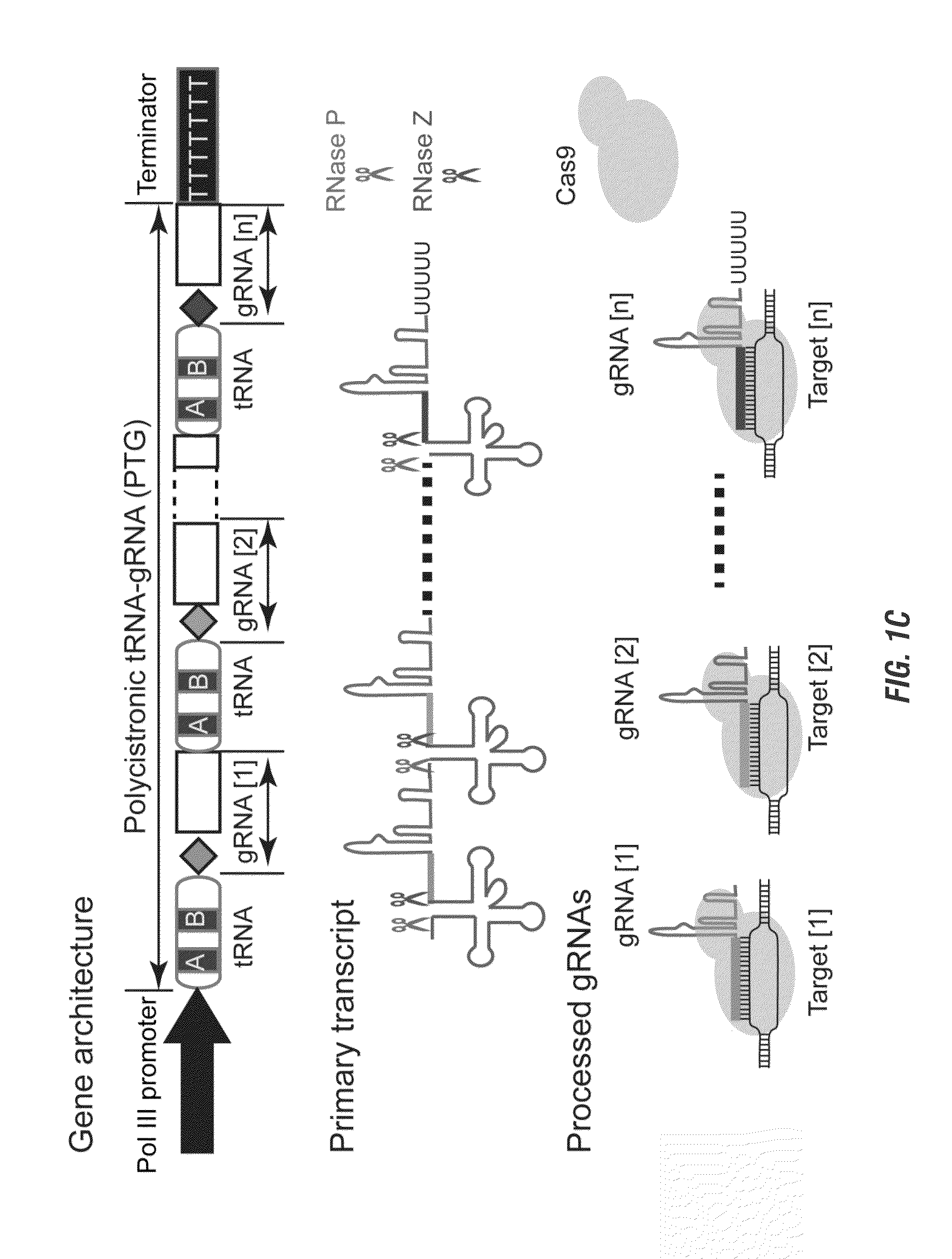
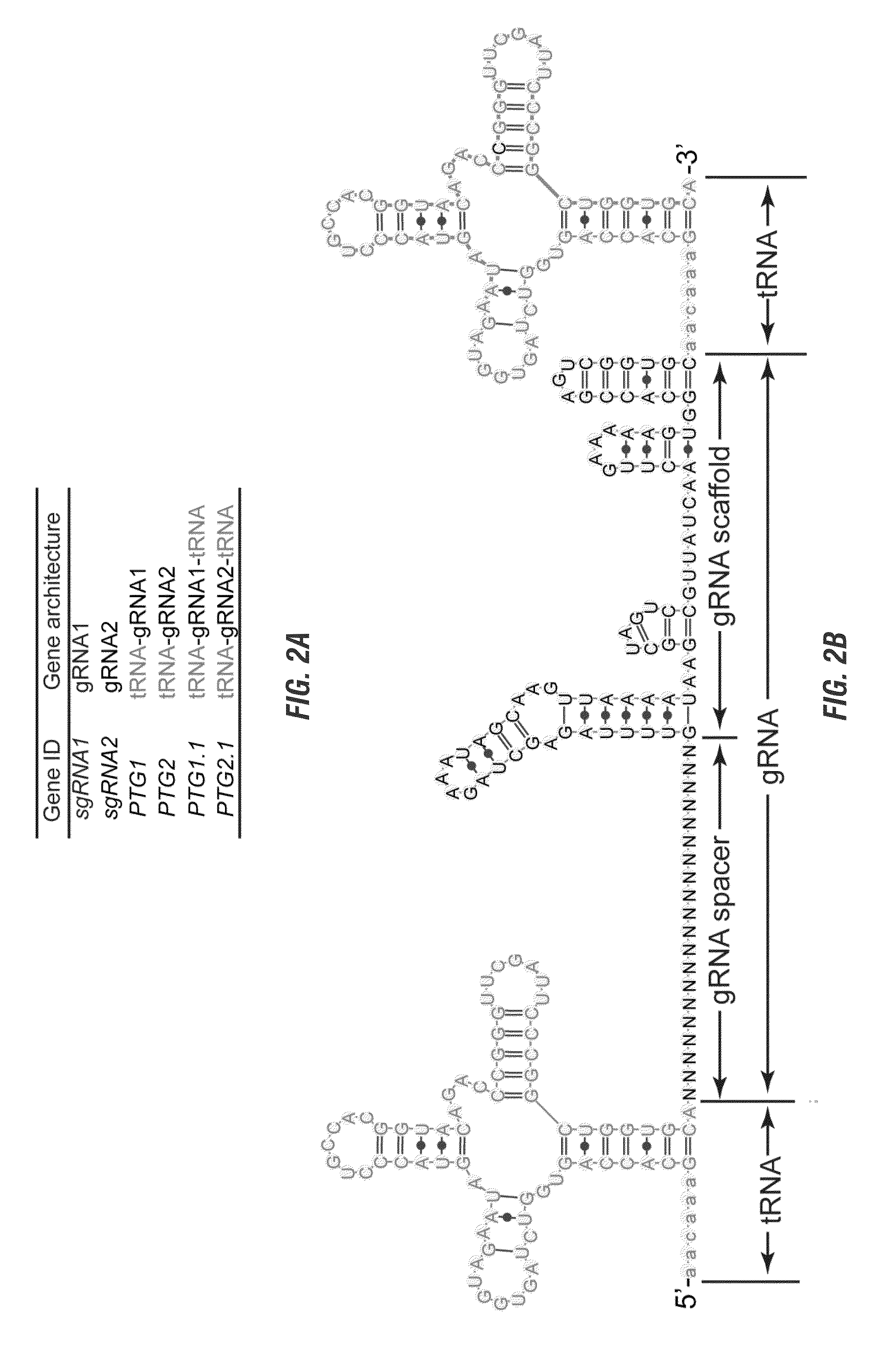
The invention includes materials and methods to generate numerous small RNAs from one polynucleotide construct (synthetic gene) to facilitate RNA-guided multiplex genome editing, modification, inhibition of expression and other RNA-based technologies. The synthetic gene / polynucleotide construct encodes polycistronic RNA components separated by tRNAs, and preferably also includes regulatory components such as a promoter or terminator to form an expression cassette. Once transcribed in a cell, the transcript is processed by the cell to multiple RNA molecules by the endogenous tRNA processing system. The system can be used for any RNA based gene manipulation method including RNA-mediated genome editing, artificial microRNA mediated gene silencing, small RNA mediated genetic manipulation, double-stranded RNA mediated gene silencing, antisense mechanisms and the like.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Compositions and methods for synthetic gene assembly
ActiveUS9677067B2FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSynthetic geneComputational biology
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
Compositions and methods for synthetic gene assembly
InactiveUS20170159044A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSynthetic geneChemistry
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
Methylotroph producing mammalian type sugar chain
ActiveUS20060148039A1FungiImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBiotechnologyHeterologous
This invention is to provide a process for producing a glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain, characterized in that the process comprises introducing an α-1,2-mannosidase gene into a methylotrophic yeast having a mutation of a sugar chain biosynthesizing enzyme gene, so that the α-1,2-mannosidase gene is expressed under the control of a potent promoter