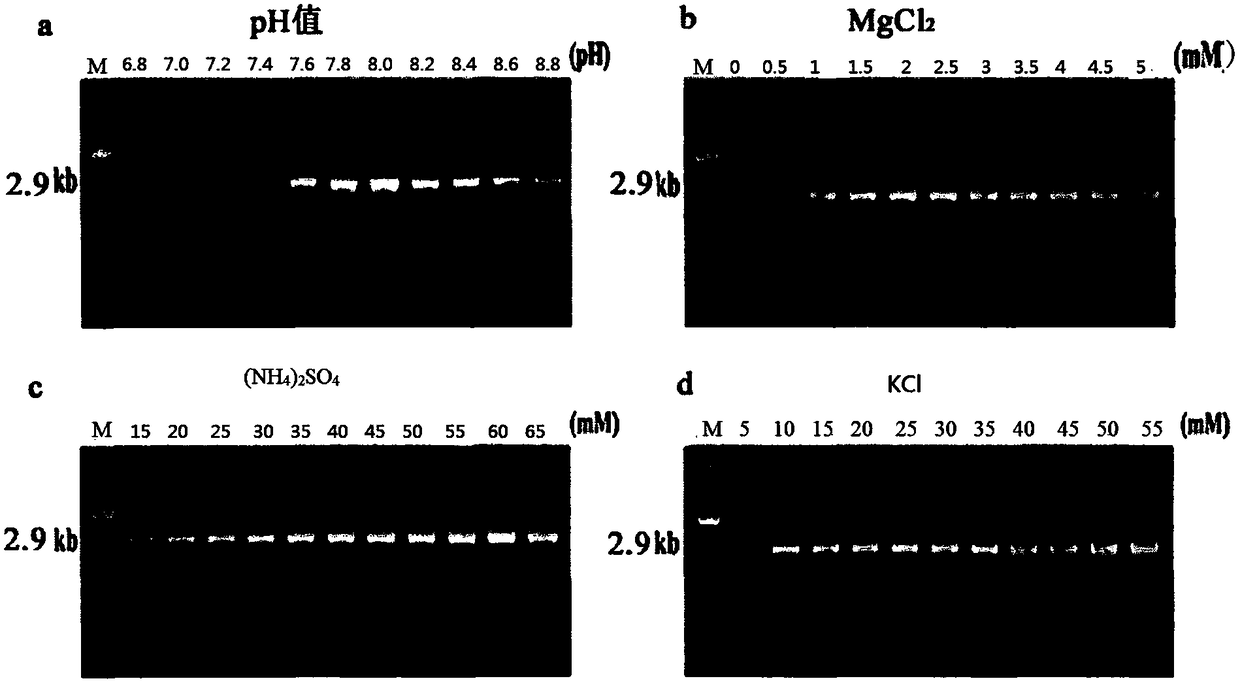
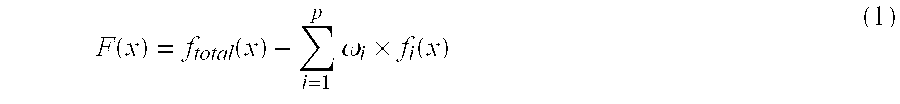Patents
Literature
202 results about "GC-content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In molecular biology and genetics, GC-content (or guanine-cytosine content) is the percentage of nitrogenous bases in a DNA or RNA molecule that are either guanine (G) or cytosine (C). This measure indicates the proportion of G and C bases out of an implied four total bases, also including adenine and thymine in DNA and adenine and uracil in RNA.
Method of Sequence Optimization for Improved Recombinant Protein Expression using a Particle Swarm Optimization Algorithm
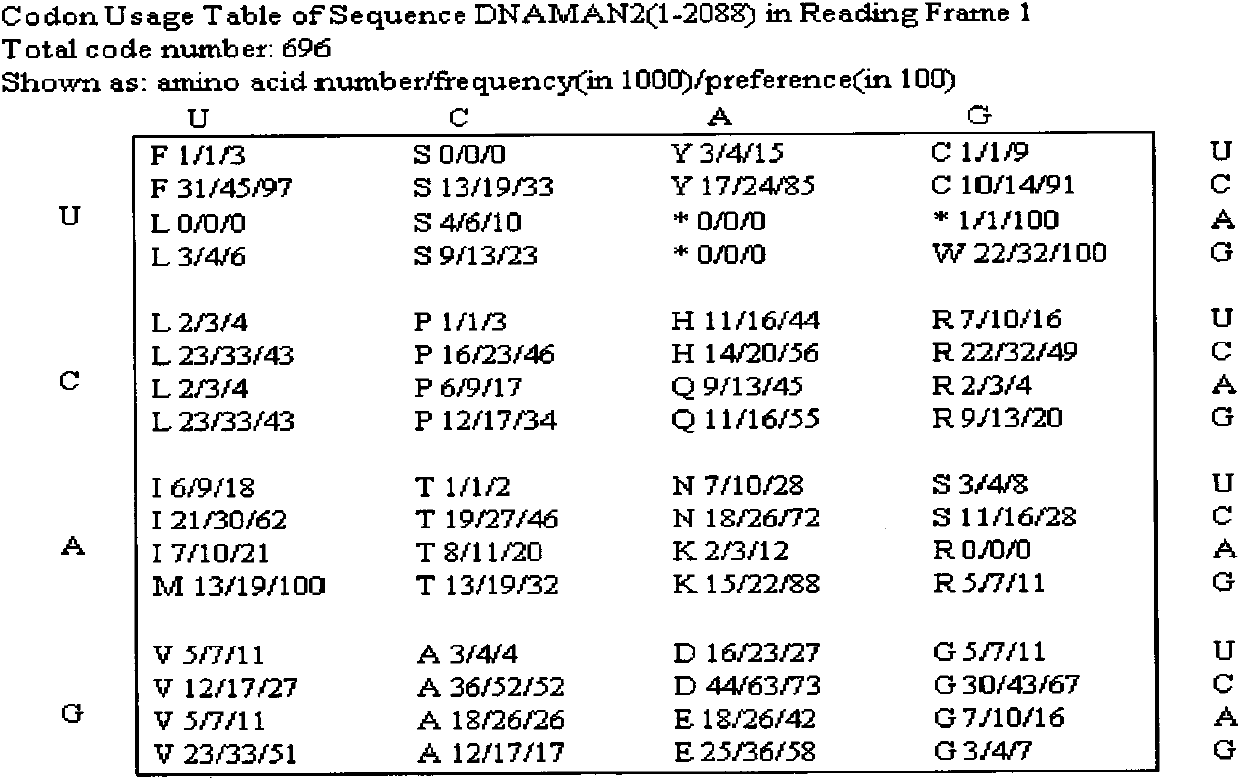
An improved gene sequence optimization method, the systematic optimization method, is described for boosting the recombinant expression of genes in bacteria, yeast, insect and mammalian cells. This general method takes into account of multiple, preferably most or all, of the parameters and factors affecting protein expression including codon usage, tRNA usage, GC-content, ribosome binding sequences, promoter, 5′-UTR, ORF and 3′-UTR sequences of the genes to improve and optimize the gene sequences to boost the protein expression of the genes in bacteria, yeast, insect and mammalian cells. In particular, the invention relates to a system and a method for sequence optimization for improved recombinant protein expression using a particle swarm optimization algorithm. The improved systematic optimization method can be incorporated into a software for more efficient optimization.
Owner:NANJING GENSCRIPT BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for detecting variation of copy numbers of genomes
ActiveCN105574361AIncreased sensitivityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsGC-contentBiology
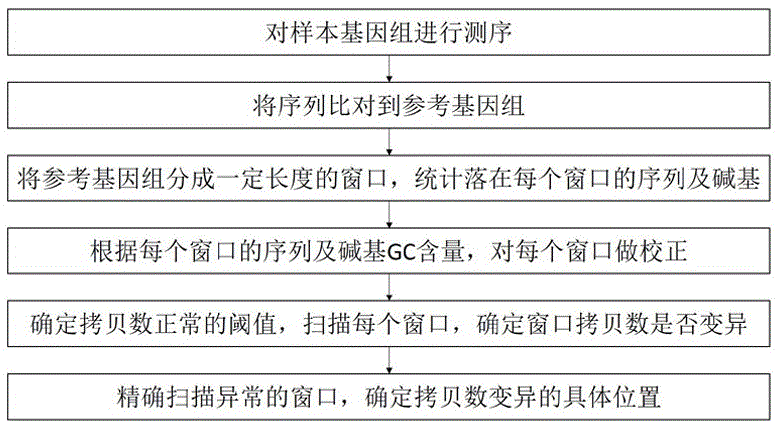
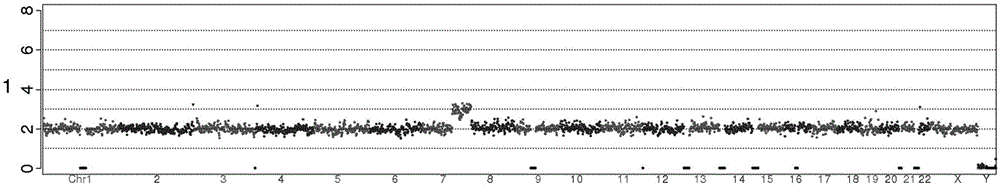
The invention relates to a method for detecting the variation of copy numbers of genomes. The method specifically comprises the following steps: sequencing sample genomes to obtain genome sequences; aligning the sequences to a reference genome to obtain the positions of the sequences on the genome; dividing the reference genome into windows with a certain length and carrying out statistics on the sequences and basic groups falling on the windows; correcting the windows according to the sequences and GC contents of the basic groups; determining threshold values with normal copy numbers, scanning the windows and determining whether the copy numbers of the windows varies; and precisely scanning the abnormal windows to determine the precise breakpoints and then determine the specific variation position of the copy numbers. According to the method, the sensitivity of the detection for the variation of the copy numbers of the genomes can be improved through utilizing three mean values, carrying out window correction, determining the threshold values with normal copy numbers, precisely scanning the abnormal windows and determining the precise breakpoints and the specific variation positions of the copy numbers; and the method is easy, simple and feasible to operate, high in efficiency, low in cost and beneficial for popularization and application.
Owner:YIKON GENOMICS SHANGHAI CO LTD
Method of sequence optimization for improved recombinant protein expression using a particle swarm optimization algorithm
An improved gene sequence optimization method, the systematic optimization method, is described for boosting the recombinant expression of genes in bacteria, yeast, insect and mammalian cells. This general method takes into account of multiple, preferably most or all, of the parameters and factors affecting protein expression including codon usage, tRNA usage, GC-content, ribosome binding sequences, promoter, 5′-UTR, ORF and 3′-UTR sequences of the genes to improve and optimize the gene sequences to boost the protein expression of the genes in bacteria, yeast, insect and mammalian cells. In particular, the invention relates to a system and a method for sequence optimization for improved recombinant protein expression using a particle swarm optimization algorithm. The improved systematic optimization method can be incorporated into a software for more efficient optimization.
