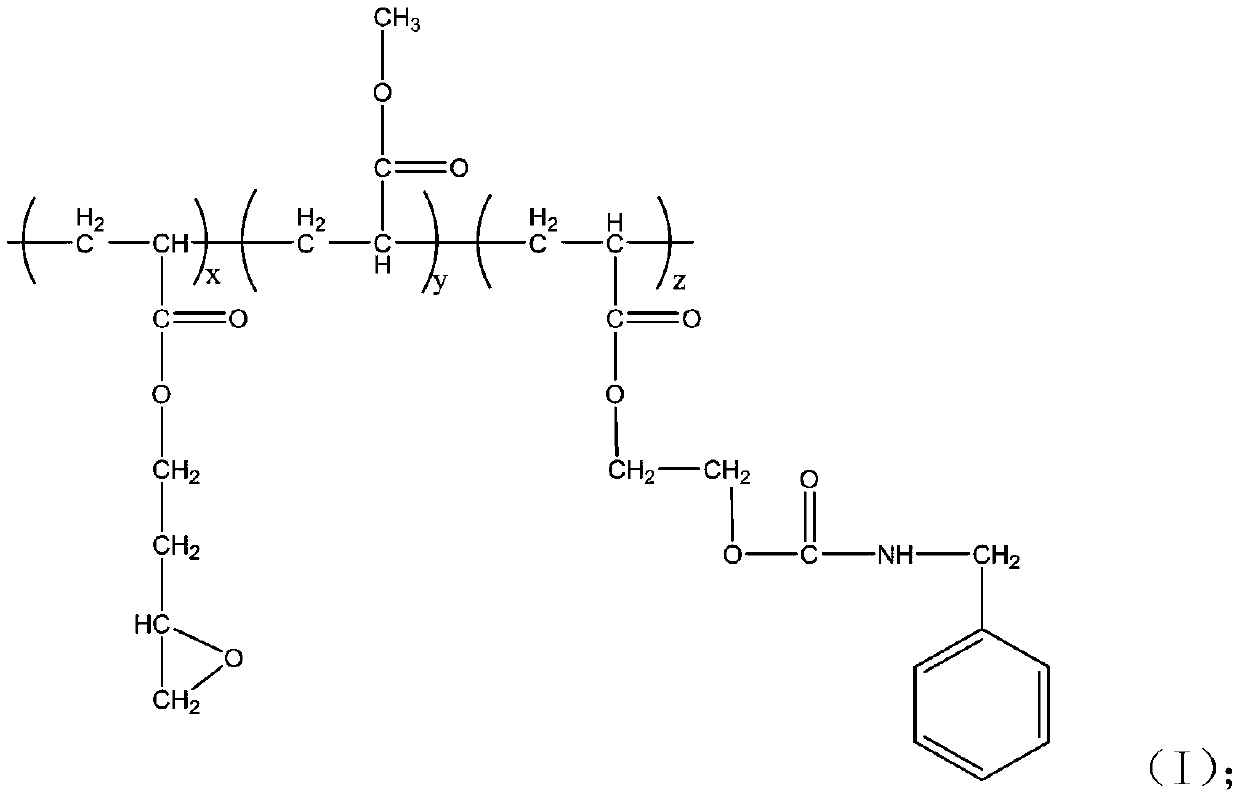
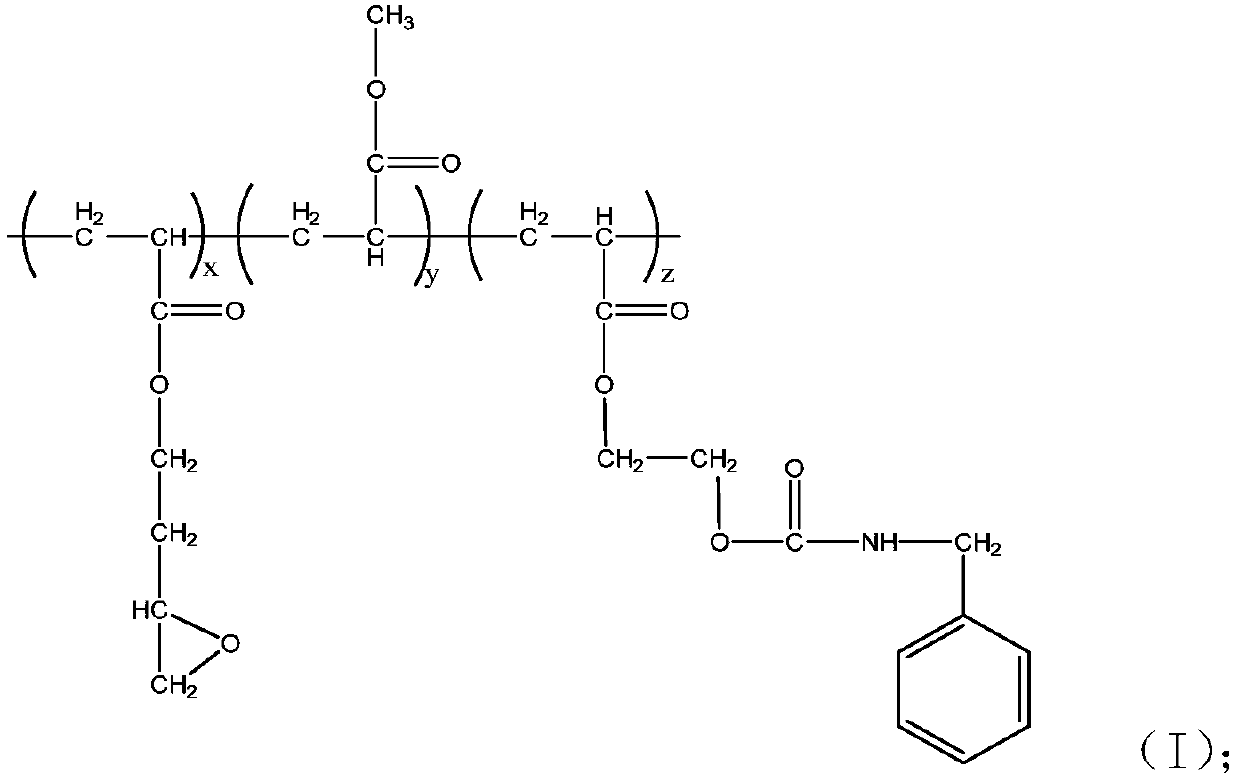
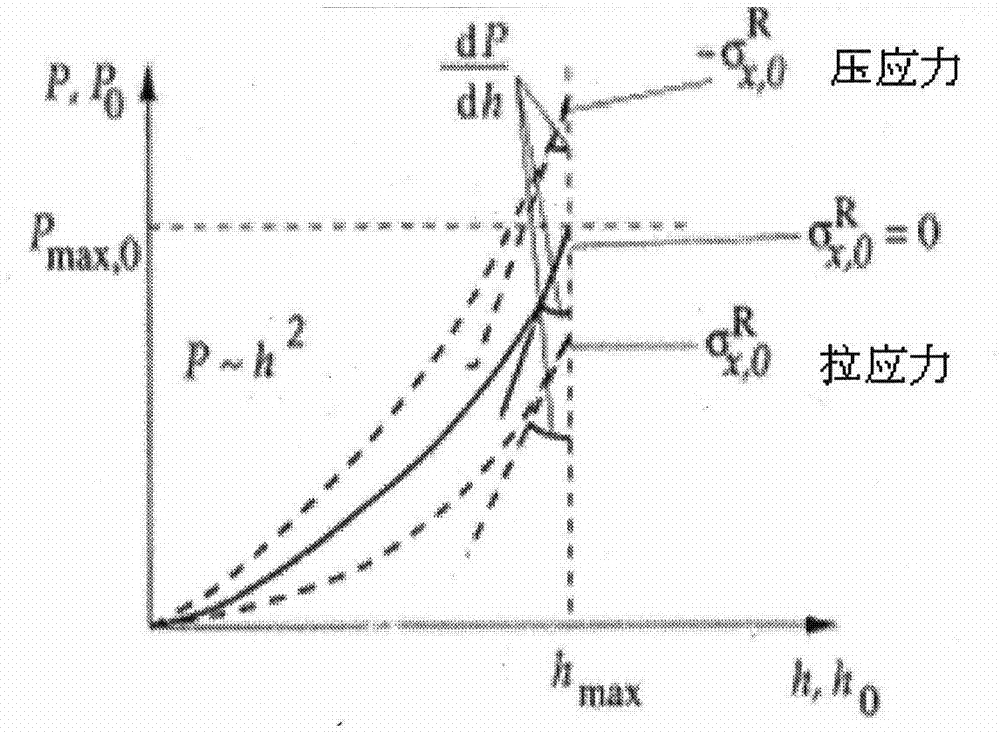
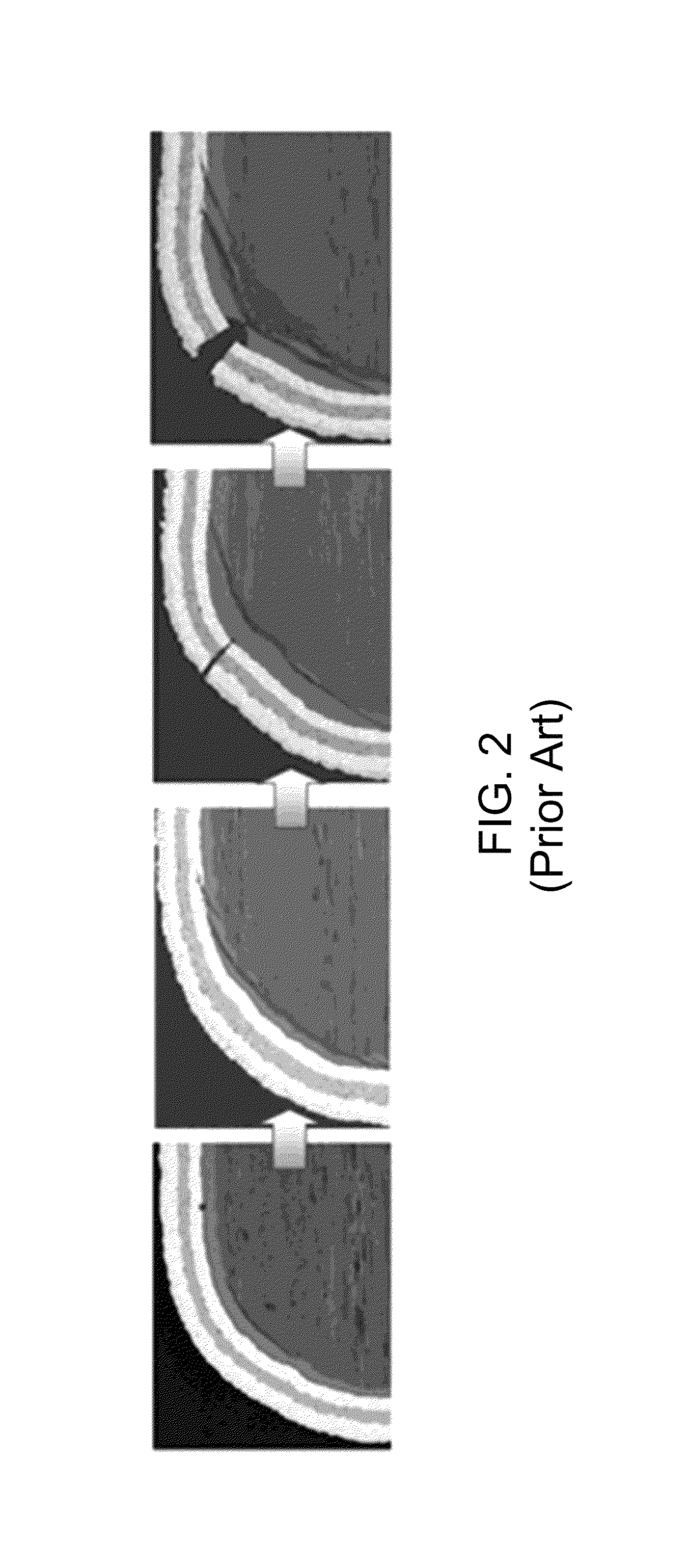
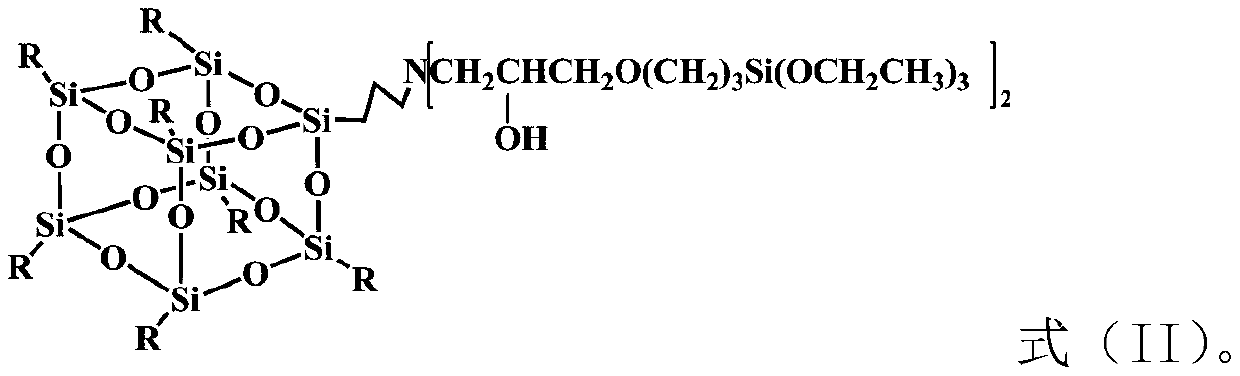Patents
Literature
77 results about "Interfacial stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
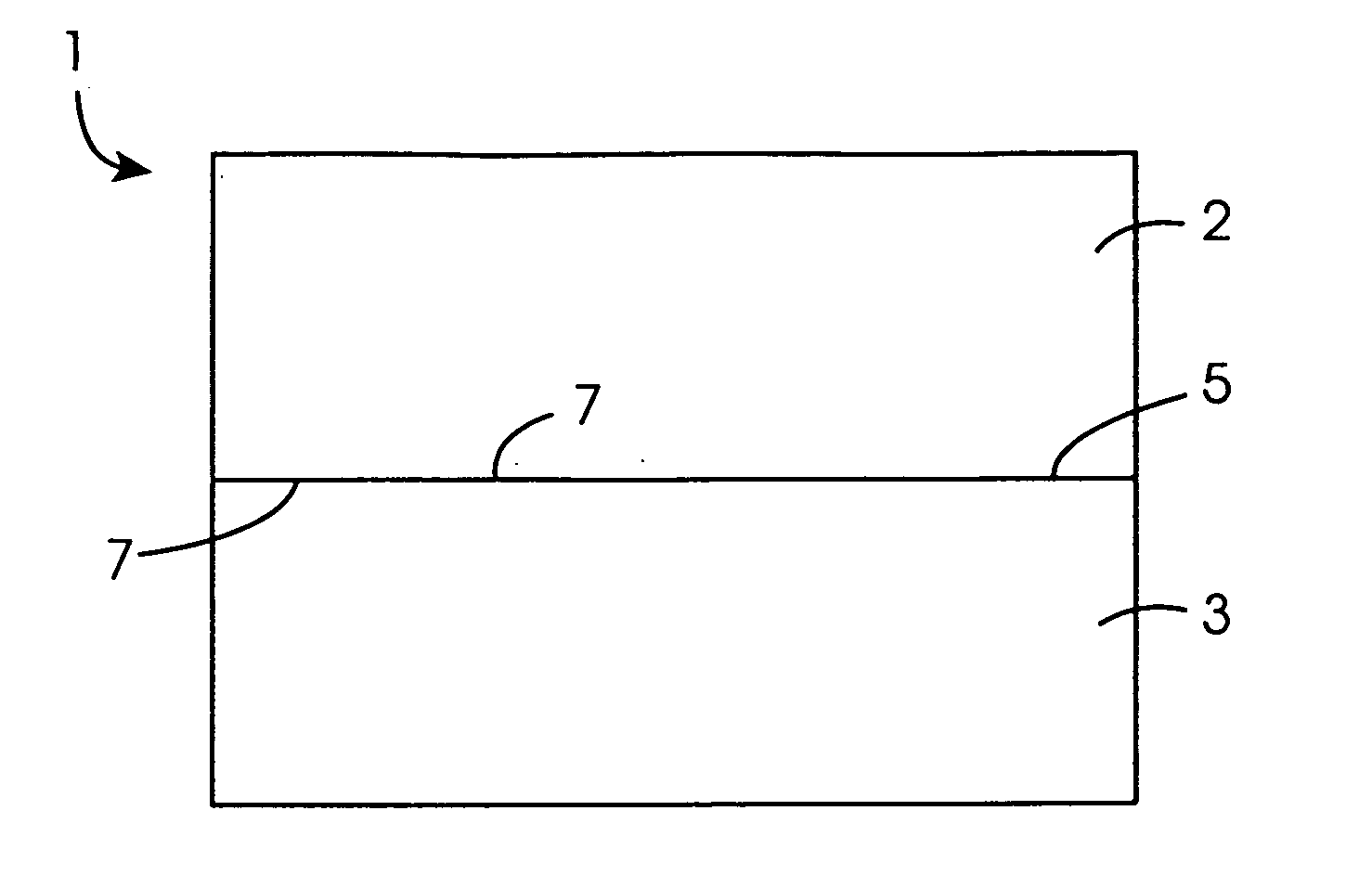
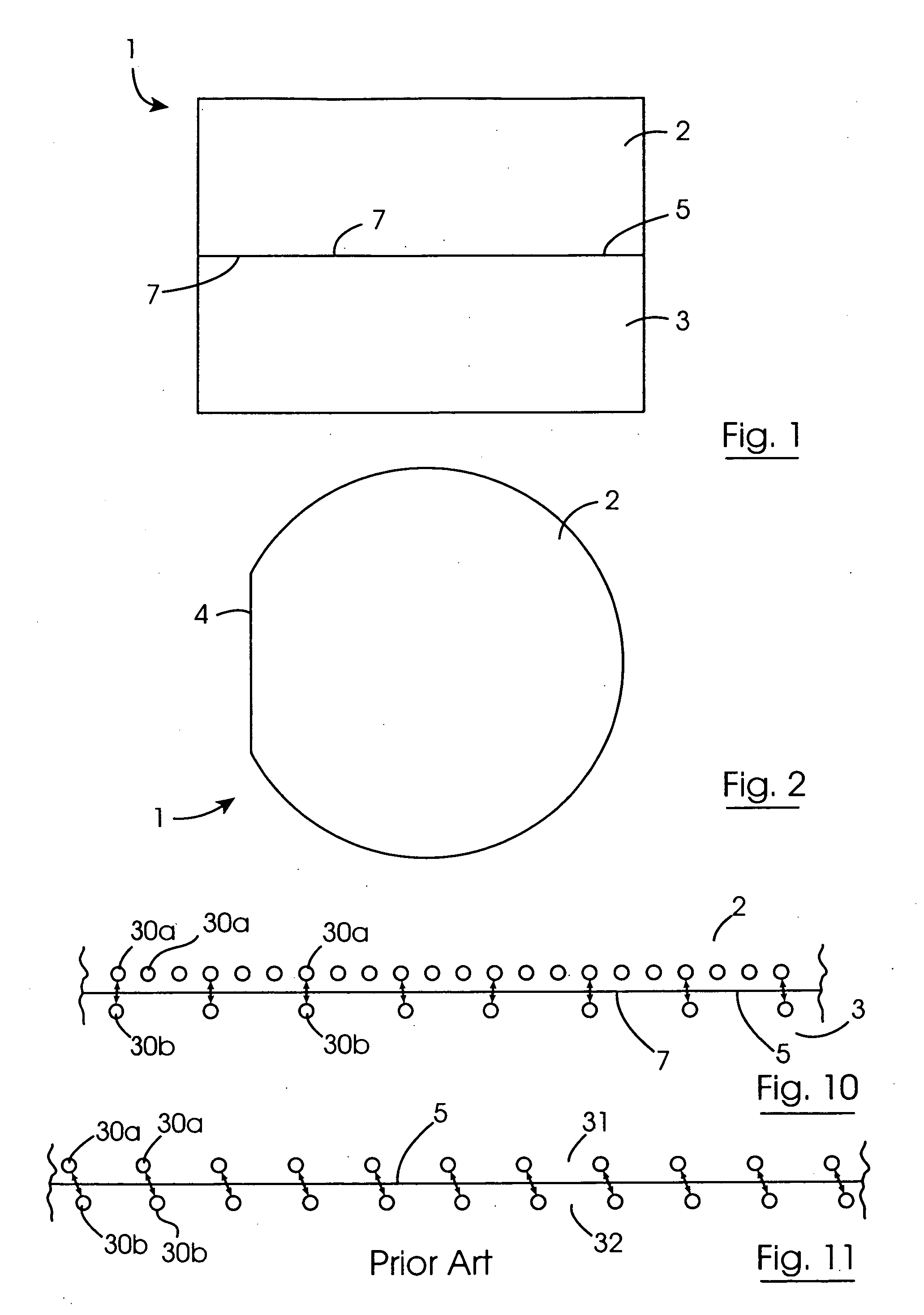
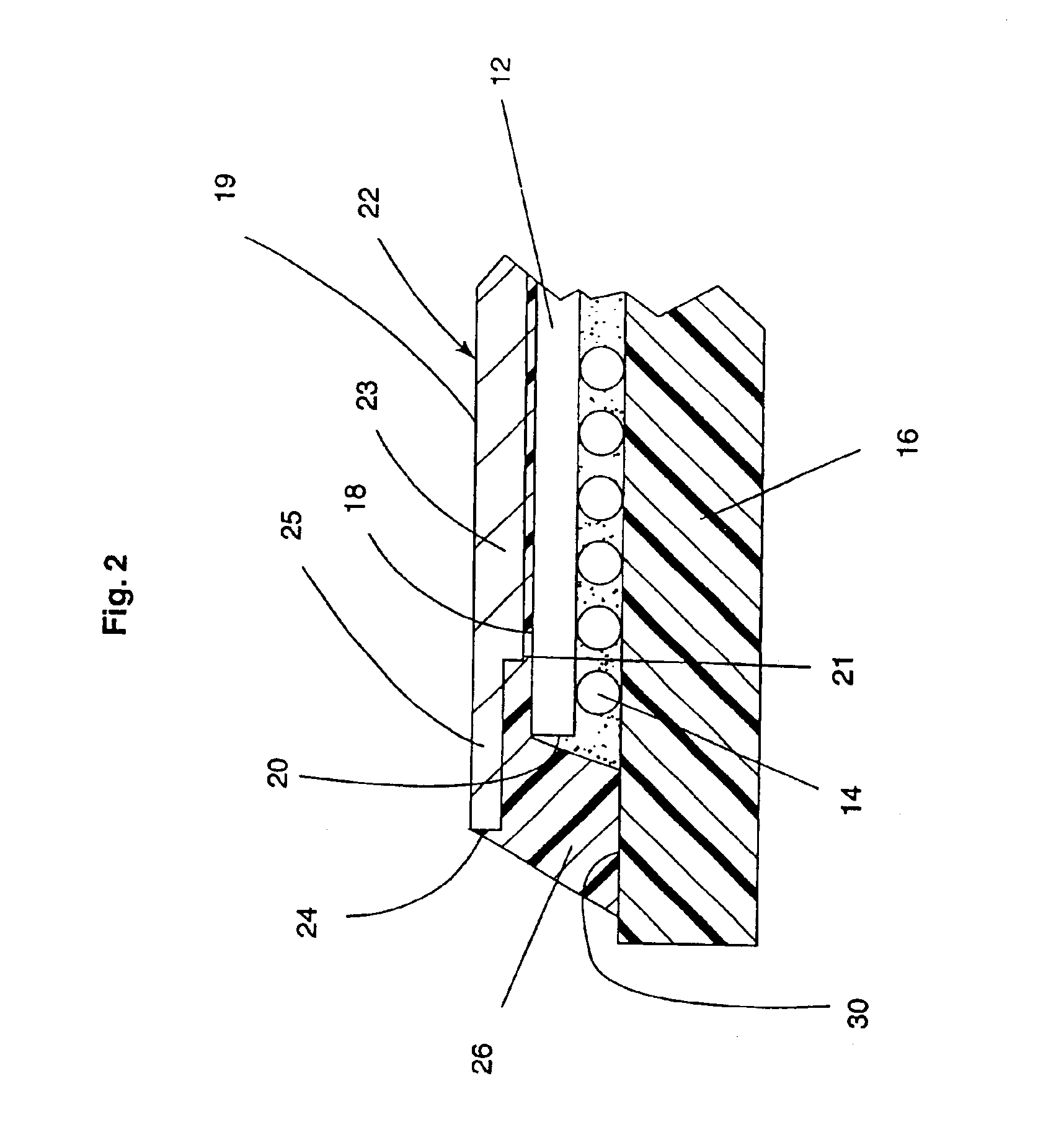
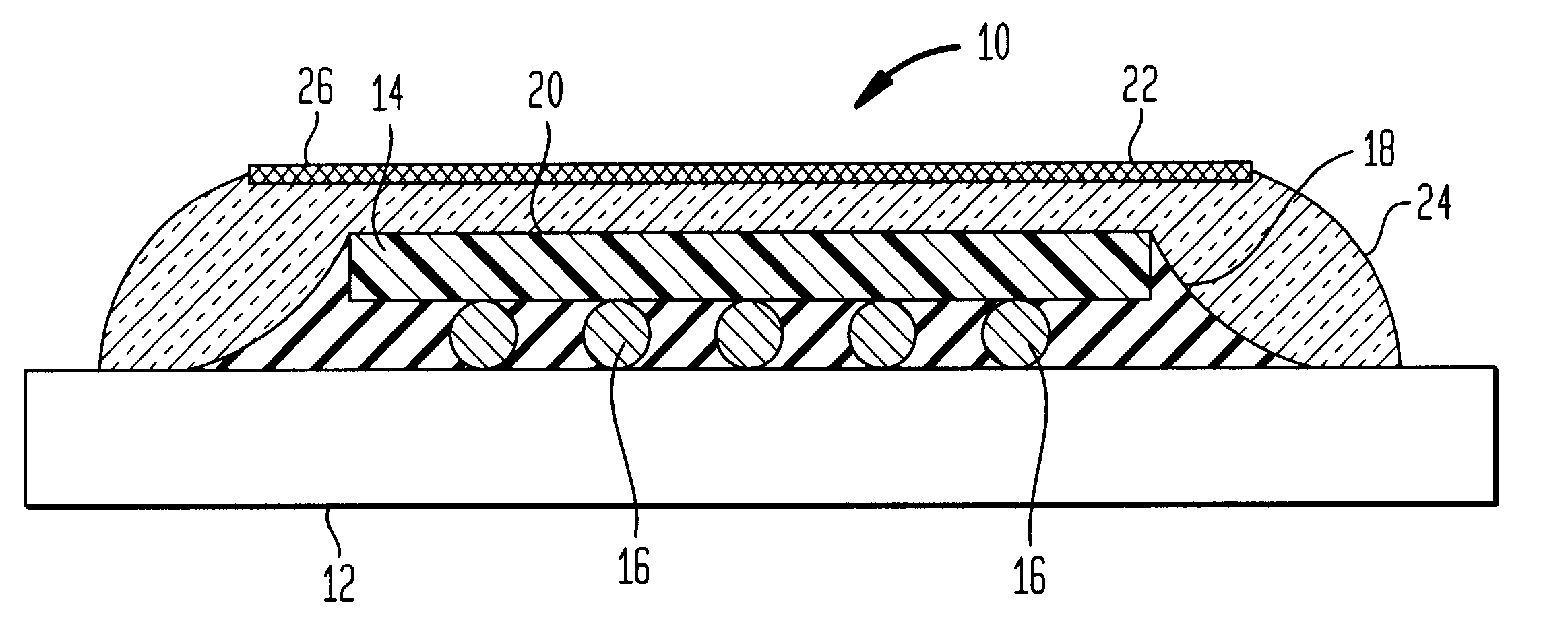
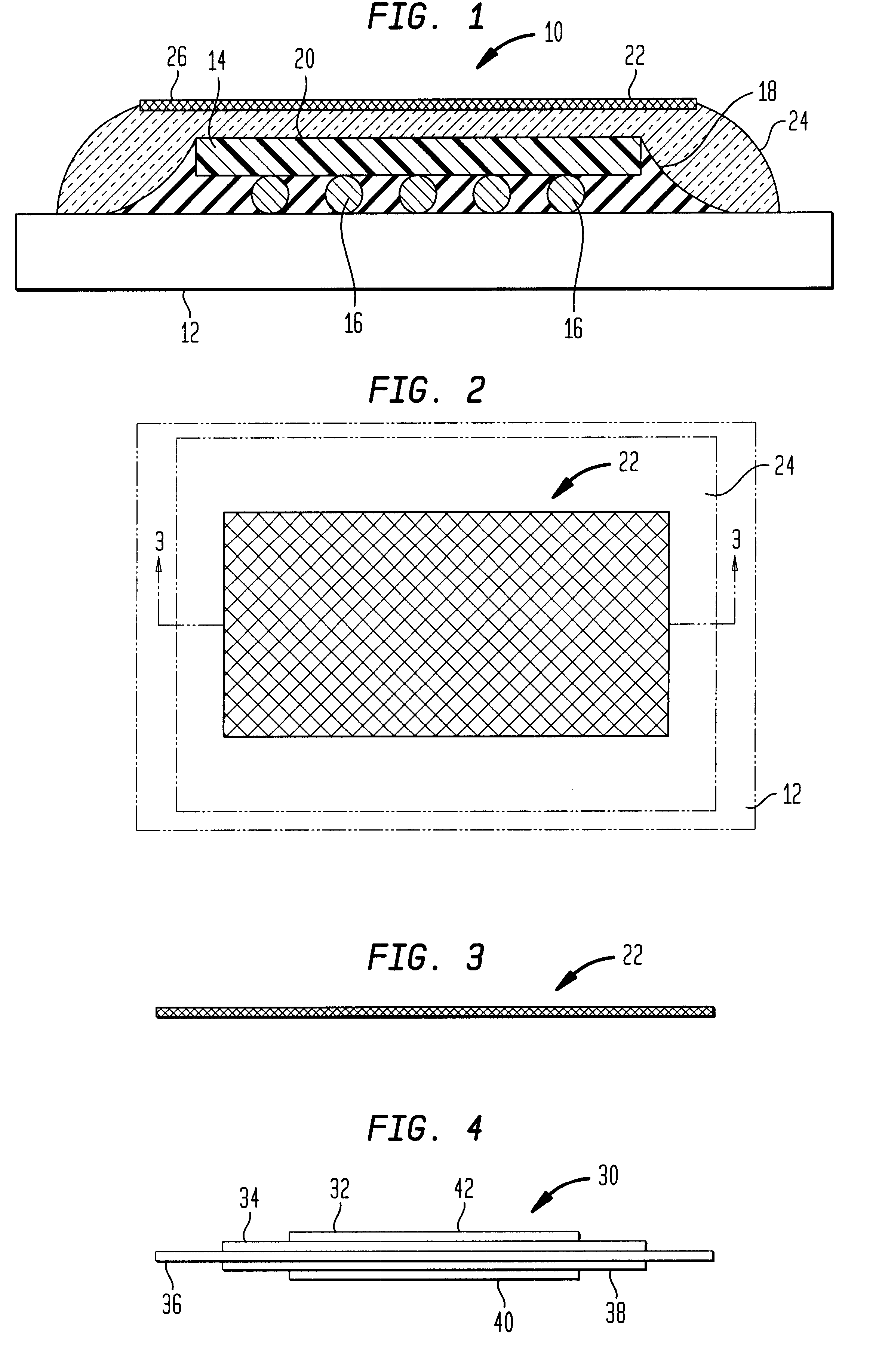
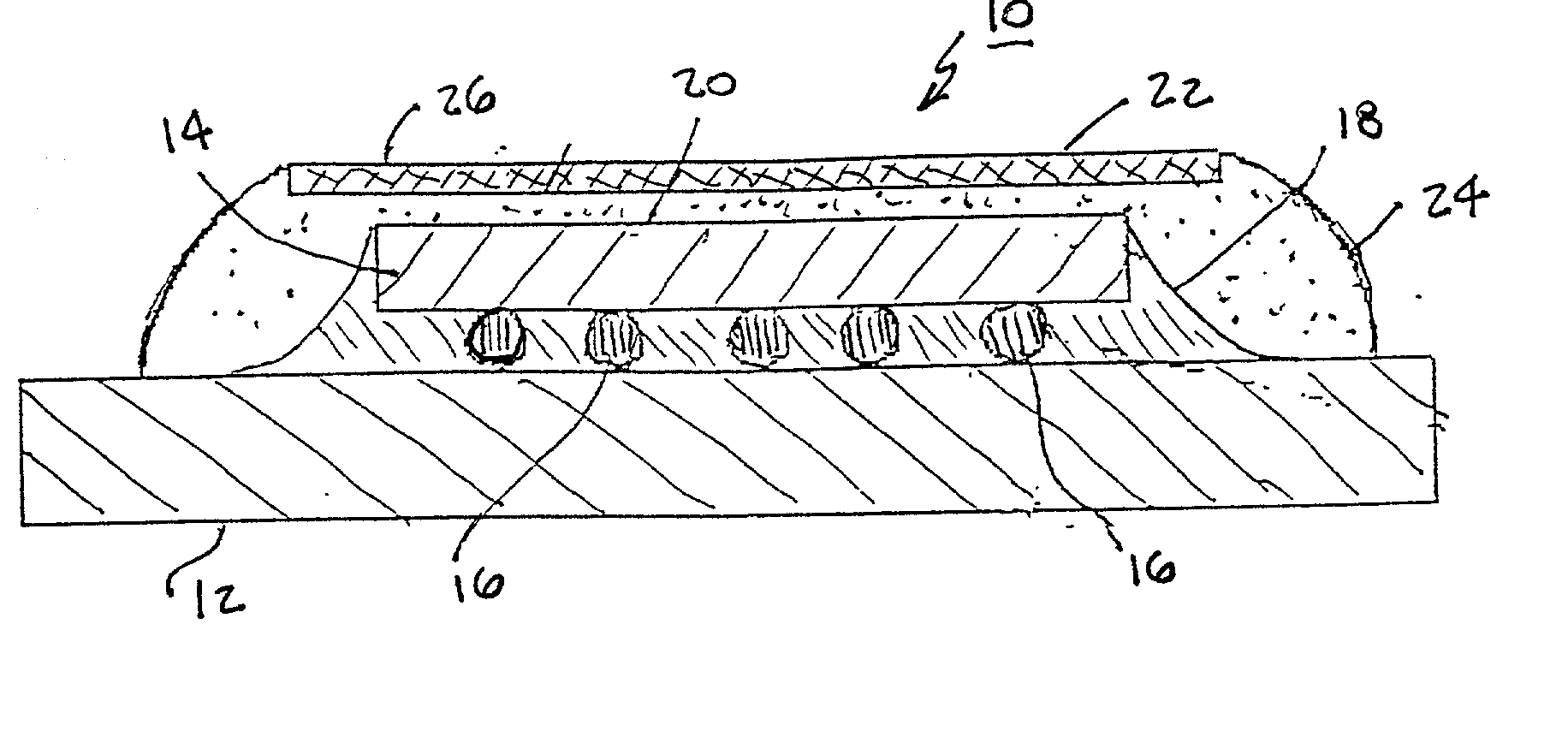
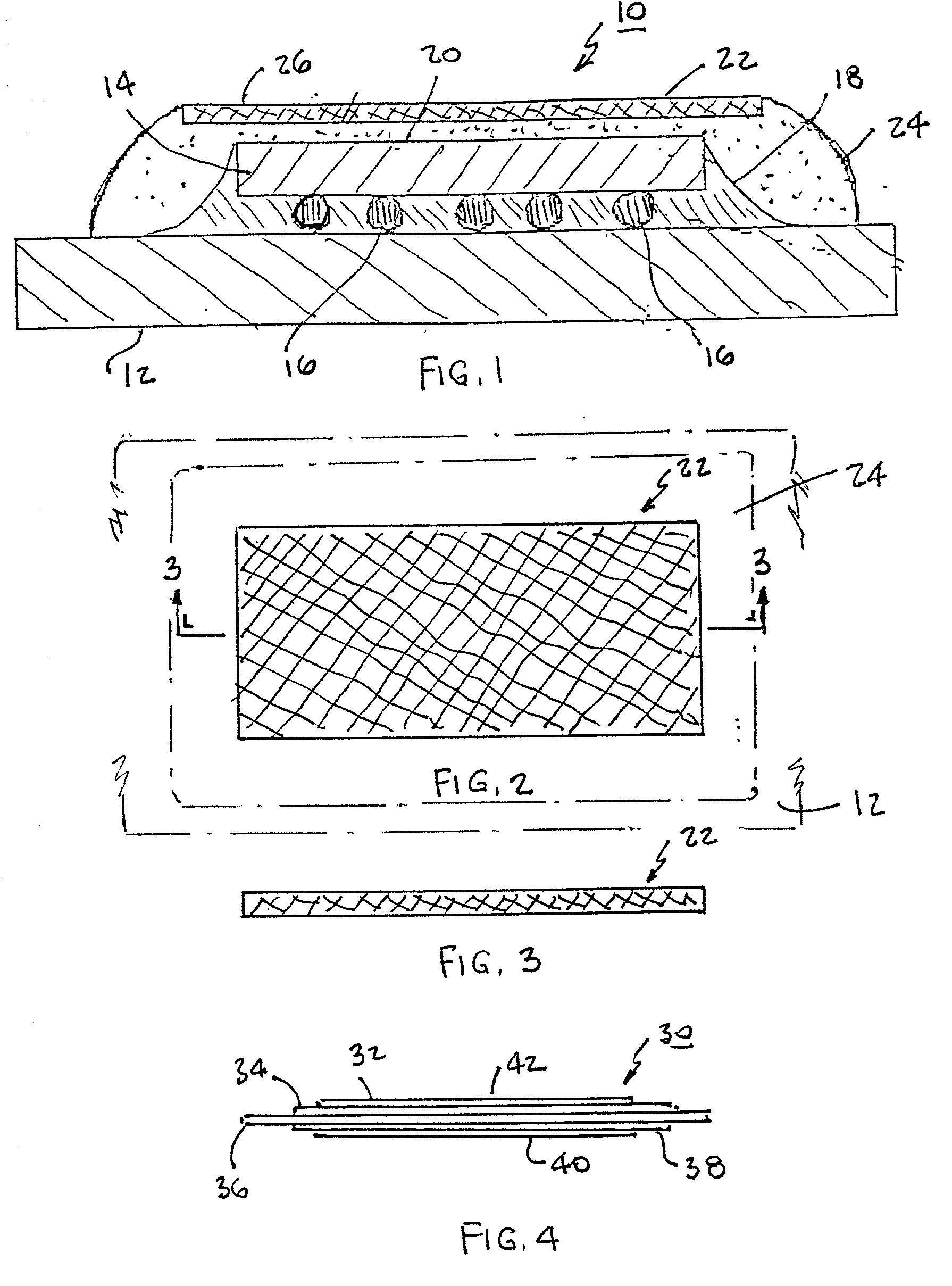
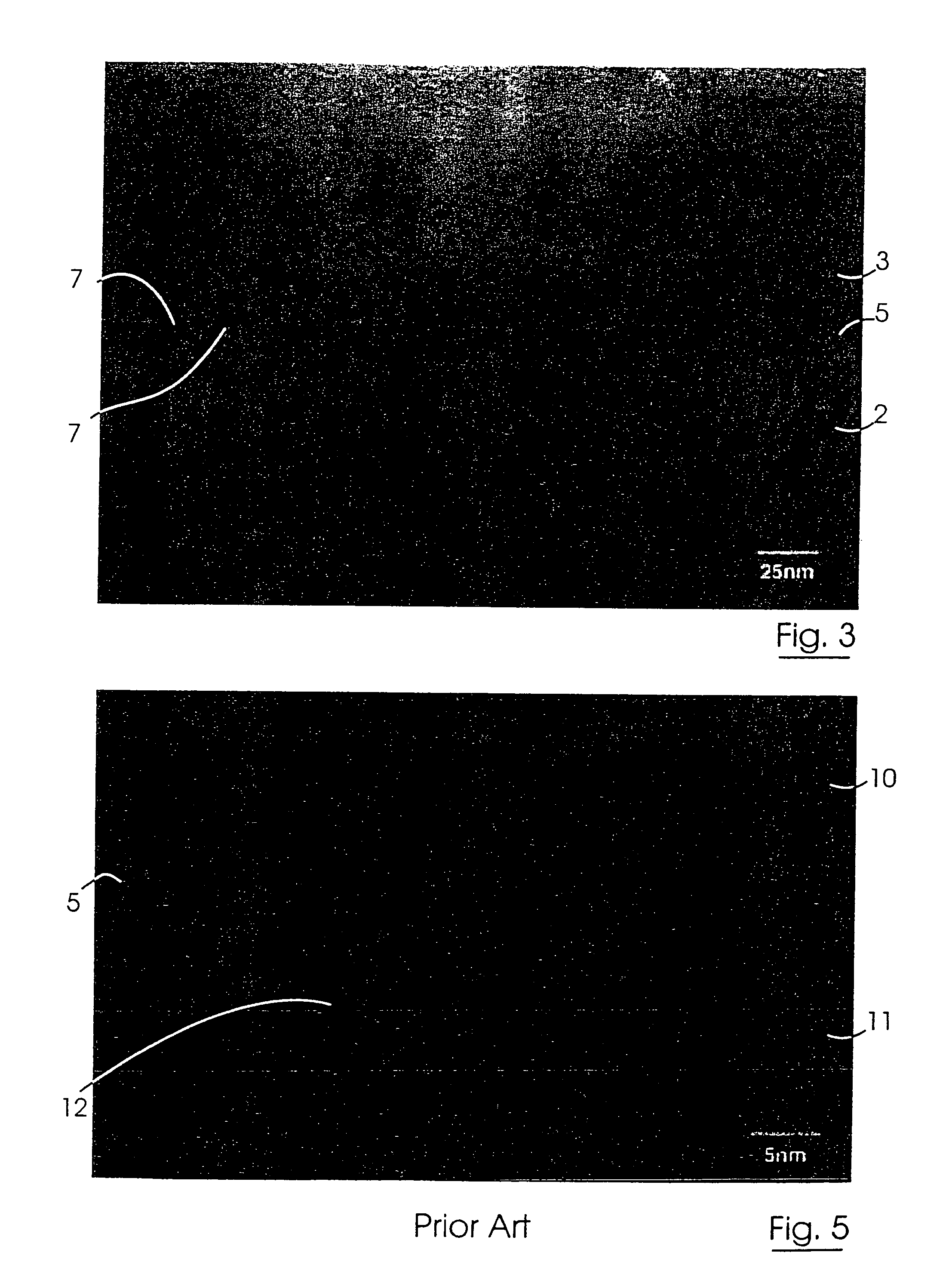
Method for direct bonding two silicon wafers for minimising interfacial oxide and stresses at the bond interface, and an SOI structure
InactiveUS20040087109A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInterfacial oxideBond interface
A semiconductor substrate (1) comprises first and second silicon wafers (2,3) directly bonded together with interfacial oxide and interfacial stresses minimised along a bond interface (5), which is defined by bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3). Interfacial oxide is minimised by selecting the first and second wafers (2,3) to be of relatively low oxygen content, well below the limit of solid solubility of oxygen in the wafers. In order to minimise interfacial stresses, the first and second wafers are selected to have respective different crystal plane orientations. The bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3) are polished and cleaned, and are subsequently dried in a nitrogen atmosphere. Immediately upon being dried, the bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3) are