in the yeast; culturing in a medium the methylotrophic yeast cells with a heterologous gene transferred thereinto; and obtaining the glycoprotein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain from the culture. Using the newly created methylotrophic yeast having a sugar chain mutation, a neutral sugar chain identical with a high mannose type sugar chain produced by mammalian cells such as human cells, or a glycoprotein comprising such a neutral sugar chain, can be produced in a large amount at a high purity. By introducing a mammalian type sugar chain biosynthesizing gene into the above-described mutant, a mammalian type sugar chain, such as a hybrid or complex, or a protein comprising a mammalian type sugar chain can be efficiently produced.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
Synthetic gene clusters
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for producing a synthetic gene or other DNA sequence
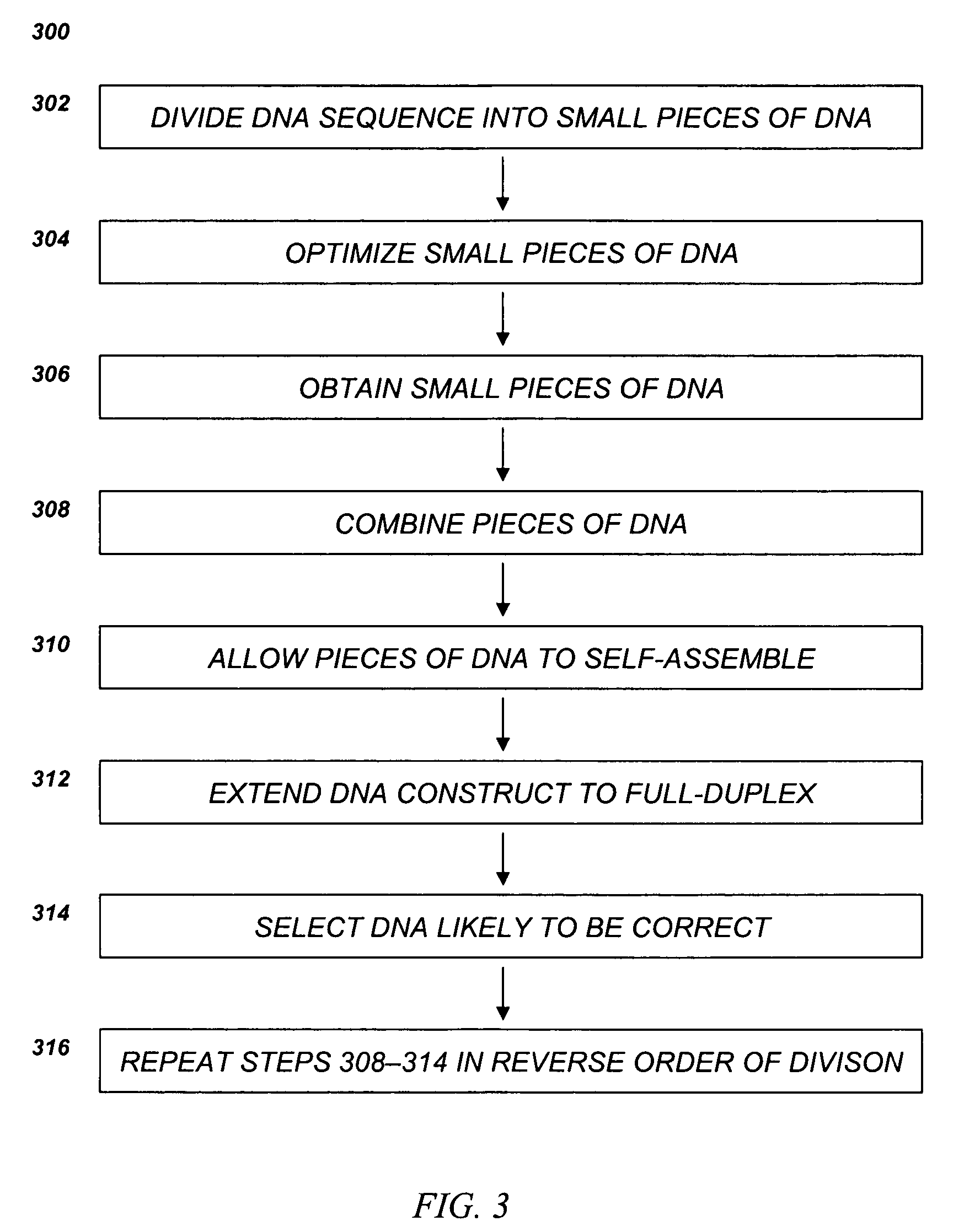
ActiveUS7262031B2Easy to assembleLikelihood of synthesizing the correct DNA sequenceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSingle strandNucleic acid sequencing
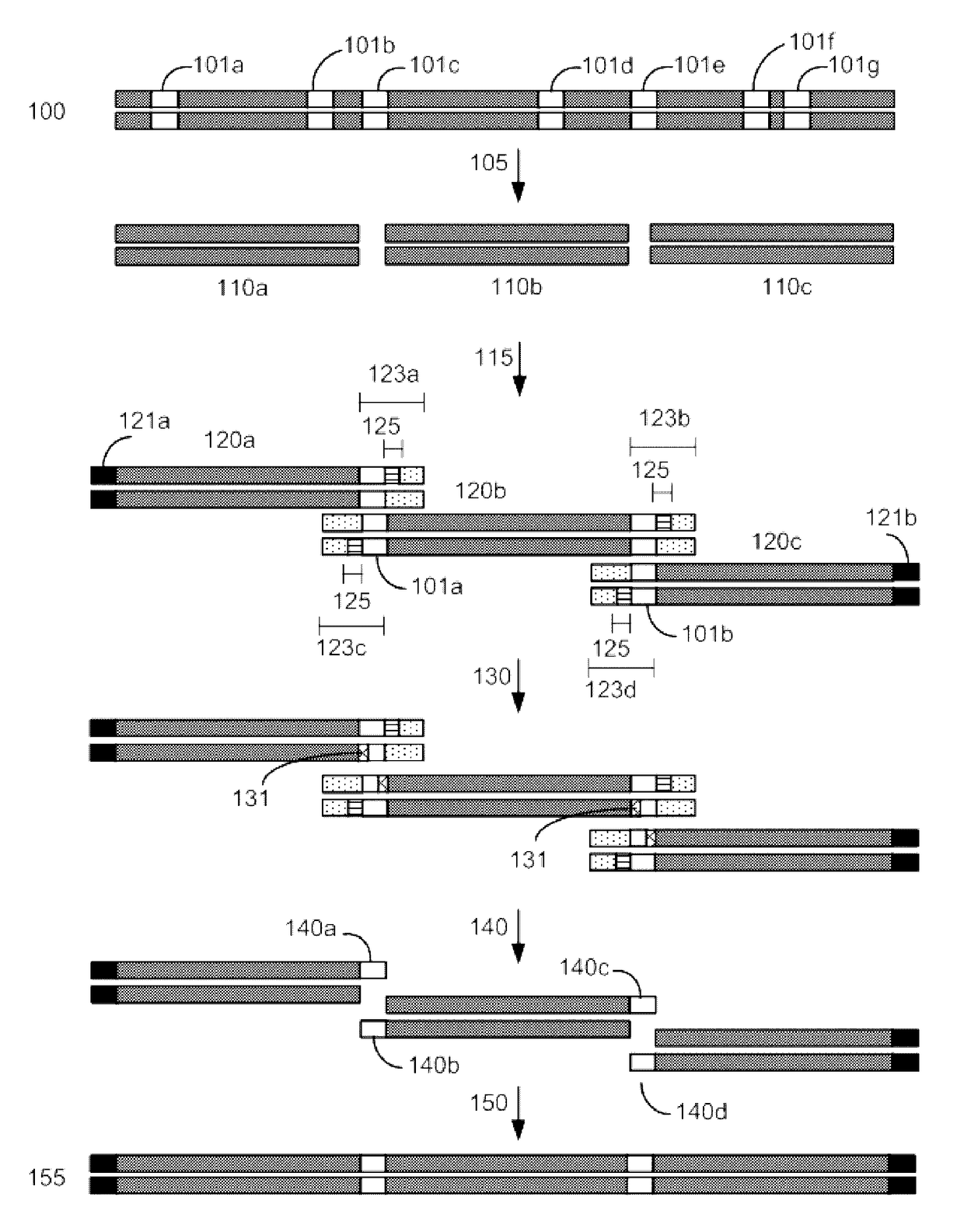
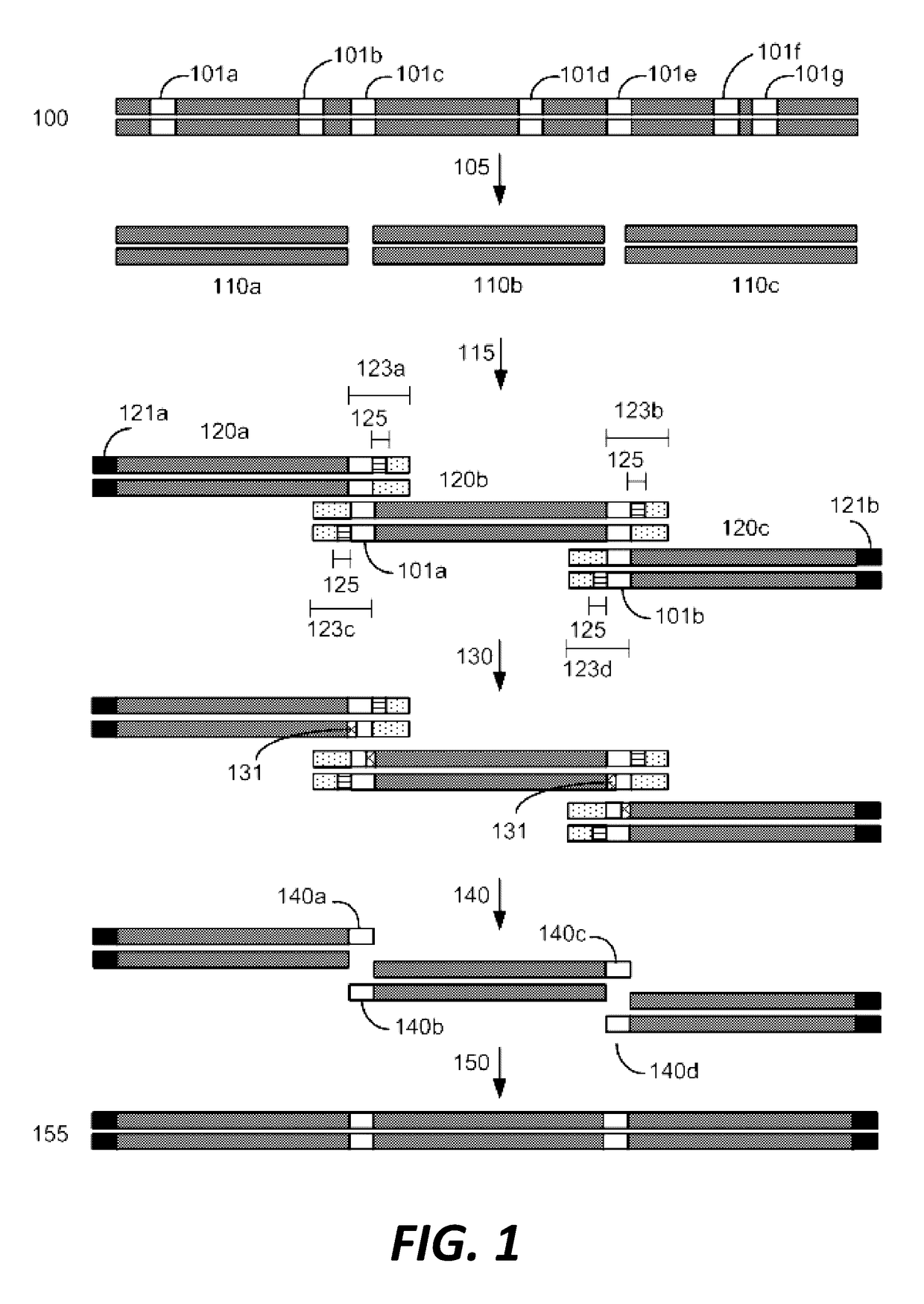
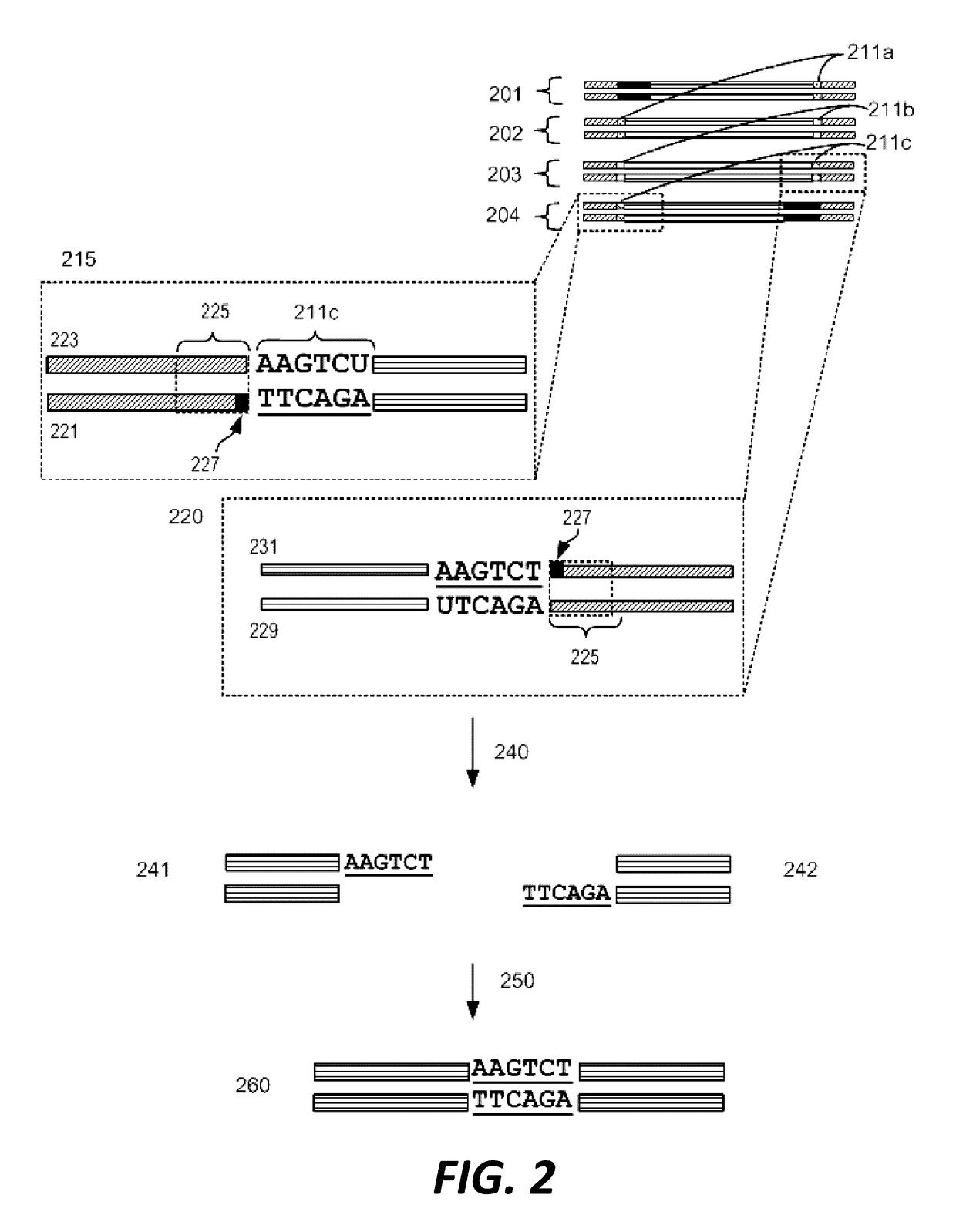
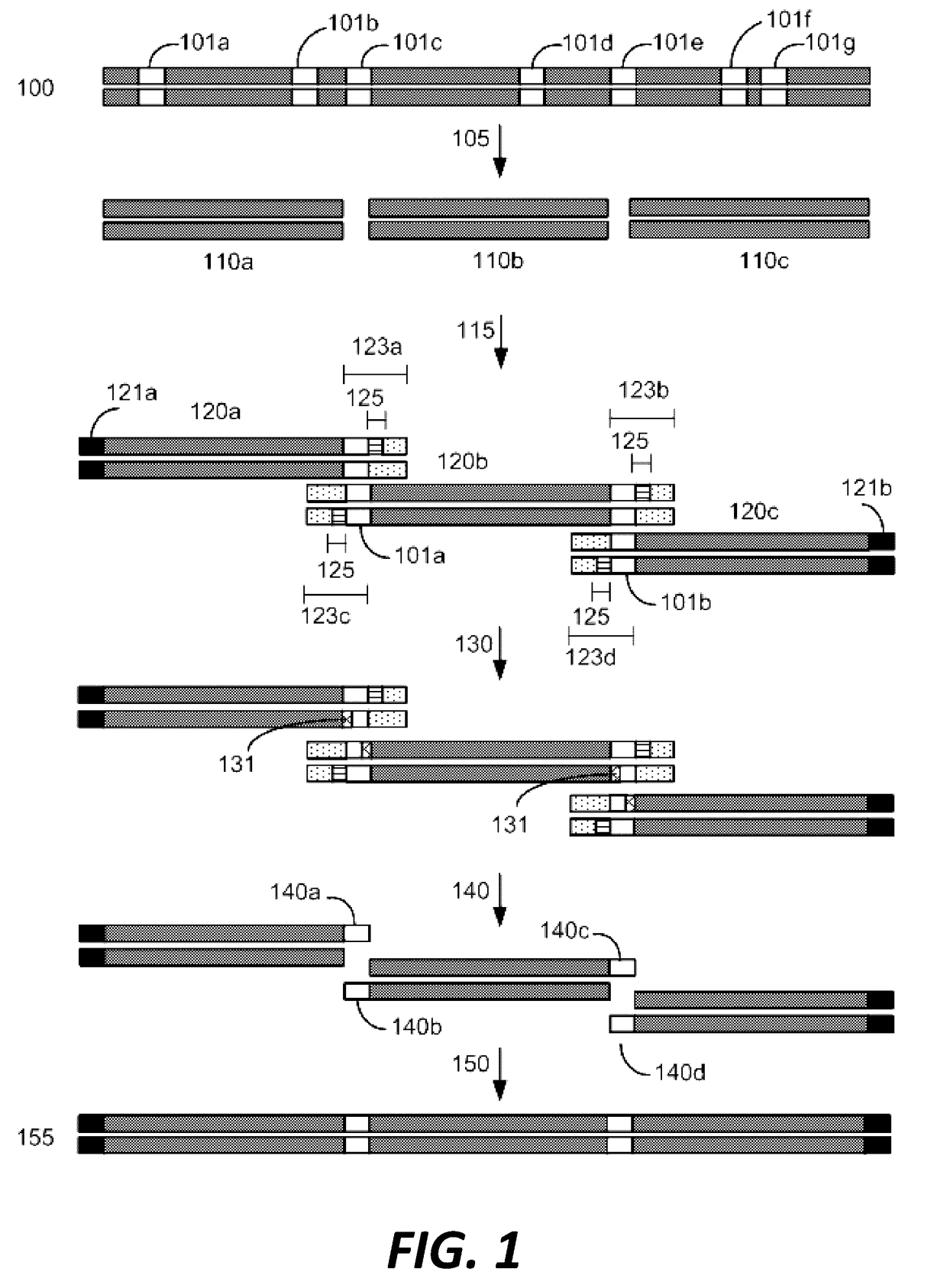
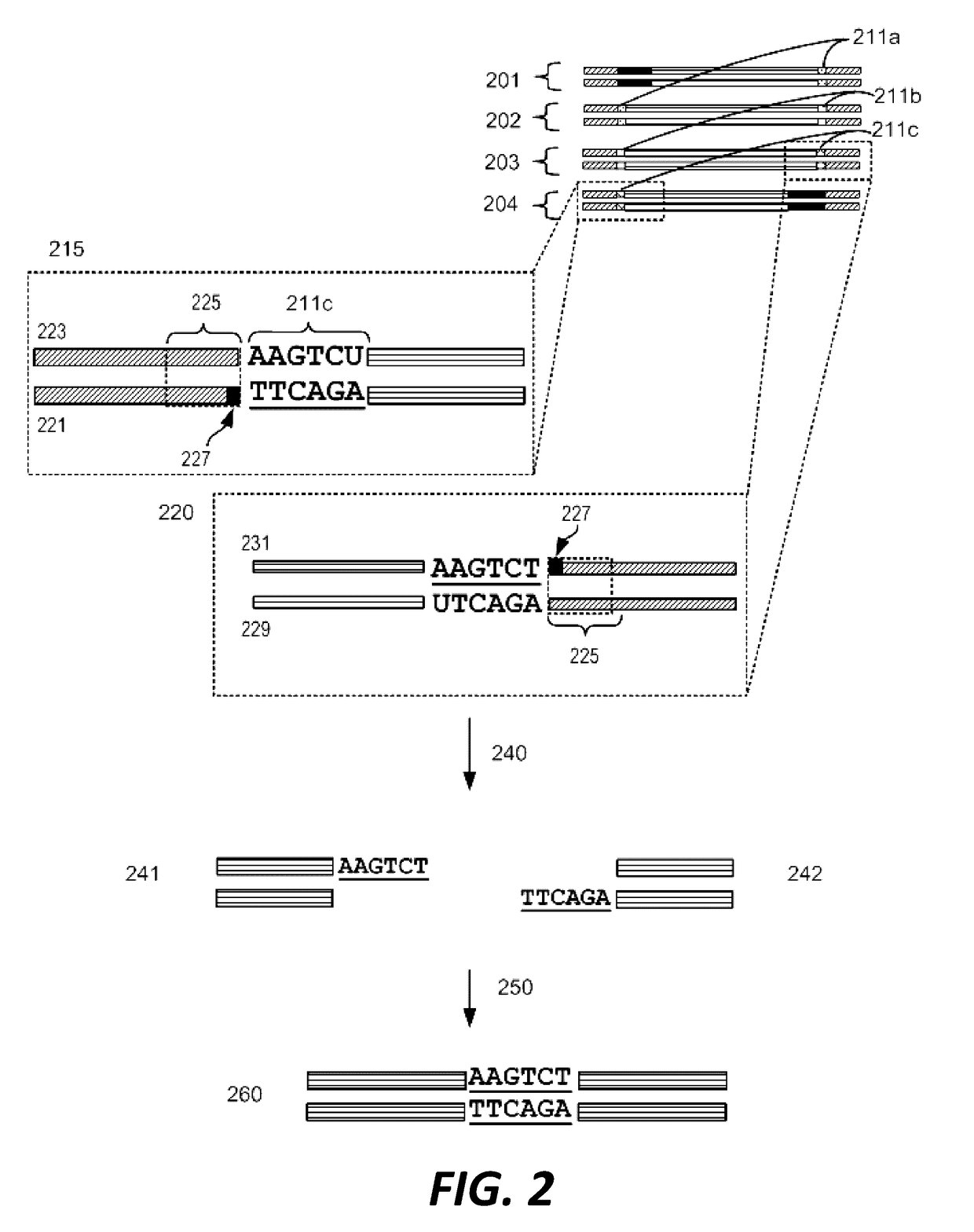
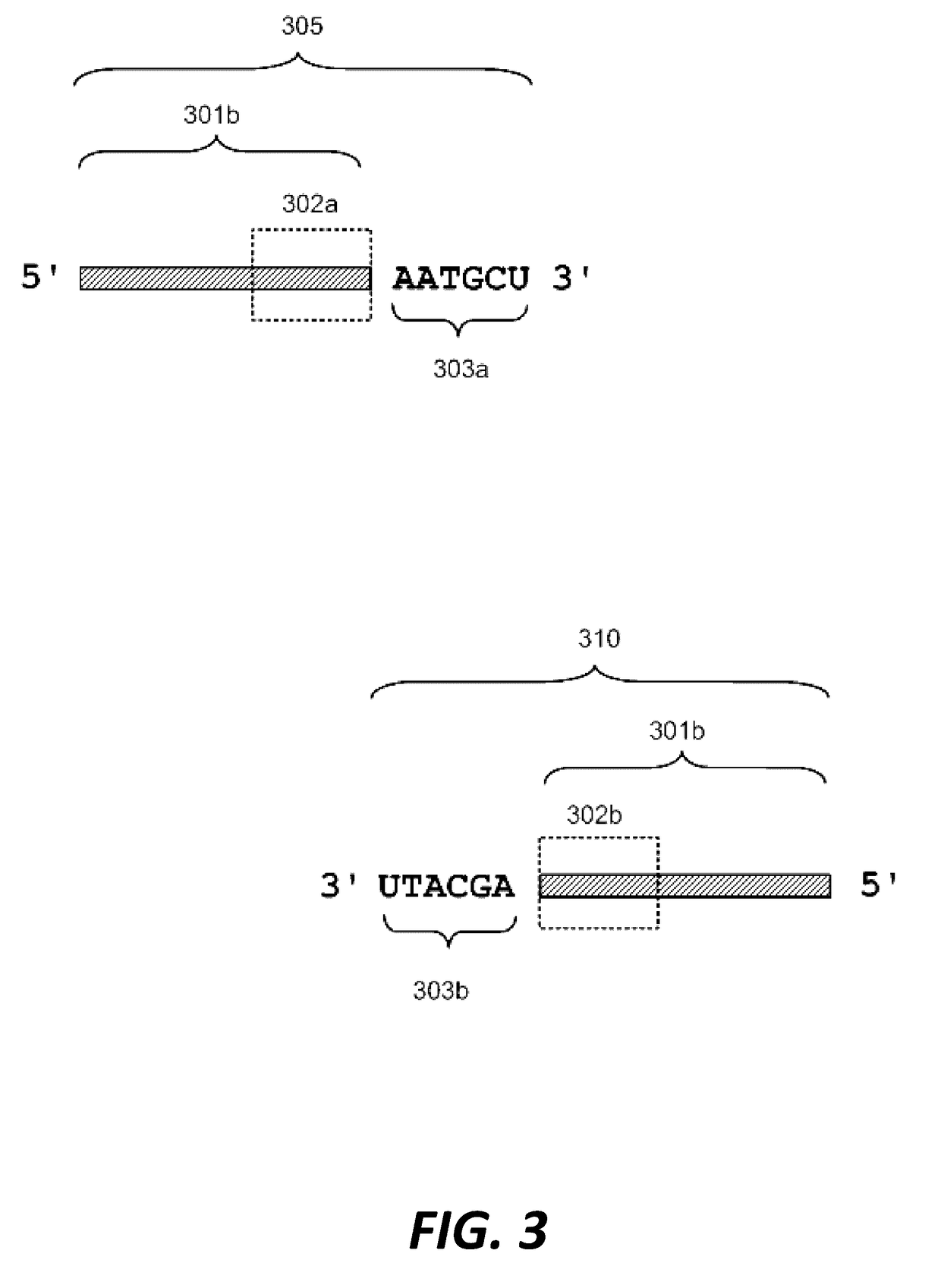
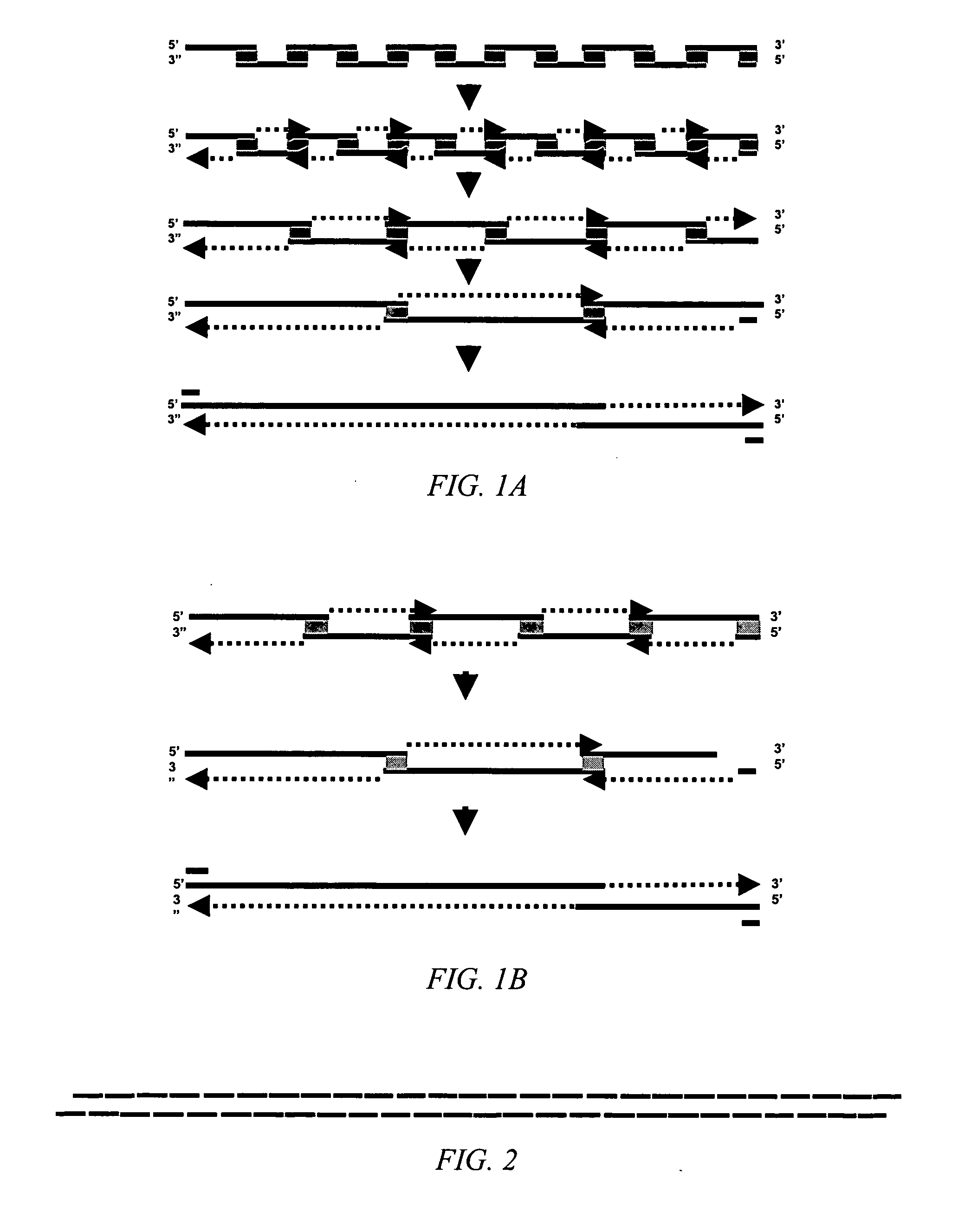
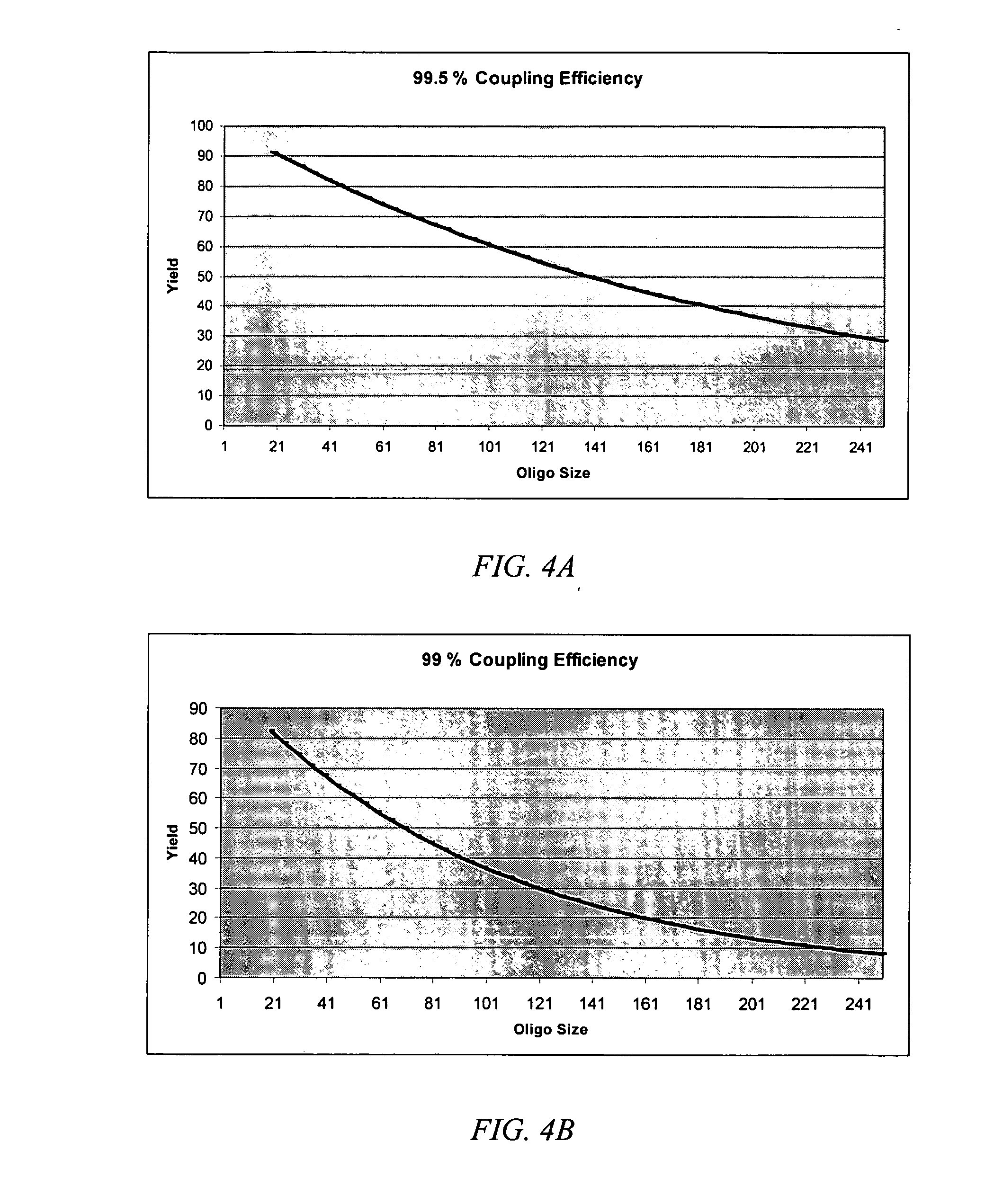
Disclosed herein is a method for synthesizing a desired nucleic acid sequence. The method comprises dividing the desired sequence into a plurality of partially overlapping segments; optimizing the melting temperatures of the overlapping regions of each segment to disfavor hybridization to the overlapping segments which are non-adjacent in the desired sequence; allowing the overlapping regions of single stranded segments which are adjacent to one another in the desired