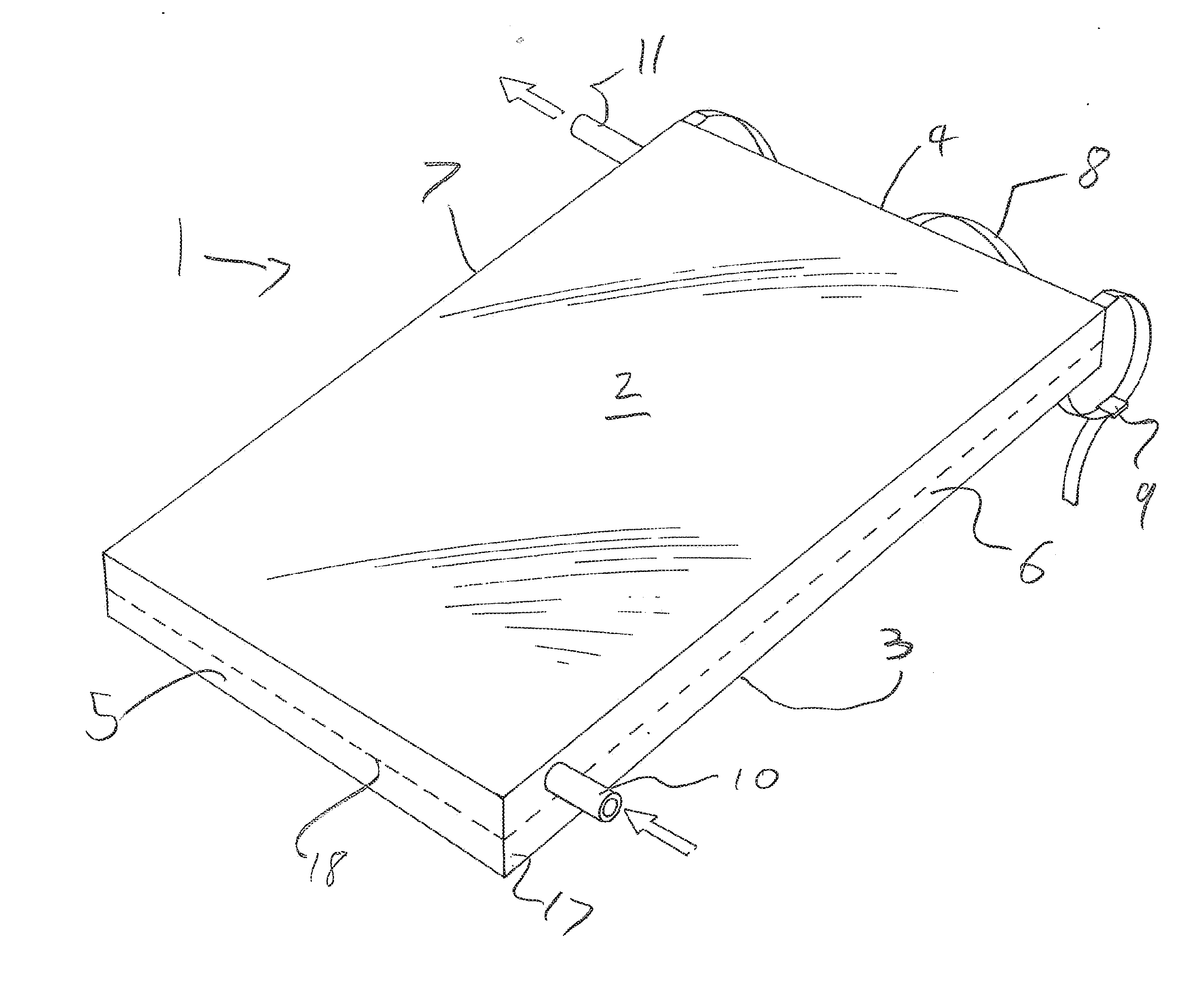
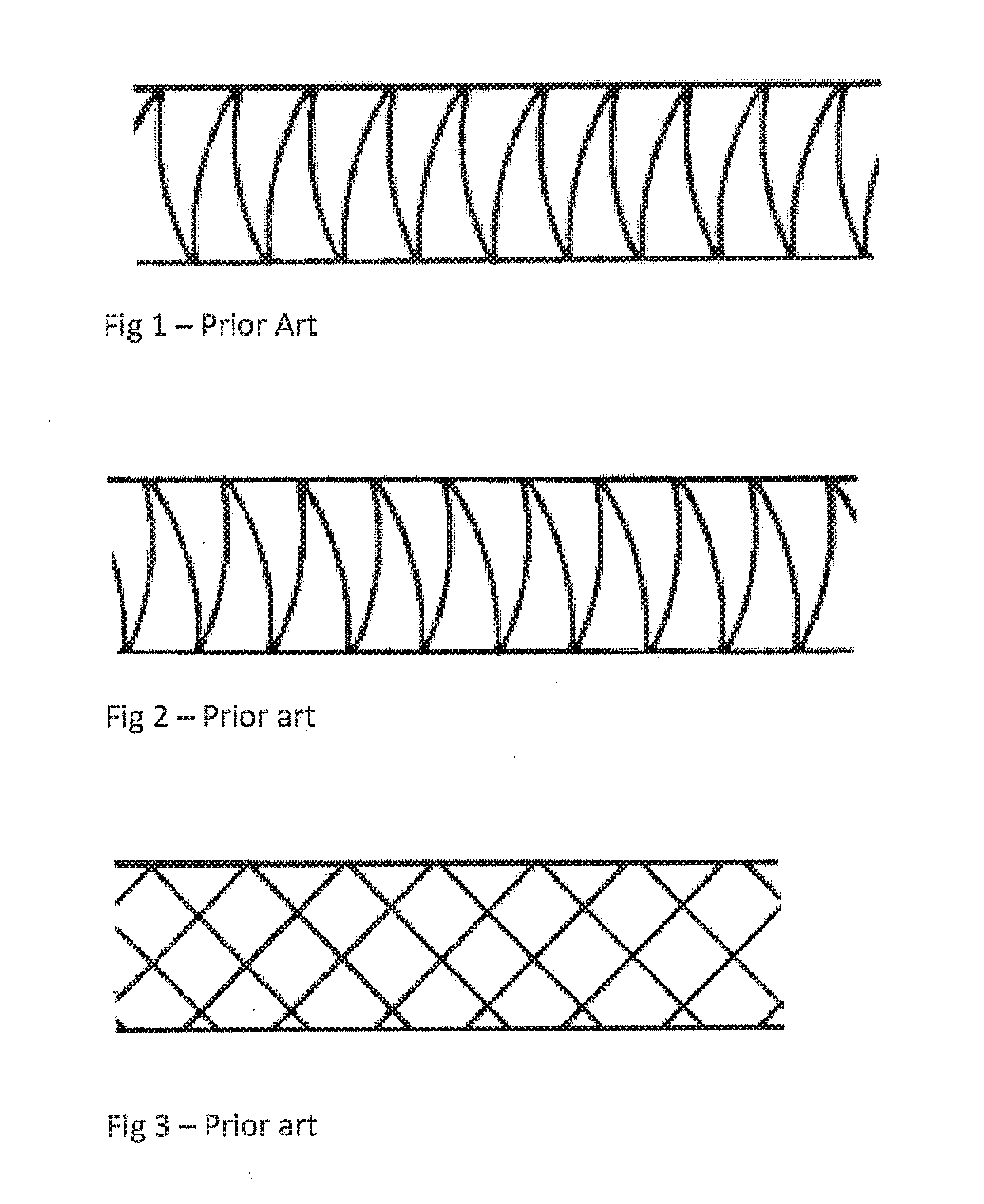
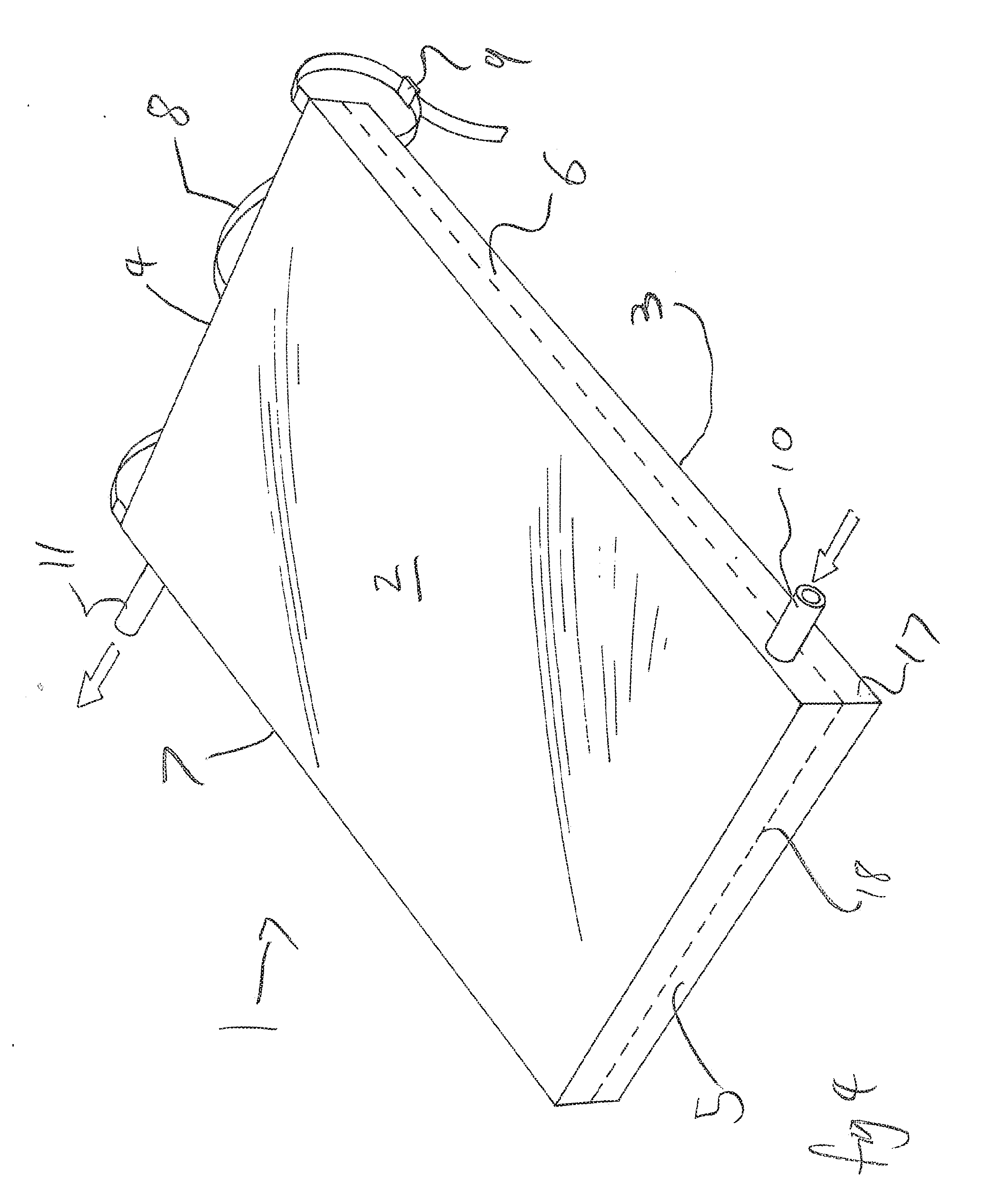
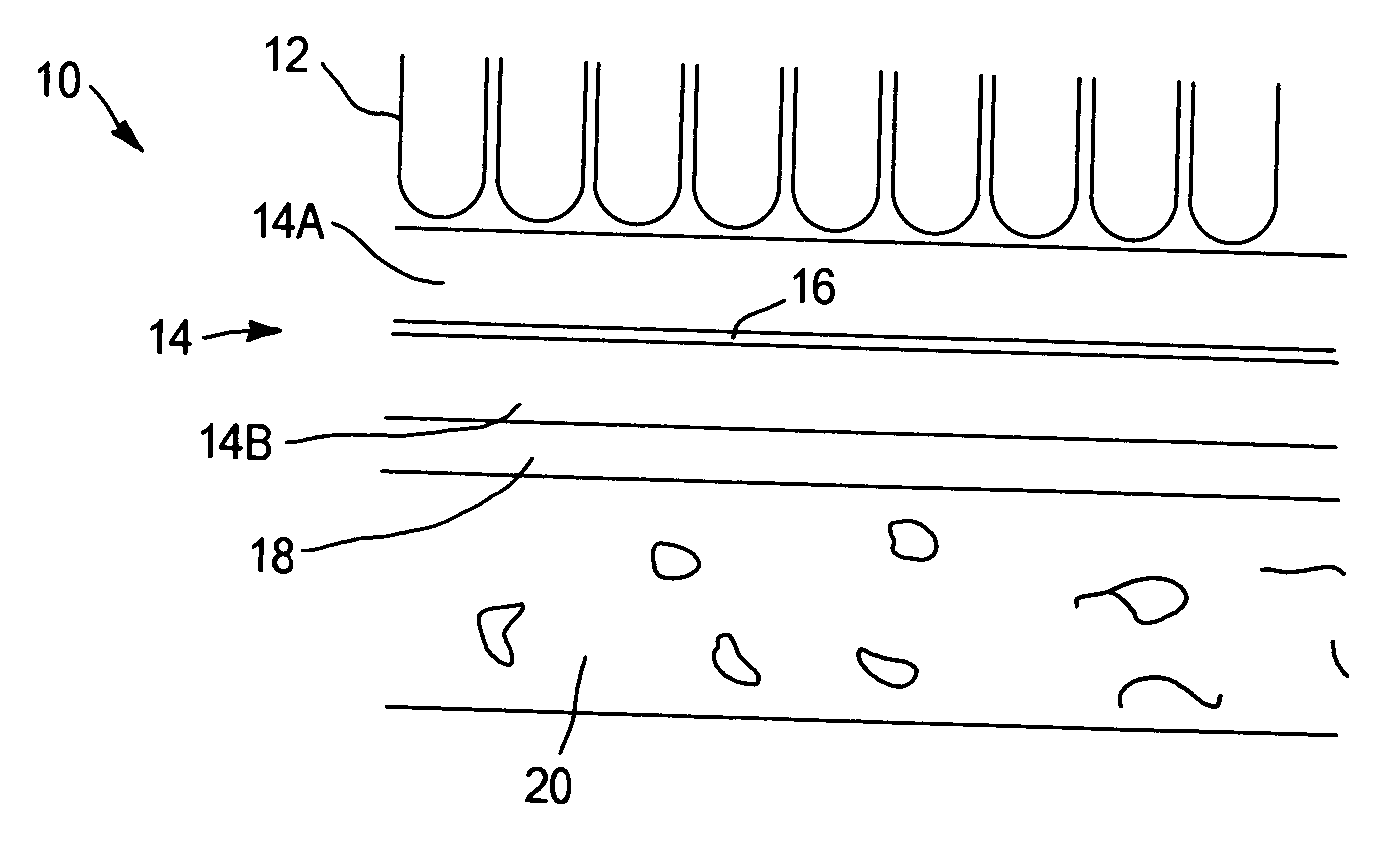
Patents
Literature
162 results about "Microfilament" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton and are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but in cells are modified by and interact with numerous other proteins. Microfilaments are usually about 7 nm in diameter and composed of two strands of actin. Microfilament functions include cytokinesis, amoeboid movement and cell motility in general, changes in cell shape, endocytosis and exocytosis, cell contractility and mechanical stability. Microfilaments are flexible and relatively strong, resisting buckling by multi-piconewton compressive forces and filament fracture by nanonewton tensile forces. In inducing cell motility, one end of the actin filament elongates while the other end contracts, presumably by myosin II molecular motors. Additionally, they function as part of actomyosin-driven contractile molecular motors, wherein the thin filaments serve as tensile platforms for myosin's ATP-dependent pulling action in muscle contraction and pseudopod advancement. Microfilaments have a tough, flexible framework which helps the cell in movement.
