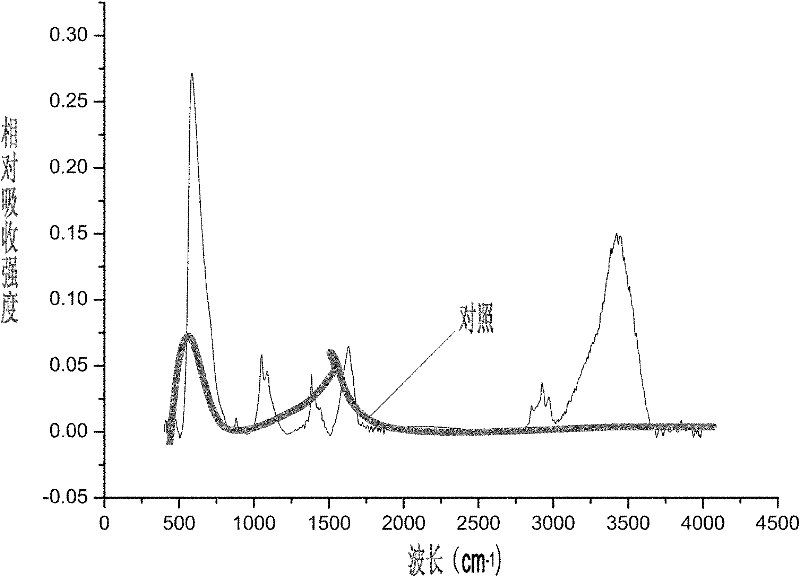
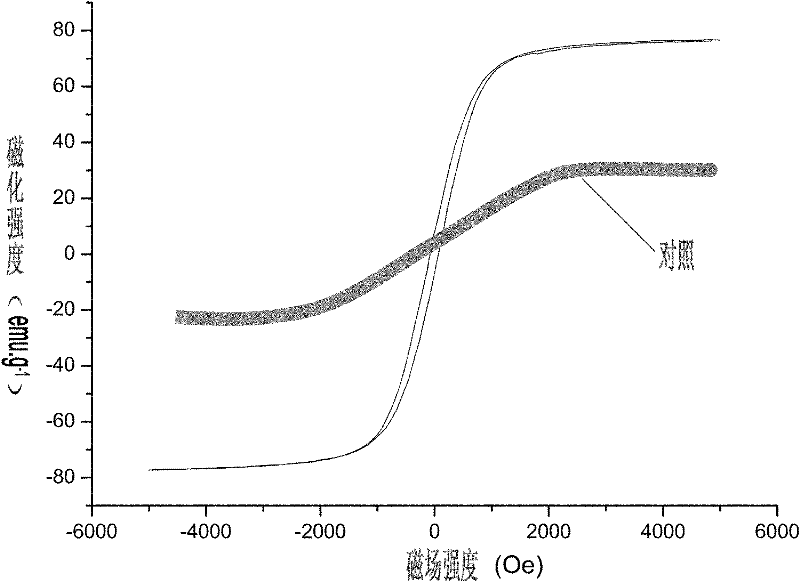
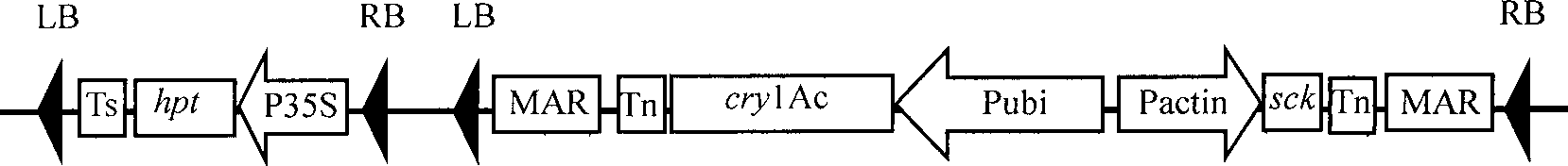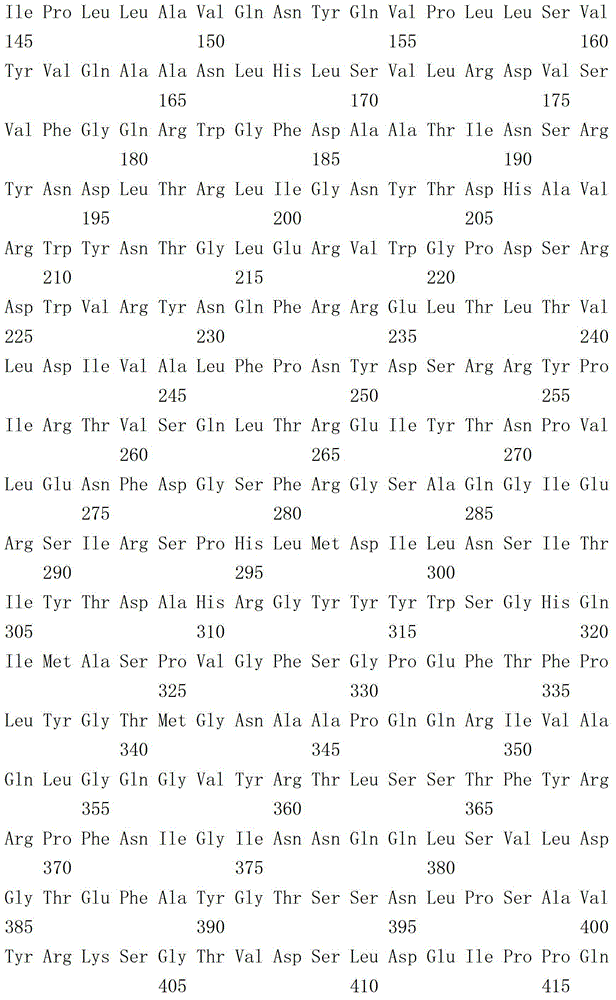Patents
Literature
99 results about "Cry1Ac" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cry1Ac protoxin is a crystal protein produced by the gram-positive bacterium, Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) during sporulation. Cry1Ac is one of the delta endotoxins produced by this bacterium which act as insecticides. Because of this, the genes for these have been introduced into commercially important crops by genetic engineering (such as cotton and corn) in order to confer pest resistance on those plants.
Synthetic genes encoding cry1ac
Compositions and methods for conferring pesticidal activity to bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions containing a synthetic nucleotide sequence encoding a Cry1Ac protein are provided. The coding sequences can be used in DNA constructs or expression cassettes for transformation and expression in plants and bacteria. Compositions also include transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, tissues, and seeds. In particular, isolated pesticidal nucleic acid molecules are provided, wherein the nucleotide sequences are set forth in SEQ ID NO:1, 2, 3, 4, 5 or 6, as well as variants and fragments thereof.
Owner:ATHENIX
Novel bacillus thuringiensis isolate
A novel bacterial strain of Bacillus thuringiensis, VBTS 2528, is described. This strain comprises genes encoding Cry1Ac, Cry 1Ca, and Cry2Aa endotoxin proteins. The invention further relates to an insecticidal composition comprising a mixture of VBTS 2528 and to methods for controlling insect pests utilizing VBTS 2528.