sequence to hybridize to one another under conditions which disfavor hybridization of non-adjacent segments; and filling in, ligating, or repairing the gaps between the overlapping regions, thereby forming a double-stranded DNA with the desired sequence. Also disclosed is a method for preventing errors in the synthesis of the nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
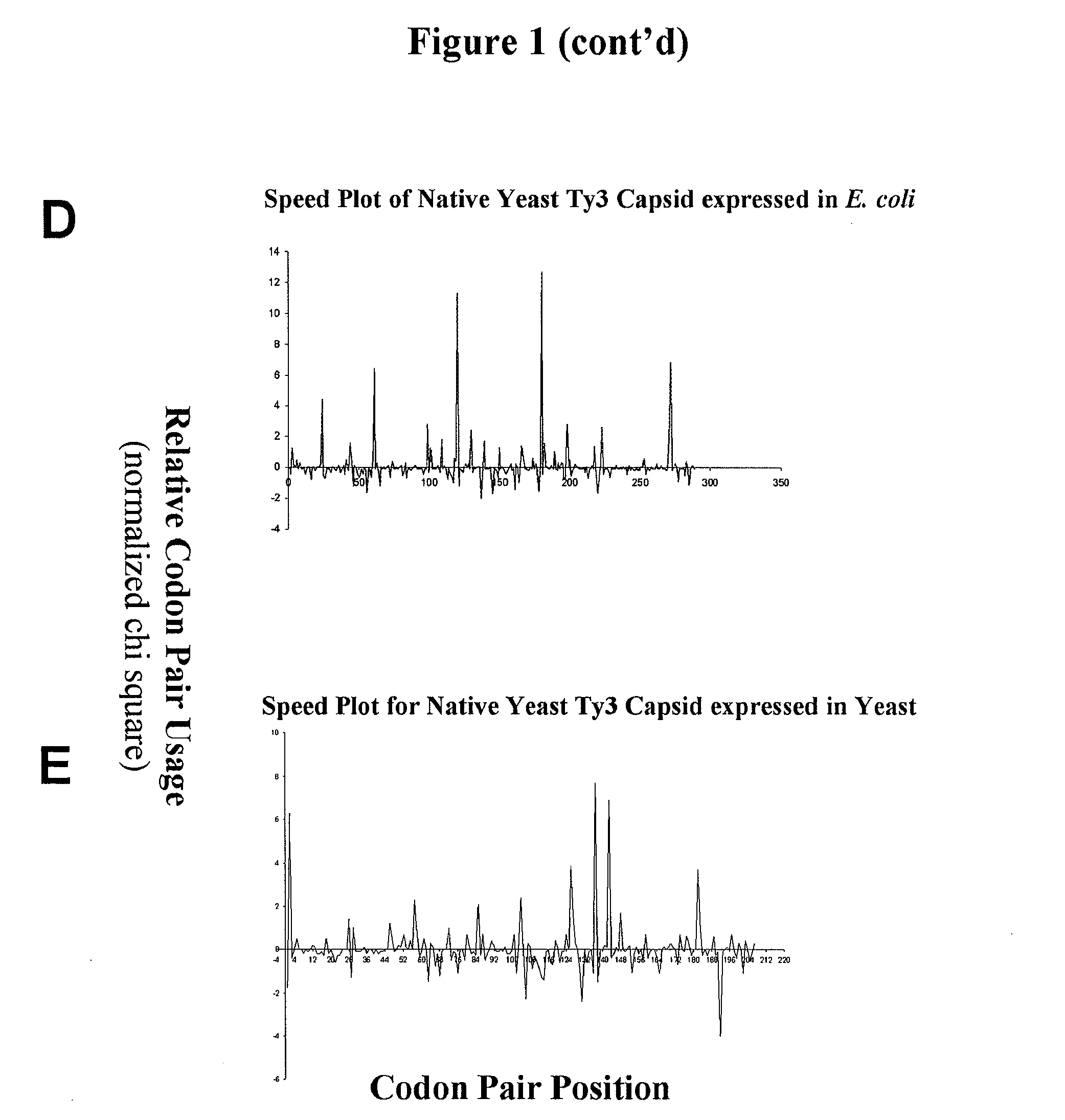
Polypepetide-encoding nucleotide sequences with refined translational kinetics and methods of making same
InactiveUS20080046192A1Reduce protein expressionEnhance protein expressionData visualisationProteomicsData setNucleotide
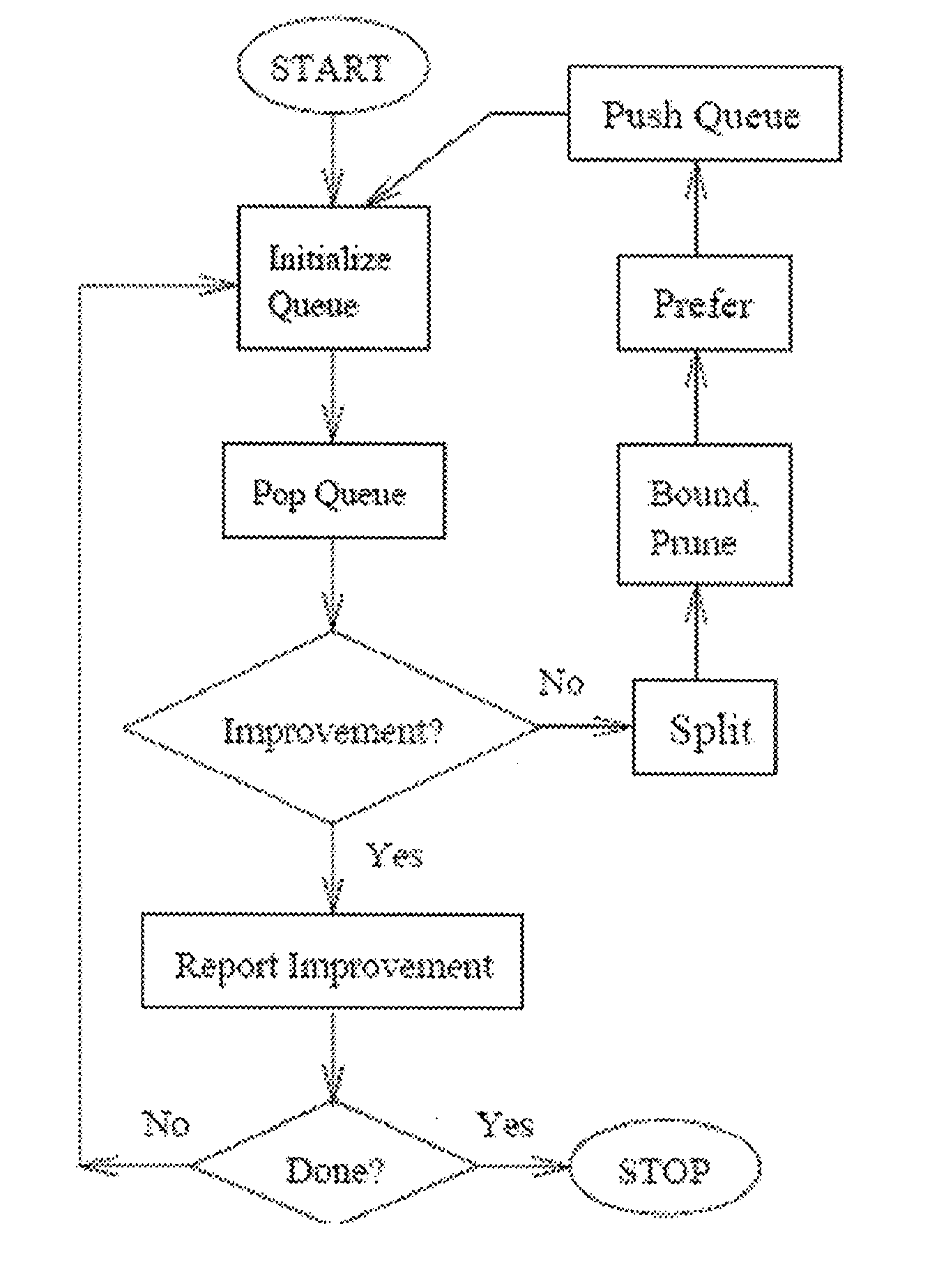
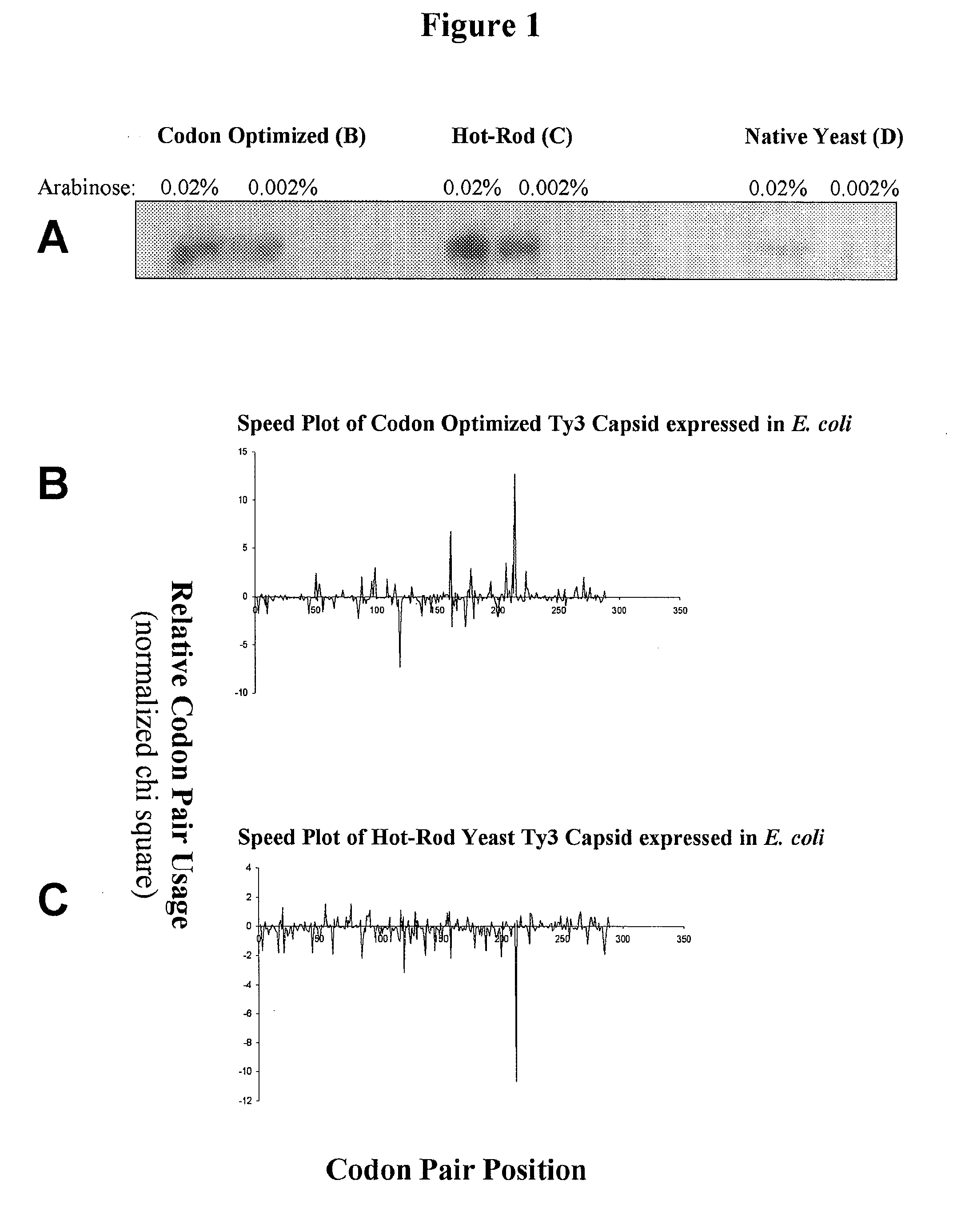
Provided are methods for creating a synthetic gene for expression in a host organism, by providing a data set representative of codon pair translational kinetics for the host organism which includes translational kinetics values of the codon pairs utilized by the host organism, providing a desired polypeptide sequence for expression in the host organism, and generating a polynucleotide sequence encoding the polypeptide sequence by analyzing candidate nucleotides to select, where possible, codon pairs that are predicted not to cause a translational pause in the host organism, with reference to the data set, thereby providing a candidate polynucleotide sequence encoding the desired polypeptide. The methods can be performed using multiple parameter nucleotide sequence optimization methods, such as branch-and-bound methods for nucleotide sequence refinement.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bacterial strain for producing farnesene and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN103243065AIncrease productionRational experimentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainCulture mediums
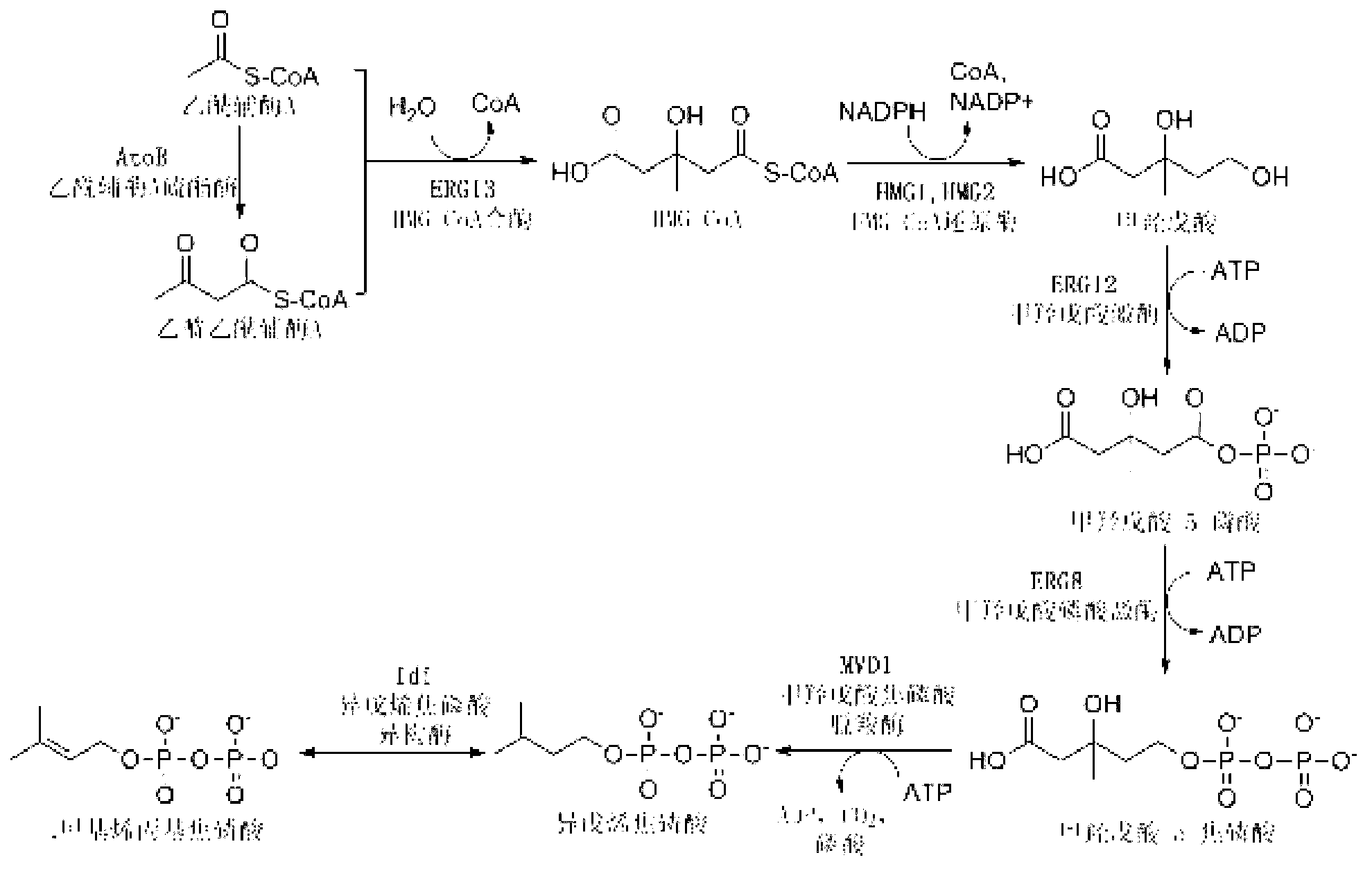
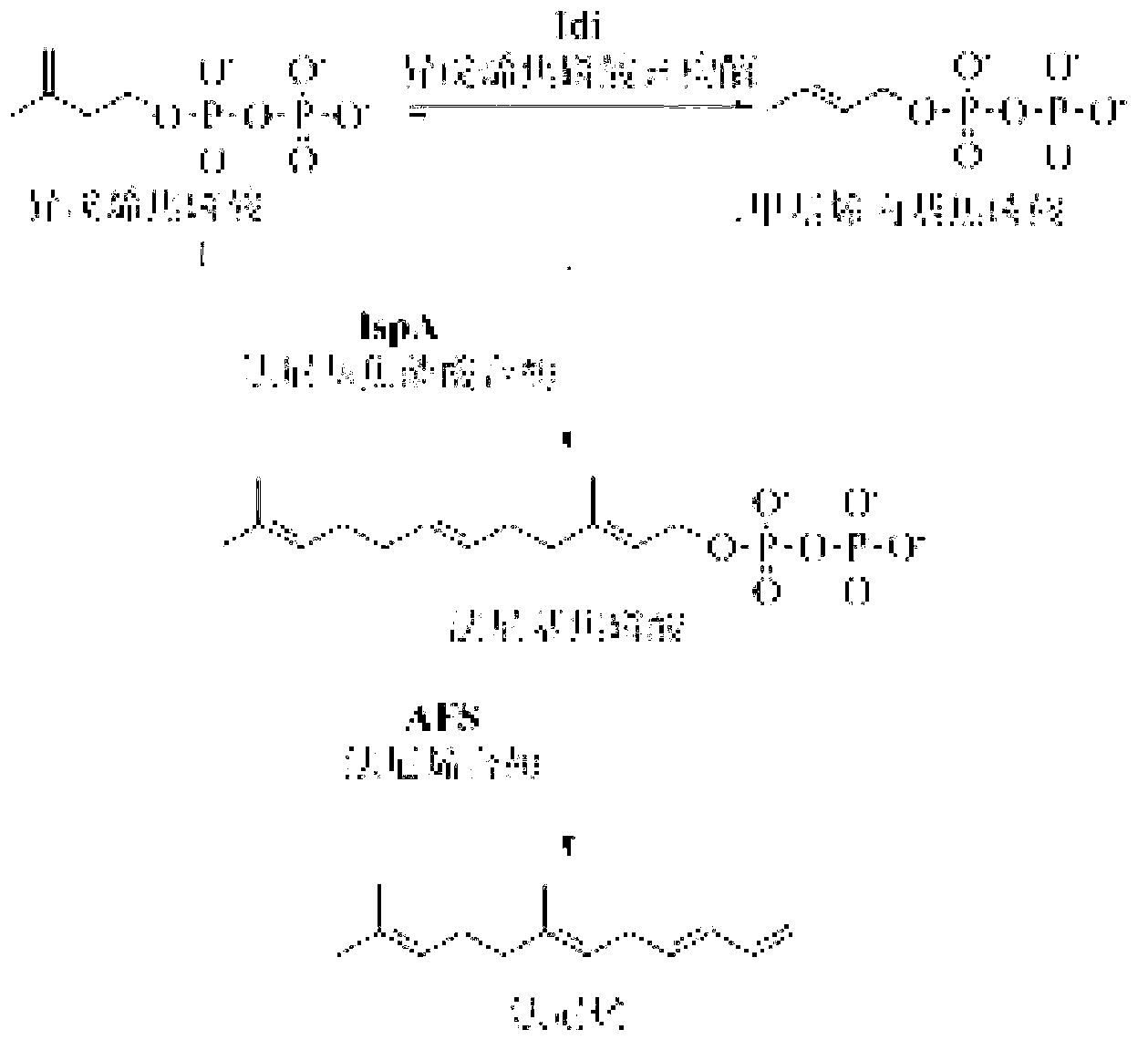