abutted together and the wafers (2,3) are subjected to a preliminary anneal at a temperature of at least 400° C. for a time period of a few hours. As soon as possible after the preliminary anneal, and preferably, within forty-eight hours of the preliminary anneal, the first and second wafers (2,3) are fusion bonded at a bond anneal temperature of approximately 1,150° C. for a time period of approximately three hours. The preliminary anneal may be omitted if fusion bonding at the bond anneal temperature is carried out within approximately six hours of the wafers (2,3) being abutted together. An SOI structure (50) may subsequently be prepared from the semiconductor structure (1) which forms a substrate layer (52) supported on a handle layer (55) with a buried insulating layer (57) between the substrate layer (52) and the handle layer (55).
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Post-treating method for steel-back aluminium-based semisolid-state clad plate
InactiveCN101117696AIncreased interfacial shear strengthSimple methodRoll mill control devicesMetal rolling arrangementsReduction rateRoom temperature
The present invention discloses a post-processing method for steel-back aluminum-base semisolid composite plates and relates to the post-processing research field of interfacial mechanical characteristic of steel-back aluminum-base semisolid composite plates. At room temperature, a steel-back aluminum-base semisolid composite plate is rolled with the reduction rate of 0.5-1.6 percent on a precision rolling mill, and the difference between shrinkages of the aluminum-base coating and the steel base in the coagulating and cooling process of the composition is redeemed by the difference between the deformation of the aluminum-base coating and the steel base produced in the rolling process, thereby, reducing the additional interfacial stress of the composite plate, simply and conveniently improving the interfacial shear strength of the composite plate, and solving the technical problems of large energy consumption and small increase amplitude of interfacial shear strength in post-processing method of diffusion annealing of aluminum-base semisolid composite plates.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Polycrystalline diamond composite sheet
ActiveCN102174877AImprove interface integrationImprove wear resistanceDrill bitsMetal layered productsPolycrystalline diamondAlloy
The invention discloses a polycrystalline diamond composite sheet. In the polycrystalline diamond composite sheet provided by the invention, a polycrystalline diamond layer is not directly combined with a hard alloy layer, but a transitional layer is added between the polycrystalline diamond layer and the hard alloy layer. The transitional layer can be a single layer or formed by multiple layers,and the compositions of the transitional layer are different from one another according to different purposes. The transitional layer is added between the polycrystalline diamond layer and the hard alloy layer, so that the interface combination condition of the polycrystalline diamond composite sheet can be improved, interfacial stress can be reduced, and the abrasion resistance and the impact-resistant toughness of the polycrystalline diamond composite sheet can be synchronously improved.