Owner:VALENT BIOSCIENCES CORP
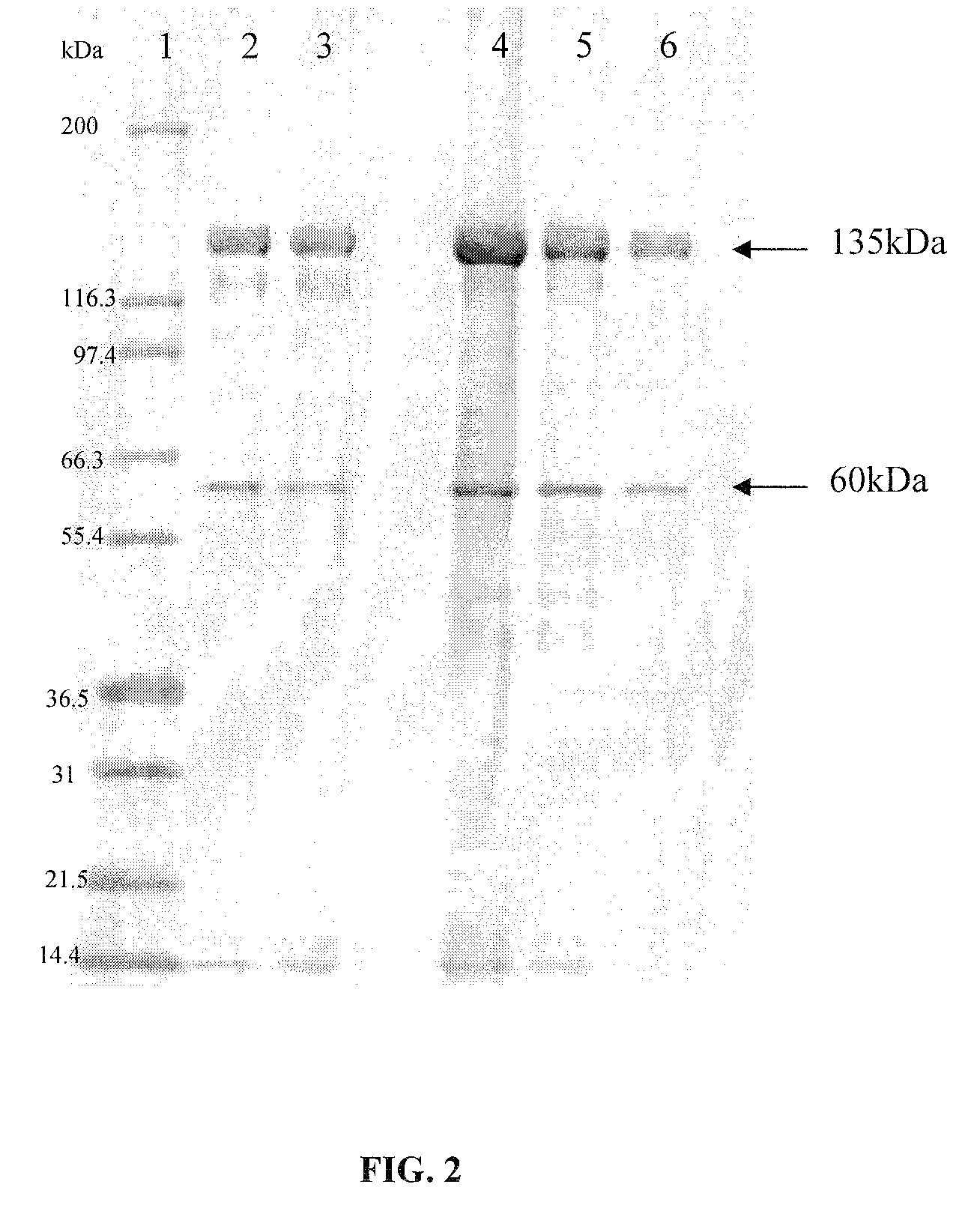
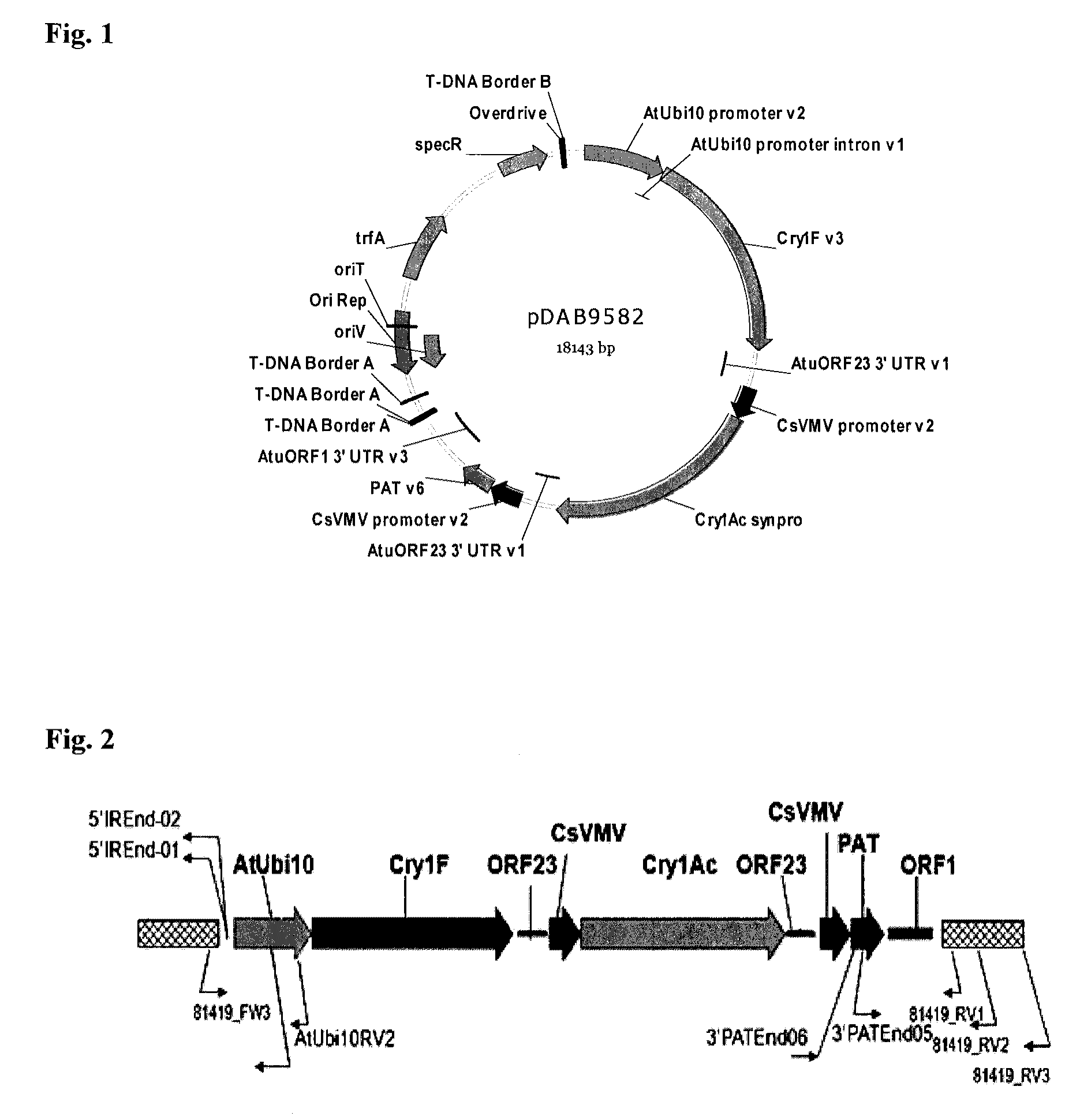
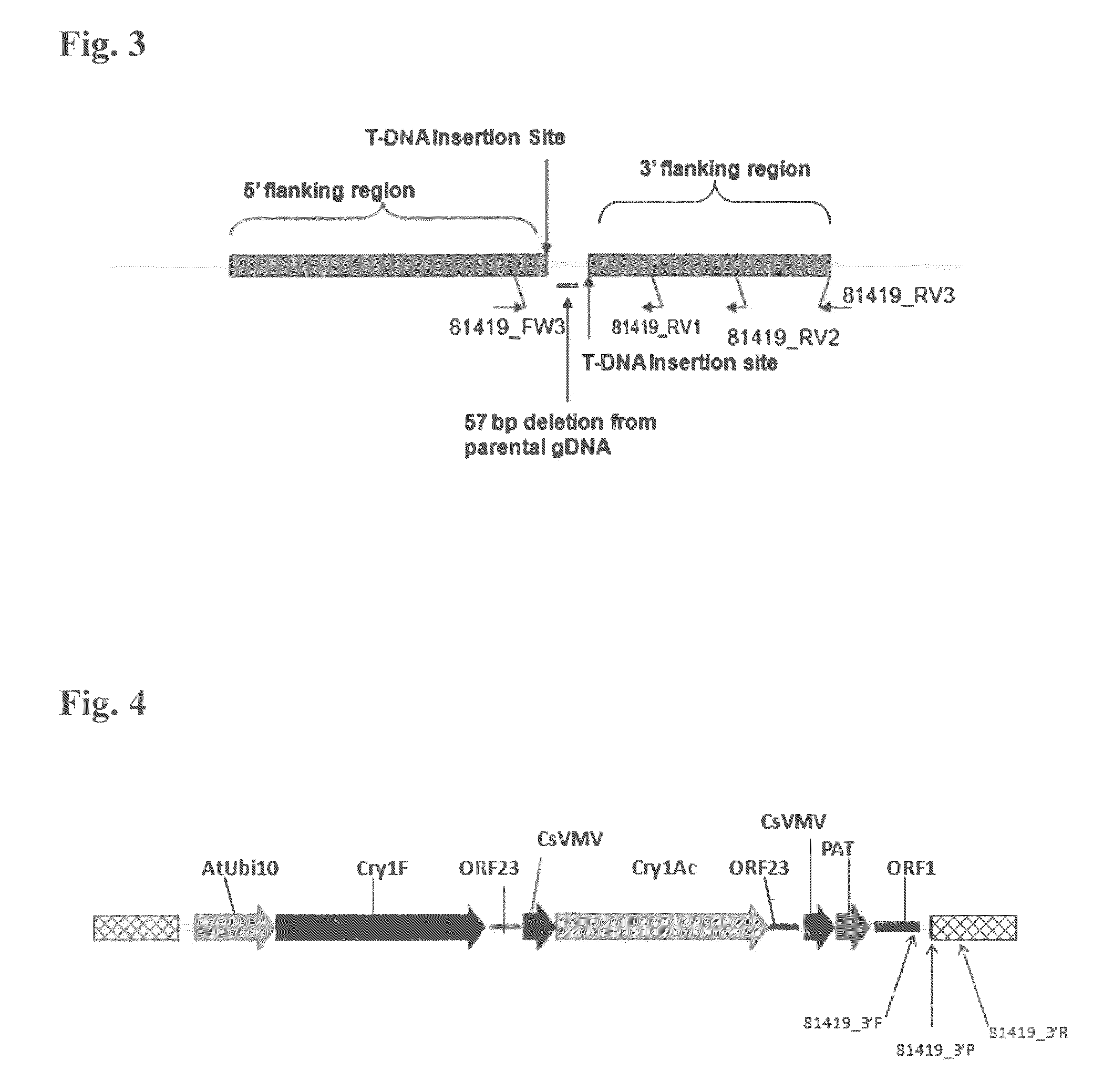
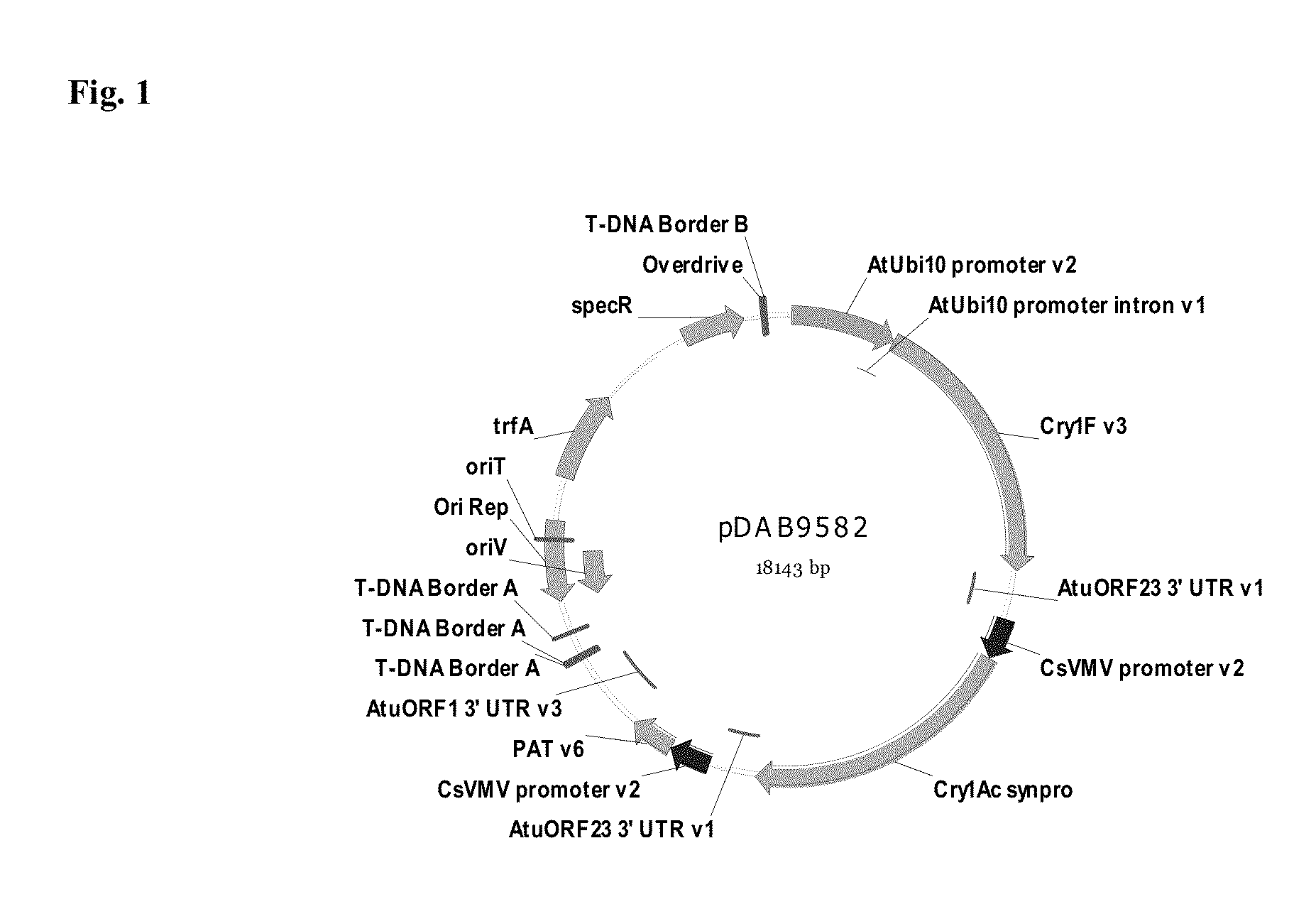
Soybean event pDAB9582.814.19.1 detection method
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Mutant Bacillus thuringiensis proteins and genes encoding the same with improved insecticidal activity and use thereof
The present disclosure discloses novel Cry1Ac mutants with improved insecticidal activity and / or spectrum against pests belong to Order lepidoptera. Also provided are transgenic plants expressing the present protein and methods for controlling Lepidopteran pest using the present mutants.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
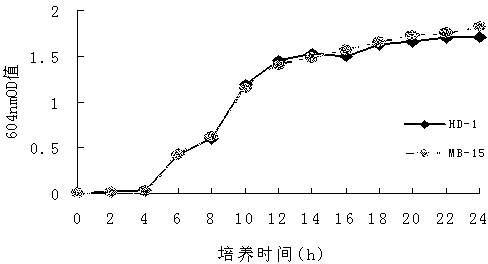
Bacillus thuringiensis MB-15 strain and preparation method of its wettable powder
InactiveCN103160449ABroad insecticidal spectrumGood control effectBiocideBacteriaCotton bollwormInsecticidal crystal proteins
The invention discloses a Bacillus thuringiensis MB-15 strain which has a broad spectrum and high virulence on vegetable lepidoptera pests, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No. 5255. The strain can form a diamond insecticidal crystal protein, contains cry1I, cry1Ac, cry2Ac and vip3Aa genes, and has high-efficiency insecticidal activity on plutella xylostella, Pieris brassicae, beet armyworm, Spodoptera litura, Helicoverpa armigera and other lepidoptera pests. The invention also relates to a preparation method of the wettable powder of strain. The wettable powder comprises the following content of main components: 40.0-50.0% of Bacillus thuringiensis MB-15 strain powder, 5.0-10.0% of a dispersant, 5.0-10.0% of a wetting agent, 0.5-1.0% of a stabilizer, 0.5-1.0% of an ultraviolet light protection agent, and 28.0-49.0% of a carrier. The wettable powder can be used to control a plurality of lepidoptera pests on vegetables, and has the characteristics of broad spectrum, high efficiency, and safety, etc.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
ABC transportprotein gene ABCH1 and application of specific dsRNA of ABCH1 in prevention and control of diamond back moth and Bt resistance treatment
The invention relates to an ABC transportprotein gene ABCH1 and an application of the specific dsRNA of ABCH1 in the prevention and control of diamond back moth and Bt resistance treatment. The invention discloses an insect ABC transportprotein gene and an application of an encoding gene ABCH1 and the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) of the insect ABC transportprotein gene, and the insect ABC transportprotein gene can specifically silence ABCH1 gene so that Bt Cry1Ac insecticidal protein-sensitive and resistant diamond back moth dies. The gene full-length nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and is used for encoding the protein as shown in the SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention also discloses ABCH1 gene specific fragments which are used for synthesis of dsRNA; after dsRNA is injected into the Bt Cry1Ac insecticidal protein-sensitive and resistant early 3-year-old diamond back moth larvae body cavity, the diamond back moth slowly develops during the growing process, which results in the death of the diamond back moth in larva and pupa stages. The invention provides a novel target for the prevention and control of field pests and Bt resistance treatment based on RNA interference and thus has good application prospects.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
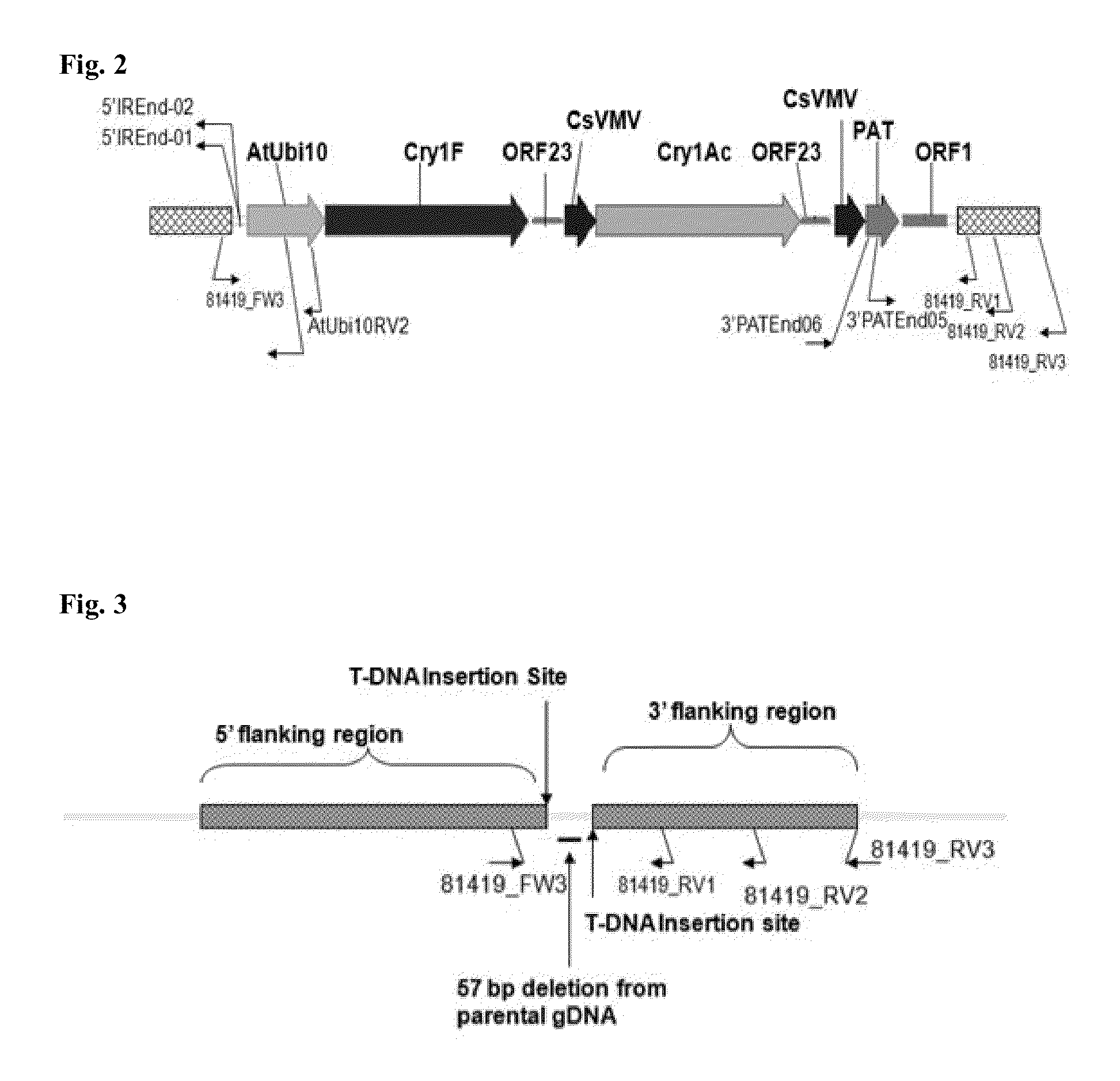
Foreign fragment flanking sequence of transgenic rice line Kefeng No. 8 containing sck/cry1Ac bivalent insect-resistant gene and use
InactiveCN101413005AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAgricultural scienceResistant genes
