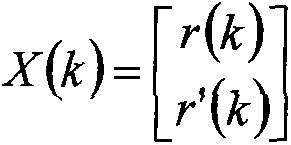Patents
Literature
252 results about "Bayesian inference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bayesian inference is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to update the probability for a hypothesis as more evidence or information becomes available. Bayesian inference is an important technique in statistics, and especially in mathematical statistics. Bayesian updating is particularly important in the dynamic analysis of a sequence of data. Bayesian inference has found application in a wide range of activities, including science, engineering, philosophy, medicine, sport, and law. In the philosophy of decision theory, Bayesian inference is closely related to subjective probability, often called "Bayesian probability".
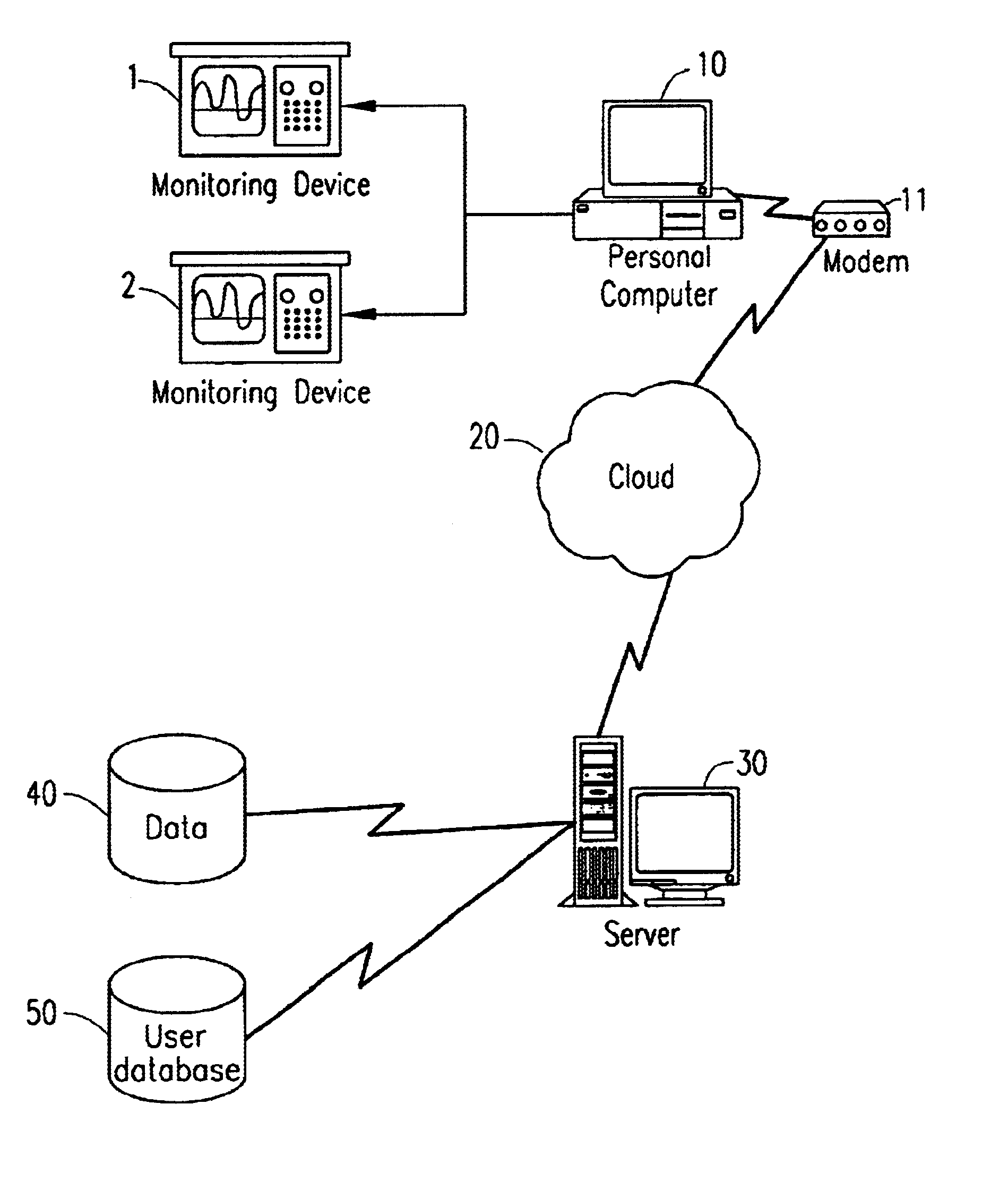
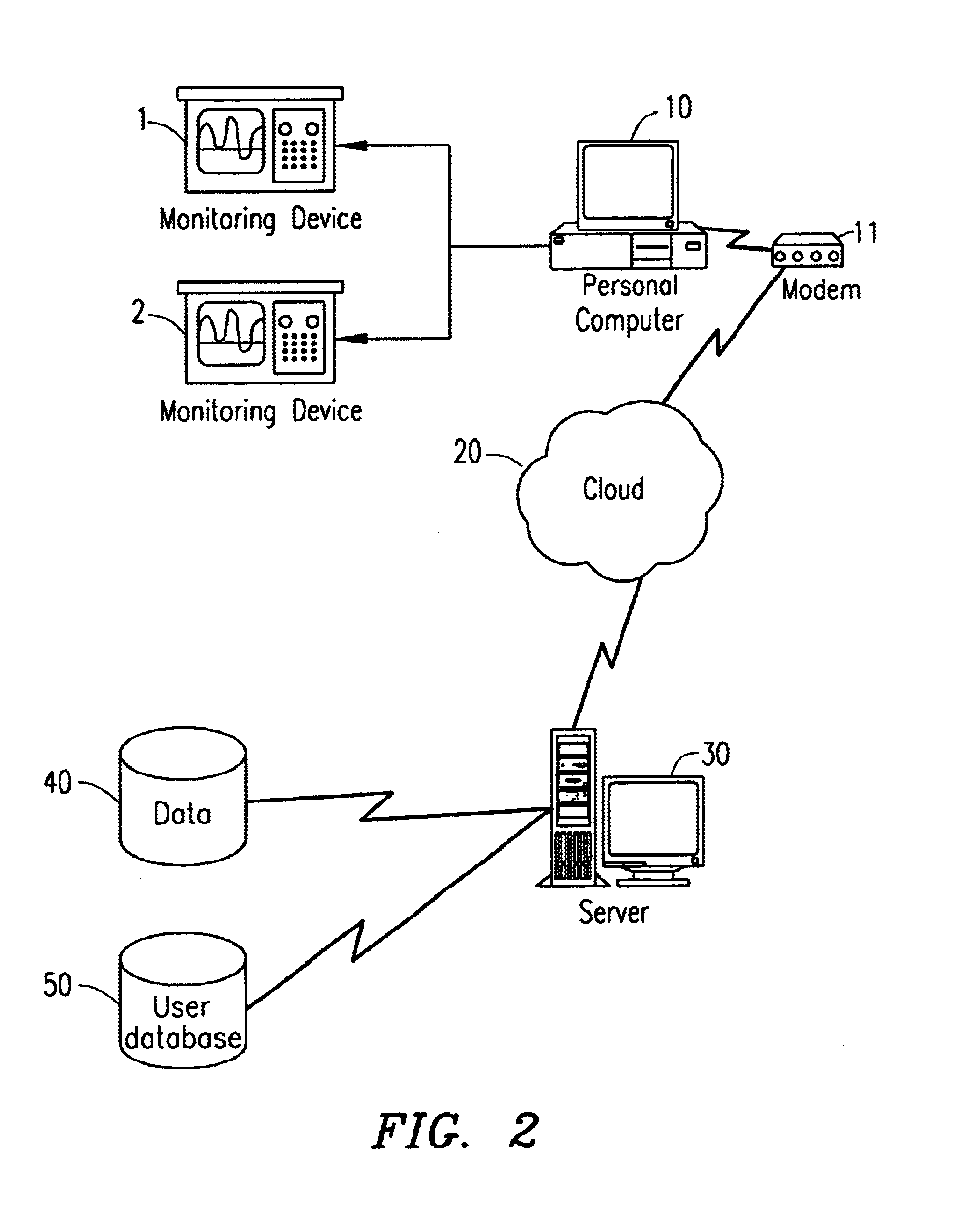
Automated medical decision making utilizing bayesian network knowledge domain modeling
InactiveUS6687685B1Reliable and statistically sound and convenient methodEasy to manageBiological neural network modelsComputer-assisted medical data acquisitionTriageMedical knowledge
The present invention relates to a system and method of medical knowledge domain modeling and automated medical decision-making, such as for online, questionnaire-based medical triage. In the present invention, information such as conditions and characteristics related to a diagnosis or disposition level is modeled in a Bayesian Network. The Bayesian Network may comprise instantiable nodes, fault nodes, intermediary nodes, a utility node and a decision node. Using Bayesian inference, the conditional probability of any pair in the network may be determined in real-time. These conditional probabilities are modified upon the input of evidence, which is typically in the form of answers to a dynamic set of questions designed to identify a diagnosis or disposition level for the patient under evaluation.
Owner:DR RED DUKE
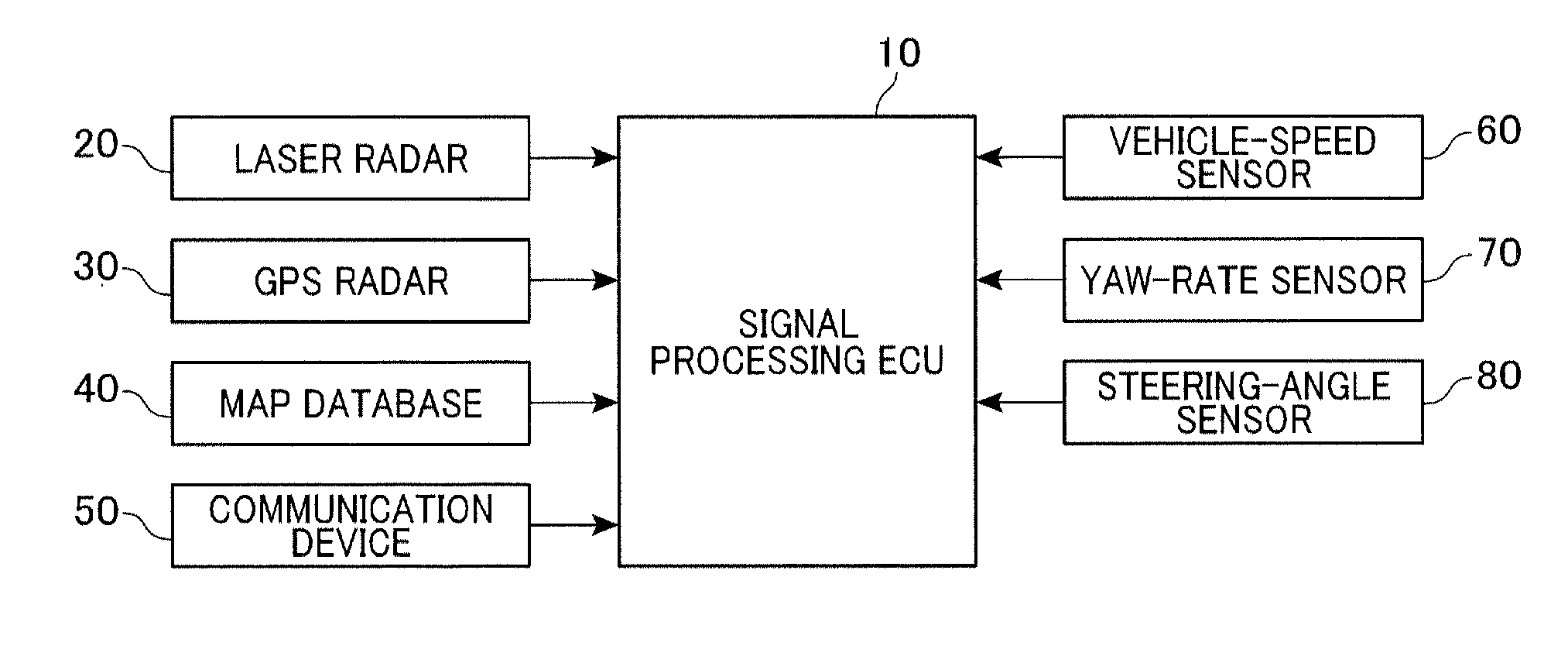
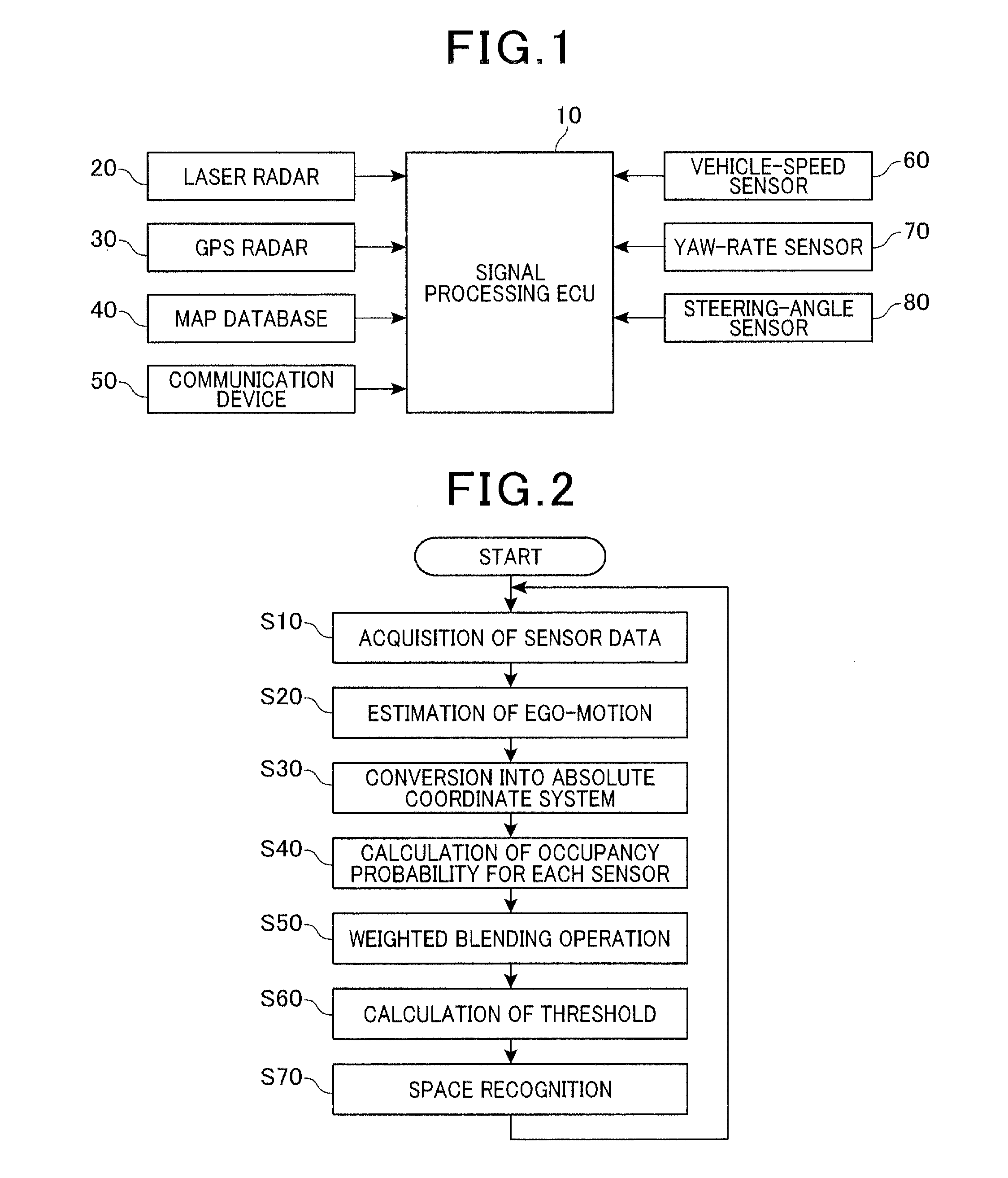
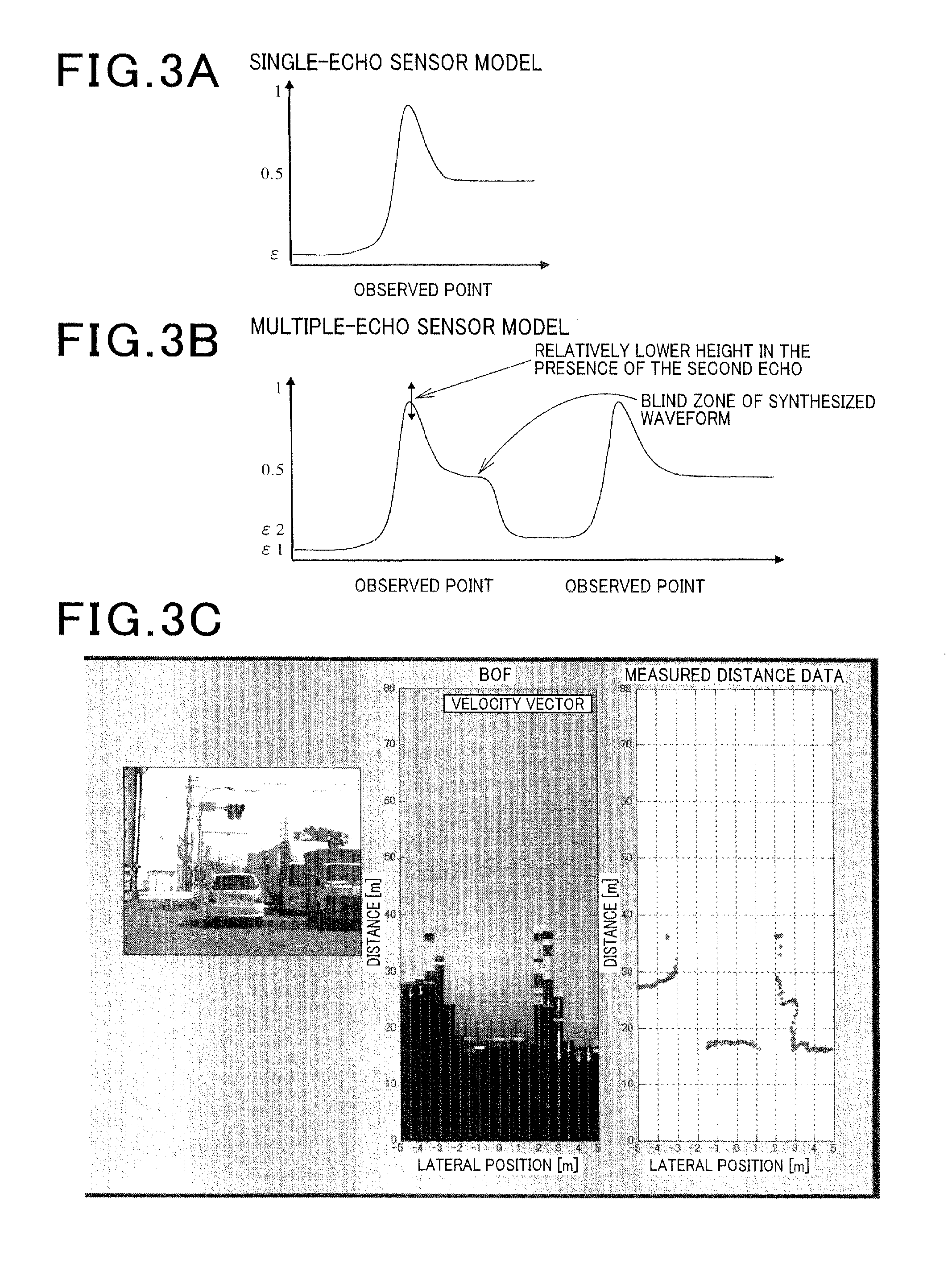
Traveling environment recognition device and method
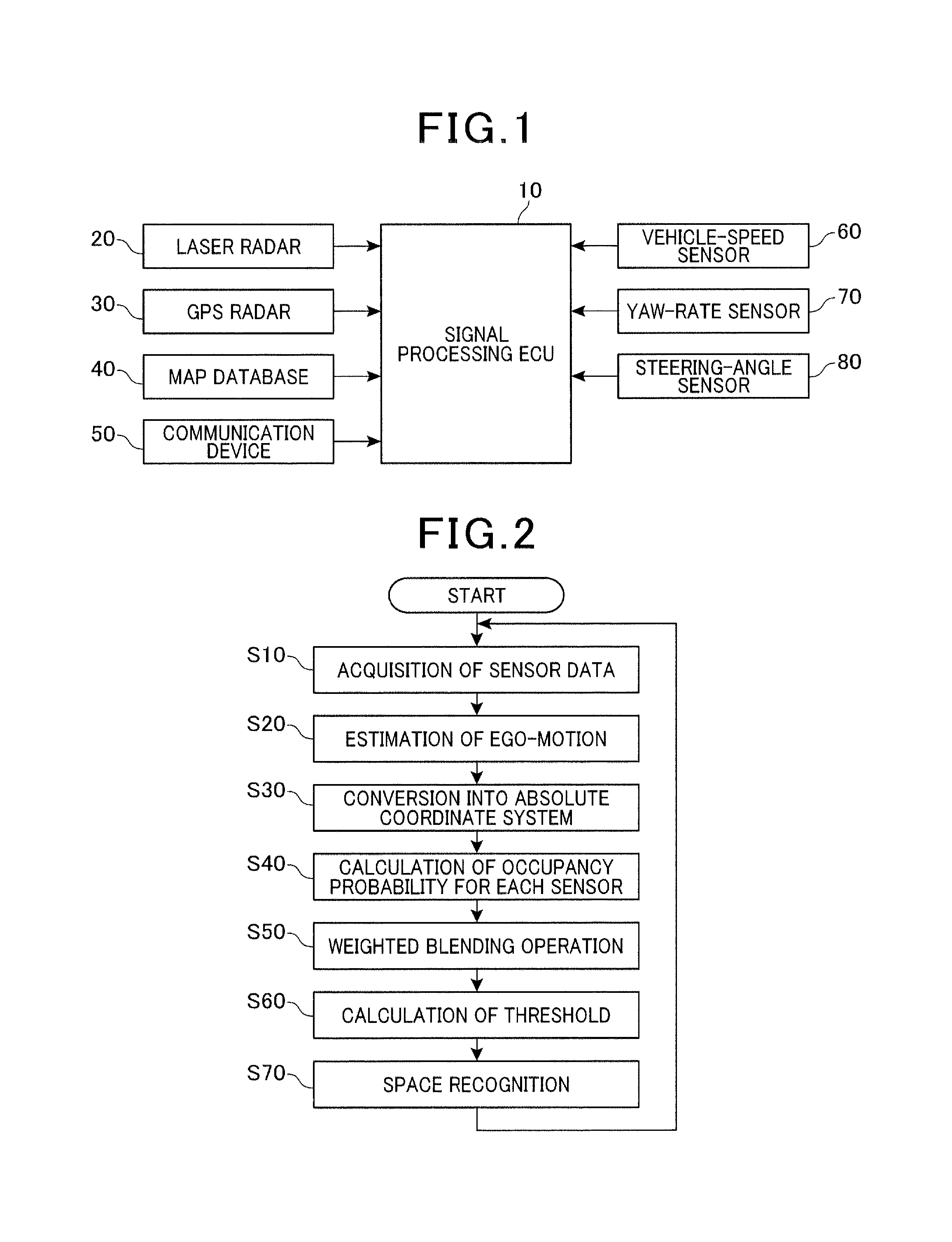
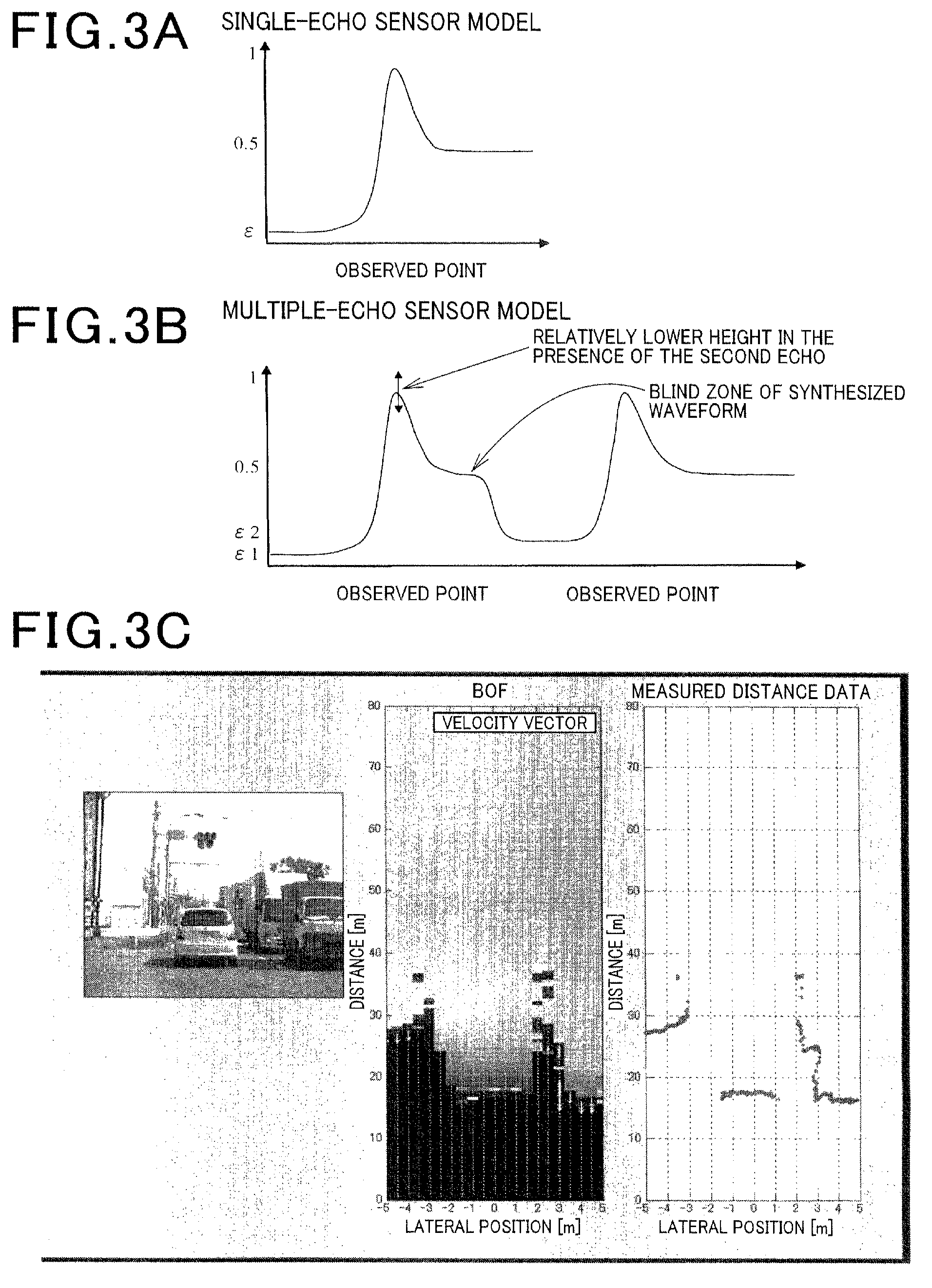
ActiveUS20120053755A1Improve accuracyAccurate occupancy probabilityDigital data processing detailsExternal condition input parametersRadarSimulation
A traveling environment recognition device capable of accurately recognizing a traveling environment of a vehicle. An occupancy grid map that stores an occupancy probability of each obstacle to traveling of the own vehicle for each cell of the occupancy grid map is generated, and the occupancy probability for each cell is updated according to Bayesian inference. More specifically, for each cell of the occupancy grid map, the occupancy probability calculated from information from a radar device, the occupancy probability calculated from information from a communication device, and the occupancy probability calculated from information from a storage device that stores map data are blended to provide an occupancy probability of the obstacles to traveling of the own vehicle, which leads to more accurate traveling environment recognition.