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for producing farnesene and an application of the bacterial strain, belonging to the field of synthetic biology. The bacterial strain for producing the farnesene contains related genes for synthesizing the farnesene through a mevalonic acid pathway and codon optimization; and the sequence of a farnesene synthetic gene afs optimized by codons is as shown by SEQ ID NO.1. The bacterial strain can be used for producing the farnesene, and a seed solution of the bacterial strain is inoculated into a culture medium containing a carbon source to carry out prokaryotic expression to obtain the farnesene. The gene for synthesizing the farnesene is subjected to codon optimization or the farnesene is synthesized by using the mevalonic acid pathway to ensure that each protein is closer to a ratio of AtoB:ERG13:tHMG1:ERG12:ERG8:MVD1:Idi:IspA:AFS=1:10:2:5:5:2:5:2:2, so that the production of the farnesene can be further promoted. By adopting the bacterial strain, the output of the farnesene is greatly improved to be more than 1g / L.
Owner:SHENZHEN ACTION TECH CO LTD
Somatic hypermutation systems
InactiveUS20120028301A1Avoid problemsDecrease and increase in rateImmunoglobulins against growth factorsRecombinant DNA-technologyActivation-induced (cytidine) deaminaseIn vivo
The present application relates to somatic hypermutation (SHM) systems and synthetic genes. Synthetic genes can be designed using computer-based approaches to increase or decrease susceptibility of a polynucleotide to somatic hypermutation. Genes of interest are inserted into the vectors and subjected to activation-induced cytidine deaminase to induce somatic hypermutation. Proteins or portions thereof encoded by the modified genes can be introduced into a SHM system for somatic hypermutation and proteins or portions thereof exhibiting a desired phenotype or function can be isolated for in vitro or in vivo diagnostic or therapeutic uses.