The invention relates to a flanking sequence for a foreign inserting fragment of a transgenic rice line Kefeng No. 8 harboring sck / crylAc double insect resistance genes and application thereof, which belong to the field of biotechnology. A flanking sequence of a 5' end is shown in SEQ ID NO1, and a flanking sequence of a 3' end is shown in SEQ ID NO2. The flanking sequence is utilized to design a specific primer for the augmentation of target DNA, which can establish sensitive and specific qualitative and quantificational PCR detection of the line specificity of the rice line Kefeng No. 8.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Coding gene of anti-Cry1Ac toxin single-chain variable fragments (scFv) and immuno-polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection method
InactiveCN102936598ACoding sequences are not readily availableEnhanced detection signalMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against bacteriaPhage antibodiesSingle-Chain Antibodies
The invention relates to a coding sequence of anti-Cry1Ac scFv and an immuno-PCR detection method for detecting Cry1Ac through the phage scFv. The scFv are obtained through elutriation in a natural phage antibody base according to the method. The method is characterized in that the specificity of the scFv is determined by a CDR region sequence in a heavy chain and light chain variable region sequence, immuno-PCR results indicate that a fluorescence detection system can be used for quantitative detection of the Cry1Ac, and the detection range is 0.2-100ng / mL. The method is fast, simple and high in flexibility; a step for marking reporter DNA molecules during an existing immuno-PCR process is avoided, the experimental operation is simplified, and potential practical values are provided.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Mutant bacillus thuringiensis proteins and genes encoding the same with improved insecticidal activity and use thereof
The present disclosure discloses novel Cry1Ac mutants with improved insecticidal activity and / or spectrum against pests belong to Order lepidoptera. Also provided are transgenic plants expressing the present protein and methods for controlling Lepidopteran pest using the present mutants.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Bacillus thuringiensis bacterial strain for strain insect disinfestations, restraining epiphyte and uses thereof
The invention relates to an insecticidal and antifungal bacillus thuringiensis bacterial strain and the application. The bacterial strain is bacillus thuringiensis 519-1, which is called as Bt 519-1 for short, the collection number is CGMCC No. 2327, the bacterial strain carries the insecticidal protein coding genes of cry1Aa, cry1Ab, cry1Ac, cry1I, cry2 and the vip3A and 70 kDa chitinase coding gene chiB. The semi-lethal concentration (LC50) to spodoptera exigua of the spore crystal complex freeze-dried powder of the bacterial strain is only 8.8Mug / mL, and the bacterial strain can inhibit the growth of 8 common plant pathogen fungal myceliums and inhibit the germination of the fungal spores completely. The usage of the bacterial strain can produce the insecticidal and anti-disease multifunctional biological pesticides, which is used for the prevention and the treatment of lepidoptera major pest spodoptera exigua and bollworm; at the same time, the bacterial strain also has the inhibition function of the plant pathogen fungi.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Method for detecting insecticidal crystal proteins Bt Cry1Ab/Ac and special enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit thereof
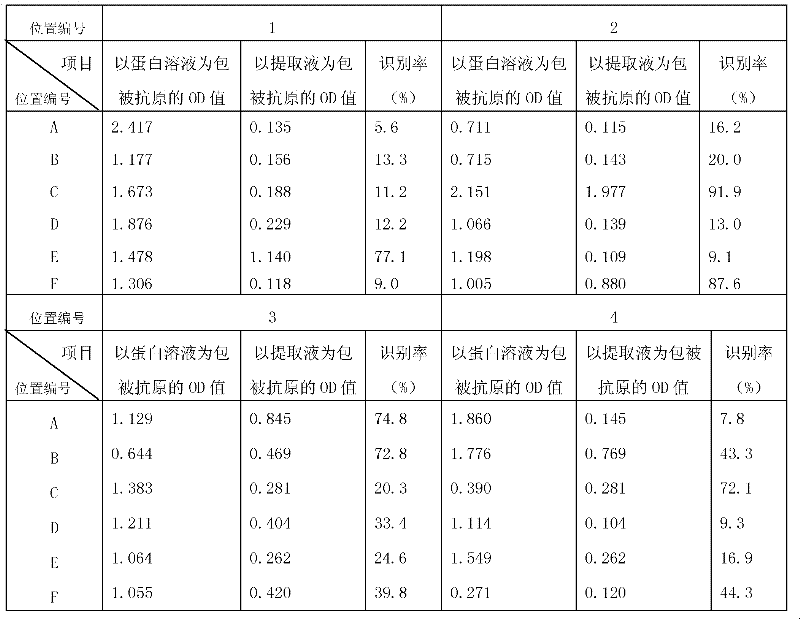
The invention discloses a method for detecting insecticidal crystal proteins Bt Cry1Ab / Ac and a special enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit thereof. An anti-Bt Cry1Ab / Ac monoclonal antibody used by the method and the kit is secreted by a hybridoma cell strain Bt2F9, and the application number of the hybridoma cell strain in CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) is CGMCC No.5162. The monoclonal antibody is obtained by simultaneously using a Bt Cry1Ac protein solution and an extracting solution of Bt Cry1Ac transgenic cotton plant leaves as a coating antigen and screening hybridoma cells through an indirect non-competitive ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) method, the monoclonal antibody has high affinity for Bt Cry1Ab / Ac protein expressed in plants, and the affinity constant is 1.03*10<9>M<-1>. The double-antibody sandwich enzyme linked immunosorbent assay kit prepared by the monoclonal antibody is used for qualitatively or quantitatively detecting proteins Bt Cry1Ab / Ac in transgenic plants such as cotton and corn, the linear detection range is 0.78-50ng / mL, and the kit has the advantages of fastness and sensitiveness.