Owner:DENSO CORP
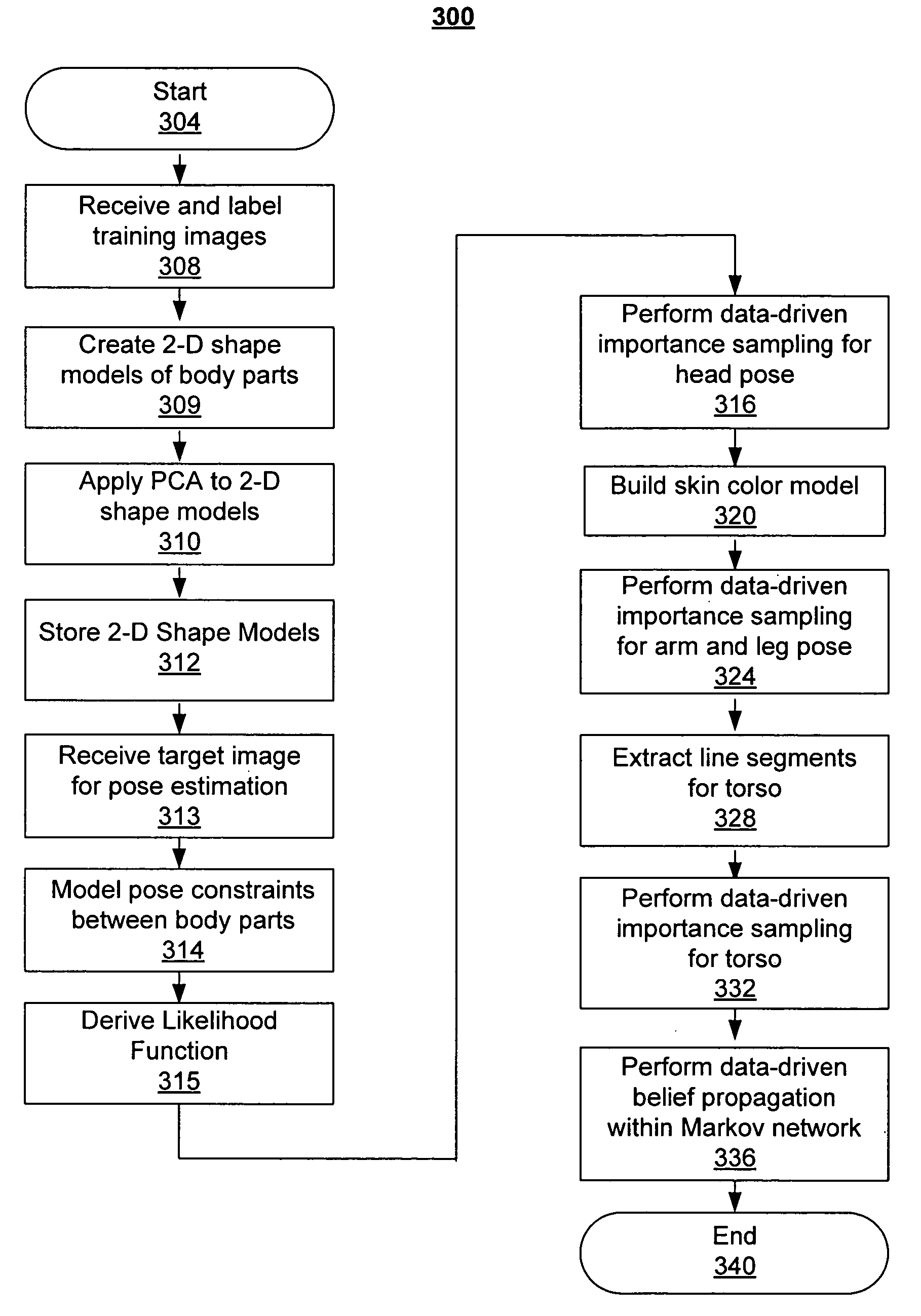
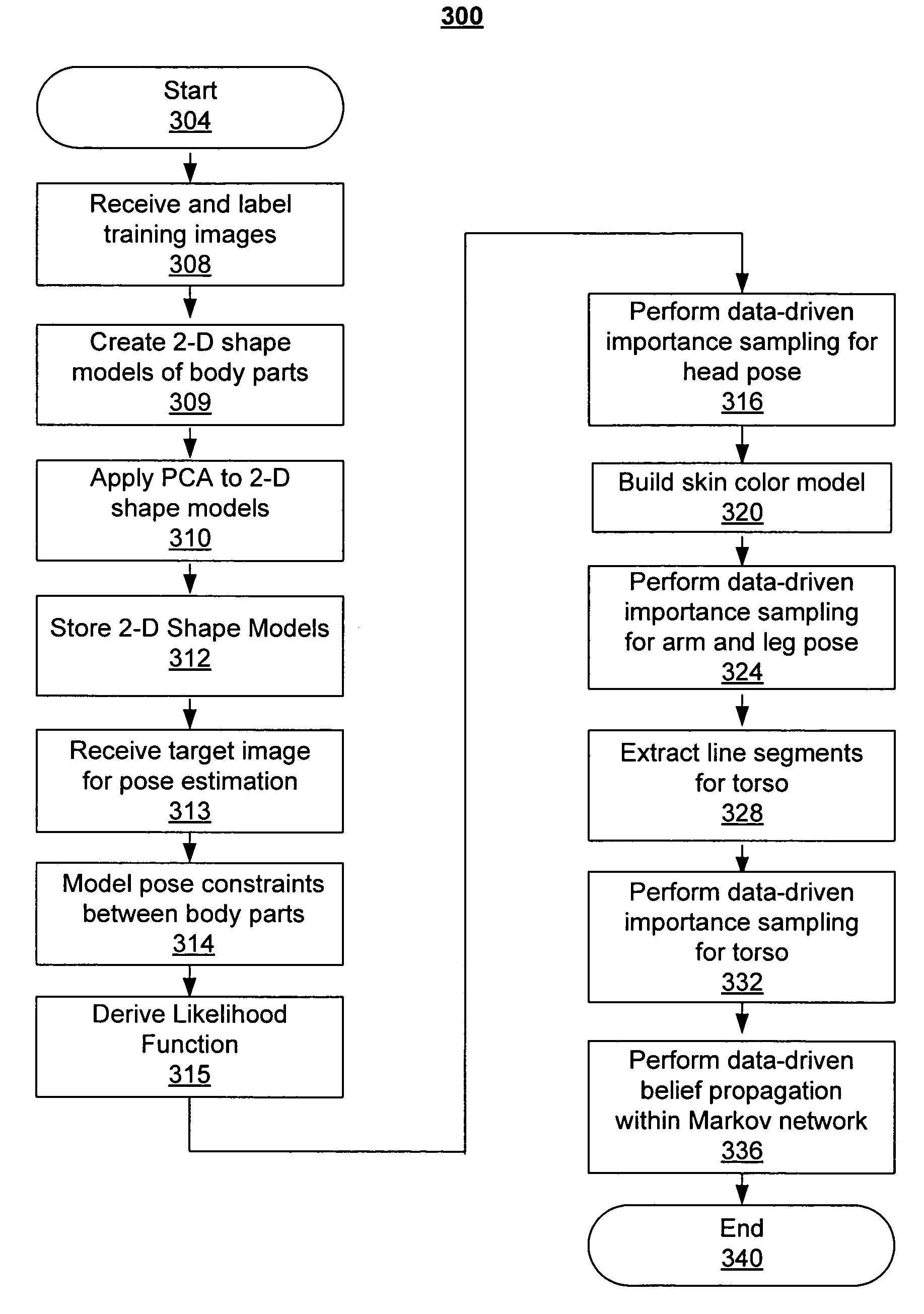
Human pose estimation with data driven belief propagation
A statistical formulation estimates two-dimensional human pose from single images. This is based on a Markov network and on inferring pose parameters from cues such as appearance, shape, edge, and color. A data-driven belief propagation Monte Carlo algorithm performs efficient Bayesian inferencing within a rigorous statistical framework. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the method in estimating human pose from single images.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
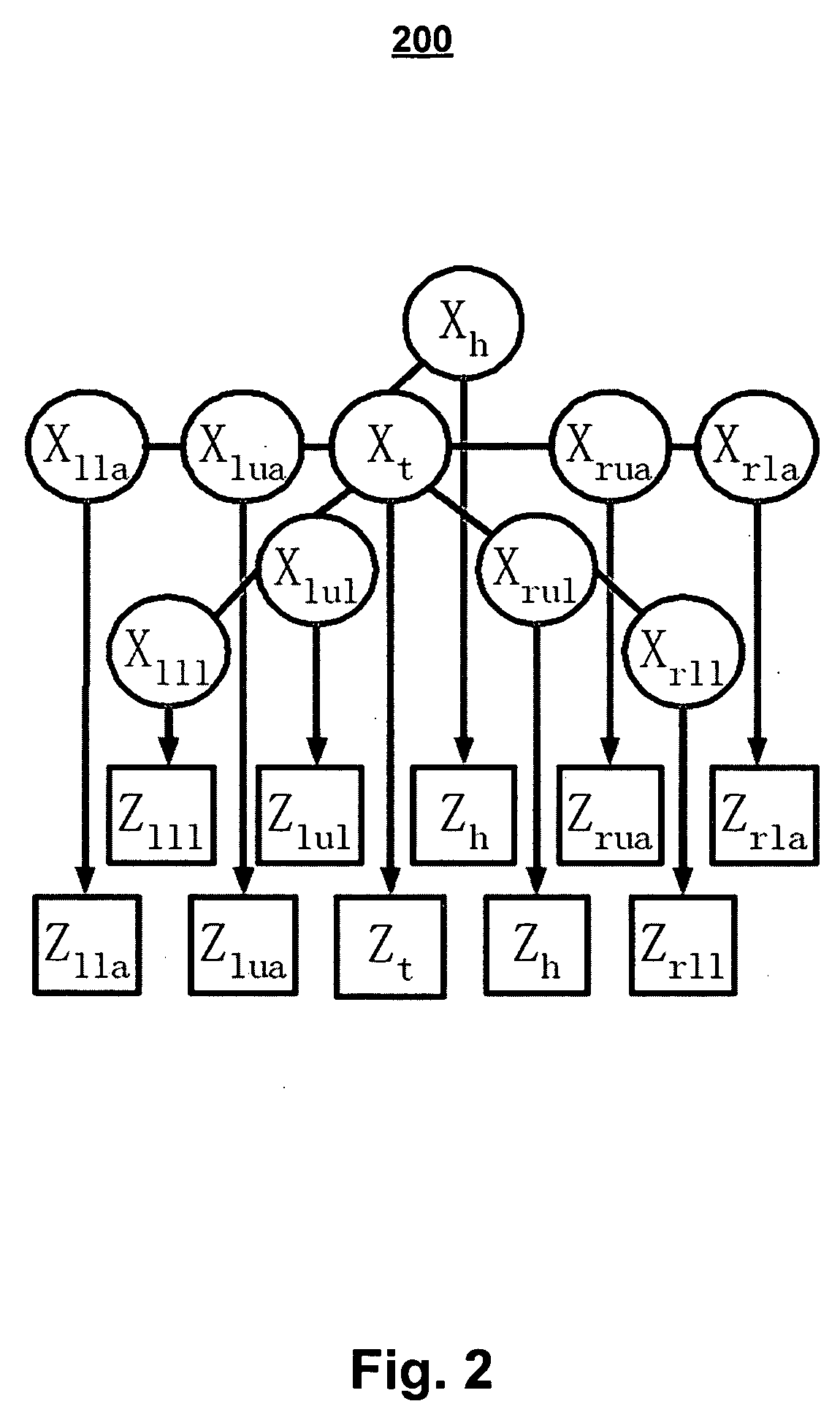
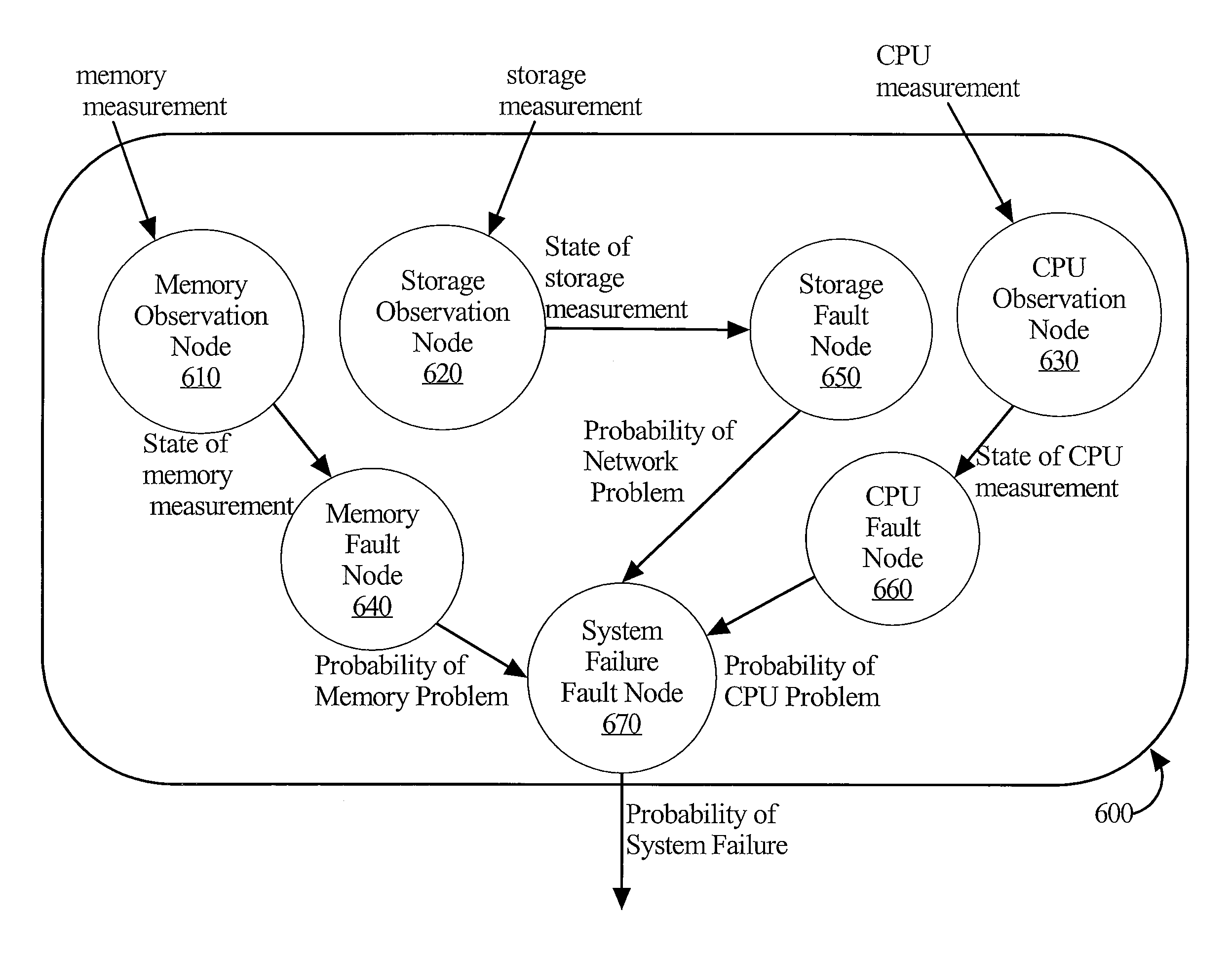
Method and apparatus for dealing with accumulative behavior of some system observations in a time series for bayesian inference with a static bayesian network model
ActiveUS20120005534A1Reliability/availability analysisNon-redundant fault processingProbit modelNetwork model
A method and apparatus are provided for determining the probability that one or more problems have occurred within a complex multi-host system. A probabilistic model representing the cause / effect relationships among potential system problems identifies the probability that a problem occurred in the system based at least on system measure states that are input into the probabilistic model. System measure states may be determined based on an aggregation of system measurement values taken periodically. Aggregating system measurement values may be performed over system measurement values that were taken during a recent time interval. A rolling count aggregation function may be used for this purpose. A rolling count function counts the number of system measurement values taken within the recent time interval that lie within a particular range of values. A system measure state may be determined based on whether the rolling count exceeds a threshold associated with the system measure.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
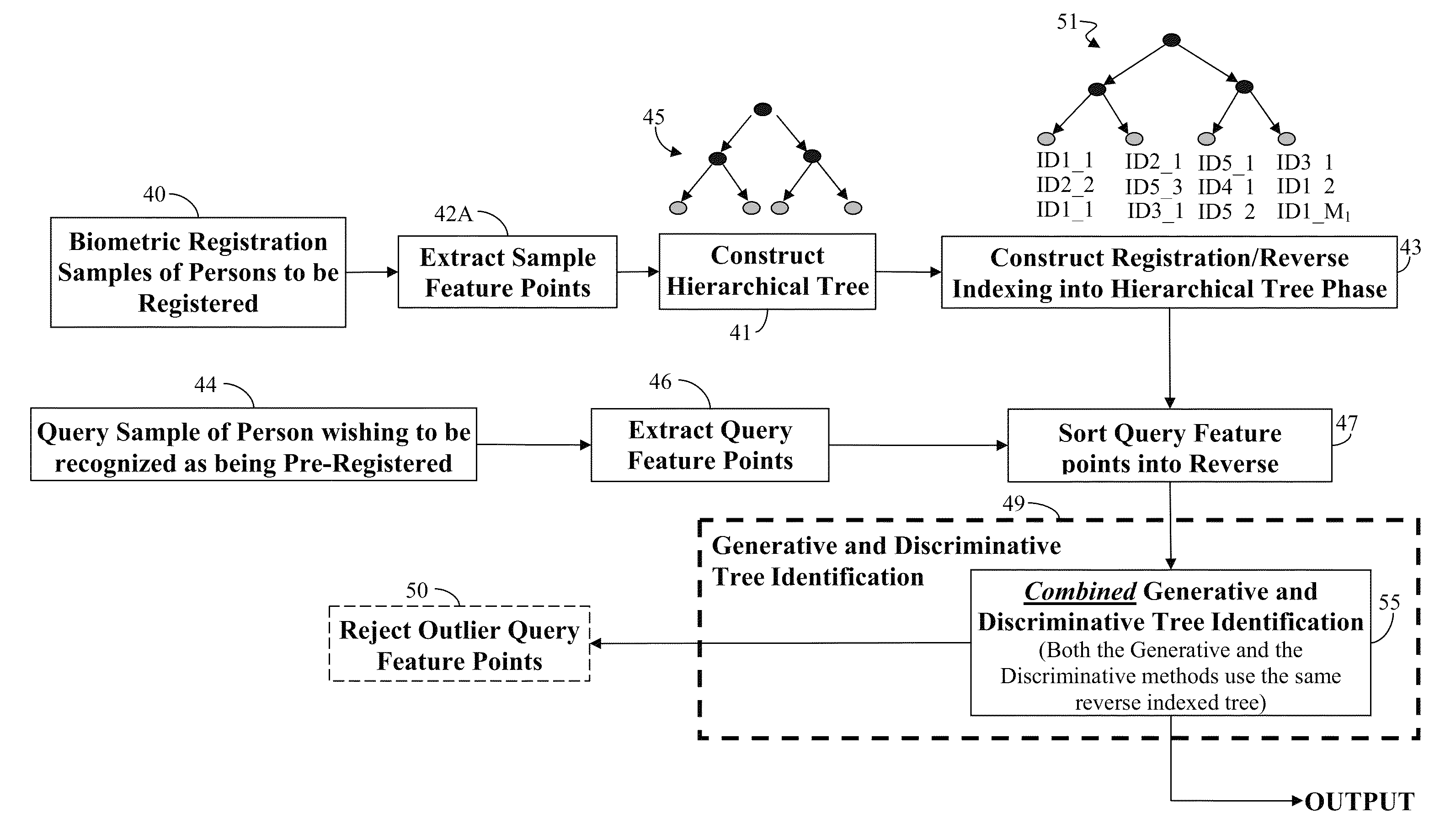
Small Vein Image Recognition and Authorization Using Constrained Geometrical Matching and Weighted Voting Under Generic Tree Model
An automated registration and authentication system combines a generative and discriminative approach to improve the matching of a query object to a database of registered objects. The discriminative approach uses a voting mechanism to identify a most likely match, and the generative approach uses ASIFT transforms to determine a best geometric match. The two results are combined using a technique base on Bayesian inference theory.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
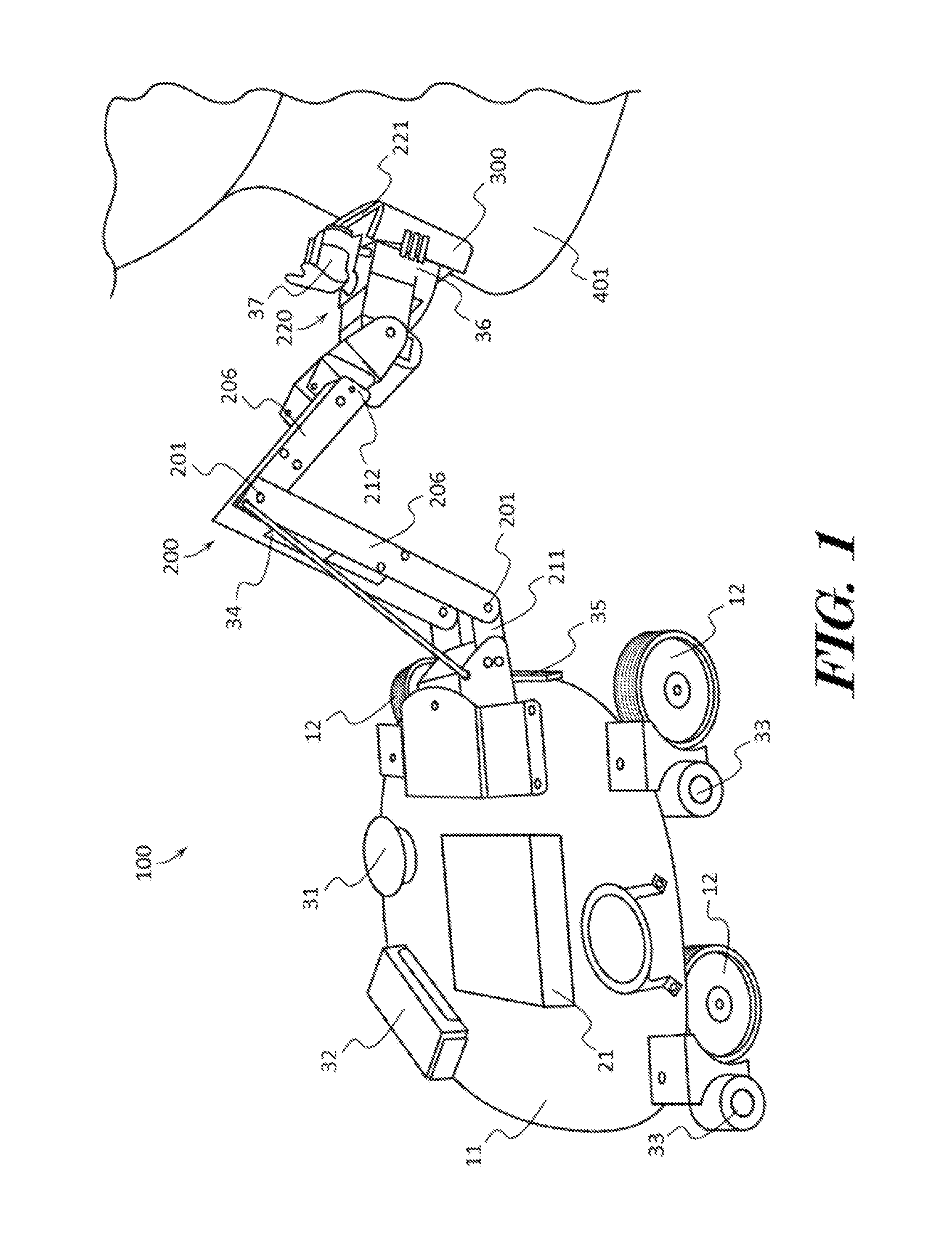
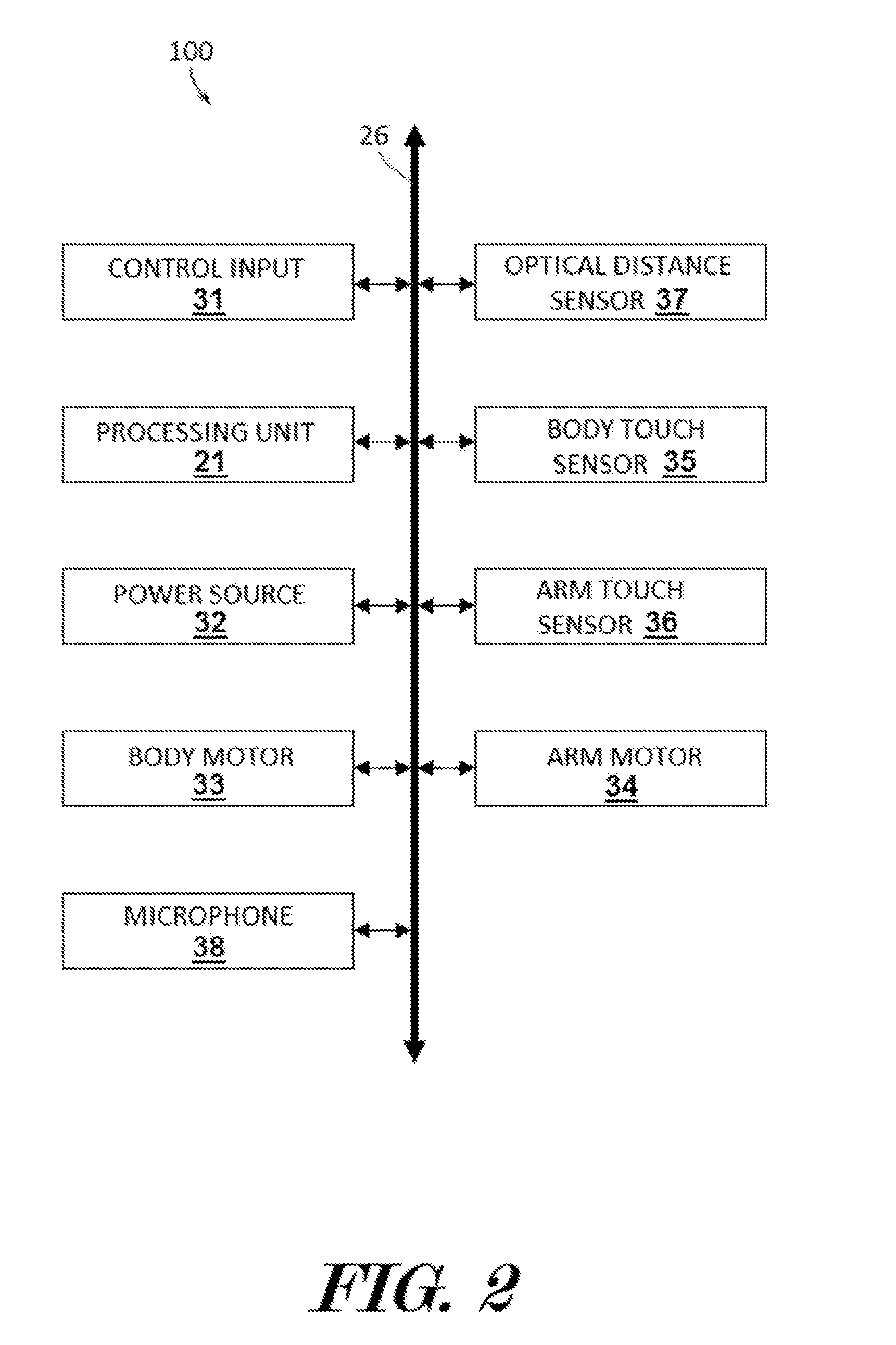
Robotic Touch Perception
ActiveUS20160158942A1Programme-controlled manipulatorComputer controlTouch PerceptionComputer vision
An apparatus such as a robot capable of performing goal oriented tasks may include one or more touch sensors to receive touch perception feedback on the location of objects and structures within an environment. A fusion engine may be configured to combine touch perception data with other types of sensor data such as data received from an image or distance sensor. The apparatus may combine distance sensor data with touch sensor data using inference models such as Bayesian inference. The touch sensor may be mounted onto an adjustable arm of a robot. The apparatus may use the data it has received from both a touch sensor and distance sensor to build a map of its environment and perform goal oriented tasks such as cleaning or moving objects.
Owner:AEOLUS ROBOTICS
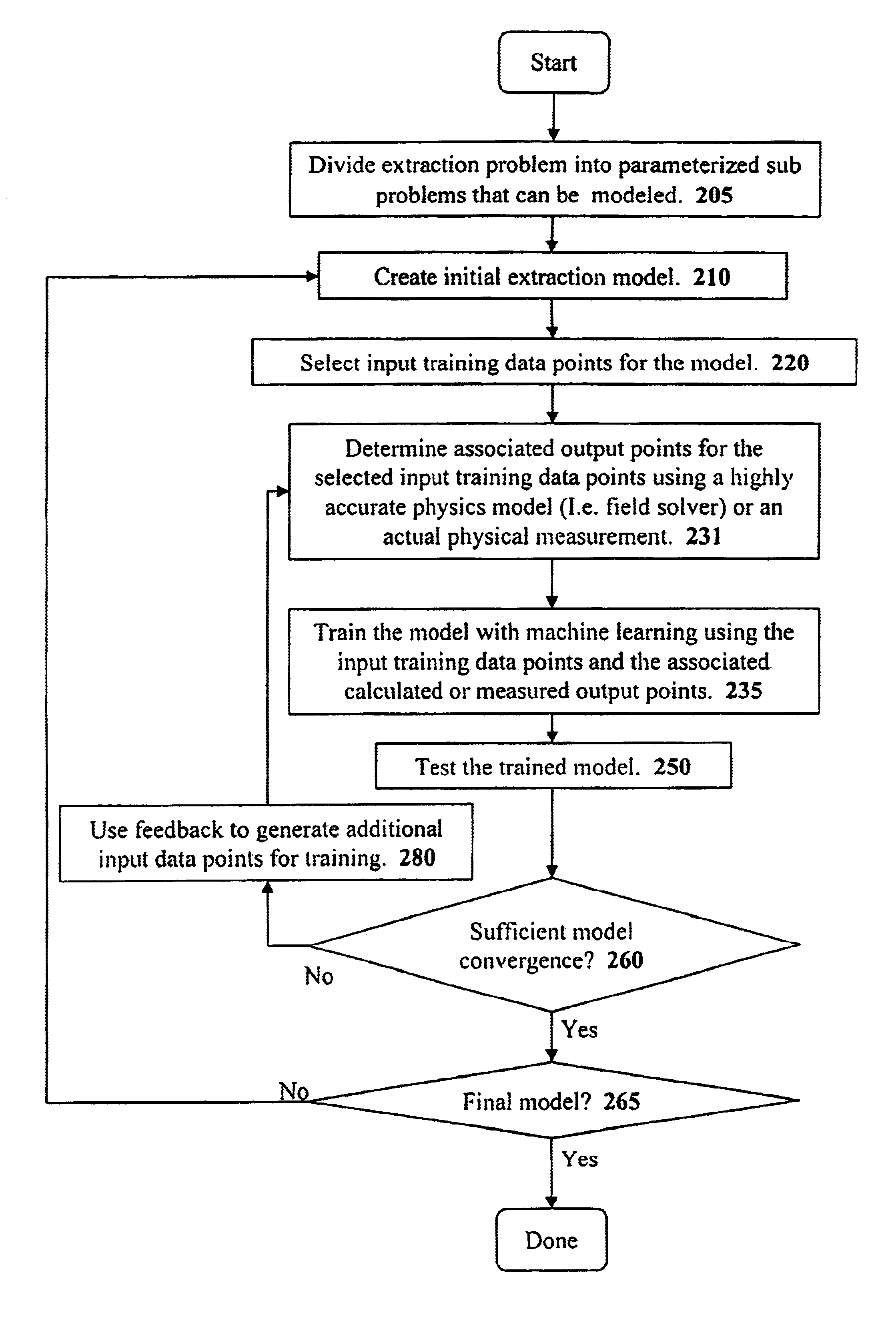
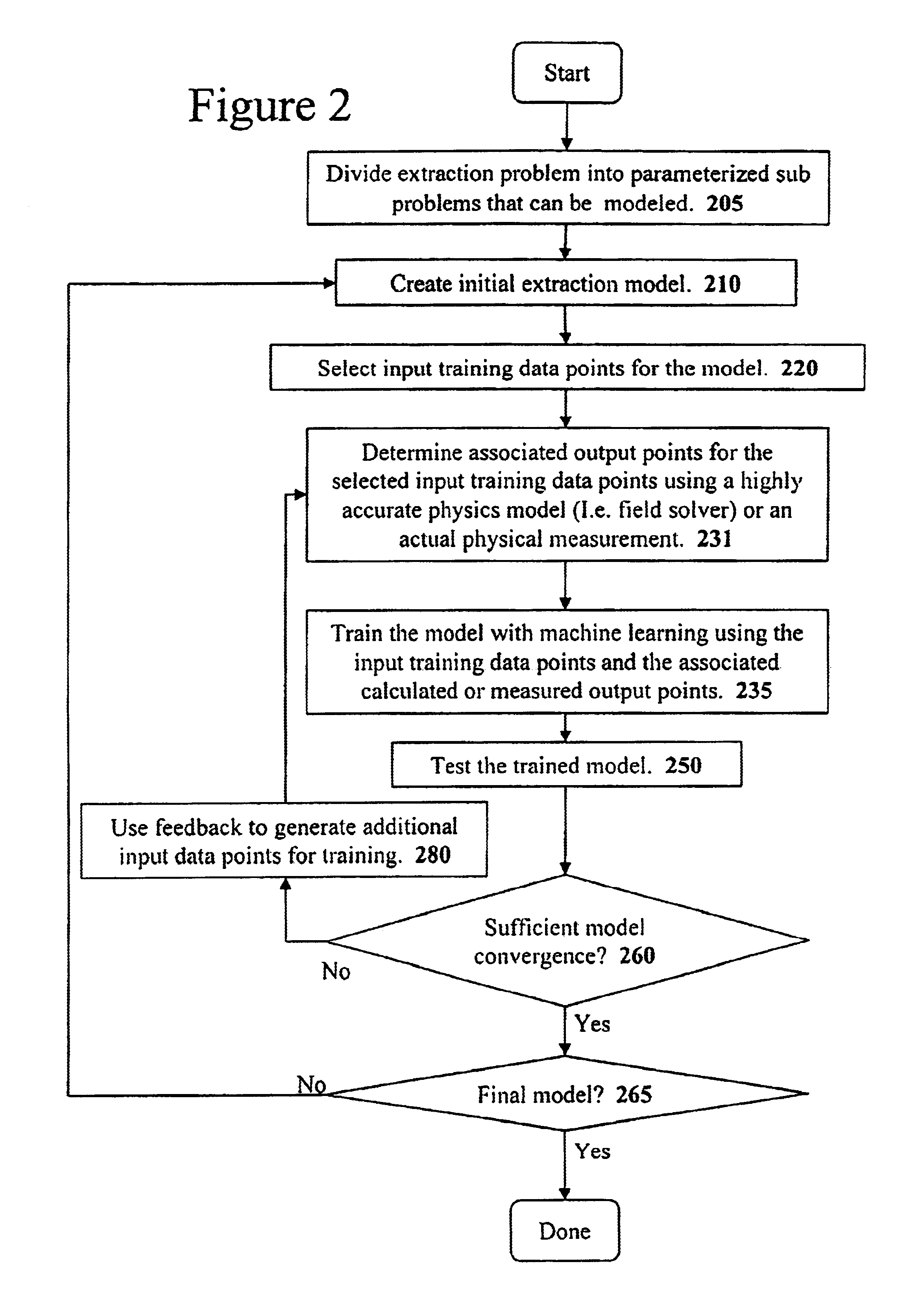
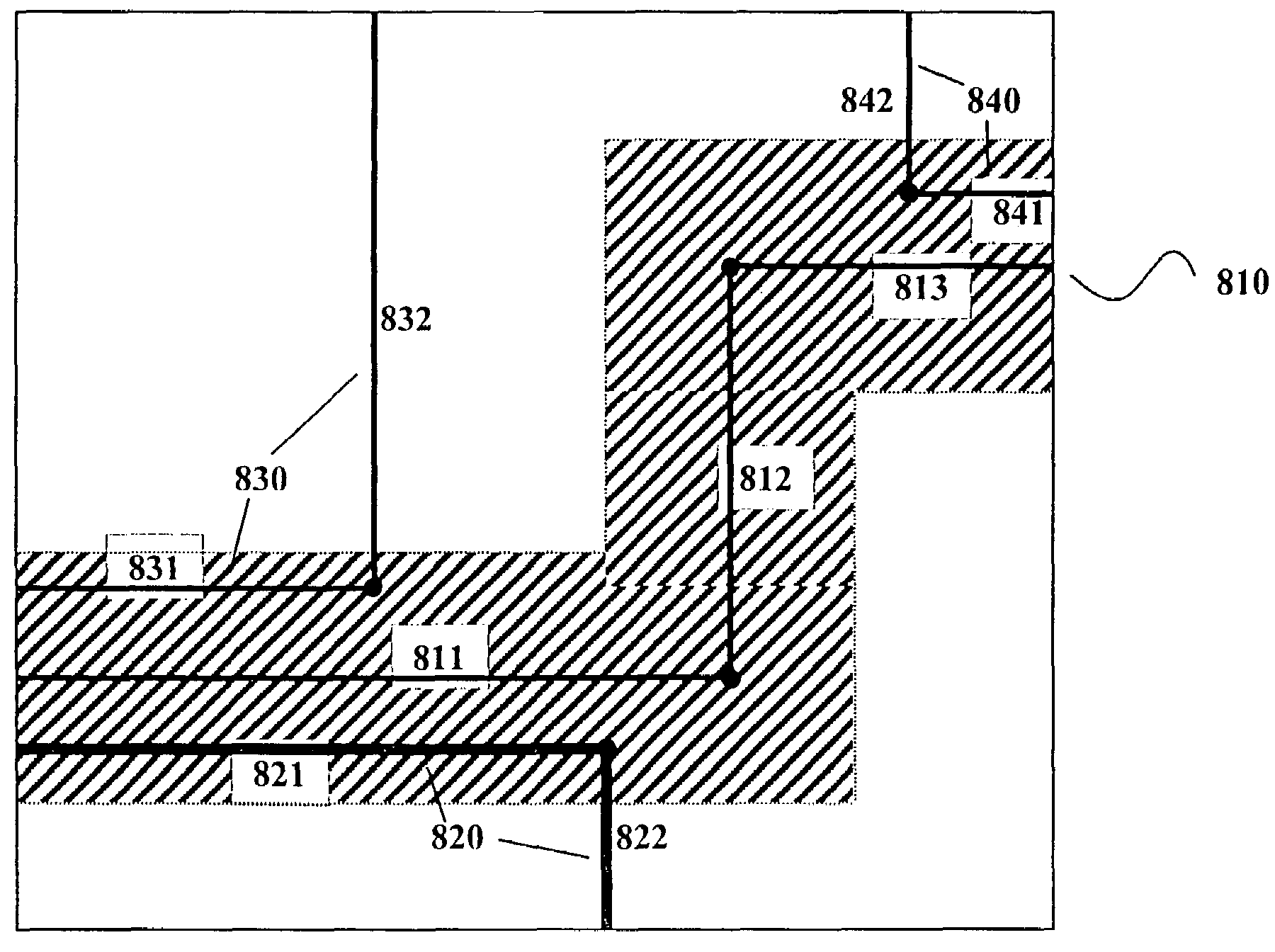
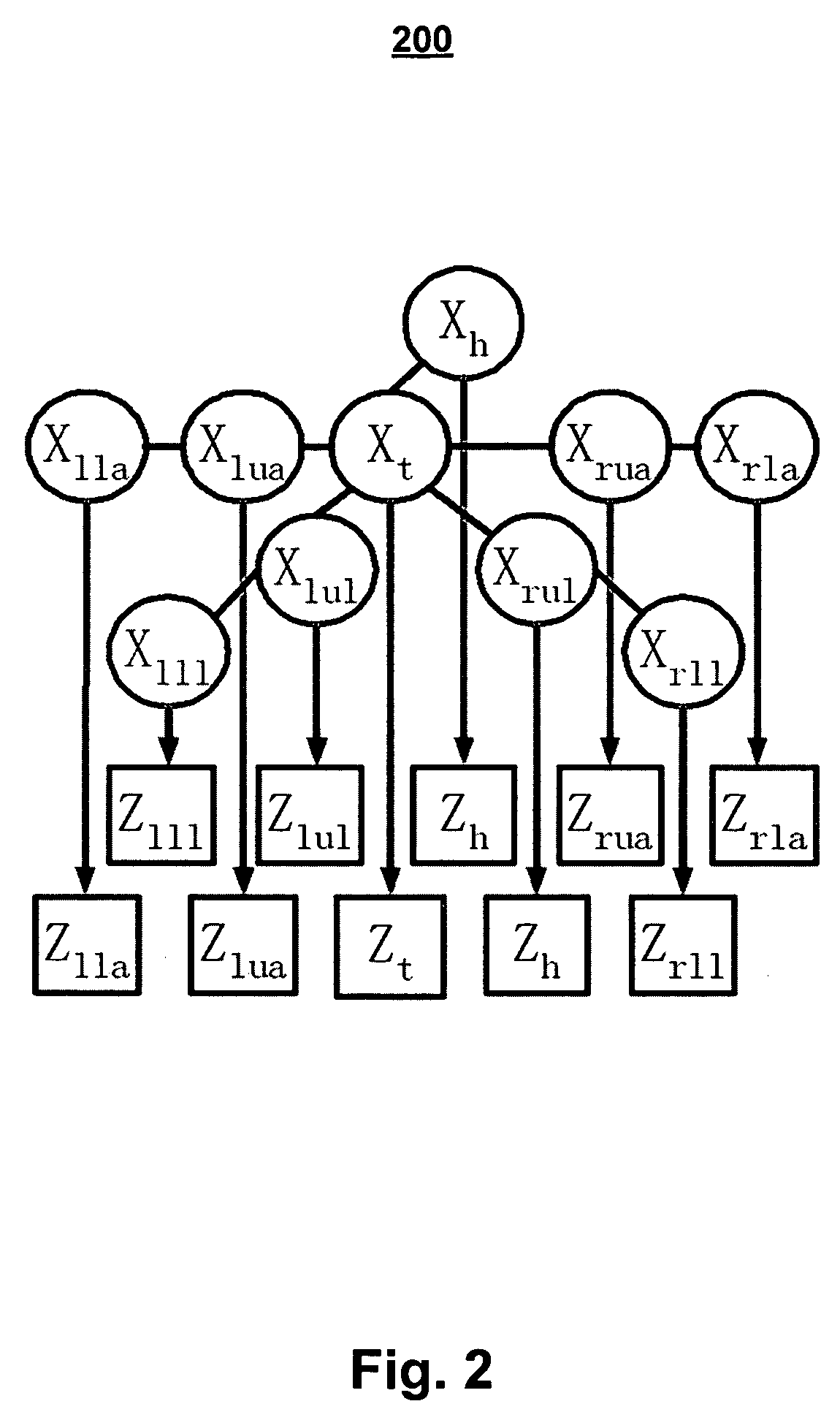
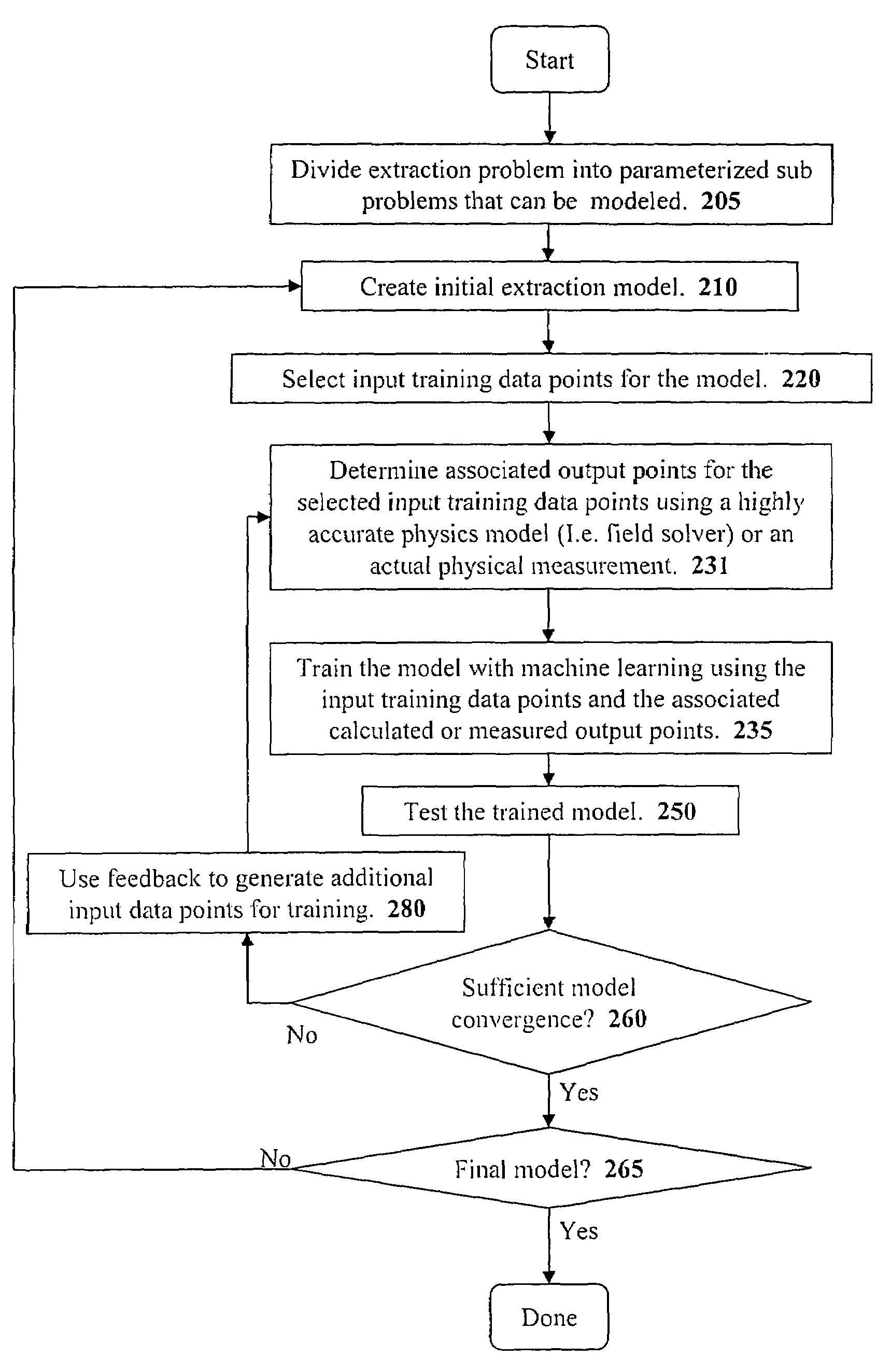
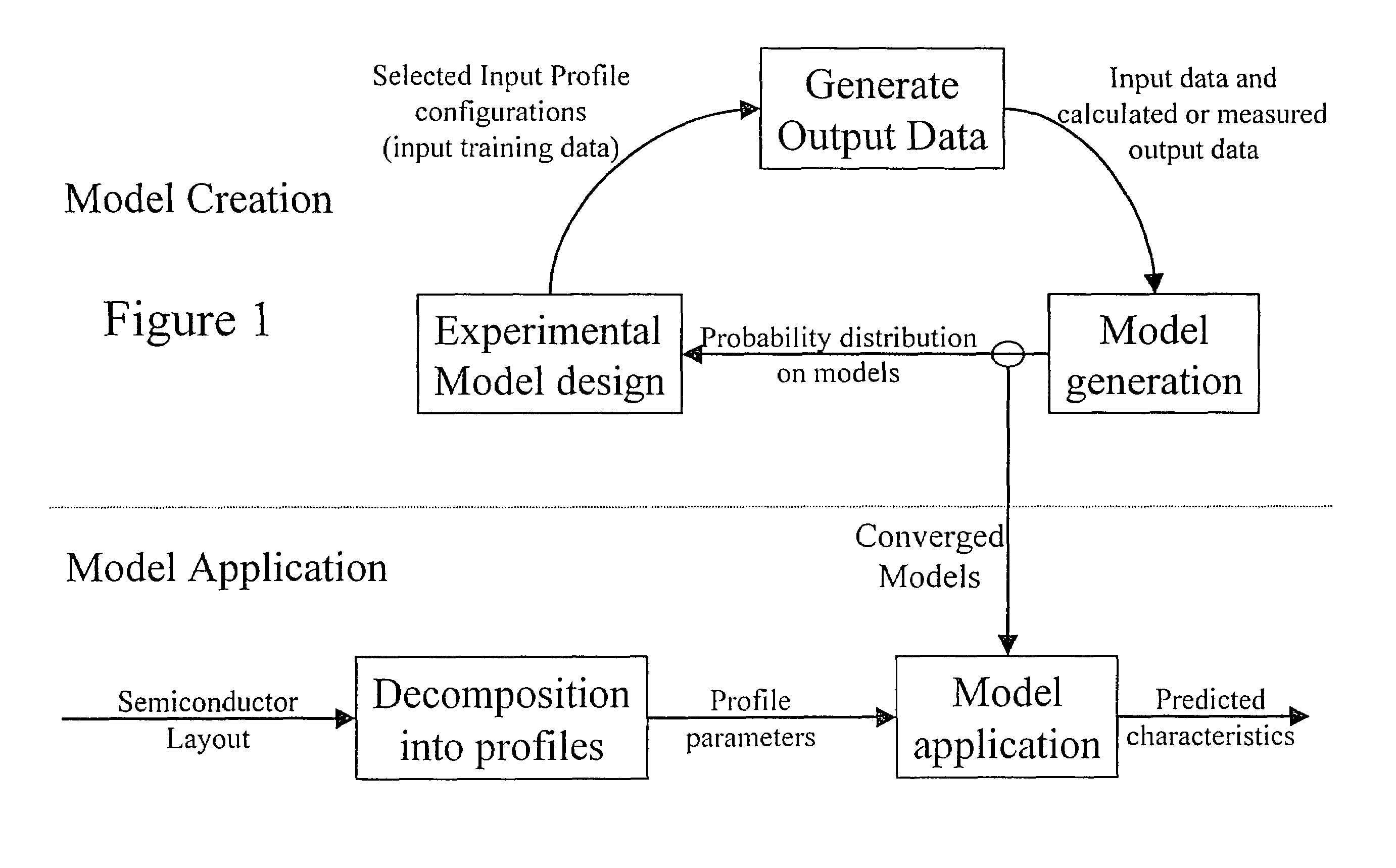
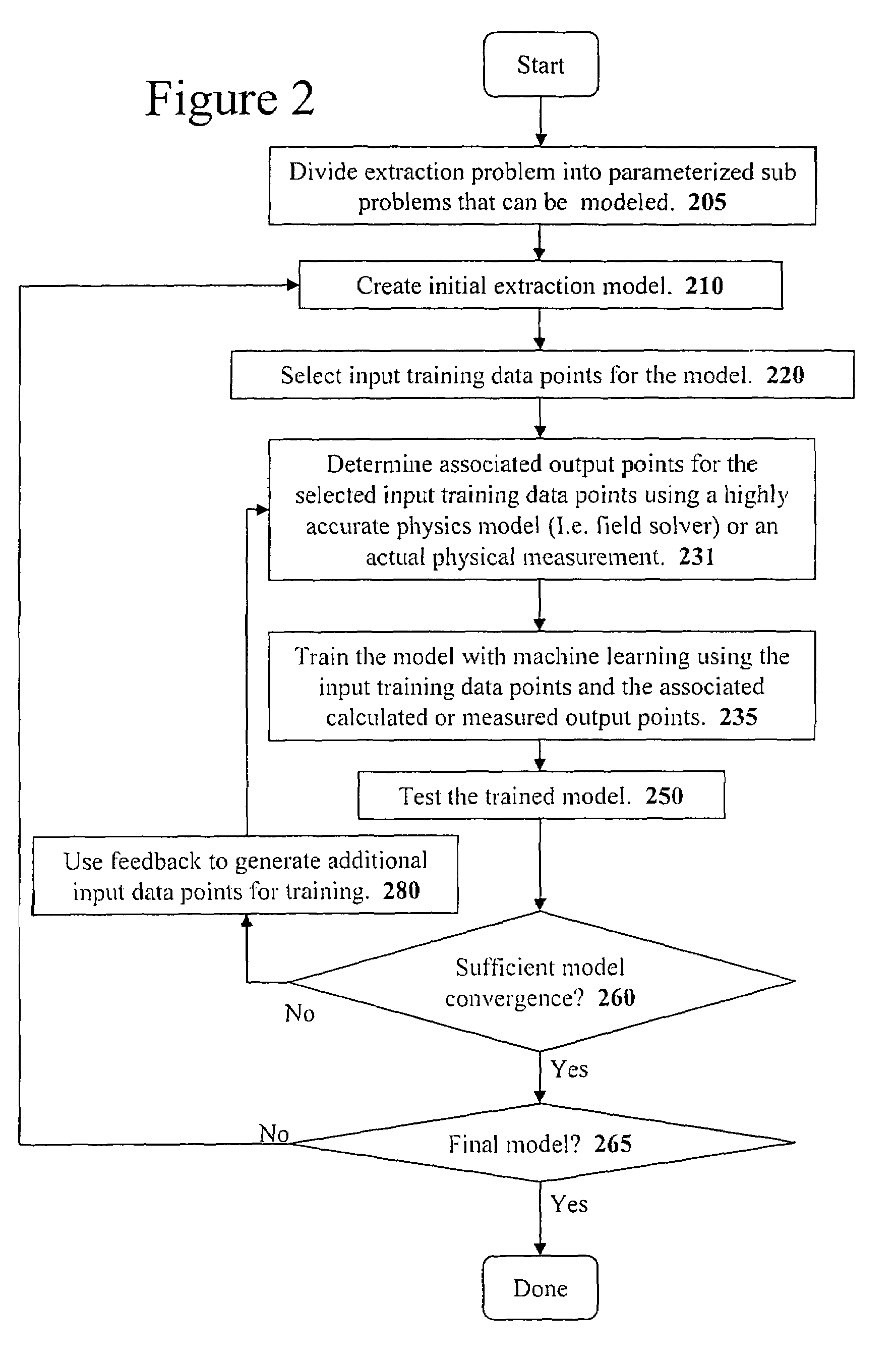
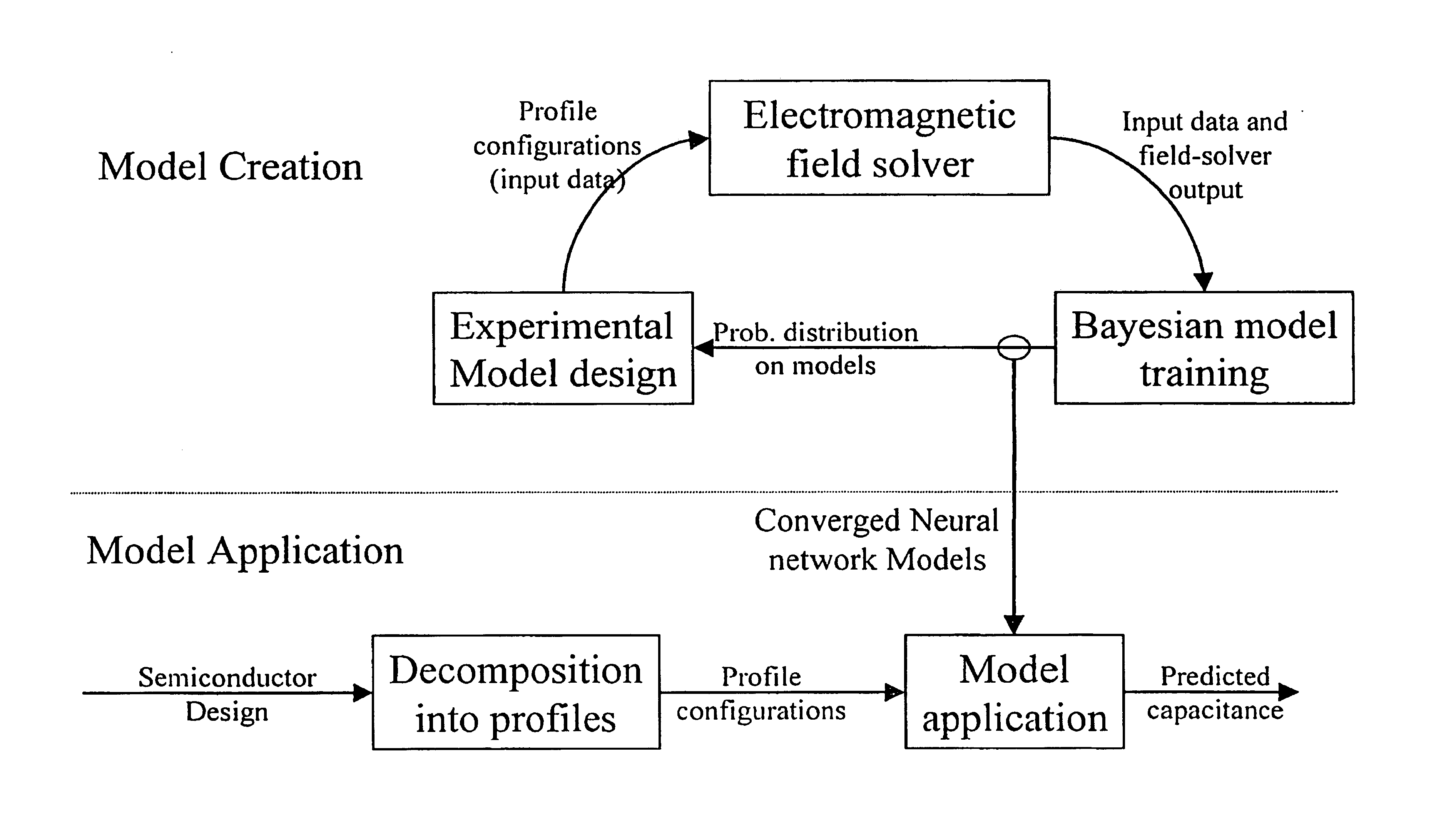
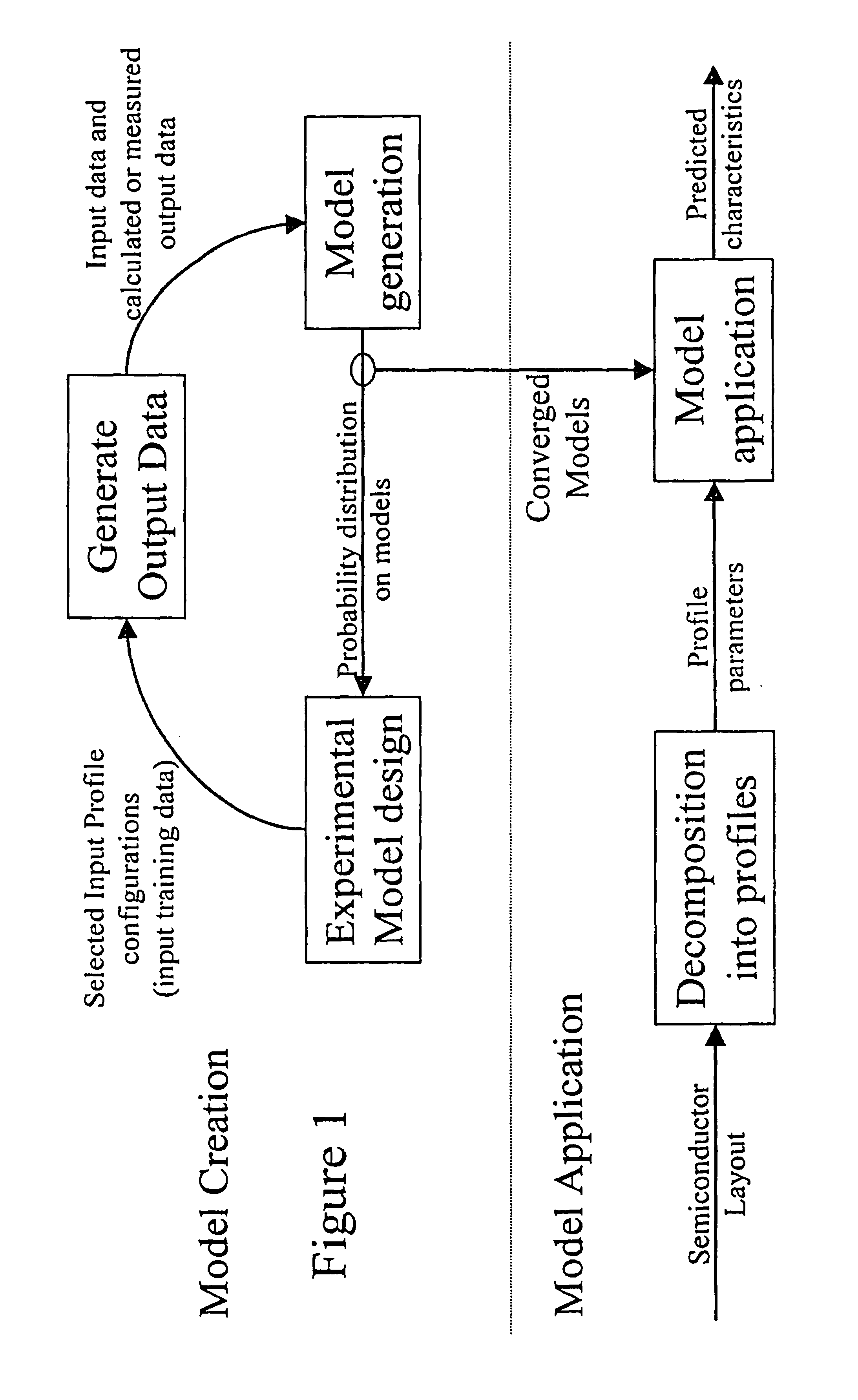
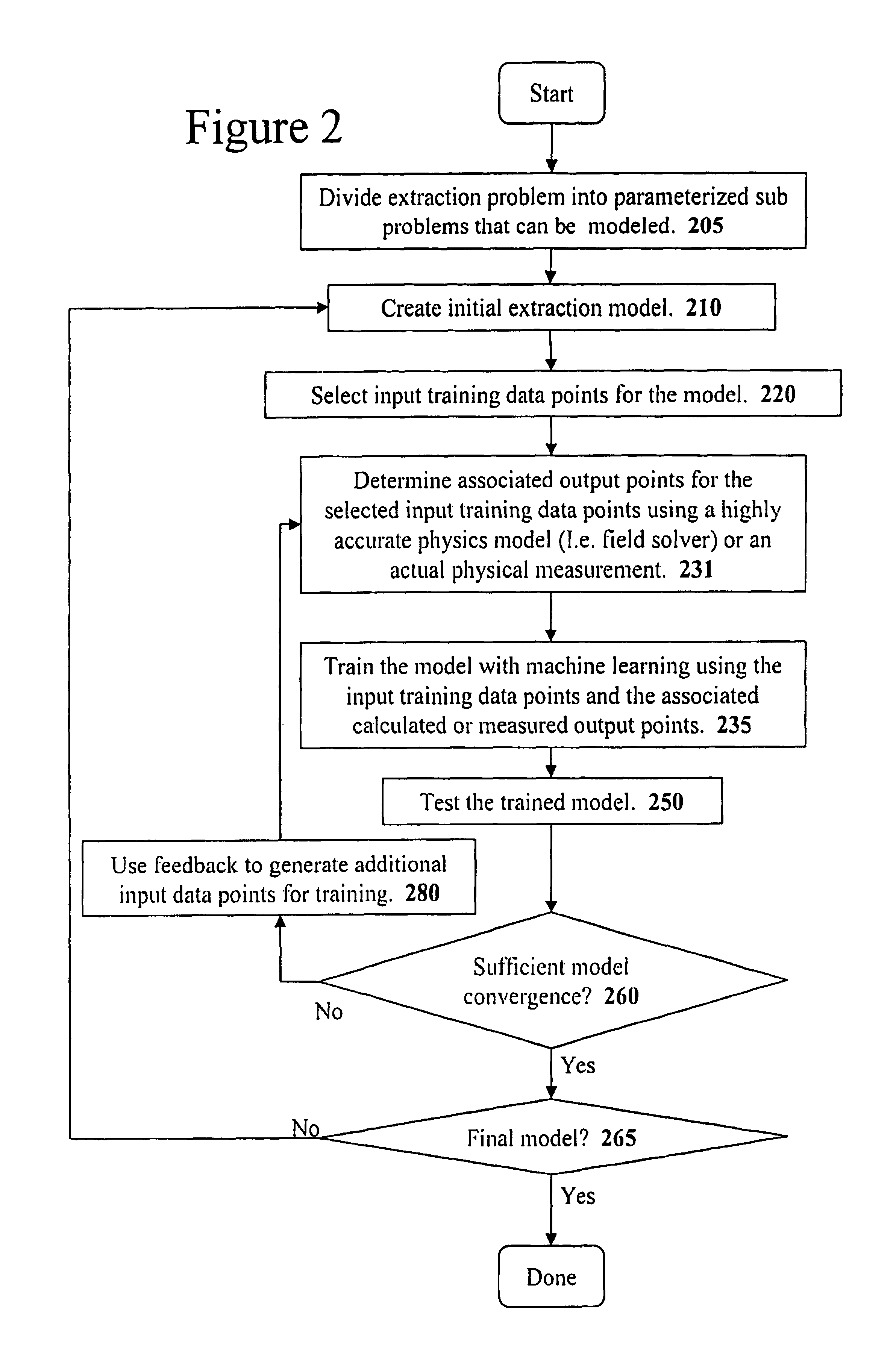
Method and apparatus for creating an extraction model using Bayesian inference
InactiveUS6883148B1Data processing applicationsComputation using non-denominational number representationPhysics basedLearning based
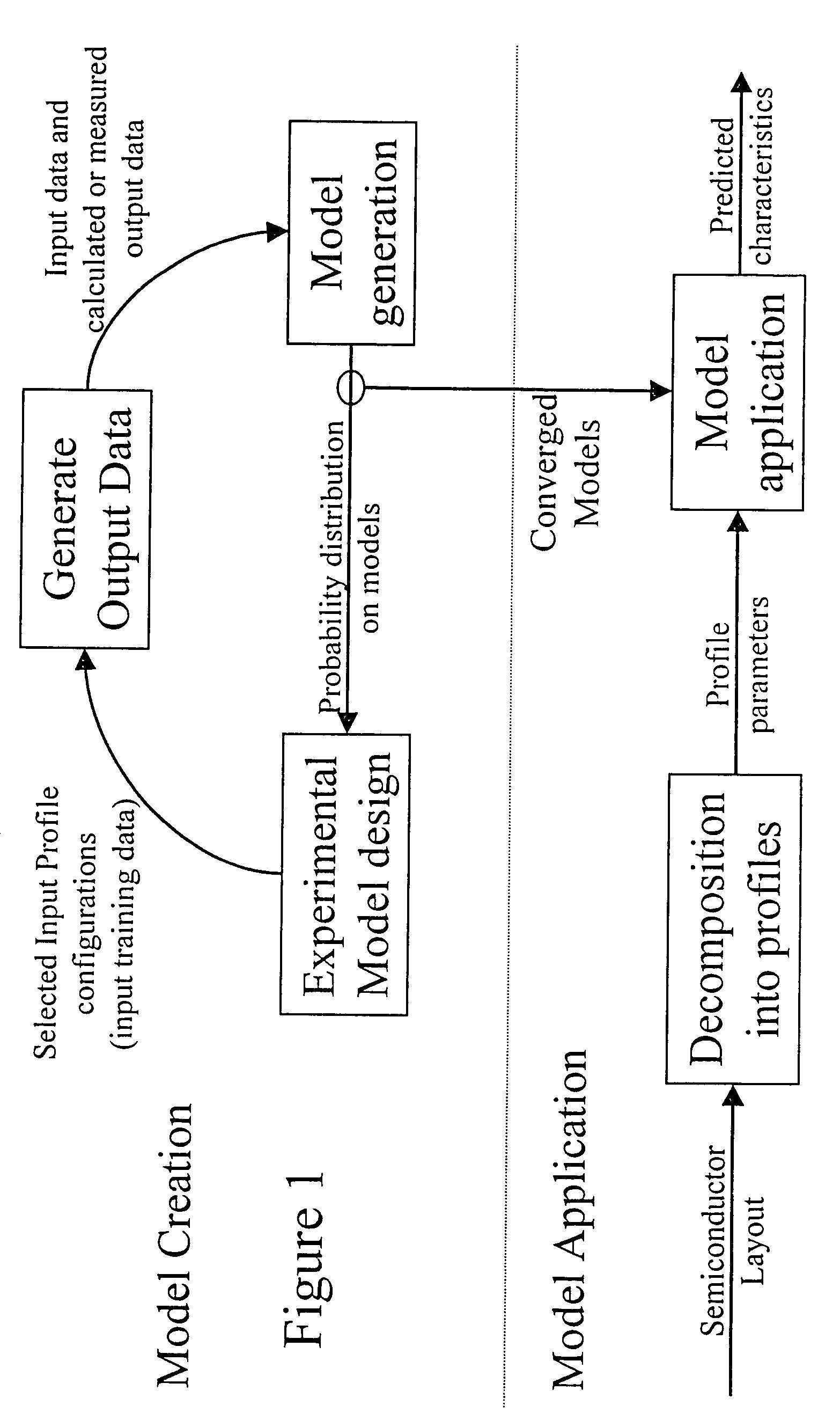
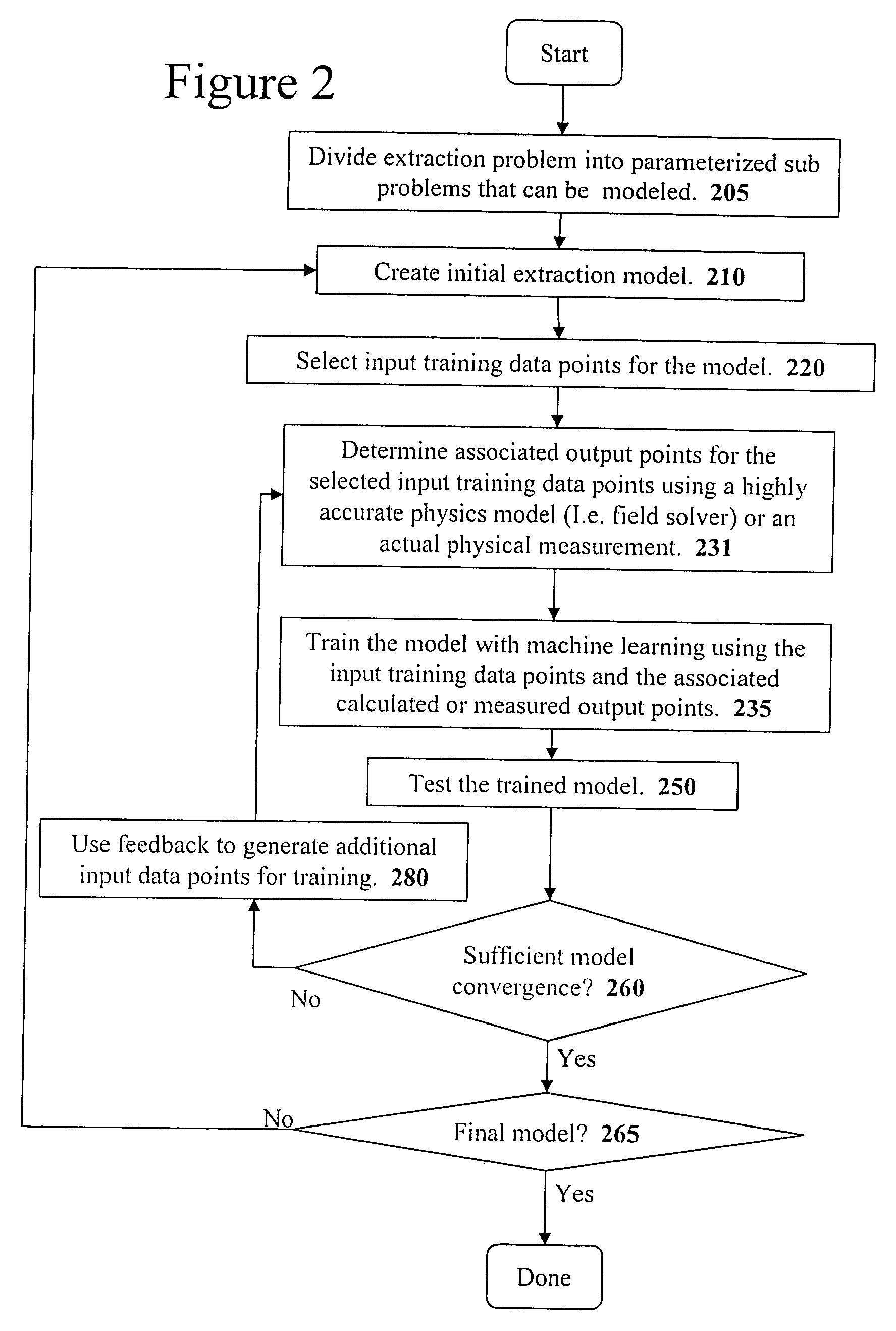
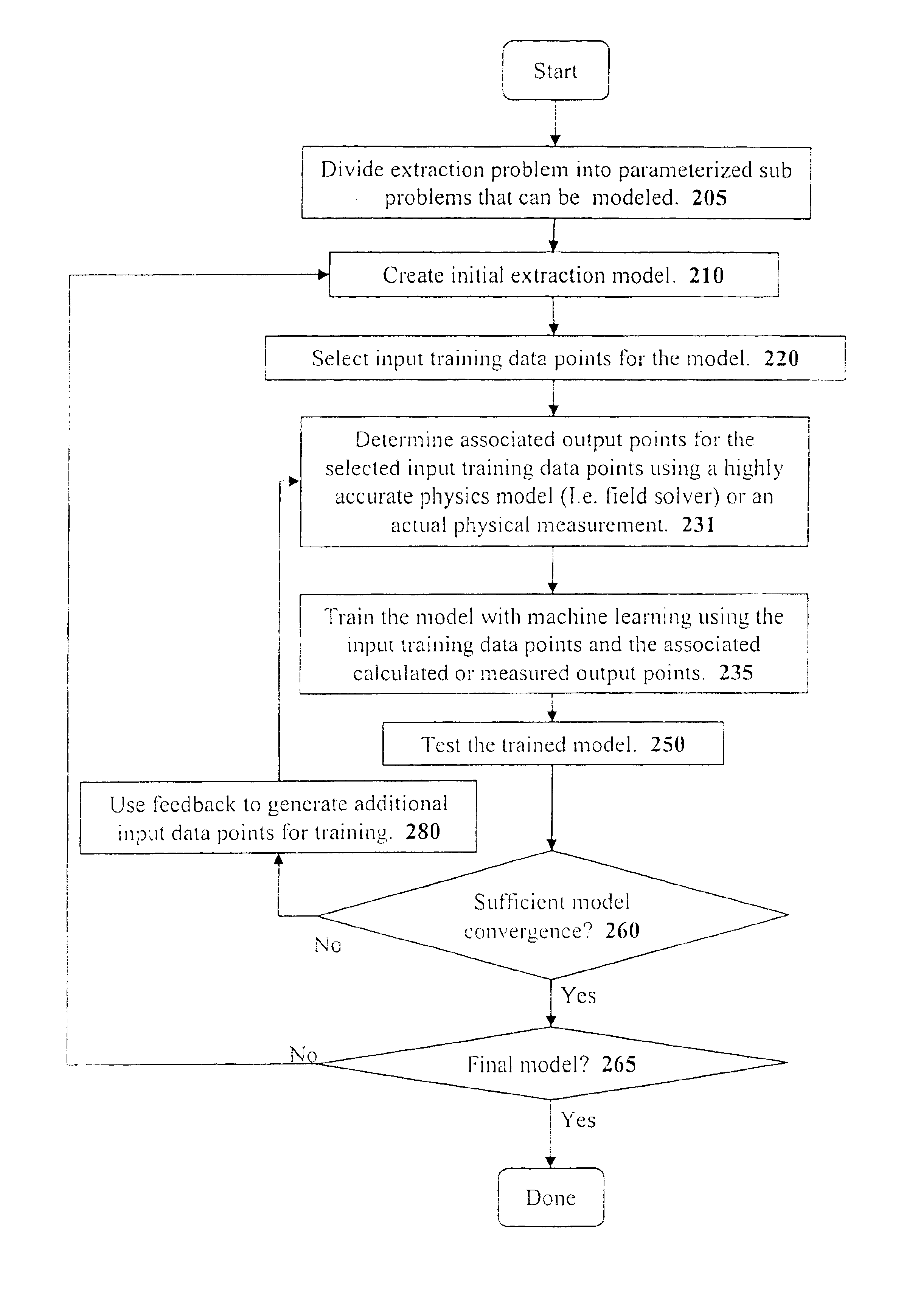
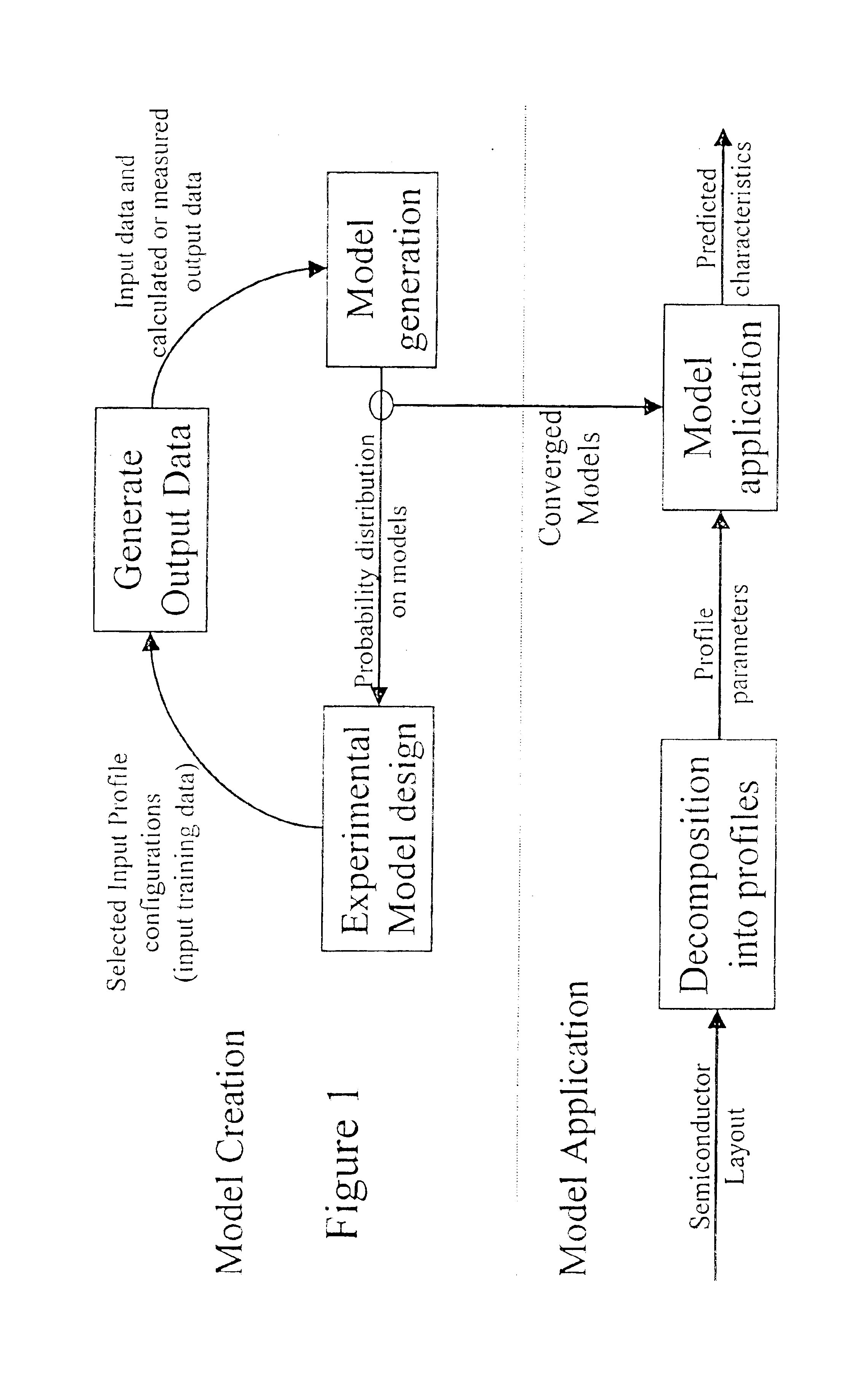
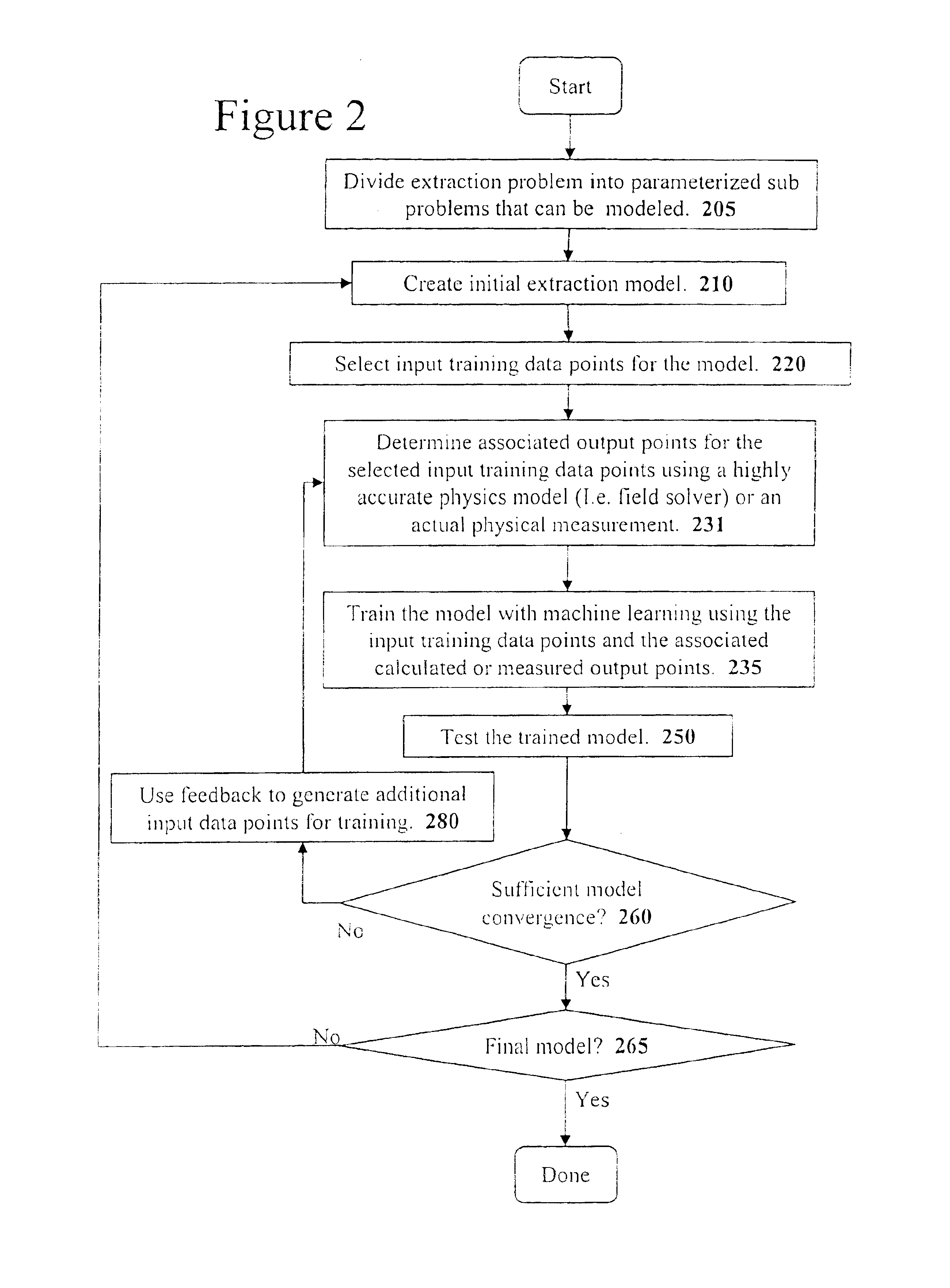
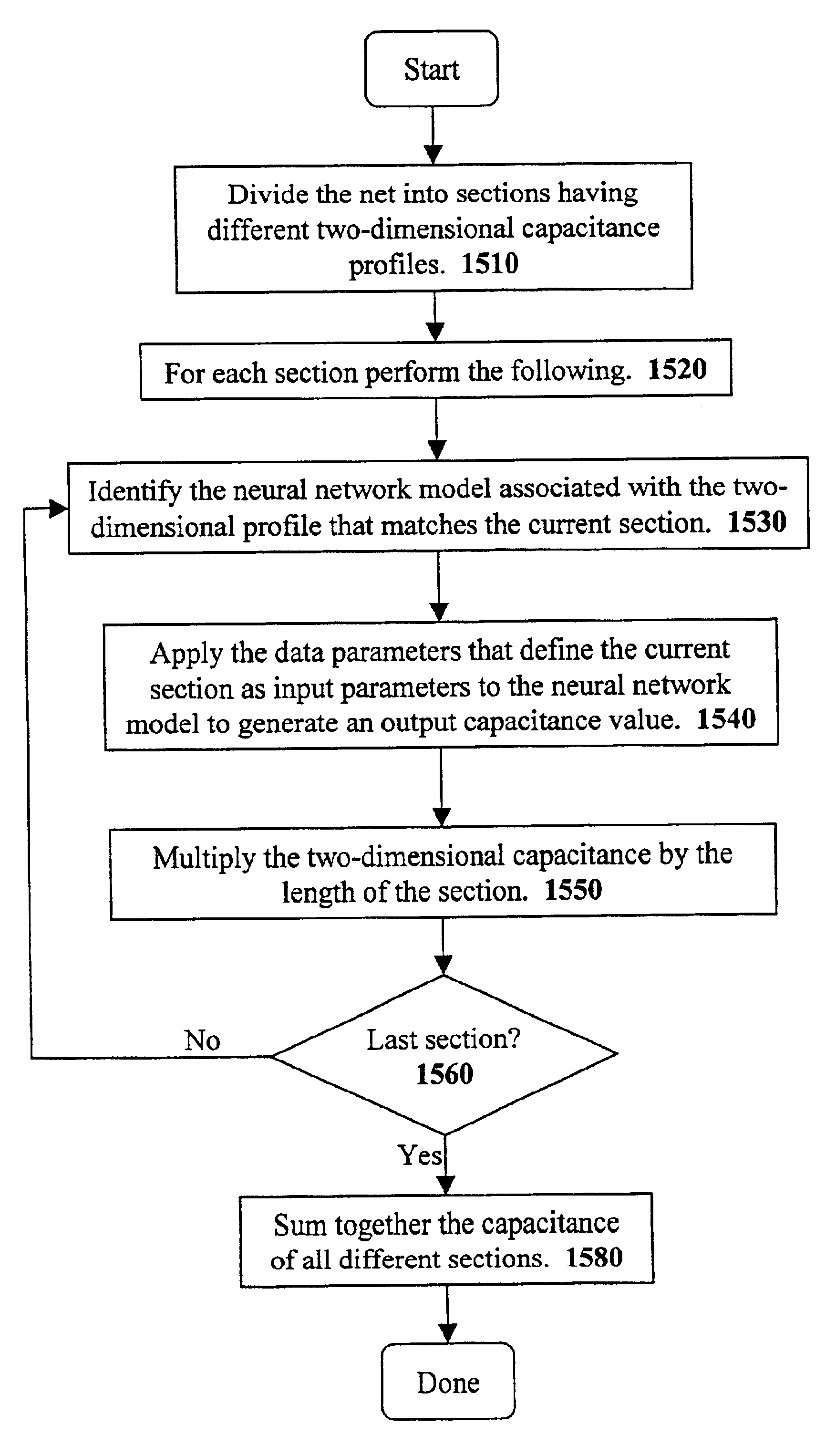
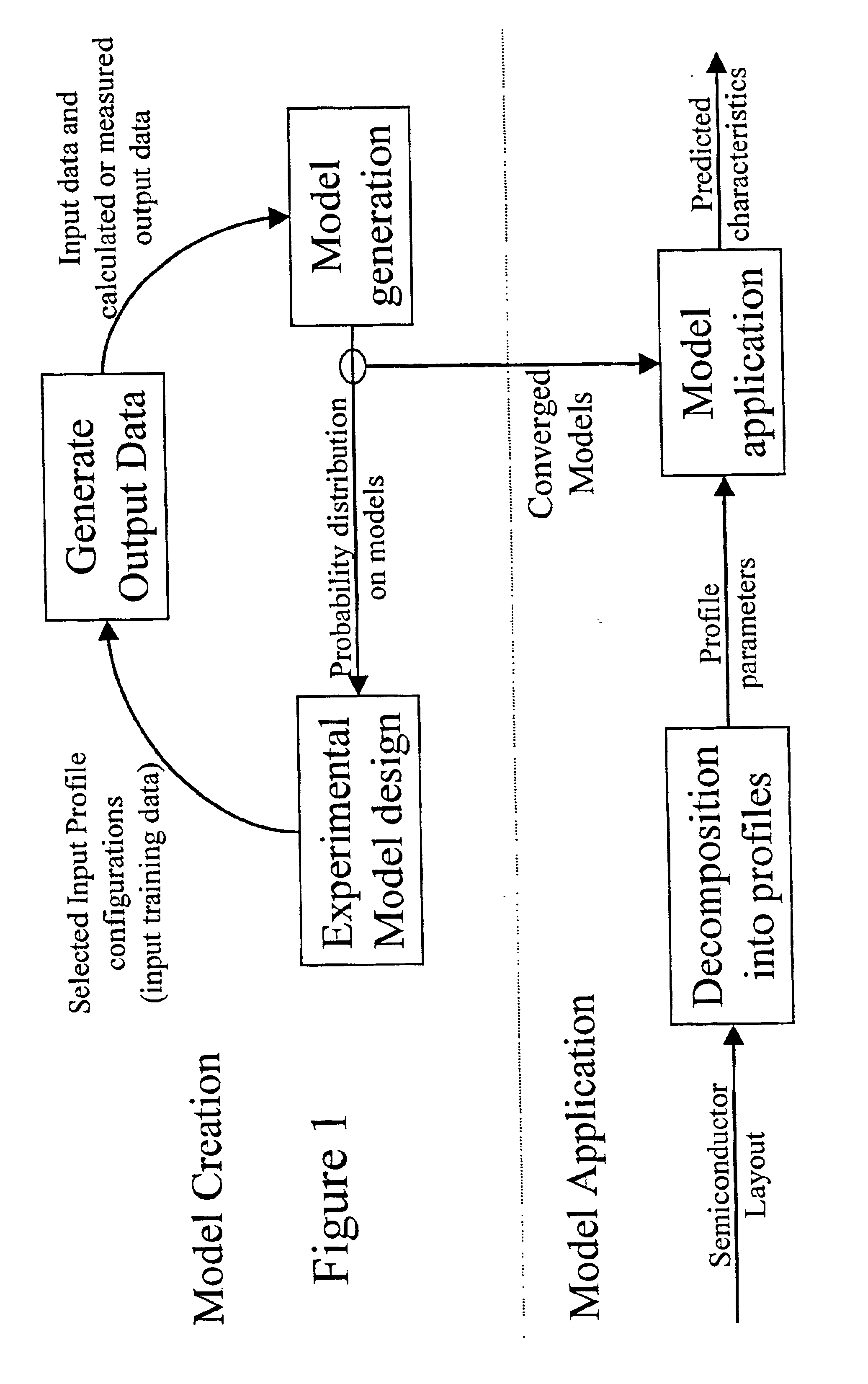
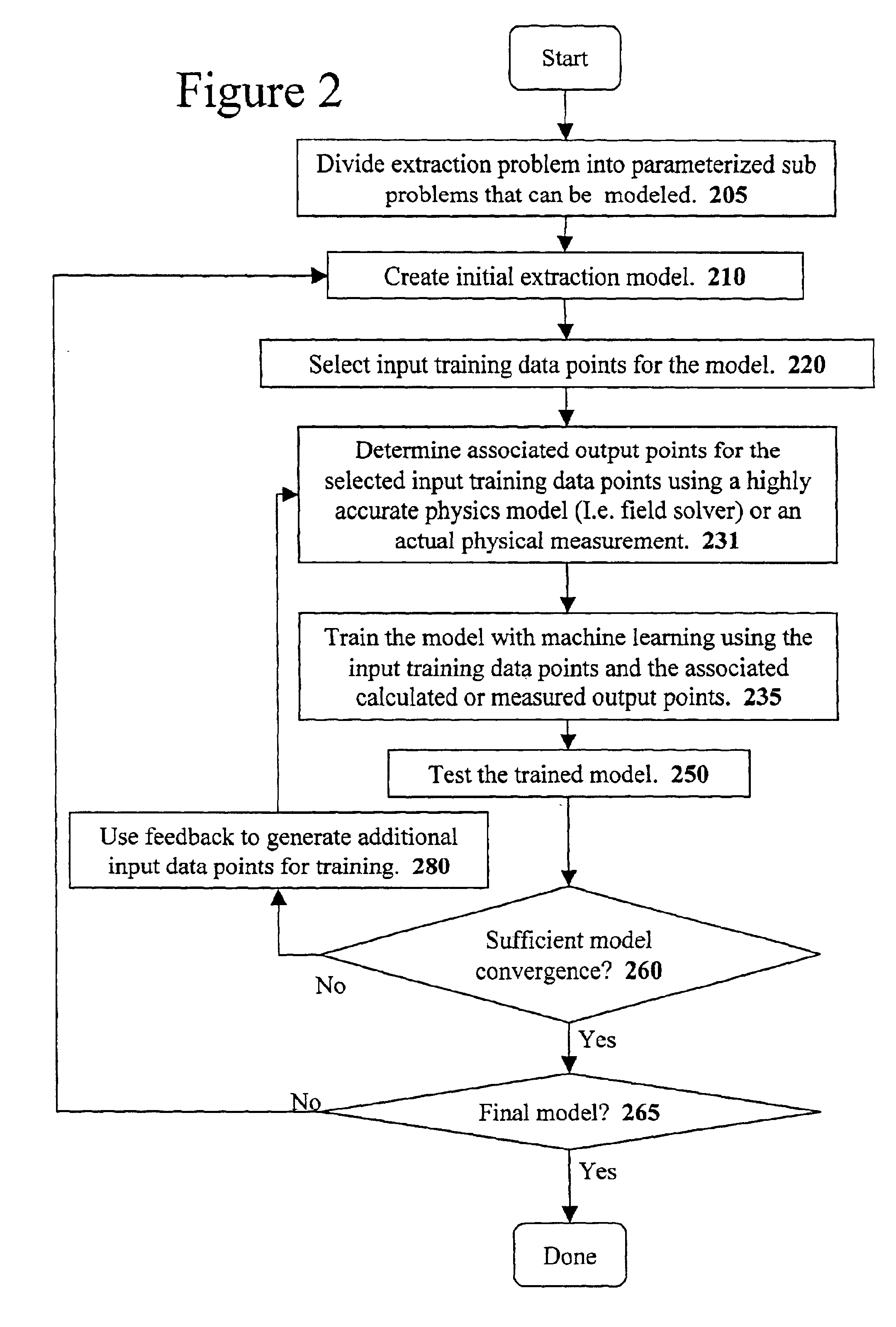
A system for using machine-learning to create a model for performing integrated circuit layout extraction is disclosed. The system of the present invention has two main phases: model creation and model application. The model creation phase comprises creating one or more extraction models using machine-learning techniques. First, a complex extraction problem is decomposed into smaller simpler extraction problems. Then, each smaller extraction problem is then analyzed to identify a set of physical parameters that fully define the smaller extraction problem. Next, models are created using machine learning techniques for all of the smaller simpler extraction problems. The machine learning is performed by first creating training data sets composed of the identified parameters from typical examples of the smaller extraction problem and the answers to those example extraction problems as solved using a highly accurate physics-based field solver. The system them uses the created training sets to train neural networks that will be used to model the extraction problems. Bayesian inference is used to train the neural networks models. Bayesian inference may be implemented with normal Monte Carlo techniques or Hybrid Monte Carlo techniques. After the creation of a set of models for each of the smaller simpler extraction problems, the machine-learning based models may be used for extraction.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Object tracking by hierarchical association of detection responses