Owner:中山市海明润超硬材料有限公司
Electronic package and method of forming
InactiveUS6933619B2Economically mass producedMinimize interfacial stressSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipEngineering
An electronic package and method of making same in which a thermally conductive member is in thermally conductive communication with a semiconductor chip encapsulated within a dielectric material that surrounds portions of a thermally conductive member, semiconductor chip, and a predefined portion of a circuitized substrate. The present invention's thermally conductive member includes two portions of different bending stiffness to assure reduced interfacial stresses between the semiconductor chip and the circuitized substrate.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Multi-bit encoded glass-coated microwire and articles composed thereof
InactiveUS20050109435A1Eliminate needInorganic material magnetismGlass/slag layered productsGratingFluorescence
A glass-coated amorphous metallic microwire is encoded with multi-bit digital information. Encoding is achieved magnetically, optically or through a combination of magnetic and optical encoding processes. Magnetic encoding is carried out by modifying the constituent magnetic domain structure through selective relief of interfacial stress between the glass coating and the amorphous metallic alloy core. It is also achieved by selective surface crystallization of the amorphous metallic core in order to produce a controlled magnetic bias field. Optical encoding is associated with the glass coating. It is readily achieved by fluorescent element deposition, patterned removal of fluorescent element coating, Bragg grating, and thermally activated pattern deposition. The magnetic and optical multi-bit encoding approaches for glass-coated amorphous metallic microwire can be used individually or collectively in either a redundant or a complementary manner. Encoded microwire of the instant invention can be assembled into tags for electronic article surveillance and into numerous other structures as well.
Owner:DEMODULATION
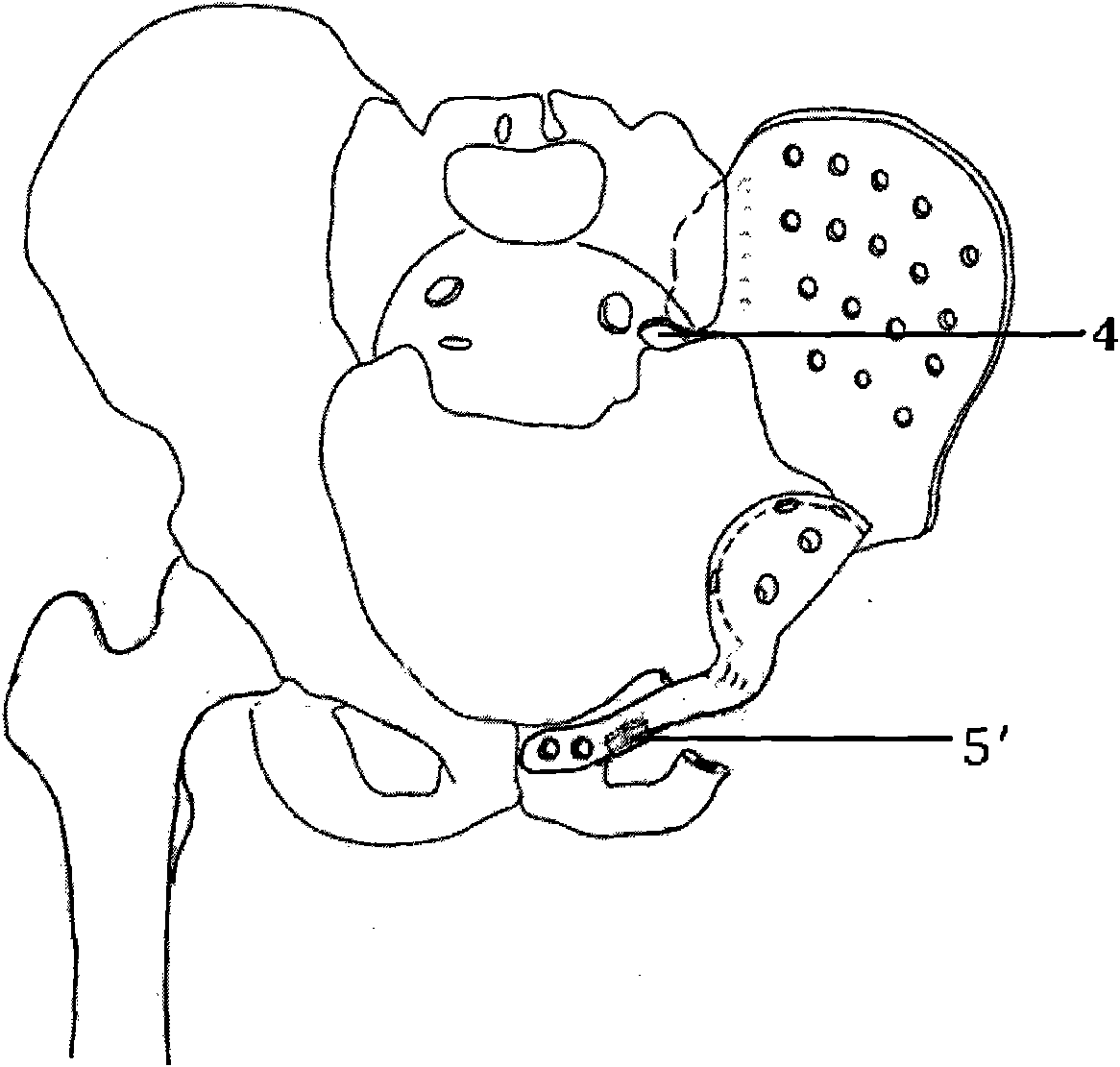
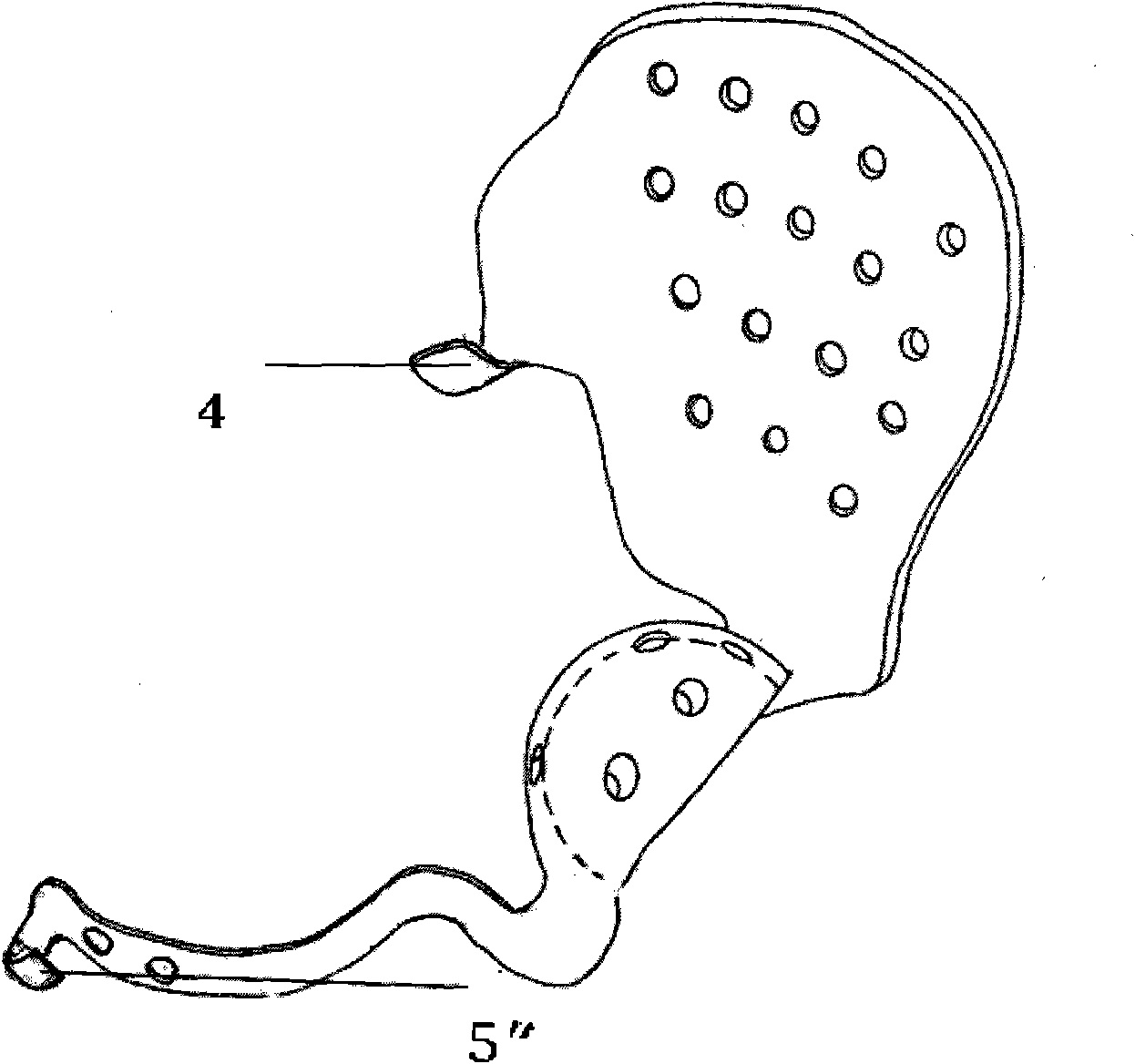
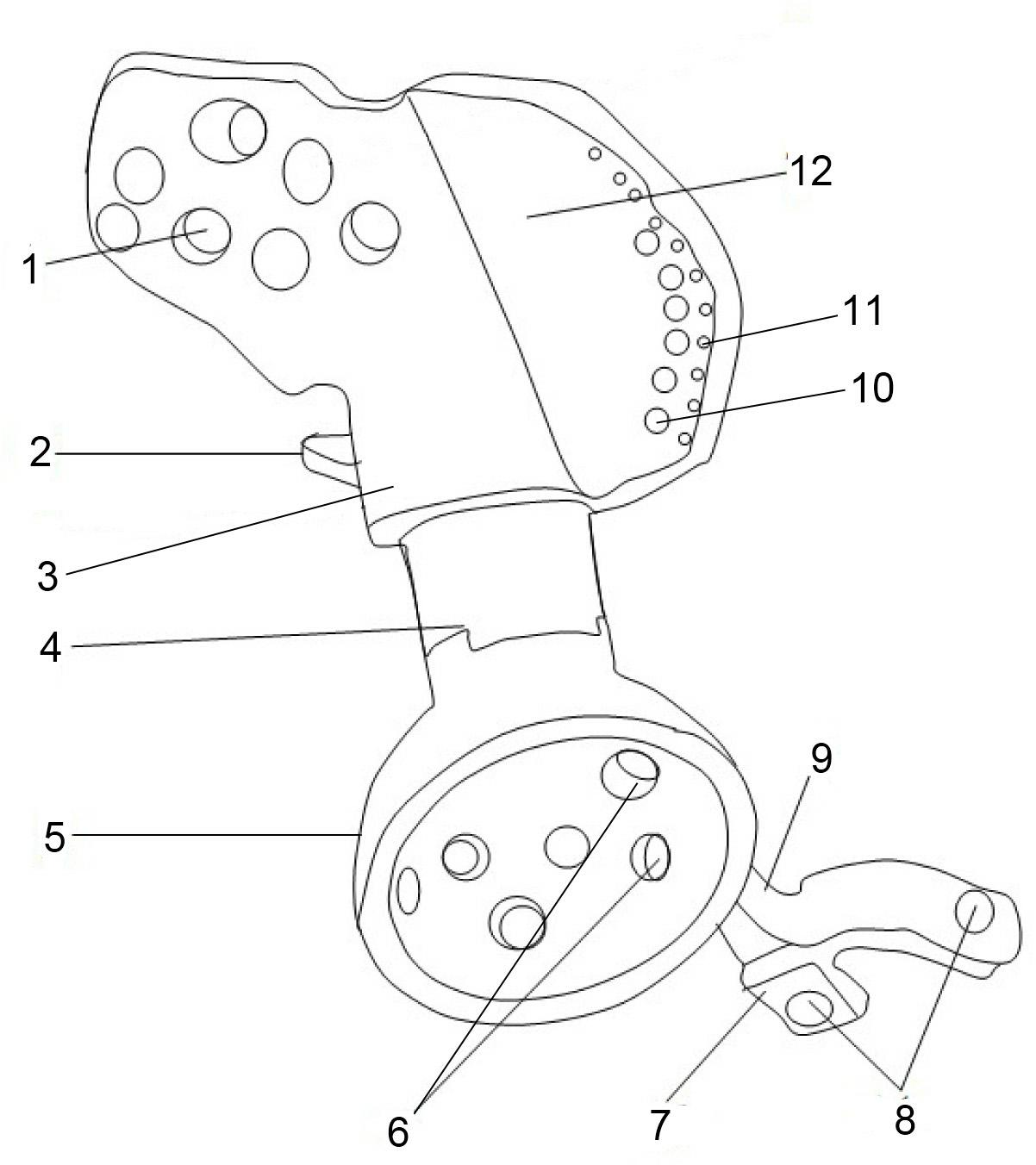
Artificial half pelvic prosthesis with support structure
InactiveCN102048598ALong-term steady decreasePrevent looseningJoint implantsAcetabular cupsNeurovascular injuryProsthesis
The invention discloses an artificial half pelvic prosthesis with a support structure, comprising an ilium side prosthesis and an acetabulum side prosthesis which are provided with a plurality of bolt holes, and a hook-like support structure arranged at the sacrum part justly is arranged at the edge end of the ilium side prosthesis; the ilium side prosthesis is hemispherical, an extension arm is arranged inwards, and a hook-like support structure arranged below the public rami at the same side or the opposite side is arranged at the tail end below the arm. In the invention, by adopting the support structure, interfacial stress between the prosthesis and the residual pelvis is converted into pressure stress from shearing or tensile stress, so as to improve the stability of the prosthesis. Moreover, a special inserted support structure or an inserted intramedullary stem structure is adopted at the connecting part of the prosthesis and a horizontal ramus of pubis, more femoral blood vessels and nerves on the surface are not needed to be exposed in the operation, the inserted type support structure or the intramedullary stem is directly inserted in the stump of the horizontal ramus of pubis, so as to simplify the operation and reduce risks of bleeding and injuring vital nerves and blood vessels.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
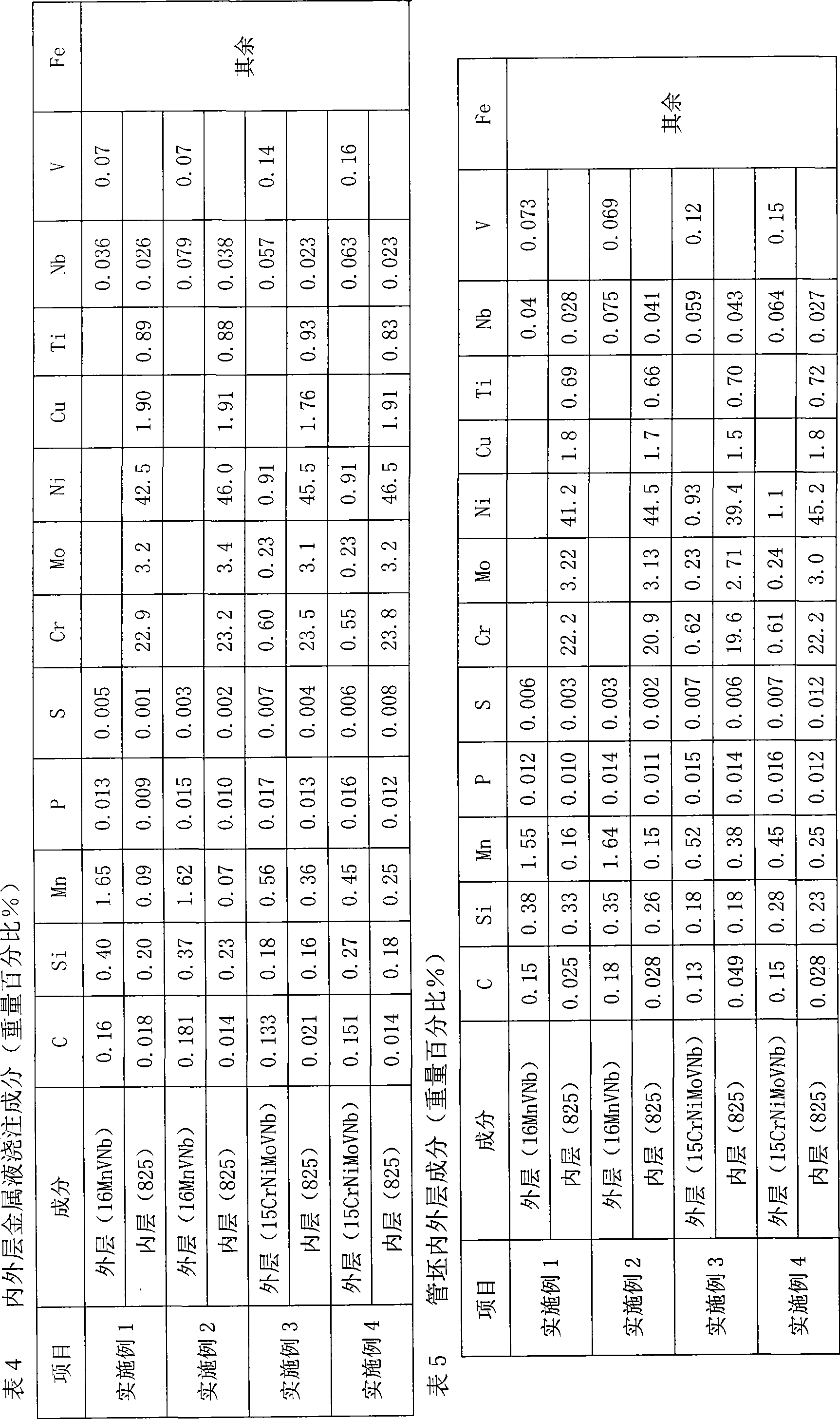
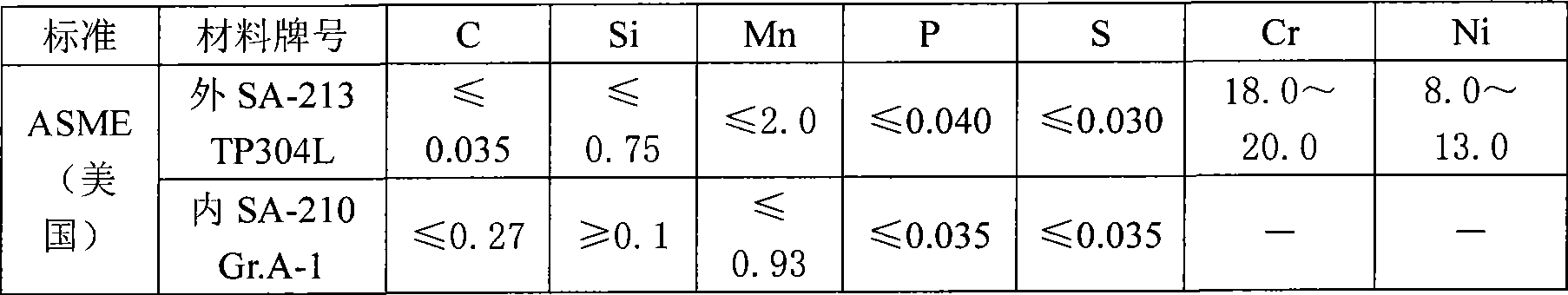
Corrosion-resistant dual metal clad tube blank and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101530898ANot easy to layerImprove securityRigid pipesExplosion weldingCorrosion resistant
A manufacturing method of a corrosion-resistant dual metal clad tube blank comprises the following steps: outer-layer molten metal is pumped into a pipe die for centrifugal pouring, the molten metal is cooled after pouring, and inner-layer molten metal is poured when internal surface temperature of the outer layer is cooled to be lower than 50-70 DEG C which is the melting point of the outer-layer molten metal; inner-layer molten metal is pumped into the pipe die for centrifugal pouring, the molten metal is cooled after pouring; cooling is stopped after the outer layer and the inner layer are completely solidified, at the moment, the inner layer and the outer layer achieve complete metallurgical bonding; wherein, the outer layer is made of X52 or X60 steel and the inner layer is made of 825 steel. A metallurgical bonding layer of a production tube obtained by carrying out extrusion or hot rolling on the tube blank manufactured by the method is several times or dozens of times as thick as a bonding layer of the dual metal tube obtained by the explosive welding process; the transition of the ingredients on the inner and outer layers is gentle, thus greatly relieving the interfacial stress between the inner layer and the outer layer, facilitating the inner layer and the outer layer not to be layered easily, improving the safety of the use of the production tube and prolonging the service life of the production tube.
