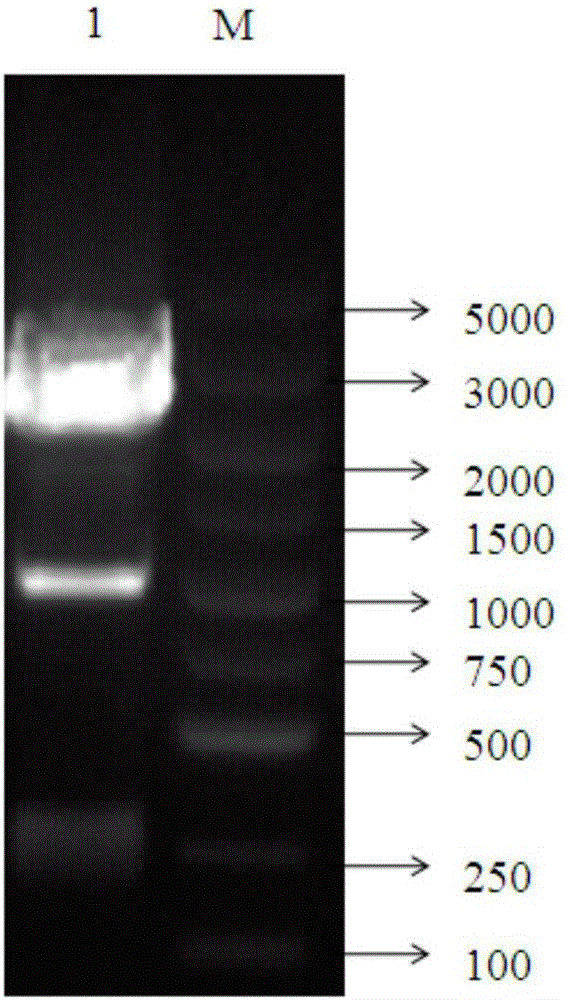
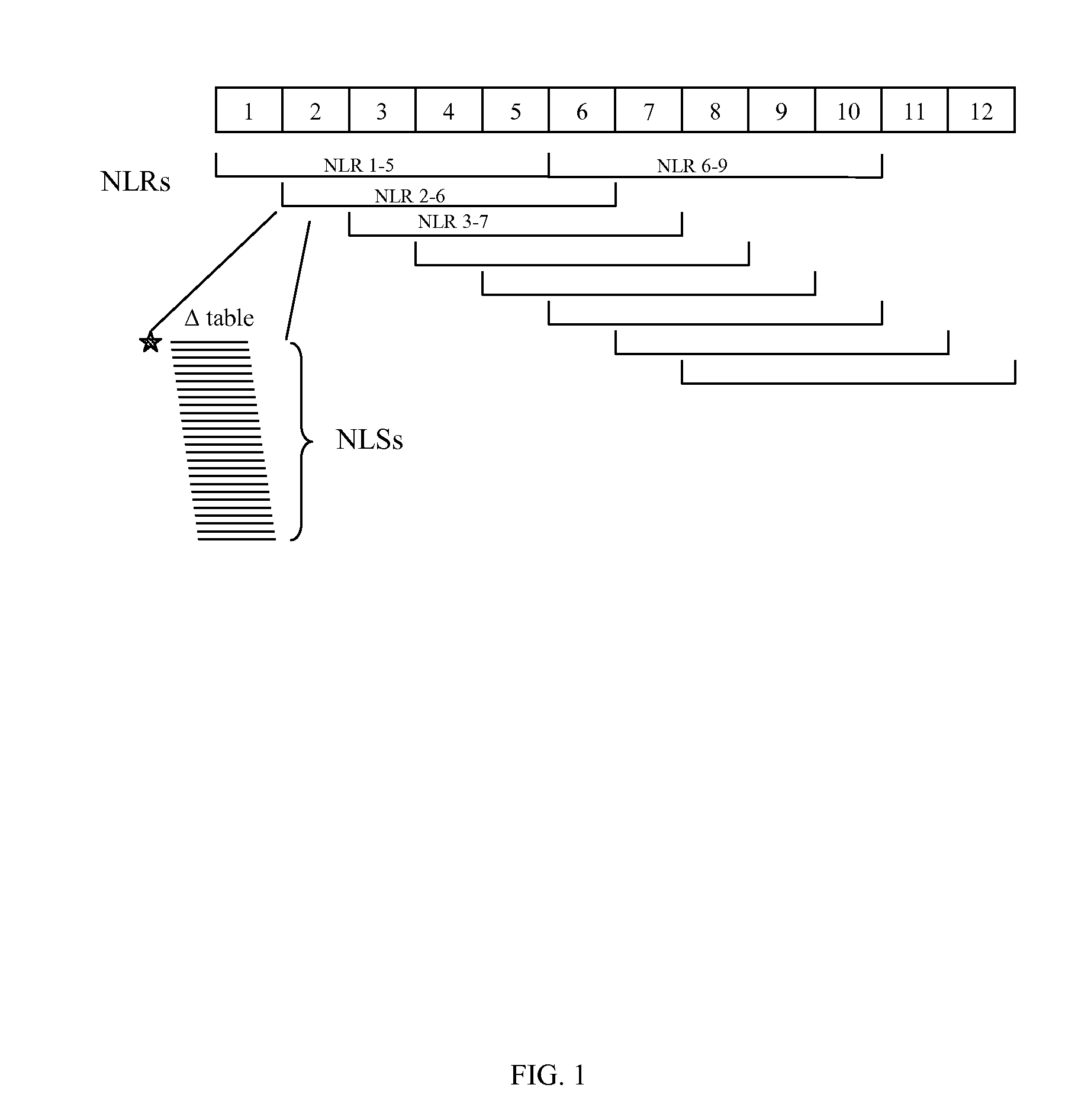
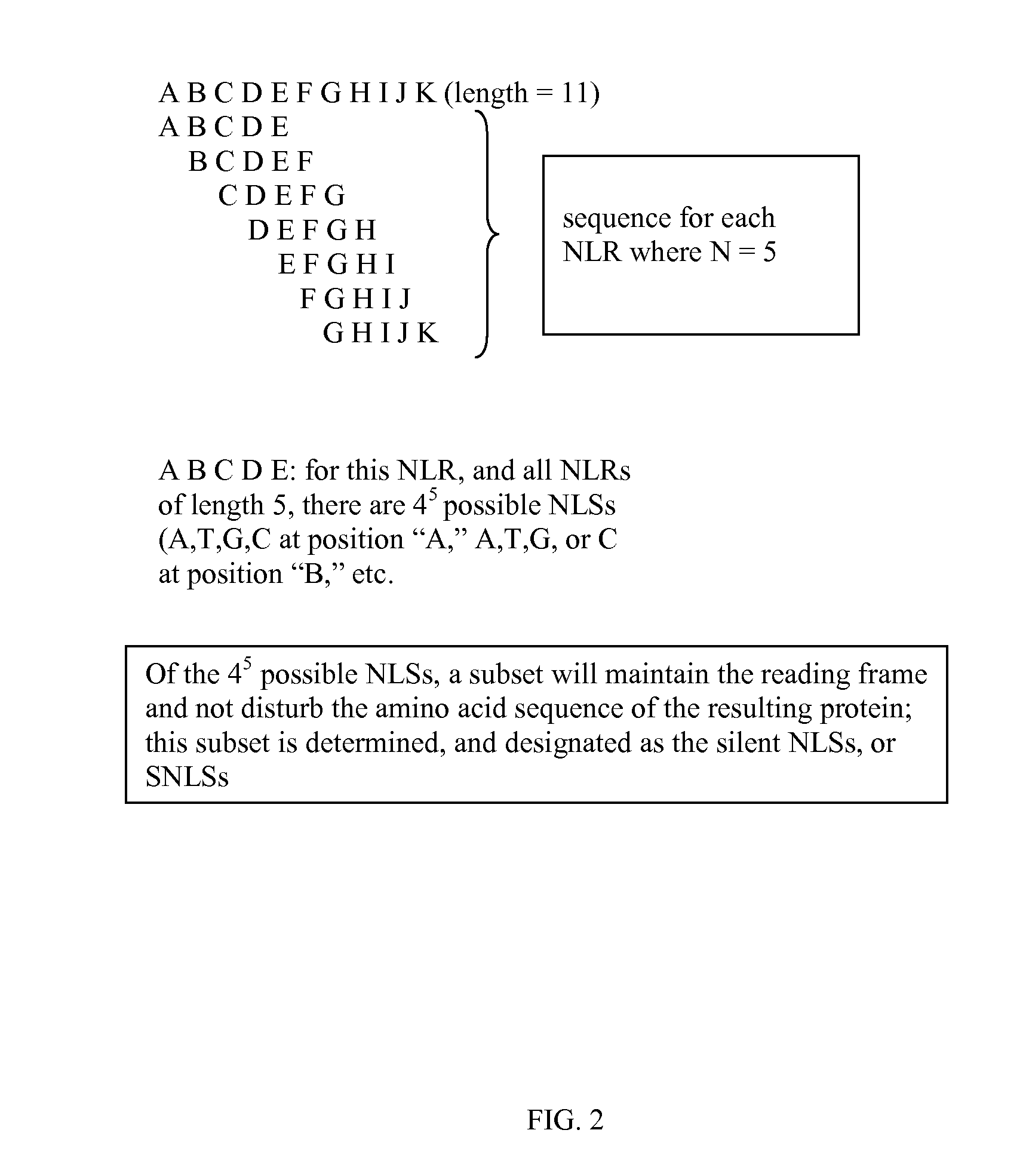
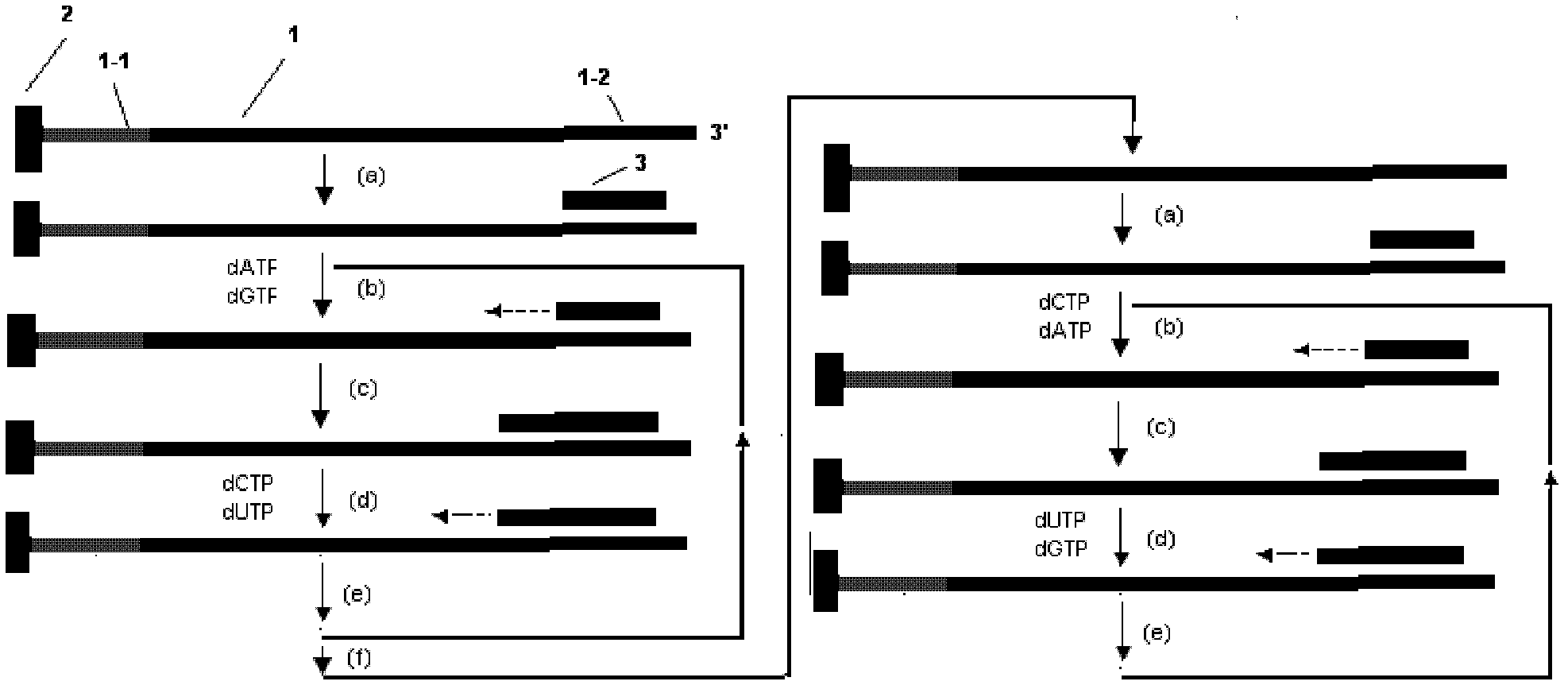
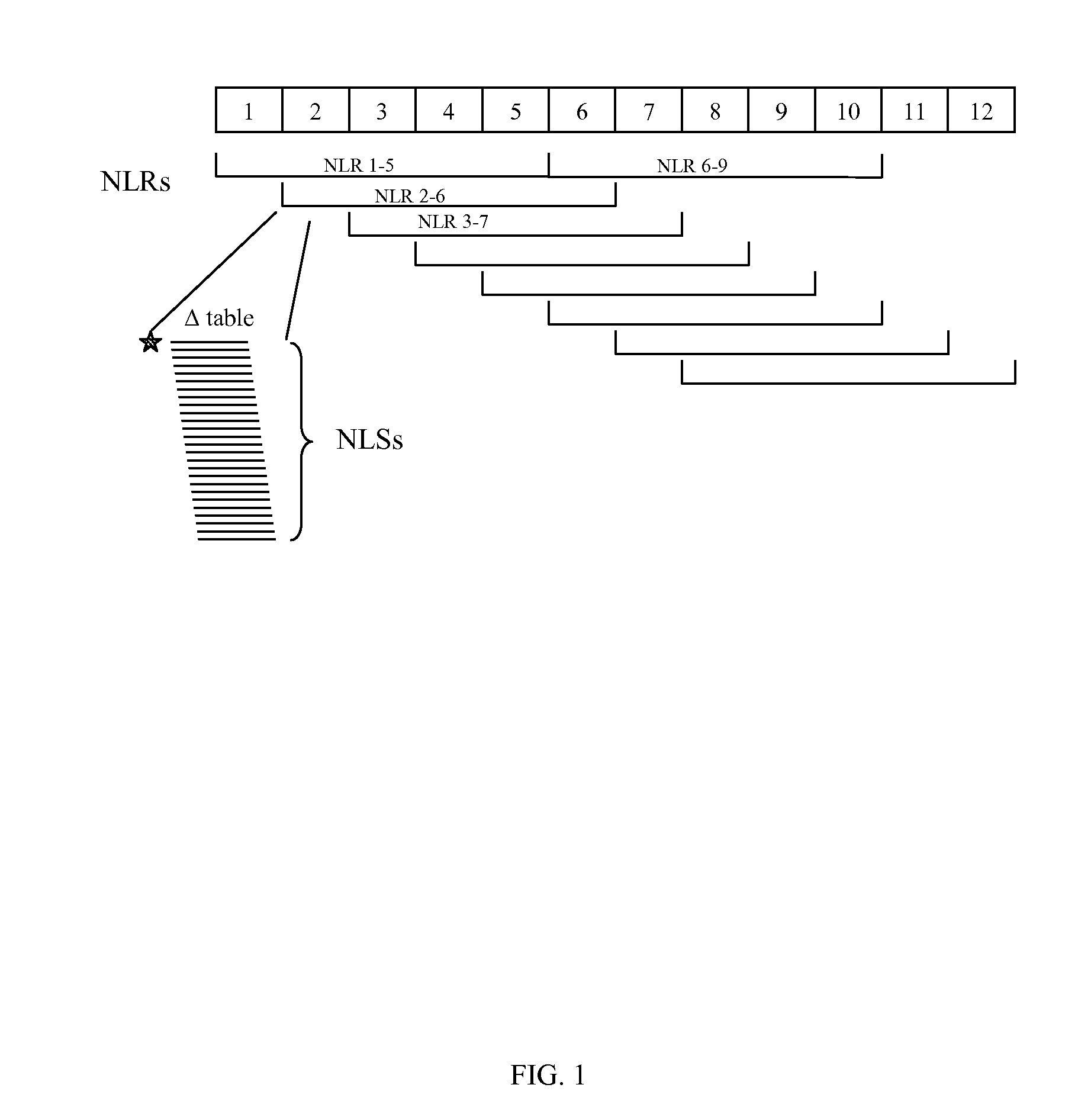
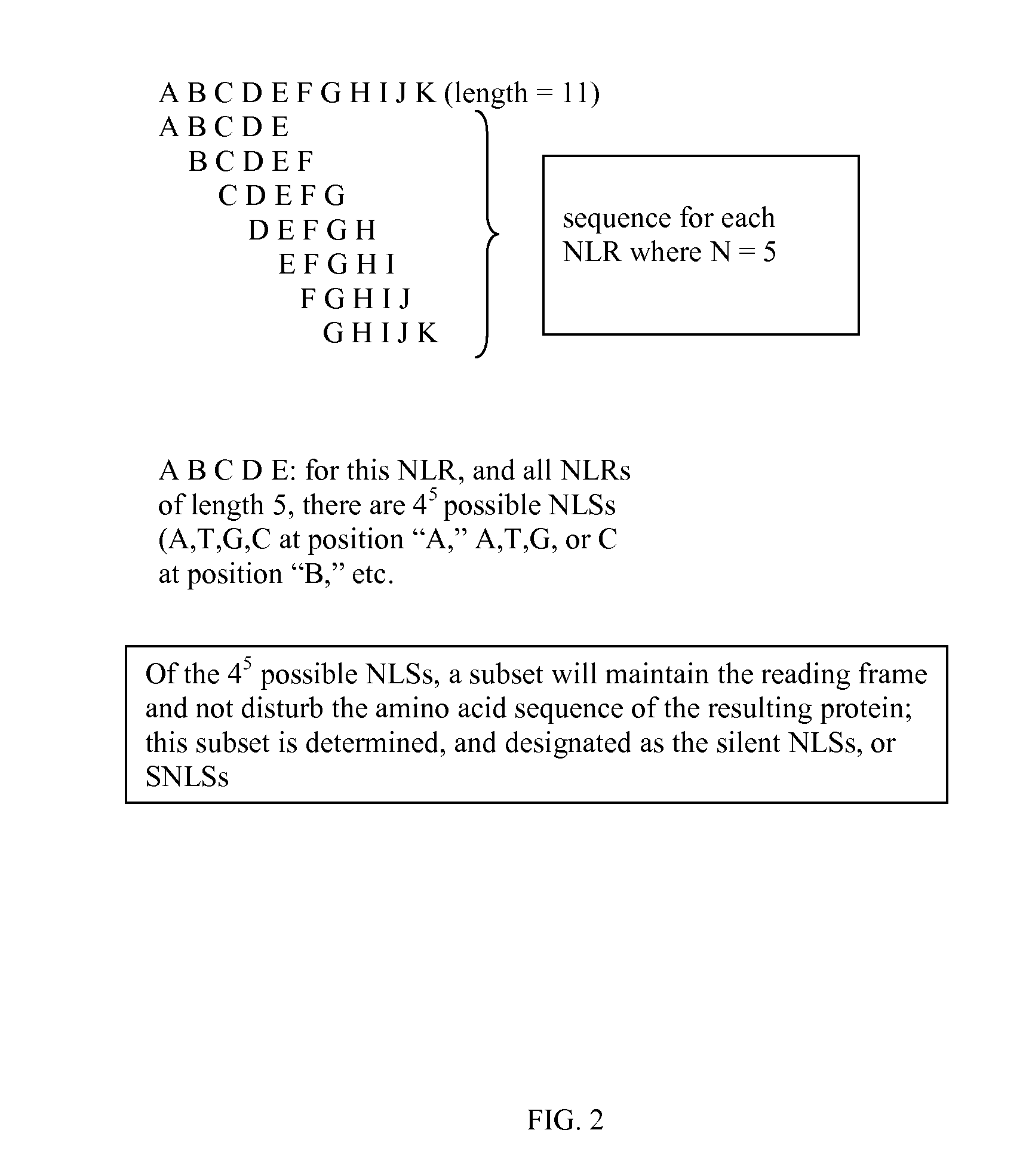
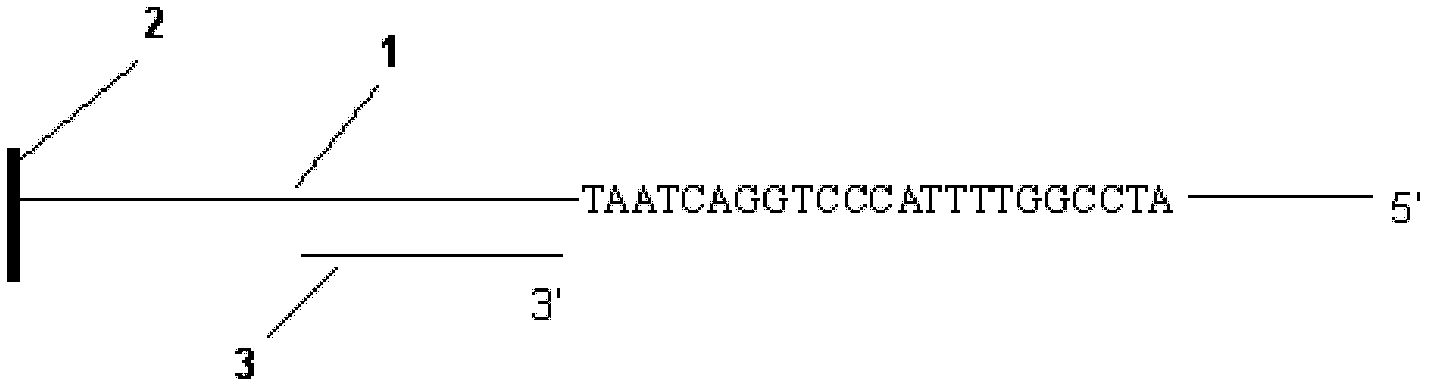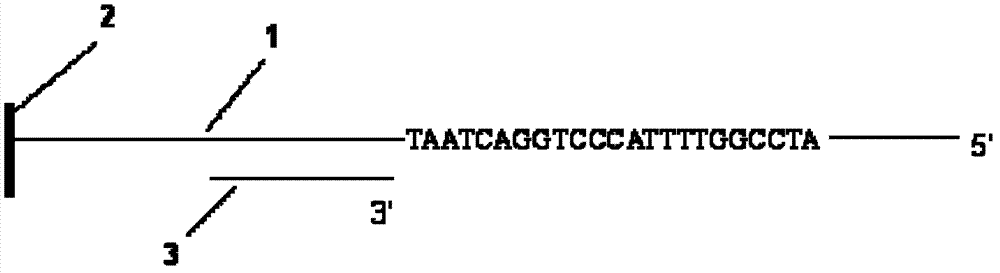Patents
Literature
50 results about "Synthetic nucleotide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methods for detecting and identifying single molecules
InactiveUS6287765B1Highly specific controlImprove securityNanotechSugar derivativesSynthetic nucleotideMolecular adsorption
Multimolecular devices and drug delivery systems prepared from synthetic heteropolymers, heteropolymeric discrete structures, multivalent heteropolymeric hybrid structures, aptameric multimolecular devices, multivalent imprints, tethered specific recognition devices, paired specific recognition devices, nonaptameric multimolecular devices and immobilized multimolecular structures are provided, including molecular adsorbents and multimolecular adherents, adhesives, transducers, switches, sensors and delivery systems. Methods for selecting single synthetic nucleotides, shape-specific probes and specifically attractive surfaces for use in these multimolecular devices are also provided. In addition, paired nucleotide-nonnucleotide mapping libraries for transposition of selected populations of selected nonoligonucleotide molecules into selected populations of replicatable nucleotide sequences are described.