Owner:NANJING GENSCRIPT BIOTECH CO LTD
Site-specific mutagenesis high temperature resistant phytase gene TP and expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN102943083AImprove stabilityHigh expressionHydrolasesAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention provides site-specific mutagenesis high temperature resistant phytase gene TP and an expression vector and application thereof. Amino acid in a specific area in a phytase amino acid sequence is mutated into praline and arginine so as to enable the phytase to have a special stable protein structure. Simultaneously, a gene sequence is optimized to synthesize a phytase gene according to pichia pastoris codon preference and GC content, recombinant plasmids are built and transferred to pichia pastoris, and positive converters are obtained through screening to conduct induction expression to obtain the high temperature resistant phytase. Experiments prove that the phytase obtained through expression of the pichia pastoris can resist high temperature plasmids with the temperature higher than 85 DEG C, and survival rate reaches 85%. Popularization and application of the high temperature resistant phytase have substantial economical benefit and social benefit on development of feed animal husbandry of our country, and simultaneously great ecological benefit can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN CHIATAI FEED TECH
Glucose oxidase mutant gene, expression and application thereof
InactiveCN101955953AIncrease secreted expressionIncrease enzyme activityFungiBacteriaYeastGlucose polymers
The invention discloses a glucose oxidase mutant gene, expression and application thereof. In the invention, 272 basic groups are changed through codon optimization and GC content change and the content of GC is reduced to 48.44% from 55.54% so as to obtain the glucose oxidase mutant gene, wherein the basic group is represented by SEQ ID NO.2. The glucose oxidase mutant gene is transferred into pichia yeast to express; the experimental result shows that the secretory expression level of the glucose oxidase mutant gene in the pichia yeast is significantly improved by comparing with the same before mutation; compared with partial research at home and abroad, the final secretory expression of the glucose oxidase mutant gene achieves high expression level, thereby building the foundation for further expansion of industrial production. The determination of enzymatic properties of the glucose oxidase mutant gene shows that the recombinant glucose oxidase protein expressed by the glucose oxidase mutant gene has good thermal stability and high enzyme activity.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
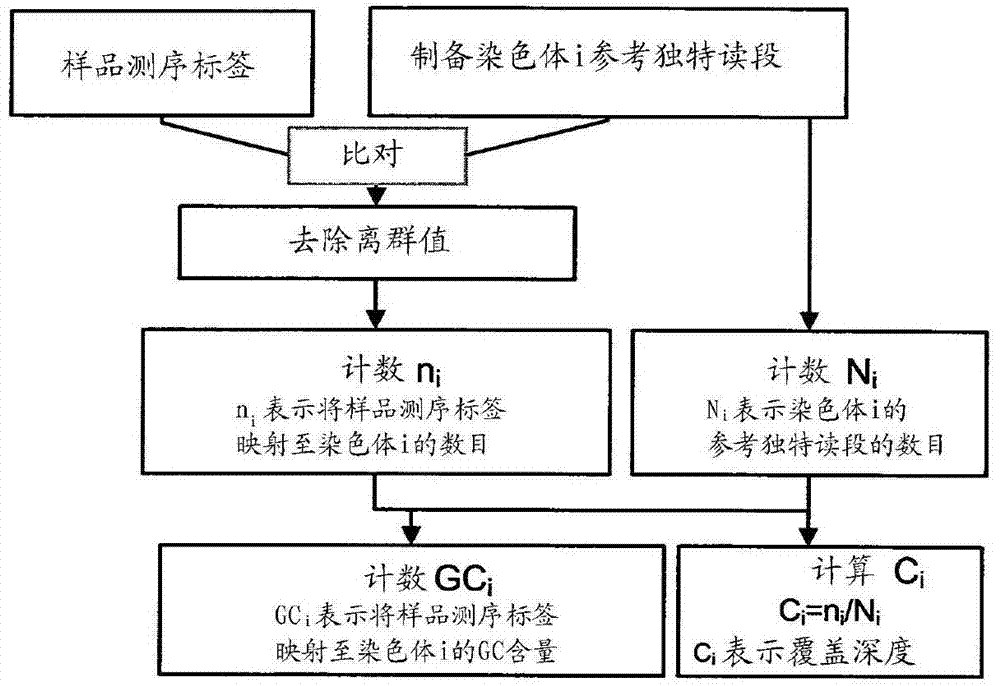
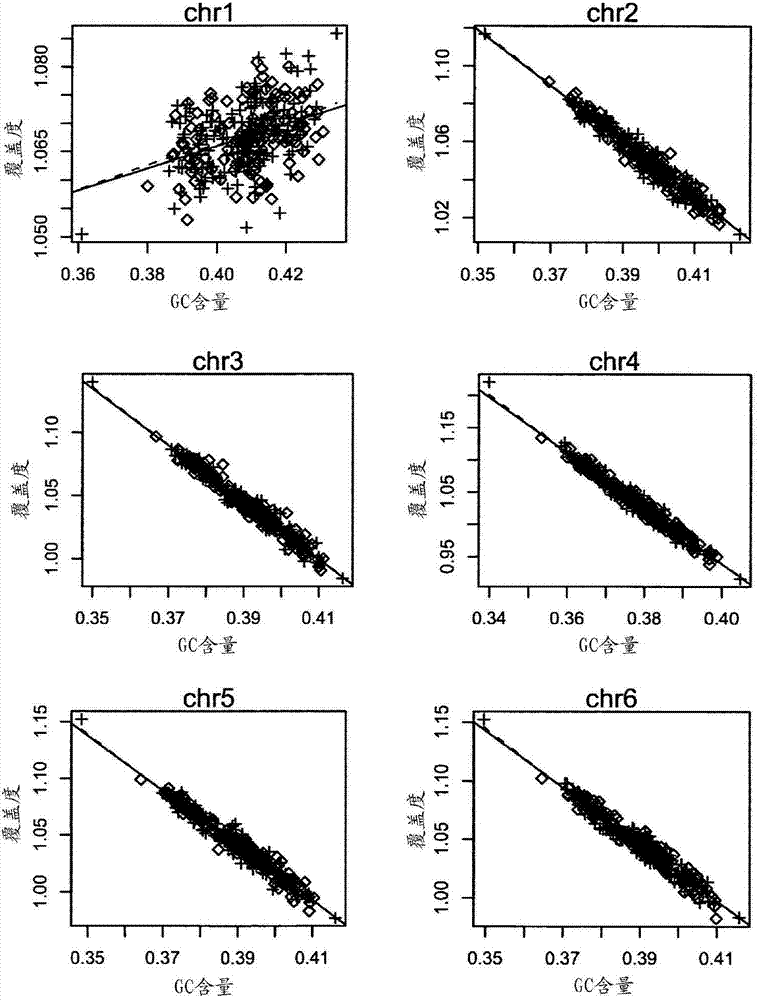
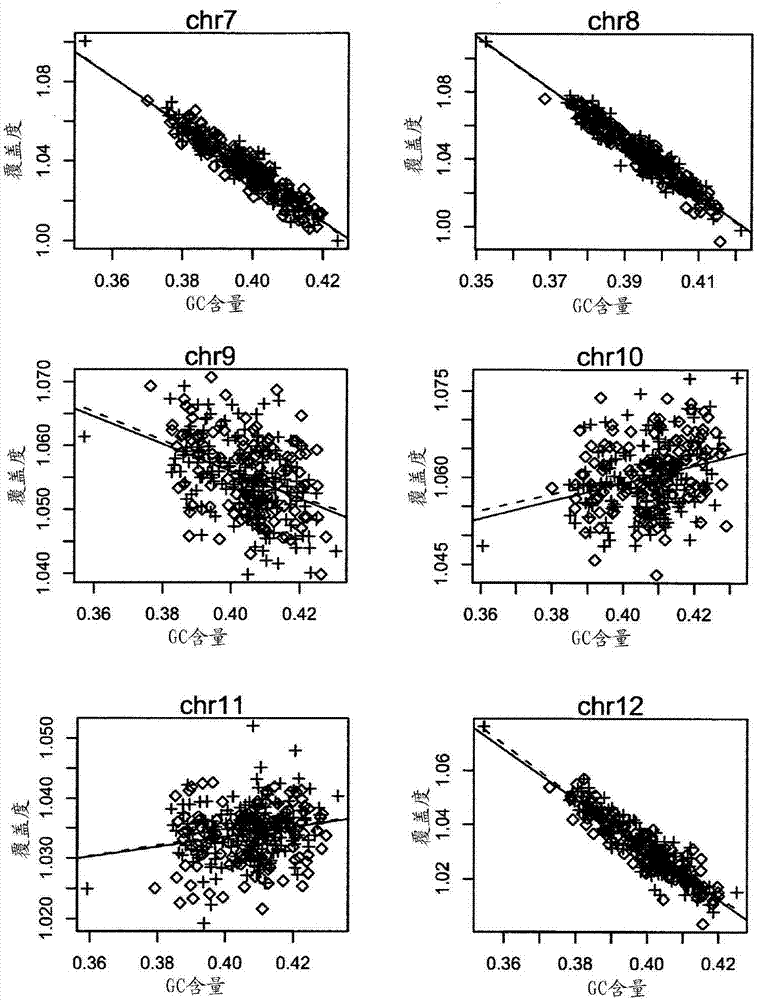
Method and device for carrying out GC correction on chromosome sequencing results
ActiveCN104120181ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHereditary disordersLarge-Scale Sequencing
The invention relates to a non-diagnostic method for noninvasively detecting fetal hereditary disorder by sequencing nucleotides from a maternal biological sample on a large scale, and further provides a method for eliminating sequencing result GC bias caused by chromosome GC content difference. The method disclosed by the invention not only enables detection to be more accurate, but also provides a non-diagnostic comprehensive method for detecting fatal aneuploidy including sex chromosomal disease cases, for example, XO, XXX, XXY, XYY, and the like.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
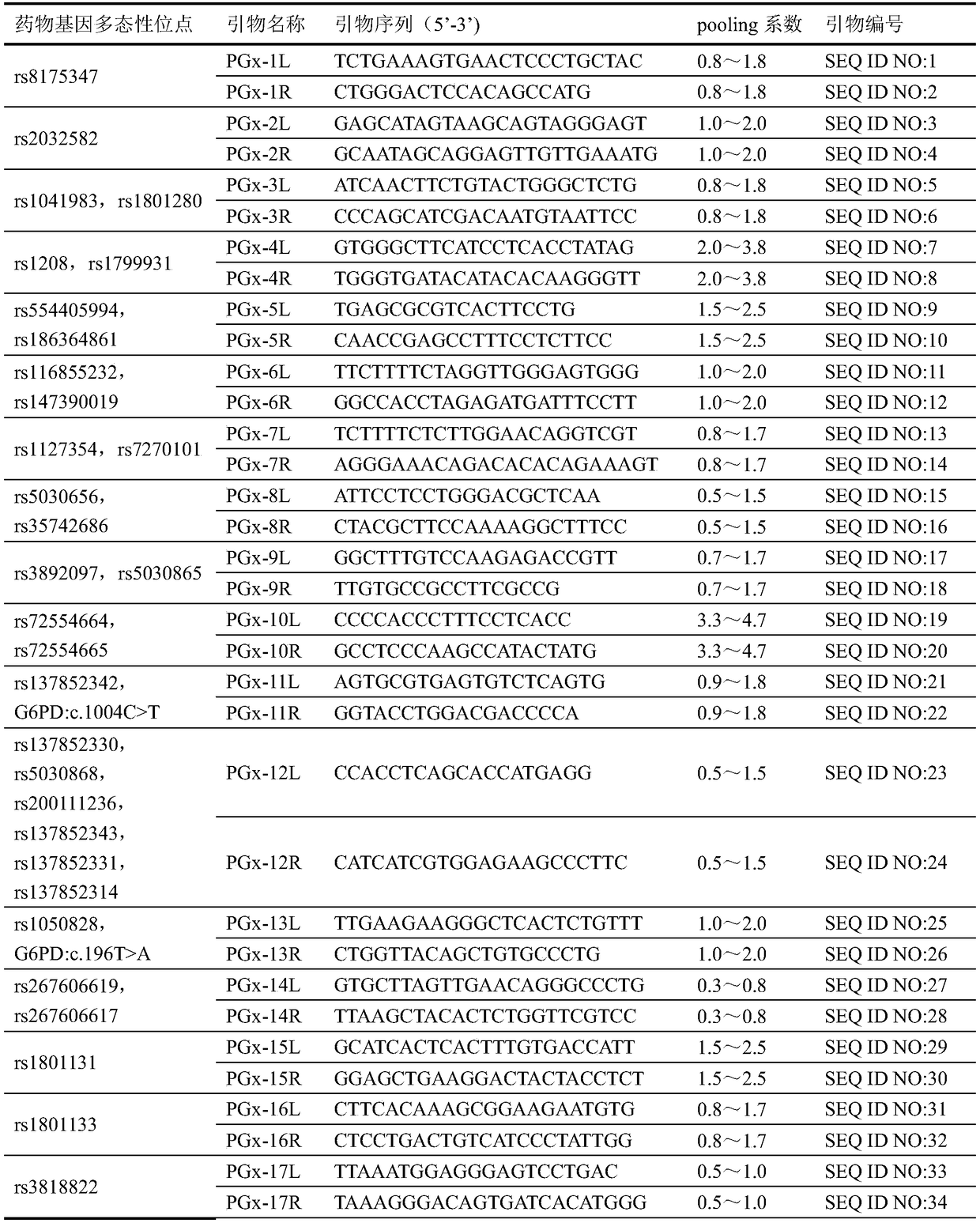
Personalized medication gene detection kit and application
ActiveCN108707658AStrong specificityAvoid mutual interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationMultiplex pcrsDried blood spot
The invention discloses a personalized medication gene detection kit and application. The personalized medication gene detection kit is suitable for multiple kinds of sample types including dried blood spots, whole blood and buccal swabs, information of all medicine gene polymorphic sites can be acquired at once, the sequencing effective rate is 50% or above, the sequencing cover degree is 100%, the average sequencing depth exceeds 3000 X, the library building success rate is larger than or equal to 98.5%, and the medicine gene polymorphic site detection accuracy is larger than or equal to 99.9%; a primer group is high in specificity and little in nonspecific amplification, interference among primers can be well overcome, under the situation of up to 186 primer sequences, one-tube multiplePCR reaction is achieved, moreover, amplicon is high in uniformity, and under the situation of large amplification area GC content difference, overall effective amplification can be conducted. The detection kit, the primer group and a library building method can be applied to personalized medication gene detection, and guidance is provided for personalized medication.
Owner:CAPITALBIO GENOMICS
Optimized gene of recombinant glucose oxidase and expression vector and application of optimized gene
ActiveCN102517304AIncrease secreted expressionIncreased GC contentFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisMrna secondary structure
The invention discloses an optimized gene of recombinant glucose oxidase and an expression vector and application of the optimized gene. On the premise that the amino acid sequence of the glucose oxidase is not changed, the gene sequence of the glucose oxidase is optimized according to pichia pastoris preferred codons by comprehensively considering the influencing factors such as use frequency ofthe codons, adjustment of GC content, deletion of instable sequences, secondary mRNA structure and the like; and the nucleotide sequence of the optimized glucose oxidase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1.The invention further provides the expression vector and a recombinant host strain containing the optimized gene of the glucose oxidase. The optimized gene is transferred to the pichia pastoris for expression, and the test results show that: compared with the gene before optimization, the secreting expression quantity of the optimized gene in the pichia pastoris is remarkably improved. The application effect tests of the glucose oxidase show that the expressed recombinant glucose oxidase has the same using effect as a commercial enzyme preparation.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Real-time fluorescence quantification PCR detection primer for quickly identifying genotypes of duck circovirus and detection method thereof
PendingCN106065419AIdentification method is simpleImprove shortcutMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescencePcr method
The invention relates to a real-time fluorescence quantification PCR detection primer for quickly identifying genotypes of duck circovirus and a detection method thereof. The sequences of the primer are described as follows: an upstream primer P1: 5'-CAGATCCCCGGGCACGAGA-3'; a downstream primer P2: 5'-CCTCACCTTCAGGGATTC-3'. The detection method includes the steps of: establishing the real-time fluorescence quantification PCR method based on SYBR Green I with the primer, wherein difference of temperature of a melting curve exists due to the difference of GC content of a nucleotide in a specific gene fragment region of gene 1-type duck circovirus and gene 2-type duck circovirus which are amplified by the primer, so that infection of the gene 1-type duck circovirus and the gene 2-type duck circovirus can be directly carried out according to the difference of Tm value in the melting curve. The method can distinguish the infection caused by the duck circovirus in different genotypes just with one group of primer, thereby providing technical fundament for healthy breeding in duck breeding industry.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY FUJIAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Newcastle disease virus/avian influenza virus H9 subtype/infectious bronchitis virus triplex fluorescence quantification detection reagent and detection method
InactiveCN105671204AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFluorescenceQuarantine
The invention relates to a newcastle disease virus / avian influenza virus H9 subtype / infectious bronchitis virus triplex fluorescence quantification detection reagent and a detection method and belongs to the technical field of animal quarantine. A newcastle disease virus M gene coding region specific sequence, an avian influenza virus H9 subtype H gene coding region specific sequence and a chicken infectious bronchitis virus M gene coding region specific sequence are selected as target regions, and on the basis of multi-sequence comparison, primer and probe design is conducted. The length of primers is about 20 basic groups, the GC content is 50-60%, a two-stage structure and repeatability do not exist in the primers, no complementary sequence exists between the primers or in the primers, and the melting temperature (Tm value) difference between the primers is smaller than 5 DEG C. In order to guarantee universal use of a newcastle disease virus probe, the length of the probe is only 13 basic groups, the probe is modified by LAN, and the Tm value of the probe is increased. The lengths of the other two virus probes are both about 25 basic groups, and the Tm values are about 5 DEG C higher than those of the primers.