Owner:HANDAN XINXING SPECIAL TUBING CO LTD
Semi-pelvic prosthesis
The invention belongs to the technical field of designing and manufacturing of prosthesis and relates to semi-pelvic prosthesis. The semi-pelvic prosthesis is characterized by being formed by connecting an ilium fixing part, acetabulum prosthesis, and a pubis connection part, wherein the ilium fixing part is used for being connected and fixed with a residual iliac wing and sacrum; the pubis connection part is used for being connected and fixed with the residual pubis on the same side or pubis on an opposite side; the ilium fixing part and the acetabulum prosthesis are connected by a tapered rotation prevention clamp port; and the acetabulum prosthesis and the pubis connection part are fixed and connected by a bolt. The semi-pelvic prosthesis has the advantages that (1) compared with assembled prosthesis, hot bending forming integrated prosthesis is disperse in stress; (2) the semi-pelvic prosthesis and the residual iliac wing are fixed by a self-locking nail, and the sacrum and the residual pubis are fixed by a self-locking nail, so that loosening of the bolt can be effectively prevented; and (3) the semi-pelvic prosthesis is provided with a flat supporting structure, so that the interfacial stress between the prosthesis and the sacrum, and between the prosthesis and the pubis can be converted from shear force or tensile stress into pressure stress, the loosening or displacement of the prosthesis is prevented, the long-term stability of the prosthesis is facilitated, and the prosthesis cannot be broken easily when complex force is applied to a human body for a long time.
Owner:THYTEC SHANGHAI
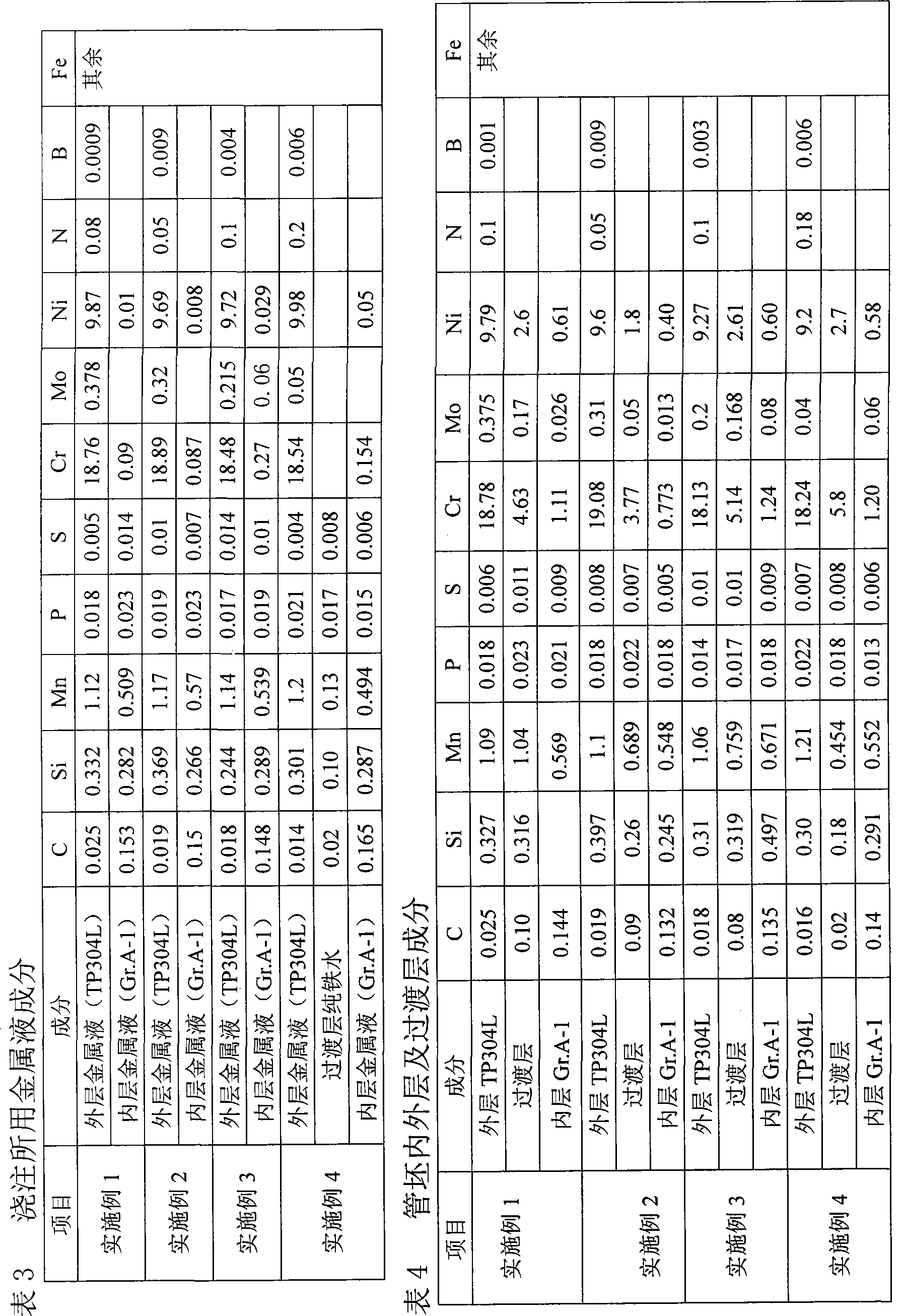
Clad tube blank of dual metal seamless steel tube used for boiler and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101530907ANot easy to layerExtended service lifeRigid pipesMetal layered productsJoint surfaceTransition layer
A clad tube blank of a dual metal seamless steel tube used for a boiler comprises an inner layer and an outer layer; a transition layer is arranged between the inner layer and the outer layer and is respectively bonded with the inner layer and the outer layer completely and metallurgically; the inner layer is cast by a Gr.A-1 material; the transition layer is cast by ferrite or inner layer materials. The transition layer is arranged between the inner layer and the outer layer of the clad tube blank and is respectively bonded with the inner layer and the outer layer completely and metallurgically, therefore, interfacial stress between joint surfaces of the inner layer and the outer layer is reduced, the tube blank is not easy to be layered and the service life of production tubes used for boilers and manufactured by the tube blank is greatly increased.
Owner:XINXING DUCTILE IRON PIPES CO LTD +1
In-situ non-crystallizing modification method for surface of metal material
InactiveCN106011847AReduce interface stressIncreasing the thicknessMetallic material coating processesMetallic materialsMetal
The invention belongs to the technical field of modification of surfaces of metal materials, and discloses an in-situ non-crystallizing modification method for the surface of a metal material. The method comprises the steps that amorphous alloy components matched with components of a metal matrix material are selected based on the components of the metal matrix material; then, required simple-substance element powder except main elements of a metal matrix is matched according to the amorphous alloy components; after being mixed, the element powder is preplaced on the surface of the metal matrix; laser is adopted to directly irradiate the mixed powder and the metal matrix to melt the mixed powder and the metal matrix and mix the melts; and an amorphous alloy is generated through the in-situ alloying reaction of the mixed element powder and the main elements of the metal matrix under the condition of quick cooling, and an amorphous alloy surface is prepared. According to the method, the interfacial stress of the amorphous alloy surface and the metal matrix is effectively reduced, the thickness of the amorphous alloy surface is increased, and the surface performance of the metal material is remarkably improved; and the amorphous alloy surface prepared through the method is different from an amorphous alloy coating prepared through a traditional method, the amorphous alloy surface is generated through the in-situ alloying reaction on the surface of the metal matrix, the interface bonding is high, and the performance is excellent.