Owner:MOLECULAR MACHINES
Synthetic genes encoding cry1ac
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions containing a synthetic nucleotide sequence encoding a Cry1Ac protein are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also include transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated pesticidal nucleic acid molecules are provided, wherein the nucleotide sequences are set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:ATHENIX
Protected nucleotide analogs
Disclosed herein are nucleotide analogs with one or more protecting groups, methods of synthesizing nucleotide analogs with one or more protecting groups and methods of treating diseases and / or conditions such as viral infections, cancer, and / or parasitic diseases with the nucleotide analogs with one or more protecting groups.
Owner:ALIOS BIOPHARMA INC
Computational methods for synthetic gene design
The present invention is drawn to methods for designing synthetic nucleotide sequences encoding polypeptides of interest. The methods involve organizing a database of sequences as a set of N-length oligomer sequences and compiling a list of probability scores for each N-length sequence. The probability scores are used to substitute one or more higher-scoring sequences into the parent nucleotide sequence to generate an optimized sequence. The nucleotide sequence of interest may be further optimized by removing either or both of unintended open reading frames or undesired short DNA elements, and / or substituting oligomer sequences to achieve a specific G:C content. These methods may be used for optimizing expression of heterologous genes in any organism, particularly in plants. The method generates synthetic sequences with a composition similar to that of a target database. These synthetic sequences may be used, for example, for regulating pesticidal activity or herbicide resistance in organisms, particularly plants or plant cells.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
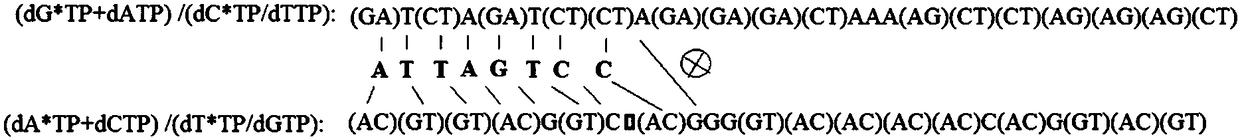
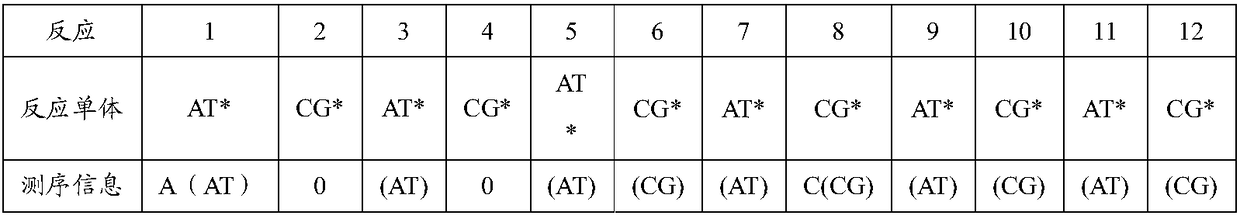
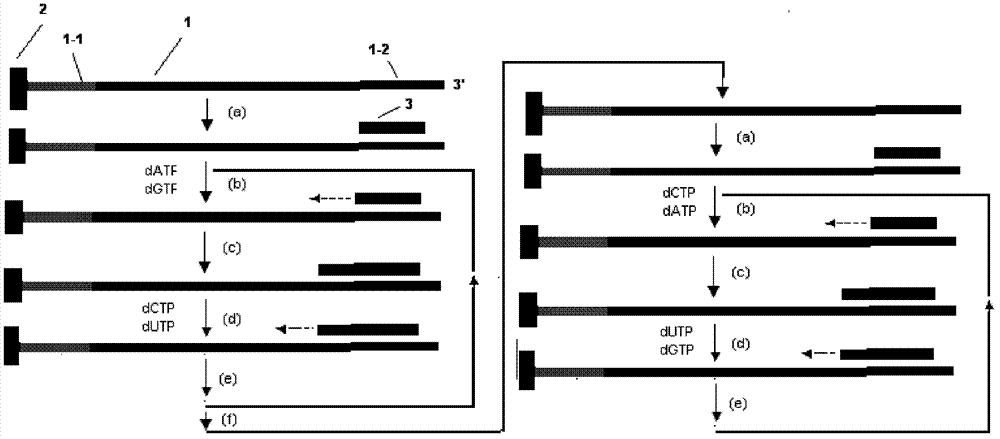
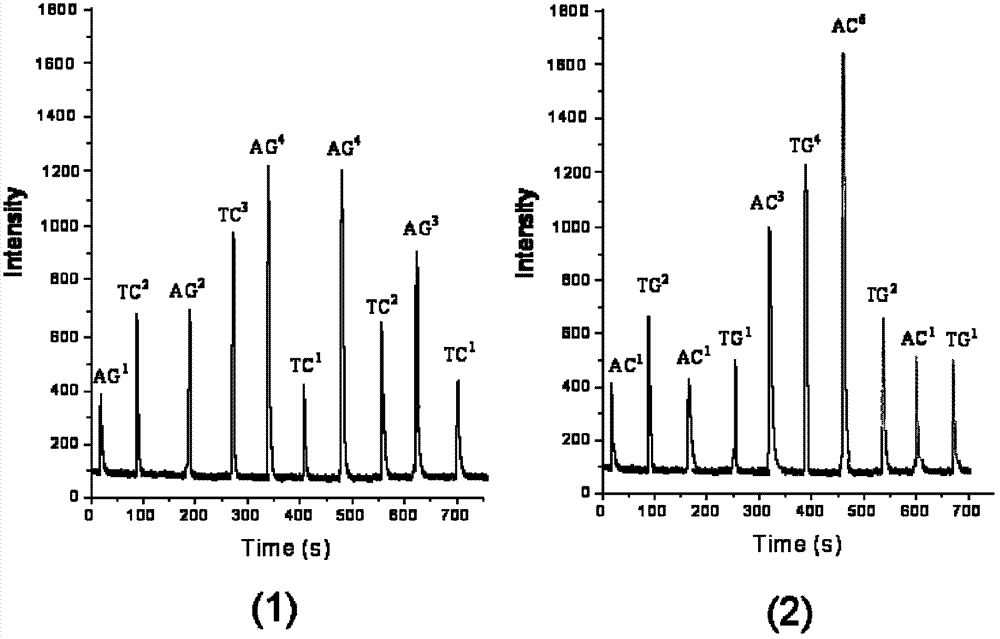
Decoding and sequencing method by real-time synthesis of two nucleotides into deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
InactiveCN102634586AIncrease the lengthLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic nucleotideDeoxycytidine triphosphate
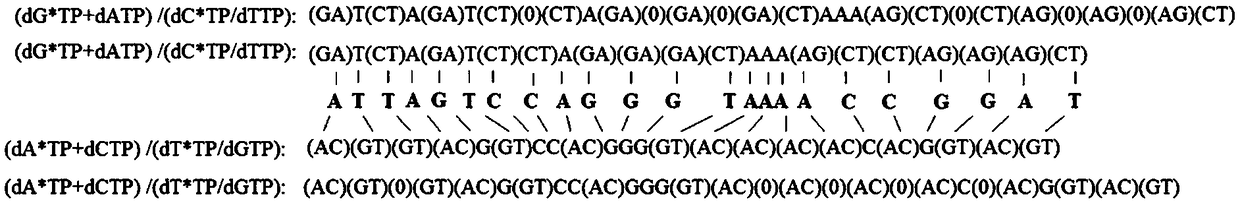
The invention discloses a decoding and sequencing method by real-time synthesis of two nucleotides into deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Single-sequencing reactions are performed on two different nucleotides of X and Y simultaneously and a base sequence fragment code of XYn is obtained according to the quantitative relation between the number of synthesizing nucleotides and the number of the detected molecules which are generated in real time. The sequencing comprises two sets of sequencing reactions on the same template; and in either set of sequencing, a cycle that two different nucleotides synthesize the sequencing reaction simultaneously is performed on deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP), deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP), deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP) and deoxy-thymidine triphosphate (dTTP) containing four nucleotides in the mode that each nucleotide is used once in a cycle. After a plurality of sequencing reactions, information of a plurality of XYn ranked according to a sequencing order by the first set is obtained. When the set of sequencing reactions is completed, denaturation is performed to eliminate the extended strand of a sequencing primer and the sequencing primer is re-crossed to perform the second set of sequencing reactions; information of a plurality of XYn ranked by the second sequencing reaction is obtained; the specific base sequence of nucleic acid fragment to be detected is assembled by decoding the information of a plurality of XYn ranked according to a sequence order by the two sets.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Human papilloma virus 18 L1 (HPV18L1) polynucleotide sequence and its expression vector, host cell and use
ActiveCN102719453AHigh yieldLow costFungiViral antigen ingredientsSynthetic nucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to a human papilloma virus 18 L1 (HPV18L1) polynucleotide sequence and its expression vector, host cell and use and especially relates to an amino acid sequence of an HPV L1 capsid protein, a synthetic nucleotide sequence for coding the amino acid sequence, a recombinant expression vector containing the synthetic nucleotide sequence, and a hansenula polymorpha expression host strain containing the synthetic nucleotide sequence. The invention also relates to a use of an HPV18L1 protein composed of the amino acid sequence and derivatives of the amino acid sequence in preparation of vaccines. Through modification of a nucleotide sequence of a gene of an HPV18L1 wide-type virus, a recombinant HPV18L1 capsid protein can be highly expressed in a hansenula polymorpha expression system and thus hansenula polymorpha expression system-based industrial production of an HPV18L1 capsid protein is realized. Compared with the existing eukaryotic expression systems, the HPV18L1 polynucleotide sequence and its expression vector and host cell have advantages of higher yield and lower cost.
Owner:天津昕因达生物技术有限公司
HPV16L1 polynucleotide sequence and expression vector, host cell and application thereof
InactiveCN102586287AHigh yieldLow costFungiViral antigen ingredientsHuman papillomavirusSynthetic nucleotide
The invention relates to an HPV16L1 polynucleotide sequence, and an expression vector, a host cell and application of the HPV16L1 polynucleotide sequence. The HPV16L1 polynucleotide sequence comprises an amino acid sequence of recombinant human papillomavirus (HPV) L1 capsid protein, a synthetic nucleotide sequence coding the amino acid sequence, and a recombinant expression vector and a hansenula polymorpha expression host strain comprising the nucleotide sequence. The invention also relates to the application of HPV16L1 protein consisting of the amino acid sequence and derivatives of the HPV16L1 polynucleotide sequence in preparing vaccine. According to the invention, by transforming the nucleotide sequence of HPV16L1 wild type virogene, the recombinant HPV16L1 capsid protein in a hansenula polymorpha system is efficiently expressed, and the HPV16L1 capsid protein can be industrially produced by using the hansenula polymorpha expression system; and compared with the conventional other eukaryotic expression systems, the hansenula polymorpha expression system has the advantages of high yield, low cost and the like.