Owner:FUJIAN ANXIN RUIJIE BIOTECH CO LTD
Expression system of bacillus thur ingiens (Bt) insecticidal protein Cry1Ac-a
InactiveCN102586286AOvercome the disadvantages of preferenceLower secondary structureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliProtein secondary structure
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and biotechnology, and relates to an expression system of a bacillus thur ingiens (Bt) insecticidal protein Cry1Ac-a. The expression system of the Bt insecticidal protein Cry1Ac-a is synthetic. The expression system of the Bt insecticidal protein Cry1Ac-a comprises expression vectors and protein Cry1Ac-a gene fragments. The protein Cry1Ac-a gene fragments are obtained by optimization according to an escherichia coli codon preference. An optimized protein Cry1Ac-a comprises 615 amino acids, and has molecular weight of 68.7KD and an isoelectric point of 5.42. The invention also relates to a method for high-efficiency expression of a protein by recombinant strain IPTG induction. The expression system of the Bt insecticidal protein Cry1Ac-a overcomes the defect of an escherichia coli expression codon preference, obviously reduces a secondary structure of a mRNA, realizes high expression of the protein Cry1Ac-a in escherichia coli, and provides a feasible solution scheme for high-efficiency and low-cost expression of the protein Cry1Ac-a.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Activated bacillus thuringiensis HLJ-66 with Bt diamond back moth resistance and application thereof
ActiveCN103695362AGood effectEasy to solveBiocideBacteriaAureobasidium sp.Insecticidal crystal proteins
The invention relates to activated bacillus thuringiensis HLJ-66 with Bt diamond back moth resistance and application thereof. The strain disclosed by the invention is bacillus thuringiensis HLJ-66, is called HLJ-66 for short and has the preservation number of CGMCCNo.8445, the preservation data of Nov. 8th in 2013 and the preservation address of No. 3, courtyard No.1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District of Beijing. The strain has toxicity for anti-Cry1Ac insecticidal crystal protein and Btk diamond back moth by toxicity biological assay screening. The strain is utilized to produce a high-efficiency broad-spectrum pesticide for preventing and treating the lepidopterous important pest of diamond back moth; and meanwhile, the strain has a good effect on resistance pests, is beneficial for preventing and treating resistance diamond back moth in the field, improves application value, is harmless for people, livestock and other animals, has no pollution to the environment and has excellent ecological benefits and excellent application and popularization prospect.
Owner:顶秀作物科技有限公司
Bacillus thuringiensis with activity on resisting Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) plutella xylostella
The invention discloses a Bacillus thuringiensis with activity on resisting Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) plutella xylostella, and relates to a Bacillus thuringiensi. The Bacillus thuringiensis is Bacillus thuringiensis AH-2 and belongs to the Bacillus, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the collection number of CGMCC No: 5220 in September 6, 2011. The Bacillus thuringiensis AH-2 has strong action on poisoning and killing Lepidoptera and Coleoptera main pests and resisting Bt and Cry1Ac toxalbumin pests. The Bacillus thuringiensis can be used for producing efficient broad-spectrum insecticide, can be used for preventing the Lepidoptera important pests such as plutella xylostella and the Coleoptera pest such as yellow mealworm, has good effect on resisting pests and is favorable for preventing and controlling field resistance plutella xylostella.