Systems, methods, and computer readable storage media are described that can provide a multi-level hierarchical framework to progressively associate detection responses, in which different methods and models are adopted to improve tracking robustness. A modified transition matrix for the Hungarian algorithm can be used to solve the association problem that considers not only initialization, termination and transition of tracklets but also false alarm hypotheses. A Bayesian inference approach can be used to automatically estimate a scene structure model as the high-level knowledge for the long-range trajectory association.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method and apparatus for creating an extraction model using Bayesian inference implemented with the Hybrid Monte Carlo method
ActiveUS7103524B1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationData setMathematical model
A system for using machine learning based upon Bayesian inference using a hybrid Monte Carlo method to create a model for performing integrated circuit layout extraction is disclosed. The system of the present invention has two main phases: model creation and model application. The model creation phase comprises creating one or more extraction models using machine-learning techniques. First, a complex extraction problem is decomposed into smaller simpler extraction problems. Then, each smaller extraction problem is then analyzed to identify a set of physical parameters that fully define the smaller extraction problem. Then, for each of the smaller simpler extraction problems, complex mathematical models are created using machine learning techniques. The machine learning is performed by first creating training data sets composed of the identified parameters from typical examples of the smaller extraction problem and the answers to those example extraction problems as solved using a highly accurate physics-based field solver. Next, the system uses Bayesian inference implemented with a hybrid Monte Carlo method to train a set of neural networks for extraction problems. After the creation of a set of models for each of the smaller simpler extraction problems, the machine-learning based models may be used for extraction.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
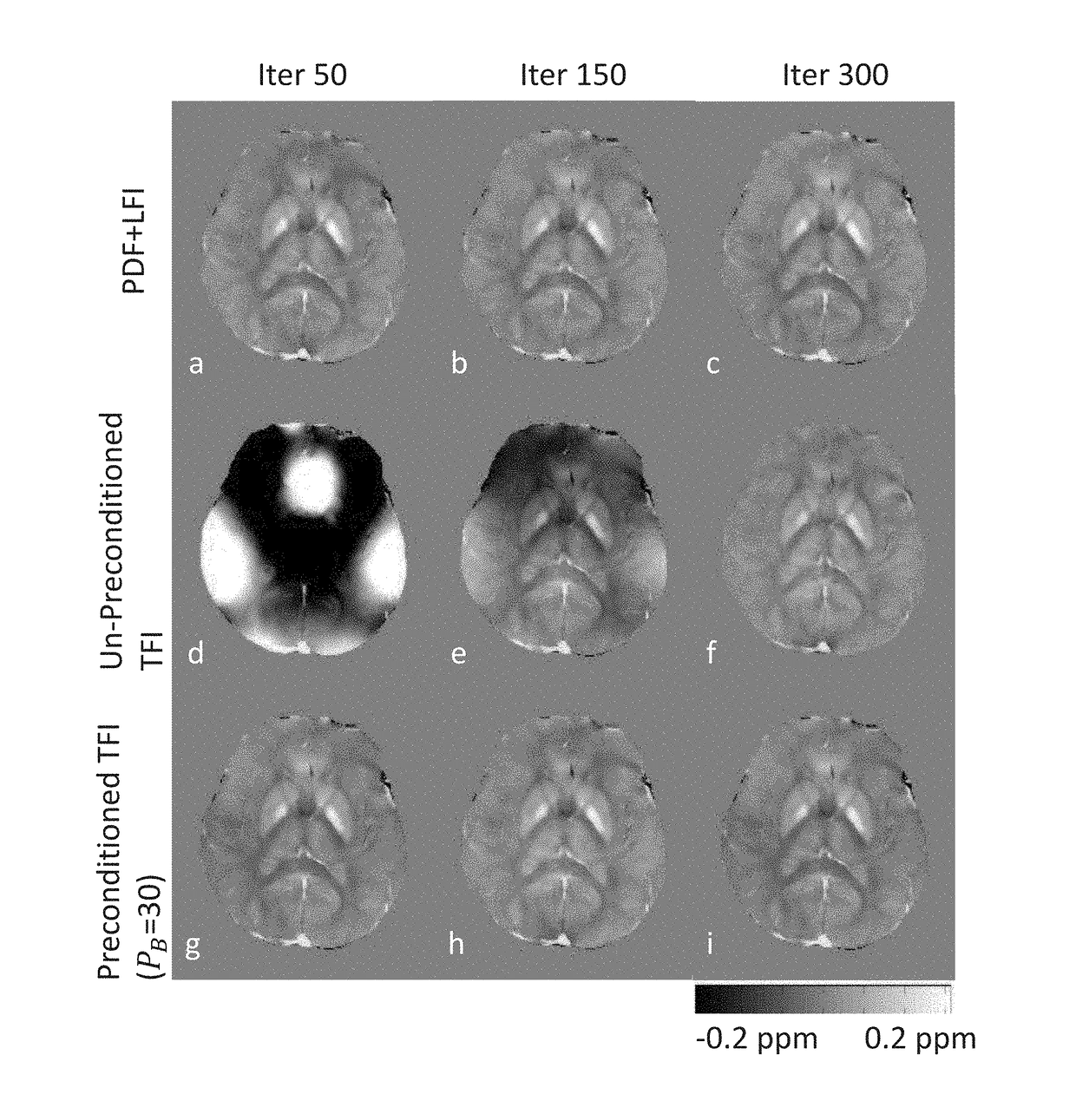
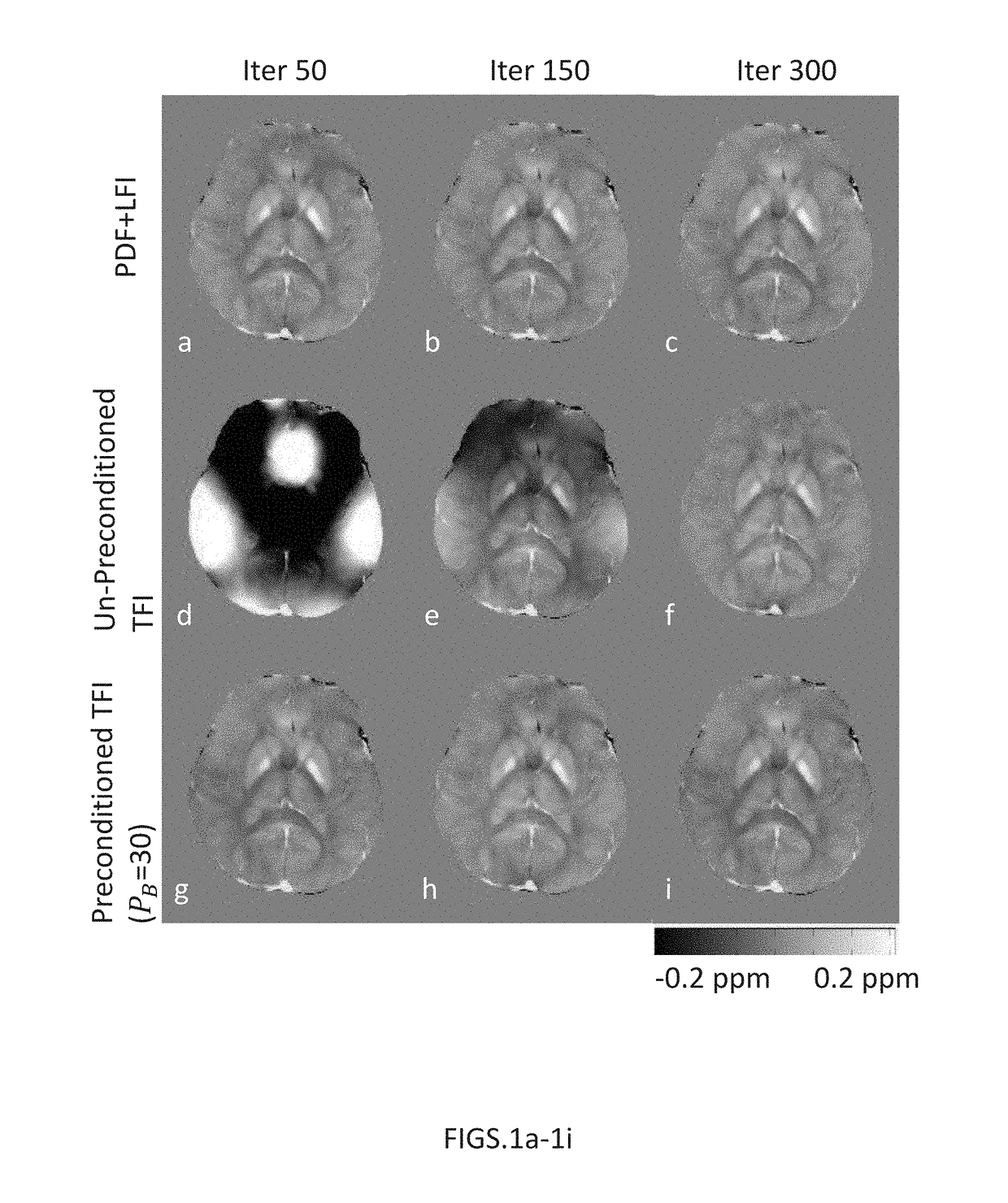
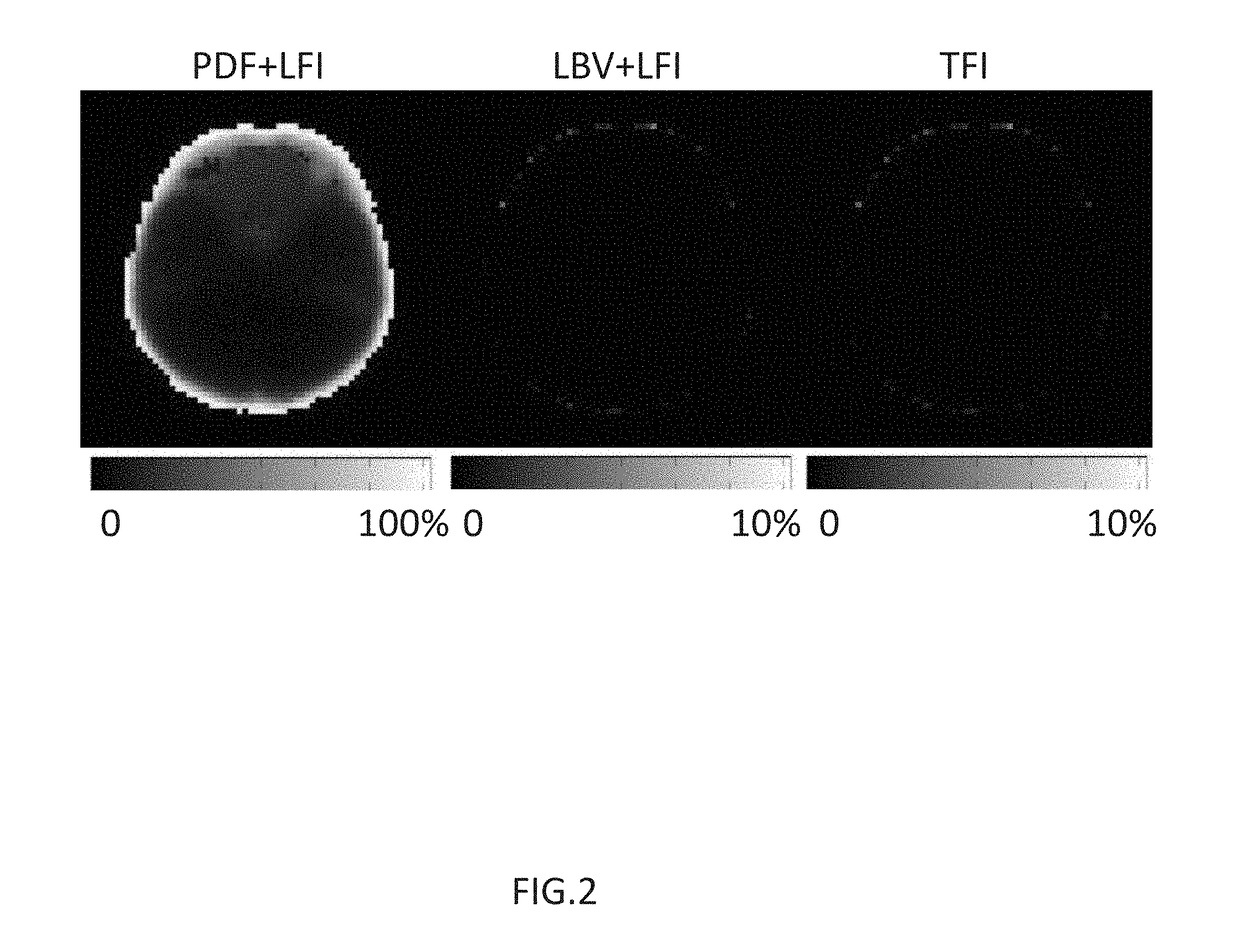
System and method of robust quantitative susceptibility mapping
ActiveUS20180321347A1Improve accuracyQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisMagnetic susceptibilityQuantitative susceptibility mapping
Exemplary quantitative susceptibility mapping methods, systems and computer-accessible medium can be provided to generate images of tissue magnetism property from complex magnetic resonance imaging data using the Bayesian inference approach, which minimizes a cost function consisting of a data fidelity term and two regularization terms. The data fidelity term is constructed directly from the complex magnetic resonance imaging data. The first prior is constructed from matching structures or information content in known morphology. The second prior is constructed from a region having an approximately homogenous and known susceptibility value and a characteristic feature on anatomic images. The quantitative susceptibility map can be determined by minimizing the cost function. Thus, according to the exemplary embodiment, system, method and computer-accessible medium can he provided for determining magnetic susceptibility information associated with at least one structure.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Human pose estimation with data driven belief propagation
A statistical formulation estimates two-dimensional human pose from single images. This is based on a Markov network and on inferring pose parameters from cues such as appearance, shape, edge, and color. A data-driven belief propagation Monte Carlo algorithm performs efficient Bayesian inferencing within a rigorous statistical framework. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the method in estimating human pose from single images.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method and apparatus for performing extraction using machine learning
InactiveUS6857112B1Improve accuracyComputer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsData setIntegrated circuit layout