Owner:王昌华
Compositions for use in security marking
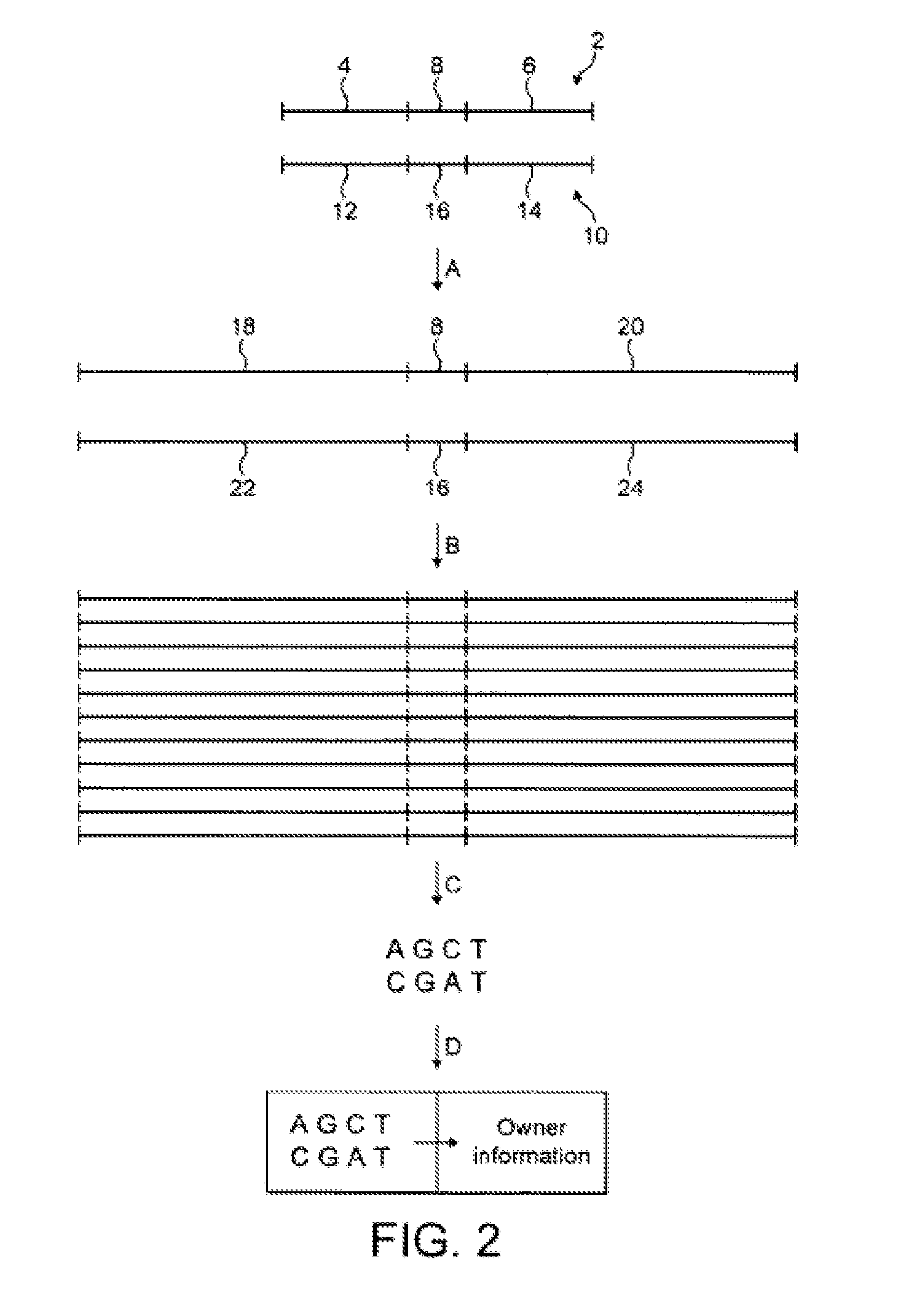
ActiveUS20120135413A1Top level identificationComplex and analysisStampsMicrobiological testing/measurementOligomerSynthetic nucleotide
A composition comprising: a plurality of identical first synthetic nucleotide oligomers; and a plurality of identical second synthetic nucleotide oligomers which are different to the first synthetic nucleotide oligomers, wherein each of the first synthetic nucleotide oligomers comprises a first primer binding sequence of bases, a first identifier sequence of three to seven bases in length, and a second primer binding sequence of bases, the first identifier sequence being disposed between the first and second primer binding sequences, wherein each of the second synthetic nucleotide oligomers comprises a third primer binding sequence of bases, a second identifier sequence of three to seven bases in length, and a fourth primer binding sequence of bases, the second identifier sequence being disposed between the third and fourth primer binding sequences, and wherein the first identifier sequence is different to the second identifier sequence.
Owner:SELECTAMARK SECURITY SYSTEMS PLC
Fluorescent nucleotides
InactiveUS7109314B2Efficient labeling of nucleic acidsReduce negative chargeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic nucleotideFluorescence
According to the present invention, there is provided a fluorescent nucleotide represented by the formula: A-B-C,wherein A represents a residue of natural or synthetic nucleotide, oligonucleotide, polynucleotide, or derivative thereof, and binds to B at a base moiety in said residue; B represents a divalent linking group or a single bond; and C represents a monovalent group derived from a fluorescent dye having 0 or 1 sulfonic acid group or phosphoric acid group in a molecule. The present invention provides useful fluorescent nucleotides for labeling nucleic acids, specifically, fluorescent nucleotides of which uptake ratio is high in synthetic reaction of nucleic acids.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
Glycosyltransferase reversibility for sugar nucleotide synthesis and microscale scanning
InactiveUS20130004979A1Simple methodEfficient synthesisBacteriaSugar derivativesNucleotideChemo enzymatic
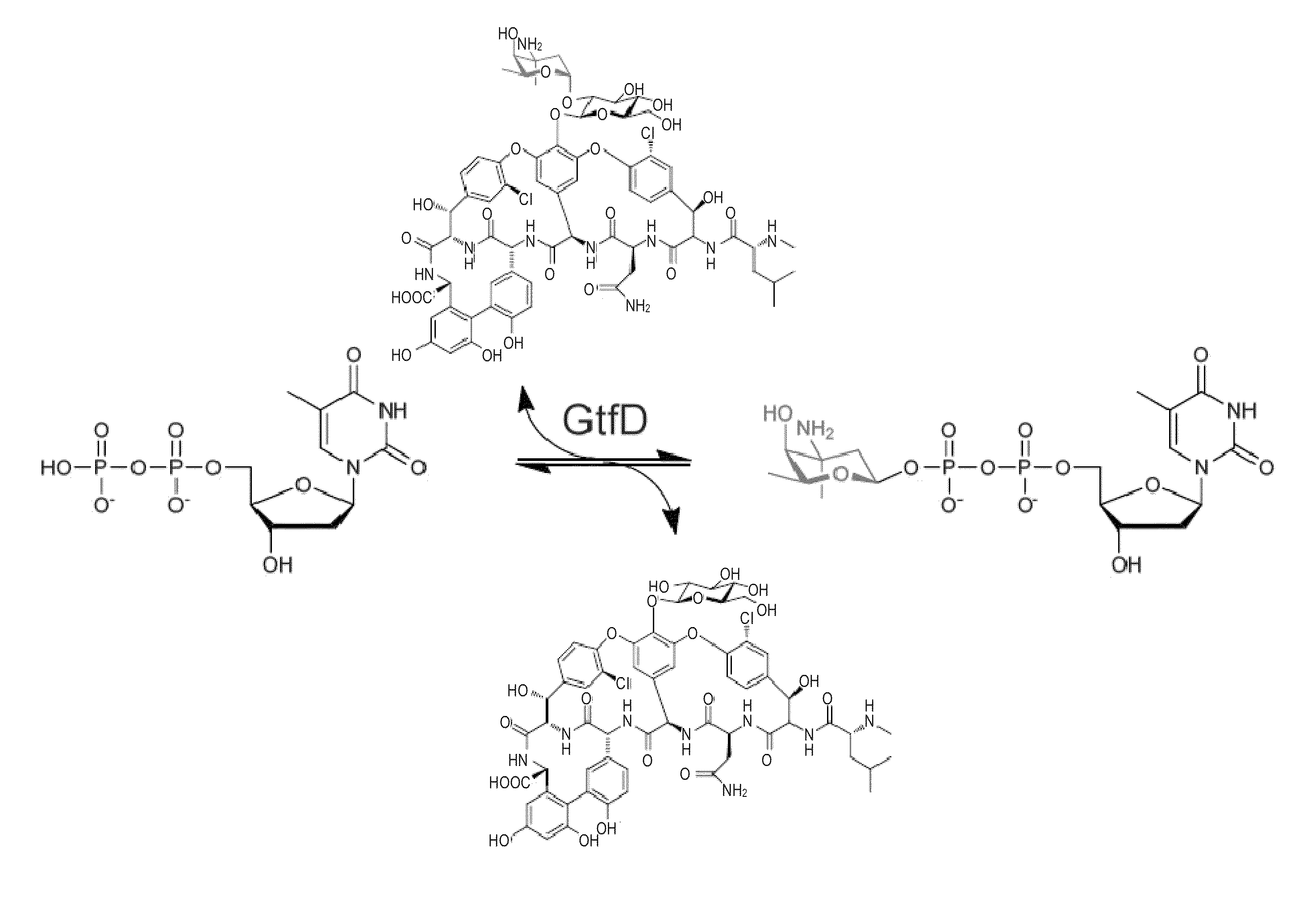
The present invention generally relates to materials and methods for exploiting glycosyltransferase reversibility for nucleotide diphosphate (NDP) sugar synthesis. The present invention provides engineered glycosyltransferase enzymes characterized by improved reaction reversibility and expanded sugar donor specificity as compared to corresponding non-mutated glycosyltransferase enzymes. Such reagents provide advantageous routes to NDP sugars for subsequent use in a variety of biomedical applications, including enzymatic and chemo-enzymatic glycorandomization.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Methods for synthesizing ribonucleotide sequence and acquiring transgenic plant
InactiveCN101173288AMicrobiological testing/measurementDepsipeptidesSynthetic nucleotideRibonucleotide synthesis
The invention discloses an artificially synthesized nucleotide sequence, which is shown by SEQ ID NO: 1. The amino acid sequence for the disinsection protein of the nucleotide sequence coding is as shown by SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also discloses a plasmid of the nucleotide sequence. The invention also disclose the use of the nucleotide sequence, which is a method of getting transgenic plant: the transgenic plant is stably guided. The invention can be used for detecting whether the nucleotide sequence is contained in the transgenic plant.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Construction of temperature-controlled aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacterium started to express excision enzyme of cellulose
ActiveCN104560741AAchieve heat shock expressionThe composition of the enzyme system is reasonableFungiMicroorganism based processesHeat shockTemperature control
The invention discloses construction of a temperature-controlled aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacterium started to express an excision enzyme of cellulose and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacterium disclosed by the invention is an aspergillus niger strain which is integrated with a gene of the excision enzyme of cellulose in a position of a heat shock protein gene. Construction of the aspergillus niger genetically engineered bacterium comprises the following steps: synthesizing a homologous recombinant fragment shown in a nucleotide sequence such as SEQ ID NO. 1; enzyme-digesting the recombinant fragment and a pWM1 plasmid by using Sa1I and then connecting transformed DH5alpha to obtain a homologous recombinant plasmid; transforming agrobacterium by using the homologous recombinant plasmid and obtaining the target strain by agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. According to the invention, heat shock expression of the excision enzyme of cellulose is realized, so that the enzyme constitution of the cellulose of aspergillus niger is reasonable, so that the catalytic capacity of the cellulose is enhanced; the strain constructed does not generate toxins and is high in safety and suitable for industrial application.