Owner:哈尔滨微华生物科技有限公司
Rapid detection of bt-cry toxins
InactiveCN1672049AEasy to implementHigh detection sensitivityBiological material analysisBiological testingCelluloseBiology
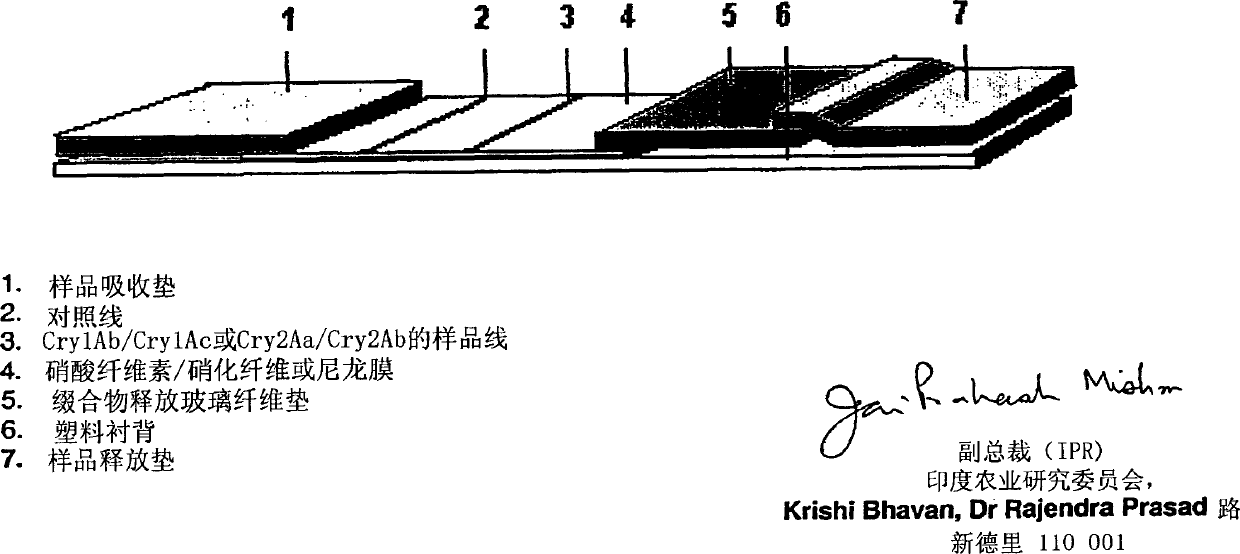
The present invention is based on the use of 1) two polyclonal IgGs against two Cry toxins, 2) Cry toxin receptors isolated from lepidopteran larvae and 3) manual striping methods to manufacture immunochromatographic strips that are useful in detecting a variety of analytes. Immunochromatographic strips, which facilitate rapid detection of analytes are expensive if made using monoclonal antibodies and cannot be affordable for Indian farmers and extension workers. The main objective of the current method was to simplify the development of the immunochromatographic detection method for Cry (Bt) toxin detection using affinity purified polyclonal antibodies specific to the analyte and also to provide a robust and easy method suitable for manufacture of 'Cry1Ac / Cry1Ab / Cry2Aa / Cry2Ab toxin' detection strips at affordable cost, under Indian conditions. Anti-Bt (anti-Cry1 Ac or anti-Cry2Aa / Ab or both) antibody or Cry receptor proteins are immobilized on a cellulose nitrate membrane by manual striping. The membrane is blocked using casein or BSA and preservatives. Anti-Bt (anti-Cry1 Ac or anti-Cry2Aa / Ab or both) antibody is labeled with gold and adsorbed on glass-fibre membrane which is placed at the bottom the membrane so as to overlap 2mm. Specificity and accuracy of the assay are greatly enhanced due to the use of antigen-affinity and Protein-A affinity purified polyclonal IgG raised in two different animals (goat and rabbit). The schematic diagram of the Cry toxin detection lateral flow strip assembly is shown in a diagram appended herewith. The strips thus made represent rapid, sensitive devices and methods for detecting the presence of Cry1Ac / Cry1Ab / Cry2Aa / Cry2Ab and crystal toxins either from transgenic plants or in Bt-fermented products.
Owner:INDIAN COUNCIL OF AGRI RES
Immune nano-magnetic particle for detecting Cry1Ab/Cry1Ac insecticidal proteins and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an immune nano-magnetic particle for detecting Cry1Ab / Cry1Ac insecticidal proteins and a preparation method thereof. The immune nano-magnetic particle for detecting Cry1Ab / Cry1Ac insecticidal proteins disclosed by the invention is coated by a polyclonal antibody resisting the Cry1Ab / Cry1Ac insecticidal proteins, and the size of the magnetic particle is 150-200nm. The immune nano-magnetic particle is prepared via the steps of: preparing a carboxyl nano-magnetic particle with high water solubility by an improved chemical precipitation method, and coupling the antibody resisting the Cry1Ab / Cry1Ac insecticidal proteins with the activated nano-magnetic particle by a chemical coupling method. The immune nano-magnetic particle is used for detecting the Cry1Ab / Cry1Ac insecticidal proteins via a chemiluminescence EIA (enzyme linked immuno assay) method; the sensitivity is high; the maximum detected protein concentration is 1000ng / ml, and the minimum detectable concentration is 1ng / ml; and magnetic enrichment is performed easily, so as to remove the interference of impurity molecules.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
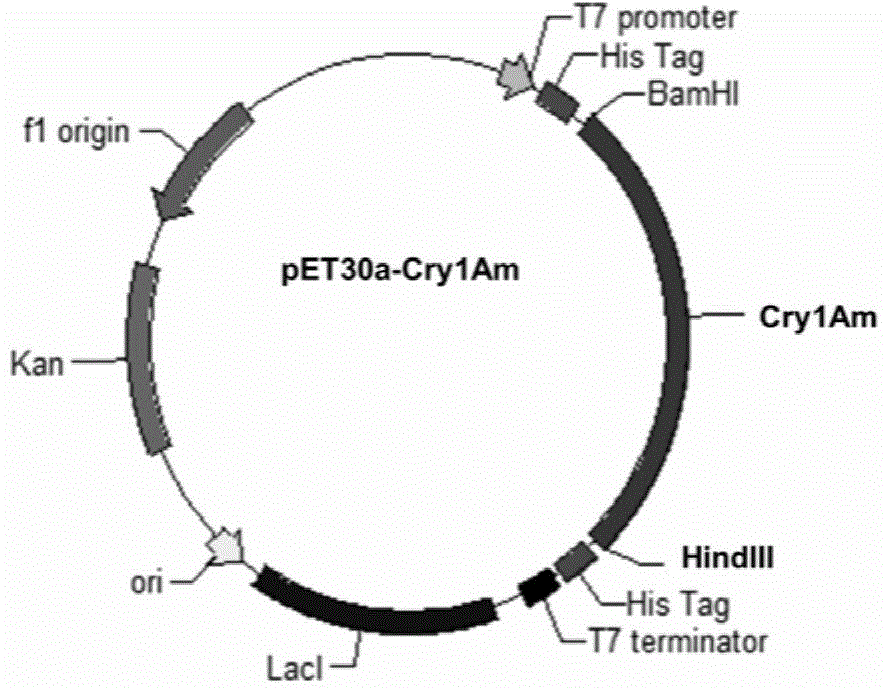
Fusion insecticidal protein Cry1Am, and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN104861074AHigh insecticidal activityEfficient killingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHybrid peptidesWild typeCry1Ac
The invention discloses a novel fusion insecticidal protein Cry1Am, and a coding gene and an application thereof. The fusion insecticidal protein has high insecticidal activity against wild type and Cry1Ab / Cry1Ac-resistant insects, and can be used for killing lepidopteran pests such as Asiatic corn borer, and for improving the insecticidal capacity of transgenic crops. The fusion insecticidal protein can effectively kill corn borers with Cry1Ac protein resistance, and can be used in insect resistance control.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
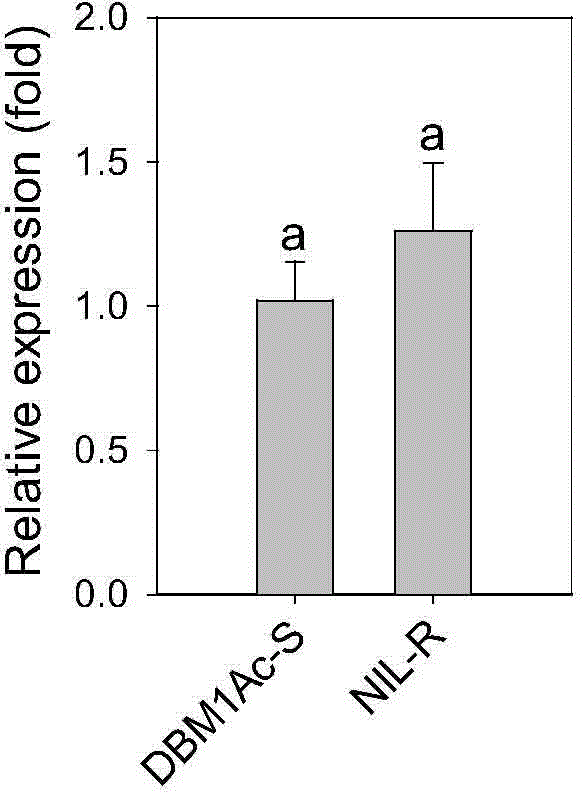
Method for detecting resistance of diamondback moth to Bt insecticidal protein Cry1Ac based on ABCC1 gene and kit thereof
InactiveCN104195253AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyForward primer
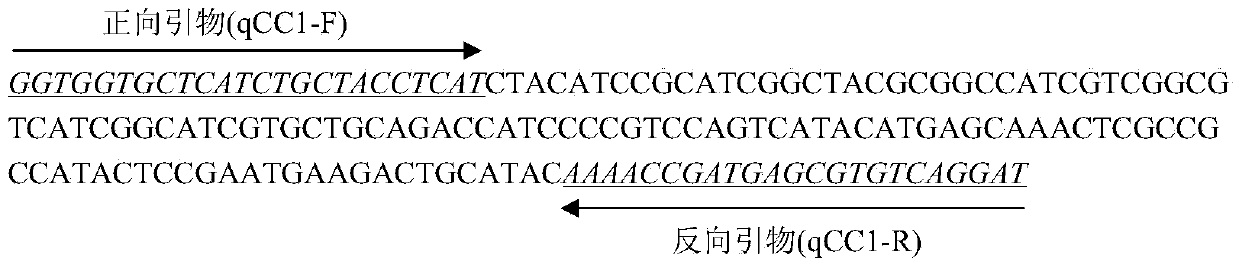
The invention discloses a real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting the resistance of a diamondback moth to Bt insecticidal protein Cry1Ac based on an ABCC1 gene and a kit thereof. The kit comprises the sequences of the following target gene specific primers: the sequence of a forward primer is shown in SEQIDNO. 2 and the sequence of a reverse primer is shown in SEQIDNO. 3. Since the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of less manpower and samples, large detection amount, high sensitivity and strong specificity and is fast, convenient, accurate and reliable, the level of the resistance of the diamondback moth to the Bt insecticidal protein Cry1Ac can be effectively detected, the method is applicable to the early rapid diagnosis of the resistance of the diamondback moth to the Bt insecticidal protein Cry1Ac and can be also used for real-time monitoring and early warning / forecasting of the resistance of the diamondback moth in the field to the Bt insecticidal protein Cry1Ac and thus the method has broad application prospects.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Microfluidic protein chip for detecting genetically modified crops and kit of microfluidic protein chip