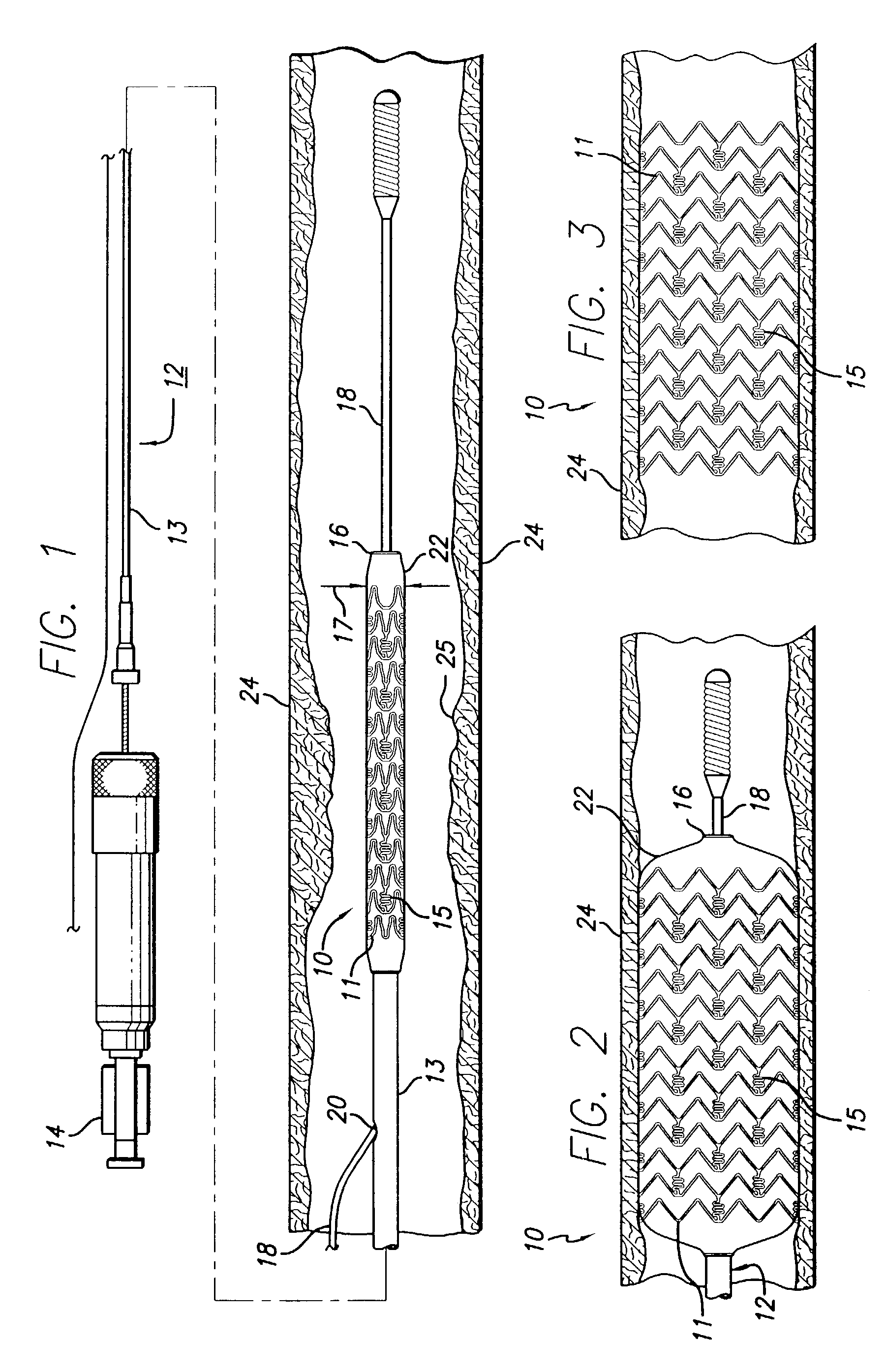
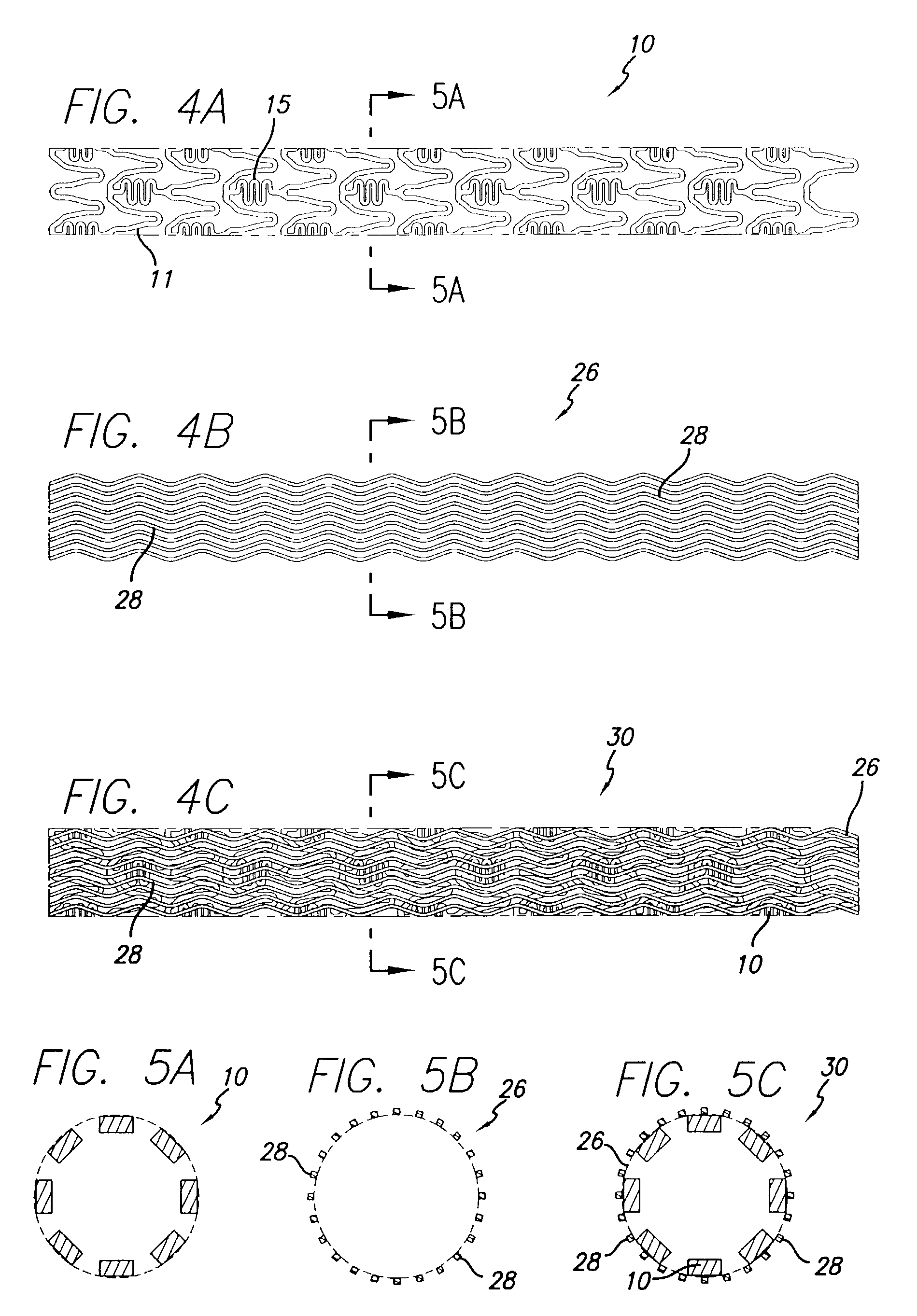
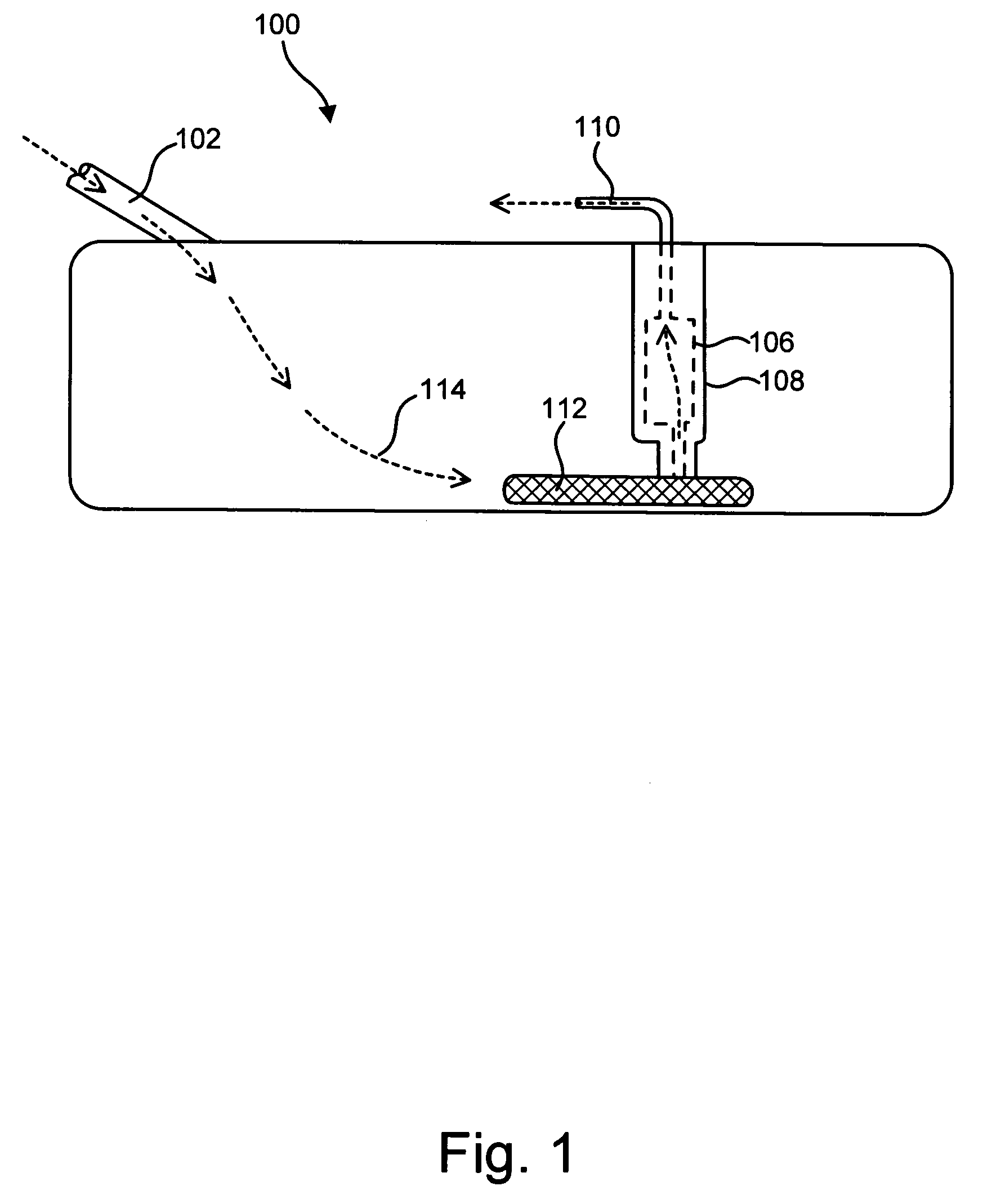
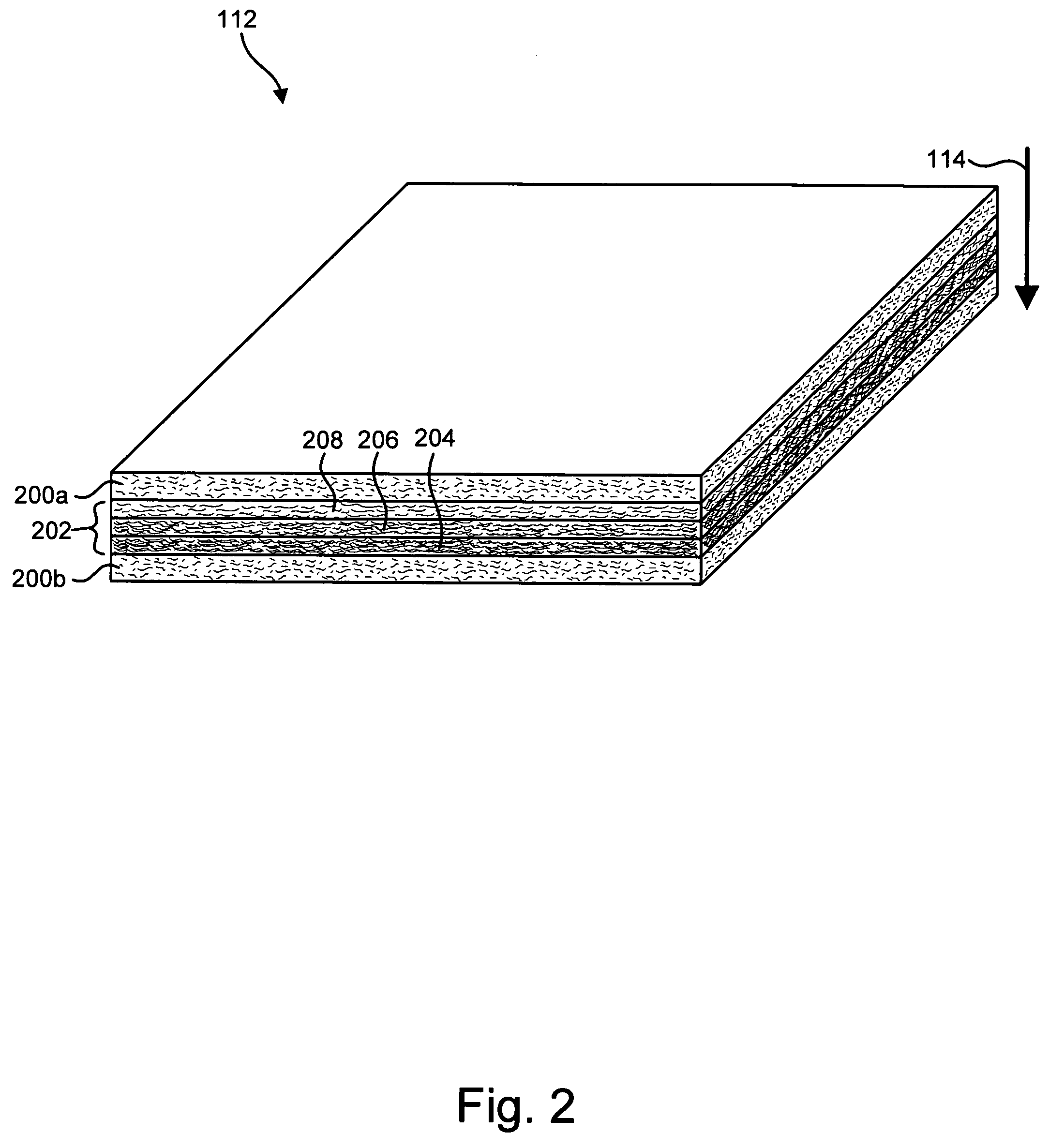
Drug-eluting stent and methods of making the same
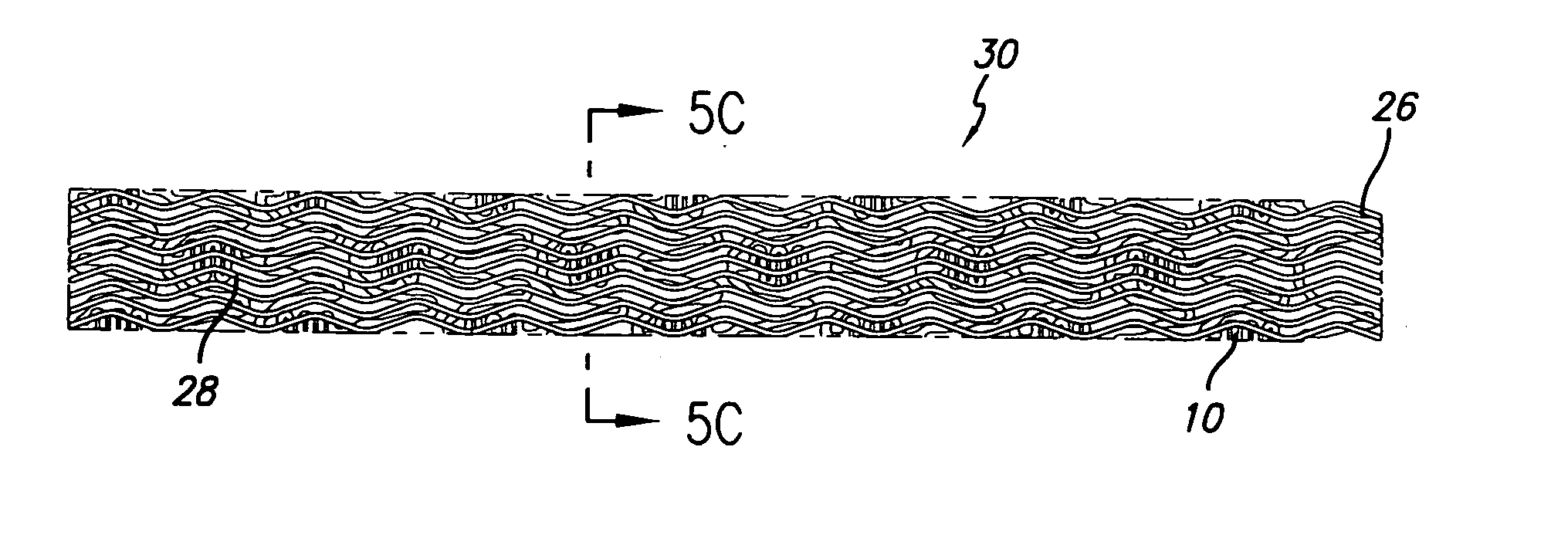
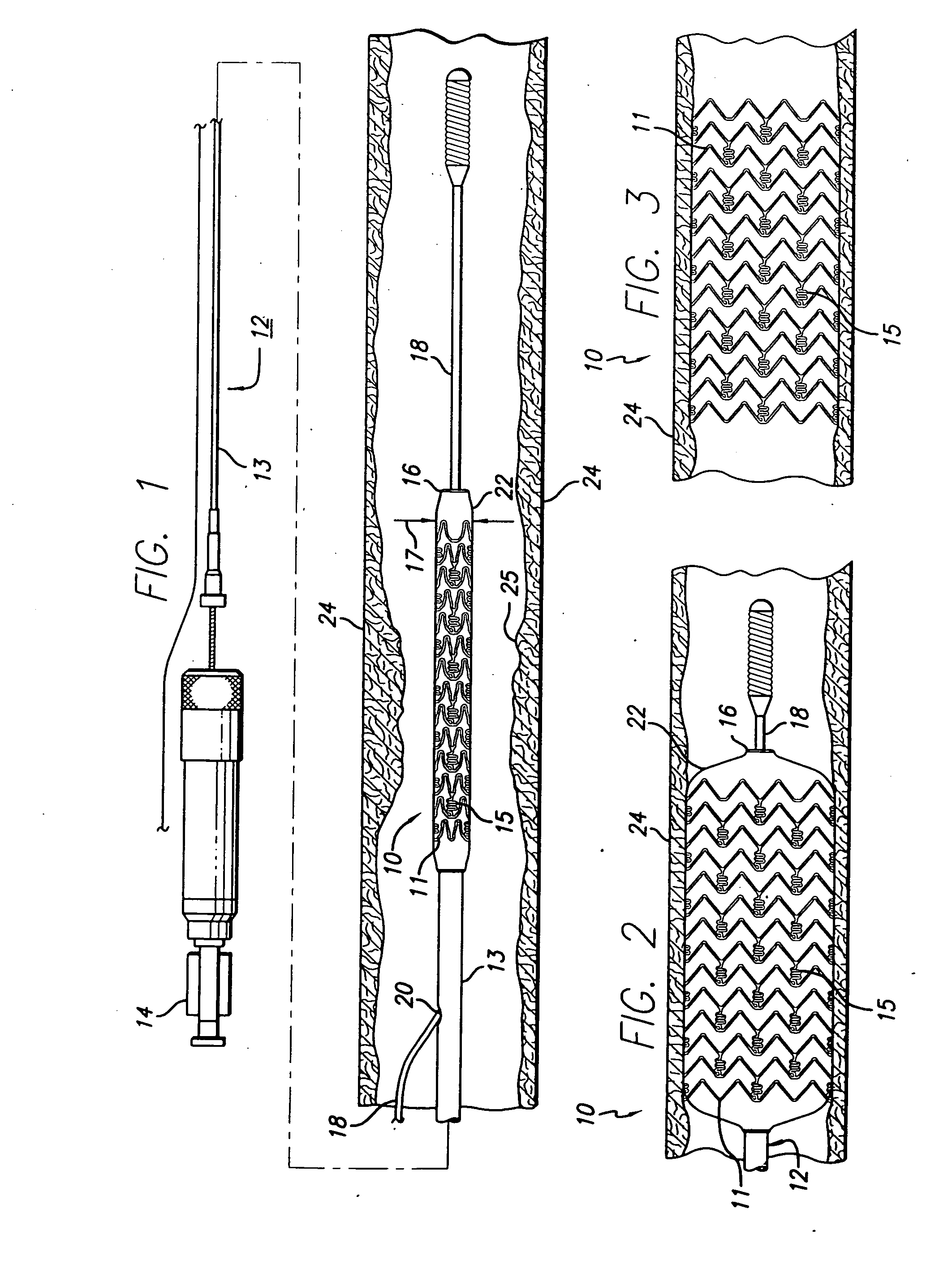
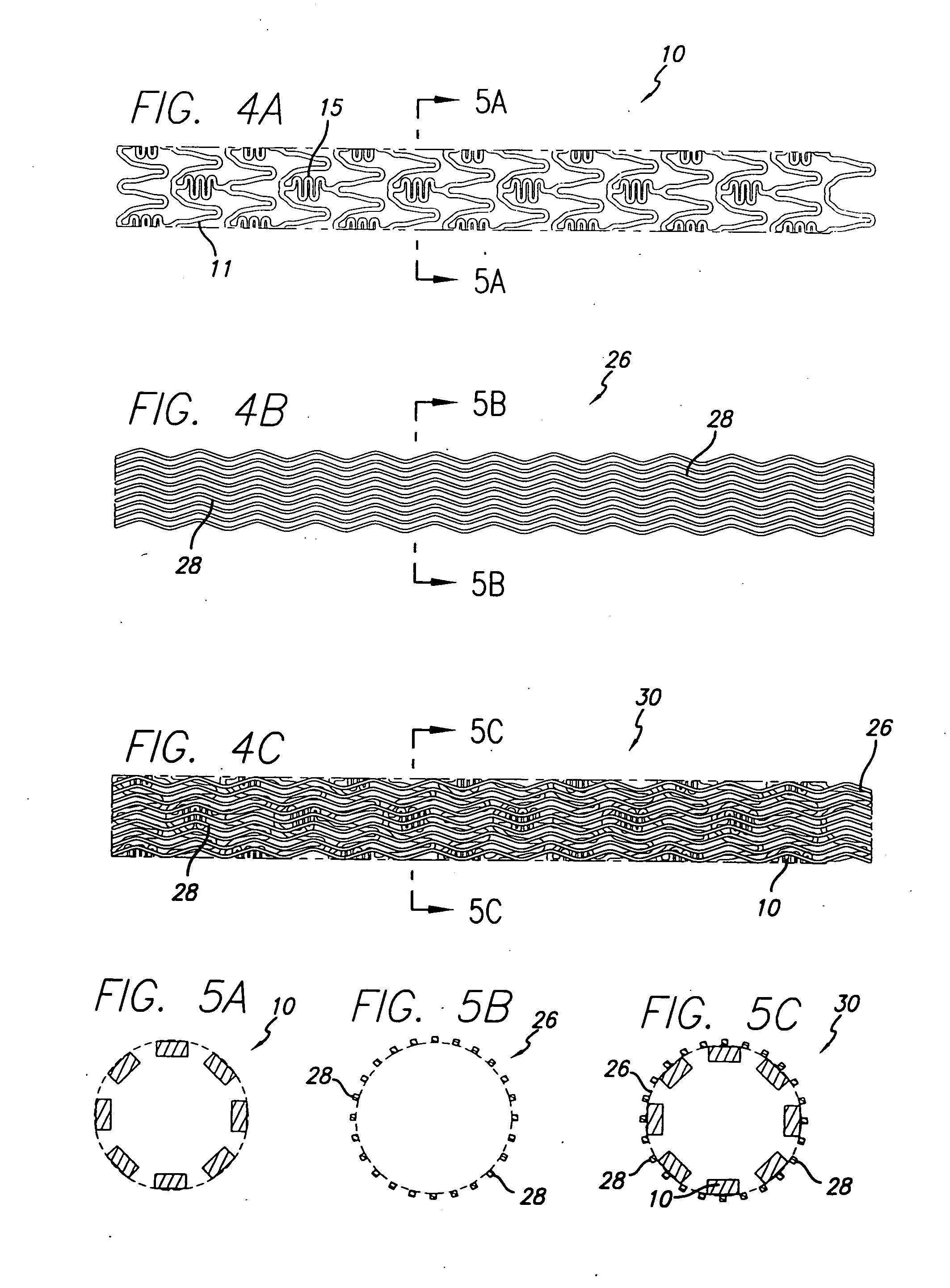
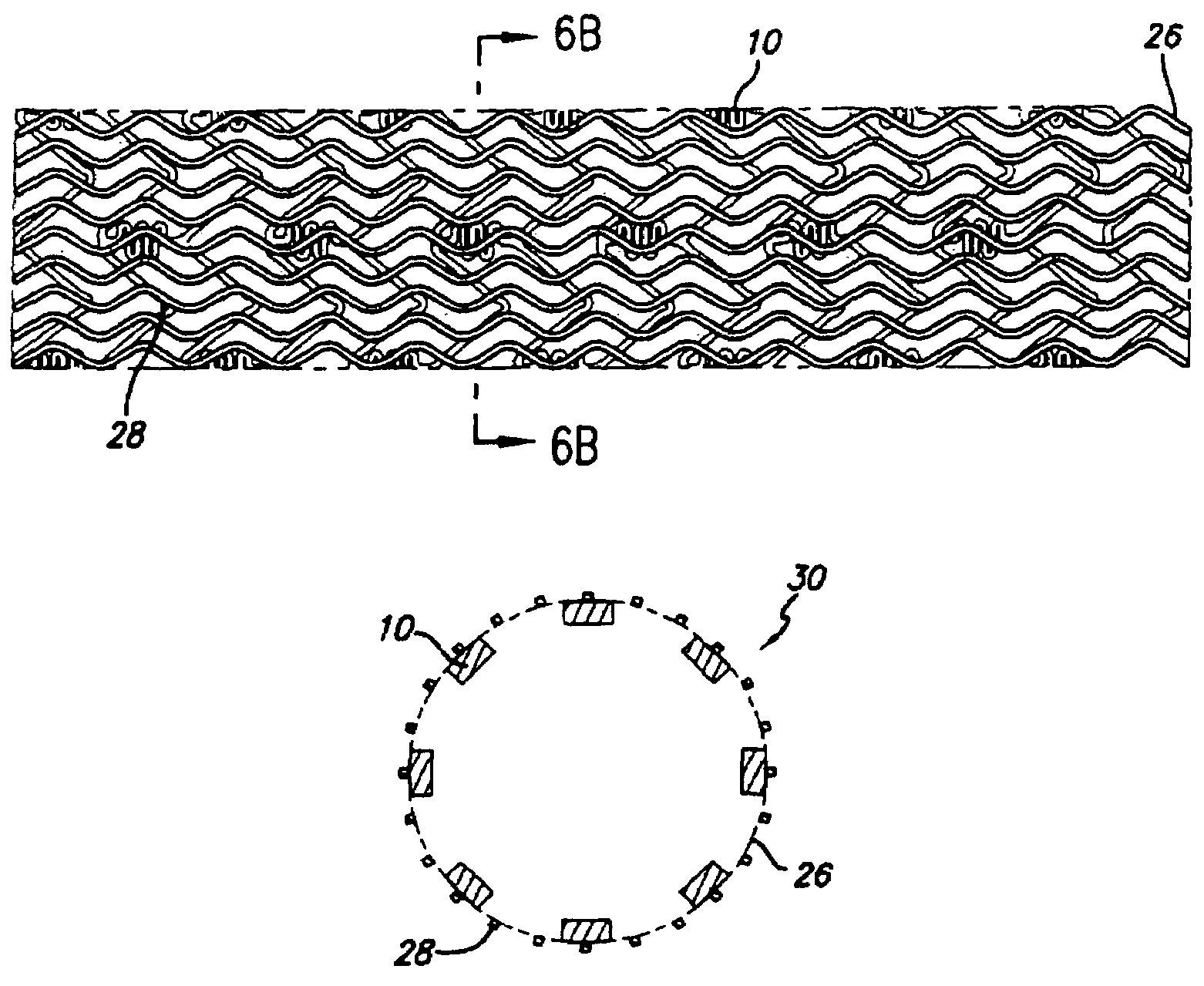
An intravascular stent having a prefabricated, patterned polymeric sleeve for controlled release of therapeutic drugs and for delivery of the therapeutic drugs in localized drug therapy in a blood vessel is disclosed. The polymeric sleeve is attached to at least a portion of an outside surface area of the stent structure. Alternatively, a plurality of individual microfilament strands are longitudinally attached to an outer surface of a stent structure in a spaced apart orientation and loaded with at least one therapeutic drug for the release thereof at a treatment site. The stent has a high degree of flexibility in the longitudinal direction, yet has adequate vessel wall coverage and radial strength sufficient to hold open an artery or other body lumen. Methods for making the same are also disclosed.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Drug-eluting stent and methods of making the same
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Preparation method of recycled polyester chip microfilaments and usage thereof
InactiveCN101747596ASimple compositionNo smellFilament/thread formingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsPolyesterLinear low-density polyethylene
The invention relates to a preparation method of recycled polyester chip microfilaments and a usage thereof, belonging to the field of plastic modification and category of composite material / alloy promoter. The polyester chip microfilament is an ideal promoter which has excellent performance, environment-friendliness, high added value, wide application range and broad market prospect and can change the mechanical property of the composite material / alloy. Recycled blow molding polyester (RPET / RPBT) is taken as main raw material, and the following formula and process are adopted for preparing the microfilament according to parts by weight: 100 parts of recycled polyester (RPET / RPBT), 5-30 parts of wire-drawing high-density polyethylene (HDPE) / polypropylene (PP) / linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE), 0.1-4 parts of crosslinking agent / chain extender / anchoring agent, 0.1-0.8 part of antioxidant, 0.5-6 parts of nucleating agent, and 1-5 parts of nucleate accelerant, and other processing aids (such as lubricant and plasticizer) / functional aids (such as fire retardant and ultraviolet absorber) can be additionally and appropriately added. The microfilament is prepared through extrusion, cooling, drawing and granulating by the reaction under 90-260 DEG C under the action of mechanical shear. The recycled polyester (RPET / RPBT) microfilament prepared in the invention can endow the composite material / alloy with excellent mechanical property.