Owner:山东省动物疫病预防与控制中心 +1
PCR amplification system and PCR amplification method for high GC content gene
The invention discloses a PCR amplification system and a PCR amplification method for high GC content gene, belonging to the technical field of biotechnology; the PCR amplification system comprises DNA polymerase, MgCl2, dNTP, upstream primer, downstream primer, DNA template and double distilled water; and the invention is characterized in that the PCR amplification system also comprises tri(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane hydrochloride, dithiothreitol, bovine serum albumin and additive. The PCR amplification technology in the invention can amplify target genes containing over 80% of GC, can amplify high GC content target genes with a length up to 1.5Kb and can successfully amplify template genes with different degrees of complexity and different sources such as people, animals, plants and microorganisms; in addition, the PCR amplification technology has less operating steps, short operating time, simple instruments and devices, thus being generally applicable to the scientific research and medical diagnosis.
Owner:陈学军
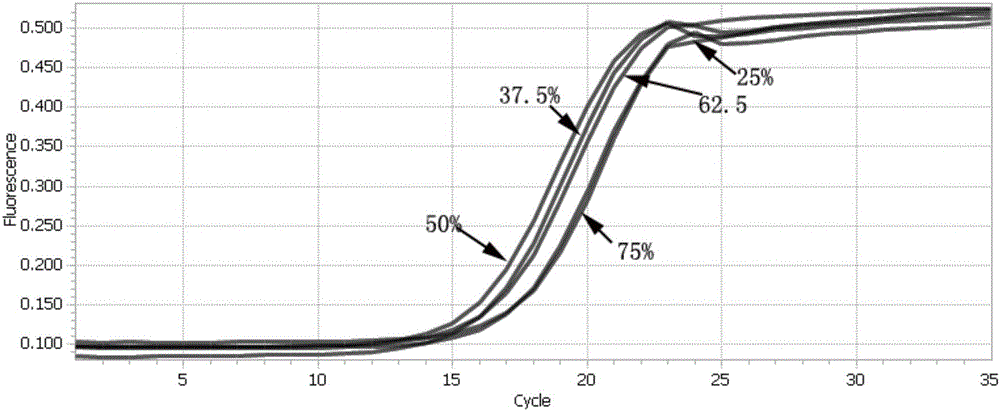
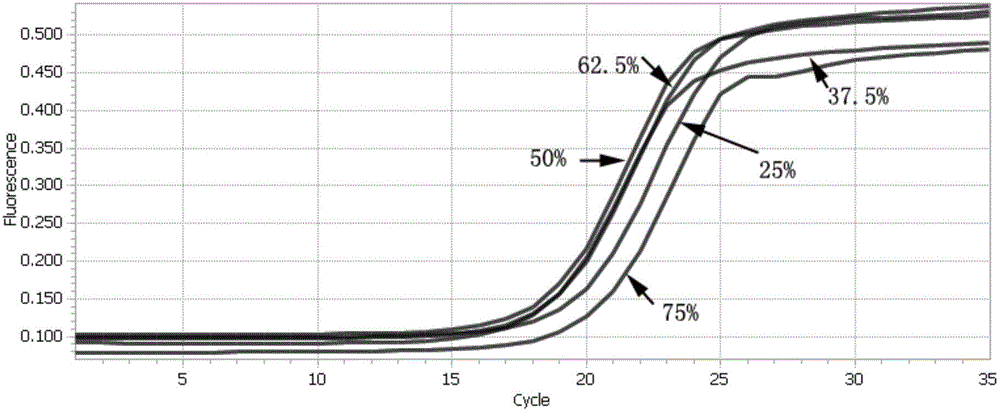
Kit and method for precise quantification of next-generation sequencing libraries different in GC content by qPCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction)
ActiveCN106434924AQuantitatively accurateReduce precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingGC-content
The invention discloses a kit and a method for precise quantification of next-generation sequencing libraries different in GC content by qPCR (quantitative polymerase chain reaction). The kit for precise quantification of the next-generation sequencing libraries different in GC content by qPCR comprises a plurality of standard samples different in GC content, library dilution liquid, qPCR premixed liquid, primers and ddH2O, wherein nucleotide sequences of the primers are as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2. The invention further provides the method of adopting the kit for precise quantification of the next-generation sequencing libraries different in GC content by qPCR. The kit and the method have advantages of precise quantification, convenience in use, wide application range, high selectivity, high sensitivity, high specificity and high stability and provide a guarantee for high-quality high-efficiency sequencing.
Owner:BEIJING TRANSGEN BIOTECH CO LTD
System and method for detecting copy number variation of cell free tumor genes
ActiveCN108875302AEliminate the effects of identificationEliminate inconsistent capture efficienciesSpecial data processing applicationsCell freeGC-content
The invention provides a system and a method for detecting copy number variation of cell free tumor genes. The average depth of each capture interval is normalized through the average sequencing depthof an overall capture area, so that the influence of change of capture efficiency caused by experiment operation errors on gene copy number identification is eliminated. In a traditional normalization method, a ratio of interval reads to all sequencing reads is adopted as a normalized value of each interval, and the influence on a result caused by inconsistent capture efficiency among different experiments is not eliminated in the traditional method. Through a method for constructing a normal training set, the problem of inconsistent capture efficiency among the capture intervals in samples due to reasons of GC content, probe concentration and the like can be eliminated, so that the false positive rate is reduced.
Owner:广州漫瑞生物信息技术有限公司
PCR amplification additive composition used for high-GC gene, and PCR amplification method of high-GC gene
InactiveCN103981172AAmplified GC contentStrong specificityDNA preparationPolyethylene glycolPcr method
The invention provides a PCR amplification additive composition used for high-GC gene. The amplification additives are selected from two or more of 7-deaza-dGTP, betaine or betaine analog, DMSO, glycerin, formamide and polyethylene glycol. Compared with additives and the prior art, the PCR additive and an amplification method can realize the amplification of target gene with the template GC content of above 80%, and can realize the successful amplification of complex gene to be used in clinic detection; a PCR amplification obtained in the invention has the advantages of high specificity, single brand and no purification, and can be directly used in subsequent operations; and the PCR method has a low requirement on DNA polymerase, and can match with various commercial PCR kits.
Owner:江苏佰龄全基因生物医学技术有限公司
Method for removing GC preferences in euchromosomes and between chromosomes as well as detection system
InactiveCN105825076AAvoid distortionIncreased sensitivitySpecial data processing applicationsAnomaly detectionHigh throughput sequence