A system for using machine-learning to create a model for performing integrated circuit layout extraction is disclosed. The system of the present invention has two main phases: model creation and model application. The model creation phase comprises creating one or more extraction models using machine-learning techniques. First, a complex extraction problem is decomposed into smaller simpler extraction problems. Then, each smaller extraction problem is then analyzed to identify a set of physical parameters that fully define the smaller extraction problem. Next, models are created using machine learning techniques for all of the smaller simpler extraction problems. The machine learning is performed by first creating training data sets composed of the identified parameters from typical examples of the smaller extraction problem and the answers to those example extraction problems as solved using a highly accurate physics-based field solver. The training sets are then used to train the models. In one embodiment, neural networks are used to model the extraction problems. Bayesian inference is employed by one embodiment in order to train the neural network models. Bayesian inference may be implemented with normal Monte Carlo techniques or Hybrid Monte Carlo techniques. After the creation of a set of models for each of the smaller simpler extraction problems, the machine-learning based models may be used for extraction.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
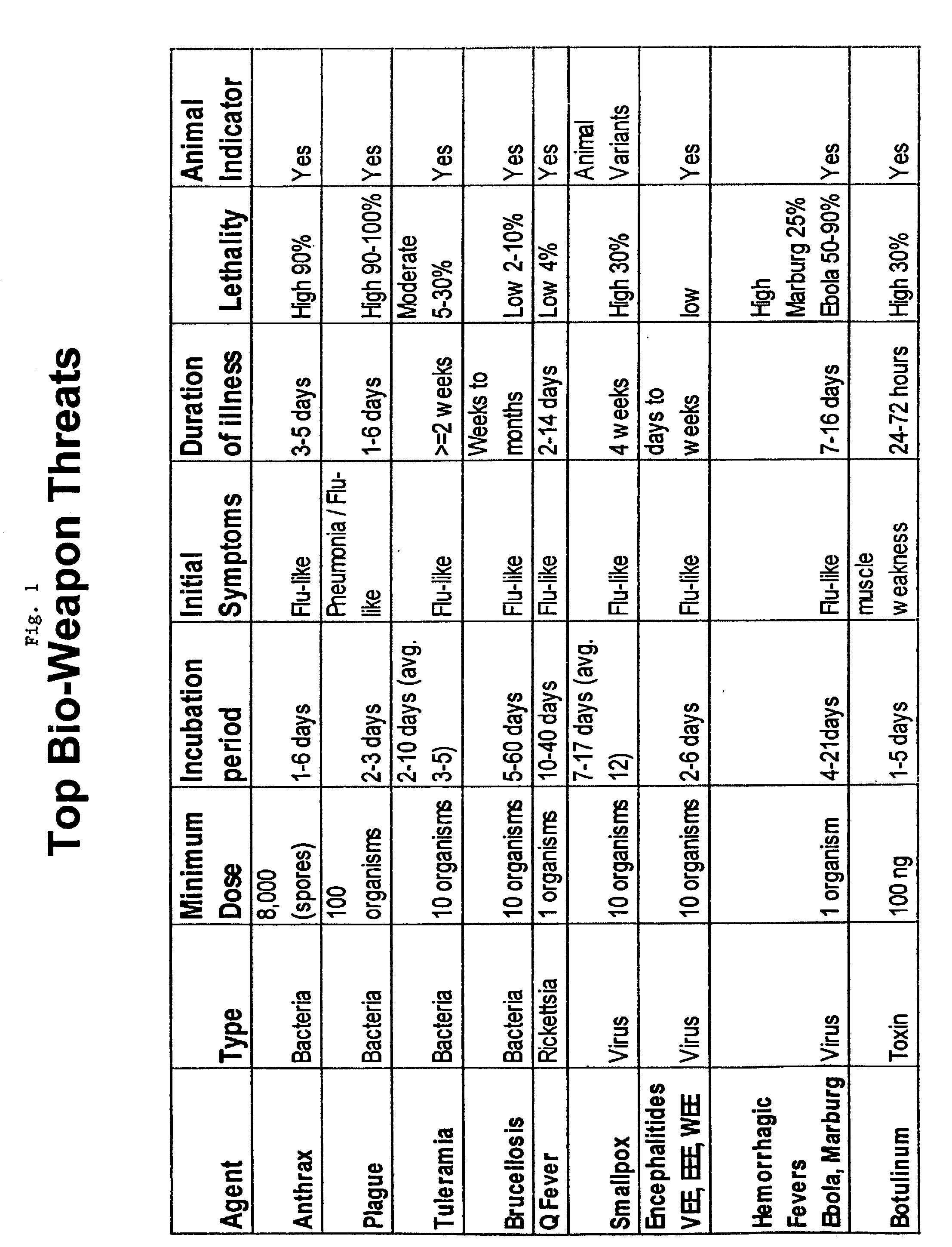
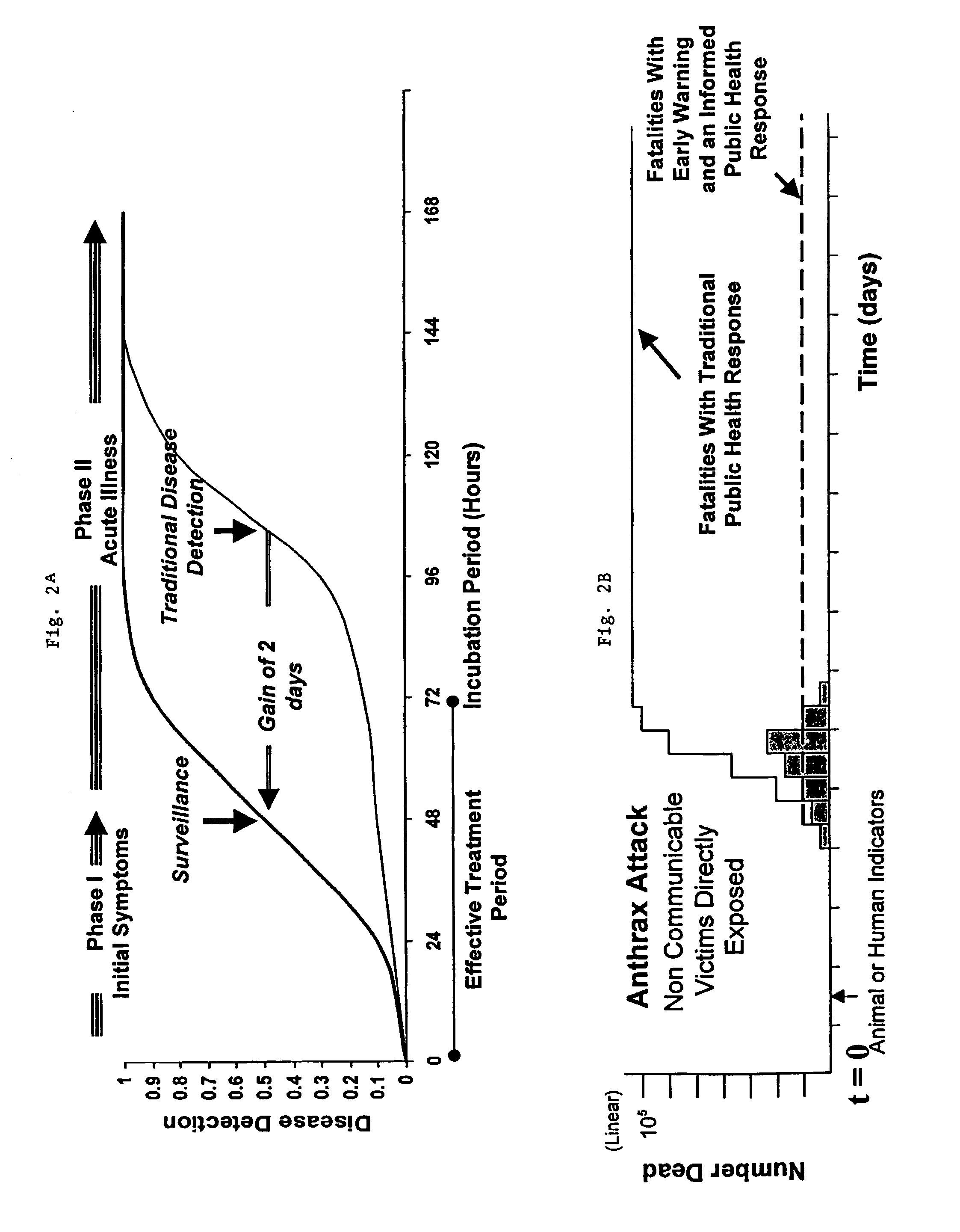
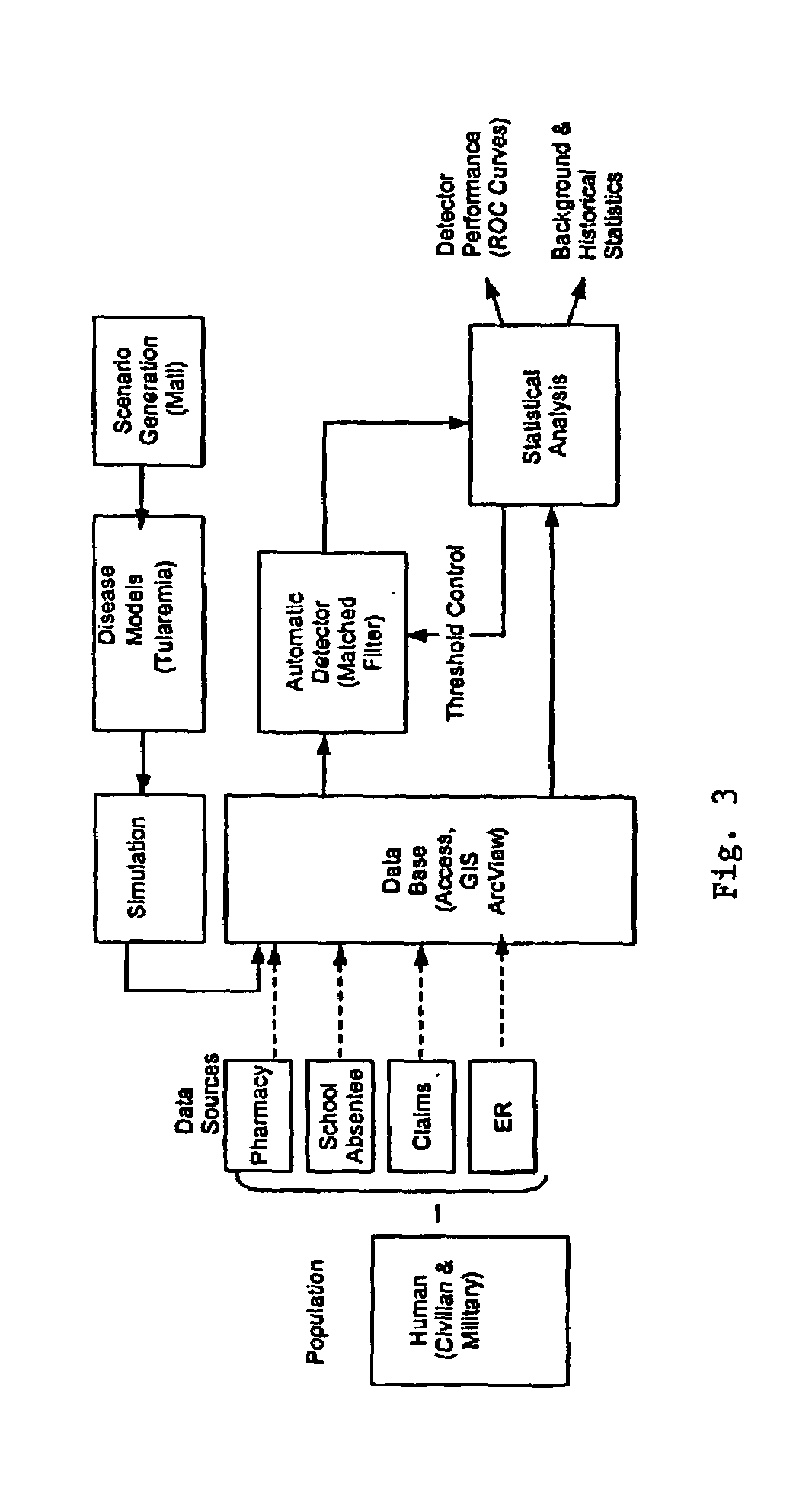
Method and system for bio-surveillance detection and alerting
InactiveUS7249006B2Save livesEarly detectionElectric testing/monitoringAnalogue computers for chemical processesData setAdaptive matching
Background noise from relevant data sets, including for example over-the-counter sales data, absenteeism data, etc., is subtracted using a background estimation algorithm that outputs residual data. The effects of hypothetical anomalous events, such as a bio-terrorist attack, on the relevant data sets are modeled to create replica data. The replica data may be based on input from epidemiologists and various scenario templates including information on disease manifestation and other intelligence. The residual data and the replica data are then matched using a detector. Types of detectors include for example adaptive matched-filter detectors, change detectors and Bayesian Inference Networks. An alarm is triggered if a real anomalous event similar to a hypothetical anomalous event is detected. A Geographical Information System (GIS) may be used to display data from individual zip codes.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method and apparatus for performing extraction using a neural network
InactiveUS6907591B1Improve accuracyDetecting faulty computer hardwareProgram controlPhysics basedNerve network
A system for using machine-learning to create a model for performing integrated circuit layout extraction is disclosed. The system of the present invention has two main phases: model creation and model application. The model creation phase comprises creating one or more extraction models using machine-learning techniques. First, a complex extraction problem is decomposed into smaller simpler extraction problems. Then, each smaller extraction problem is then analyzed to identify a set of physical parameters that fully define the smaller extraction problem. Next, models are created using machine learning techniques for all of the smaller simpler extraction problems. The machine learning is performed by first creating training data sets composed of the identified parameters from typical examples of the smaller extraction problem and the answers to those example extraction problems as solved using a highly accurate physics-based field solver. Next, the system trains a set of neural networks using the training sets. In one embodiment, Bayesian inference is used to train the neural networks that are used to model the extraction. After the creation the neural network based models for each of the smaller simpler extraction problems, the neural network based models may be used for extraction.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
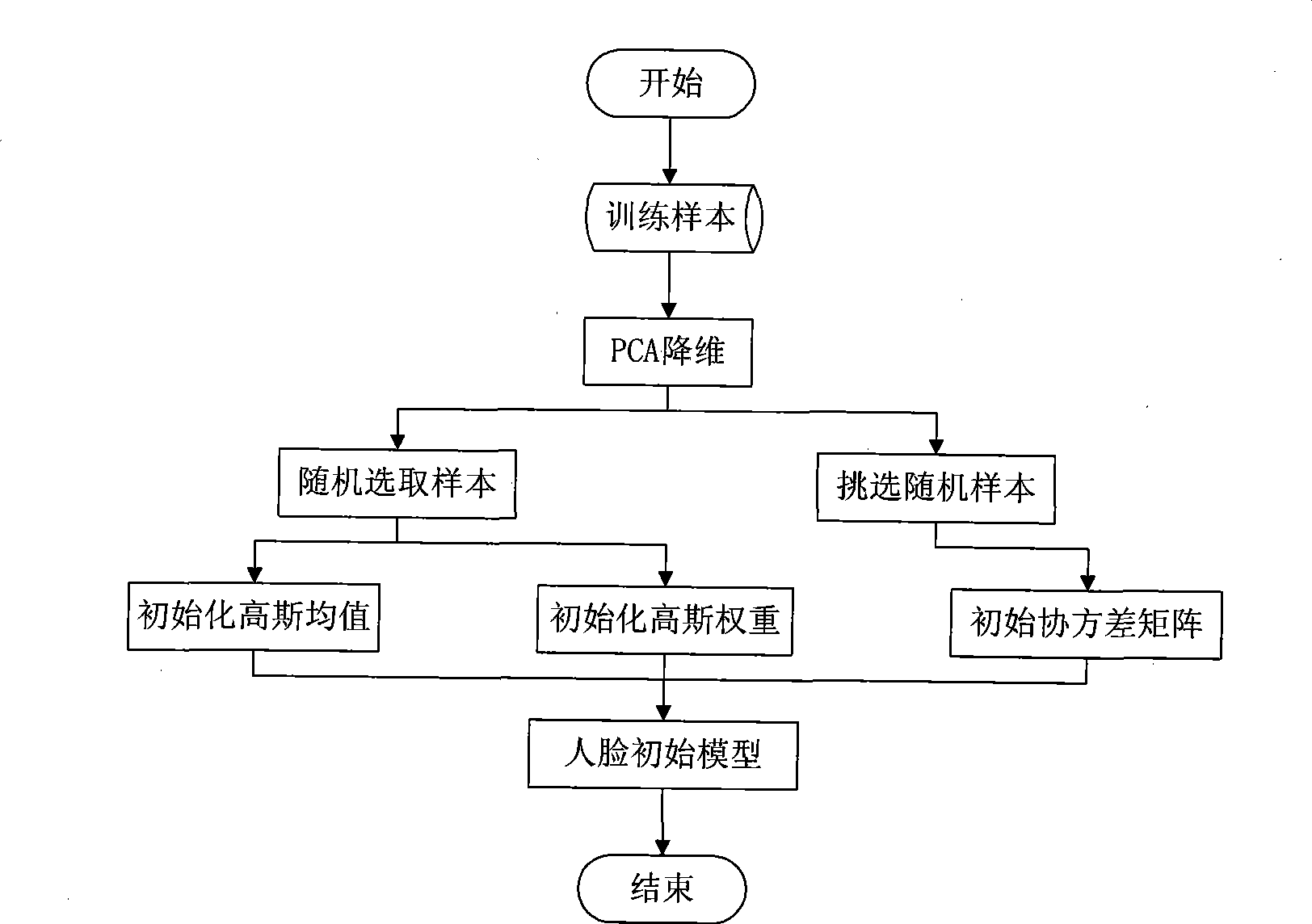
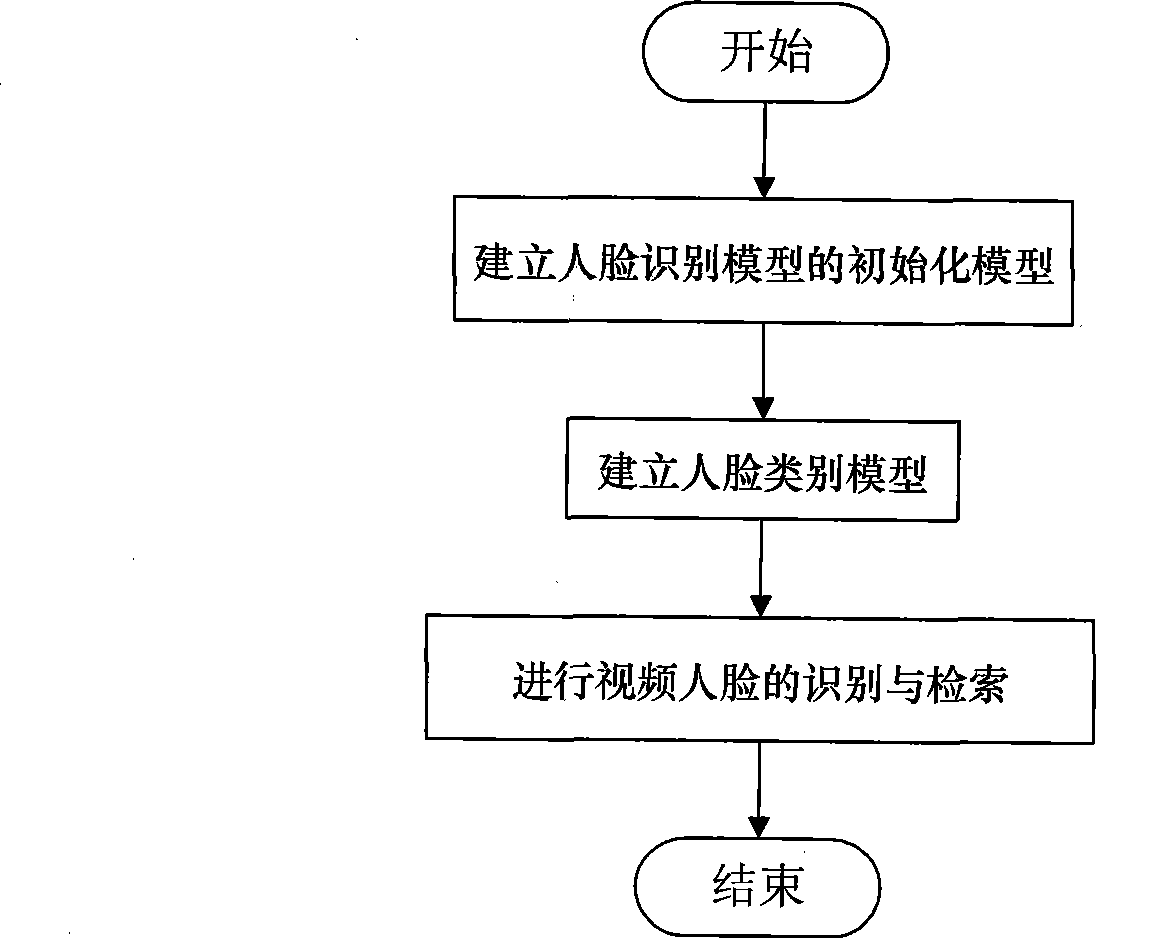
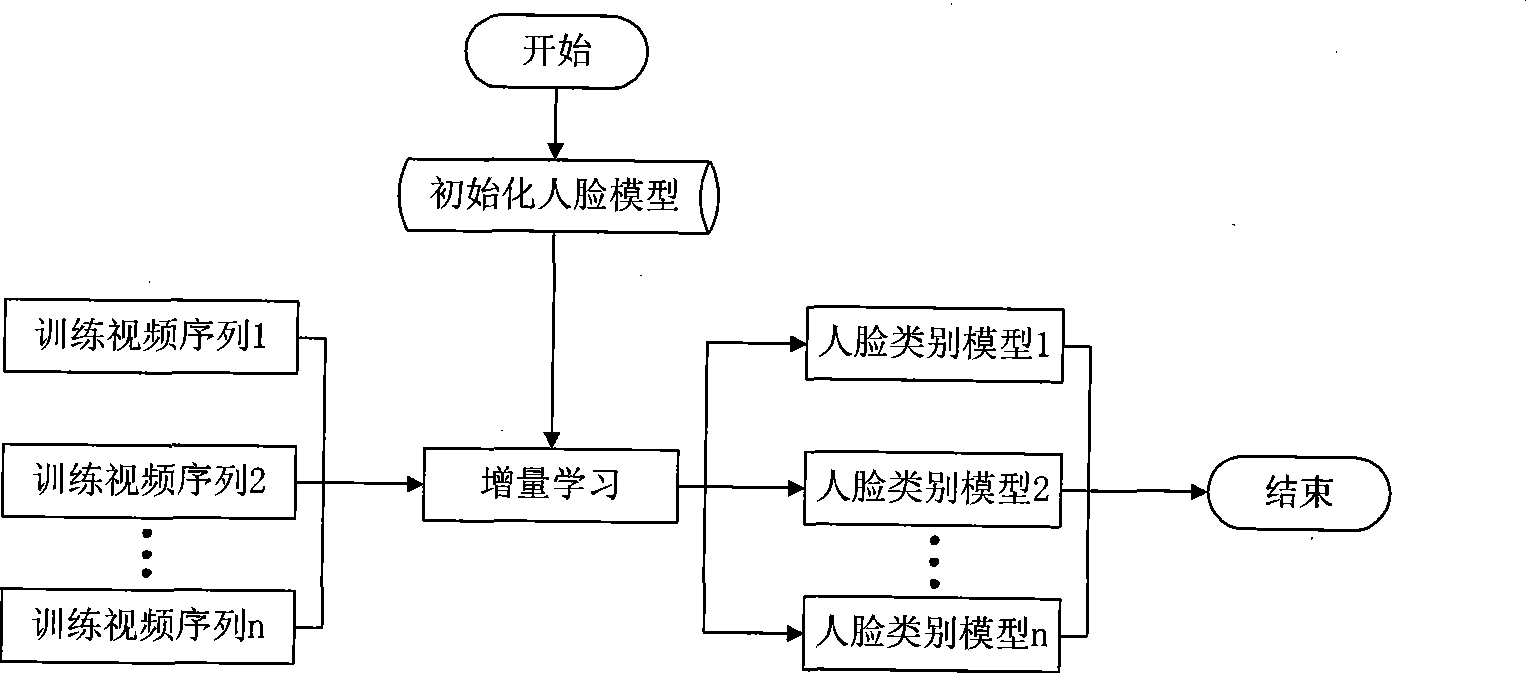
Video human face identification and retrieval method based on on-line learning and Bayesian inference
InactiveCN101464950AHigh degree of automationAdjust the number of Gaussian mixturesCharacter and pattern recognitionFrame basedIncremental learning
The invention discloses a method for recognizing and retrieving video faces based on on-line study and Bayesian inference. The method comprises the following steps: step one: establishing an initialization model of a face recognition model, (i.e. the face recognition model adopts a GMM face recognition model); step two: establishing a face category model, (i.e. the model renewal of the initialization face model is performed by adopting an incremental learning manner); step three: recognizing and retrieving video faces. The test sequence and the category model are assigned, the sequence recognition information of the accumulation video in the Bayesian inference process is utilized, the probability density function of the identity is propagated according to information of a time axis, and the method provides recognition results of the video faces for users based on the MAP rules to obtain recognition scores. The invention establishes a model training frame based on non-supervised learning completely, according to spatial distribution of the training sequence, the initialization model is evolved for the category model in different modes, and the distribution of spatial data is better fitted through adjusting Gaussian mixture number of the face category model.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
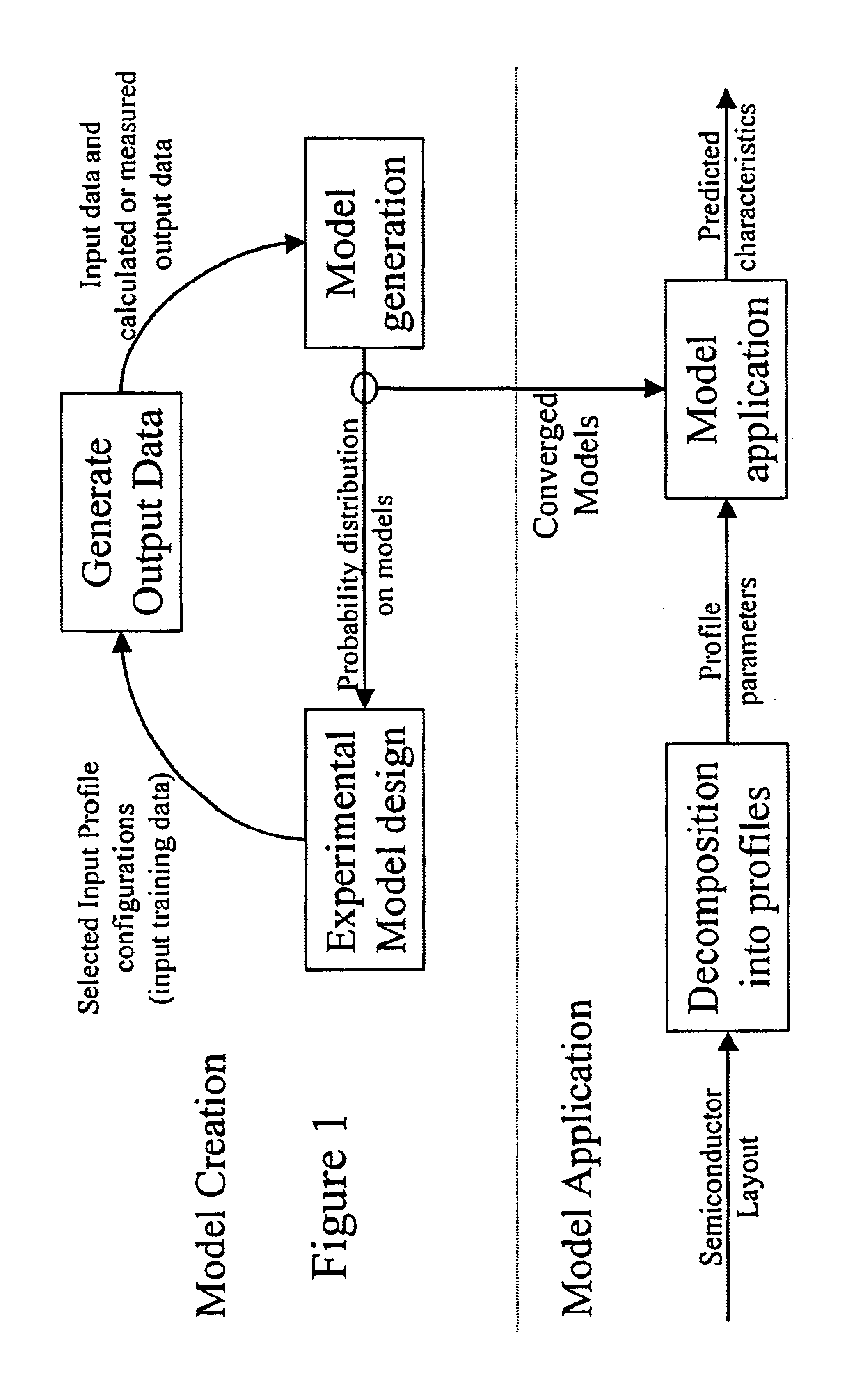
Method and apparatus for creating an extraction model
InactiveUS7051293B1Improve accuracyCAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationLearning basedPhysics based