Owner:王世和
Gradient density depth filtration system
An apparatus, system and method to provide increasingly fine gradient density depth filtration of a fluid. The apparatus may include a melt-blown filtration assembly having varying densities of melt-blown microfilaments fabricated from acetal or other substantially dimensionally stable thermoplastic. The apparatus thus facilitates efficient filtration by providing a gradient density depth filtration system compatible with various fuels, coolants, and other forms of a fluid.
Owner:CUMMINS FILTRATION IP INC
Soluble Microfilament-Generating Multicomponent Fibers
InactiveUS20070077427A1Improve solubilityFilament/thread formingConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsFiberPolymer dissolution
Owner:FIBER INNOVATION TECH
Soluble microfilament-generating multicomponent fibers
InactiveUS20060083917A1Improve solubilityConjugated synthetic polymer artificial filamentsYarnFiberPolymer dissolution
Microfilament-generating multicomponent fibers are provided that include a first polymer component and a second polymer component extruded together in separate contiguous polymer segments extending along the length of the fiber. The first polymer component comprises a synthetic melt-processable polymer that is substantially soluble in a first relatively benign solvent selected from water, aqueous caustic solution, and non-halogenated organic solvents. The second polymer component is formed from a second synthetic melt-processable polymer dimensioned to produce one or more microfilaments upon dissolution of the first polymer, and that is substantially soluble in an aqueous solvent selected from water and aqueous caustic solution. The two polymer components are dissolvable in different solvents.
Owner:FIBER INNOVATION TECH
Cartilage cell epimatrix three-dimensional porous sponge stent for tissue engineering and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101496913AFacilitate in vitro constructionPromotes regeneration in the bodyBone implantCartilage cellsCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a three-dimensional porous cartilage extracellular matrix sponge scaffold made of natural cartilage, which can compound cells further to construct tissue engineered cartilage, and can be used for clinically repairing cartilage defects. In the invention, conditions which can fully perform cell extraction and form a porous scaffold matrix are provided by processing cartilage into cartilage microfilaments, and then the cell extraction and solidification and / or strengthening treatment are performed to obtain the three-dimensional porous cartilage extracellular matrix sponge scaffold which is completely decellurized. The antigenicity and cell components are removed in the natural cartilage, and an extracellular matrix component of the cartilage is retained to obtain the scaffold with appropriate pore diameter and porosity, suitable degradation rate, good biocompatibility and certain biomechanical strength. The scaffold has the advantages of broad material sources, low cost, simple and feasible preparation technology, and good repetitiveness; and the scaffold can be widely applied in the field of tissue engineering and has good clinical application prospect.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Tissue engineering bone/cartilage double-layer scaffold and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN101574540AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationBone implantCartilage collagenCells bone
The invention discloses a tissue engineering bone / cartilage double-layer scaffold and a construction method and application in medical science. The method adopts natural cartilage and bone as materials, respectively removes the antigenicity of the cartilage and the bone through de-cell, and adopts a freezing and drying method to prepare the double-layer scaffold simultaneously suitable for growthof the two issues of the bone and the cartilage. A preparation method comprises that: acellular bone is soaked in suspension of cartilage acellular matrix microfilaments, and the double-layer scaffoldof which the upper layer is a cartilage acellular matrix three-dimensional porous spongy scaffold and the lower layer is an acellular bone scaffold is prepared by the freezing and drying method and acrosslinking method. The cartilage acellular matrix spongy scaffold part of the double-layer scaffold can be introduced with factors promoting the formation of the cartilage, and the acellular bone part can be introduced with factors promoting the formation of the bone, and the factors can be respectively inoculated with cells for forming the cartilage or the bone to construct a living tissue engineering bone / cartilage complex, which is used for repairing bone and cartilage complex defect or total joint defect clinically.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Mattress or mattress overlay
InactiveUS20160157631A1Reduce humidityEasy to compressStuffed mattressesSpring mattressesMechanical engineeringPhysics
A mattress or mattress overlay is provided, which is formed from several layers of spacer fabric. At least two layers of the spacer fabric are arranged such that the microfilaments in the layers curve in the same direction, towards the foot of the bed. Another layer can be provided, with layers which curve in the same, or a different direction, e.g. orthogonal. The top layer is more compressible than the bottom layer and the surface of the top layer of spacer fabric is provided with cuts in the heel region to reduce pressure at this high-risk bony prominence.
Owner:MEDSTROM
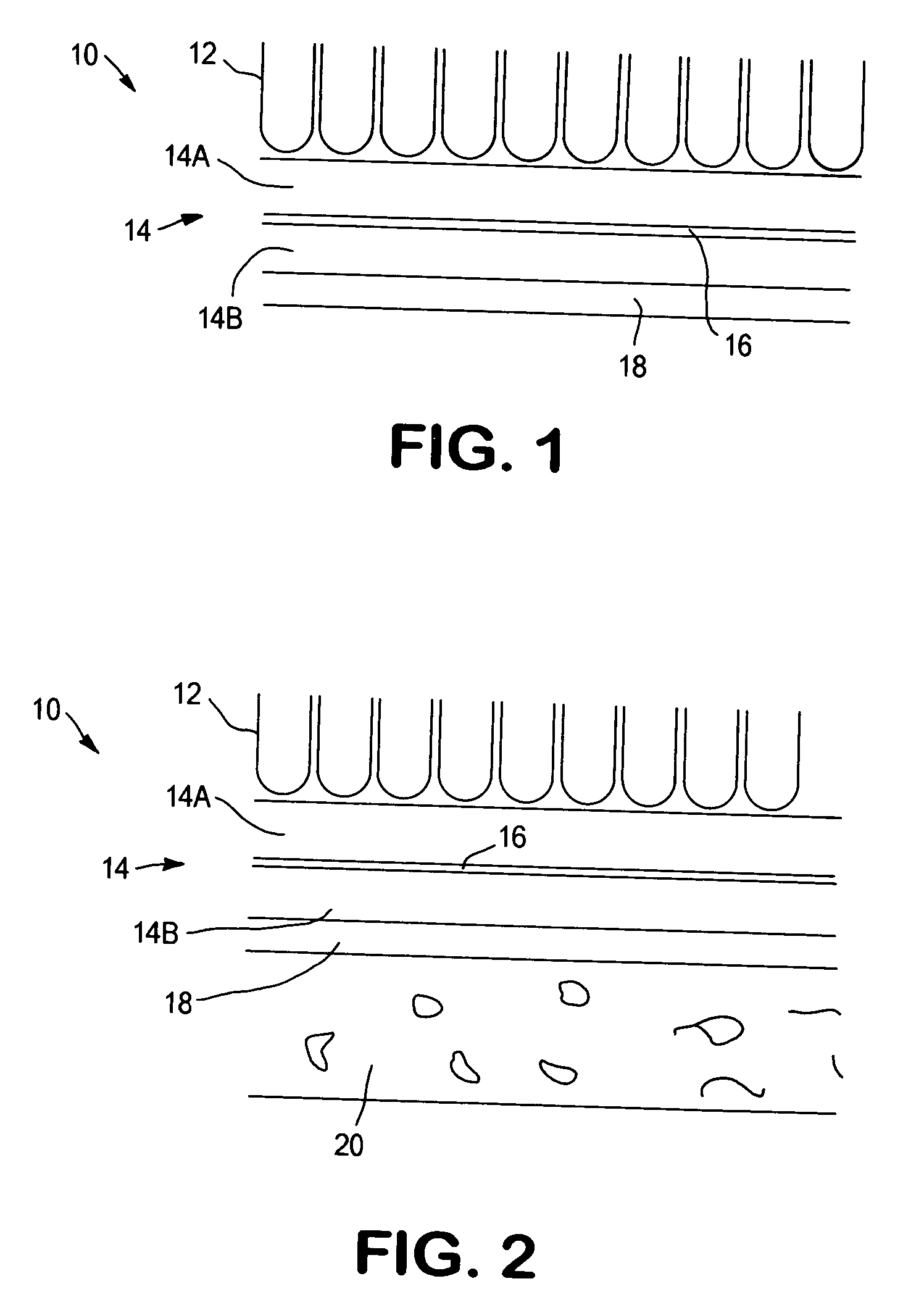