Owner:中农华威生物制药(湖北)有限公司
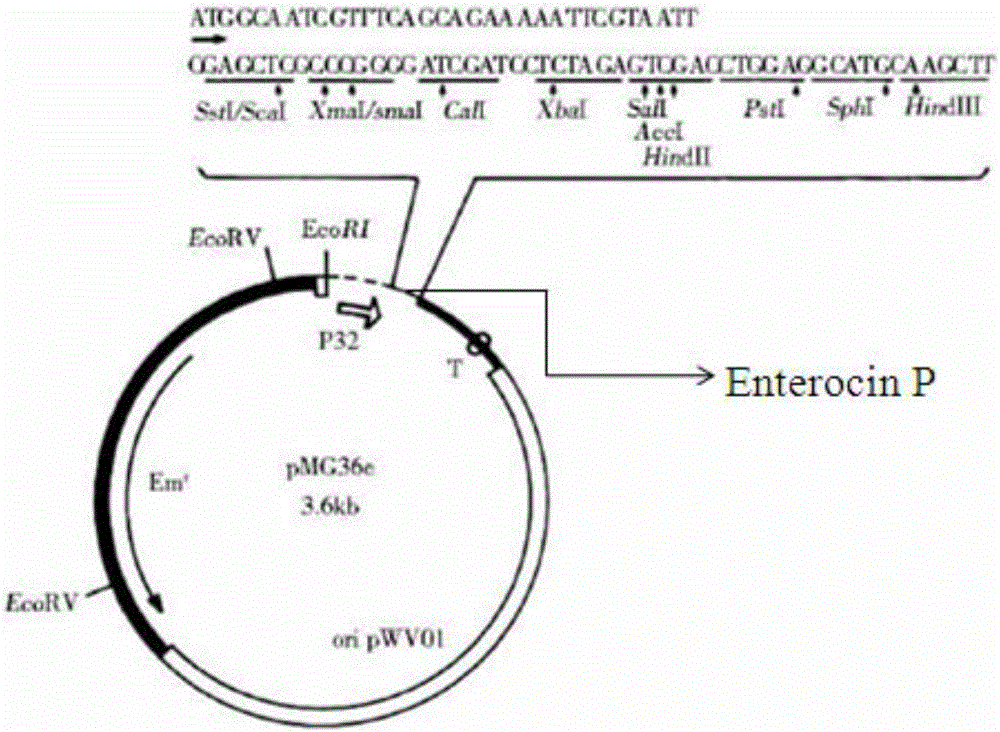
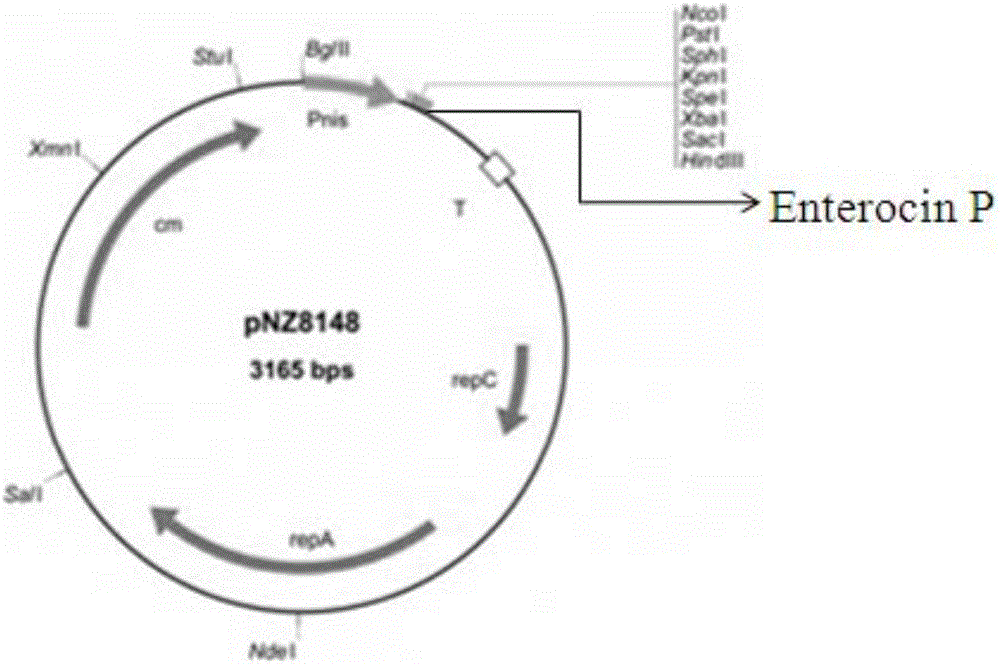
Antibacterial peptide Enterocin P and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105861522AHigh antibacterial activityNo antibiotic resistanceAccessory food factorsNucleic acid vectorSide effectAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of antibacterial peptide Enterocin P. An antibacterial peptide Enterocin P gene has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1. A mature antibacterial peptide Enterocin P coded by the antibacterial peptide Enterocin P gene has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2. The preparation method includes following steps: (1), artificially synthesizing a gene with a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:3; (2), building recombinant plasmid capable of realizing efficient expression; (3), building a gene engineering bacterium of lactococcus lactis NZ900; (4), utilizing the gene engineering bacterium to express the antibacterial peptide; (5), detecting antibacterial activity of the antibacterial peptide. The antibacterial peptide has high antibacterial activity to pathogenic bacteria and is safe, nontoxic and free of side effect.
Owner:源耀生物科技(盐城)股份有限公司
Improved method for producing 5'-flavor nucleotide
InactiveCN102382871AShort cycleUse less bacteriaHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPhosphate
The invention belongs to the technical field of biochemical engineering, relates to an improved method for producing 5'-flavor nucleotide and particularly relates to a method for constructing a gene engineering bacterium through a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) recombination technology, carrying out mutant screening on the gene engineering bacterium and utilizing the high-activity gene engineering bacterium to produce 5'-nucleotide. The method comprises the following steps: 1, through the DNA recombination technology, constructing an acid phosphatase expression vector, and converting into Escherichia coli to obtain a gene engineering bacterium capable of efficiently expressing acid phosphatase; 2, mutating the gene of the acid phosphatase, and screening the acid phosphatase having high affinity with nucleoside; and 3, using the acid phosphatase to catalyze the nucleoside and a phosphate group donor so as to synthesize the 5'-nucleotide. By using the method to realize the catalytic synthesis of the 5'-nucleotide, the invention has the characteristics of simple process, high efficiency, short period, less bacterium consumption, low cost and the like, conforms to environment protection requirements, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI FUCHANG TECH
Preparation and application of myoglobin monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN112521497AShort manufacturing timeHigh expressionImmunoglobulins against animals/humansFermentationEscherichia coliIMMUNE FLUORESCENCE
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention provides a recombinant protein. An amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein is formed by repeatedly connecting two dominantepitopes of myoglobin (Myo) in series, an escherichia coli preferred codon is adopted to convert the amino acid sequence of the recombinant protein into a corresponding nucleotide sequence, the nucleotide sequence is chemically synthesized, and a recombinant expression vector is constructed. Therefore, the expression quantity of the recombinant protein in escherichia coli is increased. The invention also relates to a phage library established by immunizing mice with the recombinant protein, a corresponding myoglobin single-chain antibody scfv sequence is obtained through selecting and screening, the obtained scfv sequence is constructed into a complete mouse IgG1 antibody sequence expression vector, a monoclonal antibody is expressed through transient HEK293F cells, the monoclonal antibody is purified, and an optimal monoclonal antibody pairing combination is determined through an immunofluorescence orthogonal experiment.