The invention discloses a method for removing GC preferences in euchromosomes and between chromosomes as well as a detection system. The detection system comprises (1) a high-throughput sequencing instrument used for obtaining a whole genome sequence of a sample through high-throughput sequencing, and (2) a computer readable medium used for executing a plurality of instructions in the following steps: a, constructing a system for removing GC deviations, b, constructing another system for removing the GC deviations, and c, constructing a detection system for detecting non euploids and normal samples in samples: judging whether the samples are the non euploids or not finally according to Z values obtained by two different corrections. With the adoption of the detection system, the GC deviations are removed, so that the fetal genetic abnormality detection with higher sensitivity can be carried out while the data distortion is avoided. The detection system is used for defining parameters used for a statistic test according to the GC content. In addition, parameters in statistical sense are obtained according to a large batch of data through a Z value statistics method, so that higher accuracy can be achieved.
Owner:杭州天译基因科技有限公司
Mixed type hot-start DNA polymerase composition, PCR amplification kit, and applications thereof
ActiveCN108546749AImprove heat resistanceLow mismatch rateMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyWild type
The invention discloses a mixed type hot-start DNA polymerase composition, a PCR amplification kit, and applications thereof. The composition comprises Taq DNA polymerase, an anti-Taq antibody, and mutant type KOD DNA polymerase. The anti-Taq antibody is capable of specifically being combined with Taq DNA polymerase. The 147th site of wild type KOD DNA polymerase is histidine, and the 147th site of mutant type KOD DNA polymerase is lysine. The experiment results show that the mismatch rate is low when the mixed type hot-start DNA polymerase composition is used for PCR amplification, the composition has the dual characteristics of high efficient amplification and high fidelity and is heat resistant in amplification, and the amplification effect is good no matter for a long DNA segment, a template with a low amount, or a template with a high GC content.
Owner:深圳市艾伟迪生物科技有限公司
Gene encoding beta-glucosidase
InactiveCN101363026AAvoid pollutionSolve the world energy crisisEnzymesGenetic engineeringBeta-glucosidaseNucleotide
The invention provides a gene of coded beta-glucosaccharase, which is called Unbgl1B and is obtained by constructing Metagenome DNA library of uncultured microorganisms of alkality contaminated soil and by the detecting and screening method of the activity of the beta-glucosaccharase of clone library, so as to be one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) DNA sequences and partial sequence thereof in sequence 1 of a sequence table; 2) DNA sequences having more than 80% of homoeology compared with the DNA sequences defined by the sequence 1 of the sequence table. The DNA in the sequence 1 of a sequence table is DNA sequences of a pGEM-3Zf(+) part of a cloning vector and DNA of exogenetic uncultured microorganisms cloned on the vector, and the exogenetic DNA segment consists of 838 basic groups; the GC content of the gene is 54.3%. The gene is used for producing the beta-glucosaccharase, so as to dissociate cellobiose into single glucose molecule.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Microorganism and method for environmental purification using the same
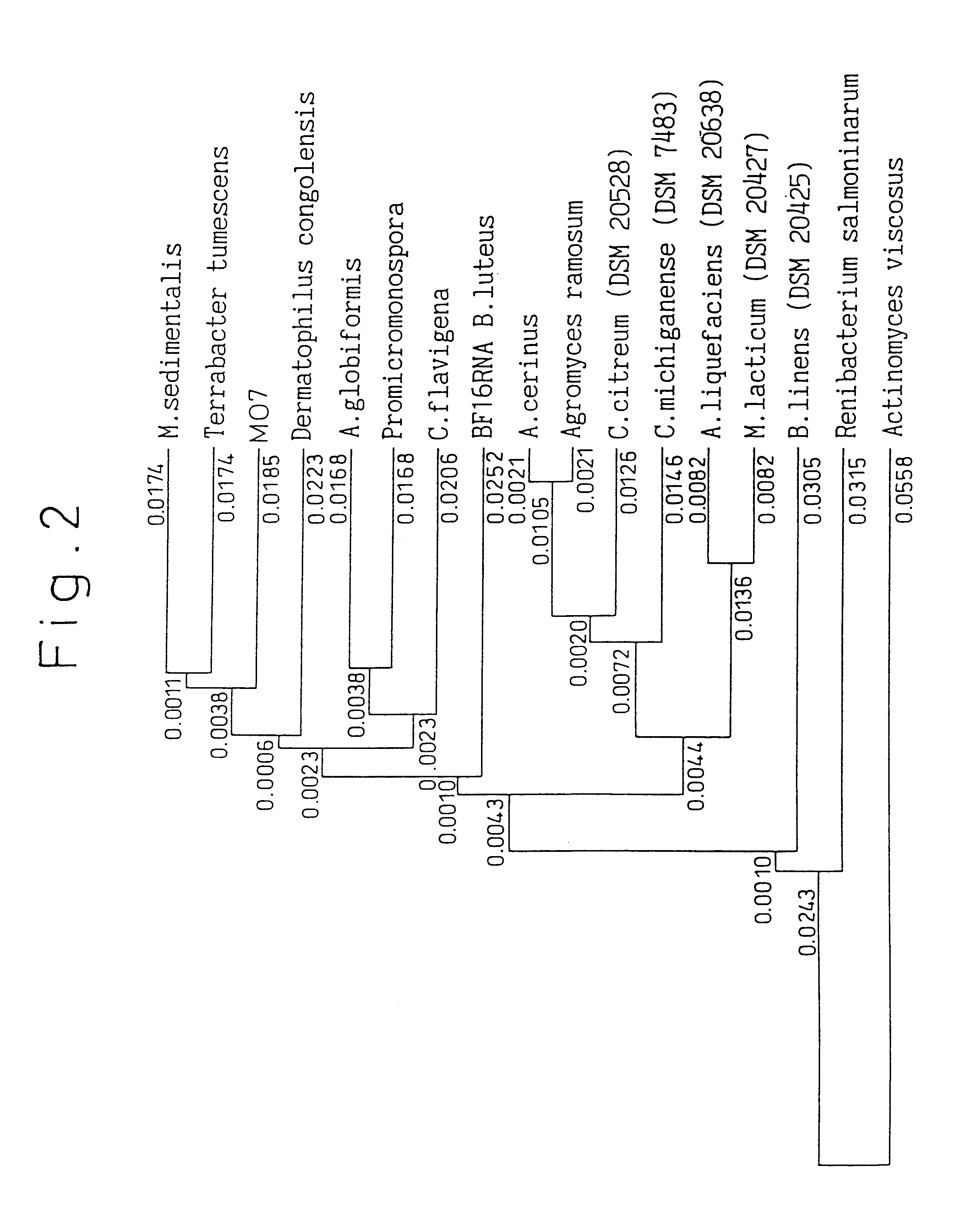
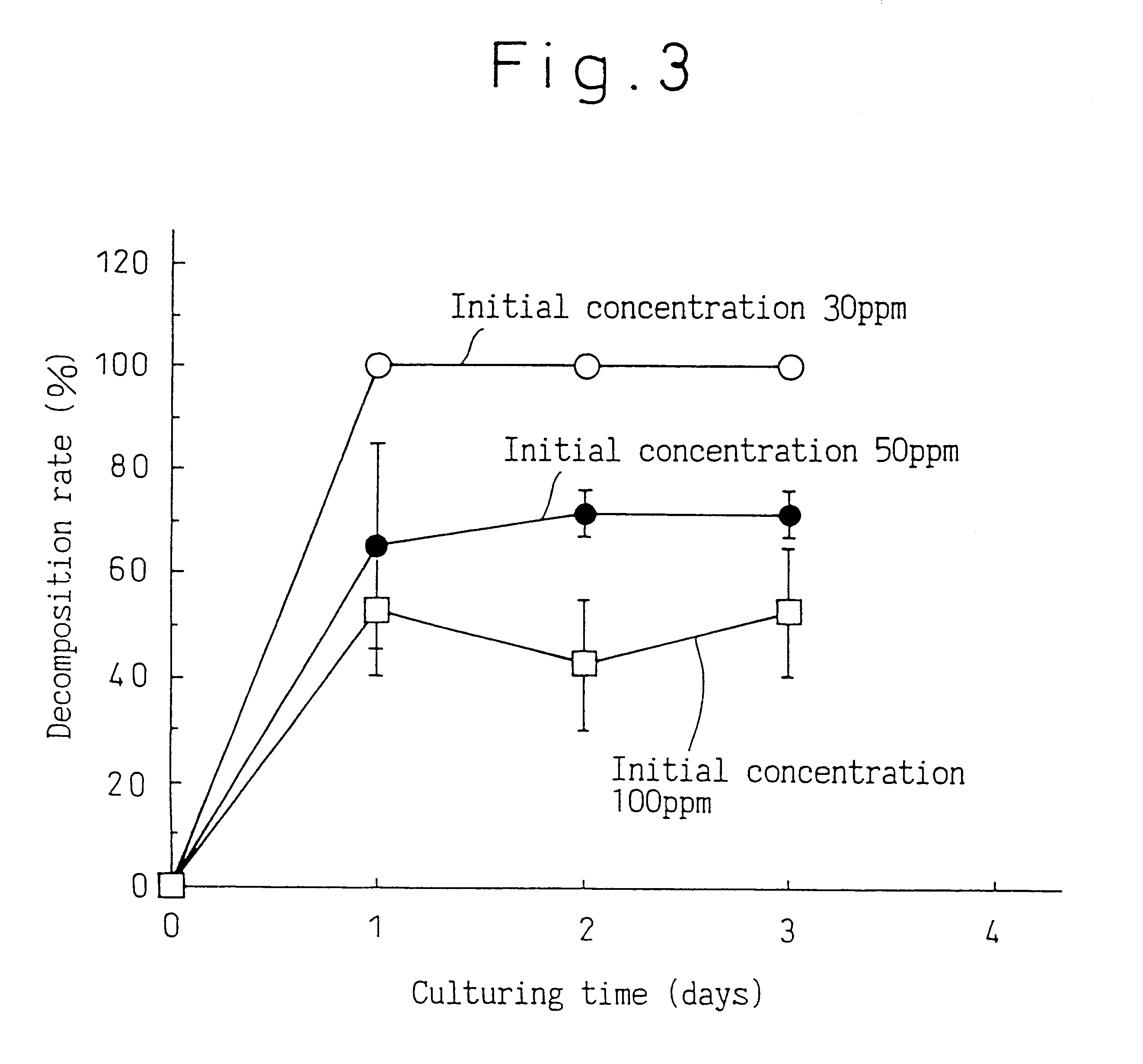
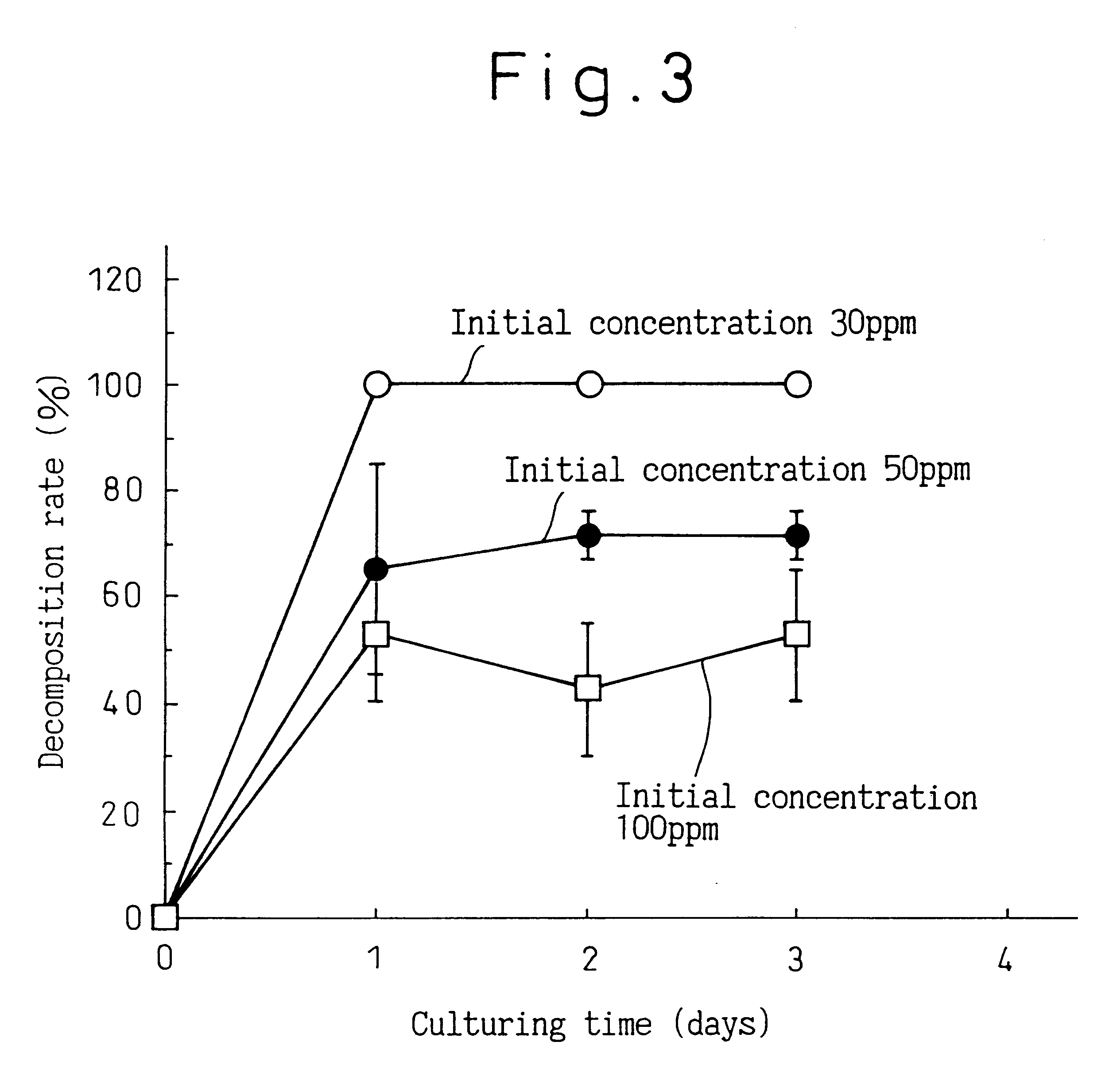
InactiveUS6521444B1Easy to penetrate into soilEfficient decompositionMicroorganismsSolid waste disposalMotilityOxygen
A novel microorganism which has the following characteristics: morphology (coccoid, rod shaped); gram staining (+), spore forming (-), motility (-), relationship to oxygen (aerobic), oxidase test (-), catalase test (+), resistance to acid (-), rod-coccus cycle (+), and GC content of DNA (mole%) (73 (by HPLC)), and which can decompose chloroethylene. The microorganism can decompose in 24 hours 30 ppm of trichloroethylene, and decompose of 100 ppm of trichloroethylene by 50%.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
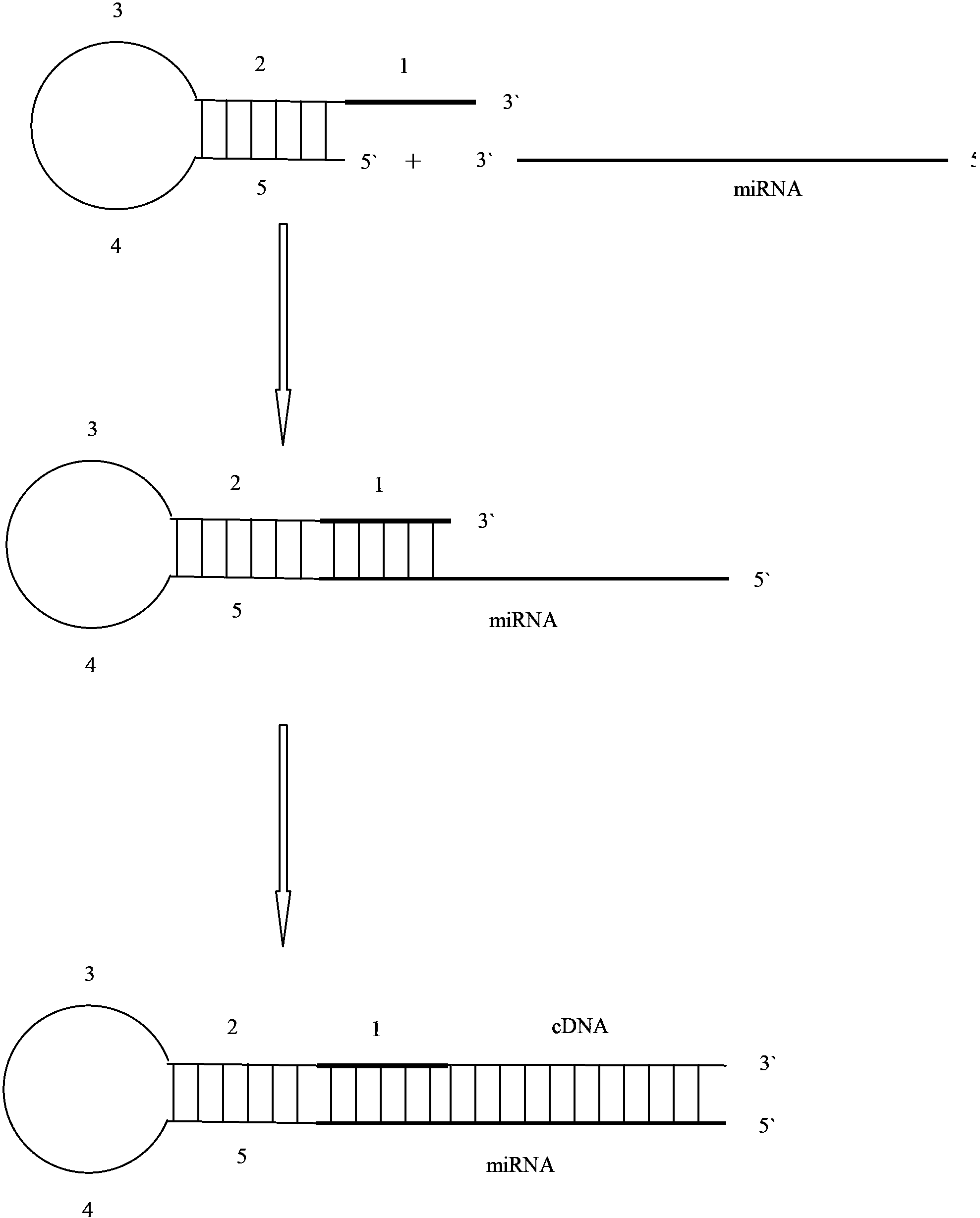
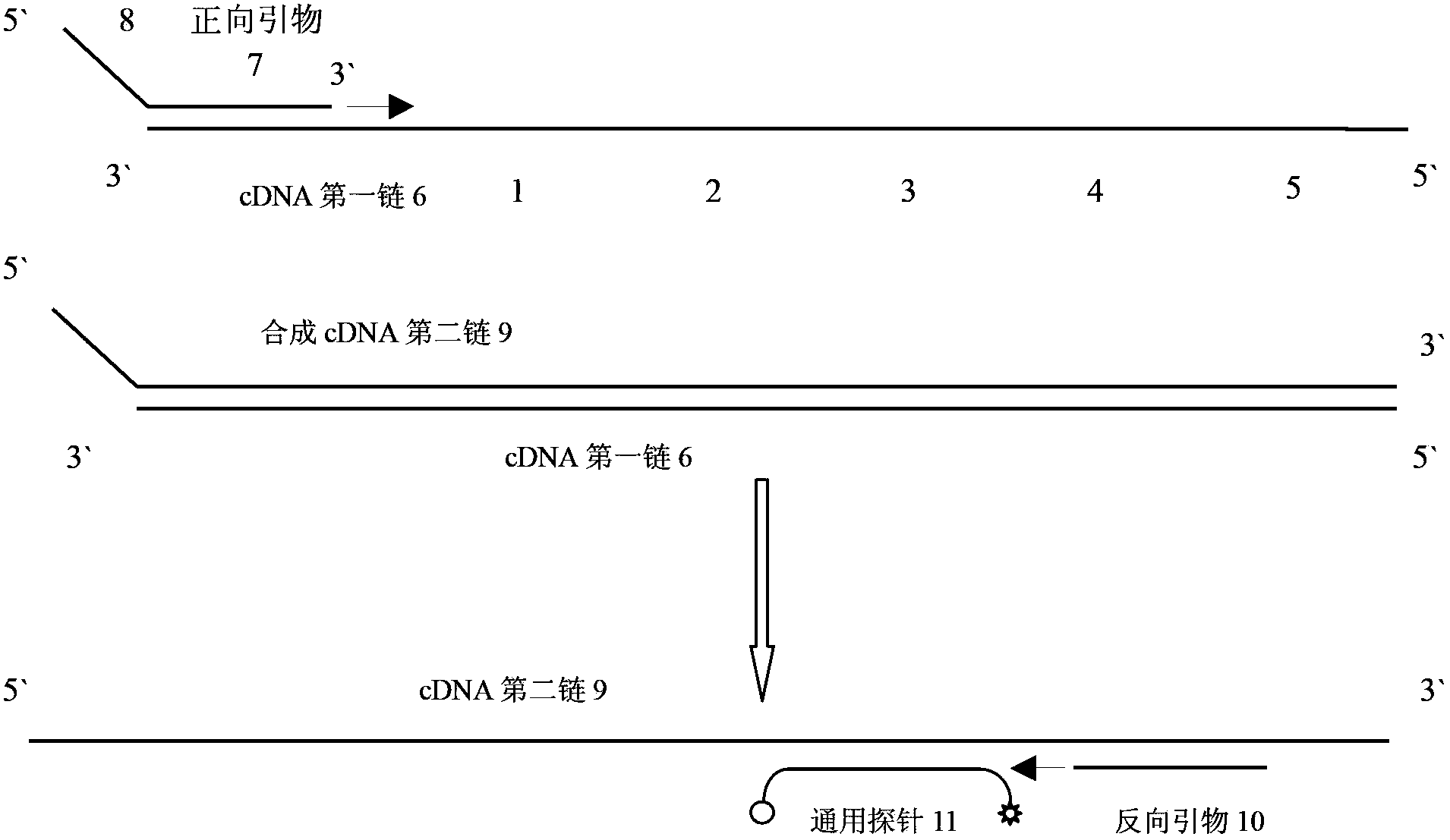
Primer for amplifying short-chain RNA (ribonucleic acid) and related method thereof
InactiveCN103509789ASimple designEasy to synthesizeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMicrobiologyNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a primer for amplifying a short-chain RNA (ribonucleic acid) and a related method thereof. The primer is oligonucleotide; a fragment of nucleotide sequence at the 5' end of the primer is fixed, and forms a structure with a nucleotide loop and a nucleotide stem; the 3' end of the primer is connected with 6 to 8 nucleotides, and is paired with the 3' end of a mature miR to form specific complementary binding; the 3' end of the nucleotide loop contains a fragment of nucleotide sequence with GC content of over 70 percent, and the fragment of nucleotide sequence is called a universal probe region; nucleotides on the 8th to 30th sites at the 5' end of the primer form a universal reverse primer region. The primer has an internal double-chain structure, and cannot be bound to a specific sequence in a nucleotide chain under the action of steric hindrance, and the reverse transcription of the sequence is avoided; the primer is only specifically paired with and bound to the 3' end for specific reverse transcription. The primer is high in specificity, easy to design, convenient to synthesize and suitable for the reverse transcription of the short-chain RNA, especially the mature miR, and the formation of a primer dimer is avoided.