Owner:ANAPTYSBIO INC
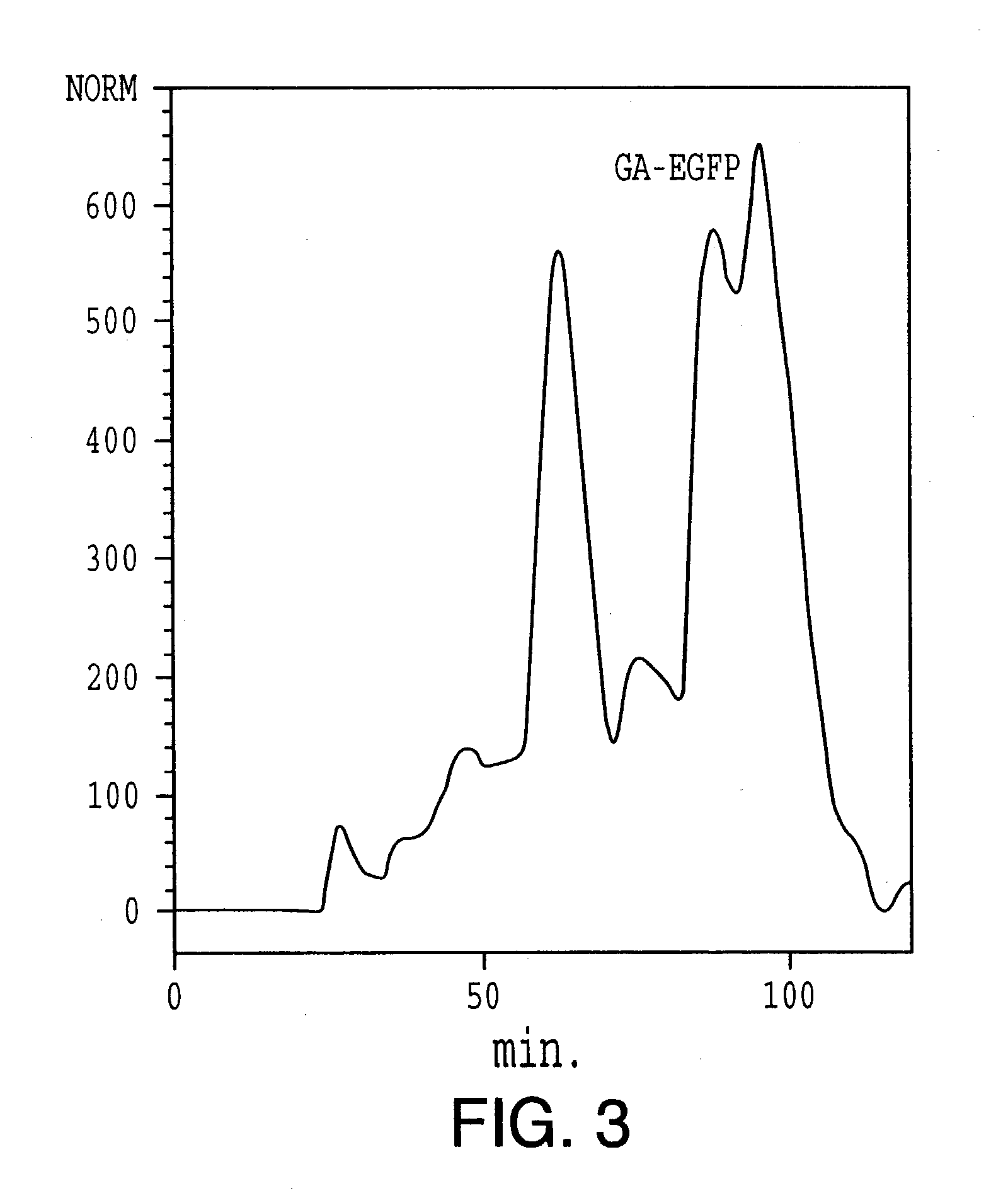
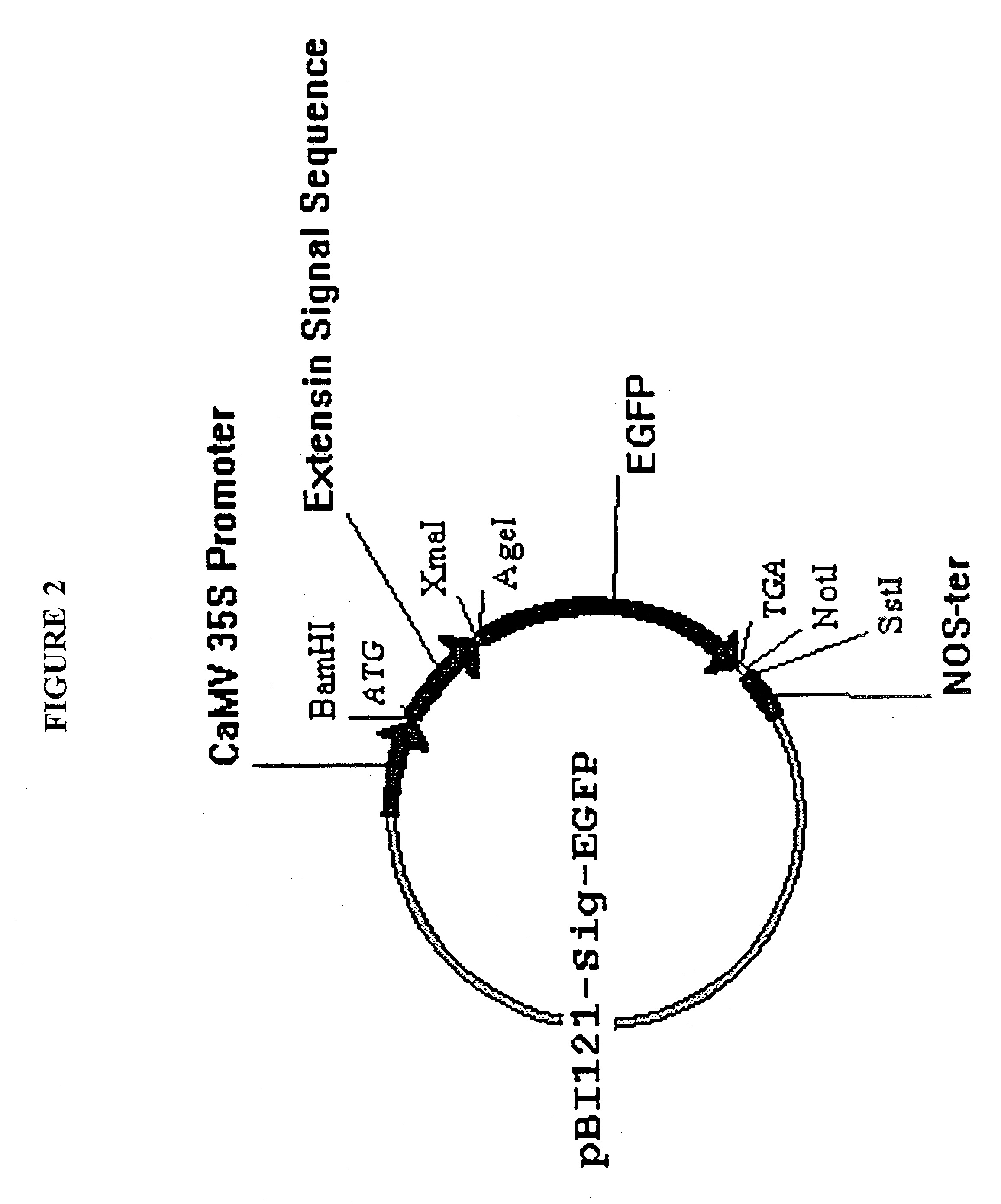
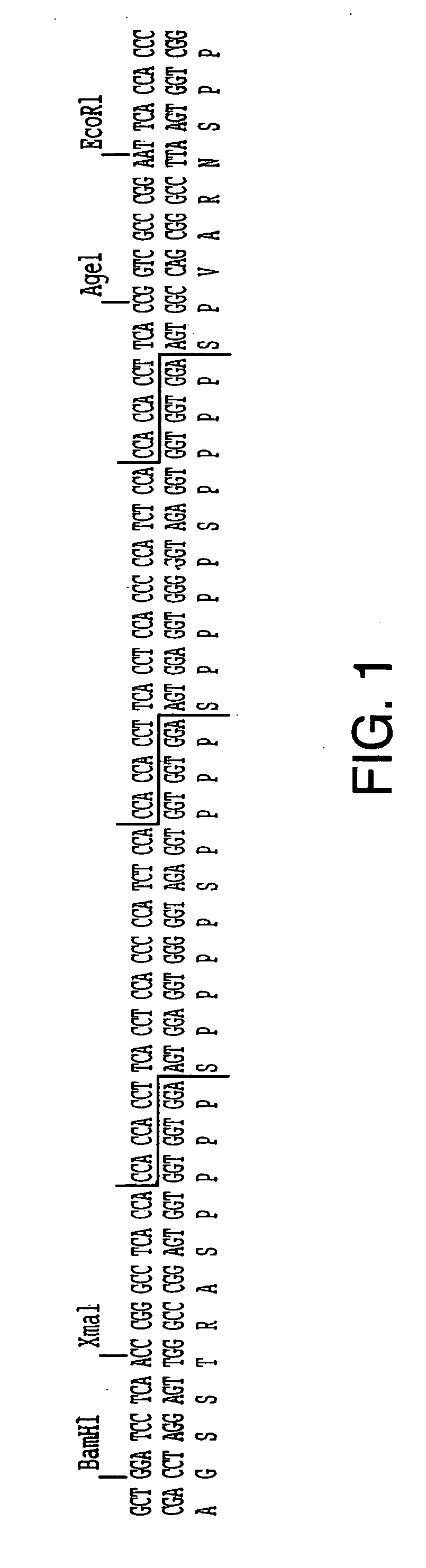
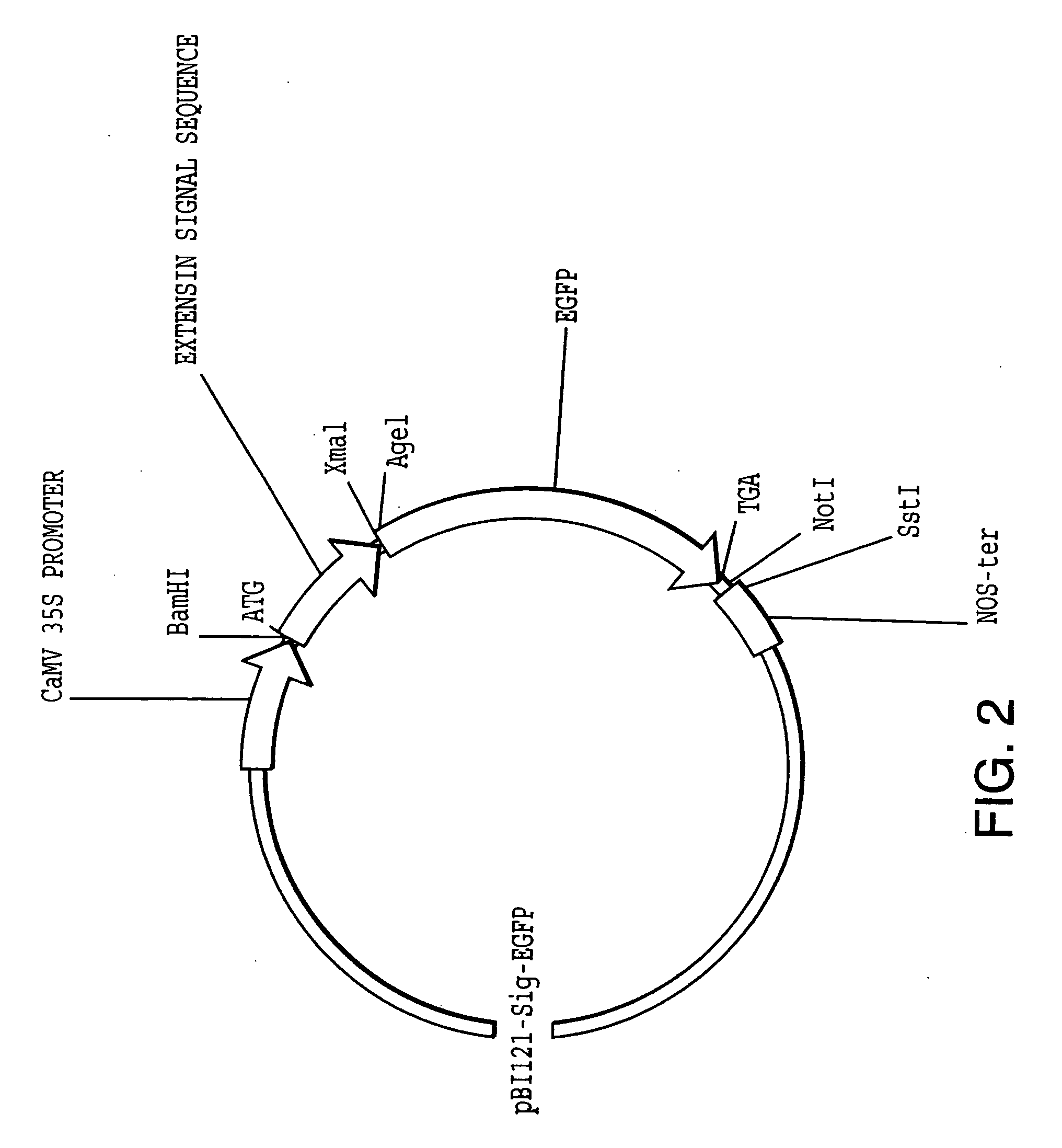
Synthetic genes for plant gums and other hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins
InactiveUS20040009555A1Easy to transformMaximizing numberPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsArabinogalactan proteinHydroxyproline
A new approach in the field of plant gums is described which presents a new solution to the production of hydroxyproline(Hyp)-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs), repetitive proline-rich proteins (RPRPs) and arabinogalactan-proteins (AGPs). The expression of synthetic genes designed from repetitive peptide sequences of such glycoproteins, including the peptide sequences of gum arabic glycoprotein (GAGP), is taught in host cells, including plant host cells.
Owner:OHIO UNIV TECH TRANSFER OFFICE TECH & ENTERPRISE BUILDING
Novel synthetic genes for plant gums
InactiveUS20040009557A1Maximize number of cellHigh activityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulinsBiotechnologyHydroxyproline
A new approach in the field of plant gums is described which presents a new solution to the production of hydroxyproline(Hyp)-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs), repetitive proline-rich proteins (RPRPs) and arabino-galactan proteins (AGPs). The expression of synthetic genes designed from repetitive peptide sequences of such glycoproteins, including the peptide sequences of gum arabic glycoprotein (GAGP), is taught in host cells, including plant host cells.
Owner:OHIO UNIV TECH TRANSFER OFFICE TECH & ENTERPRISE BUILDING
Synthetic genes for plant gums and other hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins
InactiveUS20050074838A1Maximize number of cellFacilitate slow-release drug deliveryBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyHydroxyproline
A new approach in the field of plant gums is described which presents a new solution to the production of hydroxyproline(Hyp)-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs), repetitive proline-rich proteins (RPRPs) and arabinogalactan-proteins (AGPs). The expression of synthetic genes designed from repetitive peptide sequences of such glycoproteins, including the peptide sequences of gum arabic glycoprotein (GAGP), is taught in host cells, including plant host cells.
Owner:OHIO UNIV TECH TRANSFER OFFICE TECH & ENTERPRISE BUILDING
Methods for calculating codon pair-based translational kinetics values, and methods for generating polypeptide-encoding nucleotide sequences from such values
InactiveUS20070275399A1Improve shortcomingsEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementData visualisationNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
Provided are methods for calculating codon pair translational kinetics values, creating a synthetic gene for expression in a host organism, and providing codon pair translational kinetic values. The methods typically are directed to refinement of statistical observed versus expected codon pair frequencies using one of several factors such as amino acid sequence homology, secondary or tertiary structural considerations, and empirical measurements. In some synthetic genes codon pairs are predicted not to cause a translational pause in the host organism, thereby providing a polynucleotide sequence encoding the desired polypeptide with desired translational kinetics properties. The methods can be performed using multiple parameter nucleotide sequence optimization methods, such as branch-and-bound methods for nucleotide sequence refinement.