InactiveCN102759628ADecreased probe activityHigh sensitivityBiological testingTransgelin GenePhosphate
The invention discloses a microfluidic protein chip for high-through detecting genetically modified crops. The microfluidic protein chip comprises a nucleic acid chip which is synthesized on the basis of mu ParafloTM microfluidic protein chip and contains six nucleotide sequences and 6 types of antibody-oligonucleotide composite probes, thereby simultaneously detecting 6 transgenetic proteins of trans-bacillus thuringiensis Bt insecticidal crystal protein (Cry1Ac), trans-bacillus thuringiensis Bt insecticidal crystal protein (Cry1c), trans-bacillus thuringiensis Bt insecticidal crystal protein (Cry1F), trans-bacillus thuringiensis Bt insecticidal crystal protein (Cry1Ab), soybean trypsin (SBTI) and neomycin phosphate transferase II gene (NPTII). The invention further provides a transgenic assay kit which comprises a mu ParafloTM microfluidic deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) chip which contains six types of probes, six types of antibody-oligonucleotide composite probes, six types of detection antibodies and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
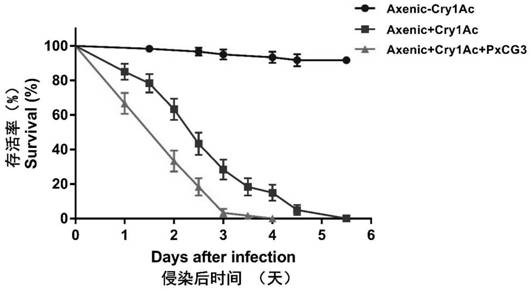
Plutella xylostella (L) Enterococcus mundtii PxG1 bacterial strain and application thereof
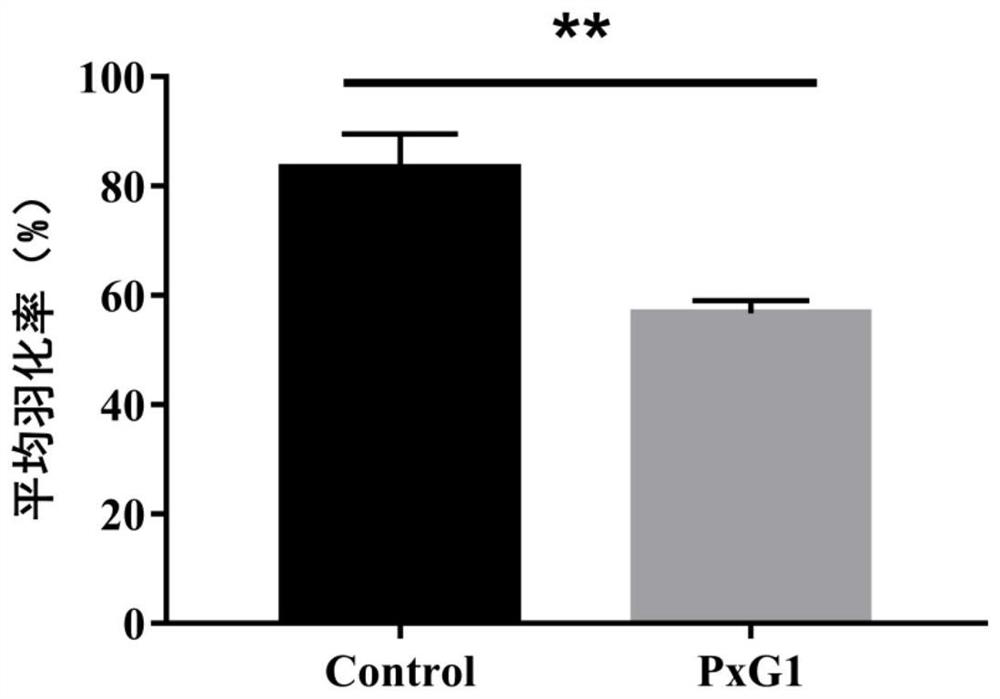
ActiveCN112175861AHigh insecticidal activityFeather reductionBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a Plutella xylostella (L) Enterococcus mundtii PxG1 bacterial strain and application thereof. The bacterial strain is collected in the GuangDong Microbial Culture Collection Center (GDMCC) on June 29th, 2020, and a culture collection number is GDMCC No: 61067. Research indicates that the eclosion rate of the Plutella xylostella (L) fed with the Enterococcus mundtii PxG1 bacterial strain is obviously lowered, and simultaneously indicates that the Enterococcus mundtii PxG1 bacterial strain has a function for improving Bt toxin insecticidal activity and carrying out synergy on Cry1Ac original toxins to quickly kill the Plutella xylostella (L), and the Enterococcus mundtii PxG1 bacterial strain can be used as a novel biological prevention and control bacterium, is usedfor preventing and controlling brassicaceae vegetable pests, and has good biological prevention and treatment potential and a good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method of purifying Bt toxalbumin from insect-resistant cotton seeds
InactiveCN103145815AReduce lossesSimple purification processPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesProtein targetProtein.monoclonal
The invention discloses a method of purifying Bt toxalbumin from insect-resistant cotton seeds. The invention provides a method of purifying Bt Cry1Ac protein from insect-resistant cotton seeds. The method comprises the following steps: (1) peeling the insect-resistant cotton seeds and then extracting total soluble protein to obtain a solution A; (2) conducting ammonium sulfate precipitation to the solution A, and centrifugally collecting the precipitate, wherein the saturation of the ammonium sulfate is 60%; (3) dissolving the precipitate obtained from the step (2), and dialyzing to obtain a solution B; and (4) conducting immuno-affinity chromatography to the solution B, collecting protein components, namely Bt toxalbumin, combined with the specificity of anti-Bt Cry1Ab / Ac protein monoclonal antibody, wherein the anti-Bt Cry1Ab / Ac protein monoclonal antibody is produced by secreting hybridoma Bt2F9 CGMCC No.5162. The method has the following advantages that the purification procedures are simplified, the purification cost is lowered, the purification time is shortened and reducing the loss of target proteins is reduced.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
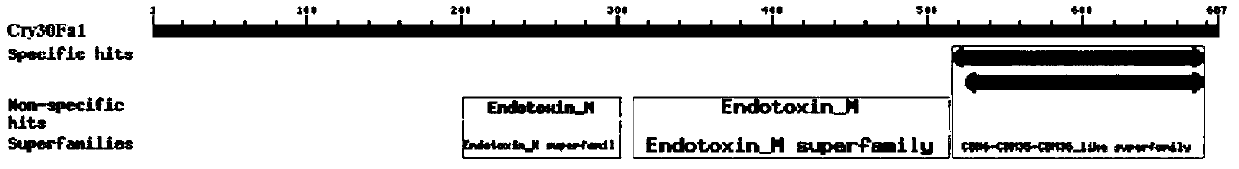
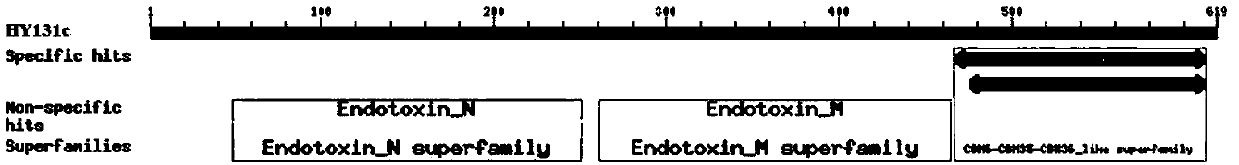
Insecticidal protein HY131c capable of resisting brown plant-hopper as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses insecticidal protein HY131c capable of resisting brown plant-hopper as well as an encoding gene and application thereof. The protein provided by the invention comprises structural domain I of Cry1Ac, structural domain II of Cry30Fa1 and structure domain III of Cry1Ac; and the protein is obtained by replacing the structural domain II in Cry1Ac protein with the structural domain II of Cry30Fa1 protein. Proved by experiment of the invention, the novel insecticidal protein provided by the invention has high toxicity to brown plant-hopper, thus providing a new strategy for resisting brown plant-hopper for rice, and having wide application prospect.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
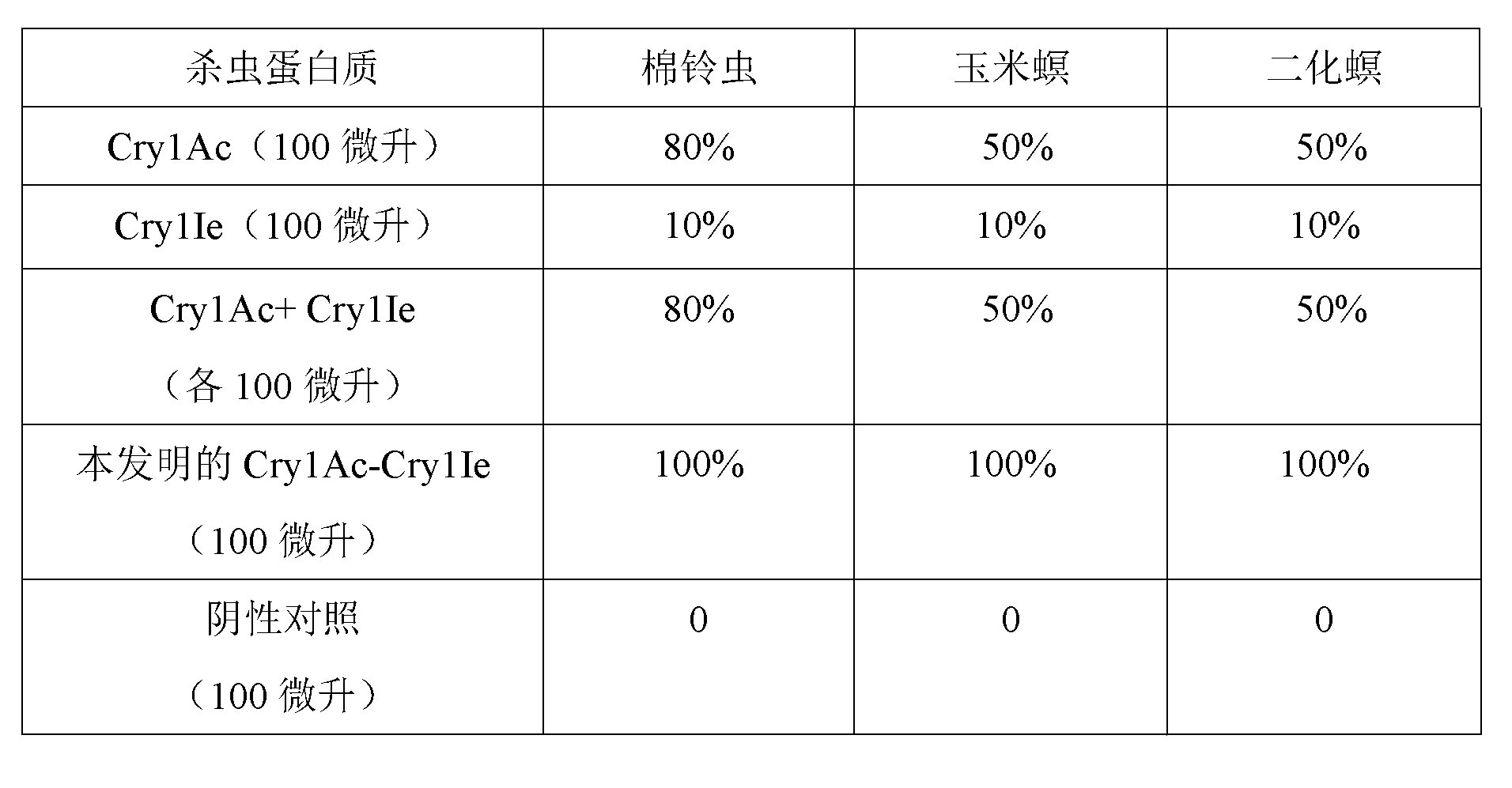
Insect-resistant fusion gene as well as insect-resistant fusion protein and application of insect-resistant fusion gene and insect-resistant fusion protein
InactiveCN103215290AHigh insecticidal activityBroad insecticidal spectrumInsecticidesHybrid peptidesBacillus thuringiensisAureobasidium sp.