Owner:杭州贤至生物科技有限公司
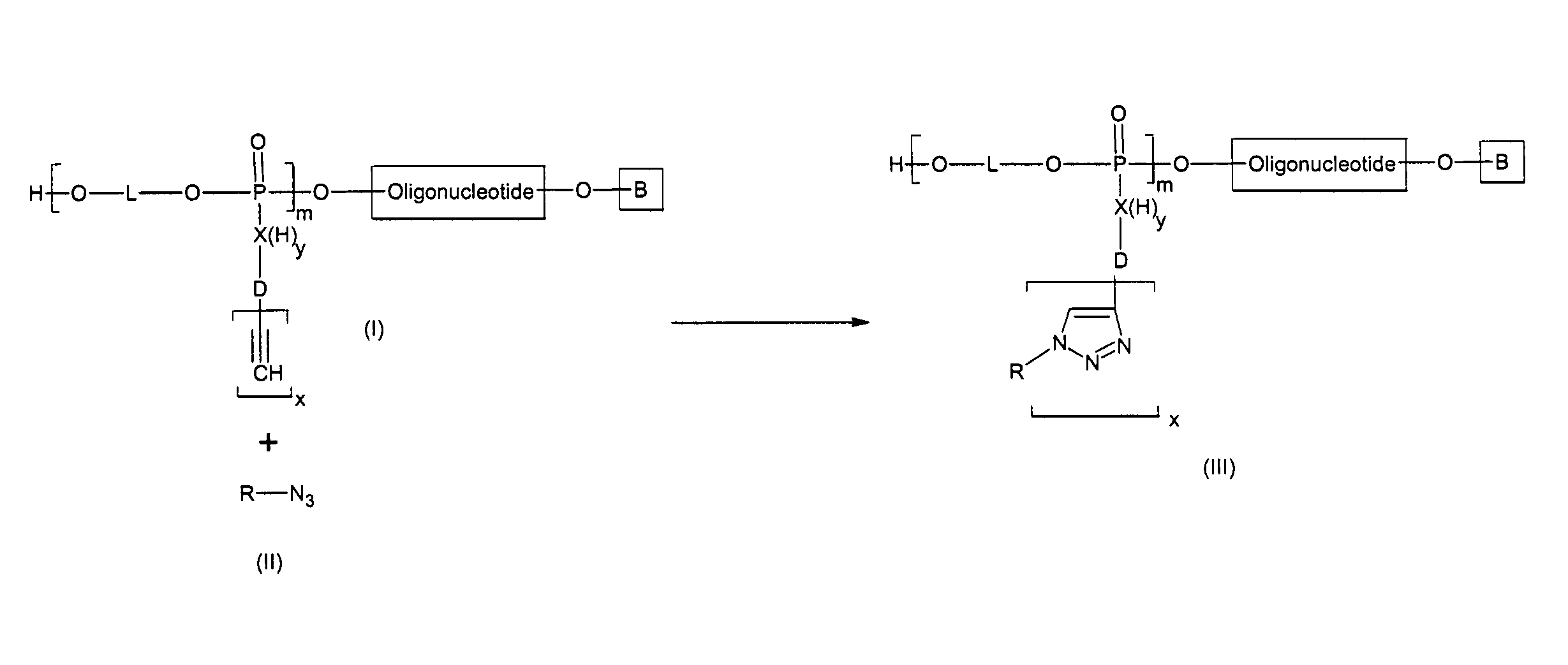
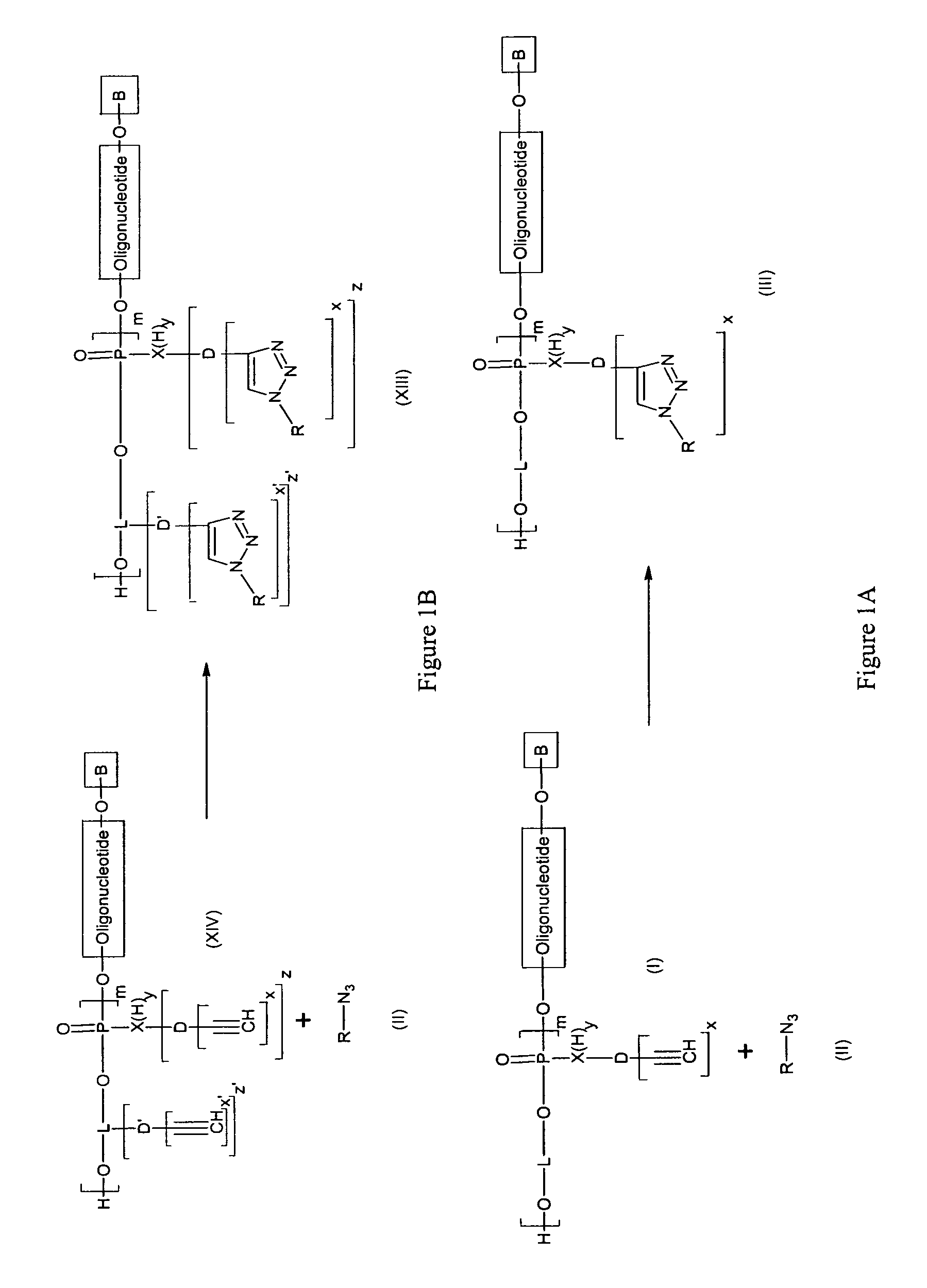
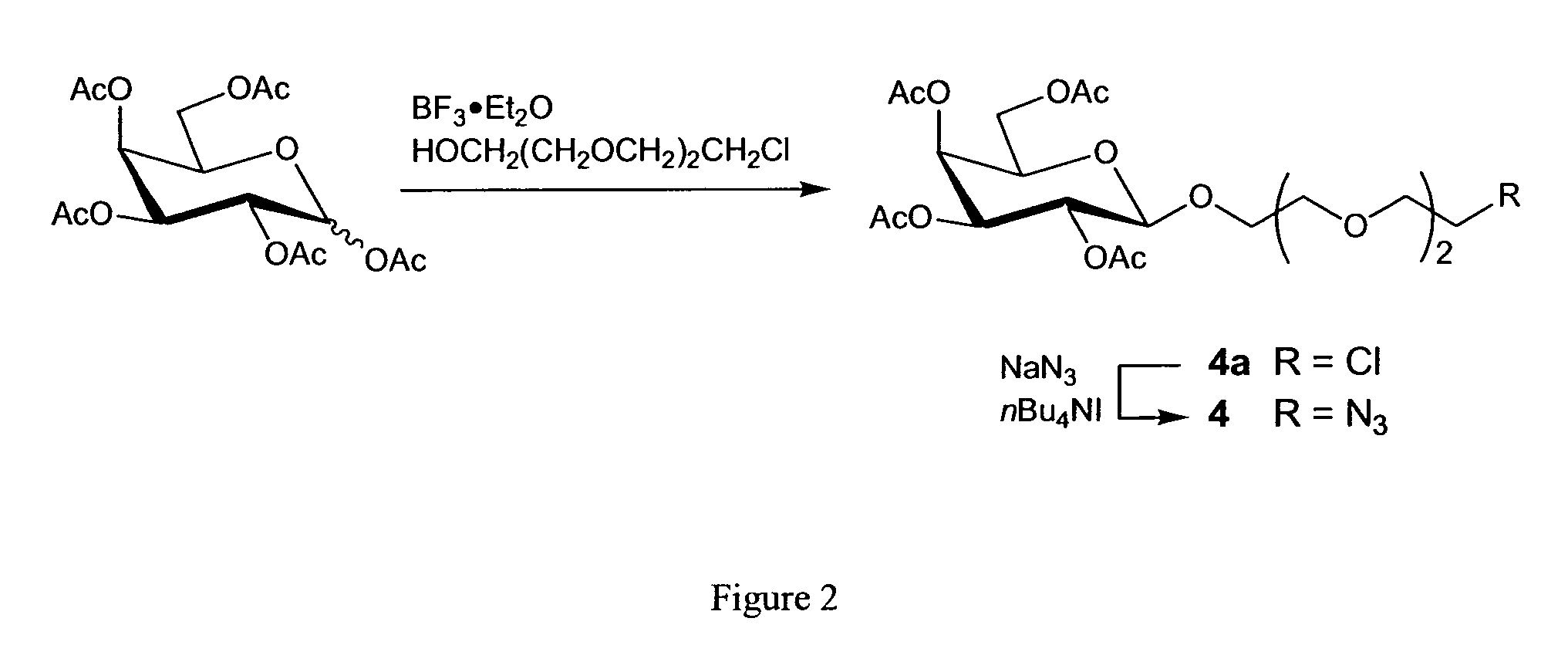
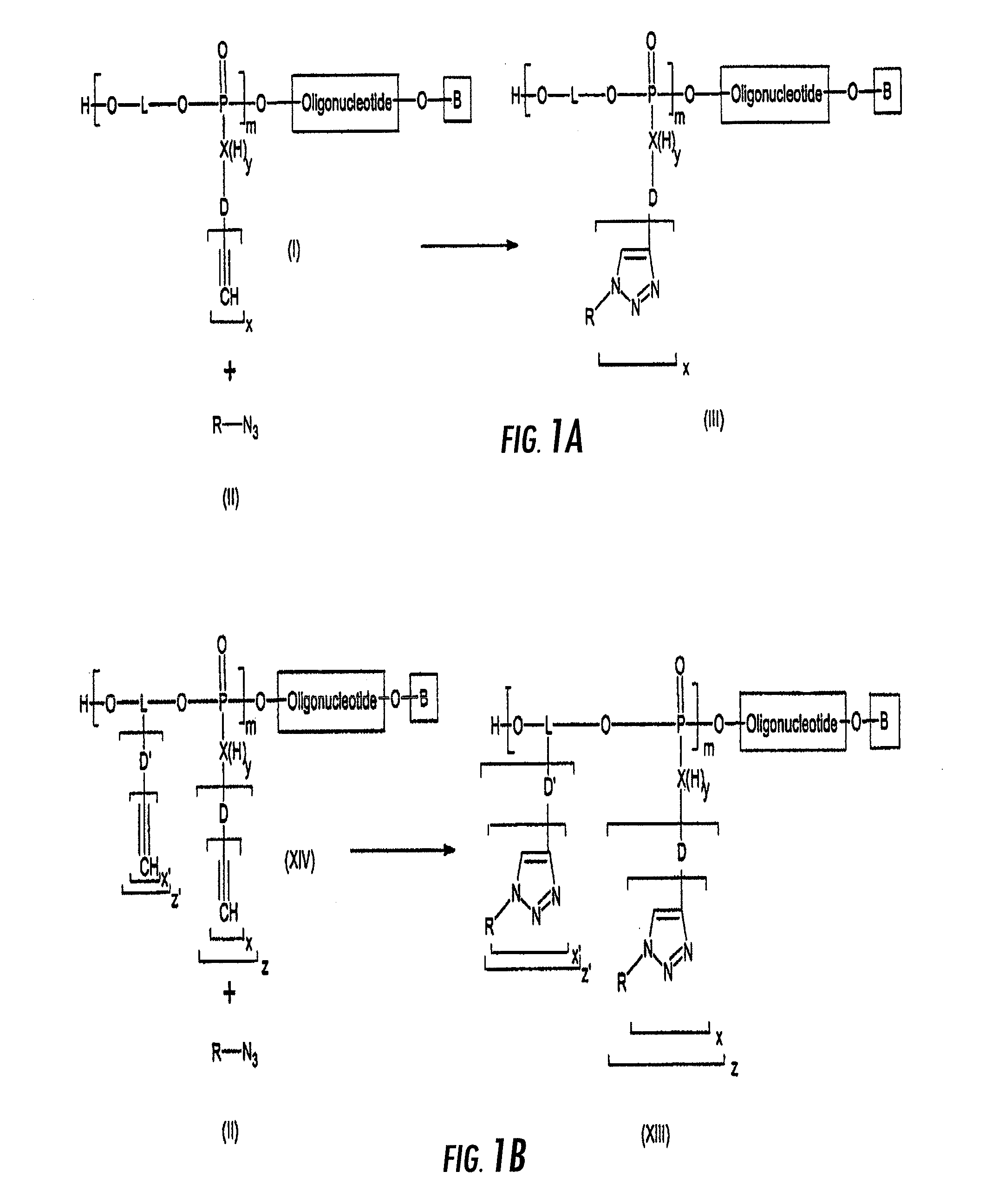
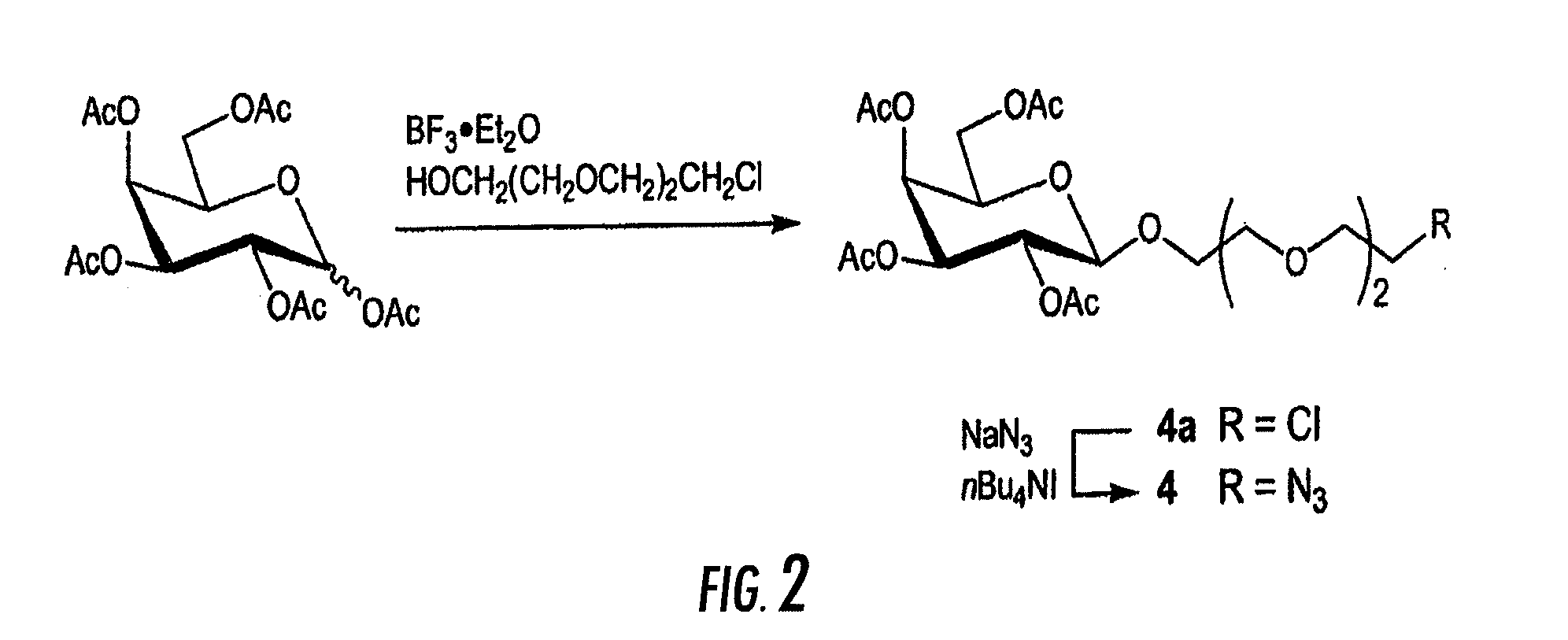
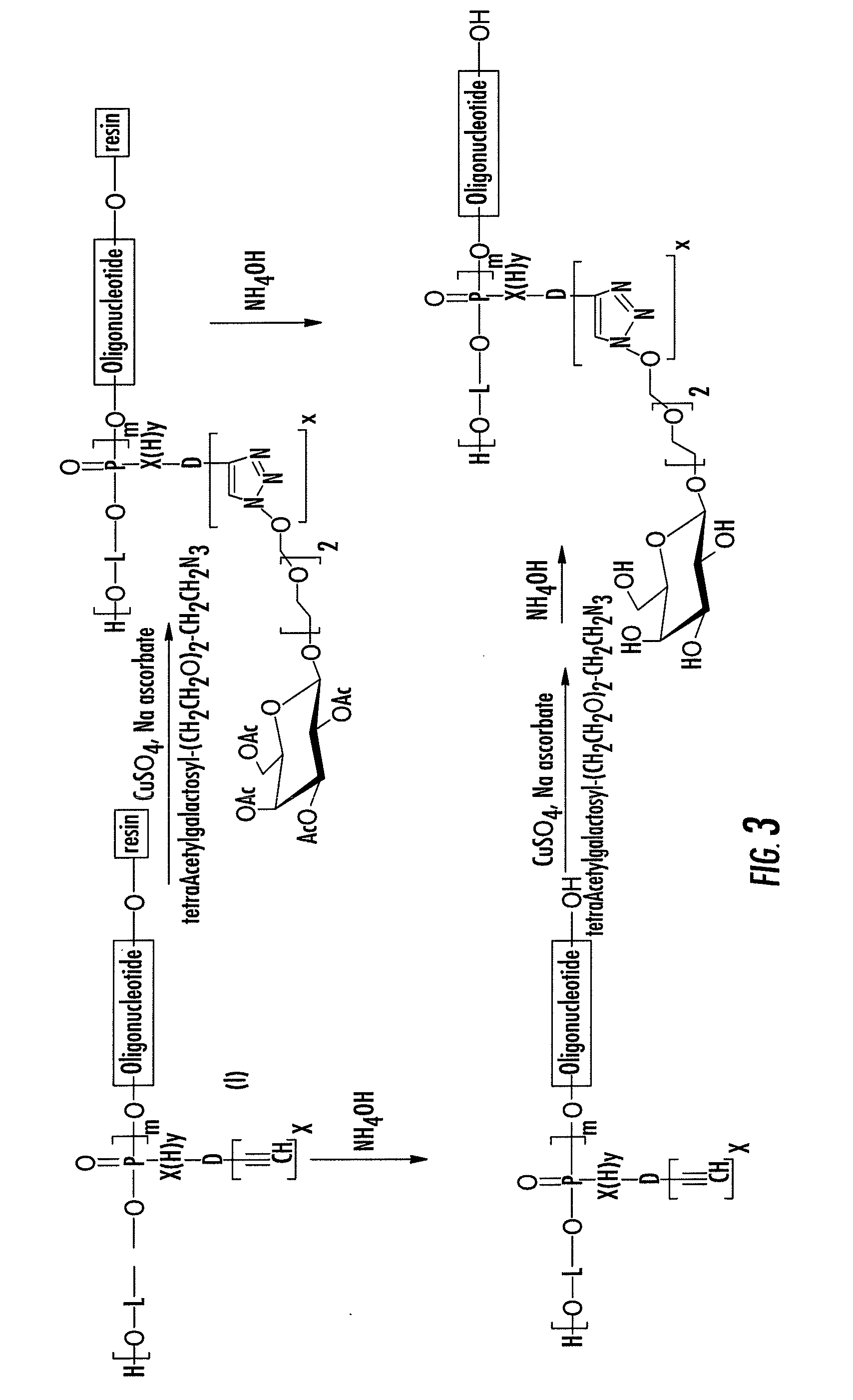
Method for the synthesis of oligonucleotide derivatives
InactiveUS7951926B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic nucleotideBiological studies
Method for the synthesis of nucleotide derivatives wherein molecules of interest are grafted on the oligonucleotide with the help of a “click chemistry” reaction between an azide function on the molecule of interest and an alkyne function on the oligonucleotide, or between an alkyne function on the molecule of interest and an azide function on the oligonucleotide.Intermediate molecules, notably alkyne functionalized oligonucleotides, grafted oligonucleotides, azide functionalized oligonucleotides, oligonucleotide micro arrays containing them and the use of those grafted oligonucleotides for biological investigation and for cell targeting.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
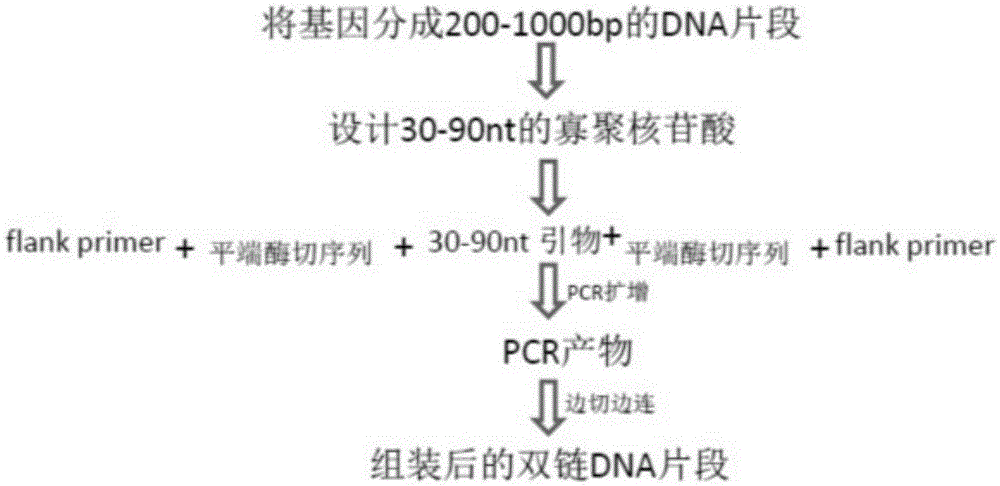
Method for high flux synthesis of nucleotide pool and assembling of double-stranded DNA from semiconductor chips
The invention relates to a method for high flux synthesis of a nucleotide pool and assembling of a double-stranded DNA from semiconductor chips. The method comprises the following steps: 1, dividing a pre-synthesized double-stranded DNA into a plurality of DNA fragments; 2, designing nucleotides by using the DNA fragments; 3, arranging a flank sequence and a recombinase digestion identification sequence to each of two ends of each of the nucleotides to synthesize nucleotide sequences, wherein the nucleotide sequences are prepared from the semiconductor chips; 4, washing out the nucleotides from the semiconductor chips; 5, carrying out PCR amplification with the flank sequence as a primer to obtain a PCR product for later use, wherein the amount of every synthesized nucleotide obtained after the PCR amplification is greatly increased; and 6, splicing the nucleotides by using he recombinase digestion PCR product, and cutting while splicing to obtain double-stranded DNA fragments. The method has the advantages of low cost and high one-time synthesis flux, and can be used in assembling of metabolism pathways, biological approaches, biological element databases or genomes.