Owner:LATHROP RICHARD H +4
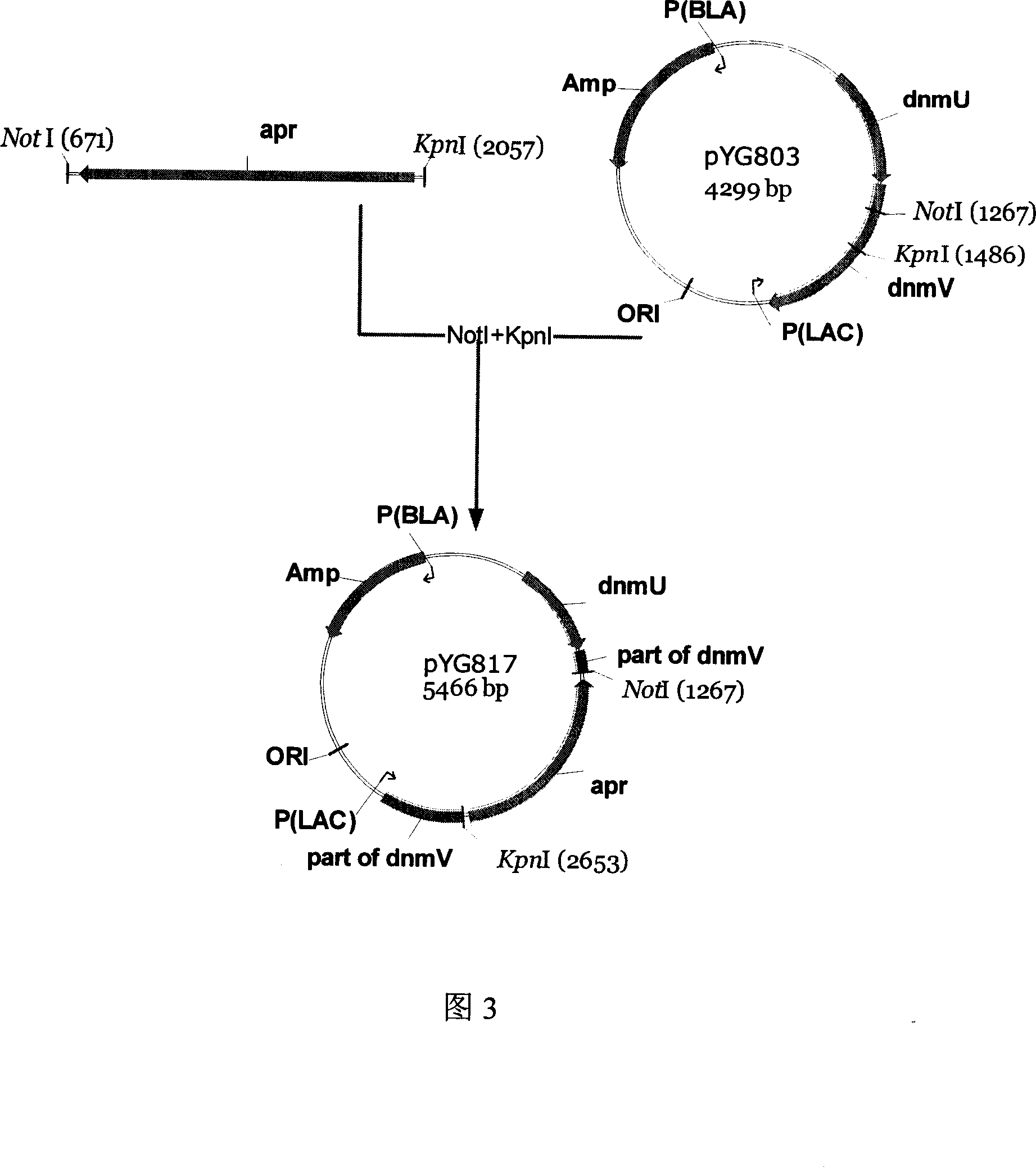
Engineering bacterium capable of producing anthracene ring antibiotics and application of the same
The invention discloses an engineering bacterium through anthracene nucleus antibiotic and appliance, which is characterized by the following: inserting or replacing restriction enzymes site of dnmV gene nucleic acid order of sky blue rufus streptomycete with antibiotic against property gene and surface cerubidin synthetic gene; blocking-up engineering bacterium of dnmV gene; or transforming expressing carrier of anthracene nucleus antibiotic synthetic gene to lead streptomycin (S.lividans)TK24; extracting expressing plasmid from S.lividans TK24; leading-in sky blue rufus streptomycete gene only with antibiotic against property gene to block dnmV gene; blocking-up abrupt change bacterium. This invention can produce cerubidin and / or analogue, such as anthracene nucleus antibiotic.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD +1
Synthetic gene encoding human carcinoembryonic antigen and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070104685A1Easy to insertEasy to removeVirusesGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideCarcinoembryonic antigen
Synthetic polynucleotides encoding human carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) are provided, the synthetic polynucleotides being codon-optimized for expression in a human cellular environment. The gene encoding CEA is commonly associated with the development of human carcinomas. The present invention provides compositions and methods to elicit or enhance immunity to the protein product expressed by the CEA tumor-associated antigen, wherein aberrant CEA expression is associated with a carcinoma or its development. This invention specifically provides adenoviral vector and plasmid constructs carrying codon-optimed human CEA and discloses their use in vaccines and pharmaceutical compositions for preventing and treating cancer.
Owner:LA MONICA NICOLA +3
Method for producing lactic acid by using glycerol
InactiveCN101255451AEasy to separate and purifyBroaden your optionsMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiodieselGlycerol
The invention is a method for producing lactic acid for a substrate by glycerin, belonging to the field of biochemical technology. The method comprises the steps that: strains containing glycerin use genes and lactic acid synthetic genes are inoculated to a glycerin-containing seed culture medium; seed liquid is added to an initial fermentation medium containing 30-80g / L glycerin for anaerobic fermentation or micro-aerobic fermentation under 37 DEG C to 55 DEG C; the pH value is adjusted by fed batch 3-4M aqueous slkali or portion-wise addition of solid CaCO<3>, when the production strength of the lactic acid is less than 0.3-0.5g / (1h); the glycerin is stopped fed batching, the fermentation is continued until the residual glycerin concentration decreased to 5g / L. The method has the advantages that: the by product glycerin in the biodiesel production process is reasonably used, and transferred to high-added-value lactic acid; the method can also be used for coupling production of biodiesel and lactic acid, by which high-added-value biodiesel and lactic acid are produced with low-cost raw material, the utilization rate of raw material is improved, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Recombinant vaccine against botulinum neurotoxin
InactiveUS20070037257A1Fast and efficient purificationBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesVaccinationRecombinant vaccines
This invention is directed to preparation and expression of synthetic genes encoding polypeptides containing protective epitopes of botulinum neurotoxin (BoNT). The invention is also directed to production of immunogenic peptides encoded by the synthetic genes, as well as recovery and purification of the immunogenic peptides from recombinant organisms. The invention is also directed to methods of vaccination against botulism using the expressed peptides.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
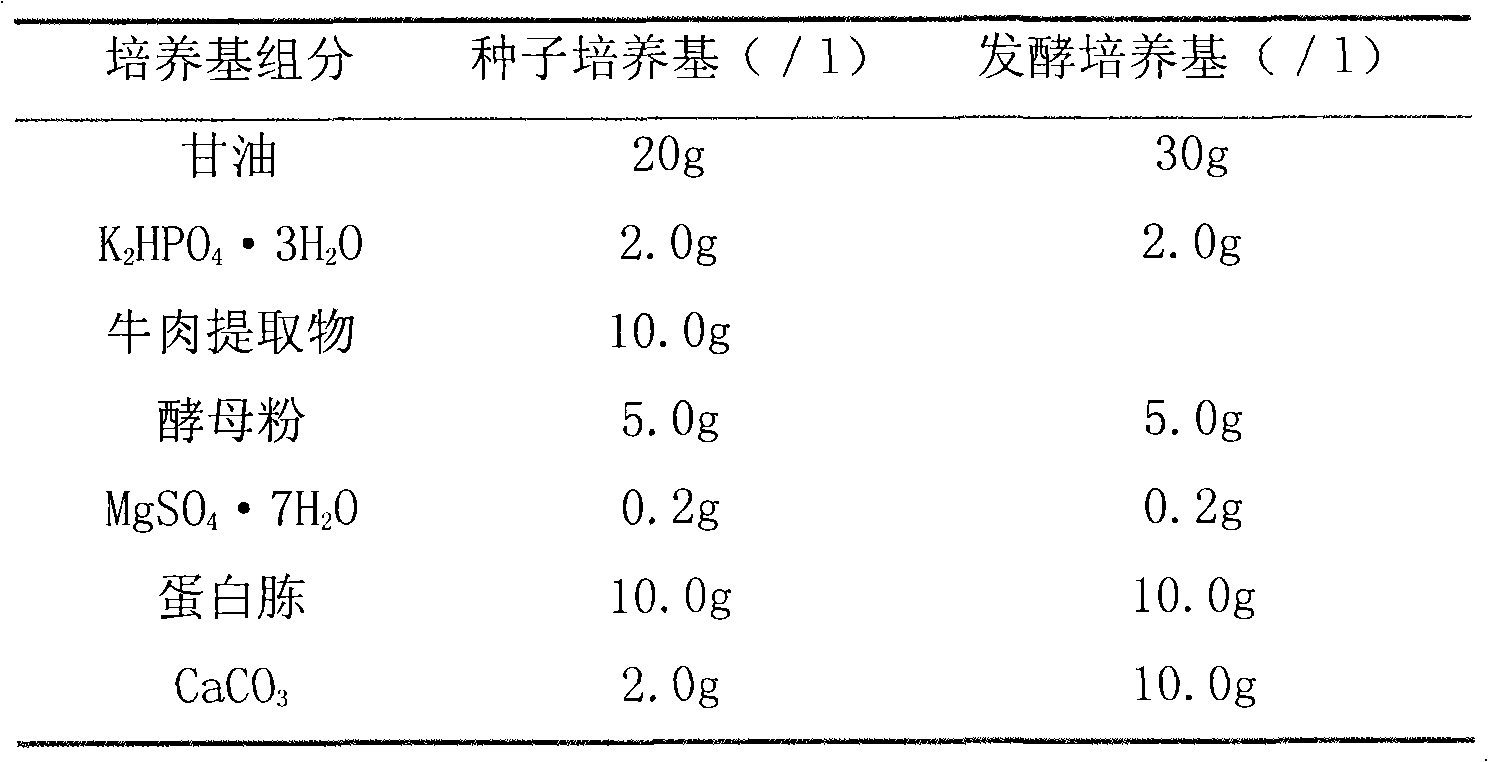
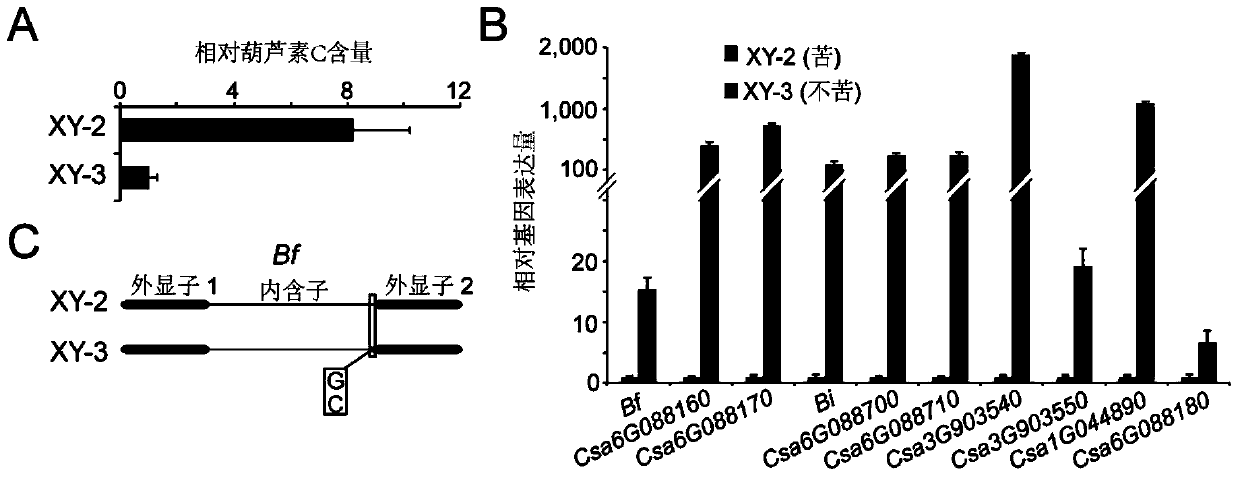
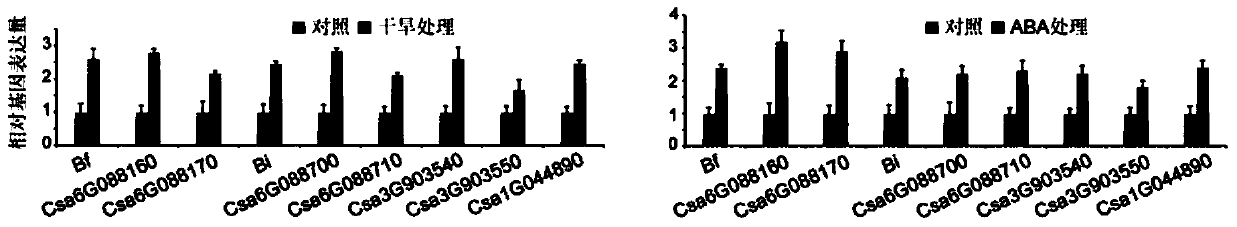
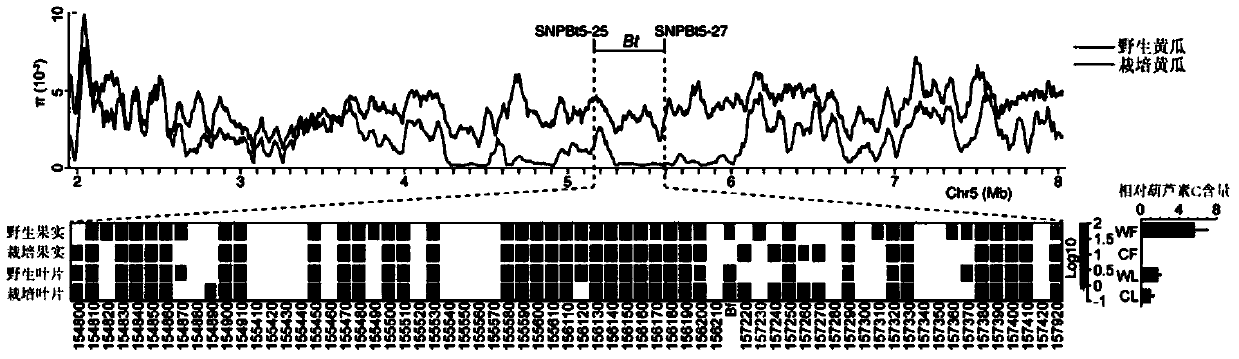
Transcription factor Csa5G157230 participating in regulation of synthesis of cucumber cucurbitacine C and application thereof