The invention belongs to the field of plant gene engineering, relates to a method for obtaining an insect-resistant fusion gene with high insect killing capacity, an insect-resistant fusion gene and an insect-resistant fusion protein with high insect killing capacity and an application of constructing insect-resistant crops by using the fusion protein. Specifically, the invention discloses an insect-resistant fusion gene. The insect-resistant fusion gene comprises a nucleotide sequence for coding bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal Cry1Ac and a nucleotide sequence for coding Cry1Ie toxin from 5' to 3'; the Cry1Ac and the Cry1Ie nucleotide are connected by an XmaI digestion site; and the two nucleotide sequences are in the same open reading frame. The invention further discloses an insect-resistant fusion protein coded by the insect-resistant fusion gene. The invention further discloses applications of the insect-resistant fusion gene and the insect-resistant fusion protein in transgenic insect-resistant crops.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Promotor of plutella xylostella Bt (Bacillus Thuringiensis) insecticidal protein Cry1Ac resistant gene MAP4K4 (Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase Kinase 4) and application thereof
InactiveCN109679955AMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesPromoter activityBacillus thuringiensis
The invention discloses a core promotor sequence for regulating expression of a plutella xylostella Bt (Bacillus Thuringiensis) Cry1Ac insecticidal protein resistant gene MAP4K4 (Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase Kinase 4), mutation sites and application of the core promotor sequence in plutella xylostella Bt Cry1Ac insecticidal protein resistance identification and field monitoring.The mutation sites are nucleotides located at a 491 site, a 474 site and 469 to 470 sites at the upstream of an initial codon ATG and are respectively named M1, M2 and M3. A nucleotide sequence of plutella xylostella Bt Cry1Ac insecticidal protein susceptible population promotor is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and a nucleotide sequence of a resistance near-isogenic line population promotor is as shownin SEQ ID NO.2. An experiment verifies that the activity of a MAP4K4 gene promotor is remarkably enhanced when M2 and M3 are in mutation at the same time. According to the core promotor sequence disclosed by the invention, the research of promotor mutation in the field of insect Bt resistance is promoted, and particularly, important theoretical and practical significances in aspects of insect Btresistance field detection and control are obtained.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
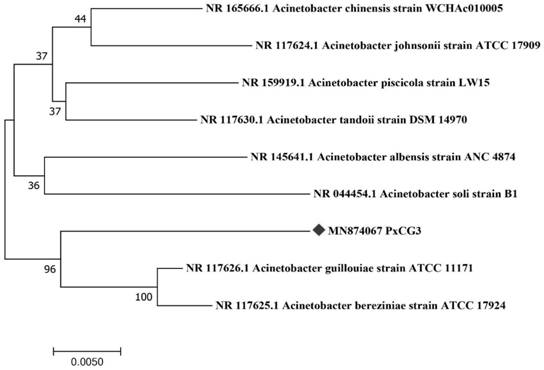
Acinetobacter guillouiae PxCG3 strain of plutella xylostella (L) and application of acinetobacter guillouiae PxCG3 strain
The invention discloses an acinetobacter guillouiae PxCG3 strain of plutella xylostella (L) and application of the acinetobacter guillouiae PxCG3 strain. The strain is preserved in guangdong microbialculture collection center (GDMCC) on August 11, 2020, and the preservation number of the strain is GDMCC No: 61134. Researches show that the acinetobacter guillouiae PxCG3 strain has the effects of improving the insecticidal activity of Bt toxin and synergizing Cry1Ac prototoxin to quickly kill the plutella xylostella (L); and the acinetobacter guillouiae PxCG3 strain can be used as a novel biological prevention and control bacterium, is used for prevention and control of cruciferous vegetable pests, and has extremely good biological prevention and control potential and application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Plutella xylostella trypsin-9 gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a plutella xylostella trypsin-9 gene and application thereof; the nucleotide sequence of the plutella xylostella trypsin-9 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, and the amino acid sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. Researches show that Trypsin-9 plays an important role in activation of Cry1Ac prototoxin in the midgut of plutella xylostella, the activation of Bt Cry1Acprototoxin in the midgut of plutella xylostella can be remarkably improved by feeding Trypsin-9, and the mortality rate of plutella xylostella is remarkably increased; after the expression of the geneTrypsin-9 of the plutella xylostella in the midgut is silenced, the digestion of the midgut of the plutella xylostella to food can be reduced, and pupation malformation is caused, so that the Trypsin-9 can be used as a molecular target for novel biological control, is used for preventing and controlling cruciferous vegetable pests, and has high biological control potential and application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Isothermal amplification method for detecting cry1Ac-transfected sugarcane