A system for using machine-learning to create a model for performing integrated circuit layout extraction is disclosed. The system of the present invention has two main phases: model creation and model application. The model creation phase comprises creating one or more extraction models using machine-learning techniques. First, a complex extraction problem is decomposed into smaller simpler extraction problems. Then, each smaller extraction problem is then analyzed to identify a set of physical parameters that fully define the smaller extraction problem. Next, models are created using machine learning techniques for all of the smaller simpler extraction problems. The machine learning is performed by first creating training data sets composed of the identified parameters from typical examples of the smaller extraction problem and the answers to those example extraction problems as solved using a highly accurate physics-based field solver. The training sets are then used to train the models. In one embodiment, neural networks are used to model the extraction problems. To train the neural network models. Bayesian inference is used in one embodiment. Bayesian inference may be implemented with normal Monte Carlo techniques or Hybrid Monte Carlo techniques. After the creation of a set of models for each of the smaller simpler extraction problems, the machine-learning based models may be used for extraction.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
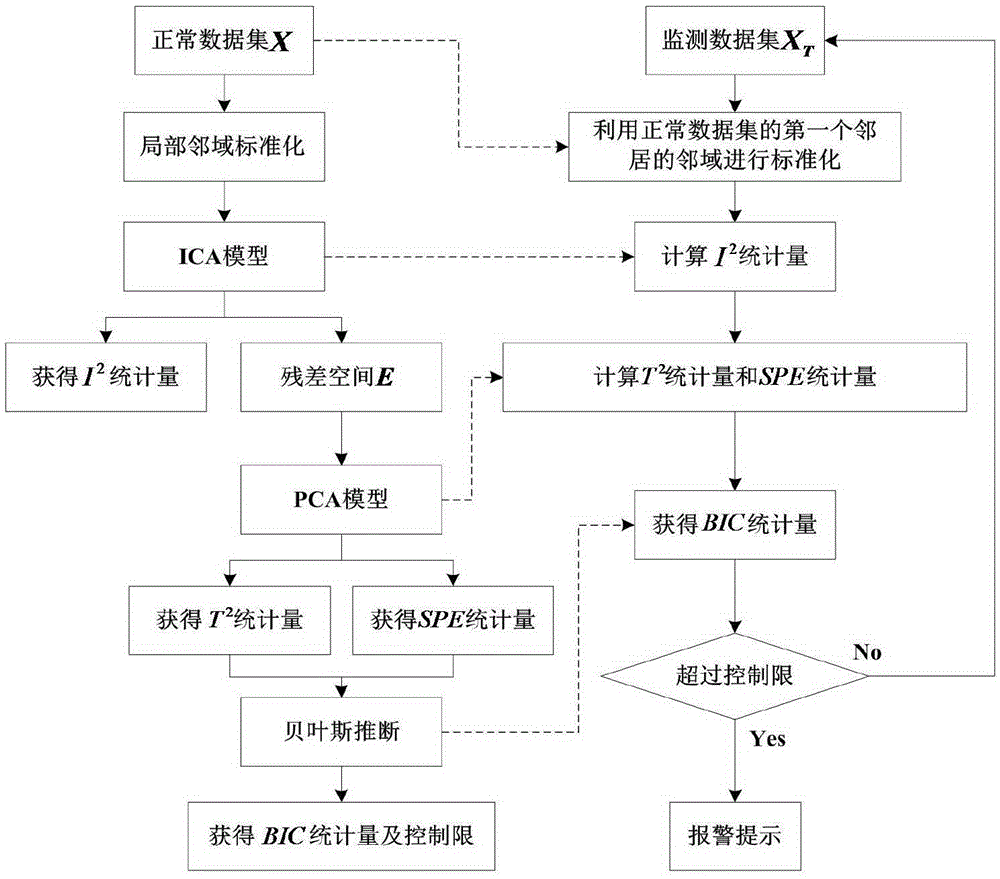
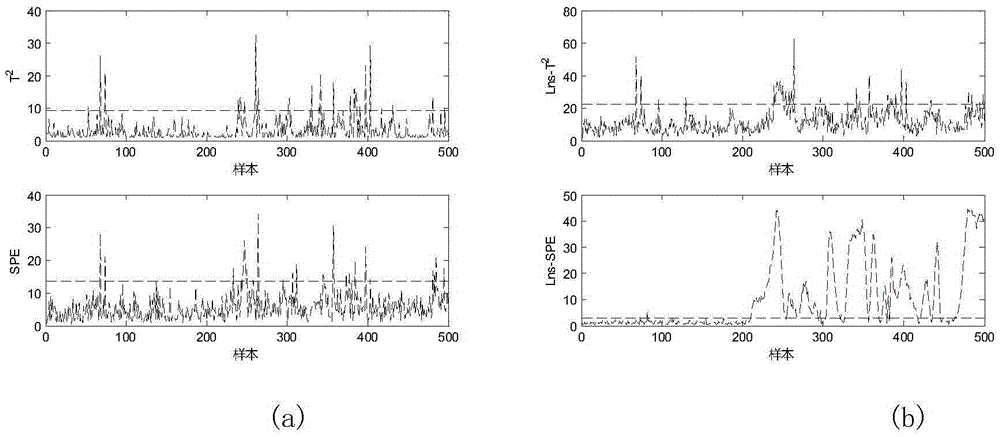
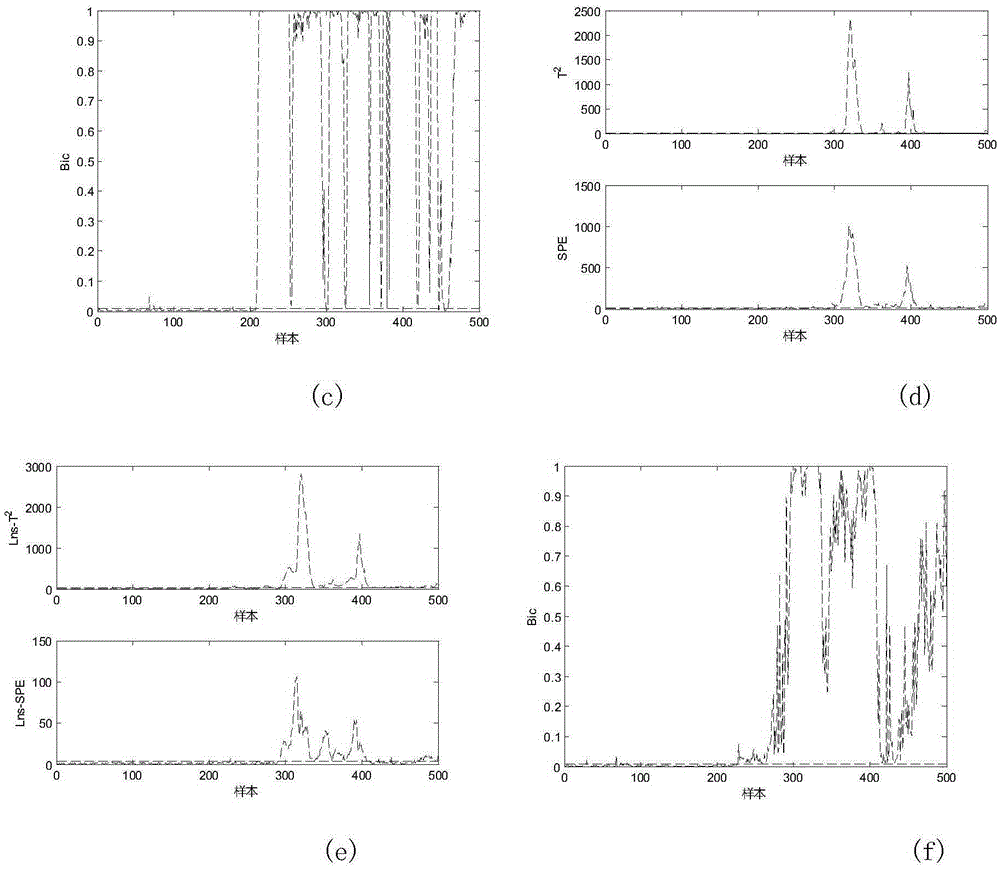
ICA-PCA multi-working condition fault diagnosis method based on local neighborhood standardization and Bayesian inference
ActiveCN105425779AEasy to observe and monitorEasy to handleProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringData setDiagnosis methods
The invention discloses an ICA-PCA multi-working condition fault diagnosis method based on local neighborhood standardization and Bayesian inference. The method firstly carries out independent sampling of each normal working condition during an industrial course to obtain a training dataset, carries out the local neighborhood standardization of the training dataset to obtain a dataset which follows single distribution, and then uses an ICA-PCA method to respectively analyze and process Gaussian features and non-Gaussian features of the dataset so as to obtain an overall model. At an online monitoring stage, independent and repeated sampling is carried out to industrial course data, a plurality of statistical quantities are acquired by applying the model to carry out analysis and processing after the local neighborhood standardization processing, then the multiple statistical quantities are combined into one statistical quantity by the Bayesian inference, and a fault diagnosis result is acquired by comparing control limits. In comparison with traditional fault diagnosis methods, the ICA-PCA multi-working condition fault diagnosis method based on the local neighborhood standardization and the Bayesian inference disclosed by the invention can simplify processing courses, improve diagnosis effects and improve course monitoring performance, and can also make workers' monitoring and observation convenient, make for avoiding safety hidden dangers and guarantee normal running of the industrial course.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for performing extraction using a model trained with Bayesian inference via a Monte Carlo method
A system for using machine learning based upon Bayesian inference using a hybrid monte carlo method to create a model for performing integrated circuit layout extraction is disclosed. The system of the present invention has two main phases: model creation and model application. The model creation phase comprises creating one or more extraction models using machine-learning techniques. First, a complex extraction problem is decomposed into smaller simpler extraction problems. Then, each smaller extraction problem is then analyzed to identify a set of physical parameters that fully define the smaller extraction problem. Next, complex mathematical models are created using machine learning techniques for all of the smaller simpler extraction problems. The machine learning is performed by first creating training data sets composed of the identified parameters from typical examples of the smaller extraction problem and the answers to those example extraction problems as solved using a highly accurate physics-based field solver. Next, the system uses Bayesian inference implemented with a Monte Carlo method to train a set of neural networks for extraction problems. After the creation of a set of models for each of the smaller simpler extraction problems, the machine-learning based models may be used for extraction.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
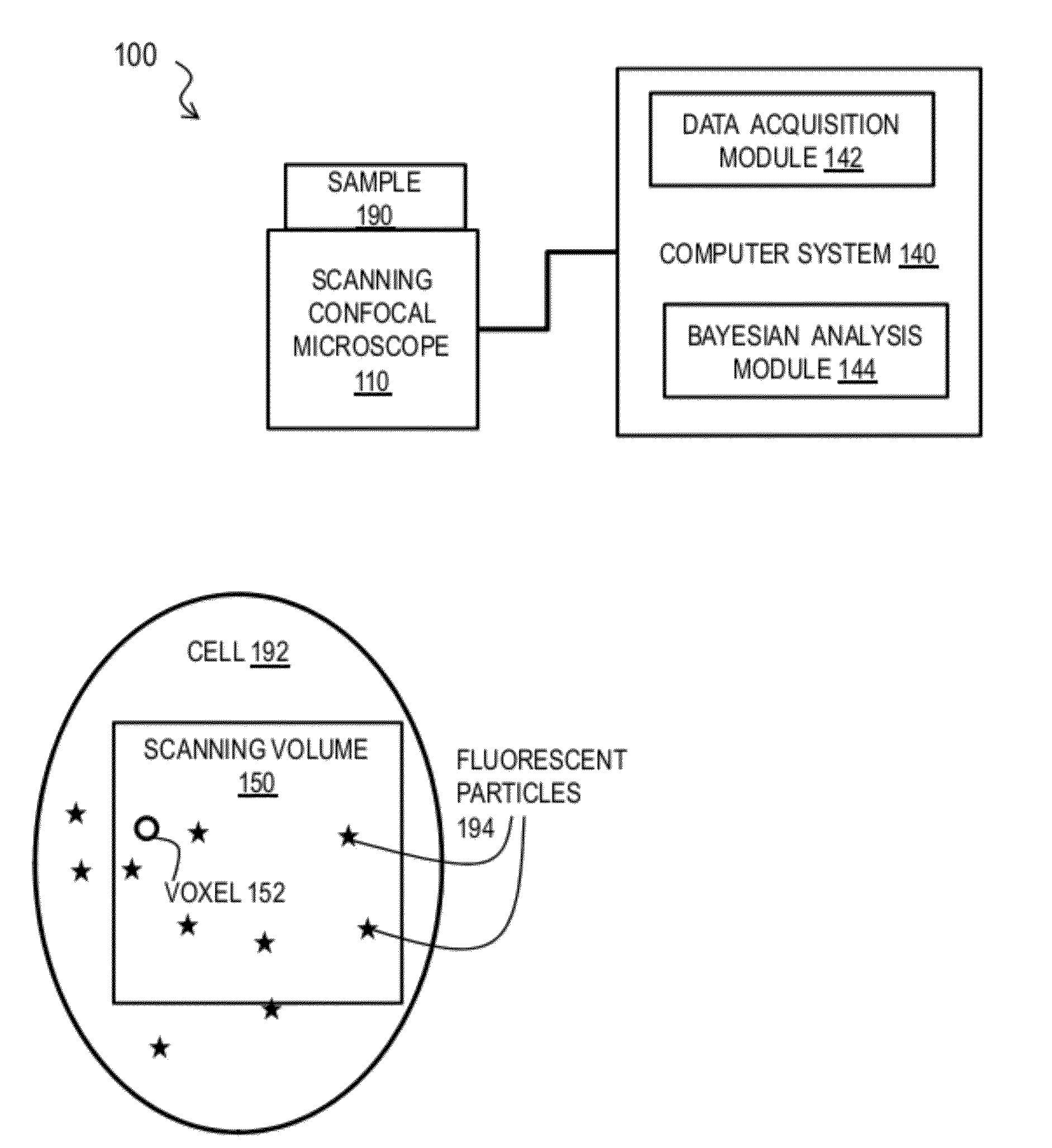
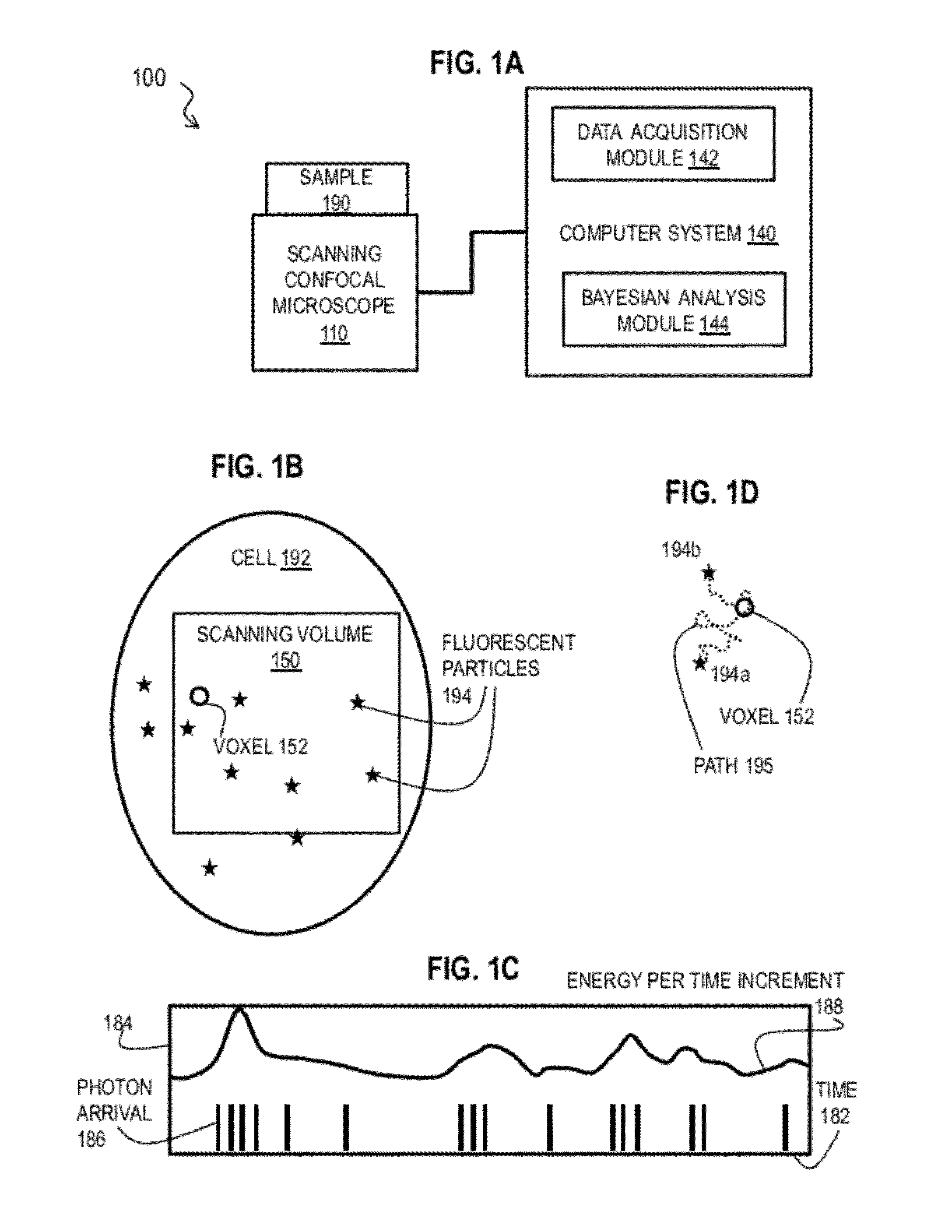
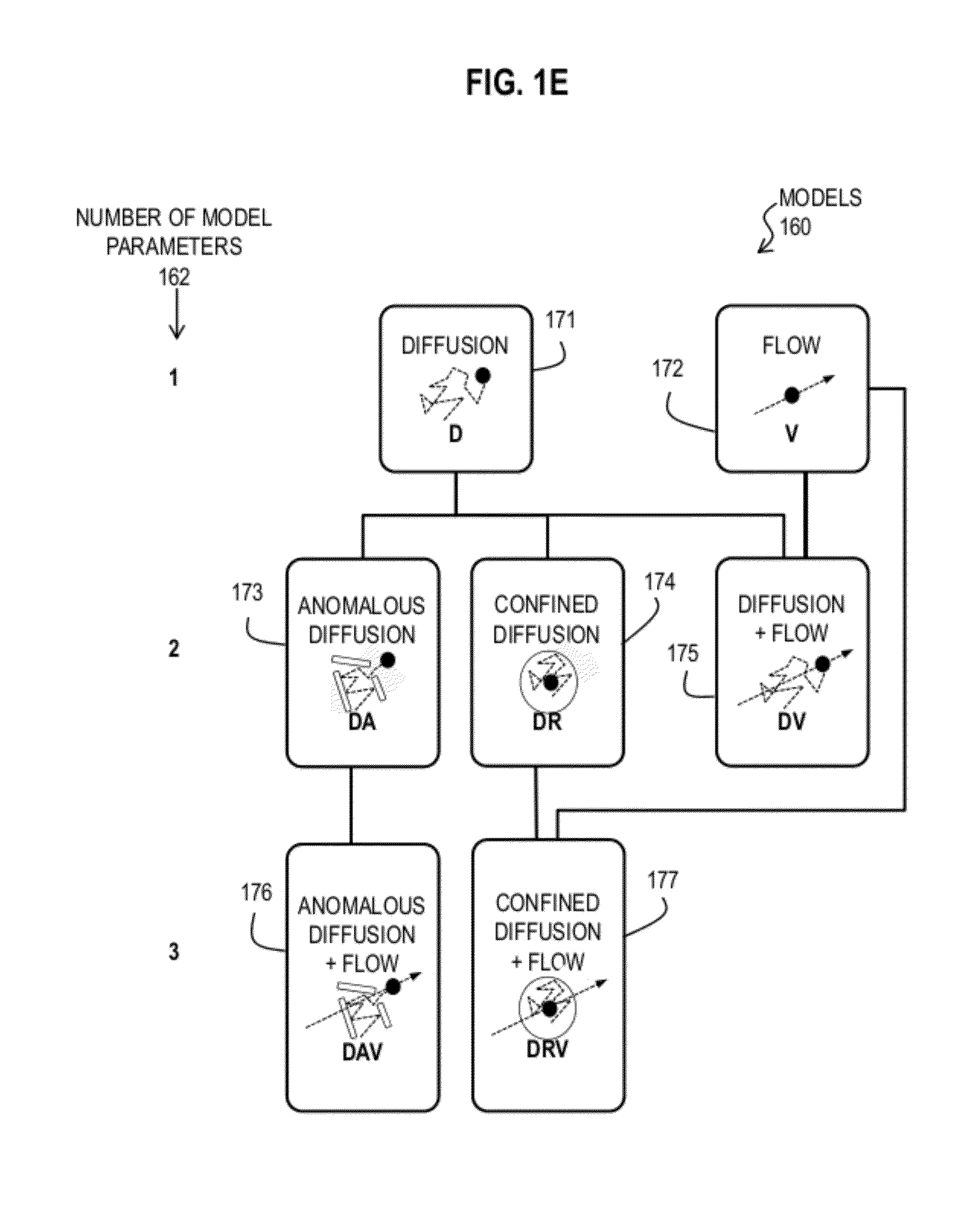
Bayesian Inference of Particle Motion and Dynamics from Single Particle Tracking and Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy
Techniques for inferring particle dynamics from certain data include determining multiple models for motion of particles in a biological sample. Each model includes a corresponding set of one or more parameters. Measured data is obtained based on measurements at one or more voxels of an imaging system sensitive to motion of particles in the biological sample; and, determining noise correlation of the measured data. Based at least in part on the noise correlation, a marginal likelihood is determined of the measured data given each model of the multiple models. A relative probability for each model is determined based on the marginal likelihood. Based at least in part on the relative probability for each model, a value is determined for at least one parameter of the set of one or more parameters corresponding to a selected model of the multiple models.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for time correlated multi-photon counting measurements