Owner:ZHOUSHAN HOSPITAL
Noninvasive detection of fetal genetic abnormality
ActiveUS20140099642A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLarge-Scale SequencingFetal aneuploidy
The current invention is directed to methods for noninvasive detection of fetal genetic abnormalities by large-scale sequencing of nucleotides from maternal biological sample. Further provided are methods to remove GC bias from the sequencing results according to the difference in GC content of a chromosome. The current invention not only makes the detection much more accurate but also represents a comprehensive method for fetal aneuploidy detection including sex chromosome disorders such as XO, XXX, XXY, and XYY, etc.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD
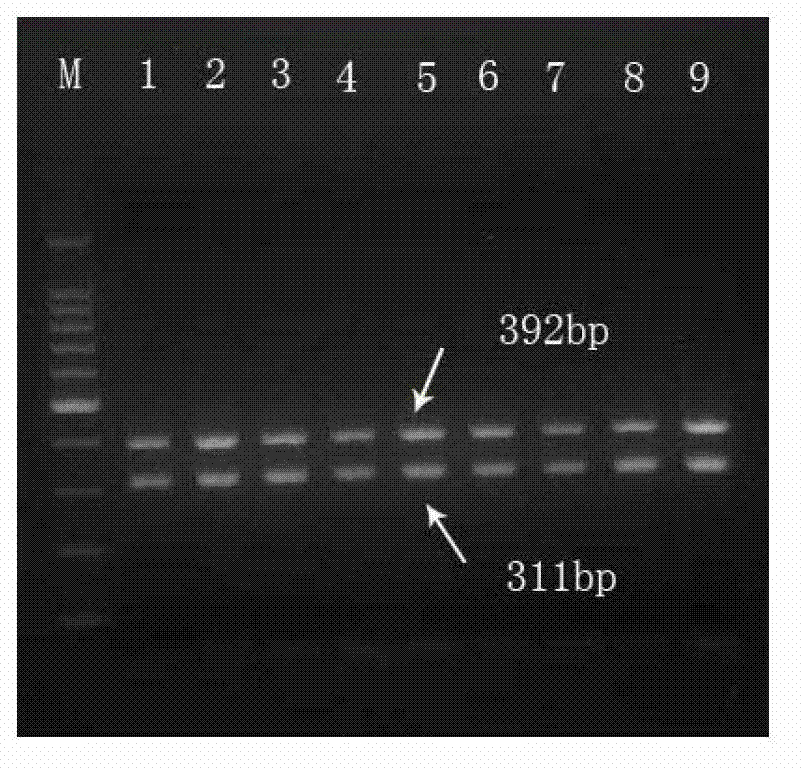
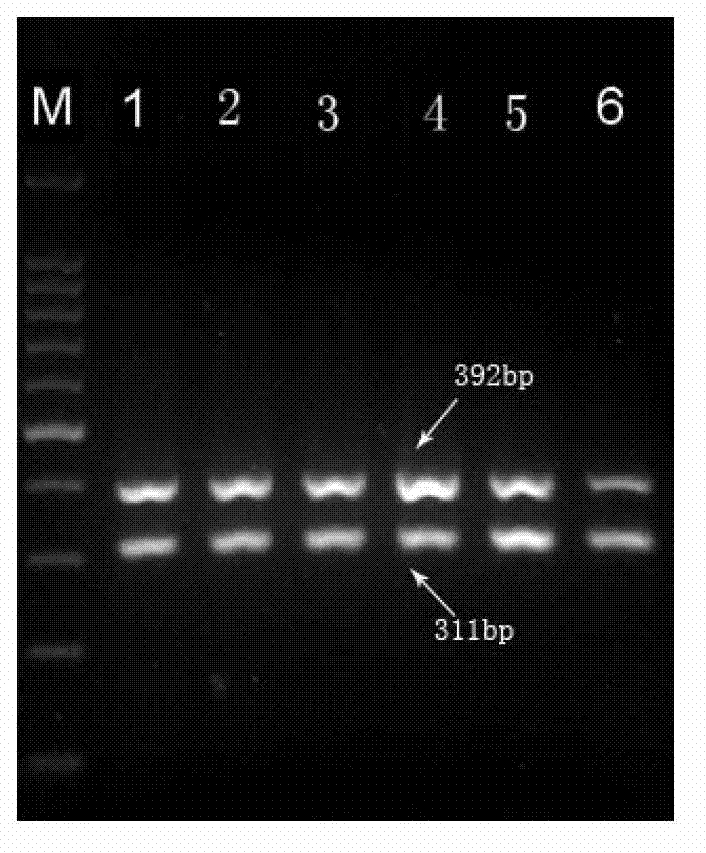
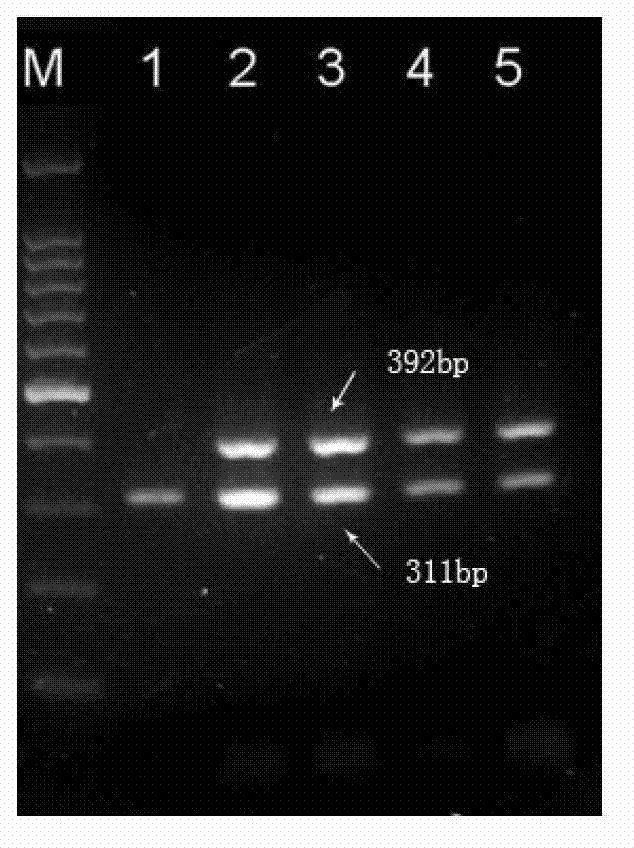
Multiple PCR primer used for simultaneously detecting infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis virus and akabane virus as well as its design method
InactiveCN103160615ARapid detectionSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAgricultural scienceInfectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus
The invention relates to a multiple PCR primer used for simultaneously detecting infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis virus and akabane virus as well as its design method, and relates to detection of infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis virus and akabane virus. The size of a PCR amplification fragment corresponded to an infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis virus primer in the multiple PCR primer is 311bp, the size of the PCR amplification fragment corresponded to akabane virus id 392bp. The method comprises the following steps: 1) designing multiple PCR primer combination; 2) screening the primer in the primer combination, keeping the primer which can not synthesize a primer dimer; 3) determining the competition advantage and disadvantage states of the kept primer, comparing GC% and base number in the kept primer, selecting the kept primer with high GC content and determining as the primer with excellent competition state, performing a step 5); otherwise, performing a step 4); 4) selecting the primer with poor competition state again, wherein the concrete step repeats the step 2) and determining the kept primer according to the step 3) again; and 5) performing amplification on the primer with the excellent competition state.
Owner:厦门佰能检验技术服务有限公司
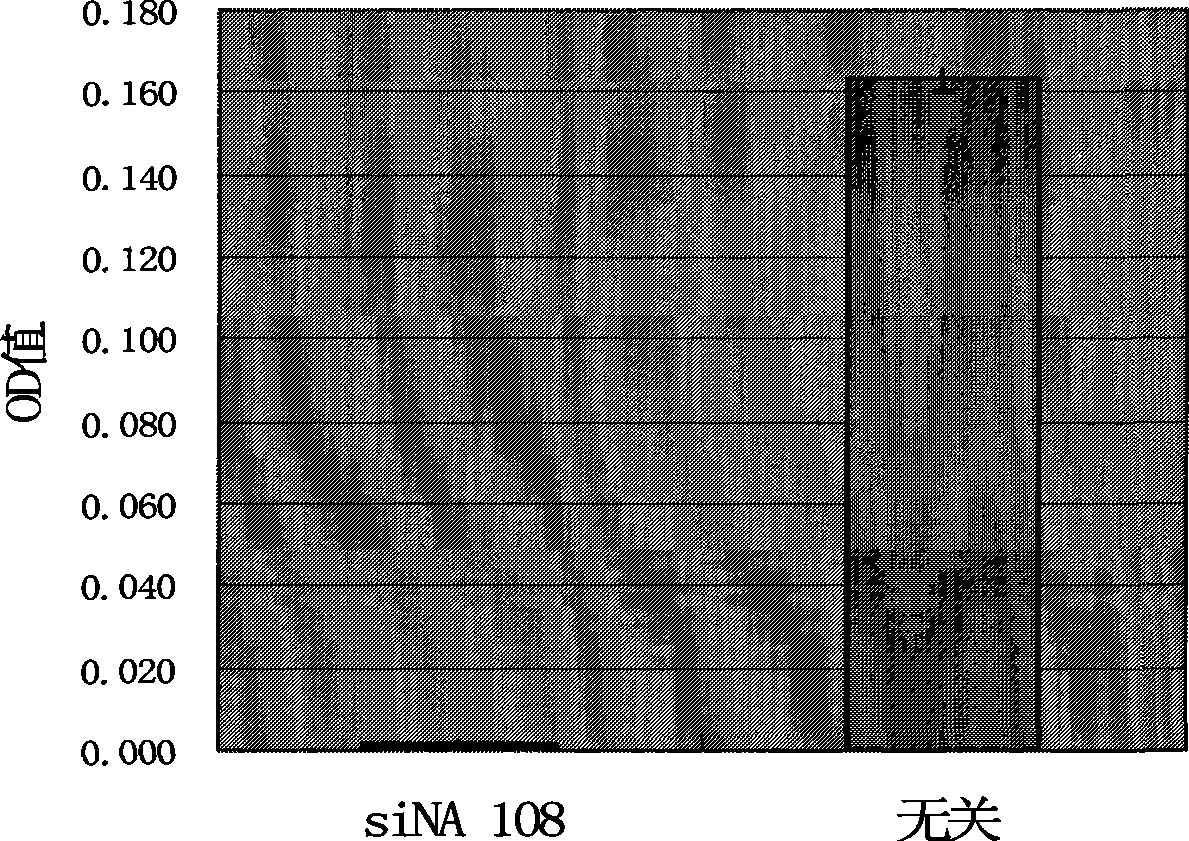
Double-chain small molecule interference nucleic acid for inhibiting and killing drug tolerant bacteria and composition thereof
InactiveCN101457222ADrug resistance is reversibleInhibition is effectiveAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesMethicillin resistance geneHuman DNA sequencing
The invention relates to a double-chain small molecule interference nucleic acid for inhibiting and killing various drug tolerance bacteria using methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aurous as represents. The siNA of the invention is a double-chain molecule with 19 base pairs. A sense strand and a antisense strand respectively have two overhanging bases dT at 5' terminals, the GC content is 40-55; the aimed target sequence is selected from the genes relative with the vital movements of copy, transcription and translation in the staphylococcus aurous genome and an mecA gene correlative with the drug tolerance; said target sequence is preserved in 900f staphylococcus aurous; said target sequence is in a conservative sequence area in more than 900f staphylococcus aurous with distinct source with all the gene sequences in the human genome; the target sequence of the said siNA double-chain molecule is selected from SEQ ID NO. 1-325, the sense strand is a corresponding DNA or RNA sequence with the target sequence and the antisense strand is a corresponding RNA or DNA with the sense strand according to the complementary base law.