The invention provides a transcription factor Csa5G157230 participating in regulation of synthesis of cucumber cucurbitacine C and application thereof. The transcription factor is one of two bHLH transcription factors (Csa5G157230 and Csa5G156220) which are found in cucumber genome firstly and used for controlling synthesis of bitter taste; the two bHLH transcription factors are used for controlling the forming of the bitter taste in fruits and leaves respectively; simple crossing of yeast, a gel tissue system and instantaneous expression of tobacco prove that the two transcription factors can be combined to a bitter taste synthesis promoter region and used for activating transcription of a synthesis gene; meanwhile, the bitter taste characteristics of cucumber plants can be restored by expressing the corresponding transcription factors in the leaves or fruits of the cucumber free of bitter taste abundantly. The invention further discloses a molecular mechanism for forming bitter taste of cucumber and provides theoretical basis for breeding cucumber free of bitter taste and molecular assisted breeding goals.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
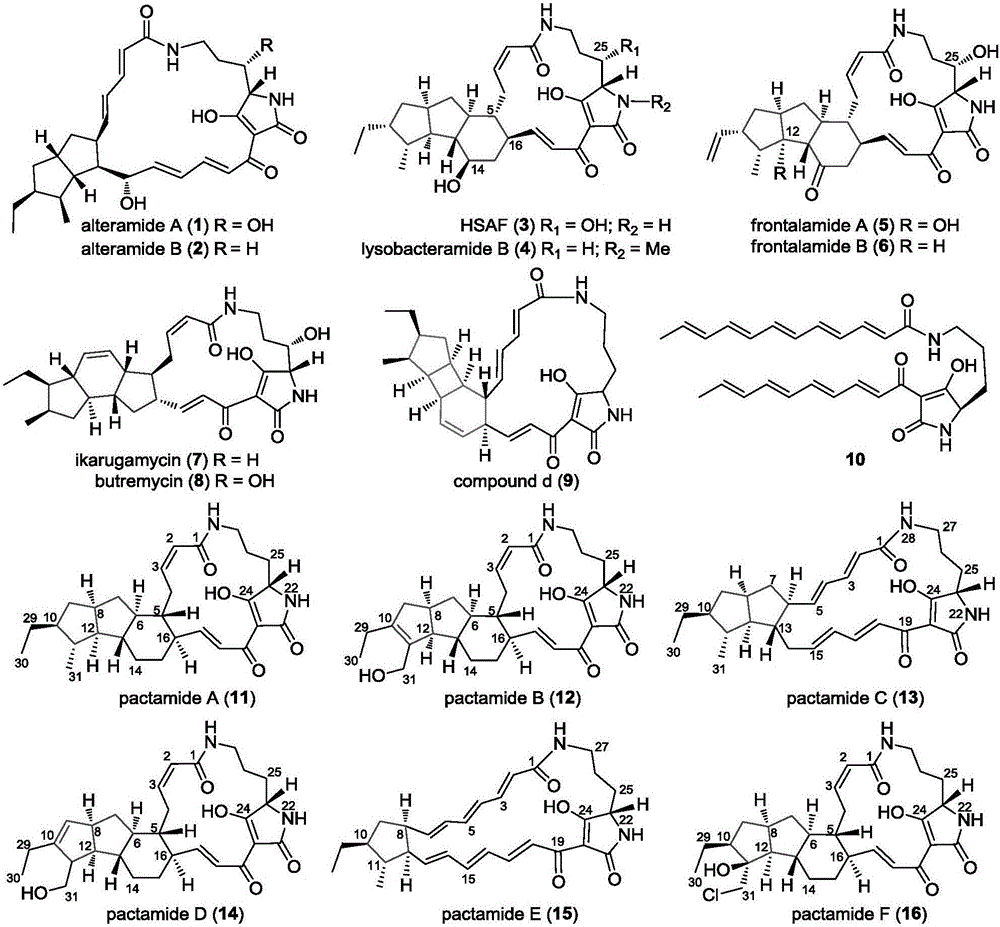
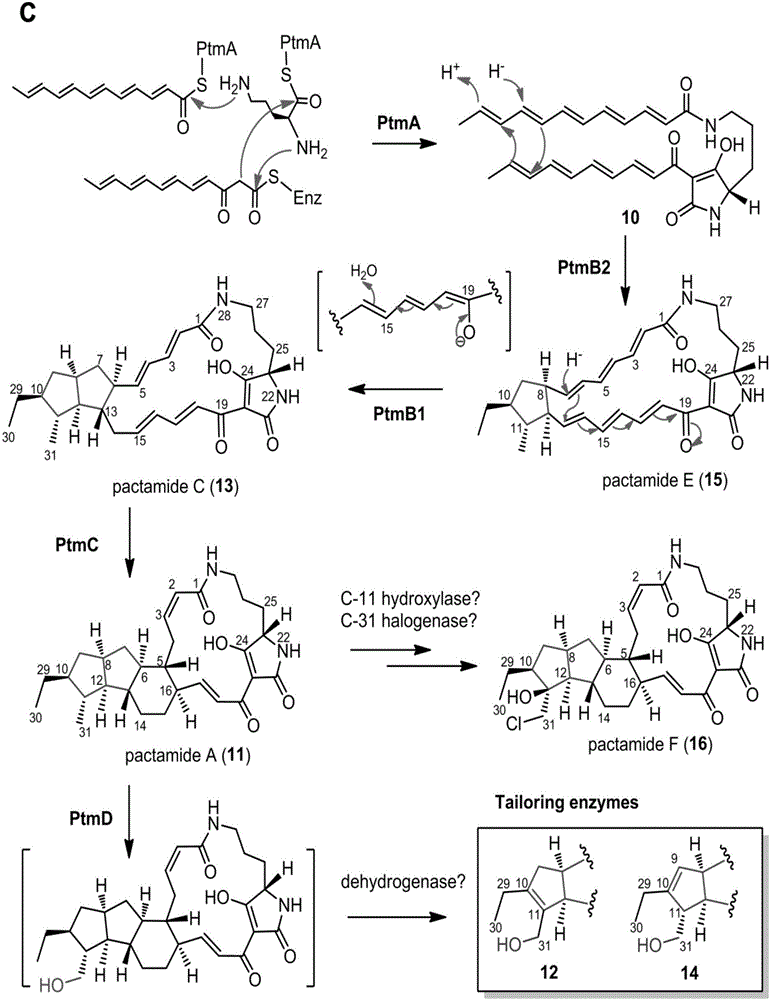
Biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and application thereof
ActiveCN106434702ABiosynthetic gene cluster activationHas antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCyclasePolyketide
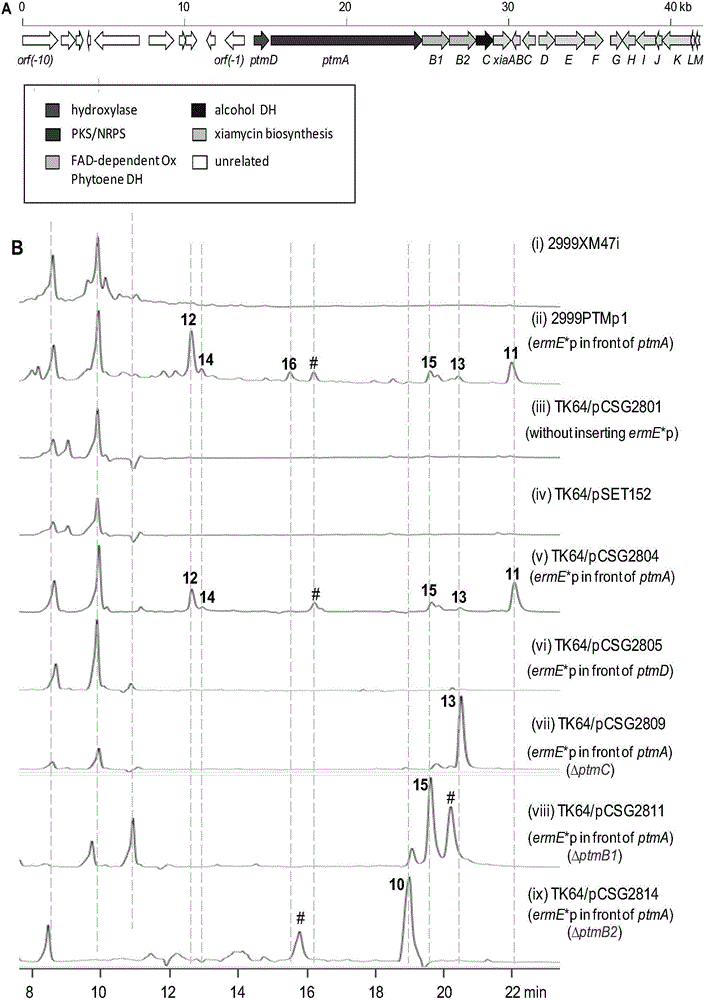
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and an application thereof. The biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide comes from (Streptomyces pactum)SCSIO 02999, and the cluster comprises five genes including heterozygous polyketone / nonribosomal peptide synthetases genes ptmA, FAD dependent redox enzyme genes ptmB1, phytoene dehydrogenase genes ptmB2, cyclase genes ptmC and hydroxylase genes ptmD. According to the biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and the application thereof, information in genes and proteins related to biosynthesis of the paquete amide provides theoretical foundations and materials for conducting genetic modification on the biosynthesis of multi-ring tetramate macrocylic lactam family. By conducting genetic modifications on the biological synthetic genes, 6 new structures antineoplastic paquete amide compounds pactamide A-F are obtained, and thus effective compound entities are provided for research and development of antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Synthetic peptides and dna sequences for treatment of multiple sclerosis
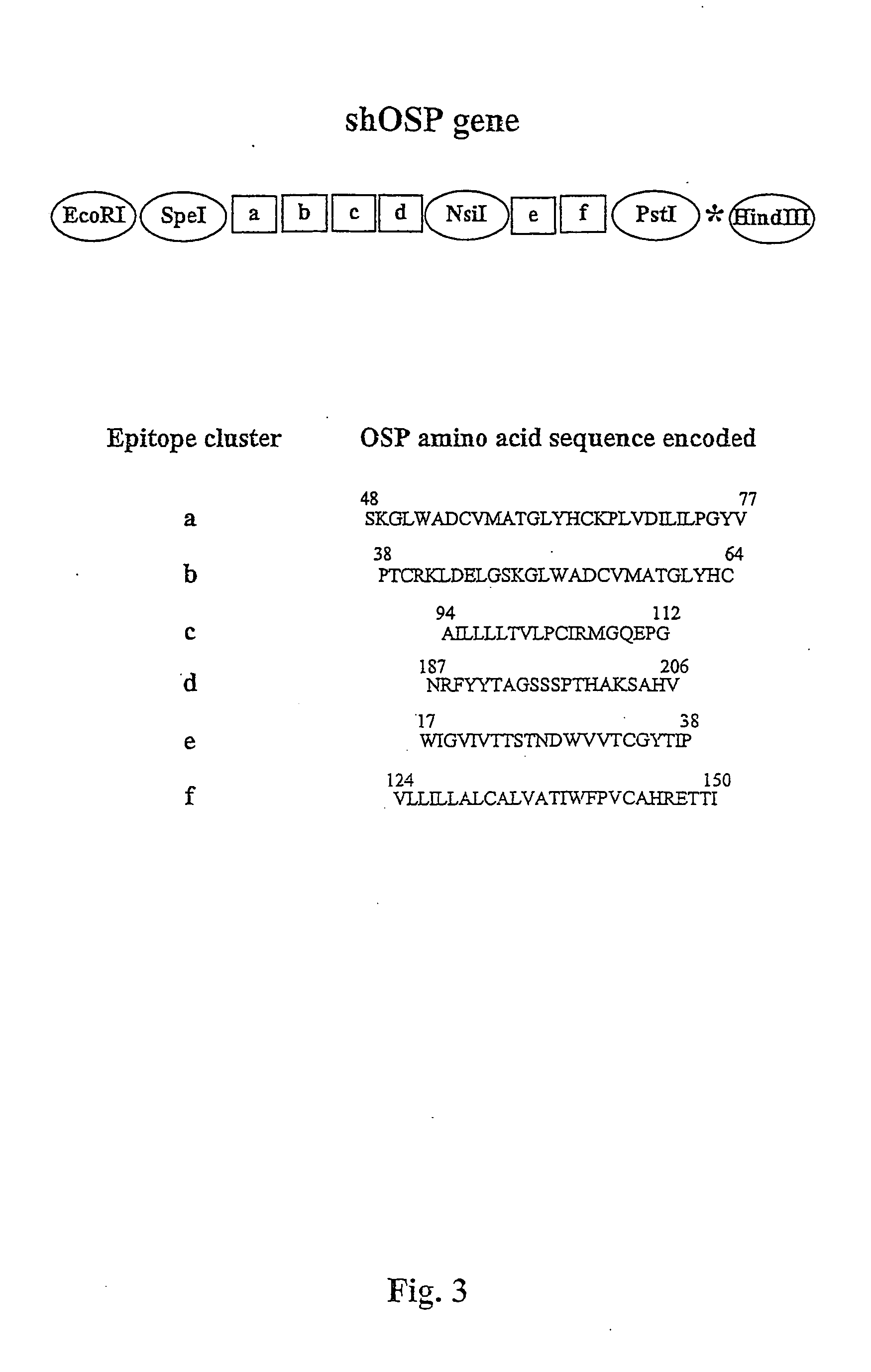
Synthetic unaltered and altered peptides comprising sequences of at least one immunogenic epitope cluster (IEC) of at least one human autoantigen related to multiple sclerosis (MS) and at least one nonameric core sequence which fits into the MS-relevant HLA-DR / DQ molecule and is flanked by 2-5 amino acids at its N- and C-termini, are provided. The alteration is preferably by substituting 1 to 3 TCR contact residues by Ala. The autoantigen is preferably MOG, MBP, OSP, MOBP and PLP. Polypeptides comprising at least two such peptides of a sole autoantigen or at least one peptide of two different autoantigens, and synthetic genes encoding them, are also provided, as well as pharmaceutical compositions for treatment and diagnostic of MS.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Method for producing a synthetic gene or other DNA sequence
InactiveUS20050106590A1Easy to assembleLikelihood of synthesizing the correct DNA sequenceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSingle strandNucleic acid sequencing
Disclosed herein is a method for synthesizing a desired nucleic acid sequence. The method comprises dividing the desired sequence into a plurality of partially overlapping segments; optimizing the melting temperatures of the overlapping regions of each segment to disfavor hybridization to the overlapping segments which are non-adjacent in the desired sequence; allowing the overlapping regions of single stranded segments which are adjacent to one another in the desired sequence to hybridize to one another under conditions which disfavor hybridization of non-adjacent segments; and filling in, ligating, or repairing the gaps between the overlapping regions, thereby forming a double-stranded DNA with the desired sequence. Also disclosed is a method for preventing errors in the synthesis of the nucleic acid sequence.