The invention provides a method and a measurement system for characterisation of luminescence properties, the method comprises irradiating the luminescent material with a pulse of excitation light, providing a triggering signal correlated to the pulse of excitation light; detecting with a photodetector such as a photomultiplier tube (PMT) a plurality of photons emitted from the luminescent material as result of the pulse of excitation light, the photodetector providing an output signal upon the event of detection of a photon; determining for each detected photon a photon arrival time and providing an output suitable for inputting to an analysing module wherein an output comprises zero, one, or more photon arrival time for each excitation, receiving said outputs in an analysing module; and determining. in the analysing module, characteristics properties of the luminescent material by performing a statistical analysis based on Bayesian inference.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE LTD
Multi-scale diffusion salient target detection method based on background and target prior
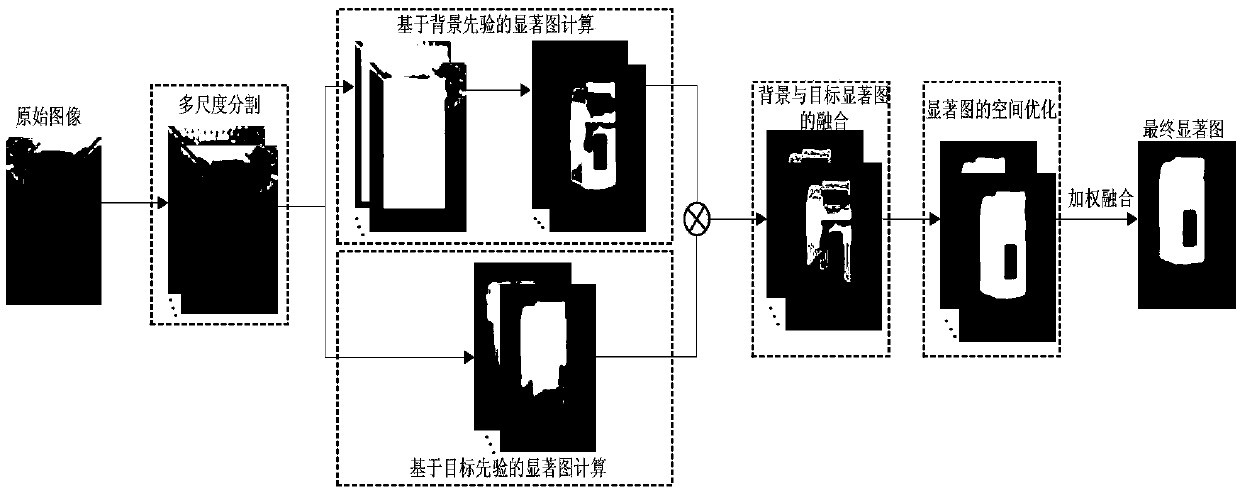
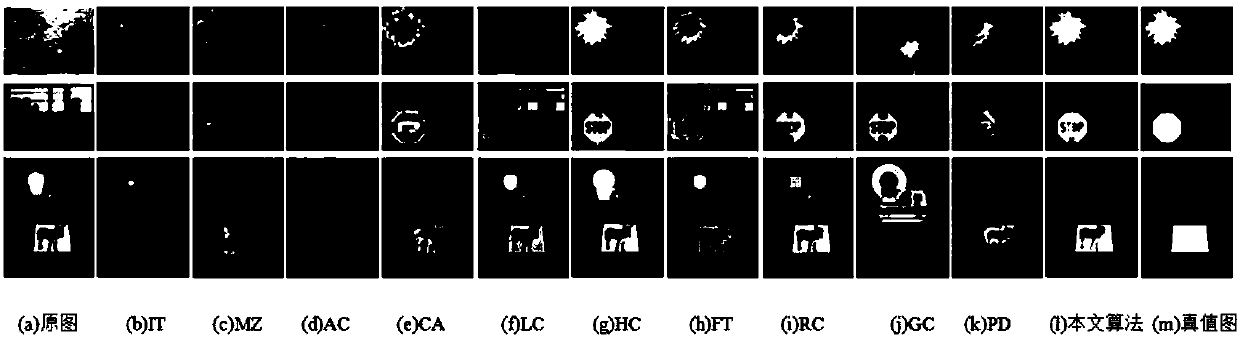
ActiveCN108549891AImprove detection accuracyImprove integrityImage enhancementImage analysisDiffusionData set
The invention discloses a multi-scale diffusion salient target detection method based on background and target priors. The multi-scale diffusion salient target detection method comprises the steps of:firstly, segmenting an image into super-pixels at different scales by utilizing a simple linear iterative clustering algorithm; secondly, regarding the periphery of the image as a background prior, and calculating a Euclidean distance between each pixel and background super-pixels in a CIELAB color space to obtain a background saliency map; thirdly, using target property as prior information to obtain a foreground saliency map; fourthly, calculating background saliency and target saliency of each super-pixel on each scale by means of Bayesian inference, so as to obtain a saliency map fusing the foreground and background priors; fifthly, selecting a manifold sorting method to propagate the saliency of each super-pixel into the whole image to obtain a spatially optimized saliency map; and finally, constructing a pixel-level saliency map through weighted summation of the saliency values at different scales. The experimental results show that the multi-scale diffusion salient target detection method disclosed by the invention can detect the salient targets more effectively than the conventional methods on four kinds of common reference data sets.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
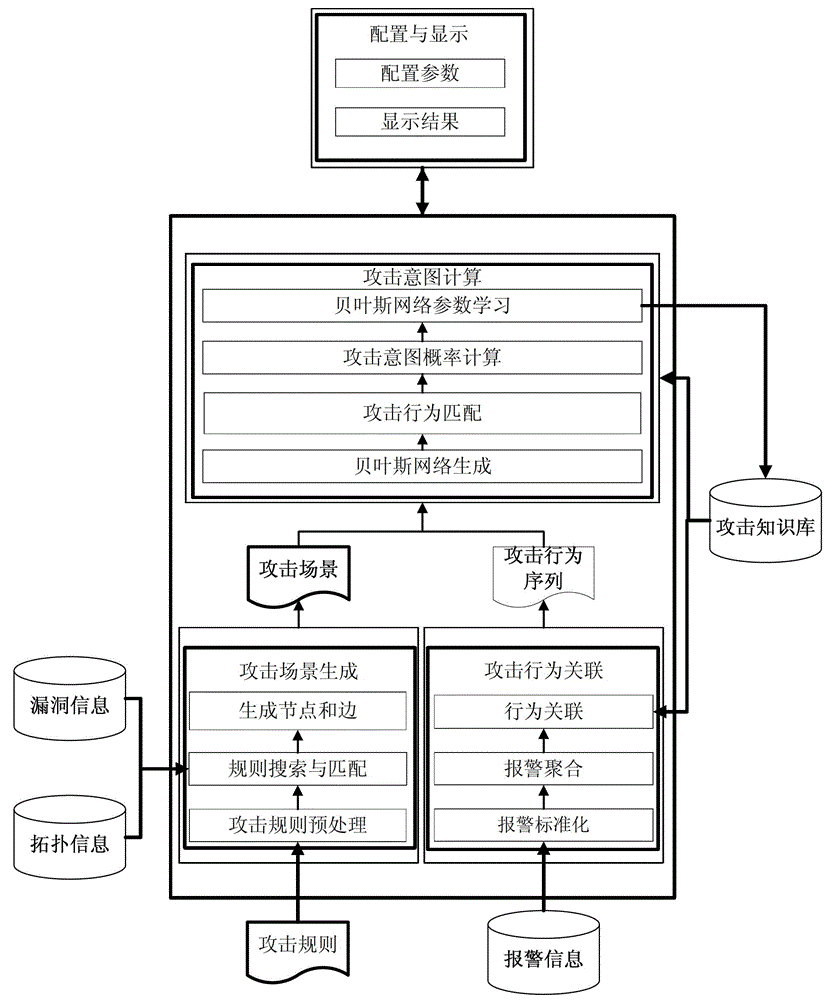
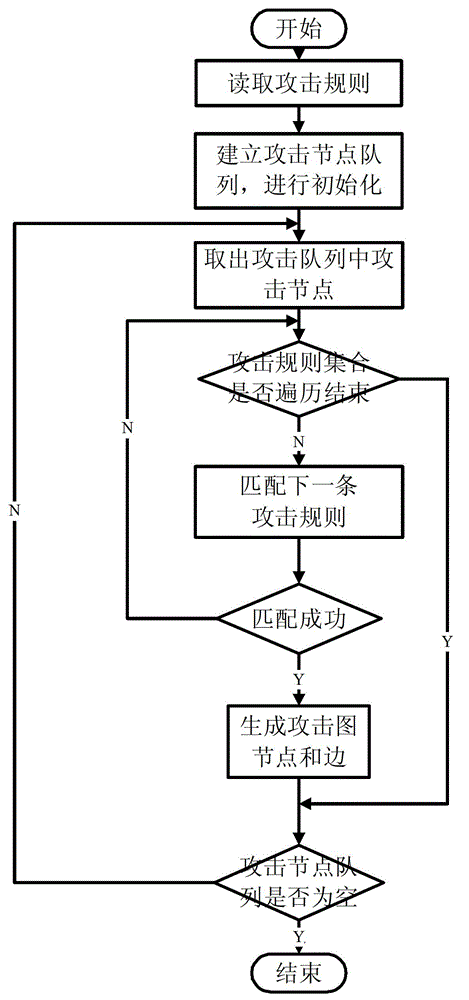
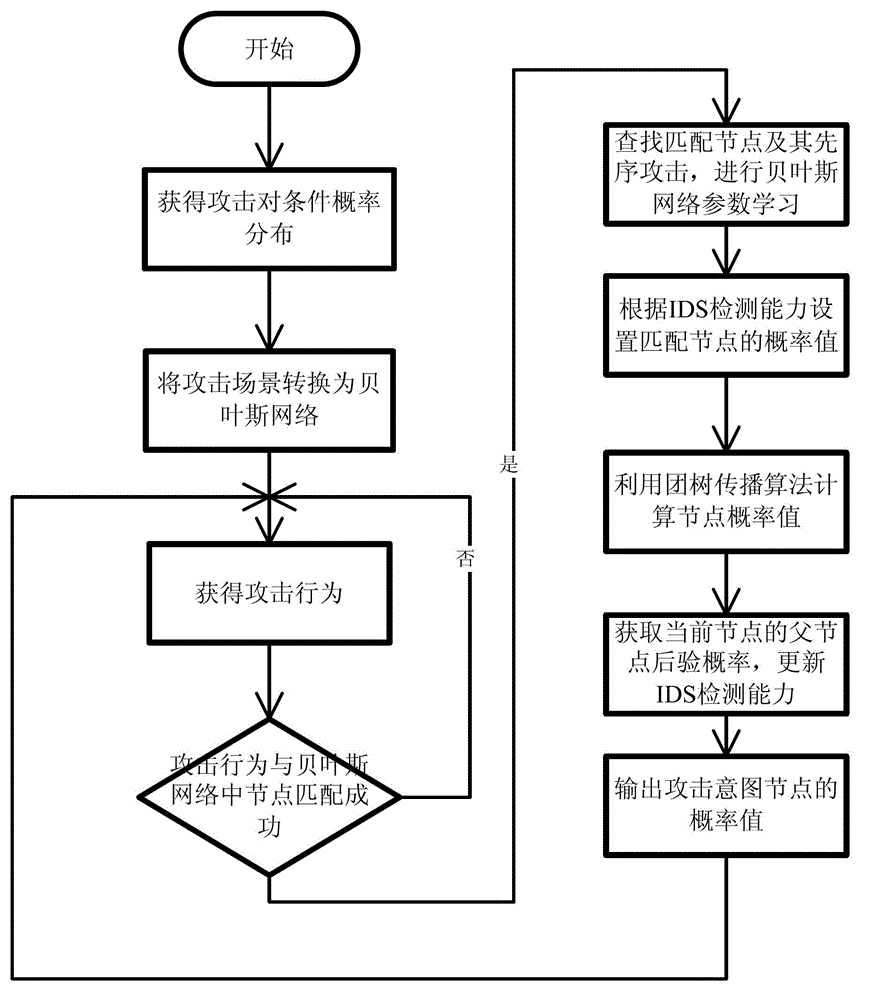
Attack intention recognition method based on Bayesian network inference
InactiveCN102724199AImprove scalabilityThe calculation result is accurateTransmissionPattern recognitionClique tree
The invention provides an attack intention recognition method based on Bayesian network inference. The attack intention recognition method is applied to the attack intention recognition of an intelligence and decision-making oriented system with a parameter learning mechanism in computer network self-organizing operation (CNSOO). The method can enable an intelligence system to recognize the attack intention of an attacker by using IDS (Intrusion Detection System) alarm information according to given host vulnerability information, network topological information and attack knowledge base and supply the attack intention to a decision-making system as a decision-making basis in a CNSOO environment. The attack intention recognition process comprises the following steps of: generating attacking scenes, fusing and matching IDS alarm information, updating conditional probability distribution caused by attacking behaviors, calculating the probability of attack intention nodes by using a clique tree propagation algorithm in the Bayesian network inference, and updating Bayesian network parameters and IDS detection capability. The calculation parameters are updated according to calculation results and historical information, so that the calculation results can be more accurate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
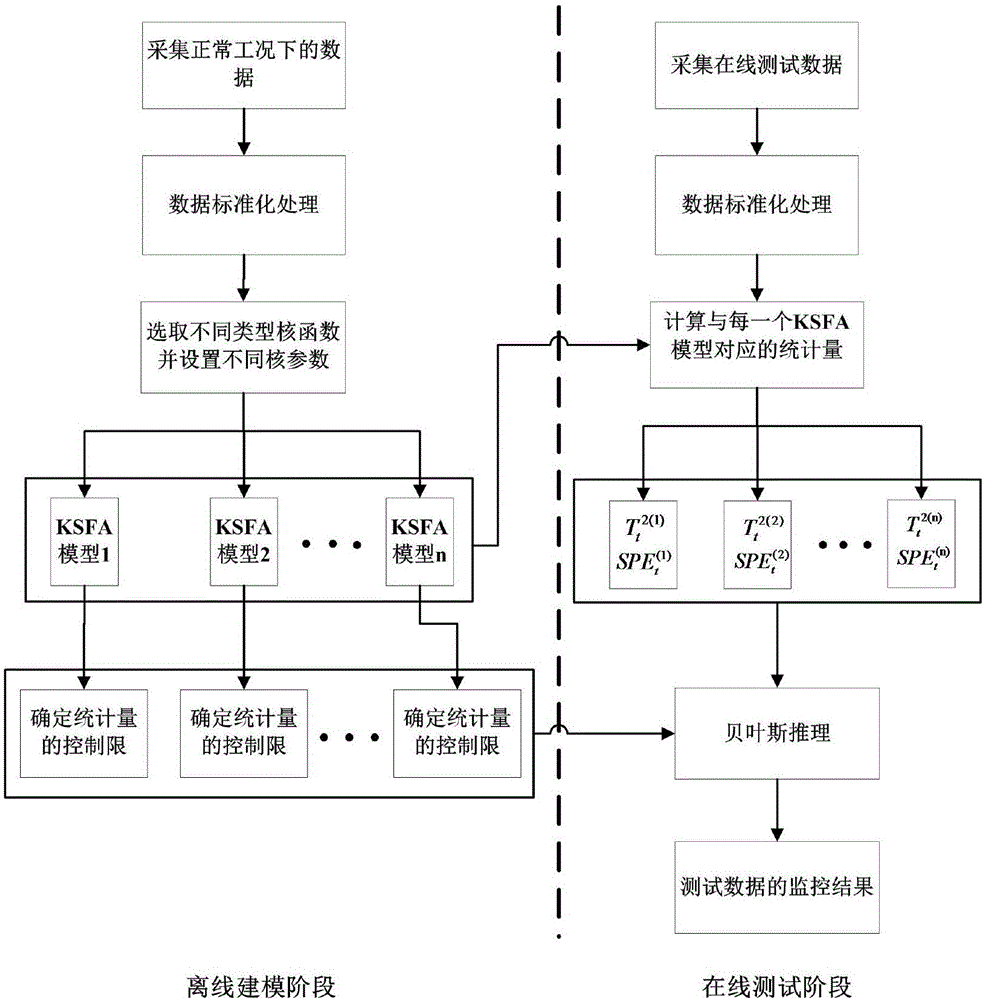
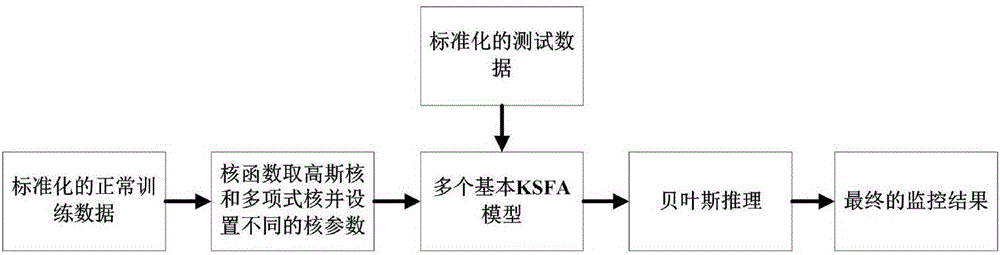
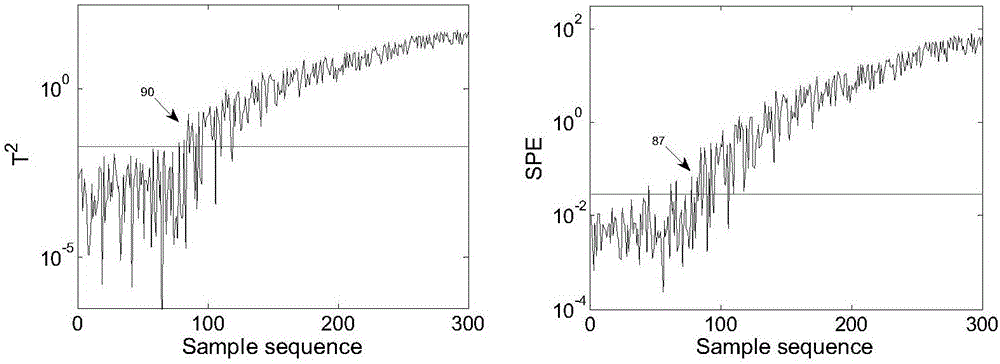
Non-linear industrial process fault detection method based on Bayes kernel slow feature analysis
ActiveCN106647718AFully extractedImprove fault detection resultsElectric testing/monitoringIntegrated monitoringAlgorithm
The invention relates to a non-linear industrial process fault detection method based on Bayes kernel slow feature analysis. After normalization processing of training data and test data, kernel functions of different types are adopted based on a conventional kernel feature analysis method, and the various kernel functions are configured with different kernel functions, and therefore a series of basic KSFA models are established. Non-linear slow features are more fully extracted from the normalized training data and the normalized test data by using the basic KSFA models, and the basic KSFA models are respectively used to monitor the process. The non-linear industrial process fault detection method is provided with Bayesian inference, and the test data monitoring results of the series of basic KSFA models are weighted in a combined manner by adopting a probability way, and finally the integrated monitoring result of a plurality of models is acquired, and therefore a fault detection result is improved, and a fault detection rate is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