Owner:常熟市大地机械铸造厂
Coupled-cap flip chip BGA package with improved cap design for reduced interfacial stresses
InactiveUS6512295B2Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesiveSemiconductor chip
Plastic ball grid array (PBGA) packages comprised of organic carriers on which are mounted and encapsulated semiconductor chips, providing for the mounting of so-called flip-chips. The chips are overlaid with a heat spreading thermally-conductive cap of a mesh-like material which is interstitially filled with an adhesive to prevent delamination caused by mismatches in the coefficients of thermal expansion, which result in contractions which cause the entire package arrangement to warp, leading to delamination between an encapsulant and cap and resulting in failure of connect joints and the ball grid arrays.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
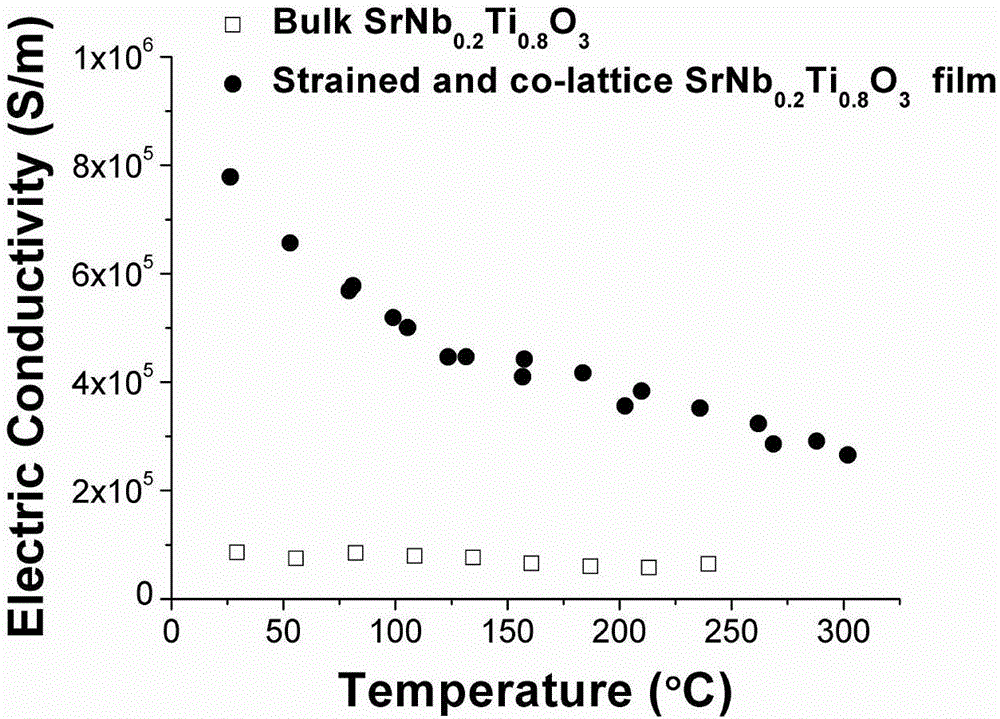
Preparation method of high-performance doping strontium titanate oxide thermoelectric film
ActiveCN106784279AIncreased Seebeck coefficientImprove the Seebeck coefficientThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsSingle crystalFilm material
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-performance doping strontium titanate perovskite oxide thermoelectric film. The method is characterized in that epitaxial coherent growth of a doping strontium titanate film material on the surface of an oxide monocrystal substrate which has the same lattice body structure and an unmatched parameter compared with the film material is realized by controlling a plasma property and a substrate condition; and an interfacial stress field is generated. A crystal structure property, an electronic structure property and a polarization characteristic of the film material, and an interfacial property between the film material and the substrate are adjusted by the stress field and the lattice distortion degree of the film material, so that thermoelectric transmission properties of the material such as conductivity and a seebeck coefficient are greatly improved. A room-temperature thermoelectric power factor of the prepared doping strontium titanate film material is 50-10000mnW / (cm*K<2>). The high-performance doping strontium titanate film material prepared by the method can be further applied to design and preparation of a thermoelectric device, so that the thermal and electric energy conversion efficiency of the prepared thermoelectric device during realization of functions such as temperature difference power generation, refrigeration and temperature sensing can be greatly improved.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
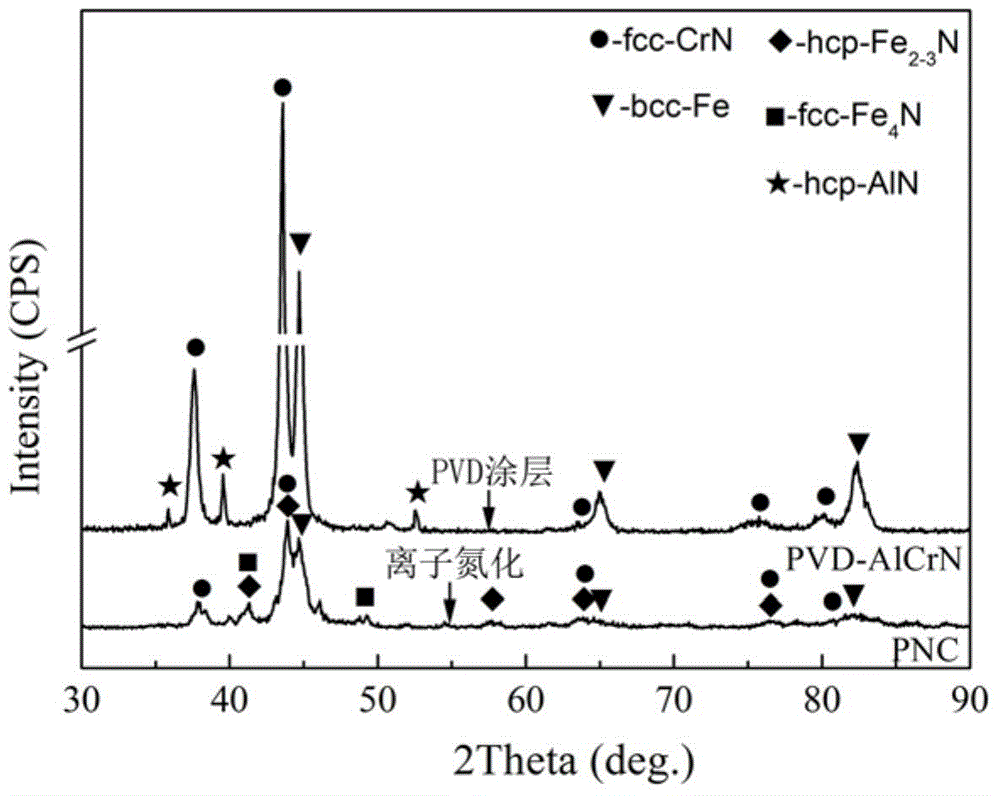
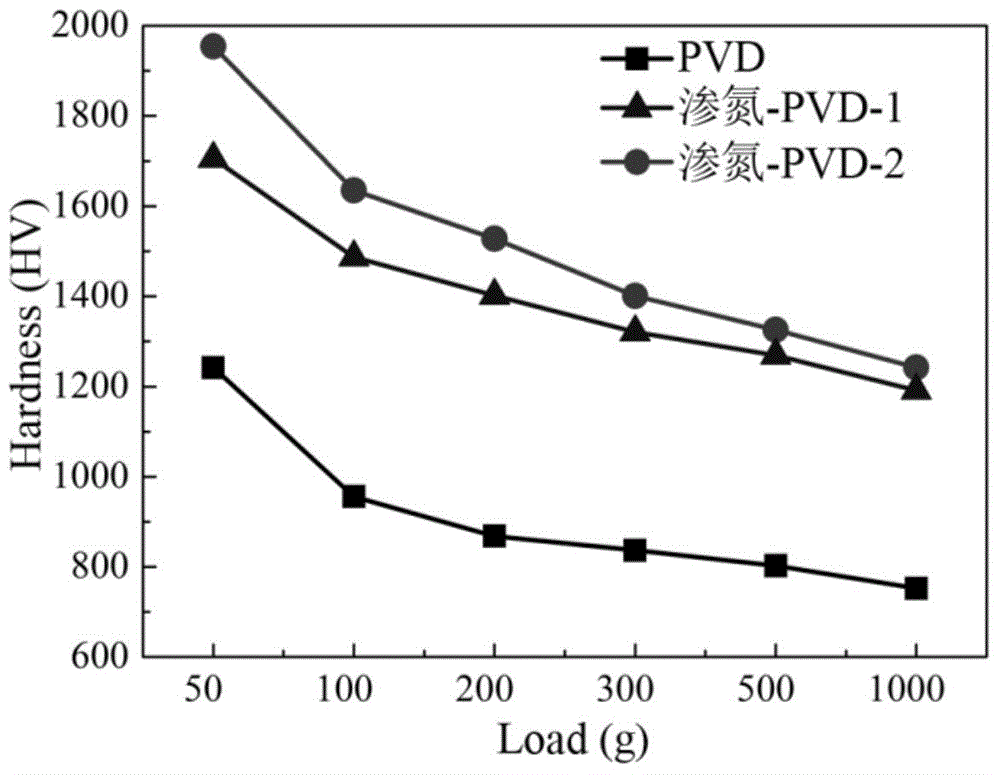
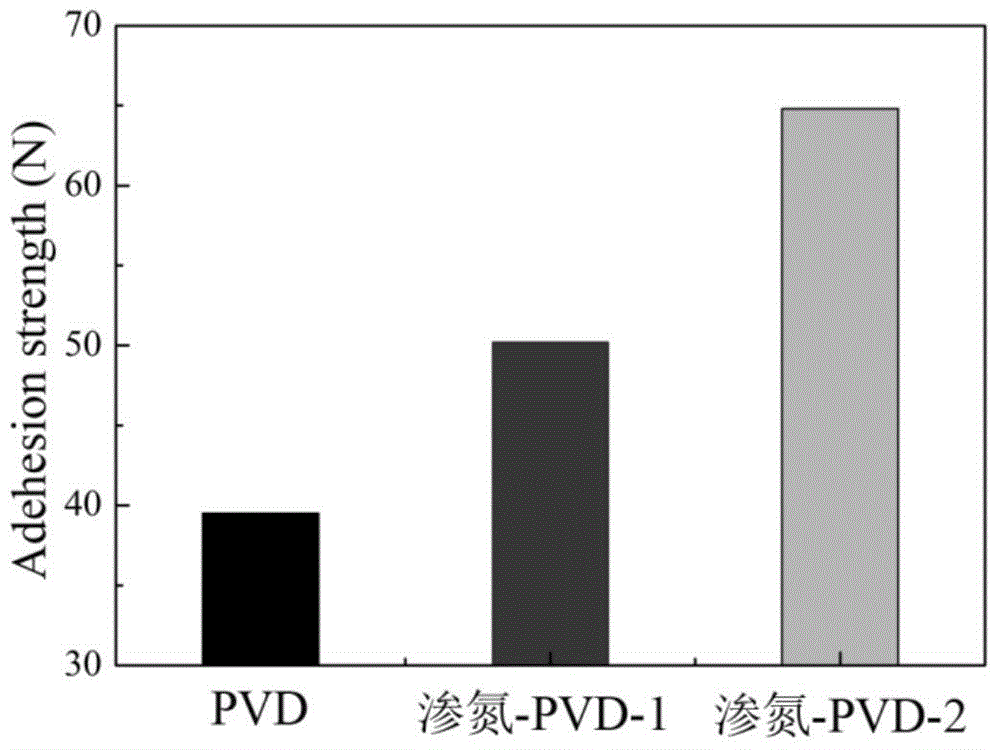
Nitriding PVD composite coating and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a nitriding PVD (Physical Vapor Decomposition) composite coating and a preparation method thereof. The internal structure of a diffusion layer comprises a nitrogen-containing oversaturated martensitic structure, a metal nitrogen compound, a metal carbon compound and Fe4N phase; the internal structure of a compound layer comprises Fe4N phase of a face-centered cubic structure, CrN phase of the face-centered cubic structure, and Fe2-3N phase of a close-packed hexagonal structure; the internal structure of a PVD hard film layer mainly comprises fcc-(Cr, Al)N phase of the face-centered cubic structure and further comprises a small number of hcp-AlN phase of the close-packed hexagonal structure, and fcc-(Ti, Al)N phase of the face-centered cubic structure. With the adoption of the reasonable technologic optimization and adjustment and control of the structure, the decomposition of the compound layer can be inhibited; the Fe4N phase and the CrN phase in the compound layer become nucleation particles for phase epitaxial growth of the PVD hard film, so as to obviously increase the film-matrix binding force; the compound layer provides powerful support for the PVD hard film; moreover, the compound layer enables the stress on the film-matrix interface to be continuously changed, so as to improve the interfacial stress concentration situation, and improve the bearing capacity, the surface hardness and other mechanical properties of the composite coating.
Owner:安徽工业大学科技园有限公司
Double-component epoxy adhesive for bonding ceramics, preparation method and using method thereof
InactiveCN102220101AReduce internal stressHigh bonding strengthNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesCarboxyl rubber adhesivesFiberCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to a double-component epoxy adhesive for bonding ceramics, a preparation method and using method thereof, belonging to the adhesive field, and aiming at solving the technical problem that the interfacial stress is overhigh owning to great difference of linear expansion coefficients when the existing epoxy adhesive is used for bonding the ceramics. The component A of the double-component epoxy adhesive is prepared by E-44 epoxy resin, E-51 epoxy resin, carboxy terminal butadiene-acrylonitrile, ground quartz, carbon fiber, carbon nano tube, SiC crystal whisker and ultraviolet absorber UV-531, the component B of the double-component epoxy adhesive is prepared by 3-diethylin propylamine, silane coupling agent KH-550, accelerating agent DMP-30 and ground quartz, and the double-component epoxy adhesive is prepared by a mixing method. When the adhesive is used, the adhesive is coated on a surface to be adhered for superimposition and solidification; and the shearing strength of the adhesive can reach more than 60MPa when the adhesive is used for bonding SiC ceramic; the bonding interface is good, an obvious mechanical embedding function is realized between an adhesive layer and a parent metal, and the defects such as cracks, air holes and the like do not exist in the adhesive layer.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Epoxy resin/carbon fiber composite material and preparation method thereof
The present invention discloses an epoxy resin / carbon fiber composite material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of carbon fiber-reinforced materials. The epoxy resin / carbon fiber composite material comprises a silicon rubber, wherein the silicon rubber is simultaneously cross-linked with the epoxy resin and carbon fibers. According to the present invention, the silicon rubber is added to the composite material to simultaneously cross-link the silicon rubber, the epoxy resin and the carbon fibers so as to prepare the composite material with the good epoxy resin, carbon fiber and silicon rubber compatibility; and the silicon rubber is added to the composite material so as to effectively reduce the interfacial stress force of the composite material and increase the strength, wherein the impact strength of the material of the present invention is increased by 30-45% compared to the conventional silicon rubber-free epoxy resin / carbon fiber composite material.
Owner:CHERY AUTOMOBILE CO LTD
Coupled-cap flip chip BGA package with improved cap design for reduced interfacial stresses
InactiveUS20020121694A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesiveSemiconductor chip
Plastic ball grid array (PBGA) packages comprised of organic carriers on which are mounted and encapsulated semiconductor chips, providing for the mounting of so-called flip-chips. The chips are overlaid with a heat spreading thermally-conductive cap of a mesh-like material which is interstitially filled with an adhesive to prevent delamination caused by mismatches in the coefficients of thermal expansion, which result in contractions which cause the entire package arrangement to warp, leading to delamination between an encapsulant and cap and resulting in failure of connect joints and the ball grid arrays.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
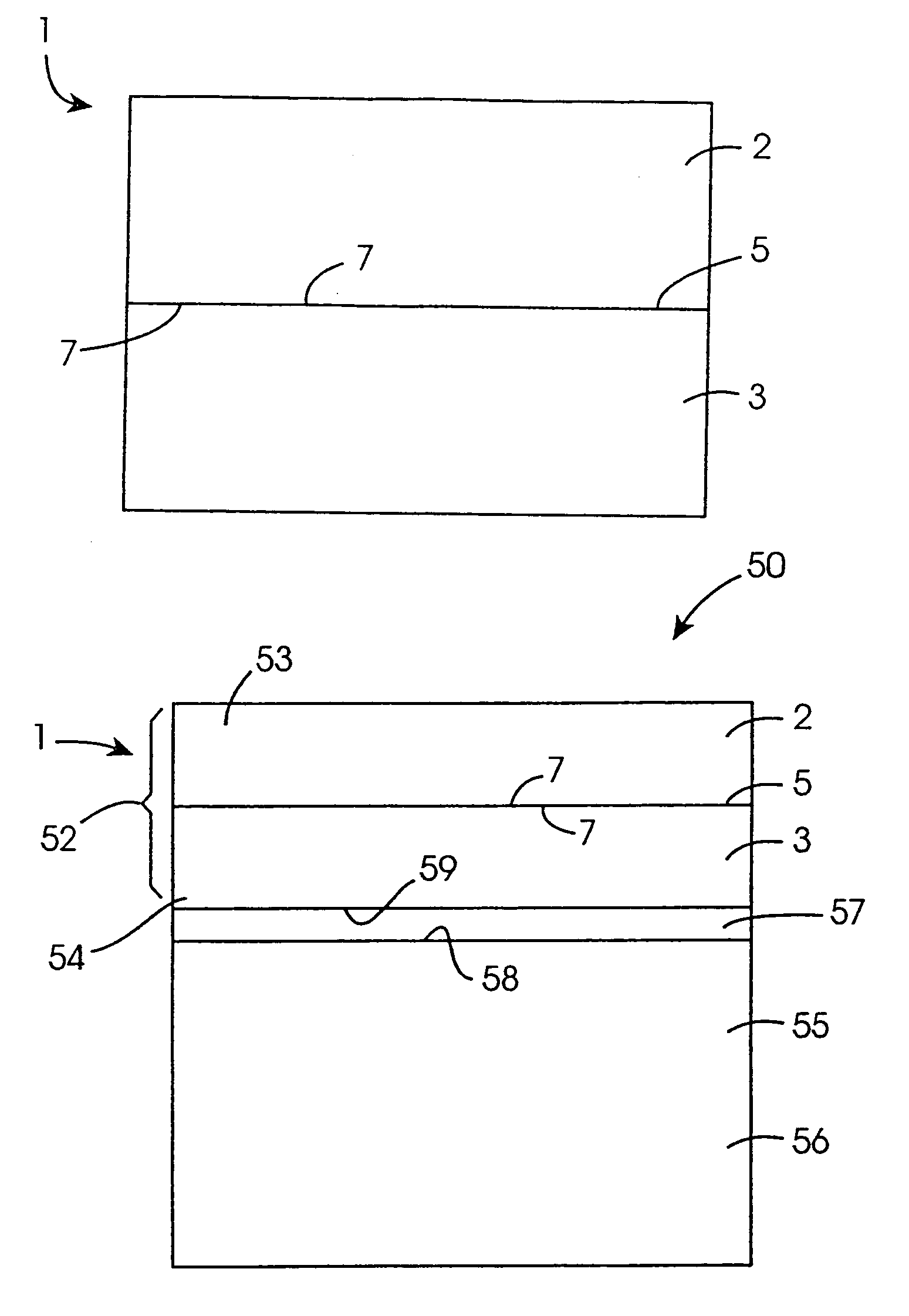
Method for direct bonding two silicon wafers for minimising interfacial oxide and stresses at the bond interface, and an SOI structure
A semiconductor substrate (1) comprises first and second silicon wafers (2,3) directly bonded together with interfacial oxide and interfacial stresses minimised along a bond interface (5), which is defined by bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3). Interfacial oxide is minimised by selecting the first and second wafers (2,3) to be of relatively low oxygen content, well below the limit of solid solubility of oxygen in the wafers. In order to minimise interfacial stresses, the first and second wafers are selected to have respective different crystal plane orientations. The bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3) are polished and cleaned, and are subsequently dried in a nitrogen atmosphere. Immediately upon being dried, the bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3) are abutted together and the wafers (2,3) are subjected to a preliminary anneal at a temperature of at least 400° C. for a time period of a few hours. As soon as possible after the preliminary anneal, and preferably, within forty-eight hours of the preliminary anneal, the first and second wafers (2,3) are fusion bonded at a bond anneal temperature of approximately 1,150° C. for a time period of approximately three hours. The preliminary anneal may be omitted if fusion bonding at the bond anneal temperature is carried out within approximately six hours of the wafers (2,3) being abutted together. An SOI structure (50) may subsequently be prepared from the semiconductor structure (1) which forms a substrate layer (52) supported on a handle layer (55) with a buried insulating layer (57) between the substrate layer (52) and the handle layer (55).