InactiveCN102965436AThe color reaction is intuitive and convenient to see the resultStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyColor reaction
The invention relates to an isothermal amplification method for detecting cry1Ac-transfected sugarcane. The method comprises the steps of extracting sugarcane template DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), establishing an isothermal amplification system and identifying an isothermal amplification product. According to the isothermal amplification method for detecting the cry1Ac-transfected sugarcane, four specific primers are designed aiming at base sequences of an exogenous target gene cry1Ac of stem-borer-resistant transgenic sugarcane, and a chain-displacement amplification reaction is carried out under the action of polymerase Bst, so that the specificity is high; meanwhile, the amplification reaction can be completed by only a water bath kettle and a normal-temperature low-speed centrifuge capable of completing instant centrifugation, so that instruments and equipment required are simple, the amplification cost is relatively lower compared with that of the conventional PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology, which needs a gel scanning system and a PCR (or real-time PCR) instrument, which are expensive, and the like, the amplification time is short, the amplification efficiency is high, and the result viewing is visual and convenient due to visual color reaction; and after the system is established, extracted DNA of a sugarcane genome directly serves as a template, so that the method is applicable to the cry1Ac-transfected sugarcane screening of laboratories and fields and the detection and tracking of cry1Ac ingredients and has the advantages of low cost, rapidness, sensitivity, simplicity and accuracy.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Human molecule-modified insecticidal protein and coding gene, design method and application thereof
ActiveCN108997494AHigh affinityStrong competitivenessBiocideImmunoglobulins against bacteriaPlutellaToxin
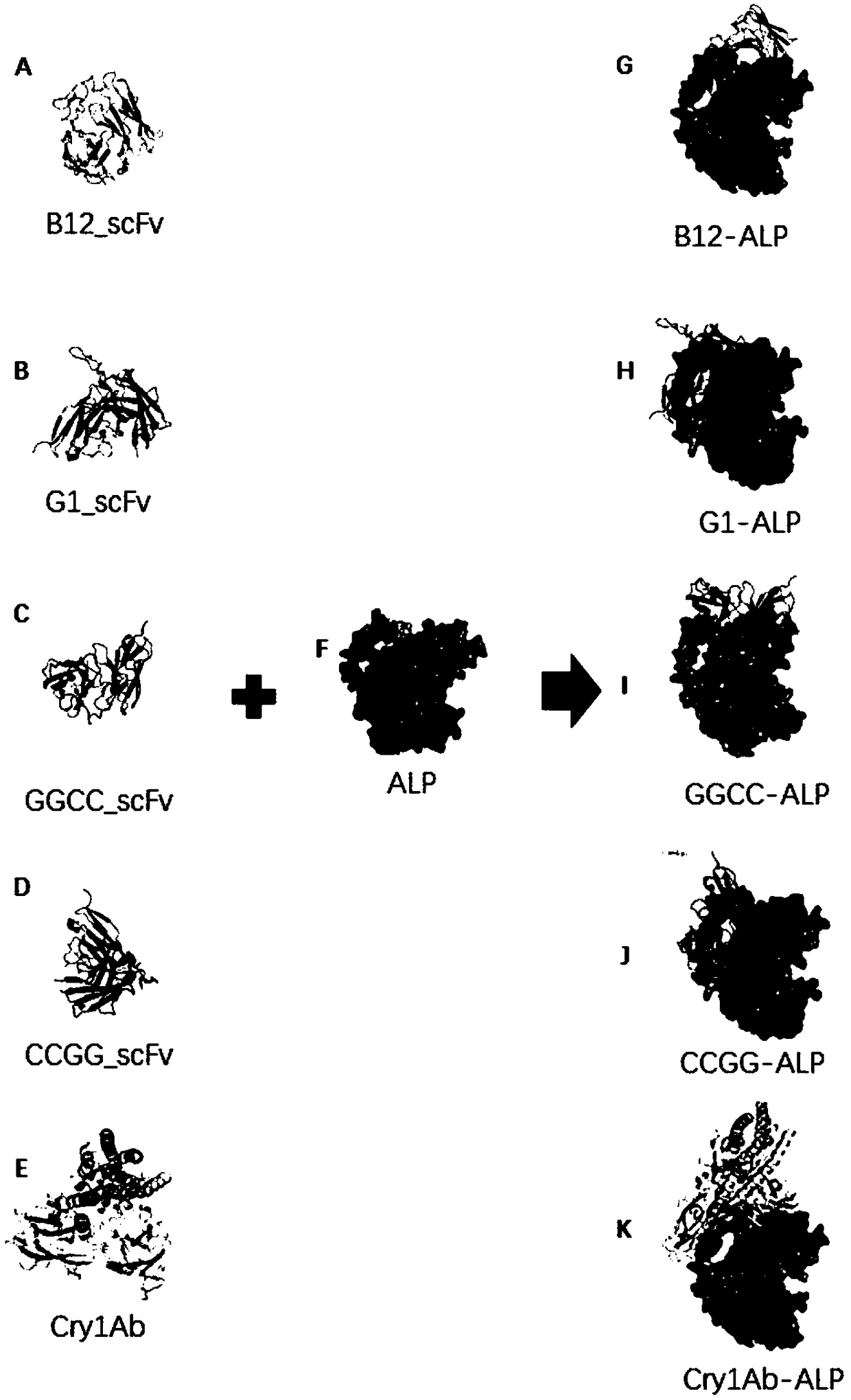
The invention provides human molecule-modified insecticidal protein and a coding gene, design method and application thereof, and belongs to the fields of genetic engineering and biological control. The invention provides the human molecule-modified insecticidal protein GGCC_scFv, wherein the human molecule-modified insecticidal protein GGCC_scFv has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The insecticidal protein GGCC_scFv has higher affinity with intestinal BBMV of Plutella xylostella than with Cry1Ab and Cry1B toxins, competes with the Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac and Cry1B toxins in combination with the intestinal BBMV of Plutella xylostella, and is a simulation of the Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac and Cry1B toxins; and it is shown through indoor insecticidal activity tests on Plutella xylostella, the fatality rate can reach 50% in 3 days, and can reach 95% in 7 days, and therefore the human molecule-modified insecticidal protein can effectively replace the Cry1A toxin, and is applied to biological control of pests.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Probe combination, liquid-phase chip and kit for transgenic corn detection, and application thereof
ActiveCN106498049AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyFluid phase
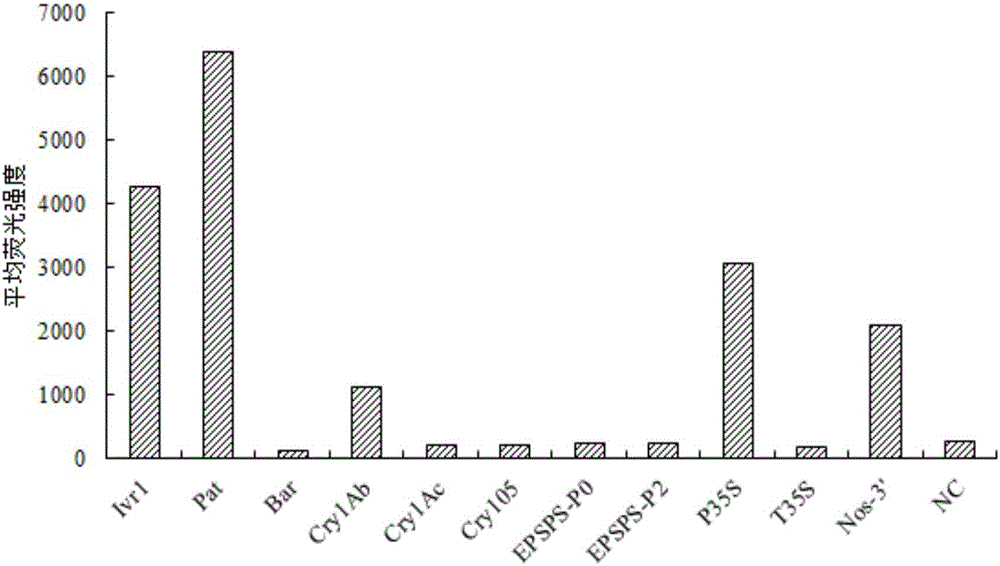
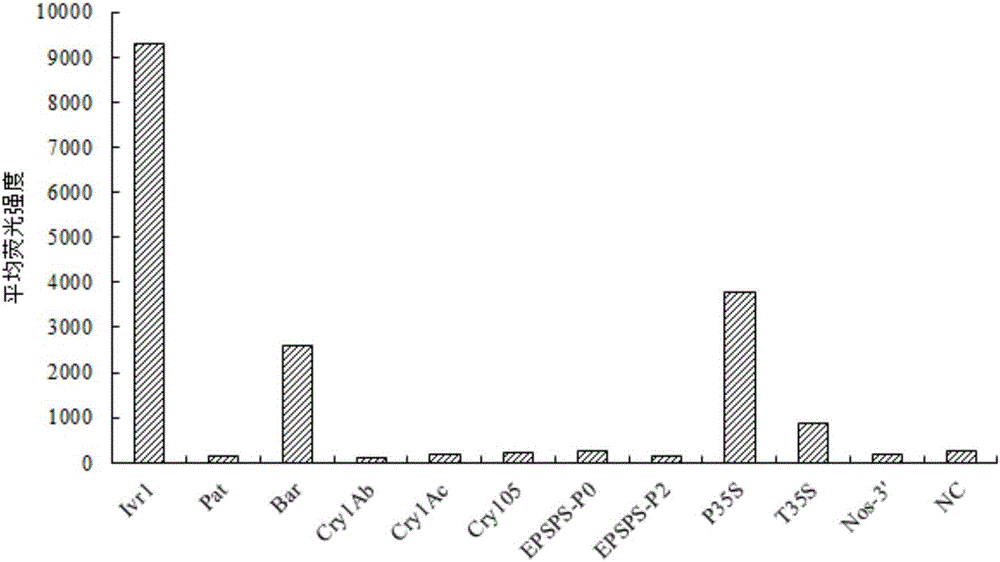
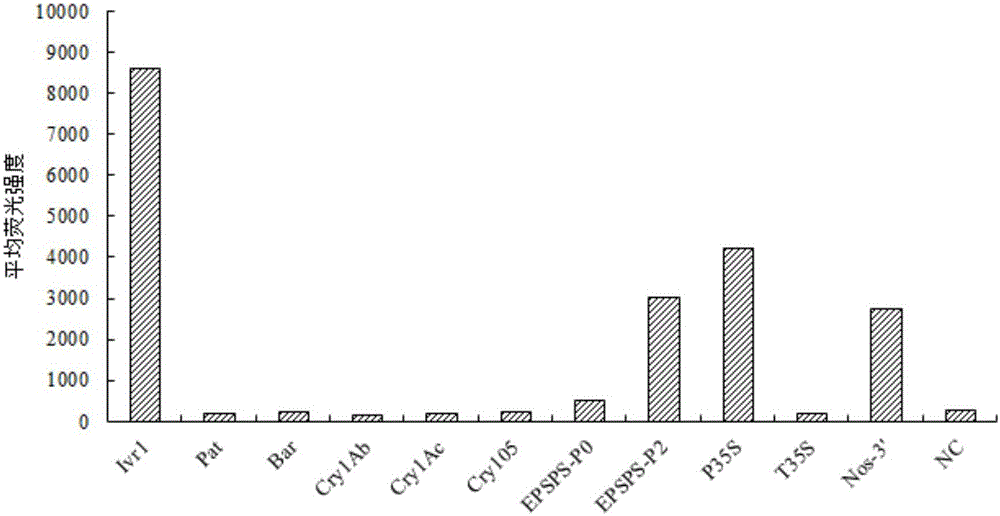
The invention provides probe combination, a liquid-phase chip and a kit for transgenic corn detection, and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of transgenic detection. The probe combination comprises 10 detection probes and a positive probe, wherein the 10 detection probes are designed according to common exogenous genes Pat, Bar, Cry1Ab, Cry1Ac, Cry105, EPSPS-P0, EPSPS-P2, P35S, T35S and Nos-3' in the transgenic corn; and the positive probe is designed according to an endogenous gene Ivr1 of the corn. The probe combination can be used for detecting whether the transgenic corn contain the above transgenic components or not after being coupled with fluorescent encoding microspheres separately, has the characteristics of simplicity in operation, high specificity, high sensitivity and large flux, and has an important function on transgenic corn detection of seed stations, institutes of agricultural sciences and border ports.
Owner:上海泽衡生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com