Owner:李宝健
Microorganism and method for environmental purification using the same
InactiveUS6171844B1Easy to penetrate into soilMinimize impactBacteriaSolid waste disposalMicroorganismSpore
A novel microorganism which has the following characteristics: morphology (coccoid, rod shaped), gram staining (+), spore forming (-), motility (-), relationship to exygen (aerobic), oxidase test (-), catalase test (+), resistance to acid (-), rod-coccus cycle (+), and GC content of DNA (mole %) (73 (by HPLC)), and which can decompose chloroethylene. The microorganism can decompose in 24 hours 30 ppm of trichloroethylene, and decompose of 100 ppm of trichloroethylene by 50%.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for improving the sensitivity of detection in determining copy number variations
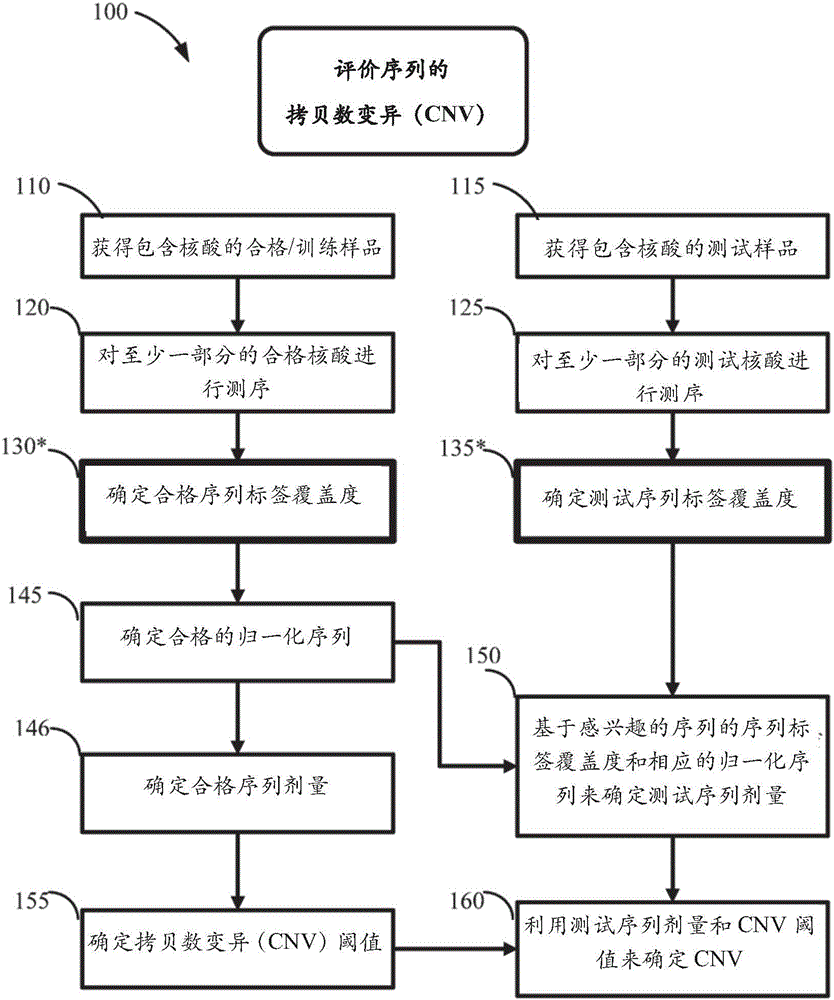
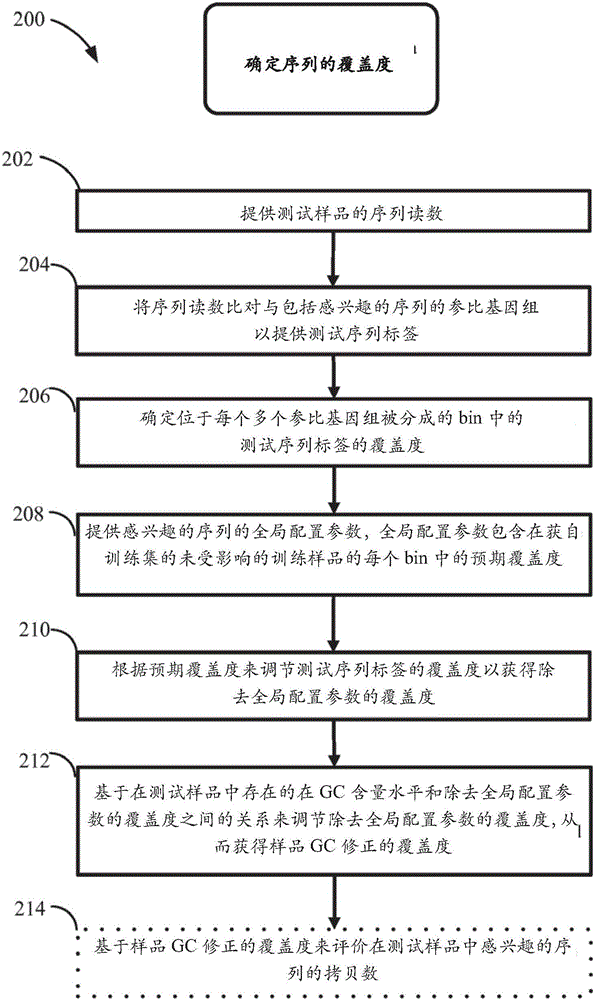
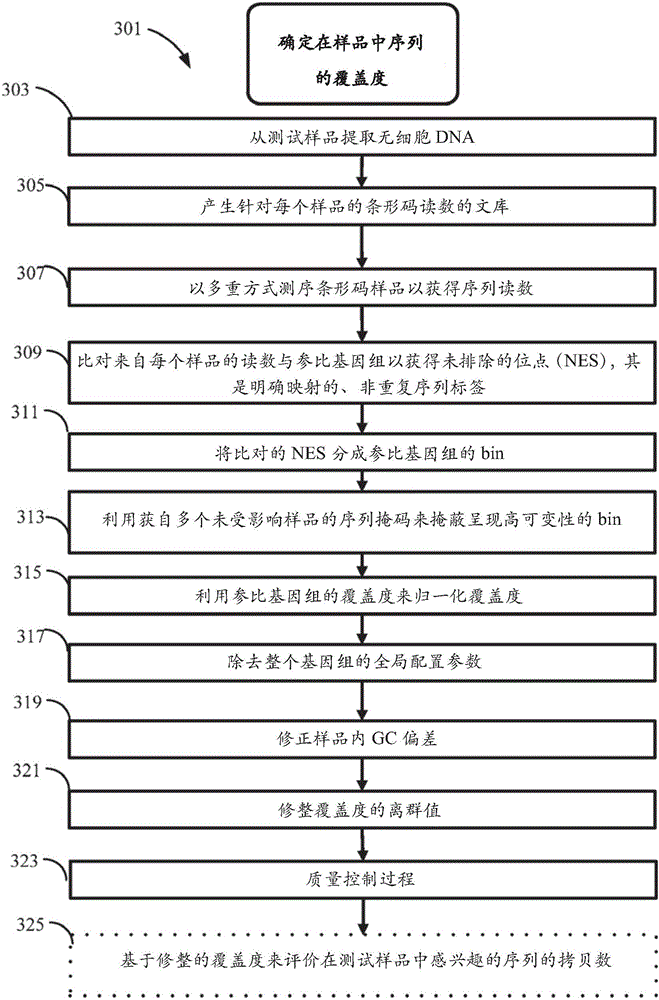
The invention discloses a method for improving the sensitivity of detection in determining copy number variations. Disclosed are methods for determining copy number variation (CNV) known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining copy number variation (CNV) of fetuses using maternal samples comprising maternal and fetal cell free DNA. In some embodiments, methods are provided for determining CNVs known or suspected to be associated with a variety of medical conditions. Some embodiments disclosed herein provide methods to improve the sensitivity and / or specificity of sequence data analysis by removing within-sample GC-content bias. In some embodiments, removal of within-sample GC-content bias is based on sequence data corrected for systematic variation common across unaffected training samples. Also disclosed are systems and computer program products for evaluation of CNV of sequences of interest.
Owner:VERINATA HEALTH INC
Lactase mutator, secretory expression method and application thereof
ActiveCN101948854AIncrease relative enzyme activityIncrease secreted expressionFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisLactase
The invention discloses a lactase mutator with optimized codon and high specific activity and a secretory expression method thereof. The lactase gene cloned in bifidobacterium animalis is optimized for codon of the gene and the GC content on condition that the amino acid sequence of the gene is not changed according to the preference of the codon of Pichia pastoris; the optimized lactase gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.2.After optimizing, 461 basic groups are changed; the percentage of GC% is lowered to 53.79% from 61.11%t; the enzymatic activity of the lactase is obviously increased after the codon is optimized. Moreover, the method shows that: since the lactase gene and protein disulfide isomerase are transformed into the Pichia pastoris cell, the relative activity of the lactase is obviously increased; and the secretory expression content of the lactase gene in the Pichia pastoris is obviously increased.
Owner:北京森根比亚生物工程技术有限公司
Method for synthesis of nucleic acids