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Preparation method of TiCN gradient coating
ActiveCN107034433AOvercoming the tendency to appear large particlesOvercome organizational defects such as stomataVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSurface layerTube furnace
The invention discloses a preparation method of a TiCN gradient coating. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1:, filling a graphite crucible with a solid carburizing agent, then, backfilling a TiN coating block into the carburizing agent, and then, sealing the graphite crucible by using a graphite cover; S2: placing the graphite crucible sealed by using the graphite cover in the step S1 into a vacuum carbon tube furnace; and then, heating from the room temperature to 800-850 DEG C under an Ar or vacuum condition, next, keeping the temperature for 4-8h to carry out carburization reaction to obtain the TiCN gradient coating. The TiCN gradient coating not only has the characteristic of gradient component distribution that the core layer is rich in nitrogen and the surface layer is rich in carbon, and the friction coefficient of the coating can be remarkably reduced; and meanwhile, solid carburization simultaneously has an annealing treatment effect, so that the interfacial stress between a matrix and the coating in a coating deposition process can be further eliminated, and the adhesive force between the coating and the matrix can be increased.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Laser forming method of gradient composite structure
ActiveCN108145160AReduce and counteract interlaminar stressHigh bonding strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyOptoelectronicsUltimate tensile strength
The invention provides a laser forming method of a gradient composite structure. The gradient composite structure is obtained through the steps of preparing of laser forming equipment, design of a laser forming technology, laser forming and the like. According to the laser forming method, by designing scanning trajectories of transition layers, the scanning trajectories between the two adjacent layers are nested mutually, so that interlayer stress between the transition layers is reduced and counteracted; and meanwhile, combination of the transition layers is converted from plane combination into stereo combination through a mutually-nested mode, so that the combination strength of the transition layers is improved, and finally the gradient composite structure which achieves component continuous transition and is small in interfacial stress and higher in overall strength is obtained.
Owner:AEROSPACE INST OF ADVANCED MATERIALS & PROCESSING TECH
Multi-bit encoded glass-coated microwire and articles composed thereof
InactiveUS7233249B2Eliminate needInorganic material magnetismGlass/slag layered productsGratingFluorescence
A glass-coated amorphous metallic microwire is encoded with multi-bit digital information. Encoding is achieved magnetically, optically or through a combination of magnetic and optical encoding processes. Magnetic encoding is carried out by modifying the constituent magnetic domain structure through selective relief of interfacial stress between the glass coating and the amorphous metallic alloy core. It is also achieved by selective surface crystallization of the amorphous metallic core in order to produce a controlled magnetic bias field. Optical encoding is associated with the glass coating. It is readily achieved by fluorescent element deposition, patterned removal of fluorescent element coating, Bragg grating, and thermally activated pattern deposition. The magnetic and optical multi-bit encoding approaches for glass-coated amorphous metallic microwire can be used individually or collectively in either a redundant or a complementary manner. Encoded microwire of the instant invention can be assembled into tags for electronic article surveillance and into numerous other structures as well.
Owner:DEMODULATION
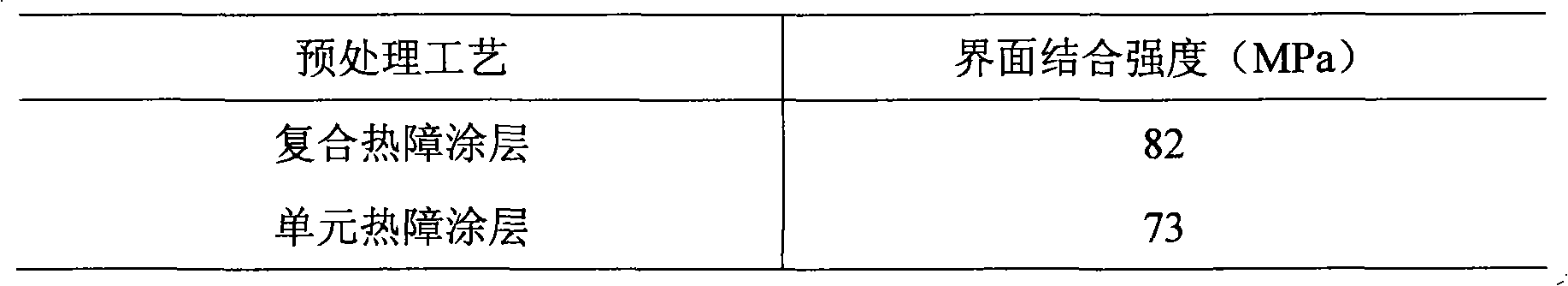
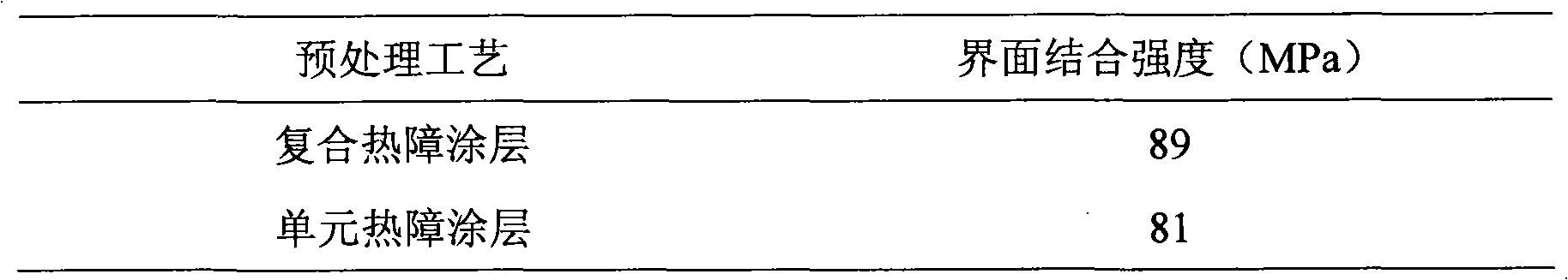
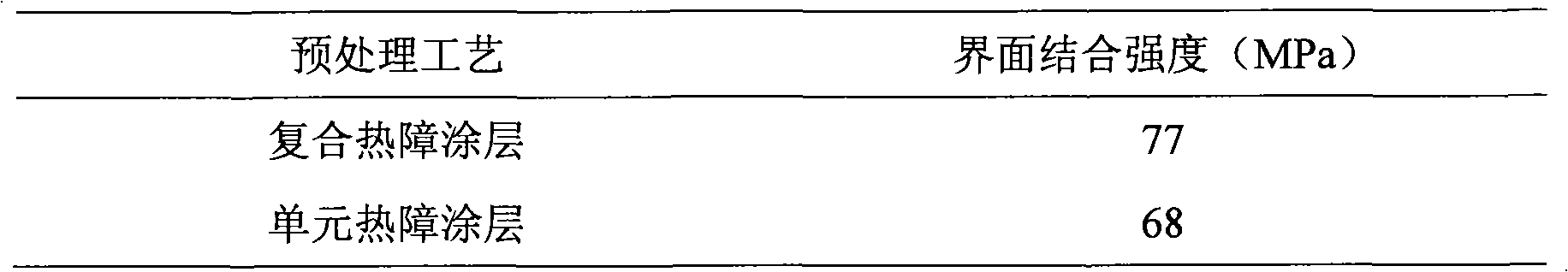
Method for preparing thermal expansion matching composite thermal barrier coating
InactiveCN101831602AImprove performanceExtended service lifeMolten spray coatingInterfacial bondAlloy
The invention discloses a method for preparing a thermal expansion matching composite thermal barrier coating, and relates to the field of surface coatings. The composite thermal barrier coating consists of a thermal barrier coating material Zr1-x-yHfxREyO2-y / 2 and a negative thermal expansion material Zr1-yREyW2-zMozO8-y / 2, wherein x is more than or equal to 0.01 and less than or equal to 1; y is more than or equal to 0.01 and less than or equal to 0.05; z is more than or equal to 0.3 and less than or equal to 1; and RE is one or more of La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Pm, SM, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, Sc and Y. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) cutting a matrix alloy into a certain size; 2) according to the thermal expansion matching principle, matching thermal barrier coating nanopowder with negative thermal expansion material micropowder; 3) performing micro / nano composition reconstruction on two kinds of prepared powder; 4) performing laser radiation on reconstructed composite particles; and 5) filling the composite particles in a powder feeder, and preparing the thermal barrier coating through vacuum plasma spraying. The thermal barrier coating prepared has small interfacial stress, high bond strength, and good mechanical property. The method has simple process, is suitable for large-scale massive production, and can prepare the composite thermal barrier coating with firm interfacial bond.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
UV-polymerizable POSS modified acrylate pressure-sensitive adhesive and a preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109868084AImprove performanceIncrease stickinessNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesMacromolecular adhesive additivesThermal expansionTemperature resistance
The invention relates to a UV-polymerizable POSS modified acrylate pressure-sensitive adhesive which comprises the following components: an acrylate copolymer, a viscosity modifier, a molecular weightmodifier, an interface promoter, POSS (polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane) and a photoinitiator. According to the invention, a UV-polymerization technique is employed to produce a POSS modified acrylate pressure-sensitive adhesive which has extremely high interfacial stress dispersion capability and can well resist the damage of thermal expansion and contraction to a material. Meanwhile, the UV-polymerization technique which has the advantages of zero solvent, no pollution, few reaction steps and high reaction efficiency is employed to produce a UV-polymerizable POSS modified acrylate pressure-sensitive adhesive. The acrylate pressure-sensitive adhesive provided by the invention is excellent in adhesion, peel strength, tensile strength and high temperature resistance.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Non-residual-stress thin film, preparation method of non-residual-stress thin film and application of non-residual-stress thin film in nanoindentation method
InactiveCN104729897APrevent measurement results from being affectedEasy to operatePreparing sample for investigationInvestigating material hardnessGas phaseSingle crystal
The invention discloses a non-residual-stress thin film. The thin film is mainly used for calculating the intensity of residual stress in an indentation method, the thin film is a metal thin film, and the metal thin film is prepared by sputtering or depositing a thin film on a single crystal through physical vapor deposition or chemical vapor deposition, and then removing the crystal. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the non-residual-stress thin film and application of the non-residual-stress thin film in a nanoindentation method. The interfacial stress, for being combined with a substrate, of a non-residual-stress thin film sample obtained is completely removed, and in the process of a nanoindentation test, the thin film can carry out non-bottom-surface support so as to prevent a bottom surface from affecting measuring results. The non-residual-stress thin film can be used for greatly improving the adaptability and the practicability of a Suresh theoretical model in a nanoindentation testing method.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
Crack-resistant environmental barrier coatings
InactiveUS9290836B2Reduce morbidityImprove system reliabilityMolten spray coatingBlade accessoriesCoating systemEngineering
Methods suitable for reducing corner cracking of environmental barrier coating systems. The methods include forming at least one layer of a first portion of the environmental barrier coating system on at least a first region of the component, performing a first heat treatment, forming at least one layer of a second portion of the environmental barrier coating system on a second region of the component, and performing a second heat treatment to the component. Edges of the first portion and edges of the second portion form an angle of at most 60° with respect to a surface of the first region of the component. During the second heat treatment, the second portion of the EBC system expands and the expansion of the second portion of the EBC system is at least partially constrained by the first portion of the EBC system to reduce tensile interfacial stresses in the EBC system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Clay adhesion test device with upward soil pushing and extruding effect and adjustable contact area and test method