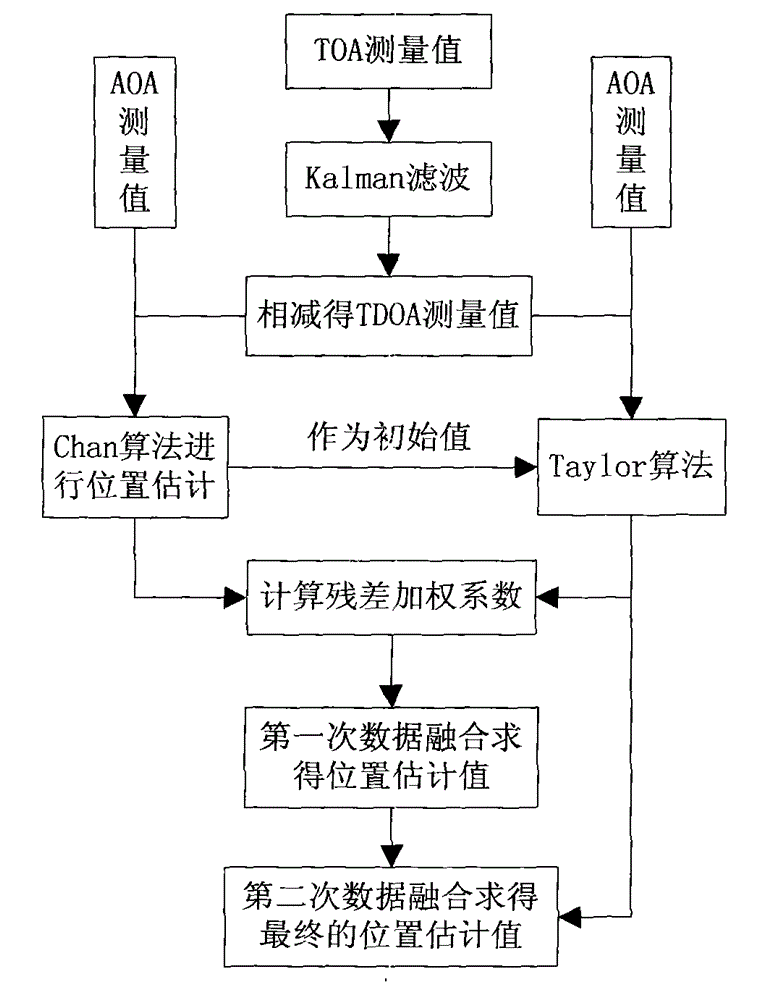
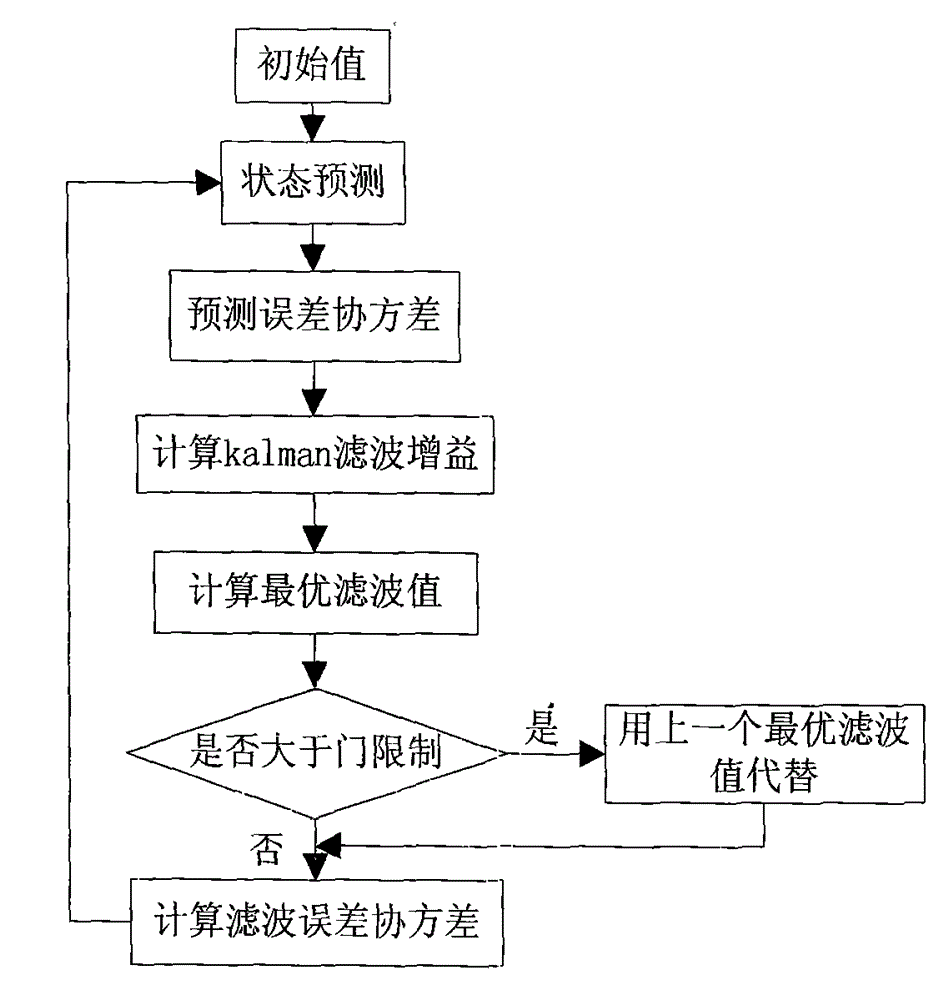
Time division-synchronization code division multiple access (TD-SCDMA) system-based method for accurately positioning underground personnel
ActiveCN103152695ASolve positioning difficultiesHigh positioning accuracyLocation information based serviceResidual methodMobile station
The invention discloses a time division-synchronization code division multiple access (TD-SCDMA) system-based method for accurately positioning underground personnel. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring time of arrival (TOA) and an angle of arrival (AOA) of a signal at a base station; de-noising a TOA value by using an improved kalman filtering algorithm; calculating a time difference of arrival (TDOA) value according to the de-noised TOA value; estimating the position of a mobile station by using a TDOA / AOA mixed Chan algorithm and a TDOA / AOA mixed Taylor algorithm; performing first data fusion on a position estimated value by using a weighted residual method to obtain a new position estimated value; and performing second data fusion on the position estimated value by using Bayesian inference to obtain the final position estimated value. By the method for accurately positioning the underground personnel, the advantages of a TD-SCDMA system and the superiority of the data fusion are utilized, a TDOA / AOA mixed data fusion positioning algorithm is adopted, the positioning accuracy is high, and the problem that the personnel in an underground coal mine are hard to position is solved.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
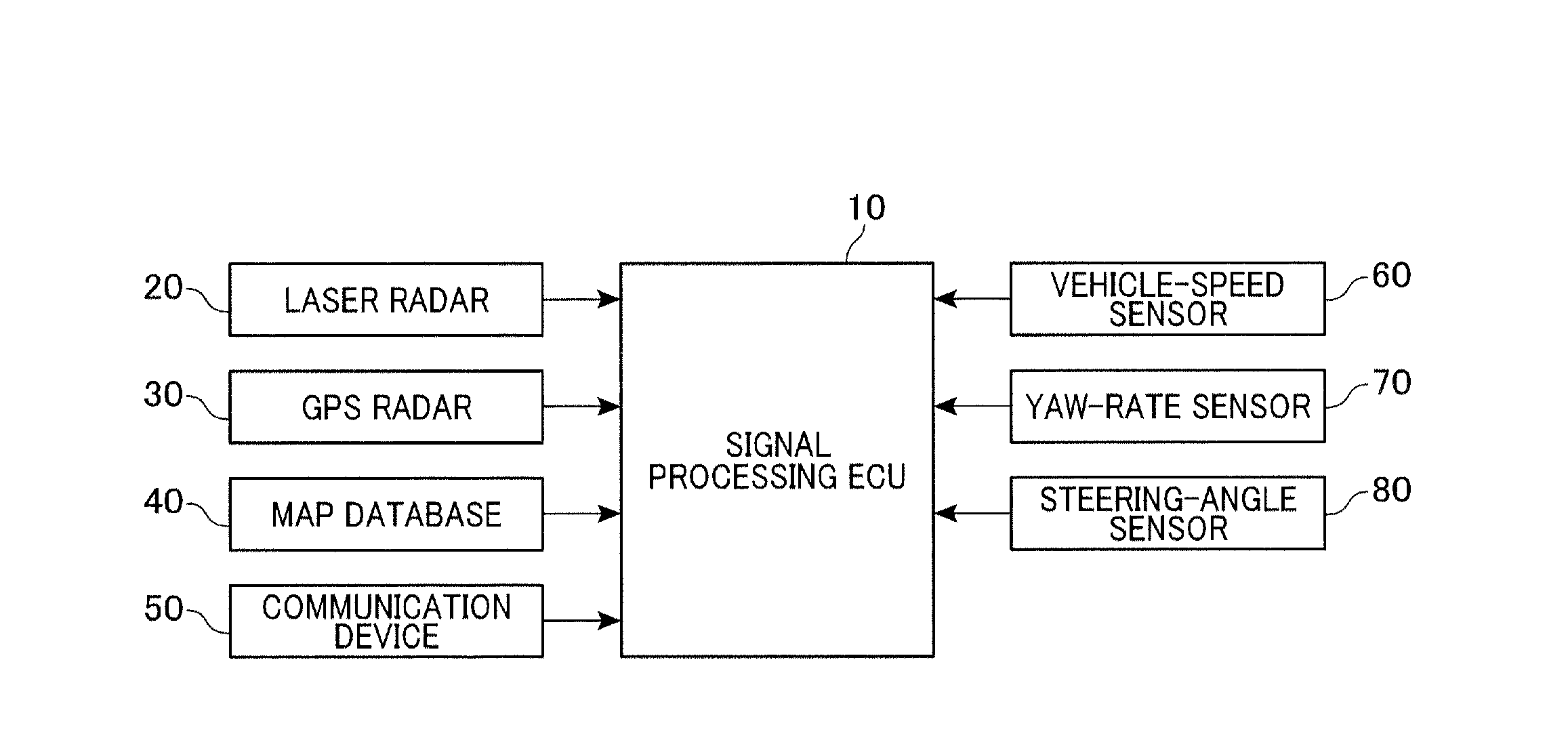
Traveling environment recognition device
ActiveUS8744744B2Improve accuracyProbability is accurateDigital data processing detailsAnti-collision systemsRadarSimulation
A traveling environment recognition device capable of accurately recognizing a traveling environment of a vehicle. An occupancy grid map that stores an occupancy probability of each obstacle to traveling of the own vehicle for each cell of the occupancy grid map is generated, and the occupancy probability for each cell is updated according to Bayesian inference. More specifically, for each cell of the occupancy grid map, the occupancy probability calculated from information from a radar device, the occupancy probability calculated from information from a communication device, and the occupancy probability calculated from information from a storage device that stores map data are blended to provide an occupancy probability of the obstacles to traveling of the own vehicle, which leads to more accurate traveling environment recognition.
Owner:DENSO CORP
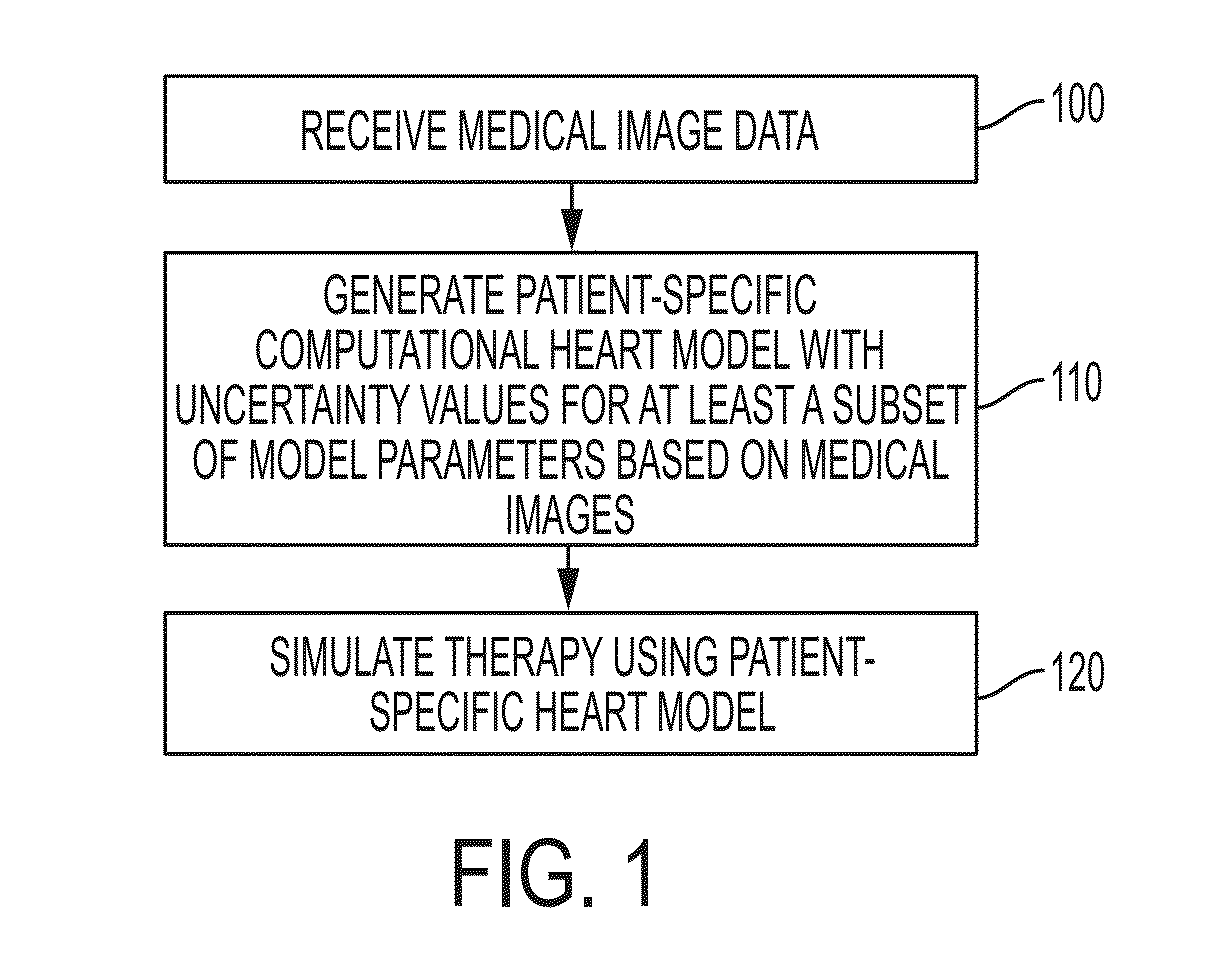
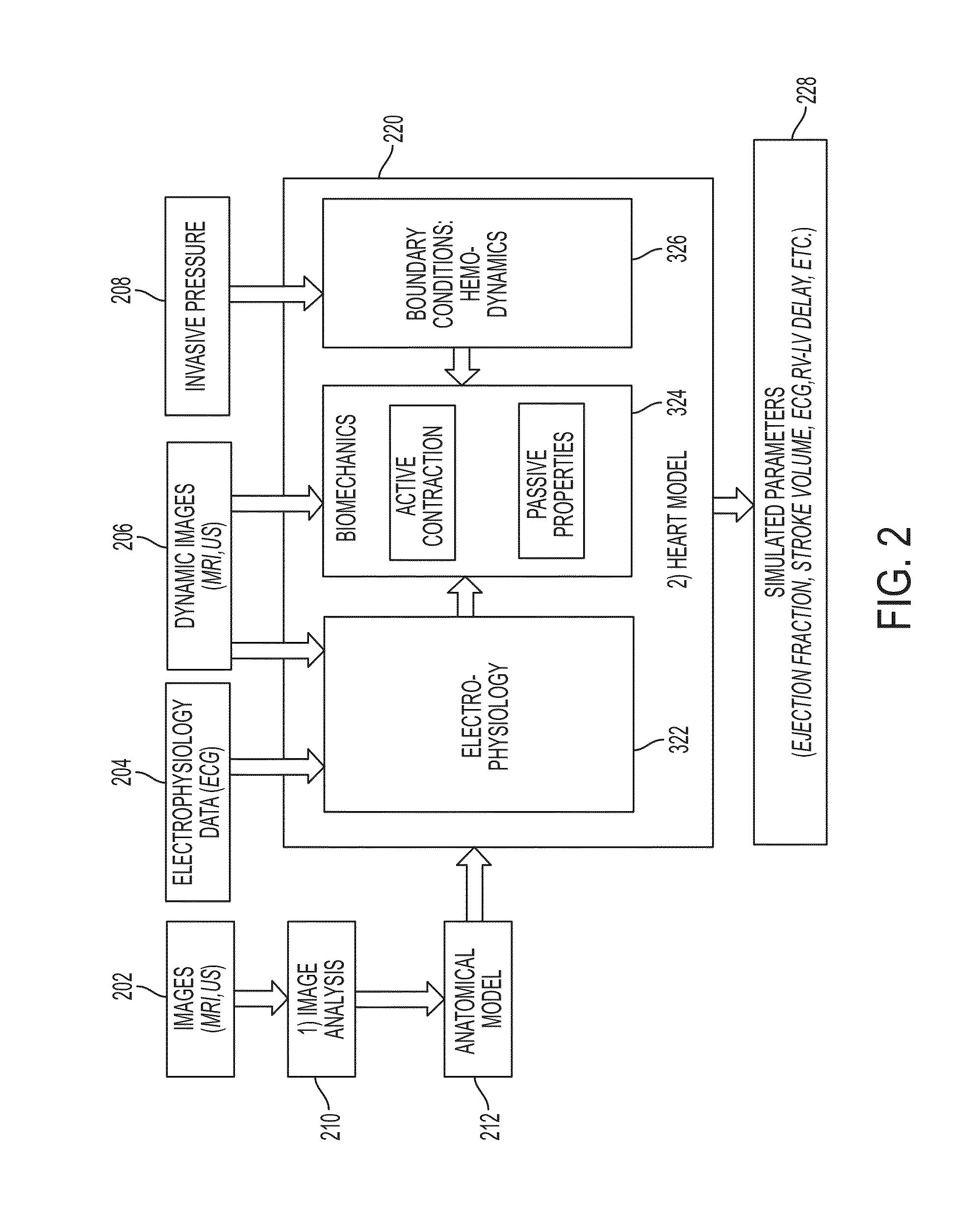
Method and System for Image-Based Estimation of Multi-Physics Parameters and Their Uncertainty for Patient-Specific Simulation of Organ Function
A method and system for estimating tissue parameters of a computational model of organ function and their uncertainty due to model assumptions, data noise and optimization limitations is disclosed. As applied to a cardiac use-case, a patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific computational heart model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical heart model. Patient-specific parameters and corresponding uncertainty values are estimated for at least a subset of parameters of the patient-specific computational heart model. A surrogate model is estimated for a forward model of cardiac function, and the surrogate model is applied within Bayesian inference to estimate the posterior probability density function of the parameter space of the forward model. Cardiac function for the patient is simulated using the patient-specific computational heart model. The estimated parameters, their uncertainty, and the computed cardiac function are displayed to the user.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
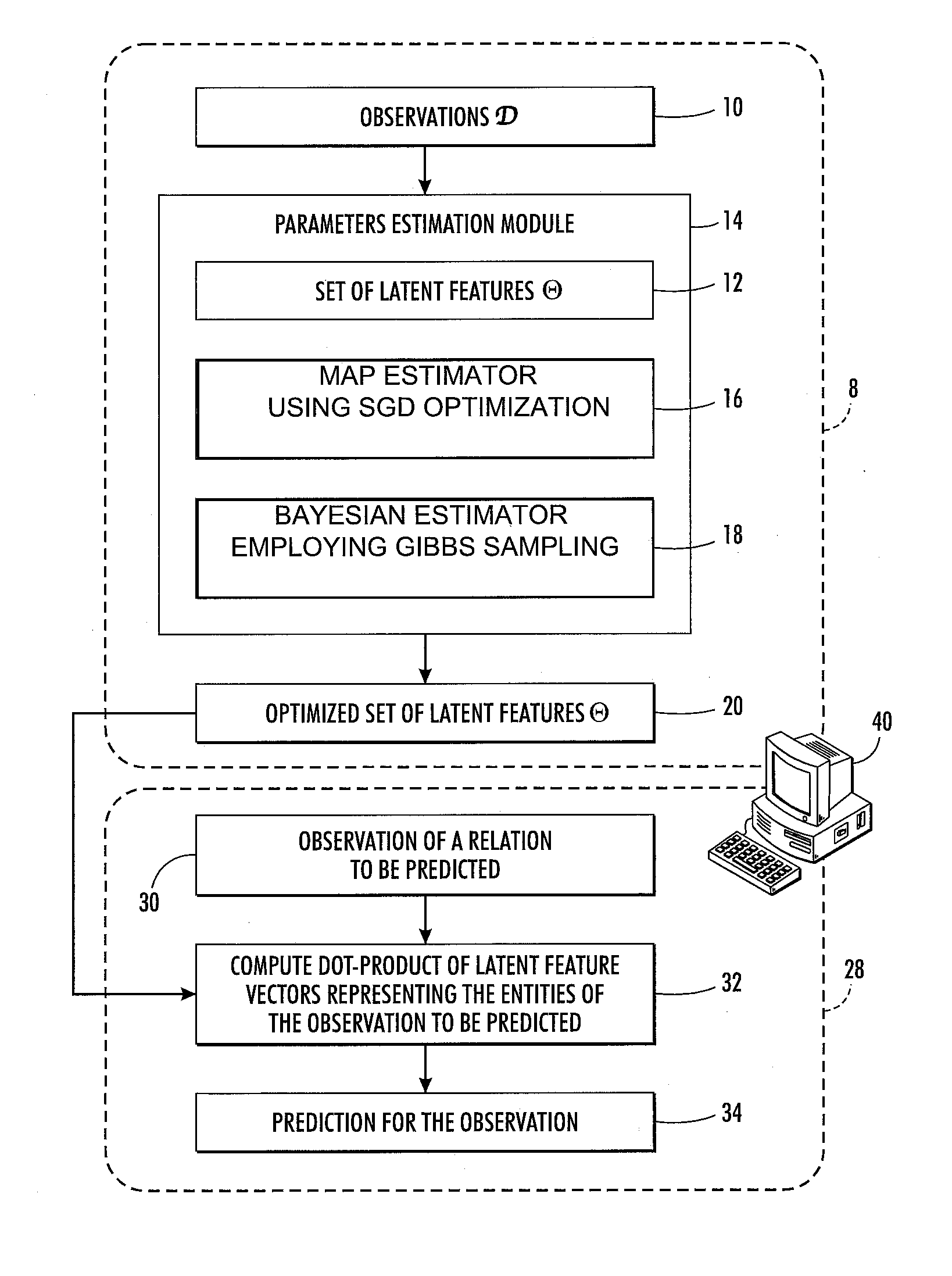
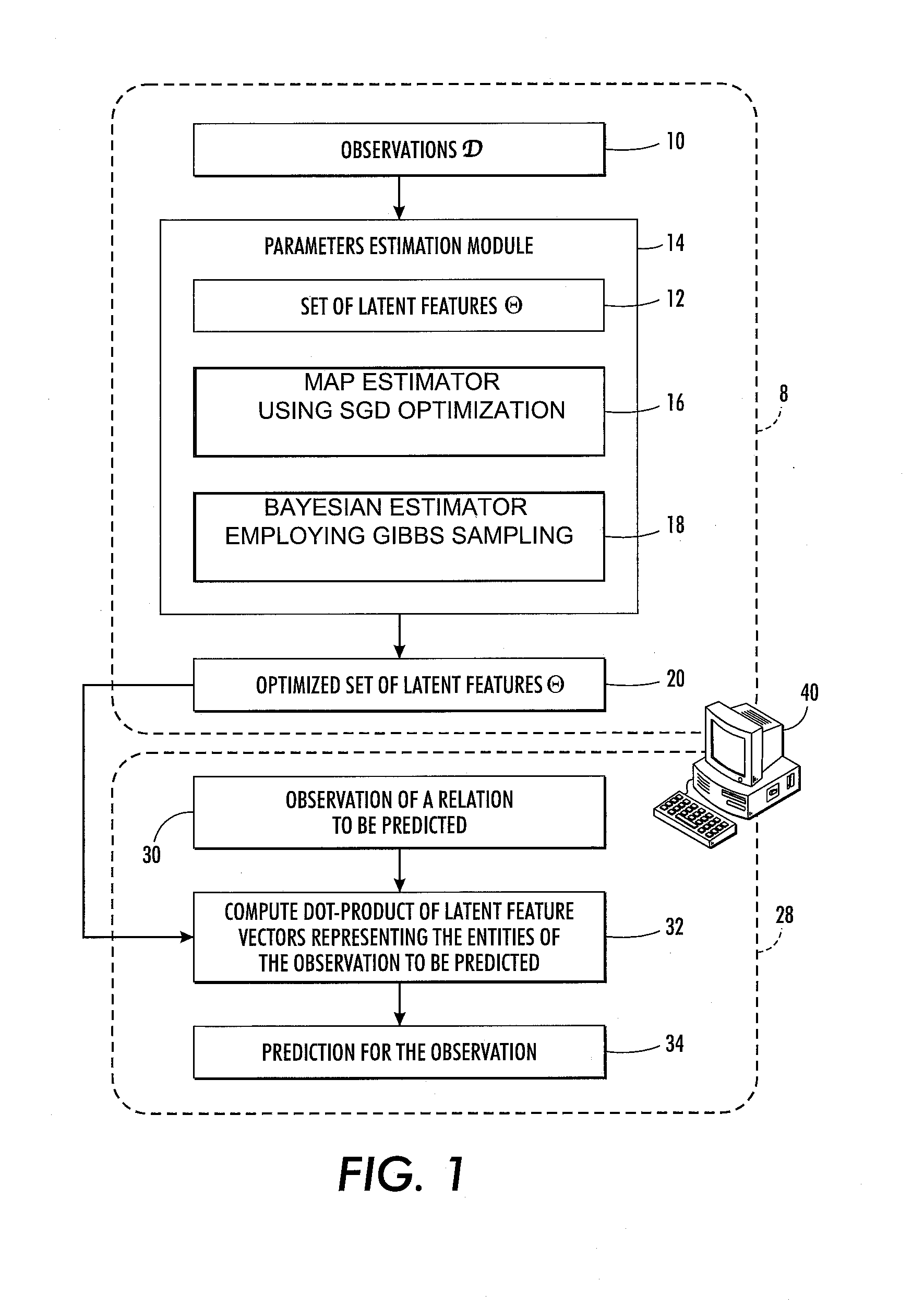
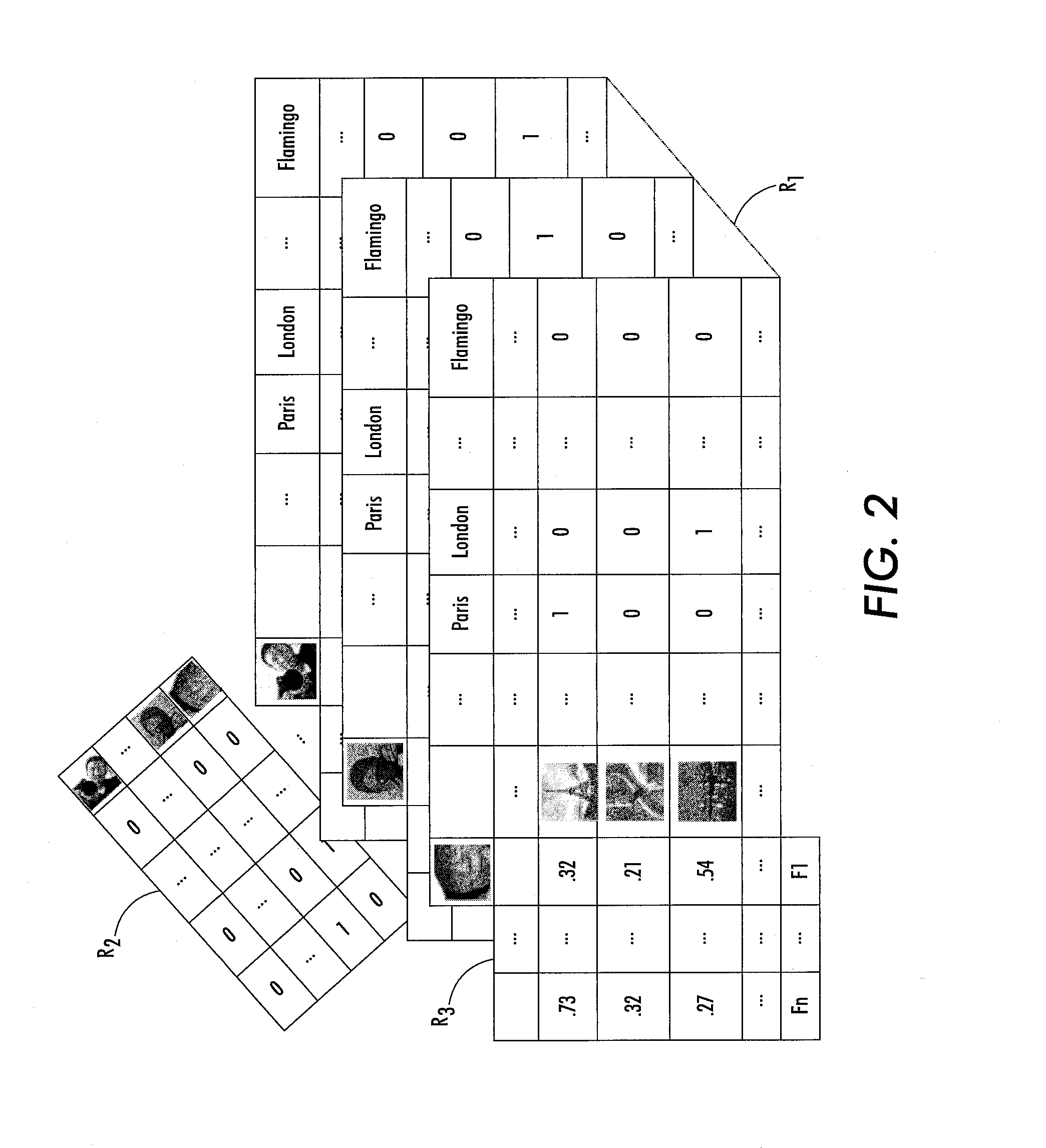
Probabilistic relational data analysis
InactiveUS20140156231A1Maximize likelihoodMathematical modelsComputation using non-denominational number representationFeature vectorProgramming language
A multi-relational data set is represented by a probabilistic multi-relational data model in which each entity of the multi-relational data set is represented by a D-dimensional latent feature vector. The probabilistic multi-relational data model is trained using a collection of observations of relations between entities of the multi-relational data set. The collection of observations includes observations of at least two different relation types. A prediction is generated for an observation of a relation between two or more entities of the multi-relational data set based on a dot product of the optimized D-dimensional latent feature vectors representing the two or more entities. The training may comprise optimizing the D-dimensional latent feature vectors to maximize likelihood of the collection of observations, for example by Bayesian inference performed using Gibbs sampling.