Owner:UNIVERSTIY OF CALIFORNIA
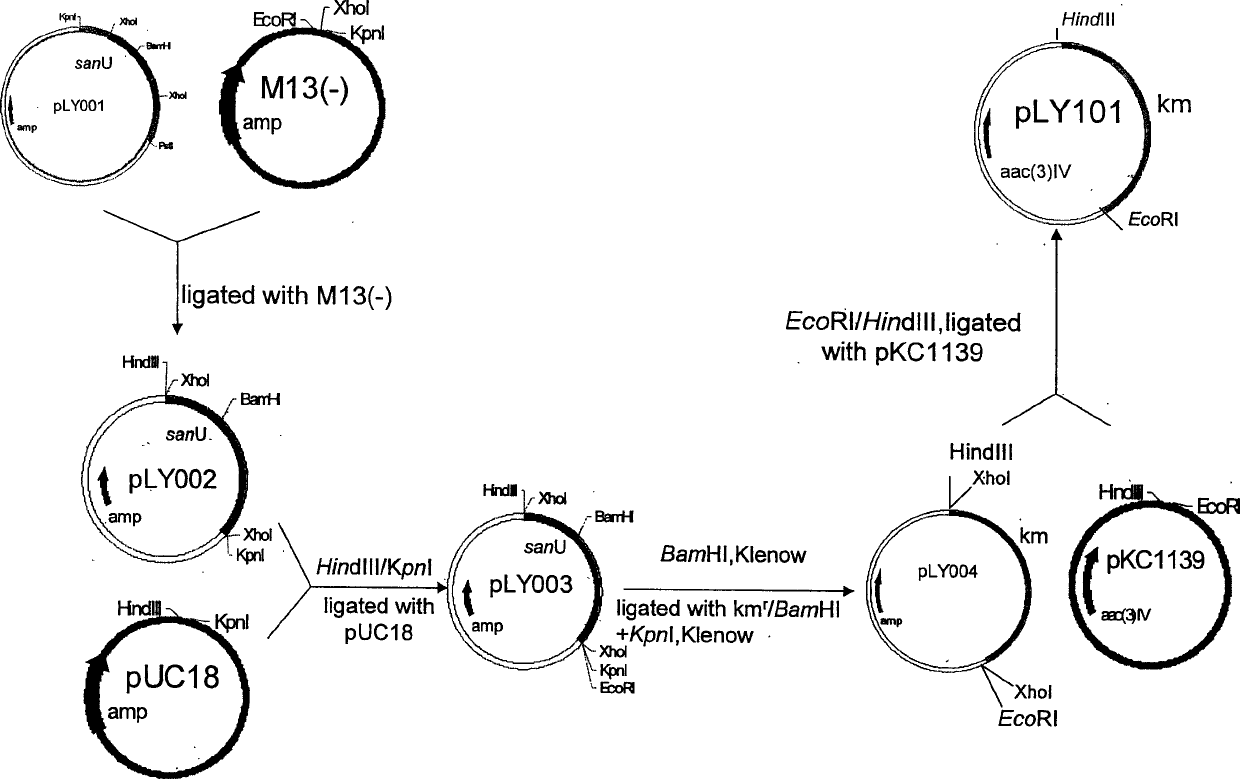
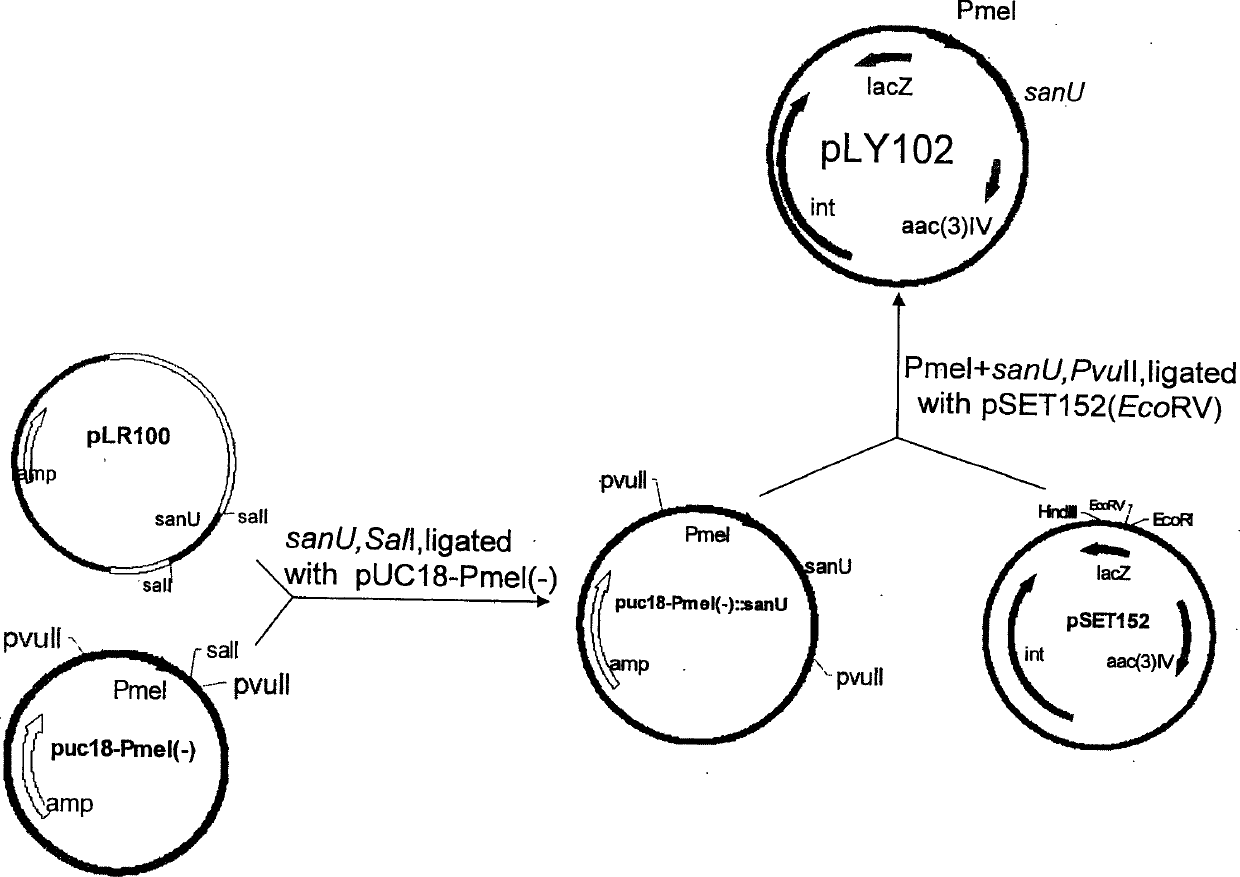
High-yield engineering bacterium of nicomycin x component and its application
The present invention belongs to the field of antibiotic gene engineering, and is especially the process of cloning nicomycin biological synthetic gene sanU from one strain of Streptomyces ansochromogenes 7100 CGMCC 4.321; connecting the synthetic gene sanU with promoter of melanin biosynthetic structure gene, cloning onto the polycloning site of integrative single-copy plamid, transforming wild Streptomyces ansochromogenes 7100 CGMCC 4.321 protoplast to obtain nicomycin X component of the recombinant engineering bacterium in the yield 2 times higher than wild strain. The high-yield engineering bacterium may be used in preparing antiseptic medicines.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant plasmid as well as preparation method and application of astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant plasmid
InactiveCN103805623ARealize accumulationBuild accuratelyMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionAstaxanthinBetaxanthins
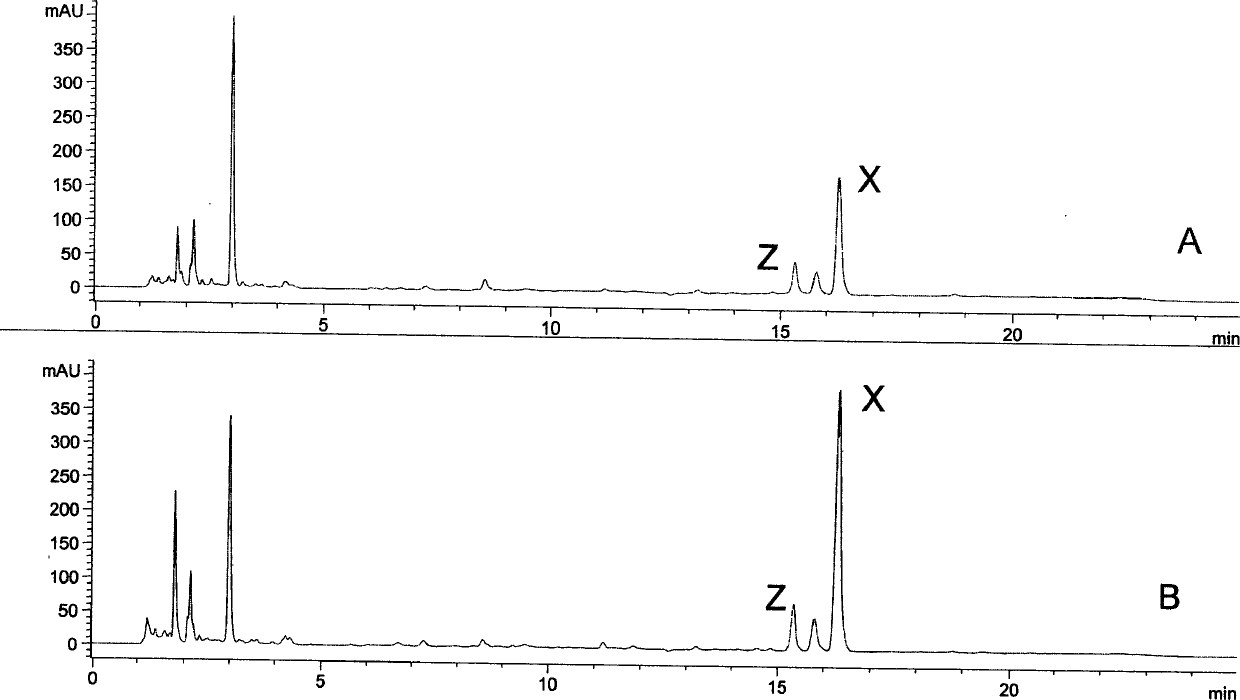
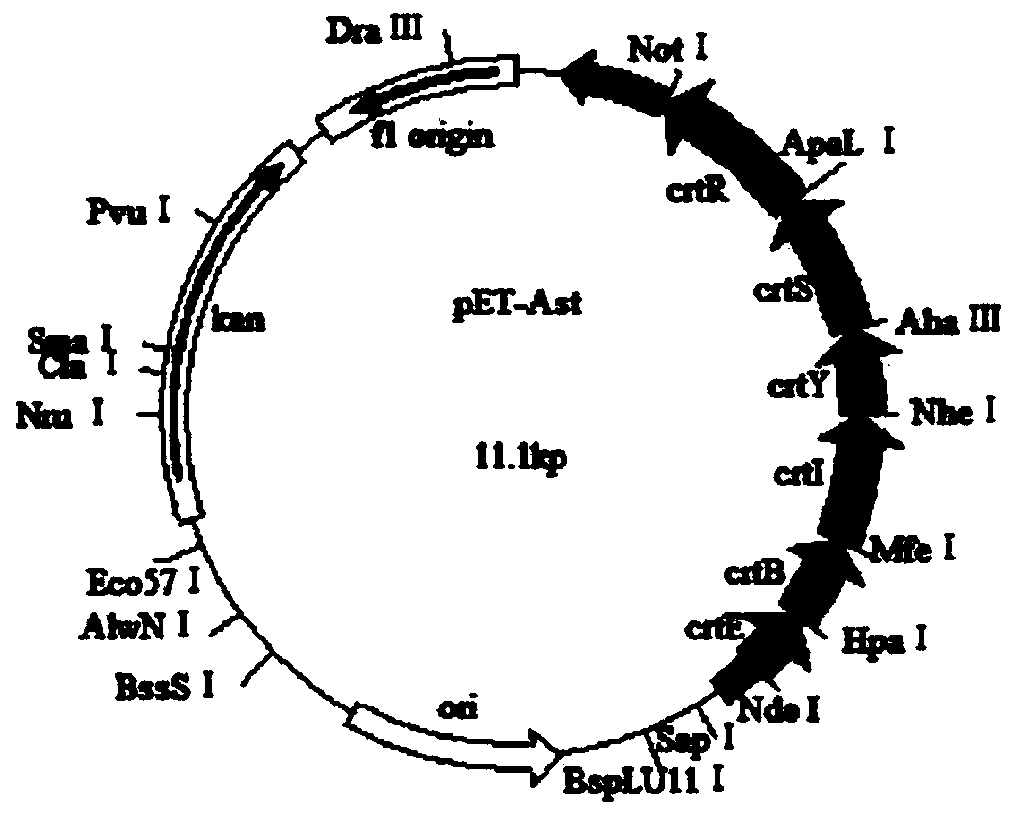
The invention discloses an astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast with a base sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast, an application of the recombinant plasmid pET-Ast to the detection of astaxanthin synthetase activity of a target receptor, and an application method. After the astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast provided by the invention is introduced to an Escherichia coli BL21 strain, the accumulation of astaxanthin in a cell body of Escherichia coli is successfully realized, so that an astaxanthin production strain can be accurately and rapidly established. The preparation method of the astaxanthin synthetic gene recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast is simple and convenient, easy to operate and low in cost. By using the method disclosed by the invention, a gene sequence to be detected in the target receptor can be replaced with a related gene sequence in the recombinant expression plasmid pET-Ast through digestion and connection, and then, the function of a gene to be detected in the target receptor can be simply and effectively detected and verified through detecting whether the astaxanthin is accumulated in a host cell body.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY
Method for increasing streptomyces secondary metabolite yield
ActiveCN107805640AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationMetaboliteStreptomyces
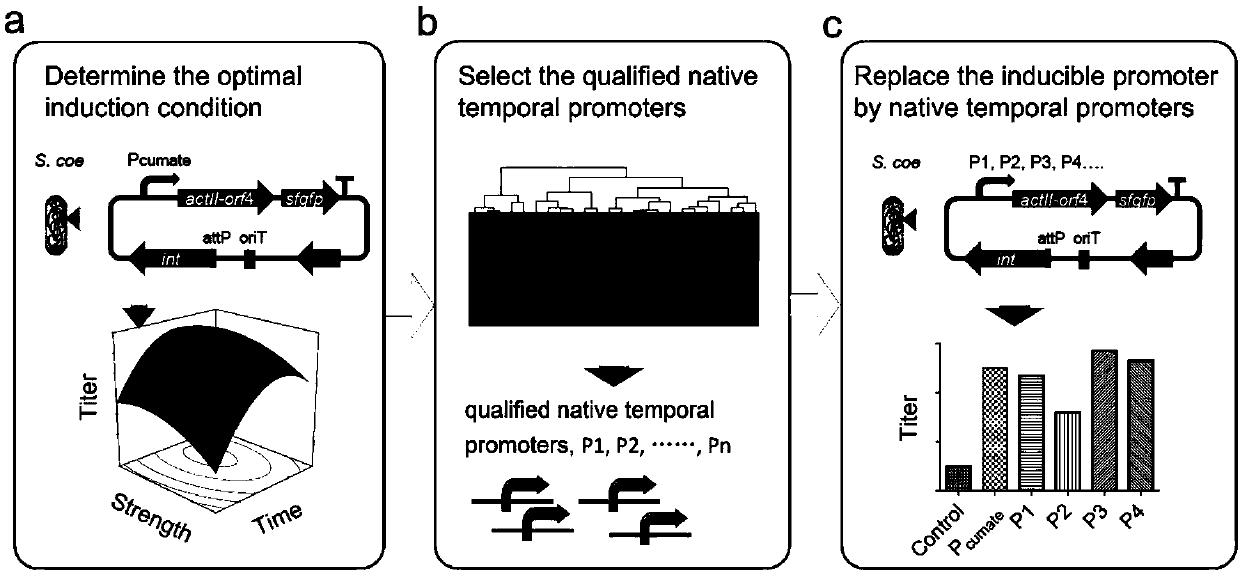
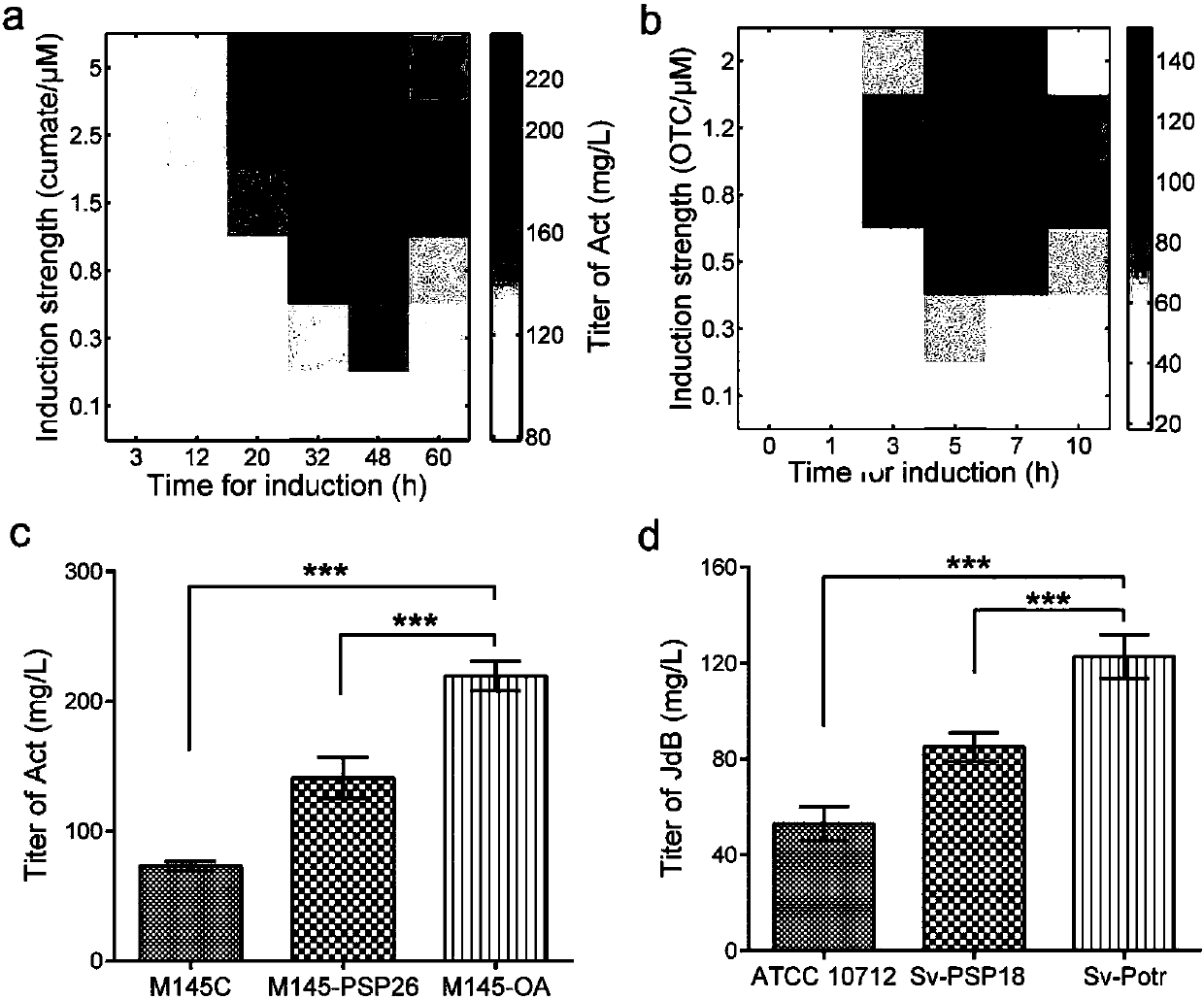
Belonging to the genetic engineering and fermentation engineering field, the invention provides a method for increasing streptomyces secondary metabolite yield. The method includes the steps of: utilizing an induction promoter to control the expression of a target secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene cluster, and determining the optimal induction condition by means of a response surface model; conducting transcriptome analysis to screen a physiological promoter with consistent control behavior to the induction promoter; and finally, preparing plasmid utilizing the physiological promoter to control the expression of the target secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene cluster, and transferring the plasmid into host bacteria for fermentation. The method provided by the invention can get rid of dependency on an inducer, and realizes self-regulation of target biosynthetic gene cluster expression and increase of the target product yield. The method provided by the invention regulates the expression of secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene cluster from the dimensions of time and intensity, makes the expression fit the physiological metabolic behaviors of the host, and is very important for increasing the yield of the target secondary metabolite in streptomyces.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com