Method for producing ethanol from lignocellulose biomaterial by use of neu-heat-resistant enzyme
A technology of lignocellulose and biomass, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, biomass pretreatment, solid-phase fermentation bioreactor, etc., can solve problems such as fiber breakage and increased accessibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
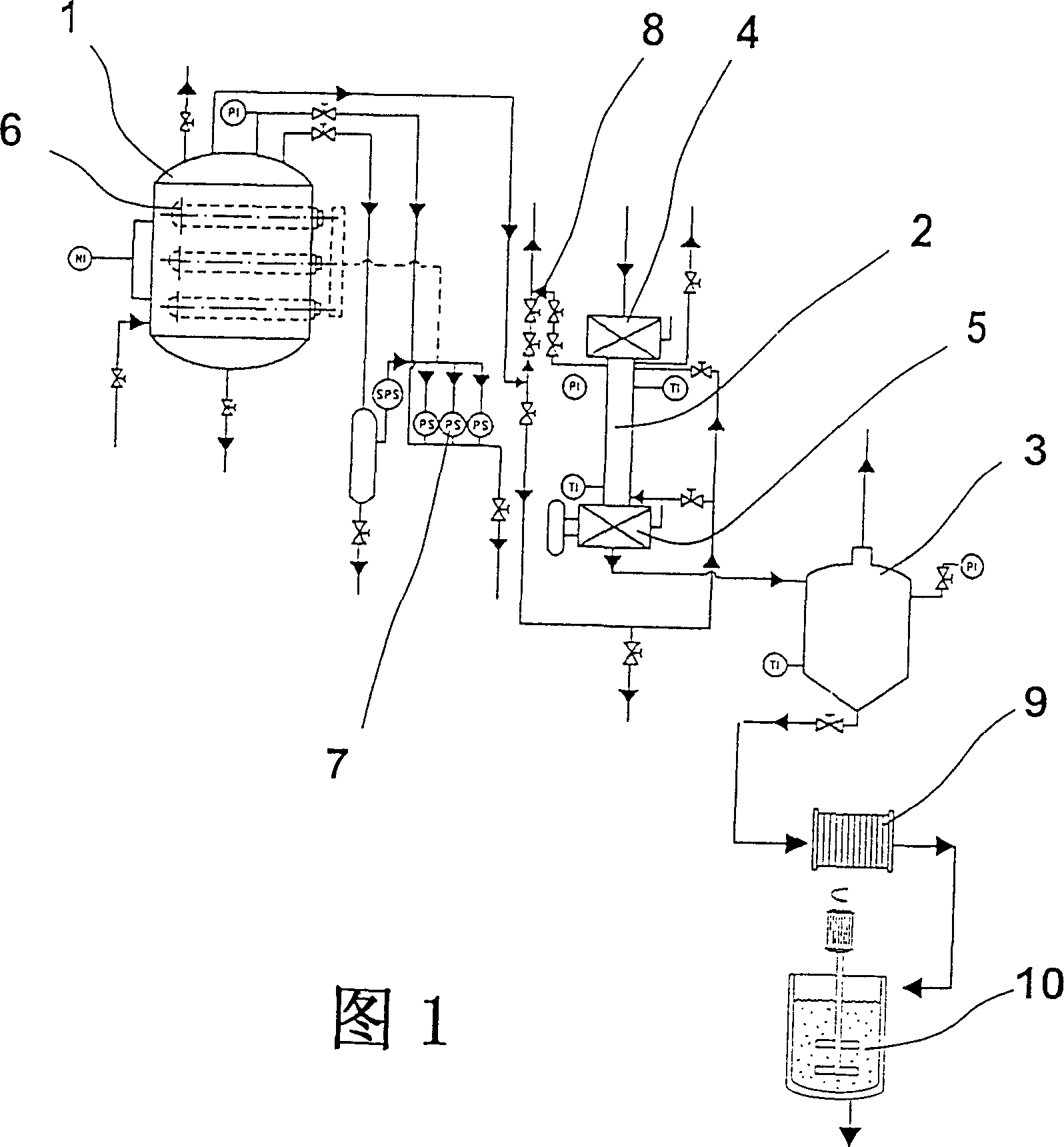
[0039] The feedstocks used in the present invention are mainly cellulose containing materials such as forestry and agricultural residues, pulp, lignocellulosic crop biomass and organic fractions of household waste. Normally, this material has been air dried and contains 10-15% moisture.
[0040] Although the material needs to be comminuted prior to pretreatment, the required particle size (15-30mm) is considerably larger than that used in other reactor designs, thereby reducing the energy consumption associated with comminuting. This steam heat treatment causes condensation and produces a wet lignocellulosic mass. Since the temperature is high enough to thermodynamically force the dissociation of liquid water, autohydrolysis occurs, producing an acidic medium and overcoming the energy barrier for hydrolysis. Since the diffusion of the vapor phase is greater than that of the liquid phase, the incorporation of vapor into the structure of the lignocellulosic material is ensured....
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| water content | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com