InactiveCN108663319AEvenly loadedUniform contact stressUsing mechanical meansMaterial weighingEngineeringBottle
The invention provides a clay adhesion test device with upward soil pushing and extruding effect and adjustable contact area and test method. The test device comprises a cylindrical soil box, an annular metal backing plate, a soil box cover plate, a fixed pulley block, a water storage bottle, a water supply bottle, a flowmeter, a balance, an air compressor, a water supply barrel, a pressure control valve, a pressure meter, a water bag, a valve, a hose and a nylon rope, wherein constant pressure is set by the air compressor and loaded to the water supply barrel, the water bag swells under the constant hydraulic pressure to produce an upward soil pushing and extruding effect, soil samples are loaded uniformly, and interfacial stress between the soil samples and the soil box cover plate is more uniform. The adhesion of the soil samples with different contact areas with the soil box cover plate is tested by replacing annular metal backing plates with different cross section areas, and by means of the annular metal backing plates, the problems about adhesion test under different contact areas and the soil samples adhering to the bottom surface of a test disc in an adhesion test are solved effectively.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Preparation method of gradient abrasion-resistant coating containing Ag nano-particles
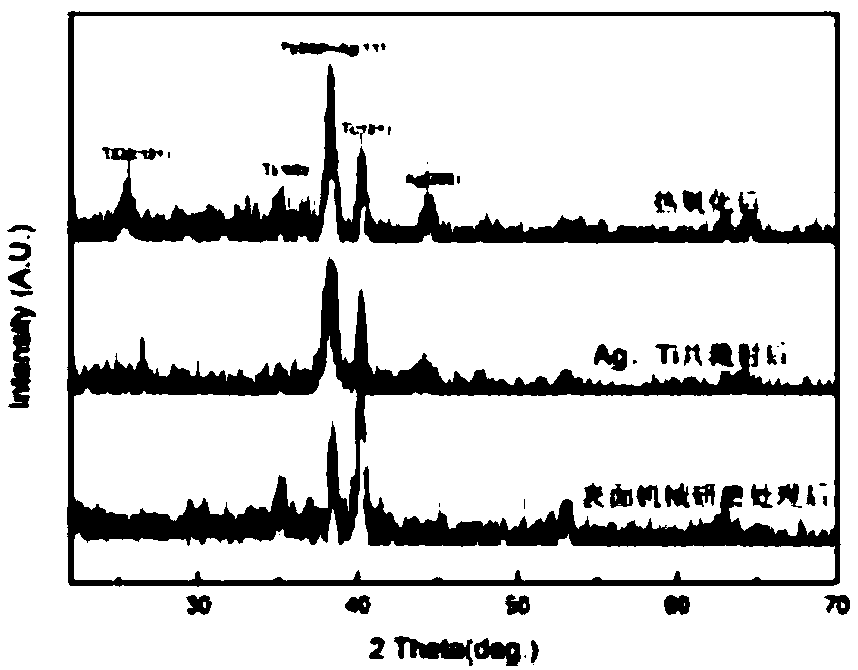
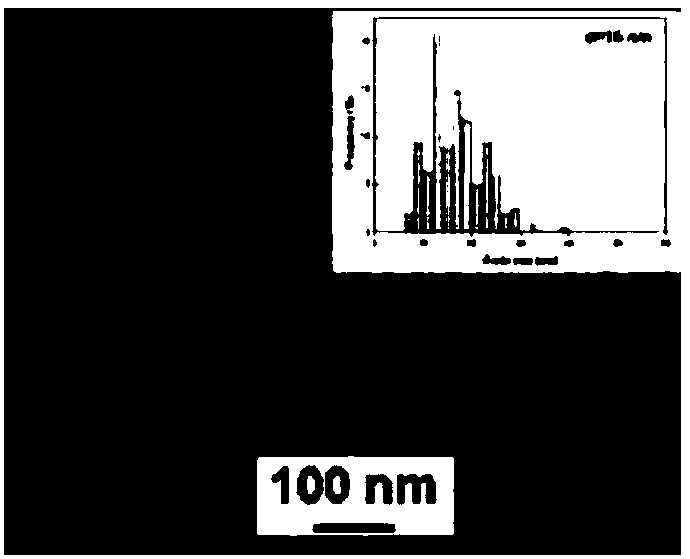
ActiveCN107779814APrevent oxidationImprove friction and wear performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringSurface layer
The invention discloses a preparation method of a gradient abrasion-resistant coating containing Ag nano-particles, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a gradient abrasion-resistant coating containing Ag nano-particles on the surface of a Ti material. The method mainly includes the steps: recrystallization annealing of the Ti material; surface mechanical attrition treatment; reactive magnetron co-sputtering; heat oxidation. According to the method, a high-toughness and high-hardness abrasion-resistant surface layer is acquired by the aid of the Ag nano-particles with good lubrication and toughness and TiO2 with high hardness, the gradient coating is designed and acquired, interfacial stress between the coating and a metal substrate is effectively improved, and bonding of the coating and the substrate is improved, so that friction and abrasion performances of the Ti material can be obviously improved.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
Method for representing bonding strength of hard film through interfacial stress of elasticoplastic deformation
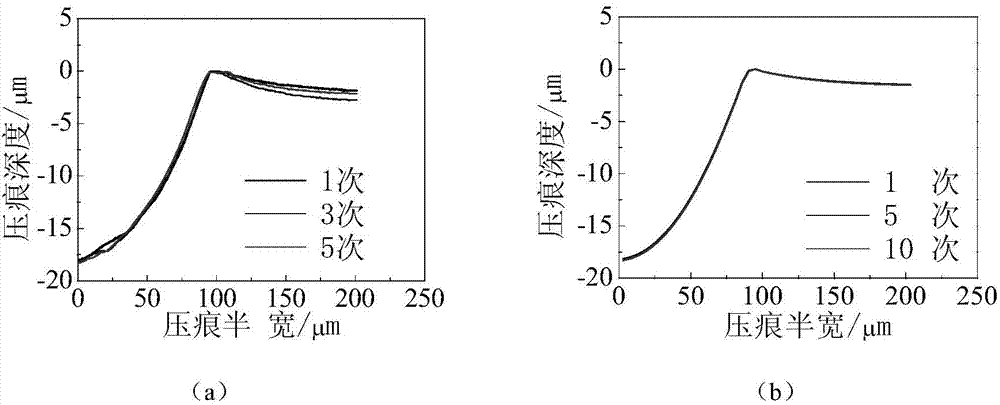
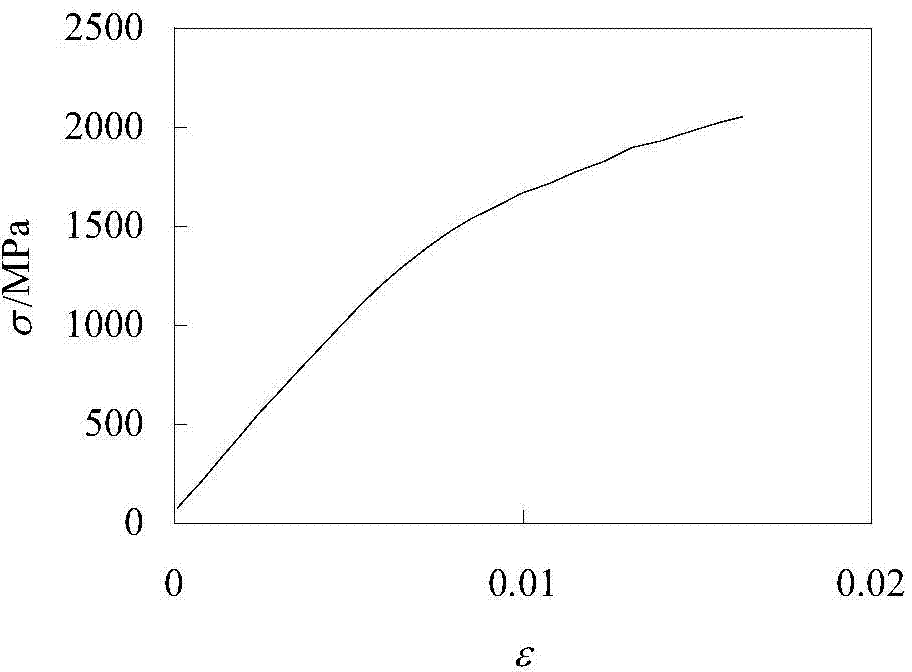
ActiveCN104502273AChange the minimum loadChange peak load ratioUsing mechanical meansSpecial data processing applicationsShear stressAlloy substrate
The invention discloses a method for representing the bonding strength of a hard film through interfacial stress of elasticoplastic deformation. The method comprises the following steps: performing circulation pressing testing on a sample of which a metal or hard alloy substrate surface is deposited with the hard film by using a circulation pressing experiment machine, so as to cause elasticoplastic deformation of a film substrate system, and finally strip off the film from the substrate because of interface fatigue; performing finite element modeling analysis according to relevant material property and practical testing conditions, acquiring the shearing stress amplitude acting at the film base interface when the film is stripped off under different circulation loads according to the solving result, and finally quantitatively representing the bonding strength of the film / substrate interface according to shearing stress amplitude-stripping week curved. The method for representing the bonding strength of a film / substrate interface is relatively reasonable and feasible, relatively accurate and quantitative in representation, relatively practical and reliable in result, and applicable to representation and evaluation on the bonding strength of hard films on metal or hard alloy surfaces which are widely used in the conventional industrial fields.
Owner:宁波云涂科技有限公司
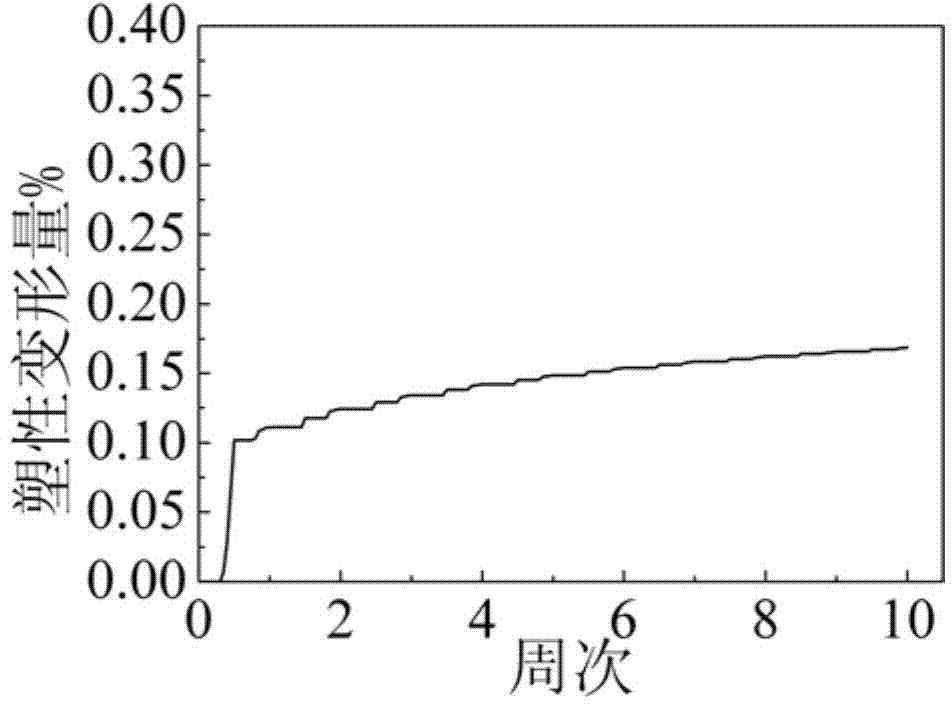
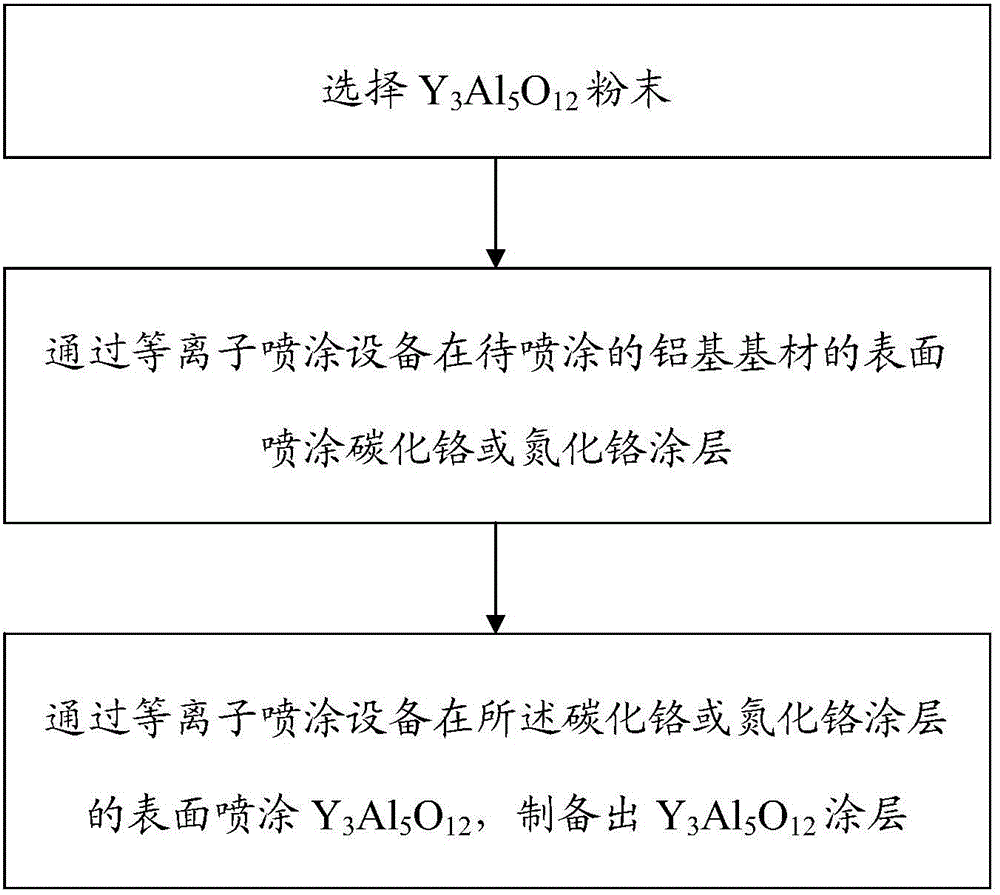
Preparation method of Y3Al5O12 coating applied to aluminum-based base material
InactiveCN105624602ARelieve interface stressEasy transitionMolten spray coatingChromium carbideEtching
The invention relates to the technical field of anticorrosive treatment of inner surfaces of technological chambers for semiconductor etching, in particular to a preparation method of a Y3Al5O12 coating applied to an aluminum-based base material. The preparation method comprises the following steps that Y3Al5O12 powder is selected; a chromium carbide or chromium nitride coating is sprayed to the surface of the aluminum-based base material to be sprayed through plasma spraying equipment; and Y3Al5O12 is sprayed to the surface of chromium carbide or chromium nitride coating through the plasma spraying equipment, so that the Y3Al5O12 coating is prepared. According to the preparation method of the Y3Al5O12 coating applied to the aluminum-based base material, the bonding phase of the chromium carbide or chromium nitride is added between the aluminum-based base material and the Y3Al5O12 coating, a good transition function between the Y3Al5O12 coating and the aluminum-based base material can be achieved, interfacial stress of the Y3Al5O12 coating and the aluminum-based base material is effectively reduced, and the interface bonding strength is improved.
Owner:北京美桥电子设备有限公司 +1
Semiconductor device and manufacture method
InactiveCN106356341AImprove cooling efficiencySpeed up heat transferMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPower semiconductor deviceCooling effect
The invention relates to the field of circuits and discloses a semiconductor device and a manufacture method. The semiconductor device comprises a circuit device, a cooling fin and a thermal interface material layer located between the circuit device and the cooling fin, wherein the circuit device and the cooling fin are arranged in a laminating manner; a packaging layer surrounds the side wall of the circuit device; a first surface of the thermal interface material layer is in thermal coupling with the circuit device and the packaging layer, and a second surface is in thermal coupling with the cooling fin. In the scheme, the packaging layer and the circuit device are both in thermal coupling with the thermal interface material layer, so that the contact area of the circuit device with the thermal interface material layer is increased, heat produced on the side wall of the circuit device can be transferred to the thermal interface material layer through the packaging layer and then transferred to the cooling fin, and the cooling effect of the semiconductor device is improved. By means of the packaging layer surrounding the circuit device, the laying area of the thermal interface material layer is increased, the area of a contact surface of the thermal interface material layer is increased, the interfacial stress is reduced, and the component reliability is improved correspondingly.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Cement concrete pavement waterproof structure with embedded seam of full-seam-opening hollow elastic tube
InactiveCN105525554AImprove waterproof performanceIncreased durabilityPaving detailsEngineeringShearing deformation
The invention discloses a cement concrete pavement waterproof structure with an embedded seam of a full-seam-opening hollow elastic tube, comprising a hollow elastic tube which is arranged in the embedded seam and can horizontally expand and contract along with the expansion and contraction of a pavement slab; the elastic tube is at least provided with an arch-shaped bulge upwards under the squeezing action of the pavement slab; the surface of the hollow elastic tube, over against the seam, is provided with an open seam of which the inside and outside are communicated; the pre-compressed magnitude of a hollow elastic waterproof part is large, so that the hollow elastic waterproof part can have relatively large extension and compression space, can adapt to deformation of a concrete slab for a long time, and especially can adapt to horizontal expansion and contraction deformation and vertical shear deformation; and when the width of a transverse seam changes with the temperature, because the compression degree of the hollow elastic waterproof part is suitable for expansion and contraction motion of the hollow elastic waterproof part, under the conditions of the expansion and contraction deformation and shear deformation of the transverse seam, by reducing the interfacial stress caused by the expansion and contraction deformation and shear deformation of the transverse seam, the joint between the transverse seam and the elastic waterproof part can not be damaged because of separation of the elastic waterproof part from the transverse seam.
Owner:CHONGQING JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com