Owner:SUZHOU HONGXUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Computational methods for synthetic gene design
ActiveUS8175813B2Microbiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesHeterologousSequence database
The present invention is drawn to methods for designing synthetic nucleotide sequences encoding polypeptides of interest. The methods involve organizing a database of sequences as a set of N-length oligomer sequences and compiling a list of probability scores for each N-length sequence. The probability scores are used to substitute one or more higher-scoring sequences into the parent nucleotide sequence to generate an optimized sequence. The nucleotide sequence of interest may be further optimized by removing either or both of unintended open reading frames or undesired short DNA elements, and / or substituting oligomer sequences to achieve a specific G:C content. These methods may be used for optimizing expression of heterologous genes in any organism, particularly in plants. The method generates synthetic sequences with a composition similar to that of a target database. These synthetic sequences may be used, for example, for regulating pesticidal activity or herbicide resistance in organisms, particularly plants or plant cells.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Preparation method and application of probiotic antibacterial peptide Enterocin B
PendingCN106086041AHigh antibacterial activityNo side effectsAccessory food factorsNucleic acid vectorEnterocin BSynthetic nucleotide
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a probiotic antibacterial peptide Enterocin B genetically engineered bacterium. A probiotic antibacterial peptide Enterocin B gene has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1. Mature antibacterial peptide Enterocin B coded by the probiotic antibacterial peptide Enterocin B gene has an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2. The preparation method includes following steps: (1), artificially synthesizing a gene with a nuceotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:3; (2), establishing recombinant plasmid supportive of efficient expression; (3), establishing a genetically engineered bacterium; (4), utilizing the genetically engineered bacterium to express the antibacterial peptide Enterocin B. The antibacterial peptide enterocin B has high bacteriostatic activity and is safet, nontoxic and free of side effect and antibiotic resistance.