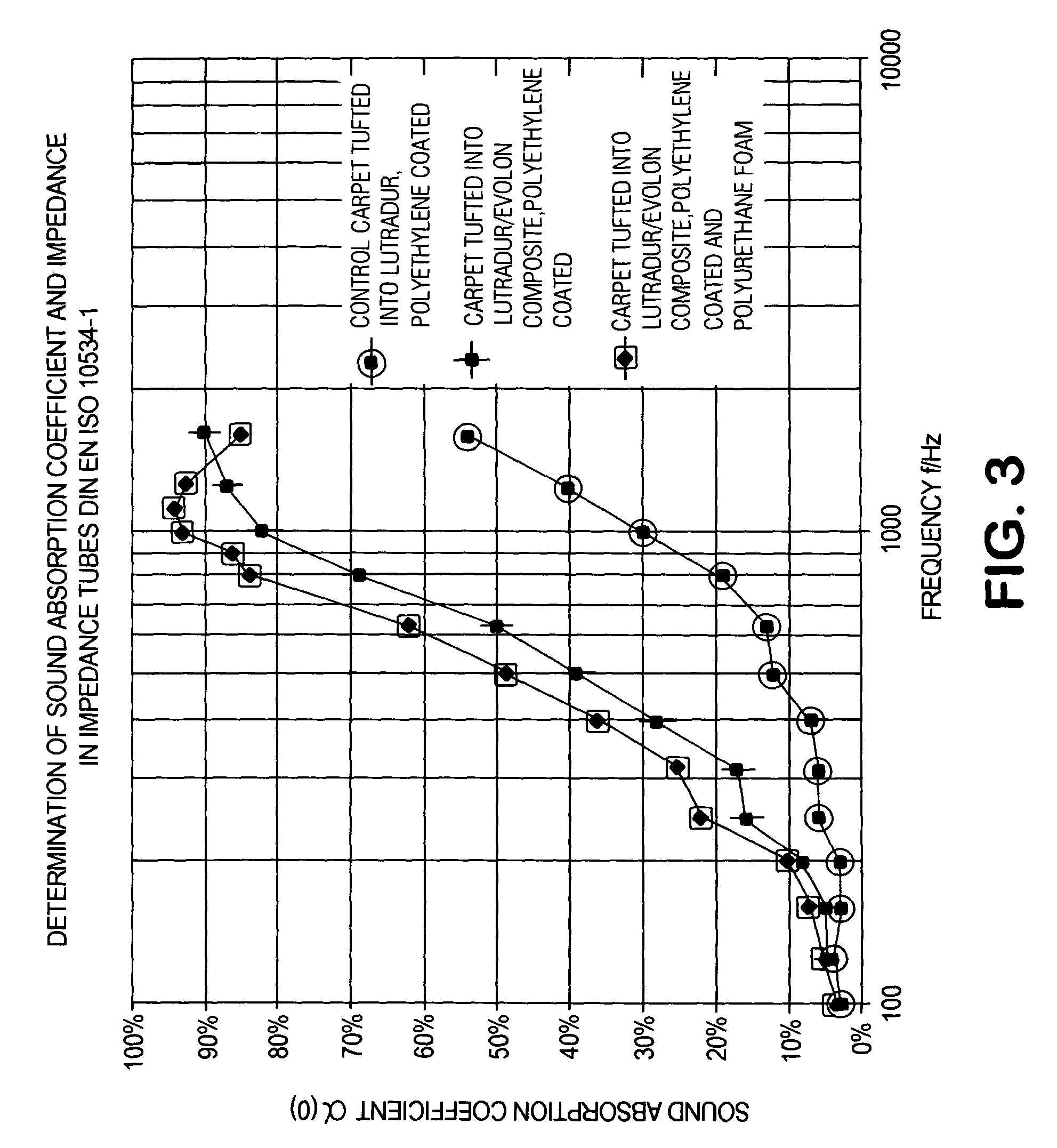
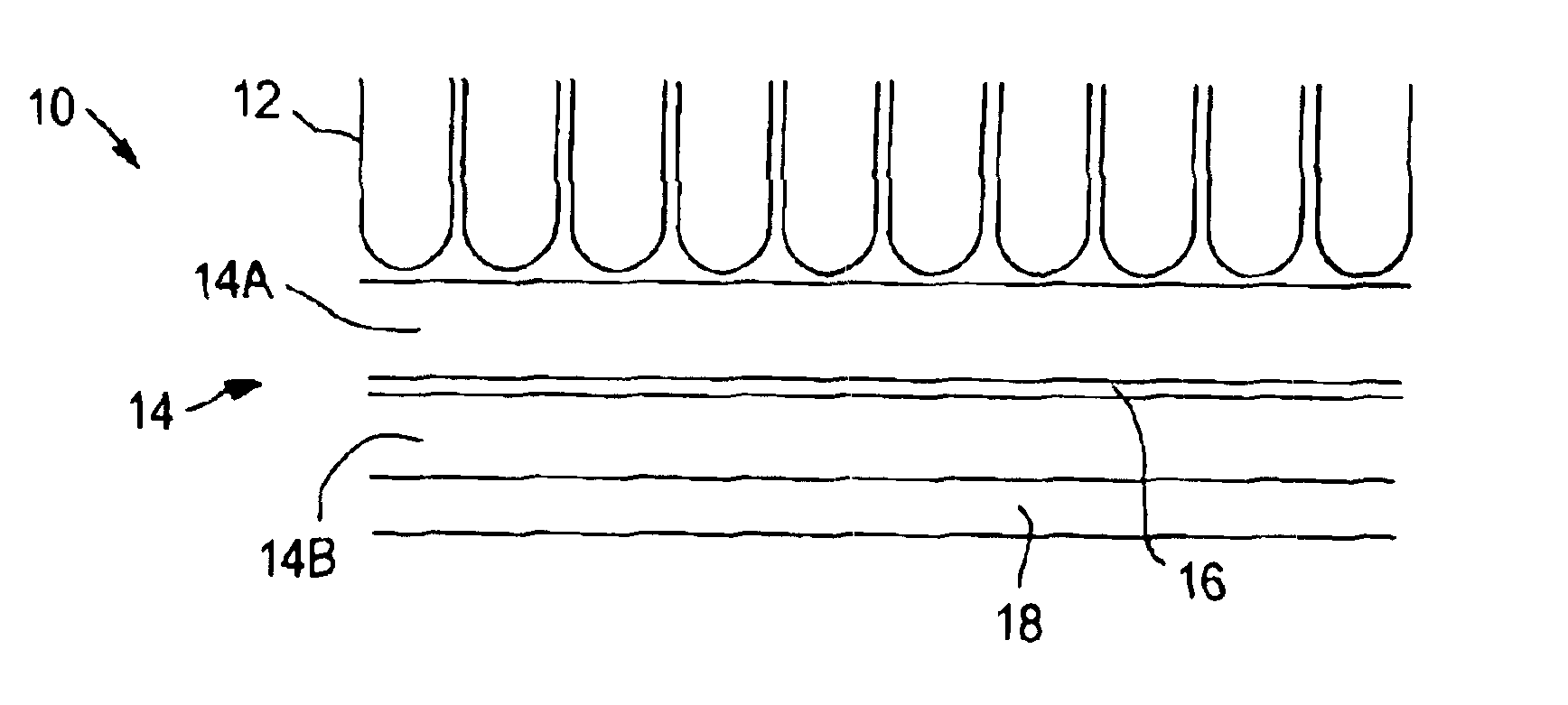
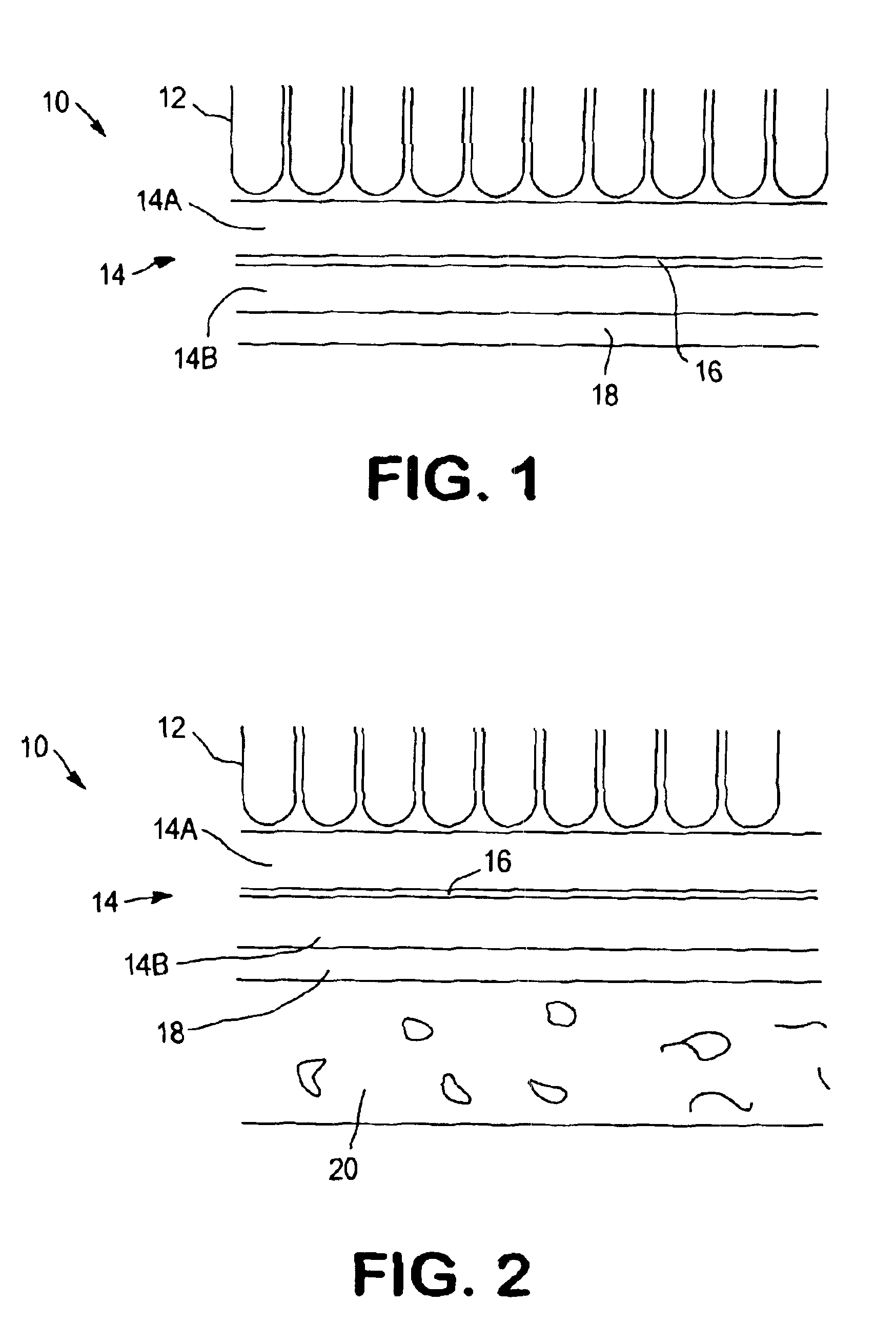
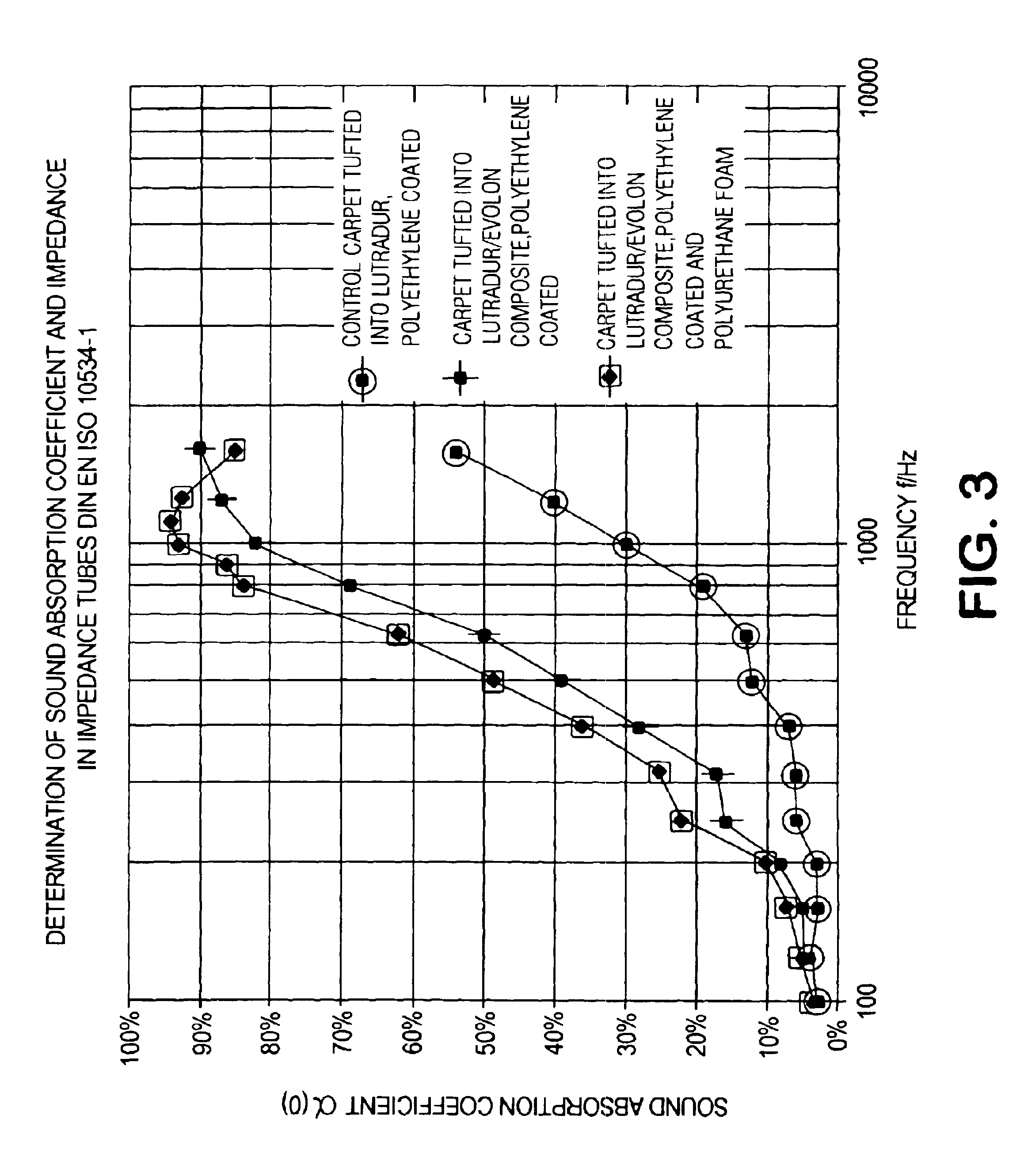
Automotive tufted carpet with enhanced acoustical properties
InactiveUS20040151870A1Improve acoustic propertiesFacilitate thermobondingVehicle arrangementsLayered productsYarnEngineering
An automotive tufted carpet with improved acoustic properties is formed with a two-part primary backing. The first backing layer is formed of a woven or non-woven material, and the second backing layer is formed of a microfilament spunlaced material possessing sound absorbing acoustic properties. The first backing layer and second backing layer are thermobonded together with an adhesive web positioned therebetween to form the two-part primary backing. Tufts of yarn are then sewn through the two-part primary backing. The resulting acoustically enhanced automotive tufted carpet may be backcoated or precoated, and may have a secondary backing adhered thereto as a matter of choice.
Owner:FREUDENBERG SPUNWEB +1
Multi-bit encoded glass-coated microwire and articles composed thereof
InactiveUS20050109435A1Eliminate needInorganic material magnetismGlass/slag layered productsGratingFluorescence
A glass-coated amorphous metallic microwire is encoded with multi-bit digital information. Encoding is achieved magnetically, optically or through a combination of magnetic and optical encoding processes. Magnetic encoding is carried out by modifying the constituent magnetic domain structure through selective relief of interfacial stress between the glass coating and the amorphous metallic alloy core. It is also achieved by selective surface crystallization of the amorphous metallic core in order to produce a controlled magnetic bias field. Optical encoding is associated with the glass coating. It is readily achieved by fluorescent element deposition, patterned removal of fluorescent element coating, Bragg grating, and thermally activated pattern deposition. The magnetic and optical multi-bit encoding approaches for glass-coated amorphous metallic microwire can be used individually or collectively in either a redundant or a complementary manner. Encoded microwire of the instant invention can be assembled into tags for electronic article surveillance and into numerous other structures as well.
Owner:DEMODULATION
Automotive tufted carpet with enhanced acoustical properties
InactiveUS6808786B2Improve acoustic propertiesFacilitate thermobondingVehicle arrangementsLayered productsYarnEngineering
An automotive tufted carpet with improved acoustic properties is formed with a two-part primary backing. The first backing layer is formed of a woven or non-woven material, and the second backing layer is formed of a microfilament spunlaced material possessing sound absorbing acoustic properties. The first backing layer and second backing layer are thermobonded together with an adhesive web positioned therebetween to form the two-part primary backing. Tufts of yarn are then sewn through the two-part primary backing. The resulting acoustically enhanced automotive tufted carpet may be backcoated or precoated, and may have a secondary backing adhered thereto as a matter of choice.
Owner:FREUDENBERG SPUNWEB +1
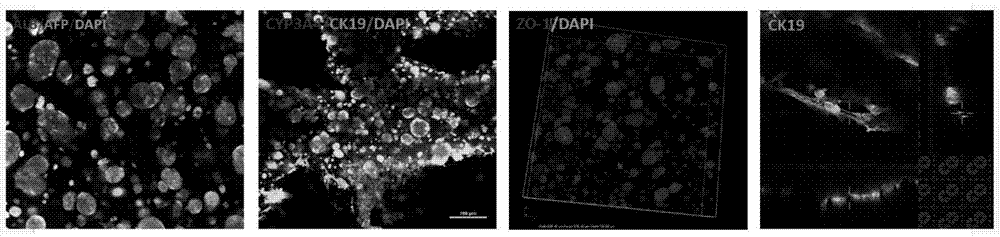
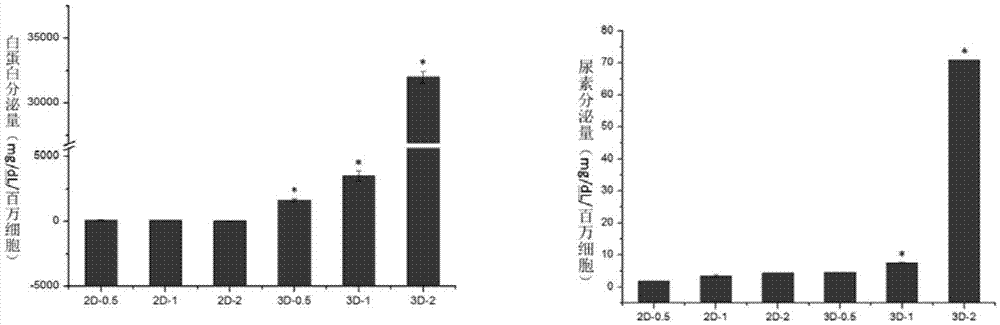
Construction method and application of in-vitro three-dimensional human liver tissue
InactiveCN106916781AFast printingImprove efficiencyHepatocytesDrug screeningDrug developmentAqueous solution
The invention relates to a construction method for in-vitro three-dimensional human liver tissue. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing a solution of seed cells with an aqueous solution of biological ink so as to obtain a cell printing solution; (2) under the control of a computer, uniformly extruding the cell printing solution with a cell printer at a set speed according to a designed path and allowing the cell printing solution to rapidly coagulate at a certain temperature so as to form gel microfilaments, and repeating the above operations so as to finish construction of a multilayer cell structure in a layer-upon-layer scanning manner; (3) subjecting the multilayer cell structure to secondary crosslinking and culturing the multilayer cell structure with a cell culture solution so as to obtain a stable multilayer cell structure; and (4) culturing the stable multilayer cell structure with an induction medium so as to obtain the in-vitro three-dimensional human liver tissue. The method provided by the invention can construct in-vitro three-dimensional human liver tissue with good functionality, and the constructed in-vitro three-dimensional human liver tissue is applicable to fields like treatment of hepatopathy, medicinal development, medicine screening, etc.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Highly oriented super microfilaments
InactiveUS20060006585A1Improve heat resistanceUse in some applicationFilament handlingArc welding apparatusThermosetting polymerInfrared beam
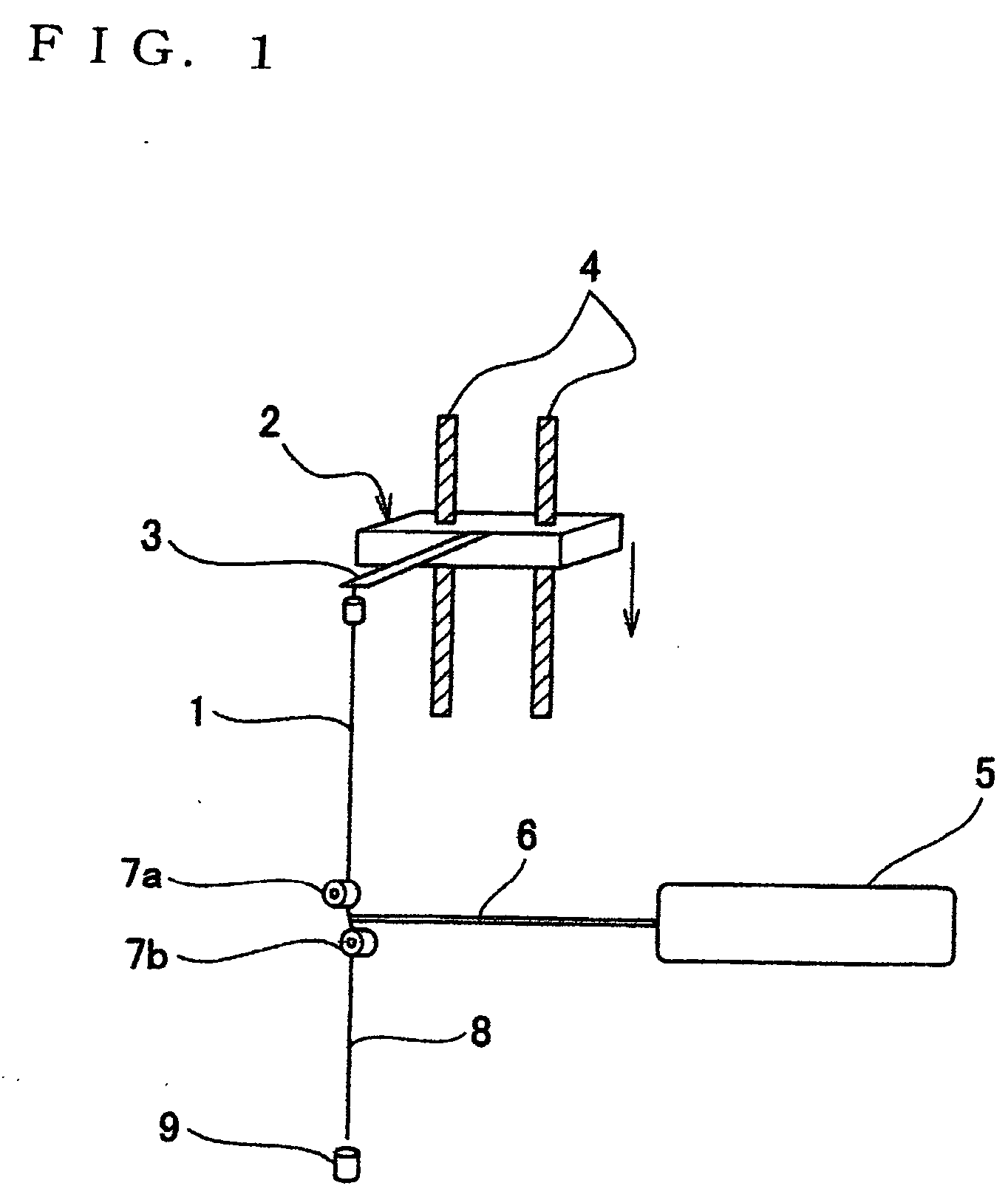
Method of and apparatus for continuously manufacturing highly oriented super micro filaments with a diameter of 5 μm or less from most of thermoplastic polymers stably by a simple and convenient means without requiring any special apparatus of high accuracy and high level, characterized in original filaments supplied from a filament supply means are heated by infrared beams and the heated filaments are drawn by tension provided by their own weight or under an applied tension of 1 MPa or less, and are drawn to 1000 times or more.