Owner:XEROX CORP
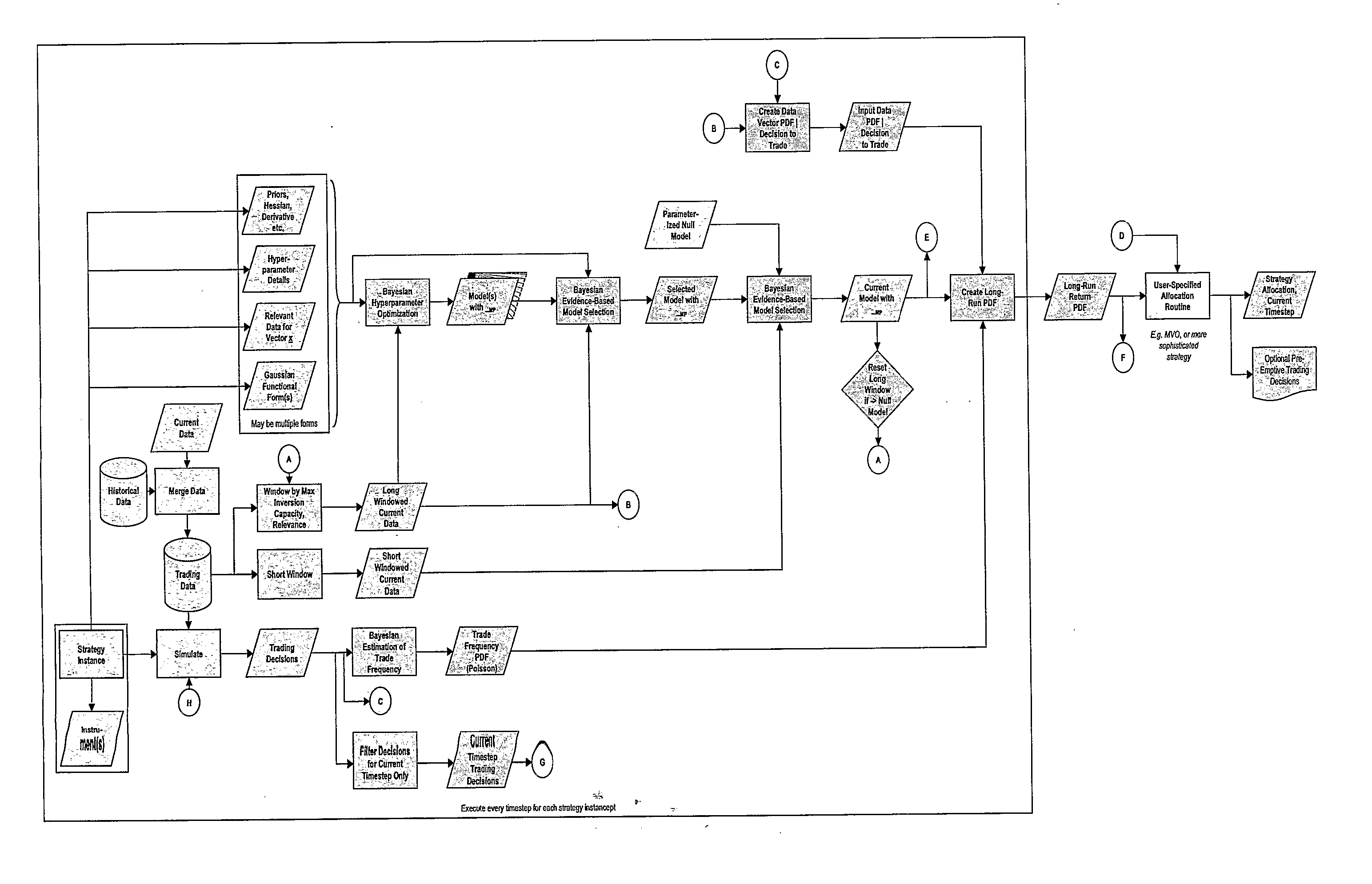
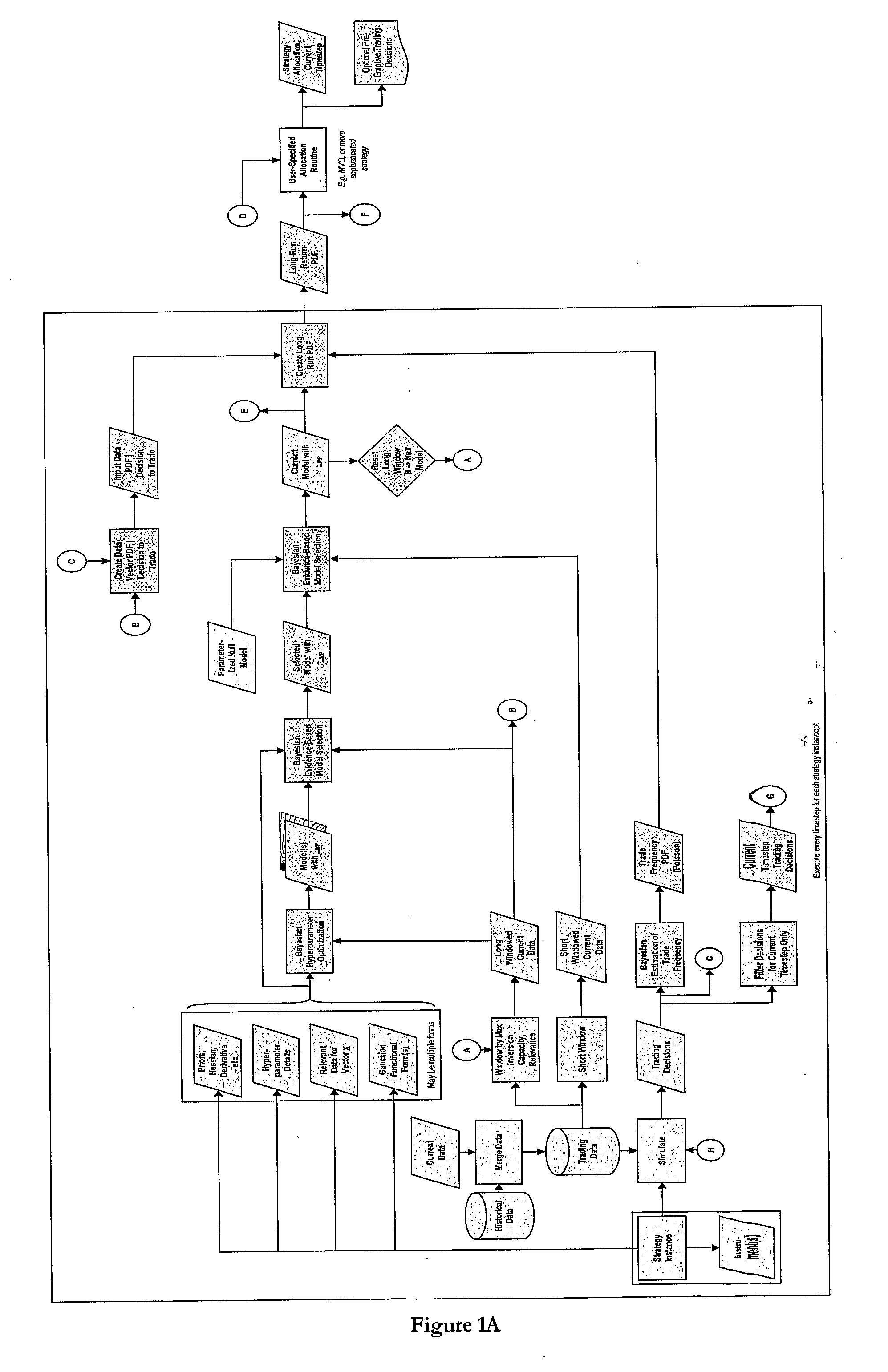
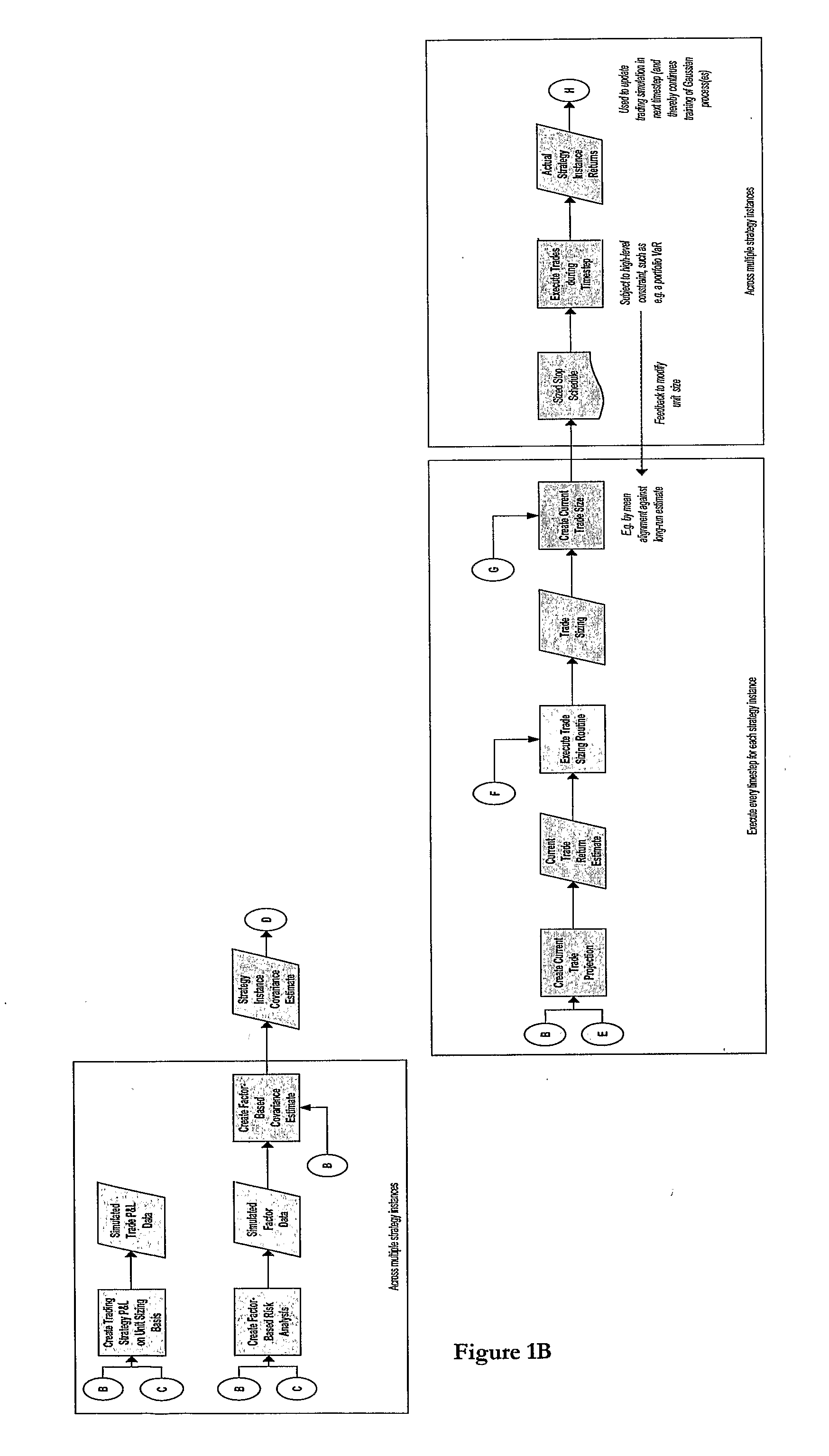
Method Of Lowering The Computational Overhead Involved In Money Management For Systematic Multi-Strategy Hedge Funds
InactiveUS20080097884A1Less computing powerLow implementation overheadFinanceComplex mathematical operationsBayesian inferenceRelevant feature
A data representation is deployed that comprises instances of a software object implementing a particular systematic trading strategy; there are multiple such instances (‘strategy instances’), each corresponding to a different trading strategy, with a strategy instance being paired with a tradable instrument. The method comprises the steps of: (a) each strategy instance providing an estimate of its returns; (b) using Bayesian inference to assess predefined characteristics of each estimate; (c) allocating capital to specific strategy instance / instrument pairings depending on the estimated returns and the associated characteristics. The object based representation is both flexible and powerful; because it directly supports a Bayesian inference, it is functionally better than known approaches because it allows characteristics, such as the reliability of the return estimates to be quantified and modelled and the accuracy of the return estimates to be improved.
Owner:ASPECT CAPITAL
Small vein image recognition and authorization using constrained geometrical matching and weighted voting under generic tree model
ActiveUS8768049B2Digital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsVeinAuthentication system
An automated registration and authentication system combines a generative and discriminative approach to improve the matching of a query object to a database of registered objects. The discriminative approach uses a voting mechanism to identify a most likely match, and the generative approach uses ASIFT transforms to determine a best geometric match. The two results are combined using a technique base on Bayesian inference theory.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
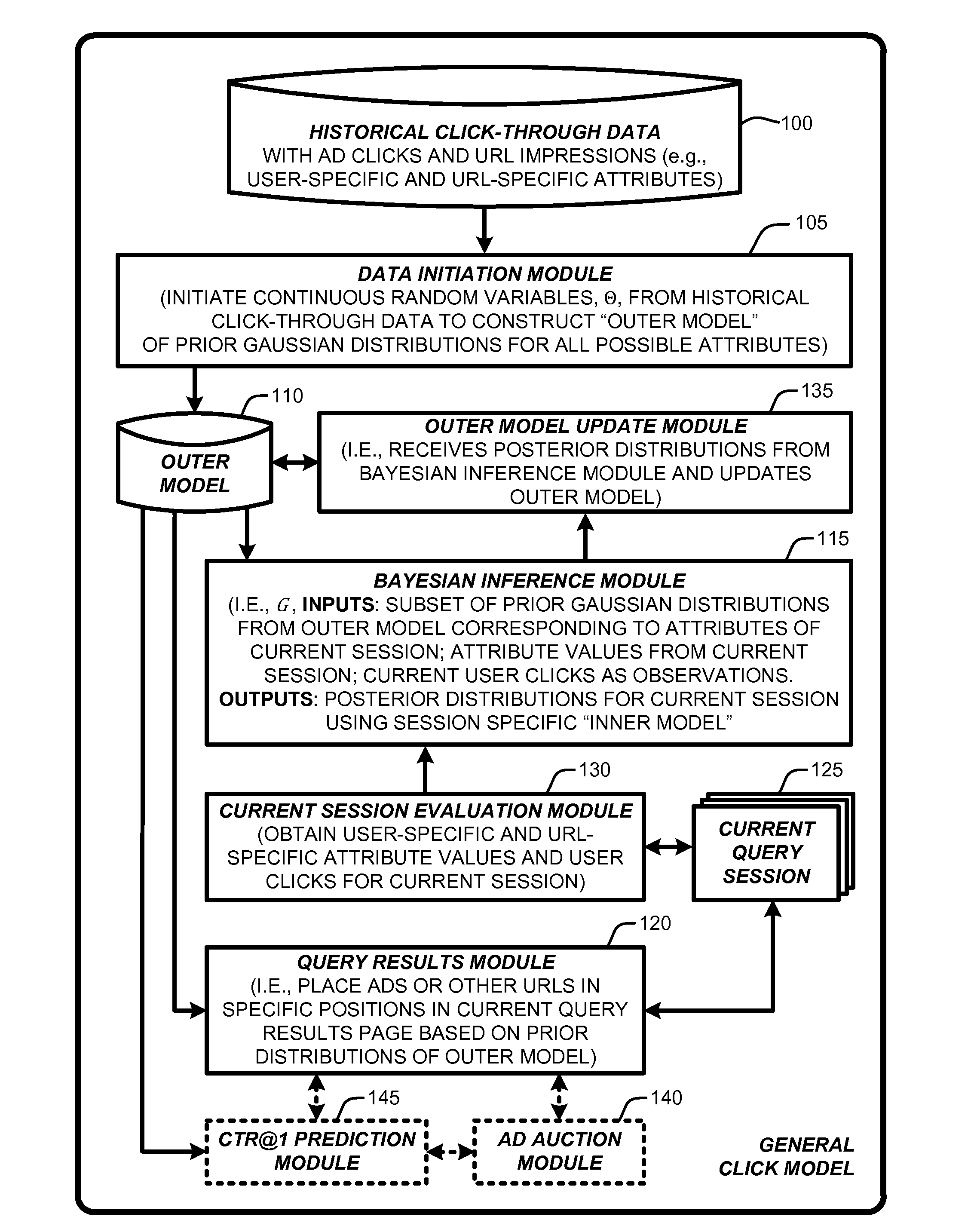
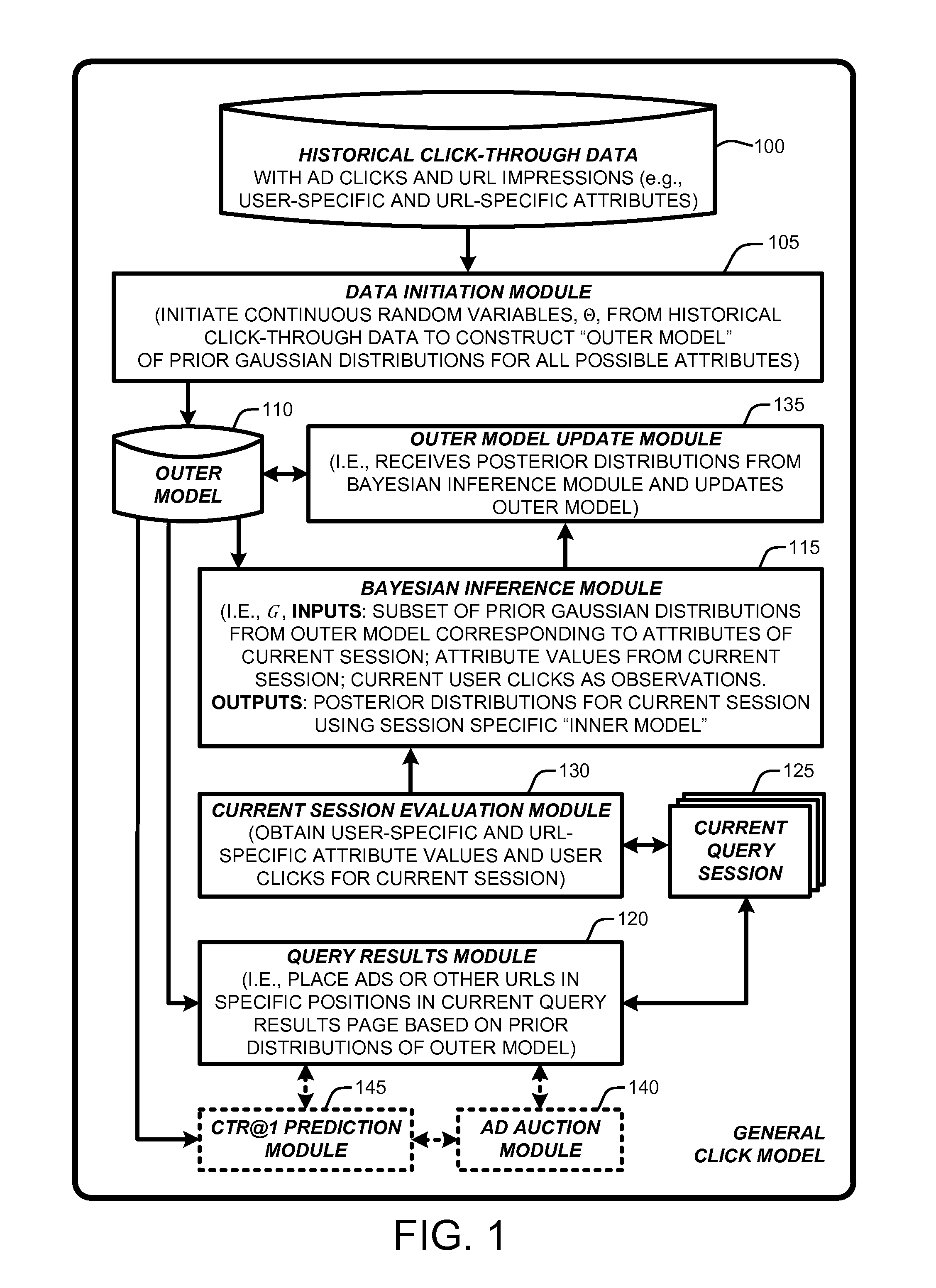
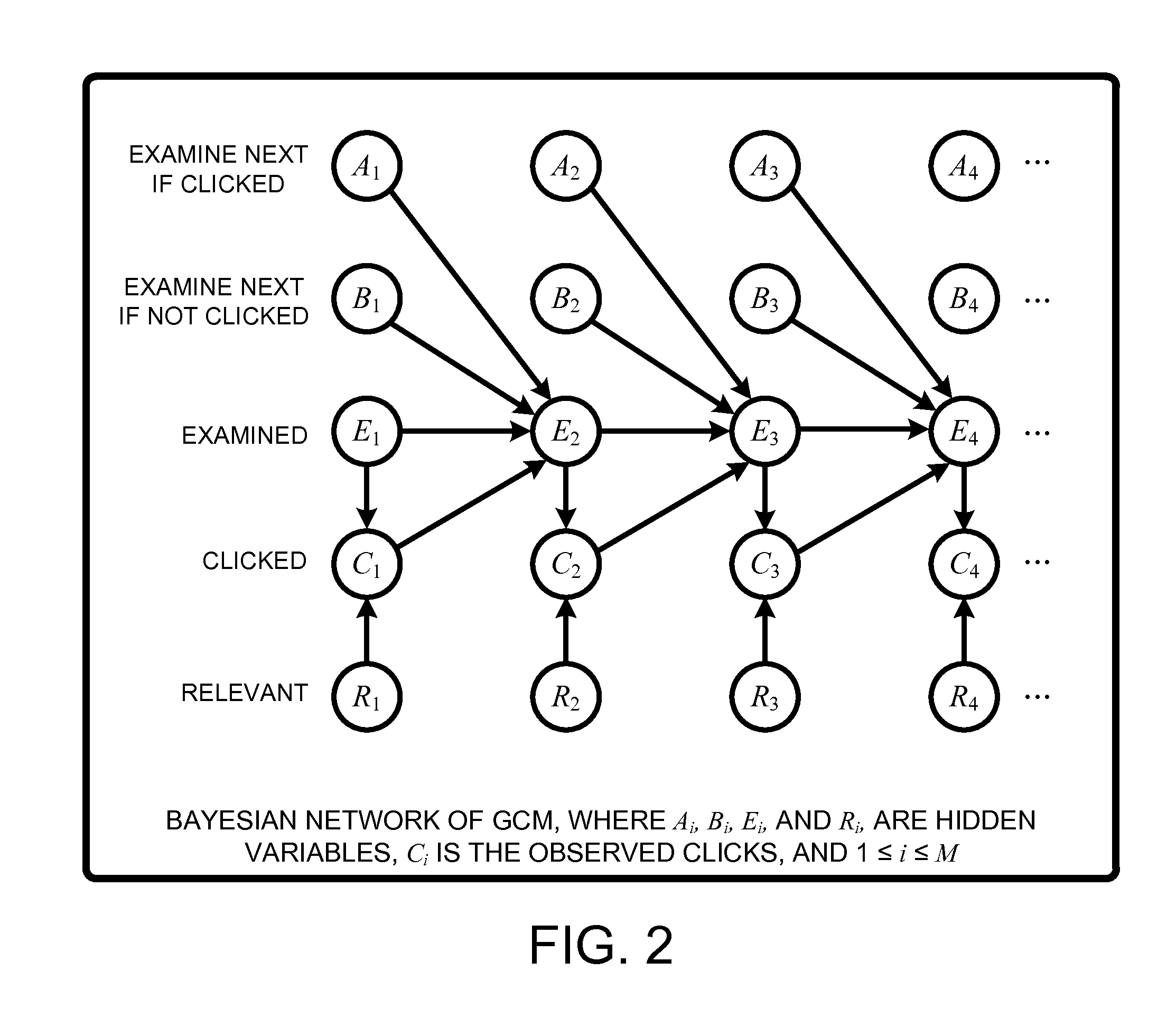
Click modeling for URL placements in query response pages
InactiveUS20110302031A1Accurate modelingDigital computer detailsKnowledge representationTailMultiple attribute
A “General Click Model” (GCM) is constructed using a Bayesian network that is inherently capable of modeling “tail queries” by building the model on multiple attribute values that are shared across queries. More specifically, the GCM learns and predicts user click behavior towards URLs displayed on a query results page returned by a search engine. Unlike conventional click modeling approaches that learn models based on individual queries, the GCM learns click models from multiple attributes, with the influence of different attribute values being measured by Bayesian inference. This provides an advantage in learning that enables the GCM to achieve improved generalization and results, especially for tail queries, than conventional click models. In addition, most conventional click models consider only position and the identity of URLs when learning the model. In contrast, the GCM considers more session-specific attributes in making a final prediction for anticipated or expected user click behaviors.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com