Owner:源耀生物科技(盐城)股份有限公司
Method for constructing cellulase high-yielding strain by expressing doubleactive protein of celluloseexonucleaseand endonuclease
ActiveCN104480139AHigh activityIncrease enzyme activityFungiMicroorganism based processesGenetic engineeringAgrobacterium tumefaciens
The invention discloses amethod for constructing a cellulase high-yielding strain by expressing doubleactive protein of celluloseexonucleaseand endonuclease, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. According to the method, coding genes provided with doubleactive protein of celluloseexonucleaseand endonucleaseare integrated to a position of an aspergillusniger heat shock protein gene with adoption of homologous recombination and genetic engineering technologies. Specifically, a homologous recombinant fragment whose nucleotide sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.1 is synthesized, is digested by Sal I and connected with pWM1 plasmid,DH 5 alpha is transformed, and homologous recombinant plasmid is obtained; the homologous recombinant plasmid is transformed to agrobacterium tumefaciens, and a cellulase high-yielding aspergillusniger strain is obtained through agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation. Expression of interest protein is increased remarkably by increasing the temperature through heat shockexpression, so that the activities of the celluloseexonucleaseand endonuclease are improved remarkably, and the enzyme activity of celluloseis improved.
Owner:中农华威生物制药(湖北)有限公司
Artificial codon optimized pseudorabies virus gE protein and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, in particular to an artificial codon-optimized pseudorabies virus gE protein as well as a coding gene and an application thereof. According tothe invention, the gE-like protein gene which can be recognized by a pseudorabies virus gE antibody is optimized and synthesized through an artificial codon, an expression vector is constructed by utilizing an artificially synthesized nucleotide sequence, and the specific recognition capability of the pseudorabies virus gE protein and the pseudorabies virus gE antibody is analyzed through westernblotting, ELISA and sequencing. The pseudorabies virus gE protein obtained by the invention can be used for preparing a differential diagnosis kit for porcine pseudorabies virus infected wild strains.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Personalized cells, tissues, and organs for transplantation from a humanized, bespoke, designated-pathogen free, (n0n-human) donor and methods and products relating to same
ActiveUS20200283737A1Minimal modificationReduce of causativeNew breed animal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitopeSynthetic nucleotide
A biological system for generating and preserving a repository of personalized, humanized transplantable cells, tissues, and organs for transplantation, wherein the biological system is biologically active and metabolically active, the biological system having genetically reprogrammed cells, tissues, and organs in a non-human animal for transplantation into a human recipient, wherein the non-human animal does not present one or more surface glycan epitopes and specific sequences from the wild-type swine's SLA is replaced with a synthetic nucleotides based on a human captured reference sequence from a human recipient's HLA.
Owner:XENOTHERAPEUTICS INC
DNA sequencing method using nucleotide and nucleotide with reversibly blocked end 3'
ActiveCN108165618AEliminate sequencing errorsImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic nucleotideA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA sequencing method using a nucleotide and a nucleotide with a reversibly blocked end 3'. X and Y* nucleotides simultaneously undergo a single sequencing reaction, whereinX represents a nucleotide with an unblocked end 3' and Y* is a nucleotide with a reversibly blocked end 3'. According to a quantitative relationship between the same number of detected molecules produced by two different nucleotides in the sequencing reaction and the number N of synthetic nucleotides, the sequencing information for a single sequencing reaction includes (N-1) specific bases X and 1or 0 coding XY. The whole sequencing process includes at least two sequencing reactions on the same template. Through comparing the two sets of sequencing information, the specific base sequence of the nucleic acid fragment to be tested is determined. Three groups of sequencing can also be performed. Through comparing the sequencing information obtained by the three sequencing reactions, the specific base sequences of the nucleic acid fragments to be tested are determined and the accuracy of sequencing is further improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Probiotic antimicrobial peptide Enterocin P, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106011153AHigh antibacterial activityNo side effectsAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsSynthetic nucleotideAntimicrobial peptides
The invention discloses a probiotic antimicrobial peptide Enterocin P, and a preparation method and application thereof. The probiotic antimicrobial peptide Enterocin P gene has nucleotide sequence disclosed as SEQ ID No.1. The mature antimicrobial peptide Enterocin P encoded by the probiotic antimicrobial peptide Enterocin P gene has amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID No.2. The preparation method of the antimicrobial peptide Enterocin P comprises the following steps: (1) synthesizing gene of which the nucleotide sequence is disclosed as SEQ ID NO:3; (2) establishing a recombinant plasmid capable of expressing the antimicrobial peptide; (3) transforming the host bacterium by using the recombinant plasmid to establish a gene engineering bacterium; (4) expressing the antimicrobial peptide by using the gene engineering bacterium; and (5) detecting the antibacterial activity of the antimicrobial peptide. The probiotic antimicrobial peptide Enterocin P has antibacterial activity on pathogenic bacteria, and can be used as an animal feed additive.
Owner:源耀生物科技(盐城)股份有限公司
Method for the Synthesis of Oligonucleotide Derivatives
Method for the synthesis of nucleotide derivatives wherein molecules of interest are grafted on the oligonucleotide with the help of a “click chemistry” reaction between an azide function on the molecule of interest and an alkyne function on the oligonucleotide, or between an alkyne function on the molecule of interest and an azide function on the oligonucleotide.Intermediate molecules, notably alkyne functionalized oligonucleotides, grafted oligonucleotides, azide functionalized oligonucleotides, oligonucleotide micro arrays containing them and the use of those grafted oligonucleotides for biological investigation and for cell targeting.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Synthetic genes encoding CRY1AC
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Mouse hepatitis virus detection
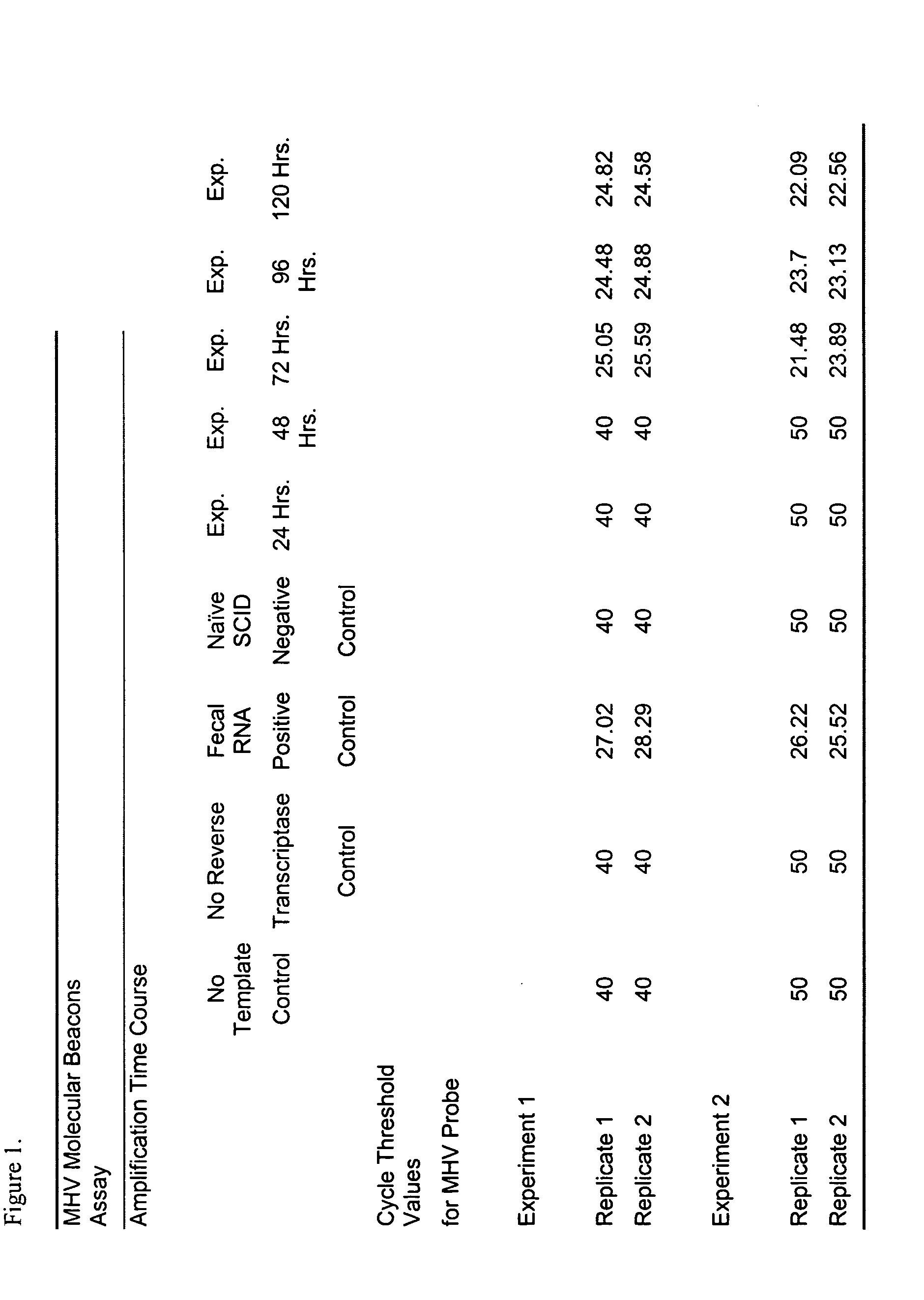
InactiveUS20050202416A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic nucleotideTest sample
The present invention relates to the identification of a nucleotide sequence that is conserved in the genome of the Mouse Hepatitis Virus (MHV) and to the design and construction of synthetic nucleotide primers and probes that target this conserved region. The invention further provides for methods and kits that use these primers and probes to detect the presence of Mouse Hepatitis virus in a test sample.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Method for synthesizing nucleotide pools in high-throughput manner by aid of semiconductor chips and assembling double-stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing nucleotide pools in a high-throughput manner by the aid of semiconductor chips and assembling double-stranded DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The method includes steps of (1), dividing pre-synthetic double-stranded DNA into a plurality of DNA fragments; (2), designing nucleotide by the aid of the DNA fragments; (3), adding sequences to two ends of a primer which is the nucleotide, synthesizing nucleotide sequences and preparing the nucleotide sequences by the aid of the semiconductor chips; (4), carrying out first-round amplification by the aid of the primer with biotin labels; (5), recombining first-round PCR (polymerase chain reaction) products by the aid of at least one type of recombinant enzymes; (6), purifying PCR mixtures; (7), carrying out second-round PCR, and assembling nucleotide fragments to obtain assembled PCR products; (8), carrying out third-round PCR amplification on the PCR products by the aid of designed head and tail primers to obtain double-stranded DNA fragments. The method has the advantages of low cost and high one-step synthesis throughput.
Owner:SUZHOU HONGXUN BIOTECH CO LTD
Compositions for use in security marking
ActiveUS10472676B2Increase the lengthShorten the lengthStampsMicrobiological testing/measurementOligomerSynthetic nucleotide
A composition comprising: a plurality of identical first synthetic nucleotide oligomers; and a plurality of identical second synthetic nucleotide oligomers which are different to the first synthetic nucleotide oligomers, wherein each of the first synthetic nucleotide oligomers comprises a first primer binding sequence of bases, a first identifier sequence of three to seven bases in length, and a second primer binding sequence of bases, the first identifier sequence being disposed between the first and second primer binding sequences, wherein each of the second synthetic nucleotide oligomers comprises a third primer binding sequence of bases, a second identifier sequence of three to seven bases in length, and a fourth primer binding sequence of bases, the second identifier sequence being disposed between the third and fourth primer binding sequences, and wherein the first identifier sequence is different to the second identifier sequence.
Owner:SELECTAMARK SECURITY SYSTEMS PLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com