Owner:YAMANASHI UNIV OF
Highly oriented super microfilaments
InactiveUS7101504B2Improves drawabilityImprove mobilityFilament handlingArc welding apparatusThermosetting polymerInfrared beam
Owner:YAMANASHI UNIV OF
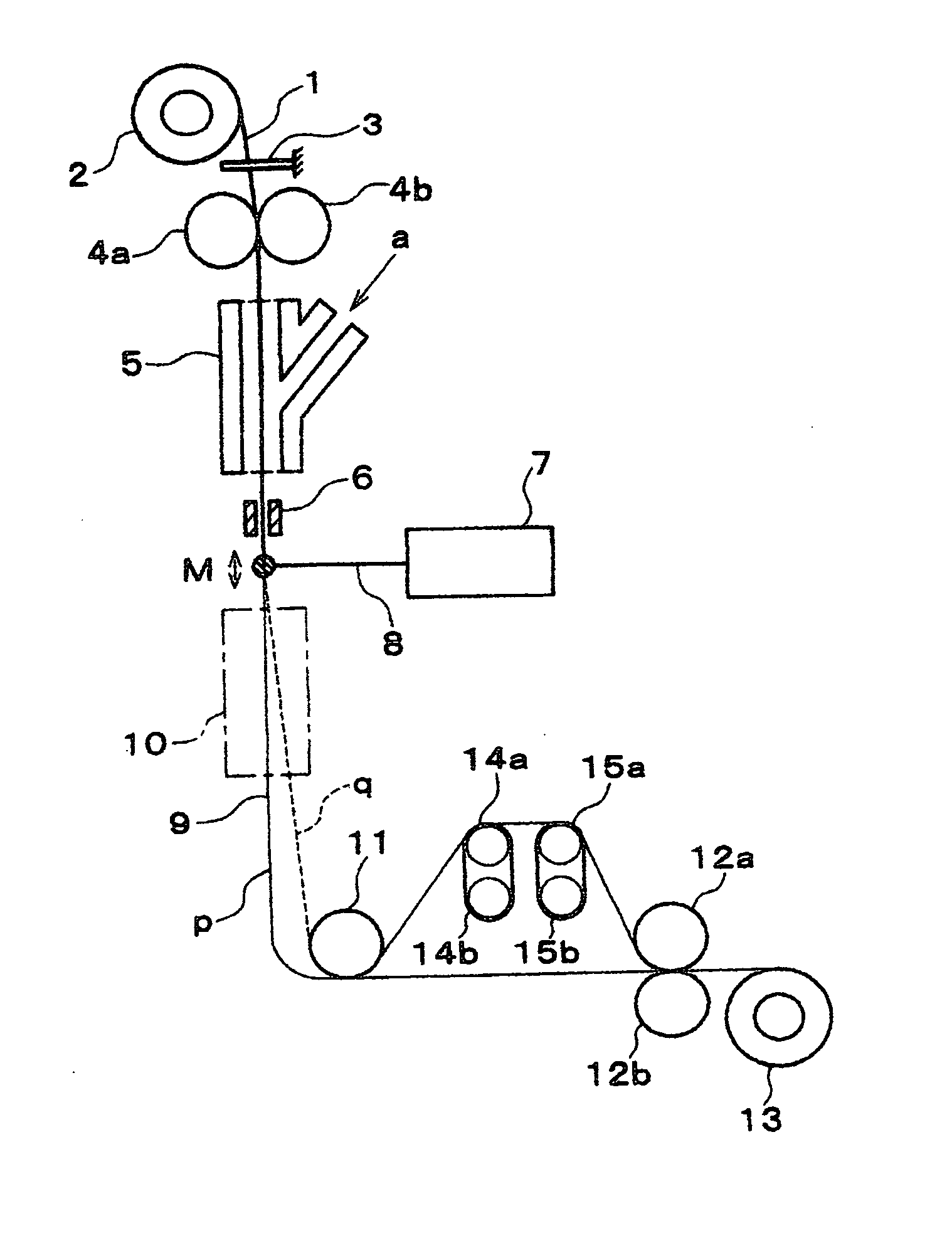
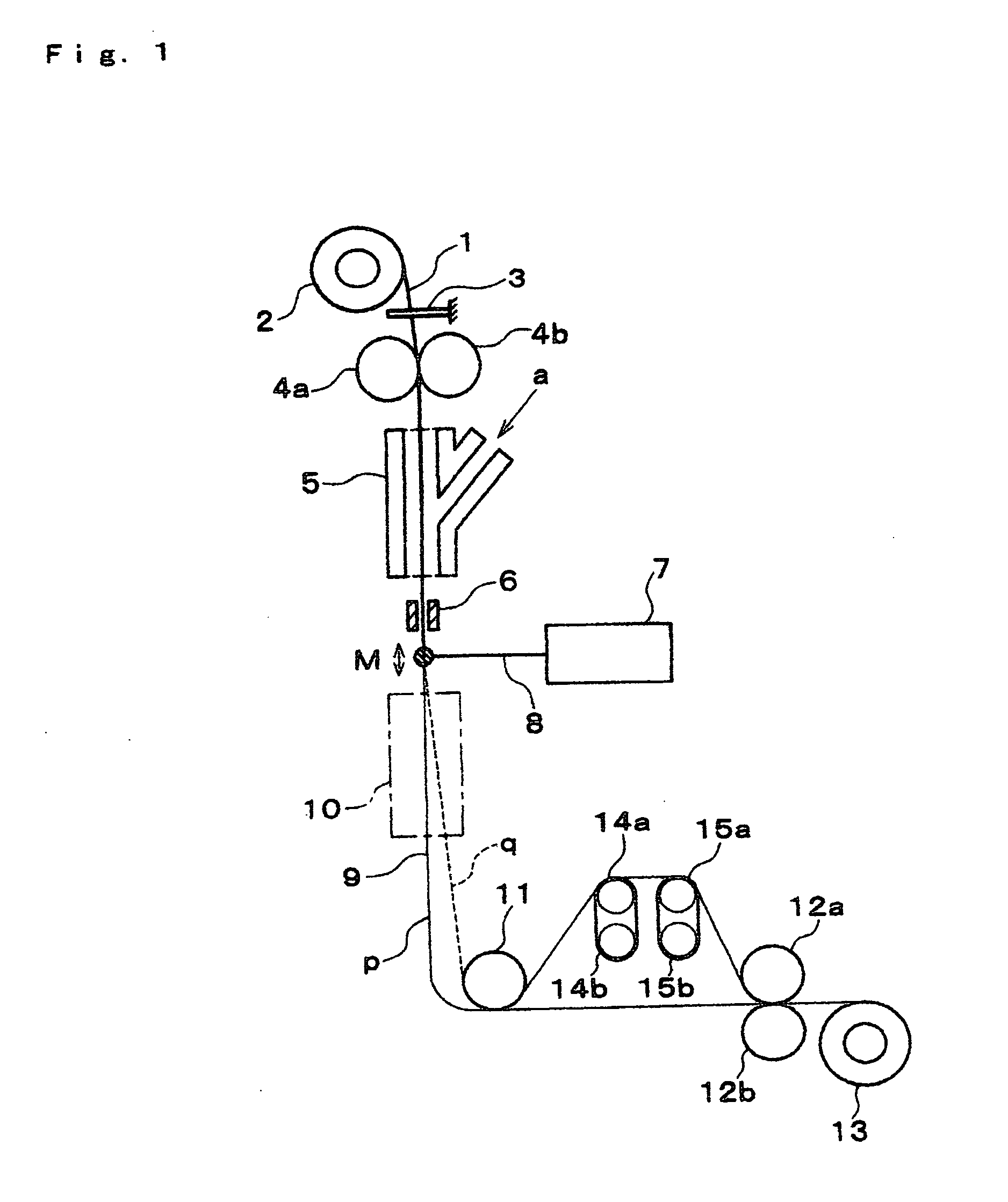
Device and method for producing microfilament yarns with high titer uniformity from thermoplastic polymers
InactiveUS6174474B1Improved textile-mechanical propertyReduce in quantityConfectionerySweetmeatsYarnDye absorption
A device and a method are disclosed, by means of which microfilament yarns made of synthetic polymers can be produced with increased uniformity of the titer, dye absorption and improved physical yarn properties at increased production speeds by means of a spinning process with spinnerets of high hole density and a central cooling unit.
Owner:OERLIKON TEXTILE GMBH & CO KG
Method and dedicated chip for preparation of micron calcium alginate filament based on microfluidic chip
ActiveCN102974410AStable and uniform formationControllable arrangementProductsReagentsControl systemCalcium alginate
The present invention provides a method and a dedicated chip for preparation of micron calcium alginate filaments based on a microfluidic chip. By using the chip and the method, calcium alginate microfilament with a minimum diameter of 20 [mu]m can be prepared, calcium alginate microfilaments interiorly including a dispersed phase of spherical structure of other materials can be prepared, and calcium alginate microfilaments with special morphology can be prepared. By using an independent fluid path and a gas path control system of the microfluidic chip, combined with a micro-injection pump and a gas pump valve system, the diameter of the calcium alginate microfilaments can be controlled; the material dispersed phase with the special structure in the microfilaments, including pitch, size, composition and sequence, can be highly-controlled arranged; and the special structure of the filaments can be adjusted. The method and the platform provided by the present invention can highly-controlled prepare calcium alginate filaments, the preparation process is stable, and morphology of the product is homogeneous, and the method is simple.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Oriented sheath core type filament
InactiveUS20060182960A1Easy to getSimple and convenient meanNon-woven fabricsYarnMechanical engineeringInfrared beam
The object of this invention is to make possible the manufacturing of sheath-core type super microfilaments from sheath-core type filaments such as hollow filaments, optical filaments and conjugate filaments continuously and stably by a simple and convenient means without requiring any apparatus of high-accuracy and high-level, characterized in that original filaments delivered from sheath-core type filament supply means are heated by infrared beams and the heated sheath-core type filaments are drawn at 100 times or more by a tension provided by the own weight or under a tension of 1 MPa or less.