InactiveUS6962780B2Reduced Pollution ChancesEfficient amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlcoholPolyol
The present invention is a method for synthesis of nucleic acids to amplify an intended nucleic acid in a region in which a GC content is rich, wherein a polyhydric alcohol and / or ammonium sulfate is present in an amplification reaction solution. According to the present invention, it is possible to amplify nucleic acids in a GC rich region efficiently and directly from a sample such as blood containing lots of PCR inhibitory substances without undergoing a process of isolating and purifying the nucleic acid, even though conducting PCR in the GC rich region tends to be difficult using conventional processes even if purified DNA is used.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Compositions for improving gene amplification
InactiveUS20120028259A1Improve polymerase performanceImprove performanceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBlood componentGC-content
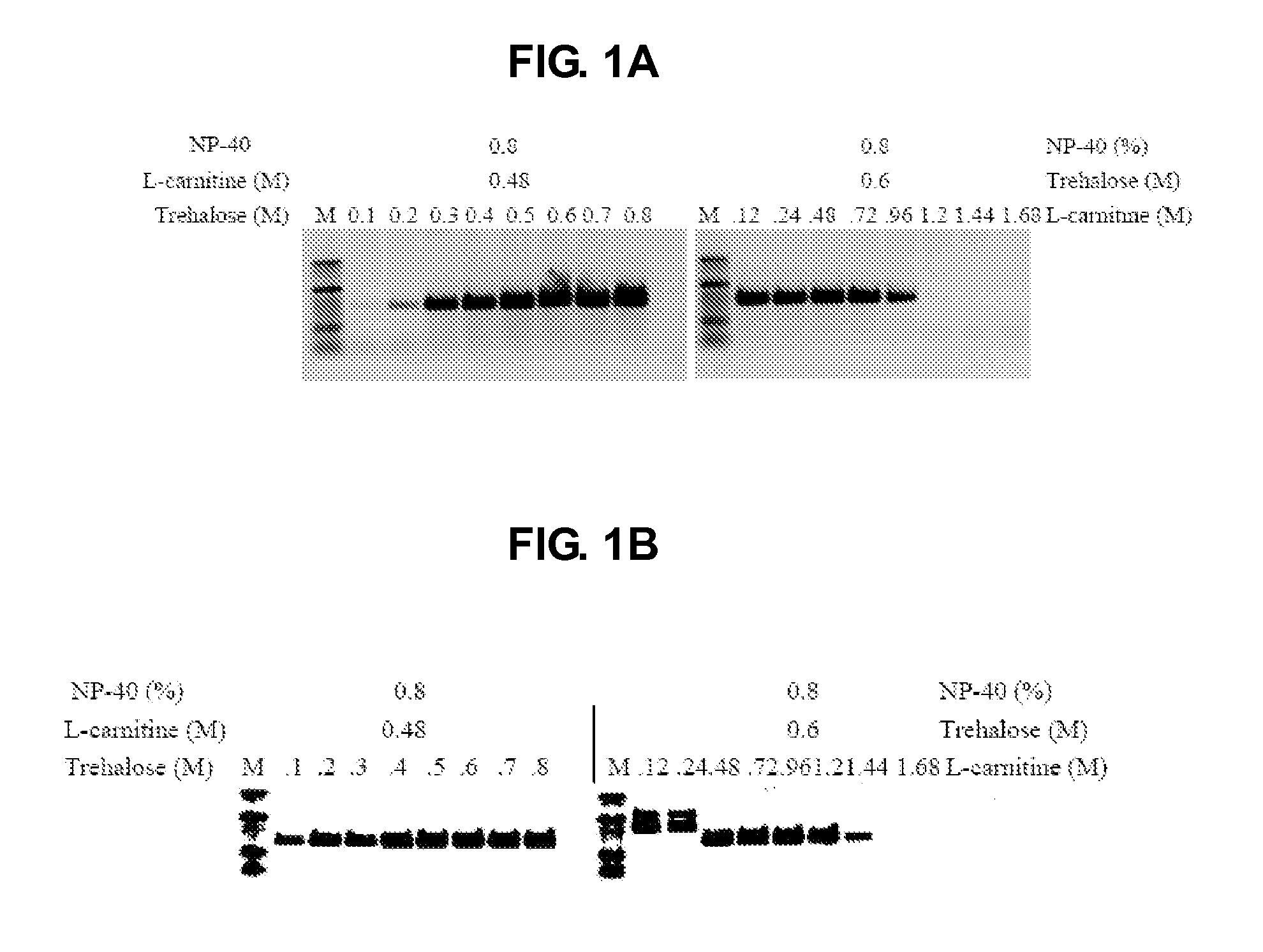
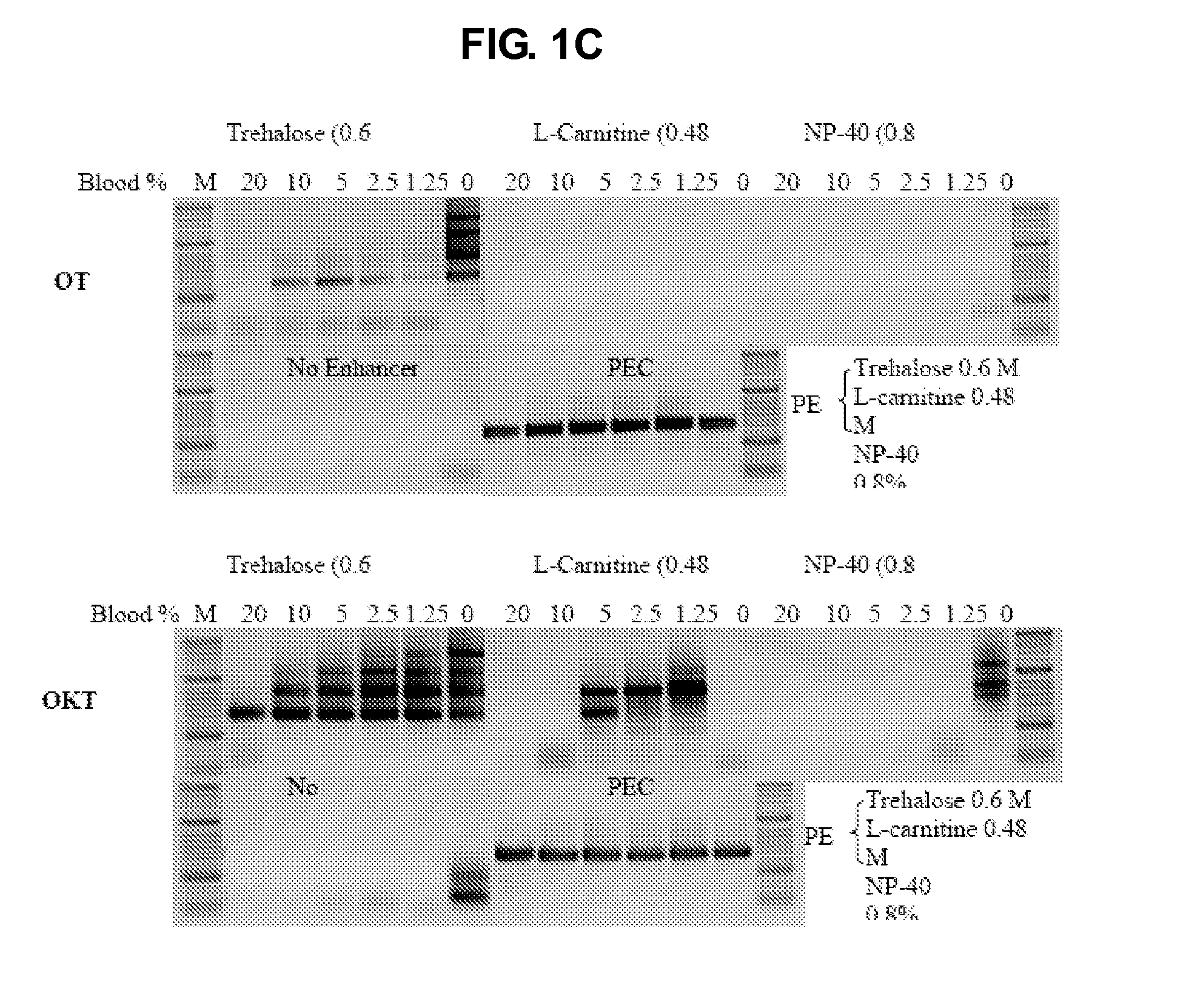
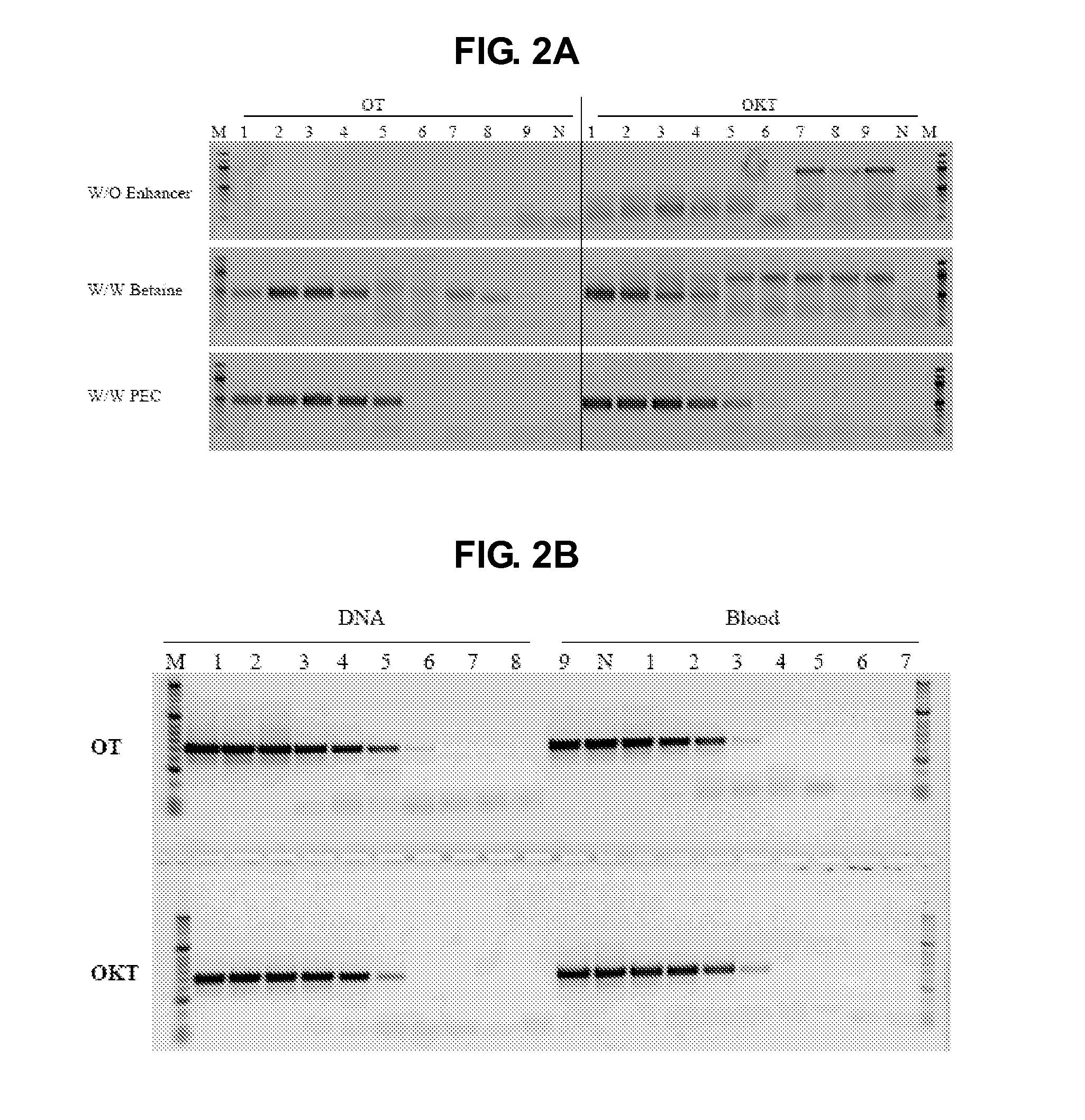
The present invention generally relates to amplfication reactions. One aspect of the invention provides amplification reaction enhancer compositions comprising trehalose, carnitine, and a non-ionic detergent, such as NP40. These enhancer compositions can improve efficiency, specificity, and sensitivity of amplification reactions in conventional and real-time PCR and RT-PCR. In addition, these compositions permit nucleic acid amplification directly in crude samples containing blood, blood components, or soil extract with little or no nucleic acid extraction prior to amplification. Another aspect of the invention provides a method of enhancing an amplification reaction containing a crude blood sample with heparin. Another improvement derived from the invention is improved detection of difficult, high GC content nucleic acid targets.
Owner:DNA POLYMERASE TECH
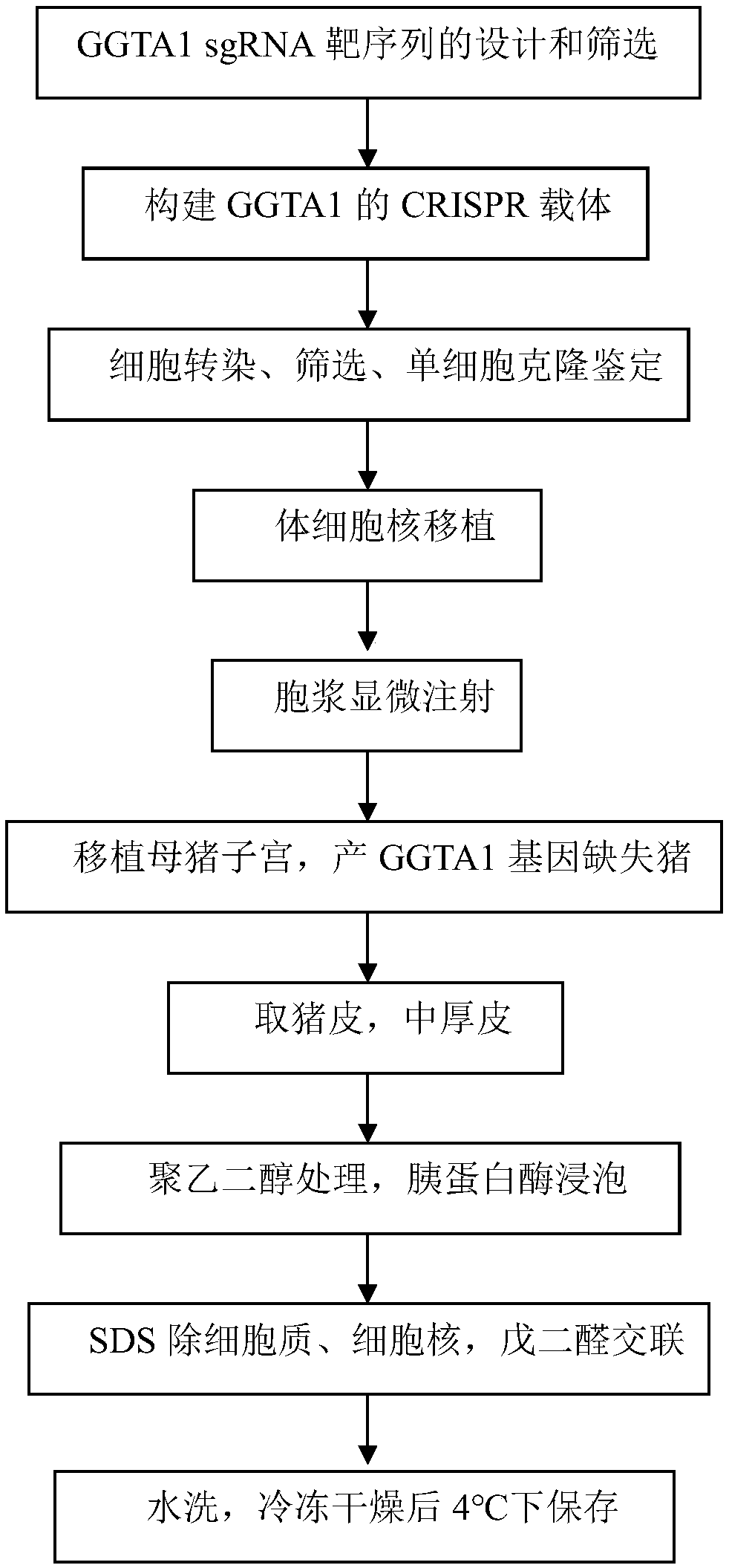
SgRNA for lowering immunogenicity, low-immunogenicity dressing and preparation method thereof
PendingCN108642054ALow immunogenicityNon-immunogenicGenetically modified cellsNucleic acid vectorBinding siteGC-content
The invention discloses a SgRNA for lowering immunogenicity, a low-immunogenicity dressing and a preparation method thereof. The sgRNA for lowering immunogenicity has a length from 18nt and 22nt; the3' end of the target sequence on the GGTA1 gene of the sgRNA contains GG, and the GC content is 40%-60%; The sgRNA does not have SNPs in the genome sequence of the target combination site; the sgRNA is compared with a pig GGTA1 gene to carry out the whole gene off-target effect analysis, and maximum 5 base mismatches are allowed in the off-target site. The low-immunogenicity dressing is pig skin,the pig skin is derived from a GGTA1 gene knockout pig. The sgRNA for lowering immunogenicity and the low-immunogenicity dressing have the advantages of low immunogenicity, even no immunogenicity, canbe used as a human skin substitute and reduce the risk of complications.