Owner:YAMANASHI UNIV OF
Drawn Biodegradable Micro-Filament
InactiveUS20070222104A1Simple and convenient meanEasy to getMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentNon-woven fabricsPolymer scienceInfrared beam
The invention resides in enabling biodegradable filament of polylactic acid, polyglycolic acid and the like to manufacture biodegradable micro-filament by simple and convenient means without needing special, high-accuracy and high-level apparatus; it is characterized in that highly molecular oriented micro-filament those of 12 μm or less and generally from 2 μm to 3 μm can be obtained by heating biodegradable filament by infrared beam and the heated original filament is drawn to 100 times or more by tension of 10 MPa or less.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF YAMANASHI
Preparation and application of nerve tissue matrix derived tissue engineering scaffold material
InactiveCN102218160AKeep natural ingredientsGood biocompatibilityCatheterProsthesisFreeze-dryingDefect repair
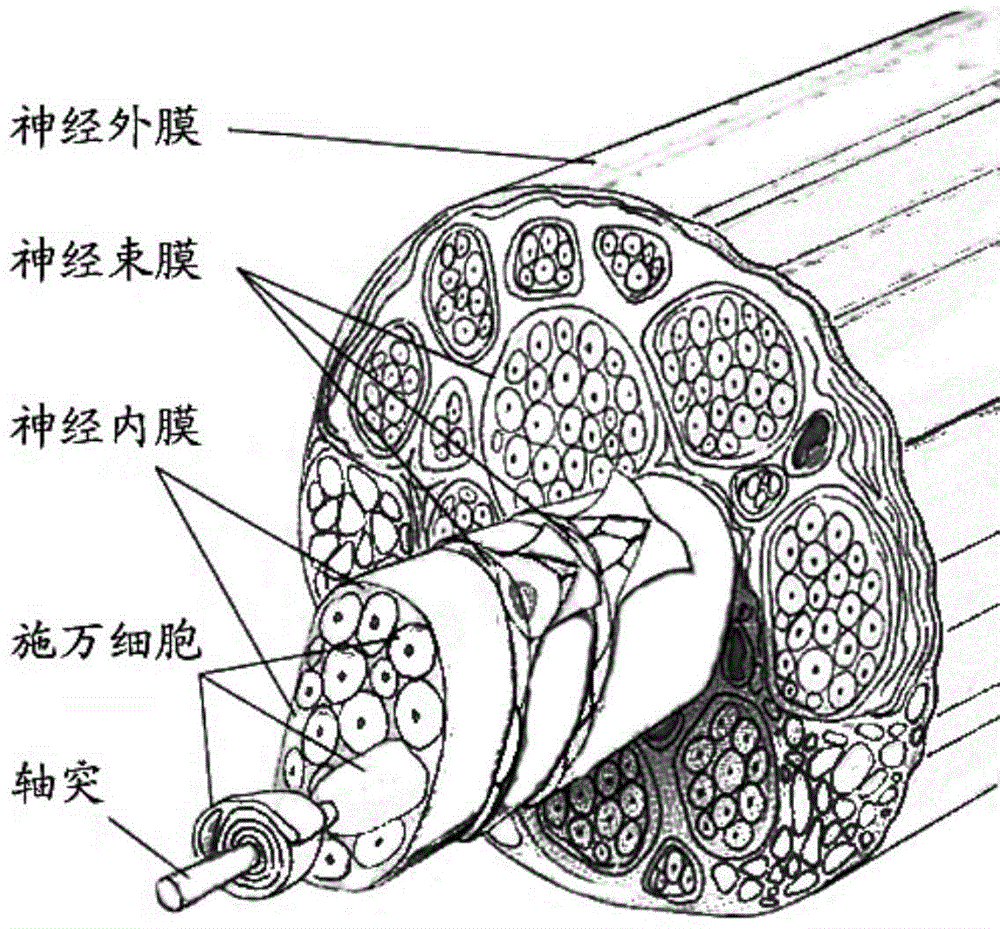
The invention discloses preparation and application of a nerve tissue matrix derived tissue engineering scaffold material. A nerve tissue is taken as a raw material, matrix components (including nano-scale collagen microfilaments, fibronectin microfilaments and laminin microfilaments) favorable for nerve regeneration are extracted by means of medicine expansion, mechanical pulverization, enzymolysis treatment, dialysis collection and the like, and immunogenicity components (including Schwann cells, phospholipid and axons) not favorable for nerve regeneration are removed. The prepared nerve tissue matrix derived material can be further prepared into a three-dimensional porous oriented scaffold through oriented crystallization, freeze drying and crosslinking separately or by matching other polymer materials, or is prepared into a nano-scale film by an electrospinning technology, and the film is wound to form a nerve regeneration catheter. The tissue engineering scaffold or catheter prepared by the method is favorable for adhesion, proliferation and migration of seed cells, promotes nerve generation and can be used for never defect repair.
Owner:卢世璧
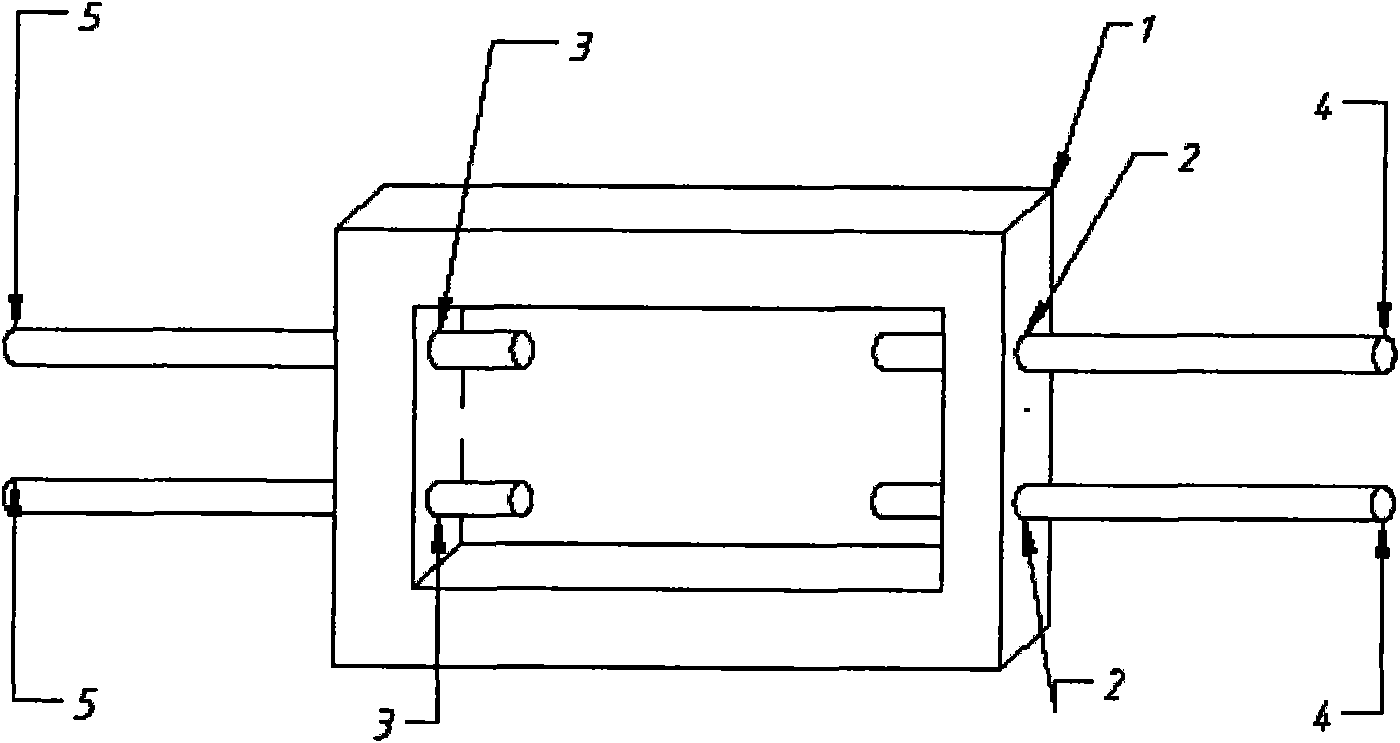
Construction method of micro point array in microchannel
InactiveCN101274469ASimple interfaceConvenient inspectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrofluidicsShell molding
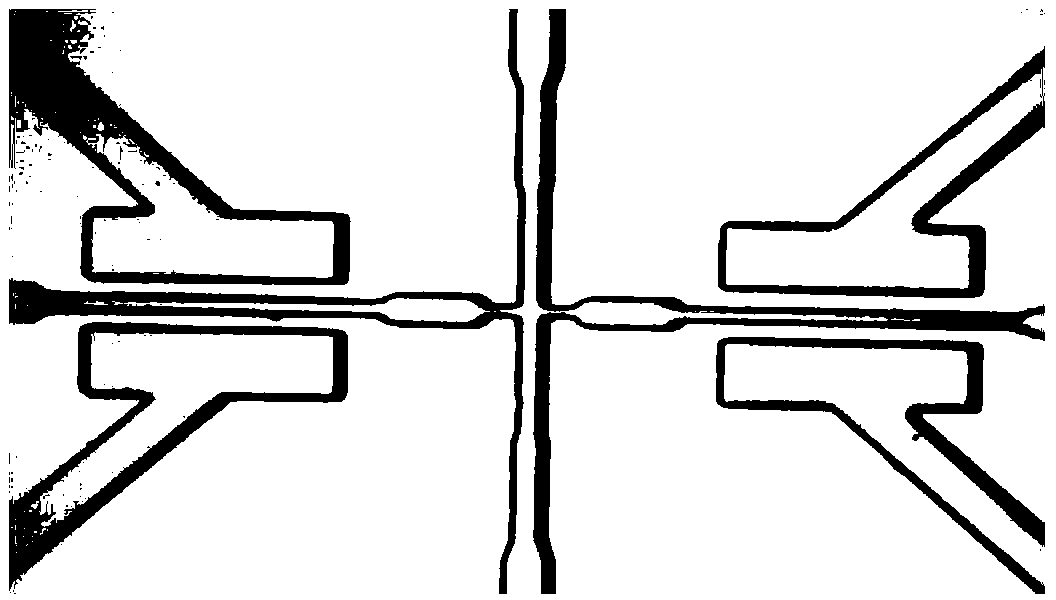
The invention provides a method for establishing a micro-point array in a micro-channel which relates to the technical field of processing of micro-channels. In the method, the main steps of arrangement, casting, etc. are adopted to cure microfilament arrays contacted in a cross manner in polymer and then the steps of demoulding, filament removal, etc. are adopted to entirely form micro-points or micro-point arrays in the micro-channel. The method of the invention is based on a molding process belonging to the soft lithography category without relying on a costly and stringent photoetching process; in addition, the method can also flexibly and differently create various surfaces, geometric shapes and sizes of different micro-point materials in different micro-flowing channels through combining and arranging material composition, geometric shapes and sizes of the crossed filaments, which results in that basic technical types of the micro-flowing and the micro-array can be closely integrated as a whole to provide a flexible and low-cost processing and manufacturing approach for the integration of the techniques of micro-fluidic control and micro-solid control.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Stent grafts
Provided is a stent graft that has superior prevention of endoleakage due to being resistant to creasing, and has superior prevention of graft migration as a result of promoting cell infiltration into gaps among microfibers in a dispersed state and forming an integrated structure with the cells in the landing zone of the stent. The stent graft according to the present invention is a stent graft comprising a stent graft fabric that has microfiber bundles consisting essentially of microfilaments having a filament linear density of 0.5 dtex or less, and said microfiber bundles having a total linear density of 10 to 60 dtex / 120 to 3000 filaments, for the warp and / or weft, and in which the porosity of the microfiber bundles is 30% to 95%, wherein said stent graft has said stent graft fabric being located in at least 1 cm range from the central end.
Owner:TERUMO KK
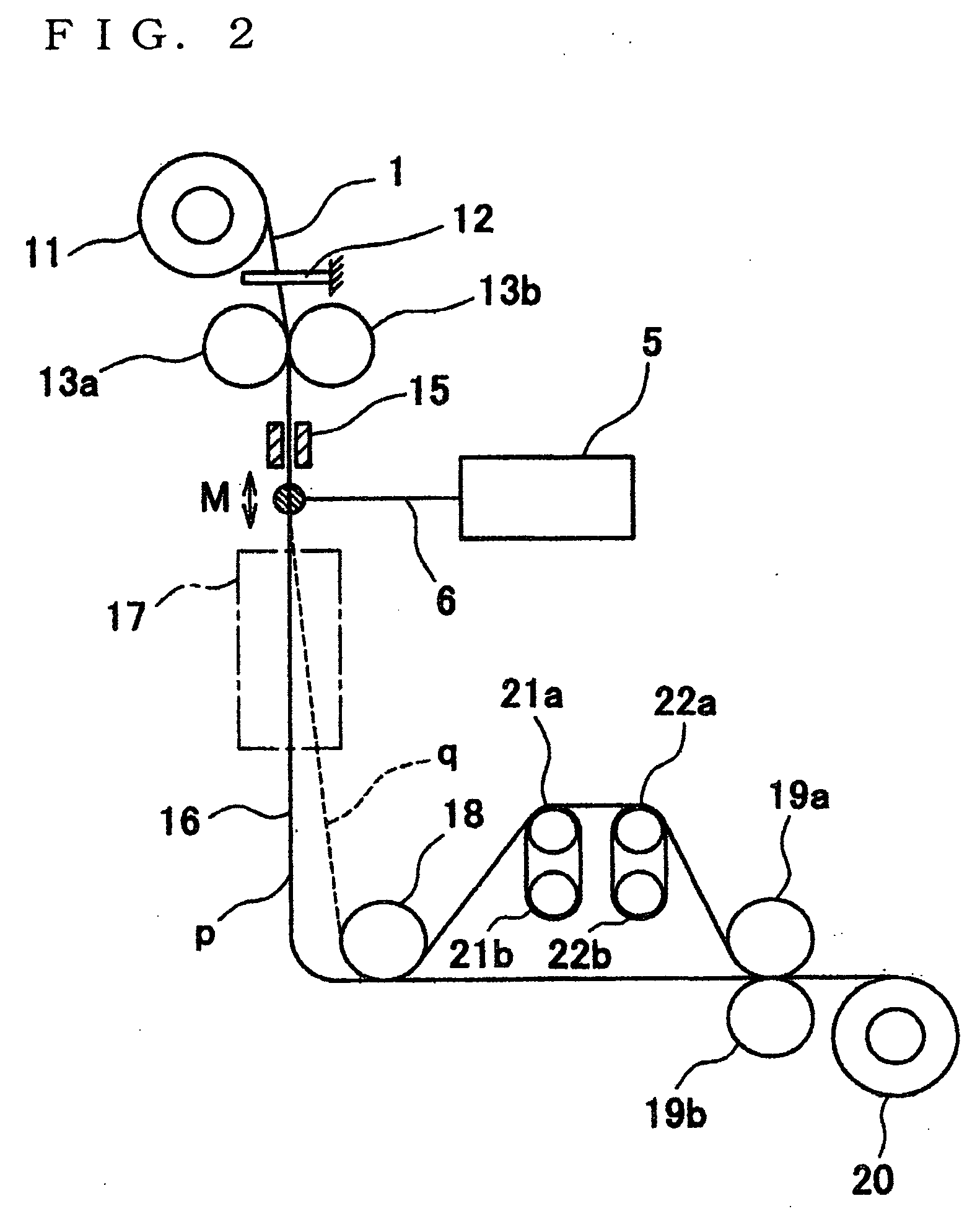
Production method and production device of ultrafine filament
ActiveUS20100148406A1Increase manufacturing costImproved molecular orientationFilament/thread formingNon-woven fabricsLight beamEngineering
The objective of the present invention is to enable a microfilament that is a nanofilament to be manufactured continuously and consistently from all thermoplastic polymers without requiring a specialized high precision.high performance apparatus and also to present the nanofilament manufactured as described. The present invention comprises a microfilament in a nanofilament region and the manufacturing means thereof wherein a original filament transferred using a filament transfer means is supplied to an orifice under pressure P1 and is heated and drawn using an infrared light beam directly under the orifice under pressure P2 (P1>P2).