Owner:武汉博杰生物医学科技有限公司 +1
Novel feruloyl esterase, mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111748538ARich sources of bacteriaRich sourcesHydrolasesFood processingEscherichia coliGenetics genomics
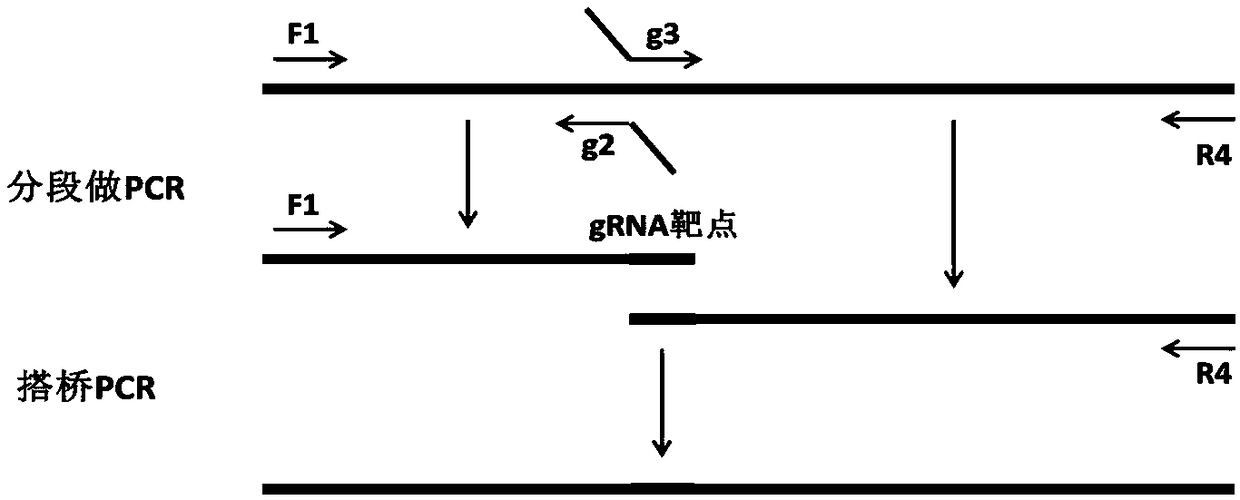
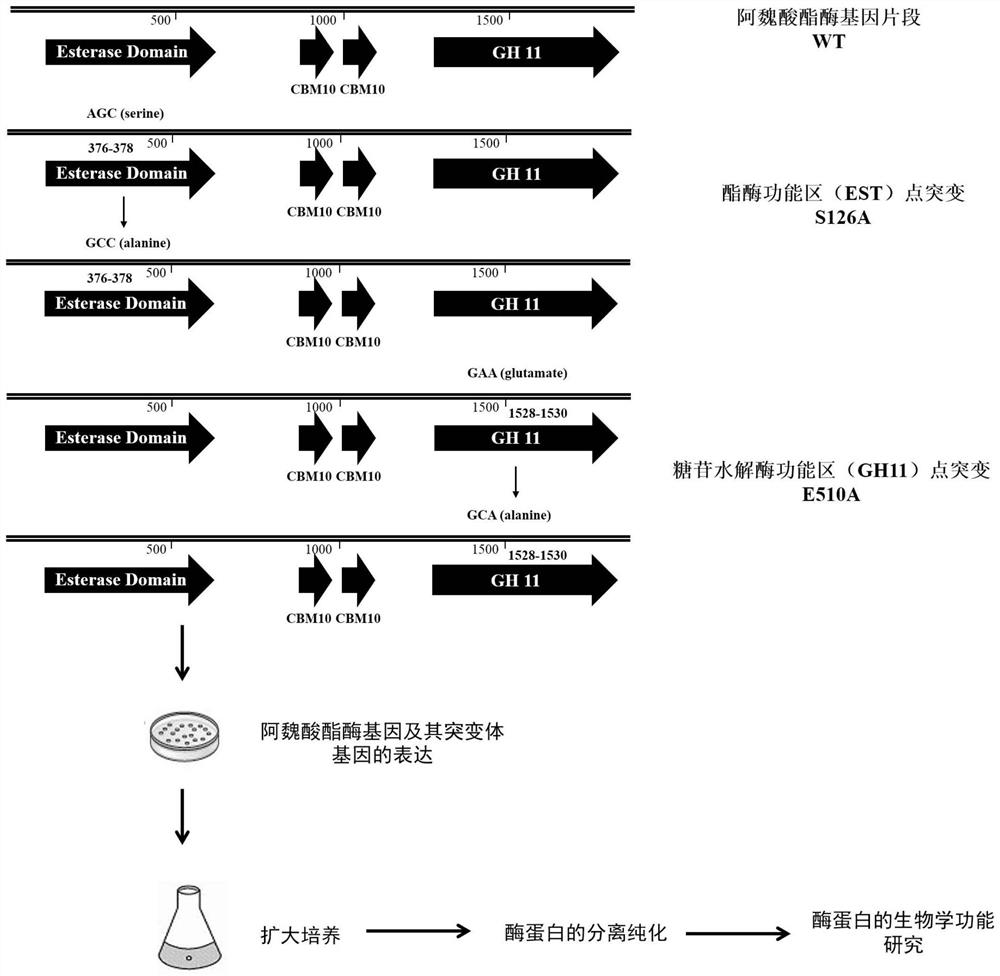
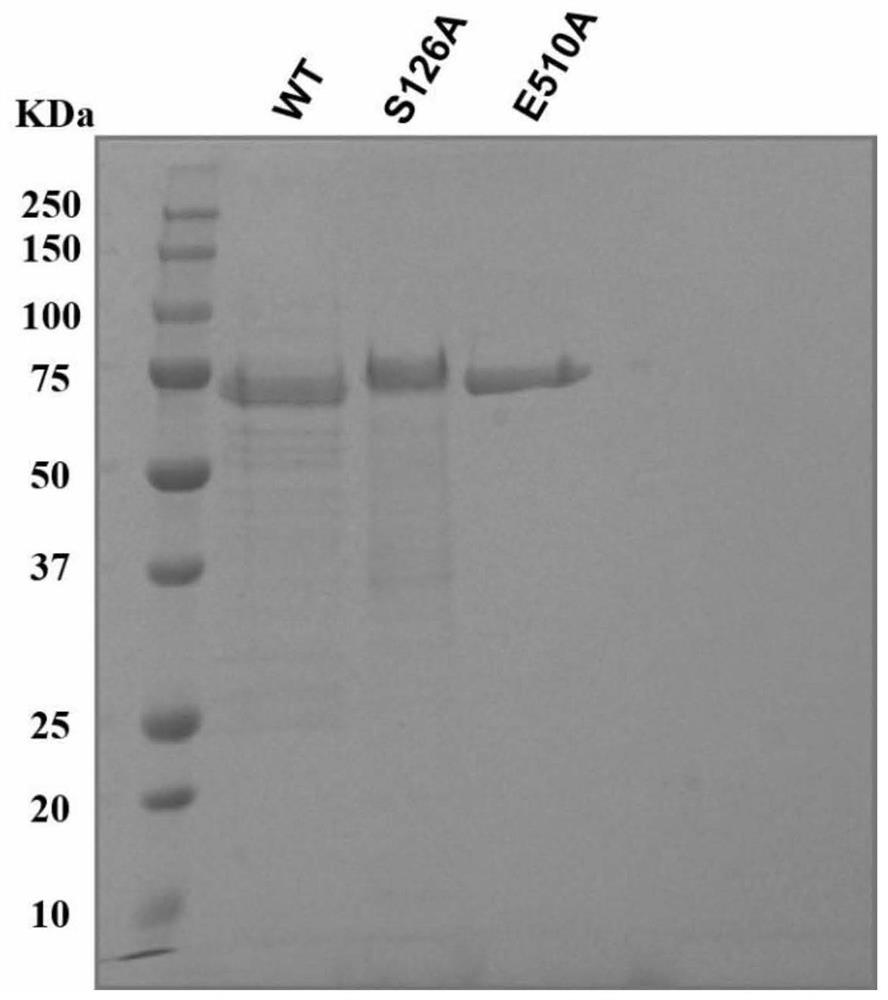
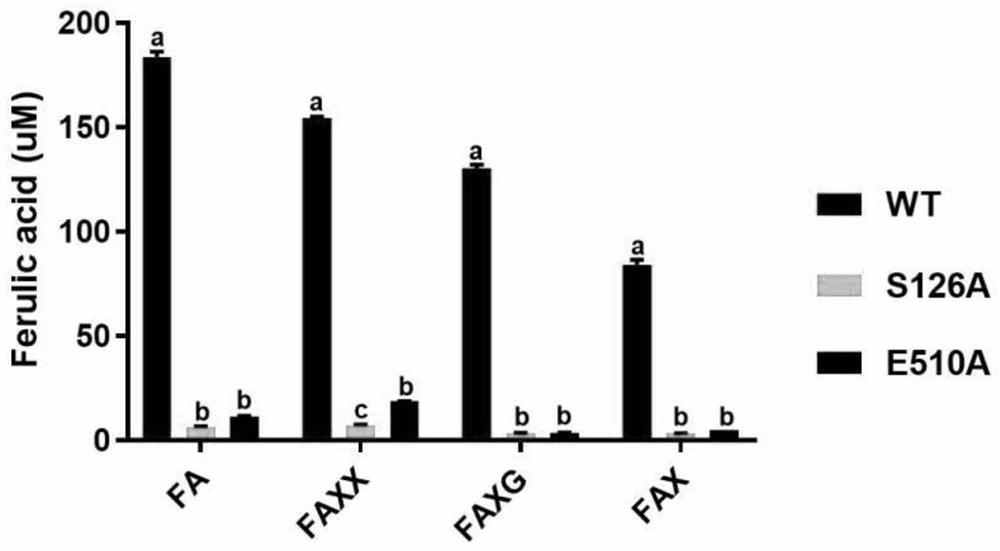
The invention discloses novel feruloyl esterase, a mutant and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, successfully screening out a feruloyl esterase gene from anaerobic fungi Neocallimatix sp. by utilizing a genomics technology; according to the preference of a prokaryotic system codon, the GC content of a feruloyl esterase gene and the secondary structure of mRNA, and codon optimization is carried out on the feruloyl esterase gene to obtain a novel feruloyl esterase gene sequence. The enzyme has an esterase regionand a glucoside hydrolase 11 region, site-specific mutagenesis is carried out on the two regions; the obtained mutant gene is also expressed in escherichia coli; separation and purification results show that the novel feruloyl esterase and the mutant thereof are successfully expressed in escherichia coli, and the esterase activity of the mutant is far lower than that of a non-mutant, so that the strain source of the feruloyl esterase is enriched, and the feruloyl esterase has theoretical guiding significance in the aspects of improving the digestibility of feed fibers and improving the production performance of animals.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
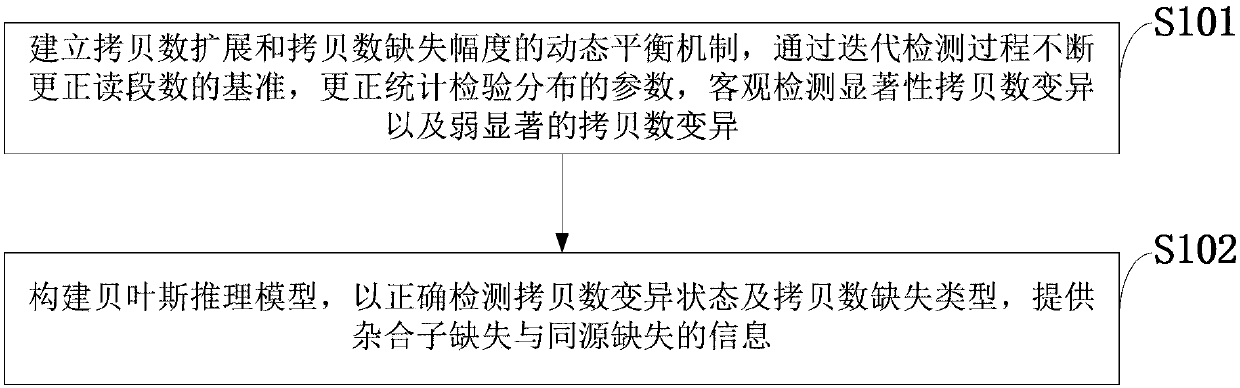
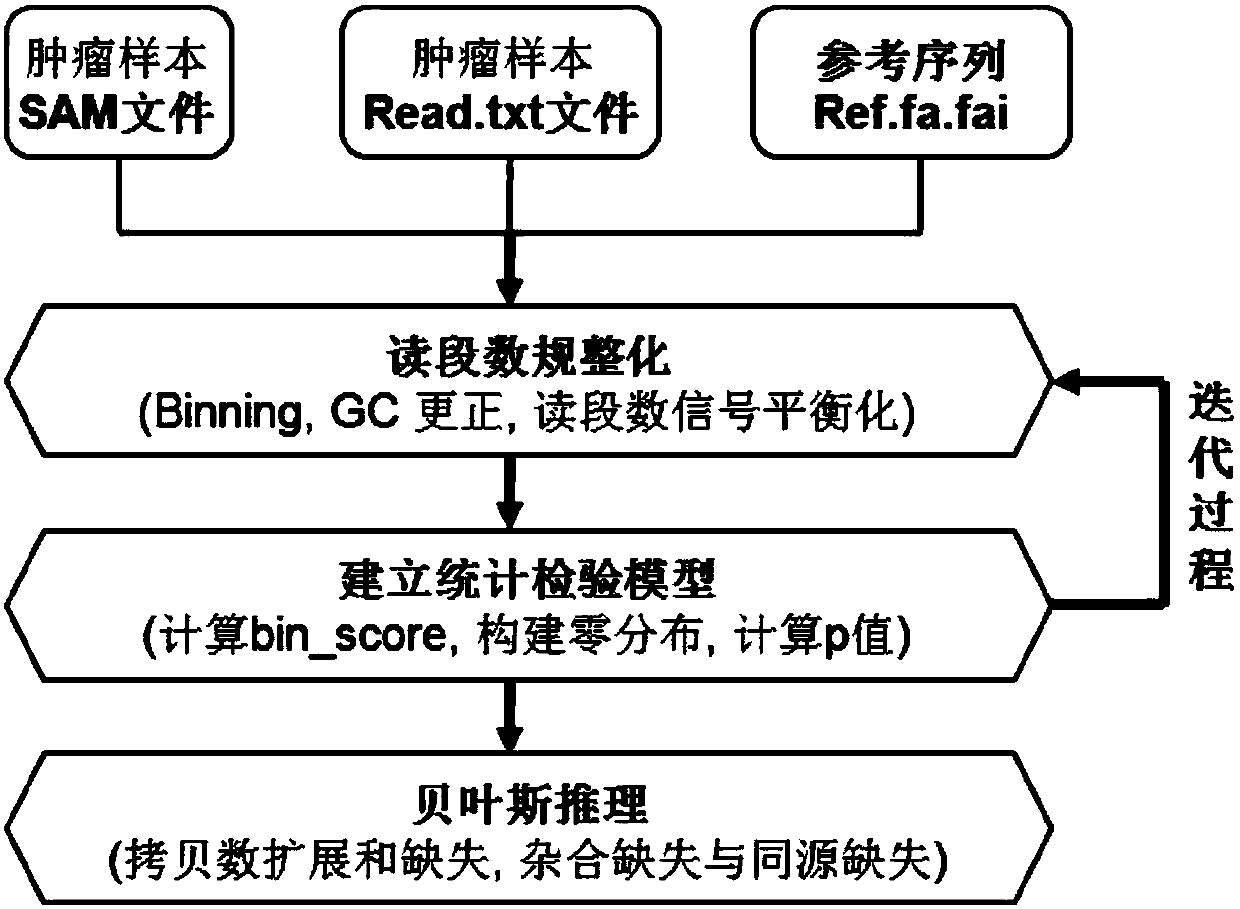
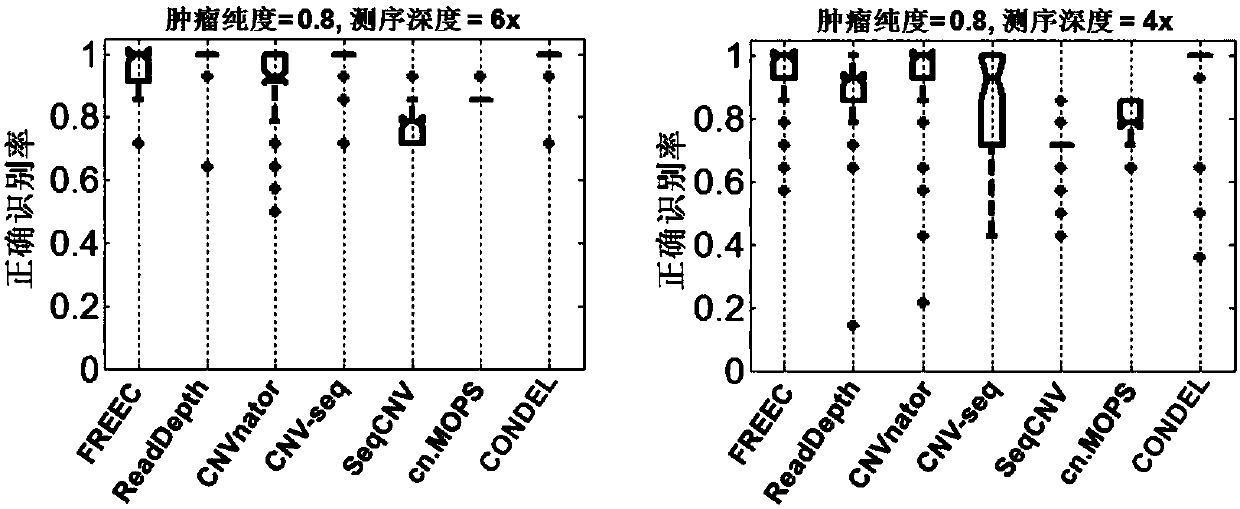
Copy number variation and deletion type detection method and computer based on single tumor sample
The invention belongs to the technical field of copy number variation detection, and discloses a copy number variation and deletion type detection method and computer based on a single tumor sample. The method includes the steps of building a dynamic balancing mechanism of a copy number extension and deletion range, iterating the detection process to constantly correct the benchmark of reading thesegment number, correcting the parameters of statistical test distribution, and objectively detecting significant copy number variation and weakly-significant copy number variation; building a Bayesian inference model, and correctly detecting the copy number variation state and the copy number deletion type. According to the method and the computer, the copy number variation state and the copy number deletion type are correctly detected, and the information of heterozygote deletion and homologous deletion is provided; the comparation quality and the comparation error problem are considered, and the whole genome GC content is reasonably corrected; the dynamic balancing mechanism of the copy number extension and deletion range is built to accurately position the benchmark of the copy numberand accurately detect the variation state of the copy number.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com