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF YAMANASHI
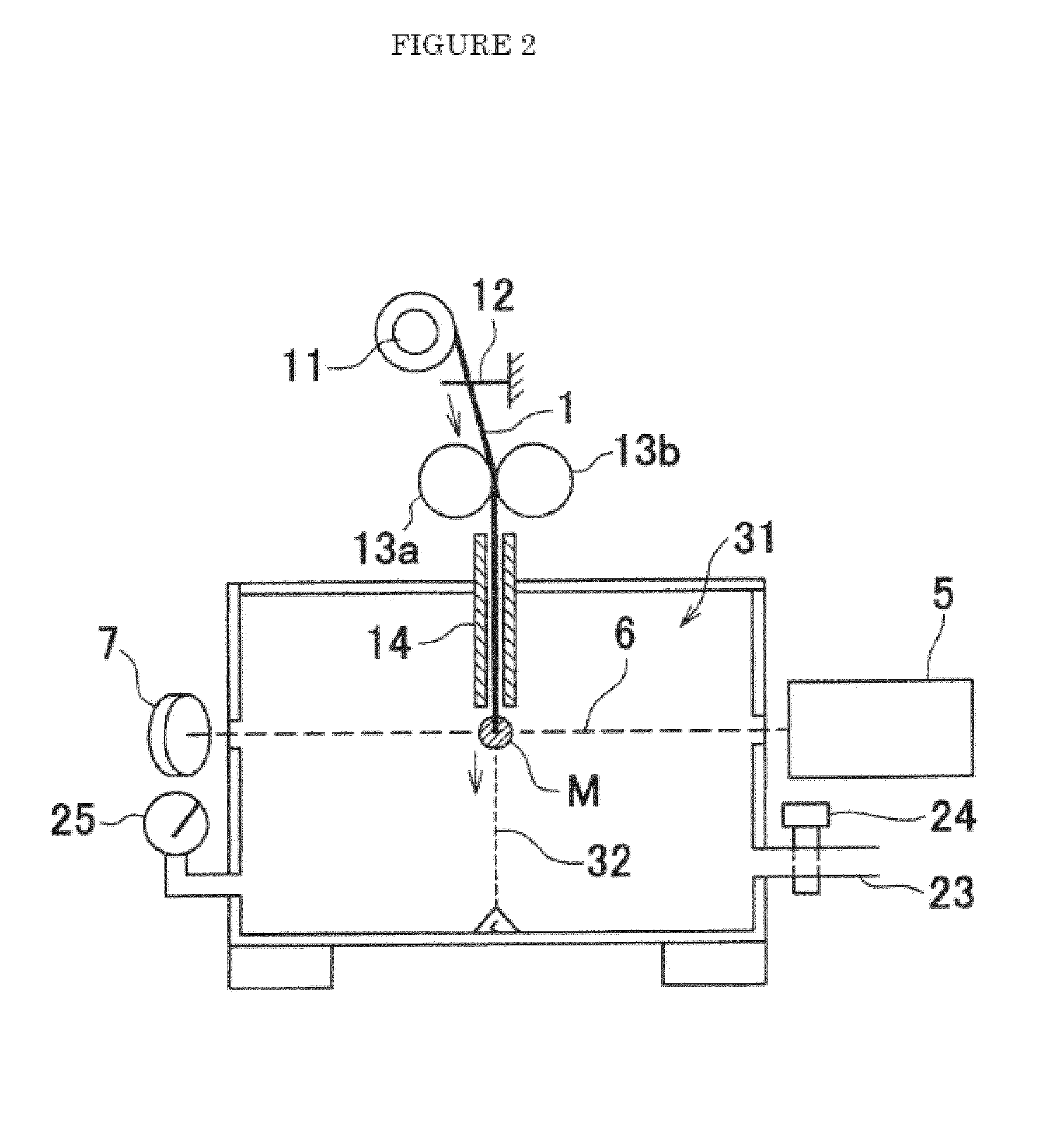
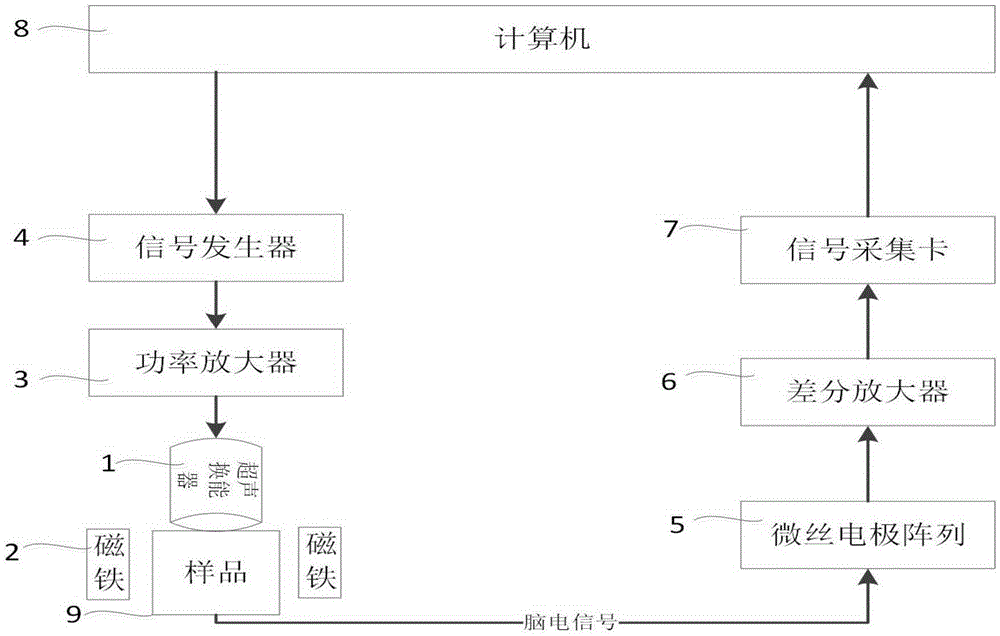
Closed-loop transcranial magnetoacoustic stimulation device
InactiveCN105251141AStimulate or inhibit activityAutomatic phase predictionUltrasound therapyElectrotherapyUltrasonic sensorClosed loop
The invention relates to a closed-loop transcranial magnetoacoustic stimulation device, which comprises a computer, a signal generator, a power amplifier, a focused ultrasonic transducer, a microfilament electrode array, a differential amplifier, a signal acquisition card and magnets, and is characterized in that the computer is communicated and connected with the signal generator through a data line, the output end of the signal generator is connected with the input end of the power amplifier through a data line, the output end of the power amplifier is connected with a signal input end of the ultrasonic transducer through a data line, the input end of the microfilament electrode array acquires cranial nerve electric signals, the output end of the microfilament electrode array is connected with the input end of the differential amplifier through a data line, the output end of the differential amplifier is connected with an A / D interface of the input end of the signal acquisition card through a data line, and the output end of the signal acquisition card is connected with the computer through a data line. A test sample is placed below the ultrasonic transducer, and two sides of the test sample are provided with the magnets respectively. The closed-loop transcranial magnetoacoustic stimulation device has the characteristics of high spatial resolution, convenient operation, accurate stimulation, no damage and the like.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Fluorescence labeling method for cotton pollen tube microfilament framework
InactiveCN101477000AOmit the step of enzymatic digestionHigh fluorescence staining efficiencyPreparing sample for investigationZoologyRefrigerated temperature
The invention relates to a method for carrying out fluorescence labeling on an actin filament framework of a cotton pollen tube, which belongs to the technical field of biology. The method comprises: perforating a glass slide to make a chamber for cultivating the pollen tube; cultivating pollen in the chamber to bourgeon the pollen tube; fixing the cultivated pollen tube by 50mm Pipes buffer solution (pH6.9) containing 4 percent of paraformaldehyde for 1 to 2 h; washing the pollen tube, and putting the pollen tube into 0.1 to 0.2 percent glycerin (or 0.1 to 0.2 percent Triton X-100) for 3 to 4 h at a room temperature (or over night in a 4 DEG C refrigerator); washing the pollen tube, and staining the pollen tube through a phalloidine labeled by TRITC(rhodamine) with the concentration of 1 to 2.5 mu g / ml; and washing the pollen tube, and then observing the pollen tube under a confocal scanning microspope. The method has the advantages of simple operation, good labeling effect and important practical application value, and can play an important part in researching the framework of a cotton pollen tube cell and fertilization reproduction.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of agarose gel microfluidic device
InactiveCN101856629AImprove sealingHigh recovery rateLaboratory glasswaresChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesConcentration gradientBiochip
The invention relates to the field of making biochips, in particular to a preparation method of an agarose gel microfluidic device. Particularly, the agarose gel microfluidic device is prepared by three steps of assigning microfilaments, pouring and solidifying, and wiredrawing. The agarose gel microfluidic device manufactured by the method has good sealing property, and the recovery rate of liquid is up to 95%. The agarose gel microfluidic device manufactured by the method can generate stable concentration gradients, and is used for observing interaction between cells and biochemical micro-environments, especially the interaction under a flow condition. The method has simple operation, and the microfluidic device can be manufactured in an ordinary lab without expensive precision instruments.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
Labeling method of apple pollen tube microfilament
The invention discloses a labeling method of an apple pollen tube microfilament. The labeling method comprises the following steps: cultivating apple pollen, curing the apple pollen, performing enzyme treatment on the apple pollen, treating the apple pollen with a surfactant, performing dye labeling, and performing scanning and imaging. The labeling method has the beneficial effect that the labeling method of gymnosperm pollen tube microfilament is referred and improved on the basis of the labeling method of pear pollen tube microfilament, dyes enter cells easier through curing, enzymolysis of cell walls and the surfactant, the interference of cell outer wall autofluorescence due to insufficient enzymolysis as TRITC-Phalloidin is applied are avoided when FITC-Phalloidin labeling is applied, so that relatively complete apple pollen tube microfilament can be stored; moreover, the labeling method is efficient and quick, can be used for obtaining relatively clear and bright pictures, thus filling up the blank of the apple pollen tube microfilament labeling, providing reference for labeling microfilament in rosaceae and angiosperm pollen tube, and achieving a high application value.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Tissue engineering nerve graft with suspension fiber scaffold and preparation method thereof
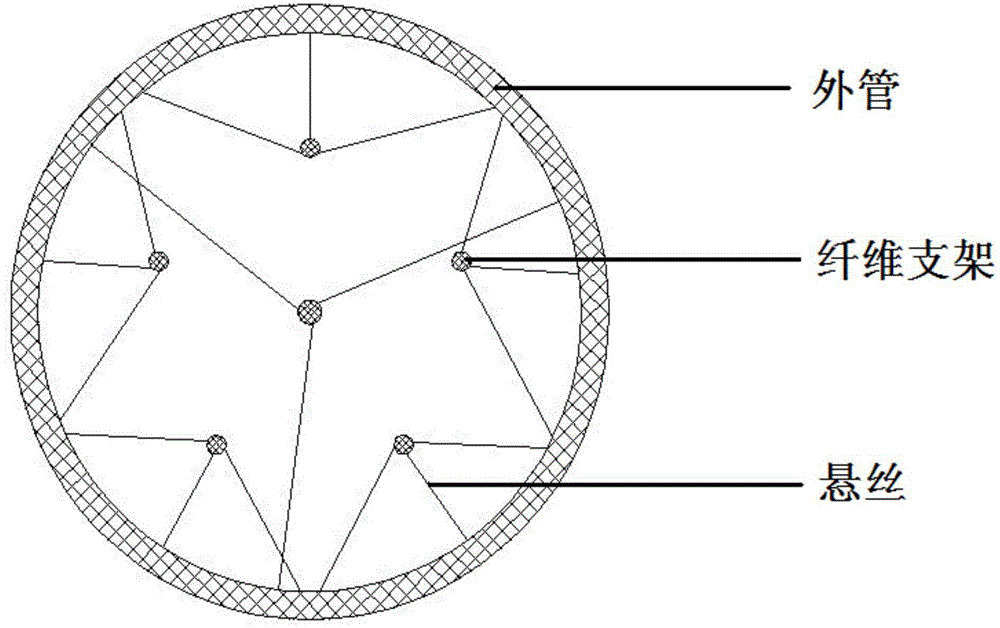
The invention discloses a tissue engineering nerve graft with a suspension fiber scaffold. The nerve graft comprises a conduit and tube fiber scaffolds. The nerve graft is characterized in that a plurality of suspensions are arranged on each fiber scaffold along the fiber length direction, and are connected with the inner wall of the conduit; and the fiber scaffolds are distributed and suspended in the conduit by virtue of the suspensions. By utilizing bio-printing technology, built-in microfilaments of a tissue engineering nerve graft can be stably and uniformly distributed in the conduit by utilizing the supporting force of the suspensions, and each fiber scaffold has an independent space to guarantee that nerve cells can directionally grow along the fiber scaffolds and cannot have error bridging, so that the success rate of operations can be greatly improved.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
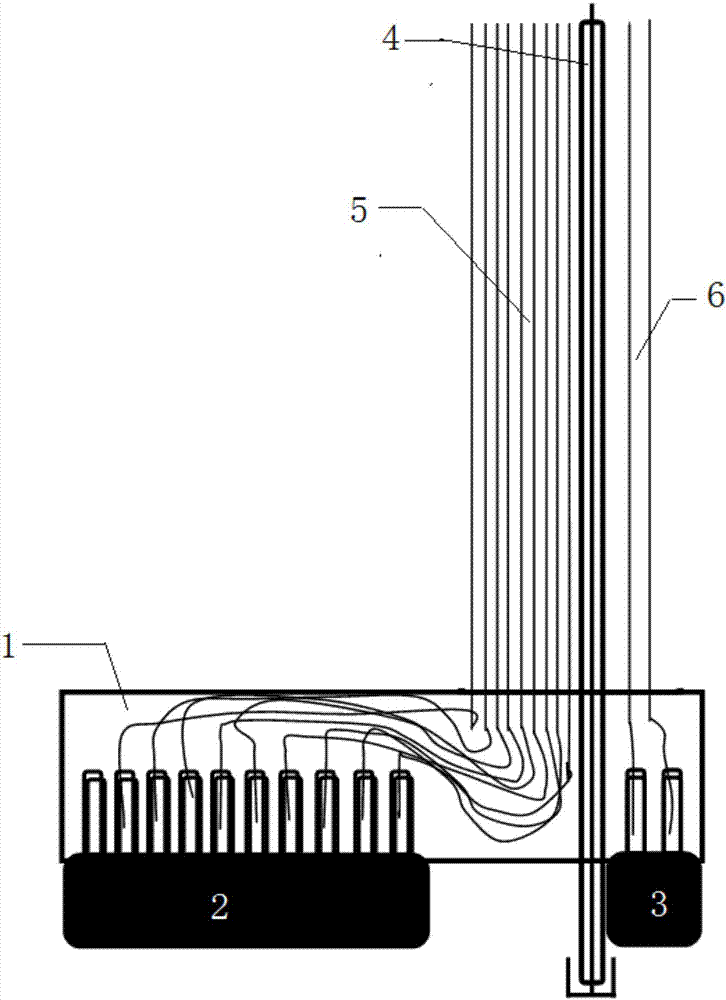
Rat-intracranial-implantation microfilament array electrode suitable for experiment and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106983953ALow costHead electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringBiochemical engineeringElectrode array
The invention discloses a rat-intracranial-implantation microfilament array electrode suitable for an experiment and a manufacturing method thereof. The electrode is formed by a plurality of electrode microfilaments, a dosing conduit and the like. The electrode microfilaments are arranged in parallel and form a microfilament measurement electrode array and a microfilament stimulation electrode array respectively. The electrode manufactured through using the method of the invention can simultaneously realize three functions of experiment rat brain electric signal recording, electrical stimulation and drug stimulation. According to a specific demand, one or any two functions can be selected. And self-manufacturing can be completed with low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CHINESE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Gumnosperm pollen tube microfilament framework fluorescent marking method and its uses
The invention discloses a method for fluorescence labeling of gymnosperm pollen tube fibril bone and its application and is to provide a method for fluorescence labeling of gymnosperm pollen tube fibril bone and the application of this method in microscope inspection of gymnosperm pollen tube fibril bone. The said labelling method includes the following steps: 1) fixing the gymnosperm pollen tube with 40-60mM Pipes cushion solution containing 2-4 % cavaform; 2) washing the pollen tube; 3) placing the pollen tube in 0.2-0.3 % glycerin to infiltrate for 30-60min; 4) washing the pollen tube; 5) dyeing the pollen tube and avoiding the sun with 150-250nM phalloidine by fluorescence labeling for 0.5-1.5h and fluorescence labeling the fibril bone. The invention is of simple operation and is quick, has small damage to the cells, and has good labeling effect, which will play an important role in study gymnosperm pollen tube cell bone and have a high actual application value.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com